- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research

Qualitative Data Analysis: What is it, Methods + Examples

In a world rich with information and narrative, understanding the deeper layers of human experiences requires a unique vision that goes beyond numbers and figures. This is where the power of qualitative data analysis comes to light.
In this blog, we’ll learn about qualitative data analysis, explore its methods, and provide real-life examples showcasing its power in uncovering insights.
What is Qualitative Data Analysis?
Qualitative data analysis is a systematic process of examining non-numerical data to extract meaning, patterns, and insights.
In contrast to quantitative analysis, which focuses on numbers and statistical metrics, the qualitative study focuses on the qualitative aspects of data, such as text, images, audio, and videos. It seeks to understand every aspect of human experiences, perceptions, and behaviors by examining the data’s richness.
Companies frequently conduct this analysis on customer feedback. You can collect qualitative data from reviews, complaints, chat messages, interactions with support centers, customer interviews, case notes, or even social media comments. This kind of data holds the key to understanding customer sentiments and preferences in a way that goes beyond mere numbers.
Importance of Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative data analysis plays a crucial role in your research and decision-making process across various disciplines. Let’s explore some key reasons that underline the significance of this analysis:
In-Depth Understanding
It enables you to explore complex and nuanced aspects of a phenomenon, delving into the ‘how’ and ‘why’ questions. This method provides you with a deeper understanding of human behavior, experiences, and contexts that quantitative approaches might not capture fully.
Contextual Insight
You can use this analysis to give context to numerical data. It will help you understand the circumstances and conditions that influence participants’ thoughts, feelings, and actions. This contextual insight becomes essential for generating comprehensive explanations.
Theory Development
You can generate or refine hypotheses via qualitative data analysis. As you analyze the data attentively, you can form hypotheses, concepts, and frameworks that will drive your future research and contribute to theoretical advances.
Participant Perspectives
When performing qualitative research, you can highlight participant voices and opinions. This approach is especially useful for understanding marginalized or underrepresented people, as it allows them to communicate their experiences and points of view.
Exploratory Research
The analysis is frequently used at the exploratory stage of your project. It assists you in identifying important variables, developing research questions, and designing quantitative studies that will follow.
Types of Qualitative Data
When conducting qualitative research, you can use several qualitative data collection methods , and here you will come across many sorts of qualitative data that can provide you with unique insights into your study topic. These data kinds add new views and angles to your understanding and analysis.
Interviews and Focus Groups
Interviews and focus groups will be among your key methods for gathering qualitative data. Interviews are one-on-one talks in which participants can freely share their thoughts, experiences, and opinions.
Focus groups, on the other hand, are discussions in which members interact with one another, resulting in dynamic exchanges of ideas. Both methods provide rich qualitative data and direct access to participant perspectives.
Observations and Field Notes
Observations and field notes are another useful sort of qualitative data. You can immerse yourself in the research environment through direct observation, carefully documenting behaviors, interactions, and contextual factors.
These observations will be recorded in your field notes, providing a complete picture of the environment and the behaviors you’re researching. This data type is especially important for comprehending behavior in their natural setting.
Textual and Visual Data
Textual and visual data include a wide range of resources that can be qualitatively analyzed. Documents, written narratives, and transcripts from various sources, such as interviews or speeches, are examples of textual data.
Photographs, films, and even artwork provide a visual layer to your research. These forms of data allow you to investigate what is spoken and the underlying emotions, details, and symbols expressed by language or pictures.
When to Choose Qualitative Data Analysis over Quantitative Data Analysis
As you begin your research journey, understanding why the analysis of qualitative data is important will guide your approach to understanding complex events. If you analyze qualitative data, it will provide new insights that complement quantitative methodologies, which will give you a broader understanding of your study topic.
It is critical to know when to use qualitative analysis over quantitative procedures. You can prefer qualitative data analysis when:
- Complexity Reigns: When your research questions involve deep human experiences, motivations, or emotions, qualitative research excels at revealing these complexities.
- Exploration is Key: Qualitative analysis is ideal for exploratory research. It will assist you in understanding a new or poorly understood topic before formulating quantitative hypotheses.
- Context Matters: If you want to understand how context affects behaviors or results, qualitative data analysis provides the depth needed to grasp these relationships.
- Unanticipated Findings: When your study provides surprising new viewpoints or ideas, qualitative analysis helps you to delve deeply into these emerging themes.
- Subjective Interpretation is Vital: When it comes to understanding people’s subjective experiences and interpretations, qualitative data analysis is the way to go.
You can make informed decisions regarding the right approach for your research objectives if you understand the importance of qualitative analysis and recognize the situations where it shines.
Qualitative Data Analysis Methods and Examples
Exploring various qualitative data analysis methods will provide you with a wide collection for making sense of your research findings. Once the data has been collected, you can choose from several analysis methods based on your research objectives and the data type you’ve collected.
There are five main methods for analyzing qualitative data. Each method takes a distinct approach to identifying patterns, themes, and insights within your qualitative data. They are:
Method 1: Content Analysis
Content analysis is a methodical technique for analyzing textual or visual data in a structured manner. In this method, you will categorize qualitative data by splitting it into manageable pieces and assigning the manual coding process to these units.
As you go, you’ll notice ongoing codes and designs that will allow you to conclude the content. This method is very beneficial for detecting common ideas, concepts, or themes in your data without losing the context.
Steps to Do Content Analysis
Follow these steps when conducting content analysis:
- Collect and Immerse: Begin by collecting the necessary textual or visual data. Immerse yourself in this data to fully understand its content, context, and complexities.
- Assign Codes and Categories: Assign codes to relevant data sections that systematically represent major ideas or themes. Arrange comparable codes into groups that cover the major themes.
- Analyze and Interpret: Develop a structured framework from the categories and codes. Then, evaluate the data in the context of your research question, investigate relationships between categories, discover patterns, and draw meaning from these connections.
Benefits & Challenges
There are various advantages to using content analysis:
- Structured Approach: It offers a systematic approach to dealing with large data sets and ensures consistency throughout the research.
- Objective Insights: This method promotes objectivity, which helps to reduce potential biases in your study.
- Pattern Discovery: Content analysis can help uncover hidden trends, themes, and patterns that are not always obvious.
- Versatility: You can apply content analysis to various data formats, including text, internet content, images, etc.
However, keep in mind the challenges that arise:
- Subjectivity: Even with the best attempts, a certain bias may remain in coding and interpretation.
- Complexity: Analyzing huge data sets requires time and great attention to detail.
- Contextual Nuances: Content analysis may not capture all of the contextual richness that qualitative data analysis highlights.
Example of Content Analysis
Suppose you’re conducting market research and looking at customer feedback on a product. As you collect relevant data and analyze feedback, you’ll see repeating codes like “price,” “quality,” “customer service,” and “features.” These codes are organized into categories such as “positive reviews,” “negative reviews,” and “suggestions for improvement.”
According to your findings, themes such as “price” and “customer service” stand out and show that pricing and customer service greatly impact customer satisfaction. This example highlights the power of content analysis for obtaining significant insights from large textual data collections.
Method 2: Thematic Analysis
Thematic analysis is a well-structured procedure for identifying and analyzing recurring themes in your data. As you become more engaged in the data, you’ll generate codes or short labels representing key concepts. These codes are then organized into themes, providing a consistent framework for organizing and comprehending the substance of the data.
The analysis allows you to organize complex narratives and perspectives into meaningful categories, which will allow you to identify connections and patterns that may not be visible at first.
Steps to Do Thematic Analysis
Follow these steps when conducting a thematic analysis:
- Code and Group: Start by thoroughly examining the data and giving initial codes that identify the segments. To create initial themes, combine relevant codes.
- Code and Group: Begin by engaging yourself in the data, assigning first codes to notable segments. To construct basic themes, group comparable codes together.
- Analyze and Report: Analyze the data within each theme to derive relevant insights. Organize the topics into a consistent structure and explain your findings, along with data extracts that represent each theme.
Thematic analysis has various benefits:
- Structured Exploration: It is a method for identifying patterns and themes in complex qualitative data.
- Comprehensive knowledge: Thematic analysis promotes an in-depth understanding of the complications and meanings of the data.
- Application Flexibility: This method can be customized to various research situations and data kinds.
However, challenges may arise, such as:
- Interpretive Nature: Interpreting qualitative data in thematic analysis is vital, and it is critical to manage researcher bias.
- Time-consuming: The study can be time-consuming, especially with large data sets.
- Subjectivity: The selection of codes and topics might be subjective.
Example of Thematic Analysis
Assume you’re conducting a thematic analysis on job satisfaction interviews. Following your immersion in the data, you assign initial codes such as “work-life balance,” “career growth,” and “colleague relationships.” As you organize these codes, you’ll notice themes develop, such as “Factors Influencing Job Satisfaction” and “Impact on Work Engagement.”
Further investigation reveals the tales and experiences included within these themes and provides insights into how various elements influence job satisfaction. This example demonstrates how thematic analysis can reveal meaningful patterns and insights in qualitative data.
Method 3: Narrative Analysis
The narrative analysis involves the narratives that people share. You’ll investigate the histories in your data, looking at how stories are created and the meanings they express. This method is excellent for learning how people make sense of their experiences through narrative.
Steps to Do Narrative Analysis
The following steps are involved in narrative analysis:
- Gather and Analyze: Start by collecting narratives, such as first-person tales, interviews, or written accounts. Analyze the stories, focusing on the plot, feelings, and characters.
- Find Themes: Look for recurring themes or patterns in various narratives. Think about the similarities and differences between these topics and personal experiences.
- Interpret and Extract Insights: Contextualize the narratives within their larger context. Accept the subjective nature of each narrative and analyze the narrator’s voice and style. Extract insights from the tales by diving into the emotions, motivations, and implications communicated by the stories.
There are various advantages to narrative analysis:
- Deep Exploration: It lets you look deeply into people’s personal experiences and perspectives.
- Human-Centered: This method prioritizes the human perspective, allowing individuals to express themselves.
However, difficulties may arise, such as:
- Interpretive Complexity: Analyzing narratives requires dealing with the complexities of meaning and interpretation.
- Time-consuming: Because of the richness and complexities of tales, working with them can be time-consuming.
Example of Narrative Analysis
Assume you’re conducting narrative analysis on refugee interviews. As you read the stories, you’ll notice common themes of toughness, loss, and hope. The narratives provide insight into the obstacles that refugees face, their strengths, and the dreams that guide them.
The analysis can provide a deeper insight into the refugees’ experiences and the broader social context they navigate by examining the narratives’ emotional subtleties and underlying meanings. This example highlights how narrative analysis can reveal important insights into human stories.
Method 4: Grounded Theory Analysis
Grounded theory analysis is an iterative and systematic approach that allows you to create theories directly from data without being limited by pre-existing hypotheses. With an open mind, you collect data and generate early codes and labels that capture essential ideas or concepts within the data.
As you progress, you refine these codes and increasingly connect them, eventually developing a theory based on the data. Grounded theory analysis is a dynamic process for developing new insights and hypotheses based on details in your data.
Steps to Do Grounded Theory Analysis
Grounded theory analysis requires the following steps:
- Initial Coding: First, immerse yourself in the data, producing initial codes that represent major concepts or patterns.
- Categorize and Connect: Using axial coding, organize the initial codes, which establish relationships and connections between topics.
- Build the Theory: Focus on creating a core category that connects the codes and themes. Regularly refine the theory by comparing and integrating new data, ensuring that it evolves organically from the data.
Grounded theory analysis has various benefits:
- Theory Generation: It provides a one-of-a-kind opportunity to generate hypotheses straight from data and promotes new insights.
- In-depth Understanding: The analysis allows you to deeply analyze the data and reveal complex relationships and patterns.
- Flexible Process: This method is customizable and ongoing, which allows you to enhance your research as you collect additional data.
However, challenges might arise with:
- Time and Resources: Because grounded theory analysis is a continuous process, it requires a large commitment of time and resources.
- Theoretical Development: Creating a grounded theory involves a thorough understanding of qualitative data analysis software and theoretical concepts.
- Interpretation of Complexity: Interpreting and incorporating a newly developed theory into existing literature can be intellectually hard.
Example of Grounded Theory Analysis
Assume you’re performing a grounded theory analysis on workplace collaboration interviews. As you open code the data, you will discover notions such as “communication barriers,” “team dynamics,” and “leadership roles.” Axial coding demonstrates links between these notions, emphasizing the significance of efficient communication in developing collaboration.
You create the core “Integrated Communication Strategies” category through selective coding, which unifies new topics.
This theory-driven category serves as the framework for understanding how numerous aspects contribute to effective team collaboration. This example shows how grounded theory analysis allows you to generate a theory directly from the inherent nature of the data.
Method 5: Discourse Analysis
Discourse analysis focuses on language and communication. You’ll look at how language produces meaning and how it reflects power relations, identities, and cultural influences. This strategy examines what is said and how it is said; the words, phrasing, and larger context of communication.
The analysis is precious when investigating power dynamics, identities, and cultural influences encoded in language. By evaluating the language used in your data, you can identify underlying assumptions, cultural standards, and how individuals negotiate meaning through communication.
Steps to Do Discourse Analysis
Conducting discourse analysis entails the following steps:
- Select Discourse: For analysis, choose language-based data such as texts, speeches, or media content.
- Analyze Language: Immerse yourself in the conversation, examining language choices, metaphors, and underlying assumptions.
- Discover Patterns: Recognize the dialogue’s reoccurring themes, ideologies, and power dynamics. To fully understand the effects of these patterns, put them in their larger context.
There are various advantages of using discourse analysis:
- Understanding Language: It provides an extensive understanding of how language builds meaning and influences perceptions.
- Uncovering Power Dynamics: The analysis reveals how power dynamics appear via language.
- Cultural Insights: This method identifies cultural norms, beliefs, and ideologies stored in communication.
However, the following challenges may arise:
- Complexity of Interpretation: Language analysis involves navigating multiple levels of nuance and interpretation.
- Subjectivity: Interpretation can be subjective, so controlling researcher bias is important.
- Time-Intensive: Discourse analysis can take a lot of time because careful linguistic study is required in this analysis.
Example of Discourse Analysis
Consider doing discourse analysis on media coverage of a political event. You notice repeating linguistic patterns in news articles that depict the event as a conflict between opposing parties. Through deconstruction, you can expose how this framing supports particular ideologies and power relations.
You can illustrate how language choices influence public perceptions and contribute to building the narrative around the event by analyzing the speech within the broader political and social context. This example shows how discourse analysis can reveal hidden power dynamics and cultural influences on communication.
How to do Qualitative Data Analysis with the QuestionPro Research suite?
QuestionPro is a popular survey and research platform that offers tools for collecting and analyzing qualitative and quantitative data. Follow these general steps for conducting qualitative data analysis using the QuestionPro Research Suite:
- Collect Qualitative Data: Set up your survey to capture qualitative responses. It might involve open-ended questions, text boxes, or comment sections where participants can provide detailed responses.
- Export Qualitative Responses: Export the responses once you’ve collected qualitative data through your survey. QuestionPro typically allows you to export survey data in various formats, such as Excel or CSV.
- Prepare Data for Analysis: Review the exported data and clean it if necessary. Remove irrelevant or duplicate entries to ensure your data is ready for analysis.
- Code and Categorize Responses: Segment and label data, letting new patterns emerge naturally, then develop categories through axial coding to structure the analysis.
- Identify Themes: Analyze the coded responses to identify recurring themes, patterns, and insights. Look for similarities and differences in participants’ responses.
- Generate Reports and Visualizations: Utilize the reporting features of QuestionPro to create visualizations, charts, and graphs that help communicate the themes and findings from your qualitative research.
- Interpret and Draw Conclusions: Interpret the themes and patterns you’ve identified in the qualitative data. Consider how these findings answer your research questions or provide insights into your study topic.
- Integrate with Quantitative Data (if applicable): If you’re also conducting quantitative research using QuestionPro, consider integrating your qualitative findings with quantitative results to provide a more comprehensive understanding.
Qualitative data analysis is vital in uncovering various human experiences, views, and stories. If you’re ready to transform your research journey and apply the power of qualitative analysis, now is the moment to do it. Book a demo with QuestionPro today and begin your journey of exploration.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

Journey Orchestration Platforms: Top 11 Platforms in 2024
May 2, 2024

Taking Action in CX – Tuesday CX Thoughts
Apr 30, 2024

QuestionPro CX Product Updates – Quarter 1, 2024
Apr 29, 2024

NPS Survey Platform: Types, Tips, 11 Best Platforms & Tools
Apr 26, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Qualitative Data Analysis Methods 101:
The “big 6” methods + examples.
By: Kerryn Warren (PhD) | Reviewed By: Eunice Rautenbach (D.Tech) | May 2020 (Updated April 2023)
Qualitative data analysis methods. Wow, that’s a mouthful.
If you’re new to the world of research, qualitative data analysis can look rather intimidating. So much bulky terminology and so many abstract, fluffy concepts. It certainly can be a minefield!
Don’t worry – in this post, we’ll unpack the most popular analysis methods , one at a time, so that you can approach your analysis with confidence and competence – whether that’s for a dissertation, thesis or really any kind of research project.
What (exactly) is qualitative data analysis?
To understand qualitative data analysis, we need to first understand qualitative data – so let’s step back and ask the question, “what exactly is qualitative data?”.
Qualitative data refers to pretty much any data that’s “not numbers” . In other words, it’s not the stuff you measure using a fixed scale or complex equipment, nor do you analyse it using complex statistics or mathematics.
So, if it’s not numbers, what is it?
Words, you guessed? Well… sometimes , yes. Qualitative data can, and often does, take the form of interview transcripts, documents and open-ended survey responses – but it can also involve the interpretation of images and videos. In other words, qualitative isn’t just limited to text-based data.
So, how’s that different from quantitative data, you ask?
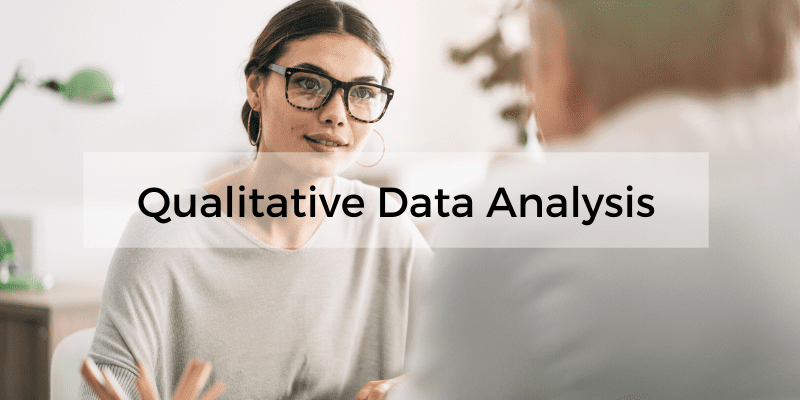
Simply put, qualitative research focuses on words, descriptions, concepts or ideas – while quantitative research focuses on numbers and statistics . Qualitative research investigates the “softer side” of things to explore and describe , while quantitative research focuses on the “hard numbers”, to measure differences between variables and the relationships between them. If you’re keen to learn more about the differences between qual and quant, we’ve got a detailed post over here .
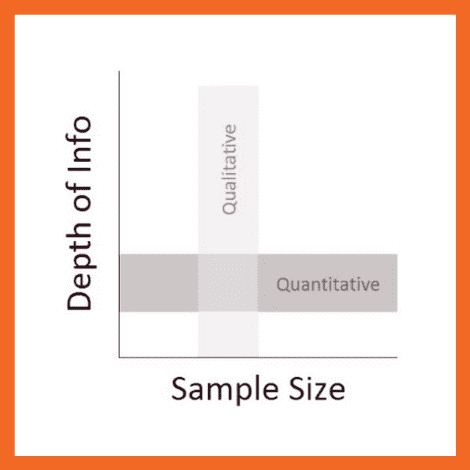
So, qualitative analysis is easier than quantitative, right?
Not quite. In many ways, qualitative data can be challenging and time-consuming to analyse and interpret. At the end of your data collection phase (which itself takes a lot of time), you’ll likely have many pages of text-based data or hours upon hours of audio to work through. You might also have subtle nuances of interactions or discussions that have danced around in your mind, or that you scribbled down in messy field notes. All of this needs to work its way into your analysis.
Making sense of all of this is no small task and you shouldn’t underestimate it. Long story short – qualitative analysis can be a lot of work! Of course, quantitative analysis is no piece of cake either, but it’s important to recognise that qualitative analysis still requires a significant investment in terms of time and effort.
Need a helping hand?
In this post, we’ll explore qualitative data analysis by looking at some of the most common analysis methods we encounter. We’re not going to cover every possible qualitative method and we’re not going to go into heavy detail – we’re just going to give you the big picture. That said, we will of course includes links to loads of extra resources so that you can learn more about whichever analysis method interests you.
Without further delay, let’s get into it.
The “Big 6” Qualitative Analysis Methods
There are many different types of qualitative data analysis, all of which serve different purposes and have unique strengths and weaknesses . We’ll start by outlining the analysis methods and then we’ll dive into the details for each.
The 6 most popular methods (or at least the ones we see at Grad Coach) are:
- Content analysis
- Narrative analysis
- Discourse analysis
- Thematic analysis
- Grounded theory (GT)
- Interpretive phenomenological analysis (IPA)
Let’s take a look at each of them…
QDA Method #1: Qualitative Content Analysis
Content analysis is possibly the most common and straightforward QDA method. At the simplest level, content analysis is used to evaluate patterns within a piece of content (for example, words, phrases or images) or across multiple pieces of content or sources of communication. For example, a collection of newspaper articles or political speeches.
With content analysis, you could, for instance, identify the frequency with which an idea is shared or spoken about – like the number of times a Kardashian is mentioned on Twitter. Or you could identify patterns of deeper underlying interpretations – for instance, by identifying phrases or words in tourist pamphlets that highlight India as an ancient country.
Because content analysis can be used in such a wide variety of ways, it’s important to go into your analysis with a very specific question and goal, or you’ll get lost in the fog. With content analysis, you’ll group large amounts of text into codes , summarise these into categories, and possibly even tabulate the data to calculate the frequency of certain concepts or variables. Because of this, content analysis provides a small splash of quantitative thinking within a qualitative method.
Naturally, while content analysis is widely useful, it’s not without its drawbacks . One of the main issues with content analysis is that it can be very time-consuming , as it requires lots of reading and re-reading of the texts. Also, because of its multidimensional focus on both qualitative and quantitative aspects, it is sometimes accused of losing important nuances in communication.
Content analysis also tends to concentrate on a very specific timeline and doesn’t take into account what happened before or after that timeline. This isn’t necessarily a bad thing though – just something to be aware of. So, keep these factors in mind if you’re considering content analysis. Every analysis method has its limitations , so don’t be put off by these – just be aware of them ! If you’re interested in learning more about content analysis, the video below provides a good starting point.
QDA Method #2: Narrative Analysis
As the name suggests, narrative analysis is all about listening to people telling stories and analysing what that means . Since stories serve a functional purpose of helping us make sense of the world, we can gain insights into the ways that people deal with and make sense of reality by analysing their stories and the ways they’re told.
You could, for example, use narrative analysis to explore whether how something is being said is important. For instance, the narrative of a prisoner trying to justify their crime could provide insight into their view of the world and the justice system. Similarly, analysing the ways entrepreneurs talk about the struggles in their careers or cancer patients telling stories of hope could provide powerful insights into their mindsets and perspectives . Simply put, narrative analysis is about paying attention to the stories that people tell – and more importantly, the way they tell them.
Of course, the narrative approach has its weaknesses , too. Sample sizes are generally quite small due to the time-consuming process of capturing narratives. Because of this, along with the multitude of social and lifestyle factors which can influence a subject, narrative analysis can be quite difficult to reproduce in subsequent research. This means that it’s difficult to test the findings of some of this research.
Similarly, researcher bias can have a strong influence on the results here, so you need to be particularly careful about the potential biases you can bring into your analysis when using this method. Nevertheless, narrative analysis is still a very useful qualitative analysis method – just keep these limitations in mind and be careful not to draw broad conclusions . If you’re keen to learn more about narrative analysis, the video below provides a great introduction to this qualitative analysis method.
QDA Method #3: Discourse Analysis
Discourse is simply a fancy word for written or spoken language or debate . So, discourse analysis is all about analysing language within its social context. In other words, analysing language – such as a conversation, a speech, etc – within the culture and society it takes place. For example, you could analyse how a janitor speaks to a CEO, or how politicians speak about terrorism.
To truly understand these conversations or speeches, the culture and history of those involved in the communication are important factors to consider. For example, a janitor might speak more casually with a CEO in a company that emphasises equality among workers. Similarly, a politician might speak more about terrorism if there was a recent terrorist incident in the country.
So, as you can see, by using discourse analysis, you can identify how culture , history or power dynamics (to name a few) have an effect on the way concepts are spoken about. So, if your research aims and objectives involve understanding culture or power dynamics, discourse analysis can be a powerful method.
Because there are many social influences in terms of how we speak to each other, the potential use of discourse analysis is vast . Of course, this also means it’s important to have a very specific research question (or questions) in mind when analysing your data and looking for patterns and themes, or you might land up going down a winding rabbit hole.
Discourse analysis can also be very time-consuming as you need to sample the data to the point of saturation – in other words, until no new information and insights emerge. But this is, of course, part of what makes discourse analysis such a powerful technique. So, keep these factors in mind when considering this QDA method. Again, if you’re keen to learn more, the video below presents a good starting point.
QDA Method #4: Thematic Analysis
Thematic analysis looks at patterns of meaning in a data set – for example, a set of interviews or focus group transcripts. But what exactly does that… mean? Well, a thematic analysis takes bodies of data (which are often quite large) and groups them according to similarities – in other words, themes . These themes help us make sense of the content and derive meaning from it.
Let’s take a look at an example.
With thematic analysis, you could analyse 100 online reviews of a popular sushi restaurant to find out what patrons think about the place. By reviewing the data, you would then identify the themes that crop up repeatedly within the data – for example, “fresh ingredients” or “friendly wait staff”.
So, as you can see, thematic analysis can be pretty useful for finding out about people’s experiences , views, and opinions . Therefore, if your research aims and objectives involve understanding people’s experience or view of something, thematic analysis can be a great choice.
Since thematic analysis is a bit of an exploratory process, it’s not unusual for your research questions to develop , or even change as you progress through the analysis. While this is somewhat natural in exploratory research, it can also be seen as a disadvantage as it means that data needs to be re-reviewed each time a research question is adjusted. In other words, thematic analysis can be quite time-consuming – but for a good reason. So, keep this in mind if you choose to use thematic analysis for your project and budget extra time for unexpected adjustments.

QDA Method #5: Grounded theory (GT)
Grounded theory is a powerful qualitative analysis method where the intention is to create a new theory (or theories) using the data at hand, through a series of “ tests ” and “ revisions ”. Strictly speaking, GT is more a research design type than an analysis method, but we’ve included it here as it’s often referred to as a method.
What’s most important with grounded theory is that you go into the analysis with an open mind and let the data speak for itself – rather than dragging existing hypotheses or theories into your analysis. In other words, your analysis must develop from the ground up (hence the name).
Let’s look at an example of GT in action.
Assume you’re interested in developing a theory about what factors influence students to watch a YouTube video about qualitative analysis. Using Grounded theory , you’d start with this general overarching question about the given population (i.e., graduate students). First, you’d approach a small sample – for example, five graduate students in a department at a university. Ideally, this sample would be reasonably representative of the broader population. You’d interview these students to identify what factors lead them to watch the video.
After analysing the interview data, a general pattern could emerge. For example, you might notice that graduate students are more likely to read a post about qualitative methods if they are just starting on their dissertation journey, or if they have an upcoming test about research methods.
From here, you’ll look for another small sample – for example, five more graduate students in a different department – and see whether this pattern holds true for them. If not, you’ll look for commonalities and adapt your theory accordingly. As this process continues, the theory would develop . As we mentioned earlier, what’s important with grounded theory is that the theory develops from the data – not from some preconceived idea.
So, what are the drawbacks of grounded theory? Well, some argue that there’s a tricky circularity to grounded theory. For it to work, in principle, you should know as little as possible regarding the research question and population, so that you reduce the bias in your interpretation. However, in many circumstances, it’s also thought to be unwise to approach a research question without knowledge of the current literature . In other words, it’s a bit of a “chicken or the egg” situation.
Regardless, grounded theory remains a popular (and powerful) option. Naturally, it’s a very useful method when you’re researching a topic that is completely new or has very little existing research about it, as it allows you to start from scratch and work your way from the ground up .

QDA Method #6: Interpretive Phenomenological Analysis (IPA)
Interpretive. Phenomenological. Analysis. IPA . Try saying that three times fast…
Let’s just stick with IPA, okay?
IPA is designed to help you understand the personal experiences of a subject (for example, a person or group of people) concerning a major life event, an experience or a situation . This event or experience is the “phenomenon” that makes up the “P” in IPA. Such phenomena may range from relatively common events – such as motherhood, or being involved in a car accident – to those which are extremely rare – for example, someone’s personal experience in a refugee camp. So, IPA is a great choice if your research involves analysing people’s personal experiences of something that happened to them.
It’s important to remember that IPA is subject – centred . In other words, it’s focused on the experiencer . This means that, while you’ll likely use a coding system to identify commonalities, it’s important not to lose the depth of experience or meaning by trying to reduce everything to codes. Also, keep in mind that since your sample size will generally be very small with IPA, you often won’t be able to draw broad conclusions about the generalisability of your findings. But that’s okay as long as it aligns with your research aims and objectives.
Another thing to be aware of with IPA is personal bias . While researcher bias can creep into all forms of research, self-awareness is critically important with IPA, as it can have a major impact on the results. For example, a researcher who was a victim of a crime himself could insert his own feelings of frustration and anger into the way he interprets the experience of someone who was kidnapped. So, if you’re going to undertake IPA, you need to be very self-aware or you could muddy the analysis.

How to choose the right analysis method
In light of all of the qualitative analysis methods we’ve covered so far, you’re probably asking yourself the question, “ How do I choose the right one? ”
Much like all the other methodological decisions you’ll need to make, selecting the right qualitative analysis method largely depends on your research aims, objectives and questions . In other words, the best tool for the job depends on what you’re trying to build. For example:
- Perhaps your research aims to analyse the use of words and what they reveal about the intention of the storyteller and the cultural context of the time.
- Perhaps your research aims to develop an understanding of the unique personal experiences of people that have experienced a certain event, or
- Perhaps your research aims to develop insight regarding the influence of a certain culture on its members.
As you can probably see, each of these research aims are distinctly different , and therefore different analysis methods would be suitable for each one. For example, narrative analysis would likely be a good option for the first aim, while grounded theory wouldn’t be as relevant.
It’s also important to remember that each method has its own set of strengths, weaknesses and general limitations. No single analysis method is perfect . So, depending on the nature of your research, it may make sense to adopt more than one method (this is called triangulation ). Keep in mind though that this will of course be quite time-consuming.
As we’ve seen, all of the qualitative analysis methods we’ve discussed make use of coding and theme-generating techniques, but the intent and approach of each analysis method differ quite substantially. So, it’s very important to come into your research with a clear intention before you decide which analysis method (or methods) to use.
Start by reviewing your research aims , objectives and research questions to assess what exactly you’re trying to find out – then select a qualitative analysis method that fits. Never pick a method just because you like it or have experience using it – your analysis method (or methods) must align with your broader research aims and objectives.

Let’s recap on QDA methods…
In this post, we looked at six popular qualitative data analysis methods:
- First, we looked at content analysis , a straightforward method that blends a little bit of quant into a primarily qualitative analysis.
- Then we looked at narrative analysis , which is about analysing how stories are told.
- Next up was discourse analysis – which is about analysing conversations and interactions.
- Then we moved on to thematic analysis – which is about identifying themes and patterns.
- From there, we went south with grounded theory – which is about starting from scratch with a specific question and using the data alone to build a theory in response to that question.
- And finally, we looked at IPA – which is about understanding people’s unique experiences of a phenomenon.
Of course, these aren’t the only options when it comes to qualitative data analysis, but they’re a great starting point if you’re dipping your toes into qualitative research for the first time.
If you’re still feeling a bit confused, consider our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through the research process to help you develop your best work.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

84 Comments
This has been very helpful. Thank you.
Thank you madam,
Thank you so much for this information
I wonder it so clear for understand and good for me. can I ask additional query?
Very insightful and useful
Good work done with clear explanations. Thank you.
Thanks so much for the write-up, it’s really good.
Thanks madam . It is very important .
thank you very good
This has been very well explained in simple language . It is useful even for a new researcher.
Great to hear that. Good luck with your qualitative data analysis, Pramod!
This is very useful information. And it was very a clear language structured presentation. Thanks a lot.
Thank you so much.
very informative sequential presentation
Precise explanation of method.
Hi, may we use 2 data analysis methods in our qualitative research?
Thanks for your comment. Most commonly, one would use one type of analysis method, but it depends on your research aims and objectives.
You explained it in very simple language, everyone can understand it. Thanks so much.
Thank you very much, this is very helpful. It has been explained in a very simple manner that even a layman understands
Thank nicely explained can I ask is Qualitative content analysis the same as thematic analysis?
Thanks for your comment. No, QCA and thematic are two different types of analysis. This article might help clarify – https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/nhs.12048
This is my first time to come across a well explained data analysis. so helpful.
I have thoroughly enjoyed your explanation of the six qualitative analysis methods. This is very helpful. Thank you!
Thank you very much, this is well explained and useful
i need a citation of your book.
Thanks a lot , remarkable indeed, enlighting to the best
Hi Derek, What other theories/methods would you recommend when the data is a whole speech?
Keep writing useful artikel.
It is important concept about QDA and also the way to express is easily understandable, so thanks for all.
Thank you, this is well explained and very useful.
Very helpful .Thanks.
Hi there! Very well explained. Simple but very useful style of writing. Please provide the citation of the text. warm regards
The session was very helpful and insightful. Thank you
This was very helpful and insightful. Easy to read and understand
As a professional academic writer, this has been so informative and educative. Keep up the good work Grad Coach you are unmatched with quality content for sure.
Keep up the good work Grad Coach you are unmatched with quality content for sure.
Its Great and help me the most. A Million Thanks you Dr.
It is a very nice work
Very insightful. Please, which of this approach could be used for a research that one is trying to elicit students’ misconceptions in a particular concept ?
This is Amazing and well explained, thanks
great overview
What do we call a research data analysis method that one use to advise or determining the best accounting tool or techniques that should be adopted in a company.
Informative video, explained in a clear and simple way. Kudos
Waoo! I have chosen method wrong for my data analysis. But I can revise my work according to this guide. Thank you so much for this helpful lecture.
This has been very helpful. It gave me a good view of my research objectives and how to choose the best method. Thematic analysis it is.
Very helpful indeed. Thanku so much for the insight.
This was incredibly helpful.
Very helpful.
very educative
Nicely written especially for novice academic researchers like me! Thank you.
choosing a right method for a paper is always a hard job for a student, this is a useful information, but it would be more useful personally for me, if the author provide me with a little bit more information about the data analysis techniques in type of explanatory research. Can we use qualitative content analysis technique for explanatory research ? or what is the suitable data analysis method for explanatory research in social studies?
that was very helpful for me. because these details are so important to my research. thank you very much
I learnt a lot. Thank you
Relevant and Informative, thanks !
Well-planned and organized, thanks much! 🙂
I have reviewed qualitative data analysis in a simplest way possible. The content will highly be useful for developing my book on qualitative data analysis methods. Cheers!
Clear explanation on qualitative and how about Case study
This was helpful. Thank you
This was really of great assistance, it was just the right information needed. Explanation very clear and follow.
Wow, Thanks for making my life easy
This was helpful thanks .
Very helpful…. clear and written in an easily understandable manner. Thank you.
This was so helpful as it was easy to understand. I’m a new to research thank you so much.
so educative…. but Ijust want to know which method is coding of the qualitative or tallying done?
Thank you for the great content, I have learnt a lot. So helpful
precise and clear presentation with simple language and thank you for that.
very informative content, thank you.
You guys are amazing on YouTube on this platform. Your teachings are great, educative, and informative. kudos!
Brilliant Delivery. You made a complex subject seem so easy. Well done.
Beautifully explained.
Thanks a lot
Is there a video the captures the practical process of coding using automated applications?
Thanks for the comment. We don’t recommend using automated applications for coding, as they are not sufficiently accurate in our experience.
content analysis can be qualitative research?
THANK YOU VERY MUCH.
Thank you very much for such a wonderful content
do you have any material on Data collection
What a powerful explanation of the QDA methods. Thank you.
Great explanation both written and Video. i have been using of it on a day to day working of my thesis project in accounting and finance. Thank you very much for your support.
very helpful, thank you so much
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- AI & NLP
- Churn & Loyalty
- Customer Experience
- Customer Journeys
- Customer Metrics
- Feedback Analysis
- Product Experience
- Product Updates
- Sentiment Analysis
- Surveys & Feedback Collection
- Try Thematic
Welcome to the community
Qualitative Data Analysis: Step-by-Step Guide (Manual vs. Automatic)
When we conduct qualitative methods of research, need to explain changes in metrics or understand people's opinions, we always turn to qualitative data. Qualitative data is typically generated through:
- Interview transcripts
- Surveys with open-ended questions
- Contact center transcripts
- Texts and documents
- Audio and video recordings
- Observational notes
Compared to quantitative data, which captures structured information, qualitative data is unstructured and has more depth. It can answer our questions, can help formulate hypotheses and build understanding.
It's important to understand the differences between quantitative data & qualitative data . But unfortunately, analyzing qualitative data is difficult. While tools like Excel, Tableau and PowerBI crunch and visualize quantitative data with ease, there are a limited number of mainstream tools for analyzing qualitative data . The majority of qualitative data analysis still happens manually.
That said, there are two new trends that are changing this. First, there are advances in natural language processing (NLP) which is focused on understanding human language. Second, there is an explosion of user-friendly software designed for both researchers and businesses. Both help automate the qualitative data analysis process.
In this post we want to teach you how to conduct a successful qualitative data analysis. There are two primary qualitative data analysis methods; manual & automatic. We will teach you how to conduct the analysis manually, and also, automatically using software solutions powered by NLP. We’ll guide you through the steps to conduct a manual analysis, and look at what is involved and the role technology can play in automating this process.
More businesses are switching to fully-automated analysis of qualitative customer data because it is cheaper, faster, and just as accurate. Primarily, businesses purchase subscriptions to feedback analytics platforms so that they can understand customer pain points and sentiment.

We’ll take you through 5 steps to conduct a successful qualitative data analysis. Within each step we will highlight the key difference between the manual, and automated approach of qualitative researchers. Here's an overview of the steps:
The 5 steps to doing qualitative data analysis
- Gathering and collecting your qualitative data
- Organizing and connecting into your qualitative data
- Coding your qualitative data
- Analyzing the qualitative data for insights
- Reporting on the insights derived from your analysis
What is Qualitative Data Analysis?
Qualitative data analysis is a process of gathering, structuring and interpreting qualitative data to understand what it represents.
Qualitative data is non-numerical and unstructured. Qualitative data generally refers to text, such as open-ended responses to survey questions or user interviews, but also includes audio, photos and video.
Businesses often perform qualitative data analysis on customer feedback. And within this context, qualitative data generally refers to verbatim text data collected from sources such as reviews, complaints, chat messages, support centre interactions, customer interviews, case notes or social media comments.
How is qualitative data analysis different from quantitative data analysis?
Understanding the differences between quantitative & qualitative data is important. When it comes to analyzing data, Qualitative Data Analysis serves a very different role to Quantitative Data Analysis. But what sets them apart?
Qualitative Data Analysis dives into the stories hidden in non-numerical data such as interviews, open-ended survey answers, or notes from observations. It uncovers the ‘whys’ and ‘hows’ giving a deep understanding of people’s experiences and emotions.
Quantitative Data Analysis on the other hand deals with numerical data, using statistics to measure differences, identify preferred options, and pinpoint root causes of issues. It steps back to address questions like "how many" or "what percentage" to offer broad insights we can apply to larger groups.
In short, Qualitative Data Analysis is like a microscope, helping us understand specific detail. Quantitative Data Analysis is like the telescope, giving us a broader perspective. Both are important, working together to decode data for different objectives.
Qualitative Data Analysis methods
Once all the data has been captured, there are a variety of analysis techniques available and the choice is determined by your specific research objectives and the kind of data you’ve gathered. Common qualitative data analysis methods include:
Content Analysis
This is a popular approach to qualitative data analysis. Other qualitative analysis techniques may fit within the broad scope of content analysis. Thematic analysis is a part of the content analysis. Content analysis is used to identify the patterns that emerge from text, by grouping content into words, concepts, and themes. Content analysis is useful to quantify the relationship between all of the grouped content. The Columbia School of Public Health has a detailed breakdown of content analysis .
Narrative Analysis
Narrative analysis focuses on the stories people tell and the language they use to make sense of them. It is particularly useful in qualitative research methods where customer stories are used to get a deep understanding of customers’ perspectives on a specific issue. A narrative analysis might enable us to summarize the outcomes of a focused case study.
Discourse Analysis
Discourse analysis is used to get a thorough understanding of the political, cultural and power dynamics that exist in specific situations. The focus of discourse analysis here is on the way people express themselves in different social contexts. Discourse analysis is commonly used by brand strategists who hope to understand why a group of people feel the way they do about a brand or product.
Thematic Analysis
Thematic analysis is used to deduce the meaning behind the words people use. This is accomplished by discovering repeating themes in text. These meaningful themes reveal key insights into data and can be quantified, particularly when paired with sentiment analysis . Often, the outcome of thematic analysis is a code frame that captures themes in terms of codes, also called categories. So the process of thematic analysis is also referred to as “coding”. A common use-case for thematic analysis in companies is analysis of customer feedback.
Grounded Theory
Grounded theory is a useful approach when little is known about a subject. Grounded theory starts by formulating a theory around a single data case. This means that the theory is “grounded”. Grounded theory analysis is based on actual data, and not entirely speculative. Then additional cases can be examined to see if they are relevant and can add to the original grounded theory.

Challenges of Qualitative Data Analysis
While Qualitative Data Analysis offers rich insights, it comes with its challenges. Each unique QDA method has its unique hurdles. Let’s take a look at the challenges researchers and analysts might face, depending on the chosen method.
- Time and Effort (Narrative Analysis): Narrative analysis, which focuses on personal stories, demands patience. Sifting through lengthy narratives to find meaningful insights can be time-consuming, requires dedicated effort.
- Being Objective (Grounded Theory): Grounded theory, building theories from data, faces the challenges of personal biases. Staying objective while interpreting data is crucial, ensuring conclusions are rooted in the data itself.
- Complexity (Thematic Analysis): Thematic analysis involves identifying themes within data, a process that can be intricate. Categorizing and understanding themes can be complex, especially when each piece of data varies in context and structure. Thematic Analysis software can simplify this process.
- Generalizing Findings (Narrative Analysis): Narrative analysis, dealing with individual stories, makes drawing broad challenging. Extending findings from a single narrative to a broader context requires careful consideration.
- Managing Data (Thematic Analysis): Thematic analysis involves organizing and managing vast amounts of unstructured data, like interview transcripts. Managing this can be a hefty task, requiring effective data management strategies.
- Skill Level (Grounded Theory): Grounded theory demands specific skills to build theories from the ground up. Finding or training analysts with these skills poses a challenge, requiring investment in building expertise.
Benefits of qualitative data analysis
Qualitative Data Analysis (QDA) is like a versatile toolkit, offering a tailored approach to understanding your data. The benefits it offers are as diverse as the methods. Let’s explore why choosing the right method matters.
- Tailored Methods for Specific Needs: QDA isn't one-size-fits-all. Depending on your research objectives and the type of data at hand, different methods offer unique benefits. If you want emotive customer stories, narrative analysis paints a strong picture. When you want to explain a score, thematic analysis reveals insightful patterns
- Flexibility with Thematic Analysis: thematic analysis is like a chameleon in the toolkit of QDA. It adapts well to different types of data and research objectives, making it a top choice for any qualitative analysis.
- Deeper Understanding, Better Products: QDA helps you dive into people's thoughts and feelings. This deep understanding helps you build products and services that truly matches what people want, ensuring satisfied customers
- Finding the Unexpected: Qualitative data often reveals surprises that we miss in quantitative data. QDA offers us new ideas and perspectives, for insights we might otherwise miss.
- Building Effective Strategies: Insights from QDA are like strategic guides. They help businesses in crafting plans that match people’s desires.
- Creating Genuine Connections: Understanding people’s experiences lets businesses connect on a real level. This genuine connection helps build trust and loyalty, priceless for any business.
How to do Qualitative Data Analysis: 5 steps
Now we are going to show how you can do your own qualitative data analysis. We will guide you through this process step by step. As mentioned earlier, you will learn how to do qualitative data analysis manually , and also automatically using modern qualitative data and thematic analysis software.
To get best value from the analysis process and research process, it’s important to be super clear about the nature and scope of the question that’s being researched. This will help you select the research collection channels that are most likely to help you answer your question.
Depending on if you are a business looking to understand customer sentiment, or an academic surveying a school, your approach to qualitative data analysis will be unique.
Once you’re clear, there’s a sequence to follow. And, though there are differences in the manual and automatic approaches, the process steps are mostly the same.
The use case for our step-by-step guide is a company looking to collect data (customer feedback data), and analyze the customer feedback - in order to improve customer experience. By analyzing the customer feedback the company derives insights about their business and their customers. You can follow these same steps regardless of the nature of your research. Let’s get started.
Step 1: Gather your qualitative data and conduct research (Conduct qualitative research)
The first step of qualitative research is to do data collection. Put simply, data collection is gathering all of your data for analysis. A common situation is when qualitative data is spread across various sources.
Classic methods of gathering qualitative data
Most companies use traditional methods for gathering qualitative data: conducting interviews with research participants, running surveys, and running focus groups. This data is typically stored in documents, CRMs, databases and knowledge bases. It’s important to examine which data is available and needs to be included in your research project, based on its scope.
Using your existing qualitative feedback
As it becomes easier for customers to engage across a range of different channels, companies are gathering increasingly large amounts of both solicited and unsolicited qualitative feedback.
Most organizations have now invested in Voice of Customer programs , support ticketing systems, chatbot and support conversations, emails and even customer Slack chats.
These new channels provide companies with new ways of getting feedback, and also allow the collection of unstructured feedback data at scale.
The great thing about this data is that it contains a wealth of valubale insights and that it’s already there! When you have a new question about user behavior or your customers, you don’t need to create a new research study or set up a focus group. You can find most answers in the data you already have.
Typically, this data is stored in third-party solutions or a central database, but there are ways to export it or connect to a feedback analysis solution through integrations or an API.
Utilize untapped qualitative data channels
There are many online qualitative data sources you may not have considered. For example, you can find useful qualitative data in social media channels like Twitter or Facebook. Online forums, review sites, and online communities such as Discourse or Reddit also contain valuable data about your customers, or research questions.
If you are considering performing a qualitative benchmark analysis against competitors - the internet is your best friend. Gathering feedback in competitor reviews on sites like Trustpilot, G2, Capterra, Better Business Bureau or on app stores is a great way to perform a competitor benchmark analysis.
Customer feedback analysis software often has integrations into social media and review sites, or you could use a solution like DataMiner to scrape the reviews.
Step 2: Connect & organize all your qualitative data
Now you all have this qualitative data but there’s a problem, the data is unstructured. Before feedback can be analyzed and assigned any value, it needs to be organized in a single place. Why is this important? Consistency!
If all data is easily accessible in one place and analyzed in a consistent manner, you will have an easier time summarizing and making decisions based on this data.
The manual approach to organizing your data
The classic method of structuring qualitative data is to plot all the raw data you’ve gathered into a spreadsheet.
Typically, research and support teams would share large Excel sheets and different business units would make sense of the qualitative feedback data on their own. Each team collects and organizes the data in a way that best suits them, which means the feedback tends to be kept in separate silos.
An alternative and a more robust solution is to store feedback in a central database, like Snowflake or Amazon Redshift .
Keep in mind that when you organize your data in this way, you are often preparing it to be imported into another software. If you go the route of a database, you would need to use an API to push the feedback into a third-party software.
Computer-assisted qualitative data analysis software (CAQDAS)
Traditionally within the manual analysis approach (but not always), qualitative data is imported into CAQDAS software for coding.
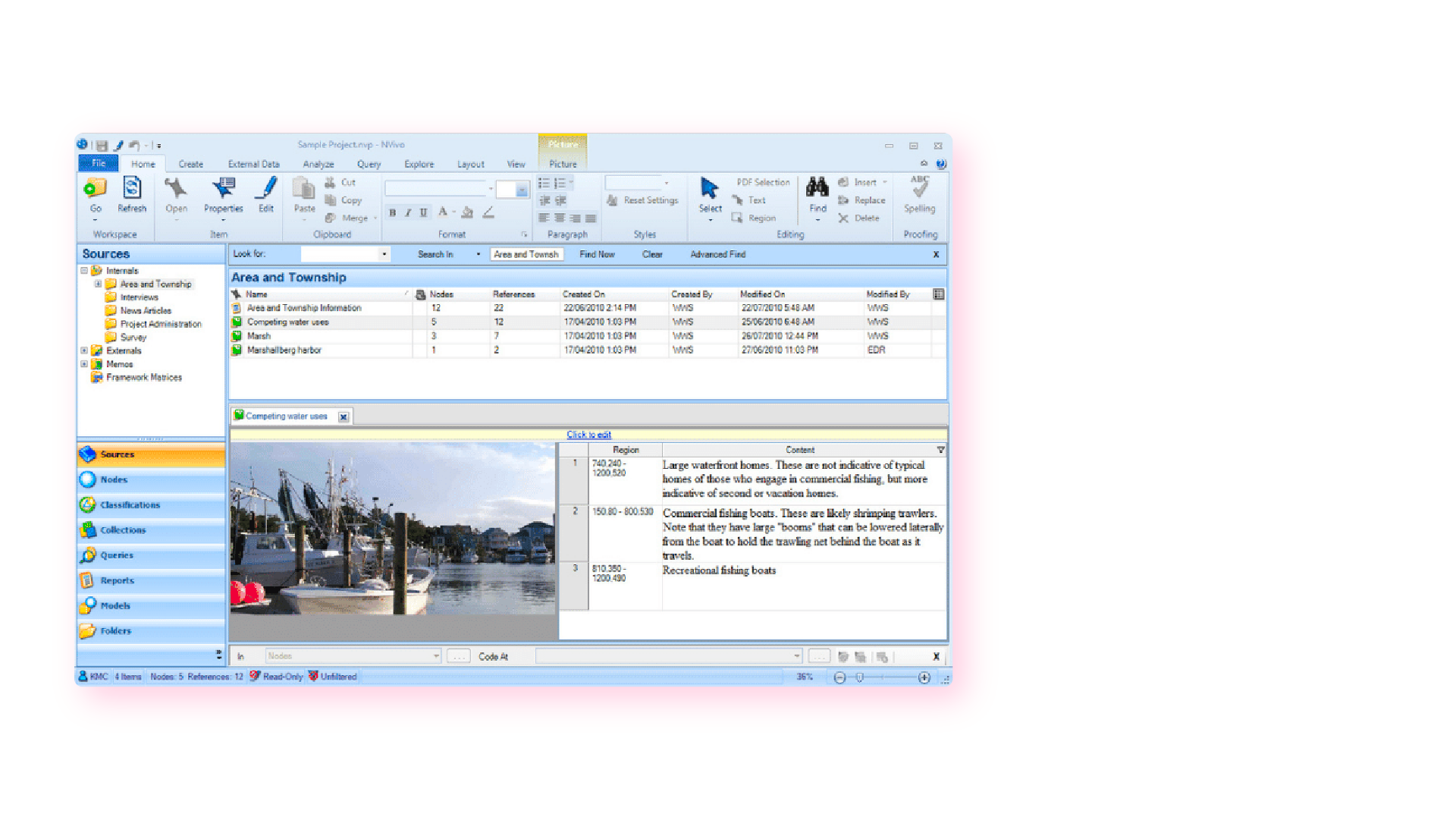
In the early 2000s, CAQDAS software was popularised by developers such as ATLAS.ti, NVivo and MAXQDA and eagerly adopted by researchers to assist with the organizing and coding of data.
The benefits of using computer-assisted qualitative data analysis software:
- Assists in the organizing of your data
- Opens you up to exploring different interpretations of your data analysis
- Allows you to share your dataset easier and allows group collaboration (allows for secondary analysis)
However you still need to code the data, uncover the themes and do the analysis yourself. Therefore it is still a manual approach.
Organizing your qualitative data in a feedback repository
Another solution to organizing your qualitative data is to upload it into a feedback repository where it can be unified with your other data , and easily searchable and taggable. There are a number of software solutions that act as a central repository for your qualitative research data. Here are a couple solutions that you could investigate:
- Dovetail: Dovetail is a research repository with a focus on video and audio transcriptions. You can tag your transcriptions within the platform for theme analysis. You can also upload your other qualitative data such as research reports, survey responses, support conversations, and customer interviews. Dovetail acts as a single, searchable repository. And makes it easier to collaborate with other people around your qualitative research.
- EnjoyHQ: EnjoyHQ is another research repository with similar functionality to Dovetail. It boasts a more sophisticated search engine, but it has a higher starting subscription cost.
Organizing your qualitative data in a feedback analytics platform
If you have a lot of qualitative customer or employee feedback, from the likes of customer surveys or employee surveys, you will benefit from a feedback analytics platform. A feedback analytics platform is a software that automates the process of both sentiment analysis and thematic analysis . Companies use the integrations offered by these platforms to directly tap into their qualitative data sources (review sites, social media, survey responses, etc.). The data collected is then organized and analyzed consistently within the platform.
If you have data prepared in a spreadsheet, it can also be imported into feedback analytics platforms.
Once all this rich data has been organized within the feedback analytics platform, it is ready to be coded and themed, within the same platform. Thematic is a feedback analytics platform that offers one of the largest libraries of integrations with qualitative data sources.

Step 3: Coding your qualitative data
Your feedback data is now organized in one place. Either within your spreadsheet, CAQDAS, feedback repository or within your feedback analytics platform. The next step is to code your feedback data so we can extract meaningful insights in the next step.
Coding is the process of labelling and organizing your data in such a way that you can then identify themes in the data, and the relationships between these themes.
To simplify the coding process, you will take small samples of your customer feedback data, come up with a set of codes, or categories capturing themes, and label each piece of feedback, systematically, for patterns and meaning. Then you will take a larger sample of data, revising and refining the codes for greater accuracy and consistency as you go.
If you choose to use a feedback analytics platform, much of this process will be automated and accomplished for you.
The terms to describe different categories of meaning (‘theme’, ‘code’, ‘tag’, ‘category’ etc) can be confusing as they are often used interchangeably. For clarity, this article will use the term ‘code’.
To code means to identify key words or phrases and assign them to a category of meaning. “I really hate the customer service of this computer software company” would be coded as “poor customer service”.
How to manually code your qualitative data
- Decide whether you will use deductive or inductive coding. Deductive coding is when you create a list of predefined codes, and then assign them to the qualitative data. Inductive coding is the opposite of this, you create codes based on the data itself. Codes arise directly from the data and you label them as you go. You need to weigh up the pros and cons of each coding method and select the most appropriate.
- Read through the feedback data to get a broad sense of what it reveals. Now it’s time to start assigning your first set of codes to statements and sections of text.
- Keep repeating step 2, adding new codes and revising the code description as often as necessary. Once it has all been coded, go through everything again, to be sure there are no inconsistencies and that nothing has been overlooked.
- Create a code frame to group your codes. The coding frame is the organizational structure of all your codes. And there are two commonly used types of coding frames, flat, or hierarchical. A hierarchical code frame will make it easier for you to derive insights from your analysis.
- Based on the number of times a particular code occurs, you can now see the common themes in your feedback data. This is insightful! If ‘bad customer service’ is a common code, it’s time to take action.
We have a detailed guide dedicated to manually coding your qualitative data .
Using software to speed up manual coding of qualitative data
An Excel spreadsheet is still a popular method for coding. But various software solutions can help speed up this process. Here are some examples.
- CAQDAS / NVivo - CAQDAS software has built-in functionality that allows you to code text within their software. You may find the interface the software offers easier for managing codes than a spreadsheet.
- Dovetail/EnjoyHQ - You can tag transcripts and other textual data within these solutions. As they are also repositories you may find it simpler to keep the coding in one platform.
- IBM SPSS - SPSS is a statistical analysis software that may make coding easier than in a spreadsheet.
- Ascribe - Ascribe’s ‘Coder’ is a coding management system. Its user interface will make it easier for you to manage your codes.
Automating the qualitative coding process using thematic analysis software
In solutions which speed up the manual coding process, you still have to come up with valid codes and often apply codes manually to pieces of feedback. But there are also solutions that automate both the discovery and the application of codes.
Advances in machine learning have now made it possible to read, code and structure qualitative data automatically. This type of automated coding is offered by thematic analysis software .
Automation makes it far simpler and faster to code the feedback and group it into themes. By incorporating natural language processing (NLP) into the software, the AI looks across sentences and phrases to identify common themes meaningful statements. Some automated solutions detect repeating patterns and assign codes to them, others make you train the AI by providing examples. You could say that the AI learns the meaning of the feedback on its own.
Thematic automates the coding of qualitative feedback regardless of source. There’s no need to set up themes or categories in advance. Simply upload your data and wait a few minutes. You can also manually edit the codes to further refine their accuracy. Experiments conducted indicate that Thematic’s automated coding is just as accurate as manual coding .
Paired with sentiment analysis and advanced text analytics - these automated solutions become powerful for deriving quality business or research insights.
You could also build your own , if you have the resources!
The key benefits of using an automated coding solution
Automated analysis can often be set up fast and there’s the potential to uncover things that would never have been revealed if you had given the software a prescribed list of themes to look for.
Because the model applies a consistent rule to the data, it captures phrases or statements that a human eye might have missed.
Complete and consistent analysis of customer feedback enables more meaningful findings. Leading us into step 4.
Step 4: Analyze your data: Find meaningful insights
Now we are going to analyze our data to find insights. This is where we start to answer our research questions. Keep in mind that step 4 and step 5 (tell the story) have some overlap . This is because creating visualizations is both part of analysis process and reporting.
The task of uncovering insights is to scour through the codes that emerge from the data and draw meaningful correlations from them. It is also about making sure each insight is distinct and has enough data to support it.
Part of the analysis is to establish how much each code relates to different demographics and customer profiles, and identify whether there’s any relationship between these data points.
Manually create sub-codes to improve the quality of insights
If your code frame only has one level, you may find that your codes are too broad to be able to extract meaningful insights. This is where it is valuable to create sub-codes to your primary codes. This process is sometimes referred to as meta coding.
Note: If you take an inductive coding approach, you can create sub-codes as you are reading through your feedback data and coding it.
While time-consuming, this exercise will improve the quality of your analysis. Here is an example of what sub-codes could look like.
You need to carefully read your qualitative data to create quality sub-codes. But as you can see, the depth of analysis is greatly improved. By calculating the frequency of these sub-codes you can get insight into which customer service problems you can immediately address.
Correlate the frequency of codes to customer segments
Many businesses use customer segmentation . And you may have your own respondent segments that you can apply to your qualitative analysis. Segmentation is the practise of dividing customers or research respondents into subgroups.
Segments can be based on:
- Demographic
- And any other data type that you care to segment by
It is particularly useful to see the occurrence of codes within your segments. If one of your customer segments is considered unimportant to your business, but they are the cause of nearly all customer service complaints, it may be in your best interest to focus attention elsewhere. This is a useful insight!
Manually visualizing coded qualitative data
There are formulas you can use to visualize key insights in your data. The formulas we will suggest are imperative if you are measuring a score alongside your feedback.
If you are collecting a metric alongside your qualitative data this is a key visualization. Impact answers the question: “What’s the impact of a code on my overall score?”. Using Net Promoter Score (NPS) as an example, first you need to:
- Calculate overall NPS
- Calculate NPS in the subset of responses that do not contain that theme
- Subtract B from A
Then you can use this simple formula to calculate code impact on NPS .
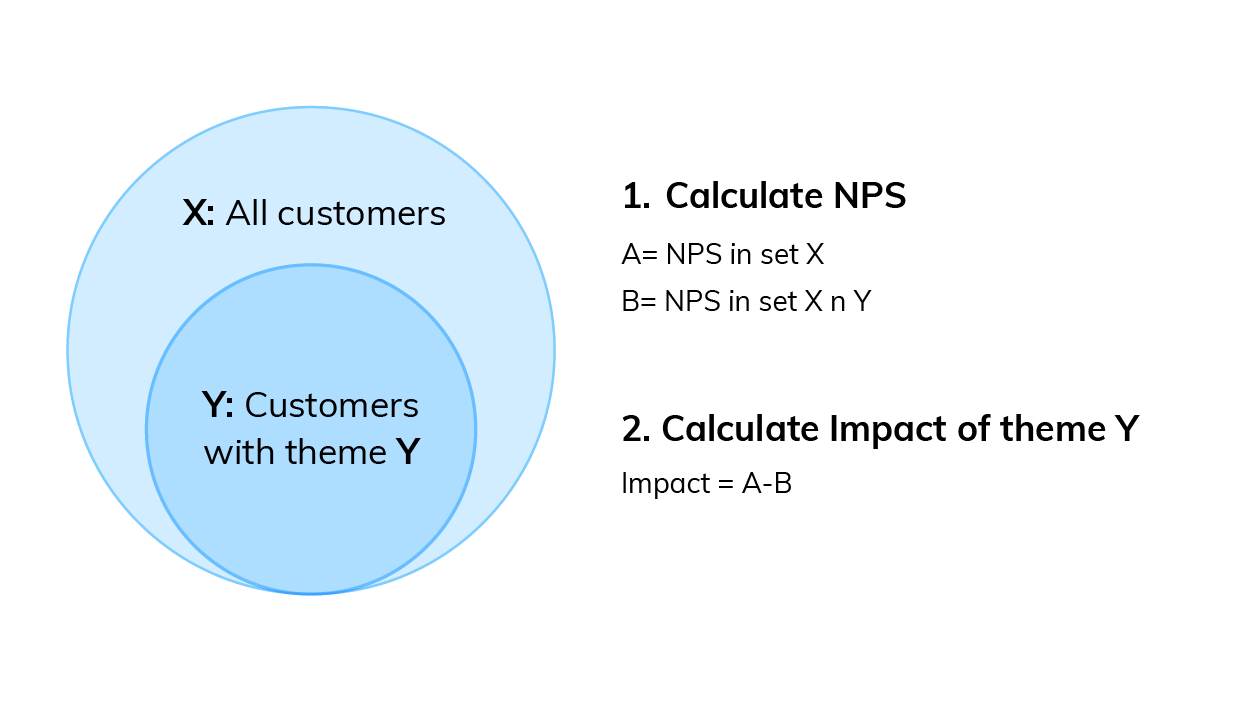
You can then visualize this data using a bar chart.
You can download our CX toolkit - it includes a template to recreate this.
Trends over time
This analysis can help you answer questions like: “Which codes are linked to decreases or increases in my score over time?”
We need to compare two sequences of numbers: NPS over time and code frequency over time . Using Excel, calculate the correlation between the two sequences, which can be either positive (the more codes the higher the NPS, see picture below), or negative (the more codes the lower the NPS).
Now you need to plot code frequency against the absolute value of code correlation with NPS. Here is the formula:
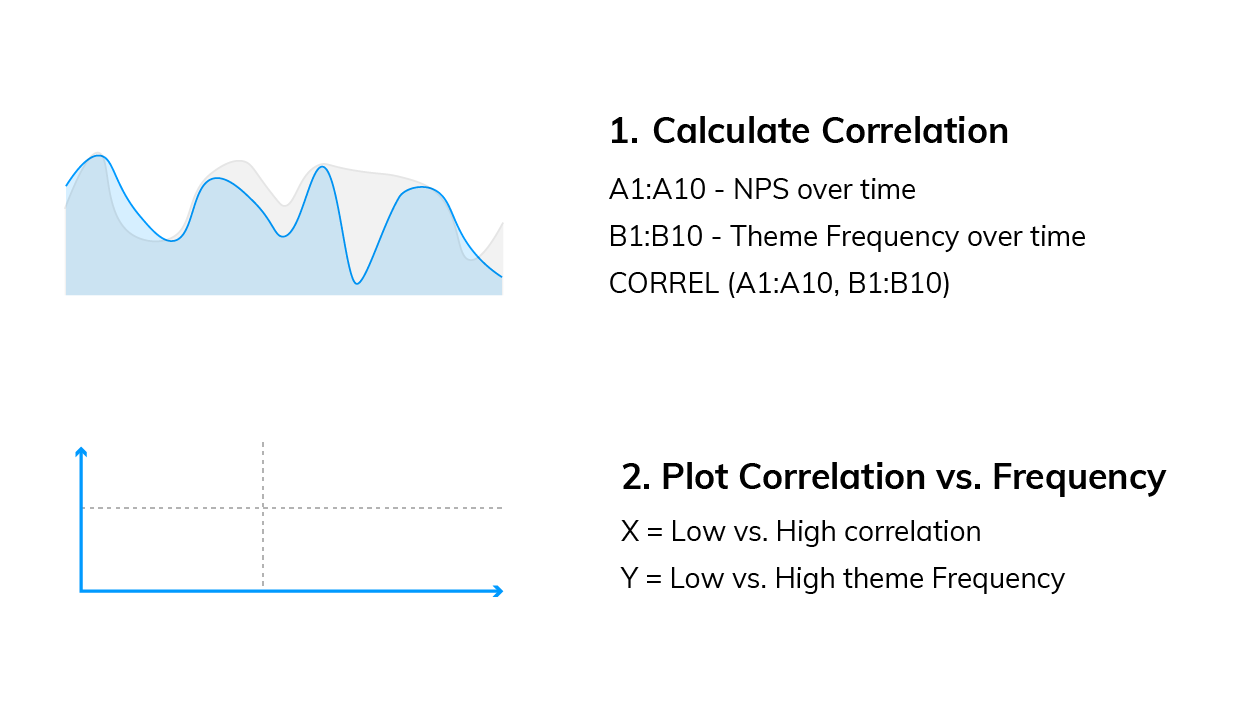
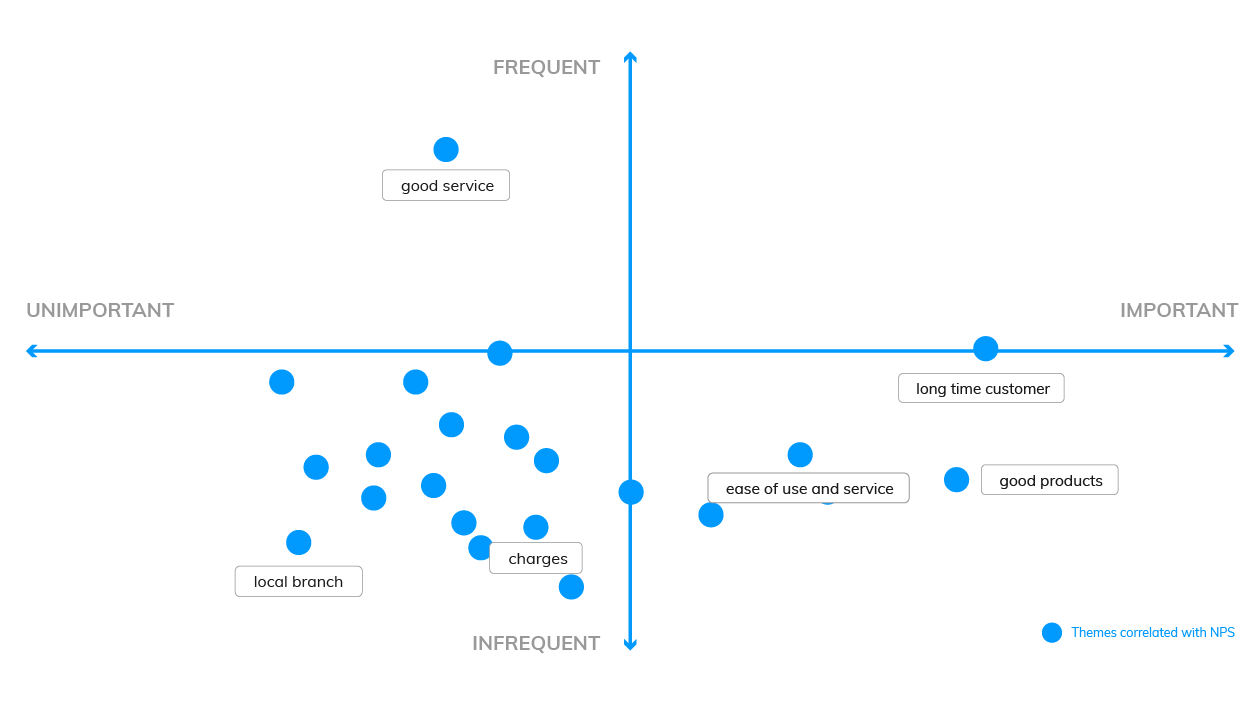
The visualization could look like this:
These are two examples, but there are more. For a third manual formula, and to learn why word clouds are not an insightful form of analysis, read our visualizations article .
Using a text analytics solution to automate analysis
Automated text analytics solutions enable codes and sub-codes to be pulled out of the data automatically. This makes it far faster and easier to identify what’s driving negative or positive results. And to pick up emerging trends and find all manner of rich insights in the data.
Another benefit of AI-driven text analytics software is its built-in capability for sentiment analysis, which provides the emotive context behind your feedback and other qualitative textual data therein.
Thematic provides text analytics that goes further by allowing users to apply their expertise on business context to edit or augment the AI-generated outputs.
Since the move away from manual research is generally about reducing the human element, adding human input to the technology might sound counter-intuitive. However, this is mostly to make sure important business nuances in the feedback aren’t missed during coding. The result is a higher accuracy of analysis. This is sometimes referred to as augmented intelligence .
Step 5: Report on your data: Tell the story
The last step of analyzing your qualitative data is to report on it, to tell the story. At this point, the codes are fully developed and the focus is on communicating the narrative to the audience.
A coherent outline of the qualitative research, the findings and the insights is vital for stakeholders to discuss and debate before they can devise a meaningful course of action.
Creating graphs and reporting in Powerpoint
Typically, qualitative researchers take the tried and tested approach of distilling their report into a series of charts, tables and other visuals which are woven into a narrative for presentation in Powerpoint.
Using visualization software for reporting
With data transformation and APIs, the analyzed data can be shared with data visualisation software, such as Power BI or Tableau , Google Studio or Looker. Power BI and Tableau are among the most preferred options.
Visualizing your insights inside a feedback analytics platform
Feedback analytics platforms, like Thematic, incorporate visualisation tools that intuitively turn key data and insights into graphs. This removes the time consuming work of constructing charts to visually identify patterns and creates more time to focus on building a compelling narrative that highlights the insights, in bite-size chunks, for executive teams to review.
Using a feedback analytics platform with visualization tools means you don’t have to use a separate product for visualizations. You can export graphs into Powerpoints straight from the platforms.
Conclusion - Manual or Automated?
There are those who remain deeply invested in the manual approach - because it’s familiar, because they’re reluctant to spend money and time learning new software, or because they’ve been burned by the overpromises of AI.
For projects that involve small datasets, manual analysis makes sense. For example, if the objective is simply to quantify a simple question like “Do customers prefer X concepts to Y?”. If the findings are being extracted from a small set of focus groups and interviews, sometimes it’s easier to just read them
However, as new generations come into the workplace, it’s technology-driven solutions that feel more comfortable and practical. And the merits are undeniable. Especially if the objective is to go deeper and understand the ‘why’ behind customers’ preference for X or Y. And even more especially if time and money are considerations.
The ability to collect a free flow of qualitative feedback data at the same time as the metric means AI can cost-effectively scan, crunch, score and analyze a ton of feedback from one system in one go. And time-intensive processes like focus groups, or coding, that used to take weeks, can now be completed in a matter of hours or days.
But aside from the ever-present business case to speed things up and keep costs down, there are also powerful research imperatives for automated analysis of qualitative data: namely, accuracy and consistency.
Finding insights hidden in feedback requires consistency, especially in coding. Not to mention catching all the ‘unknown unknowns’ that can skew research findings and steering clear of cognitive bias.
Some say without manual data analysis researchers won’t get an accurate “feel” for the insights. However, the larger data sets are, the harder it is to sort through the feedback and organize feedback that has been pulled from different places. And, the more difficult it is to stay on course, the greater the risk of drawing incorrect, or incomplete, conclusions grows.
Though the process steps for qualitative data analysis have remained pretty much unchanged since psychologist Paul Felix Lazarsfeld paved the path a hundred years ago, the impact digital technology has had on types of qualitative feedback data and the approach to the analysis are profound.
If you want to try an automated feedback analysis solution on your own qualitative data, you can get started with Thematic .

Community & Marketing
Tyler manages our community of CX, insights & analytics professionals. Tyler's goal is to help unite insights professionals around common challenges.
We make it easy to discover the customer and product issues that matter.
Unlock the value of feedback at scale, in one platform. Try it for free now!
- Questions to ask your Feedback Analytics vendor
- How to end customer churn for good
- Scalable analysis of NPS verbatims
- 5 Text analytics approaches
- How to calculate the ROI of CX
Our experts will show you how Thematic works, how to discover pain points and track the ROI of decisions. To access your free trial, book a personal demo today.
Recent posts
Watercare is New Zealand's largest water and wastewater service provider. They are responsible for bringing clean water to 1.7 million people in Tamaki Makaurau (Auckland) and safeguarding the wastewater network to minimize impact on the environment. Water is a sector that often gets taken for granted, with drainage and
Become a qualitative theming pro! Creating a perfect code frame is hard, but thematic analysis software makes the process much easier.
Qualtrics is one of the most well-known and powerful Customer Feedback Management platforms. But even so, it has limitations. We recently hosted a live panel where data analysts from two well-known brands shared their experiences with Qualtrics, and how they extended this platform’s capabilities. Below, we’ll share the

Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative data refers to non-numeric information such as interview transcripts, notes, video and audio recordings, images and text documents. Qualitative data analysis can be divided into the following five categories:
1. Content analysis . This refers to the process of categorizing verbal or behavioural data to classify, summarize and tabulate the data.
2. Narrative analysis . This method involves the reformulation of stories presented by respondents taking into account context of each case and different experiences of each respondent. In other words, narrative analysis is the revision of primary qualitative data by researcher.
3. Discourse analysis . A method of analysis of naturally occurring talk and all types of written text.
4. Framework analysis . This is more advanced method that consists of several stages such as familiarization, identifying a thematic framework, coding, charting, mapping and interpretation.
5. Grounded theory . This method of qualitative data analysis starts with an analysis of a single case to formulate a theory. Then, additional cases are examined to see if they contribute to the theory.
Qualitative data analysis can be conducted through the following three steps:
Step 1: Developing and Applying Codes . Coding can be explained as categorization of data. A ‘code’ can be a word or a short phrase that represents a theme or an idea. All codes need to be assigned meaningful titles. A wide range of non-quantifiable elements such as events, behaviours, activities, meanings etc. can be coded.
There are three types of coding:
- Open coding . The initial organization of raw data to try to make sense of it.
- Axial coding . Interconnecting and linking the categories of codes.
- Selective coding . Formulating the story through connecting the categories.
Coding can be done manually or using qualitative data analysis software such as
NVivo, Atlas ti 6.0, HyperRESEARCH 2.8, Max QDA and others.
When using manual coding you can use folders, filing cabinets, wallets etc. to gather together materials that are examples of similar themes or analytic ideas. Manual method of coding in qualitative data analysis is rightly considered as labour-intensive, time-consuming and outdated.
In computer-based coding, on the other hand, physical files and cabinets are replaced with computer based directories and files. When choosing software for qualitative data analysis you need to consider a wide range of factors such as the type and amount of data you need to analyse, time required to master the software and cost considerations.
Moreover, it is important to get confirmation from your dissertation supervisor prior to application of any specific qualitative data analysis software.
The following table contains examples of research titles, elements to be coded and identification of relevant codes:
Qualitative data coding
Step 2: Identifying themes, patterns and relationships . Unlike quantitative methods , in qualitative data analysis there are no universally applicable techniques that can be applied to generate findings. Analytical and critical thinking skills of researcher plays significant role in data analysis in qualitative studies. Therefore, no qualitative study can be repeated to generate the same results.
Nevertheless, there is a set of techniques that you can use to identify common themes, patterns and relationships within responses of sample group members in relation to codes that have been specified in the previous stage.
Specifically, the most popular and effective methods of qualitative data interpretation include the following:
- Word and phrase repetitions – scanning primary data for words and phrases most commonly used by respondents, as well as, words and phrases used with unusual emotions;
- Primary and secondary data comparisons – comparing the findings of interview/focus group/observation/any other qualitative data collection method with the findings of literature review and discussing differences between them;
- Search for missing information – discussions about which aspects of the issue was not mentioned by respondents, although you expected them to be mentioned;
- Metaphors and analogues – comparing primary research findings to phenomena from a different area and discussing similarities and differences.
Step 3: Summarizing the data . At this last stage you need to link research findings to hypotheses or research aim and objectives. When writing data analysis chapter, you can use noteworthy quotations from the transcript in order to highlight major themes within findings and possible contradictions.
It is important to note that the process of qualitative data analysis described above is general and different types of qualitative studies may require slightly different methods of data analysis.
My e-book, The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Dissertation in Business Studies: a step by step approach contains a detailed, yet simple explanation of qualitative data analysis methods . The e-book explains all stages of the research process starting from the selection of the research area to writing personal reflection. Important elements of dissertations such as research philosophy, research approach, research design, methods of data collection and data analysis are explained in simple words. John Dudovskiy

- Subject List
- Take a Tour
- For Authors
- Subscriber Services
- Publications
- African American Studies
- African Studies
- American Literature
- Anthropology
- Architecture Planning and Preservation
- Art History
- Atlantic History
- Biblical Studies
- British and Irish Literature
- Childhood Studies
- Chinese Studies
- Cinema and Media Studies
- Communication
- Criminology
- Environmental Science
- Evolutionary Biology
- International Law
- International Relations
- Islamic Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Latino Studies
- Linguistics
- Literary and Critical Theory
- Medieval Studies
- Military History
- Political Science
- Public Health
- Renaissance and Reformation
- Social Work
- Urban Studies
- Victorian Literature
- Browse All Subjects
How to Subscribe
- Free Trials
In This Article Expand or collapse the "in this article" section Qualitative Data Analysis Techniques
Introduction, general overviews.
- Semiotic Analysis
- Text Mining
- Discourse Analysis
- Classical Content Analysis
- Schema Analysis
- Latent Content Analysis
- Manifest Content Analysis
- Keywords-in-context
- Constant Comparison Analysis
- Membership Categorization Analysis
- Narrative Analysis
- Conversation Analysis
- Ethnographic Decision Model Analysis
- Critical Discourse Analysis
- Frame or Framing Analysis
- Social Semiotic Analysis
- Domain Analysis
- Taxonomic Analysis
- Componential Analysis
- Theme Analysis
- Dialogical Narrative Analysis
- Qualitative Comparative Analysis
- Multimodal Discourse Analysis (MDA)
- Dimensional Analysis
- Framework Analysis
- Secondary Data Analysis
- Interpretative Phenomenological Analysis (IPA)
- Consensual Qualitative Research
- Situational Analysis
- Micro-Interlocutor Analysis
- Rhetorical Analysis
- Systematic Data Integration
- Nonverbal Communication Analysis
Related Articles Expand or collapse the "related articles" section about
About related articles close popup.
Lorem Ipsum Sit Dolor Amet
Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Aliquam ligula odio, euismod ut aliquam et, vestibulum nec risus. Nulla viverra, arcu et iaculis consequat, justo diam ornare tellus, semper ultrices tellus nunc eu tellus.
- Action Research in Education
- Grounded Theory
- Literature Reviews
- Mixed Methods Research
- Narrative Research in Education
- Qualitative Research Design
- Quantitative Research Designs in Educational Research
- Researcher Development and Skills Training within the Context of Postgraduate Programs
Other Subject Areas
Forthcoming articles expand or collapse the "forthcoming articles" section.
- English as an International Language for Academic Publishing
- Girls' Education in the Developing World
- History of Education in Europe
- Find more forthcoming articles...
- Export Citations
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Qualitative Data Analysis Techniques by Anthony J. Onwuegbuzie , Magdalena Denham LAST REVIEWED: 30 June 2014 LAST MODIFIED: 30 June 2014 DOI: 10.1093/obo/9780199756810-0078
Qualitative research can be traced back to ancient times; however, the use of qualitative methods began to be formalized in certain disciplines (e.g., sociology, anthropology) only in the 19th century. Broadly speaking, qualitative research involves an in-depth examination of human experiences and human behavior, with the goal of obtaining insights into everyday experiences and meaning attached to these experiences of individuals (via qualitative methodologies such as biography, autobiography, life history, oral history, autoethnography, case study) and groups (via qualitative methodologies such as phenomenology, ethnography, grounded theory), which, optimally, can lead to understanding the meaning of behaviors from the study participant’s/group’s perspective. Qualitative researchers tend to investigate not just what, where , and when , but more importantly the why and how of events, experiences, and behaviors. Thus, qualitative researchers are much more likely to study smaller but focused samples than large samples. In general, qualitative research studies primarily involve the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data (i.e., information) that naturally occur. Of these steps, the analysis of data arguably represents one of the most difficult steps—if not the most difficult step—of the qualitative research process because it involves a systematic exploration of meaning and the achievement of verstehen (i.e., understanding). More specifically, qualitative data analysis is a process that comprises multiple phases, and from which findings are extracted or emerge. These phases include examining, cleaning, organizing, reducing, exploring, describing, explaining, displaying, interrogating, categorizing, pattern finding, transforming, correlating, consolidating, comparing, integrating, synthesizing, and interpreting data, in ways that allow researchers to see patterns, to identify categories and themes, to develop typologies, to discover relationships, to cultivate explanations, to extract interpretations, to develop critiques, to generate or to advance theories, and/or the like, with the goal of meaning making. A criticism of qualitative data analysis is that because it typically involves examination of data extracted from small, nonrandom samples, findings stemming from any qualitative analysis usually are not generalizable beyond the local research participants. However, what is a limitation for one purpose (i.e., generalization of findings to the population the sample was drawn from), is a strength for another purpose. Specifically, the examination of relatively small samples allows qualitative researchers to collect (maximally) rich data (e.g., via in-depth interviews, focus groups, observations, images, nonverbal communication). This, in turn, makes it more likely that as a result of the qualitative data analysis, verstehen will be achieved.
The analysis of data represents the most important and difficult step in the qualitative research process. Therefore, the purpose of this entry is to document the history and development of qualitative analytical approaches. In particular, described here are thirty-four formal qualitative data-analysis approaches that were identified from an exhaustive search of the literature. This OBO entry not only extends the work of Onwuegbuzie, et al. 2011 —which identified twenty-three analysis approaches—but by adding numerous other qualitative data analysis approaches, it also extends these works by documenting the origin of each analysis approach, mapping it onto the nine moments described in Denzin and Lincoln 2011 and outlining the sources of qualitative data that it can analyze. With respect to the latter, see Leech and Onwuegbuzie 2008 with typology wherein the following four major sources of qualitative data prevail: talk, observations, images, and documents. Specifically, talk represents data that are extracted directly from the voices of the participants using data collection techniques such as individual interviews and focus groups. Observations involve the collection of data by systematically watching or perceiving one or more events, interactions, or nonverbal communication to address or to inform the research question(s). Images represent still (e.g., drawings, photographs) or moving (e.g., videos) visual data that are observed or perceived. Documents represent the collection of text that exists either in printed or digital form. As Miles and Huberman 1994 declared: “The strengths of qualitative data rest on the competence with which their analysis is carried out” (p. 10). By only being aware of a few qualitative data-analysis approaches, a qualitative researcher might make the data fit the analysis rather than select the most appropriate data-analysis approach given the underlying research elements such as the research question, researcher’s lens, and sampling and design characteristics. In contrast, by being aware of the array of qualitative data-analysis approaches, as well as how and when to conduct them, a qualitative researcher is in a better position not only to conduct analyses that have integrity but also to conduct analyses that emerge as findings emerge. Thus, qualitative researchers likely would put themselves in a better position for making meaning if they adopt a constructivist approach to qualitative data analysis. However, this can only occur if they have an awareness of multiple ways of analyzing qualitative data. This goal helps to establish the significance of the current work in this field.
Denzin, Norman K., and Yvonna S. Lincoln. 2011. Introduction: The discipline and practice of qualitative research. In Sage handbook of qualitative research . 4th ed. Edited by Norman K. Denzin and Yvonna S. Lincoln, 1–25. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
The authors document the history of qualitative research. This history spans nine moments, starting with they call the “traditional” moment and continuing through to the ninth moment, which they call the “fractured future,” which is the present moment.
Leech, Nancy L., and Anthony J. Onwuegbuzie. 2008. Qualitative data analysis: A compendium of techniques and a framework for selection for school psychology research and beyond. School Psychology Quarterly 23:587–604.
DOI: 10.1037/1045-3830.23.4.587
The authors describe the following eighteen qualitative analysis techniques: method of constant comparison analysis, keywords-in-context, word count, classical content analysis, domain analysis, taxonomic analysis, componential analysis, conversation analysis, discourse analysis, secondary analysis, membership categorization analysis, narrative analysis, qualitative comparative analysis, semiotics, manifest content analysis, latent content analysis, text mining, and micro-interlocutor analysis.
Miles, Matthew B., and A. Michael Huberman. 1994. Qualitative data analysis: An expanded sourcebook . 2d ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
In this groundbreaking book, the authors conceptualize and describe nineteen within-case analyses (i.e., partially ordered display, time-ordered display, role-ordered display, and conceptually ordered display) and eighteen cross-case analyses (i.e., partially ordered display, case-ordered display, time-ordered display, and conceptually ordered display. Thus, this work is the most comprehensive guidebook to qualitative analysis to date.
Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J., Nancy L. Leech, and Kathleen M. T. Collins. 2011. Toward a new era for conducting mixed analyses: The role of quantitative dominant and qualitative dominant crossover mixed analyses. In The Sage handbook of innovation in social research methods . Edited by Malcolm Williams and Paul W. Vogt, 353–384. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
In this book chapter, the authors introduce a unified framework for combining qualitative analysis and quantitative analysis—which they call a mixed analysis—regardless of whether the researcher is oriented toward quantitative research or mixed research.
back to top
Users without a subscription are not able to see the full content on this page. Please subscribe or login .
Oxford Bibliographies Online is available by subscription and perpetual access to institutions. For more information or to contact an Oxford Sales Representative click here .
- About Education »
- Meet the Editorial Board »
- Academic Achievement
- Academic Audit for Universities
- Academic Freedom and Tenure in the United States
- Adjuncts in Higher Education in the United States
- Administrator Preparation
- Adolescence
- Advanced Placement and International Baccalaureate Courses
- Advocacy and Activism in Early Childhood
- African American Racial Identity and Learning
- Alaska Native Education
- Alternative Certification Programs for Educators
- Alternative Schools
- American Indian Education
- Animals in Environmental Education
- Art Education
- Artificial Intelligence and Learning
- Assessing School Leader Effectiveness
- Assessment, Behavioral
- Assessment, Educational
- Assessment in Early Childhood Education
- Assistive Technology
- Augmented Reality in Education
- Beginning-Teacher Induction
- Bilingual Education and Bilingualism
- Black Undergraduate Women: Critical Race and Gender Perspe...
- Blended Learning
- Case Study in Education Research
- Changing Professional and Academic Identities
- Character Education
- Children’s and Young Adult Literature
- Children's Beliefs about Intelligence
- Children's Rights in Early Childhood Education
- Citizenship Education
- Civic and Social Engagement of Higher Education
- Classroom Learning Environments: Assessing and Investigati...
- Classroom Management
- Coherent Instructional Systems at the School and School Sy...
- College Admissions in the United States
- College Athletics in the United States
- Community Relations
- Comparative Education
- Computer-Assisted Language Learning
- Computer-Based Testing
- Conceptualizing, Measuring, and Evaluating Improvement Net...
- Continuous Improvement and "High Leverage" Educational Pro...
- Counseling in Schools
- Critical Approaches to Gender in Higher Education
- Critical Perspectives on Educational Innovation and Improv...
- Critical Race Theory
- Crossborder and Transnational Higher Education
- Cross-National Research on Continuous Improvement
- Cross-Sector Research on Continuous Learning and Improveme...
- Cultural Diversity in Early Childhood Education
- Culturally Responsive Leadership
- Culturally Responsive Pedagogies
- Culturally Responsive Teacher Education in the United Stat...
- Curriculum Design
- Data Collection in Educational Research
- Data-driven Decision Making in the United States
- Deaf Education
- Desegregation and Integration
- Design Thinking and the Learning Sciences: Theoretical, Pr...
- Development, Moral
- Dialogic Pedagogy
- Digital Age Teacher, The
- Digital Citizenship
- Digital Divides
- Disabilities
- Distance Learning
- Distributed Leadership
- Doctoral Education and Training
- Early Childhood Education and Care (ECEC) in Denmark
- Early Childhood Education and Development in Mexico
- Early Childhood Education in Aotearoa New Zealand
- Early Childhood Education in Australia
- Early Childhood Education in China
- Early Childhood Education in Europe
- Early Childhood Education in Sub-Saharan Africa
- Early Childhood Education in Sweden
- Early Childhood Education Pedagogy
- Early Childhood Education Policy
- Early Childhood Education, The Arts in
- Early Childhood Mathematics
- Early Childhood Science
- Early Childhood Teacher Education
- Early Childhood Teachers in Aotearoa New Zealand
- Early Years Professionalism and Professionalization Polici...
- Economics of Education
- Education For Children with Autism
- Education for Sustainable Development
- Education Leadership, Empirical Perspectives in
- Education of Native Hawaiian Students
- Education Reform and School Change
- Educational Statistics for Longitudinal Research
- Educator Partnerships with Parents and Families with a Foc...
- Emotional and Affective Issues in Environmental and Sustai...
- Emotional and Behavioral Disorders
- Environmental and Science Education: Overlaps and Issues
- Environmental Education
- Environmental Education in Brazil
- Epistemic Beliefs
- Equity and Improvement: Engaging Communities in Educationa...
- Equity, Ethnicity, Diversity, and Excellence in Education
- Ethical Research with Young Children
- Ethics and Education
- Ethics of Teaching
- Ethnic Studies
- Evidence-Based Communication Assessment and Intervention
- Family and Community Partnerships in Education
- Family Day Care
- Federal Government Programs and Issues
- Feminization of Labor in Academia
- Finance, Education
- Financial Aid
- Formative Assessment
- Future-Focused Education
- Gender and Achievement
- Gender and Alternative Education
- Gender, Power and Politics in the Academy
- Gender-Based Violence on University Campuses
- Gifted Education
- Global Mindedness and Global Citizenship Education
- Global University Rankings
- Governance, Education
- Growth of Effective Mental Health Services in Schools in t...
- Higher Education and Globalization
- Higher Education and the Developing World
- Higher Education Faculty Characteristics and Trends in the...
- Higher Education Finance
- Higher Education Governance
- Higher Education Graduate Outcomes and Destinations
- Higher Education in Africa
- Higher Education in China
- Higher Education in Latin America
- Higher Education in the United States, Historical Evolutio...
- Higher Education, International Issues in
- Higher Education Management
- Higher Education Policy
- Higher Education Research
- Higher Education Student Assessment
- High-stakes Testing
- History of Early Childhood Education in the United States
- History of Education in the United States
- History of Technology Integration in Education
- Homeschooling
- Inclusion in Early Childhood: Difference, Disability, and ...
- Inclusive Education
- Indigenous Education in a Global Context
- Indigenous Learning Environments
- Indigenous Students in Higher Education in the United Stat...
- Infant and Toddler Pedagogy
- Inservice Teacher Education
- Integrating Art across the Curriculum
- Intelligence
- Intensive Interventions for Children and Adolescents with ...
- International Perspectives on Academic Freedom
- Intersectionality and Education
- Knowledge Development in Early Childhood
- Leadership Development, Coaching and Feedback for
- Leadership in Early Childhood Education
- Leadership Training with an Emphasis on the United States
- Learning Analytics in Higher Education
- Learning Difficulties
- Learning, Lifelong
- Learning, Multimedia
- Learning Strategies
- Legal Matters and Education Law
- LGBT Youth in Schools
- Linguistic Diversity
- Linguistically Inclusive Pedagogy
- Literacy Development and Language Acquisition
- Mathematics Identity
- Mathematics Instruction and Interventions for Students wit...
- Mathematics Teacher Education
- Measurement for Improvement in Education
- Measurement in Education in the United States
- Meta-Analysis and Research Synthesis in Education
- Methodological Approaches for Impact Evaluation in Educati...
- Methodologies for Conducting Education Research
- Mindfulness, Learning, and Education
- Motherscholars
- Multiliteracies in Early Childhood Education
- Multiple Documents Literacy: Theory, Research, and Applica...
- Multivariate Research Methodology
- Museums, Education, and Curriculum
- Music Education
- Native American Studies
- Nonformal and Informal Environmental Education
- Note-Taking
- Numeracy Education
- One-to-One Technology in the K-12 Classroom
- Online Education
- Open Education
- Organizing for Continuous Improvement in Education
- Organizing Schools for the Inclusion of Students with Disa...
- Outdoor Play and Learning
- Outdoor Play and Learning in Early Childhood Education
- Pedagogical Leadership
- Pedagogy of Teacher Education, A
- Performance Objectives and Measurement
- Performance-based Research Assessment in Higher Education
- Performance-based Research Funding
- Phenomenology in Educational Research
- Philosophy of Education
- Physical Education
- Podcasts in Education
- Policy Context of United States Educational Innovation and...
- Politics of Education
- Portable Technology Use in Special Education Programs and ...
- Post-humanism and Environmental Education
- Pre-Service Teacher Education
- Problem Solving
- Productivity and Higher Education
- Professional Development
- Professional Learning Communities
- Program Evaluation
- Programs and Services for Students with Emotional or Behav...
- Psychology Learning and Teaching
- Psychometric Issues in the Assessment of English Language ...
- Qualitative Data Analysis Techniques
- Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Research Samp...
- Queering the English Language Arts (ELA) Writing Classroom
- Race and Affirmative Action in Higher Education
- Reading Education
- Refugee and New Immigrant Learners
- Relational and Developmental Trauma and Schools
- Relational Pedagogies in Early Childhood Education
- Reliability in Educational Assessments
- Religion in Elementary and Secondary Education in the Unit...
- Researcher Development and Skills Training within the Cont...
- Research-Practice Partnerships in Education within the Uni...
- Response to Intervention
- Restorative Practices
- Risky Play in Early Childhood Education
- Scale and Sustainability of Education Innovation and Impro...
- Scaling Up Research-based Educational Practices
- School Accreditation
- School Choice
- School Culture
- School District Budgeting and Financial Management in the ...
- School Improvement through Inclusive Education
- School Reform
- Schools, Private and Independent
- School-Wide Positive Behavior Support
- Science Education
- Secondary to Postsecondary Transition Issues
- Self-Regulated Learning
- Self-Study of Teacher Education Practices
- Service-Learning
- Severe Disabilities
- Single Salary Schedule
- Single-sex Education
- Single-Subject Research Design
- Social Context of Education
- Social Justice
- Social Network Analysis
- Social Pedagogy
- Social Science and Education Research
- Social Studies Education
- Sociology of Education
- Standards-Based Education
- Statistical Assumptions
- Student Access, Equity, and Diversity in Higher Education
- Student Assignment Policy
- Student Engagement in Tertiary Education
- Student Learning, Development, Engagement, and Motivation ...
- Student Participation
- Student Voice in Teacher Development
- Sustainability Education in Early Childhood Education
- Sustainability in Early Childhood Education
- Sustainability in Higher Education
- Teacher Beliefs and Epistemologies
- Teacher Collaboration in School Improvement
- Teacher Evaluation and Teacher Effectiveness
- Teacher Preparation
- Teacher Training and Development
- Teacher Unions and Associations
- Teacher-Student Relationships
- Teaching Critical Thinking
- Technologies, Teaching, and Learning in Higher Education
- Technology Education in Early Childhood
- Technology, Educational
- Technology-based Assessment
- The Bologna Process
- The Regulation of Standards in Higher Education
- Theories of Educational Leadership
- Three Conceptions of Literacy: Media, Narrative, and Gamin...
- Tracking and Detracking
- Traditions of Quality Improvement in Education
- Transformative Learning
- Transitions in Early Childhood Education
- Tribally Controlled Colleges and Universities in the Unite...
- Understanding the Psycho-Social Dimensions of Schools and ...
- University Faculty Roles and Responsibilities in the Unite...
- Using Ethnography in Educational Research
- Value of Higher Education for Students and Other Stakehold...
- Virtual Learning Environments
- Vocational and Technical Education
- Wellness and Well-Being in Education
- Women's and Gender Studies
- Young Children and Spirituality
- Young Children's Learning Dispositions
- Young Children's Working Theories
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
Powered by:
- [66.249.64.20|81.177.182.174]
- 81.177.182.174
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Language Acquisition
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Media
- Music and Culture
- Music and Religion
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Society
- Law and Politics
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Medical Ethics
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Games
- Computer Security
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Ethics
- Business History
- Business Strategy
- Business and Technology
- Business and Government
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic History
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Systems
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Theory
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Politics and Law
- Public Policy
- Public Administration
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous chapter
- Next chapter >

29 Qualitative Data Analysis Strategies
Johnny Saldaña, School of Theatre and Film, Arizona State University
- Published: 02 September 2020
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
This chapter provides an overview of selected qualitative data analysis strategies with a particular focus on codes and coding. Preparatory strategies for a qualitative research study and data management are first outlined. Six coding methods are then profiled using comparable interview data: process coding, in vivo coding, descriptive coding, values coding, dramaturgical coding, and versus coding. Strategies for constructing themes and assertions from the data follow. Analytic memo writing is woven throughout as a method for generating additional analytic insight. Next, display and arts-based strategies are provided, followed by recommended qualitative data analytic software programs and a discussion on verifying the researcher’s analytic findings.
Qualitative Data Analysis Strategies
Anthropologist Clifford Geertz ( 1983 ) charmingly mused, “Life is just a bowl of strategies” (p. 25). Strategy , as I use it here, refers to a carefully considered plan or method to achieve a particular goal. The goal in this case is to develop a write-up of your analytic work with the qualitative data you have been given and collected as part of a study. The plans and methods you might employ to achieve that goal are what this article profiles.
Some may perceive strategy as an inappropriate, if not manipulative, word, suggesting formulaic or regimented approaches to inquiry. I assure you that is not my intent. My use of strategy is dramaturgical in nature: Strategies are actions that characters in plays take to overcome obstacles to achieve their objectives. Actors portraying these characters rely on action verbs to generate belief within themselves and to motivate them as they interpret their lines and move appropriately on stage.
What I offer is a qualitative researcher’s array of actions from which to draw to overcome the obstacles to thinking to achieve an analysis of your data. But unlike the prescripted text of a play in which the obstacles, strategies, and outcomes have been predetermined by the playwright, your work must be improvisational—acting, reacting, and interacting with data on a moment-by-moment basis to determine what obstacles stand in your way and thus what strategies you should take to reach your goals.
Another intriguing quote to keep in mind comes from research methodologist Robert E. Stake ( 1995 ), who posited, “Good research is not about good methods as much as it is about good thinking” (p. 19). In other words, strategies can take you only so far. You can have a box full of tools, but if you do not know how to use them well or use them creatively, the collection seems rather purposeless. One of the best ways we learn is by doing . So, pick up one or more of these strategies (in the form of verbs) and take analytic action with your data. Also keep in mind that these are discussed in the order in which they may typically occur, although humans think cyclically, iteratively, and reverberatively, and each research project has its unique contexts and needs. Be prepared for your mind to jump purposefully and/or idiosyncratically from one strategy to another throughout the study.
Qualitative Data Analysis Strategy: To Foresee
To foresee in qualitative data analysis (QDA) is to reflect beforehand on what forms of data you will most likely need and collect, which thus informs what types of data analytic strategies you anticipate using. Analysis, in a way, begins even before you collect data (Saldaña & Omasta, 2018 ). As you design your research study in your mind and on a text editing page, one strategy is to consider what types of data you may need to help inform and answer your central and related research questions. Interview transcripts, participant observation field notes, documents, artifacts, photographs, video recordings, and so on are not only forms of data but also foundations for how you may plan to analyze them. A participant interview, for example, suggests that you will transcribe all or relevant portions of the recording and use both the transcription and the recording itself as sources for data analysis. Any analytic memos (discussed later) you make about your impressions of the interview also become data to analyze. Even the computing software you plan to employ will be relevant to data analysis because it may help or hinder your efforts.
As your research design formulates, compose one to two paragraphs that outline how your QDA may proceed. This will necessitate that you have some background knowledge of the vast array of methods available to you. Thus, surveying the literature is vital preparatory work.
Qualitative Data Analysis Strategy: To Survey
To survey in QDA is to look for and consider the applicability of the QDA literature in your field that may provide useful guidance for your forthcoming data analytic work. General sources in QDA will provide a good starting point for acquainting you with the data analysis strategies available for the variety of methodologies or genres in qualitative inquiry (e.g., ethnography, phenomenology, case study, arts-based research, mixed methods). One of the most accessible (and humorous) is Galman’s ( 2013 ) The Good, the Bad, and the Data , and one of the most richly detailed is Frederick J. Wertz et al.’s ( 2011 ) Five Ways of Doing Qualitative Analysis . The author’s core texts for this chapter come from The Coding Manual for Qualitative Researchers (Saldaña, 2016 ) and Qualitative Research: Analyzing Life (Saldaña & Omasta, 2018 ).
If your study’s methodology or approach is grounded theory, for example, then a survey of methods works by authors such as Barney G. Glaser, Anselm L. Strauss, Juliet Corbin, and, in particular, the prolific Kathy Charmaz ( 2014 ) may be expected. But there has been a recent outpouring of additional book publications in grounded theory by Birks and Mills ( 2015 ), Bryant ( 2017 ), Bryant and Charmaz ( 2019 ), and Stern and Porr ( 2011 ), plus the legacy of thousands of articles and chapters across many disciplines that have addressed grounded theory in their studies.
Fields such as education, psychology, social work, healthcare, and others also have their own QDA methods literature in the form of texts and journals, as well as international conferences and workshops for members of the profession. It is important to have had some university coursework and/or mentorship in qualitative research to suitably prepare you for the intricacies of QDA, and you must acknowledge that the emergent nature of qualitative inquiry may require you to adopt analysis strategies that differ from what you originally planned.
Qualitative Data Analysis Strategy: To Collect
To collect in QDA is to receive the data given to you by participants and those data you actively gather to inform your study. Qualitative data analysis is concurrent with data collection and management. As interviews are transcribed, field notes are fleshed out, and documents are filed, the researcher uses opportunities to carefully read the corpus and make preliminary notations directly on the data documents by highlighting, bolding, italicizing, or noting in some way any particularly interesting or salient portions. As these data are initially reviewed, the researcher also composes supplemental analytic memos that include first impressions, reminders for follow-up, preliminary connections, and other thinking matters about the phenomena at work.
Some of the most common fieldwork tools you might use to collect data are notepads, pens and pencils; file folders for hard-copy documents; a laptop, tablet, or desktop with text editing software (Microsoft Word and Excel are most useful) and Internet access; and a digital camera and voice recorder (functions available on many electronic devices such as smartphones). Some fieldworkers may even employ a digital video camera to record social action, as long as participant permissions have been secured. But everything originates from the researcher. Your senses are immersed in the cultural milieu you study, taking in and holding onto relevant details, or significant trivia , as I call them. You become a human camera, zooming out to capture the broad landscape of your field site one day and then zooming in on a particularly interesting individual or phenomenon the next. Your analysis is only as good as the data you collect.
Fieldwork can be an overwhelming experience because so many details of social life are happening in front of you. Take a holistic approach to your entrée, but as you become more familiar with the setting and participants, actively focus on things that relate to your research topic and questions. Keep yourself open to the intriguing, surprising, and disturbing (Sunstein & Chiseri-Strater, 2012 , p. 115), because these facets enrich your study by making you aware of the unexpected.
Qualitative Data Analysis Strategy: To Feel
To feel in QDA is to gain deep emotional insight into the social worlds you study and what it means to be human. Virtually everything we do has an accompanying emotion(s), and feelings are both reactions and stimuli for action. Others’ emotions clue you to their motives, values, attitudes, beliefs, worldviews, identities, and other subjective perceptions and interpretations. Acknowledge that emotional detachment is not possible in field research. Attunement to the emotional experiences of your participants plus sympathetic and empathetic responses to the actions around you are necessary in qualitative endeavors. Your own emotional responses during fieldwork are also data because they document the tacit and visceral. It is important during such analytic reflection to assess why your emotional reactions were as they were. But it is equally important not to let emotions alone steer the course of your study. A proper balance must be found between feelings and facts.

Qualitative Data Analysis Strategy: To Organize
To organize in QDA is to maintain an orderly repository of data for easy access and analysis. Even in the smallest of qualitative studies, a large amount of data will be collected across time. Prepare both a hard drive and hard-copy folders for digital data and paperwork, and back up all materials for security from loss. I recommend that each data unit (e.g., one interview transcript, one document, one day’s worth of field notes) have its own file, with subfolders specifying the data forms and research study logistics (e.g., interviews, field notes, documents, institutional review board correspondence, calendar).
For small-scale qualitative studies, I have found it quite useful to maintain one large master file with all participant and field site data copied and combined with the literature review and accompanying researcher analytic memos. This master file is used to cut and paste related passages together, deleting what seems unnecessary as the study proceeds and eventually transforming the document into the final report itself. Cosmetic devices such as font style, font size, rich text (italicizing, bolding, underlining, etc.), and color can help you distinguish between different data forms and highlight significant passages. For example, descriptive, narrative passages of field notes are logged in regular font. “Quotations, things spoken by participants, are logged in bold font.” Observer’s comments, such as the researcher’s subjective impressions or analytic jottings, are set in italics.
Qualitative Data Analysis Strategy: To Jot
To jot in QDA is to write occasional, brief notes about your thinking or reminders for follow-up. A jot is a phrase or brief sentence that will fit on a standard-size sticky note. As data are brought and documented together, take some initial time to review their contents and jot some notes about preliminary patterns, participant quotes that seem vivid, anomalies in the data, and so forth.
As you work on a project, keep something to write with or to voice record with you at all times to capture your fleeting thoughts. You will most likely find yourself thinking about your research when you are not working exclusively on the project, and a “mental jot” may occur to you as you ruminate on logistical or analytic matters. Document the thought in some way for later retrieval and elaboration as an analytic memo.
Qualitative Data Analysis Strategy: To Prioritize
To prioritize in QDA is to determine which data are most significant in your corpus and which tasks are most necessary. During fieldwork, massive amounts of data in various forms may be collected, and your mind can be easily overwhelmed by the magnitude of the quantity, its richness, and its management. Decisions will need to be made about the most pertinent data because they help answer your research questions or emerge as salient pieces of evidence. As a sweeping generalization, approximately one half to two thirds of what you collect may become unnecessary as you proceed toward the more formal stages of QDA.
To prioritize in QDA is also to determine what matters most in your assembly of codes, categories, patterns, themes, assertions, propositions, and concepts. Return to your research purpose and questions to keep you framed for what the focus should be.
Qualitative Data Analysis Strategy: To Analyze
To analyze in QDA is to observe and discern patterns within data and to construct meanings that seem to capture their essences and essentials. Just as there are a variety of genres, elements, and styles of qualitative research, so too are there a variety of methods available for QDA. Analytic choices are most often based on what methods will harmonize with your genre selection and conceptual framework, what will generate the most sufficient answers to your research questions, and what will best represent and present the project’s findings.
Analysis can range from the factual to the conceptual to the interpretive. Analysis can also range from a straightforward descriptive account to an emergently constructed grounded theory to an evocatively composed short story. A qualitative research project’s outcomes may range from rigorously achieved, insightful answers to open-ended, evocative questions; from rich descriptive detail to a bullet-point list of themes; and from third-person, objective reportage to first-person, emotion-laden poetry. Just as there are multiple destinations in qualitative research, there are multiple pathways and journeys along the way.
Analysis is accelerated as you take cognitive ownership of your data. By reading and rereading the corpus, you gain intimate familiarity with its contents and begin to notice significant details as well as make new connections and insights about their meanings. Patterns, categories, themes, and their interrelationships become more evident the more you know the subtleties of the database.
Since qualitative research’s design, fieldwork, and data collection are most often provisional, emergent, and evolutionary processes, you reflect on and analyze the data as you gather them and proceed through the project. If preplanned methods are not working, you change them to secure the data you need. There is generally a postfieldwork period when continued reflection and more systematic data analysis occur, concurrent with or followed by additional data collection, if needed, and the more formal write-up of the study, which is in itself an analytic act. Through field note writing, interview transcribing, analytic memo writing, and other documentation processes, you gain cognitive ownership of your data; and the intuitive, tacit, synthesizing capabilities of your brain begin sensing patterns, making connections, and seeing the bigger picture. The purpose and outcome of data analysis is to reveal to others through fresh insights what we have observed and discovered about the human condition. Fortunately, there are heuristics for reorganizing and reflecting on your qualitative data to help you achieve that goal.
Qualitative Data Analysis Strategy: To Pattern
To pattern in QDA is to detect similarities within and regularities among the data you have collected. The natural world is filled with patterns because we, as humans, have constructed them as such. Stars in the night sky are not just a random assembly; our ancestors pieced them together to form constellations like the Big Dipper. A collection of flowers growing wild in a field has a pattern, as does an individual flower’s patterns of leaves and petals. Look at the physical objects humans have created and notice how pattern oriented we are in our construction, organization, and decoration. Look around you in your environment and notice how many patterns are evident on your clothing, in a room, and on most objects themselves. Even our sometimes mundane daily and long-term human actions are reproduced patterns in the form of routines, rituals, rules, roles, and relationships (Saldaña & Omasta, 2018 ).
This human propensity for pattern-making follows us into QDA. From the vast array of interview transcripts, field notes, documents, and other forms of data, there is this instinctive, hardwired need to bring order to the collection—not just to reorganize it but to look for and construct patterns out of it. The discernment of patterns is one of the first steps in the data analytic process, and the methods described next are recommended ways to construct them.
Qualitative Data Analysis Strategy: To Code
To code in QDA is to assign a truncated, symbolic meaning to each datum for purposes of qualitative analysis—primarily patterning and categorizing. Coding is a heuristic—a method of discovery—to the meanings of individual sections of data. These codes function as a way of patterning, classifying, and later reorganizing them into emergent categories for further analysis. Different types of codes exist for different types of research genres and qualitative data analytic approaches, but this chapter will focus on only a few selected methods. First, a code can be defined as follows:
A code in qualitative data analysis is most often a word or short phrase that symbolically assigns a summative, salient, essence-capturing, and/or evocative attribute for a portion of language-based or visual data. The data can consist of interview transcripts, participant observation field notes, journals, documents, open-ended survey responses, drawings, artifacts, photographs, video, Internet sites, e-mail correspondence, academic and fictional literature, and so on. The portion of data coded … can range in magnitude from a single word to a full paragraph, an entire page of text or a stream of moving images.… Just as a title represents and captures a book or film or poem’s primary content and essence, so does a code represent and capture a datum’s primary content and essence. (Saldaña, 2016 , p. 4)
One helpful precoding task is to divide or parse long selections of field note or interview transcript data into shorter stanzas . Stanza division unitizes or “chunks” the corpus into more manageable paragraph-like units for coding assignments and analysis. The transcript sample that follows illustrates one possible way of inserting line breaks between self-standing passages of interview text for easier readability.
Process Coding
As a first coding example, the following interview excerpt about an employed, single, lower middle-class adult male’s spending habits during a difficult economic period in the United States is coded in the right-hand margin in capital letters. The superscript numbers match the beginning of the datum unit with its corresponding code. This method is called process coding (Charmaz, 2014 ), and it uses gerunds (“-ing” words) exclusively to represent action suggested by the data. Processes can consist of observable human actions (e.g., BUYING BARGAINS), mental or internal processes (e.g., THINKING TWICE), and more conceptual ideas (e.g., APPRECIATING WHAT YOU’VE GOT). Notice that the interviewer’s (I) portions are not coded, just the participant’s (P). A code is applied each time the subtopic of the interview shifts—even within a stanza—and the same codes can (and should) be used more than once if the subtopics are similar. The central research question driving this qualitative study is, “In what ways are middle-class Americans influenced and affected by an economic recession?”
Different researchers analyzing this same piece of data may develop completely different codes, depending on their personal lenses, filters, and angles. The previous codes are only one person’s interpretation of what is happening in the data, not a definitive list. The process codes have transformed the raw data units into new symbolic representations for analysis. A listing of the codes applied to this interview transcript, in the order they appear, reads:
BUYING BARGAINS
QUESTIONING A PURCHASE
THINKING TWICE
STOCKING UP
REFUSING SACRIFICE
PRIORITIZING
FINDING ALTERNATIVES
LIVING CHEAPLY
NOTICING CHANGES
STAYING INFORMED
MAINTAINING HEALTH
PICKING UP THE TAB
APPRECIATING WHAT YOU’VE GOT
Coding the data is the first step in this approach to QDA, and categorization is just one of the next possible steps.
Qualitative Data Analysis Strategy: To Categorize
To categorize in QDA is to cluster similar or comparable codes into groups for pattern construction and further analysis. Humans categorize things in innumerable ways. Think of an average apartment or house’s layout. The rooms of a dwelling have been constructed or categorized by their builders and occupants according to function. A kitchen is designated as an area to store and prepare food and to store the cooking and dining materials, such as pots, pans, and utensils. A bedroom is designated for sleeping, a closet for clothing storage, a bathroom for bodily functions and hygiene, and so on. Each room is like a category in which related and relevant patterns of human action occur. There are exceptions now and then, such as eating breakfast in bed rather than in a dining area or living in a small studio apartment in which most possessions are contained within one large room (but nonetheless are most often organized and clustered into subcategories according to function and optimal use of space).
The point is that the patterns of social action we designate into categories during QDA are not perfectly bounded. Category construction is our best attempt to cluster the most seemingly alike things into the most seemingly appropriate groups. Categorizing is reorganizing and reordering the vast array of data from a study because it is from these smaller, larger, and meaning-rich units that we can better grasp the particular features of each one and the categories’ possible interrelationships with one another.
One analytic strategy with a list of codes is to classify them into similar clusters. The same codes share the same category, but it is also possible that a single code can merit its own group if you feel it is unique enough. After the codes have been classified, a category label is applied to each grouping. Sometimes a code can also double as a category name if you feel it best summarizes the totality of the cluster. Like coding, categorizing is an interpretive act, because there can be different ways of separating and collecting codes that seem to belong together. The cut-and-paste functions of text editing software are most useful for exploring which codes share something in common.
Below is my categorization of the 15 codes generated from the interview transcript presented earlier. Like the gerunds for process codes, the categories have also been labeled as “-ing” words to connote action. And there was no particular reason why 15 codes resulted in three categories—there could have been less or even more, but this is how the array came together after my reflections on which codes seemed to belong together. The category labels are ways of answering why they belong together. For at-a-glance differentiation, I place codes in CAPITAL LETTERS and categories in upper- and lowercase Bold Font :
Category 1: Thinking Strategically
Category 2: Spending Strategically
Category 3: Living Strategically
Notice that the three category labels share a common word: strategically . Where did this word come from? It came from analytic reflection on the original data, the codes, and the process of categorizing the codes and generating their category labels. It was the analyst’s choice based on the interpretation of what primary action was happening. Your categories generated from your coded data do not need to share a common word or phrase, but I find that this technique, when appropriate, helps build a sense of unity to the initial analytic scheme.
The three categories— Thinking Strategically, Spending Strategically , and Living Strategically —are then reflected on for how they might interact and interplay. This is where the next major facet of data analysis, analytic memos, enters the scheme. But a necessary section on the basic principles of interrelationship and analytic reasoning must precede that discussion.
Qualitative Data Analysis Strategy: To Interrelate
To interrelate in QDA is to propose connections within, between, and among the constituent elements of analyzed data. One task of QDA is to explore the ways our patterns and categories interact and interplay. I use these terms to suggest the qualitative equivalent of statistical correlation, but interaction and interplay are much more than a simple relationship. They imply interrelationship . Interaction refers to reverberative connections—for example, how one or more categories might influence and affect the others, how categories operate concurrently, or whether there is some kind of domino effect to them. Interplay refers to the structural and processual nature of categories—for example, whether some type of sequential order, hierarchy, or taxonomy exists; whether any overlaps occur; whether there is superordinate and subordinate arrangement; and what types of organizational frameworks or networks might exist among them. The positivist construct of cause and effect becomes influences and affects in QDA.
There can even be patterns of patterns and categories of categories if your mind thinks conceptually and abstractly enough. Our minds can intricately connect multiple phenomena, but only if the data and their analyses support the constructions. We can speculate about interaction and interplay all we want, but it is only through a more systematic investigation of the data—in other words, good thinking—that we can plausibly establish any possible interrelationships.
Qualitative Data Analysis Strategy: To Reason
To reason in QDA is to think in ways that lead to summative findings, causal probabilities, and evaluative conclusions. Unlike quantitative research, with its statistical formulas and established hypothesis-testing protocols, qualitative research has no standardized methods of data analysis. Rest assured, there are recommended guidelines from the field’s scholars and a legacy of analysis strategies from which to draw. But the primary heuristics (or methods of discovery) you apply during a study are retroductive, inductive, substructive, abductive , and deductive reasoning.
Retroduction is historic reconstruction, working backward to figure out how the current conditions came to exist. Induction is what we experientially explore and infer to be transferable from the particular to the general, based on an examination of the evidence and an accumulation of knowledge. Substruction takes things apart to more carefully examine the constituent elements of the whole. Abduction is surmising from a range of possibilities that which is most likely, those explanatory hunches of plausibility based on clues. Deduction is what we generally draw and conclude from established facts and evidence.
It is not always necessary to know the names of these five ways of reasoning as you proceed through analysis. In fact, you will more than likely reverberate quickly from one to another depending on the task at hand. But what is important to remember about reasoning is:
to examine the evidence carefully and make reasonable inferences;
to base your conclusions primarily on the participants’ experiences, not just your own;
not to take the obvious for granted, because sometimes the expected will not happen;
your hunches can be right and, at other times, quite wrong; and
to logically yet imaginatively think about what is going on and how it all comes together.
Futurists and inventors propose three questions when they think about creating new visions for the world: What is possible (induction)? What is plausible (abduction)? What is preferable (deduction)? These same three questions might be posed as you proceed through QDA and particularly through analytic memo writing, which is substructive and retroductive reflection on your analytic work thus far.
Qualitative Data Analysis Strategy: To Memo
To memo in QDA is to reflect in writing on the nuances, inferences, meanings, and transfer of coded and categorized data plus your analytic processes. Like field note writing, perspectives vary among practitioners as to the methods for documenting the researcher’s analytic insights and subjective experiences. Some advise that such reflections should be included in field notes as relevant to the data. Others advise that a separate researcher’s journal should be maintained for recording these impressions. And still others advise that these thoughts be documented as separate analytic memos. I prescribe the latter as a method because it is generated by and directly connected to the data themselves.
An analytic memo is a “think piece” of reflective free writing, a narrative that sets in words your interpretations of the data. Coding and categorizing are heuristics to detect some of the possible patterns and interrelationships at work within the corpus, and an analytic memo further articulates your retroductive, inductive, substructive, abductive, and deductive thinking processes on what things may mean. Though the metaphor is a bit flawed and limiting, think of codes and their consequent categories as separate jigsaw puzzle pieces and their integration into an analytic memo as the trial assembly of the complete picture.
What follows is an example of an analytic memo based on the earlier process coded and categorized interview transcript. It is intended not as the final write-up for a publication, but as an open-ended reflection on the phenomena and processes suggested by the data and their analysis thus far. As the study proceeds, however, initial and substantive analytic memos can be revisited and revised for eventual integration into the final report. Note how the memo is dated and given a title for future and further categorization, how participant quotes are occasionally included for evidentiary support, and how the category names are bolded and the codes kept in capital letters to show how they integrate or weave into the thinking:
April 14, 2017 EMERGENT CATEGORIES: A STRATEGIC AMALGAM There’s a popular saying: “Smart is the new rich.” This participant is Thinking Strategically about his spending through such tactics as THINKING TWICE and QUESTIONING A PURCHASE before he decides to invest in a product. There’s a heightened awareness of both immediate trends and forthcoming economic bad news that positively affects his Spending Strategically . However, he seems unaware that there are even more ways of LIVING CHEAPLY by FINDING ALTERNATIVES. He dines at all-you-can-eat restaurants as a way of STOCKING UP on meals, but doesn’t state that he could bring lunch from home to work, possibly saving even more money. One of his “bad habits” is cigarettes, which he refuses to give up; but he doesn’t seem to realize that by quitting smoking he could save even more money, not to mention possible health care costs. He balks at the idea of paying $2.00 for a soft drink, but doesn’t mind paying $6.00–$7.00 for a pack of cigarettes. Penny-wise and pound-foolish. Addictions skew priorities. Living Strategically , for this participant during “scary times,” appears to be a combination of PRIORITIZING those things which cannot be helped, such as pet care and personal dental care; REFUSING SACRIFICE for maintaining personal creature-comforts; and FINDING ALTERNATIVES to high costs and excessive spending. Living Strategically is an amalgam of thinking and action-oriented strategies.
There are several recommended topics for analytic memo writing throughout the qualitative study. Memos are opportunities to reflect on and write about:
A descriptive summary of the data;
How the researcher personally relates to the participants and/or the phenomenon;
The participants’ actions, reactions, and interactions;
The participants’ routines, rituals, rules, roles, and relationships;
What is surprising, intriguing, or disturbing (Sunstein & Chiseri-Strater, 2012 , p. 115);
Code choices and their operational definitions;
Emergent patterns, categories, themes, concepts, assertions, and propositions;
The possible networks and processes (links, connections, overlaps, flows) among the codes, patterns, categories, themes, concepts, assertions, and propositions;
An emergent or related existent theory;
Any problems with the study;
Any personal or ethical dilemmas with the study;
Future directions for the study;
The analytic memos generated thus far (i.e., metamemos);
Tentative answers to the study’s research questions; and
The final report for the study. (adapted from Saldaña & Omasta, 2018 , p. 54)
Since writing is analysis, analytic memos expand on the inferential meanings of the truncated codes, categories, and patterns as a transitional stage into a more coherent narrative with hopefully rich social insight.
Qualitative Data Analysis Strategy: To Code—A Different Way
The first example of coding illustrated process coding, a way of exploring general social action among humans. But sometimes a researcher works with an individual case study in which the language is unique or with someone the researcher wishes to honor by maintaining the authenticity of his or her speech in the analysis. These reasons suggest that a more participant-centered form of coding may be more appropriate.
In Vivo Coding
A second frequently applied method of coding is called in vivo coding. The root meaning of in vivo is “in that which is alive”; it refers to a code based on the actual language used by the participant (Strauss, 1987 ). The words or phrases in the data record you select as codes are those that seem to stand out as significant or summative of what is being said.
Using the same transcript of the male participant living in difficult economic times, in vivo codes are listed in the right-hand column. I recommend that in vivo codes be placed in quotation marks as a way of designating that the code is extracted directly from the data record. Note that instead of 15 codes generated from process coding, the total number of in vivo codes is 30. This is not to suggest that there should be specific numbers or ranges of codes used for particular methods. In vivo codes, however, tend to be applied more frequently to data. Again, the interviewer’s questions and prompts are not coded, just the participant’s responses:
The 30 in vivo codes are then extracted from the transcript and could be listed in the order they appear, but this time they are placed in alphabetical order as a heuristic to prepare them for analytic action and reflection:
“ALL-YOU-CAN-EAT”
“ANOTHER DING IN MY WALLET”
“BAD HABITS”
“CHEAP AND FILLING”
“COUPLE OF THOUSAND”
“DON’T REALLY NEED”
“HAVEN’T CHANGED MY HABITS”
“HIGH MAINTENANCE”
“INSURANCE IS JUST WORTHLESS”
“IT ALL ADDS UP”
“LIVED KIND OF CHEAP”
“NOT A BIG SPENDER”
“NOT AS BAD OFF”
“NOT PUTTING AS MUCH INTO SAVINGS”
“PICK UP THE TAB”
“SCARY TIMES”
“SKYROCKETED”
“SPENDING MORE”
“THE LITTLE THINGS”
“THINK TWICE”
“TWO-FOR-ONE”
Even though no systematic categorization has been conducted with the codes thus far, an analytic memo of first impressions can still be composed:
March 19, 2017 CODE CHOICES: THE EVERYDAY LANGUAGE OF ECONOMICS After eyeballing the in vivo codes list, I noticed that variants of “CHEAP” appear most often. I recall a running joke between me and a friend of mine when we were shopping for sales. We’d say, “We’re not ‘cheap,’ we’re frugal .” There’s no formal economic or business language in this transcript—no terms such as “recession” or “downsizing”—just the everyday language of one person trying to cope during “SCARY TIMES” with “ANOTHER DING IN MY WALLET.” The participant notes that he’s always “LIVED KIND OF CHEAP” and is “NOT A BIG SPENDER” and, due to his employment, “NOT AS BAD OFF” as others in the country. Yet even with his middle class status, he’s still feeling the monetary pinch, dining at inexpensive “ALL-YOU-CAN-EAT” restaurants and worried about the rising price of peanut butter, observing that he’s “NOT PUTTING AS MUCH INTO SAVINGS” as he used to. Of all the codes, “ANOTHER DING IN MY WALLET” stands out to me, particularly because on the audio recording he sounded bitter and frustrated. It seems that he’s so concerned about “THE LITTLE THINGS” because of high veterinary and dental charges. The only way to cope with a “COUPLE OF THOUSAND” dollars worth of medical expenses is to find ways of trimming the excess in everyday facets of living: “IT ALL ADDS UP.”
Like process coding, in vivo codes could be clustered into similar categories, but another simple data analytic strategy is also possible.
Qualitative Data Analysis Strategy: To Outline
To outline in QDA is to hierarchically, processually, and/or temporally assemble such things as codes, categories, themes, assertions, propositions, and concepts into a coherent, text-based display. Traditional outlining formats and content provide not only templates for writing a report but also templates for analytic organization. This principle can be found in several computer-assisted qualitative data analysis software (CAQDAS) programs through their use of such functions as “hierarchies,” “trees,” and “nodes,” for example. Basic outlining is simply a way of arranging primary, secondary, and subsecondary items into a patterned display. For example, an organized listing of things in a home might consist of the following:
Large appliances
Refrigerator
Stove-top oven
Microwave oven
Small appliances
Coffee maker
Dining room
In QDA, outlining may include descriptive nouns or topics but, depending on the study, it may also involve processes or phenomena in extended passages, such as in vivo codes or themes.
The complexity of what we learn in the field can be overwhelming, and outlining is a way of organizing and ordering that complexity so that it does not become complicated. The cut-and-paste and tab functions of a text editing page enable you to arrange and rearrange the salient items from your preliminary coded analytic work into a more streamlined flow. By no means do I suggest that the intricate messiness of life can always be organized into neatly formatted arrangements, but outlining is an analytic act that stimulates deep reflection on both the interconnectedness and the interrelationships of what we study. As an example, here are the 30 in vivo codes generated from the initial transcript analysis, arranged in such a way as to construct five major categories:
Now that the codes have been rearranged into an outline format, an analytic memo is composed to expand on the rationale and constructed meanings in progress:
March 19, 2017 NETWORKS: EMERGENT CATEGORIES The five major categories I constructed from the in vivo codes are: “SCARY TIMES,” “PRIORTY,” “ANOTHER DING IN MY WALLET,” “THE LITTLE THINGS,” and “LIVED KIND OF CHEAP.” One of the things that hit me today was that the reason he may be pinching pennies on smaller purchases is that he cannot control the larger ones he has to deal with. Perhaps the only way we can cope with or seem to have some sense of agency over major expenses is to cut back on the smaller ones that we can control. $1,000 for a dental bill? Skip lunch for a few days a week. Insulin medication to buy for a pet? Don’t buy a soft drink from a vending machine. Using this reasoning, let me try to interrelate and weave the categories together as they relate to this particular participant: During these scary economic times, he prioritizes his spending because there seems to be just one ding after another to his wallet. A general lifestyle of living cheaply and keeping an eye out for how to save money on the little things compensates for those major expenses beyond his control.
Qualitative Data Analysis Strategy: To Code—In Even More Ways
The process and in vivo coding examples thus far have demonstrated only two specific methods of 33 documented approaches (Saldaña, 2016 ). Which one(s) you choose for your analysis depends on such factors as your conceptual framework, the genre of qualitative research for your project, the types of data you collect, and so on. The following sections present four additional approaches available for coding qualitative data that you may find useful as starting points.
Descriptive Coding
Descriptive codes are primarily nouns that simply summarize the topic of a datum. This coding approach is particularly useful when you have different types of data gathered for one study, such as interview transcripts, field notes, open-ended survey responses, documents, and visual materials such as photographs. Descriptive codes not only help categorize but also index the data corpus’s basic contents for further analytic work. An example of an interview portion coded descriptively, taken from the participant living in tough economic times, follows to illustrate how the same data can be coded in multiple ways:
For initial analysis, descriptive codes are clustered into similar categories to detect such patterns as frequency (i.e., categories with the largest number of codes) and interrelationship (i.e., categories that seem to connect in some way). Keep in mind that descriptive coding should be used sparingly with interview transcript data because other coding methods will reveal richer participant dynamics.
Values Coding
Values coding identifies the values, attitudes, and beliefs of a participant, as shared by the individual and/or interpreted by the analyst. This coding method infers the “heart and mind” of an individual or group’s worldview as to what is important, perceived as true, maintained as opinion, and felt strongly. The three constructs are coded separately but are part of a complex interconnected system.
Briefly, a value (V) is what we attribute as important, be it a person, thing, or idea. An attitude (A) is the evaluative way we think and feel about ourselves, others, things, or ideas. A belief (B) is what we think and feel as true or necessary, formed from our “personal knowledge, experiences, opinions, prejudices, morals, and other interpretive perceptions of the social world” (Saldaña, 2016 , p. 132). Values coding explores intrapersonal, interpersonal, and cultural constructs, or ethos . It is an admittedly slippery task to code this way because it is sometimes difficult to discern what is a value, attitude, or belief since they are intricately interrelated. But the depth you can potentially obtain is rich. An example of values coding follows:
For analysis, categorize the codes for each of the three different constructs together (i.e., all values in one group, attitudes in a second group, and beliefs in a third group). Analytic memo writing about the patterns and possible interrelationships may reveal a more detailed and intricate worldview of the participant.
Dramaturgical Coding
Dramaturgical coding perceives life as performance and its participants as characters in a social drama. Codes are assigned to the data (i.e., a “play script”) that analyze the characters in action, reaction, and interaction. Dramaturgical coding of participants examines their objectives (OBJ) or wants, needs, and motives; the conflicts (CON) or obstacles they face as they try to achieve their objectives; the tactics (TAC) or strategies they employ to reach their objectives; their attitudes (ATT) toward others and their given circumstances; the particular emotions (EMO) they experience throughout; and their subtexts (SUB), or underlying and unspoken thoughts. The following is an example of dramaturgically coded data:
Not included in this particular interview excerpt are the emotions the participant may have experienced or talked about. His later line, “that’s another ding in my wallet,” would have been coded EMO: BITTER. A reader may not have inferred that specific emotion from seeing the line in print. But the interviewer, present during the event and listening carefully to the audio recording during transcription, noted that feeling in his tone of voice.
For analysis, group similar codes together (e.g., all objectives in one group, all conflicts in another group, all tactics in a third group) or string together chains of how participants deal with their circumstances to overcome their obstacles through tactics:
OBJ: SAVING MEAL MONEY → TAC: SKIPPING MEALS + COUPONS
Dramaturgical coding is particularly useful as preliminary work for narrative inquiry story development or arts-based research representations such as performance ethnography. The method explores how the individuals or groups manage problem solving in their daily lives.
Versus Coding
Versus (VS) coding identifies the conflicts, struggles, and power issues observed in social action, reaction, and interaction as an X VS Y code, such as MEN VS WOMEN, CONSERVATIVES VS LIBERALS, FAITH VS LOGIC, and so on. Conflicts are rarely this dichotomous; they are typically nuanced and much more complex. But humans tend to perceive these struggles with an US VS THEM mindset. The codes can range from the observable to the conceptual and can be applied to data that show humans in tension with others, themselves, or ideologies.
What follows are examples of versus codes applied to the case study participant’s descriptions of his major medical expenses:
As an initial analytic tactic, group the versus codes into one of three categories: the Stakeholders , their Perceptions and/or Actions , and the Issues at stake. Examine how the three interrelate and identify the central ideological conflict at work as an X VS Y category. Analytic memos and the final write-up can detail the nuances of the issues.
Remember that what has been profiled in this section is a broad brushstroke description of just a few basic coding processes, several of which can be compatibly mixed and matched within a single analysis (see Saldaña’s 2016 The Coding Manual for Qualitative Researchers for a complete discussion). Certainly with additional data, more in-depth analysis can occur, but coding is only one approach to extracting and constructing preliminary meanings from the data corpus. What now follows are additional methods for qualitative analysis.
Qualitative Data Analysis Strategy: To Theme
To theme in QDA is to construct summative, phenomenological meanings from data through extended passages of text. Unlike codes, which are most often single words or short phrases that symbolically represent a datum, themes are extended phrases or sentences that summarize the manifest (apparent) and latent (underlying) meanings of data (Auerbach & Silverstein, 2003 ; Boyatzis, 1998 ). Themes, intended to represent the essences and essentials of humans’ lived experiences, can also be categorized or listed in superordinate and subordinate outline formats as an analytic tactic.
Below is the interview transcript example used in the previous coding sections. (Hopefully you are not too fatigued at this point with the transcript, but it is important to know how inquiry with the same data set can be approached in several different ways.) During the investigation of the ways middle-class Americans are influenced and affected by an economic recession, the researcher noticed that participants’ stories exhibited facets of what he labeled economic intelligence , or EI (based on the formerly developed theories of Howard Gardner’s multiple intelligences and Daniel Goleman’s emotional intelligence). Notice how theming interprets what is happening through the use of two distinct phrases—ECONOMIC INTELLIGENCE IS (i.e., manifest or apparent meanings) and ECONOMIC INTELLIGENCE MEANS (i.e., latent or underlying meanings):
Unlike the 15 process codes and 30 in vivo codes in the previous examples, there are now 14 themes to work with. They could be listed in the order they appear, but one initial heuristic is to group them separately by “is” and “means” statements to detect any possible patterns (discussed later):
EI IS TAKING ADVANTAGE OF UNEXPECTED OPPORTUNITY
EI IS BUYING CHEAP
EI IS SAVING A FEW DOLLARS NOW AND THEN
EI IS SETTING PRIORITIES
EI IS FINDING CHEAPER FORMS OF ENTERTAINMENT
EI IS NOTICING PERSONAL AND NATIONAL ECONOMIC TRENDS
EI IS TAKING CARE OF ONE’S OWN HEALTH
EI MEANS THINKING BEFORE YOU ACT
EI MEANS SACRIFICE
EI MEANS KNOWING YOUR FLAWS
EI MEANS LIVING AN INEXPENSIVE LIFESTYLE
EI MEANS YOU CANNOT CONTROL EVERYTHING
EI MEANS KNOWING YOUR LUCK
There are several ways to categorize the themes as preparation for analytic memo writing. The first is to arrange them in outline format with superordinate and subordinate levels, based on how the themes seem to take organizational shape and structure. Simply cutting and pasting the themes in multiple arrangements on a text editing page eventually develops a sense of order to them. For example:
A second approach is to categorize the themes into similar clusters and to develop different category labels or theoretical constructs . A theoretical construct is an abstraction that transforms the central phenomenon’s themes into broader applications but can still use “is” and “means” as prompts to capture the bigger picture at work:
Theoretical Construct 1: EI Means Knowing the Unfortunate Present
Supporting Themes:
Theoretical Construct 2: EI Is Cultivating a Small Fortune
Theoretical Construct 3: EI Means a Fortunate Future
What follows is an analytic memo generated from the cut-and-paste arrangement of themes into “is” and “means” statements, into an outline, and into theoretical constructs:
March 19, 2017 EMERGENT THEMES: FORTUNE/FORTUNATELY/UNFORTUNATELY I first reorganized the themes by listing them in two groups: “is” and “means.” The “is” statements seemed to contain positive actions and constructive strategies for economic intelligence. The “means” statements held primarily a sense of caution and restriction with a touch of negativity thrown in. The first outline with two major themes, LIVING AN INEXPENSIVE LIFESTYLE and YOU CANNOT CONTROL EVERYTHING also had this same tone. This reminded me of the old children’s picture book, Fortunately/Unfortunately , and the themes of “fortune” as a motif for the three theoretical constructs came to mind. Knowing the Unfortunate Present means knowing what’s (most) important and what’s (mostly) uncontrollable in one’s personal economic life. Cultivating a Small Fortune consists of those small money-saving actions that, over time, become part of one’s lifestyle. A Fortunate Future consists of heightened awareness of trends and opportunities at micro and macro levels, with the understanding that health matters can idiosyncratically affect one’s fortune. These three constructs comprise this particular individual’s EI—economic intelligence.
Again, keep in mind that the examples for coding and theming were from one small interview transcript excerpt. The number of codes and their categorization would increase, given a longer interview and/or multiple interviews to analyze. But the same basic principles apply: codes and themes relegated into patterned and categorized forms are heuristics—stimuli for good thinking through the analytic memo-writing process on how everything plausibly interrelates. Methodologists vary in the number of recommended final categories that result from analysis, ranging anywhere from three to seven, with traditional grounded theorists prescribing one central or core category from coded work.
Qualitative Data Analysis Strategy: To Assert
To assert in QDA is to put forward statements that summarize particular fieldwork and analytic observations that the researcher believes credibly represent and transcend the experiences. Educational anthropologist Frederick Erickson ( 1986 ) wrote a significant and influential chapter on qualitative methods that outlined heuristics for assertion development . Assertions are declarative statements of summative synthesis, supported by confirming evidence from the data and revised when disconfirming evidence or discrepant cases require modification of the assertions. These summative statements are generated from an interpretive review of the data corpus and then supported and illustrated through narrative vignettes—reconstructed stories from field notes, interview transcripts, or other data sources that provide a vivid profile as part of the evidentiary warrant.
Coding or theming data can certainly precede assertion development as a way of gaining intimate familiarity with the data, but Erickson’s ( 1986 ) methods are a more admittedly intuitive yet systematic heuristic for analysis. Erickson promotes analytic induction and exploration of and inferences about the data, based on an examination of the evidence and an accumulation of knowledge. The goal is not to look for “proof” to support the assertions, but to look for plausibility of inference-laden observations about the local and particular social world under investigation.
Assertion development is the writing of general statements, plus subordinate yet related ones called subassertions and a major statement called a key assertion that represents the totality of the data. One also looks for key linkages between them, meaning that the key assertion links to its related assertions, which then link to their respective subassertions. Subassertions can include particulars about any discrepant related cases or specify components of their parent assertions.
Excerpts from the interview transcript of our case study will be used to illustrate assertion development at work. By now, you should be quite familiar with the contents, so I will proceed directly to the analytic example. First, there is a series of thematically related statements the participant makes:
“Buy one package of chicken, get the second one free. Now that was a bargain. And I got some.”
“With Sweet Tomatoes I get those coupons for a few bucks off for lunch, so that really helps.”
“I don’t go to movies anymore. I rent DVDs from Netflix or Redbox or watch movies online—so much cheaper than paying over ten or twelve bucks for a movie ticket.”
Assertions can be categorized into low-level and high-level inferences . Low-level inferences address and summarize what is happening within the particulars of the case or field site—the micro . High-level inferences extend beyond the particulars to speculate on what it means in the more general social scheme of things—the meso or macro . A reasonable low-level assertion about the three statements above collectively might read, The participant finds several small ways to save money during a difficult economic period . A high-level inference that transcends the case to the meso level might read, Selected businesses provide alternatives and opportunities to buy products and services at reduced rates during a recession to maintain consumer spending.
Assertions are instantiated (i.e., supported) by concrete instances of action or participant testimony, whose patterns lead to more general description outside the specific field site. The author’s interpretive commentary can be interspersed throughout the report, but the assertions should be supported with the evidentiary warrant . A few assertions and subassertions based on the case interview transcript might read as follows (and notice how high-level assertions serve as the paragraphs’ topic sentences):
Selected businesses provide alternatives and opportunities to buy products and services at reduced rates during a recession to maintain consumer spending. Restaurants, for example, need to find ways during difficult economic periods when potential customers may be opting to eat inexpensively at home rather than spending more money by dining out. Special offers can motivate cash-strapped clientele to patronize restaurants more frequently. An adult male dealing with such major expenses as underinsured dental care offers: “With Sweet Tomatoes I get those coupons for a few bucks off for lunch, so that really helps.” The film and video industries also seem to be suffering from a double-whammy during the current recession: less consumer spending on higher-priced entertainment, resulting in a reduced rate of movie theater attendance (recently 39 percent of the American population, according to a CNN report); coupled with a media technology and business revolution that provides consumers less costly alternatives through video rentals and Internet viewing: “I don’t go to movies anymore. I rent DVDs from Netflix or Redbox or watch movies online—so much cheaper than paying over ten or twelve bucks for a movie ticket.”
To clarify terminology, any assertion that has an if–then or predictive structure to it is called a proposition since it proposes a conditional event. For example, this assertion is also a proposition: “Special offers can motivate cash-strapped clientele to patronize restaurants more frequently.” Propositions are the building blocks of hypothesis testing in the field and for later theory construction. Research not only documents human action but also can sometimes formulate statements that predict it. This provides a transferable and generalizable quality in our findings to other comparable settings and contexts. And to clarify terminology further, all propositions are assertions, but not all assertions are propositions.
Particularizability —the search for specific and unique dimensions of action at a site and/or the specific and unique perspectives of an individual participant—is not intended to filter out trivial excess but to magnify the salient characteristics of local meaning. Although generalizable knowledge is difficult to formulate in qualitative inquiry since each naturalistic setting will contain its own unique set of social and cultural conditions, there will be some aspects of social action that are plausibly universal or “generic” across settings and perhaps even across time.
To work toward this, Erickson advocates that the interpretive researcher look for “concrete universals” by studying actions at a particular site in detail and then comparing those actions to actions at other sites that have also been studied in detail. The exhibit or display of these generalizable features is to provide a synoptic representation, or a view of the whole. What the researcher attempts to uncover is what is both particular and general at the site of interest, preferably from the perspective of the participants. It is from the detailed analysis of actions at a specific site that these universals can be concretely discerned, rather than abstractly constructed as in grounded theory.
In sum, assertion development is a qualitative data analytic strategy that relies on the researcher’s intense review of interview transcripts, field notes, documents, and other data to inductively formulate, with reasonable certainty, composite statements that credibly summarize and interpret participant actions and meanings and their possible representation of and transfer into broader social contexts and issues.
Qualitative Data Analysis Strategy: To Display
To display in QDA is to visually present the processes and dynamics of human or conceptual action represented in the data. Qualitative researchers use not only language but also illustrations to both analyze and display the phenomena and processes at work in the data. Tables, charts, matrices, flow diagrams, and other models and graphics help both you and your readers cognitively and conceptually grasp the essence and essentials of your findings. As you have seen thus far, even simple outlining of codes, categories, and themes is one visual tactic for organizing the scope of the data. Rich text, font, and format features such as italicizing, bolding, capitalizing, indenting, and bullet pointing provide simple emphasis to selected words and phrases within the longer narrative.
Think display was a phrase coined by methodologists Miles and Huberman ( 1994 ) to encourage the researcher to think visually as data were collected and analyzed. The magnitude of text can be essentialized into graphics for at-a-glance review. Bins in various shapes and lines of various thicknesses, along with arrows suggesting pathways and direction, render the study a portrait of action. Bins can include the names of codes, categories, concepts, processes, key participants, and/or groups.
As a simple example, Figure 29.1 illustrates the three categories’ interrelationship derived from process coding. It displays what could be the apex of this interaction, LIVING STRATEGICALLY, and its connections to THINKING STRATEGICALLY, which influences and affects SPENDING STRATEGICALLY.
Three categories’ interrelationship derived from process coding.
Figure 29.2 represents a slightly more complex (if not playful) model, based on the five major in vivo codes/categories generated from analysis. The graphic is used as a way of initially exploring the interrelationship and flow from one category to another. The use of different font styles, font sizes, and line and arrow thicknesses is intended to suggest the visual qualities of the participant’s language and his dilemmas—a way of heightening in vivo coding even further.
In vivo categories in rich text display
Accompanying graphics are not always necessary for a qualitative report. They can be very helpful for the researcher during the analytic stage as a heuristic for exploring how major ideas interrelate, but illustrations are generally included in published work when they will help supplement and clarify complex processes for readers. Photographs of the field setting or the participants (and only with their written permission) also provide evidentiary reality to the write-up and help your readers get a sense of being there.
Qualitative Data Analysis Strategy: To Narrate
To narrate in QDA is to create an evocative literary representation and presentation of the data in the form of creative nonfiction. All research reports are stories of one kind or another. But there is yet another approach to QDA that intentionally documents the research experience as story, in its traditional literary sense. Narrative inquiry serves to plot and story-line the participant’s experiences into what might be initially perceived as a fictional short story or novel. But the story is carefully crafted and creatively written to provide readers with an almost omniscient perspective about the participants’ worldview. The transformation of the corpus from database to creative nonfiction ranges from systematic transcript analysis to open-ended literary composition. The narrative, however, should be solidly grounded in and emerge from the data as a plausible rendering of social life.
The following is a narrative vignette based on interview transcript selections from the participant living through tough economic times:
Jack stood in front of the soft drink vending machine at work and looked almost worriedly at the selections. With both hands in his pants pockets, his fingers jingled the few coins he had inside them as he contemplated whether he could afford the purchase. Two dollars for a twenty-ounce bottle of Diet Coke. Two dollars. “I can practically get a two-liter bottle for that same price at the grocery store,” he thought. Then Jack remembered the upcoming dental surgery he needed—that would cost one thousand dollars—and the bottle of insulin and syringes he needed to buy for his diabetic, high maintenance cat—almost two hundred dollars. He sighed, took his hands out of his pockets, and walked away from the vending machine. He was skipping lunch that day anyway so he could stock up on dinner later at the cheap-but-filling all-you-can-eat Chinese buffet. He could get his Diet Coke there.
Narrative inquiry representations, like literature, vary in tone, style, and point of view. The common goal, however, is to create an evocative portrait of participants through the aesthetic power of literary form. A story does not always have to have a moral explicitly stated by its author. The reader reflects on personal meanings derived from the piece and how the specific tale relates to one’s self and the social world.
Qualitative Data Analysis Strategy: To Poeticize
To poeticize in QDA is to create an evocative literary representation and presentation of the data in poetic form. One approach to analyzing or documenting analytic findings is to strategically truncate interview transcripts, field notes, and other pertinent data into poetic structures. Like coding, poetic constructions capture the essence and essentials of data in a creative, evocative way. The elegance of the format attests to the power of carefully chosen language to represent and convey complex human experience.
In vivo codes (codes based on the actual words used by participants themselves) can provide imagery, symbols, and metaphors for rich category, theme, concept, and assertion development, in addition to evocative content for arts-based interpretations of the data. Poetic inquiry takes note of what words and phrases seem to stand out from the data corpus as rich material for reinterpretation. Using some of the participant’s own language from the interview transcript illustrated previously, a poetic reconstruction or “found poetry” might read as follows:
Scary Times Scary times … spending more (another ding in my wallet) a couple of thousand (another ding in my wallet) insurance is just worthless (another ding in my wallet) pick up the tab (another ding in my wallet) not putting as much into savings (another ding in my wallet) It all adds up. Think twice: don’t really need skip Think twice, think cheap: coupons bargains two-for-one free Think twice, think cheaper: stock up all-you-can-eat (cheap—and filling) It all adds up.
Anna Deavere Smith, a verbatim theatre performer, attests that people speak in forms of “organic poetry” in everyday life. Thus, in vivo codes can provide core material for poetic representation and presentation of lived experiences, potentially transforming the routine and mundane into the epic. Some researchers also find the genre of poetry to be the most effective way to compose original work that reflects their own fieldwork experiences and autoethnographic stories.
Qualitative Data Analysis Strategy: To Compute
To compute in QDA is to employ specialized software programs for qualitative data management and analysis. The acronym for computer-assisted qualitative data analysis software is CAQDAS. There are diverse opinions among practitioners in the field about the utility of such specialized programs for qualitative data management and analysis. The software, unlike statistical computation, does not actually analyze data for you at higher conceptual levels. These CAQDAS software packages serve primarily as a repository for your data (both textual and visual) that enables you to code them, and they can perform such functions as calculating the number of times a particular word or phrase appears in the data corpus (a particularly useful function for content analysis) and can display selected facets after coding, such as possible interrelationships. Basic software such as Microsoft Word and Excel provides utilities that can store and, with some preformatting and strategic entry, organize qualitative data to enable the researcher’s analytic review. The following Internet addresses are listed to help in exploring selected CAQDAS packages and obtaining demonstration/trial software; video tutorials are available on the companies’ websites and on YouTube:
ATLAS.ti: http://www.atlasti.com
Dedoose: http://www.dedoose.com
HyperRESEARCH: http://www.researchware.com
MAXQDA: http://www.maxqda.com
NVivo: http://www.qsrinternational.com
QDA Miner: http://www.provalisresearch.com
Quirkos: http://www.quirkos.com
Transana: http://www.transana.com
V-Note: http://www.v-note.org
Some qualitative researchers attest that the software is indispensable for qualitative data management, especially for large-scale studies. Others feel that the learning curve of most CAQDAS programs is too lengthy to be of pragmatic value, especially for small-scale studies. From my own experience, if you have an aptitude for picking up quickly on the scripts and syntax of software programs, explore one or more of the packages listed. If you are a novice to qualitative research, though, I recommend working manually or “by hand” for your first project so you can focus exclusively on the data and not on the software.
Qualitative Data Analysis Strategy: To Verify
To verify in QDA is to administer an audit of “quality control” to your analysis. After your data analysis and the development of key findings, you may be thinking to yourself, “Did I get it right?” “Did I learn anything new?” Reliability and validity are terms and constructs of the positivist quantitative paradigm that refer to the replicability and accuracy of measures. But in the qualitative paradigm, other constructs are more appropriate.
Credibility and trustworthiness (Lincoln & Guba, 1985 ) are two factors to consider when collecting and analyzing the data and presenting your findings. In our qualitative research projects, we must present a convincing story to our audiences that we “got it right” methodologically. In other words, the amount of time we spent in the field, the number of participants we interviewed, the analytic methods we used, the thinking processes evident to reach our conclusions, and so on should be “just right” to assure the reader that we have conducted our jobs soundly. But remember that we can never conclusively prove something; we can only, at best, convincingly suggest. Research is an act of persuasion.
Credibility in a qualitative research report can be established in several ways. First, citing the key writers of related works in your literature review is essential. Seasoned researchers will sometimes assess whether a novice has “done her homework” by reviewing the bibliography or references. You need not list everything that seminal writers have published about a topic, but their names should appear at least once as evidence that you know the field’s key figures and their work.
Credibility can also be established by specifying the particular data analysis methods you employed (e.g., “Interview transcripts were taken through two cycles of process coding, resulting in three primary categories”), through corroboration of data analysis with the participants themselves (e.g., “I asked my participants to read and respond to a draft of this report for their confirmation of accuracy and recommendations for revision”), or through your description of how data and findings were substantiated (e.g., “Data sources included interview transcripts, participant observation field notes, and participant response journals to gather multiple perspectives about the phenomenon”).
Data scientist W. Edwards Deming is attributed with offering this cautionary advice about making a convincing argument: “Without data, you’re just another person with an opinion.” Thus, researchers can also support their findings with relevant, specific evidence by quoting participants directly and/or including field note excerpts from the data corpus. These serve both as illustrative examples for readers and to present more credible testimony of what happened in the field.
Trustworthiness, or providing credibility to the writing, is when we inform the reader of our research processes. Some make the case by stating the duration of fieldwork (e.g., “Forty-five clock hours were spent in the field”; “The study extended over a 10-month period”). Others put forth the amounts of data they gathered (e.g., “Sixteen individuals were interviewed”; “My field notes totaled 157 pages”). Sometimes trustworthiness is established when we are up front or confessional with the analytic or ethical dilemmas we encountered (e.g., “It was difficult to watch the participant’s teaching effectiveness erode during fieldwork”; “Analysis was stalled until I recoded the entire data corpus with a new perspective”).
The bottom line is that credibility and trustworthiness are matters of researcher honesty and integrity . Anyone can write that he worked ethically, rigorously, and reflexively, but only the writer will ever know the truth. There is no shame if something goes wrong with your research. In fact, it is more than likely the rule, not the exception. Work and write transparently to achieve credibility and trustworthiness with your readers.
The length of this chapter does not enable me to expand on other QDA strategies such as to conceptualize, theorize, and write. Yet there are even more subtle thinking strategies to employ throughout the research enterprise, such as to synthesize, problematize, and create. Each researcher has his or her own ways of working, and deep reflexivity (another strategy) on your own methodology and methods as a qualitative inquirer throughout fieldwork and writing provides you with metacognitive awareness of data analysis processes and possibilities.
Data analysis is one of the most elusive practices in qualitative research, perhaps because it is a backstage, behind-the-scenes, in-your-head enterprise. It is not that there are no models to follow. It is just that each project is contextual and case specific. The unique data you collect from your unique research design must be approached with your unique analytic signature. It truly is a learning-by-doing process, so accept that and leave yourself open to discovery and insight as you carefully scrutinize the data corpus for patterns, categories, themes, concepts, assertions, propositions, and possibly new theories through strategic analysis.
Auerbach, C. F. , & Silverstein, L. B. ( 2003 ). Qualitative data: An introduction to coding and analysis . New York, NY: New York University Press.
Google Scholar
Google Preview
Birks, M. , & Mills, J. ( 2015 ). Grounded theory: A practical guide (2nd ed.). London, England: Sage.
Boyatzis, R. E. ( 1998 ). Transforming qualitative information: Thematic analysis and code development . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Bryant, A. ( 2017 ). Grounded theory and grounded theorizing: Pragmatism in research practice. New York, NY: Oxford.
Bryant, A. , & Charmaz, K. (Eds.). ( 2019 ). The Sage handbook of current developments in grounded theory . London, England: Sage.
Charmaz, K. ( 2014 ). Constructing grounded theory: A practical guide through qualitative analysis (2nd ed.). London, England: Sage.
Erickson, F. ( 1986 ). Qualitative methods in research on teaching. In M. C. Wittrock (Ed.), Handbook of research on teaching (3rd ed., pp. 119–161). New York, NY: Macmillan.
Galman, S. C. ( 2013 ). The good, the bad, and the data: Shane the lone ethnographer’s basic guide to qualitative data analysis. Walnut Creek, CA: Left Coast Press.
Geertz, C. ( 1983 ). Local knowledge: Further essays in interpretive anthropology . New York, NY: Basic Books.
Lincoln, Y. S. , & Guba, E. G. ( 1985 ). Naturalistic inquiry . Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Miles, M. B. , & Huberman, A. M. ( 1994 ). Qualitative data analysis (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Saldaña, J. ( 2016 ). The coding manual for qualitative researchers (3rd ed.). London, England: Sage.
Saldaña, J. , & Omasta, M. ( 2018 ). Qualitative research: Analyzing life . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Stake, R. E. ( 1995 ). The art of case study research . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Stern, P. N. , & Porr, C. J. ( 2011 ). Essentials of accessible grounded theory . Walnut Creek, CA: Left Coast Press.
Strauss, A. L. ( 1987 ). Qualitative analysis for social scientists . Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.
Sunstein, B. S. , & Chiseri-Strater, E. ( 2012 ). FieldWorking: Reading and writing research (4th ed.). Boston, MA: Bedford/St. Martin’s.
Wertz, F. J. , Charmaz, K. , McMullen, L. M. , Josselson, R. , Anderson, R. , & McSpadden, E. ( 2011 ). Five ways of doing qualitative analysis: Phenomenological psychology, grounded theory, discourse analysis, narrative research, and intuitive inquiry . New York, NY: Guilford Press.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Learn / Guides / Qualitative data analysis guide
Back to guides
5 qualitative data analysis methods
Qualitative data uncovers valuable insights that help you improve the user and customer experience. But how exactly do you measure and analyze data that isn't quantifiable?
There are different qualitative data analysis methods to help you make sense of qualitative feedback and customer insights, depending on your business goals and the type of data you've collected.
Before you choose a qualitative data analysis method for your team, you need to consider the available techniques and explore their use cases to understand how each process might help you better understand your users.
This guide covers five qualitative analysis methods to choose from, and will help you pick the right one(s) based on your goals.
Content analysis
Thematic analysis
Narrative analysis
Grounded theory analysis
Discourse analysis
5 qualitative data analysis methods explained
Qualitative data analysis ( QDA ) is the process of organizing, analyzing, and interpreting qualitative research data—non-numeric, conceptual information, and user feedback—to capture themes and patterns, answer research questions, and identify actions to improve your product or website.
Step 1 in the research process (after planning ) is qualitative data collection. You can use behavior analytics software—like Hotjar —to capture qualitative data with context, and learn the real motivation behind user behavior, by collecting written customer feedback with Surveys or scheduling an in-depth user interview with Engage .
Use Hotjar’s tools to collect feedback, uncover behavior trends, and understand the ‘why’ behind user actions.
1. Content analysis
Content analysis is a qualitative research method that examines and quantifies the presence of certain words, subjects, and concepts in text, image, video, or audio messages. The method transforms qualitative input into quantitative data to help you make reliable conclusions about what customers think of your brand, and how you can improve their experience and opinion.
Conduct content analysis manually (which can be time-consuming) or use analysis tools like Lexalytics to reveal communication patterns, uncover differences in individual or group communication trends, and make broader connections between concepts.
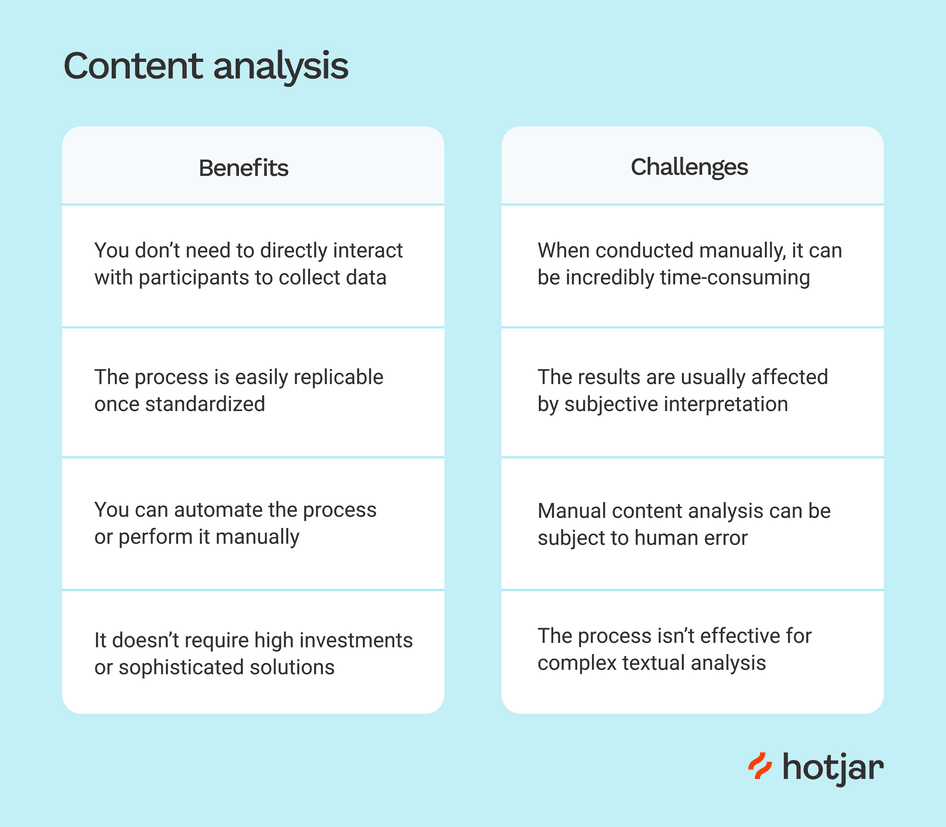
How content analysis can help your team
Content analysis is often used by marketers and customer service specialists, helping them understand customer behavior and measure brand reputation.
For example, you may run a customer survey with open-ended questions to discover users’ concerns—in their own words—about their experience with your product. Instead of having to process hundreds of answers manually, a content analysis tool helps you analyze and group results based on the emotion expressed in texts.
Some other examples of content analysis include:
Analyzing brand mentions on social media to understand your brand's reputation
Reviewing customer feedback to evaluate (and then improve) the customer and user experience (UX)
Researching competitors’ website pages to identify their competitive advantages and value propositions
Interpreting customer interviews and survey results to determine user preferences, and setting the direction for new product or feature developments
Content analysis was a major part of our growth during my time at Hypercontext.
[It gave us] a better understanding of the [blog] topics that performed best for signing new users up. We were also able to go deeper within those blog posts to better understand the formats [that worked].
2. Thematic analysis
Thematic analysis helps you identify, categorize, analyze, and interpret patterns in qualitative study data , and can be done with tools like Dovetail and Thematic .
While content analysis and thematic analysis seem similar, they're different in concept:
Content analysis can be applied to both qualitative and quantitative data , and focuses on identifying frequencies and recurring words and subjects
Thematic analysis can only be applied to qualitative data, and focuses on identifying patterns and themes
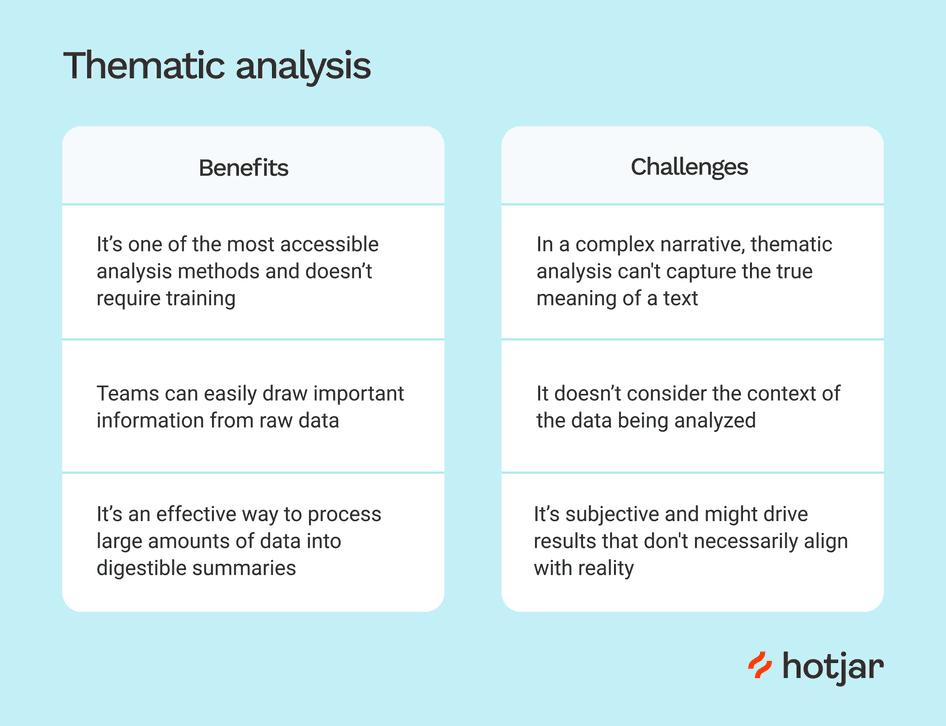
How thematic analysis can help your team
Thematic analysis can be used by pretty much anyone: from product marketers, to customer relationship managers, to UX researchers.
For example, product teams use thematic analysis to better understand user behaviors and needs and improve UX . Analyzing customer feedback lets you identify themes (e.g. poor navigation or a buggy mobile interface) highlighted by users and get actionable insight into what they really expect from the product.
💡 Pro tip: looking for a way to expedite the data analysis process for large amounts of data you collected with a survey? Try Hotjar’s AI for Surveys : along with generating a survey based on your goal in seconds, our AI will analyze the raw data and prepare an automated summary report that presents key thematic findings, respondent quotes, and actionable steps to take, making the analysis of qualitative data a breeze.
3. Narrative analysis
Narrative analysis is a method used to interpret research participants’ stories —things like testimonials , case studies, focus groups, interviews, and other text or visual data—with tools like Delve and AI-powered ATLAS.ti .
Some formats don’t work well with narrative analysis, including heavily structured interviews and written surveys, which don’t give participants as much opportunity to tell their stories in their own words.
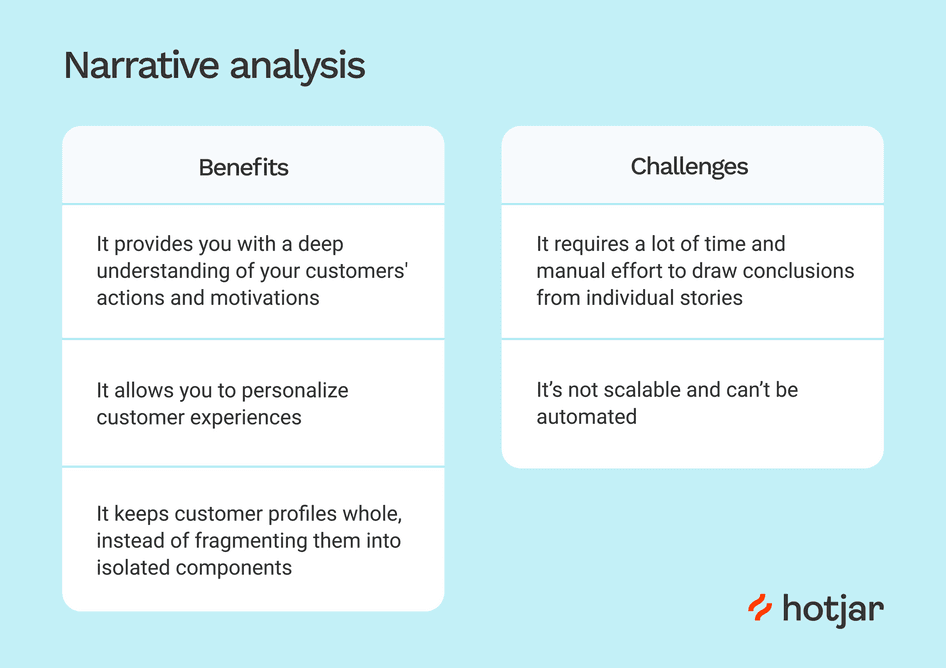
How narrative analysis can help your team
Narrative analysis provides product teams with valuable insight into the complexity of customers’ lives, feelings, and behaviors.
In a marketing research context, narrative analysis involves capturing and reviewing customer stories—on social media, for example—to get in-depth insight into their lives, priorities, and challenges.
This might look like analyzing daily content shared by your audiences’ favorite influencers on Instagram, or analyzing customer reviews on sites like G2 or Capterra to gain a deep understanding of individual customer experiences. The results of this analysis also contribute to developing corresponding customer personas .
💡 Pro tip: conducting user interviews is an excellent way to collect data for narrative analysis. Though interviews can be time-intensive, there are tools out there that streamline the workload.
Hotjar Engage automates the entire process, from recruiting to scheduling to generating the all-important interview transcripts you’ll need for the analysis phase of your research project.
4. Grounded theory analysis
Grounded theory analysis is a method of conducting qualitative research to develop theories by examining real-world data. This technique involves the creation of hypotheses and theories through qualitative data collection and evaluation, and can be performed with qualitative data analysis software tools like MAXQDA and NVivo .
Unlike other qualitative data analysis techniques, this method is inductive rather than deductive: it develops theories from data, not the other way around.
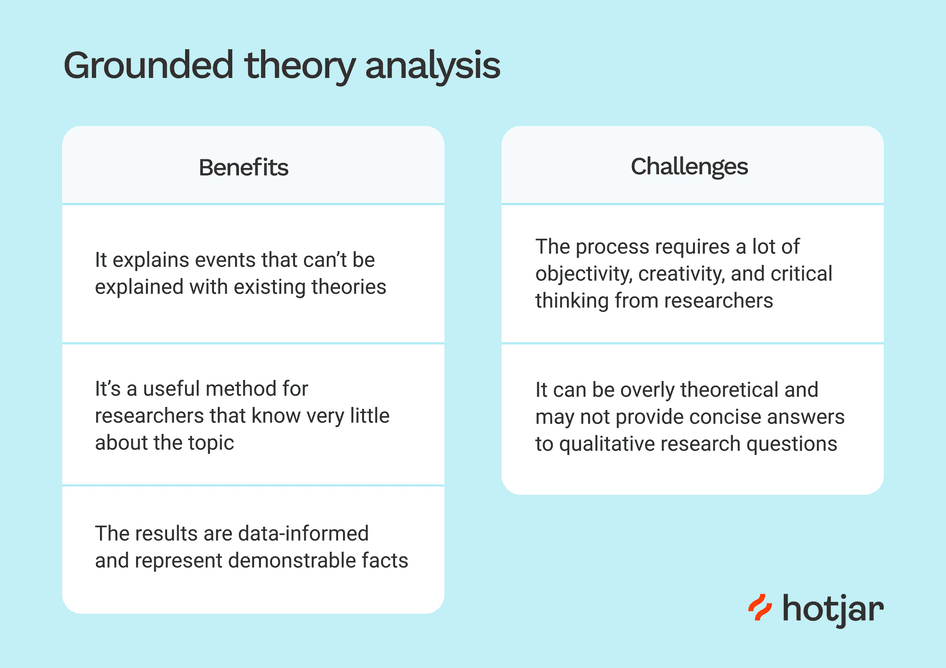
How grounded theory analysis can help your team
Grounded theory analysis is used by software engineers, product marketers, managers, and other specialists who deal with data sets to make informed business decisions.
For example, product marketing teams may turn to customer surveys to understand the reasons behind high churn rates , then use grounded theory to analyze responses and develop hypotheses about why users churn, and how you can get them to stay.
Grounded theory can also be helpful in the talent management process. For example, HR representatives may use it to develop theories about low employee engagement, and come up with solutions based on their research findings.
5. Discourse analysis
Discourse analysis is the act of researching the underlying meaning of qualitative data. It involves the observation of texts, audio, and videos to study the relationships between information and its social context.
In contrast to content analysis, this method focuses on the contextual meaning of language: discourse analysis sheds light on what audiences think of a topic, and why they feel the way they do about it.
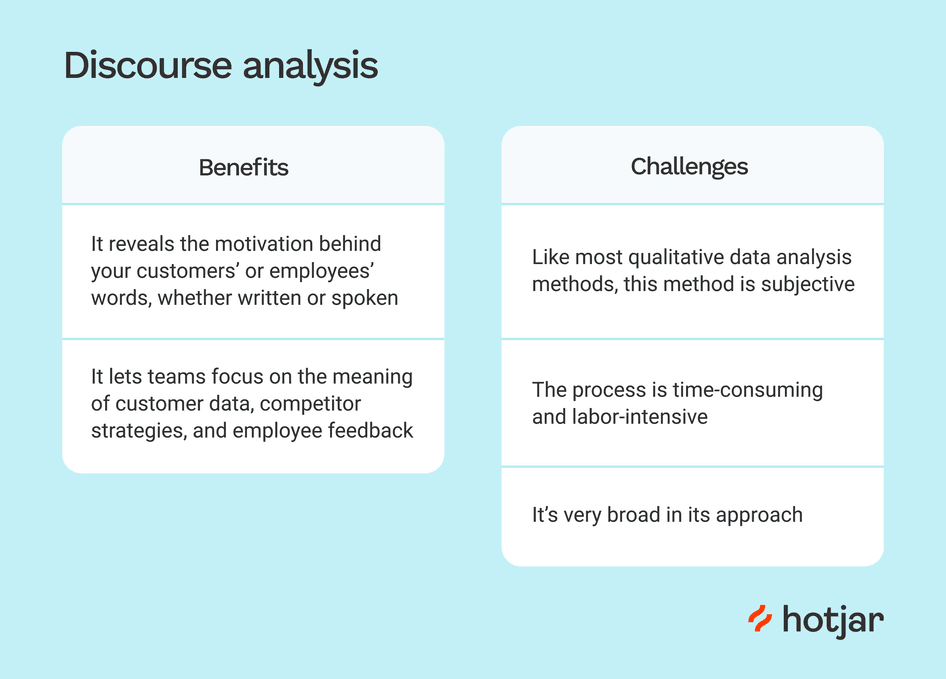
How discourse analysis can help your team
In a business context, this method is primarily used by marketing teams. Discourse analysis helps marketers understand the norms and ideas in their market , and reveals why they play such a significant role for their customers.
Once the origins of trends are uncovered, it’s easier to develop a company mission, create a unique tone of voice, and craft effective marketing messages.
Which qualitative data analysis method should you choose?
While the five qualitative data analysis methods we list above are all aimed at processing data and answering research questions, these techniques differ in their intent and the approaches applied.
Choosing the right analysis method for your team isn't a matter of preference—selecting a method that fits is only possible once you define your research goals and have a clear intention. When you know what you need (and why you need it), you can identify an analysis method that aligns with your research objectives.
Gather qualitative data with Hotjar
Use Hotjar’s product experience insights in your qualitative research. Collect feedback, uncover behavior trends, and understand the ‘why’ behind user actions.
FAQs about qualitative data analysis methods
What is the qualitative data analysis approach.
The qualitative data analysis approach refers to the process of systematizing descriptive data collected through interviews, focus groups, surveys, and observations and then interpreting it. The methodology aims to identify patterns and themes behind textual data, and other unquantifiable data, as opposed to numerical data.
What are qualitative data analysis methods?
Five popular qualitative data analysis methods are:
What is the process of qualitative data analysis?
The process of qualitative data analysis includes six steps:
Define your research question
Prepare the data
Choose the method of qualitative analysis
Code the data
Identify themes, patterns, and relationships
Make hypotheses and act
Qualitative data analysis guide
Previous chapter
QDA challenges
Next chapter

Data & Finance for Work & Life

Data Analysis for Qualitative Research: 6 Step Guide
Data analysis for qualitative research is not intuitive. This is because qualitative data stands in opposition to traditional data analysis methodologies: while data analysis is concerned with quantities, qualitative data is by definition unquantified . But there is an easy, methodical approach that anyone can take use to get reliable results when performing data analysis for qualitative research. The process consists of 6 steps that I’ll break down in this article:
- Perform interviews(if necessary )
- Gather all documents and transcribe any non-paper records
- Decide whether to either code analytical data, analyze word frequencies, or both
- Decide what interpretive angle you want to take: content analysis , narrative analysis, discourse analysis, framework analysis, and/or grounded theory
- Compile your data in a spreadsheet using document saving techniques (windows and mac)
- Identify trends in words, themes, metaphors, natural patterns, and more
To complete these steps, you will need:
- Microsoft word
- Microsoft excel
- Internet access
You can get the free Intro to Data Analysis eBook to cover the fundamentals and ensure strong progression in all your data endeavors.
What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is not the same as quantitative research. In short, qualitative research is the interpretation of non-numeric data. It usually aims at drawing conclusions that explain why a phenomenon occurs, rather than that one does occur. Here’s a great quote from a nursing magazine about quantitative vs qualitative research:
“A traditional quantitative study… uses a predetermined (and auditable) set of steps to confirm or refute [a] hypothesis. “In contrast, qualitative research often takes the position that an interpretive understanding is only possible by way of uncovering or deconstructing the meanings of a phenomenon. Thus, a distinction between explaining how something operates (explanation) and why it operates in the manner that it does (interpretation) may be [an] effective way to distinguish quantitative from qualitative analytic processes involved in any particular study.” (bold added) (( EBN ))
Learn to Interpret Your Qualitative Data
This article explain what data analysis is and how to do it. To learn how to interpret the results, visualize, and write an insightful report, sign up for our handbook below.

Step 1a: Data collection methods and techniques in qualitative research: interviews and focus groups
Step 1 is collecting the data that you will need for the analysis. If you are not performing any interviews or focus groups to gather data, then you can skip this step. It’s for people who need to go into the field and collect raw information as part of their qualitative analysis.
Since the whole point of an interview and of qualitative analysis in general is to understand a research question better, you should start by making sure you have a specific, refined research question . Whether you’re a researcher by trade or a data analyst working on one-time project, you must know specifically what you want to understand in order to get results.
Good research questions are specific enough to guide action but open enough to leave room for insight and growth. Examples of good research questions include:
- Good : To what degree does living in a city impact the quality of a person’s life? (open-ended, complex)
- Bad : Does living in a city impact the quality of a person’s life? (closed, simple)
Once you understand the research question, you need to develop a list of interview questions. These questions should likewise be open-ended and provide liberty of expression to the responder. They should support the research question in an active way without prejudicing the response. Examples of good interview questions include:
- Good : Tell me what it’s like to live in a city versus in the country. (open, not leading)
- Bad : Don’t you prefer the city to the country because there are more people? (closed, leading)
Some additional helpful tips include:
- Begin each interview with a neutral question to get the person relaxed
- Limit each question to a single idea
- If you don’t understand, ask for clarity
- Do not pass any judgements
- Do not spend more than 15m on an interview, lest the quality of responses drop
Focus groups
The alternative to interviews is focus groups. Focus groups are a great way for you to get an idea for how people communicate their opinions in a group setting, rather than a one-on-one setting as in interviews.
In short, focus groups are gatherings of small groups of people from representative backgrounds who receive instruction, or “facilitation,” from a focus group leader. Typically, the leader will ask questions to stimulate conversation, reformulate questions to bring the discussion back to focus, and prevent the discussion from turning sour or giving way to bad faith.
Focus group questions should be open-ended like their interview neighbors, and they should stimulate some degree of disagreement. Disagreement often leads to valuable information about differing opinions, as people tend to say what they mean if contradicted.
However, focus group leaders must be careful not to let disagreements escalate, as anger can make people lie to be hurtful or simply to win an argument. And lies are not helpful in data analysis for qualitative research.
Step 1b: Tools for qualitative data collection
When it comes to data analysis for qualitative analysis, the tools you use to collect data should align to some degree with the tools you will use to analyze the data.
As mentioned in the intro, you will be focusing on analysis techniques that only require the traditional Microsoft suite programs: Microsoft Excel and Microsoft Word . At the same time, you can source supplementary tools from various websites, like Text Analyzer and WordCounter.
In short, the tools for qualitative data collection that you need are Excel and Word , as well as web-based free tools like Text Analyzer and WordCounter . These online tools are helpful in the quantitative part of your qualitative research.
Step 2: Gather all documents & transcribe non-written docs
Once you have your interviews and/or focus group transcripts, it’s time to decide if you need other documentation. If you do, you’ll need to gather it all into one place first, then develop a strategy for how to transcribe any non-written documents.
When do you need documentation other than interviews and focus groups? Two situations usually call for documentation. First , if you have little funding , then you can’t afford to run expensive interviews and focus groups.
Second , social science researchers typically focus on documents since their research questions are less concerned with subject-oriented data, while hard science and business researchers typically focus on interviews and focus groups because they want to know what people think, and they want to know today.
Non-written records
Other factors at play include the type of research, the field, and specific research goal. For those who need documentation and to describe non-written records, there are some steps to follow:
- Put all hard copy source documents into a sealed binder (I use plastic paper holders with elastic seals ).
- If you are sourcing directly from printed books or journals, then you will need to digitalize them by scanning them and making them text readable by the computer. To do so, turn all PDFs into Word documents using online tools such as PDF to Word Converter . This process is never full-proof, and it may be a source of error in the data collection, but it’s part of the process.
- If you are sourcing online documents, try as often as possible to get computer-readable PDF documents that you can easily copy/paste or convert. Locked PDFs are essentially a lost cause .
- Transcribe any audio files into written documents. There are free online tools available to help with this, such as 360converter . If you run a test through the system, you’ll see that the output is not 100%. The best way to use this tool is as a first draft generator. You can then correct and complete it with old fashioned, direct transcription.
Step 3: Decide on the type of qualitative research
Before step 3 you should have collected your data, transcribed it all into written-word documents, and compiled it in one place. Now comes the interesting part. You need to decide what you want to get out of your research by choosing an analytic angle, or type of qualitative research.
The available types of qualitative research are as follows. Each of them takes a unique angle that you must choose to get what information you want from the analysis . In addition, each of them has a different impact on the data analysis for qualitative research (coding vs word frequency) that we use.
Content analysis
Narrative analysis, discourse analysis.
- Framework analysis, and/or
Grounded theory
From a high level, content, narrative, and discourse analysis are actionable independent tactics, whereas framework analysis and grounded theory are ways of honing and applying the first three.
- Definition : Content analysis is identify and labelling themes of any kind within a text.
- Focus : Identifying any kind of pattern in written text, transcribed audio, or transcribed video. This could be thematic, word repetition, idea repetition. Most often, the patterns we find are idea that make up an argument.
- Goal : To simplify, standardize, and quickly reference ideas from any given text. Content analysis is a way to pull the main ideas from huge documents for comparison. In this way, it’s more a means to an end.
- Pros : The huge advantage of doing content analysis is that you can quickly process huge amounts of texts using simple coding and word frequency techniques we will look at below. To use a metaphore, it is to qualitative analysis documents what Spark notes are to books.
- Cons : The downside to content analysis is that it’s quite general. If you have a very specific, narrative research question, then tracing “any and all ideas” will not be very helpful to you.
- Definition : Narrative analysis is the reformulation and simplification of interview answers or documentation into small narrative components to identify story-like patterns.
- Focus : Understanding the text based on its narrative components as opposed to themes or other qualities.
- Goal : To reference the text from an angle closer to the nature of texts in order to obtain further insights.
- Pros : Narrative analysis is very useful for getting perspective on a topic in which you’re extremely limited. It can be easy to get tunnel vision when you’re digging for themes and ideas from a reason-centric perspective. Turning to a narrative approach will help you stay grounded. More importantly, it helps reveal different kinds of trends.
- Cons : Narrative analysis adds another layer of subjectivity to the instinctive nature of qualitative research. Many see it as too dependent on the researcher to hold any critical value.
- Definition : Discourse analysis is the textual analysis of naturally occurring speech. Any oral expression must be transcribed before undergoing legitimate discourse analysis.
- Focus : Understanding ideas and themes through language communicated orally rather than pre-processed on paper.
- Goal : To obtain insights from an angle outside the traditional content analysis on text.
- Pros : Provides a considerable advantage in some areas of study in order to understand how people communicate an idea, versus the idea itself. For example, discourse analysis is important in political campaigning. People rarely vote for the candidate who most closely corresponds to his/her beliefs, but rather for the person they like the most.
- Cons : As with narrative analysis, discourse analysis is more subjective in nature than content analysis, which focuses on ideas and patterns. Some do not consider it rigorous enough to be considered a legitimate subset of qualitative analysis, but these people are few.
Framework analysis
- Definition : Framework analysis is a kind of qualitative analysis that includes 5 ordered steps: coding, indexing, charting, mapping, and interpreting . In most ways, framework analysis is a synonym for qualitative analysis — the same thing. The significant difference is the importance it places on the perspective used in the analysis.
- Focus : Understanding patterns in themes and ideas.
- Goal : Creating one specific framework for looking at a text.
- Pros : Framework analysis is helpful when the researcher clearly understands what he/she wants from the project, as it’s a limitation approach. Since each of its step has defined parameters, framework analysis is very useful for teamwork.
- Cons : It can lead to tunnel vision.
- Definition : The use of content, narrative, and discourse analysis to examine a single case, in the hopes that discoveries from that case will lead to a foundational theory used to examine other like cases.
- Focus : A vast approach using multiple techniques in order to establish patterns.
- Goal : To develop a foundational theory.
- Pros : When successful, grounded theories can revolutionize entire fields of study.
- Cons : It’s very difficult to establish ground theories, and there’s an enormous amount of risk involved.
Step 4: Coding, word frequency, or both
Coding in data analysis for qualitative research is the process of writing 2-5 word codes that summarize at least 1 paragraphs of text (not writing computer code). This allows researchers to keep track of and analyze those codes. On the other hand, word frequency is the process of counting the presence and orientation of words within a text, which makes it the quantitative element in qualitative data analysis.
Video example of coding for data analysis in qualitative research
In short, coding in the context of data analysis for qualitative research follows 2 steps (video below):
- Reading through the text one time
- Adding 2-5 word summaries each time a significant theme or idea appears
Let’s look at a brief example of how to code for qualitative research in this video:
Click here for a link to the source text. 1
Example of word frequency processing
And word frequency is the process of finding a specific word or identifying the most common words through 3 steps:
- Decide if you want to find 1 word or identify the most common ones
- Use word’s “Replace” function to find a word or phrase
- Use Text Analyzer to find the most common terms
Here’s another look at word frequency processing and how you to do it. Let’s look at the same example above, but from a quantitative perspective.
Imagine we are already familiar with melanoma and KITs , and we want to analyze the text based on these keywords. One thing we can do is look for these words using the Replace function in word
- Locate the search bar
- Click replace
- Type in the word
- See the total results
Here’s a brief video example:
Another option is to use an online Text Analyzer. This methodology won’t help us find a specific word, but it will help us discover the top performing phrases and words. All you need to do it put in a link to a target page or paste a text. I pasted the abstract from our source text, and what turns up is as expected. Here’s a picture:

Step 5: Compile your data in a spreadsheet
After you have some coded data in the word document, you need to get it into excel for analysis. This process requires saving the word doc as an .htm extension, which makes it a website. Once you have the website, it’s as simple as opening that page, scrolling to the bottom, and copying/pasting the comments, or codes, into an excel document.
You will need to wrangle the data slightly in order to make it readable in excel. I’ve made a video to explain this process and places it below.
Step 6: Identify trends & analyze!
There are literally thousands of different ways to analyze qualitative data, and in most situations, the best technique depends on the information you want to get out of the research.
Nevertheless, there are a few go-to techniques. The most important of this is occurrences . In this short video, we finish the example from above by counting the number of times our codes appear. In this way, it’s very similar to word frequency (discussed above).
A few other options include:
- Ranking each code on a set of relevant criteria and clustering
- Pure cluster analysis
- Causal analysis
We cover different types of analysis like this on the website, so be sure to check out other articles on the home page .
How to analyze qualitative data from an interview
To analyze qualitative data from an interview , follow the same 6 steps for quantitative data analysis:
- Perform the interviews
- Transcribe the interviews onto paper
- Decide whether to either code analytical data (open, axial, selective), analyze word frequencies, or both
- Compile your data in a spreadsheet using document saving techniques (for windows and mac)
- Source text [ ↩ ]
About the Author
Noah is the founder & Editor-in-Chief at AnalystAnswers. He is a transatlantic professional and entrepreneur with 5+ years of corporate finance and data analytics experience, as well as 3+ years in consumer financial products and business software. He started AnalystAnswers to provide aspiring professionals with accessible explanations of otherwise dense finance and data concepts. Noah believes everyone can benefit from an analytical mindset in growing digital world. When he's not busy at work, Noah likes to explore new European cities, exercise, and spend time with friends and family.
File available immediately.

Notice: JavaScript is required for this content.

- Privacy Policy

Home » Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types and Guide
Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types and Guide
Table of Contents

Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding people’s beliefs, attitudes, behaviors, and experiences through the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. It seeks to answer research questions through the examination of subjective data, such as interviews, focus groups, observations, and textual analysis.
Qualitative research aims to uncover the meaning and significance of social phenomena, and it typically involves a more flexible and iterative approach to data collection and analysis compared to quantitative research. Qualitative research is often used in fields such as sociology, anthropology, psychology, and education.
Qualitative Research Methods

Qualitative Research Methods are as follows:
One-to-One Interview
This method involves conducting an interview with a single participant to gain a detailed understanding of their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs. One-to-one interviews can be conducted in-person, over the phone, or through video conferencing. The interviewer typically uses open-ended questions to encourage the participant to share their thoughts and feelings. One-to-one interviews are useful for gaining detailed insights into individual experiences.
Focus Groups
This method involves bringing together a group of people to discuss a specific topic in a structured setting. The focus group is led by a moderator who guides the discussion and encourages participants to share their thoughts and opinions. Focus groups are useful for generating ideas and insights, exploring social norms and attitudes, and understanding group dynamics.
Ethnographic Studies
This method involves immersing oneself in a culture or community to gain a deep understanding of its norms, beliefs, and practices. Ethnographic studies typically involve long-term fieldwork and observation, as well as interviews and document analysis. Ethnographic studies are useful for understanding the cultural context of social phenomena and for gaining a holistic understanding of complex social processes.
Text Analysis
This method involves analyzing written or spoken language to identify patterns and themes. Text analysis can be quantitative or qualitative. Qualitative text analysis involves close reading and interpretation of texts to identify recurring themes, concepts, and patterns. Text analysis is useful for understanding media messages, public discourse, and cultural trends.
This method involves an in-depth examination of a single person, group, or event to gain an understanding of complex phenomena. Case studies typically involve a combination of data collection methods, such as interviews, observations, and document analysis, to provide a comprehensive understanding of the case. Case studies are useful for exploring unique or rare cases, and for generating hypotheses for further research.
Process of Observation
This method involves systematically observing and recording behaviors and interactions in natural settings. The observer may take notes, use audio or video recordings, or use other methods to document what they see. Process of observation is useful for understanding social interactions, cultural practices, and the context in which behaviors occur.
Record Keeping
This method involves keeping detailed records of observations, interviews, and other data collected during the research process. Record keeping is essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the data, and for providing a basis for analysis and interpretation.
This method involves collecting data from a large sample of participants through a structured questionnaire. Surveys can be conducted in person, over the phone, through mail, or online. Surveys are useful for collecting data on attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors, and for identifying patterns and trends in a population.
Qualitative data analysis is a process of turning unstructured data into meaningful insights. It involves extracting and organizing information from sources like interviews, focus groups, and surveys. The goal is to understand people’s attitudes, behaviors, and motivations
Qualitative Research Analysis Methods
Qualitative Research analysis methods involve a systematic approach to interpreting and making sense of the data collected in qualitative research. Here are some common qualitative data analysis methods:
Thematic Analysis
This method involves identifying patterns or themes in the data that are relevant to the research question. The researcher reviews the data, identifies keywords or phrases, and groups them into categories or themes. Thematic analysis is useful for identifying patterns across multiple data sources and for generating new insights into the research topic.
Content Analysis
This method involves analyzing the content of written or spoken language to identify key themes or concepts. Content analysis can be quantitative or qualitative. Qualitative content analysis involves close reading and interpretation of texts to identify recurring themes, concepts, and patterns. Content analysis is useful for identifying patterns in media messages, public discourse, and cultural trends.
Discourse Analysis
This method involves analyzing language to understand how it constructs meaning and shapes social interactions. Discourse analysis can involve a variety of methods, such as conversation analysis, critical discourse analysis, and narrative analysis. Discourse analysis is useful for understanding how language shapes social interactions, cultural norms, and power relationships.
Grounded Theory Analysis
This method involves developing a theory or explanation based on the data collected. Grounded theory analysis starts with the data and uses an iterative process of coding and analysis to identify patterns and themes in the data. The theory or explanation that emerges is grounded in the data, rather than preconceived hypotheses. Grounded theory analysis is useful for understanding complex social phenomena and for generating new theoretical insights.
Narrative Analysis
This method involves analyzing the stories or narratives that participants share to gain insights into their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs. Narrative analysis can involve a variety of methods, such as structural analysis, thematic analysis, and discourse analysis. Narrative analysis is useful for understanding how individuals construct their identities, make sense of their experiences, and communicate their values and beliefs.
Phenomenological Analysis
This method involves analyzing how individuals make sense of their experiences and the meanings they attach to them. Phenomenological analysis typically involves in-depth interviews with participants to explore their experiences in detail. Phenomenological analysis is useful for understanding subjective experiences and for developing a rich understanding of human consciousness.
Comparative Analysis
This method involves comparing and contrasting data across different cases or groups to identify similarities and differences. Comparative analysis can be used to identify patterns or themes that are common across multiple cases, as well as to identify unique or distinctive features of individual cases. Comparative analysis is useful for understanding how social phenomena vary across different contexts and groups.
Applications of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research has many applications across different fields and industries. Here are some examples of how qualitative research is used:
- Market Research: Qualitative research is often used in market research to understand consumer attitudes, behaviors, and preferences. Researchers conduct focus groups and one-on-one interviews with consumers to gather insights into their experiences and perceptions of products and services.
- Health Care: Qualitative research is used in health care to explore patient experiences and perspectives on health and illness. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with patients and their families to gather information on their experiences with different health care providers and treatments.
- Education: Qualitative research is used in education to understand student experiences and to develop effective teaching strategies. Researchers conduct classroom observations and interviews with students and teachers to gather insights into classroom dynamics and instructional practices.
- Social Work : Qualitative research is used in social work to explore social problems and to develop interventions to address them. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with individuals and families to understand their experiences with poverty, discrimination, and other social problems.
- Anthropology : Qualitative research is used in anthropology to understand different cultures and societies. Researchers conduct ethnographic studies and observe and interview members of different cultural groups to gain insights into their beliefs, practices, and social structures.
- Psychology : Qualitative research is used in psychology to understand human behavior and mental processes. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with individuals to explore their thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
- Public Policy : Qualitative research is used in public policy to explore public attitudes and to inform policy decisions. Researchers conduct focus groups and one-on-one interviews with members of the public to gather insights into their perspectives on different policy issues.
How to Conduct Qualitative Research
Here are some general steps for conducting qualitative research:
- Identify your research question: Qualitative research starts with a research question or set of questions that you want to explore. This question should be focused and specific, but also broad enough to allow for exploration and discovery.
- Select your research design: There are different types of qualitative research designs, including ethnography, case study, grounded theory, and phenomenology. You should select a design that aligns with your research question and that will allow you to gather the data you need to answer your research question.
- Recruit participants: Once you have your research question and design, you need to recruit participants. The number of participants you need will depend on your research design and the scope of your research. You can recruit participants through advertisements, social media, or through personal networks.
- Collect data: There are different methods for collecting qualitative data, including interviews, focus groups, observation, and document analysis. You should select the method or methods that align with your research design and that will allow you to gather the data you need to answer your research question.
- Analyze data: Once you have collected your data, you need to analyze it. This involves reviewing your data, identifying patterns and themes, and developing codes to organize your data. You can use different software programs to help you analyze your data, or you can do it manually.
- Interpret data: Once you have analyzed your data, you need to interpret it. This involves making sense of the patterns and themes you have identified, and developing insights and conclusions that answer your research question. You should be guided by your research question and use your data to support your conclusions.
- Communicate results: Once you have interpreted your data, you need to communicate your results. This can be done through academic papers, presentations, or reports. You should be clear and concise in your communication, and use examples and quotes from your data to support your findings.
Examples of Qualitative Research
Here are some real-time examples of qualitative research:
- Customer Feedback: A company may conduct qualitative research to understand the feedback and experiences of its customers. This may involve conducting focus groups or one-on-one interviews with customers to gather insights into their attitudes, behaviors, and preferences.
- Healthcare : A healthcare provider may conduct qualitative research to explore patient experiences and perspectives on health and illness. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with patients and their families to gather information on their experiences with different health care providers and treatments.
- Education : An educational institution may conduct qualitative research to understand student experiences and to develop effective teaching strategies. This may involve conducting classroom observations and interviews with students and teachers to gather insights into classroom dynamics and instructional practices.
- Social Work: A social worker may conduct qualitative research to explore social problems and to develop interventions to address them. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with individuals and families to understand their experiences with poverty, discrimination, and other social problems.
- Anthropology : An anthropologist may conduct qualitative research to understand different cultures and societies. This may involve conducting ethnographic studies and observing and interviewing members of different cultural groups to gain insights into their beliefs, practices, and social structures.
- Psychology : A psychologist may conduct qualitative research to understand human behavior and mental processes. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with individuals to explore their thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
- Public Policy: A government agency or non-profit organization may conduct qualitative research to explore public attitudes and to inform policy decisions. This may involve conducting focus groups and one-on-one interviews with members of the public to gather insights into their perspectives on different policy issues.
Purpose of Qualitative Research
The purpose of qualitative research is to explore and understand the subjective experiences, behaviors, and perspectives of individuals or groups in a particular context. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis, qualitative research aims to provide in-depth, descriptive information that can help researchers develop insights and theories about complex social phenomena.
Qualitative research can serve multiple purposes, including:
- Exploring new or emerging phenomena : Qualitative research can be useful for exploring new or emerging phenomena, such as new technologies or social trends. This type of research can help researchers develop a deeper understanding of these phenomena and identify potential areas for further study.
- Understanding complex social phenomena : Qualitative research can be useful for exploring complex social phenomena, such as cultural beliefs, social norms, or political processes. This type of research can help researchers develop a more nuanced understanding of these phenomena and identify factors that may influence them.
- Generating new theories or hypotheses: Qualitative research can be useful for generating new theories or hypotheses about social phenomena. By gathering rich, detailed data about individuals’ experiences and perspectives, researchers can develop insights that may challenge existing theories or lead to new lines of inquiry.
- Providing context for quantitative data: Qualitative research can be useful for providing context for quantitative data. By gathering qualitative data alongside quantitative data, researchers can develop a more complete understanding of complex social phenomena and identify potential explanations for quantitative findings.
When to use Qualitative Research
Here are some situations where qualitative research may be appropriate:
- Exploring a new area: If little is known about a particular topic, qualitative research can help to identify key issues, generate hypotheses, and develop new theories.
- Understanding complex phenomena: Qualitative research can be used to investigate complex social, cultural, or organizational phenomena that are difficult to measure quantitatively.
- Investigating subjective experiences: Qualitative research is particularly useful for investigating the subjective experiences of individuals or groups, such as their attitudes, beliefs, values, or emotions.
- Conducting formative research: Qualitative research can be used in the early stages of a research project to develop research questions, identify potential research participants, and refine research methods.
- Evaluating interventions or programs: Qualitative research can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions or programs by collecting data on participants’ experiences, attitudes, and behaviors.
Characteristics of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is characterized by several key features, including:
- Focus on subjective experience: Qualitative research is concerned with understanding the subjective experiences, beliefs, and perspectives of individuals or groups in a particular context. Researchers aim to explore the meanings that people attach to their experiences and to understand the social and cultural factors that shape these meanings.
- Use of open-ended questions: Qualitative research relies on open-ended questions that allow participants to provide detailed, in-depth responses. Researchers seek to elicit rich, descriptive data that can provide insights into participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Sampling-based on purpose and diversity: Qualitative research often involves purposive sampling, in which participants are selected based on specific criteria related to the research question. Researchers may also seek to include participants with diverse experiences and perspectives to capture a range of viewpoints.
- Data collection through multiple methods: Qualitative research typically involves the use of multiple data collection methods, such as in-depth interviews, focus groups, and observation. This allows researchers to gather rich, detailed data from multiple sources, which can provide a more complete picture of participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Inductive data analysis: Qualitative research relies on inductive data analysis, in which researchers develop theories and insights based on the data rather than testing pre-existing hypotheses. Researchers use coding and thematic analysis to identify patterns and themes in the data and to develop theories and explanations based on these patterns.
- Emphasis on researcher reflexivity: Qualitative research recognizes the importance of the researcher’s role in shaping the research process and outcomes. Researchers are encouraged to reflect on their own biases and assumptions and to be transparent about their role in the research process.
Advantages of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research offers several advantages over other research methods, including:
- Depth and detail: Qualitative research allows researchers to gather rich, detailed data that provides a deeper understanding of complex social phenomena. Through in-depth interviews, focus groups, and observation, researchers can gather detailed information about participants’ experiences and perspectives that may be missed by other research methods.
- Flexibility : Qualitative research is a flexible approach that allows researchers to adapt their methods to the research question and context. Researchers can adjust their research methods in real-time to gather more information or explore unexpected findings.
- Contextual understanding: Qualitative research is well-suited to exploring the social and cultural context in which individuals or groups are situated. Researchers can gather information about cultural norms, social structures, and historical events that may influence participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Participant perspective : Qualitative research prioritizes the perspective of participants, allowing researchers to explore subjective experiences and understand the meanings that participants attach to their experiences.
- Theory development: Qualitative research can contribute to the development of new theories and insights about complex social phenomena. By gathering rich, detailed data and using inductive data analysis, researchers can develop new theories and explanations that may challenge existing understandings.
- Validity : Qualitative research can offer high validity by using multiple data collection methods, purposive and diverse sampling, and researcher reflexivity. This can help ensure that findings are credible and trustworthy.
Limitations of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research also has some limitations, including:
- Subjectivity : Qualitative research relies on the subjective interpretation of researchers, which can introduce bias into the research process. The researcher’s perspective, beliefs, and experiences can influence the way data is collected, analyzed, and interpreted.
- Limited generalizability: Qualitative research typically involves small, purposive samples that may not be representative of larger populations. This limits the generalizability of findings to other contexts or populations.
- Time-consuming: Qualitative research can be a time-consuming process, requiring significant resources for data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
- Resource-intensive: Qualitative research may require more resources than other research methods, including specialized training for researchers, specialized software for data analysis, and transcription services.
- Limited reliability: Qualitative research may be less reliable than quantitative research, as it relies on the subjective interpretation of researchers. This can make it difficult to replicate findings or compare results across different studies.
- Ethics and confidentiality: Qualitative research involves collecting sensitive information from participants, which raises ethical concerns about confidentiality and informed consent. Researchers must take care to protect the privacy and confidentiality of participants and obtain informed consent.
Also see Research Methods
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide

Leon and Anne Goldberg Professor of Humanities, Sociology and Anthropology
Massachusetts Institute of Technology

Senior Associate Dean for Open Learning
Professor of History
Vice President for Open Learning
Valid Certificate ID: c0e4f509-ad1e-4851-a3b3-f5256c729af6
- Terms of Services
- Privacy Policy
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.

StatPearls [Internet].
Qualitative study.
Steven Tenny ; Janelle M. Brannan ; Grace D. Brannan .
Affiliations
Last Update: September 18, 2022 .
- Introduction
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems. [1] Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervene or introduce treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypotheses as well as further investigate and understand quantitative data. Qualitative research gathers participants' experiences, perceptions, and behavior. It answers the hows and whys instead of how many or how much. It could be structured as a stand-alone study, purely relying on qualitative data or it could be part of mixed-methods research that combines qualitative and quantitative data. This review introduces the readers to some basic concepts, definitions, terminology, and application of qualitative research.
Qualitative research at its core, ask open-ended questions whose answers are not easily put into numbers such as ‘how’ and ‘why’. [2] Due to the open-ended nature of the research questions at hand, qualitative research design is often not linear in the same way quantitative design is. [2] One of the strengths of qualitative research is its ability to explain processes and patterns of human behavior that can be difficult to quantify. [3] Phenomena such as experiences, attitudes, and behaviors can be difficult to accurately capture quantitatively, whereas a qualitative approach allows participants themselves to explain how, why, or what they were thinking, feeling, and experiencing at a certain time or during an event of interest. Quantifying qualitative data certainly is possible, but at its core, qualitative data is looking for themes and patterns that can be difficult to quantify and it is important to ensure that the context and narrative of qualitative work are not lost by trying to quantify something that is not meant to be quantified.
However, while qualitative research is sometimes placed in opposition to quantitative research, where they are necessarily opposites and therefore ‘compete’ against each other and the philosophical paradigms associated with each, qualitative and quantitative work are not necessarily opposites nor are they incompatible. [4] While qualitative and quantitative approaches are different, they are not necessarily opposites, and they are certainly not mutually exclusive. For instance, qualitative research can help expand and deepen understanding of data or results obtained from quantitative analysis. For example, say a quantitative analysis has determined that there is a correlation between length of stay and level of patient satisfaction, but why does this correlation exist? This dual-focus scenario shows one way in which qualitative and quantitative research could be integrated together.
Examples of Qualitative Research Approaches
Ethnography
Ethnography as a research design has its origins in social and cultural anthropology, and involves the researcher being directly immersed in the participant’s environment. [2] Through this immersion, the ethnographer can use a variety of data collection techniques with the aim of being able to produce a comprehensive account of the social phenomena that occurred during the research period. [2] That is to say, the researcher’s aim with ethnography is to immerse themselves into the research population and come out of it with accounts of actions, behaviors, events, etc. through the eyes of someone involved in the population. Direct involvement of the researcher with the target population is one benefit of ethnographic research because it can then be possible to find data that is otherwise very difficult to extract and record.
Grounded Theory
Grounded Theory is the “generation of a theoretical model through the experience of observing a study population and developing a comparative analysis of their speech and behavior.” [5] As opposed to quantitative research which is deductive and tests or verifies an existing theory, grounded theory research is inductive and therefore lends itself to research that is aiming to study social interactions or experiences. [3] [2] In essence, Grounded Theory’s goal is to explain for example how and why an event occurs or how and why people might behave a certain way. Through observing the population, a researcher using the Grounded Theory approach can then develop a theory to explain the phenomena of interest.
Phenomenology
Phenomenology is defined as the “study of the meaning of phenomena or the study of the particular”. [5] At first glance, it might seem that Grounded Theory and Phenomenology are quite similar, but upon careful examination, the differences can be seen. At its core, phenomenology looks to investigate experiences from the perspective of the individual. [2] Phenomenology is essentially looking into the ‘lived experiences’ of the participants and aims to examine how and why participants behaved a certain way, from their perspective . Herein lies one of the main differences between Grounded Theory and Phenomenology. Grounded Theory aims to develop a theory for social phenomena through an examination of various data sources whereas Phenomenology focuses on describing and explaining an event or phenomena from the perspective of those who have experienced it.
Narrative Research
One of qualitative research’s strengths lies in its ability to tell a story, often from the perspective of those directly involved in it. Reporting on qualitative research involves including details and descriptions of the setting involved and quotes from participants. This detail is called ‘thick’ or ‘rich’ description and is a strength of qualitative research. Narrative research is rife with the possibilities of ‘thick’ description as this approach weaves together a sequence of events, usually from just one or two individuals, in the hopes of creating a cohesive story, or narrative. [2] While it might seem like a waste of time to focus on such a specific, individual level, understanding one or two people’s narratives for an event or phenomenon can help to inform researchers about the influences that helped shape that narrative. The tension or conflict of differing narratives can be “opportunities for innovation”. [2]
Research Paradigm
Research paradigms are the assumptions, norms, and standards that underpin different approaches to research. Essentially, research paradigms are the ‘worldview’ that inform research. [4] It is valuable for researchers, both qualitative and quantitative, to understand what paradigm they are working within because understanding the theoretical basis of research paradigms allows researchers to understand the strengths and weaknesses of the approach being used and adjust accordingly. Different paradigms have different ontology and epistemologies . Ontology is defined as the "assumptions about the nature of reality” whereas epistemology is defined as the “assumptions about the nature of knowledge” that inform the work researchers do. [2] It is important to understand the ontological and epistemological foundations of the research paradigm researchers are working within to allow for a full understanding of the approach being used and the assumptions that underpin the approach as a whole. Further, it is crucial that researchers understand their own ontological and epistemological assumptions about the world in general because their assumptions about the world will necessarily impact how they interact with research. A discussion of the research paradigm is not complete without describing positivist, postpositivist, and constructivist philosophies.
Positivist vs Postpositivist
To further understand qualitative research, we need to discuss positivist and postpositivist frameworks. Positivism is a philosophy that the scientific method can and should be applied to social as well as natural sciences. [4] Essentially, positivist thinking insists that the social sciences should use natural science methods in its research which stems from positivist ontology that there is an objective reality that exists that is fully independent of our perception of the world as individuals. Quantitative research is rooted in positivist philosophy, which can be seen in the value it places on concepts such as causality, generalizability, and replicability.
Conversely, postpositivists argue that social reality can never be one hundred percent explained but it could be approximated. [4] Indeed, qualitative researchers have been insisting that there are “fundamental limits to the extent to which the methods and procedures of the natural sciences could be applied to the social world” and therefore postpositivist philosophy is often associated with qualitative research. [4] An example of positivist versus postpositivist values in research might be that positivist philosophies value hypothesis-testing, whereas postpositivist philosophies value the ability to formulate a substantive theory.
Constructivist
Constructivism is a subcategory of postpositivism. Most researchers invested in postpositivist research are constructivist as well, meaning they think there is no objective external reality that exists but rather that reality is constructed. Constructivism is a theoretical lens that emphasizes the dynamic nature of our world. “Constructivism contends that individuals’ views are directly influenced by their experiences, and it is these individual experiences and views that shape their perspective of reality”. [6] Essentially, Constructivist thought focuses on how ‘reality’ is not a fixed certainty and experiences, interactions, and backgrounds give people a unique view of the world. Constructivism contends, unlike in positivist views, that there is not necessarily an ‘objective’ reality we all experience. This is the ‘relativist’ ontological view that reality and the world we live in are dynamic and socially constructed. Therefore, qualitative scientific knowledge can be inductive as well as deductive.” [4]
So why is it important to understand the differences in assumptions that different philosophies and approaches to research have? Fundamentally, the assumptions underpinning the research tools a researcher selects provide an overall base for the assumptions the rest of the research will have and can even change the role of the researcher themselves. [2] For example, is the researcher an ‘objective’ observer such as in positivist quantitative work? Or is the researcher an active participant in the research itself, as in postpositivist qualitative work? Understanding the philosophical base of the research undertaken allows researchers to fully understand the implications of their work and their role within the research, as well as reflect on their own positionality and bias as it pertains to the research they are conducting.
Data Sampling
The better the sample represents the intended study population, the more likely the researcher is to encompass the varying factors at play. The following are examples of participant sampling and selection: [7]
- Purposive sampling- selection based on the researcher’s rationale in terms of being the most informative.
- Criterion sampling-selection based on pre-identified factors.
- Convenience sampling- selection based on availability.
- Snowball sampling- the selection is by referral from other participants or people who know potential participants.
- Extreme case sampling- targeted selection of rare cases.
- Typical case sampling-selection based on regular or average participants.
Data Collection and Analysis
Qualitative research uses several techniques including interviews, focus groups, and observation. [1] [2] [3] Interviews may be unstructured, with open-ended questions on a topic and the interviewer adapts to the responses. Structured interviews have a predetermined number of questions that every participant is asked. It is usually one on one and is appropriate for sensitive topics or topics needing an in-depth exploration. Focus groups are often held with 8-12 target participants and are used when group dynamics and collective views on a topic are desired. Researchers can be a participant-observer to share the experiences of the subject or a non-participant or detached observer.
While quantitative research design prescribes a controlled environment for data collection, qualitative data collection may be in a central location or in the environment of the participants, depending on the study goals and design. Qualitative research could amount to a large amount of data. Data is transcribed which may then be coded manually or with the use of Computer Assisted Qualitative Data Analysis Software or CAQDAS such as ATLAS.ti or NVivo. [8] [9] [10]
After the coding process, qualitative research results could be in various formats. It could be a synthesis and interpretation presented with excerpts from the data. [11] Results also could be in the form of themes and theory or model development.
Dissemination
To standardize and facilitate the dissemination of qualitative research outcomes, the healthcare team can use two reporting standards. The Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research or COREQ is a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. [12] The Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR) is a checklist covering a wider range of qualitative research. [13]
Examples of Application
Many times a research question will start with qualitative research. The qualitative research will help generate the research hypothesis which can be tested with quantitative methods. After the data is collected and analyzed with quantitative methods, a set of qualitative methods can be used to dive deeper into the data for a better understanding of what the numbers truly mean and their implications. The qualitative methods can then help clarify the quantitative data and also help refine the hypothesis for future research. Furthermore, with qualitative research researchers can explore subjects that are poorly studied with quantitative methods. These include opinions, individual's actions, and social science research.
A good qualitative study design starts with a goal or objective. This should be clearly defined or stated. The target population needs to be specified. A method for obtaining information from the study population must be carefully detailed to ensure there are no omissions of part of the target population. A proper collection method should be selected which will help obtain the desired information without overly limiting the collected data because many times, the information sought is not well compartmentalized or obtained. Finally, the design should ensure adequate methods for analyzing the data. An example may help better clarify some of the various aspects of qualitative research.
A researcher wants to decrease the number of teenagers who smoke in their community. The researcher could begin by asking current teen smokers why they started smoking through structured or unstructured interviews (qualitative research). The researcher can also get together a group of current teenage smokers and conduct a focus group to help brainstorm factors that may have prevented them from starting to smoke (qualitative research).
In this example, the researcher has used qualitative research methods (interviews and focus groups) to generate a list of ideas of both why teens start to smoke as well as factors that may have prevented them from starting to smoke. Next, the researcher compiles this data. The research found that, hypothetically, peer pressure, health issues, cost, being considered “cool,” and rebellious behavior all might increase or decrease the likelihood of teens starting to smoke.
The researcher creates a survey asking teen participants to rank how important each of the above factors is in either starting smoking (for current smokers) or not smoking (for current non-smokers). This survey provides specific numbers (ranked importance of each factor) and is thus a quantitative research tool.
The researcher can use the results of the survey to focus efforts on the one or two highest-ranked factors. Let us say the researcher found that health was the major factor that keeps teens from starting to smoke, and peer pressure was the major factor that contributed to teens to start smoking. The researcher can go back to qualitative research methods to dive deeper into each of these for more information. The researcher wants to focus on how to keep teens from starting to smoke, so they focus on the peer pressure aspect.
The researcher can conduct interviews and/or focus groups (qualitative research) about what types and forms of peer pressure are commonly encountered, where the peer pressure comes from, and where smoking first starts. The researcher hypothetically finds that peer pressure often occurs after school at the local teen hangouts, mostly the local park. The researcher also hypothetically finds that peer pressure comes from older, current smokers who provide the cigarettes.
The researcher could further explore this observation made at the local teen hangouts (qualitative research) and take notes regarding who is smoking, who is not, and what observable factors are at play for peer pressure of smoking. The researcher finds a local park where many local teenagers hang out and see that a shady, overgrown area of the park is where the smokers tend to hang out. The researcher notes the smoking teenagers buy their cigarettes from a local convenience store adjacent to the park where the clerk does not check identification before selling cigarettes. These observations fall under qualitative research.
If the researcher returns to the park and counts how many individuals smoke in each region of the park, this numerical data would be quantitative research. Based on the researcher's efforts thus far, they conclude that local teen smoking and teenagers who start to smoke may decrease if there are fewer overgrown areas of the park and the local convenience store does not sell cigarettes to underage individuals.
The researcher could try to have the parks department reassess the shady areas to make them less conducive to the smokers or identify how to limit the sales of cigarettes to underage individuals by the convenience store. The researcher would then cycle back to qualitative methods of asking at-risk population their perceptions of the changes, what factors are still at play, as well as quantitative research that includes teen smoking rates in the community, the incidence of new teen smokers, among others. [14] [15]
Qualitative research functions as a standalone research design or in combination with quantitative research to enhance our understanding of the world. Qualitative research uses techniques including structured and unstructured interviews, focus groups, and participant observation to not only help generate hypotheses which can be more rigorously tested with quantitative research but also to help researchers delve deeper into the quantitative research numbers, understand what they mean, and understand what the implications are. Qualitative research provides researchers with a way to understand what is going on, especially when things are not easily categorized. [16]
- Issues of Concern
As discussed in the sections above, quantitative and qualitative work differ in many different ways, including the criteria for evaluating them. There are four well-established criteria for evaluating quantitative data: internal validity, external validity, reliability, and objectivity. The correlating concepts in qualitative research are credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability. [4] [11] The corresponding quantitative and qualitative concepts can be seen below, with the quantitative concept is on the left, and the qualitative concept is on the right:
- Internal validity--- Credibility
- External validity---Transferability
- Reliability---Dependability
- Objectivity---Confirmability
In conducting qualitative research, ensuring these concepts are satisfied and well thought out can mitigate potential issues from arising. For example, just as a researcher will ensure that their quantitative study is internally valid so should qualitative researchers ensure that their work has credibility.
Indicators such as triangulation and peer examination can help evaluate the credibility of qualitative work.
- Triangulation: Triangulation involves using multiple methods of data collection to increase the likelihood of getting a reliable and accurate result. In our above magic example, the result would be more reliable by also interviewing the magician, back-stage hand, and the person who "vanished." In qualitative research, triangulation can include using telephone surveys, in-person surveys, focus groups, and interviews as well as surveying an adequate cross-section of the target demographic.
- Peer examination: Results can be reviewed by a peer to ensure the data is consistent with the findings.
‘Thick’ or ‘rich’ description can be used to evaluate the transferability of qualitative research whereas using an indicator such as an audit trail might help with evaluating the dependability and confirmability.
- Thick or rich description is a detailed and thorough description of details, the setting, and quotes from participants in the research. [5] Thick descriptions will include a detailed explanation of how the study was carried out. Thick descriptions are detailed enough to allow readers to draw conclusions and interpret the data themselves, which can help with transferability and replicability.
- Audit trail: An audit trail provides a documented set of steps of how the participants were selected and the data was collected. The original records of information should also be kept (e.g., surveys, notes, recordings).
One issue of concern that qualitative researchers should take into consideration is observation bias. Here are a few examples:
- Hawthorne effect: The Hawthorne effect is the change in participant behavior when they know they are being observed. If a researcher was wanting to identify factors that contribute to employee theft and tells the employees they are going to watch them to see what factors affect employee theft, one would suspect employee behavior would change when they know they are being watched.
- Observer-expectancy effect: Some participants change their behavior or responses to satisfy the researcher's desired effect. This happens in an unconscious manner for the participant so it is important to eliminate or limit transmitting the researcher's views.
- Artificial scenario effect: Some qualitative research occurs in artificial scenarios and/or with preset goals. In such situations, the information may not be accurate because of the artificial nature of the scenario. The preset goals may limit the qualitative information obtained.
- Clinical Significance
Qualitative research by itself or combined with quantitative research helps healthcare providers understand patients and the impact and challenges of the care they deliver. Qualitative research provides an opportunity to generate and refine hypotheses and delve deeper into the data generated by quantitative research. Qualitative research does not exist as an island apart from quantitative research, but as an integral part of research methods to be used for the understanding of the world around us. [17]
- Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Qualitative research is important for all members of the health care team as all are affected by qualitative research. Qualitative research may help develop a theory or a model for health research that can be further explored by quantitative research. Much of the qualitative research data acquisition is completed by numerous team members including social works, scientists, nurses, etc. Within each area of the medical field, there is copious ongoing qualitative research including physician-patient interactions, nursing-patient interactions, patient-environment interactions, health care team function, patient information delivery, etc.
- Review Questions
- Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
- Comment on this article.
Disclosure: Steven Tenny declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Janelle Brannan declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Grace Brannan declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
- Cite this Page Tenny S, Brannan JM, Brannan GD. Qualitative Study. [Updated 2022 Sep 18]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
In this Page
Bulk download.
- Bulk download StatPearls data from FTP
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- Suicidal Ideation. [StatPearls. 2024] Suicidal Ideation. Harmer B, Lee S, Duong TVH, Saadabadi A. StatPearls. 2024 Jan
- Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas. [Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022] Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas. Crider K, Williams J, Qi YP, Gutman J, Yeung L, Mai C, Finkelstain J, Mehta S, Pons-Duran C, Menéndez C, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1; 2(2022). Epub 2022 Feb 1.
- Macromolecular crowding: chemistry and physics meet biology (Ascona, Switzerland, 10-14 June 2012). [Phys Biol. 2013] Macromolecular crowding: chemistry and physics meet biology (Ascona, Switzerland, 10-14 June 2012). Foffi G, Pastore A, Piazza F, Temussi PA. Phys Biol. 2013 Aug; 10(4):040301. Epub 2013 Aug 2.
- Review Evidence Brief: The Effectiveness Of Mandatory Computer-Based Trainings On Government Ethics, Workplace Harassment, Or Privacy And Information Security-Related Topics [ 2014] Review Evidence Brief: The Effectiveness Of Mandatory Computer-Based Trainings On Government Ethics, Workplace Harassment, Or Privacy And Information Security-Related Topics Peterson K, McCleery E. 2014 May
- Review Public sector reforms and their impact on the level of corruption: A systematic review. [Campbell Syst Rev. 2021] Review Public sector reforms and their impact on the level of corruption: A systematic review. Mugellini G, Della Bella S, Colagrossi M, Isenring GL, Killias M. Campbell Syst Rev. 2021 Jun; 17(2):e1173. Epub 2021 May 24.
Recent Activity
- Qualitative Study - StatPearls Qualitative Study - StatPearls
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Qualitative Data Analysis Just Got Easier: Quick Start Your Data Analysis with MAXQDA. Intuitive and Easy-to-Use Qualitative Data Analysis Software. Start Your Free Trial!
Method 1: Content Analysis. Content analysis is a methodical technique for analyzing textual or visual data in a structured manner. In this method, you will categorize qualitative data by splitting it into manageable pieces and assigning the manual coding process to these units.
QDA Method #1: Qualitative Content Analysis. Content analysis is possibly the most common and straightforward QDA method. At the simplest level, content analysis is used to evaluate patterns within a piece of content (for example, words, phrases or images) or across multiple pieces of content or sources of communication. For example, a collection of newspaper articles or political speeches.
Qualitative Data Analysis methods. Once all the data has been captured, there are a variety of analysis techniques available and the choice is determined by your specific research objectives and the kind of data you've gathered. Common qualitative data analysis methods include: Content Analysis. This is a popular approach to qualitative data ...
For many researchers unfamiliar with qualitative research, determining how to conduct qualitative analyses is often quite challenging. Part of this challenge is due to the seemingly limitless approaches that a qualitative researcher might leverage, as well as simply learning to think like a qualitative researcher when analyzing data. From framework analysis (Ritchie & Spencer, 1994) to content ...
Aims of Qualitative Data Analysis The analysis of qualitative data can have several aims. The first aim may be to describe a phenomenon in some or greater detail. The phenomenon can be the subjective experi-ences of a specific individual or group (e.g. the way people continue to live after a fatal diagnosis). This can focus on the case (indi-
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and analyzing numerical data for statistical analysis. Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, history, etc. Qualitative research question examples
5. Grounded theory. This method of qualitative data analysis starts with an analysis of a single case to formulate a theory. Then, additional cases are examined to see if they contribute to the theory. Qualitative data analysis can be conducted through the following three steps: Step 1: Developing and Applying Codes.
analysis process, as it does in the design and data collection phase. Qualitative research methods are not "routinized", meaning there are many different ways to think about qualitative research and the creative approaches that can be used. Good qualitative research contributes to science via a
By only being aware of a few qualitative data-analysis approaches, a qualitative researcher might make the data fit the analysis rather than select the most appropriate data-analysis approach given the underlying research elements such as the research question, researcher's lens, and sampling and design characteristics.
Qualitative data analysis is a slow process of moving backwards and forwards between the research question (RQ), theory, and your data from the transcribed interviews while thinking about the context of your study. Although it takes time, it is essential to be systematic and rigorous to create trustworthy findings.
This chapter provides an overview of selected qualitative data analysis strategies with a particular focus on codes and coding. Preparatory strategies for a qualitative research study and data management are first outlined. Six coding methods are then profiled using comparable interview data: process coding, in vivo coding, descriptive coding ...
Step 1: Organizing the Data. "Valid analysis is immensely aided by data displays that are focused enough to permit viewing of a full data set in one location and are systematically arranged to answer the research question at hand." (Huberman and Miles, 1994, p. 432) The best way to organize your data is to go back to your interview guide.
How to conduct qualitative research? Given that qualitative research is characterised by flexibility, openness and responsivity to context, the steps of data collection and analysis are not as separate and consecutive as they tend to be in quantitative research [13, 14].As Fossey puts it: "sampling, data collection, analysis and interpretation are related to each other in a cyclical ...
5 qualitative data analysis methods explained. Qualitative data analysis is the process of organizing, analyzing, and interpreting qualitative research data—non-numeric, conceptual information, and user feedback—to capture themes and patterns, answer research questions, and identify actions to improve your product or website.Step 1 in the research process (after planning) is qualitative ...
How to analyze qualitative data from an interview. To analyze qualitative data from an interview, follow the same 6 steps for quantitative data analysis: Perform the interviews. Transcribe the interviews onto paper. Decide whether to either code analytical data (open, axial, selective), analyze word frequencies, or both.
Qualitative data analysis is an umbrella term that encompasses many steps and processes. The term describes ways we work with data collected with qualitative methods, which can take many forms. We might have field notes or research journal entries, written or verbal responses to questions, media or audio files, visual data such as photographs ...
Qualitative Research. Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding people's beliefs, attitudes, behaviors, and experiences through the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. It seeks to answer research questions through the examination of subjective data, such as interviews, focus ...
This paper presents a variety of data analysis techniques described by various qualitative researchers, such as LeCompte and Schensul, Wolcott, and Miles and Huberman. It further shares several ...
INTRODUCTION. In an earlier paper, 1 we presented an introduction to using qualitative research methods in pharmacy practice. In this article, we review some principles of the collection, analysis, and management of qualitative data to help pharmacists interested in doing research in their practice to continue their learning in this area.
Thematic analysis is a method of data analysis in qualitative research that most researchers use, and it is flexible because it can be applied and utilized broadly across various epistemologies ...
Though the data analysis phase of qualitative research is more difficult to execute rapidly compared to other steps (e.g., project planning, data collecion, and transcription), there are ways to expedite the data analysis phase, so that the organization, coding, analysis, and reduction of data can be handled in a more streamlined manner ...
In some cases, qualitative data can also include pictorial display, audio or video clips (e.g. audio and visual recordings of patients, radiology film, and surgery videos), or other multimedia materials. Data analysis is the part of qualitative research that most distinctively differentiates from quantitative research methods.
Data analysis is a challenging and exciting stage of the qualitative research process. It requires a mix of creativity and systematic searching, a blend of inspiration and diligent detection. Fortunately (or not), there is no clear-cut set of conventions governing the processes involved in the analysis of qualitative data instead of that of ...
This is to certify that Hugo Alonso Valverde Parra has successfully completed Qualitative Research Methods: Data Coding and Analysis Nov. 1, 2022 - Nov. 18, 2023 Susan Silbey. Leon and Anne Goldberg Professor of Humanities, Sociology and Anthropology. Massachusetts Institute of Technology ...
Qualitative research gathers participants' experiences, perceptions, and behavior. It answers the hows and whys instead of how many or how much. It could be structured as a stand-alone study, purely relying on qualitative data or it could be part of mixed-methods research that combines qualitative and quantitative data.
A novel (nonlinear) mathematical model for the transmission of Coronavirus 19 (COVID-19) with eight compartments and considering the impact of vaccination is examined in this manuscript. The qualitative behavior of the system such as the boundedness of solutions, the basic reproduction number, and the stability of the equilibrium points is investigated in detail. Some domestic real data ...