An Undergraduate's Guide to Funding and Publishing Research
- URECA and other SBU Research Programs and Opportunities
- Funding Your Research
- Publishing Your Research: Why and How?
- Publishing Your Research: List of Undergraduate Journals

SBU's own publications
Note that among the journals listed here are SBU's own publications such as SBU Brooklogue , Young Investigator's Review and the Stony Brook Undergraduate History Journal .
How do I know whether my discipline is considered a Humanities or Social Science field?
Humanities includes fields such as Art History, Classics, English, Comparative Literature, History, Musicology, and Philosophy. Sometimes History can be considered broadly as either a Humanities or Social Science discipline, but for the sake of this list, most history journals are listed in the Arts & Humanities category. Likewise, Women's, Gender, and Sexuality Studies and related fields often use methods from both Humanities and Social Science research, so you might find related topics on either the Humanities or Social Science list. Psychology is another borderline discipline that might be classified as either a social science or STEM field. For the sake of this list, Psychology is listed with the Social Sciences. STEM fields are those affiliated with science, technology, engineering, or math.
Journals that publish undergraduate research
There are many journals that focus specifically on publishing undergraduate research. The Council on Undergraduate Research (CUR) keeps an ever growing list of journals that feature undergraduate work . However, many of those listed by CUR are hosted by a specific institution and might only publish the work of their own students, and others might not be peer-reviewed or have publishing fees, so read the descriptions carefully. And, as always, carefully review each journal's website, published articles, and the author submission guidelines before submitting your work.
Below is a list of selected journals that SBU undergraduates are eligible to submit to, organized into the following categories:
- Broad Scope: Journals that publish research in any disciplinary area.
- Arts and Humanities : Fields such as Art History, Classics, English, Comparative Literature, Cultural Studies, History, Musicology, Philosophy, Theology, and Writing & Rhetoric. Sometimes History-related fields are also classified as a Social Science, but on this page, most history journals are in the Arts & Humanities category.
- Social Sciences: Fields such as Sociology, Psychology, Economics, International Affairs, Geography, Sustainability, Political Science, and Human Rights are included here.
- STEM : Fields in the hard sciences, technology, engineering and mathematics.
Broad Scope: Journals that publish research in any discipline
- Aletheia: The Alpha Chi Journal of Undergraduate Scholarship Peer-reviewed journal for undergraduate scholarship run by the Alpha Chi National College Honor Society.
- American Journal of Undergraduate Research (AJUR) AJUR is a national, independent, faculty peer-reviewed, open-source, quarterly, multidisciplinary student research journal.
- Butler Journal of Undergraduate Research (BJUR) Submission of original, scholarly research articles is open to undergraduates from any accredited college or university. BJUR publishes scholarship across the humanities, social sciences, and natural sciences.
- Discussions: The Undergraduate Research Journal of Case Western Reserve University The journal accepts research papers written by current undergraduate students from accredited colleges and universities around the globe. The research can be on any topic.
- Inquiries: Social Sciences, Arts, & Humanities An open access academic journal focusing on publishing high quality original work across a range of disciplines, especially on work in the social sciences, arts, and humanities.
- International Journal of Undergraduate Research & Creative Activities (IJURCA) Peer-reviewed, open-access journal dedicated to the publication of outstanding scholarship by undergraduates and their mentors. Accepts submissions from all academic disciplines, including original research in the the form of articles and literature reviews, as well as creative work in a variety of media.
- Journal of Student Research Multidisciplinary and faculty-reviewed journal devoted to the rapid dissemination of current research done by high school, undergraduate, and graduate students.
- Midwest Journal of Undergraduate Research Multidisciplinary scholarly journal produced by a team of Monmouth College student editors and faculty members with peer and faculty reviewers for each article.
- SBU Brooklogue SBU's exclusively undergraduate, peer-reviewed journal for humanities and social sciences.
- Undergraduate Research Journal Double-blind, educator-reviewed print and electronic journal published annually. A forum for multidisciplinary undergraduate research and creative endeavors including case studies, conceptual pieces, creative writing, journalism writings, literature reviews, original art, photography, and scientific studies. Highlights mentored undergraduate scholarly products across all disciplines from all types of higher education institutions.
- UReCA: The NCHC Journal of Undergraduate Research & Creative Activity The official undergraduate journal of the National Collegiate Honors Council. Submissions are accepted from undergraduates in the following categories: STEM, Social Science, Humanities, Fine Art, and Creative Writing.
Arts and Humanities
- Animus: The Undergraduate Classical Journal of the University of Chicago Supports undergraduate scholarship in the Classics and related fields.
- Apollon Undergraduate Journal A peer-reviewed journal run by faculty and students at Fairfield University. Any undergraduate student whose research was produced through coursework in the humanities may submit.
- Archive: An Undergraduate Journal of History Accepts submissions of History scholarship, including scholarly papers, articles, book reviews, and historical essays from undergraduate students of all majors from colleges and universities in the U.S. or abroad.
- Berkeley Undergraduate Journal of Classics Original manuscripts on any topic related to Classics from undergraduate students in any major at an institution which confers a bachelor's degree are eligible to submit.
- Clio's Scroll: The Berkeley Undergraduate History Journal The journal publishes articles by undergraduates and recent graduates of any university on historical topics.
- Dies Ligibiles: An Undergraduate Journal of Medieval Studies The journal accepts research papers, book reviews, translations, and art in English, French, and Spanish from any undergraduate student at any college or university. The work must pertain to the time period 400 - 1600 CE.
- Epistemai: An Undergraduate Philosophy Journal A student-run philosophy journal at the University of Minnesota Twin Cities. The journal publishes short, original philosophical work done by undergraduates from universities across the country, and internationally.
- Falsafa: Undergraduate Journal of Philosophy Run by the Philosophy Club at the University of California, Irvine, this journal highlights philosophical ideas and research by undergraduates.
- Forbes & Fifth This undergraduate journal of the Dietrich School of Arts and Sciences at the University of Pittsburgh considers both scholarly and creative work from students at any accredited university in the world.
- The Gettysburg College Journal of the Civil War Era Open access peer-reviewed undergraduate journal that publishes academic essays, public history essays, and book reviews on the Civil War Era.
- History Matters: An Undergraduate Journal of Historical Research An undergraduate history journal published annually by the Department of History at Appalachian State University. The journal is indexed by EBSCOhost's America: History and Life.
- Journal of Art History and Museum Studies (JAHMS) An undergraduate peer-reviewed journal that publishes undergraduate scholarship by a diverse coalition of student artists and historians.
- The Kennesaw Tower: Undergraduate Foreign Language Research Journal Annual undergraduate double blind and peer-reviewed journal publishes scholarly work of advanced undergraduates students in Chinese, FLED, French, German, Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish.
- Mysterion: The Theology Journal of Boston College Publishes undergraduate research from around the world on topics related to theology.
- Nota Bene: Canadian Undergraduate Journal of Musicology Publishes essays written by undergraduate students from universities around the world. Topics include historical musicology, ethnomusicology, popular music studies, music theory, music education, and interdisciplinary subjects. Double blind review by professors across Canada.
- The Oswald Review: An International Journal of Undergraduate Research and Criticism in the Discipline of English Published annually, and requiring a faculty member's endorsement, the refereed journal in indexed in EBSCO and accepts undergraduate criticism and research in the field of English from students throughout the U.S. and abroad.
- Queen City Writers: a journal of undergraduate writing & composing Refereed journal that publishes essays and multimedia work by undergraduate students affiliated with any post-secondary institution. Topics covered include writing, rhetoric, reading, pedagogy, literacy broadly conceived, popular culture and media, community discourses and multimodal and digital composing.
- Rock Creek Review An undergraduate journal edited, produced and published at Heidelberg University in partnership with the English Department. The journal publishes literary research from schools around the world for an annual publication. Check the website for the "call for papers," which will explain the theme of the next issue.
- RhetTech Undergraduate Journal Run by students at James Madison University, this journal showcases exemplary work being done in undergraduate writing, rhetoric, and technical communication courses around the country.
- Simpliciter: Brandies Philosophy Journal Run by students at Brandeis University, this journal aims to recognize excellent works of philosophy produced by undergraduates from universities anywhere in the world.
- sprinkle: an undergraduate journal of feminist and queer studies A peer-reviewed journal devoted to the diverse voices of emerging scholar-activists, authors, and artists in Women's Gender & Queer Studies and related fields. First established at McGill University, sprinkle is now published at Cal Poly San Luis Obispo and welcomes submissions from around the world.
- Stance: An International Undergraduate Philosophy Journal Peer-reviewed journal publishes original work by undergraduates from around the world.
- Stony Brook Undergraduate History Journal Peer-reviewed publication that showcases the research of SBU students writing about history at the local, national and international levels.
- UC Berkeley Comparative Literature Undergraduate Journal Publishes undergraduate research in comparative texts and media, treating a broad range of topics including theoretical literary discourse, international trends in literature, and comparisons for national literature. Showcases the best work across the U.S. and also highlight more contemplative writing by students regarding multicultural issues, culture shock, or transnational experiences such as studying abroad.
- UC Santa Barbara Undergraduate Journal of History A space for undergraduates to share original research other scholarly works of history. Reviewed by graduate students with faculty mentorship.
- The Word: The Stanford Journal of Student Hiphop Research Continually solicits research papers and blog content related to hiphop culture. An open-source, open peer-refereed journal. Open to undergraduates from any college or university.
- Xchanges: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Technical Communication, Rhetoric, and Writing Across the Curriculum The fall issues publishes these and research projects of upper-level undergraduate students. Submissions may be traditional articles or multimodal "webtexts." Based in the English Department at the University of New Mexico.
- Yale Historical Review Welcomes works from undergraduates at any institution on any historically relevant topic.
- Young Scholars in Writing (YSW) An international peer-reviewed journal. Publishes original research and theoretical articles by undergraduates of all majors and years on the subjects of rhetoric, writing, writers, discourse, language, and related topics.
Social Sciences
- Afkar: The Undergraduate Journal of Middle East Studies International peer-reviewed journal that accepts research articles, essays, and book reviews that focus on the politics, history, culture, and society of the Middle East and North Africa.
- Al Noor Boston College's Middle Eastern Studies journal. It is run by undergraduates and publishes work from students around the world.
- Chicago Journal of Foreign Policy: University of Chicago's Premiere Undergraduate Journal of International Affairs Accepts submissions from undergraduates from around the world on articles related to foreign policy, international relations, and related topics, preferably pertaining to the period since 1945..
- Compass: An Undergraduate Journal of American Political Ideas A joint project of Northern Illinois University and Arizona State University, Compass publishes work related to American democracy understood in the broad contexts of political philosophy, history, literature, economics, and culture.
- Consilience: The Journal of Sustainable Development To encourage an international community to think more broadly, deeply, and analytically about sustainable development, the journal publishes work by students, researchers, professors, and practitioners from a variety of academic fields and geographic regions.
- Critique: a worldwide student journal of politics Peer-reviewed journal that publishes scholarship by students of political science. The journal is recognized by the American Political Science Association and indexed by EBSCO.
- The Developing Economist Student-run undergraduate economics research journal, published with support from the Longhorn Chapter of the Omicron Delta Epsilon Economics Honor Society and the Department of Economics at the University of Texas at Austin.
- Issues in Political Economy Co-edited by undergraduates at Elon University and the University of Mary Washington, the journal publishes undergraduate research in the field of economics and is indexed in Cabell's Directory of Publishing Opportunities in Economics and Finance.
- Journal of Integrated Social Sciences A web-based, peer-reviewed journal committed to the scholarly investigation of social phenomena. We especially encourage students and their faculty advisors to submit the results of their investigations in Psychology, Sociology, and Gender Studies.
- Journal of Interpersonal Relations, Intergroup Relations, and Identity (JIRIRI) Affiliated with the Universite de Montreal, the international peer-reviewed journal publishes the work of undergraduates on new theoretical ideas in the fields of psychology, identity, interpersonal and intergroup relations. It publishes both theoretical and empirical articles.
- Journal of Politics and Society Published by the student group Helvidius at Columbia University, the journal focuses on undergraduate interdisciplinary research in the social sciences.
- The Journal of Undergraduate Ethnic Minority Psychology (JUEMP) Open access, double blind, peer-reviewed journal devoted to publishing research authored or co-authored by undergraduates. The journal is especially interested in submissions that are from ethnic minorities perspectives, that focus on the thoughts and behaviors of ethnic minority populations, or both.
- New Errands: The Undergraduate Journal of American Studies Sponsored by The Eastern American Studies Association and the American Studies Program at Penn State Harrisburg, this journal publishes undergraduate research in the field of American Studies.
- The Philosophy, Politics, and Economics Review International undergraduate journal housed in the Kellogg Center for Philosophy, Politics, and Economics at Virginia Tech. Through a double blind review process, the journal publishes original research in the humanities and social sciences from undergraduates worldwide.
- Process: Journal of Multidisciplinary Undergraduate Scholarship Published quarterly, the journal publishes undergraduate writings that rigorously engage with issues of social justice, transformative education, politics, identity, and cultural production. Publishes both critical essays and non-traditional or multimodal compositions.
- Righting Wrongs: A Journal of Human Rights Based at Webster University's Institute for Human Rights and Humanitarian Studies, this peer-reviewed academic journal publishes undergraduate research papers, book reviews, opinion pieces, and photo essays that explore human rights issues.
- Social Moments: A Student Journal of Social Relations Interdisciplinary peer-reviewed journal examining the social and cultural world through a social science lens. All undergraduate and graduate students are invited to submit work in any social science discipline.
- Sociology between the Gaps: Forgotten and Neglected Topics Undergraduates, graduates, and professionals in sociology and related fields may submit their articles, books and film reviews, and point of view essays. Double blind peer review.
- Undergraduate Economic Review (UER) Supported by the Department of Economics and The Ames Library at Illinois Wesleyan University, this is an open access peer-reviewed journal that publishes undergraduate research in the field of economics from around the world.
- Undergraduate Journal of Global Citizenship Based at Fairfield University, the journal publishes undergraduate research on topics related to International Studies such as global awareness, interdependence, environmental responsibility, social justice, humanitarianism, and other themes that promote the understanding of global citizenship.
- Undergraduate Journal of Service Learning & Community-Based Research Refereed, multidisciplinary, open access undergraduate journal that publishes articles from students all around the world. Accepted articles contribute to the literature on service learning and community-based research through reflection, research, or analysis. Based at University of North Carolina Wilmington.
- The Undergraduate Research Journal of Psychology at UCLA (URJP) Based at UCLA, but accepting submissions of undergraduate research from institutions all over the world, this peer-reviewed journal aims to empower undergraduate students to engage in and with research and facilitate scientific conversation and inquiry in the field of psychology.
STEM Fields
- Columbia Undergraduate Science Journal (CUSJ) Open access science journal that publishes manuscripts resulting from significant scientific research or analysis. Each paper undergoes a double-blind peer review process and a faculty review by the CUSJ Faculty Advisory Board.
- EvoS: The Evolutional Studies Consortium A peer-reviewed open access journal, EvoS welcomes work from all academic disciplines and interdisciplinary scholarship that incorporates evolutionary theory.
- Illumin Magazine: A Review of Engineering in Everyday Life An online magazine dedicated to exploring the science and technology behind the things we encounter every day. Features the work of University of Southern California undergraduate engineers, as well as submissions from universities across the U.S.
- Impulse: The Premier Undergraduate Neuroscience Journal International online neuroscience journal for undergraduate publications.
- International Journal of Exercise Science This journal engages undergraduate and graduate students in scholarly activity as both authors and reviewers. Articles on exercise science undergo peer review.
- Intersect: The Stanford Journal of Science, Technology, and Society An open access international science, technology, and society research journal that accepts undergraduate, graduate, and PhD submissions at the intersection of history, culture, sociology, art, literature, business, law, health, and design with science and technology. Students from around the world are invited to submit.
- Involve: A Journal of Mathematics High quality mathematical research involving students from all academic levels. Submissions should include substantial faculty input; faculty co-authorship is required and the submission should come from a faculty member.
- Journal of Undergraduate Chemistry Research Peer-reviewed journal that publishes undergraduate students' work in chemistry, including analytical, organic, inorganic, physical, polymers, and biochemistry.
- Journal of Undergraduate Kinesiology Research Published by the Kinesiology Department at the University of Wisconsin Eau Claire, the peer-reviewed, journal is dedicated to original undergraduate research in Kinesiology. Currently, the research originates from students at the University of Wisconsin, but undergraduates from all institutions are invited to submit.
- Journal of Undergraduate Reports in Physics (JURP) Peer-reviewed publication of the Society of Physics Students comprised of undergraduate research, outreach, and scholarly reporting.
- Journal of Young Investigators (JYI) JYI publishes original work in the sciences written by undergraduates mentored by a faculty member. The mission of the journal is to improve undergraduate science training by providing innovative, high quality educational experiences in science writing, publication, and the peer-review process.
- Psi Chi Journal Undergraduate, graduate, and faculty submissions welcome year round to this peer-reviewed psychology journal.
- Rose-Hulman Undergraduate Mathematics Journal Devoted entirely to papers written by undergraduates on topics in the mathematical sciences. Sponsored by the Mathematics Department at Rose-Hulman Institute of Technology, the journal accepts submissions from undergraduates around the world and faculty co-authors are not permitted.
- RURALS: Review of Undergraduate Research in Agricultural and Life Sciences Faculty-refereed international journal devoted to the publication of high quality research by undergraduates in all agricultural research problem areas.
- SIAM Undergraduate Research Online (SIURO) Run by the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM), SIURO publishes articles written by undergraduates from all over the world in the field of computational mathematics. Each paper must be submitted with a letter from a faculty advisor.
- Spectrum Published by the University of Alberta, this multidisciplinary journal publishes research completed by undergraduates in a variety of formats including research articles, review articles, music, video, visual arts, and creative writing.
- Spora: A Journal of Biomathematics Published by Illinois State, this is an open access refereed research journal dedicated to publishing high quality manuscripts by undergraduate or graduate students that describe mathematical and statistical techniques to solve problems in biological settings, as well as in experimental biology. Requires an article processing charge.
- PUMP Journal of Undergraduate Research PUMP stands for Preparing Undergraduate Mathematicians for Ph.D.s, and the journal publishes articles by undergraduates students who want to pursue doctoral studies in the Mathematical Sciences. The journal especially encourages submissions by students from underrepresented groups. Topics include pure and applied mathematics and statistics and authors may submit research papers, papers containing new proofs of known results, and expository papers which propose original points of view.
- Undergraduate Journal of Experimental Microbiology and Immunology (UJEMI+) Based at the University of British Columbia, the journal has two versions -- one that publishes only UBC students (UJEMI) and the other that is open to external submissions (UJEMI+). Dedicated to the publication of undergraduate articles in fields related to microbiology and immunology, the journal requires a formal endorsement from a course instructor or researcher who mentored the student authors.
- Young Investigator's Review Stony Brook's own student-run science journal!
- << Previous: Publishing Your Research: Why and How?
- Next: Contact >>
- Last Updated: Mar 26, 2024 11:42 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.stonybrook.edu/undergraduate_research
- Request a Class
- Hours & Locations
- Ask a Librarian
- Special Collections
- Library Faculty & Staff
Library Administration: 631.632.7100
- Stony Brook Home
- Campus Maps
- Web Accessibility Information
- Accessibility Barrier Report Form

Comments or Suggestions? | Library Webmaster

Except where otherwise noted, this work by SBU Libraries is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License .
The Journal of Purdue Undergraduate Research
Home > Libraries > LIBRARIESPUBLISHING > SPS > SPSOAJ > JPUR
The Journal of Purdue Undergraduate Research has been established to publish outstanding research papers written by Purdue undergraduates from all disciplines who have completed faculty-mentored research projects. The journal is run by students, but behind the scenes is a unique partnership between Purdue University Press and other departments of Purdue University Libraries, working with Purdue Marketing and Media and the Writing Lab, based in the Department of English. Publication of JPUR is sponsored by the Office of the Provost at Purdue University.
We are now accepting submissions for Volume 14 to be published in August 2024. The final deadline for the 2024 volume is February 15, 2024 . To submit your proposal, please use the "Submit Proposal" link on the left-hand navigation bar.
Student Opportunities
JPUR is an Open Access journal. This means that it uses a funding model that does not charge readers or their institutions for access. Readers may freely read, download, copy, distribute, print, search, or link to the full texts of articles. This journal is covered under the CC BY-NC-ND license. If you have concerns about the submission or publication terms for the Journal of Purdue Undergraduate Research , please contact the Journal Coordinator at [email protected].
Who is reading JPUR right now?
Current volume: volume 13 (2023).
Editorial Jenna Rickus
Clouds in the Ancient Lunar Atmosphere: Water Ice Nucleation on Aerosol Simulants Mariana C. Aguilar
Parentally Exposed Zebrafish Larvae Have Altered Craniofacial Measurements: Multigeneration Developmental Atrazine Toxicity Isabelle Akoro
A Computational Profile Of Invasive Lionfish In Belize: A New Insight on a Destructive Species Joshua E. Balan
Machine Learning of Big Data: A Gaussian Regression Model to Predict the Spatiotemporal Distribution of Ground Ozone Jerry Gu
Characterizing Differential Reflectivity Calibration Dependence on Environmental Temperature Using the X-band Teaching and Research Radar (XTRRA): Looking for a Relationship between Temperature and Differential Reflectivity Bias Emma Miller
Genome-Wide Mutagenesis to Investigate the N-Terminal Methylome: The Protective Effects of Hsp31 and Other Methylated Proteins in Yeast James Rooney and Jacob Lindsey
Trauma, Recovery, and Adolescent Relationships in Stephen Chbosky’s The Perks of Being a Wallflower: An In-Depth Analysis Rachel Rosen
The Role of Vocal Development Patterns: Predicting Neurogenetic Risk in Infancy Using Early Vocal Development and Sex Alyssa Cregg, Rachel Siela, Olivia Battaglia, Kaylee Bobay, Madison Chin, Athena Fordwor, Conghao Gao, Deeksha Handa, Erin Lee, Tiernan McDivitt, Grace Strabala, Victoria Tuell, and Laurel Williams
Biodiesel Transesterification of Spent Coffee Grounds Using DBU as a Catalyst: Using DBU to Make Biodiesel from Coffee Grounds Christopher Stepherson, Pericles Karras, Amy Ha, Phuc Tan Nguyen, Abigail Pati, Jacob Hejazi, Soheil Hussain, Elizabeth De Young, and Shuaicheng Fu
Sales of Cage-Free Eggs: The Impact of Proposition 12 on Egg Prices and Consumer Welfare in California Mingcong Xie
Research Snapshots
Dining Out Behavior in China and the Implications in the Post-COVID-19 Era Ji Yong Kwon
Evaluating the Efficacy of IPM Strategies Against Insect Pests of Collards Elliott Masterson
Laboratory Screening of Sorghum Lines for Incompatibility: A Postattachment Resistance Mechanism to the Parasitic Weed Striga hermonthica Cameron Matthews
Gossypium hirsutum as a Study Species to Understand Plant Responses to Drought Stress Sam Schafer
Lake Michigan Shoreline Landowner Survey Colby Smock
Tourism Insights: ESG in Lodging and Hospitality Emily Cassanmagnago
Monon Neighborhood Livability Study Abigail Dimmick
UPLeft: Pick Up Leftovers, Uplift Those in Need Veronica Galles
To Innovate or Integrate: A Story of Mergers and Acquisitions in the Video Game Industry Charlie Geis and Dustin Rabin
Standard Improvements to Policy for Maintaining a High Leasing Rate on Commercial Properties Scott Morical
Microfinancing and Entrepreneurship in Cocoa Refinement in Côte d’Ivoire Erin Soro
“We Flourish”: The Role of BIPOC Parents in Diversifying Children’s Literature Kayla Neal
Liquid Nitrogen Shrink-Fitting Process Natalie Harvey
Smartphone Color Error Analysis Mackenna Hawes
Is Northwest Indiana Prepared to Be a “Climate Haven”? Luke Carl Jorgensen
Changes in Russian Media Language in Turbulent Times Evan Landau
Design and Development of an Inert Controlled Environmental Chamber for Evaluation of Contaminant Mass Transfer Brian Magnuson and Zachary Limaye
Tree Localization in a Plantation Using Ultra Wideband Signals Akshat Verma
Developmental Atrazine Exposure Modifies Expression of Synucleins Isabelle Akoro
Active Herbicide Ingredients in Roundup Ready Xtend Products, Glyphosate and Dicamba, Results in Hypoactivity in Zebrafish Larvae When Exposed During Development Ryker Bond
Analyzing Health Care Delivery Costs from 2011 to 2020 in the Emergency Departments and Overall Hospital Costs Jacob A. Corey
Formulation of Preservation Solutions for Model Generation with In Vivo Tissue Morphology Holly Pickett
Comparing Effects of Atrazine Exposure on Neuroendocrine Molecular Targets at Two Developmental Exposure Periods in the Zebrafish Jenna Swihart
Monitoring of Caucasus Heritage Sites Facing Cultural Genocide Peyton Edelbrock
Laughter and Madness: The Comic Horror of Evil Dead II David Gowan
Examining the Examiner: An Amicus Brief on Conflicts Between Forensic Technology and Indigenous Religious Freedoms in Favor of Virtual Autopsies Peyton James
Efficacy of the Pedagogical, Cultural, and Advocacy Programming at Purdue University Asian American and Asian Resource and Cultural Center Michael Kuczajda
American Foreign Policy and Public Opinion of the Crimean War (1853–1856) Anurag Shah
The Effects of Wildfire Aerosol Emissions on Air Quality Emma Braun and Audrey Shirley
Model Selection Through Cross-Validation for Supervised Learning Tasks with Manifold Data Derek Brown
Exploring the Evolution of Callose Synthase in Green Plants Giovanna Durante
The Cross-Linguistic and Cross-Situational Association Between Accentedness and Its Impact as Rated by Speakers Makaila Groves
Toward Improved Global Food Security: Uncovering How Tomatoes Fight Root-Knot Nematodes Chingyan H. Huang
Does Having Air Conditioning Affect Friendship Formation in the First Two Months of College? Zachariah Hunt
The Impact of Accessible Data on Cyberstalking Elise Kwan
NeuroArt: Presenting a Tool for Self-Regulation Emma Niecikowski
Promises and Risks of Applying AI Medical Imaging to Early Detection of Cancers, and Regulation for AI Medical Imaging Yiyao Zhang
Out of the Box
Digitizing Delphi: Educating Audiences Through Virtual Reconstruction Kate Koury
Interview: Bethany McGowan and Matthew Hannah Catie Gilhooly
Interview: Michael Kirchner Catie Gilhooly
Alumni Spotlights
Alumni Spotlight: Chufan Gao
Alumni Spotlight: Caleb Hettinger
Alumni Spotlight: Emerald Obie
Alumni Spotlight: Emma Wallens
Cover Image Research Summary
Back Matter
Dr. Krystal R. Hans and undergraduate student researchers in the Hans Lab (courtesy of Purdue University/John Underwood).
- About This Journal
- Editorial Board
- Tips for Authors
- JPUR Stories
- Submit Article
- Most Popular Papers
- Receive Email Notices or RSS

Advanced Search
ISSN: 2158-4052
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright
A national, peer reviewed, multidisciplinary research journal
American Journal of Undergraduate Research (AJUR) is a national, independent, faculty peer-reviewed, open-source, quarterly, multidisciplinary student research journal, established in 2002. Our mission is to peer-review, publish on the web and in print, and index scholarly and creative manuscripts written by undergraduates and with undergraduates’ participation, at no cost to authors. The journal is indexed internationally by EBSCO and Crossref , and each manuscript receives a DOI number. AJUR ‘s entire content, by invitation, is archived by the United States Library of Congress . AJUR makes a unique contribution because of the high standards for content, rigorous review process, and ease of accessibility to the public and professionals. It accepts submissions from outside the United States, provided the submissions would be of broad interest to US and international readers. AJUR ’s print ISSN is 1536-4585 and the web ISSN is 2375-8732. The editorial board of AJUR consists of approximately sixty professional subject editors in a wide variety of fields. Printed copies are available in the special collections section of Penfield Library . Up-to-date information about AJUR can be found at https://ajuronline.org/ .
The submission publishing process, our expectations, and the editorial workflow are described at the “ Submissions and Review ” link button above. You may see AJUR’s Current Issue or Archives by clicking the corresponding links/buttons above. Please read more about the AJUR and see our editorial board using the “ History and Editors ” link.
Please consider being a sponsor of AJUR , a not-for-profit organization. Thank you for your interest and for your support of undergraduate research.
Any questions? Please check our Q&A page. To reach the editor of AJUR, send an e-mail to ajureditor[at]gmail.com

- Get Curious
- Talk to People
- Take Action
- Inspire Others
- Events and Outcomes
- JHU At-A-Glance
- Students and Schools
- Ready to Hire?
- Mentor Students
- Hire Students
- “When U Grow Up” Podcast
A student’s guide to undergraduate research
- Share This: Share A student’s guide to undergraduate research on Facebook Share A student’s guide to undergraduate research on LinkedIn Share A student’s guide to undergraduate research on X
Originally written by Shiwei Wang for Nature journal in March 2019.
Participating in original research during your undergraduate studies can greatly expand your learning experience. However, finding the project can be a challenging task, so here’s a short but comprehensive guide that can help you get the most out of an undergraduate research opportunity.
Choose the right lab
Learn to think like a scientist. A lot of people start their undergraduate research by glancing at the faculty list and e-mailing multiple professors whose work seems interesting. Although this might get you a position somewhere, it is not the most effective approach. Before looking at labs, dive into the science to find out which areas fascinate you. Read a lot, go to talks, and talk to your professors not just about their classes, but about science in general as well.
Subscribe to e-mail newsletters from journals such as Nature and Science. Try to read research highlights and science news regularly. Podcasts and articles by, for example, Nature, Science, Scientific American or Quanta can also be interesting sources of information. Follow academics, journals and universities on Twitter. Start your undergraduate research by learning more about science, thinking like a scientist and working out what you love.
Look for questions, not subjects. You might have chosen a major to study, but don’t let this limit your search for research labs. Modern labs are interdisciplinary and very different from what you do in undergrad labs. Instead of limiting your search to your department, try to look at labs in all related departments. Choose labs on the basis of the questions they’re trying to answer.
Mentoring is as important as research. Contact group members to learn about your prospective laboratory’s environment. Are the group members close? Is the lab friendly or competitive and condescending? Is the lab head hands-off or hands-on? The size of the group is also important. If you join a small group, you’ll have a higher chance of being mentored directly by your principal investigator, whereas in a big group, you are more likely to be mentored by a postdoctoral researcher or graduate student.
Reach out with confidence. Once you’ve determined that the research programme interests you and the group dynamic is healthy, send the principal investigator an e-mail. Make sure to explain why you’re interested in working in the lab and that you have spoken to other lab members. Be patient if they don’t reply. If you don’t receive a response after a week or so, send a second e-mail or reach out in other ways, such as by asking group members to enquire for you.
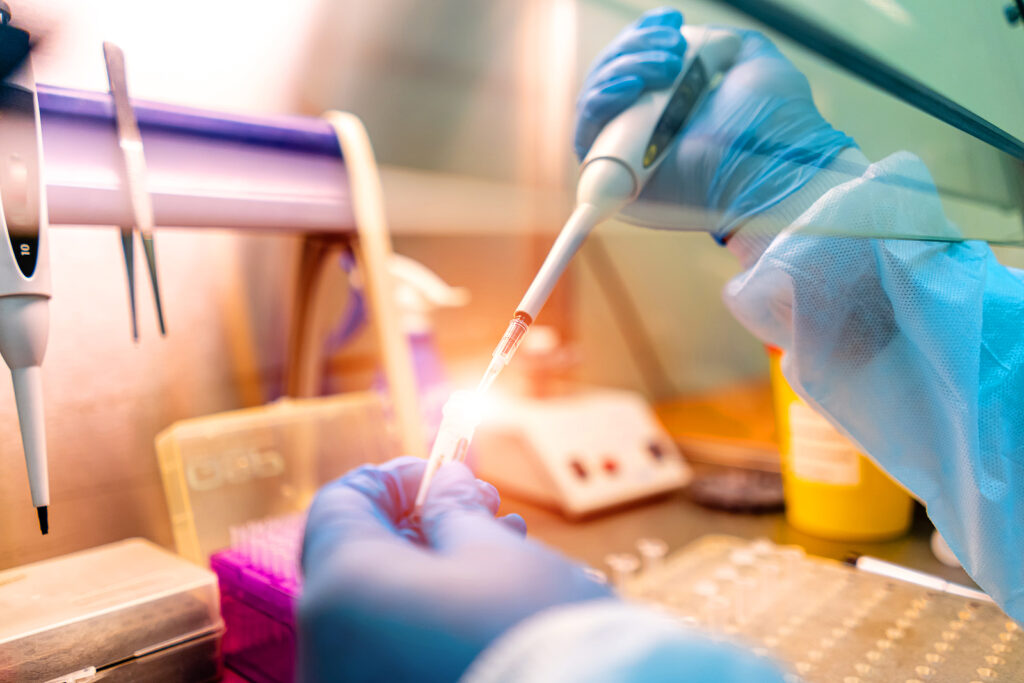
Get the most out of the experience
Start your research with reading, and keep on reading. Usually, the principal investigator will assign you a mentor and a project. Ask for literature to read: learning about the state of the field and why the work is important will help you to push the project forward. Read about your field as well as other, totally unrelated fields. As an undergraduate, you have the freedom to change your major and your future plans. Make sure to strike a balance between reading and conducting experiments. It’s hard to do both at the same time, but it will make you a better scientist.
Set specific goals for yourself and let your mentors know. Think about what you want from your research and how much time you are willing to put in. Besides learning the techniques, do you want to learn how to analyse results and design experiments? Do you want to learn how to write proposals by applying for undergraduate research grants? Do you want to improve your presentation skills by going to conferences? Do you want to potentially finish a project for publication? Working out what you want to achieve will help you to direct your time effectively.
Research takes time. Don’t blame yourself if experiments don’t work or the project is not moving forward as fast as you expected. Science is about failing and trying again. Getting used to and coping with frustration is part of the learning curve of research.
Find a healthy balance. University is already a lot of work, and research will only take up more time. When planning your schedule, try to allocate large blocks of time (whole afternoons or individual days) to research. Rushing through a procedure could be unsafe and will often produce useless results. Always plan extra time for experiments. Consider working less in the lab during exam weeks so you don’t get overwhelmed. Talk to your mentor about your schedule and feelings regularly, so that you can arrange experiments at times that suit you, and you can keep on top of your mental health.
Find financial support. If you wish to do research at your own institution over the summer, your institution might offer funding to cover your expenses. If you want to go to another university, you can apply for funding from that institution’s undergraduate research programme, or from foundations, companies or academic societies. For example, the US National Science Foundation offers a Research Experiences for Undergraduates programme. Universities, foundations and academic societies might also offer grants to cover your travel expense to various conferences. Don’t let money limit what you want to do. Talk to senior students or professors, or search online to find all the opportunities!
Always think about the big picture. Your undergraduate research doesn’t define what you’re going to do after your degree. Keep reading and taking classes outside your comfort zone. Explore and learn as much as possible. Working out what you love is the best preparation you can get for the rest of your career.
Read the full article on the Nature website.
To find a research opportunity at Johns Hopkins University, visit the Hopkins Office of Undergraduate Research website .

Announcements:
Links to resources: For Reviewers For Authors In Focus In Action
Brief About:
The Minnesota Undergraduate Research & Academic Journal is an academic journal dedicated to the academic research of undergraduate students. It is a student-run publication, with students as the reviewers, authors, and editorial board, that strives toward a diverse representation of work from all subjects and fields. Students are encouraged to submit research in a variety of formats and platforms, whether it be by text, photo or video. As the university’s first multi-disciplinary, undergraduate research journal, MURAJ aims to stay committed to its values of diversity and broad scope by publishing work from all areas of research and from students in all ranges of their undergraduate career.
Read more about us !
Current Issue
Vol. 5 No. 4 (2022): Minnesota Undergraduate Research & Academic Journal

Journal Cover Artist: Tony Miller
MURAJ’s interdisciplinary annual publication compiles distinguished academic pieces composed by undergraduate authors. Each piece is subject to a rigorous peer-review process completed by our experienced University of Minnesota undergraduate reviewers. Our excellent authors demonstrate the breadth and depth of undergraduate research in Minnesota and nationwide.
Published: 2022-06-03
Letter from the Editor
Muraj 2021-2022 vol. 5 no. 4 masthead, biological, animal, and health sciences, defining a cultural context to underutilized crops in the minnesota food system a systems mapping approach, effects of ph changes on zebrafish microbiome, inhibition of mct1 to reduce tumor invasion during early malignant progression in hnscc, mesalamine and immunosuppressant treatment in crohn’s disease, the relation between the brain-gut axis and parkinson's disease, business, law and politics, an insight into the world of spac fraud, an investigation of intent and genocide in the 1930s kazakh famine, the effect of wage increases on judicial corruption, political stability and agriculture: a case study of egypt, diversified studies, constructed value systems across interpersonal relationships, finding the sun: an effort in retracting and relearning one’s past, engineering and physical science, utilizing the hamiltonian dynamics to study resonant interactions of whistler-mode waves and electrons in the solar wind, environmental, conservation, and plant science, optimizing carrot growth in static hydroponic systems, mathematics and computer science, a statistical investigation on workforce automation, muraj: in creation.

Rape Culture

Literature and History
Expanding queer indigenous traditions as a vehicle of futurity, a flame fate dares not move a sapphic reading of katherine philips, social sciences, education and communication, african americans and type 2 diabetes: social determinants of health in prevalence and outcomes, an analysis of icelandic pagan rituals and norse mythology, economic growth of the republic of armenia versus caucasus region during the period 2017– 2019: a case study, ethics and discrimination in the hiring process: an overview of gender and race, government transparency and data: foia evidence from law enforcement agencies, masculinity development, gender stereotypes, and gender equality, pandilleros y políticos: cyclical violence in el salvador, psycholinguistic indicators of anxiety during white self-reflection on racial privilege, trust in the new normal: the effect of face mask wearing on perceived trustworthiness.
The copyright of these individual works published by the University of Minnesota Libraries Publishing remains with the original creator or editorial team. For uses beyond those covered by law or the Creative Commons license, permission to reuse should be sought directly from the copyright owner listed on each article.


ConnectUR 2024.
Undergraduate Research: What’s Next?
The dual-experience conference will focus on revealing what is on the horizon for students, faculty, and institutions in undergraduate research, scholarship, and creative inquiry, even as we pause to take notice of how far we have come.

Featured Event
Proposal Writing Institute
July 11-15, 2024 University of Wisconsin-River Falls

FEATURED UR STORY
Center of UR Shares Their Keys to Success

Some of Our Institutional Members


Papers and Presentations
Main navigation, presenting at a conference provides many opportunities to professionalize your work.
- Develop the skill to write succinctly about your work in a compelling way.
- Receive valuable feedback on your presentation.
- Learn about the latest developments in your field or discipline.
- Meet your peers and other researchers from different schools and learn about possible graduate programs.
Talk to your faculty mentor about submitting abstracts to appropriate conferences in your field.
Undergraduate Research Student Grants support students presenting their work at peer reviewed scholarly conferences. Learn more about Undergraduate Research Conference Grants here .
Publishing a paper
Complete your independent project by writing a research paper, for possible submission to journals at Stanford or outside Stanford. You may also consider presenting your work in more accessible forms in newspapers, magazines, radio, and on the web.
Seek recommendations from your faculty mentor about the appropriate outlet for your work.
Consider the opportunities for publication offered by the Stanford Undergraduate Research Journal and other student journals on campus.
Volunteer Project Presentation
Undergraduate Research also encourages current student volunteers to present their project posters or to speak about their project experiences to students who are not yet engaged in these pursuits. Some of these info session events may be dorm presentations with Undergraduate Research staff, and you may like to consider contributing especially to your first year or sophomore year dorms. Please indicate the sites where you would like to give such a presentation. You will be playing a part in guiding students as they explore their interests and begin their own independent projects!

Home > Journal Publishing > Active Journals > KJUR
The Kennesaw Journal of Undergraduate Research ( KJUR ) is a peer-reviewed scholarly journal dedicated to promoting academic study and achievement among undergraduate students at Kennesaw State University. This journal seeks to encourage inquiry among undergraduates by providing them with an avenue for spreading and exchanging knowledge through publication of their research.
Current Issue: Volume 10, Issue 1 (2023)
Reckoning Roanoke: A Historiographical Examination of the Lost Colony Anna K. Poole
The Survival of Manuscripts: Resistance, Adoption, and Adaptation to Gutenberg's Printing Press in Early Modern Europe Kaitlin Jean Kojali
Perceived Phantoms: A Phenomenological Observation of Spirituality in Atsumori Nicholas C. Gilomen
- Journal Home
- About This Journal
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Author Fact Sheet ( PDF )
- Reviewer Guidelines ( PDF )
- Internship Opportunities
- Submit Article
- Most Popular Papers
- Receive Email Notices or RSS
Advanced Search
ISSN: 2474-4921
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright
Journal of Student Research
Journal of Student Research (JSR) is an Academic, Multidisciplinary, and Faculty-reviewed Journal (Houston, Texas) devoted to the Rapid Dissemination of Current Research Published by High School Edition , Undergraduate and Graduate students.
Articles Indexed in Scholarly Databases

The journal seeks articles that are novel, integrative, and accessible to a broad audience, including an array of disciplines. The content of the journal ranges from Applied research to Theoretical research. In general, papers on all topics are welcome to submit. The journal uses an automated process from manuscript submission to publication. Manuscript submission, peer review, and publication are all handled online, and the journal automates all clerical steps during peer review.
Trusted By Student Authors Globally

Focus and Scope
Students strive to be successful at publications, and with JSR, authors aspiring to publish will receive scholarly feedback after the reviews of their submissions are received. This feedback will help authors identify areas of improvement to their submission and help them better understand the process to be successful at publication. Once published, we strive to provide a global platform for our authors to showcase their work.

Faculty-Refereed Review Process
This journal uses a double-blind review, which means that both the reviewer and author identities are concealed from the reviewers, and vice versa, throughout the review process. Authors need to ensure that their manuscripts do not give away their identity to facilitate this. To find out more about the review process, please visit the Author Guidelines page. We invite teachers and faculty interested in reviewing articles for this journal; please visit our Reviewers page for more information.
Open Access Policy
This journal provides access to its published content on the principle that making research freely available to the public supports a greater global exchange of knowledge. Learn more about Open Access .
Authors Retain Copyright
Articles published in this journal are under a Creative Commons License , and the authors retain the copyright to their work.
Announcements
Call for papers: volume 13 issue 3.
If you are an undergraduate or graduate student at a college or university aspiring to publish, we are accepting submissions. Submit Your Article Now!
Deadline: 11:59 p.m. May 31, 2024

The MIT education: Undergraduate research
One of the earliest programs of its kind in the United States, the Undergraduate Research Opportunities Program (UROP) supports thousands of projects each year with 94% of MIT graduating seniors conducting research, for pay or for credit, during their undergraduate years.
In 1969, Margaret MacVicar, then a 26-year-old MIT professor (and alumna), established UROP with funding from the inventor Edwin Land . Since then, MIT has spent well over $100 million on the UROP program—redefining the nature of research at MIT. Hundreds of academic papers published each year draw on UROP research, and most undergraduates will be included as coauthors on them.
Every scientist was once a novice: UROP gives you a point of entry to begin work that can last a lifetime.
Hands-on research
Through UROP you can perform hands-on research projects with faculty mentorship. The projects span every stage of the process of academic inquiry, beginning with the drafting of a plan, continuing through the process of conducting research, and often resulting in coauthored papers, conference presentations, and even the occasional invention—and you can take part for pay or credit.
How to UROP
You may apply for advertised UROP positions or propose your own . Or conduct your research at MIT, off campus , or even internationally . You may UROP at any time 01 Although, informally, we'd advise you that maybe get your feet under you first. First-year UROPs are often possible but only sometimes prudent. during your MIT career.
- Although, informally, we'd advise you that maybe get your feet under you first. First-year UROPs are often possible but only sometimes prudent. back to text ↑
Related blogs
MIT Cancer Research The history and future of cancer research at MIT.
- by Matt McGann '00
- March 29, 2006
“This is not a smoking gun for superfluidity. This is a cannon.” Physics Breakthrough at MIT
- June 22, 2005
Can You Save the World’s Oceans? Who, me? Yes, you.
- by Chris S. '11
- December 8, 2007
- 27 comments
An Early History of International Students at MIT studying the people MIT made, and the people who made MIT
- by Yuliya K. '18
- February 9, 2017
Life as a Physics Major- Research and Junior Lab(Part 2) Long and verbose. But I hope you find time to read it.
- by Lulu L. '09
- January 29, 2008
- 29 comments
Procrastination in the Time of Corona i have so much time and so many ways to procrastinate my work
- by Nisha D. '21
- March 24, 2020
- Search This Site All UCSD Sites Faculty/Staff Search Term
- Contact & Directions
- Climate Statement
- Cognitive Behavioral Neuroscience
- Cognitive Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Adjunct Faculty
- Non-Senate Instructors
- Researchers
- Psychology Grads
- Affiliated Grads
- New and Prospective Students
- Honors Program
- Experiential Learning
- Programs & Events
- Psi Chi / Psychology Club
- Prospective PhD Students
- Current PhD Students
- Area Brown Bags
- Colloquium Series
- Anderson Distinguished Lecture Series
- Speaker Videos
- Undergraduate Program
Academic and Writing Resources
- Writing Research Papers
Writing Research Papers
Information and resources.
One of the most important skills that you can learn in this department is how to write a research paper. For many of you, this will be in fulfillment of the Psychology B.S. Degree Research Paper requirement and/or the Psychology Honors Program Thesis requirement. You may also be writing an American Psychological Association (APA) formatted research paper for a Psychology course (such as a term paper or a summary of an empirical research paper). In some cases, such as for certain job, graduate school, and fellowship applications, you may be asked to provide a writing sample; a well-written research paper can be ideal for that purpose. The ability to write research papers is crucial for those who wish to pursue graduate school and research careers. To assist with these potential goals, we’ve gathered important information and helpful tips for you.
Should I Use a Specific Format and Style?
In the psychological sciences, it is common for research papers to adhere to the guidelines of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (papers in other fields often use APA format as well). APA guidelines not only specify the types of sections that a research paper should have, but also the order of those sections, the manner in which scholarly sources should be cited in the text and in a separate references section, appropriate methods of reporting experimental and statistical results, the proper use of language, and other details. A well-written psychology research paper typically follows those guidelines .
How to Write a Successful Research Paper in APA Style
For more information on writing research papers in APA style, please checking out the following pages. Here you’ll find details on multiple aspects of the research paper writing process, ranging from how the paper should be structured to how to write more effectively.
- Structure and Format – the critical components of each section of an APA-formatted research paper (Introduction, Methods, and on), as well as how those sections should be formatted according to APA guidelines.
► Structure of Research Papers in APA Style
► Formatting Research Papers in APA Style
- Finding, Evaluating, and Citing References – how to search databases, how to obtain references, how to take notes when reading references, what types of references to use, how to include in-text citations, and how to create an APA-formatted reference list.
► Using Databases and Finding References
► What Types of References Are Appropriate for Research Papers?
► Evaluating References and Taking Notes
► Citing References in APA Style
- Writing a Literature Review, the Writing Process, and Improving Writing – how to write a literature review (an overview or summary of prior research, which is a common technique of introducing a research topic in the early sections of a paper), as well as recommendations for the writing process, improving clarity and conciseness, examples of adequate and better paragraphs, and links to resources on improving writing.
► Writing Literature Reviews
► Writing Process and Revising
► Improving Scientific Writing
- Avoiding Plagiarism – how to make sure that your research paper represents your writing and ideas and does not erroneously or unethically appropriate the works of others.
► Academic Integrity and Avoiding Plagiarism
- How-To Videos – for video guides to the different major sections of research papers, plus literature reviews and references, please see the following:
► Writing Research Papers Videos
In addition, you may be interested in downloading “ How to Write a Research Paper in APA Style ”, a comprehensive guide developed by Prof. Emma Geller, “ Tips for Writing APA Style Research Papers ” (a short summary of multiple aspects of the paper-writing process), and an Example B.S. Degree Research Paper written in APA Style .

Workshops and Downloadable Resources
- For in-person discussion of the process of writing research papers, please consider attending this department’s “Writing Research Papers” workshop (for dates and times, please check the undergraduate workshops calendar).
- How to Write APA Style Research Papers (a comprehensive guide) [ PDF ]
- Tips for Writing APA Style Research Papers (a brief summary) [ PDF ]
- Example APA Style Research Paper (for B.S. Degree – empirical research) [ PDF ]
- Example APA Style Research Paper (for B.S. Degree – literature review) [ PDF ]
Further Resources
- OASIS Language and Writing Program
- UCSD Writing Programs and Resources
- UCSD Muir College Writing Hub
- UCSD Writing Hub
External Resources
- APA Style Guide from the Purdue University Online Writing Lab (OWL)
- APA Tutorial on the Basics of APA Style
- EasyBib Guide to Writing and Citing in APA Format
- Formatting APA Style Papers in Microsoft Word
- How to Write an APA Style Research Paper from Hamilton University
- Online Learning: Plagiarism and Paraphrasing
- Sample APA Formatted Paper with Comments
- Sample APA Formatted Paper
- Tips for Writing a Paper in APA Style
- WikiHow Guide to Writing APA Research Papers
Back to top
- Research Paper Structure
- Formatting Research Papers
- Using Databases and Finding References
- What Types of References Are Appropriate?
- Evaluating References and Taking Notes
- Citing References
- Writing a Literature Review
- Writing Process and Revising
- Improving Scientific Writing
- Academic Integrity and Avoiding Plagiarism
- Writing Research Papers Videos
- Effective Studying
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Ann Med Surg (Lond)
- v.81; 2022 Sep

Undergraduate students' involvement in research: Values, benefits, barriers and recommendations
- Yusuff Adebayo Adebisi
a Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Ibadan, Ibadan, Nigeria
b Global Health Focus, Abuja, Nigeria
Developing, maintaining, and sustaining undergraduate research initiatives can benefit academic institutions, faculty mentors, and students. As the world evolves, more research is required to advance knowledge and innovation in all fields. This implies that students must be prepared for today's knowledge-driven world. Research in the medical and health sciences has stalled in many developing countries, where a dual burden of communicable and noncommunicable diseases is prevalent. In this article, I discuss the values and benefits of undergraduate healthcare students participating in research and scientific publishing, as well as the challenges they face. I also make recommendations to encourage undergraduates to get involved in research. The potential of undergraduate research has not yet been fully realized. Undergraduate research's main objectives are to teach students how to do research and to help them acquire skills that they can use beyond the academic environment. Undergraduate research will complement rather than conflict with university education and should go beyond the mandatory terminal year thesis and must cover the entire course of their studies. The key to successful undergraduate research participation is for students to see and understand the importance of rigor, academic integrity, and responsible research conduct. This means academic institutions should carefully plan research programs, activities, and courses for students. Building capacity in research has a long-term impact on valuable learning outcomes as undergraduate students prepare for professional service. Stakeholders and educational authorities must invest in strengthening undergraduate involvement in research.
1. Introduction
As the world evolves, the need for research grows, and it remains a factor of key importance in creating a knowledge-driven economy and supporting development initiatives as well as driving innovations across all fields [ 1 ]. It is becoming more and more important to increase undergraduate student involvement in research [ 2 ]. Academic institutions, faculty mentors, and students can all benefit from developing, maintaining, and sustaining undergraduate research initiatives. By integrating research into their academic courses and giving them a strong academic foundation, students can strengthen their autonomous critical thinking abilities as well as their oral and written communication skills, among others. As students are ready for professional service, the research process affects important learning goals that have a lasting impact. All students should be prepared for the contemporary knowledge-driven world because, today, doing research is not just for academics but also for individuals and institutions interested in knowledge creation and advancement.
The advancement and innovation of all fields, including the health sciences and related areas, depends on research [ 3 ]. Society can benefit greatly from health-related research [ 4 ], which can provide vital insights into disease trends and risk factors, treatment outcomes or public health interventions, care patterns, costs and usage of healthcare services, and more. By doing research to find solutions to problems that are currently unknown, we can close knowledge gaps and change the way healthcare professionals work as well as how we respond to public health issues. With the increase in health concerns ravaging the world [ [5] , [6] , [7] ], it is clear that research is indispensable – whether it be tackling diseases of poverty, performing clinical trials, responding to the rise of chronic diseases, improving access to medicines, increasing vaccines uptake, containing local epidemics, developing innovation in treatment plans, or ensuring that marginalized populations have access to HIV care treatments, among others. This suggests that there is a pressing need to advance knowledge creation and utilization, and that gathering local, grassroots data at all levels of healthcare is important.
Research in the medical and health sciences has seen a downturn in many developing countries [ 8 ], where a double burden of communicable and non-communicable diseases is highly prevalent. The development of undergraduate health sciences students' research capacity is a key intervention to address this issue. With the support of faculties, it is possible for undergraduate students to learn about and participate actively in research. In this article, I discuss the values and benefits of undergraduate healthcare students' involvement in research and scientific publishing, as well as the challenges they face. I also provide recommendations to advance undergraduates’ involvement in research.
2. Values and benefits of undergraduate research
Involving undergraduate students in research should go beyond the mandatory terminal year thesis and must cover the entire course of their studies. There are myriads of benefits to involving (healthcare) students in research and scientific publishing at the undergraduate level. Research is a methodical process of investigation that includes data collection and analysis, the recording of significant information, and subsequent analysis and interpretation of that information in accordance with the protocols defined by specific academic and professional disciplines [ 9 ]. This implies that conducting research is an important way to improve students’ ability to think critically and solve problems, both of which are essential throughout their career as healthcare professionals. Critical thinking abilities have been linked to better patient outcomes, higher patient care quality, and improved safety outcomes [ 10 ]. While problem-solving focuses on identifying and resolving issues, critical thinking entails asking insightful questions and critiquing solutions. Early exposure of healthcare students to the value of research is a critical strategy for increasing their interest in and attitude toward it. Table 1 highlights the achievements of some students that engaged in research as undergraduates.
Examples of students that got involved in research as undergraduate and their achievements.
The elements required for professional competency in the health fields are covered in healthcare student curricula. This includes understanding of the fundamental theories and literature in the field of study, as well as knowledge of the terminology or technical language specific to health sciences. Incorporating research methodology and the hypothesis-driven scientific process can help to build on this foundation while also stimulating independent critical thinking. By involving undergraduate students in research, they can build trust in the scientific process. Besides that, independent thinking can give an undergraduate student the confidence to draw their own conclusions based on available evidence. No doubt that undergraduate students who took part in research projects will have greater thought independence, a stronger intrinsic motivation to learn, and a more active role in their learning. As a result, as undergraduates prepare for their respective professions, the research process has a very positive impact on their practice.
Students who participate in research may have the chance to develop the advanced writing abilities needed for science publishing and communication [ 11 ]. Even though healthcare students write a lot throughout their time in college, many still struggle to write in a way that is considered acceptable. This is due to the fact that students frequently plagiarize in writing assignments since there is usually little to no formal training on academic writing, and some institutions pay less attention to this. It has also become more challenging for students to express themselves in their own words during academic assessments as a result of the encouragement to memorize academic information verbatim by some teachers. Writing is difficult, but it is a skill that can be honed. Improving students' writing skills is much easier if proper attention is paid to strengthening their capacity for and involvement in the academic research process. This will be useful to them throughout their career, whether they choose to be academic or not.
Investing in academic writing skills among students, particularly in developing countries, is critical for improving scientific outputs on health issues confronting the region. It is not enough to know how to conduct research; academic writing is also important. Additionally, it is crucial for academic institutions to encourage students to present their research work at scientific conferences, which are frequently restricted to postgraduate students. This gives them the chance to collaborate more frequently with faculty members while also giving them another learning opportunity and boosting their confidence and presentation skills. Students who make significant contributions to the intellectual aspect of a research should not be relegated to acknowledgement section of the paper but should be included as co-authors. Furthermore, students should not be denied first authorship because of power dynamics. This will definitely improve students’ attitude towards research.
Through research, students can observe how the theories and concepts they have learned are applied. The active learning aspect of research allows students to connect with their own interests, which is not possible in a passive learning setting. If a research culture and thought process are instilled in healthcare students as they progress through the academic institution in a more systematic, logical, and integrated manner, it will be easier for them to understand what they are learning and will promote active participation in class. This is due to the fact that students who conduct research will be able to understand the research process and how scientists think and work on problems; learn about different lab techniques (as needed); develop skills in data analysis and interpretation; and be able to integrate theory and practice. Further, undergraduates should be involved in research as early as possible because it allows them to identify, develop, and nurture their interests while being open-minded to other areas. This will make choosing and transitioning into research area of choice much easier for them as they pursue postgraduate studies. Because of the high-level of interest and fundamental knowledge gained through undergraduate research participation, it will be possible to increase the enthusiasm, completion rates, and quality of academic research at the postgraduate level. Besides that, undergraduate research allows students to decide whether or not they want to pursue a career in research.
Due to the opportunity for students to pursue their individual interests, research experiences have been linked to a boost in students' motivation to learn [ 12 ]. This means undergraduates will have the chance to take more control over their own learning experiences and have their intellectual curiosity piqued by research. Student-faculty research mentoring relationships frequently develop over time. In contrast to what is possible in the classroom, students form a distinct type of interaction with their research mentor. Most of the time, the interaction is more intense and lasts longer. It frequently serves as the foundation for lifelong friendships and career guidance. When students are looking for jobs or graduate schools, faculty research mentors are an excellent source of recommendations and advice. Additionally, students gain experience working in a research team, which typically involves group work, stronger relationships with colleagues and faculty members, and the development of communication skills. All of which are qualities that employers are increasingly looking for. The key to successful undergraduate research participation is for students to see and understand the importance of rigor, academic integrity, and responsible research conduct. This means academic institutions should carefully plan research programs, activities, and courses for students.
One of the most significant benefits of student research participation is the possibility of publishing articles in peer-reviewed journals. This will also give students early exposure to the process and concept of scientific publishing. Students who submit their manuscript to a reputable journal for publication can also benefit from peer review, which allows them to improve their paper and learn more from the reviewers’ comments. Also, undergraduate students who are exposed to the scientific publishing process early on will be less likely to become victims of predatory journals. Students with publishing experience may be inspired and motivated to pursue a career in research. Having publication allows students to improve their resumes and graduate school applications. Publishing counts as research experience and demonstrates that undergraduate students who have published are enthusiastic about research. As an active learning process, research requires students to frame questions, devise a strategy for testing their hypotheses, analyze data, and write clearly to report their findings, among other things. The research experiences, skills, and knowledge students acquire at the undergraduate level will better prepare them for many of their future endeavors, including careers and postgraduate study. In addition to exposing students to conducting original/primary research, it is important to engage them in secondary research activities including writing reviews, correspondence, commentary, viewpoints, book chapters, and more. Secondary research improves students' writing abilities and thought processes, enables the construction of intelligent arguments, enhances their capacity to use scientific databases to find evidence, and teaches them how to engage in constructive criticism, among others.
While the benefits of undergraduate research to students have been highlighted in the preceding paragraphs, academic institutions can also benefit from engaging undergraduates in research [ 13 ]. Teams conducting research benefit from the enthusiasm and energy of curious undergraduate students. They frequently keep asking for more tasks to complete since they are eager to learn. Undergraduate students often pose inquiries that can be quite perceptive and, perhaps rather unintentionally, alter the way advisors approach research problems and better improve the quality of scientific output from such institutions. In contrast to how faculty research mentors interact with graduate students and other senior team members, undergraduate researchers need responses to inquiries in unique ways, which usually facilitate an opportunity for multidirectional intense learning.
Furthermore, undergraduate students' contributions to peer-reviewed publications and local, regional, national, or international research presentations at conferences and other scientific gatherings will benefit the university or institution's visibility in the scientific community and attract more funding. Students can actively contribute to scientific knowledge provided they are motivated and have the necessary research knowledge and abilities. I serve as a practical example. At the undergraduate level, I published more than 50 articles (including both primary and secondary research) in peer-reviewed journals on a diverse range of public health issues, including the COVID-19 pandemic. While still an undergraduate, I received research and travel grants and presented scientific papers both locally and internationally. This captured the attention of the media, and many undergraduates are now inspired to participate in research more than ever. With the right support systems in place, undergraduates' contributions to scientific literature can be valuable, benefiting not only the student but also the academic institution and society. Imagine a university where students receive the assistance they require to develop their capacity for scientific publishing and research. Such an institution would contribute more to science and knowledge creation, raising their profile in the process. Undergraduate research initiatives are an untapped gold mine if they are nurtured, funded, and supported adequately.
3. Barriers and challenges facing involvement of undergraduate students in research
Healthcare undergraduates interested in research face a number of challenges that have been documented in academic literature. In this section, I conducted a rapid unsystematic review of primary studies and used Table 2 to summarize the challenges and barriers facing undergraduate research identified in randomly selected academic papers.
Barriers and challenges facing healthcare students’ involvement in research.
The rapid review of the fifteen (15) original studies in Table 2 revealed the major barriers and challenges limiting undergraduate student involvement in research across different countries. The findings of the reviewed studies were clearly similar. The key barriers and challenges to undergraduate involvement in research can be divided into three categories: a significant lack of knowledge and skills to participate in research; little to no faculty support, mentorship, funding and motivation for undergraduates to participate in research; and structural barriers limiting student involvement in research such as lack of time due to the loaded curriculum, dearth of research facilities as well as lack of major plans and strategies for undergraduate research.
4. Recommendations
There is an urgent need for stakeholders all over the world to look into the issues and devise tailored strategies to increase the involvement of (healthcare) students in research. Here are my eight (8) recommendations to advance the involvement of undergraduate students in research:
- 1. Research methods and processes should be taught to students as early as their second year of college. Even though some universities only cover research methodologies in the final year, it is essential to include more content on scientific writing and research methods as a mandatory course throughout the whole academic program. Undergraduate teaching curricula and approaches should promote inquiry-based learning. All professional classes' academic curricula might include regular discussions of new advances in the medical and health sciences, and the academic departments might be tasked with organizing these conversations. Long-term, this practice would foster a research aptitude in undergraduate students since opportunity like these would stimulate their minds.
- 2. As part of academic program, students should be evaluated for their interest in research and assigned suitable researchers to serve as their research mentors. Faculty research mentors must also be compensated. Lecturers do not receive credit for mentoring students for publications or research projects. Credit points should be awarded for each peer-reviewed publication attributed to such mentorship to encourage faculty-student research collaboration and motivate them to serve as research mentors for undergraduates. Mandatory structured mentorship programs are desperately needed.
- 3. During the undergraduate program, students should have the opportunity to participate in more research trainings, internships, and placements locally and internationally. This will contribute significantly to students' research skills and experience.
- 4. Students should be encouraged to publish at least two papers, either primary or secondary research, in peer-reviewed journals before graduation. Besides that, the final year thesis must be published and must be on a topic with the potential to make or drive impact.
- 5. Encourage undergraduate students to participate in scientific meetings, conferences, and seminars and to present their research, project, ideas or innovation in such gathering. Funding should be provided for undergraduate research conferences so that students can share their work, learn from the experiences of others, and improve institutional collaboration. This is a worthwhile investment towards advancing knowledge creation and utilization.
- 6. Existing undergraduate journals (e.g., International Journal of Medical Students), student research capacity building initiatives (e.g., Global Health Focus), undergraduate research funding initiatives, and other efforts aimed at promoting student involvement in research should be supported in order to provide more opportunities for students to participate in research.
- 7. A platform should be established to celebrate, provide incentives, and awards to undergraduates who contribute to the advancement of scientific knowledge. More students will be inspired to participate in research as a result of this. Funding (e.g., travel grant, research grant, etc.) should be made more accessible to students that have demonstrated remarkable passion for knowledge creation.
- 8. More research should be conducted across academic institutions to better understand the local barriers that prevent undergraduates from participating in research.
5. Conclusion
Undergraduate research is a treasure trove that has yet to be fully tapped. The primary goal of undergraduate research is to teach students how to conduct research and to develop necessary skills that can be applied outside of the academic setting. Bolstering undergraduate research will complement, rather than conflict with, university education. There is an urgent need to develop global and local initiatives as well as strengthen current initiatives to further encourage undergraduate students to participate in research and scientific publishing.
Sources of funding
Ethical approval.
Not Required.
Not Required
Author contribution
I conceptualized, wrote and revised the paper. I agreed to and approved the final publication of this article.
Registration of research studies
- 1. Name of the registry: Not applicable
- 2. Unique Identifying number or registration ID: Not applicable
- 3. Hyperlink to your specific registration (must be publicly accessible and will be checked): Not applicable
Declaration of competing interest
How Undergraduates Benefit From Doing Research
Undergraduate research isn't just for STEM subjects.
Benefits of Undergraduate Research

Getty Images
Studies show students who participate in research earn better grades, are more likely to graduate and are better equipped for graduate school or careers.
Jessica Stewart understands from personal experience the value of doing research as a college undergraduate. In her junior year at the University of California, Berkeley , Stewart worked with art historian Darcy Grimaldo Grigsby on her book, "Colossal," researching the Suez Canal, Eiffel Tower and other massive art and engineering monuments.
She loved the research so much that she went on to get her Ph.D. in art history. Almost 20 years after working on "Colossal," Stewart now directs the program that gave her the opportunity: UC Berkeley’s Undergraduate Research Apprenticeship Program.
But the initial benefit of doing undergraduate research was even more practical. When she was deciding which projects to apply for as an undergraduate, she got to explore many academic disciplines. This process opened her eyes.
“From the moment I set foot on campus, URAP allowed me to see what kinds of ideas I could study,” Stewart says. “The research and credit are great, but there’s this wayfinding side, too, where students can learn who researchers are, what research looks like and fields they may not have had any exposure to.”
A long tradition at some universities, mentored research projects are now offered at undergraduate institutions around the U.S. While many programs started out focused on science, today most universities offer opportunities across disciplines, including all aspects of STEM as well as architecture, business and theater arts.
No matter the subject area, research participation is an asset for undergrads. Studies show students who participate earn better grades , are more likely to graduate and are better equipped for graduate school or careers.
“It’s often most transformative for nontraditional learners and underrepresented students,” Stewart says. “They learn to triangulate life experience and studies in ways that may not have been intuitive for them. It greatly improves academic performance, retention and persistence.”
Research Roots in STEM
Every year, 6,000 undergraduates participate in research experiences through the National Science Foundation, mostly during the summer. Projects span nearly 20 subject areas , such as astronomy and ocean sciences. Most take place in the U.S., but some research is done abroad, including a marine sciences project at the Bermuda Institute of Ocean Sciences.
Experiences like these increase students’ confidence in their research skills and boost awareness of what graduate school will be like, according to a 2018 study . They also help students identify whether they want to pursue a science career.
“It’s one of the best ways to recruit students into STEM careers and retain them,” says Corby Hovis, a program director at the NSF's Division of Undergraduate Education. “That’s why we do it. It’s an effective way to get students from classrooms into doing STEM.”
The NSF is especially interested in applications from students who might not have had past opportunities to do research, including those who are the first in their families to attend college, and Black and Latino students.
Research institutions apply for NSF grants to mentor undergraduate students and guide them through participation in an ongoing project. For students, the experience includes orientation and training, as well as a stipend and allowances for housing and travel. In most cases, students write a paper about their contribution to research and may even present at a conference or seminar.
Some opportunities require that students have specific math courses under their belts, but all focus on helping students build other skills, aside from lab or research techniques, that they’ll need for future academic work or careers.
“Communicating clearly the results of research is a skill that could carry over into any field,” Hovis says. “The teamwork and cohort experience not only encourages them to continue in science, but (is) translatable to any number of other activities they will do later on.”
Connecting With Faculty
At the Massachusetts Institute of Technology , research has been part of the undergraduate experience for more than 50 years. Some students choose the school specifically for this reason, and more than 90% of students participate. As at other schools, research is part of a bigger initiative around experiential learning, which also includes service learning and study abroad .
The biggest challenge for students is usually figuring out what kind of research they’re interested in.
“We depend on students to do some of that footwork,” says Michael Bergren, director of MIT's Undergraduate Research Opportunities Program. “There are a lot of supports, but at the end of the day a student needs to understand what they’re interested in, who's doing the work they’re interested in and what the steps are to participating in that research.”
But there is hand-holding, if needed. Before applying to work on a project, students have to approach the lead faculty member and introduce themselves.
“This is really intimidating. We don’t take that for granted,” Bergren says. “Part of life skills development is approaching a lab or faculty member and advocating for themselves.”
Peers offer tips about how to navigate that face-to-face encounter, such as find out a faculty member's office hours, send an email with a resume attached and attend a departmental event.
The networking doesn’t stop there. Get to know which graduate students work on the project, talk to other students who might be exploring the same opportunities and make sure you know what the work involves.
“As the research progresses, deliverables amp up,” Bergren says. “You may find you need to put more time into this right when finals are happening.”
The Future of Undergraduate Research
Some undergraduate researchers might share their work at academic conferences or seminars, or even be published in journals. Some might participate in the Council on Undergraduate Research annual conference , the largest symposium of its kind. Every year, more than 4,000 students attend a graduate school and career fair and present work that spans the disciplines.
Students have come to expect that they’ll get a chance to do research as undergrads, says Lindsay Currie, the council's director.
“More recent generations grew up in a different climate. They learned by doing in classrooms,” Currie says. “That, combined with a workforce that expects people to have lived experience, means students want to be able to say that they’ve already done research as part of their coursework.”
What’s next, Currie says, is universities that integrate research into coursework so that students start a project their first year and continue through their time in college. Working with a network of universities, the Council on Undergraduate Research has completed a study of how schools can modify their curricula to incorporate research from the very beginning.
“Starting as freshmen, students would work on research that would build,” Currie says. “This would be significantly more advanced projects that would be consistent across the particular department. This is how they’re going to teach, because they know students benefit from doing.”
Tips to Make Your Final College Choice

2024 Best Colleges

Search for your perfect fit with the U.S. News rankings of colleges and universities.
College Admissions: Get a Step Ahead!
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S. News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
Ask an Alum: Making the Most Out of College
You May Also Like
Protests boil over on college campuses.
Lauren Camera April 22, 2024

Supporting Low-Income College Applicants
Shavar Jeffries April 16, 2024

Supporting Black Women in Higher Ed
Zainab Okolo April 15, 2024

Law Schools With the Highest LSATs
Ilana Kowarski and Cole Claybourn April 11, 2024

Today NAIA, Tomorrow Title IX?
Lauren Camera April 9, 2024

Grad School Housing Options
Anayat Durrani April 9, 2024

How to Decide if an MBA Is Worth it
Sarah Wood March 27, 2024

What to Wear to a Graduation
LaMont Jones, Jr. March 27, 2024

FAFSA Delays Alarm Families, Colleges
Sarah Wood March 25, 2024

Help Your Teen With the College Decision
Anayat Durrani March 25, 2024

Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- 15 April 2024
- Correction 22 April 2024
Revealed: the ten research papers that policy documents cite most
- Dalmeet Singh Chawla 0
Dalmeet Singh Chawla is a freelance science journalist based in London.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar

Policymakers often work behind closed doors — but the documents they produce offer clues about the research that influences them. Credit: Stefan Rousseau/Getty
When David Autor co-wrote a paper on how computerization affects job skill demands more than 20 years ago, a journal took 18 months to consider it — only to reject it after review. He went on to submit it to The Quarterly Journal of Economics , which eventually published the work 1 in November 2003.
Autor’s paper is now the third most cited in policy documents worldwide, according to an analysis of data provided exclusively to Nature . It has accumulated around 1,100 citations in policy documents, show figures from the London-based firm Overton (see ‘The most-cited papers in policy’), which maintains a database of more than 12 million policy documents, think-tank papers, white papers and guidelines.
“I thought it was destined to be quite an obscure paper,” recalls Autor, a public-policy scholar and economist at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge. “I’m excited that a lot of people are citing it.”
The most-cited papers in policy
Economics papers dominate the top ten papers that policy documents reference most.
Data from Overton as of 15 April 2024
The top ten most cited papers in policy documents are dominated by economics research; the number one most referenced study has around 1,300 citations. When economics studies are excluded, a 1997 Nature paper 2 about Earth’s ecosystem services and natural capital is second on the list, with more than 900 policy citations. The paper has also garnered more than 32,000 references from other studies, according to Google Scholar. Other highly cited non-economics studies include works on planetary boundaries, sustainable foods and the future of employment (see ‘Most-cited papers — excluding economics research’).
These lists provide insight into the types of research that politicians pay attention to, but policy citations don’t necessarily imply impact or influence, and Overton’s database has a bias towards documents published in English.
Interdisciplinary impact
Overton usually charges a licence fee to access its citation data. But last year, the firm worked with the publisher Sage to release a free web-based tool , based in Thousand Oaks, California, that allows any researcher to find out how many times policy documents have cited their papers or mention their names. Overton and Sage said they created the tool, called Sage Policy Profiles, to help researchers to demonstrate the impact or influence their work might be having on policy. This can be useful for researchers during promotion or tenure interviews and in grant applications.
Autor thinks his study stands out because his paper was different from what other economists were writing at the time. It suggested that ‘middle-skill’ work, typically done in offices or factories by people who haven’t attended university, was going to be largely automated, leaving workers with either highly skilled jobs or manual work. “It has stood the test of time,” he says, “and it got people to focus on what I think is the right problem.” That topic is just as relevant today, Autor says, especially with the rise of artificial intelligence.
Most-cited papers — excluding economics research
When economics studies are excluded, the research papers that policy documents most commonly reference cover topics including climate change and nutrition.
Walter Willett, an epidemiologist and food scientist at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston, Massachusetts, thinks that interdisciplinary teams are most likely to gain a lot of policy citations. He co-authored a paper on the list of most cited non-economics studies: a 2019 work 3 that was part of a Lancet commission to investigate how to feed the global population a healthy and environmentally sustainable diet by 2050 and has accumulated more than 600 policy citations.
“I think it had an impact because it was clearly a multidisciplinary effort,” says Willett. The work was co-authored by 37 scientists from 17 countries. The team included researchers from disciplines including food science, health metrics, climate change, ecology and evolution and bioethics. “None of us could have done this on our own. It really did require working with people outside our fields.”
Sverker Sörlin, an environmental historian at the KTH Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm, agrees that papers with a diverse set of authors often attract more policy citations. “It’s the combined effect that is often the key to getting more influence,” he says.

Has your research influenced policy? Use this free tool to check
Sörlin co-authored two papers in the list of top ten non-economics papers. One of those is a 2015 Science paper 4 on planetary boundaries — a concept defining the environmental limits in which humanity can develop and thrive — which has attracted more than 750 policy citations. Sörlin thinks one reason it has been popular is that it’s a sequel to a 2009 Nature paper 5 he co-authored on the same topic, which has been cited by policy documents 575 times.
Although policy citations don’t necessarily imply influence, Willett has seen evidence that his paper is prompting changes in policy. He points to Denmark as an example, noting that the nation is reformatting its dietary guidelines in line with the study’s recommendations. “I certainly can’t say that this document is the only thing that’s changing their guidelines,” he says. But “this gave it the support and credibility that allowed them to go forward”.
Broad brush
Peter Gluckman, who was the chief science adviser to the prime minister of New Zealand between 2009 and 2018, is not surprised by the lists. He expects policymakers to refer to broad-brush papers rather than those reporting on incremental advances in a field.
Gluckman, a paediatrician and biomedical scientist at the University of Auckland in New Zealand, notes that it’s important to consider the context in which papers are being cited, because studies reporting controversial findings sometimes attract many citations. He also warns that the list is probably not comprehensive: many policy papers are not easily accessible to tools such as Overton, which uses text mining to compile data, and so will not be included in the database.

The top 100 papers
“The thing that worries me most is the age of the papers that are involved,” Gluckman says. “Does that tell us something about just the way the analysis is done or that relatively few papers get heavily used in policymaking?”
Gluckman says it’s strange that some recent work on climate change, food security, social cohesion and similar areas hasn’t made it to the non-economics list. “Maybe it’s just because they’re not being referred to,” he says, or perhaps that work is cited, in turn, in the broad-scope papers that are most heavily referenced in policy documents.
As for Sage Policy Profiles, Gluckman says it’s always useful to get an idea of which studies are attracting attention from policymakers, but he notes that studies often take years to influence policy. “Yet the average academic is trying to make a claim here and now that their current work is having an impact,” he adds. “So there’s a disconnect there.”
Willett thinks policy citations are probably more important than scholarly citations in other papers. “In the end, we don’t want this to just sit on an academic shelf.”
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-00660-1
Updates & Corrections
Correction 22 April 2024 : The original version of this story credited Sage, rather than Overton, as the source of the policy papers’ citation data. Sage’s location has also been updated.
Autor, D. H., Levy, F. & Murnane, R. J. Q. J. Econ. 118 , 1279–1333 (2003).
Article Google Scholar
Costanza, R. et al. Nature 387 , 253–260 (1997).
Willett, W. et al. Lancet 393 , 447–492 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Steffen, W. et al. Science 347 , 1259855 (2015).
Rockström, J. et al. Nature 461 , 472–475 (2009).
Download references
Reprints and permissions
Related Articles

India’s 50-year-old Chipko movement is a model for environmental activism
Correspondence 23 APR 24
The Middle East’s largest hypersaline lake risks turning into an environmental disaster zone
More work is needed to take on the rural wastewater challenge

CERN’s impact goes way beyond tiny particles
Spotlight 17 APR 24
The economic commitment of climate change
Article 17 APR 24

Last-mile delivery increases vaccine uptake in Sierra Leone
Article 13 MAR 24
Postdoctoral Associate- Computational Spatial Biology
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Staff Scientist - Genetics and Genomics
Technician - senior technician in cell and molecular biology.
APPLICATION CLOSING DATE: 24.05.2024 Human Technopole (HT) is a distinguished life science research institute founded and supported by the Italian ...
Human Technopole
Postdoctoral Fellow
The Dubal Laboratory of Neuroscience and Aging at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) seeks postdoctoral fellows to investigate the ...
San Francisco, California
University of California, San Francsico
Postdoctoral Associate
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Skip to the content of this page , the main menu , the secondary menu , Google Translate , the site search form or go to the the site home page .
Join us April 18
Yolanda suarez-balcazar and fabricio balcazar are leading authors of article recently recognized among the most cited papers.
Erika Chavez
Wednesday, April 24, 2024
Yolanda Suarez-Balcazar, department of Occupational Therapy, and Fabricio Balcazar, department of Disability and Human Development are leading authors of “ Promoting justice through community-based research: International case studies ,” an article recently recognized among the most cited papers published in the American Journal of Community Psychology between January 1, 2022 and December 31, 2023. Other co-authors include researchers from Spain, Peru and Italy.
Follow Inside AHS
- Social Media
- MEMBERS IN THE NEWS
- SCHOOL & PROGRAM UPDATES
- GLOBAL ACTION
- FACULTY & STAFF HONORS
- MEMBER RESEARCH & REPORTS
- STUDENT & ALUMNI ACHIEVEMENTS
- PARTNER NEWS
EXPLORE THE FRIDAY LETTER

The Health Survey Research Methods Conference Call for Papers

The twelfth Health Survey Research Methods Conference (HSRMC) will continue the series that began 50 years ago to discuss innovative survey research methods that improve the quality of health survey data. The next conference will be held in Williamsburg, VA, from March 4-7, 2025, and HSRMC is seeking abstracts by June 30, 2024 for papers to be presented at the conference.
Abstracts can include general overview papers that summarize and integrate current knowledge, papers that identify and address future research challenges, innovative theoretical essays, and other papers that describe new empirical research that advances the field of survey methods and their application to health-related issues. All abstracts must be submitted online between April 1 and June 30, 2024. Submitted abstracts will be reviewed by the HSRMC steering committee. Read more about the 2025 call and learn more about the history of the HSRMC .
Centre for Academic Primary Care
New centre for applied excellence in skin and allergy research.

CAESAR Team (from left): Dr Phuong Hua, Dr Andrew Turner, Dr Roxanne Parslow, Professor Matt Ridd, Dr Raquel Granell, Catriona Rutter.
25 April 2024
The University of Bristol is home to a new Centre for Applied Excellence in Skin and Allergy Research (CAESAR), which has been established to improve the diagnosis and treatment of common skin and allergy problems in primary care.
Directed by Matthew Ridd , GP and Professor of Primary Health Care at the Centre for Academic Primary Care , it comprises a multi-disciplinary group of 20 people with a focus on childhood eczema and food allergy.
Professor Ridd and CAESAR are supported by a National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) Research Professorship award to build capacity and accelerate progress in answering questions of importance to patients with skin and/or allergy problems.
The majority of people with skin and allergy conditions are looked after by their GP. However, there are many uncertainties about how best to look after even common problems. For example, the main treatments for eczema are moisturisers (emollients) and flare control creams (topical corticosteroids). These have been around for decades, yet we still don’t how to use them together optimally or indeed how to support carers and patients with eczema to look after their skin.
During its first five years, CAESAR will work on the Transforming Outcomes for Paediatric Allergy in Primary Care (TOPIC) programme. Underpinned by strong public, patient and stakeholder involvement, supporting equality, diversity and inclusion, it will address the following research questions:
- What are the most effective and safe ways to use emollients and topical corticosteroids to treat children with eczema in primary care?
- Does an eczema clinic in primary care improve disease control in children?
- What are the priorities for food allergy research in children?
- What awareness is there of early allergen introduction advice, is it being followed and is it preventing food allergy?
The NIHR Research Professorships scheme funds and supports research leaders of the future to improve the health and wealth of the nation through research. It also aims to strengthen and benefit health, public health and care research leadership at the highest academic levels.
CAESAR sits within the Centre for Academic Primary Care , NIHR School for Primary Care Research (SPCR), University of Bristol. It works closely with the Bristol Trials Centre and builds on existing studies ( TIGER , ATHENA ) and collaborations. The centre also hosts the Society for Academic Primary Care (SAPC) and NIHR SPCR Skin and Allergy specialist interest groups.
Dr Andrew Turner , Research Manager of CAESAR, said: “We’re thrilled to launch CAESAR and our ambitious plans to accelerate progress in answering common, practical questions in primary care. With a commitment to excellence, our Centre endeavours to make a lasting impact, driving positive change in our community and beyond.”
Professor Matthew Ridd, GP and Director of CAESAR, said: “I’m delighted to have been given this opportunity to set up the Centre and lead much-needed research to address the needs of patients, carers and the NHS in this area.”
For more information, visit the CAESAR website .
Further information
About the national institute for health and care research.
The mission of the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) is to improve the health and wealth of the nation through research. We do this by:
Funding high quality, timely research that benefits the NHS, public health and social care;
- Investing in world-class expertise, facilities and a skilled delivery workforce to translate discoveries into improved treatments and services;
- Partnering with patients, service users, carers and communities, improving the relevance, quality and impact of our research;
- Attracting, training and supporting the best researchers to tackle complex health and social care challenges;
- Collaborating with other public funders, charities and industry to help shape a cohesive and globally competitive research system;
- Funding applied global health research and training to meet the needs of the poorest people in low- and middle-income countries.
NIHR is funded by the Department of Health and Social Care. Its work in low- and middle-income countries is principally funded through UK Aid from the UK government.
The NIHR is the research partner of the NHS, public health and social care.
About the Centre for Academic Primary Care
The Centre for Academic Primary Care (CAPC) at the University of Bristol is a leading centre for primary care research in the UK, one of nine forming the NIHR School for Primary Care Research. It sits within Bristol Medical School, an internationally recognised centre of excellence for population health research and teaching. Follow on X: @capcbristol and on LinkedIn .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Intersections features features student essays, research papers, and capstone theses in the Arts, Humanities, and Social Sciences. There are no established deadlines as submissions are accepted on a rolling basis. ... The Midwest Journal of Undergraduate Research is an academic peer-reviewed journal, produced under the direction of student ...
A forum for multidisciplinary undergraduate research and creative endeavors including case studies, conceptual pieces, creative writing, journalism writings, literature reviews, original art, photography, and scientific studies. ... Open access peer-reviewed undergraduate journal that publishes academic essays, public history essays, and book ...
The Journal of Purdue Undergraduate Research has been established to publish outstanding research papers written by Purdue undergraduates from all disciplines who have completed faculty-mentored research projects. The journal is run by students, but behind the scenes is a unique partnership between Purdue University Press and other departments of Purdue University Libraries, working with ...
Welcome to the Journal of Undergraduate Research & Scholarly Excellence! JURSE is a peer-reviewed, undergraduate journal registered with the Library of Congress that accepts submissions of any subject, from any undergraduate institution. We receive hundreds of submissions for publication every year, from institutions ranging from small liberal ...
As an academic paper can have anywhere from five to hundreds of sources, I would also suggest using a citation manager as you write. This will save you from having to constantly update the sources in the paper as you add and revise. Submitting the Paper. In my case, my PI submitted the paper and is the primary contact with the journal.
American Journal of Undergraduate Research (AJUR) is a national, independent, faculty peer-reviewed, open-source, quarterly, multidisciplinary student research journal, established in 2002. Our mission is to peer-review, publish on the web and in print, and index scholarly and creative manuscripts written by undergraduates and with undergraduates' participation, at no cost to authors.
As an undergraduate, you have the freedom to change your major and your future plans. Make sure to strike a balance between reading and conducting experiments. It's hard to do both at the same ...
A student's guide to undergraduate research. Published on August 16, 2021. Originally written by Shiwei Wang for Nature journal in March 2019. Participating in original research during your undergraduate studies can greatly expand your learning experience. However, finding the project can be a challenging task, so here's a short but ...
The Minnesota Undergraduate Research & Academic Journal is an academic journal dedicated to the academic research of undergraduate students. It is a student-run publication, with students as the reviewers, authors, and editorial board, that strives toward a diverse representation of work from all subjects and fields. Students are encouraged to ...
A complete research paper in APA style that is reporting on experimental research will typically contain a Title page, Abstract, Introduction, Methods, Results, Discussion, and References sections. 1 Many will also contain Figures and Tables and some will have an Appendix or Appendices. These sections are detailed as follows (for a more in ...
A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides analysis, interpretation, and argument based on in-depth independent research. Research papers are similar to academic essays, but they are usually longer and more detailed assignments, designed to assess not only your writing skills but also your skills in scholarly research ...
Please contact Natalie Jones, customer and volunteer experience manager at [email protected] or 202-783-4810. The Council on Undergraduate Research is committed to inclusivity and diversity in all of its activities; therefore, CUR will increase and nurture participation of individuals and groups that have been traditionally underrepresented in ...
Publishing a paper. Complete your independent project by writing a research paper, for possible submission to journals at Stanford or outside Stanford. You may also consider presenting your work in more accessible forms in newspapers, magazines, radio, and on the web. Seek recommendations from your faculty mentor about the appropriate outlet ...
The Kennesaw Journal of Undergraduate Research (KJUR) is a peer-reviewed scholarly journal dedicated to promoting academic study and achievement among undergraduate students at Kennesaw State University. This journal seeks to encourage inquiry among undergraduates by providing them with an avenue for spreading and exchanging knowledge through publication of their research.
The ability to integrate theory and practice. However, participation in an undergraduate research experience also benefited students in areas that can reach beyond academia ( 3 ). Having tolerance for obstacles. Learning to work independently. Understanding how knowledge is constructed.
Journal of Student Research (JSR) is an Academic, Multidisciplinary, and Faculty-reviewed Journal (Houston, Texas) devoted to the Rapid Dissemination of Current Research Published by High School Edition, Undergraduate and Graduate students. Articles Indexed in Scholarly Databases. The journal seeks articles that are novel, integrative, and ...
Hundreds of academic papers published each year draw on UROP research, and most undergraduates will be included as coauthors on them. Every scientist was once a novice: UROP gives you a point of entry to begin work that can last a lifetime. Hands-on research. Through UROP you can perform hands-on research projects with faculty mentorship.
For more information on writing research papers in APA style, please checking out the following pages. Here you'll find details on multiple aspects of the research paper writing process, ranging from how the paper should be structured to how to write more effectively. Structure and Format - the critical components of each section of an APA ...
1. Introduction. As the world evolves, the need for research grows, and it remains a factor of key importance in creating a knowledge-driven economy and supporting development initiatives as well as driving innovations across all fields [].It is becoming more and more important to increase undergraduate student involvement in research [].Academic institutions, faculty mentors, and students can ...
The logistics of conducting research with undergraduate students, let alone co-authoring papers with them, can appear daunting, and faculty incentives for doing so vary . However, we optimistically speculate that the rewards of teaching students to be contributing scientists may make a greater impact than the science itself ( 1 - 4 ).
1. Introduction. As the world evolves, the need for research grows, and it remains a factor of key importance in creating a knowledge-driven economy and supporting development initiatives as well as driving innovations across all fields [1].It is becoming more and more important to increase undergraduate student involvement in research [2].Academic institutions, faculty mentors, and students ...
Benefits of Undergraduate Research. Studies show students who participate in research earn better grades, are more likely to graduate and are better equipped for graduate school or careers ...
Read about their experiences with undergraduate research. Undergraduate Research Opportunities. More than 550 students participated in this year's Undergraduate Research Creative Activity conference, which included 406 presentations on topics from human performance and nutrition to apparel and textiles. That number has rapidly grown in recent ...
The top ten most cited papers in policy documents are dominated by economics research; the number one most referenced study has around 1,300 citations.
Yolanda Suarez-Balcazar, department of Occupational Therapy, and Fabricio Balcazar, department of Disability and Human Development are leading authors of "Promoting justice through community-based research: International case studies," an article recently recognized among the most cited papers published in the American Journal of Community Psychology between January 1, 2022 and December 31 ...
The twelfth Health Survey Research Methods Conference will continue the series that began 50 years ago to discuss innovative survey research methods that improve the quality of. health survey data. The next conference will be held in Williamsburg, VA, from March 4-7, 2025, and HSRMC is seeking abstracts by June 30, 2024 for papers to be presented at the conference.
Undergraduate Research Abstracts _____ Sofia Lozano-Samper Poster Location: U6 Title: What Determines the Changing Food Security of Syrian Refugees in ... This paper explores how declining marriage rates, especially among Black women, impact Social Security wealth inequality. Using percen le rank OLS regression, I show that despite greater
Directed by Matthew Ridd, GP and Professor of Primary Health Care at the Centre for Academic Primary Care, it comprises a multi-disciplinary group of 20 people with a focus on childhood eczema and food allergy.. Professor Ridd and CAESAR are supported by a National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) Research Professorship award to build capacity and accelerate progress in answering ...
whose overall performance, as measured by both academic benchmarks and internal testing, rivals that of models such as Mixtral 8x7B and GPT-3.5 (e.g., phi-3-mini achieves 69% on MMLU and 8.38 on MT-bench), despite being small enough to be deployed on a phone. The innovation lies entirely in