- How to Cite
- Language & Lit
- Rhyme & Rhythm
- The Rewrite
- Search Glass

General Statement Vs. Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a succinct statement of the arguments you'll be making in a paper and is a critical component of any well-written work. A general statement, by contrast, is any declarative sentence providing supporting information or transitioning to a new topic. While both sentence structures play an important role in writing, a paper without a thesis statement can end up poorly organized with no central argument.
Role in Paper
Your thesis defines the topic and focus of your paper. Even if your paper is not an argumentative paper, you'll still need a thesis that defines your scope. For example, in a paper summarizing "Romeo and Juliet," your thesis might briefly outline three general plot themes. Your general statements should then expand upon your thesis by giving supplemental information and commentary. In some papers, the primary thesis is in the first paragraph, and then each subsequent paragraph contains a mini-thesis. For example, the "Romeo and Juliet" paper might use one paragraph to outline each plot theme, with a mini-thesis at the beginning of the paragraph providing more information about the plot theme.
Your thesis makes a central argument upon which your paper will focus. General statements either lead up to this argument by providing background information or support the argument by presenting and analyzing data. General statements are also an important part of a conclusion. You can use them to outline directions for future research or to address unsettled research debates, for example. Some students mistakenly make a general statement when they need to make a thesis statement. For example, "Poverty is a social problem" is a general statement that does not outline an argument. On the other hand, "School programs designed to counteract the effect of poverty can help undermine the long-lasting effects of low family income" is a compelling thesis statement.
Paper Structure
Both your thesis statement and general statements play roles in structuring your paper. Your thesis limits your focus to a single argument or two, and general statements support this argument. In a sociology paper, your thesis might argue that childhood poverty is the best predictor of adult poverty. General statements might then give facts about childhood poverty, statements about how to end poverty or information on the psychological ramifications of poverty. However, your general statements should not veer outside of the limited focus of your thesis. A paragraph full of general statements about how teen pregnancy contributes to poverty would likely confuse the focus of your paper.
Supporting the Thesis
The primary role of a general statement is to support your thesis. In the introductory paragraph, general statements can also build up to your thesis by providing relevant background. You might, for example, make the general statement that "Philosophers have long debated when it is ethical to kill someone," then follow up with a thesis explaining when killing is ethical or how a particular philosopher attacks this ethical dilemma.
- Purdue Online Writing Lab: Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements
- Indiana University Bloomington: How to Write a Thesis Statement
- University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign: Writing Tips -- Thesis Statements
- Louisiana Tech: Thesis Exercises -- What a Thesis Is Not
Van Thompson is an attorney and writer. A former martial arts instructor, he holds bachelor's degrees in music and computer science from Westchester University, and a juris doctor from Georgia State University. He is the recipient of numerous writing awards, including a 2009 CALI Legal Writing Award.

Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
- I nfographics
- Show AWL words
- Subscribe to newsletter
- What is academic writing?
- Academic Style
- What is the writing process?
- Understanding the title
- Brainstorming
- Researching
- First draft
- Proofreading
- Report writing
- Compare & contrast
- Cause & effect
- Problem-solution
- Classification
- Essay structure
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Book review
- Research proposal
- Thesis/dissertation
- What is cohesion?
- Cohesion vs coherence
- Transition signals
- What are references?
- In-text citations
- Reference sections
- Reporting verbs
- Band descriptors
Show AWL words on this page.
Levels 1-5: grey Levels 6-10: orange
Show sorted lists of these words.
Any words you don't know? Look them up in the website's built-in dictionary .
Choose a dictionary . Wordnet OPTED both
Introduction How to get an essay started
Getting started can often be difficult. Even professional writers say that the hardest part of writing is the beginning. Writing an introduction to an essay can therefore seem a daunting task, though it need not be so difficult, as long as you understand the purpose and the structure of the introduction. An example essay has been given to help you understand both of these, and there is a checklist at the end which you can use for editing your introduction.
Purpose of the introduction
When writing an introduction to an academic essay, it is useful to remember the main purpose of the introduction. In general, the introduction will introduce the topic to the reader by stating what the topic is and giving some general background information. This will help the reader to understand what you are writing about, and show why the topic is important. The introduction should also give the overall plan of the essay.
In short, the main purpose of the introduction is to:
- introduce the topic of the essay;
- give a general background of the topic;
- indicate the overall plan of the essay.
This last purpose is perhaps the most important, and is the reason why many writers choose to write the introduction last , after they have written the main body , because they need to know what the essay will contain before they can give a clear plan.
Structure of the introduction
Although essays vary in length and content, most essays will have the same overall structure, including the introduction. The structure is related to the purpose mentioned above. The introduction to an essay should have the following two parts:
- general statements (to introduce the topic and give the background);
- a thesis statement (to show the structure).
General statements
The general statements will introduce the topic of the essay and give background information. The background information for a short essay will generally just be one or two sentences. The general statements should become more and more specific thesis statement , which is the most specific sentence of the introduction--> as the introduction progresses, leading the reader into the essay (some writers talk about "attracting the readers' attention", though for an academic essay, this is less important). For longer essays, the general statements could include one or more definitions , or could classify the topic, and may cover more than one paragraph.
The following is an example of background statements for a short essay ( given below ):
Although they were invented almost a hundred years ago, for decades cars were only owned by the rich. Since the 60s and 70s they have become increasingly affordable, and now most families in developed nations, and a growing number in developing countries, own a car.
These sentences introduce the topic of the essay (cars) and give some background to this topic (situation in the past, the situation now). These sentences lead nicely into the thesis statement (see below).
Thesis statement
The thesis statement is the most important part of the introduction. It gives the reader clear information about the content of the essay, which will help them to understand the essay more easily. The thesis states the specific topic, and often lists the main (controlling) ideas that will be discussed in the main body. It may also indicate how the essay will be organised, e.g. in chronological order, order of importance, advantages/disadvantages, cause/effect. It is usually at the end of the introduction, and is usually (but not always) one sentence long.
In short, the thesis statement:
- states the specific topic of the essay;
- often lists the main (controlling) ideas of the essay;
- may indicate the method of organisation of the essay;
- is usually at the end of the introduction;
- is usually one sentence.
Here is an example of a thesis statement with no subtopics mentioned:
While cars have undoubted advantages, they also have significant drawbacks.
This thesis statement tells us the specific topic of the essay (advantages and disadvantages of cars) and the method of organisation (advantages should come first, disadvantages second). It is, however, quite general, and may have been written before the writer had completed the essay.
In the following thesis statement, the subtopics are named:
While cars have undoubted advantages, of which their convenience is the most apparent, they have significant drawbacks, most notably pollution and traffic problems.
This thesis gives us more detail, telling us not just the topic (advantages and disadvantages of cars) and the method of organisation (advantages first, disadvantages second), but also tells us the main ideas in the essay (convenience, pollution, traffic problems). This essay will probably have three paragraphs in the main body.
Example essay
Below is a discussion essay which looks at the advantages and disadvantages of car ownership. This essay is used throughout the essay writing section to help you understand different aspects of essay writing. Here it focuses on the thesis statement and general statements of the introduction (mentioned on this page), topic sentences , controlling ideas, and the summary and final comment of the conclusion. Click on the different areas (in the shaded boxes to the right) to highlight the different structural aspects in this essay.
Although they were invented almost a hundred years ago, for decades cars were only owned by the rich. Since the 60s and 70s they have become increasingly affordable, and now most families in developed nations, and a growing number in developing countries, own a car. While cars have undoubted advantages, of which their convenience is the most apparent, they have significant drawbacks, most notably pollution and traffic problems . The most striking advantage of the car is its convenience. When travelling long distance, there may be only one choice of bus or train per day, which may be at an unsuitable time. The car, however, allows people to travel at any time they wish, and to almost any destination they choose. Despite this advantage, cars have many significant disadvantages, the most important of which is the pollution they cause. Almost all cars run either on petrol or diesel fuel, both of which are fossil fuels. Burning these fuels causes the car to emit serious pollutants, such as carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and nitrous oxide. Not only are these gases harmful for health, causing respiratory disease and other illnesses, they also contribute to global warming, an increasing problem in the modern world. According to the Union of Concerned Scientists (2013), transportation in the US accounts for 30% of all carbon dioxide production in that country, with 60% of these emissions coming from cars and small trucks. In short, pollution is a major drawback of cars. A further disadvantage is the traffic problems that they cause in many cities and towns of the world. While car ownership is increasing in almost all countries of the world, especially in developing countries, the amount of available roadway in cities is not increasing at an equal pace. This can lead to traffic congestion, in particular during the morning and evening rush hour. In some cities, this congestion can be severe, and delays of several hours can be a common occurrence. Such congestion can also affect those people who travel out of cities at the weekend. Spending hours sitting in an idle car means that this form of transport can in fact be less convenient than trains or aeroplanes or other forms of public transport. In conclusion, while the car is advantageous for its convenience , it has some important disadvantages, in particular the pollution it causes and the rise of traffic jams . If countries can invest in the development of technology for green fuels, and if car owners can think of alternatives such as car sharing, then some of these problems can be lessened.
Union of Concerned Scientists (2013). Car Emissions and Global Warming. www.ucsusa.org/clean vehicles/why-clean-cars/global-warming/ (Access date: 8 August, 2013)

GET FREE EBOOK
Like the website? Try the books. Enter your email to receive a free sample from Academic Writing Genres .
Below is a checklist for an essay introduction. Use it to check your own writing, or get a peer (another student) to help you.
Next section
Find out how to structure the main body of an essay in the next section.
Previous section
Go back to the previous section about essay structure .

Author: Sheldon Smith ‖ Last modified: 26 January 2022.
Sheldon Smith is the founder and editor of EAPFoundation.com. He has been teaching English for Academic Purposes since 2004. Find out more about him in the about section and connect with him on Twitter , Facebook and LinkedIn .
Compare & contrast essays examine the similarities of two or more objects, and the differences.
Cause & effect essays consider the reasons (or causes) for something, then discuss the results (or effects).
Discussion essays require you to examine both sides of a situation and to conclude by saying which side you favour.
Problem-solution essays are a sub-type of SPSE essays (Situation, Problem, Solution, Evaluation).
Transition signals are useful in achieving good cohesion and coherence in your writing.
Reporting verbs are used to link your in-text citations to the information cited.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
Published on September 14, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on November 21, 2023.
A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master’s program or a capstone to a bachelor’s degree.
Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation , it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete. It relies on your ability to conduct research from start to finish: choosing a relevant topic , crafting a proposal , designing your research , collecting data , developing a robust analysis, drawing strong conclusions , and writing concisely .
Thesis template
You can also download our full thesis template in the format of your choice below. Our template includes a ready-made table of contents , as well as guidance for what each chapter should include. It’s easy to make it your own, and can help you get started.
Download Word template Download Google Docs template
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Thesis vs. thesis statement, how to structure a thesis, acknowledgements or preface, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review, methodology, reference list, proofreading and editing, defending your thesis, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about theses.
You may have heard the word thesis as a standalone term or as a component of academic writing called a thesis statement . Keep in mind that these are two very different things.
- A thesis statement is a very common component of an essay, particularly in the humanities. It usually comprises 1 or 2 sentences in the introduction of your essay , and should clearly and concisely summarize the central points of your academic essay .
- A thesis is a long-form piece of academic writing, often taking more than a full semester to complete. It is generally a degree requirement for Master’s programs, and is also sometimes required to complete a bachelor’s degree in liberal arts colleges.
- In the US, a dissertation is generally written as a final step toward obtaining a PhD.
- In other countries (particularly the UK), a dissertation is generally written at the bachelor’s or master’s level.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
The final structure of your thesis depends on a variety of components, such as:
- Your discipline
- Your theoretical approach
Humanities theses are often structured more like a longer-form essay . Just like in an essay, you build an argument to support a central thesis.
In both hard and social sciences, theses typically include an introduction , literature review , methodology section , results section , discussion section , and conclusion section . These are each presented in their own dedicated section or chapter. In some cases, you might want to add an appendix .
Thesis examples
We’ve compiled a short list of thesis examples to help you get started.
- Example thesis #1: “Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the ‘Noble Savage’ on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807” by Suchait Kahlon.
- Example thesis #2: “’A Starving Man Helping Another Starving Man’: UNRRA, India, and the Genesis of Global Relief, 1943-1947″ by Julian Saint Reiman.
The very first page of your thesis contains all necessary identifying information, including:
- Your full title
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date.
Sometimes the title page also includes your student ID, the name of your supervisor, or the university’s logo. Check out your university’s guidelines if you’re not sure.
Read more about title pages
The acknowledgements section is usually optional. Its main point is to allow you to thank everyone who helped you in your thesis journey, such as supervisors, friends, or family. You can also choose to write a preface , but it’s typically one or the other, not both.
Read more about acknowledgements Read more about prefaces
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
An abstract is a short summary of your thesis. Usually a maximum of 300 words long, it’s should include brief descriptions of your research objectives , methods, results, and conclusions. Though it may seem short, it introduces your work to your audience, serving as a first impression of your thesis.
Read more about abstracts
A table of contents lists all of your sections, plus their corresponding page numbers and subheadings if you have them. This helps your reader seamlessly navigate your document.
Your table of contents should include all the major parts of your thesis. In particular, don’t forget the the appendices. If you used heading styles, it’s easy to generate an automatic table Microsoft Word.
Read more about tables of contents
While not mandatory, if you used a lot of tables and/or figures, it’s nice to include a list of them to help guide your reader. It’s also easy to generate one of these in Word: just use the “Insert Caption” feature.
Read more about lists of figures and tables
If you have used a lot of industry- or field-specific abbreviations in your thesis, you should include them in an alphabetized list of abbreviations . This way, your readers can easily look up any meanings they aren’t familiar with.
Read more about lists of abbreviations
Relatedly, if you find yourself using a lot of very specialized or field-specific terms that may not be familiar to your reader, consider including a glossary . Alphabetize the terms you want to include with a brief definition.
Read more about glossaries
An introduction sets up the topic, purpose, and relevance of your thesis, as well as expectations for your reader. This should:
- Ground your research topic , sharing any background information your reader may need
- Define the scope of your work
- Introduce any existing research on your topic, situating your work within a broader problem or debate
- State your research question(s)
- Outline (briefly) how the remainder of your work will proceed
In other words, your introduction should clearly and concisely show your reader the “what, why, and how” of your research.
Read more about introductions
A literature review helps you gain a robust understanding of any extant academic work on your topic, encompassing:
- Selecting relevant sources
- Determining the credibility of your sources
- Critically evaluating each of your sources
- Drawing connections between sources, including any themes, patterns, conflicts, or gaps
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing work. Rather, your literature review should ultimately lead to a clear justification for your own research, perhaps via:
- Addressing a gap in the literature
- Building on existing knowledge to draw new conclusions
- Exploring a new theoretical or methodological approach
- Introducing a new solution to an unresolved problem
- Definitively advocating for one side of a theoretical debate
Read more about literature reviews
Theoretical framework
Your literature review can often form the basis for your theoretical framework, but these are not the same thing. A theoretical framework defines and analyzes the concepts and theories that your research hinges on.
Read more about theoretical frameworks
Your methodology chapter shows your reader how you conducted your research. It should be written clearly and methodically, easily allowing your reader to critically assess the credibility of your argument. Furthermore, your methods section should convince your reader that your method was the best way to answer your research question.
A methodology section should generally include:
- Your overall approach ( quantitative vs. qualitative )
- Your research methods (e.g., a longitudinal study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., interviews or a controlled experiment
- Any tools or materials you used (e.g., computer software)
- The data analysis methods you chose (e.g., statistical analysis , discourse analysis )
- A strong, but not defensive justification of your methods
Read more about methodology sections
Your results section should highlight what your methodology discovered. These two sections work in tandem, but shouldn’t repeat each other. While your results section can include hypotheses or themes, don’t include any speculation or new arguments here.
Your results section should:
- State each (relevant) result with any (relevant) descriptive statistics (e.g., mean , standard deviation ) and inferential statistics (e.g., test statistics , p values )
- Explain how each result relates to the research question
- Determine whether the hypothesis was supported
Additional data (like raw numbers or interview transcripts ) can be included as an appendix . You can include tables and figures, but only if they help the reader better understand your results.
Read more about results sections
Your discussion section is where you can interpret your results in detail. Did they meet your expectations? How well do they fit within the framework that you built? You can refer back to any relevant source material to situate your results within your field, but leave most of that analysis in your literature review.
For any unexpected results, offer explanations or alternative interpretations of your data.
Read more about discussion sections
Your thesis conclusion should concisely answer your main research question. It should leave your reader with an ultra-clear understanding of your central argument, and emphasize what your research specifically has contributed to your field.
Why does your research matter? What recommendations for future research do you have? Lastly, wrap up your work with any concluding remarks.
Read more about conclusions
In order to avoid plagiarism , don’t forget to include a full reference list at the end of your thesis, citing the sources that you used. Choose one citation style and follow it consistently throughout your thesis, taking note of the formatting requirements of each style.
Which style you choose is often set by your department or your field, but common styles include MLA , Chicago , and APA.
Create APA citations Create MLA citations
In order to stay clear and concise, your thesis should include the most essential information needed to answer your research question. However, chances are you have many contributing documents, like interview transcripts or survey questions . These can be added as appendices , to save space in the main body.
Read more about appendices
Once you’re done writing, the next part of your editing process begins. Leave plenty of time for proofreading and editing prior to submission. Nothing looks worse than grammar mistakes or sloppy spelling errors!
Consider using a professional thesis editing service or grammar checker to make sure your final project is perfect.
Once you’ve submitted your final product, it’s common practice to have a thesis defense, an oral component of your finished work. This is scheduled by your advisor or committee, and usually entails a presentation and Q&A session.
After your defense , your committee will meet to determine if you deserve any departmental honors or accolades. However, keep in mind that defenses are usually just a formality. If there are any serious issues with your work, these should be resolved with your advisor way before a defense.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation shouldn’t take up more than 5–7% of your overall word count.
If you only used a few abbreviations in your thesis or dissertation , you don’t necessarily need to include a list of abbreviations .
If your abbreviations are numerous, or if you think they won’t be known to your audience, it’s never a bad idea to add one. They can also improve readability, minimizing confusion about abbreviations unfamiliar to your reader.
When you mention different chapters within your text, it’s considered best to use Roman numerals for most citation styles. However, the most important thing here is to remain consistent whenever using numbers in your dissertation .
A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical first steps in your writing process. It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding what kind of research you’d like to undertake.
Generally, an outline contains information on the different sections included in your thesis or dissertation , such as:
- Your anticipated title
- Your abstract
- Your chapters (sometimes subdivided into further topics like literature review , research methods , avenues for future research, etc.)
A thesis is typically written by students finishing up a bachelor’s or Master’s degree. Some educational institutions, particularly in the liberal arts, have mandatory theses, but they are often not mandatory to graduate from bachelor’s degrees. It is more common for a thesis to be a graduation requirement from a Master’s degree.
Even if not mandatory, you may want to consider writing a thesis if you:
- Plan to attend graduate school soon
- Have a particular topic you’d like to study more in-depth
- Are considering a career in research
- Would like a capstone experience to tie up your academic experience
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, November 21). What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 1, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/thesis/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation & thesis outline | example & free templates, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, 10 research question examples to guide your research project, what is your plagiarism score.
- Skip to Content
- Skip to Main Navigation
- Skip to Search

Indiana University Bloomington Indiana University Bloomington IU Bloomington

- Mission, Vision, and Inclusive Language Statement
- Locations & Hours
- Undergraduate Employment
- Graduate Employment
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Newsletter Archive
- Support WTS
- Schedule an Appointment
- Online Tutoring
- Before your Appointment
- WTS Policies
- Group Tutoring
- Students Referred by Instructors
- Paid External Editing Services
- Writing Guides
- Scholarly Write-in
- Dissertation Writing Groups
- Journal Article Writing Groups
- Early Career Graduate Student Writing Workshop
- Workshops for Graduate Students
- Teaching Resources
- Syllabus Information
- Course-specific Tutoring
- Nominate a Peer Tutor
- Tutoring Feedback
- Schedule Appointment
- Campus Writing Program
Writing Tutorial Services
How to write a thesis statement, what is a thesis statement.
Almost all of us—even if we don’t do it consciously—look early in an essay for a one- or two-sentence condensation of the argument or analysis that is to follow. We refer to that condensation as a thesis statement.
Why Should Your Essay Contain a Thesis Statement?
- to test your ideas by distilling them into a sentence or two
- to better organize and develop your argument
- to provide your reader with a “guide” to your argument
In general, your thesis statement will accomplish these goals if you think of the thesis as the answer to the question your paper explores.
How Can You Write a Good Thesis Statement?
Here are some helpful hints to get you started. You can either scroll down or select a link to a specific topic.
How to Generate a Thesis Statement if the Topic is Assigned How to Generate a Thesis Statement if the Topic is not Assigned How to Tell a Strong Thesis Statement from a Weak One
How to Generate a Thesis Statement if the Topic is Assigned
Almost all assignments, no matter how complicated, can be reduced to a single question. Your first step, then, is to distill the assignment into a specific question. For example, if your assignment is, “Write a report to the local school board explaining the potential benefits of using computers in a fourth-grade class,” turn the request into a question like, “What are the potential benefits of using computers in a fourth-grade class?” After you’ve chosen the question your essay will answer, compose one or two complete sentences answering that question.
Q: “What are the potential benefits of using computers in a fourth-grade class?” A: “The potential benefits of using computers in a fourth-grade class are . . .”
A: “Using computers in a fourth-grade class promises to improve . . .”
The answer to the question is the thesis statement for the essay.
[ Back to top ]
How to Generate a Thesis Statement if the Topic is not Assigned
Even if your assignment doesn’t ask a specific question, your thesis statement still needs to answer a question about the issue you’d like to explore. In this situation, your job is to figure out what question you’d like to write about.
A good thesis statement will usually include the following four attributes:
- take on a subject upon which reasonable people could disagree
- deal with a subject that can be adequately treated given the nature of the assignment
- express one main idea
- assert your conclusions about a subject
Let’s see how to generate a thesis statement for a social policy paper.
Brainstorm the topic . Let’s say that your class focuses upon the problems posed by changes in the dietary habits of Americans. You find that you are interested in the amount of sugar Americans consume.
You start out with a thesis statement like this:
Sugar consumption.
This fragment isn’t a thesis statement. Instead, it simply indicates a general subject. Furthermore, your reader doesn’t know what you want to say about sugar consumption.
Narrow the topic . Your readings about the topic, however, have led you to the conclusion that elementary school children are consuming far more sugar than is healthy.
You change your thesis to look like this:
Reducing sugar consumption by elementary school children.
This fragment not only announces your subject, but it focuses on one segment of the population: elementary school children. Furthermore, it raises a subject upon which reasonable people could disagree, because while most people might agree that children consume more sugar than they used to, not everyone would agree on what should be done or who should do it. You should note that this fragment is not a thesis statement because your reader doesn’t know your conclusions on the topic.
Take a position on the topic. After reflecting on the topic a little while longer, you decide that what you really want to say about this topic is that something should be done to reduce the amount of sugar these children consume.
You revise your thesis statement to look like this:
More attention should be paid to the food and beverage choices available to elementary school children.
This statement asserts your position, but the terms more attention and food and beverage choices are vague.
Use specific language . You decide to explain what you mean about food and beverage choices , so you write:
Experts estimate that half of elementary school children consume nine times the recommended daily allowance of sugar.
This statement is specific, but it isn’t a thesis. It merely reports a statistic instead of making an assertion.
Make an assertion based on clearly stated support. You finally revise your thesis statement one more time to look like this:
Because half of all American elementary school children consume nine times the recommended daily allowance of sugar, schools should be required to replace the beverages in soda machines with healthy alternatives.
Notice how the thesis answers the question, “What should be done to reduce sugar consumption by children, and who should do it?” When you started thinking about the paper, you may not have had a specific question in mind, but as you became more involved in the topic, your ideas became more specific. Your thesis changed to reflect your new insights.
How to Tell a Strong Thesis Statement from a Weak One
1. a strong thesis statement takes some sort of stand..
Remember that your thesis needs to show your conclusions about a subject. For example, if you are writing a paper for a class on fitness, you might be asked to choose a popular weight-loss product to evaluate. Here are two thesis statements:
There are some negative and positive aspects to the Banana Herb Tea Supplement.
This is a weak thesis statement. First, it fails to take a stand. Second, the phrase negative and positive aspects is vague.
Because Banana Herb Tea Supplement promotes rapid weight loss that results in the loss of muscle and lean body mass, it poses a potential danger to customers.
This is a strong thesis because it takes a stand, and because it's specific.
2. A strong thesis statement justifies discussion.
Your thesis should indicate the point of the discussion. If your assignment is to write a paper on kinship systems, using your own family as an example, you might come up with either of these two thesis statements:
My family is an extended family.
This is a weak thesis because it merely states an observation. Your reader won’t be able to tell the point of the statement, and will probably stop reading.
While most American families would view consanguineal marriage as a threat to the nuclear family structure, many Iranian families, like my own, believe that these marriages help reinforce kinship ties in an extended family.
This is a strong thesis because it shows how your experience contradicts a widely-accepted view. A good strategy for creating a strong thesis is to show that the topic is controversial. Readers will be interested in reading the rest of the essay to see how you support your point.
3. A strong thesis statement expresses one main idea.
Readers need to be able to see that your paper has one main point. If your thesis statement expresses more than one idea, then you might confuse your readers about the subject of your paper. For example:
Companies need to exploit the marketing potential of the Internet, and Web pages can provide both advertising and customer support.
This is a weak thesis statement because the reader can’t decide whether the paper is about marketing on the Internet or Web pages. To revise the thesis, the relationship between the two ideas needs to become more clear. One way to revise the thesis would be to write:
Because the Internet is filled with tremendous marketing potential, companies should exploit this potential by using Web pages that offer both advertising and customer support.
This is a strong thesis because it shows that the two ideas are related. Hint: a great many clear and engaging thesis statements contain words like because , since , so , although , unless , and however .
4. A strong thesis statement is specific.
A thesis statement should show exactly what your paper will be about, and will help you keep your paper to a manageable topic. For example, if you're writing a seven-to-ten page paper on hunger, you might say:
World hunger has many causes and effects.
This is a weak thesis statement for two major reasons. First, world hunger can’t be discussed thoroughly in seven to ten pages. Second, many causes and effects is vague. You should be able to identify specific causes and effects. A revised thesis might look like this:
Hunger persists in Glandelinia because jobs are scarce and farming in the infertile soil is rarely profitable.
This is a strong thesis statement because it narrows the subject to a more specific and manageable topic, and it also identifies the specific causes for the existence of hunger.
Produced by Writing Tutorial Services, Indiana University, Bloomington, IN
Writing Tutorial Services social media channels
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Developing Strong Thesis Statements

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
These OWL resources will help you develop and refine the arguments in your writing.
The thesis statement or main claim must be debatable
An argumentative or persuasive piece of writing must begin with a debatable thesis or claim. In other words, the thesis must be something that people could reasonably have differing opinions on. If your thesis is something that is generally agreed upon or accepted as fact then there is no reason to try to persuade people.
Example of a non-debatable thesis statement:
This thesis statement is not debatable. First, the word pollution implies that something is bad or negative in some way. Furthermore, all studies agree that pollution is a problem; they simply disagree on the impact it will have or the scope of the problem. No one could reasonably argue that pollution is unambiguously good.
Example of a debatable thesis statement:
This is an example of a debatable thesis because reasonable people could disagree with it. Some people might think that this is how we should spend the nation's money. Others might feel that we should be spending more money on education. Still others could argue that corporations, not the government, should be paying to limit pollution.
Another example of a debatable thesis statement:
In this example there is also room for disagreement between rational individuals. Some citizens might think focusing on recycling programs rather than private automobiles is the most effective strategy.
The thesis needs to be narrow
Although the scope of your paper might seem overwhelming at the start, generally the narrower the thesis the more effective your argument will be. Your thesis or claim must be supported by evidence. The broader your claim is, the more evidence you will need to convince readers that your position is right.
Example of a thesis that is too broad:
There are several reasons this statement is too broad to argue. First, what is included in the category "drugs"? Is the author talking about illegal drug use, recreational drug use (which might include alcohol and cigarettes), or all uses of medication in general? Second, in what ways are drugs detrimental? Is drug use causing deaths (and is the author equating deaths from overdoses and deaths from drug related violence)? Is drug use changing the moral climate or causing the economy to decline? Finally, what does the author mean by "society"? Is the author referring only to America or to the global population? Does the author make any distinction between the effects on children and adults? There are just too many questions that the claim leaves open. The author could not cover all of the topics listed above, yet the generality of the claim leaves all of these possibilities open to debate.
Example of a narrow or focused thesis:
In this example the topic of drugs has been narrowed down to illegal drugs and the detriment has been narrowed down to gang violence. This is a much more manageable topic.
We could narrow each debatable thesis from the previous examples in the following way:
Narrowed debatable thesis 1:
This thesis narrows the scope of the argument by specifying not just the amount of money used but also how the money could actually help to control pollution.
Narrowed debatable thesis 2:
This thesis narrows the scope of the argument by specifying not just what the focus of a national anti-pollution campaign should be but also why this is the appropriate focus.
Qualifiers such as " typically ," " generally ," " usually ," or " on average " also help to limit the scope of your claim by allowing for the almost inevitable exception to the rule.
Types of claims
Claims typically fall into one of four categories. Thinking about how you want to approach your topic, or, in other words, what type of claim you want to make, is one way to focus your thesis on one particular aspect of your broader topic.
Claims of fact or definition: These claims argue about what the definition of something is or whether something is a settled fact. Example:
Claims of cause and effect: These claims argue that one person, thing, or event caused another thing or event to occur. Example:
Claims about value: These are claims made of what something is worth, whether we value it or not, how we would rate or categorize something. Example:
Claims about solutions or policies: These are claims that argue for or against a certain solution or policy approach to a problem. Example:
Which type of claim is right for your argument? Which type of thesis or claim you use for your argument will depend on your position and knowledge of the topic, your audience, and the context of your paper. You might want to think about where you imagine your audience to be on this topic and pinpoint where you think the biggest difference in viewpoints might be. Even if you start with one type of claim you probably will be using several within the paper. Regardless of the type of claim you choose to utilize it is key to identify the controversy or debate you are addressing and to define your position early on in the paper.
Thesis and Purpose Statements
Use the guidelines below to learn the differences between thesis and purpose statements.
In the first stages of writing, thesis or purpose statements are usually rough or ill-formed and are useful primarily as planning tools.
A thesis statement or purpose statement will emerge as you think and write about a topic. The statement can be restricted or clarified and eventually worked into an introduction.
As you revise your paper, try to phrase your thesis or purpose statement in a precise way so that it matches the content and organization of your paper.
Thesis statements
A thesis statement is a sentence that makes an assertion about a topic and predicts how the topic will be developed. It does not simply announce a topic: it says something about the topic.
Good: X has made a significant impact on the teenage population due to its . . . Bad: In this paper, I will discuss X.
A thesis statement makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of the paper. It summarizes the conclusions that the writer has reached about the topic.
A thesis statement is generally located near the end of the introduction. Sometimes in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or an entire paragraph.
A thesis statement is focused and specific enough to be proven within the boundaries of the paper. Key words (nouns and verbs) should be specific, accurate, and indicative of the range of research, thrust of the argument or analysis, and the organization of supporting information.
Purpose statements
A purpose statement announces the purpose, scope, and direction of the paper. It tells the reader what to expect in a paper and what the specific focus will be.
Common beginnings include:
“This paper examines . . .,” “The aim of this paper is to . . .,” and “The purpose of this essay is to . . .”
A purpose statement makes a promise to the reader about the development of the argument but does not preview the particular conclusions that the writer has drawn.
A purpose statement usually appears toward the end of the introduction. The purpose statement may be expressed in several sentences or even an entire paragraph.
A purpose statement is specific enough to satisfy the requirements of the assignment. Purpose statements are common in research papers in some academic disciplines, while in other disciplines they are considered too blunt or direct. If you are unsure about using a purpose statement, ask your instructor.
This paper will examine the ecological destruction of the Sahel preceding the drought and the causes of this disintegration of the land. The focus will be on the economic, political, and social relationships which brought about the environmental problems in the Sahel.
Sample purpose and thesis statements
The following example combines a purpose statement and a thesis statement (bold).
The goal of this paper is to examine the effects of Chile’s agrarian reform on the lives of rural peasants. The nature of the topic dictates the use of both a chronological and a comparative analysis of peasant lives at various points during the reform period. . . The Chilean reform example provides evidence that land distribution is an essential component of both the improvement of peasant conditions and the development of a democratic society. More extensive and enduring reforms would likely have allowed Chile the opportunity to further expand these horizons.
For more tips about writing thesis statements, take a look at our new handout on Developing a Thesis Statement.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Developing a Thesis Statement
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects
Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing

OASIS: Writing Center
Writing a paper: thesis statements, basics of thesis statements.
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper. Specific means the thesis deals with a narrow and focused topic, appropriate to the paper's length. Arguable means that a scholar in your field could disagree (or perhaps already has!).
Strong thesis statements address specific intellectual questions, have clear positions, and use a structure that reflects the overall structure of the paper. Read on to learn more about constructing a strong thesis statement.
Being Specific
This thesis statement has no specific argument:
Needs Improvement: In this essay, I will examine two scholarly articles to find similarities and differences.
This statement is concise, but it is neither specific nor arguable—a reader might wonder, "Which scholarly articles? What is the topic of this paper? What field is the author writing in?" Additionally, the purpose of the paper—to "examine…to find similarities and differences" is not of a scholarly level. Identifying similarities and differences is a good first step, but strong academic argument goes further, analyzing what those similarities and differences might mean or imply.
Better: In this essay, I will argue that Bowler's (2003) autocratic management style, when coupled with Smith's (2007) theory of social cognition, can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover.
The new revision here is still concise, as well as specific and arguable. We can see that it is specific because the writer is mentioning (a) concrete ideas and (b) exact authors. We can also gather the field (business) and the topic (management and employee turnover). The statement is arguable because the student goes beyond merely comparing; he or she draws conclusions from that comparison ("can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover").
Making a Unique Argument
This thesis draft repeats the language of the writing prompt without making a unique argument:
Needs Improvement: The purpose of this essay is to monitor, assess, and evaluate an educational program for its strengths and weaknesses. Then, I will provide suggestions for improvement.
You can see here that the student has simply stated the paper's assignment, without articulating specifically how he or she will address it. The student can correct this error simply by phrasing the thesis statement as a specific answer to the assignment prompt.
Better: Through a series of student interviews, I found that Kennedy High School's antibullying program was ineffective. In order to address issues of conflict between students, I argue that Kennedy High School should embrace policies outlined by the California Department of Education (2010).
Words like "ineffective" and "argue" show here that the student has clearly thought through the assignment and analyzed the material; he or she is putting forth a specific and debatable position. The concrete information ("student interviews," "antibullying") further prepares the reader for the body of the paper and demonstrates how the student has addressed the assignment prompt without just restating that language.

Creating a Debate
This thesis statement includes only obvious fact or plot summary instead of argument:
Needs Improvement: Leadership is an important quality in nurse educators.
A good strategy to determine if your thesis statement is too broad (and therefore, not arguable) is to ask yourself, "Would a scholar in my field disagree with this point?" Here, we can see easily that no scholar is likely to argue that leadership is an unimportant quality in nurse educators. The student needs to come up with a more arguable claim, and probably a narrower one; remember that a short paper needs a more focused topic than a dissertation.
Better: Roderick's (2009) theory of participatory leadership is particularly appropriate to nurse educators working within the emergency medicine field, where students benefit most from collegial and kinesthetic learning.
Here, the student has identified a particular type of leadership ("participatory leadership"), narrowing the topic, and has made an arguable claim (this type of leadership is "appropriate" to a specific type of nurse educator). Conceivably, a scholar in the nursing field might disagree with this approach. The student's paper can now proceed, providing specific pieces of evidence to support the arguable central claim.
Choosing the Right Words
This thesis statement uses large or scholarly-sounding words that have no real substance:
Needs Improvement: Scholars should work to seize metacognitive outcomes by harnessing discipline-based networks to empower collaborative infrastructures.
There are many words in this sentence that may be buzzwords in the student's field or key terms taken from other texts, but together they do not communicate a clear, specific meaning. Sometimes students think scholarly writing means constructing complex sentences using special language, but actually it's usually a stronger choice to write clear, simple sentences. When in doubt, remember that your ideas should be complex, not your sentence structure.
Better: Ecologists should work to educate the U.S. public on conservation methods by making use of local and national green organizations to create a widespread communication plan.
Notice in the revision that the field is now clear (ecology), and the language has been made much more field-specific ("conservation methods," "green organizations"), so the reader is able to see concretely the ideas the student is communicating.
Leaving Room for Discussion
This thesis statement is not capable of development or advancement in the paper:
Needs Improvement: There are always alternatives to illegal drug use.
This sample thesis statement makes a claim, but it is not a claim that will sustain extended discussion. This claim is the type of claim that might be appropriate for the conclusion of a paper, but in the beginning of the paper, the student is left with nowhere to go. What further points can be made? If there are "always alternatives" to the problem the student is identifying, then why bother developing a paper around that claim? Ideally, a thesis statement should be complex enough to explore over the length of the entire paper.
Better: The most effective treatment plan for methamphetamine addiction may be a combination of pharmacological and cognitive therapy, as argued by Baker (2008), Smith (2009), and Xavier (2011).
In the revised thesis, you can see the student make a specific, debatable claim that has the potential to generate several pages' worth of discussion. When drafting a thesis statement, think about the questions your thesis statement will generate: What follow-up inquiries might a reader have? In the first example, there are almost no additional questions implied, but the revised example allows for a good deal more exploration.
Thesis Mad Libs
If you are having trouble getting started, try using the models below to generate a rough model of a thesis statement! These models are intended for drafting purposes only and should not appear in your final work.
- In this essay, I argue ____, using ______ to assert _____.
- While scholars have often argued ______, I argue______, because_______.
- Through an analysis of ______, I argue ______, which is important because_______.
Words to Avoid and to Embrace
When drafting your thesis statement, avoid words like explore, investigate, learn, compile, summarize , and explain to describe the main purpose of your paper. These words imply a paper that summarizes or "reports," rather than synthesizing and analyzing.
Instead of the terms above, try words like argue, critique, question , and interrogate . These more analytical words may help you begin strongly, by articulating a specific, critical, scholarly position.
Read Kayla's blog post for tips on taking a stand in a well-crafted thesis statement.
Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Search our website or email us .
Read our website accessibility and accommodation statement .
- Previous Page: Introductions
- Next Page: Conclusions
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students
Online Guide to Writing and Research
The writing process, explore more of umgc.
- Online Guide to Writing
Thesis Statement and Controlling Idea
So what? This is the question you will get asked if your thesis statement, or main idea, is not obvious in your paper. Your thesis statement is the most important part of your writing; without it, your paper doesn’t have a main point or stance. A thesis statement states the purpose and topic of your writing, and the controlling idea indicates the direction and, often, the writing strategy you will adopt.

Generally, your thesis is placed at the end of your introduction and is a concise and simple sentence that combines your topic and your position on the topic. Like a road map, your thesis lets your readers know what to expect from the rest of your paper. Your body paragraphs support it, and your essay lacks direction without it.
It is important to keep in mind that this early in your writing, your thesis statement is really a working thesis that you use to begin thinking about your topic. You may revise this thesis many times before you are finished thinking and ready to write your final draft. Below are some sample thesis statements.
YOUR TOPIC + POSITION ON TOPIC = THESIS STATEMENT
Thesis statement do's and don'ts.
Present an argument, stance, or claim. Can your audience argue with it?
Provide a key to the organization of your paper. Can you construct body paragraphs that support it?
Mirror the assignment prompt. Are you following what is expected of you?
Present the thesis at the end of the introduction.
Answer the question: “so what?”
Present an argument that can be supported by reputable research. Is your argument logical?
Embrace the “how” and “why” elements. It’s a great strategy to present the problem, examine why it’s a problem, and show how it can be fixed.
Include announcement style language like “this paper will discuss” or “this will be shown in this essay.”
Be informative only with no argument or stance, such as, “Some high school seniors decide to take a gap year.”
Include overly broad or generalized statements like, “Kids of this generation are lazy.”
Force the reader to guess what the paper will prove or discuss
Be questions.
Key Takeaways
Your thesis is one statement at the end of your introduction and should be clear, concise, and arguable.
Without a thesis, your paper lacks direction and purpose.
Mailing Address: 3501 University Blvd. East, Adelphi, MD 20783 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License . © 2022 UMGC. All links to external sites were verified at the time of publication. UMGC is not responsible for the validity or integrity of information located at external sites.
Table of Contents: Online Guide to Writing
Chapter 1: College Writing
How Does College Writing Differ from Workplace Writing?
What Is College Writing?
Why So Much Emphasis on Writing?
Chapter 2: The Writing Process
Doing Exploratory Research
Getting from Notes to Your Draft
Introduction
Prewriting - Techniques to Get Started - Mining Your Intuition
Prewriting: Targeting Your Audience
Prewriting: Techniques to Get Started
Prewriting: Understanding Your Assignment
Rewriting: Being Your Own Critic
Rewriting: Creating a Revision Strategy
Rewriting: Getting Feedback
Rewriting: The Final Draft
Techniques to Get Started - Outlining
Techniques to Get Started - Using Systematic Techniques
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Freewriting
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Summarizing Your Ideas
Writing: Outlining What You Will Write
Chapter 3: Thinking Strategies
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone: Style Through Vocabulary and Diction
Critical Strategies and Writing
Critical Strategies and Writing: Analysis
Critical Strategies and Writing: Evaluation
Critical Strategies and Writing: Persuasion
Critical Strategies and Writing: Synthesis
Developing a Paper Using Strategies
Kinds of Assignments You Will Write
Patterns for Presenting Information
Patterns for Presenting Information: Critiques
Patterns for Presenting Information: Discussing Raw Data
Patterns for Presenting Information: General-to-Specific Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Specific-to-General Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Summaries and Abstracts
Supporting with Research and Examples
Writing Essay Examinations
Writing Essay Examinations: Make Your Answer Relevant and Complete
Writing Essay Examinations: Organize Thinking Before Writing
Writing Essay Examinations: Read and Understand the Question
Chapter 4: The Research Process
Planning and Writing a Research Paper
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Ask a Research Question
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Cite Sources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Collect Evidence
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Decide Your Point of View, or Role, for Your Research
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Draw Conclusions
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Find a Topic and Get an Overview
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Manage Your Resources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Outline
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Survey the Literature
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Work Your Sources into Your Research Writing
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Human Resources
Research Resources: What Are Research Resources?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Electronic Resources
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Print Resources
Structuring the Research Paper: Formal Research Structure
Structuring the Research Paper: Informal Research Structure
The Nature of Research
The Research Assignment: How Should Research Sources Be Evaluated?
The Research Assignment: When Is Research Needed?
The Research Assignment: Why Perform Research?
Chapter 5: Academic Integrity
Academic Integrity
Giving Credit to Sources
Giving Credit to Sources: Copyright Laws
Giving Credit to Sources: Documentation
Giving Credit to Sources: Style Guides
Integrating Sources
Practicing Academic Integrity
Practicing Academic Integrity: Keeping Accurate Records
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Paraphrasing Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Quoting Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Summarizing Your Sources
Types of Documentation
Types of Documentation: Bibliographies and Source Lists
Types of Documentation: Citing World Wide Web Sources
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - APA Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - CSE/CBE Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - Chicago Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - MLA Style
Types of Documentation: Note Citations
Chapter 6: Using Library Resources
Finding Library Resources
Chapter 7: Assessing Your Writing
How Is Writing Graded?
How Is Writing Graded?: A General Assessment Tool
The Draft Stage
The Draft Stage: The First Draft
The Draft Stage: The Revision Process and the Final Draft
The Draft Stage: Using Feedback
The Research Stage
Using Assessment to Improve Your Writing
Chapter 8: Other Frequently Assigned Papers
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Article and Book Reviews
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Reaction Papers
Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Adapting the Argument Structure
Writing Arguments: Purposes of Argument
Writing Arguments: References to Consult for Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Anticipate Active Opposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Determine Your Organization
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Develop Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Introduce Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - State Your Thesis or Proposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Write Your Conclusion
Writing Arguments: Types of Argument
Appendix A: Books to Help Improve Your Writing
Dictionaries
General Style Manuals
Researching on the Internet
Special Style Manuals
Writing Handbooks
Appendix B: Collaborative Writing and Peer Reviewing
Collaborative Writing: Assignments to Accompany the Group Project
Collaborative Writing: Informal Progress Report
Collaborative Writing: Issues to Resolve
Collaborative Writing: Methodology
Collaborative Writing: Peer Evaluation
Collaborative Writing: Tasks of Collaborative Writing Group Members
Collaborative Writing: Writing Plan
General Introduction
Peer Reviewing
Appendix C: Developing an Improvement Plan
Working with Your Instructor’s Comments and Grades
Appendix D: Writing Plan and Project Schedule
Devising a Writing Project Plan and Schedule
Reviewing Your Plan with Others
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a thesis statement + examples

What is a thesis statement?
Is a thesis statement a question, how do you write a good thesis statement, how do i know if my thesis statement is good, examples of thesis statements, helpful resources on how to write a thesis statement, frequently asked questions about writing a thesis statement, related articles.
A thesis statement is the main argument of your paper or thesis.
The thesis statement is one of the most important elements of any piece of academic writing . It is a brief statement of your paper’s main argument. Essentially, you are stating what you will be writing about.
You can see your thesis statement as an answer to a question. While it also contains the question, it should really give an answer to the question with new information and not just restate or reiterate it.
Your thesis statement is part of your introduction. Learn more about how to write a good thesis introduction in our introduction guide .
A thesis statement is not a question. A statement must be arguable and provable through evidence and analysis. While your thesis might stem from a research question, it should be in the form of a statement.
Tip: A thesis statement is typically 1-2 sentences. For a longer project like a thesis, the statement may be several sentences or a paragraph.
A good thesis statement needs to do the following:
- Condense the main idea of your thesis into one or two sentences.
- Answer your project’s main research question.
- Clearly state your position in relation to the topic .
- Make an argument that requires support or evidence.
Once you have written down a thesis statement, check if it fulfills the following criteria:
- Your statement needs to be provable by evidence. As an argument, a thesis statement needs to be debatable.
- Your statement needs to be precise. Do not give away too much information in the thesis statement and do not load it with unnecessary information.
- Your statement cannot say that one solution is simply right or simply wrong as a matter of fact. You should draw upon verified facts to persuade the reader of your solution, but you cannot just declare something as right or wrong.
As previously mentioned, your thesis statement should answer a question.
If the question is:
What do you think the City of New York should do to reduce traffic congestion?
A good thesis statement restates the question and answers it:
In this paper, I will argue that the City of New York should focus on providing exclusive lanes for public transport and adaptive traffic signals to reduce traffic congestion by the year 2035.
Here is another example. If the question is:
How can we end poverty?
A good thesis statement should give more than one solution to the problem in question:
In this paper, I will argue that introducing universal basic income can help reduce poverty and positively impact the way we work.
- The Writing Center of the University of North Carolina has a list of questions to ask to see if your thesis is strong .
A thesis statement is part of the introduction of your paper. It is usually found in the first or second paragraph to let the reader know your research purpose from the beginning.
In general, a thesis statement should have one or two sentences. But the length really depends on the overall length of your project. Take a look at our guide about the length of thesis statements for more insight on this topic.
Here is a list of Thesis Statement Examples that will help you understand better how to write them.
Every good essay should include a thesis statement as part of its introduction, no matter the academic level. Of course, if you are a high school student you are not expected to have the same type of thesis as a PhD student.
Here is a great YouTube tutorial showing How To Write An Essay: Thesis Statements .


- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

5.2: Identifying Thesis Statements and Topic Sentences
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 25748
Being able to identify the purpose and thesis of a text, as you’re reading it, takes practice. This section will offer you that practice.
One fun strategy for developing a deeper understanding the material you’re reading is to make a visual “map” of the ideas. Mind maps, whether hand-drawn or done through computer programs, can be fun to make, and help put all the ideas of an essay you’re reading in one easy-to-read format.
Your understanding of what the “central” element of the mind map is might change as you read and re-read. Developing the central idea of your mind map is a great way to help you determine the reading’s thesis.
Figure 2.5. 1
- Hand-drawn Mind Map
Locating Explicit and Implicit Thesis Statements
In academic writing, the thesis is often explicit : it is included as a sentence as part of the text. It might be near the beginning of the work, but not always–some types of academic writing leave the thesis until the conclusion.
Journalism and reporting also rely on explicit thesis statements that appear very early in the piece–the first paragraph or even the first sentence.
Works of literature, on the other hand, usually do not contain a specific sentence that sums up the core concept of the writing. However, readers should finish the piece with a good understanding of what the work was trying to convey. This is what’s called an implicit thesis statement: the primary point of the reading is conveyed indirectly, in multiple locations throughout the work. (In literature, this is also referred to as the theme of the work.)
Academic writing sometimes relies on implicit thesis statements, as well.
This video offers excellent guidance in identifying the thesis statement of a work, no matter if it’s explicit or implicit.
Topic Sentences
We’ve learned that a thesis statement conveys the primary message of an entire piece of text. Now, let’s look at the next level of important sentences in a piece of text: topic sentences in each paragraph.
A useful metaphor would be to think of the thesis statement of a text as a general: it controls all the major decisions of the writing. There is only one thesis statement in a text. Topic sentences, in this relationship, serve as captains: they organize and sub-divide the overall goals of a writing into individual components. Each paragraph will have a topic sentence.
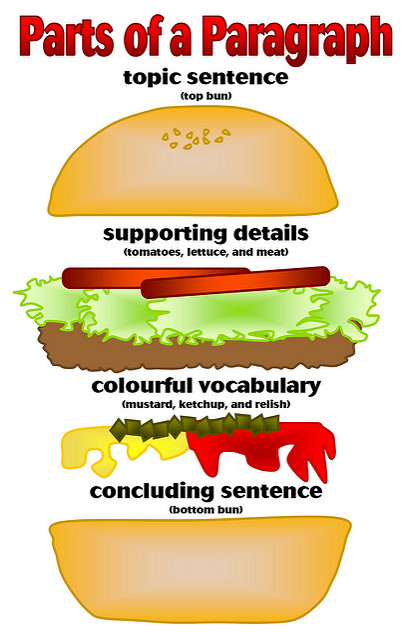
Figure 2.5. 2
It might be helpful to think of a topic sentence as working in two directions simultaneously. It relates the paragraph to the essay’s thesis, and thereby acts as a signpost for the argument of the paper as a whole, but it also defines the scope of the paragraph itself. For example, consider the following topic sentence:
Many characters in Lorraine Hansberry’s play A Raisin in the Sun have one particular dream in which they are following, though the character Walter pursues his most aggressively.
If this sentence controls the paragraph that follows, then all sentences in the paragraph must relate in some way to Walter and the pursuit of his dream.
Topic sentences often act like tiny thesis statements. Like a thesis statement, a topic sentence makes a claim of some sort. As the thesis statement is the unifying force in the essay, so the topic sentence must be the unifying force in the paragraph. Further, as is the case with the thesis statement, when the topic sentence makes a claim, the paragraph which follows must expand, describe, or prove it in some way. Topic sentences make a point and give reasons or examples to support it.
The following diagram illustrates how a topic sentence can provide more focus to the general topic at hand.
Placement of Topic Sentences
What if I told you that the topic sentence doesn’t necessarily need to be at the beginning? This might be contrary to what you’ve learned in previous English or writing classes, and that’s okay. Certainly, when authors announce a topic clearly and early on in a paragraph, their readers are likely to grasp their idea and to make the connections that they want them to make.
However, when authors are writing for a more sophisticated academic audience—that is an audience of college-educated readers—they will often use more sophisticated organizational strategies to build and reveal ideas in their writing. One way to think about a topic sentence, is that it presents the broadest view of what authors want their readers to understand. This is to say that they’re providing a broad statement that either announces or brings into focus the purpose or the meaning for the details of the paragraph. If the topic sentence is seen as the broadest view, then every supporting detail will bring a narrower—or more specific—view of the same topic.
With this in mind, take some time to contemplate the diagrams in the figure below. The widest point of each diagram (the bases of the triangles) represents the topic sentence of the paragraph. As details are presented, the topic becomes narrower and more focused. The topic can precede the details, it can follow them, it can both precede and follow them, or the details can surround the topic. There are surely more alternatives than those that are presented here, but this gives you an idea of some of the possible paragraph structures and possible placements for the topic sentence of a paragraph.
Consider some of the following examples of different topic sentence placements in a paragraph from a review essay of the beloved children’s book, The Cat in the Hat , by Dr. Seuss. Paragraph structures are labeled according to the diagrams presented above, and topic sentences are identified by red text.
Topic Sentence-Details-Topic Sentence
A good children’s book requires an exciting plot and a problem with which children can sympathize. In The Cat in the Hat there is plenty of action, depicted in the wild antics of the cat, and later in the amazing but dangerous and messy tricks of Thing 1 and Thing 2. All this excitement and action naturally draws children into the story and keeps the plot moving forward at a pace that maintains their interest. There is also tension to be resolved. The fish senses danger and constantly warns the children not to participate in the cat’s perilous stunts. And later, as the mother’s return becomes more imminent, the children begin to heed the fish’s warning and finally wish to contain the chaos and clean up the mess, but how? While this plot is fantastic enough to fuel any child’s imagination, it also contains a problem with which any child can relate: a mess and the threat of a parent’s disapproval. The careful balance of action, tension, and relatability is what makes this book an enduring childhood favorite.
Topic Sentence-Details
The careful balance of action, tension, and relatability is what makes Dr. Seuss’s The Cat in the Hat an enduring childhood favorite. In The Cat in the Hat there is plenty of action, depicted in the wild antics of the cat, and later in the amazing but dangerous and messy tricks of Thing 1 and Thing 2. All this excitement and action naturally draws children into the story and keeps the plot moving forward at a pace that maintains their interest. There is also tension to be resolved. The fish senses danger and constantly warns the children not to participate in the cat’s perilous stunts. And later, as the mother’s return becomes more imminent, the children begin to heed the fish’s warning and finally wish to contain the chaos and clean up the mess, but how? While this plot is fantastic enough to fuel any child’s imagination, it also contains a problem with which any child can relate: a mess and the threat of a parent’s disapproval.
You can relocate the topic sentence to the end here, and you’ll have an example of the Details-Topic Sentence method of organizing the paragraph.
Details-Topic Sentence-Details
In The Cat in the Hat there is plenty of action, depicted in the wild antics of the cat, and later in the amazing but dangerous and messy tricks of Thing 1 and Thing 2. All this excitement and action naturally draws children into the story and keeps the plot moving forward at a pace that maintains their interest. The careful balance of action, tension, and relatability is what makes Dr. Seuss’s The Cat in the Hat an enduring childhood favorite. There is definitely tension to be resolved here. The fish senses danger and constantly warns the children not to participate in the cat’s perilous stunts. And later, as the mother’s return becomes more imminent, the children begin to heed the fish’s warning and finally wish to contain the chaos and clean up the mess, but how? While this plot is fantastic enough to fuel any child’s imagination, it also contains a problem with which any child can relate: a mess and the threat of a parent’s disapproval.
Explicit and Implicit Topic Sentences
Similar to thesis statements, topic sentences may be explicit or implicit.
Consider the following paragraph from an essay titled “The Bothersome Beauty of Pigeons,” by author and Boise State writing professor, Bruce Ballenger. It’s important to note that this is a personal narrative essay rather than a more traditional academic essay, but the paragraph provides a good example of an implied topic. In this essay Ballenger takes the time to consider the beauty of pigeons, a bird that’s usually thought of as nothing more than a nuisance. Just prior to this paragraph, Ballenger talks about how he used a fake owl to scare away pigeons on his property. He goes on to explain,
My pigeons moved next door where an elderly couple feed them bird seed and have the time and willingness to clean up after their new charges; so it seems, in this case, things have worked out for everyone. But the large flocks still haunt the piazzas in Florence and Venice, the squares in London, and similar places in nearly every city across the globe. Despite their ability to distinguish between a Van Gogh and a Chagall, pigeons still deposit droppings that deface the great marble statues and facades–the works of art and architecture that are part of our human heritage–and yet people still buy bags of seed for about a dollar and pose for photographs, drenched in doves. Meanwhile, officials in these cities continue, sometimes quietly, to wage war against the birds (“Introduction”).
Here, Ballenger seems to be saying that in spite of the attempts of so many to rid themselves of the pigeons, others are still drawn to them and will feed them and encourage them to come back. His main idea seems to be that the battle against pigeons is a losing proposition, but he doesn’t come out and say so. His message in this paragraph is implied. Do you think this paragraph would be improved with an explicit topic sentence?
EXERCISE 1: Identify the Topic and Focus
Choose a piece of writing, perhaps an essay or some news articles found online, and for each paragraph identify (1) the topic and (2) the more focused idea. Remember, the topic sentence applies more focus to the broader topic to help narrow the scope of the paragraph. For example, the topic of a paragraph might be school lunches. The more focused idea of that same paragraph might be the idea of having students plant school gardens as a way to help incorporate more fresh produce in the menu.
License and Attributions:
CC licensed content, Previously shared:
Basic Reading and Writing. Authored by: Lumen. Located at: https://human.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Composition/Book:_Basic_Reading_and_Writing_(Lumen)/ Module_2:_Critical_Reading/2.05:_Identifying_Thesis_Statements License: CC BY: Attribution.
Adaptions: Reformatted, some content removed to fit a broader audience.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Identifying Thesis Statements, Claims, and Evidence
Thesis statements, claims, and evidence, introduction.
The three important parts of an argumentative essay are:
- A thesis statement is a sentence, usually in the first paragraph of an article, that expresses the article’s main point. It is not a fact; it’s a statement that you could disagree with. Therefore, the author has to convince you that the statement is correct.
- Claims are statements that support the thesis statement, but like the thesis statement, are not facts. Because a claim is not a fact, it requires supporting evidence.
- Evidence is factual information that shows a claim is true. Usually, writers have to conduct their own research to find evidence that supports their ideas. The evidence may include statistical (numerical) information, the opinions of experts, studies, personal experience, scholarly articles, or reports.
Each paragraph in the article is numbered at the beginning of the first sentence.
Paragraphs 1-7
Identifying the Thesis Statement. Paragraph 2 ends with this thesis statement: “People’s prior convictions should not be held against them in their pursuit of higher learning.” It is a thesis statement for three reasons:
- It is the article’s main argument.
- It is not a fact. Someone could think that peoples’ prior convictions should affect their access to higher education.
- It requires evidence to show that it is true.
Finding Claims. A claim is statement that supports a thesis statement. Like a thesis, it is not a fact so it needs to be supported by evidence.
You have already identified the article’s thesis statement: “People’s prior convictions should not be held against them in their pursuit of higher learning.”
Like the thesis, a claim be an idea that the author believes to be true, but others may not agree. For this reason, a claim needs support.
- Question 1. Can you find a claim in paragraph 3? Look for a statement that might be true, but needs to be supported by evidence.
Finding Evidence.
Paragraphs 5-7 offer one type of evidence to support the claim you identified in the last question. Reread paragraphs 5-7.
- Question 2. Which word best describes the kind of evidence included in those paragraphs: A report, a study, personal experience of the author, statistics, or the opinion of an expert?
Paragraphs 8-10
Finding Claims
Paragraph 8 makes two claims:
- “The United States needs to have more of this transformative power of education.”
- “The country [the United States] incarcerates more people and at a higher rate than any other nation in the world.”
Finding Evidence
Paragraphs 8 and 9 include these statistics as evidence:
- “The U.S. accounts for less than 5 percent of the world population but nearly 25 percent of the incarcerated population around the globe.”
- “Roughly 2.2 million people in the United States are essentially locked away in cages. About 1 in 5 of those people are locked up for drug offenses.”
Question 3. Does this evidence support claim 1 from paragraph 8 (about the transformative power of education) or claim 2 (about the U.S.’s high incarceration rate)?
Question 4. Which word best describes this kind of evidence: A report, a study, personal experience of the author, statistics, or the opinion of an expert?
Paragraphs 11-13
Remember that in paragraph 2, Andrisse writes that:
- “People’s prior convictions should not be held against them in their pursuit of higher learning.” (Thesis statement)
- “More must be done to remove the various barriers that exist between formerly incarcerated individuals such as myself and higher education.” (Claim)
Now, review paragraphs 11-13 (Early life of crime). In these paragraphs, Andrisse shares more of his personal story.
Question 5. Do you think his personal story is evidence for statement 1 above, statement 2, both, or neither one?
Question 6. Is yes, which one(s)?
Question 7. Do you think his personal story is good evidence? Does it persuade you to agree with him?
Paragraphs 14-16
Listed below are some claims that Andrisse makes in paragraph 14. Below each claim, please write the supporting evidence from paragraphs 15 and 16. If you can’t find any evidence, write “none.”
Claim: The more education a person has, the higher their income.
Claim: Similarly, the more education a person has, the less likely they are to return to prison.
Paragraphs 17-19
Evaluating Evidence
In these paragraphs, Andrisse returns to his personal story. He explains how his father’s illness inspired him to become a doctor and shares that he was accepted to only one of six biomedical graduate programs.
Do you think that this part of Andrisse’s story serves as evidence (support) for any claims that you’ve identified so far? Or does it support his general thesis that “people’s prior convictions should not be held against them in pursuit of higher learning?” Please explain your answer.
Paragraphs 20-23
Andrisse uses his personal experience to repeat a claim he makes in paragraph 3, that “more must be done to remove the various barriers that exist between formerly incarcerated individuals such as myself and higher education.”
To support this statement, he has to show that barriers exist. One barrier he identifies is the cost of college. He then explains the advantages of offering Pell grants to incarcerated people.
What evidence in paragraphs 21-23 support his claim about the success of Pell grants?
Paragraphs 24-28 (Remove questions about drug crimes from federal aid forms)
In this section, Andrisse argues that federal aid forms should not ask students about prior drug convictions. To support that claim, he includes a statistic about students who had to answer a similar question on their college application.
What statistic does he include?
In paragraph 25, he assumes that if a question about drug convictions discourages students from applying to college, it will probably also discourage them from applying for federal aid.
What do you think about this assumption? Do you think it’s reasonable or do you think Andrisse needs stronger evidence to show that federal aid forms should not ask students about prior drug convictions?
Supporting English Language Learners in First-Year College Composition Copyright © by Breana Bayraktar is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

7.2 The Topic, General Purpose, Specific Purpose, and Thesis
Before any work can be done on crafting the body of your speech or presentation, you must first do some prep work—selecting a topic, formulating a general purpose, a specific purpose statement, and crafting a central idea, or thesis statement. In doing so, you lay the foundation for your speech by making important decisions about what you will speak about and for what purpose you will speak. These decisions will influence and guide the entire speechwriting process, so it is wise to think carefully and critically during these beginning stages.
Selecting a Topic
Generally, speakers focus on one or more interrelated topics—relatively broad concepts, ideas, or problems that are relevant for particular audiences. The most common way that speakers discover topics is by simply observing what is happening around them—at their school, in their local government, or around the world. Student government leaders, for example, speak or write to other students when their campus is facing tuition or fee increases, or when students have achieved something spectacular, like lobbying campus administrators for lower student fees and succeeding. In either case, it is the situation that makes their speeches appropriate and useful for their audience of students and university employees. More importantly, they speak when there is an opportunity to change a university policy or to alter the way students think or behave in relation to a particular event on campus.
But you need not run for president or student government in order to give a meaningful speech. On the contrary, opportunities abound for those interested in engaging speech as a tool for change. Perhaps the simplest way to find a topic is to ask yourself a few questions, including:
• What important events are occurring locally, nationally and internationally? • What do I care about most? • Is there someone or something I can advocate for? • What makes me angry/happy? • What beliefs/attitudes do I want to share? • Is there some information the audience needs to know?
Students speak about what is interesting to them and their audiences. What topics do you think are relevant today? There are other questions you might ask yourself, too, but these should lead you to at least a few topical choices. The most important work that these questions do is to locate topics within your pre-existing sphere of knowledge and interest. David Zarefsky (2010) also identifies brainstorming as a way to develop speech topics, a strategy that can be helpful if the questions listed above did not yield an appropriate or interesting topic. Starting with a topic you are already interested in will likely make writing and presenting your speech a more enjoyable and meaningful experience. It means that your entire speechwriting process will focus on something you find important and that you can present this information to people who stand to benefit from your speech.
Once you have answered these questions and narrowed your responses, you are still not done selecting your topic. For instance, you might have decided that you really care about breeds of dogs. This is a very broad topic and could easily lead to a dozen different speeches. To resolve this problem, speakers must also consider the audience to whom they will speak, the scope of their presentation, and the outcome they wish to achieve.
Formulating the Purpose Statements
By honing in on a very specific topic, you begin the work of formulating your purpose statement . In short, a purpose statement clearly states what it is you would like to achieve. Purpose statements are especially helpful for guiding you as you prepare your speech. When deciding which main points, facts, and examples to include, you should simply ask yourself whether they are relevant not only to the topic you have selected, but also whether they support the goal you outlined in your purpose statement. The general purpose statement of a speech may be to inform, to persuade, to celebrate, or to entertain. Thus, it is common to frame a specific purpose statement around one of these goals. According to O’Hair, Stewart, and Rubenstein, a specific purpose statement “expresses both the topic and the general speech purpose in action form and in terms of the specific objectives you hope to achieve” (2004). For instance, the home design enthusiast might write the following specific purpose statement: At the end of my speech, the audience will learn the pro’s and con’s of flipping houses. In short, the general purpose statement lays out the broader goal of the speech while the specific purpose statement describes precisely what the speech is intended to do. Some of your professors may ask that you include the general purpose and add the specific purpose.
Writing the Thesis Statement
The specific purpose statement is a tool that you will use as you write your talk, but it is unlikely that it will appear verbatim in your speech. Instead, you will want to convert the specific purpose statement into a central idea, or thesis statement that you will share with your audience.
Depending on your instructor’s approach, a thesis statement may be written two different ways. A thesis statement may encapsulate the main points of a speech in just a sentence or two, and be designed to give audiences a quick preview of what the entire speech will be about. The thesis statement for a speech, like the thesis of a research-based essay, should be easily identifiable and ought to very succinctly sum up the main points you will present. Some instructors prefer that your thesis, or central idea, be a single, declarative statement providing the audience with an overall statement that provides the essence of the speech, followed by a separate preview statement.
If you are a Harry Potter enthusiast, you may write a thesis statement (central idea) the following way using the above approach: J.K. Rowling is a renowned author of the Harry Potter series with a Cinderella like story having gone from relatively humble beginnings, through personal struggles, and finally success and fame.
Writing the Preview Statement
However, some instructors prefer that you separate your thesis from your preview statement . A preview statement (or series of statements) is a guide to your speech. This is the part of the speech that literally tells the audience exactly what main points you will cover. If you were to open your Waze app, it would tell you exactly how to get there. Best of all, you would know what to look for! So, if we take our J.K Rowling example, let’s rewrite that using this approach separating out the thesis and preview:
J.K. Rowling is a renowned author of the Harry Potter series with a Cinderella like rags to riches story. First, I will tell you about J.K. Rowling’s humble beginnings. Then, I will describe her personal struggles as a single mom. Finally, I will explain how she overcame adversity and became one of the richest women in the United Kingdom.
There is no best way to approach this. This is up to your instructor.
Writing the Body of Your Speech
Once you have finished the important work of deciding what your speech will be about, as well as formulating the purpose statement and crafting the thesis, you should turn your attention to writing the body of your speech. All of your main points are contained in the body, and normally this section is prepared well before you ever write the introduction or conclusion. The body of your speech will consume the largest amount of time to present; and it is the opportunity for you to elaborate on facts, evidence, examples, and opinions that support your thesis statement and do the work you have outlined in the specific purpose statement. Combining these various elements into a cohesive and compelling speech, however, is not without its difficulties, the first of which is deciding which elements to include and how they ought to be organized to best suit your purpose.
clearly states what it is you would like to achieve
“expresses both the topic and the general speech purpose in action form and in terms of the specific objectives you hope to achieve" (O'Hair, Stewart, & Rubenstein, 2004)
single, declarative sentence that captures the essence or main point of your entire presentation
the part of the speech that literally tells the audience exactly what main points you will cover
Introduction to Speech Communication Copyright © 2021 by Individual authors retain copyright of their work. is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

- [email protected]
- Shapiro Library
- SNHU Library Frequently Asked Questions
FAQ: What is a thesis statement and how do I write one?
- 7 Academic Integrity & Plagiarism
- 60 Academic Support, Writing Help, & Presentation Help
- 27 Access/Remote Access
- 7 Accessibility
- 9 Building/Facilities
- 7 Career/Job Information
- 26 Catalog/Print Books
- 26 Circulation
- 128 Citing Sources
- 14 Copyright
- 310 Databases
- 24 Directions/Location
- 18 Faculty Resources/Needs
- 7 Hours/Contacts
- 2 Innovation Lab & Makerspace/3D Printing
- 25 Interlibrary Loan
- 43 IT/Computer/Printing Support
- 3 Library Instruction
- 37 Library Technology Help
- 6 Multimedia
- 17 Online Programs
- 19 Periodicals
- 25 Policies
- 8 RefWorks/Citation Managers
- 4 Research Guides (LibGuides)
- 217 Research Help
- 23 University Services
Last Updated: Apr 01, 2024 Views: 5
What is a thesis statement.
A thesis statement is a sentence that states the main idea of your paper. It is not just a statement of fact, but a statement of position. What argument are you making about your topic? Your thesis should answer that question.
How long should my thesis statement be?
Thesis statements are often just one sentence. Keep thesis statements concise, without extra words or information. If you are having trouble keeping your thesis statement to one sentence, consider the following:
- Is your thesis is specific enough?
- Does your thesis directly supports your paper?
- Does your thesis accurately describes your purpose or argue your claim?
Can I see some example thesis statements?
The following websites have examples of thesis statements:
- Thesis Statements This link opens in a new window (UNC)
- Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements This link opens in a new window (OWL at Purdue)
- Writing an Effective Thesis Statement This link opens in a new window (Indiana River State College)
These web resources may be helpful if you are looking for examples. However, be sure to evaluate any sources you use! The Shapiro Library cannot vouch for the accuracy of information provided on external websites.
Where can I find more information?
Video tutorials.
- The Persuasive Thesis: How to Write an Argument This link opens in a new window (SNHU Academic Support)
- Research and Citation Playlist This link opens in a new window (SNHU Academic Support)
- Planning a Paper series: Drafting a Thesis Statement This link opens in a new window ( Infobase Learning Cloud - SNHU Login Required)
More Information
- Build a Critical Analysis Thesis This link opens in a new window (SNHU Academic Support)
- Build a Compare & Contrast Thesis This link opens in a new window (SNHU Academic Support)
- Build a History Thesis This link opens in a new window (SNHU Academic Support)
- Build a Persuasive Thesis This link opens in a new window (SNHU Academic Support)
Further Help
This information is intended to be a guideline, not expert advice. Please speak to your instructor about the appropriate way to craft thesis statements for your class assignments and projects.
Campus Students
To access Academic Support, visit your Brightspace course and select “Tutoring and Mentoring” from the Academic Support pulldown menu.
Online Students
To access help with citations and more, visit the Academic Support via modules in Brightspace:
- Academic Support Overview: Getting Help with your Schoolwork This link opens in a new window
- Share on Facebook
Was this helpful? Yes 0 No 0
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) are a self-serve option for users to search and find answers to their questions.
Use the search box above to type your question to search for an answer or browse existing FAQs by group, topic, etc.
Tell Me More
Link to Question Form
More assistance.
Submit a Question
Related FAQs

8.2 The Topic, General Purpose, Specific Purpose, and Thesis
Before any work can be done on crafting the body of your speech or presentation, you must first do some prep work—selecting a topic, formulating a general purpose, a specific purpose statement, and crafting a central idea, or thesis statement. In doing so, you lay the foundation for your speech by making important decisions about what you will speak about and for what purpose you will speak. These decisions will influence and guide the entire speechwriting process, so it is wise to think carefully and critically during these beginning stages.
Understanding the General Purpose
Before any work on a speech can be done, the speaker needs to understand the general purpose of the speech. The general purpose is what the speaker hopes to accomplish and will help guide in the selection of a topic. The instructor generally provides the general purpose for a speech, which falls into one of three categories. A general purpose to inform would mean that the speaker is teaching the audience about a topic, increasing their understanding and awareness, or providing new information about a topic the audience might already know. Informative speeches are designed to present the facts, but not give the speaker’s opinion or any call to action. A general purpose to persuade would mean that the speaker is choosing the side of a topic and advocating for their side or belief. The speaker is asking the audience to believe in their stance, or to take an action in support of their topic. A general purpose to entertain often entails short speeches of ceremony, where the speaker is connecting the audience to the celebration. You can see how these general purposes are very different. An informative speech is just facts, the speaker would not be able to provide an opinion or direction on what to do with the information, whereas a persuasive speech includes the speaker’s opinions and direction on what to do with the information. Before a speaker chooses a topic, they must first understand the general purpose.
Selecting a Topic
Generally, speakers focus on one or more interrelated topics—relatively broad concepts, ideas, or problems that are relevant for particular audiences. The most common way that speakers discover topics is by simply observing what is happening around them—at their school, in their local government, or around the world. Opportunities abound for those interested in engaging speech as a tool for change. Perhaps the simplest way to find a topic is to ask yourself a few questions, including:
- What important events are occurring locally, nationally, and internationally?
- What do I care about most?
- Is there someone or something I can advocate for?
- What makes me angry/happy?
- What beliefs/attitudes do I want to share?
- Is there some information the audience needs to know?
Students speak about what is interesting to them and their audiences. What topics do you think are relevant today? There are other questions you might ask yourself, too, but these should lead you to at least a few topical choices. The most important work that these questions do is to locate topics within your pre-existing sphere of knowledge and interest. Topics should be ideas that interest the speaker or are part of their daily lives. In order for a topic to be effective, the speaker needs to have some credibility or connection to the topic; it would be unfair to ask the audience to donate to a cause that the speaker has never donated to. There must be a connection to the topic for the speaker to be seen as credible. David Zarefsky (2010) also identifies brainstorming as a way to develop speech topics, a strategy that can be helpful if the questions listed above did not yield an appropriate or interesting topic. Brainstorming involves looking at your daily activities to determine what you could share with an audience. Perhaps if you work out regularly or eat healthy, you could explain that to an audience, or demonstrate how to dribble a basketball. If you regularly play video games, you may advocate for us to take up video games or explain the history of video games. Anything that you find interesting or important might turn into a topic. Starting with a topic you are already interested in will make writing and presenting your speech a more enjoyable and meaningful experience. It means that your entire speechwriting process will focus on something you find important and that you can present this information to people who stand to benefit from your speech. At this point, it is also important to consider the audience before choosing a topic. While we might really enjoy a lot of different things that could be topics, if the audience has no connection to that topic, then it wouldn’t be meaningful for the speaker or audience. Since we always have a diverse audience, we want to make sure that everyone in the audience can gain some new information from the speech. Sometimes, a topic might be too complicated to cover in the amount of time we have to present, or involve too much information then that topic might not work for the assignment, and finally if the audience can not gain anything from a topic then it won’t work. Ultimately, when we choose a topic we want to pick something that we are familiar with and enjoy, we have credibility and that the audience could gain something from. Once you have answered these questions and narrowed your responses, you are still not done selecting your topic. For instance, you might have decided that you really care about breeds of dogs. This is a very broad topic and could easily lead to a dozen different speeches. To resolve this problem, speakers must also consider the audience to whom they will speak, the scope of their presentation, and the outcome they wish to achieve.
Formulating the Purpose Statements
By honing in on a very specific topic, you begin the work of formulating your purpose statement. In short, a purpose statement clearly states what it is you would like to achieve. Purpose statements are especially helpful for guiding you as you prepare your speech. When deciding which main points, facts, and examples to include, you should simply ask yourself whether they are relevant not only to the topic you have selected, but also whether they support the goal you outlined in your purpose statement. The general purpose statement of a speech may be to inform, to persuade, to celebrate, or to entertain. Thus, it is common to frame a specific purpose statement around one of these goals. According to O’Hair, Stewart, and Rubenstein, a specific purpose statement “expresses both the topic and the general speech purpose in action form and in terms of the specific objectives you hope to achieve” (2004). The specific purpose is a single sentence that states what the audience will gain from this speech, or what will happen at the end of the speech. The specific purpose is a combination of the general purpose and the topic and helps the speaker to focus in on what can be achieved in a short speech.
To go back to the topic of a dog breed, the general purpose might be to inform, a specific purpose might be: To inform the audience about how corgis became household pets. If the general purpose is to persuade the specific purpose might be: to persuade the audience that dog breeds deemed “dangerous” should not be excluded from living in the cities. In short, the general purpose statement lays out the broader goal of the speech while the specific purpose statement describes precisely what the speech is intended to do. The specific purpose should focus on the audience and be measurable, if I were to ask the audience before I began the speech how many people know how corgis became household pets, they could raise their hand, and if I ask at the end of my speech how many people know how corgis became household pets, I should see a lot more hands. The specific purpose is the “so what” of the speech, it helps the speaker focus on the audience and take a bigger idea of a topic and narrow it down to what can be accomplished in a short amount of time.
Writing the Thesis Statement
The specific purpose statement is a tool that you will use as you write your speech, but it is unlikely that it will appear verbatim in your speech. Instead, you will want to convert the specific purpose statement into a central idea, or thesis statement that you will share with your audience. Just like in a written paper, where the thesis comes in the first part of the paper, in a speech, the thesis comes within the first few sentences of the speech. The thesis must be stated and tells the audience what to expect in this speech. A thesis statement may encapsulate the main idea of a speech in just a sentence or two and be designed to give audiences a quick preview of what the entire speech will be about. The thesis statement should be a single, declarative statement followed by a separate preview statement. If you are a Harry Potter enthusiast, you may write a thesis statement (central idea) the following way using the above approach: J.K. Rowling is a renowned author of the Harry Potter series with a Cinderella-like story of a rise to fame.
Writing the Preview Statement
A preview statement (or series of statements) is a guide to your speech. This is the part of the speech that literally tells the audience exactly what main points you will cover. If you were to get on any freeway, there would be a green sign on the side of the road that tells you what cities are coming up—this is what your preview statement does; it tells the audience what points will be covered in the speech. Best of all, you would know what to look for! So, if we take our J.K Rowling example, the thesis and preview would look like this: J.K. Rowling is a renowned author of the Harry Potter series with a Cinderella-like rags-to-riches story. First, I will tell you about J.K. Rowling’s humble beginnings. Then, I will describe her personal struggles as a single mom. Finally, I will explain how she overcame adversity and became one of the richest women in the United Kingdom.
Writing the Body of Your Speech
Once you have finished the important work of deciding what your speech will be about, as well as formulating the purpose statement and crafting the thesis, you should turn your attention to writing the body of your speech. The body of your speech consists of 3–4 main points that support your thesis and help the audience to achieve the specific purpose. Creating main points helps to chunk the information you are sharing with your audience into an easy-to-understand organization. Choosing your main points will help you focus in on what information you want to share with the audience in order to prove your thesis. Since we can’t tell the audience everything about our topic, we need to choose our main points to make sure we can share the most important information with our audience. All of your main points are contained in the body, and normally this section is prepared well before you ever write the introduction or conclusion. The body of your speech will consume the largest amount of time to present, and it is the opportunity for you to elaborate on your supporting evidence, such as facts, statistics, examples, and opinions that support your thesis statement and do the work you have outlined in the specific purpose statement. Combining these various elements into a cohesive and compelling speech, however, is not without its difficulties, the first of which is deciding which elements to include and how they ought to be organized to best suit your purpose.
clearly states what it is you would like to achieve
“expresses both the topic and the general speech purpose in action form and in terms of the specific objectives you hope to achieve” (O'Hair, Stewart, & Rubenstein, 2004)
single, declarative sentence that captures the essence or main point of your entire presentation
It’s About Them: Public Speaking in the 21st Century Copyright © 2022 by LOUIS: The Louisiana Library Network is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
General Statement Vs. Thesis Statement. A thesis statement is a succinct statement of the arguments you'll be making in a paper and is a critical component of any well-written work. A general statement, by contrast, is any declarative sentence providing supporting information or transitioning to a new topic. While both sentence structures play ...
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
This thesis statement tells us the specific topic of the essay (advantages and disadvantages of cars) and the method of organisation (advantages should come first, disadvantages second). It is, however, quite general, and may have been written before the writer had completed the essay. In the following thesis statement, the subtopics are named:
A thesis statement . . . Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic. Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper. Is focused and specific enough to be "proven" within the boundaries of your paper. Is generally located near the end ...
For the reader, the thesis statement: Serves as a "map" to guide the reader through the paper. In the same way the thesis helps you organize your paper, the thesis helps organize the reader's thinking. Once a solid thesis is presented, the reader will understand that all of the evidence presented is in service of proving the thesis.
**Thesis s •A thesis statement can appear as one sentence (see examples C and D) or several sentences (see examples A and B); this is dependent on the requirements of your rhetorical context. ** Note: these are general guidelines for constructing a strong thesis statement and topic sentences in a thesis driven essay; always refer to your ...
Tips for Writing Your Thesis Statement. 1. Determine what kind of paper you are writing: An analytical paper breaks down an issue or an idea into its component parts, evaluates the issue or idea, and presents this breakdown and evaluation to the audience.; An expository (explanatory) paper explains something to the audience.; An argumentative paper makes a claim about a topic and justifies ...
A thesis statement is a very common component of an essay, particularly in the humanities. It usually comprises 1 or 2 sentences in the introduction of your essay, and should clearly and concisely summarize the central points of your academic essay. A thesis is a long-form piece of academic writing, often taking more than a full semester to ...
How to Tell a Strong Thesis Statement from a Weak One 1. A strong thesis statement takes some sort of stand. Remember that your thesis needs to show your conclusions about a subject. For example, if you are writing a paper for a class on fitness, you might be asked to choose a popular weight-loss product to evaluate. Here are two thesis statements:
Using paper checkers responsibly. Pollution is bad for the environment. This thesis statement is not debatable. First, the word pollution implies that something is bad or negative in some way. Furthermore, all studies agree that pollution is a problem; they simply disagree on the impact it will have or the scope of the problem.
A thesis statement makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of the paper. It summarizes the conclusions that the writer has reached about the topic. A thesis statement is generally located near the end of the introduction. Sometimes in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or an entire ...
When drafting your thesis statement, avoid words like explore, investigate, learn, compile, summarize, and explain to describe the main purpose of your paper. These words imply a paper that summarizes or "reports," rather than synthesizing and analyzing. Instead of the terms above, try words like argue, critique, question, and interrogate.
A thesis statement states the purpose and topic of your writing, and the controlling idea indicates the direction and, often, the writing strategy you will adopt. Your thesis is like a road map, guiding your readers so that they know what to expect. Generally, your thesis is placed at the end of your introduction and is a concise and simple ...
It is a brief statement of your paper's main argument. Essentially, you are stating what you will be writing about. Organize your papers in one place. Try Paperpile. No credit card needed. Get 30 days free. You can see your thesis statement as an answer to a question. While it also contains the question, it should really give an answer to the ...
The main idea, thesis statement, and topic sentences all provide structure to an essay. It is important for both readers and writers to understand the roles of each of these in order to maintain ...
We've learned that a thesis statement conveys the primary message of an entire piece of text. Now, let's look at the next level of important sentences in a piece of text: topic sentences in each paragraph. A useful metaphor would be to think of the thesis statement of a text as a general: it controls all the major decisions of the writing.
Thesis Statements, Claims, and Evidence Introduction. The three important parts of an argumentative essay are: A thesis statement is a sentence, usually in the first paragraph of an article, that expresses the article's main point. It is not a fact; it's a statement that you could disagree with.
The general purpose statement of a speech may be to inform, to persuade, to celebrate, or to entertain. Thus, it is common to frame a specific purpose statement around one of these goals. According to O'Hair, Stewart, and Rubenstein, a specific purpose statement "expresses both the topic and the general speech purpose in action form and in ...
A thesis statement is a sentence that states the main idea of your paper. It is not just a statement of fact, but a statement of position. What argument are you making about your topic? Your thesis should answer that question. How long should my thesis statement be? Thesis statements are often just one sentence. Keep thesis statements concise ...
The thesis statement should be a single, declarative statement followed by a separate preview statement. If you are a Harry Potter enthusiast, you may write a thesis statement (central idea) the following way using the above approach: J.K. Rowling is a renowned author of the Harry Potter series with a Cinderella-like story of a rise to fame.
This is an example of general statements moving towards specific statements. General statements can also be used to tell the main idea of a book or article. They can provide an overall synopsis or ...
The thesis statement provides the scope, purpose and direction of your paper. It is specific and focused. An example for an APA format paper might include: Example. Focused interviews and examination of published research indicate that college students report increased satisfaction in attending classes with cultural diversity. Community ...