Home / Guides / Citation Guides / MLA Format / How to Cite an Essay in MLA

How to Cite an Essay in MLA
The guidelines for citing an essay in MLA format are similar to those for citing a chapter in a book. Include the author of the essay, the title of the essay, the name of the collection if the essay belongs to one, the editor of the collection or other contributors, the publication information, and the page number(s).
Citing an Essay
Mla essay citation structure.
Last, First M. “Essay Title.” Collection Title, edited by First M. Last, Publisher, year published, page numbers. Website Title , URL (if applicable).
MLA Essay Citation Example
Gupta, Sanjay. “Balancing and Checking.” Essays on Modern Democracy, edited by Bob Towsky, Brook Stone Publishers, 1996, pp. 36-48. Essay Database, www . databaseforessays.org/modern/modern-democracy.
MLA Essay In-text Citation Structure
(Last Name Page #)
MLA Essay In-text Citation Example
Click here to cite an essay via an EasyBib citation form.
MLA Formatting Guide
MLA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Sample Paper
- Works Cited
- MLA 8 Updates
- MLA 9 Updates
- View MLA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all MLA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
To cite your sources in an essay in MLA style, you need to have basic information including the author’s name(s), chapter title, book title, editor(s), publication year, publisher, and page numbers. The templates for in-text citations and a works-cited-list entry for essay sources and some examples are given below:
In-text citation template and example:
For citations in prose, use the first name and surname of the author on the first occurrence. For subsequent citations, use only the surname(s). In parenthetical citations, always use only the surname of the author(s).
Citation in prose:
First mention: Annette Wheeler Cafarelli
Subsequent occurrences: Wheeler Cafarelli
Parenthetical:
….(Wheeler Cafarelli).
Works-cited-list entry template and example:
The title of the chapter is enclosed in double quotation marks and uses title case. The book or collection title is given in italics and uses title case.
Surname, First Name. “Title of the Chapter.” Title of the Book , edited by Editor(s) Name, Publisher, Publication Year, page range.
Cafarelli, Annette Wheeler. “Rousseau and British Romanticism: Women and British Romanticism.” Cultural Interactions in the Romantic Age: Critical Essays in Comparative Literature , edited by Gregory Maertz. State U of New York P, 1998, pp. 125–56.
To cite an essay in MLA style, you need to have basic information including the author(s), the essay title, the book title, editor(s), publication year, publisher, and page numbers. The templates for citations in prose, parenthetical citations, and works-cited-list entries for an essay by multiple authors, and some examples, are given below:
For citations in prose, use the first name and surname of the author (e.g., Mary Strine).
For sources with two authors, use both full author names in prose (e.g., Mary Strine and Beth Radick).
For sources with three or more authors, use the first name and surname of the first author followed by “and others” or “and colleagues” (e.g., Mary Strine and others). In subsequent citations, use only the surname of the first author followed by “and others” or “and colleagues” (e.g., Strine and others).
In parenthetical citations, use only the author’s surname. For sources with two authors, use two surnames (e.g., Strine and Radick). For sources with three or more author names, use the first author’s surname followed by “et al.”
First mention: Mary Strine…
Subsequent mention: Strine…
First mention: Mary Strine and Beth Radick…
Subsequent mention: Strine and Radick…
First mention: Mary Strine and colleagues …. or Mary Strine and others
Subsequent occurrences: Strine and colleagues …. or Strine and others
…. (Strine).
….(Strine and Radick).
….(Strine et al.).
The title of the essay is enclosed in double quotation marks and uses title case. The book or collection title is given in italics and uses title case.
Surname, First Name, et al. “Title of the Essay.” Title of the Book , edited by Editor(s) Name, Publisher, Publication Year, page range.
Strine, Mary M., et al. “Research in Interpretation and Performance Studies: Trends, Issues, Priorities.” Speech Communication: Essays to Commemorate the 75th Anniversary of the Speech Communication Association , edited by Gerald M. Phillips and Julia T. Wood, Southern Illinois UP, 1990, pp. 181–204.
MLA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
- Human Editing
- Free AI Essay Writer
- AI Outline Generator
- AI Paragraph Generator
- Paragraph Expander
- Essay Expander
- Literature Review Generator
- Research Paper Generator
- Thesis Generator
- Paraphrasing tool
- AI Rewording Tool
- AI Sentence Rewriter
- AI Rephraser
- AI Paragraph Rewriter
- Summarizing Tool
- AI Content Shortener
- Plagiarism Checker
- AI Detector
- AI Essay Checker
- Citation Generator
- Reference Finder
- Book Citation Generator
- Legal Citation Generator
- Journal Citation Generator
- Reference Citation Generator
- Scientific Citation Generator
- Source Citation Generator
- Website Citation Generator
- URL Citation Generator
- Proofreading Service
- Editing Service
- AI Writing Guides
- AI Detection Guides
- Citation Guides
- Grammar Guides
- Paraphrasing Guides
- Plagiarism Guides
- Summary Writing Guides
- STEM Guides
- Humanities Guides
- Language Learning Guides
- Coding Guides
- Top Lists and Recommendations
- AI Detectors
- AI Writing Services
- Coding Homework Help
- Citation Generators
- Editing Websites
- Essay Writing Websites
- Language Learning Websites
- Math Solvers
- Paraphrasers
- Plagiarism Checkers
- Reference Finders
- Spell Checkers
- Summarizers
- Tutoring Websites
Most Popular
How to cite a blog.
13 days ago
How to Cite a Tweet
How to cite photos, how to cite a newspaper article.
10 days ago
What Is a Reference Source?
How to cite evidence.
Image: unsplash.com

Citing textual evidence is critical to academic writing, professional communications, and even everyday discussions where arguments need to be supported by facts. Your ability to reference specific parts of a text improves credibility and strengthens your arguments, allowing you to present a well-rounded and persuasive case. For this reason, we wanted to give you a quick overview of how to cite evidence effectively, using one method in particular – the RACE strategy .
Introduction to Citing Text Evidence
The core reason for citing evidence is to lend credibility to an argument , showing the audience that the points being made are not just based on personal opinion but are backed by solid references. This practice is foundational in academic settings. There, the questions that students need to respond to are often constructed in a way that requires citing of evidence to support their answers. However, how can we make this process more quick and effectice? The answer lies in the RACE strategy, which is a special framework called to streamlines the process of citing textual evidence.
What is the RACE Strategy?
The RACE strategy stands for Restate, Answer, Cite evidence, and Explain. It is a methodical approach designed to help individuals construct well-structured answers that include textual proof. Let’s break down this method a little bit so you have some kind of impression on what we are going to talk about further.
- Restating the question or prompt in the introduction of the answer helps the writer to set the stage for a clear response.
- The direct answer, taht follows afterwards, presents the key point or thesis of the question.
- After we’e given an answer, we can move on to citing evidence, where we will integrate specific examples from the text to support the answer.
- Finally, we can move on to explaining our evidence. Here, it’s important to elaborating on how the cited examples support the argument we made.
This structured approach not only helps in organizing thoughts but also makes sure that the necessary components of a well-supported argument are present. Just like how to cite the constitution you have to be precise and factual. Let’s explore each step with actual examples to better illustrate how this strategy can help you with the process of citing textual evidence.
Restating basically means paraphrasing the original question or statement within your answer. This step demonstrates your understanding of the question and sets the stage for your response.
By answering directly, you respond to the question and therefore briefly present your main argument or thesis. You should stay clear and concise here, providing a straightforward statement of your position or understanding.
Cite Evidence
Citing evidence is where you integrate specific examples from the text to support your answer. This involves quoting or paraphrasing passages and pointing out where in the text your evidence can be found. Don’t forget to use quotation marks appropriately for direct quotes and to provide context for your citations or let a legal citation machine handle it.
For instance, to support the theme of racial injustice, you might cite evidence by saying,
When explaining, you elaborat on how your cited evidence supports your answer. This step connects your evidence back to your main argument, demonstrating a deeper understanding of the text.
After citing evidence, an explanation could be structured the following way,
To put it all together, here’s how an integrated response using the RACE strategy might look:
Response : ⬇

“The novel ‘To Kill a Mockingbird’ primarily explores themes such as racial injustice and the loss of innocence. One of the central themes is racial injustice, which is depicted through the trial of Tom Robinson and its impact on the town of Maycomb. Harper Lee illustrates this theme through the character of Atticus Finch, who states, ‘In our courts, when it’s a white man’s word against a black man’s, the white man always wins.’ (Lee, 1960, p. 295). This quote highlights the deeply ingrained racial biases within the judicial system of Maycomb, underscoring the novel’s critique of racial injustice and its effects on individuals and society as a whole.”
By following the RACE strategy and using actual examples, you can effectively structure clear and relevant responses that add depth to your argumentation. This method not only help in organizing thoughts but also in demonstrating a deep understanding of the text and its main topics.
However, there are a few nuances that you have to be aware of. The first one is the use of quotation marks. Don’t forget them when referencing direct quotes from a text, as they indicate that you took those words verbatim. Furthermore, you have to understand and use citation styles relevant to the discipline or context you write on. This will help you appropriately format your references and avoid unintentional plagiarizing. A quick tip: sentence starters and tags for dialogue can also help with introduction of quoted or paraphrased evidence effectively, as they let the reader or listener easily follow the argument’s progression.
Adapting the RACE Strategy for Distance Learning
Even in the case of distance learnign , the RACE strategy remains a valuable tool for teaching students how to cite evidence effectively. Digital resources such as Google Docs often offer collaborative platforms where teachers can share templates, sentence stems, and color-coded examples to guide students through the response building process.
Moreover, interactive activities facilitated through online tools, can further engage students in practicing citing evidence, with digital resources providing immediate feedback and opportunities for revision. This adaptation help develop the skill of citing textual evidence even in a remote learning setting.
It’s hard to argue that citing textual evidence is useful skill that can help you get far in your academic writing as well as in other more professional fields. Following the RACE strategy and using our tips on referencing, you, as students, can create well-structured and compelling responses (which no professor could argue with).
How can I use the RACE strategy to improve my essay writing?
You can use the RACE strategy to structure your paragraphs or entire essays by ensuring that each section includes a restatement of the question (if applicable), a clear answer or thesis statement, cited evidence from your sources, and an explanation of how this evidence supports your argument. This approach can enhance clarity, coherence, and persuasiveness.
What are some tips for effectively citing evidence in my writing?
Some tips for effectively citing evidence are: using direct quotes from the text with proper quotation marks, paraphrasing accurately while maintaining the original meaning, providing specific examples, and ensuring that your citations are relevant and support your argument. Always include page numbers or other locator information if available.
Is the RACE strategy useful for standardized tests or only for classroom assignments?
The RACE strategy is beneficial for a wide range of writing tasks, including standardized tests, classroom assignments, and even professional writing. Its structured approach to constructing responses makes it a valuable tool for any situation requiring evidence-based writing.
Follow us on Reddit for more insights and updates.
Comments (0)
Welcome to A*Help comments!
We’re all about debate and discussion at A*Help.
We value the diverse opinions of users, so you may find points of view that you don’t agree with. And that’s cool. However, there are certain things we’re not OK with: attempts to manipulate our data in any way, for example, or the posting of discriminative, offensive, hateful, or disparaging material.
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
More from Citation Guides

How To Cite A Source With No Author

How To Cite A Lecture in MLA

Remember Me
What is your profession ? Student Teacher Writer Other
Forgotten Password?
Username or Email
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
In-Text Citations: The Basics

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Note: This page reflects the latest version of the APA Publication Manual (i.e., APA 7), which released in October 2019. The equivalent resource for the older APA 6 style can be found here .
Reference citations in text are covered on pages 261-268 of the Publication Manual. What follows are some general guidelines for referring to the works of others in your essay.
Note: On pages 117-118, the Publication Manual suggests that authors of research papers should use the past tense or present perfect tense for signal phrases that occur in the literature review and procedure descriptions (for example, Jones (1998) found or Jones (1998) has found ...). Contexts other than traditionally-structured research writing may permit the simple present tense (for example, Jones (1998) finds ).

APA Citation Basics
When using APA format, follow the author-date method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the year of publication for the source should appear in the text, like, for example, (Jones, 1998). One complete reference for each source should appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
If you are referring to an idea from another work but NOT directly quoting the material, or making reference to an entire book, article or other work, you only have to make reference to the author and year of publication and not the page number in your in-text reference.
On the other hand, if you are directly quoting or borrowing from another work, you should include the page number at the end of the parenthetical citation. Use the abbreviation “p.” (for one page) or “pp.” (for multiple pages) before listing the page number(s). Use an en dash for page ranges. For example, you might write (Jones, 1998, p. 199) or (Jones, 1998, pp. 199–201). This information is reiterated below.
Regardless of how they are referenced, all sources that are cited in the text must appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
In-text citation capitalization, quotes, and italics/underlining
- Always capitalize proper nouns, including author names and initials: D. Jones.
- If you refer to the title of a source within your paper, capitalize all words that are four letters long or greater within the title of a source: Permanence and Change . Exceptions apply to short words that are verbs, nouns, pronouns, adjectives, and adverbs: Writing New Media , There Is Nothing Left to Lose .
( Note: in your References list, only the first word of a title will be capitalized: Writing new media .)
- When capitalizing titles, capitalize both words in a hyphenated compound word: Natural-Born Cyborgs .
- Capitalize the first word after a dash or colon: "Defining Film Rhetoric: The Case of Hitchcock's Vertigo ."
- If the title of the work is italicized in your reference list, italicize it and use title case capitalization in the text: The Closing of the American Mind ; The Wizard of Oz ; Friends .
- If the title of the work is not italicized in your reference list, use double quotation marks and title case capitalization (even though the reference list uses sentence case): "Multimedia Narration: Constructing Possible Worlds;" "The One Where Chandler Can't Cry."
Short quotations
If you are directly quoting from a work, you will need to include the author, year of publication, and page number for the reference (preceded by "p." for a single page and “pp.” for a span of multiple pages, with the page numbers separated by an en dash).
You can introduce the quotation with a signal phrase that includes the author's last name followed by the date of publication in parentheses.
If you do not include the author’s name in the text of the sentence, place the author's last name, the year of publication, and the page number in parentheses after the quotation.
Long quotations
Place direct quotations that are 40 words or longer in a free-standing block of typewritten lines and omit quotation marks. Start the quotation on a new line, indented 1/2 inch from the left margin, i.e., in the same place you would begin a new paragraph. Type the entire quotation on the new margin, and indent the first line of any subsequent paragraph within the quotation 1/2 inch from the new margin. Maintain double-spacing throughout, but do not add an extra blank line before or after it. The parenthetical citation should come after the closing punctuation mark.
Because block quotation formatting is difficult for us to replicate in the OWL's content management system, we have simply provided a screenshot of a generic example below.

Formatting example for block quotations in APA 7 style.
Quotations from sources without pages
Direct quotations from sources that do not contain pages should not reference a page number. Instead, you may reference another logical identifying element: a paragraph, a chapter number, a section number, a table number, or something else. Older works (like religious texts) can also incorporate special location identifiers like verse numbers. In short: pick a substitute for page numbers that makes sense for your source.
Summary or paraphrase
If you are paraphrasing an idea from another work, you only have to make reference to the author and year of publication in your in-text reference and may omit the page numbers. APA guidelines, however, do encourage including a page range for a summary or paraphrase when it will help the reader find the information in a longer work.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Using Evidence: Citing Sources Properly
Citing sources properly is essential to avoiding plagiarism in your writing. Not citing sources properly could imply that the ideas, information, and phrasing you are using are your own, when they actually originated with another author. Plagiarism doesn't just mean copy and pasting another author's words. Review Amber's blog post, "Avoiding Unintentional Plagiarism," for more information! Plagiarism can occur when authors:
- Do not include enough citations for paraphrased information,
- Paraphrase a source incorrectly,
- Do not use quotation marks, or
- Directly copy and paste phrasing from a source without quotation marks or citations.
Read more about how to avoid these types of plagiarism on the following subpages and review the Plagiarism Detection & Revision Skills video playlist on this page. For more information on avoiding plagiarism, see our Plagiarism Prevention Resource Kit .
Also make sure to consult our resources on citations to learn about the correct formatting for citations.
What to Consider
Citation issues can appear when writers use too much information from a source, rather than including their own ideas and commentary on sources' information. Here are some factors to consider when citing sources:
Remember that the cited material should illustrate rather than substitute for your point. Make sure your paper is more than a collection of ideas from your sources; it should provide an original interpretation of that material. For help with creating this commentary while also avoiding personal opinion, see our Commentary vs. Opinion resource.
The opening sentence of each paragraph should be your topic sentence , and the final sentence in the paragraph should conclude your point and lead into the next. Without these aspects, you leave your reader without a sense of the paragraph's main purpose. Additionally, the reader may not understand your reasons for including that material.
All material that you cite should contribute to your main argument (also called a thesis or purpose statement). When reading the literature, keep that argument in mind, noting ideas or research that speaks specifically to the issues in your particular study. See our synthesis demonstration for help learning how to use the literature in this way.
Most research papers should include a variety of sources from the last 3-5 years. You may find one particularly useful study, but try to balance your references to that study with research from other authors. Otherwise, your paper becomes a book report on that one source and lacks richness of theoretical perspective.
Direct quotations are best avoided whenever possible. While direct quotations can be useful for illustrating a rhetorical choice of your author, in most other cases paraphrasing the material is more appropriate. Using your own words by paraphrasing will better demonstrate your understanding and will allow you to emphasize the ways in which the ideas contribute to your paper's main argument.
Plagiarism Detection & Revising Skills Video Playlist

Citing Sources Video Playlist

Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Search our website or email us .
Read our website accessibility and accommodation statement .
- Previous Page: Synthesis
- Next Page: Not Enough Citations
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
Generate accurate APA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- APA Style 7th edition
How to Cite in APA Format (7th edition) | Guide & Generator

This citation guide outlines the most important citation guidelines from the 7th edition APA Publication Manual (2020). Scribbr also offers free guides for the older APA 6th edition , MLA Style , and Chicago Style .
Generate accurate APA citations with Scribbr
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text.
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Apa in-text citations, apa references, formatting the apa reference page, free lecture slides, frequently asked questions.
In-text citations are brief references in the running text that direct readers to the reference entry at the end of the paper. You include them every time you quote or paraphrase someone else’s ideas or words to avoid plagiarism .
An APA in-text citation consists of the author’s last name and the year of publication (also known as the author-date system). If you’re citing a specific part of a source, you should also include a locator such as a page number or timestamp. For example: (Smith, 2020, p. 170) .
Parenthetical vs. narrative citation
The in-text citation can take two forms: parenthetical and narrative. Both types are generated automatically when citing a source with Scribbr’s APA Citation Generator.
- Parenthetical citation: According to new research … (Smith, 2020) .
- Narrative citation: Smith (2020) notes that …
Multiple authors and corporate authors
The in-text citation changes slightly when a source has multiple authors or an organization as an author. Pay attention to punctuation and the use of the ampersand (&) symbol.
Missing information
When the author, publication date or locator is unknown, take the steps outlined below.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
APA references generally include information about the author , publication date , title , and source . Depending on the type of source, you may have to include extra information that helps your reader locate the source.
Reference examples
Citing a source starts with choosing the correct reference format. Use Scribbr’s Citation Example Generator to learn more about the format for the most common source types. Pay close attention to punctuation, capitalization, and italicization.
Generate APA citations for free
It is not uncommon for certain information to be unknown or missing, especially with sources found online. In these cases, the reference is slightly adjusted.
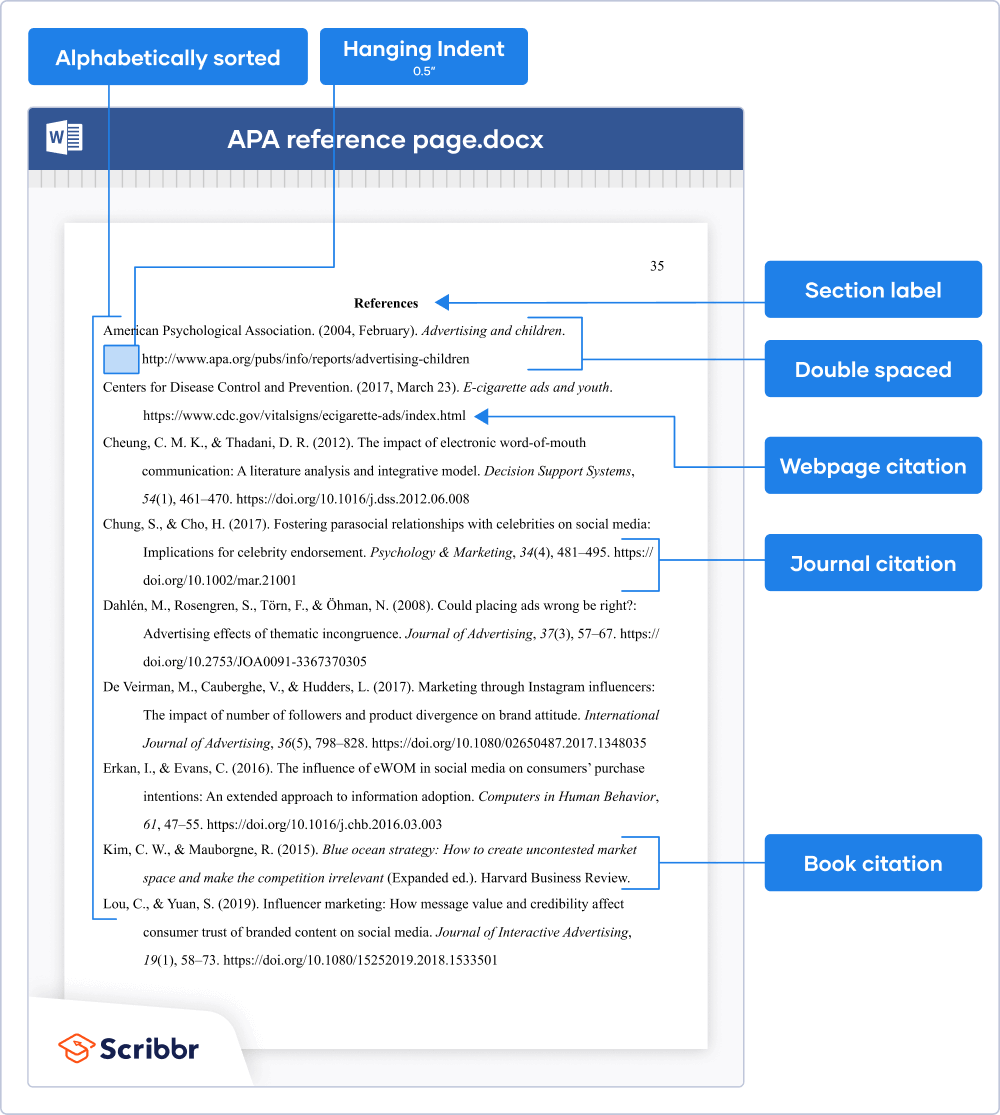
On the first line of the page, write the section label “References” (in bold and centered). On the second line, start listing your references in alphabetical order .
Apply these formatting guidelines to the APA reference page:
- Double spacing (within and between references)
- Hanging indent of ½ inch
- Legible font (e.g. Times New Roman 12 or Arial 11)
- Page number in the top right header
Which sources to include
On the reference page, you only include sources that you have cited in the text (with an in-text citation ). You should not include references to personal communications that your reader can’t access (e.g. emails, phone conversations or private online material).
Are you a teacher or professor looking to introduce your students to APA Style? Download our free introductory lecture slides, available for Google Slides and Microsoft PowerPoint.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
Are your APA in-text citations flawless?
The AI-powered APA Citation Checker points out every error, tells you exactly what’s wrong, and explains how to fix it. Say goodbye to losing marks on your assignment!
Get started!

When no individual author name is listed, but the source can clearly be attributed to a specific organization—e.g., a press release by a charity, a report by an agency, or a page from a company’s website—use the organization’s name as the author in the reference entry and APA in-text citations .
When no author at all can be determined—e.g. a collaboratively edited wiki or an online article published anonymously—use the title in place of the author. In the in-text citation, put the title in quotation marks if it appears in plain text in the reference list, and in italics if it appears in italics in the reference list. Shorten it if necessary.
When you quote or paraphrase a specific passage from a source, you need to indicate the location of the passage in your APA in-text citation . If there are no page numbers (e.g. when citing a website ) but the text is long, you can instead use section headings, paragraph numbers, or a combination of the two:
(Caulfield, 2019, Linking section, para. 1).
Section headings can be shortened if necessary. Kindle location numbers should not be used in ebook citations , as they are unreliable.
If you are referring to the source as a whole, it’s not necessary to include a page number or other marker.
The abbreviation “ et al. ” (meaning “and others”) is used to shorten APA in-text citations with three or more authors . Here’s how it works:
Only include the first author’s last name, followed by “et al.”, a comma and the year of publication, for example (Taylor et al., 2018).
APA Style usually does not require an access date. You never need to include one when citing journal articles , e-books , or other stable online sources.
However, if you are citing a website or online article that’s designed to change over time, it’s a good idea to include an access date. In this case, write it in the following format at the end of the reference: Retrieved October 19, 2020, from https://www.uva.nl/en/about-the-uva/about-the-university/about-the-university.html
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- Beginner's guide to APA in-text citation
- Setting Up the APA Reference Page | Formatting & References (Examples)
- APA 7th edition: The most notable changes
More interesting articles
- APA Footnotes | Format & Examples
- APA format for academic papers and essays
- APA headings and subheadings
- APA running head
- APA Title Page (7th edition) | Template for Students & Professionals
- Creating an APA Style table of contents
- Creating APA reference entries
- Direct quotes in APA Style
- How to create an APA Style appendix
- How to format tables and figures in APA Style
- How to write an APA methods section
- How to write an APA results section
- How to write and format an APA abstract
- Ordering works on the APA reference page
- Reporting Statistics in APA Style | Guidelines & Examples
- Writing in APA Style: Language guidelines
Scribbr APA Citation Checker
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
When you cite a work that appears inside a larger source (for instance, an article in a periodical or an essay in a collection), cite the author of the internal source (i.e., the article or essay). For example, to cite Albert Einstein's article "A Brief Outline of the Theory of Relativity," which was published in Nature in 1921, you might write ...
As a writer, you need to supply the most relevant evidence for claims and counterclaims based on what you know about your audience. Your claim is your position on the subject, while a counterclaim is a point that someone with an opposing view may raise. Pointing out the strengths and limitations of your evidence in a way that anticipates the ...
Quotes should always be cited (and indicated with quotation marks), and you should include a page number indicating where in the source the quote can be found. Example: Quote with APA Style in-text citation. Evolution is a gradual process that “can act only by very short and slow steps” (Darwin, 1859, p. 510).
An in-text citation can be included in one of two ways as shown below: 1. Put all the citation information at the end of the sentence: 2. Include author name as part of the sentence (if author name unavailable, include title of work): Each source cited in-text must also be listed on your Works Cited page. RefWorks includes a citation builder ...
Create manual citation. The guidelines for citing an essay in MLA format are similar to those for citing a chapter in a book. Include the author of the essay, the title of the essay, the name of the collection if the essay belongs to one, the editor of the collection or other contributors, the publication information, and the page number (s).
Citing textual evidence is critical to academic writing, professional communications, and even everyday discussions where arguments need to be supported by facts. Your ability to reference specific parts of a text improves credibility and strengthens your arguments, allowing you to present a well-rounded and persuasive case.
APA Citation Basics. When using APA format, follow the author-date method of in-text citation. This means that the author's last name and the year of publication for the source should appear in the text, like, for example, (Jones, 1998). One complete reference for each source should appear in the reference list at the end of the paper.
To quote a source, copy a short piece of text word for word and put it inside quotation marks. To paraphrase a source, put the text into your own words. It’s important that the paraphrase is not too close to the original wording. You can use the paraphrasing tool if you don’t want to do this manually.
Citing sources properly is essential to avoiding plagiarism in your writing. Not citing sources properly could imply that the ideas, information, and phrasing you are using are your own, when they actually originated with another author. Plagiarism doesn't just mean copy and pasting another author's words. Review Amber's blog post, "Avoiding ...
On the first line of the page, write the section label “References” (in bold and centered). On the second line, start listing your references in alphabetical order. Apply these formatting guidelines to the APA reference page: Double spacing (within and between references) Hanging indent of ½ inch.