

Essay on Social Problems in India
Students are often asked to write an essay on Social Problems in India in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Social Problems in India
Introduction.
India, a diverse country, faces numerous social issues. These problems are deeply rooted in the country’s history, culture, and socio-economic conditions.
Poverty is a significant problem. Despite economic growth, a large population still lives below the poverty line. They lack basic necessities like food, shelter, and clothing.
Illiteracy is another major issue. Many children, especially in rural areas, do not have access to quality education. This hinders their future prospects.
Gender Inequality
Gender inequality is prevalent. Women often face discrimination, limiting their opportunities. This hampers social and economic progress.
Addressing these social problems is crucial for India’s development. Collective efforts from government, society, and individuals are needed to bring about change.
Also check:
- Speech on Social Problems in India
250 Words Essay on Social Problems in India
India, a diverse and culturally rich country, faces a multitude of social issues. These problems, deeply rooted in the socio-economic fabric of the nation, are a significant impediment to its growth and development.
Despite India’s rapid economic growth, poverty remains a pressing issue. The World Bank estimates that 22% of India’s population lives below the poverty line. Poverty not only leads to poor living conditions but also fuels other social issues like illiteracy and child labor.
Illiteracy is another major social problem. Even though the literacy rate has improved over the years, the quality of education remains a concern. Illiteracy fuels unemployment and social inequality, making it a vicious cycle that is hard to break.
India ranks low in gender equality indices. Discrimination, violence against women, and female foeticide are grim realities. The patriarchal mindset and societal norms often suppress women’s rights and opportunities.
Caste System
The caste system, although constitutionally abolished, continues to influence societal interactions and opportunities. It perpetuates discrimination and social exclusion, affecting the lower castes’ socio-economic status.
Addressing these social problems requires comprehensive efforts from the government, civil society, and individuals. Policies need to be effectively implemented, and societal attitudes must change. Only then can India truly progress towards an inclusive and equitable society.
500 Words Essay on Social Problems in India
India, a diverse and culturally rich nation, is not immune to social issues. Despite its vast resources and significant economic growth, it continues to grapple with numerous social problems that hinder its development and affect the lives of its citizens.
Poverty is one of the most pressing social issues in India. Despite being one of the world’s fastest-growing economies, a significant portion of India’s population lives below the poverty line. Poverty is a complex issue interlinked with other social problems like illiteracy, unemployment, and social inequality. It is a vicious cycle that needs to be broken through comprehensive socio-economic reforms.
Illiteracy is another significant social problem in India. Despite the Right to Education Act, many children in India do not have access to quality education. This lack of education perpetuates poverty, as it limits individuals’ ability to secure well-paying jobs and improve their living conditions. Illiteracy also hampers social and economic progress at a national level.
Despite constitutional guarantees of gender equality, India continues to struggle with deep-seated gender biases. Women face numerous challenges, including lower wages, limited access to education, and widespread violence. The skewed sex ratio due to female foeticide is a grim reflection of the societal preference for male children. Empowering women and ensuring their equal participation in all aspects of life is crucial for India’s social and economic progress.
Caste-based Discrimination
Caste-based discrimination is a unique and deeply rooted social problem in India. Despite legal prohibitions, the caste system continues to influence many aspects of social life, including marriage, education, and employment. This systemic discrimination exacerbates social inequality and hinders social mobility.
Corruption is a pervasive social issue affecting India’s political, economic, and social fabric. It undermines trust in public institutions, hampers economic development, and perpetuates social inequality. Tackling corruption requires strong political will, effective legal mechanisms, and active citizen participation.
Addressing these social problems is crucial for India’s progress. It requires a multifaceted approach that includes effective government policies, active civil society participation, and a change in societal attitudes. Education, gender equality, and social justice should be at the forefront of this effort. While the task is enormous, the potential for change and progress is equally significant. By confronting these issues head-on, India can pave the way for a more inclusive, equitable, and prosperous society.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Unemployment in India
- Essay on Indian Politics
- Essay on Role of Youth in Modern India
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- IAS Preparation
- UPSC Preparation Strategy
- Social Issues In India
Social Issues in India - Major Classifications
Social issues in India are in plenty and they need to be addressed systematically to achieve social justice and economic justice to all the citizens of India. The founding fathers of India were keen on addressing the social issues of India by framing the constitution accordingly. Information on the major social issues will help the aspirants of the IAS Exam .
Classification of Social Issues
The below table gives a broad classification of major social issues in India.
Gender Issues
The details of 3 major gender issues are given below.
- As per the report of the Economic Survey 2017-18, there are 63 million missing women in India.
- Missing women are women who are not alive due to foeticide or infanticide.
- As per the World Economic Forum, India is ranked very low at 87th position in the “Global Gender Parity Report.”
- Indian Government launched the ‘Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao’ scheme to address the problem of the gender gap.
- The government has been carrying out information campaigns to address the problems by bringing in behavioural change in society.
Read about Gender Inequality in India in the linked article.
Triple Talaq
- Many Muslim-majority countries have banned triple talaq.
- To bring equality and justice to women, the Government of India has passed the Triple Talaq Bill, henceforth all declarations of talaq including written and electronic forms will be null and void.
Use the information given in the Triple Talaq Essay to substantiate your answers in the Mains exam.
Sexual Harassment at Workplace
- The government passed the Sexual Harassment at Workplace (Prevention, Prohibition, and Redressal) Act in 2013.
- It aims to protect the rights of women in any workplace in any capacity.
Learn in detail about Sexual Harassment at the Workplace in the linked article.
Poverty Report
- As per the World Bank Brookings Institute report, as of May 2018, there are only 73 million people in the poorest of the poor index.
- As per the report, 44 people in India are taken out of poverty every minute.
- If the growth continues at the same pace, then 50 million people will move out of poverty by 2022.
- India is no longer the country with the highest poverty.
Read about Poverty-related topics from the links given below:
Caste Related Issues
The details of caste-related issues are given below .
Lynchings because of caste-related issues occur in the country. There was no specific section to handle mob lynchings under the IPC but under the new Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, there is a provision for life imprisonment or death for such a crime. The Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita “adds murder or grievous hurt by five or more people on specified grounds, as an offence. These grounds include race, caste, sex, language, or personal belief. The punishment for such murder is life imprisonment or death”.
Information and Broadcasting Advisory
- Information and Broadcasting Ministry has issued an advisory that the word ‘Dalit’ can no longer be used, this is as per the directive of the Bombay High Court and Madhya Pradesh High Courts. This is because the word found no mention in the Constitution of India or any statute.
- There was another directive from the Social Justice and Empowerment Ministry to use only the term ‘Scheduled Castes’.
Implications of Caste Census
- The next caste census will take place in 2021, the problems associated with it is that it will encourage caste-based politics rather than concentrating on developmental activities. Also, there will be strong sentiments for or against reservations.
This is also one of the major social issues in India. The details are given below.
Changing Pattern of Migration
- As per recent reports, the number of women migrating in India is increasing at a faster pace than men. Marriage continues to play an important role in the migration of women; however, now other economic factors like employment, business, and education are also playing an important role in migration.
Know about Migration from India’s context in the linked article.
Plight of Migrants
- There has been an increase in violence against migrants coming to a state from different parts of the country.
- Lack of job opportunities for the locals has led to growing resentment against the migrants who are dubbed ‘outsiders’
Learn the challenges of migration that are mentioned in the linked article.
A country’s sustainable progress is dependent on the availability of healthy human resources. With a deteriorating environment and unhealthy lifestyle, health is turning out to be one of the major social issues in India.
Impact of Air Pollution
- As per the India State-Level Disease Burden Initiative report, India faces 26% of the world’s premature deaths and disease burden due to air pollution.
- 1 in 8 deaths in India was attributed to air pollution, which makes it a leading risk factor for death.
- Poor air quality is responsible for heart ailments as well.
Campaign against Drugs
- The drug menace is extremely severe in Punjab.
- Punjab’s prisons are overcrowded with drug users and peddlers.
- Punjab set up a Special Task Force to tackle the menace.
Substance Abuse in India
- As per a recent report released by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, India has 6 crore alcohol addicts
- More than 3 crore Indians are using cannabis products.
- 8.5 lakh people in India inject drugs.
Know the relevant facts about Drug Abuse in India from the linked article.
Other Issues
Increasing Youth Suicides
- As per reports from the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) between 2014 and 2016; 26,476 students committed suicide in India. Of these around 7,500 committed suicide due to failure in various examinations.
- The main blame lies with India’s education system.
- The education system has not been able to generate enough jobs.
Social Issues in India- UPSC Notes:- Download PDF Here
The above details would help candidates prepare for UPSC 2024 .
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
IAS 2024 - Your dream can come true!
Download the ultimate guide to upsc cse preparation.
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Essay on Social Issues in India for Students in 2000 Words
On this page, you will read an Essay on Social Issues in India for Students in 2000 Words. In India and Every society has specific problems that commonly refer to social issues or social problems. It is a problem that affects a significant percentage of the population or community in a country or world.
So, let’s Start the Essay on Social Issues in India
Table of Contents
What are Social Issues?
Social issues (social problems, social evil, and social conflict) refer to any undesirable state that opposes the society or part of society. This is an unwanted social situation, which often raises problems; continue that is harmful to society.
Social problems cause many problems by factors that are beyond the control of one person and cause many conflicts for moral reasons.
The drawback of all Social Issues
There are many drawbacks to all social issues. This includes:
- Social issues are situations that have adverse and harmful consequences for society.
- Social issues arise when people leave from nature or society from an ideal situation.
- Almost all social issues have some common origins.
- Many of them are interrogating, and if one solves, the other will also resolve.
- Social issues have a massive lousy impact on society and can affect any part of it.
- Social issues need a common approach to the solution.
- Almost everywhere, societies in this world have social issues.
- India is struggling with many social issues such as the caste system, child labor, illiteracy, gender inequality, superstition, religious conflicts, and more. It is a critical time for society to free itself from these undesirable social evils.
Major Social Issues in India
The main social issues in India are briefly discussed below in the following order-
- Caste system
- Child labor
- Child Marriage
- Gender Inequality
- Domestic Violence against Women
- Sexual Violence and Harassment to Women
- Child Sex Abuse
- Communalism
- Dowry system
- Superstition
- Religious Conflicts
- Untouchability
- Child Trafficking
- Over – Population
1. The caste system
The caste system is a system for determining the class or assigning a status to people from birth. The causes, effects, and solutions of the caste system in India are described below:
The main reason for creating the caste system in India is the caste assignment based on professional specialization. Four classes of the caste system: Four classes include:
- Brahmins – priesthood class.
- Kshatriyas – a class of warriors and rulers.
- Vaishyas – a commercial class.
- Sudras – the lowest of four traditional classes involved in household members and workers, etc.
The caste system has many disadvantages, such as:
- Promotes inequality
- Undemocratic by nature
- False differentiation in superiority and inferiority
- It increases the difference between people from the upper and lower caste.
- People fall victim to the caste.
Education will help people realize the disadvantages of the caste system. There is a need for broad social change for equality. There should include special classes in schools that give children value and moral education. Thanks to better learning and economic progress, people belonging to different castes mix and cooperate.
Poverty means a situation in which it does not fulfill the basic needs of people. This is a vicious circle and means no money or material goods.
The significant causes of poverty are:
When resources and opportunities are limited, and the population is high, there is an unemployment situation that ultimately leads to poverty.
Poor people will always have to rely on others to survive. Poor food quality can lead to poor nutrition. Poor people have less freedom to choose their profession. Poverty can affect the morality and self-esteem of people living in extreme difficulties. It also causes stress, which ultimately affects interpersonal relationships.
Low living standards prevail among poor people. When many people live in poverty, the opportunities for developing the country’s economy become limited. Increasing employment opportunities can control debt.
The government should take further steps towards charity, trust, and some transparency when spending money in these social institutions. The education system should reform and initiatives to attract more children to attain the school.
3. Child labor
Child labor is a system of involving children in any business activity. Child labor means involving underage children. The main reasons for child labor in India are:
- Unemployment
- Illiteracy and
- A low standard of living
If the above problems resolve by Indian society, then the country will have fewer social issues. When the family is poor, they often have no choice but to send their children to work. Because of parents’ unemployment, children do not receive the proper education and forces to engage in child labor.
Adverse effects of child labor are:
Child labor is a cruel practice. It hinders personal development, destroys their childhood. Child labor deprives the opportunity to play, make friends, dreams, relax, and enjoy all critical aspects of a healthy, desirable childhood. Children are the upcoming pillars of the country and engaging them in child labor will weaken these pillars.
The primary solution to the problem of child labor is:
Provide education and knowledge to children. If the parent’s income increases, children get an education. The government will have to take further steps to enforce labor law properly. As the employment opportunity of adults will increase, it reduces child labor.
Child labor is an unfortunate and disturbing phenomenon that unfortunately still needs to be eliminated in many parts of the world, including India.
4. Illiteracy
Illiteracy describes the inability to read and/or write. Because of the problem of unemployment and poverty, children have no chance of proper education. Many people remain illiterate because of physical or mental disabilities. Other social evils like the caste system and gender inequalities also cause illiteracy. One of the leading causes of crime is illiteracy.
Most illiterate people are unaware of the advantages of maintaining cleanliness and hygiene . Illiterates have difficulty in getting a good job and earning. Overpopulation is a massive increase in the number of people and is causing by some factors.
The only and best way to eliminate illiteracy from society is education. The government should take steps to promote free education for the backward class of society in government schools. The government is also looking at the fact that people receive fair pay for their work.
5. The dowry system
Dowry is one of the worst practices widespread in Indian society. There is a tradition of asking for a dowry at the time of marriage and greed among the groom’s family for quick and easy money. People are also asking for a dowry to keep up status.
The main problems of the dowry system in society are:
The bride’s family, which usually belongs to the middle and low classes, face its bitter side. Parents often take out a loan for their daughter’s marriage. Most times, observing the lousy situation of their parents, the bride becomes mentally affected. Sometimes psychological torture caused by dowry leads to suicidal tendencies.
6. Religious conflicts:
Religious conflicts are among the most severe social issues today.
The difference in beliefs: people belonging to different religions have different views.Lack of education: People who want to spread violence in the name of religion can easily mislead illiterate people. Sometimes, conflicts between communities lead to violence and crime.
The solution to religious violence lies only in the hands of Societies.
7. Children’s marriage
Child marriage in India has been practiced for centuries, and children are married before their physical and mental maturity. Regardless of its roots, child marriage is a gross violation of human rights, leaving physical, psychological, and emotional scars for life.
Second, economically weak and large families encourage this practice because it helps to send girls early. While the boy’s marriage provides additional help in household and business operations.
Awareness-raising: all stakeholders should be alert and convinced of the adverse effects of child marriage. Checking loopholes in law: shortcomings need to be corrected to strengthen the law.
8. Gender Inequality
The problem of gender inequality is historical. The sociological reality behind this structure is the transition from a matriarchal society, which is more egalitarian, to a patriarchal society.
Although economic and technological progress has changed the social structure, the problem of gender inequality still exists, even in modern, urbanized societies.
The problem of the education system
In all areas of men-dominated society, including the structure of the state, the education system, the health care system, security forces, and the judiciary, there is a male culture and a sense of power.
In the education system, equal opportunities must be guaranteed for all children, regardless of gender, and the government should ensure this practice is implemented.
The program should be non-discriminatory and textbooks, especially in terms of language, should be prepared under the principles of gender equality.
9. Domestic violence against women
This form of domestic violence is the most common. The most common causes of harassment and torture of women are dissatisfaction with the dowry and abusing women for more, arguing with a partner, refusing sex with him, neglecting children, leaving home without telling the partner, improper cooking or on time, engaging in new matters, not caring for my parents-in-law, etc.
Many other factors in urban areas lead to differences at the beginning and then are domestic violence. Violence against young widows is also increasing in India.
Other forms of physical abuse of women also include beating, grabbing, burdening them with bullying, public humiliation, and neglecting health problems.
10. Starvation
Although the concept of food security was coined 17 years ago, humanity has been fighting hunger and thrust since ancient times. A new global partnership to reduce extreme poverty and set several time-bound targets with a deadline of 2015, known as the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs), is expected to give new impetus to the cause of food security.
The reasons for this disturbing phenomenon are different in each case. The physical availability of food at both macro and micro levels can be negatively affected due to the lack of local production, natural and human-made disasters, seasonal changes, water scarcity, poor infrastructure, insufficient storage capacity, stockpiling, and even legal problems.
However, factors that impede food absorption include a lack of clean drinking water, inadequate health, hygiene and sanitation, a low level of literacy and a fiscal cushion for governments for public sector development programs that would help ensure essential service delivery.
11. Terrorism
Terrorism not only kills the innocent but it also undermines democratic governance, even in mature democracies such as the United States and much of Europe, India, and other parts of the world.
To eliminate the threat that terrorism poses to democracy , the United States and its allies should continue to emphasize sharing intelligence and make such efforts.
12. Sexual harassment and the violation of women’s rights
Violence against women and girls is a severe violation of human rights. Decades of mobilization of civil society and women’s movements have put the end of gender-based violence high on the list of national and international priorities.
We should work with governments to develop particular national action plans to prevent and counter-violence against women, strengthening coordination between the actors required for lasting and meaningful operation.
13. Sexual exploitation of children
In recent years, it reflects the reality of how child pornography is produced. Sexual exploitation of children is a severe problem in our society, and it happens more often than people realize it.
Based on reports submitted to Cybertip, the Studies show that most criminals do not have criminal records. The sexual exploitation of children covers a wide range of behaviors and situations.
14. Untouchability
This is a practice in which people from the lower caste are kept far away, deprived of social equality and suffering from touch disabilities. These are considered contaminating or polluting the people of the higher castes.
The word “untouchable” refers to a despised and degraded portion of the Hindu population. Untouchables occupy the lowest place in society and have been subjecting to various types of social, cultural, and other restrictions. Eve Govt has been worked a lot on this issue, but few are still happening in rural areas.
15. Child trafficking
Child trafficking is a crime that uses girls and boys for many purposes, including forced labor and sex. It is associated with criminal activity and corruption. Further, smuggling and exploitation are posing an increasing risk to children worldwide.
When human trafficking occurs, children are often victims of trafficking for commercial sexual exploitation or for work, such as domestic service, factory work, agricultural work, mining, or forced to fight conflicts.
16. Overpopulation
Overpopulation is a condition in which the human population increases to the extent that exceeds the carrying capacity of the ecological system. In an overcrowded environment, the number of people is higher than the number of necessary survival materials, such as transportation, water, shelter, food, or social facilities. This is regularly contributing to the deterioration of the environment, the quality of life, and even the collapse of the ecosystem.
Conclusion of Essay on Social Issues in India
Society can solve social issues themselves. These issues make up a barrier to the progress of society, which is why we should work together to end them. If we do not unite against them, social issues will continue to grow. It can be solved only through mass consciousness, education, humanity, and a positive attitude.
I hope you like this Essay on Social Issues for Students.
4 thoughts on “Essay on Social Issues in India for Students in 2000 Words”
It is really helpful… Thank you uploading such a nice things!
beau contenu si utile!???? Merci
It is really helpful in our annual Exam tq u????
It realy help me but I also want essay on Consumer Awareness
Leave a comment Cancel reply
- Top Colleges
- Top Courses
- Entrance Exams
- Admission 2024
- Study Abroad
- Study in Canada
- Study in UK
- Study in USA
- Study in Australia
- Study in Germany
- IELTS Material
- Scholarships
- Sarkari Exam
- Visual Stories
- College Compare
- Write a review
- Login/ Register
- Login / Register
Top 10 Social Issues Topics for Students

Manali Ganguly ,
Mar 4, 2024
Share it on:
The social issues topics for the UPSC exam are unemployment, poverty, gender inequality, illiteracy, religious intolerance, child-labour, women-safety, and overpopulation among others.

The social issues topics for the UPSC exam include gender bias and inequality, unemployment, child labour, corruption, illiteracy, religious disharmony, caste and creed differences, and superstitions. These social issues are recurrent in India since the time India was a British colony.
After 76 years of independence, these social issues are recurrent in India. These topics on social issues are important from the perspective of the UPSC exam. Candidates must take a note of all the topics discussed below.
Table of Contents
Social Issues in India: An Overview
Top 10 social issues topics in india.
- Gender Inequality
- Unemployment
- Women’s Safety
- Child Abuse
Top 100 Social Issues Topics For Students
The term ‘social issues’ implies the problems that are inherent within the society. It could be anything ranging from gender inequality to unemployment. The social issues can be said to be a condition that is detrimental in nature, to society and the individual. These are undesirable happenings within the society that need rectification.
The social issues that are prevalent in India include such issues as gender distinction, untouchability, caste differences, religious intolerance, sexual abuse, illiteracy, corruption and a lot more. The socio-economic problems that were common when India was a British colony, are prevalent till today.
Also Check: 100+ Speech Topics for College Students
While India became independent 76 years ago, the socio-economic issues have remained persistent throughout. The most common social issues faced by the Indians have been listed below:
1. Corruption
This is one of the most prevalent social issues. Corruption is a problem that looms large in Indian society. This vice is present in almost all spheres, starting from the political issues to the workplace issues. Money laundering and scams are the most heard-of news in the present times.
2. Gender Inequality
This is one of the social issues topics that are important from the UPSC exam point of view. Gender bias and gender inequality is a major problem that is being addressed, but at a very slow pace. While equality is present in the papers, the reality is very different. A number of campaigns vouching for gender equality are emerging in the present times. However, the inherent difference in thought doesn't seem to go away. The gender-bias and gap can only be reduced once society changes its outlook.
There is yet another gender inequality that plays when it comes to the third gender. There is still a very small number of organisations and workplaces giving an option for the third gender. Their social acceptance is also very low. These social issues need to be addressed to clean the society of the evil of gender inequality.
Also Check : Important UPSC Essay Topics from Previous Years
3. Population
One of the major social issues topics is the population of India. The country is teeming with overpopulation. This is also one of the root causes of unemployment. Population is exploding. Awareness campaigns are being arranged to make people understand the evils of overpopulation. However, despite all such campaigns and measures, there has been very little improvement. Overpopulation is the biggest hurdle in the country’s progress.
4. Unemployment
Unemployment has a direct impact on the progress of the society and the nation as a whole. The most eminent reason, which is also one of the major social issues topics, is the lack of opportunities. The work opportunity is not evenly distributed. There are privileged classes that enjoy all the benefits at the cost of other classes.
The public sector and government sector jobs must be increased to meet the population. The unemployment rate in India, as of June 2023, was 8.16% as per the Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy. Steps must be taken to eradicate the major problem of unemployment.
Also Check : 100+ Speech Topics for College Students
5. Women’s Safety
This is another of the major social issues topics. The safety of women has always been a question in the country. With so much development in the other fields of life, the safety issue remains dormant. Till the present time, most of the places are not considered safe for women.
The number of women-abuse and physical abuse cases are on the rise. Almost every day, a new rape case comes up. A number of women-centric schemes have been introduced. There is a constant effort to safeguard women, but the effort is not very effective. While the living standards of women have somewhat improved in the urban areas, the condition in the remote areas or villages is appalling. This issue needs immediate addressing.
Poverty refers to the availability of financial resources to sustain a basic living, which include the most basic needs of life. This is one of the major social issues topics. Poverty is, in fact, the biggest problem that country has to reckon with. The division of wealth among the citizens has a major impact on the status of the country. The financial resources are not equally divided.
7. Illiteracy
Literacy rates are good in the city, but in the remote areas and villages, the rate of illiteracy is higher. Child-labour in the villages and remote areas as well as the city suburbs is one of the biggest reasons contributing to the problem. The number of schools and colleges in the suburbs and villages is not adequate. This has an impact on the literacy rate directly.
Also Check : Easy Topics for Group Discussion
8. Healthcare
The healthcare care system also needs to be improved in all parts of the country. Though the healthcare system is very good and is equipped with all the modern technologies in the cities and metropolitan areas, the healthcare system is not adequate in the other parts of the country. This is yet another among the major social issues topics to be addressed.
9. Violence
This is one major social vice that must be corrected. Violence in all forms is gaining prominence. Violence during the elections, during a protest-rally, or in a political rally, can be seen every now and then. In fact, violence has become a part of the protests shown by the student-unions in the colleges and universities.
10. Child-Abuse
The rate of child-abuse has grown in the present times. Child- abuse refers to every form of abuse including psychological, sexual, or physical abuse. The maltreatment of a child in any form is considered an abuse on the child. There are rights protecting the child, for example, POCSO against sexual abuse. Despite all the rights and acts to protect the children, the cases of child abuse are only rising.
Also Check: Best Career Options For Girls in India
The students must prepare themselves with social issues topics for essays. Both at the secondary and higher secondary school levels as well as for the UPSC exams, the social issues topics are important. Listed down are 100 top social issues topics for the students to prepare for the exams:
- Women Empowerment
- Child-Abuse
- Inadequate Healthcare
- Dowry System
- Juvenile Delinquency
- Urbanisation
- Infanticide
- Tradition vs. Modernity
- Work Opportunities
- Higher Education in India
- Lack of Infrastructure
- Economic Inequality
- Discrimination
- Social Justice
- Teenage Pregnancy
- Substance Abuse
- Gun Control
- Animal Rights
- Homelessness
- Untouchability
- Religious Intolerance
- The aftermath of Covid 19
- Deforestation
- Climate Change
- Environment Abuse
- Pros and Cons of Online Education
- Work from Home Culture
- Political Polarisation
- Body shaming
- Poverty-based discrimination in the society
- Labour Laws
- Child-Labour
- Right to education
- Vices of polygamy
- Racism in the workplace
- Child Rights
- LGBT Community
- Rights for the third gender
- Ethnic cleansing
- Religious bias in the political parties
- Hate Speech on social media
- Gender discrimination in the workplace
- Domestic Violence
- The impact of #MeToo
- Role of Men in the Era of Feminism
- Position of Women in the Modern Society
- Moral Policing
- Reservation of seats in talent acquiring
- Improper distribution of wealth
- Social shaming
- Inability of Muslim women to initiate divorce
- Impact of online games on lives
- Impact of virtual life on teens
- Pros and cons of digitization
- Inadequate infrastructure of rural India
- Improper hygiene in rural India
- Shopping malls vs marketplace
- Fees structure of schools
- Shaming in school for grades
- Misuse of labour
- Pros and cons of work from home
- Impact of realistic movies on life of teens
- Intolerance in teens
- Imbibing the west: Pros and cons
- Modern schools
- Discrimination on the basis ability to speak in English
- Plight of a migrant
- Changing laws for migration
- Youth suicides
- Farmer disharmony
- Controversy on the term Dalit
- Lynch culture
- Sexual harassment at the workplace
- Causes of poverty in India
POST YOUR COMMENT
Related articles.

Jiwaji University Syllabus 2024: Download PDF

Kerala University Private Registration 2024
![essay topics on social issues in india Durg University Syllabus 2024: Download PDF [All Courses]](https://media.getmyuni.com/assets/images/articles/articles-87bf8f18c2334f59b6155fa59e572d77.webp)
Durg University Syllabus 2024: Download PDF [All Courses]

DTU Seat Matrix 2024: Check Course Wise Seat Matrix

Top 9 Free Online Certificate Courses by Government of India

JNTUK Revaluation Results 2024 - Link @jntukresults.edu.in

CUET Exam City Intimation Slip 2024 (Apr 30)
Get Free Scholarship worth 25000 INR

6 Major Social Issues in India: Causes and Measures
India suffers from a host of social issues ranging from poverty to gendered violence. This article covers the concept of social issues and highlights the different experiences of rural and urban sectors. Further, it studies six important social issues namely poverty, unemployment, illiteracy, the caste system, gendered violence and communalism by analyzing their causes and the specific measures adopted to combat them.
What Are Social Issues?

An individual problem is one that affects only a particular individual or group. On the other hand, public issues are those faced by society as a whole. A social issue is when a situation is deemed less than the social ideal. It must result in unfavourable circumstances that can only be handled collectively. India has undergone many changes in the last decades. Social change brings with it a new set of circumstances wherein an otherwise overlooked issue might be given importance. For example, the population explosion in India was not viewed as a serious issue until the 1950s. It is also important to note that any problem only becomes a social issue when enough number of people find it undesirable. Sati was not deemed a social issue until Raja Ram Mohan Roy criticized the practice and a considerable number of people started supporting him (Ahuja 2014).
Rural versus Urban Social Issues
Many scholars have identified fundamental differences between the causes and consequences of issues experienced the rural and urban sectors.
The rural sector has five identifying characteristics. Firstly, people are either directly or indirectly dependent upon agriculture. Next, the upper caste citizens are the largest landholders. Thirdly, the roles and values of rural people are traditional. Also, the farmers receive inadequate compensation for their hard work. Finally, people are scattered in rural areas as compared to urban cities. This isolation means that their access to services like banks, hospitals and schools is also minimal.
Read: Farmers’ suicides in India
On the other hand, the urban sector is characterized by the concentration of large populations in small areas. This results in many issues such as slums, high crime rates, pollution, drug abuse and unemployment. Also, cities are highly interdependent on every small part. For example, a strike by bus workers could result in many problems for the functioning of a city.
Poverty can be defined as the inability to secure the minimum standard of living appropriate to society. According to the Planning Commission, 22% of India’s population lived below the poverty line in 2012.
Causes of Poverty
The sociologist David Elesh determined three causes of poverty namely individual, culture of poverty and social structure. The first ideology is propagated by those who believe that if an individual ends up in poverty, it is their own fault and due to a lack of hard work and initiative. This thought is rooted in the functionalist approach of sociology. It maintains that poverty is a good thing for society since it propagates the survival of the fittest. The culture of poverty concept was introduced in 1959 by Oscar Lewis. He believed that the lifestyle of the lower socio-economic classes fostered behaviours and attitudes associated with poverty. Hence, no amount of economic rehabilitation could help alleviate the poor. Finally, the social structure approach was propagated by sociologist Herbert Gans . He associated poverty with unjust social conditions and pointed out that the middle and higher classes had a vested interest in the poor. For example, the existence of the poor helped alleviate their social status. Thus, they had no interest in changing the social structure (Ahuja 2014).
Within the Indian context, many unique causes of poverty have been identified. The first is the rapidly rising population. This year, the population reached 138.72 crores which was a 1.26% increase from last year. Such a high population raised the demand for consumption of a limited number of resources. The second is low agricultural productivity due to lack of capital, technology and fragmented land holding. The next cause is unemployment which is present in the form of both underemployment and disguised unemployment in the agricultural sector. Social factors have also contributed to poverty through the caste system , gendered laws of inheritance and a lack of infrastructure. Finally, political factors such as the British exploitation of natural resources also led to a weakened Indian economy.
Poverty Alleviation Programs
The Indian government has launched many poverty alleviation programs for the rural and urban poor. A few major schemes have been described below. The Indira Awaas Yojna (IAY) was launched to aid the construction of houses for those belonging to scheduled tribes, scheduled castes, freed bonded laborers and the rural poor living below the poverty line. The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGA) was introduced in 2005 all over India. Under this scheme, every rural household was guaranteed 100 days of wage employment in the form of unskilled manual labor each fiscal year. Finally, the food security scheme introduced in 2003 distributed allocated amounts of food grains to priority and antyodya households for free. This scheme covered almost 75% of the rural and 50% of the urban population (Ahuja 2014).
Unemployment
Unemployment has often been described as the most significant social issue in society. This is because an individual is dependent on their work for both their livelihood and their status. Sociologically, unemployment is defined as the inability to find remunerative work in the face of both potential and desire to earn. The three elements of unemployment are that the individual must be capable, willing and making an effort to be gainfully employed.
Types of Unemployment
There are three major classifications of unemployment, namely, seasonal, cyclical and technological.
Seasonal unemployment is a characteristic of the agricultural sector. Any cultivator in India is unemployed for almost four to six months every year. Workers at some manufacturing units like ice or sugar factories are also seasonally unemployed due to the nature of the work.
Cyclical unemployment is a result of the ups and downs in business. For example, an entrepreneur earning high profits might invest them in a startup thus creating employment. But when they start suffering losses, they might reduce the number of workers present in their industries.
Technological unemployment is caused because of the introduction of new technologies that displace manual labor. The adoption of automation in almost every industry has resulted in a loss of economic security for the average man (Ahuja 2014).
Causes of Unemployment
Sociologists have suggested that unemployment is a result of both economic and social factors.
Degrading social status means that many people consider themselves overqualified for certain jobs and thus prefer to remain unemployed. For example, many youths consider teaching in universities to be a prestigious job whereas teaching in a school is looked down upon.
Geographical immobility refers to surplus labor in one location and inadequate labor in another. People may be unable to move to areas with higher job opportunities due to a lack of information, language barriers or family responsibilities. For example, women in rural areas often lose out on paid work because they do not get the opportunity to migrate to cities like their husbands.
Population explosion has led to increased unemployment due to the limited number of job opportunities in the economy. Many people lose out on work due to personal reasons such as lack of education or experience or even illness and disability. The high rates of unemployment increase the dependency on parents to provide for their children and for the government to assume responsibility for them.
The defective education system fails to give importance to primary education and vocational training. The benefits of education are mostly availed only by middle- and high-income youth with access to private schools and universities. The conditions in most government schools are unsuitable for studying and are often a result for many girls to drop out (Ahuja 2014).
Remedial Measures
The Indian government has recognized the issue of unemployment within the country. They have taken many steps in the form of employment generation schemes. The MGNREGA scheme mentioned previously is one major measure. Unemployment cannot be solved by making India more labour-intensive which has been suggested in the past. Instead, the focus should be on educating the youth and making them employable within the upcoming service sector.
Unemployment: Definition, Types, Causes, Solutions and The Way Ahead
As mentioned in the previous section, illiteracy is a major barrier to development since it results in unskilled labor. According to the Census Commission of India, literacy refers to any person who can read and write with understanding in a recognized Indian language. The 2011 census revealed that the literacy rate of India was around 74% with many regional variations and gender disparities. All over India, Kerala has the highest literacy rate and Bihar the lowest.
Measures to Eradicate Illiteracy
Many programs have been introduced by the government in accordance with the education policies of India. A few of these have been mentioned below.
The National Adult Education (NAE) program was introduced in 1978 to promoted education within the age group of 15-35 years. The Rural Functional Literacy (RFL) program is a sub-program of the NAE and was launched in 1986. It aimed at creating awareness among adults about the numerous government schemes they could benefit from. Moreover, it involved student volunteers from universities in teaching adults. Finally, the National Literacy Mission was launched in 1988 by Rajiv Gandhi and aimed at involving volunteer agencies in the mission to educate illiterate persons all over the country (Ahuja 2014).
Caste System
The Indian caste system is based on the cultural features of hierarchy, pollution and purity. It subscribes to the doctrines of Karma and Dharma. The Indian government introduced the category of Scheduled Castes (SCs) to the constitution in 1935. Currently, SCs constitute around 16% of the Indian population. The main issues faced by Dalits are those of untouchability, exploitation, exclusion from religious and educational institutions and social discrimination.
Dalit Empowerment Measures
The government’s approach towards the upliftment of SCs was based on two ideas. The first was to overcome deprivations in terms of education, housing and employment that the SCs have inherited due to their historical exclusion from society. The second was to encourage their participation in the economic, social and political processes of the country.
Protective measures included acts such as the protection of the Civil Rights Act passed in 1976 and the Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes Prevention of Atrocities Act passed in 1989. Together, these acts protected Dalits from untouchability, discrimination and violence in public places. Reservation policies within educational institutions, government services and political bodies are also a part of protective measures. These ensure adequate participation of SCs in public spheres though they are restricted to only the government sectors.
Development measures were introduced within the educational, economic and social spheres. To increase educational development the government has attempted to include reservations within educational institutions, provide financial support and coaching facilities and emphasized on girls education. Economic empowerment includes distribution of land to landless laborers and implementation of wage labor programs. Finally, social welfare schemes to increase access to sanitation, housing, drinking water and electricity have been introduced by the government (Thorat 2009).
Read: Dalit and Backward Classes Movements
Gendered Violence
Women have always been victims of exploitation and violence within the Indian subcontinent. Violence against women consists of criminal, domestic and social violence. Criminal violence consists of rape, murder, female foeticide and abduction. Domestic violence includes wife battering, dowry deaths and sexual violence. Social violence comprises eve-teasing, inheritance laws favouring men etc.
The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) released that 33,356 cases of rape were reported all over India in 2018. Most of these are instances where the rapist is known to the victim. Moreover, these statistics fail to reveal the high number of rapes that are not even reported by the victim. Instances of rape cut across geographical locations, class and caste. Female employees are raped by employers, women inmates are raped by superintendents, female patients are raped by hospital staff and domestic helpers by their employers. Within the context of marriage, violence against women becomes harder to navigate. The Indian constitution does not recognize marital rape as a criminal offence (Ahuja 2014).
Measures to Prevent Women’s Harassment
The government in collaboration with volunteer organizations has taken a few steps for the safety of women. Shelters for women suffering from abusive husbands or in-laws have been established. But such accommodations suffer from issues of overcrowding and a lack of financial support. Helplines for women have been publicized by the police in various cities such as New Delhi. Legal institutions that provide free legal assistance to women have also been promoted by the government. But despite all these measures, the most important change that is required to combat women’s harassment is a change in attitude. The patriarchal society of India has oppressed women for too long. This pattern needs to change by taking small steps such as ending victim-blaming for sexual and violent assaults.
Communalism
Communalism refers to attempts to overemphasize the importance of religious identity and stimulate communal violence between different religious groups. Within India, tensions between Hindus, Muslims and Sikhs have been present since the India-Pakistan partition. Muslims, Sikhs and other religious minorities are protected by the Indian constitution under provisions for justice, tolerance, equality and freedom. Despite these provisions, communal violence has been a part of India since independence. The recent case of the Babri Masjid and associated riots is a popular example of religious discord. Violence can take many forms of mass mobilizations, insurgency and riots. Usually, communal violence is more politically motivated than fueled by religion. Hindu- Muslim riots in Andhra Pradesh in 1990 led to more than a hundred deaths (Ahuja 2014).
Prescriptive Measures
India has suffered at the hands of communalism for too long. The government and the citizens must work together towards harmony. Symbolic gestures are not enough for Muslims as they must be empowered through literacy and employment. Secularism must be promoted through education. Moreover, communal minded politicians should be boycotted during elections and the police and military must be sensitized and encouraged to adopt a secular outlook.
This article has covered many social issues faced by Indian citizens on a daily basis. It is essential that such problems be recognized by individuals and governments alike so that they may work together towards a better future.
Ahuja, R. (2014). Social problems in India . Jaipur: Rawat Publications.
Thorat, S. (2009). Dalits in India: Search for a common destiny . New Delhi: SAGE Publications India Pvt. http://dx.doi.org/10.4135/9788132101086.n1
Arushi is a sociology and environmental studies. She is passionate about writing and researching about these two fields. She has a keen interest in social work and has collaborated with many volunteering programs in the past. Her hobbies include horse riding, trekking and painting.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
ImportantIndia.com
Indian History, Festivals, Essays, Paragraphs, Speeches.
Essay on Social Issues in India (causes, effects and solutions)
Category: Essays and Paragraphs , Social Issues in India On February 2, 2019 By Team Work
Social Issues in India
Introduction .
Every society has some problems, and these are commonly termed as social issues . It is a problem that is affecting a considerable percentage of a nation’s or global population or society.
Social issues (also social problem, social evil, and social conflict) refers to any undesirable condition that is opposed either by the whole society or by a section of the society. It is an unwanted social condition, often objectionable, the continuance of which is harmful for the society.
Social issues are caused by some factors that are beyond the control of a single individual and cause a lot of conflict on the moral grounds.
There are some common characteristics of all social problems. This include:
- Social problems are those situations that have bad and injurious consequences for society.
- Social problems arise when there is a deviation of the people or the nature of society from the ideal situation.
- Almost all social problems have some common origin.
- Many of the social issues are interconnected, and if one is solved, then others also get solved.
- Social problems have a huge impact on society and may affect any section of the society.
- Social issues need a collective approach to be solved.
- Almost all societies in this world have social issues.
India is facing a large number of social issues such as caste system, child labour, illiteracy, gender inequality, superstitions, religious conflicts, and many more. It is high time that the society gets relief from these undesirable social evils.
Major Social Issues: We have prepared a list of major social issues in India. They are briefly discussed below in the following order:
- Caste system
- Child labour
- Child marriage
- Low status of women
- Gender inequality at work
- Dowry system
- Sati practice
- Superstition
- Sanitation and cleanliness
- Religious conflicts
- Juvenile delinquency
1. Caste system
Introduction: Caste system is a system of defining class or assigning status to individuals from the time of birth. In India, the caste system is mainly profession based. India has been a victim of caste system since ages.
The causes, effects and solutions of Caste system in India are discussed below:
Causes: The main reason behind the growth of Caste system in India is the assignment of caste based on job specialization. There were different types of jobs in the society which were done by the people based on their capability. This division of job based on specialization resulted into caste system.
Four classes of Caste system: The four classes includes:
- The Brahmins – the priestly class. They were mainly engaged in religious and priestly activities. They were also appointed as advisors to the Kings.
- The Kshatriyas – the warrior and ruler class. They were mainly engaged in warfare activities.
- The Vaishyas – the trader class. They were mainly engaged in business, agriculture, and trading activities.
- The Sudras – the lowest of the four traditional class engaged as domestic servants and laborers, etc.
Negative effects of Caste system: Caste system has many disadvantages such as:
- Encourages untouchability,
- Promotes Inequality,
- Undemocratic in nature,
- Fake differentiation in superiority and inferiority.
- Increases gap between upper and lower caste people.
People are victimized by caste. There is discrimination which divides the society, and anti-social elements take advantage of this. Caste system is also a danger towards the National integration of the country. Caste system is a major cause for many inhuman and immoral social practices such as untouchability, child marriage, sati system (sati pratha), etc.
- Education will help the people to become aware of the disadvantages of Caste system.
- There is a need for widespread social change in favor of equality of human-beings. Caste system can be discouraged through social education in rural areas.
- There should be special classes at schools that imparts value and moral education to the children.
- Superstitious people are extremely fearful and discourage any change in social norms. Education will help shed away superstition, which in turn, will help shed casteism as well.
- With better education and economic progress, people belonging to diverse caste get opportunity to mix and work together. Many of them become friends while working together on a project.
Introduction: Poverty refers to a situation when people’s basic needs are not fulfilled. When people doesn’t have the necessary food to eat or clothes to wear or shelter to stay then its called poverty. Life becomes very difficult for people with income is below the poverty line (BPL).
Poverty is a vicious circle and is the lack of money or material possessions. Social, political, as well as economic elements, contribute to poverty. It leads to a lack of basic life necessities and comfort. Illiteracy is a major cause and effect of poverty. These people have a low standard of living and poverty is the cause of many social evils.
The causes, effects and solutions for poverty in India are discussed below:
Causes: The major reasons or causes of poverty are:
- People don’t get proper education which leads to poverty. People are poor because they are illiterate, and they are illiterate because they cannot afford education. Illiteracy and poverty stays side-by-side. They both are the cause and effect of each other.
- In case where the resources and opportunities are limited and the population is high, there arises a situation of joblessness which ultimately leads to poverty.
- When a large number of people live in poverty, there is limited scope for the development of country’s economy.
- Some natural and environmental problems such as lack of rainfall, drought, etc. often lead to poverty. There are many other reasons also like caste system, unemployment, etc.
Effects: The negative effects of poverty are mentioned below:
- Poor people will always have to depend on others to survive.
- Low quality foods may leads to bad nutrition.
- Poor people have less liberty for the choice of profession.
- Poverty may affect the moral and self-esteem of people living in extreme hardship.
- Poverty also results in building stress which ultimately affects the relationship of people.
- The low standard of living prevails among poor people.
Solutions: The solutions for poverty are discussed below:
- Poverty can be checked by increasing job opportunities. It will decrease the rate of unemployment which ultimately results in decrease of poverty in economy.
- Government should take more steps towards charity, trusts and have some transparency while spending money in those social institutions.
- There is a need for initiatives of paid leave to the workers.
- The education system should be reformed and initiatives should be taken to bring more children to schools.
3. Child labour
Introduction: Child labour is a system of involving children in any economic activity. Children at the age of playing engage themselves into economic activity for their family. Child labour can be seen throughout the country in a wide way.
Child labour means getting children who are minors of age to do work. Even if children are paid for the labour that they perform, child labour is still deeply wrong.
The causes, effects and solution of Child labour are briefly mentioned below:
Causes : The major causes of child labour in India are:
- Unemployment,
- Illiteracy, and
- Low standard of living.
If the above problems can be resolved from the Indian society, then the country will have less social issues.
When a family is poor, they often have no choice but to send their children out to work. If the child’s parents or other relatives are sick, or poor, more pressure will be put on children to go out to work to provide for themselves and their families.
Due to unemployment of the parents, children do not get proper education and are forced to get involved in child labour. Educated people are less likely to engage their child as child labours. In general, educated people want to keep up a certain level of standard and live a respectable life. On the contrary, illiterate people are not even aware of the evil effects of child labour.
Effects: The negative effects or major disadvantages of child labour include:
- Child labour is an inhuman practice. The mental growth of the children engaged in child labour is checked.
- Children get less time and opportunity to go to school. They are unable to participate fully in education. They are deprived from education which makes them illiterate.
- Child labour obstructs personal growth. The standard of living of people remains low.
- Child labour destroys their childhood. Child labour does not only limit children’s ability to grow emotionally and to relish a period of carefree innocence before they are launched into adulthood.
- Child Labour deprives children of the ability to play, to make friends, to daydream, to relax, and to enjoy all of the key aspects of a normal, desirable childhood.
- Children are the future pillars of the economy and involving them into child labour will only make those pillars weak. Ultimately, child labour affects the country’s growth.
Solution: The main solution to child labour is:
- Imparting education and knowledge to children.
- If incomes of the parents can be increased then it is possible for the children’s to get education.
- Government will have to take more steps towards proper enforcement of labour laws.
- People who are employed and are above the poverty line should take steps towards replacing child workers with adult workers. It will benefit not only the society, but the country at large.
Child labour is an extremely sad and worrying phenomenon that unfortunately still needs to be eradicated in many parts of the world, including India.
4. Child marriage
Introduction: Child marriage refers to the marriage of individuals below the prescribed limit of age. Marriage is to be considered legal as per the Indian Law, when the groom’s age is 21 and above and bride’s age is 18 and above.
Though, child marriage has caused problems to both and boys and girls, the most severe victims of the evil practice are the girls.
The causes, effects and solutions for the social problem of child marriage are given below:
Causes: The causes or the main reason behind the child marriage is the poor economic condition of the family of the marriage parties.
Besides there are other reasons also for child marriage like illiteracy, providing security to their daughters by marrying them to secured person, child trafficking, etc.
Negative effects of child marriage: The negative effects of child marriage include the following:
- Due to child marriage, the girls become pregnant at an early age. Since their bodies are not properly developed to have kids, it may lead to early maternal death. In many of the cases, the infant baby’s health doesn’t seem good.
- Child marriage also leads to illiteracy and poverty. A girl who is married at an early age is deprived of opportunities for education and personal growth.
- Due to less compatibility and understanding, relationship between the couples hampers.
Solution: Education is the only and the best way to stop child marriage. Educated people from society should raise voice against child marriage.
Gender equality and women education is very important to stop the evil practice of child marriage. The girls become extremely dependent upon her parents because of lack of education. As such, she is not in a position to speak against the will of her parents. If a girl gets equal opportunity to get educated, then she will be in a better position to decide, what that is best for her future.
Government should take steps to enforce the laws on child marriage. The problem of child marriage can be solved by raising awareness about the disadvantages of child marriage.
5. Illiteracy
Introduction: Illiteracy refers to the inability to read and/or write. The problem of illiteracy is a major social issue in India. The problem has spread through-out the country in a wide way. It is one of the most dangerous obstacles in the economy’s growth. People with no education find it difficult to get jobs and remain poor. They are at risk of poor diet, manual jobs, worse physical and mental health. It impacts their social situations too.
The major causes, negative effects and solutions of the problem of Illiteracy in India are discussed below:
Reason: The major reasons of illiteracy in India are discussed below:
- Since many adults in India are illiterate, they don’t understand the importance of getting education for their children.
- Due to the problem of unemployment and poverty, children get little opportunity for proper education.
- Many people stay illiterate due to some physical or mental disabilities.
- Other social evils like caste system, gender inequality also cause illiteracy.
Negative effects/ Disadvantages:
- One of the major cause for crimes is illiteracy. Due to illiteracy issue, rates of crime are gradually increasing and health, productivity and growth of the country is gradually decreasing.
- Most illiterate people are unaware of the benefits of maintaining cleanliness and hygiene.
- Illiterate people find it very difficulty to secure a good job and earn livelihood. If a person is looking for a means to earn and work, but is not getting it then it is known as unemployment. This social problem leads to frustration.
- Overpopulation is a huge increase in the number of people, and it is caused by some factors out of which illiteracy is a major one.
Solution: The only and the best way to eradicate illiteracy from the society are by education.
The scheme for mid-day meals at schools is a welcome step.
Government should take steps to promote free education for the backward class of the society in government schools.
Government also look at the matter that people get fair payment for their work. Appropriate steps should be taken to create more employment opportunities for adults, so that they can educate their children by sending them to school.
6. Low status of women
Introduction: Low status of women refers to the inferior position of women (in comparison to men) in the society. This reflects the narrow mindset of the society. It is seen all over the country, but widely prevalent in the backward areas.
The causes, negative impact, and solutions of the problem of low status of women are briefly discussed below:
Causes: Narrow mindset of the society is the main reasons behind this problem. Women in India are considered inferior than men since ages. A large part of the society believes that men are more capable to earn more than their women. It is widely seen that the male members of the family try to control the activities of the female members, which leads to the low status of women.
Negative impact: The negative impact of the lower status of women are:
- Women do not get the adequate chance to do something to contribute to the society.
- Since the status of women in society is low, people want a boy child instead of a girl child. This intensifies the problem of female foeticide.
Solution: The solution to the problem is:
- The empowerment of women is of utmost importance for solving the problem.
- Awareness must be created to change the narrow mindset of the society. Campaigns must be launched to acknowledge the role and contribution of women in the society.
- Education can also help to solve the problem of low status of women in the society.
- Mass-media campaigns should be promoted.
7. Gender inequality at work:
Introduction: Inequality at work refers to any type of discrimination in working environment based on caste, gender, race, color, etc. But gender inequality at work means discrimination or unequal treatment between male and female workers.
Causes: The main reason behind the issue of gender inequality at work is the mindset and culture.
The ego of male members prevents the female members to enjoy equal position at work places. People also do this because of un-awareness.
Impact and effects: The main impact of gender inequality at work is that society gets shrink and deprived of the minds of the female worker. It also gives rise to low status of women issue in the society.
Solution: The solution for social issue of gender inequality at work is in the hands of people themselves. People should start training and impart proper education for gender equality.
People should also change their perception that women will get less salary in comparison to men. For that, people should introduce successful business women as the role model at their workplaces.
8. Dowry system
Introduction: Dowry is one of the most evil practices that are prevalent in the Indian society. Dowry system is actually the transfer of money, property and other valuable assets of bride’s family to the groom’s family on the eve of marriage.
Reason: There are several reasons of prevailing dowry system in the society like:
- Tradition of asking for dowry at the time of marriage.
- The greed among the family of groom for quick and easy money.
- People also ask for dowry for maintaining status.
Disadvantages: The major disadvantages of Dowry system in the society is:
- The bride’s family who generally belong to middle and low-class has to face the bitter-side of it. Bride’s family spend lavishly during the marriage. Because of this social evil, some families lose huge money.
- Parents often take loan for their daughter’s marriage.
- In many cases, by watching the poor situation of their parents, bride becomes mentally affected.
- Sometimes, the mental torture due to dowry leads to suicidal tendencies.
- Many cases of dowry deaths have been seen in past years.
- Emotional torture and divorce are other evil effects of dowry system.
Solution: The solution to stop the practice of this evil system is in our hands only.
- People should stop discrimination between a boy and a girl.
- Girls should also be allowed to have their education and proper knowledge.
- Awareness must be created and for these people with the help of media.
- Last, but not the least, parents should change the thoughts of dowry from their mind and children should stand against their family for doing this.
9. Sati System (Sati Practice)
Introduction: Sati system or pratha is one of the cruelest, evil, inhuman and immoral social practices prevailing in our country.
Sati system refers to the act of committing suicide by the widowed women on the funeral pyre of his husband. This is an inhuman act.
In 1987, Roop Kanwar committed sati at the age of 18. After this incident, both the State and the Central Government enacted acts to abolish the Sati system.
Disadvantages: The main disadvantages are:
- Sati System in itself is an inhuman practice.
- Women are deprived of their basic right to live their life.
- Sati system also shows the domination of men over the women.
- Sati system reduces the self-respect of women and brings down the status of women in the society.
Causes: The causes behind the Sati system are:
- To maintain the status: As people of high caste were not allowed to marry with low-caste, so after the death of her husband, she was burned alive only to save the status
- Sati was also committed to save her sexuality with the other member of the society.
- Sati was also practiced by women to show her love and devotion towards her husband.
- In the backward areas where widows were treated as untouchables were forced to commit sati.
Solution: The solutions for the evil practice of sati are:
- Educating the people through mass communication.
- Bringing a change in the perspective of the people that a widow person cannot marry with anyone.
Government has already enacted the Sati Prevention Law. Sati Practice is illegal in India. The evil is rapidly diminishing from the Indian Society. However, awareness has to be created to stop the sati practice completely.
10. Superstition
Introduction: Superstition refers to the irrational beliefs of supernatural forces. Superstition is one of the major social issues affecting the entire country.
It’s a belief of human beings that there are some supernatural causes behind the bad events. Science doesn’t believe in this type of supernatural causality because science always tries to give scientific explanation for every event. But, deep down inside human beings have their own belief.
There are many superstitions prevailing in the country. Human beings have the tendency to believe bad before the good.
Reason: The main reason behind superstitions is:
- Fear: Fear is the main obstacles for everything. Superstition arises due to human fear.
- Lack of Knowledge: Basically superstition arises due to lack of knowledge.
- Religion, tradition and social practices are others causes of superstition.
Disadvantages: The major disadvantages of being superstitious are:
- Fear: People start to think less broadly and always develop constant fear in mind. This fear affects not only the individual but also his family and society.
- Waste time and energy: People waste of much time and efforts.
- People stop for few seconds whenever they sneeze. All these arise due to human fear and imagination.
Solution: The main solution is to get knowledge and education because knowing nothing causes fear in mind which ultimately arise superstition.
By adjusting or gaining knowledge, mind can develop the reason behind the occurrence of superstition and one can understand very well that these things doesn’t affect anybody’s life.
Also by being always positive, one can get rid of those superstitions.
11. Sanitation and cleanliness
Introduction: Sanitation and cleanliness is a basic problem and one of the important social issues of our country. People should clean their areas and take care of personal hygiene to stay healthy and away from any diseases.
People should clean the areas of keeping food; clean their area of staying to promote cleanliness. People should maintain adequate sewage disposal system so that the public health is not put at risk.
Disadvantages: There are many casualties of not having sanitation and proper cleanliness.
- People suffer from various diseases such as diarrhea, malnutrition, dengue, malaria and many more.
- It also suffers children’s development.
Reason: The major reason behind this is the carelessness and laziness of people themselves. The people themselves create the problem of dirt and unhealthy environment.
People think of their own only and do not think of others. People do not mind to throw garbage in open areas which may negatively affect the environment.
Solution: The solution is in the hands of the people itself.
- People have to start to make their area clean and stay healthy.
- People should make a proper area for sanitation so that public health will not suffer.
- Mass awareness programmes are already initiated by different institutions, organisations and government bodies to save human race.
12. Religious conflicts
Introduction: Religious conflicts are among the most harmful social issues of today. Sometimes violence, war, conflict, etc. arises because of religious fanaticism.
Causes: The causes are briefly discussed as follows:
- Difference in beliefs: People belonging to different religions have difference in their beliefs. This difference often leads to conflict.
- Lack of education: Illiterate people can be easily mis-guided by people who want to spread violence in the name of religion.
Negative effects: Sometimes conflicts between communities leads to violence and crimes. People become fearful and it affects the overall progress of the country. The lack of communal harmony in society leads to disunity.
Solutions: The solution for religious violence is in the hands of the people only. People should gain proper knowledge and develop better understanding. By removing the thoughts of cruelty, one can correctly judge what’s right or wrong. Awareness must be created and for this media will be very useful.
13. Beggary
Introduction: Beggary is another social problem in our country. People who are in extreme situation of need and poverty are called beggars. The state of being a beggar is called beggary.
Causes: There are many causes behind the beggary problem in India. Some of the reasons behind beggary are poverty, unemployment, illiteracy, social customs, physical disability, mental state, disease and many more.
Impacts and effects: The main disadvantages of beggary is that
- Beggars largely depend on what they get from the people and this is in fact a big problem because they start to depend totally on this and stop finding any other source of income.
- Now, they have become burden to the society and they in fact forcefully made their children to do the same.
- The cruelest part of beggary is that they sometimes allow doing anything to their own body for money. They are sometimes forced to cut their hands or legs.
Solution: Government has to take large initiatives to remove the problem of beggary from the society like providing job security, recruiting more employees in the Governmental sectors and many more. Beggary problem can also be in control if the children who are begging can be put in the Govt. schools for education because education is the main key to eradicate any social problem.
14. Juvenile delinquency
Introduction: Juvenile delinquency is also termed as Teenage Crime. Basically, juvenile delinquency refers to the crimes committed by minors. The crimes by teenage boys or girls are generally done without having proper knowledge of it as they know very little about the world.
Negative effects: The crimes by minors affects not only the children but to the family and the society. Children’s are the future generations of the country. Education of the children is hampered and the status and reputation of the family also goes down. People become less secured and there is always a sense of tension and distress.
Causes: There are numerous reasons behind Juvenile delinquency, such as:
- Lack of knowledge: They know very little about the outside world. They sometimes commit crime unknowingly.
- Trauma: Trauma of any childhood or teenage incident may have negative effect on mind.
- Violent films and movies: Watching any stuff like murder, violence, etc. may again negatively affect the mind of the teenager.
- Family Disturbance also cause for the crime.
Solutions: There are many organisations who deal with the problem of Juvenile delinquency. They are established to help those children who are involved in it. They increase their thinking ability and decision-making skills. They start to understand the meaning of Juvenile delinquency and the results of it. There are rehabilitation centres and consultancies also run by the Government who treat those children and make them a good person.
- History of Mughal Empire
- Modern History of India
- Important India
- Indian Geography
- Report an Article
- Terms of Use, Privacy Policy, Cookie Policy, and Copyrights.
The multiple faces of inequality in India
Post-doctoral research fellow in economics, Centre de Sciences Humaines de New Delhi
Disclosure statement
Tista Kundu a reçu des financements de AXA Research Fund.
View all partners
Known for its caste system, India is often thought of as one of the world’s most unequal countries. The 2022 World Inequality Report (WIR), headed by leading economist Thomas Piketty and his protégé, Lucas Chancel, did nothing to improve this reputation. Their research showed that the gap between the rich and the poor in India is at a historical high, with the top 10% holding 57% of national income – more than the average of 50% under British colonial rule (1858-1947). In contrast, the bottom half accrued only 13% of national revenue. A February report by Oxfam noted 2021 alone saw 84% of households suffer a loss of income while the number of Indian billionaires grew from 102 to 142.
Both reports highlight not only the problem of revenue inequality but also of opportunity. While there may be disagreement between left and right on the ethics of equality, there is a consensus that everyone should be given the chance to succeed and the principle of fairness – and not factors such as birth, region, race, gender, ethnicity or family backgrounds – ought to lay the foundations of a level playing field for all.
Drawing from the latest pre-pandemic database from the Periodic Labour Force Survey of 2018-19, our research confirms this is far from the case in India. On the one hand, the country has had a consistently high GDP growth rate of more than 7% for nearly two decades, the exception being the period around the 2008 financial crisis. On the other hand, this income has failed to trickle down to India’s marginalised communities, with preliminary results pointing to a higher level of inequality of opportunity in the country than in Brazil or Guatemala.
Precarity as well as a large shadow economy also plague the country’s labour market. Even before the pandemic, only 30% to 40% of regular salaried adult Indian earners had job contracts or social securities such as national pension schemes, provident fund or health insurance. For self-employed workers, the situation is even more critical, even though these constituted nearly 60% of the Indian labour force in 2019.
Castes, gender and background still determine life chances
Our research indicated that at least 30% of earning inequality is still determined by caste, gender and family backgrounds. The seriousness of this figure becomes clear when it’s compared with rates of the world’s most egalitarian countries, such as Finland and Norway, where the respective estimates are below 10% for a similar set of social and family attributes.
The caste system is a distinctive feature of Indian inequality. Emerging around 1500 BC, the hereditary social classification draws its origins from occupational hierarchy. Ancient Indian society was thought to be divided in four Varnas or castes: Brahmins (the priests), Khatriyas (the soldiers), Vaishyas (the traders) and Shudras (the servants), in order of hierarchy. Apart from the above four, there were the “untouchables” or Dalits (the oppressed), as they are called now, who were prohibited to come into contact with any of the upper castes. These groups were further subdivided in thousands of sub-castes or Jatis , with complicated internal hierarchy, eventually merged into fewer manageable categories under the British colonisation period.

The Indian constitution secures the rights of the Scheduled Castes (SC), Scheduled Tribes (ST) and Other Backward Class (OBC) through a caste-based reservation quota, by virtue of which a certain portion of higher-education admissions, public sector jobs, political or legislative representations, are reserved for them. Despite this, there is a notable earning inequality between these social categories and the rest of the population, who consists of no more than 30% to 35% of Indian population. Adopting a data-driven approach we find that, on average, SC, ST and OBC still earn less than the rest.
While unique, the caste system is not the only source of unfairness. Indeed, it accounts for less than 7% of inequality of opportunity, something that’s in itself laudable. We will need to add criteria such as gender and family background differences to explain 30% of inequality.
In a country where femicides and rapes regularly make headlines, it comes as no surprise that women from marginalised social groups are often subject to a “double disadvantage”. For some states such as Rajasthan (in the country’s northwest), Andhra Pradesh (south), Maharashtra (centre), we find even upper-caste women enjoy fewer educational opportunities than men from the marginalised SC/ST communities. Even among the graduates, while the national average employment rate for males is 70%, it is below 30% for the females.
A temporary byproduct of rising growth?
Rising inequality could be dismissed as a temporary byproduct of rapid growth on the grounds of Simon Kuznets’ famous hypothesis , according to which inequality rises with rapid growth before eventually subsiding. However, there is no guarantee of this, least of all because widening gap between rich and poor is not only limited to fast-growing countries such as India. Indeed, a 2019 study found that the growth-inequality relationship often reflects inequality of opportunity and prospects of growth are relatively dim for economies with a bumpy distribution of opportunities.
Despite sporadic evidence of converging caste or gender gaps, our research shows an intricate web of social hierarchy has been cast over every aspect of life in India. It is true that some deprived castes may withdraw from school early to explore traditional jobs available to their caste-based networks – thereby limiting their opportunities. However, are they responsible for such choices or it is the precariousness of the Indian economy that pushes them down such routes? There is no straightforward answer to these questions, even if some of the “bad choices” that individuals make can result more from pressure than choice.
Given the complicated intertwining of various forms of hierarchy in India, broad policies targeting inequality may have less success than anticipated. Dozens of factors other than caste, gender or family background feed into inequality, including home sanitation, school facilities, domestic violence, access to basic infrastructure such as electricity, water or healthcare, crime rates, political stability of the locality, environmental risks and many more.
Better data would allow researchers studying India to capture the contours of its society and also help gauge the effectiveness of policies intended to expand opportunities for the neediest.

Created in 2007 to help accelerate and share scientific knowledge on key societal issues, the AXA Research Fund has supported nearly 700 projects around the world conducted by researchers in 38 countries. To learn more, visit the site of the AXA Research Fund or follow on Twitter @AXAResearchFund.
- Caste system
- The Conversation France
- Axa Research Fund (English)
- Sexism at work
- India caste system

Project Offier - Diversity & Inclusion


Senior Lecturer - Earth System Science

Sydney Horizon Educators (Identified)

Deputy Social Media Producer

Associate Professor, Occupational Therapy

Social Issues in India
India is an ancient country and according to some estimates, Indian civilization is about five thousand years of age. Therefore, it is natural that its society will also be very old and complex. Throughout its long period of history, India has witnessed and received several waves of immigrants such as Aryans, Muslims etc. These people brought with themselves their own ethnic varieties and cultures and contributed to India’s diversity, richness and vitality.
Therefore, Indian society is a complex mix of diverse cultures, people, beliefs and languages which may have come from anywhere but now is a part of this vast country. This complexity and richness gives Indian society a unique appearance of a very vibrant and colorful cultural country.
Major Problems in India
- Untouchability
- Overpopulation
Child Marriage
Child Labour
- Gender Inequality
- Domestic Violence against Women
- Sexual Violence against Women
- Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace
- Child Sexual Abuse
- Communalism
- Religious Violence
- Marital Rape
- Child Trafficking
- Bonded Labour
Reasons of Social Problems:
But the very same complexity brings with itself complex nature of social problems and issues. In fact every society of the world has their social issues unique to their society. So does Indian society. Indian society is very rooted in religious beliefs; there are people of different religious beliefs such as Hindus, Muslims, Jains, Sikhs, Parsis etc. These all adds to the socio-cultural varieties of the country. India’s social problems are also rooted in the religious practices and beliefs of it people. Almost all forms of social issues and problems find their origin in the religious and cultural practices of the people of India. These social problems are developed in a long period of times and are still continuing in one form or other.
Furthermore, India has witnessed several wars of large proportions; several foreign invaders attacked India in its long history among whom few made this country as their own and tried to force their socio-religious practices which also deteriorated social conditions; the long period of British rule crippled the country and had thrown it into backwardness. Thus, many such reasons may be cited for India’s social problems but the fact remains that we have these issues and only we can solve them.
Forms of Social Issues in India
Poverty is a condition in which a household is not able to fulfill its basic needs for survival i.e. food, clothing and shelter. Poverty is a widespread condition in India. Since Independence, poverty is a prevalent concern. It is the twenty-first century and poverty still is a persistent menace in the country. India happens to be country wherein the disparities between the haves and the have-notes are extremely wide. It needs to be taken into account that although the economy has shown some visible signs of progress in the last two decades, this progress been uneven across various sectors or areas. The growth rates are higher in Gujarat and Delhi as compared to Bihar and Uttar Pradesh. Nearly half of the population doesn’t have proper shelter, access to a decent sanitation system, villages do not have a nearby water source, and villages also do not have a secondary school and lack of proper roads. Some sections of the society like the Dalits are not even included in the poverty list maintained by the concerned authorities assigned by the government. They’re groups that are marginalized in the society.
The element which further complicates and deteriorates the situation is the government subsidies system which has leakages in the distribution system. They never reach the households.
Illiteracy is a condition which becomes a blot on the development of nation. India possesses the largest illiterate population. Illiteracy in India is a problem which has complex dimensions attached to it. Illiteracy in India is more or less concerned with different forms of disparities that exist in the country. There are gender imbalances, income imbalances, state imbalances, caste imbalances, technological barriers which shape the literacy rates that exist in the country. The Indian government though has launched several schemes to combat the menace of illiteracy but due to the poor conditions of sanitation and expensive private education and defective mid-day meal schemes, illiteracy still prevails. Not only the government, but every literate person needs to accept the eradication of illiteracy as a personal goal. Each and every contribution by a literate person can make a contribution to eradicate the menace.
According to the United Nations report, India has the second highest number of child marriages. Marriage is considered to be a sacred union between two mature and consenting individuals who are ready to accept each other and share responsibilities for a lifetime. With respect to this context, child marriages happen to be an unsound institution. Child marriage mars the innocence of childhood. The Indian Constitution provides for prohibitions against child marriage through various laws and enactments. The first law that was designed was the Child Marriage Restraint Act of 1929 which extended to the whole of India except Jammu and Kashmir. This act defines the ages of an adult male and female. Also, sex with minors is a criminal offence under Section 376 of the Indian Penal Code. Proper media sensitization is required for a major change to take place. While on one hand, it is stated that child marriage will still take nearly fifty years to be eradicated, genuine efforts, strict enforcements of the legal provisions and change the scenarios to a great extent.
Starvation is a condition characterized by the deficiency in calorie energy intake and is a serious form of malnutrition which ultimately leads to death if not taken care about. Historically, starvation has been constant across various human cultures apart from India. Starvation can take place in a country due to many reasons like war, famine, the disparities between the rich and the poor and so on. Malnutrition conditions like kwashiorkor and marasmus can also develop into serious causes of starvation. Generally, the conditions of kwashiorkor and marasmus arise when people are taking diets which are not rich in nutrients (proteins, vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates, fats and fiber). In the context of India, it becomes needless to say that the food distribution system is flawed. The Supreme Court has issued orders over the past decades directing the government to take measures like mid-day meal schemes and the provision of health care schemes for pregnant and lactating women. The National Food Security Bill which has become a landmark act does seem to show promises with respect to its measures of the identification of the poor and the needy, redressal mechanisms for grievances and children’s entitlements. But, this bill also is not without its cons. Clear mechanisms with respect to the identification of beneficiaries have not been defined. The indicators of the poor need to be made specific. They are vague in description.
Child labour typically means the employment of children in any work with or without payment. Child labour is not only limited to India, it happens to be a global phenomenon. As far as India is concerned, the issue is a vicious one as children in India have historically been helping parents at their farms and other primitive activities. Over population, illiteracy, poverty, debt trap are some of the common causes which are instrumental in this issue. Overburdened, debt-trapped parents fail to understand the importance of a normal childhood under the pressures of their own troubles and thus it leads to the poor emotional and mental balance of a child’s brain which is not prepared to undertake rigorous field or domestic tasks. Multinational companies also recruit children in garment industries for more work and less pay which is absolutely unethical. Child labour as a global concern has been raised on international platforms as well. Abolition of child trafficking , elimination of poverty, free and compulsory education, and basic standards of living can reduce the problem to a great extent. The World Band, International Monetary Fund can help in eradicating poverty by providing loan to the developing countries. Strict implementation of labour laws is also essential in order to prevent exploitation by parties or multinational companies.
Homosexuality
Homosexuality is still considered a ‘taboo’ in India. India today is one of the fastest developing nations with impressive economic growth rates. But is the growth rate enough to imply that India is a developing nation. A nation is also characterized by the way it treats its people. With respect to this prerogative, the way India looks at homosexuality is certainly not the way to look at it. Homosexuality is considered as a disease by most sections of the society and there are only a few sections of the society who welcome homosexuality. Homosexuality thus is also regarded as a criminal offence in India. Homosexuality is a ‘criminal offence’ under Section 377 of the Indian Penal Code dating back to 1861 with punishments up to ten years which makes it all the more hard to believe that India is a progressive nation and that we are the 21 st century inhabitants of the country. Although, this subject did see the light of the day when the Delhi High Court legalized gay sex among consenting adults holding that making it a criminal offence violates fundamental human rights way back in the year 2009 as a result of persuasive struggles carried out by Gay Rights activists and foundations.
In December 2013, the Supreme Court passed a controversial order making gay sex illegal quashing the Delhi High Court’s decision on the matter. In January 2014, the Supreme Court also refused to review the petition against its order on gay sex being criminalized. Needless to remark, the refusal drew flak internationally for violating fundamental rights. To sum up, homosexuality needs tolerance both by the country and its citizens. It is certainly not a disease hence it doesn’t require any treatment. According to my viewpoint, the organizations which have been instrumental with the emancipation of the LGBT community (Example- Naz Foundation) should continue with their protests because slowly but surely people are changing their perceptions towards this subject.
Other varied forms of social problems related to issues such as Casteism , Untouchability , Bonded Labour , Gender Inequality , Dowry , Domestic Violence against Women , Sexual Violence against Women , Child Sexual Abuse , Communalism , Religious Violence , Issues related to SC/STs, Marital Rape , Sexual Harassment of Women at Workplace , Child Trafficking , Overpopulation etc.
The list may go on and it is not a comprehensive list. There are several other social issues and problems ailing the country but above mentioned ones are really pressing issues which need immediate attention.
It is not so that social ills have not been fought with; in fact from the ancients times in our country there have been various social-cultural reformers such as Budha, Mahavira, Kabir, Gurunanak, Raja Ram Mohun Roy, Mahatma Gandhi, Dr. Ambedkar, Vinoba Bhave etc who have tried to fight those evils throughout their lives; they have succeeded also to a certain extent. But still the country is facing these socio-cultural problems in various degrees which is an unfortunate reality of 21 st century India.
Present Scenario:
We try to present our country as a modern, forward looking nation of the world and it’s true that India is making strides in the world as a nation with encouraging developments in scientific, economic and technological fields, but as far as social developments are concerned it is still one of the lowest ranked countries of the world. India’s Human Development Index (HDI) rank for 2013 is 135 out of 187 countries of the world which are listed in the report. This shows the sorry state of affairs as far as India’s situation on social indicators is concerned. This also shows that we as a society are still people of orthodox beliefs in a negative sense who do not want to believe in the concept of equality and brotherhood of all.
Though several Governmental and non-governmental (NGOs) bodies are working towards improving the existing situation in the social fields but results are not very encouraging. Perhaps the problem lies in the very deep rooted beliefs in the minds of people of the country which is not letting the situation to change. For instance : the issue of Female Feticides is one of the shameful practices in our country. Though there are various prohibitory measures the Government and NGOs have taken but the practice is continuing. The real reason for this is the Patriarchy system of society of our country which considers male as the superior authority and women as subordinate to them. Therefore, very strong desire of having a male child in comparison to female child led to the shameful practice of female feticides. Thus, it is belief system or the cultural conditioning of the people which is not letting the society to change at a fast pace.
Though there have been several positive changes in the society such as now girls are also going to school in vast majority and their employment ratio is also increasing; illiteracy as whole is decreasing; conditions of SC/STs are also improving etc but situation is far from satisfactory.
We witness inequality against women in our own homes, sexual violence against women can be heard on daily basis, female feticide is continuing, religious-communal violence is on the rise, untouchabilty is still a reality, child labor is widely practiced etc.
Therefore, there is a lot needs to be done for the situation to improve. And without changing the mind set and beliefs of the people it is a very difficult task. For this purpose educating people about various social problems and sensitizing them towards changing their way of thinking is the best way forward. Because without people trying to change themselves, any governmental or non-governmental efforts will prove as a half-measure. If we want to make India as a true world leader and a modern 21 st country of the world, it is imperative that that we make an improvement on our social front.
In the next pages we will discuss some of the pressing and urgent social issues facing our country, their genesis, their outlook, efforts taken to fight them and present scenario etc.
Related Information:
Social Reformers of India
- India Today
- Business Today
- Reader’s Digest
- Harper's Bazaar
- Brides Today
- Cosmopolitan
- Aaj Tak Campus
- India Today Hindi
Get 72% off on an annual Print +Digital subscription of India Today Magazine
Socio-political issues: consent and dissent, a majority are in favor of a uniform civil code, a two-child policy, amending farm laws and regulating social media, but there are many who are scared to protest and opinion over whether democracy is in danger or not remains divided.

Poverty in India Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on poverty in india.
Poverty refers to a situation in which a person remain underprivileged from the basic necessities of life. In addition, the person does not have an inadequate supply of food, shelter, and clothes. In India, most of the people who are suffering from poverty cannot afford to pay for a single meal a day. Also, they sleep on the roadside; wear dirty old clothes. In addition, they do not get proper healthy and nutritious food, neither medicine nor any other necessary thing.

Causes of Poverty
The rate of poverty in India is increasing because of the increase in the urban population. The rural people are migrating to cities to find better employment. Most of these people find an underpaid job or an activity that pays only for their food. Most importantly, around crores of urban people are below the poverty line and many of the people are on the borderline of poverty.
Besides, a huge number of people live in low-lying areas or slums. These people are mostly illiterate and in spite of efforts their condition remains the same and there is no satisfactory result.
Furthermore, there are many reasons that we can say are the major cause of poverty in India. These causes include corruption, growing population, poor agriculture , the wide gap of rich and poor, old customs, illiteracy, unemployment and few more. A large section of people are engaged in an agricultural activity but the activity pays very less in comparison to the work done by employees.
Also, more population needs more food, houses and money and in the lack of these facilities the poverty grows very quickly. In addition, being extra poor and extra rich also widens the gap between the rich and poor.
Moreover, the rich are growing richer and the poor are getting poorer creating an economic gap that is difficult to fill up.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Effects of Poverty
It affects people living in a lot of ways. Also, it has various effects that include illiteracy, reduced nutrition and diet, poor housing, child labor, unemployment , poor hygiene and lifestyle, and feminization of poverty, etc. Besides, this poor people cannot afford a healthy and balanced diet, nice clothes, proper education , a stable and clean house, etc. because all these facilities require money and they don’t even have money to feed two meals a day then how can they afford to pay for these facilities.
The Solutions for Ending Poverty
For solving the problem of poverty it is necessary for us to act quickly and correctly. Some of the ways of solving these problems are to provide proper facilities to farmers . So, that they can make agriculture profitable and do not migrate to cities in search of employment.
Also, illiterate people should be given the required training so that they can live a better life. To check the rising population, family planning should be followed. Besides, measures should be taken to end corruption, so that we can deal with the gap between rich and poor.
In conclusion, poverty is not the problem of a person but of the whole nation. Also, it should be deal with on an urgent basis by the implementation of effective measures. In addition, eradication of poverty has become necessary for the sustainable and inclusive growth of people, society, country, and economy .
FAQs about Poverty in India Essay
Q.1 List some ways to end poverty in India. A.1 Some ways to end poverty in India are:
- Develop a national poverty reduction plan
- Equal access to healthcare and education
- Sanitation facility
- Food, water, shelter, and clothing facility
- Enhance economic growth with targeted action
Q.2 Which is the poorest state in India? A.2 Chhattisgarh is the poorest state of the country.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Study Today
Largest Compilation of Structured Essays and Exams
Social Issues & Problem in India Essay | Types | Paragraph | Speech
December 20, 2017 by Study Mentor Leave a Comment
India is a great country, but diverse by some social issues. Many of the issues happen in our country. India has got the many experiences from history. Social issues have majorly taken place in India. Because of the religion India is becoming diverse most of the people follow some religion and some are against them.
Table of Contents
There are many social issues in India
In India many of the people are suffering from poverty and day by day it is increasing. In poverty people are surviving for food, cloth and for home as well.
Many of the people in India belong to the poor locality. Because of inflation poverty is increasing.
Poverty is also due to large number of population. In village area people are not aware of sanitation due to lake of water. There is also comparison between people due to castes.
People are illiterate because they cannot afford education. Resources and opportunity are limited and the population is very high because of this there is limited scope of country’s development.
Effects of poverty
People have to depend on others for their survival. They have very less liberty of choice. It can affect the moral of people. It results in extreme stress for people.
How to overcome poverty
- By increasing job opportunities.
- Government should take more steps to overcome poverty.
- Education system should be reformed.
In India there is lot of problem due to illiteracy. People are not enough literate to understand something. Due to lack of literacy, India is undeveloped. It has very complex dimension. Because of illiteracy there is problem of gender imbalance, income balances and technological imbalances.
The Indian government has done many works to spread message about importance of literacy, they have launched many schemes to attract people toward learn and also they have included mid-day meals.
Causes of illiteracy
- Gender inequality .
- Some physical or mental disability.
- Due to problem of unemployment and poverty, children get less opportunity to get educated.
Effects of illiteracy
- Major cause of crime is illiteracy.
- Illiterate people find problems for job.
- They are unaware of benefits of maintaining hygiene.
- Government should take steps to promote education for backward class people.
- Government should take steps for the betterment of children education.
Child Marriage
Child marriage is illegal issue of society. India has 2 nd highest number of child marriages. In India there are laws concerned to child marriage some people follows them some doesn’t.
The Indian constitution provides laws against child marriage.
Marriage should be considered legal when the boy’s age is 21 and girl’s age is 18 and above. It causes problem to both girl and boy both mentally and physically.
Causes of child marriage are
- Poor economic condition.
- Providing security to girl by marrying them to secured person.
Negative Effects of child marriage
- Girl becomes pregnant at early age, since there bodies are not properly developed.
- It leads to illiteracy and poverty.
- Relationship between couples hampers.
- Education is the only best possible solution to stop child marriage.
- Educated society and person should raise their voice against child marriage.
- Government should take steps against child marriage.
Child labour
It means employment of children in any work, because of the poverty many children are forced to do this; some are doing it for their survival. In the age of learning they are forced to do labouring. Overpopulation , illiteracy, poverty, debt trap they all are some issues because of which children are forced for child labouring. Children at the age of playing, they do work.
Causes of child labour
- Unemployment
Due to lack of money some parents are not able to provide their children proper education, even poor people are not aware of the fact about child labour.
Effects of child labour
- Mental level of children remains small.
- Children get less opportunity to go to school.
- It destroys their childhood.
Solution to child labour
- Providing education to children.
- People who are rich and below poverty line should take steps to replace child labours. It will truly benefit our country.
Religious matter
In India there are many religions, and Indian society is rooted in religious beliefs. Different types of religions are Hindu, Muslims, Jains, Sikhs, and Parsis etc.
Different religions contain different culture.
It is the main root of social issue in India, and the origin of social practices.
Also in these religions caste system is there, Main reason of casteism is due to job assignment according to caste.
Negative effects of caste system are
- Untouchability
- Differentiation between people.
- Gap between upper and lower caste people.
Solution of caste system
To aware people about disadvantages of caste system. There should be special classes in school of moral education. With proper education people will get opportunity to work and learn together.
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Top Trending Essays in March 2021
- Essay on Pollution
- Essay on my School
- Summer Season
- My favourite teacher
- World heritage day quotes
- my family speech
- importance of trees essay
- autobiography of a pen
- honesty is the best policy essay
- essay on building a great india
- my favourite book essay
- essay on caa
- my favourite player
- autobiography of a river
- farewell speech for class 10 by class 9
- essay my favourite teacher 200 words
- internet influence on kids essay
- my favourite cartoon character
Brilliantly
Content & links.
Verified by Sur.ly
Essay for Students
- Essay for Class 1 to 5 Students
Scholarships for Students
- Class 1 Students Scholarship
- Class 2 Students Scholarship
- Class 3 Students Scholarship
- Class 4 Students Scholarship
- Class 5 students Scholarship
- Class 6 Students Scholarship
- Class 7 students Scholarship
- Class 8 Students Scholarship
- Class 9 Students Scholarship
- Class 10 Students Scholarship
- Class 11 Students Scholarship
- Class 12 Students Scholarship
STAY CONNECTED
- About Study Today
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
Scholarships
- Apj Abdul Kalam Scholarship
- Ashirwad Scholarship
- Bihar Scholarship
- Canara Bank Scholarship
- Colgate Scholarship
- Dr Ambedkar Scholarship
- E District Scholarship
- Epass Karnataka Scholarship
- Fair And Lovely Scholarship
- Floridas John Mckay Scholarship
- Inspire Scholarship
- Jio Scholarship
- Karnataka Minority Scholarship
- Lic Scholarship
- Maulana Azad Scholarship
- Medhavi Scholarship
- Minority Scholarship
- Moma Scholarship
- Mp Scholarship
- Muslim Minority Scholarship
- Nsp Scholarship
- Oasis Scholarship
- Obc Scholarship
- Odisha Scholarship
- Pfms Scholarship
- Post Matric Scholarship
- Pre Matric Scholarship
- Prerana Scholarship
- Prime Minister Scholarship
- Rajasthan Scholarship
- Santoor Scholarship
- Sitaram Jindal Scholarship
- Ssp Scholarship
- Swami Vivekananda Scholarship
- Ts Epass Scholarship
- Up Scholarship
- Vidhyasaarathi Scholarship
- Wbmdfc Scholarship
- West Bengal Minority Scholarship
- Click Here Now!!
Mobile Number
Have you Burn Crackers this Diwali ? Yes No

Social Issues in India- Contemporary Major Current Problems in India
Social Issues in India are discussed in this post. Indian society has progressed over time, with advancements in a variety of disciplines. Know major issues in India here.

Table of Contents
Social Issues in India: Indian society has progressed over time, with advancements in a variety of disciplines. However, there are socio-cultural issues that must be recognised and addressed in every community. People’s safety, particularly that of vulnerable groups such as women, children, and the elderly, is a key issue in modern Indian culture.
Social Issues in India
Casteism, dowry, communalism, drunkenness, drug addiction, and other key socio-cultural concerns need to be addressed today. The topics covered here are not exhaustive. There are other more concerns that the country as a whole, as well as individual regions and communities, must address.

Current Social Issues in India (Political)- Casteism
Castes are rigid and at times even oppressive social groups, in which lifestyle, occupation, and social position are passed down through the generations. The caste system in India dates back to ancient times and has been influenced by numerous ruling elites throughout mediaeval, early modern, and modern India, particularly the Mughal Empire and the British Raj. Varna and jati, the two notions that make up the caste system, can be thought of as separate degrees of analysis.
After gaining independence in 1947, India implemented a number of affirmative action programmes aimed at helping historically underprivileged populations. These measures included reserving a certain number of spots in higher education and government jobs for these groups. Read About: What is the National Enblem of India?

Social Issues in India- Dowry System
In India, the dowry system refers to the items, such as cash, and permanent or personal property that the bride’s family pays to the groom, his parents, and relatives as a condition of marriage. Dowry is simply a financial payment or a present given to the groom’s family in addition to the bride, and it comprises cash, jewelry, electrical appliances, furniture, bedding, crockery, utensils, vehicles, and other household items that assist the newlyweds in setting up their home. In Arabic, dowry is referred to as Dahez. Dowry is referred to as Aaunnpot in India’s far east.
Read About: Important Amendments of Indian Constitution

Social issues in India- Communalism
The religious and cultural diversity of India gives rise to communalism as a political concept. It has been used as a political propaganda tool to generate divisions, tensions, and divisions amongst groups based on religious and ethnic identity, resulting in communal hatred and violence.
People of various faiths coexisted amicably in ancient Indian civilization.
Perhaps the first Indian prophet to introduce the concept of secularism was Buddha. Meanwhile, kings like Ashoka pursued a policy of religious tolerance and harmony.
The introduction of Islam in medieval India was marked by rare acts of violence, such as the destruction of Hindu temples by Mahmud Ghazni and the attack on Hindus, Jains, and Buddhists by Mahmud of Ghor. While religion played a significant role in people’s lives, there was no community philosophy or politics.
Rulers like Akbar and Sher Shah Suri adopted a religious policy of tolerance for many cultures and traditions practiced throughout the country. Some sectarian kings, such as Aurangzeb, were, nonetheless, among the least tolerant of other religious practices.
It originated as a result of British colonial impact and Indian social strata’s response as a modern phenomenon.
Read About: Second Battel of Panipat
Social issues in India- Gender-Based Discrimination
In every profession, our Constitution guarantees men and women equal rights. Women now have the ability to vote, inherit, and own property. In reality, the Constitution stipulates that the government shall promote the interests of the weaker parts of the population with great attention. Since independence, several laws have been established to advance the interests of women. These rules govern marriage, property inheritance, divorce, and dowry, among other things. The Equal Remuneration Act of 1976 was passed to ensure that men and women were paid equally for equivalent work.
Despite these restrictions, however, we still see a lot of prejudice against women.
In India, women face discrimination in a variety of areas, including health, education, and employment. The girls are responsible for the dowry, and they must leave their parents’ home after marriage. Furthermore, parents desire to produce male offspring in order to protect their old age. Because they are girls, many female babies are aborted, abandoned, purposefully neglected, and underfed. Read About: Partition of Bengal
Social issues in India- Drugs addiction
Drug misuse is frequently accompanied by a negative social impact on the community. The current article focuses on drug abuse’s negative impact on industry, education and training, and the family, as well as its role in the violence, crime, financial difficulties, housing issues, homelessness, and vagrancy.
Social Problems in India
India, being a diverse and populous country, faces a range of social issues. Here are some of the prominent ones:
- Poverty : India has a significant population living below the poverty line, leading to inadequate access to basic necessities like food, clean water, and shelter.
- Gender Inequality : Despite progress, gender disparities still exist in India, including unequal access to education, limited economic opportunities for women, and issues related to gender-based violence.
- Caste System : The caste system, although officially abolished, continues to influence Indian society. Discrimination and violence against lower-caste individuals, often referred to as Dalits, persist.
- Religious Tensions : India is home to multiple religions, and religious tensions and communal violence occasionally arise, particularly between Hindus and Muslims.
- Child Labor : Child labor remains a problem in some parts of India, with children being forced to work in hazardous conditions instead of receiving an education.
- Education Gap : There is a significant gap in the quality of education between urban and rural areas. Many children in rural regions lack access to quality education.
- Healthcare Challenges : Access to healthcare is uneven across the country. Rural areas often lack adequate medical facilities, and healthcare expenses can be a burden for many.
- Corruption : Corruption is prevalent in various sectors, from politics to public services, which hinders economic development and social progress.
- Environmental Issues : Rapid urbanization and industrialization have led to environmental problems such as air pollution, water pollution, and deforestation.
- Overpopulation : India’s population continues to grow, putting pressure on resources and infrastructure, which can exacerbate many of these social problems.
Current Issue in India
Here are some prominent issues:
- COVID-19 Pandemic: India faced significant challenges during the COVID-19 pandemic, including healthcare infrastructure strain, vaccine distribution, and the emergence of new variants.
- Economic Challenges: The Indian economy faced challenges such as job losses, economic contraction, and a slowdown in various sectors due to the pandemic.
- Agricultural Protests: Farmers’ protests against new agricultural laws gained widespread attention and continued to be a major issue in some parts of the country.
- Air Pollution: Major Indian cities, including Delhi, faced severe air pollution, leading to health problems and environmental concerns.
- Political Unrest: Political tensions and debates over various issues, including citizenship laws and regional autonomy, were ongoing.
- Social Issues: India continued to grapple with social issues such as gender inequality, caste-based discrimination, and violence against women.
- Environmental Concerns: Deforestation, wildlife conservation, and water scarcity were some of the environmental issues facing the country.
- Education and Healthcare: Challenges in providing quality education and healthcare to all sections of society remained.
- Cybersecurity: With increasing digitization, India faced cybersecurity challenges, including data breaches and cyberattacks.
- Infrastructure Development: The need for infrastructure development and improving transportation networks continued to be a priority.
Contemporary Issues in India
some key contemporary issues that have been of concern in India:
- COVID-19 Pandemic: India, like the rest of the world, has been dealing with the COVID-19 pandemic. Issues related to healthcare infrastructure, vaccine distribution, and the economic impact of lockdowns have been prominent.
- Economic Challenges: India has faced economic challenges, including job losses, economic inequality, and a need for economic reforms to stimulate growth.
- Environmental Concerns: Environmental issues such as air pollution, deforestation, and climate change have been a growing concern. Air quality in many Indian cities is often poor.
- Farmers’ Protests: In 2020 and 2021, farmers in India protested against new agricultural laws. These protests raised concerns about farmers’ livelihoods and agricultural reforms.
- Religious and Communal Tensions: India has faced communal tensions and religious conflicts in recent years, leading to debates about secularism and religious freedom.
- Education and Digital Divide: The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the digital divide in education, with many students lacking access to online learning resources.
- Women’s Safety: Women’s safety remains a critical issue, with incidents of violence and harassment leading to discussions about gender equality and legal reforms.
- Cybersecurity and Privacy: As India becomes more digitally connected, concerns about cybersecurity and the protection of personal data have grown.
- Political Issues: Political debates, elections, and issues related to governance and accountability continue to be central to India’s contemporary landscape.
- Healthcare Infrastructure: The pandemic exposed weaknesses in India’s healthcare infrastructure, leading to discussions about the need for improvements and investments.
Top 10 Current Major Problems in India
Top 10 Current major problems in India is given below.
1. Corruption
2. Illiteracy
3. Education System
4. Basic Sanitation
5. Healthcare System
7. Pollution
8. Women’s Safety
9. Infrastructure
10. Unemployment

Sharing is caring!
What exactly is a social problem?
A social problem is a societal issue that makes it difficult for individuals to reach their full potential.
Give some examples of Social Issues.
Social issues include poverty, unemployment, uneven opportunity, racism, and starvation.
Why do societal problems arise?
Individual or group disagreements in culture can also contribute to societal issues. This is referred to as the interaction viewpoint. The clash of cultures and religions in a society is one of the causes of societal difficulties. Culture and religion have a strong influence on people.
What is the current situation?
A current issue is anything that is occurring right now and has an impact on a certain group or society as a whole.
What is the difference between a problem and an issue?
A problem necessitates immediate resolution, but an issue necessitates discussion or debate.
Hi, I am Brajesh (M.Tech, MCA), I Professional Educator having 3 years of experience in school education sector. Aim to provide JEE, NEET, CUET, and Other Entrance exams information in a simple way to help students find clarity and confidence. I provide here easily accessible content on Exam Notifications, Syllabus, Admit Cards, and Results.

Trending Articles
- TS Inter Results 2024 Link
- TS Inter Topper List 2024

CBSE Board Exam 2024
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus 2024
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2024
- CBSE Previous Year Papers
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Previous Year paper
- CUET Participating College & Universities
- JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main Syllabus 2024
- JEE Main Exam Analysis 2023
- NEET 2024
- NEET Syllabus 2024
- NEET State wise Cut off
- NEET Rank Predictor
- NEET OMR Sheet
- NEET College Predictor
Recent Posts
Important exams, ncert solutions.
- NCERT Class 12
- NCERT Class 11
- NCERT Class 10
- NCERT Class 9
NCERT Books
School syllabus.
- CBSE Class 12
- CBSE Class 11
- CBSE Class 10
- CBSE Class 9
- JEE Mains 2024
Our Other Websites
- Teachers Adda
- Bankers Adda
- Adda Malayalam
- Adda Punjab
- Current Affairs
- Defence Adda
- Adda Bengali
- Engineers Adda
- Adda Marathi
- Adda School

Get all your queries solved in one single place. We at Adda247 school strive each day to provide you the best material across the online education industry. We consider your struggle as our motivation to work each day.
Download Adda247 App
Follow us on
- Responsible Disclosure Program
- Cancellation & Refunds
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
Gender issues in India: an amalgamation of research
Subscribe to global connection, shamika ravi and shamika ravi former brookings expert, economic advisory council member to the prime minister and secretary - government of india nirupama jayaraman nj nirupama jayaraman.
March 10, 2017
Content from the Brookings Institution India Center is now archived . After seven years of an impactful partnership, as of September 11, 2020, Brookings India is now the Centre for Social and Economic Progress , an independent public policy institution based in India.
The views are of the author(s).
Forty-two years have passed since the United Nations first decided to commemorate March 8 th as International Women’s Day, marking a historical transition in the feminist movement. Gender remains a critically important and largely ignored lens to view development issues across the world. On this past occasion of International Women’s Day 2017, here is an amalgamation of gendered learning outcomes across various crucial themes for public policy in India, emerging from Brookings India’s past research on political economy, financial inclusion and health.
Political Economy
In 2016, India ranked 130 out of 146 in the Gender Inequality Index released by the UNDP. It is evident that a stronger turn in political discourse is required, taking into consideration both public and private spaces. The normalization of intra-household violence is a huge detriment to the welfare of women. Crimes against women have doubled in the period between 1991 and 2011. NFHS data reports that 37 per cent of married women in India have experienced physical or sexual violence by a spouse while 40 per cent have experienced physical, sexual or emotional violence by a spouse. While current policy discourse recommends employment as a form of empowerment for women, data presents a disturbing correlation between female participation in labour force and their exposure to domestic violence. The NFHS-3 reports that women employed at any time in the past 12 months have a much higher prevalence of violence (39-40 per cent) than women who were not employed (29 per cent). The researchers advocate a multi-faceted approach to women’s empowerment beyond mere labour force participation, taking into consideration extra-household bargaining power.
Read more at: “ Beginning a new conversation on Women ”.
Gender inequality extends across various facets of society. Political participation is often perceived as a key factor to rectify this situation. However, gender bias extends to electoral politics and representative governance as well. The relative difference between male and female voters is the key to understanding gender inequality in politics. While the female voter turnout has been steadily increasing, the number of female candidates fielded by parties has not increased. More women contest as independents, which does not provide the cover for extraneous costs otherwise available when they are part of a political party.
However, women also act as agents of political change for other women. In the Bihar elections in 2005, when re-elections were held, the percentage of female voters had increased from 42.5 to 44.5 per cent while those of male voters declined from 50 to 47 per cent in the interim period of eight months. As a direct result, 37 per cent of the constituencies saw anti-incumbency voting. The average growth rate of women voters was nearly three times in those constituencies where there was a difference in the winning party. District-wise disaggregation of voter registration also supports this hypothesis in the case of Bihar indicating the percolation of the winds of change. This illustration proves that women are no longer under the complete control of the men in their family in terms of electoral participation. The situation is only bound to improve from here. With the introduction of Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs), vulnerable sections like women now have more freedom of choice in their vote. Further, poll related incidents of violence against women have significantly decreased since the phased introduction of EVMs across multi-level elections in India.
Read more at:
- Interview on Gender Inequality in Politics
- Women voters can tip the scales in Bihar
- Using technology to Strengthen Democracy
Related Content
Shamika Ravi
March 8, 2019
Mudit Kapoor, Deepak Agrawal, Shamika Ravi, Ambuj Roy, S V Subramanian, Randeep Guleria
August 8, 2019
Geetika Dang
September 4, 2019
Extending the conversation to political representation is the next phase in the conversation. Women make up merely 22 per cent of lower houses in parliaments around the world and in India, this number is less than half at 10.8 per cent in the outgoing Lok Sabha. A steady increase in female voter participation has been observed across India, wherein the sex ratio of voters (number of female voters vis-à-vis male) has increased from 715 in the 1960s to 883 in the 2000s. Our studies have shown that women are more likely to contest elections in states with a skewed gender ratio. In the case of more developed states, they seek representation through voting leading to an increase in voter participation.
The situation can be rectified by providing focused reservation for those constituencies with a skewed sex ratio. Reducing the entry costs (largely non-pecuniary in nature – cultural barriers, lack of exposure) for women in order to create a pipeline of female leaders is another solution. These missing women, either as voters or leaders point to the gross negligence of women at all ages.
Read more at: Missing Women in Indian Democracy
Financial Inclusion
In the developing world, women have traditionally been the focus of efforts of financial inclusion. They have proved to be better borrowers (40 per cent of Grameen Bank’s clients were women in 1983. By 2000, the number had risen to 90 per cent) – largely attributed to the fact that they are less mobile as compared to men and more susceptible to peer pressure. However, institutions in microfinance are exposed to the trade-off between market growth and social development since having more female clients lead to the inevitable drip-down of social incentives. As an attempt to overcome this hurdle, a larger role can be played by donors with a gender driven agenda, for the financial inclusion sector will drive the idea further.
Gendered contextualisation of products is highly necessary for microfinance institutions (MFIs) – men and women do not ascribe to choices in a similar fashion. Trends emerging from prior research indicates that when health insurance coverage was held under the MFI sector, by both men and women, women benefited from the coverage only so far as they were the holders and not using spousal status (if their husbands were insured). Thus healthcare seeking behaviour becomes an important factor to be considered in insurance coverage under the MFIs.
The JAM trinity – Jan Dhan Yojana, Aadhar, Mobile – can be used to improve financial inclusion from a gender perspective as well. The metrics to consider would be the number of Jan Dhan accounts held by women, percentage of women holding Aadhar cards and access to mobile connectivity for women.
Read more at: A trade-off between Growth and Social Objectives Exists for Microfinance Institutions
In terms of healthcare focusing on women, the Janani Suraksha Yojana (JSY) and National Health Mission are vital to the policy landscape. The JSY has improved maternal healthcare in India through the emphasis on institutional deliveries. Increase of 22 per cent in deliveries in government hospitals, was mirrored by an 8 per cent decline in childbirth at private hospitals and a 16 per cent decline in childbirth at home. The National Health Mission’s ASHA led to greater awareness and education of pregnant women as well as an increase in institutional maternal and neonatal healthcare. Improved infrastructure for maternal and neo-natal has been observed in community hospitals, in addition to the introduction of ambulance services.
A gendered increase in seek care is observed with a large 13 per cent increase in the number of women who report being sick in the last 15 days, driving the overall reportage. Further, an eight per cent decline in rural women seeking private healthcare, has been reported, while a 58 per cent increase in women seeking hospitalization has been reported. Further disaggregated, the data shows a 75.7 per cent increase for rural women seeking healthcare. The overall increase in usage of public hospitals is almost entirely driven by rural women who saw an increase of 24.6 per cent in utilisation of public hospitals over the 10 years (2004-2014). Our results show that the JSY had a significant, positive impact on overall hospitalisation of women in India. It increased the probability of a woman being hospitalised by approximately 1.3 per cent.
Read more at: Health and Morbidity in India
The healthcare sector in India has largely focused on maternal healthcare for women. The importance of research on mental health has been ignored in policy discourse. The significant relationship that mental health bears on violence has also been explored in further research. Every fifth suicide in India is that of a housewife (18 per cent overall) – the reportage of suicide deaths has been most consistent among housewives as a category, than other categories. India is the country with the largest rate of female deaths due to ‘intentional violence’.
Our work on childhood violence shows that girls are twice more likely to face sexual violence than boys before the age of 18. Larger the population of educated females in the country, lesser is the incidence of childhood violence at home – including lesser violent discipline, physical punishment as well as psychological aggression. Additionally, the lifetime experience of sexual violence by girls is strongly correlated with the adolescent fertility rate in a country. Further, a strong relationship is observed between female experience of sexual violence and female labour force participation within a country. The results show that the higher the labour force participation by women in a country, the higher is the incidence of sexual violence against them. This could be indicative of adverse working conditions within labour markets, and the difficulty of access to labour markets by young women in a country.

- Over the Past two decades, every fifth suicide in India is by a housewife
- What Explains Childhood Violence
Related Books
Robert E. Litan, Paul R. Masson, Michael Pomerleano
September 1, 2001
Katherine N. Probst, Don Fullerton, Robert E. Litan, Paul R. Portney
December 1, 2010
Kenneth Robinson
October 1, 1996
Global Economy and Development
Rahul Tongia, Anurag Sehgal, Puneet Kamboj
Online Only
3:00 am - 4:40 am IST
Saneet Chakradeo
August 18, 2020

Call us @ 08069405205

Search Here

- An Introduction to the CSE Exam
- Personality Test
- Annual Calendar by UPSC-2024
- Common Myths about the Exam
- About Insights IAS
- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director's Desk
- Meet Our Team
- Our Branches
- Careers at Insights IAS
- Daily Current Affairs+PIB Summary
- Insights into Editorials
- Insta Revision Modules for Prelims
- Current Affairs Quiz
- Static Quiz
- Current Affairs RTM
- Insta-DART(CSAT)
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Prelims 2024
- Secure (Mains Answer writing)
- Secure Synopsis
- Ethics Case Studies
- Insta Ethics
- Weekly Essay Challenge
- Insta Revision Modules-Mains
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Mains
- Secure (Archive)
- Anthropology
- Law Optional
- Kannada Literature
- Public Administration
- English Literature
- Medical Science
- Mathematics
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Monthly Magazine: CURRENT AFFAIRS 30
- Content for Mains Enrichment (CME)
- InstaMaps: Important Places in News
- Weekly CA Magazine
- The PRIME Magazine
- Insta Revision Modules-Prelims
- Insta-DART(CSAT) Quiz
- Insta 75 days Revision Tests for Prelims 2022
- Insights SECURE(Mains Answer Writing)
- Interview Transcripts
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Prelims
- Answer Keys for Prelims PYQs
- Solve Prelims PYQs
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Mains
- UPSC CSE Syllabus
- Toppers from Insights IAS
- Testimonials
- Felicitation
- UPSC Results
- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Ancient Indian History
- Medieval Indian History
- Modern Indian History
- World History
- World Geography
- Indian Geography
- Indian Society
- Social Justice
- International Relations
- Agriculture
- Environment & Ecology
- Disaster Management
- Science & Technology
- Security Issues
- Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude

- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Enivornment & Ecology
WEEKLY UPSC IAS ESSAY WRITING CHALLENGE
Following are the topics on which our followers have written (and writing essays) every Sunday to hone their essay writing skills. The topics are chosen based on UPSC previous year topics. Writing one essay on each Sunday will help you get better marks in this paper.
ESSAY STRATEGY by Topper – Rank 1 CSE 2017
ESSAY STRATEGY by Topper – Rank 25 CSE 2015
ESSAY STRATEGY by Topper – Rank 40 CSE 2015
- [VIDEO] How to Improve Marks in Essay and Ethics Papers?
- [VIDEO] How to Write Philosophical Essays
WEEKLY UPSC IAS ESSAY WRITING CHALLENGES – 2024
- April 21, 2024 : Well done is better than well said.
- April 14, 2024 : Consistency is the last refuge of the unimaginative.
- April 07, 2024 : Came from plant, use it; made in plant, don’t.
- March 30, 2024 : A Business That Makes Nothing More Than Money Is Poor Business
- March 24, 2024 : If Voting Really Made Difference, They Would Not Let Us Do It
- March 17, 2024 : Cinema Is Not A Slice Of Life, But A Piece Of Cake.
- March 10, 2024 : Education Can give skill, but a liberal education can give dignity
- March 3, 2024 : Sometimes when you lose your way you find yourself
- February 25, 2024 : Who Looks Inside Awakes, Who Looks Outside Dream
- February 18, 2024 : Never Let School Interfere With Your Education
- February 11, 2024 : Whoever Controls the Media Controls the Mind
- February 04, 2024 : A certain darkness is needed to see the stars
- January 28, 2024 : Those who cannot remember the past are condemned to repeat it
- January 21, 2024 : Subtle Is powerful
- January 14, 2024 : The power of community to create health is far greater than any physician, clinic or hospital.
- January 07, 2024 : Give them Quality. That’s The Best Kind of Advertising
WEEKLY UPSC IAS ESSAY WRITING CHALLENGES – 2023
- December 31, 2023 : The only antidote to mental suffering is physical pain
- December 24, 2023 : All Great Changes Are Preceded By Chaos
- December 17, 2023 : We are drowning in information, but starved for Knowledge
- December 10, 2023 : Violence Is the last resort of the incompetent
- December 03, 2023 : Be a Voice, Not an Echo
- November 26, 2023 : A Society that has more justice is the society that needs less charity
- November 19, 2023 : Sell Your Cleverness and Buy Bewilderment
- November 12, 2023 : love takes off the masks that we fear we cannot live without and know we cannot live within
- November 5, 2023 : Clothes Make The Man
- October 29, 2023 : Education is what remains after one has forgotten what one has learned in school.
- October 22, 2023 : Mathematics is the music of reason
- October 15, 2023 : Girls are weighed down by restrictions, boys with demands – two equally harmful disciplines
- October 08, 2023 : Inspiration for creativity springs from the effort to look for the magical in the mundane.
- October 01, 2023 : Not All Who Wander Are Lost
- September 24, 2023 : Visionary Decision-Making happens at the intersection of intuition and logic
- September 17, 2023 : Thinking Is Like A game. It does not begin unless there is an opposition team.
- September 10, 2023 : Unless we have well-educated people, we are vulnerable on National Security
- September 03, 2023 : Harsh Laws are, at times, better than No laws
- August 27, 2023 : Nations Do Not Die From Invasion. They Die From Internal Rottenness
- August 20, 2023 : In Individuals, insanity is rare; In groups, parties and nations, it is the rule.
- August 13, 2023 : Economics Is Too Important To Leave To The Economists.
- August 06, 2023 : A self without a book-shelf is naked.
- July 30, 2023 : Wrong Choices Lead To Right Places
- July 23, 2023 : Credit where credit is due.
- July 16, 2023 : A right is not what someone gives you; it’s what no one can take away from you.
- July 9, 2023 : The measure of intelligence is the ability to change
- July 2, 2023 : Do what you can, with what you have, where you are.
- June 25, 2023 : In the long run , the sword will always be conquered by the spirit
- June 18, 2023 : The company you keep determines your Success
- June 11, 2023 : A disciplined mind brings happiness.
- June 4, 2023 : Our moral responsibility is not to stop the future but to shape it
- May 28, 2023 : Action breeds confidence and courage
- May 21, 2023 : A library is a hospital for the mind
- May 14, 2023 : Self-Education is Life-Long Curiosity
- May 7, 2023 : Silence is Spurious Golden
- April 30, 2023 : The price of greatness is responsibility
- April 23, 2023 : Progress is impossible without change
- April 16, 2023 : The Impact of Artificial Intelligence.
- April 9, 2023 : People would rather believe than know.
- April 2, 2023 : Prioritizing education technology for global growth
- March 26, 2023 : Technology is a weapon against poverty
- March 19, 2023 : Every choice you make makes you
- March 12, 2023 : Patience is a virture ; virtue is a grace
- March 5, 2023 : Before any fight, it is the fight of mind
- February 26, 2023 : The Measure of a man is what he does with Power.
- February 19, 2023 : When you kill time, you kill life.
- February 12, 2023 : Delayed success mostly stays forever.
- February 05, 2023 : The wound is the place where the Light enters you.
- January 29, 2023 : Doubt is an uncomfortable condition, but certainty is a ridiculous one.
- January 22, 2023 : I am what I am, so take me as I am
- January 15, 2023 : Real learning comes about when the competitive spirit has ceased
- January 08, 2023 : Time hurts but it also heals. It punishes but it rewards too- it is the greatest teacher ever for a human.
- January 01, 2023 : The Beginning is the End and the End is The Beginning.
WEEKLY UPSC IAS ESSAY WRITING CHALLENGES – 2022
- December 25, 2022 : To tolerate is purely an act of mind
- December 18, 2022 : The arc of moral universe is long, but it bends towards justice
- December 11, 2022 : Religion is a culture of faith; Science is a culture of doubt.
- December 04, 2022 : My best friend is a person who will give me a book I have not read
- November 27, 2022 : Everything comes to him who hustles while he waits
- November 20, 2022 : We are always blind as we want to be
- November 13, 2022 : By your stumbling, the world is perfected.
- November 6, 2022 : You cannot step twice in the same river
- October 30, 2022 : Just because you have a choice, it does not mean that any of them has to be right.
- October 23, 2022 : A smile is the chosen vehicle for all ambiguities
- October 16, 2022 : The time to repair the roof is when the sun is shining
- October 9, 2022 : A ship in harbour is safe, but that is not what ship is for
- October 2, 2022 : History is a series of victories won by the scientific man over the romantic man
- September 25, 2022 : Poets are the unacknowledged legislators of the world
- September 18, 2022 : Forests are the best case studies for economic excellence
- September 11, 2022 : Culture changes with economic development.
- September 4 2022 : We don’t see things as they are, we see them as we are.
- August 28 2022 : The obstacle is the path.
- August 21 2022 : What is to give light must endure burning.
- August 14 2022 : “He who has never learned to obey cannot be a good commander.” Aristotle.
- August 7 2022 : Any fool can know. The point is to understand.” Albert Einstein
- July 31, 2022 : A bad conscience is easier to cope with than a bad reputation. Friedrich Nietzsche.
- July 24, 2022 : Time is all we have and don’t
- July 17, 2022 : Life fritters away when distractions become your lifestyle
- July 10, 2022 : After every darkness comes the dawn July 10, 2022 : After every darkness comes the dawn
- July 3, 2022 : Mind – a beautiful servant? Or a dangerous master?
- June 26, 2022 : Education Breeds Peace
- June 19, 2022 : A great leader is never angry
- June 12, 2022 : That which hurts, instructs; That which instructs, creates; Creates Wonders!
- June 05, 2022 : Don’t let what you cannot do interfere with what you can do
- May 29, 2022 : The journey is a reward as well as destination
- May 22, 2022 : Imagination creates reality
- May 15, 2022 : The curious paradox is, only if we accept things as they are, things can change
- May 08, 2022: The whole problem with the world is that fools and fanatics are so certain of themselves, while wiser people are so full of doubts
- May 01, 2022: Loyalty To Country Always. Loyalty To Government Only When It Deserves
- April 24, 2022: Successful Investing Is Anticipating The Anticipations of Others
- April 17, 2022: Courage is resistance to fear, mastery of fear, not absence of fear
- April 10, 2022 : Tell me and I forget. Teach me and I remember. Involve me and I learn
- April 03, 2022 : Forgiveness is the final form of love
- March 27, 2022 : The world of reality has its limits; the world of imagination is boundless
- March 20, 2022 : Reason has always existed, but not always in a reasonable form.
- March 13, 2022 : Everything we hear is an opinion; not a fact
- March 5, 2022 : There are better practices to “best practices”
- February 27, 2022 : History repeats itself first as a tragedy second as a farce.
- February 20, 2022 : What is research, but a blind date with knowledge!
- February 13, 2022 : Hand that rocks the cradle rules the world
- February 6, 2022 : The real is rational and the rational is real.
- January 30, 2022 : Philosophy of Wantlessness Is Utopian, while the philosophy of materialism is chimera.
- January 23, 2022 : Your perception of me is a reflection of you; my reaction to you is an awareness of me.
- January 16, 2022 : The process of self-discovery has now been technologically outsourced.
- January 09, 2022 : Knowing oneself is the beginning of all wisdom
- January 02, 2022 : Biased Media Is A Real Threat To Indian Democracy
WEEKLY UPSC IAS ESSAY WRITING CHALLENGES – 2021
- December 26, 2021 : What Gets Measured Gets Managed
- December 19, 2021 : The enemy of stability is complacency
- December 12, 2021 : A clear conscience fears no accusation
- December 05, 2021 : Power of vested interests is vastly exaggerated compared with the gradual encroachment of ideas
- November 28, 2021 : The whole is more than a sum of its parts
- November 21, 2021 : Scientific and technological progress cannot be equated with the progress of humanity
- November 14, 2021 : The price of our vitality is the sum of all our fears
- November 7, 2021 : Lawlessness is the result of failure to cultivate a sense of self-evaluation
- October 30, 2021 : What you do makes a difference, and you have to decide what kind of difference you want to make
- October 24, 2021 : Science for the economic freedom of humanity
- October 17, 2021 : An interdependent world cannot be an inequitable world
- October 03, 2021 : Strength comes from an indomitable Will
- SEPTEMBER 26, 2021 : Ethnocracy and concentration of power can derail even an affluent nation
- SEPTEMBER 19, 2021 : Conservation is a state of harmony between men and land.
- SEPTEMBER 12, 2021 : Culture of entitlement comes with unreasonable expectations and insecurities
- SEPTEMBER 5, 2021 : Literacy is a vital skill that enhances dignity, improves health outcomes, empowers people to access their rights and bolsters opportunities
- AUGUST 29, 2021 : A parliamentary system of government rests on a functioning opposition as ‘no democracy can do without it’.
- AUGUST 22, 2021 : Development must lead to dismantle all kinds of human unfreedom
- AUGUST 15, 2021 : Sport is a reflection of larger social phenomena
- AUGUST 8, 2021 : Every social stratum has its own Common Sense and its own good sense
- AUGUST 1, 2021 : Capitalism without competition is not Capitalism. It is Exploitation.
- JULY 25, 2021 : We don’t have to sacrifice a Strong Economy for a Healthy Environment
- JULY 18,2021 : We Need not a social conscience, but a social consciousness.
- JULY 11, 2021 : The cure for evils of democracy is more democracy.
- JULY 04, 2021 : No Constitution by itself achieves perfect justice
- JUNE 27, 2021 : Our world has achieved brilliance without conscience.
- JUNE 20, 2021 : Our common humanity demands that we make the impossible possible.
- JUNE 13, 2021 : Without courage we cannot practice any other virtue with consistency. We can’t be kind, true, merciful, generous, or honest.
- JUNE 06, 2021 : The political problem of mankind is to combine three things: economic efficiency, social justice and individual liberty.
- MAY 30, 2021 : Economics without ethics is a caricature & ethics without economics is a fairy tale.
- MAY 23 , 2021 : Indecisiveness is the rival of Progression
- MAY 16 , 2021 : Time changes everything except something within us which is always surprised by change.
- May 09, 2021 : The possession of arbitrary power has always, the world over, tended irresistibly to destroy humane sensibility, magnanimity, and truth
- May 02, 2021 : The truth of character is expressed through choice of act ions
- April 25, 2021 : It is not our differences that divide us; It is our inability to recognise, accept, and celebrate those differences.
- April 18, 2021 : Nothing in the world is more dangerous than sincere ignorance and conscientious stupidity.
- April 11, 2021 : Solutions emerge if situations are not forced
- April 04, 2021 : Morality is subservient to materialistic values in present times
- March 28, 2021 : Prejudice is a burden that confuses the past, threatens the future and renders the present inaccessible
- March 21, 2021 : Our major social problems are not the cause of our decadence but are a reflection of it
- March 14, 2021 : The Future of Multilateralism : Towards a responsible Globalization
- March 07, 2021 : Subtlety may deceive you; Integrity never will
- February 28, 2021 :Technology as the silent factor in international relations
- February 21, 2021 :Patriarchy is the least noticed yet the most significant structure of social inequality
- February 14, 2021:There can be no social justice without economic prosperity but economic prosperity without social justice is meaningless
- February 07, 2021: Culture is what we are civilization is what we have
- January 31, 2021: Simplicity is the ultimate sophistication
- January 24, 2021: Ships do not sink because of water around them , ships sink because of water that gets into them
- January 17, 2021: Mindful manifesto is the catalyst to a tranquil self
- January 10, 2021: Life is long journey between human being and being humane
- January 03, 2021: The Covid pandemic has revealed the urgent need for effective governance everywhere”
- December 27, 2020: Challenges of 21st Century – insurmountable?
- December 20, 2020: Too much Democracy is Detrimental to Development
- December 13, 2020: Happiness is not an ideal of reason, but of imagination.
WEEKLY UPSC IAS ESSAY WRITING CHALLENGES – 2020
- December 06, 2020 : As you Start to walk on the way, the Way appears
- November 29, 2020: Need of the Hour is to Maximise Possibilities of Agriculture in India
- November 22, 2020: The survival of democracy depends on its ability to lower social uncertainty
- November 15, 2020: There is no greatness where there is no simplicity
- November 08, 2020: Inequality can be Reduced by the Power of the Market rather than the Government
- November 01, 2020: Civil liberties are fundamental to the functioning of modern democracies
- October 25, 2020: Artificial Intelligence is Not All Evil – It can Promote Social Good Too
- October 18, 2020: Wherever law ends, tyranny begins
- October 11, 2020:Hyper-globalism is threat to human prosperity
- September 27, 2020: Our World is in a Surplus of Multilateral Challenges and a Deficit of Solutions
- September 20, 2020: In India Agriculture and the Farmer are both the Victims of Narrow Political Vision
- September 13, 2020: India Needs Aggressive and Pragmatic Neighbourhood Policy
- September 6, 2020: “The greatest discovery of all time is that a person can change his future by merely changing his attitude .
- August 30, 2020: The worst form of inequality is to try to make unequal things equal
- August 23, 2020: Justice will not be served until those who are unaffected are as outraged as those who are.
- August 16, 2020: Life without liberty is like a body without spirit.
- August 09, 2020: Strive not to be a success, but rather to be of value
- August 02, 2020: New Education Policy 2020: A Progressive Policy with Diverse Challenges
- July 26, 2020: In a democracy, the individual enjoys not only the ultimate power but carries the ultimate responsibility
- July 19, 2020: Education is a progressive discovery of our own ignorance
- July 12, 2020: The human spirit must prevail over technology
- July 05, 2020: When the power of love overcomes the love of power the world will know peace.
- June 28, 2020: Today India Needs ‘Harmony in Diversity’, Not Unity in Diversity.
- June 21, 2020: A people without the knowledge of their past history, origin and culture is like a tree without roots.
- June 14, 2020: Post Independence, the Issue of Land is at the Core of India’s Non-Achievement of Its Development Aspirations
- June 7, 2020: Never Let a Good Crisis Go to Waste
- May 31, 2020: Despite Challenges, To be a Healthy and Successful Nation, India must Ensure Universal Health Coverage
- May 24, 2020: Nearly all men can stand adversity, but if you want to test a man’s character, give him power.
- May 17, 2020:The test of our progress is not whether we add more to the abundance of those who have much it is whether we provide enough for those who have too little
- May 10, 2020: Urban Exclusion of Migrant Workers in India is a Reality and Needs Urgent Robust Policy Measures
- May 03, 2020: Uncertainty should ignite creativity, not depravity
- April 26, 2020: The fool doth think he is wise but the wise man knows himself to be a fool
- April 19, 2020: Social Harmony, not Social Distancing, is the final solution to all our problems
- April 12, 2020: It is our choices, that show what we truly are, far more than our abilities
- April 05, 2020: Education must also train one for quick, resolute and effective thinking
- March 29, 2020: “Problems cannot be solved at the same level of awareness that created them”
- March 22, 2020: In order to understand the world one has to turn away from it on occasion
- March 15, 2020: Pandemics such as COVID-19, though Catastrophic, are in the end Meant to Reset Humanity and its Priorities
- March 08, 2020: Those who have wisdom have all: Fools with all have nothing
- March 01, 2020: Indifferentism is the worst kind of disease that can affect people.
- [VIDEO] Perspectives on Essay Topic of Feb 23
- February 23, 2020: To ease another’s heartache is to forget one’s own.
- February 16, 2020 : When civil services does its job, people will not need social service
- February 09, 2020 : The greatest threat to our planet is the belief that someone else will save it.
- February 02, 2020: Ability will get you success, Character will keep you successful.
- January 26, 2020: Media’s duty is to inform public, not manufacture opinion.
- January 19, 2020: Freedom is not worth having if it does not include the freedom to make mistakes
- January 12, 2020 : Women who seek to be equal with men lack ambition
- J anuary 5, 2020 : All war is a symptom of man’s failure as a thinking animal
- December 29, 2019 : There cannot be daily democracy without daily citizenship
- December 22, 2019: War is the ultimate Price we pay for lasting Peace
- December 15, 2019 : Inclusivity and Plurality are the hallmarks of a peaceful society
- December 08, 2019: Justice Loses Character if it becomes Revenge
- December 01. 2019: Economic Growth and Development are Shaped by the Societies in which they Operate
- November 24, 2019: Social Media is the Fourth Pillar of Democracy
- November 17, 2019: Media is No More a Fourth Pillar of Democracy
- November 10, 2019: Rise of Artificial Intelligence: the threat of jobless future or better job opportunities through reskilling and upskilling
- November 03, 2019:Biased media is a real threat to Indian democracy
- October 27, 2019: Neglect of primary health care and education in India are reasons for its backwardness
- October 20, 2019: South Asian societies are woven not around the state, but around their plural cultures and plural identities
- October 13, 2019: Courage to accept and dedication to improve are two keys to success
- October 06, 2019: Best for an individual is not necessarily best for the society
- September 29, 2019: Values are not what humanity is, but what humanity ought to be
- September 22, 2019: Wisdom finds truth
WEEKLY UPSC IAS ESSAY WRITING CHALLENGES – 2019
- September 15, 2019: Kashmir Problem – Historical Injustice or Misguided Geopolitics?
- September 08, 2019: India’s Space Ambitions – Are they Welfarist?
- September 01, 2019: India – $5 Trillion Economy: Dream or Reality?
- August 25, 2019 Knowledge will give you power, but character respect.
- August 18, 2019 The mind is everything. What you think you become.
- August 11, 2019: Virtue is Knowledge
- August 04, 2019: Inclusive governance begets Inclusive growth
- July 28, 2019: India’s headache: Unemployment or Underemployment?
- July 21, 2019: The road to science and spirituality are opposite, but we should tread both
- July 14, 2019: India is a leading power, rather than just a balancing power
- July 07, 2019: Should the world embrace democratic socialism or progressive capitalism?
- June 30, 2019: Impact of Digital Revolution on Human Wellbeing
- June 23, 20 19: Contentment is natural wealth, luxury is artificial poverty
- June 16, 2019: The definition of happiness is the full use of your powers, along the lines of excellence.
- June 09, 2019: Not Corruption, Communalism is the Greatest Threat India is facing Today
- May 19, 2019: First they ignore you, then they laugh at you, then they fight you, then you win.
- May 12, 2019: Never interrupt your enemy when he is making a mistake
- May 05, 2019: Happiness equals reality minus expectations
- April 28, 2019: Political correctness is tyranny with manners
- April 21, 2019: The only thing necessary for the triumph of evil is for good men to do nothing.
- April 07, 2019: Dogma is the sacrifice of wisdom to consistency
- March 31, 2019: The true measure of a man is how he treats someone who can do him absolutely no good.
- March 24, 2019: Terrorism has No Religion
- March 17, 2019: Money and Religion – Great Unifiers of Humankind?
- March 10, 2019: Tradition becomes our security, and when the mind is secure it is in decay
- March 03, 2019: Innovation distinguishes between a leader and a follower
- February 24,2019: Knowledge speaks, but wisdom listens
- February 17, 2019: Problems worthy of attack prove their worth by fighting back
- February 10, 2019: Nothing in the world is more dangerous than sincere ignorance and conscientious stupidity.
- February 03, 2019: You can avoid reality, but you cannot avoid the consequences of avoiding reality
- January 27, 2019: Glory is fleeting, but obscurity is forever
- January 20, 2019: All that we are is the result of what we have thought.
- January 12, 2019: All differences in this world are of degree, and not of kind, because oneness is the secret of everything.
- January 06, 2019: National security is Irreversibly linked to good economic growth
WEEKLY UPSC IAS ESSAY WRITING CHALLENGES – 2018
- December 28, 2018: To plan for smart development, governments and business must recognize nature’s role in supporting economic activity
- December 23, 2018: Government Surveillance – Good or Bad?
- December 16, 2018: Trade Wars – Economic or Geopolitical?
- December 02, 2018: Immigration is Not a Threat, but Fundamentally it’s an Economic Issue
- November 25, 2018: A people that values its privileges above its principles loses both
- November 18, 2018: “The past’ is a permanent dimension of human consciousness and values
- November 11, 2018: A good life is one inspired by love and guided by knowledge
- November 04, 2018: Management of Indian border disputes – a complex task
- October 28, 2018: Alternative technologies for a climate change resilient India
- October 21, 2018: Poverty anywhere is a threat to prosperity everywhere
- October 14, 2018: Reality does not conform to the ideal, but confirms it
- October 07, 2018: Customary morality cannot be a guide to modern life
- September 30, 2018: Commercialization of Space : Importance and the need for regulation
- September 23, 2018: E-commerce as a new form of trade and its challenges to India.
- September 16, 2018: Ability is nothing without opportunity
- September 09, 2018: Death Penalty eliminates Criminals, not Crime.
- September 02, 2018: Dissent is the foundation of democracy.
- August 26, 2018: Mars Mission and Mob lynchings are two obverse faces of India
- August 19, 2018: Strengthening Land Rights Strengthens Development
- August 12, 2018: Age of Big Data: Data is the New Oil, History is its oldest bank
- August 05, 2018: Strong Institutions and fair procedures, not personalities constitute the fundamentals of good governance
- July 29, 2018: Social reform is a myth if places of worship are open only to all castes and not to all genders.
- July 22, 2018: Section 377, not the carnal acts banned under it is ‘against the order of nature ‘
- July 15, 2018: Schooling Is Not Education
- July 08, 2018: Sometimes it takes a natural disaster to reveal a social disaster.
- July 01, 2018: Normal human activity is worse for nature than the greatest nuclear accident in history
- June 24, 2018: Gender Sensitive Indian Society is Prerequisite for Women and Child Empowerment
- June 17, 2018: Where Should India Invest More – Human Capital or Human Development?
- June 10, 2018: Has Democracy Taken Backseat Due to the Rise of Populists and Demagogues?
- June 03, 2018: We won’t have a society ,if we destroy the environment
- May 27, 2018: Can Development and Environment Protection Go Together?
- May 20, 2018: Governor is the Choke Point of Federal Circuit of India
- May 13, 2018: Anonymity is the Best and the Worst Feature of Urbanism
- May 06, 2018: A man is but the product of his thoughts; what he thinks, he becomes
- April 29, 2018: Guaranteeing Right to Vote may Establish a Democracy, But Ensuring it’s Right Use Only Will Bring a True Democracy
- April 22, 2018: Stereotyping is an Ideological Force Which Hinders and Endangers Consolidation of India
- April 15, 2018: Can Education and legislation Address Violence Against Women and Children in India?
- April 8, 2018: Banking Crisis in India – Failure of Governance and Regulation?
- April 1, 2018: Privacy is the fountainhead of all other rights
- March 25, 2018: Impact of Technology on Human Relations and Human Productivity
- March 18, 2018: India’s Focus should be on Ease of Living, not on Easy of Doing Business
- March 11, 2018: A friend to everybody is a friend to nobody
- March 04, 2018: Capitalism can not Bring Inclusive Growth
- February 25, 2018: The unprecedented advance of technologies facilitate individual empowerment but at the cost of Institutions and Democratic societies
- February 18, 2018: Threats being Faced by Liberal Democratic Systems are both Dangerous and Permanent
- February 11, 2018: For India, Stigmatised Capitalism is Better than Crony Socialism
- February 04, 2018: Art, freedom and creativity will change society faster than politics.
- January 28, 2018: Politics of Identity is the Politics of the Weak
- January 21, 2018: Poverty is the parent of revolution and crime
- January 14, 2018: Peace cannot be kept by force; it can only be achieved by understanding
- January 07, 2018: The Root Cause of Agrarian Distress in India – Failure of Policies or Failure of Governance?
WEEKLY UPSC IAS ESSAY WRITING CHALLENGES – 2017
- December 31, 2017: Impact of the new economic measures on fiscal ties between the union and states in India
- December 24, 2017: Fulfilment of ‘new woman’ in India is a myth
- December 17, 2017: Joy is the simplest form of gratitude.
- December 10, 2017: Farming has lost the ability to be a source of subsistence for majority of farmers in India
- December 03, 2017: Destiny of a nation is shaped in its classrooms
- November 19, 2017: Has the Non- Alignment Movement(NAM) lost its relevance in a multipolar world
- November 12, 2017: Social media is inherently a selfish medium.
- November 04, 2017: We may brave human laws but cannot resist natural laws
- October 29, 2017: Gratitude is not only the greatest of virtues, but the parent of all the others.
- October 22, 2017: Harith Diwali, Swasth Diwali : What measures are needed to deal with Festivity and Air Pollution?
- October 15, 2017: Biggest Threat to Humanity – Moral Crisis or Climate Change?
- October 08, 2017: The monsoon is a defining aspect of India’s nationhood
- October 01, 2017: India’s Infrastructure Story – Why is India not able to Build like China?
- September 24, 2017: Impact of Digital Technologies on Globalisation
- September 17, 2017: Urbanisation and Solid Waste Management in India – Challenges and Opportunities
- September 10,2017: Gender Equality and Peace: Are They Connected?
- September 03, 2017: Recent Natural Disasters – What do they Reveal about Humanity?
- August 27, 2017: Godmen – A Threat to Indian Society and Culture
- August 20, 2017: Corruption in India: Neither Systemic Reforms nor Surgical Strikes would End it
- August 13,2017: Interrelationship between Gender Equality and Sustainable Development
- August 06, 2017: Utility and relevance of Parliament in our polity
- July 30, 2017: Caste System – Source of India’s Eternal Inequality?
- July 23, 2017: Indian Democracy, Media and Public Opinion – Does Public Opinion Matter in Policymaking?
- July 16, 2017: Poverty and Environment – Their Interrelationship is the Key to Sustainable World
- July 09, 2017: Soft Power is India’s Strength, not its Weakness
- July 02, 2017: Technology and Jobs – Is Technology a Curse?
- June 25, 2017: Democracy’s Relevance in the Face of New Global Threats
- June 18, 2017: Federalism in India – Competitive or Cooperative?
- June 11, 2017: Peace, Environment and Development: Are these Interrelated?
- June 04, 2017: Role of Technology in Development – Is Technology Helping or Hindering Development?
- May 28, 2017: Poverty is a State of Mind
- May 21, 2017: Does India Need Superpower Status?
- May 14, 2017: India’s Achilles Heel – Lack of Ambition or Lack of Leadership in Achieving Greatness?
- May 07, 2017: Don’t limit a child to your own learning, for he was born in another time.
- April 29, 2017: The greatest happiness of the greatest number is the foundation of morals and legislation
- April 23, 2017: To conquer fear is the beginning of wisdom
- April 16, 2017: One-Party-Dominant System – Is it Good for India?
- April 09, 2017: Should Youth in India Consider Politics as Career?
- April 02, 2017: Can World Save Succeeding Generations from the Scourge of War?
- March 26, 2017: Low, stagnating female labour-force participation in India: An anomaly or an outcome of economic reforms?
- March 19, 2017: When a man is denied the right to live the life he believes in, he has no choice but to become an outlaw
- March 12, 2017: The marks humans leave are too often scars
- March 05, 2017: Environmental Challenges and Geopolitics: How to save our Environment?
- February 27, 2017: Radical Solutions are Needed to Address Today’s Radical Problems
- February 19, 2017: India’s Importance in the Post-truth World
- February 12, 2017: The Role of Politics in Development
- February 05, 2017: Facts do not cease to exist because they are ignored
- January 29, 2017: Building Walls and Banning Refugees – Does this Help Humanity?
- January 22, 2017: Digital economy: A leveller or a source of economic inequality
- January 15, 2017: Cyberspace and internet: Blessing or curse to the human civilization in the long run
- January 08, 2017: Water disputes between states in federal India
- January 01, 2017: Need brings greed, if greed increases it spoils breed
WEEKLY UPSC IAS ESSAY WRITING CHALLENGES – 2016
- (December 25, 2016) – Cooperative federalism: Myth or reality
- (December 18, 2016) – Innovation is the key determinant of economic growth and social welfare
- (December 11, 2016) – Near jobless growth in India: An anomaly or an outcome of economic reforms
- (December 04, 2016) – If development is not engendered, it is endangered
- (November 27, 2016) – Social media is better at breaking things than at making things
- (November 20, 2016) – Deglobalization is good for the world
- (November 12, 2016) – Democracy is the worst form of government, except for all the others
- (November 06, 2016) – It is not inequality which is the real misfortune, it is dependence
- (October 30, 2016) – Reducing Poverty while also Conserving Nature is an Impossible Task
- (October 23, 2016) – Poverty can be eliminated by putting science at the heart of development
- (October 16, 2016) – People shouldn’t be afraid of their government. Governments should be afraid of their people
- (October 09, 2016) – Better Access is Key to Inclusive Cities
- (October 02, 2016) – The weaker sections of Indian society – Are their Rights and Access to Justice Getting Better?
- (September 25, 2016) – Imagination is more important than intelligence
- (September 18, 2016) – Science is organized knowledge. Wisdom is organized life
- (September 11, 2016) – Not what we have But what we enjoy, constitutes our abundance
- (September 04, 2016) – It is the mark of an educated mind to be able to entertain a thought without accepting it
- (August 28, 2016) – If one can Address Moral Crisis, many of World’s Problems can be Solved
- (August 21, 2016) – Overdependence on Technology will Advance Human Development
- (August 14, 2016) – Geography may remain the same ; history need not
- (August 07, 2016) – Knowing yourself is the beginning of all wisdom
- (July 31, 2016) – To live is the rarest thing in the world. Most people exist, that is all
- (July 24, 2016) – True knowledge exists in knowing that you know nothing
- (July 17, 2016) – We Can Not Fight Terrorism – We have to Live With it
- (July 10, 2016) – A house divided against itself cannot stand
- (July 02, 2016) – When the going gets tough, the tough get going
- (June 26, 2016) – India a Reluctant Participant in the New Global Order?
- (June 19, 2016) – Inclusiveness in India – Still a Dream?
- (June 12, 2016) – No one can make you feel inferior without your consent
- (June 05, 2016) – Not everything that can be counted counts, and not everything that counts can be counted
- (May 29, 2016) – It is hard to free fools from the chains they revere
- (May 22, 2016) – Honest disagreement is often a good sign of progress
- (May 15, 2016) – Fire is a good servant but a bad master
- (May 08, 2016) – The grass is always greener on the other side of the fence
- (May 01, 2016) – Labour Reforms in India and its Role in Economic Development
- (April 24, 2016) – It takes a whole village to raise a child
- (April 17, 2016) – Trust take years to Build, Seconds to Break
- (April 10, 2016) – Cleanliness is next to Godliness
- (April 03, 2016) – Honesty is the Best Policy
- (March 27, 2016) – Before criticizing a man, walk a mile in his shoes
- (March 20, 2016) – Caste System – India’s Enduring Curse
- (March 13, 2016) – Fortune favors the bold
- (March 06, 2016) – Quick but steady wins the race
- (February 28, 2016) – Dreams which should not let India sleep
- (February 21, 2016) – Lending hands to someone is better than giving a dole
- (February 14, 2016) – Technology cannot replace manpower
- (February 7, 2016) – Character of an institution is reflected in its leader
- (January 31, 2016) – Can Capitalism bring Inclusive Growth?
- (January 24, 2016) – Crisis Faced in India – Moral or Economic?
- (January 17, 2016) – Too many cooks spoil the broth
- (January 10, 2016) – The Best Things in Life are Free
- (January 3, 2016) – Don’t count your chickens before they hatch.
WEEKLY ESSAY WRITING CHALLENGES – 2015
- 27 December 2015
- 20 December 2015
- 13 December 2015
- 06 December 2015
- 28 November 2015
- 21 November 2015
- 15 November 2015
- 08 November 2015
- 01 November 2015
- 25 October 2015
- 18 October 2015
- 11 October 2015
- 04 October 2015
- 27 September 2015
- 20 September 2015
- 13 September 2015
- 06 September 2015
- 31 August 2015
- 30 August 2015
- 23 August 2015
- 16 August 2015
- 09 August 2015
- 01 August 2015
- 26 July 2015
- 19 July 2015
- 12 July 2015
- 05 July 2015
- 28 June 2015
- 21 June 2015
- 14 June 2015
- 07 June 2015
- 31 May 2015
- 24 May 2015
- 17 May 2015
- 10 May 2015
- 03 May 2015
- 26 April 2015
- 19 April 2015
- 12 April 2015
- 05 April 2015
- 29 March 2015
- 22 March 2015
- 15 March 2015
- 01 March 2015
- 22 February 2015
- 15 February 2015
- 08 February 2015
- 01 February 2015
- 25 January 2015
- 18 January 2015
- 11 January 2015
- 04 January 2015

- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director’s Desk
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Prelims
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Mains
- Environment & Ecology
- Science & Technology

Social Issues in india- Historical and Contemporary
Social Issues through the Ages in Indian Society:-
- The Indian society, being part of an ancient civilisation, has passed through different historical phases. The Vedic period in India sowed the seeds of a civilisation – characterised by the emergence of sophisticated philosophy, religion, astrology, science and medicine. Its institutional base centered around Varnashram and caste, emphasis on rituals, higher position of ritual performers over others and the sacrifice of animals. The following were the major social issues and problems in the early phase of the Indian civilisation.
- Conflict between the two major social groups, i.e., the Aryans and the Dasas Dasyu as mentioned in the Vedic texts.
- Increasing rigidity of social hierarchy,
- Emphasis on the observance of rituals,
- Sacrifice of animals.
- Jainism and Budhism emerged as a protest against these practices. It is to be noted that during the Vedic and the post-Vedic periods, the social position of Women was quite high. The child marriages were not common in this period.
- India’s contact with Islam has passed through the phases of conflict, gradual accommodation, increasing synthesis and the revival of communal antagonism. With the advent of the Muslim rule in India, two major trends were visible in the Indian Society:
- The first was the trend of the growing insularity and attitude of avoidance towards others. This strengthened the notion of the purity – pollution and practice of untouchability. The rigid restrictions on the sea – voyage were imposed on the people in this period. As a consequence, firstly, it reduced the spirit of enterprise and adventure among the Indians. Secondly, it minimised contacts of Indians with the outside world. During the early phase of invasions and conflicts, the practice of Sati and the child-marriage developed as a defense mechanism among the Hindus. Only a small section of the Muslim population immigrated to India from Afghanistan, Iran, Turkey and the Arab countries. The rest of them were local people who accepted Islam. Due to contacts with Hinduism and conversion, the Muslim in India were also influenced by caste-system. Thus, the social hierarchies were introduced even among the Muslims in India.
- The second trend was in the form of the emulation of the customs of the Muslim rulers by the elite and section of the upper caste Hindus. This encouraged the adoption of the practice of Pardah (veil to cover the face) by the upper caste women in north India. In the medieval period, the Bhakti movement, reassert the humanist elements of the Indian civilisation by preaching equality, speaking against rituals, the caste rigidity and untouchability. The practices of untouchability, child marriage, sati, infanticide, organised thagi (cheating) increased in the Indian Society particularly during the declining phase of the Mughal empire. Even the religious beliefs encouraged the addiction of tobacco, hashish and opium.
- By the early part of the 19th Century, the colonial administration in India was fully established. After 1820, it adopted a reformist zeal. There were several. social reform programmes to eradicate the practices of Sati and the Thagi – widely prevalent during this period. In the early 19th Century, the questions related to the social problems of sati, remarriage of widows, spread of modern education, evils of child marriage and of untouchability were raised by social reformers.
- Brahmosamaj–led by Raja Rammohan Roy,
- Aryasamaj–led by Swami Dayanand Sarawati
- Prarthana Samaj–led by Mahadeva Govind Ranade,
- Ramakrishna Mission–inspired by Ramkrishna Paramhansa and led by Swami Vivekanand.
- These reform movements opposed the practice of untouchability, Sati, infanticide and propagated in favour of the remarriage of widows and the modern education. Due to the tireless efforts of Raja Rammohan Roy, the practice of Sati was legally abolished in 1829. The Arya Samaj contributed significantly in weakening the caste-rigidity and reducing the practice of untouchability in the Punjab, Haryana and the Western Uttar Pradesh. The activities of the Prarthana Samaj were mainly confined to the Bombay Presidency. The Ram Krishna Mission contributed significantly in the field of educations and health services..
Social Issues: Contemporary Phase:-
- Socio-Cultural Issues: communalism, untouchability, population explosion, child-abuse, problems of the scheduled castes, the scheduled tribes, the backward classes, women, alcoholism and drug addiction,
- Socio-Economic Issues: poverty, unemployment, black money;
- Socio-Politici-Legal Issues: crime, delinquency, violence, terrorism
- These classifications are only the purpose of narration. They are closely interrelated with each other. Poverty is an economic as well as a social issue. Similarly, Communalism is closely linked with economic factors. The Crime and Delinquency are having legal overtones but they are closely related to the social and economic factors.
- As there were organised social movements against social Issues in the previous phases of the Indian society, similarly, concerted social and political movements were launched in the contemporary period against communalism, casteism, untouchability, illiteracy, alcoholism and drug addiction. Gandhi– as the leader of the national movement after 1919, devoted a considerable part of his action-programme for the uplift of Harijans, Adivasis and Women. He tried to reorganise education and village industries. He fought relentlessly against communalism, untouchability and alcoholism.
- In the contemporary period, there are organised movements of women, Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, backwards castes and labour to protect their interests. There are voluntary organisations working against ecological degradation, drug addiction and child abuse in India.
Social Issues Arising out of Structural Transformation:-
- Sanskritisation
- Westernisation,
- Modernisation.
- Sanskritisation is a process through which lower castes achieved upward social mobility and change either by adventure or by emulating the customs and rituals of the upper castes. It is a cultural process but changes in social status and occupations as a consequence of the upward mobility brought about by sanskritisation makes it also a structural process.
- The contact with the West, particularly with England, set in motion another process of transformation in India known as Westernisation. It is characterized by Western patterns of administration, legal system and education through the medium of the English language. Under the impact of the Western way of life, a sizeable section of educated and urbanised Indian adopted Western style of dress, food,drink, speech and manners. The emulation of the West inculcated the values of Western democracy, industrialisation and capitalism. There are cultural as well as structural aspects of Westernisation. It brought about structural changes by the growth of modern occupations related with modern education, economy and industry, emergence of urban centres with the introduction of colonial administration and the rise of urban middle class under the impact of education, administration, judiciary and press.
- Modernisation and westernization are closely related in the Indian context. The major components of modernisation such as education, political participation, urbanisation, migration, mobility, money, market, modern technology, communication-network and industrilisation were introduced by the colonial administration. They received an impetus in the post-independence period.
- The independent India adopted a modern constitution, founded a secular democratic state and followed the policy of planned socio-economic development, democratic decentralisation and the policy of protective discrimination for the weaker sections. The real question is how these patterns of structural transformation have generated social new issues in India? The processes of transformation–represented by sanskritisation, westernisation and modernisation have been, by and large, smooth and gradual in the Indian context.
Issues arising out of Structural Breakdown and Inconsistencies:-
- The following two concepts may help us in understanding the relationship between structural transformation and social Issues through the ages and Contemporary times:
- structural breakdown, and
- structural inconsistencies.
- The concept of the ‘Structural Breakdown’ means the systemic rigidity which tries to resist or retard social transformation and thus leads to the breakdown of the system or the social disorganisation. In the Third World Countries, there is a growing urge for modernisation in the post-independence period. These countries borrowed parliamentary democracy, adult franchise, modern constitution without the supporting structural base of economy, industrialisation, modern technology, literacy and normative base of rationality, civic culture and secular values. As a result, in several of the ex-colonial societies – democracy could not function successfully. The ethinic, communal, tribal, caste and regional aspirations have become so strong that they are eroding even the basic structures of democracy, modern state and civic society. This is so obvious in the case of India, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, and in many countries of Africa. The impact of social transformation on the Indian society is visible in the following manner.
- On the one hand, three patterns of transformation as mentioned earlier, has created new problems of adjustment,
- On the other hand, occasionally, the process of social transformation has been resisted. In this context, we may cite the examples of the resistance of the urge of the upward social mobility of the Scheduled Castes and the Scheduled Tribes, denial of the rightful claims of women, and obstructing land reforms by hook or crook.
- In the Indian context, Structural Inconsistencies are also visible. They are symptoms as well as the cause of social disorganisation and social problems. By structural inconsistencies is meant the existence of two opposite substructures within the same structure which are not consistent with each other. In India, on the one hand, there are highly sophisticated modern metropolitan upper and upper middle classes influenced by consumerism. On the other hand, there is a large number of the Indian people who live in inaccessible tribal and rural areas and who might have not seen even a train. A small section of the Indian society belongs to the jet age, whereas, a large Indian population even today depend on the bullock-cart. This situation is the clear indicator of the gap between the rich and the poor, the rural and the urban creating a gulf between the different groups and strata. These structural inconsistencies are the indicators of poverty, inequality, inaccessibility and deprivation existing in Indian society.
Social Issues arising out of Indias Stance of Soft State:-
- Gunnar Myrdal in his book ‘Asian Drama’ discuses the problems posed by modernisation in several Asian countries – including India. He feels that strong states, effective governments with their capacity to take hard decisions and strict enforcement of the rule of law are the major features of modern European society but in South Asian countries in general and in India in particular, an approach is being followed by the ruling elite in the post-independence period which has been termed as the policy of ‘soft-state’ by Myrdal.
- The democratisation of polity has further strengthened this policy. It has weakened the capacity of state in enforcing the rule of law. As a result, there is an increasing rate of crime, violence, terrorism, violation of law, corruption in the public life and the criminalisation of politics.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Social Issues In India Project For Class – 12
Table of Contents
1- INTRODUCTION
Social concerns are issues that significantly affect people’s lives and society. These problems might include everything from poverty, injustice, and prejudice in the matters of healthcare, education, and the environment. In this project, we’ll look at one of today’s most important societal challenges and how it affects both people and communities.
We will investigate the root causes of [ social issue ] and how it manifests in our society throughout this research. We will also examine how this problem affects various groups, including [insert examples of groups that are impacted, such as women, children, or minorities]. Additionally, we will look at recent attempts and fixes intended to solve [social issue].
We want to use this initiative to motivate people and communities to take action toward a more just and equitable society by increasing knowledge of the complexity of [social issue].
Millions of people worldwide are impacted by poverty, which is a complicated and multidimensional socioeconomic issue. Poverty, which is defined as the absence of the means of subsistence, can have a significant negative effect on people, families, and communities. We will examine the causes, effects, and potential solutions to this enduring social issue of poverty in this study.
Wide-ranging effects of poverty on people’s life include health inequalities, restricted access to opportunities and education, and greater vulnerability to crime and violence. Give examples of how poverty impacts people and communities in your region or nation.
Although attempts have been made to reduce poverty, this societal issue nevertheless poses a serious challenge to governments, charities, and communities all over the world. The policies and programmes now in place to combat poverty, such as social welfare measures, initiatives for job training and education, and microfinance programs, will be examined in this study.
Through this project, we seek to increase awareness of poverty as a social problem and spur action to build more just and equitable society.
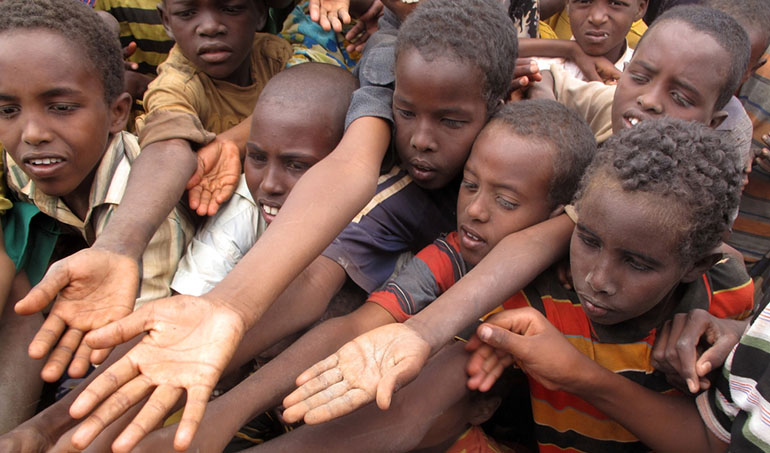

3- CAUSES OF POVERTY IN INDIA
India is the second-most populated nation in the world with a population of over 1.3 billion. India continues to struggle with poverty despite recent economic growth and progress that have been swift. More than 270 million Indians, who make less than $1.90 a day, live below the poverty line, according to the World Bank. The causes of poverty in India and how it impacts people and communities across will be examined in this research.
For effective policies and actions to be developed and implemented to solve this societal challenge, it is essential to understand the causes of poverty. We will examine current measures, such as social welfare programs, job and education programs, and microfinance programs, in our project to reduce poverty in India.
We believe that this project will increase public knowledge of the underlying causes of poverty in India and motivate action to build a more just and equitable society.
4- EFFECT OF POVERTY
Millions of people around the world are impacted by poverty, which has terrible effects on people, families, and communities. Every element of life, including health, education, work, and access to needs, can be significantly impacted by poverty. In this research, we will investigate the effects of poverty on people and communities as well as the ways in which it supports injustice and inequality.
Poverty not only has an immediate negative impact on people, but it also feeds social injustice and institutional inequity. Other forms of marginalization, such as bias against certain races, genders, or castes, are frequently linked to poverty. In addition to contributing to social and political marginalization, poverty can also create cycles of poverty that last for several generations.
With the help of this research, we seek to better understand how poverty affects both individuals and society as a whole and to spur action for the development of more just and equitable societies.
5- CASE STUDIES ON POVERTY
Millions of individuals around the world are impacted by the complicated and varied social problem of poverty. While statistics might make poverty challenging to comprehend, case studies can give a more intimate and human perspective on how poverty affects people. In order to better understand how poverty contributes to structural inequality and social injustice, we will look at case studies of poor people and communities.
We want to offer a more nuanced picture of the effects of poverty on people and communities through these case studies. Additionally, we want to emphasise the fortitude and tenacity of those who are poor and the need of using community-based approaches to solve poverty and its problems.
Through this initiative, we want to encourage people to take action in the direction of more just and equitable communities, where everyone has access to the tools and chances they need to prosper.
In various civilizations all throughout the world, notably in South Asia, where it is still widely practiced in many groups, dowry has a long history. When a couple gets married, the bride’s family is required to give the groom’s family some property or money. This is referred to as the “dowry.” While the dowry’s original purpose was to give the bride financial stability in the event of her husband’s passing, it has since evolved into a means of abuse and exploitation for many women. In this research, we will investigate the practice of dowry, its cultural and historical origins, and the manner in which it contributes to violence against women and gender inequality.

In many parts of the world, including South Asia where it is frequently considered as a necessary expense for families trying to arrange a marriage for their daughter, dower has become a ubiquitous social issue. The need to pay a sizable dowry can put a financial strain on the family of the bride and, in extreme circumstances, end in violence and abuse directed against the bride. As it implies that women are viewed as financial liabilities rather than valuable members of society, the practise of dowry furthers gender inequality.
Through this study, we will investigate how dowries affect women’s lives and how they contribute to violence against women and gender inequality. We will also look at the current dowry-related activities, such as community-based programmes and legal reforms, as well as the difficulties still facing this practise.
Through this initiative, we seek to increase public awareness of the negative effects of dowries and motivate action to build more just and equitable communities where women are valued and respected as full participants in society.
7- ORIGIN OF DOWRY
For ages, various societies all throughout the world have used the dowry system. While dowry practises differ from culture to culture, the fundamental idea of a bride’s family giving money or property to the groom’s family at the time of marriage is universal. A multitude of cultural, historical, and economic variables have influenced the development of dowry, making it a complicated and varied concept. In this study, we will investigate the dowry’s historical development in various cultural and historical situations.
From ancient Rome through mediaeval Europe to contemporary South Asia, dowry has been used in varied forms around the world. The practise of dowry has several justifications, some of which are economic, such as ways to give the bride financial security or to make up for the loss of a potential worker for the groom’s family. Dowry may also be related to societal considerations like the need to uphold family honour or maintain social standing.
Through this study, we will investigate the intricate history and cultural influences that have shaped the development of dowry. We will also look at how dowries have changed and evolved across cultures and circumstances, as well as how these changes have affected gender dynamics and social dynamics.
Through this study, we seek to learn more about the history of dowry and how it has influenced and been influenced by cultural and historical circumstances. We also seek to raise awareness of the ways that dowries support social injustice and gender inequality, and to motivate action to build more just and equitable communities where women are recognised and valued as full participants in society.
8- DOWRY IS AN ILLEGAL ACT
In many parts of the world, especially in South Asia, where it is still common in many cultures, the practise of dowry has long been a source of debate and cause for concern. Many nations have passed legislation outlawing the practise of dowry and giving women legal protection in an effort to address this problem. In order to end the practise of dowry and the violence and abuse it causes against women, the Dowry Prohibition Act was passed in India in 1961. In this study, we’ll look at the Dowry Prohibition Act’s history, development, and effects on the dowry industry in India.
The Dowry Prohibition Act was a significant piece of Indian legislation that sought to outlaw the practise of dowry and protect women from it. The act makes it illegal to give or receive dowry and makes it a crime that is punishable by jail time and/or a fine. The act also establishes dowry prohibition officers to look into dowry-related complaints and provides rules for the avoidance of dowry harassment.
We will investigate the history, breadth, and effects of the Dowry Prohibition Act in-depth through this research. We will also look at the difficulties that still exist in executing the law, including the pervasive societal and cultural attitudes that support the practise of dowry and the demand for more information and education on the subject.
Through this project, we seek to raise awareness of the role that legal frameworks have in addressing societal issues like dowry and to motivate action in the direction of building more just and equitable communities where women are cherished and respected as equal members of society.
9- DOWRY CASE STUDY
Millions of women and their families continue to be affected by the dowry tradition, which has been a chronic problem in many cultures around the world. Even though the practise of dowry is outlawed in many nations, it nevertheless exists in a number of forms and frequently results in violence, abuse, and discrimination against women. In this research, we’ll look at a dowry case study and investigate how the practise has influenced the lives of women, families, and communities.
Dowry can put enormous pressure on families to live up to the expectations of the groom’s family because it is frequently viewed as a symbol of social prestige and a source of financial security. This pressure can result in a range of abuses, such as domestic violence, harassment, and in the worst cases, even murder. The practise of dowry remains a problem throughout most of the world, especially in South Asia, despite the efforts of governments and activists to end it.
In this project, we will look at a dowry case study, concentrating on the experiences of the women and families impacted by this custom. We will examine the different dowry-related kinds of discrimination and abuse, as well as how these abuses may affect women’s and families’ lives. We will also look at the obstacles activists and organisations confront in their fight against the practise of dowry.
Through this initiative, we seek to raise awareness of the effects of dowries on women and families and to motivate action in the direction of the development of more just and equitable communities, where women are appreciated and respected as full participants in society.
10- CHILD LABOR
Millions of children worldwide are impacted by the global problem of child labor, which is frequently associated with poverty and a lack of educational opportunities. Working kids frequently miss out on childhood, education, and the chance to reach their full potential. In this project, we will investigate the problem of child labour and look at its sources, effects, and attempts at prevention.
There are many different types of child labor, including domestic work, agricultural work, and employment in factories and mines. Children who labour are frequently put in risky and exploitative situations and run the risk of suffering from physical, emotional, and psychological problems. The problem of child employment persists in many parts of the world, especially in developing nations, despite the efforts of governments and organisations to address it.
Through this study, we will explore the economic, social, and cultural aspects that contribute to the persistence of child labor, as well as its causes and effects. We will also look at the initiatives taken by governments, groups, and people to address the problem of child labor, including laws and initiatives designed to protect children’s rights and deal with its underlying causes.
Through this initiative, we seek to increase public awareness of the problem of child labour and motivate action to build more just and equitable communities where kids are safe and given the tools they need to reach their full potential.

11- TYPES OF CHILD LABOUR
Child labour is a complicated problem that affects kids of various ages and socioeconomic situations worldwide. Although the phrase “child labour” frequently conjures up pictures of kids toiling away in factories or mines, it actually refers to a wide range of activities that can harm kids’ development, education, and health. In this study, we will investigate the many forms of child work, looking at its traits, frequency, and effects on kids.
Hazardous and non-hazardous kinds of child labour exist, and it can take place in a range of locales such as homes, streets, and workplaces. Domestic work, agricultural work, and employment in factories and mines are a few of the most prevalent types of child labour. Children who participate in these activities are frequently subjected to risky situations, long hours, and low remuneration, and they run the risk of suffering bodily, emotional, and psychological harm.
Through this research, we will investigate the various forms of child labor, looking at each one’s distinctive traits and the difficulties they provide for kids’ development, education, and well-being. We will also look at the causes of various forms of child labor, such as poverty, a lack of educational opportunities, and cultural and societal standards.
Through this initiative, we seek to increase public awareness of the various forms of child labour and encourage action to build more just and equitable communities where kids are protected and given the tools they need to reach their full potential.
12- CAUSES AND EFFECT
Child labour is a complicated subject that is influenced by numerous economic, social, and cultural elements. It has a significant negative impact on children’s health, development, and education. It is essential to comprehend child labour’s causes and effects in order to establish methods that will effectively address the problem and advance the welfare of children everywhere. In this project, we’ll look at the root causes of child labour and consider how it affects kids, families, and communities.
The root reasons of child labour are complex and include elements like poverty, limited educational opportunities, and societal and cultural norms that place little importance on children’s education and general well-being. These elements frequently interact with one another to produce a complicated web of conditions that forces kids into the labour force. Child labour has a variety of detrimental repercussions on children’s development, education, and overall health as well as on their families and communities.
Through this study, we will explore the economic, social, and cultural aspects of child labour’s persistence as well as its underlying causes. We will also look at how child labour affects children, their families, communities, and how it contributes to social injustice and continued poverty.
In order to create more equitable and just societies where children are safeguarded and given the opportunity to attain their full potential, we want to increase public understanding of child labour’s fundamental causes and far-reaching effects.
13- CASE STUDIES ON CHILD LABOR
Millions of children worldwide are impacted by the widespread problem of child labor, which robs them of their childhoods and prevents them from pursuing their educations and realising their full potential. Although there are many distinct types of child labor, each one involves a violation of children’s rights and a failing on the part of society to safeguard its most defenceless citizens. We will look at a specific case study of child labour in this project, examining the conditions that lead to the kid’s exploitation, the effects on the child and their family, and the initiatives taken to address the problem.
In the case study we’ll be looking at, a young child was made to labour in risky circumstances in a factory where they were exposed to harmful chemicals, long hours, and low pay. The youngster’s family was struggling to make ends meet because they were so poor, so the money the child brought in was crucial. The rigours of the job interfered with the child’s education, and the dangerous conditions had an adverse effect on their health.
Through this research, we will thoroughly examine the case study, examining the underlying reasons why the child was exploited and the effects it had on the child’s health, development, and education. We will also look at the measures taken to address the problem, such as the assistance programmes for the child and their family and broader legislative and lobbying initiatives to end child labour.
Through this project, we want to increase public awareness of child labour’s harmful effects on children and their families. We can better appreciate the complicated problems that lead to child labour and the efforts being taken to address them by looking at specific case studies.
In conclusion, socioeconomic problems including poverty, dowry, and child labour are intricate, diverse concerns with significant repercussions for people, families, and societies. These problems are caused by several economic, social, and cultural causes, therefore resolving them will take all-encompassing and coordinated action. We have learned more about the underlying causes and effects of poverty, the history and repercussions of dowries, and the forms, causes, and effects of child labour as a result of our investigation into these issues.
Despite the difficulties these societal concerns provide, several efforts are being undertaken to address them. There are numerous strategies that can be used to address these problems and advance social justice and equity, from grassroots community activities to global policy and advocacy campaigns. We can contribute to the creation of a more just and equitable world where everyone has the chance to realise their full potential by increasing awareness of these concerns and working to support these initiatives.
In the end, dealing with social difficulties necessitates a commitment to understanding, empathy, and group action. We can make the world more just and equitable for everyone by acknowledging the humanity of those impacted by poverty, dowry, and child labour and collaborating to improve their well-being.
Certificate of Completion
I, [Your Name], a student of Class 12 at [Your School/College Name], am proud to receive this certificate for successfully completing the project on “Social Issues in India. ” This project delved into the complex and significant societal challenges that affect people and communities in our country.
Throughout this project, I thoroughly investigated and analyzed various social issues, including poverty, dowry, and child labor. I examined their root causes, effects, and the measures taken to address these problems. This research has provided me with valuable insights into the complexities of social issues and the need for collective action to build a more just and equitable society.
I express my heartfelt gratitude to [Teacher’s Name], my project guide, for their unwavering support, guidance, and encouragement throughout this project. Their expertise and mentorship have been instrumental in deepening my understanding of the social issues in India and helping me shape my research effectively.
I would also like to extend my thanks to [School/College Name] for providing me with the opportunity to explore and analyze the critical social issues prevalent in our country. This project has not only enriched my knowledge but also heightened my awareness of the importance of addressing these issues to create a better society.
With great pride, I accept this certificate, symbolizing my dedication and hard work in completing the project on “Social Issues in India. “
In order to download the PDF, You must follow on Youtube. Once done, Click on Submit
Subscribed? Click on Confirm
Download Social Issues In India Project For Class – 12 PDF
Related articles.

Automated Roti and Puri Maker Press project

The Oil Skimmer RC Boat

Secure Digi Locker Application Project

Software Piracy Protection Project
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.

Please Enable JavaScript in your Browser to Visit this Site.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Key facts about the abortion debate in America
The U.S. Supreme Court’s June 2022 ruling to overturn Roe v. Wade – the decision that had guaranteed a constitutional right to an abortion for nearly 50 years – has shifted the legal battle over abortion to the states, with some prohibiting the procedure and others moving to safeguard it.
As the nation’s post-Roe chapter begins, here are key facts about Americans’ views on abortion, based on two Pew Research Center polls: one conducted from June 25-July 4 , just after this year’s high court ruling, and one conducted in March , before an earlier leaked draft of the opinion became public.
This analysis primarily draws from two Pew Research Center surveys, one surveying 10,441 U.S. adults conducted March 7-13, 2022, and another surveying 6,174 U.S. adults conducted June 27-July 4, 2022. Here are the questions used for the March survey , along with responses, and the questions used for the survey from June and July , along with responses.
Everyone who took part in these surveys is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
A majority of the U.S. public disapproves of the Supreme Court’s decision to overturn Roe. About six-in-ten adults (57%) disapprove of the court’s decision that the U.S. Constitution does not guarantee a right to abortion and that abortion laws can be set by states, including 43% who strongly disapprove, according to the summer survey. About four-in-ten (41%) approve, including 25% who strongly approve.
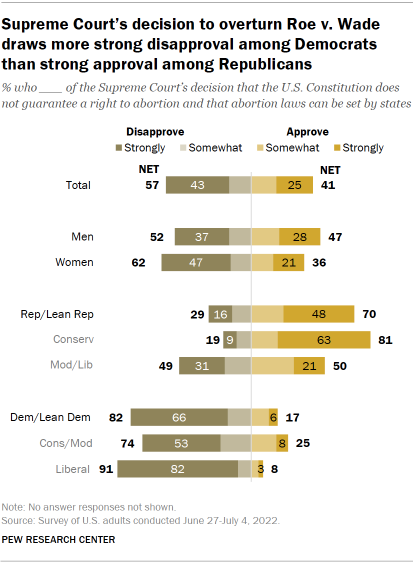
About eight-in-ten Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents (82%) disapprove of the court’s decision, including nearly two-thirds (66%) who strongly disapprove. Most Republicans and GOP leaners (70%) approve , including 48% who strongly approve.
Most women (62%) disapprove of the decision to end the federal right to an abortion. More than twice as many women strongly disapprove of the court’s decision (47%) as strongly approve of it (21%). Opinion among men is more divided: 52% disapprove (37% strongly), while 47% approve (28% strongly).
About six-in-ten Americans (62%) say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, according to the summer survey – little changed since the March survey conducted just before the ruling. That includes 29% of Americans who say it should be legal in all cases and 33% who say it should be legal in most cases. About a third of U.S. adults (36%) say abortion should be illegal in all (8%) or most (28%) cases.
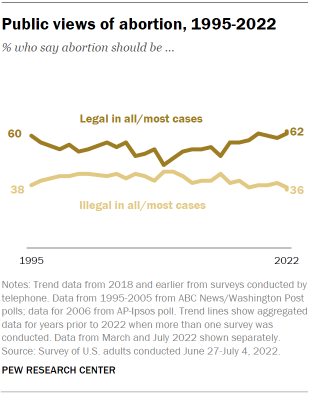
Generally, Americans’ views of whether abortion should be legal remained relatively unchanged in the past few years , though support fluctuated somewhat in previous decades.
Relatively few Americans take an absolutist view on the legality of abortion – either supporting or opposing it at all times, regardless of circumstances. The March survey found that support or opposition to abortion varies substantially depending on such circumstances as when an abortion takes place during a pregnancy, whether the pregnancy is life-threatening or whether a baby would have severe health problems.
While Republicans’ and Democrats’ views on the legality of abortion have long differed, the 46 percentage point partisan gap today is considerably larger than it was in the recent past, according to the survey conducted after the court’s ruling. The wider gap has been largely driven by Democrats: Today, 84% of Democrats say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, up from 72% in 2016 and 63% in 2007. Republicans’ views have shown far less change over time: Currently, 38% of Republicans say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, nearly identical to the 39% who said this in 2007.
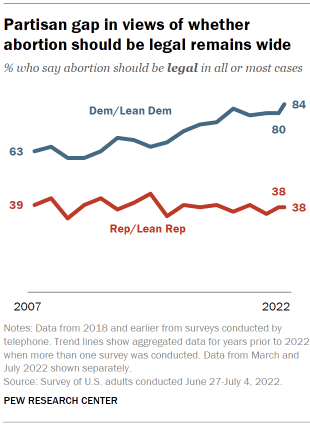
However, the partisan divisions over whether abortion should generally be legal tell only part of the story. According to the March survey, sizable shares of Democrats favor restrictions on abortion under certain circumstances, while majorities of Republicans favor abortion being legal in some situations , such as in cases of rape or when the pregnancy is life-threatening.
There are wide religious divides in views of whether abortion should be legal , the summer survey found. An overwhelming share of religiously unaffiliated adults (83%) say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, as do six-in-ten Catholics. Protestants are divided in their views: 48% say it should be legal in all or most cases, while 50% say it should be illegal in all or most cases. Majorities of Black Protestants (71%) and White non-evangelical Protestants (61%) take the position that abortion should be legal in all or most cases, while about three-quarters of White evangelicals (73%) say it should be illegal in all (20%) or most cases (53%).
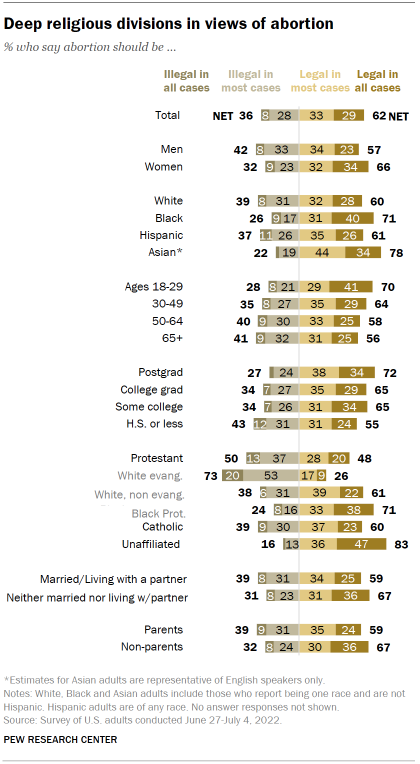
In the March survey, 72% of White evangelicals said that the statement “human life begins at conception, so a fetus is a person with rights” reflected their views extremely or very well . That’s much greater than the share of White non-evangelical Protestants (32%), Black Protestants (38%) and Catholics (44%) who said the same. Overall, 38% of Americans said that statement matched their views extremely or very well.
Catholics, meanwhile, are divided along religious and political lines in their attitudes about abortion, according to the same survey. Catholics who attend Mass regularly are among the country’s strongest opponents of abortion being legal, and they are also more likely than those who attend less frequently to believe that life begins at conception and that a fetus has rights. Catholic Republicans, meanwhile, are far more conservative on a range of abortion questions than are Catholic Democrats.
Women (66%) are more likely than men (57%) to say abortion should be legal in most or all cases, according to the survey conducted after the court’s ruling.
More than half of U.S. adults – including 60% of women and 51% of men – said in March that women should have a greater say than men in setting abortion policy . Just 3% of U.S. adults said men should have more influence over abortion policy than women, with the remainder (39%) saying women and men should have equal say.
The March survey also found that by some measures, women report being closer to the abortion issue than men . For example, women were more likely than men to say they had given “a lot” of thought to issues around abortion prior to taking the survey (40% vs. 30%). They were also considerably more likely than men to say they personally knew someone (such as a close friend, family member or themselves) who had had an abortion (66% vs. 51%) – a gender gap that was evident across age groups, political parties and religious groups.
Relatively few Americans view the morality of abortion in stark terms , the March survey found. Overall, just 7% of all U.S. adults say having an abortion is morally acceptable in all cases, and 13% say it is morally wrong in all cases. A third say that having an abortion is morally wrong in most cases, while about a quarter (24%) say it is morally acceptable in most cases. An additional 21% do not consider having an abortion a moral issue.
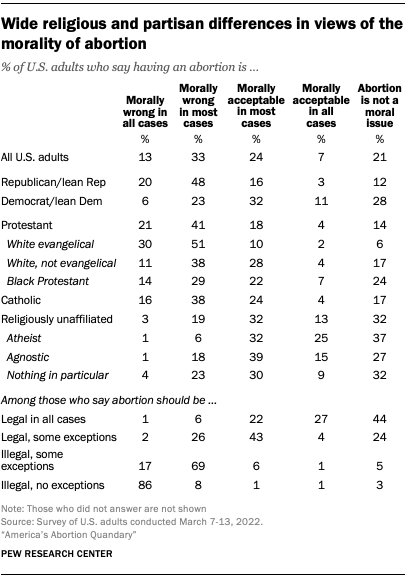
Among Republicans, most (68%) say that having an abortion is morally wrong either in most (48%) or all cases (20%). Only about three-in-ten Democrats (29%) hold a similar view. Instead, about four-in-ten Democrats say having an abortion is morally acceptable in most (32%) or all (11%) cases, while an additional 28% say it is not a moral issue.
White evangelical Protestants overwhelmingly say having an abortion is morally wrong in most (51%) or all cases (30%). A slim majority of Catholics (53%) also view having an abortion as morally wrong, but many also say it is morally acceptable in most (24%) or all cases (4%), or that it is not a moral issue (17%). Among religiously unaffiliated Americans, about three-quarters see having an abortion as morally acceptable (45%) or not a moral issue (32%).
- Religion & Abortion
Jane Doe is a a research analyst focusing on social and demographic research at Pew Research Center
What the data says about abortion in the U.S.
Support for legal abortion is widespread in many countries, especially in europe, nearly a year after roe’s demise, americans’ views of abortion access increasingly vary by where they live, by more than two-to-one, americans say medication abortion should be legal in their state, most latinos say democrats care about them and work hard for their vote, far fewer say so of gop, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Through an essay on social issues, we will learn why they are harmful and what types of social issues we face. ... For instance, in India, you will find a lot of social issues which the country is facing. ... Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas. Major Social Issues. There are a lot of social issues we are facing right now ...
250 Words Essay on Social Problems in India Introduction. India, a diverse and culturally rich country, faces a multitude of social issues. These problems, deeply rooted in the socio-economic fabric of the nation, are a significant impediment to its growth and development. Poverty. Despite India's rapid economic growth, poverty remains a ...
As per the report of the Economic Survey 2017-18, there are 63 million missing women in India. Missing women are women who are not alive due to foeticide or infanticide. As per the World Economic Forum, India is ranked very low at 87th position in the "Global Gender Parity Report.". Indian Government launched the 'Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao ...
6. Religious conflicts: Religious conflicts are among the most severe social issues today. The difference in beliefs: people belonging to different religions have different views.Lack of education: People who want to spread violence in the name of religion can easily mislead illiterate people.
Women's Safety - Even after several measures to uplift the standard of living of women in India, when it comes to women's freedom and safety, India lags. Domestic Violence, rape, and the portrayal of women in media, among other issues, should be addressed immediately. Unemployment - Unemployment is now widespread among young people.
Top 100 Social Issues Topics For Students; Social Issues in India: An Overview. The term 'social issues' implies the problems that are inherent within the society. It could be anything ranging from gender inequality to unemployment. The social issues can be said to be a condition that is detrimental in nature, to society and the individual ...
This article covers the concept of social issues and highlights the different experiences of rural and urban sectors. Further, it studies six important social issues namely poverty, unemployment, illiteracy, the caste system, gendered violence and communalism by analyzing their causes and the specific measures adopted to combat them.
India is facing a large number of social issues such as caste system, child labour, illiteracy, gender inequality, superstitions, religious conflicts, and many more. It is high time that the society gets relief from these undesirable social evils. Major Social Issues: We have prepared a list of major social issues in India.
Indian public opinion on national conditions. 1 Indian adults certainly recognize that their personal economic well-being has benefited greatly from strong national economic performance: Indian economic growth has averaged 7.3% per year since 2014. Roughly two-thirds (65%) say the financial situation of average people in India is better today ...
The caste system is a distinctive feature of Indian inequality. Emerging around 1500 BC, the hereditary social classification draws its origins from occupational hierarchy. Ancient Indian society ...
Forms of Social Issues in India. Poverty. Poverty is a condition in which a household is not able to fulfill its basic needs for survival i.e. food, clothing and shelter. Poverty is a widespread condition in India. Since Independence, poverty is a prevalent concern. It is the twenty-first century and poverty still is a persistent menace in the ...
The latest Mood of the Nation (MOTN) survey shows that 45 per cent of respondents believe democracy is in danger—a 3 percentage point rise since the MOTN poll in January 2021. A little over half of those surveyed (51 per cent) feel people are scared to protest or offer views publicly, which reflects a disturbing trend. A majority are in favor ...
Essay On Social Issues: India is a diverse country with people from various walks of life, with different cultural and ethnic backgrounds. There are mostly 9 main religions and various sub-castes in each of them. With 28 states and 8 union territories, India is truly is a glorification of unity in diversity. But the phrase unity […]
FAQs about Poverty in India Essay. Q.1 List some ways to end poverty in India. A.1 Some ways to end poverty in India are: Develop a national poverty reduction plan. Equal access to healthcare and education. Sanitation facility. Food, water, shelter, and clothing facility. Enhance economic growth with targeted action.
social issues. The editors tried their best to represent all the matters fruitfully to enhance the provisions of social issues as India is facing a large number of social issues such as caste system, juvenile delinquency, illiteracy, gender inequality, malnutrition, human trafficking, and many more. It is high time that the society
In poverty people are surviving for food, cloth and for home as well. Many of the people in India belong to the poor locality. Because of inflation poverty is increasing. Poverty is also due to large number of population. In village area people are not aware of sanitation due to lake of water. There is also comparison between people due to castes.
Social Issues in India. Casteism, dowry, communalism, drunkenness, drug addiction, and other key socio-cultural concerns need to be addressed today. The topics covered here are not exhaustive. There are other more concerns that the country as a whole, as well as individual regions and communities, must address.
A steady increase in female voter participation has been observed across India, wherein the sex ratio of voters (number of female voters vis-à-vis male) has increased from 715 in the 1960s to 883 ...
UPSC IAS Essay writing practice for Mains essay paper is crucial in getting good marks in essay paper. Insights posts new essay topic every sunday. Call us ... March 21, 2021 : Our major social problems are not the cause of our decadence but are a reflection of it ... 2020: Post Independence, the Issue of Land is at the Core of India's Non ...
India, highlighting the economic, social, and political costs associated with gender disparities. Fourthly, to study about that what are the solutions to reduce the ineq uality in India. Hypothesis
The following were the major social issues and problems in the early phase of the Indian civilisation. Conflict between the two major social groups, i.e., the Aryans and the Dasas Dasyu as mentioned in the Vedic texts. Increasing rigidity of social hierarchy, Emphasis on the observance of rituals, Sacrifice of animals.
1- INTRODUCTION. Social concerns are issues that significantly affect people's lives and society. These problems might include everything from poverty, injustice, and prejudice in the matters of healthcare, education, and the environment. In this project, we'll look at one of today's most important societal challenges and how it affects ...
For Prelims: Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019, NALSA Judgement 2014, Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Rules, 2020,... 12 Feb 2024 Social Issues. A Multifaceted Approach to Population Management. This editorial is based on "Charting a path for the population committee" which was published in The Hindu on 09/02/2024.
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions.
The wider gap has been largely driven by Democrats: Today, 84% of Democrats say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, up from 72% in 2016 and 63% in 2007. Republicans' views have shown far less change over time: Currently, 38% of Republicans say abortion should be legal in all or most cases, nearly identical to the 39% who said this ...
Chaos ensued in the United Arab Emirates after the country witnessed the heaviest rainfall in 75 years, with some areas recording more than 250 mm of precipitation in fewer than 24 hours, the ...