SWOTAnalytica.com
Swot analysis of competing against bling hbr case study.
Home >> Hbr >> Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study

Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study SWOT Analysis
Introduction.

K-C (Kimberly Clark) and P&G (Procter and Gambler) are 2 huge competitors in the disposable Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study market of the U.S. The non reusable Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study was created in Sweden, and was introduced to America in the late 1940s. In the early years, the Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study were utilized with attaching pins and plastic trousers, which was typically viewed as ineffectiveness in keeping both the babies and the parents dry. The innovation of the non reusable Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study case analysis appeared to be an appealing concept for both the firms and both the firms participated in the disposable industry after having various researches. Throughout the previous 3 years, both the companies were having a hard time in order to establish the best method to make the Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study byusing various innovations with a goal to gain the big pie of consumer in the market and build a competitive edge over one another. Both the business have actually done numerous innovations in the Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study and kept doing researches to improve the quality of the Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study case help and make a competitive position in the industry. K-C (Kimberly Clark) and P&G (Procter and Gambler) used different strategies in order to acquire high revenue margins to please their customers. Both the gamers dominated the market with P&G and K-C having a market share of 49% and 32% respectively. Both players in the industry reacted to the techniques of each other very successfully and came up with different modified and appealing non reusable Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study (Mclellan, 1999).
Problem Statement
Both the dominating gamers of the non reusable industry are dealing with various problems while combating a competitive war. The competitive struggle involves abroad series of problems including financial restrictions, fast product development, worldwide threats and opportunities, diversity choices and public pressure on environmental issues, the entryway of overseas business in the industry along with numerous technological advancement. In addition, P&G has actually introduced its recent development and K-Cis yet to decide that how to respond to this development. The entryway of P&G gender-specific non reusable Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study case solution in the market have forced K-C to test a similar item to avoid the danger of declining market share. The manager has to decide on how to respond to the brand-new development of P&G to maintainits present market position.
Situational Analysis
Porter’s five forces model:, the threat of new entrants:.
The danger of brand-new entrants in the Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study market in the U.S is considered to be low, due to the fact that the Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study market is alreadycomposed of dominating players, which is why the entryway of newbies in the market would not impact the existing gamers. The market of the Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study is really saturated, and the rivalry amongst the rivals is already high which is creating numerous obstacles for the beginner to make their location in the market. It requiresa substantial startup expense as well as a strong research study to go into the market.High advertising cost and the strong supply chain network has actually decreased the intensity of the brand-new entrants' risk in the Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study market.
Bargaining Power of Buyer:

Bargaining Power of Supplier:
The bargaining power of purchasers in the Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study industry is thought about to be high to moderate. Few gamers in the market, such as: K-C makes its own plastic for Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study, which moderate the bargaining power of supplier. There is not any substitute available in the market thatcould be used for making non reusable Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study, for that reason, it reinforces the bargaining power of the provider.
The threat of Substitute:
The danger of replacement is extremely high in the US Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study industry. The major factor behind the high danger of substitution is due to low differentiation amongst the items and the readily schedule of the substitute of Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study, such as: cotton or washable napkins.
Competitive Rivalry:
Competitive competition in the disposable Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study industry is intense. It can be evaluated by the existing Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study case solution war between two dominant gamers in the industry. Both spend much of their amounts in advertising and R&D activities in order to get more market share. Additionally, the products are truly identical, the switching cost is considered to be zero and the players in the market utilize different strategies in order to get the marketplace share.
Porter’s Five Forces Model
Swot analysis:.

One of the primary strength of K-C is that the business is mostly focusing on brand-new production technology. The company has a strong history of innovation, and is among the dominating players in the US Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study industry, due to its strong brand. Like P&G, the business has actually not completely concentrated on the innovation of Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study case solution. The company also focuses on its other departments with an objective of diverting its success. The company is highly experienced in the individual care category and has a strong circulation network. One of the strengths of the business is that the business formulates its techniques after having a thorough analysis and by measuring its profitability. (Sammut-Bonnici & Galea, 2015).
Weaknesses:
Another weak point of the company is that the companyentered into the Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study case analysis industry after P&G's entryway, which t is why the business does not have the first mover advantage. The business is utilizing old approaches in the process of producing its Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study.However, the rivals of the business have actually developed new techniques of manufacturing Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study, which are considered to be cost reliable and help the business in cutting their overhead cost.
Opportunities:
Advertisingcan help the company to improve its sales and success by spreading awareness among the customers concerning the new functions of the product being introduced by the business. The company has a chance to utilize an innovative technology in the manufacturing of Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study, which could result in the reduction of per-unit cost leading the business to be ableto offer its Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study at a lower expense to the price sensitive customers. Furthermore, the company has a chance to focus on the modification of its Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study by providingadvanced and ecological friendly features in the products.
The change in government policies relating to Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study production is thought about to be one of the greatest threats for the business. By having a fast change in technology, thenew developments in the market may increase the success of the company.
SWOT Analysis
Pestle analysis:, political factors:.
The political scenario in the U.S seems to be quiet steady. Many political aspects carry the propensity to effect the efficiency of a company, such as: strict regulation concerning the disposal of the solid waste increase the opportunities for the company and improve sales. Non reusable Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study are considered to be moredangerous and harmful for the environment in comparison to material Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study, due making use of non-biodegradable plastic in non reusable Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study.Therefore it is highly slammed by ecological neighborhoods. Due to this element, the business that areselling disposable Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study are extremely impacted by the political forces in comparison to the business that are offering material basedCompeting Against Bling Hbr Case Study. These forces can be lowered if the business starts usingbiodegradable plastic technology, like the one that is being utilized in Japan.
Economic Factors:

Social Factors:
In the U.S, the concerns of the females are changing, because now every woman wishes to be independent, for which they have inclined towards pursuing their expert lives, which often cause a hold-up in the kid birth. There are more than 70% ofwomen operating in the United States. As working ladies prefer more time saving items, than the products that take in more time, due to their hectic schedules.Therefore, they choose disposable Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study case help over fabric or fabricCompeting Against Bling Hbr Case Study. Additionally, the disposalincome of U.S is high due to which the ladies can manage the extra cost for Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study rather than utilizing fabric Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study.
Technological Factors:
Due to an extreme competitors in the market and with a supreme aim of getting bigger pie in the market, the company has actually been revealing an interest in moving towards the technological advancement. The extreme technological forces have forced the business to spend more on its R&D sector to make technological enhancements and development possible. The environmental concerns likewise require the business to move towards the use of high technology, which is considered to be ecological friendly and containsless use of non-biodegradable plastics, which likewise helps in handling the business's products' diversification.
Environmental Factors:
Due to making use of non-biodegradable plastics; the market has been facinghuge criticism by the environmental neighborhoods. The plastics usedin Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study case help trigger contamination and position a risk to the health of people. In order to avoid thecriticism over the industry, K-C and P&G both have actually performed different recycling tasks, andare making considerable efforts to adopt the Japanese technology of producing non reusable Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study with reducedand no percent non-biodegradable plastic.
Legal Factors:
The disposal solid waste act 1976 limits the companies to use non-biodegradable plastics in their Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study, due to which the cost of the business's Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study would increase. Different groups put pressure on the industry to use ecological friendly techniques and equipment, which likewise impose restrictions and oblige the business to use ecofriendly practices, otherwise the companycould be faced with harsh criticism and a number of legal notifications.
PETEL Analysis
Reactive and anticipatory change.

P&G adopted technological improvement later and also accepted the quality advancement technique when other countries were currently using that, which is why P&G was dealing with some decreasing trends in its sales as compared to Kimbie's and Huggies.
Kimbies and Clark examined the capacity in the market concerning the acceptance of the sterilized items then they started focusing on making the fluff pulp item so that the tissue could get attracted towards using more sanitized product.
Anticipatory modifications refer to the changes that a management should carry out after preparing a change strategy. It is an organized change that might be executed for the improvement of any business.
When it chose to embrace the technological advancement, kimbies and Clark was bringing the modification. Increased the sales profits for K-C since of this approval of technological improvement their Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study called Huggies.
Suggested Alternatives
Alternative-1: introduction of specific gender disposable competing against bling hbr case study case help at national level:.
Among the recommended alternatives to K-C is that the company ought to present its gender particular disposable Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study at the nationwide level. The reason behind the present of gender specific alternative is that the introduction would enhance the competitive position of the company. The benefits and drawbacks of the introduction of specific gender non reusable Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study at the international level are as follows:
- Signals to be responsive in the market against the competitors' activities.
- Permits the business to cover more group sector and maintain its competitive edge.
- The launch of gender specific Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study would preserve the competitive position of K-C in the United States Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study market.
- It would avoid the danger of catching more market share by P&G through it's His and Her disposable Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study.
- The extra set expense would be required in order to make and market the item, such as: marketing and marketing expense which ultimately affect the profitability of the company.
- The item is new to the market and customers, and the action of the clients towards the item is unknown, which untimely increases the uncertainty about the product.
- The item is brand-new to the market, so it also tends of possess high opportunities of failure.
Alternative-2:Introduce Similar Product with Few Modification
Another suggestive alternative for the business is that the company can also present a comparable item to its competitor in order to keep its competitive position in the market. The pros and cons are as follows:
- The intro of a comparable product would help the company to keep its competitive position in the industry.
- Modification in the comparable item would bring in new client, whichwould help the business to gain more market share in addition to toimprove its profitability.
- It would prove to be a brand-new product, and Particular Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study would be the extension of the features in the existing item.
- Adjustment may offer first mover benefit to the company.
- The unknown response by the clients towards the modification.
- Intensive capital is requiredforthe introduction of brand-new product.
- Chances of failure of the brand-new item.
Alternative-3: Focus On Geographical Expansion
Another suggestive option is that the business can focus on geographical growth. The advantages and disadvantages of this option are as follows:
- Improve brand acknowledgment and success of the company throughits worldwide presence.
- Attract brand-new clients by engaging in the new markets.
- The company has a possibility to accomplish economies of scale through international sales.
- Improve the profitability and competitive position of the business.
- Numerous cultures and environmental barriers among different nations.
- Substantial capital investment is needed forthe geographical growth.
- K-C may fail to get potential sales from worldwide markets with an extreme competition and hard competitors with high innovations.
Alternative-4:Invest In Technology and Advertising
Another suggestive option is that the business should purchase advertising and marketing activities and adopt high technological equipment. The pros and cons of this alternative are as follows:
- Advertising draws in new customers, which enhances the customer base of the business.
- Advance technology helps the company to adopt advance procedure through which the companywould be able to cut its numerous overhead expenses and import production capacity.
- It would offer a high sales development to K-C than particular disposable products, as the marketplace segment has more possible to grow as compared to thesaturated market sector of non reusable Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study.
- Enhances the credibility of the business, because the new technology would be environmentally friendly.
- The clients would be able to gain an insight of the features being presented in the business's product
- Huge capital expense is required in upgrading the technology and marketing activities.
- Strategies of the business would be simple to imitate.
- The trained workforce would be needed to deal with the new product of the business.
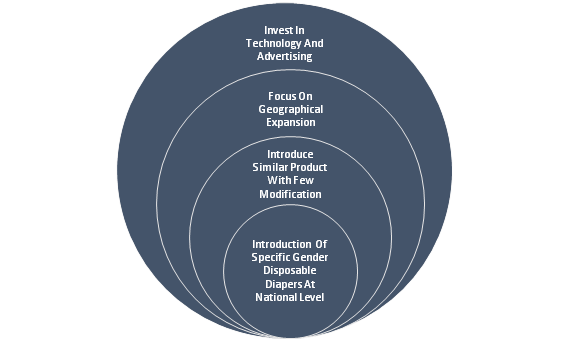
Recommendation
On the basis of the above analysis, it is advised that the business must focus on the introduction of a similar product than its competitors, who have actually currently introduced few adjustments and have their major focus on geographical growths. The factor behind recommending these options are: introduction of comparable item with couple of modifications would help the business to bring in more consumers and would increase the portfolio of the company. In addition, couple of modifications would supply safety to the business from any legal obligations. Through an expansion, the business would have the ability to enhance its consumer base and would have a new market for its present product, which would ultimately improve the success and sales of the companyand supply a competitive edge to the company.
On the basis of analysis, it is concluded that both the business have actually been controlling the Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study case analysis market from the last 4 decades. They are competinghighly on the introduction of brand-new innovations to lower their expenses, improvean existing item or to present brand-new ones. Both the business have taken the competition to different markets by making their presences intothe worldwide markets and having production plants in various local areas throughout the Europe and Asia. In order to increase its sales, the company should move towards geographical expansion. This would help the business to improve its customer base and would allow it to keep its competitive position in the Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study' market. Additionally, the business must customize its products in order to acquire the attention of the customer towards its product, and to inhabit a significant market position.
Copyright © - All Rights Reserved - SWOTAnalytica.com

Provide details on what you need help with along with a budget and time limit. Questions are posted anonymously and can be made 100% private.

Studypool matches you to the best tutor to help you with your question. Our tutors are highly qualified and vetted.

Your matched tutor provides personalized help according to your question details. Payment is made only after you have completed your 1-on-1 session and are satisfied with your session.

- Homework Q&A
- Become a Tutor
All Subjects
Mathematics
Programming
Health & Medical
Engineering
Computer Science
Foreign Languages
Access over 20 million homework & study documents
Competing against bling.
Sign up to view the full document!

24/7 Homework Help
Stuck on a homework question? Our verified tutors can answer all questions, from basic math to advanced rocket science !

Similar Documents
working on a homework question?
Studypool is powered by Microtutoring TM
Copyright © 2024. Studypool Inc.
Studypool is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university.
Ongoing Conversations

Access over 20 million homework documents through the notebank
Get on-demand Q&A homework help from verified tutors
Read 1000s of rich book guides covering popular titles

Sign up with Google
Sign up with Facebook
Already have an account? Login
Login with Google
Login with Facebook
Don't have an account? Sign Up
- Forgot Password
Get 10% Off on Your Next Order
Subscribe now to get your discount coupon *Only correct email will be accepted
Enter Your Verification Code
Approx. ~ 1 page(s)
Total Price
Thank you for your email subscription. Check your email to get Coupon Code.
Marketing Mix (4Ps) Analysis of COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY
Posted by Addison on Jul-19-2022
About 4Ps Model
The 4p model of marketing comprises elements of the product, price, promotion, and place (Chernev, 2018; Kucuk, 2017). The model is commonly referred to as the marketing mix. The marketing mix of the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY allows and facilitates it in achieving its marketing objectives as well as in positively influencing the target audience (Baines, Fill, & Rosengren, 2017). The elements identified in the marketing mix are typically used by the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY for marketing its product and service, and for brand development and building activities. These elements are critically fundamental for the development and creation of marketing plans and marketing strategies by the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY – especially for developing and sustaining competitive advantage (Chernev, 2018; Stead & Hastings, 2018; Grewal & Levy, 2021). COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY ensures that the elements identified for the marketing mix model work together cohesively, and complement each other in all its marketing strategies and plans (Abratt & Bendixen, 2018; Deepak & Jeyakumar, 2019).
The product refers to the actual good or service that is being marketed to the consumers by COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY, and which will be consumed by the target audience of the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY (Groucutt & Hopkins, 2015). The product or the service being offered by COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY largely aims to fulfill a market need and demand, as well as works to create demand by providing a unique and fulfilling customer experience (Stead & Hastings, 2018; Sahaf, 2019).
Product quality for COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY largely refers to how well the company is able to satisfy the customers’ needs and demands through its product and service offerings (Baines, Fill, & Rosengren, 2017; Deepak & Jeyakumar, 2019). In addition to this, the product quality for COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY further includes the adherence of the company and its product and service offerings to industry standards and benchmarks as well as the ability of the same to serve its meaning and purpose comprehensively (Iacobucci, 2021; Groucutt & Hopkins, 2015; Chernev, 2018).
Customer demand fulfillment
The ability of the product and service to fulfill customer demands as well as its purpose, and to work efficiently and effectively are important facets of product quality for COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY (Iacobucci, 2021; Deepak & Jeyakumar, 2019). COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY ensures that its products are available for customers at affordable prices by controlling internal costs (Wu & Li, 2018).
The warranty extended by COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY includes the guarantee that the company to its customers regarding the functioning and the quality of the purchased food and service (Abratt & Bendixen, 2018). In addition, COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY’s warranty also includes any compensation that the company has promised to give the customers in case the product and service fall short of the marketed benefits and functionalities (Išoraitė, 2016; Grewal & Levy, 2021; Kucuk, 2017).
COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY focuses thoroughly on the packaging and makes sure it includes the process of designing, evaluating, and developing a container for the products and services being manufactured and marketed (Deepak & Jeyakumar, 2019; Baines, Fill, & Rosengren, 2017). The packaging of the product and the service allows COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY to highlight the product's purpose, as well as provides ease in transportation, gives room for more prolonged shelf life, and creates a unique and delightful customer experience (Kareh, 2018; Park, 2020).
The COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY invests in developing brands out of its products and service offerings. This means that the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY engages in brand-building activities for its offerings i.e. associating specific designs and communications with its products to ensure differentiation, and easier communication with the target audience (Gillespie & Swan, 2021).
Building the brand
The branding-building activities undertaken by the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY ensure that its target audience is better able to relate to the offerings (Abratt & Bendixen, 2018). Through this, the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY ensures higher loyalty and repeat purchases, as well as positive perception creation for its offerings (Khan, 2014; Kareh, 2018).
Product features or characteristics refer to the product traits and attributes present in the offerings of COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY that allow the company to successfully deliver unique value to customers through the products and services manufactured and offered (Varadarajan, 2015; Kotler & Keller, 2021). The product traits and features also allow COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY to create points of differentiation from the competition for its offering (Kotler & Keller, 2021; Park, 2020).
Product style
COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY makes sure to focus on the design and the look of the product, and the ability of the same to meet the expectations and lifestyle of the target audience (Groucutt & Hopkins, 2015). The COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY ensures that the product style and design complement its features and purpose.
Functionality
COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY makes sure that the product manufactured fulfills its purpose, and meets customer expectations (Abratt & Bendixen, 2018). COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY focuses on the product design, and how well it is able to fulfill the demands of the customers, as well as fill in the market gap (Baines, Fill, & Rosengren, 2017)
COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY products provide the customers with an exceptional and unique experience upon consumption (Kotler & Keller, 2021). This experience includes interaction with the products that leads to different unique and positive customer feelings and helps the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY maintain differentiation from the competition (Varadarajan, 2015; Kotabe & Helsen, 2020).
Availability
COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY ensures that its product and service offerings are available for its target consumers at various retail setups. The easy availability ensures that consumers are able to purchase the offerings of COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY from various locations, allowing the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY to create an advantage over competing players (Kotler & Keller, 2021; Chernev, 2018).
Convenience
One point of focus for COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY in its product offering is convenience. The COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY ensures that its products and service are easy and convenient to use. The factor of convenience allows COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY to enjoy a higher consumption rate, as well as increased sales and trials (Kotabe & Helsen, 2020; Kucuk, 2017).
After-sales service
COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY caters to after-sales queries and demands of customers, which also includes processes of returns as well as exchanges. The after-sales service of company COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY is detrimental and critical in determining customer satisfaction with its offerings (Iacobucci, 2021; Chernev, 2018).
COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY has different SKUs in the product available. COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY has its products available in various SKU sizes which helps the company boost its sales, as different customer groups have different demands for the product quantity – depending on their usage, income as well as lifestyle (Grewal & Levy, 2021; Deepak & Jeyakumar, 2019).
The element of price in the marketing mix refers to the value that customers pay for the service or the product offered by COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY. The pricing strategy and the price of the offerings are critical because it determines three success for COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY by directly influencing the profit levels and revenue for the company (Kotabe & Helsen, 2020; Kotler & Keller, 2021; Deepak & Jeyakumar, 2019).
One of the ways through which the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY influences its pricing strategies is through offering discounts on its product and service offerings. Discounted pricing for the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY means that COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY decreases the price of the product and service in order to generate interest, or even unload excessive inventory and stock; as well as for boosting sales (Baines, Fill, & Rosengren, 2017).
COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY makes room for margins through the additional value charged in price over the cost – which allows the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY to build profit for its offerings (Kucuk, 2017). The margins available to the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY largely depend on the offering and its quality itself, in addition to the brand equity and brand value of the company.
Payment method
A significant factor of the pricing element of the marketing mix for the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY includes the payment methods that the company offers (Kotler & Keller, 2021; Abratt & Bendixen, 2018). Since the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY largely operates distribution to retail via agents and retailers, it ensures the inclusion of different payment methods. This includes digital payment, cash payment, as well as credit allowances (Grewal & Levy, 2021; Groucutt & Hopkins, 2015).
Pricing strategy
Penetrative pricing strategy.
For COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY, the penetrative pricing strategy is adopted as it allows the company higher trial generation of its products and services in the desired target market, as well as allows the building of a broader reach for its product offerings by ensuring easier affordability (Baines, Fill, & Rosengren, 2017).
Introductory pricing strategy
For new products that the company launches, COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY ensures to adopt an introductory pricing strategy. This means that the company prices its products and service offerings at relatively lower prices than the competition. This introductory pricing strategy allows the company to increase trial generation, achieve higher penetration, as well as lead to the generation of increased brand awareness and recall (Kucuk, 2017).
Aggressive/competitive pricing strategy
For existing products, COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY uses a competitive and aggressive pricing strategy. This ensures that the products are available readily at competitive prices. Aggressive and competitive pricing strategies allow the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY to experience high rates of growth and experience by allowing the buildup of consumer loyalty and following based largely on product attributes and quality instead of price– leading to the generation of higher brand equity and value for COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY (Deepak & Jeyakumar, 2019).
The element of place within the 4Ps model of the marketing mix largely refers to the locations where company COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY stocks its product and service offerings for consumers' accessibility and purchase. COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY ensures to include all possible placements which are easily accessible to and available for the company's target audience (Iacobucci, 2021; Išoraitė, 2016). With the advancement of technology, COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY has expanded the placement of its products beyond the traditional brick-and-mortar retail spaces, to include modern Omni channel retail platforms as well (Iacobucci, 2021).
Physical stores/retail
The physical retail and stores i.e. the traditional brick and mortar spaces continue to be the prioritized locations for product placement by COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY (Iacobucci, 2021; Groucutt & Hopkins, 2015; Abratt & Bendixen, 2018).
Retail types
These include hypermarkets, upper markets, and smaller grocery stores - all of which allow increased accessibility and availability of COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY’s products and services to its target audience. Physical retail has a higher footfall and allows direct interaction of the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY brand and its product offerings with the consumers (Groucutt & Hopkins, 2015; Groucutt & Hopkins, 2015; Chernev, 2018).
The COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY also stocks its products on e-commerce retail shops – such as amazon. This allows the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY higher access and penetration in other markets, as well as in secondary consumer groups. Moreover, e-commerce retailing is more cost-effective for the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY (Wu & Li, 2018; Chernev, 2018; Baines, Fill, & Rosengren, 2017).
Company-owned website
In addition to stocking products with other e-trailers, the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY also manages orders through its own website, where consumers can place orders for COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY’s products directly. This allows the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY greater control over stock and inventory management, as well as distribution networks – allowing the buildup of stronger relations with consumers.
Lastly, the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY also takes limited orders through social media pages and platforms (Wu & Li, 2018; Baines, Fill, & Rosengren, 2017).
Aggregators
Another way through which COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY uses e-commerce is by stocking its offerings with aggregators (Kucuk, 2017). This allows the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY to maximize its reach and increase penetration. At the same time, it also allows increased trial generation and repeats purchases for the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY product offerings (Išoraitė, 2016; Groucutt & Hopkins, 2015).
Specialty stores
Interestingly, the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY also stocks its products with specialty stores (Grewal & Levy, 2021). This gives the company direct exposure to its target market and audience and allows the consumers to directly interact with the brand and its offerings- without too much clutter (Kotler & Keller, 2021; Gillespie & Swan, 2021). The specialty stores are located in prime locations, and allow COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY higher penetration and reach, leading to increased brand awareness for its product offerings (Groucutt & Hopkins, 2015; Išoraitė, 2016).

Direct sales
The COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY also has a trained sales team for making direct sales (Kotler & Keller, 2021). COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY targets not only B2C consumers but also B2-B consumers (Chernev, 2018; Grewal & Levy, 2021). Both these categories, also make use of direct marketing whereby the sales agents and teams visit the target audience and business directly and detail the product features and benefits (Kotler & Keller, 2021; Groucutt & Hopkins, 2015).
B2B and direct sales
COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY’s team makes sales instantly during field visits for the company (Sahaf, 2019; Stead & Hastings, 2018). The target audience is carefully profiled and selected by the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY so that the sales representatives are able to filter out the clutter (Gillespie & Swan, 2021; Išoraitė, 2016). COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY is able to easily contact and communicate with the desired business groups only (Groucutt & Hopkins, 2015; Abratt & Bendixen, 2018).
Inventory management
COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY effectively manages its inventory and fulfills the retailer's demand in time to ensure that it manages customer relations efficiently – and does not lose any customers. COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY has also introduced automation in inventory management which allows it to improve efficiency and speed, and reduce error rates (Park, 2020; Gillespie & Swan, 2021; Kucuk, 2017).
Transportation
For COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY, this includes choosing cos effective transportation means for inventory handling, as well as order deliveries to customers, as well as retailers. The company uses third-party transportation, as well as manages its own in-house transportation networks for ensuring on-time order deliveries (Abratt & Bendixen, 2018; Chernev, 2018; Grewal & Levy, 2021).
The element of promotion in the marketing mix for COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY largely refers to the tactics and activities of communication that the company has adopted for promoting its products and services – including the brand, and its offerings, as well as other product features, characteristics, and activities (Varadarajan, 2015; Gillespie & Swan, 2021). The communication is largely targeted toward the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY's target audience and is aimed to increase brand awareness, brand loyalty as well as sales of the company (Wu & Li, 2018; Grewal & Levy, 2021).
Direct marketing
For its more specific products and offerings, COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY uses direct marketing. COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY directly emails potential customers- especially its B2B consumers for detailing its product offerings and features. COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY uses personalized messages and captures new clients and customers for the business. In addition to direct emailing, the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY also makes use of telemarketing and direct mail for targeting audiences through direct marketing (Chernev, 2018; Sahaf, 2019).
In-store promotion
COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY also focuses on in-store promotions for appealing to the customers, and boosting sales as well as raising brand awareness and profile of its offerings (Baines, Fill, & Rosengren, 2017). For COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY, the in-store promotions include offering price discounts, loyalty points, and flash sales for its products. In addition, the company also invests in building up the POS within the store locations (Stead & Hastings, 2018; Groucutt & Hopkins, 2015).
Social media marketing
One of the more contemporary forms of marketing and promotion for COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY includes social media marketing. The company has an official presence and profiles on social media platforms such as Facebook and Instagram, and regularly uses these platforms to promote its offerings, and product features and characteristics (Stead & Hastings, 2018). In addition, these platforms are also used by COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY to inform consumers about using sales and discounts to increase in-store footfall.
Traditional advertising
The COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY continues to use traditional marketing tactics and promotional platforms as well – largely for mass marketing purposes. The company especially focuses on TV advertisements, ad print media advertising for this purpose (Išoraitė, 2016; Iacobucci, 2021).
TV advertisements are generally placed in prime time for higher visibility and reach by COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY. The TV advertisements use functional as well as emotional appeals to communicate the message of the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY to the audiences (Iacobucci, 2021; Stead & Hastings, 2018).
Print media and advertisements are published in newspapers and magazines – both of which are generally consumed in high proportion by the broader target audience of the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY (Chernev, 2018; Iacobucci, 2021; Stead & Hastings, 2018).
The COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY also places advertisements on the radio to appeal to a segment of the target population. The radio communications by the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY are usually shorter and focus on functional appeal only (Park, 2020; Išoraitė, 2016; Groucutt & Hopkins, 2015).
Integrated marketing communications
The advertisement and promotional messages by COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY for all mediums and channels however are built on an integrated plan, and ensure that they reflect messages and communication that is similar to the overall campaign to void confusion and discrepancies (Gillespie & Swan, 2021; Kotler & Keller, 2021). The use of integrated marketing and integrated media has allowed the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY to build strong relations with the consumers through prompting conversations and discussions directly with them (Deepak & Jeyakumar, 2019; Sahaf, 2019; Stead & Hastings, 2018).
The 4p model or the marketing mix is an important aspect of brand building and development for the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY and significantly guides the company in the chalking out of its strategic marketing goals and plans. The marketing mix model or the 4P model has helped the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY in increasing its products’ and services’ reach and penetration and witness high levels of expansion and growth. The model has also led COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY towards a better understanding of its target audience and consumers. This understanding, in turn, has fostered strong emotional relations and increased loyalty on part of consumers towards the company – leading to an overall increase in the brand value and brand equity, as well as higher levels of brand affiliation, brand awareness, and brand recall. Together, the marketing mix has helped the company boost its sales and revenue by aligning its offerings with the needs and demands of the consumers, and the market more effectively and efficiently.
Abratt, R., & Bendixen, M. (2018). Strategic marketing: Concepts and cases. New York, United States: Routledge.
Baines, P., Fill, C., & Rosengren, S. (2017). Marketing. New York, United States: Oxford University Press.
Chernev, A. (2018). Strategic marketing management. Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: Cerebellum Press.
Deepak, R., & Jeyakumar, S. (2019). Marketing management. New Delhi, India: Educreation Publishing.
Gillespie, K., & Swan, K. (2021). Global marketing. New York, United States: Routledge.
Grewal, D., & Levy, M. (2021). M: marketing. New York, United States: McGraw-Hill Education.
Groucutt, J., & Hopkins, C. (2015). Marketing. London: Macmillan International Higher Education.
Iacobucci, D. (2021). Marketing management. Boston, Massachusetts, United States: Cengage Learning.
Išoraitė, M. (2016). Marketing mix theoretical aspects. International Journal of Research-Granthaalayah, 4(6), 25-37.
Kareh, A. (2018). Evolution of the four Ps: Revisiting the marketing mix. Retrieved June 2022, from https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbesagencycouncil/2018/01/03/evolution-of-the-four-ps-revisiting-the-marketing-mix/
Khan, M. (2014). The concept of ‘marketing mix’and its elements. International journal of information, business and management, 6(2), 95-107.
Kotabe, M., & Helsen, K. (2020). Global marketing management. Hoboken, New Jersey, United States: John Wiley & Sons.
Kotler, P., & Keller, K. (2021). Marketing Management (15th global edition). London, United Kingdom: Pearson Education Limited.
Kucuk, S. (2017). Marketing and Marketing Mix. In Visualizing Marketing (pp. 3-7). London, United Kingdom: Palgrave Macmillan.
Park, S. (2020). Marketing management (Vol. 3). Retrieved June 2022, from https://books.google.com.pk/books/about/Marketing_Management.html?id=p6v7DwAAQBAJ&redir_esc=y
Sahaf, A. (2019). Strategic marketing: Making decisions for strategic advantage. New Delhi, India: PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd.
Stead, M., & Hastings, G. (2018). Advertising in the social marketing mix: getting the balance right. In Social Marketing (pp. 29-43). London, England: Psychology Press.
Varadarajan, R. (2015). Strategic marketing, marketing strategy and market strategy. AMS review , 5(3), 78-90.
Wu, Y., & Li, E. (2018). Marketing mix, customer value, and customer loyalty in social commerce: A stimulus-organism-response perspective. Internet Research., 28(1), 74-104.
Related Article
- PESTEL Analysis of COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY
- Hofstede Cultural Model of COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY
- Net Present Value (NPV) Analysis of COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY
- Corporate Social Responsibility of COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY
- COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Analysis
- VRIO Analysis of COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY
- COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY Case Solution
- Marketing Strategy for COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY
- Blue Ocean Strategy of COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY
9414 Students
Can’t be wrong.
Ph.D Experts
Latest Feedback
Jamilah Belouafi
Ashton Corey
Joshua Carvey
Business Management
Lilous Kevin
Calculate the Price of Your Order
(Approximately - 0.0 Pages)
Next Article
- LIFE'S WORK: ALICE WATERS Marketing Mix
- COMPETING AGAINST BLING (COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY) Marketing Mix
- STAFFING AT THE STRATEGIC CONSULTING GROUP: THE S WORD (STUDENT SPREADSHEET) Marketing Mix
- A PERFORMANCE PROBLEM Marketing Mix
- THE FACILITATIVE LEADERS' LAST RESORT Marketing Mix
- INGREDIENT BRANDING & SUPPLY CHAIN TRANSPARENCY IN YHE JEANSWEAR INDUSTRY: THE ISKO CASE Marketing Mix
- AIRBUS AND BOEING: SUPERJUMBO DECISIONS, STUDENT SPREADSHEET Marketing Mix
- ONE COST OF INCREASED GLOBALIZATION: MORE INDUSTRIAL ACCIDENTS Marketing Mix
- HOW SERVICE COMPANIES CAN EARN CUSTOMER TRUST AND KEEP IT Marketing Mix
- TO BE OR NOT TO BE A PROJECT MANAGER Marketing Mix
Previuos Article
- Making the Case Marketing Mix
- Joe Smith's Closing Analysis (B) Marketing Mix
- Joe Smith's Closing Analysis (A), Spanish Version Marketing Mix
- GMAC: The Pipeline Marketing Mix
- On Writing Teaching Notes Well Marketing Mix
- Exxon Corp.: Trouble at Valdez Marketing Mix
- Ashland Oil, Inc.: Trouble at Floreffe (A) Marketing Mix
- Ashland Oil, Inc.: Trouble at Floreffe (B) Marketing Mix
- Ashland Oil, Inc.: Trouble at Floreffe (C) Marketing Mix
- Ashland Oil, Inc.: Trouble at Floreffe (D) Marketing Mix
Be a great writer or hire a greater one!
Academic writing has no room for errors and mistakes. If you have BIG dreams to score BIG, think out of the box and hire EssayPandas with BIG enough reputation.
Our Guarantees
- Quality assured
- Proof of no plagiarism
- Qualified writers
- Data security
- 24/7 support
- On time delivery
Interesting Fact
Most recent surveys suggest that around 76 % students try professional academic writing services at least once in their lifetime!
Related Services

Essay Writing Service

Dissertation writing

Report Writing

Research Paper
Get tailored help the way you need it on any academic task..
We are here to help. Chat with us on WhatsApp for any queries.
Sales Support

Product details

Brought to you by:

Competing Against Bling (HBR Case Study and Commentary), Chinese Version
By: Stephen Nason, Joseph Salvacruz, J.P. Stevenson, Kent Wong, Martin Ganz
Wei Song oversees Greater China for Rochat & Schmid, a 100-year-old Swiss maker of luxury timepieces. China is a critical market for the firm, but sales of watches have stalled there. The firm's…
- Length: 6 page(s)
- Publication Date: May 1, 2017
- Discipline: Marketing
- Product #: R1703N-PDF-CHI
What's included:
- Educator Copy
$4.95 per student
degree granting course
$8.95 per student
non-degree granting course
Get access to this material, plus much more with a free Educator Account:
- Access to world-famous HBS cases
- Up to 60% off materials for your students
- Resources for teaching online
- Tips and reviews from other Educators
Already registered? Sign in
- Student Registration
- Non-Academic Registration
- Included Materials
Wei Song oversees Greater China for Rochat & Schmid, a 100-year-old Swiss maker of luxury timepieces. China is a critical market for the firm, but sales of watches have stalled there. The firm's competitors are going after China's luxury shoppers, who are younger and flashier than the traditional customer base, with new gem-encrusted products that offer "bling." To compete with them, Pearl Zhang, Song's VP of marketing, wants to launch a campaign featuring a Chinese singer with a huge social media following among Millennials. But Simon Carbonnier, R&S's chief creative officer back in Switzerland, is dead set against celebrity endorsements and anything that deviates from the brand's long-term value of "understated elegance." Should Song fight for Pearl's new campaign--or not? Expert commentary on this case study is provided by Kent Wong and Martin Ganz.
This HBR Case Study includes both the case and the commentary. For teaching purposes, this reprint is also available in two other versions: case study-only, reprint R1703X, and commentary-only, R1703Z.
May 1, 2017
Discipline:
Geographies:
Industries:
Retail and consumer goods, Retail trade
Harvard Business Review Digital Article
R1703N-PDF-CHI
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
Don't have an account? Sign up now
Already have an account login, get 10% off on your next order.
Subscribe now to get your discount coupon *Only correct email will be accepted
(Approximately ~ 0.0 Page)
Total Price
Thank you for your email subscription. Check your email to get Coupon Code.
VRIO Analysis of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY
Posted by Zachary Edwards on Mar-22-2018
The VRIO Analysis of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY will look at each of its internal resources one by one to assess whether these provide sustained competitive advantage. The COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY VRIO Analysis also mentions at each stage whether these resources could be improved to provide a greater competitive advantage. Lastly, the resources analysed are summarised as to whether they offer sustained competitive advantage, has an unused competitive advantage, temporary competitive advantage, competitive parity or competitive disadvantage.
- The COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY VRIO Analysis shows that the financial resources of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY are highly valuable as these help in investing into external opportunities that arise. These also help COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY in combating external threats.
- According to the VRIO Analysis of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY, its local food products are a valuable resource as these are highly differentiated. This makes the perceived value for these by customers high. These are also valued more than the competition by customers due to the differentiation in these products.
- The COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY VRIO Analysis shows that COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY's employees are a valuable resource to the firm. A significant portion of the workforce is highly trained, and this leads to more productive output for the organisation. The employees are also loyal, and retention levels for the organisation are high. All of this translates into greater value for the end consumers of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY's products.
- According to the VRIO Analysis of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY, its patents are a valuable resource as these allow the firm to sell its products without competitive interference. This results in greater revenue for COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY. These patents also provide COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY with licensing revenue when it licenses these patents out to other manufacturers.
- The COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY VRIO Analysis shows that COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY’s distribution network is a valuable resource. This helps it in reaching out to more and more customers. This ensures greater revenues for COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY. It also ensures that promotion activities translate into sales as the products are easily available.
- According to the VRIO Analysis of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY, its cost structure is not a valuable resource. This is because the methods of production lead to greater costs than that of competition, which affects the overall profits of the firm. Therefore, its cost structure is a competitive disadvantage that needs to be worked on.
- The COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY VRIO Analysis shows that the research and development at COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY is not a valuable resource. This is because research and development are costing more than the benefits it provides in the form of innovation. There have been very few innovative features and breakthrough products in the past few years. Therefore, research and development are a competitive disadvantage for COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY. It is recommended that the research and development teams are improved, and costs are cut for these.
- The financial resources of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY are found to be rare according to the VRIO Analysis of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY. Strong financial resources are only possessed by a few companies in the industry.
- The local food products are found to be not rare as identified by COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY VRIO Analysis. These are easily provided in the market by other competitors. This means that competitors can use these resources in the same way as COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY and inhibit competitive advantage. This means that the local food products result in competitive parity for COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY. As this resource is valuable, COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY can still make use of this resource.
- The employees of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY are a rare resource as identified by the VRIO Analysis of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY. These employees are highly trained and skilled, which is not the case with employees in other firms. The better compensation and work environment ensure that these employees do not leave for other firms.
- The patents of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY are a rare resource as identified by the COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY VRIO Analysis. These patents are not easily available and are not possessed by competitors. This allows COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY to use them without interference from the competition.
- The distribution network of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY is a rare resource as identified by the VRIO Analysis of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY. This is because competitors would require a lot of investment and time to come up with a better distribution network than that of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY. These are also possessed by very few firms in the industry.
- The financial resources of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY are costly to imitate as identified by the COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY VRIO Analysis. These resources have been acquired by the company through prolonged profits over the years. New entrants and competitors would require similar profits for a long period of time to accumulate these amounts of financial resources.
- The local food products are not that costly to imitate as identified by the VRIO Analysis of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY. These can be acquired by competitors as well if they invest a significant amount in research and development. These also do not require years long experience. Therefore, the local food products by COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY provide it with a temporary competitive advantage that competitors can too acquire in the long run.
- The employees of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY are also not costly to imitate as identified by the COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY VRIO Analysis. This is because other firms can also train their employees to improve their skills. These companies can also hire employees from COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY by offering better compensation packages, work environment, benefits, growth opportunities etc. This makes the employees of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY a resource that provides a temporary competitive advantage. Competition can acquire these in the future.
- The patents of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY are very difficult to imitate as identified by the VRIO Analysis of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY. This is because it is not legally allowed to imitate a patented product. Similar resources to be developed and getting a patent for them is also a costly process.
- The distribution network of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY is also very costly to imitate by competition as identified by the COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY VRIO Analysis. This has been developed over the years gradually by COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY. Competitors would have to invest a significant amount if they are to imitate a similar distribution system.
Organisation
- The financial resources of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY are organised to capture value as identified by the VRIO Analysis of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY. These resources are used strategically to invest in the right places; making use of opportunities and combatting threats. Therefore, these resources prove to be a source of sustained competitive advantage for COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY.
- The Patents of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY are not well organised as identified by the COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY VRIO Analysis. This means that the organisation is not using these patents to their full potential. An unused competitive advantage exists that can be changed into a sustainable competitive advantage if COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY starts selling patented products before the patents expire.
- The distribution network of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY is organised as identified by the VRIO Analysis of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY. COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY uses this network to reach out to its customers by ensuring that products are available on all of its outlets. Therefore, these resources prove to be a source of sustained competitive advantage for COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY.
From the VRIO Analysis of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY, it was identified that the financial resources and distribution network provide a sustained competitive advantage. The patents are a source of unused competitive advantage. There exists a temporary competitive advantage for employees. There exists a competitive parity for local food products. Lastly, the cost structure of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY is a competitive disadvantage. Research and Development is also a competitive disadvantage.
Warning! This article is only an example and cannot be used for research or reference purposes. If you need help with something similar, please submit your details here .
9414 Students can’t be wrong
PhD Experts
Frankly Sean
Fast and quick delivery made me put trust and completely depend on this service. I will refer this service to friends.
Deniz Zemir
I like the professionalism and the commitment of this service to work. I would like to advise this service to everyone.
I will recommend this service because I'm completely satisfied with its performance. Thank you so much!
Annie Peter
The process was very easy and fast. I always get paper on time. Very prompt and reliable service. Highly recommended!
Calculate the Price
(approx ~ 0.0 page), total price $0, next articles.
- STAFFING AT THE STRATEGIC CONSULTING GROUP: THE S WORD (STUDENT SPREADSHEET) Vrio Analysis
- A PERFORMANCE PROBLEM Vrio Analysis
- THE FACILITATIVE LEADERS' LAST RESORT Vrio Analysis
- INGREDIENT BRANDING & SUPPLY CHAIN TRANSPARENCY IN YHE JEANSWEAR INDUSTRY: THE ISKO CASE Vrio Analysis
- AIRBUS AND BOEING: SUPERJUMBO DECISIONS, STUDENT SPREADSHEET Vrio Analysis
- ONE COST OF INCREASED GLOBALIZATION: MORE INDUSTRIAL ACCIDENTS Vrio Analysis
- HOW SERVICE COMPANIES CAN EARN CUSTOMER TRUST AND KEEP IT Vrio Analysis
- TO BE OR NOT TO BE A PROJECT MANAGER Vrio Analysis
- 3P TURBO – CROSS BORDER INVESTMENT IN BRAZIL Vrio Analysis
- FERRARI: THE 2015 INITIAL PUBLIC OFFERING (STUDENT SPREADSHEET) Vrio Analysis
Previous Articles
- LIFE'S WORK: ALICE WATERS Vrio Analysis
- COMPETING AGAINST BLING (HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY) Vrio Analysis
- STATE STREET'S CEO ON CREATING EMPLOYMENT FOR AT RISK YOUTHS Vrio Analysis
- RECLAIM YOUR COMMUTE Vrio Analysis
- ABOVE ALL, ACKNOWLEDGE THE PAIN Vrio Analysis
- LINEAR THINKING IN A NONLINEAR WORLD Vrio Analysis
- THE WORLD'S NEXT GREAT MANUFACTURING CENTER Vrio Analysis
- WHAT'S YOUR DATA STRATEGY? Vrio Analysis
- THE PROBLEM WITH PRODUCT PROLIFERATION Vrio Analysis
- NEURODIVERSITY AS A COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE Vrio Analysis
Be a great writer or hire a greater one!
Academic writing has no room for errors and mistakes. If you have BIG dreams to score BIG, think out of the box and hire Case48 with BIG enough reputation.

Our Guarantees
Zero plagiarism, best quality, qualified writers, absolute privacy, timely delivery.
Interesting Fact
Most recent surveys suggest that around 76 % students try professional academic writing services at least once in their lifetime!
Allow Our Skilled Essay Writers to Proficiently Finish Your Paper.
We are here to help. Chat with us on WhatsApp for any queries.
Customer Representative

Leadership & Managing People

Case Study: How Should an Understated Luxury Brand Compete Against Bling?

Case Study: How Should an Understated Luxury Brand Compete Against Bling? ^ H03HXT
Want to buy more than 1 copy? Contact: [email protected]
Product Description
Publication Date: February 28, 2017
How should a Swiss watchmaker stand out in China?

This Product Also Appears In
Buy together, related products.

Competing Against Bling (HBR Case Study)

A Time to Lead with Purpose and Humanity

Competing Against Bling (Commentary for HBR Case Study)
Copyright permissions.
If you'd like to share this PDF, you can purchase copyright permissions by increasing the quantity.
Order for your team and save!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Competing Against Bling. Wei Song noticed the fashion models first, preening in their chiffon-and-lace gowns. They flanked the entrance to Shanguang Jewelers' flagship store on Nanjing Road. A ...
How can an understated watch brand stand out against flashier, gem-encrusted offerings in China?Wei Song oversees Greater China for Rochat & Schmid, a 100-ye...
Competing Against Bling (HBR Case Study) By: Stephen Nason, Joseph Salvacruz, J.P. Stevenson. Wei Song oversees Greater China for Rochat & Schmid, a 100-year-old Swiss maker of luxury timepieces. China is a critical market for the firm, but sales of watches have stalled there. The firm's….
Harvard business review marketing case study: competing against bling stephen nason, joseph salvacruz, and jp stevenson from the magazine 2017) gabriel ... TAX-Chap 2-3 Question And Answer; Frq - fro for college. board ... Case Study Competing Against Bling. University: Harvard University. Course: business management (bmanagement) 999+ Documents.
Competing Against Bling HBR Case Study and Commentary. Management article -Reference no. R1703N Authors: Stephen Nason ... Originally published in: "Harvard Business Review", 2017 Revision date: 26-Jul-2017 Length: 6 pages Topics: Advertising campaigns; Brand management. View full details
The non reusable Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study was created in Sweden, and was introduced to America in the late 1940s. In the early years, the Competing Against Bling Hbr Case Study were utilized with attaching pins and plastic trousers, which was typically viewed as ineffectiveness in keeping both the babies and the parents dry.
Unformatted Attachment Preview. Running head: COMPETING AGAINST BLING Competing Against Bling Name Institution 1 COMPETING AGAINST BLING 2 Competing Against Bling You are Wei Song -how do you characterize the problems you face in the Chinese fashion watch In the situation where I am Wei Song the director of Rochat & Schmid (R&S) a Swiss maker ...
Competing Against Bling (HBR Case Study and Commentary) By: Stephen Nason, Joseph Salvacruz, J.P. Stevenson, Kent Wong, Martin Ganz. Wei Song oversees Greater China for Rochat & Schmid, a 100-year-old Swiss maker of luxury timepieces. China is a critical market for the firm, but sales of watches have stalled there. The firm's…. Length: 6 page ...
Competing Against Bling: HBR Case Study. concept: "How can an understated watch brand stand out against flashier, gem-encrusted offerings in China?". · The artwork on this website is protected by copyright and may not be used for any commercial or non-commercial purpose without the express written permission of the copyright holder.
The 4p model of marketing comprises elements of the product, price, promotion, and place (Chernev, 2018; Kucuk, 2017). The model is commonly referred to as the marketing mix. The marketing mix of the COMPETING AGAINST BLING HBR CASE STUDY AND COMMENTARY allows and facilitates it in achieving its marketing objectives as well as in positively ...
Stephen Nason, Joseph Salvacruz, and. JP Stevenson. February 28, 2017. Wei Song noticed the fashion models first. Preening in chiffon-and-lace gowns, they flanked the entrance to Shanguang ...
The case solution first identifies the central issue to the COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY case study, and the relevant stakeholders affected by this issue. This is known as the problem identification stage. After this, the relevant tools and models are used, which help in the case study analysis and case study solution.
"When you're competing against bling, it's important to remember that you're not just competing for market share. You're competing for the attention of consumers." In the video, they discuss how many companies were attempting to compete with Apple by offering similar products and services, but they didn't realize that they were also competing ...
Harvard Business Review is pleased to announce the 2016 McKinsey Award winners. ... Case Study: Competing Against Bling. Marketing ... The authors' studies show that well-integrated executives ...
Competing Against Bling HBR Case Study. Management article -Reference no. R1703X Authors: Stephen Nason (Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) - Business School); Joseph SALVACRUZ (Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) - Business School); JP Stevenson (Harvard Business School)
HBR Case Competing Against Bling (HBR Case Study and Commentary), Chinese Version. By: Stephen Nason, Joseph Salvacruz, J.P. Stevenson, Kent Wong, Martin Ganz. Wei Song oversees Greater China for Rochat & Schmid, a 100-year-old Swiss maker of luxury timepieces. China is a critical market for the firm, but sales of watches have stalled there.
VRIO Analysis of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY - The VRIO Analysis of COMPETING AGAINST BLING COMMENTARY FOR HBR CASE STUDY will look at each of its internal resources one by one to assess…
Case Study: How Should an Understated Luxury Brand Compete Against Bling? by Stephen Nason , J.P. Stevenson , Joseph Salvacruz. , $8.95. (USD) Format: