Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates

How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved April 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, what is your plagiarism score.
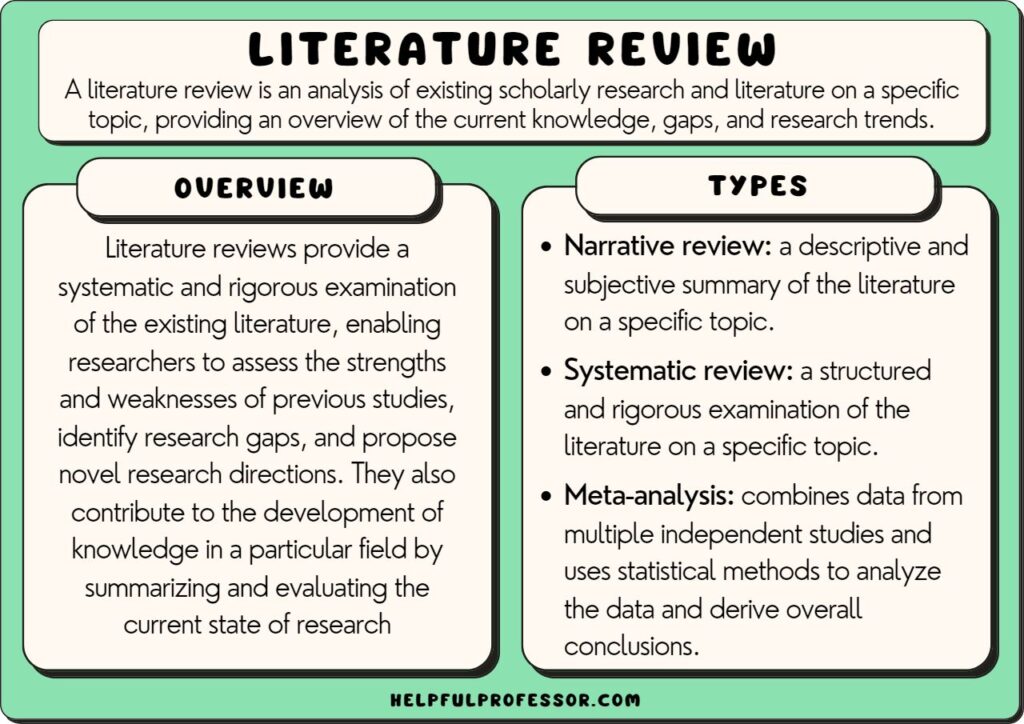
15 Literature Review Examples
Literature reviews are a necessary step in a research process and often required when writing your research proposal . They involve gathering, analyzing, and evaluating existing knowledge about a topic in order to find gaps in the literature where future studies will be needed.
Ideally, once you have completed your literature review, you will be able to identify how your research project can build upon and extend existing knowledge in your area of study.
Generally, for my undergraduate research students, I recommend a narrative review, where themes can be generated in order for the students to develop sufficient understanding of the topic so they can build upon the themes using unique methods or novel research questions.
If you’re in the process of writing a literature review, I have developed a literature review template for you to use – it’s a huge time-saver and walks you through how to write a literature review step-by-step:
Get your time-saving templates here to write your own literature review.
Literature Review Examples
For the following types of literature review, I present an explanation and overview of the type, followed by links to some real-life literature reviews on the topics.
1. Narrative Review Examples
Also known as a traditional literature review, the narrative review provides a broad overview of the studies done on a particular topic.
It often includes both qualitative and quantitative studies and may cover a wide range of years.
The narrative review’s purpose is to identify commonalities, gaps, and contradictions in the literature .
I recommend to my students that they should gather their studies together, take notes on each study, then try to group them by themes that form the basis for the review (see my step-by-step instructions at the end of the article).
Example Study
Title: Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations
Citation: Vermeir, P., Vandijck, D., Degroote, S., Peleman, R., Verhaeghe, R., Mortier, E., … & Vogelaers, D. (2015). Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. International journal of clinical practice , 69 (11), 1257-1267.
Source: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/ijcp.12686
Overview: This narrative review analyzed themes emerging from 69 articles about communication in healthcare contexts. Five key themes were found in the literature: poor communication can lead to various negative outcomes, discontinuity of care, compromise of patient safety, patient dissatisfaction, and inefficient use of resources. After presenting the key themes, the authors recommend that practitioners need to approach healthcare communication in a more structured way, such as by ensuring there is a clear understanding of who is in charge of ensuring effective communication in clinical settings.
Other Examples
- Burnout in United States Healthcare Professionals: A Narrative Review (Reith, 2018) – read here
- Examining the Presence, Consequences, and Reduction of Implicit Bias in Health Care: A Narrative Review (Zestcott, Blair & Stone, 2016) – read here
- A Narrative Review of School-Based Physical Activity for Enhancing Cognition and Learning (Mavilidi et al., 2018) – read here
- A narrative review on burnout experienced by medical students and residents (Dyrbye & Shanafelt, 2015) – read here
2. Systematic Review Examples
This type of literature review is more structured and rigorous than a narrative review. It involves a detailed and comprehensive plan and search strategy derived from a set of specified research questions.
The key way you’d know a systematic review compared to a narrative review is in the methodology: the systematic review will likely have a very clear criteria for how the studies were collected, and clear explanations of exclusion/inclusion criteria.
The goal is to gather the maximum amount of valid literature on the topic, filter out invalid or low-quality reviews, and minimize bias. Ideally, this will provide more reliable findings, leading to higher-quality conclusions and recommendations for further research.
You may note from the examples below that the ‘method’ sections in systematic reviews tend to be much more explicit, often noting rigid inclusion/exclusion criteria and exact keywords used in searches.
Title: The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review
Citation: Roman, S., Sánchez-Siles, L. M., & Siegrist, M. (2017). The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review. Trends in food science & technology , 67 , 44-57.
Source: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092422441730122X
Overview: This systematic review included 72 studies of food naturalness to explore trends in the literature about its importance for consumers. Keywords used in the data search included: food, naturalness, natural content, and natural ingredients. Studies were included if they examined consumers’ preference for food naturalness and contained empirical data. The authors found that the literature lacks clarity about how naturalness is defined and measured, but also found that food consumption is significantly influenced by perceived naturalness of goods.
- A systematic review of research on online teaching and learning from 2009 to 2018 (Martin, Sun & Westine, 2020) – read here
- Where Is Current Research on Blockchain Technology? (Yli-Huumo et al., 2016) – read here
- Universities—industry collaboration: A systematic review (Ankrah & Al-Tabbaa, 2015) – read here
- Internet of Things Applications: A Systematic Review (Asghari, Rahmani & Javadi, 2019) – read here
3. Meta-analysis
This is a type of systematic review that uses statistical methods to combine and summarize the results of several studies.
Due to its robust methodology, a meta-analysis is often considered the ‘gold standard’ of secondary research , as it provides a more precise estimate of a treatment effect than any individual study contributing to the pooled analysis.
Furthermore, by aggregating data from a range of studies, a meta-analysis can identify patterns, disagreements, or other interesting relationships that may have been hidden in individual studies.
This helps to enhance the generalizability of findings, making the conclusions drawn from a meta-analysis particularly powerful and informative for policy and practice.
Title: Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s Disease Risk: A Meta-Meta-Analysis
Citation: Sáiz-Vazquez, O., Puente-Martínez, A., Ubillos-Landa, S., Pacheco-Bonrostro, J., & Santabárbara, J. (2020). Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease risk: a meta-meta-analysis. Brain sciences, 10(6), 386.
Source: https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060386
O verview: This study examines the relationship between cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Researchers conducted a systematic search of meta-analyses and reviewed several databases, collecting 100 primary studies and five meta-analyses to analyze the connection between cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease. They find that the literature compellingly demonstrates that low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels significantly influence the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
- The power of feedback revisited: A meta-analysis of educational feedback research (Wisniewski, Zierer & Hattie, 2020) – read here
- How Much Does Education Improve Intelligence? A Meta-Analysis (Ritchie & Tucker-Drob, 2018) – read here
- A meta-analysis of factors related to recycling (Geiger et al., 2019) – read here
- Stress management interventions for police officers and recruits (Patterson, Chung & Swan, 2014) – read here
Other Types of Reviews
- Scoping Review: This type of review is used to map the key concepts underpinning a research area and the main sources and types of evidence available. It can be undertaken as stand-alone projects in their own right, or as a precursor to a systematic review.
- Rapid Review: This type of review accelerates the systematic review process in order to produce information in a timely manner. This is achieved by simplifying or omitting stages of the systematic review process.
- Integrative Review: This review method is more inclusive than others, allowing for the simultaneous inclusion of experimental and non-experimental research. The goal is to more comprehensively understand a particular phenomenon.
- Critical Review: This is similar to a narrative review but requires a robust understanding of both the subject and the existing literature. In a critical review, the reviewer not only summarizes the existing literature, but also evaluates its strengths and weaknesses. This is common in the social sciences and humanities .
- State-of-the-Art Review: This considers the current level of advancement in a field or topic and makes recommendations for future research directions. This type of review is common in technological and scientific fields but can be applied to any discipline.
How to Write a Narrative Review (Tips for Undergrad Students)
Most undergraduate students conducting a capstone research project will be writing narrative reviews. Below is a five-step process for conducting a simple review of the literature for your project.
- Search for Relevant Literature: Use scholarly databases related to your field of study, provided by your university library, along with appropriate search terms to identify key scholarly articles that have been published on your topic.
- Evaluate and Select Sources: Filter the source list by selecting studies that are directly relevant and of sufficient quality, considering factors like credibility , objectivity, accuracy, and validity.
- Analyze and Synthesize: Review each source and summarize the main arguments in one paragraph (or more, for postgrad). Keep these summaries in a table.
- Identify Themes: With all studies summarized, group studies that share common themes, such as studies that have similar findings or methodologies.
- Write the Review: Write your review based upon the themes or subtopics you have identified. Give a thorough overview of each theme, integrating source data, and conclude with a summary of the current state of knowledge then suggestions for future research based upon your evaluation of what is lacking in the literature.
Literature reviews don’t have to be as scary as they seem. Yes, they are difficult and require a strong degree of comprehension of academic studies. But it can be feasibly done through following a structured approach to data collection and analysis. With my undergraduate research students (who tend to conduct small-scale qualitative studies ), I encourage them to conduct a narrative literature review whereby they can identify key themes in the literature. Within each theme, students can critique key studies and their strengths and limitations , in order to get a lay of the land and come to a point where they can identify ways to contribute new insights to the existing academic conversation on their topic.
Ankrah, S., & Omar, A. T. (2015). Universities–industry collaboration: A systematic review. Scandinavian Journal of Management, 31(3), 387-408.
Asghari, P., Rahmani, A. M., & Javadi, H. H. S. (2019). Internet of Things applications: A systematic review. Computer Networks , 148 , 241-261.
Dyrbye, L., & Shanafelt, T. (2016). A narrative review on burnout experienced by medical students and residents. Medical education , 50 (1), 132-149.
Geiger, J. L., Steg, L., Van Der Werff, E., & Ünal, A. B. (2019). A meta-analysis of factors related to recycling. Journal of environmental psychology , 64 , 78-97.
Martin, F., Sun, T., & Westine, C. D. (2020). A systematic review of research on online teaching and learning from 2009 to 2018. Computers & education , 159 , 104009.
Mavilidi, M. F., Ruiter, M., Schmidt, M., Okely, A. D., Loyens, S., Chandler, P., & Paas, F. (2018). A narrative review of school-based physical activity for enhancing cognition and learning: The importance of relevancy and integration. Frontiers in psychology , 2079.
Patterson, G. T., Chung, I. W., & Swan, P. W. (2014). Stress management interventions for police officers and recruits: A meta-analysis. Journal of experimental criminology , 10 , 487-513.
Reith, T. P. (2018). Burnout in United States healthcare professionals: a narrative review. Cureus , 10 (12).
Ritchie, S. J., & Tucker-Drob, E. M. (2018). How much does education improve intelligence? A meta-analysis. Psychological science , 29 (8), 1358-1369.
Roman, S., Sánchez-Siles, L. M., & Siegrist, M. (2017). The importance of food naturalness for consumers: Results of a systematic review. Trends in food science & technology , 67 , 44-57.
Sáiz-Vazquez, O., Puente-Martínez, A., Ubillos-Landa, S., Pacheco-Bonrostro, J., & Santabárbara, J. (2020). Cholesterol and Alzheimer’s disease risk: a meta-meta-analysis. Brain sciences, 10(6), 386.
Vermeir, P., Vandijck, D., Degroote, S., Peleman, R., Verhaeghe, R., Mortier, E., … & Vogelaers, D. (2015). Communication in healthcare: a narrative review of the literature and practical recommendations. International journal of clinical practice , 69 (11), 1257-1267.
Wisniewski, B., Zierer, K., & Hattie, J. (2020). The power of feedback revisited: A meta-analysis of educational feedback research. Frontiers in Psychology , 10 , 3087.
Yli-Huumo, J., Ko, D., Choi, S., Park, S., & Smolander, K. (2016). Where is current research on blockchain technology?—a systematic review. PloS one , 11 (10), e0163477.
Zestcott, C. A., Blair, I. V., & Stone, J. (2016). Examining the presence, consequences, and reduction of implicit bias in health care: a narrative review. Group Processes & Intergroup Relations , 19 (4), 528-542

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
- How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
- Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
- Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
- Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
- Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
- Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
- Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

How to write a good literature review
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- Life Sciences Papers: 9 Tips for Authors Writing in Biological Sciences
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, how to use paperpal to generate emails &..., ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., do plagiarism checkers detect ai content, word choice problems: how to use the right..., how to avoid plagiarism when using generative ai..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., types of plagiarism and 6 tips to avoid..., how to write an essay introduction (with examples)..., similarity checks: the author’s guide to plagiarism and....
- UWF Libraries
Literature Review: Conducting & Writing
- Sample Literature Reviews
- Steps for Conducting a Lit Review
- Finding "The Literature"
- Organizing/Writing
- APA Style This link opens in a new window
- Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window
- MLA Style This link opens in a new window
Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts
Have an exemplary literature review.
- Literature Review Sample 1
- Literature Review Sample 2
- Literature Review Sample 3
Have you written a stellar literature review you care to share for teaching purposes?
Are you an instructor who has received an exemplary literature review and have permission from the student to post?
Please contact Britt McGowan at [email protected] for inclusion in this guide. All disciplines welcome and encouraged.
- << Previous: MLA Style
- Next: Get Help! >>
- Last Updated: Mar 22, 2024 9:37 AM
- URL: https://libguides.uwf.edu/litreview
105 Literature Review Topics + How-to Guide [2024]
![topic of literature review example 105 Literature Review Topics + How-to Guide [2024]](https://studycorgi.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/front-view-hardback-books-1-353x528.jpg)
A literature review is a variant of curtsy in scientific circles. It presents your acknowledgment that you are not the first to tackle the issue. Your predecessors have made progress in answering your research question, and you plan to start from the point they finished.
This article features examples of literature review topics on multiple knowledge areas. Additionally, you will find exhaustive disambiguation of all the types of a literature review, as well as its purposes, definition, outline, and formatting.
- 🔝 Top 15 Topics
- ✍️ Writing Tips
- Political Science
- Criminal Justice
🔗 References
🔝 top 15 literature review topics.
- What does the science say about extraterrestrial life?
- Redesigning organisms in synthetic biology: Where are we at now?
- Equality of human rights at the international level.
- Why do genes happen to be active or inactive?
- Legalizing physician-assisted suicide.
- Can an adult person change their native language?
- The most efficient study programs.
- The ethics of using surveillance cameras.
- The effect of reading fiction on your brain.
- British imperialism in India.
- What is kindness: A philosophical approach.
- Modern technologies can sift out fake news.
- Multiculturalism: A romantic myth or today’s reality?
- The demographics of liberal worldview in the US.
- Chronic fatigue: Literature review and hypotheses.
✍️ Literature Review Writing Tips
Speaking of a literature review , the definition is too broad to be used as writing guidance. It is an overview of credible materials on a particular research question. A literature review usually becomes chapter 1 in dissertations and theses , allowing to explore the current knowledge on the topic. It evaluates academic and professional articles, journal publications, books, and web-based resources.
A literature review is an indispensable part of a research paper. It serves many purposes, some of which are not evident.
What Is the Purpose of a Literature Review?
- To draw the background context;
- To compare your results with previous research;
- To justify your research methods;
- To frame research gaps and show the scientific novelty of your project;
- To explain the social value of your work;
- To demonstrate your knowledge of the referenced literature;
- To train your analytical thinking.
Types of Literature Review
Below you’ll find the 6 types of literature reviews.
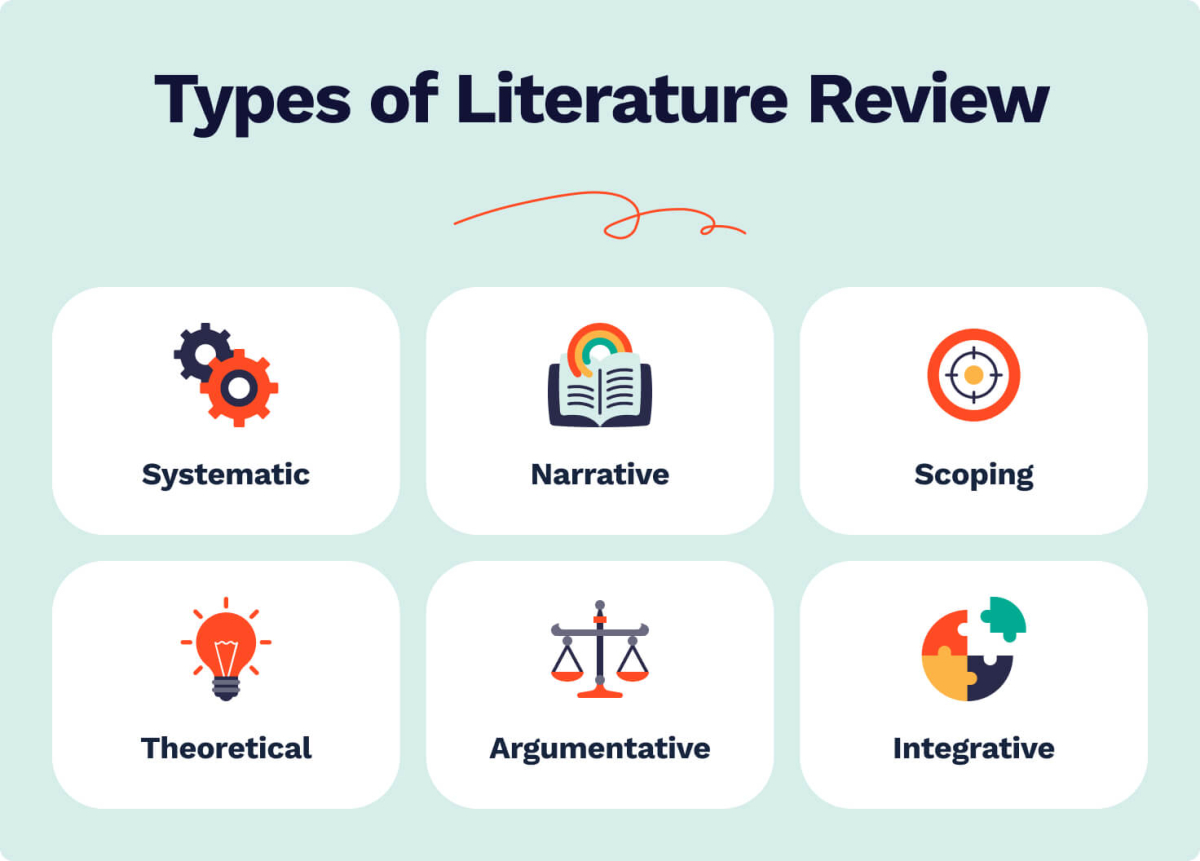
Systematic Review
A systematic literature review is a most comprehensive and data-oriented type. It defines the timeframe of the selected literature and is subdivided into two categories:
- Meta-analysis ( deductive research through standardized statistical procedures)
- Meta-synthesis (inductive study by non-statistical qualitative methods)
Narrative Review
It is also called a traditional or critical literature review. The purpose is to summarize the available material, critique it, and identify the gaps and inconsistencies. This type works well for almost any research question, provided it is sufficiently focused and limited in time or subject matter.
Scoping Review
As the name implies, it estimates the scope of available literature on a literature review topic. Unlike a systematic literature review, which aims to find the most specific research question, this type looks for the most general one. It answers the question of what else can be researched in the field.
Theoretical Review
A theoretical literature review explores the pool of theories that have so far accumulated on a concept. It lists the existing ideas, their relationships, and gaps. The purpose is to develop hypotheses to be tested in the experimental section.
Argumentative Review
This type provides the most selective literature review to prove or refute an argument already established in the research literature. However, this is also the most biased review among all types.
Integrative Review
This literature review integrates, synthesizes, and critiques the available secondary data to develop new research frameworks and perspectives.
Systematic Review vs. Literature Review vs. Annotated Bibliography
Literature Review Outline
How long should a literature review be? It depends on the assignment requirements and your outline.
A literature review is often used as a part of a more general research paper. In such a case, you can limit yourself to the standard introduction –main body – conclusion formula.
In all the other situations, use the following literature review outline.
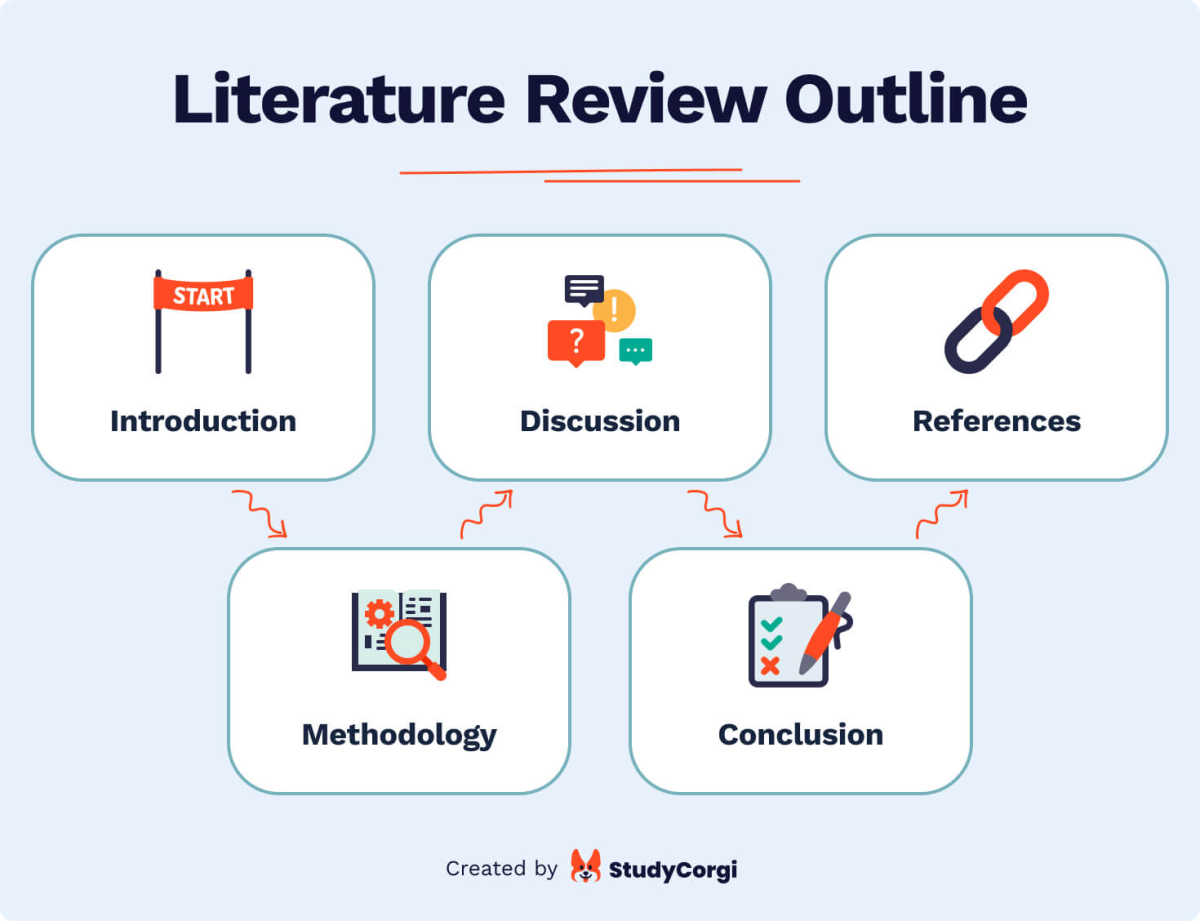
- Introduction Trace the scope and highlight the importance of your review. Why did you choose the given topic or research question? How does it contribute to the previous study?
- Methodology We have listed the types of literature review above. Depending on your purposes, select one and explain why your choice is the best. You can also specify which logic you used while choosing the sources for your review.
- Discussion It is the central part of the text which compares, contrasts, and explains the relationships between various ideas you found in the bibliography items.
- Conclusion Are you satisfied with the result of your work? How will it help further research? Which gaps have you spotted, and which hypothesis could you generate?
- List of references As in any research paper, this is an indispensable part of your literature review. Be sure to follow the format requirements as provided below.
Literature Review Format
All citation styles require you to indicate the author’s name, book title, publication year, number of pages, and volume or issue number. This data is available in any printed edition, as publishers use it to identify their products.
It may sound simple until you discover that each citation style has a multi-page list of nuanced details specific to this format and inapplicable to any other.
Browse the guides for each of the most popular types below.
APA style is a format for scholarly documents. It is particularly popular in the fields of social and behavioral sciences. APA is well-known for its simplicity in source references. Thus, a vast majority of American universities and colleges prefer this format.
MLA style manual is an abridged version of the MLA Handbook published by the Modern Language Association. It was created for students to assist in their research aspirations. Its 8 th edition is addressed to secondary-school and undergraduate university and college teachers and students. The style is popular in humanities (modern languages, literature, cultural studies, and related disciplines).
Chicago style (also called CMS or CMOS) is a style guide for American English. The University of Chicago Press first published it in 1906. Since then, it has had 17 editions and has become one of the most popular citation styles in the US. The guide instructs on editorial practice, grammar, document preparation, formatting, and even the use of the singular “they.”
💡 Literature Review Topics
Literature review topics in education.
- How can we make classrooms more inclusive ?
- Flipped classroom approach.
- Waldorf schools and their concept.
- How do ADHD symptoms affect a student’s learning abilities?
- Educational leadership.
- Methods of tracking the performance of schoolchildren.
- How can token economy diminish off-task behavior in students with autism?
- Resegregation in US schools.
- Is bilingual education realizable in contemporary schools?
- Growing violence incidents in educational institutions.
Political Science Literature Review Topics
- Gender cosmopolitanism in Sweden .
- Security policy is based on political ideology .
- The emotional effect of populism .
- The theory and classification of political speeches.
- Global measures in COVID-19 response.
- The international politics of the Arab world.
- How do we select our leaders ?
- Officials in politics: Emotional labor .
- Relational peace between countries.
- The invisible force holding countries together.
Criminal Justice Literature Review Topics
- The problematic issues of prosecution and legal enforcement in Eastern Europe.
- Track the evolution of international criminal justice practices.
- Crime prevention methods.
- The evolution of criminology as a social science.
- The cycle of domestic violence : Theory and statistics.
- The patterns in child abuse perpetrators.
- Randomized experimental designs in criminology .
- Current measures to stop human trafficking in the US.
- How should we punish environmental crimes?
- Terrorism : Approaches to its definitions.
Sociology Literature Review Topics
- Does coded language help us fight racial inequality ?
- Workplace bullying.
- International conflicts in terms of social representation theory.
- Gender and sexual activity.
- Is our society liberal or conservative ?
- Single African American parents.
- Racial salary gap in the US.
- Substance abuse and health care costs for employers.
- Does federal aid succeed at fighting urban poverty?
- How does hate speech spur desensitization?
Nursing Literature Review Topics
- Practice in the field of healthcare.
- Evidence-based nursing practice.
- Traumatic brain injury.
- Alzheimer’s disease.
- Pressure ulcers study.
- Post-operative readmission rates.
- Nursing ratios and nosocomial infections.
- Patient fall prevention study.
- Emergency room wait time.
- Electronic health records.
Psychology Literature Review Topics
- Parents’ experiences of caring for a child with ASD
- The long-term consequences of child abuse
- The neurology of depression .
- Explore the psychological effects of loud noise.
- Why is it so hard to accept what contradicts our beliefs?
- The psychological mechanisms of compulsive eating.
- Why are some people more prone to discrimination and prejudice?
- Self-protection against grief .
- Non-verbal communication rates in different cultures.
- Love : Chemistry or feeling?
Biology Literature Review Topics
- Camouflage in plants.
- Color differences in male and female bird species.
- Acceptability of genetic engineering.
- Natural reforestation: Too long to wait.
- Why are domestic plants weaker than wild ones?
- Hepcidin: importance, production, regulation.
- How can we edit DNA sequences ?
- Which anti- COVID vaccines are the most effective and why?
- Cancer : An umbrella term for many diseases.
- Species that are important to our ecology.
Easy Literature Review Topics
- Sustainable agriculture : Our future reality.
- Vegetarianism.
- The scientific background behind music therapy .
- Stono revolt.
- The latest findings in stopping brain aging.
- Articles on cyber security of young children.
- Data-driven personalization : Prospects and achievements.
- Importance of the literature review in research.
- Critical literature review of digital signature.
- Reviewing quantitative academic literature and data.
❓ Literature Review Topics FAQ
❓ what is discussed in literature review.
A literature review discusses the texts that are the most relevant to your research question. It summarizes, compares, evaluates, and critiques the available literature to find the points of intersection and blind spots. As a result, you will develop a specific topic for further research or pose a hypothesis.
❓ What are the 3 parts of literature review?
The three parts of this academic genre are the same as those of any other research paper. The introduction explores the background and importance of the topic. The main body analyzes the selected texts. It may also contain a methodology section that explains why you chose such or another literary review type. The conclusion outlines the perspectives of your research.
❓ What are the four stages of literature review?
- Formulating the problem (which topic is under study and what are its constituent parts?);
- Searching the literature (making up the preliminary bibliography list to be described in the literature review);
- Evaluating the data (which sources are the most significant in our understanding of the topic?);
- Analyzing and interpreting the essential findings.
- Literature Reviews – UNC Writing Center
- Learn how to write a review of literature
- Writing a Literature Review // Purdue Writing Lab
- Types of Literature Reviews – Systematic Reviews
- How to Conduct a Literature Review
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter X
- Share to LinkedIn
You might also like
The necklace: summary, themes, and a short story analysis, dulce et decorum est 101: summary, analysis, & questions and answers, literature review: outline, strategies, and examples [2024].
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 2 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Literature Review – Types Writing Guide and Examples
Literature Review – Types Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Literature Review
Definition:
A literature review is a comprehensive and critical analysis of the existing literature on a particular topic or research question. It involves identifying, evaluating, and synthesizing relevant literature, including scholarly articles, books, and other sources, to provide a summary and critical assessment of what is known about the topic.
Types of Literature Review
Types of Literature Review are as follows:
- Narrative literature review : This type of review involves a comprehensive summary and critical analysis of the available literature on a particular topic or research question. It is often used as an introductory section of a research paper.
- Systematic literature review: This is a rigorous and structured review that follows a pre-defined protocol to identify, evaluate, and synthesize all relevant studies on a specific research question. It is often used in evidence-based practice and systematic reviews.
- Meta-analysis: This is a quantitative review that uses statistical methods to combine data from multiple studies to derive a summary effect size. It provides a more precise estimate of the overall effect than any individual study.
- Scoping review: This is a preliminary review that aims to map the existing literature on a broad topic area to identify research gaps and areas for further investigation.
- Critical literature review : This type of review evaluates the strengths and weaknesses of the existing literature on a particular topic or research question. It aims to provide a critical analysis of the literature and identify areas where further research is needed.
- Conceptual literature review: This review synthesizes and integrates theories and concepts from multiple sources to provide a new perspective on a particular topic. It aims to provide a theoretical framework for understanding a particular research question.
- Rapid literature review: This is a quick review that provides a snapshot of the current state of knowledge on a specific research question or topic. It is often used when time and resources are limited.
- Thematic literature review : This review identifies and analyzes common themes and patterns across a body of literature on a particular topic. It aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the literature and identify key themes and concepts.
- Realist literature review: This review is often used in social science research and aims to identify how and why certain interventions work in certain contexts. It takes into account the context and complexities of real-world situations.
- State-of-the-art literature review : This type of review provides an overview of the current state of knowledge in a particular field, highlighting the most recent and relevant research. It is often used in fields where knowledge is rapidly evolving, such as technology or medicine.
- Integrative literature review: This type of review synthesizes and integrates findings from multiple studies on a particular topic to identify patterns, themes, and gaps in the literature. It aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current state of knowledge on a particular topic.
- Umbrella literature review : This review is used to provide a broad overview of a large and diverse body of literature on a particular topic. It aims to identify common themes and patterns across different areas of research.
- Historical literature review: This type of review examines the historical development of research on a particular topic or research question. It aims to provide a historical context for understanding the current state of knowledge on a particular topic.
- Problem-oriented literature review : This review focuses on a specific problem or issue and examines the literature to identify potential solutions or interventions. It aims to provide practical recommendations for addressing a particular problem or issue.
- Mixed-methods literature review : This type of review combines quantitative and qualitative methods to synthesize and analyze the available literature on a particular topic. It aims to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the research question by combining different types of evidence.
Parts of Literature Review
Parts of a literature review are as follows:
Introduction
The introduction of a literature review typically provides background information on the research topic and why it is important. It outlines the objectives of the review, the research question or hypothesis, and the scope of the review.
Literature Search
This section outlines the search strategy and databases used to identify relevant literature. The search terms used, inclusion and exclusion criteria, and any limitations of the search are described.
Literature Analysis
The literature analysis is the main body of the literature review. This section summarizes and synthesizes the literature that is relevant to the research question or hypothesis. The review should be organized thematically, chronologically, or by methodology, depending on the research objectives.
Critical Evaluation
Critical evaluation involves assessing the quality and validity of the literature. This includes evaluating the reliability and validity of the studies reviewed, the methodology used, and the strength of the evidence.
The conclusion of the literature review should summarize the main findings, identify any gaps in the literature, and suggest areas for future research. It should also reiterate the importance of the research question or hypothesis and the contribution of the literature review to the overall research project.
The references list includes all the sources cited in the literature review, and follows a specific referencing style (e.g., APA, MLA, Harvard).
How to write Literature Review
Here are some steps to follow when writing a literature review:
- Define your research question or topic : Before starting your literature review, it is essential to define your research question or topic. This will help you identify relevant literature and determine the scope of your review.
- Conduct a comprehensive search: Use databases and search engines to find relevant literature. Look for peer-reviewed articles, books, and other academic sources that are relevant to your research question or topic.
- Evaluate the sources: Once you have found potential sources, evaluate them critically to determine their relevance, credibility, and quality. Look for recent publications, reputable authors, and reliable sources of data and evidence.
- Organize your sources: Group the sources by theme, method, or research question. This will help you identify similarities and differences among the literature, and provide a structure for your literature review.
- Analyze and synthesize the literature : Analyze each source in depth, identifying the key findings, methodologies, and conclusions. Then, synthesize the information from the sources, identifying patterns and themes in the literature.
- Write the literature review : Start with an introduction that provides an overview of the topic and the purpose of the literature review. Then, organize the literature according to your chosen structure, and analyze and synthesize the sources. Finally, provide a conclusion that summarizes the key findings of the literature review, identifies gaps in knowledge, and suggests areas for future research.
- Edit and proofread: Once you have written your literature review, edit and proofread it carefully to ensure that it is well-organized, clear, and concise.
Examples of Literature Review
Here’s an example of how a literature review can be conducted for a thesis on the topic of “ The Impact of Social Media on Teenagers’ Mental Health”:
- Start by identifying the key terms related to your research topic. In this case, the key terms are “social media,” “teenagers,” and “mental health.”
- Use academic databases like Google Scholar, JSTOR, or PubMed to search for relevant articles, books, and other publications. Use these keywords in your search to narrow down your results.
- Evaluate the sources you find to determine if they are relevant to your research question. You may want to consider the publication date, author’s credentials, and the journal or book publisher.
- Begin reading and taking notes on each source, paying attention to key findings, methodologies used, and any gaps in the research.
- Organize your findings into themes or categories. For example, you might categorize your sources into those that examine the impact of social media on self-esteem, those that explore the effects of cyberbullying, and those that investigate the relationship between social media use and depression.
- Synthesize your findings by summarizing the key themes and highlighting any gaps or inconsistencies in the research. Identify areas where further research is needed.
- Use your literature review to inform your research questions and hypotheses for your thesis.
For example, after conducting a literature review on the impact of social media on teenagers’ mental health, a thesis might look like this:
“Using a mixed-methods approach, this study aims to investigate the relationship between social media use and mental health outcomes in teenagers. Specifically, the study will examine the effects of cyberbullying, social comparison, and excessive social media use on self-esteem, anxiety, and depression. Through an analysis of survey data and qualitative interviews with teenagers, the study will provide insight into the complex relationship between social media use and mental health outcomes, and identify strategies for promoting positive mental health outcomes in young people.”
Reference: Smith, J., Jones, M., & Lee, S. (2019). The effects of social media use on adolescent mental health: A systematic review. Journal of Adolescent Health, 65(2), 154-165. doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2019.03.024
Reference Example: Author, A. A., Author, B. B., & Author, C. C. (Year). Title of article. Title of Journal, volume number(issue number), page range. doi:0000000/000000000000 or URL
Applications of Literature Review
some applications of literature review in different fields:
- Social Sciences: In social sciences, literature reviews are used to identify gaps in existing research, to develop research questions, and to provide a theoretical framework for research. Literature reviews are commonly used in fields such as sociology, psychology, anthropology, and political science.
- Natural Sciences: In natural sciences, literature reviews are used to summarize and evaluate the current state of knowledge in a particular field or subfield. Literature reviews can help researchers identify areas where more research is needed and provide insights into the latest developments in a particular field. Fields such as biology, chemistry, and physics commonly use literature reviews.
- Health Sciences: In health sciences, literature reviews are used to evaluate the effectiveness of treatments, identify best practices, and determine areas where more research is needed. Literature reviews are commonly used in fields such as medicine, nursing, and public health.
- Humanities: In humanities, literature reviews are used to identify gaps in existing knowledge, develop new interpretations of texts or cultural artifacts, and provide a theoretical framework for research. Literature reviews are commonly used in fields such as history, literary studies, and philosophy.
Role of Literature Review in Research
Here are some applications of literature review in research:
- Identifying Research Gaps : Literature review helps researchers identify gaps in existing research and literature related to their research question. This allows them to develop new research questions and hypotheses to fill those gaps.
- Developing Theoretical Framework: Literature review helps researchers develop a theoretical framework for their research. By analyzing and synthesizing existing literature, researchers can identify the key concepts, theories, and models that are relevant to their research.
- Selecting Research Methods : Literature review helps researchers select appropriate research methods and techniques based on previous research. It also helps researchers to identify potential biases or limitations of certain methods and techniques.
- Data Collection and Analysis: Literature review helps researchers in data collection and analysis by providing a foundation for the development of data collection instruments and methods. It also helps researchers to identify relevant data sources and identify potential data analysis techniques.
- Communicating Results: Literature review helps researchers to communicate their results effectively by providing a context for their research. It also helps to justify the significance of their findings in relation to existing research and literature.
Purpose of Literature Review
Some of the specific purposes of a literature review are as follows:
- To provide context: A literature review helps to provide context for your research by situating it within the broader body of literature on the topic.
- To identify gaps and inconsistencies: A literature review helps to identify areas where further research is needed or where there are inconsistencies in the existing literature.
- To synthesize information: A literature review helps to synthesize the information from multiple sources and present a coherent and comprehensive picture of the current state of knowledge on the topic.
- To identify key concepts and theories : A literature review helps to identify key concepts and theories that are relevant to your research question and provide a theoretical framework for your study.
- To inform research design: A literature review can inform the design of your research study by identifying appropriate research methods, data sources, and research questions.
Characteristics of Literature Review
Some Characteristics of Literature Review are as follows:
- Identifying gaps in knowledge: A literature review helps to identify gaps in the existing knowledge and research on a specific topic or research question. By analyzing and synthesizing the literature, you can identify areas where further research is needed and where new insights can be gained.
- Establishing the significance of your research: A literature review helps to establish the significance of your own research by placing it in the context of existing research. By demonstrating the relevance of your research to the existing literature, you can establish its importance and value.
- Informing research design and methodology : A literature review helps to inform research design and methodology by identifying the most appropriate research methods, techniques, and instruments. By reviewing the literature, you can identify the strengths and limitations of different research methods and techniques, and select the most appropriate ones for your own research.
- Supporting arguments and claims: A literature review provides evidence to support arguments and claims made in academic writing. By citing and analyzing the literature, you can provide a solid foundation for your own arguments and claims.
- I dentifying potential collaborators and mentors: A literature review can help identify potential collaborators and mentors by identifying researchers and practitioners who are working on related topics or using similar methods. By building relationships with these individuals, you can gain valuable insights and support for your own research and practice.
- Keeping up-to-date with the latest research : A literature review helps to keep you up-to-date with the latest research on a specific topic or research question. By regularly reviewing the literature, you can stay informed about the latest findings and developments in your field.
Advantages of Literature Review
There are several advantages to conducting a literature review as part of a research project, including:
- Establishing the significance of the research : A literature review helps to establish the significance of the research by demonstrating the gap or problem in the existing literature that the study aims to address.
- Identifying key concepts and theories: A literature review can help to identify key concepts and theories that are relevant to the research question, and provide a theoretical framework for the study.
- Supporting the research methodology : A literature review can inform the research methodology by identifying appropriate research methods, data sources, and research questions.
- Providing a comprehensive overview of the literature : A literature review provides a comprehensive overview of the current state of knowledge on a topic, allowing the researcher to identify key themes, debates, and areas of agreement or disagreement.
- Identifying potential research questions: A literature review can help to identify potential research questions and areas for further investigation.
- Avoiding duplication of research: A literature review can help to avoid duplication of research by identifying what has already been done on a topic, and what remains to be done.
- Enhancing the credibility of the research : A literature review helps to enhance the credibility of the research by demonstrating the researcher’s knowledge of the existing literature and their ability to situate their research within a broader context.
Limitations of Literature Review
Limitations of Literature Review are as follows:
- Limited scope : Literature reviews can only cover the existing literature on a particular topic, which may be limited in scope or depth.
- Publication bias : Literature reviews may be influenced by publication bias, which occurs when researchers are more likely to publish positive results than negative ones. This can lead to an incomplete or biased picture of the literature.
- Quality of sources : The quality of the literature reviewed can vary widely, and not all sources may be reliable or valid.
- Time-limited: Literature reviews can become quickly outdated as new research is published, making it difficult to keep up with the latest developments in a field.
- Subjective interpretation : Literature reviews can be subjective, and the interpretation of the findings can vary depending on the researcher’s perspective or bias.
- Lack of original data : Literature reviews do not generate new data, but rather rely on the analysis of existing studies.
- Risk of plagiarism: It is important to ensure that literature reviews do not inadvertently contain plagiarism, which can occur when researchers use the work of others without proper attribution.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How To Write A Literature Review - A Complete Guide

Table of Contents
A literature review is much more than just another section in your research paper. It forms the very foundation of your research. It is a formal piece of writing where you analyze the existing theoretical framework, principles, and assumptions and use that as a base to shape your approach to the research question.
Curating and drafting a solid literature review section not only lends more credibility to your research paper but also makes your research tighter and better focused. But, writing literature reviews is a difficult task. It requires extensive reading, plus you have to consider market trends and technological and political changes, which tend to change in the blink of an eye.
Now streamline your literature review process with the help of SciSpace Copilot. With this AI research assistant, you can efficiently synthesize and analyze a vast amount of information, identify key themes and trends, and uncover gaps in the existing research. Get real-time explanations, summaries, and answers to your questions for the paper you're reviewing, making navigating and understanding the complex literature landscape easier.
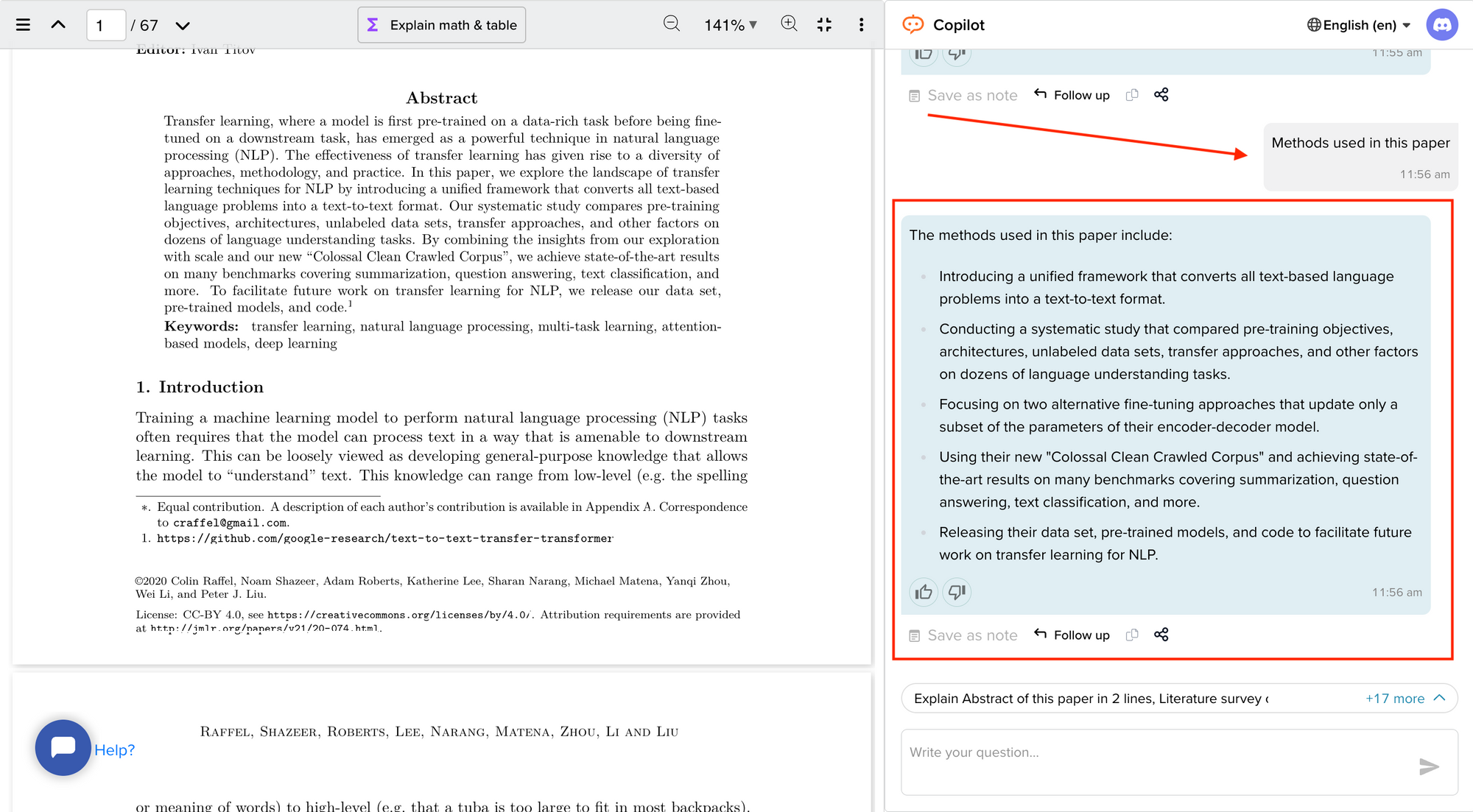
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything from the definition of a literature review, its appropriate length, various types of literature reviews, and how to write one.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is a collation of survey, research, critical evaluation, and assessment of the existing literature in a preferred domain.
Eminent researcher and academic Arlene Fink, in her book Conducting Research Literature Reviews , defines it as the following:
“A literature review surveys books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated.
Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have explored while researching a particular topic, and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within a larger field of study.”
Simply put, a literature review can be defined as a critical discussion of relevant pre-existing research around your research question and carving out a definitive place for your study in the existing body of knowledge. Literature reviews can be presented in multiple ways: a section of an article, the whole research paper itself, or a chapter of your thesis.
A literature review does function as a summary of sources, but it also allows you to analyze further, interpret, and examine the stated theories, methods, viewpoints, and, of course, the gaps in the existing content.
As an author, you can discuss and interpret the research question and its various aspects and debate your adopted methods to support the claim.
What is the purpose of a literature review?
A literature review is meant to help your readers understand the relevance of your research question and where it fits within the existing body of knowledge. As a researcher, you should use it to set the context, build your argument, and establish the need for your study.
What is the importance of a literature review?
The literature review is a critical part of research papers because it helps you:
- Gain an in-depth understanding of your research question and the surrounding area
- Convey that you have a thorough understanding of your research area and are up-to-date with the latest changes and advancements
- Establish how your research is connected or builds on the existing body of knowledge and how it could contribute to further research
- Elaborate on the validity and suitability of your theoretical framework and research methodology
- Identify and highlight gaps and shortcomings in the existing body of knowledge and how things need to change
- Convey to readers how your study is different or how it contributes to the research area
How long should a literature review be?
Ideally, the literature review should take up 15%-40% of the total length of your manuscript. So, if you have a 10,000-word research paper, the minimum word count could be 1500.
Your literature review format depends heavily on the kind of manuscript you are writing — an entire chapter in case of doctoral theses, a part of the introductory section in a research article, to a full-fledged review article that examines the previously published research on a topic.
Another determining factor is the type of research you are doing. The literature review section tends to be longer for secondary research projects than primary research projects.
What are the different types of literature reviews?
All literature reviews are not the same. There are a variety of possible approaches that you can take. It all depends on the type of research you are pursuing.
Here are the different types of literature reviews:
Argumentative review
It is called an argumentative review when you carefully present literature that only supports or counters a specific argument or premise to establish a viewpoint.
Integrative review
It is a type of literature review focused on building a comprehensive understanding of a topic by combining available theoretical frameworks and empirical evidence.
Methodological review
This approach delves into the ''how'' and the ''what" of the research question — you cannot look at the outcome in isolation; you should also review the methodology used.
Systematic review
This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research and collect, report, and analyze data from the studies included in the review.
Meta-analysis review
Meta-analysis uses statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects than those derived from the individual studies included within a review.
Historical review
Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, or phenomenon emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and identify future research's likely directions.
Theoretical Review
This form aims to examine the corpus of theory accumulated regarding an issue, concept, theory, and phenomenon. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories exist, the relationships between them, the degree the existing approaches have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested.
Scoping Review
The Scoping Review is often used at the beginning of an article, dissertation, or research proposal. It is conducted before the research to highlight gaps in the existing body of knowledge and explains why the project should be greenlit.
State-of-the-Art Review
The State-of-the-Art review is conducted periodically, focusing on the most recent research. It describes what is currently known, understood, or agreed upon regarding the research topic and highlights where there are still disagreements.
Can you use the first person in a literature review?
When writing literature reviews, you should avoid the usage of first-person pronouns. It means that instead of "I argue that" or "we argue that," the appropriate expression would be "this research paper argues that."
Do you need an abstract for a literature review?
Ideally, yes. It is always good to have a condensed summary that is self-contained and independent of the rest of your review. As for how to draft one, you can follow the same fundamental idea when preparing an abstract for a literature review. It should also include:
- The research topic and your motivation behind selecting it
- A one-sentence thesis statement
- An explanation of the kinds of literature featured in the review
- Summary of what you've learned
- Conclusions you drew from the literature you reviewed
- Potential implications and future scope for research
Here's an example of the abstract of a literature review
Is a literature review written in the past tense?
Yes, the literature review should ideally be written in the past tense. You should not use the present or future tense when writing one. The exceptions are when you have statements describing events that happened earlier than the literature you are reviewing or events that are currently occurring; then, you can use the past perfect or present perfect tenses.
How many sources for a literature review?
There are multiple approaches to deciding how many sources to include in a literature review section. The first approach would be to look level you are at as a researcher. For instance, a doctoral thesis might need 60+ sources. In contrast, you might only need to refer to 5-15 sources at the undergraduate level.
The second approach is based on the kind of literature review you are doing — whether it is merely a chapter of your paper or if it is a self-contained paper in itself. When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. In the second scenario, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
Quick tips on how to write a literature review
To know how to write a literature review, you must clearly understand its impact and role in establishing your work as substantive research material.
You need to follow the below-mentioned steps, to write a literature review:
- Outline the purpose behind the literature review
- Search relevant literature
- Examine and assess the relevant resources
- Discover connections by drawing deep insights from the resources
- Structure planning to write a good literature review
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review
As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications. You must be able to the answer below questions before you start:
- How many sources do I need to include?
- What kind of sources should I analyze?
- How much should I critically evaluate each source?
- Should I summarize, synthesize or offer a critique of the sources?
- Do I need to include any background information or definitions?
Additionally, you should know that the narrower your research topic is, the swifter it will be for you to restrict the number of sources to be analyzed.
2. Search relevant literature
Dig deeper into search engines to discover what has already been published around your chosen topic. Make sure you thoroughly go through appropriate reference sources like books, reports, journal articles, government docs, and web-based resources.
You must prepare a list of keywords and their different variations. You can start your search from any library’s catalog, provided you are an active member of that institution. The exact keywords can be extended to widen your research over other databases and academic search engines like:
- Google Scholar
- Microsoft Academic
- Science.gov
Besides, it is not advisable to go through every resource word by word. Alternatively, what you can do is you can start by reading the abstract and then decide whether that source is relevant to your research or not.
Additionally, you must spend surplus time assessing the quality and relevance of resources. It would help if you tried preparing a list of citations to ensure that there lies no repetition of authors, publications, or articles in the literature review.
3. Examine and assess the sources
It is nearly impossible for you to go through every detail in the research article. So rather than trying to fetch every detail, you have to analyze and decide which research sources resemble closest and appear relevant to your chosen domain.
While analyzing the sources, you should look to find out answers to questions like:
- What question or problem has the author been describing and debating?
- What is the definition of critical aspects?
- How well the theories, approach, and methodology have been explained?
- Whether the research theory used some conventional or new innovative approach?
- How relevant are the key findings of the work?
- In what ways does it relate to other sources on the same topic?
- What challenges does this research paper pose to the existing theory
- What are the possible contributions or benefits it adds to the subject domain?
Be always mindful that you refer only to credible and authentic resources. It would be best if you always take references from different publications to validate your theory.
Always keep track of important information or data you can present in your literature review right from the beginning. It will help steer your path from any threats of plagiarism and also make it easier to curate an annotated bibliography or reference section.
4. Discover connections
At this stage, you must start deciding on the argument and structure of your literature review. To accomplish this, you must discover and identify the relations and connections between various resources while drafting your abstract.
A few aspects that you should be aware of while writing a literature review include:
- Rise to prominence: Theories and methods that have gained reputation and supporters over time.
- Constant scrutiny: Concepts or theories that repeatedly went under examination.
- Contradictions and conflicts: Theories, both the supporting and the contradictory ones, for the research topic.
- Knowledge gaps: What exactly does it fail to address, and how to bridge them with further research?
- Influential resources: Significant research projects available that have been upheld as milestones or perhaps, something that can modify the current trends
Once you join the dots between various past research works, it will be easier for you to draw a conclusion and identify your contribution to the existing knowledge base.
5. Structure planning to write a good literature review
There exist different ways towards planning and executing the structure of a literature review. The format of a literature review varies and depends upon the length of the research.
Like any other research paper, the literature review format must contain three sections: introduction, body, and conclusion. The goals and objectives of the research question determine what goes inside these three sections.
Nevertheless, a good literature review can be structured according to the chronological, thematic, methodological, or theoretical framework approach.
Literature review samples
1. Standalone
2. As a section of a research paper
How SciSpace Discover makes literature review a breeze?
SciSpace Discover is a one-stop solution to do an effective literature search and get barrier-free access to scientific knowledge. It is an excellent repository where you can find millions of only peer-reviewed articles and full-text PDF files. Here’s more on how you can use it:
Find the right information
Find what you want quickly and easily with comprehensive search filters that let you narrow down papers according to PDF availability, year of publishing, document type, and affiliated institution. Moreover, you can sort the results based on the publishing date, citation count, and relevance.
Assess credibility of papers quickly
When doing the literature review, it is critical to establish the quality of your sources. They form the foundation of your research. SciSpace Discover helps you assess the quality of a source by providing an overview of its references, citations, and performance metrics.
Get the complete picture in no time
SciSpace Discover’s personalized suggestion engine helps you stay on course and get the complete picture of the topic from one place. Every time you visit an article page, it provides you links to related papers. Besides that, it helps you understand what’s trending, who are the top authors, and who are the leading publishers on a topic.
Make referring sources super easy
To ensure you don't lose track of your sources, you must start noting down your references when doing the literature review. SciSpace Discover makes this step effortless. Click the 'cite' button on an article page, and you will receive preloaded citation text in multiple styles — all you've to do is copy-paste it into your manuscript.
Final tips on how to write a literature review
A massive chunk of time and effort is required to write a good literature review. But, if you go about it systematically, you'll be able to save a ton of time and build a solid foundation for your research.
We hope this guide has helped you answer several key questions you have about writing literature reviews.
Would you like to explore SciSpace Discover and kick off your literature search right away? You can get started here .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. how to start a literature review.
• What questions do you want to answer?
• What sources do you need to answer these questions?
• What information do these sources contain?
• How can you use this information to answer your questions?
2. What to include in a literature review?
• A brief background of the problem or issue
• What has previously been done to address the problem or issue
• A description of what you will do in your project
• How this study will contribute to research on the subject
3. Why literature review is important?
The literature review is an important part of any research project because it allows the writer to look at previous studies on a topic and determine existing gaps in the literature, as well as what has already been done. It will also help them to choose the most appropriate method for their own study.
4. How to cite a literature review in APA format?
To cite a literature review in APA style, you need to provide the author's name, the title of the article, and the year of publication. For example: Patel, A. B., & Stokes, G. S. (2012). The relationship between personality and intelligence: A meta-analysis of longitudinal research. Personality and Individual Differences, 53(1), 16-21
5. What are the components of a literature review?
• A brief introduction to the topic, including its background and context. The introduction should also include a rationale for why the study is being conducted and what it will accomplish.
• A description of the methodologies used in the study. This can include information about data collection methods, sample size, and statistical analyses.
• A presentation of the findings in an organized format that helps readers follow along with the author's conclusions.
6. What are common errors in writing literature review?
• Not spending enough time to critically evaluate the relevance of resources, observations and conclusions.
• Totally relying on secondary data while ignoring primary data.
• Letting your personal bias seep into your interpretation of existing literature.
• No detailed explanation of the procedure to discover and identify an appropriate literature review.
7. What are the 5 C's of writing literature review?
• Cite - the sources you utilized and referenced in your research.
• Compare - existing arguments, hypotheses, methodologies, and conclusions found in the knowledge base.
• Contrast - the arguments, topics, methodologies, approaches, and disputes that may be found in the literature.
• Critique - the literature and describe the ideas and opinions you find more convincing and why.
• Connect - the various studies you reviewed in your research.
8. How many sources should a literature review have?
When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. if it is a self-contained paper in itself, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
9. Can literature review have diagrams?
• To represent an abstract idea or concept
• To explain the steps of a process or procedure
• To help readers understand the relationships between different concepts
10. How old should sources be in a literature review?
Sources for a literature review should be as current as possible or not older than ten years. The only exception to this rule is if you are reviewing a historical topic and need to use older sources.
11. What are the types of literature review?
• Argumentative review
• Integrative review
• Methodological review
• Systematic review
• Meta-analysis review
• Historical review
• Theoretical review
• Scoping review
• State-of-the-Art review
12. Is a literature review mandatory?
Yes. Literature review is a mandatory part of any research project. It is a critical step in the process that allows you to establish the scope of your research, and provide a background for the rest of your work.
But before you go,
- Six Online Tools for Easy Literature Review
- Evaluating literature review: systematic vs. scoping reviews
- Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review
- Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples

You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Writer Service >
- Topic Collections
120 Fresh and Thought-Provoking Topics for Literature Reviews in Different Disciplines
A literature review is an account of the scholarly works published on a topic. It is different from an annotated bibliography – and far more interesting at that. Instead of being just a list of summaries, a literature review synthesizes the information from all available sources in an overall relationship to your guiding concept. This may be the problem you are discussing, a statement you are arguing, a theory you are verifying, etc.
The goals of a literature review may vary:
- giving a historical overview of the research in the field
- summarizing the existing state of the topic
- finding a problem or a gap in the research field
- developing a new theory, etc.
That is why good literature review topics are often formulated as research questions. This type of paper is not an easy writing. You will need to parse immense volumes of information, synthesize and summarize coherently. You also need to devote plenty of time to reading.
This post contains a list of literature review topics suggested for various subjects. However, when choosing the most fitting one to dig into, ask yourself, what are the passions that you can apply to this research? This assignment will take a while, so you will need more than just a good study discipline to soldier on. A bit of enthusiasm and intrinsic motivation will get you much farther.
Literature Review Topics Examples on English and World Literature
Some of the suggestions in this post are linked to literature review examples in our free database. By clicking on a title, you get to a corresponding sample page, where you can read the entire text. If the topic you like isn't linked, but you would like to read an example, you can order it. We will arrange the most qualified paper writer to prepare it for you exclusively.
Ready? Let's start with topics for literature review papers on English and World Literature.
- Phoenix as a symbol for endurance in a worn path
- The novel Intuition by Allegra Goodman
- Nathaniel Hawthorne's The Birthmark through Girard's Lens
- Ender's Game by an Orson Scott Card
- Depiction of freedom and happiness in Brave New World
- Feminism and Post-Colonialism in Margaret Atwood's Oryx and Crake and Suzanne Collins's The Hunger Games
- Rationality, logic, and mathematics in the novel The Curious Incident Of The Dog In The Night-Time
- Victims of their time as a character type in the World literature
- The last days of Judas Iscariot : a play by Stephen Adly Guirgis
- The use of symbolism in Kafka's prose
- Naturalism in American literature
- Grotesque and Sublime in the prose of Edgar Allan Poe
Lit Review Topic Ideas on Science and Technology
Next are some literature review topic ideas on science and technology.
- Electronic library and effects of its implementation
- Benjamin Franklin: scientist and inventor
- Virtual Reality, science fiction, and society today
- Science, Technology, and Society as a field of knowledge
- Frederick Winslow Taylor and the principles of scientific management
- What is the future of work
- Concepts of science and technology
- The Abolition of Man by C.S. Lewis and influence of technological advancement on man and nature
- Types of machine learning
- Internet of Things and biometrics: implications, benefits, threats
- Emotional intelligence and natural language processing
- SmartCity projects that have already been implemented and their lessons
As the field is vast, we can barely scratch the surface with these suggestions. To help you with brainstorming, here are a few tips on how to choose good topics for a literature review yourself:
- Make sure the topic ties nicely with class requirements as well as your interests
- Do some preliminary research to see if there is enough literature on your topic
- Scale up if the information is scarce or down if there are too many sources to handle
- Use sources recommended for reading in the class materials
- Supplement the list with only trustworthy scholarly sources
Follow these guidelines, and you are on a path to some great ideas!
Psychology Literature Review Topics
When brainstorming topics on psychology, don't forget about the subdisciplines: biopsychology, social, educational, organizational, etc. If the suggestions below won't be enough, try looking for inspiration in Biology, Sociology, Education, or Business. The most exciting topics are often at the intersection of different areas of knowledge!
- Tricyclic antidepressants vs. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) in treatment of depression
- Stress, its causes, effects, and coping strategies
- The family system and psychology
- Tibetan compassion practices: working with terror, trauma, and transcendence
- Behaviorism psychology
- Culture and psychopathology
- Correlation between diet and cognitive functions in primary school students
- The evolutionary role of phobias and intrusive thoughts
- Popular psychology and its implications
- PTSD in mass disasters survivors: immediate relief and long-term assistance
- Cults and vulnerable populations
- False memories and gaslighting
Nursing Literature Review Topics
Nursing lit review topics are probably the most diverse in scale, as you can see from the examples below. They can describe a larger issue or a concrete solution applied to a narrowly defined problem. Following this principle, you can modify our lit review topics suggestions zooming out or in on the subject material.
- Legalization of medical marijuana and its effects on the youth
- Health effects of fiber: research findings
- Achieving higher levels of education and training for nurses
- Organic foods and cardiovascular disease
- The importance of Central Venous Line (CVL) and Central Venous Access Devices (CVAD)
- What effects do different types of music have on humans and their mental health?
- The use of laboratory-grown organs for transplantation
- The role of xylitol in alleviating dry mouth
- The detection of tar and nicotine content of cigarette smoke extract using HPLC
- Rheumatoid arthritis: etiology, diagnosis, vulnerable populations
- Mobility aids for the elderly and quality of life
- The role of play in the recuperation of hospitalized children
Education Literature Review Topics
To get more ideas from these literature review topic examples, try isolating an issue and put it in another educational context. For instance, student motivation in primary school vs. middle school or sleep deprivation in high school vs. college. This should give you plenty of material for brainstorming.
- Simulation education for crisis prevention program
- A critical consideration of the new pedagogy in its relation to modern science
- Lack of students interest in studying science
- Discovery-based learning and student-centered learning with a focus on mathematics at a high school level
- The adverse effects of sleep deprivation on academic performance: a college student's struggle
- Gender bias in special education programs
- Higher education for senior citizens: challenges and best practices
- Significant challenges of the teaching profession in the US
- Factors contributing to international student mobility
- Student motivation in private vs. state colleges
- Benefits and challenges of homeschooling for students and families
- Correlation between workload, stress levels, and self-esteem in middle-school students
Sociology Literature Review Topics
The best advice on finding current sociology topics is to look at the challenges your community faces. Become the first one to notice and address these issues!
- Are video games affecting our current and future students ?
- Ways to prevent social media bullying
- Spanking of children in the USA
- The relation of poverty and exposure to crime in adolescent men
- Transgender discrimination
- The link between science and Utopia in Utopia and the New Atlantis
- Effectiveness of group therapy in social work
- Peer pressure, depression, and causes of suicide in the adolescents
- Religious separatism social issues connected with it
- Causes and effects of domestic abuse
- Physical appearance and social status
- Race, nationality, ethnicity, and identity
Political Science Literature Review Topics
Political science is one of the more formal disciplines on this list. Being heavy with abstract concepts, it doesn't lend itself easily to casual brainstorming. Well, at least start with these:
- Electoral College, its functions, and role in public life
- Why American and the British IPE are so different
- Contingency planning
- Effects of political gerrymandering
- American political parties
- The present urban regimes in Canada
- International policies and domestic regulations: precedence and clashes
- Tolerance as a political virtue
- Grassroots activism and its impact on state and federal law
- National security and constitutional freedoms
- Historical analysis of anarchism
- The effect of social media on civic engagement
Criminal Justice Literature Review Topics
Criminal justice is a complex field. It's ripe with variance and challenges – which is good for topic ideas at least. And you have state, federal, and international levels to add more variables.
- Juvenile justice and the Missouri model
- Car-related crime in the USA
- An analysis of the impact of sexual harassment/sexual assault in the military
- The process of the arbitration without the involvement of national courts
- Serial killers and profiling
- Policing and criminal justice systems
- Psychological effects of cyberbullying on adolescents
- Sexual human trafficking from the Central America region
- Human sex-trafficking: the Canadian perspective
- Gender and racial bias in criminal investigations
- Possible ethical and legal dilemmas of using sniffer dogs
- Sting operations vs. entrapment: ethics and regulations
Chemistry and Biology Literature Review Topics
Biology is fascinating. It has something for everyone: from biochemistry and genetics to ecosystems and nature preservation. Here are some suggestions to guide your choice:
- Brain size correlation
- Haruko Obokata, ethics of stem cells research, and scientific misconduct
- Genomic and molecular genetics major and its perspectives for students
- DNA use in mass disasters
- DNA detection from dried blood spots
- Captive breeding of marine mammals: pros and cons
- The Dynamics of ER and mitochondria
- Biomarkers in gastric cancer treatment
- The chemistry behind gene splicing
- Carcinogens and hyper-processed foods
- Primates and monkeys as potential sources of novel zoonotic infections
- Natural gases, ecosystems, and the global warming
Business and Marketing Literature Review Topics
Finally, here are some business and marketing topics as well. These disciplines might be relatively new, but they are among the most dynamic and information-rich – which means great fun to explore.
- Effectiveness of neuromarketing in comparison to traditional marketing methods
- Green supply chain management
- Effectiveness of e-marketing to non-profit making organizations
- The value of information
- Shareholder engagement/activism and corporate performance
- The relationship between ethics, stress, and productivity in the workplace
- The role of integrity in business
- Client confidentiality and its role in a prosperous business
- Businesses, their impact on the community, and social responsibility
- Startup fundraising stages
- Innovative marketing in the age of instant feedback: risks and possibilities
- Strategies for staff motivation

Jana Rooheart
Jana Rooheart came to WOWESSAYS™ with a mission to put together and then slice and dice our vast practical experience in crafting all kinds of academic papers. Jana is an aspired blogger with rich expertise in psychology, digital learning tools, and creative writing. In this blog, she willingly shares tricks of pencraft and mind-altering ideas about academic writing any student will find utterly beneficial.
Share with friends using:

275 words = 1 page double-spaced
Looking for essays to inspire you? We have samples of all types on any topic under the sun!
Other pages.
- Teacher Book Reviews
- Coordinator Term Papers
- Bunch Term Papers
- Attendant Term Papers
- Drill Term Papers
- Acre Term Papers
- Deposition Term Papers
- Nexus Term Papers
- Businessman Term Papers
- Abdomen Term Papers
- How Microcredit Help Poor People Term Paper Example
- Online Dating Or Conventional Dating Essay Examples
- Article Review On Also As Would Be Obvious To Any Researcher Of Diplomacy Use Of Force And Diplomacy
- African Slave Trade Essay Examples
- Free Research Paper On Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
- Outliers Analysis Essays Examples
- Free Essay About Definition Of Student
- Project Management Case Study Essay Sample
- Free Smartphone Essay Sample
- Models Of Organizational Change Research Paper Examples
- Free Portraits Of Reconciliation Course Work Sample
- Good Legal Principles Case Study Example
- Good Example Of Essay On The Benefits Of College Education To Students
- Term Paper On Comprehensive Article Review
- Sex In The 21sr Century Media Essay Samples
- Hard Rock Case Studies Example
- Free Critical Thinking On Shared Decision Making
- Great Barrington Essays
- Manuel Zelaya Essays
- Charles Taylor Essays
- Eliza Essays
- You Tube Essays
- Grammy Essays
- National Health Insurance Essays
- Phillips Curve Essays
- Strategic Importance Essays
- Decision Support Systems Essays
- Natalie Essays
- Alessi Essays
- Snow White And The Seven Dwarfs Essays
- Okonkwo Essays
- Impacting Essays
- Pullman Company Essays
Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline
Reference management. Clean and simple.
What is a literature review? [with examples]

What is a literature review?
The purpose of a literature review, how to write a literature review, the format of a literature review, general formatting rules, the length of a literature review, literature review examples, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, related articles.
A literature review is an assessment of the sources in a chosen topic of research.
In a literature review, you’re expected to report on the existing scholarly conversation, without adding new contributions.
If you are currently writing one, you've come to the right place. In the following paragraphs, we will explain:
- the objective of a literature review
- how to write a literature review
- the basic format of a literature review
Tip: It’s not always mandatory to add a literature review in a paper. Theses and dissertations often include them, whereas research papers may not. Make sure to consult with your instructor for exact requirements.
The four main objectives of a literature review are:
- Studying the references of your research area
- Summarizing the main arguments
- Identifying current gaps, stances, and issues
- Presenting all of the above in a text
Ultimately, the main goal of a literature review is to provide the researcher with sufficient knowledge about the topic in question so that they can eventually make an intervention.
The format of a literature review is fairly standard. It includes an:
- introduction that briefly introduces the main topic
- body that includes the main discussion of the key arguments
- conclusion that highlights the gaps and issues of the literature
➡️ Take a look at our guide on how to write a literature review to learn more about how to structure a literature review.
First of all, a literature review should have its own labeled section. You should indicate clearly in the table of contents where the literature can be found, and you should label this section as “Literature Review.”
➡️ For more information on writing a thesis, visit our guide on how to structure a thesis .
There is no set amount of words for a literature review, so the length depends on the research. If you are working with a large amount of sources, it will be long. If your paper does not depend entirely on references, it will be short.
Take a look at these three theses featuring great literature reviews:
- School-Based Speech-Language Pathologist's Perceptions of Sensory Food Aversions in Children [ PDF , see page 20]
- Who's Writing What We Read: Authorship in Criminological Research [ PDF , see page 4]
- A Phenomenological Study of the Lived Experience of Online Instructors of Theological Reflection at Christian Institutions Accredited by the Association of Theological Schools [ PDF , see page 56]
Literature reviews are most commonly found in theses and dissertations. However, you find them in research papers as well.
There is no set amount of words for a literature review, so the length depends on the research. If you are working with a large amount of sources, then it will be long. If your paper does not depend entirely on references, then it will be short.
No. A literature review should have its own independent section. You should indicate clearly in the table of contents where the literature review can be found, and label this section as “Literature Review.”
The main goal of a literature review is to provide the researcher with sufficient knowledge about the topic in question so that they can eventually make an intervention.
Academic Writing
- Strategies for Writing
- Punctuation
- Plagiarism & Self-Plagiarism
How to Build a Literature Review
- PRISMA - Systematic reviews & meta-analyses
- Other Resources
- Using Zotero for Bibliographies
- Abstract Writing Tips
- Writing Assistance
- Locating a Journal
- Assessing Potential Journals
- Finding a Publisher
- Types of Peer Review
- Author Rights & Responsibilities
- Copyright Considerations
- What is a Lit Review?
- Why Write a Lit Review?
Structure of a Literature Review
Preliminary steps for literature review.
- Basic Example
- More Examples
What is a Literature Review?
A literature review is a comprehensive summary and analysis of previously published research on a particular topic. Literature reviews should give the reader an overview of the important theories and themes that have previously been discussed on the topic, as well as any important researchers who have contributed to the discourse. This review should connect the established conclusions to the hypothesis being presented in the rest of the paper.
What a Literature Review Is Not:
- Annotated Bibliography: An annotated bibliography summarizes and assesses each resource individually and separately. A literature review explores the connections between different articles to illustrate important themes/theories/research trends within a larger research area.
- Timeline: While a literature review can be organized chronologically, they are not simple timelines of previous events. They should not be a list of any kind. Individual examples or events should be combined to illustrate larger ideas or concepts.
- Argumentative Paper: Literature reviews are not meant to be making an argument. They are explorations of a concept to give the audience an understanding of what has already been written and researched about an idea. As many perspectives as possible should be included in a literature review in order to give the reader as comprehensive understanding of a topic as possible.
Why Write a Literature Review?
After reading the literature review, the reader should have a basic understanding of the topic. A reader should be able to come into your paper without really knowing anything about an idea, and after reading the literature, feel more confident about the important points.
A literature review should also help the reader understand the focus the rest of the paper will take within the larger topic. If the reader knows what has already been studied, they will be better prepared for the novel argument that is about to be made.
A literature review should help the reader understand the important history, themes, events, and ideas about a particular topic. Connections between ideas/themes should also explored. Part of the importance of a literature review is to prove to experts who do read your paper that you are knowledgeable enough to contribute to the academic discussion. You have to have done your homework.
A literature review should also identify the gaps in research to show the reader what hasn't yet been explored. Your thesis should ideally address one of the gaps identified in the research. Scholarly articles are meant to push academic conversations forward with new ideas and arguments. Before knowing where the gaps are in a topic, you need to have read what others have written.
As mentioned in other tabs, literature reviews should discuss the big ideas that make up a topic. Each literature review should be broken up into different subtopics. Each subtopic should use groups of articles as evidence to support the ideas. There are several different ways of organizing a literature review. It will depend on the patterns one sees in the groups of articles as to which strategy should be used. Here are a few examples of how to organize your review:
Chronological
If there are clear trends that change over time, a chronological approach could be used to organize a literature review. For example, one might argue that in the 1970s, the predominant theories and themes argued something. However, in the 1980s, the theories evolved to something else. Then, in the 1990s, theories evolved further. Each decade is a subtopic, and articles should be used as examples.
Themes/Theories
There may also be clear distinctions between schools of thought within a topic, a theoretical breakdown may be most appropriate. Each theory could be a subtopic, and articles supporting the theme should be included as evidence for each one.
If researchers mainly differ in the way they went about conducting research, literature reviews can be organized by methodology. Each type of method could be a subtopic, and articles using the method should be included as evidence for each one.
- Define your research question
- Compile a list of initial keywords to use for searching based on question
- Search for literature that discusses the topics surrounding your research question
- Assess and organize your literature into logical groups
- Identify gaps in research and conduct secondary searches (if necessary)
- Reassess and reorganize literature again (if necessary)
- Write review
Here is an example of a literature review, taken from the beginning of a research article. You can find other examples within most scholarly research articles. The majority of published scholarship includes a literature review section, and you can use those to become more familiar with these reviews.
Source: Perceptions of the Police by LGBT Communities

There are many books and internet resources about literature reviews though most are long on how to search and gather the literature. How to literally organize the information is another matter.
Some pro tips:
- Be thoughtful in naming the folders, sub-folders, and sub, sub-folders. Doing so really helps your thinking and concepts within your research topic.
- Be disciplined to add keywords under the tabs as this will help you search for ALL the items on your concepts/topics.
- Use the notes tab to add reminders, write bibliography/annotated bibliography
- Your literature review easily flows from your statement of purpose (SoP). Therefore, does your SoP say clearly and exactly the intent of your research? Your research assumption and argument is obvious?
- Begin with a topic outline that traces your argument. pg99: "First establish the line of argumentation you will follow (the thesis), whether it is an assertion, a contention, or a proposition.
- This means that you should have formed judgments about the topic based on the analysis and synthesis of the literature you are reviewing."
- Keep filling it in; flushing it out more deeply with your references
Other Resources/Examples
- ISU Writing Assistance The Julia N. Visor Academic Center provides one-on-one writing assistance for any course or need. By focusing on the writing process instead of merely on grammar and editing, we are committed to making you a better writer.
- University of Toronto: The Literature Review Written by Dena Taylor, Health Sciences Writing Centre
- Purdue OWL - Writing a Lit Review Goes over the basic steps
- UW Madison Writing Center - Review of Literature A description of what each piece of a literature review should entail.
- USC Libraries - Literature Reviews Offers detailed guidance on how to develop, organize, and write a college-level research paper in the social and behavioral sciences.
- Creating the literature review: integrating research questions and arguments Blog post with very helpful overview for how to organize and build/integrate arguments in a literature review
- Understanding, Selecting, and Integrating a Theoretical Framework in Dissertation Research: Creating the Blueprint for Your “House” Article focusing on constructing a literature review for a dissertation. Still very relevant for literature reviews in other types of content.
A note that many of these examples will be far longer and in-depth than what's required for your assignment. However, they will give you an idea of the general structure and components of a literature review. Additionally, most scholarly articles will include a literature review section. Looking over the articles you have been assigned in classes will also help you.
- Understanding, Selecting, and Integrating a Theoretical Framework in Dissertation Research: Creating the Blueprint for Your “House” Excellent article detailing how to construct your literature review.
- Sample Literature Review (Univ. of Florida) This guide will provide research and writing tips to help students complete a literature review assignment.
- Sociology Literature Review (Univ. of Hawaii) Written in ASA citation style - don't follow this format.
- Sample Lit Review - Univ. of Vermont Includes an example with tips in the footnotes.
Attribution
Content on this page was provided by Grace Allbaugh
- << Previous: Writing a Literature Review
- Next: PRISMA - Systematic reviews & meta-analyses >>
- Last Updated: Dec 6, 2023 3:23 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.illinoisstate.edu/academicwriting
Additional Links
- Directions and Parking
- Accessibility Services
- Library Spaces
- Staff Directory
- How it works
Published by Nicolas at January 16th, 2024 , Revised On January 23, 2024
Literature Review Examples – How To Write One?
A literature review is a critical analysis of existing scholarly literature on a particular topic. It is often required as part of academic assignments, such as research papers , theses, and dissertations. However, writing a good literature review can be challenging, especially for first-time students.
Table of Contents
This blog will guide you on how to write a literature review and provide you with exceptional literature review examples that work well in the universities in Canada for your assistance. Let’s get started.
What Is A Literature Review?
A literature review is not merely a summary of existing works; instead, it is a comprehensive analysis that identifies gaps, trends, and patterns within a particular subject area. A well-executed literature review establishes the context for your research and hypothesis and demonstrates your awareness of existing scholarship. Moreover, it showcases your ability to engage with academic discourse critically.
Purpose Of A Literature Review
The purpose of a literature review is to:
- Demonstrate your knowledge of the existing literature on your topic.
- Identify the key themes, debates, and gaps in the literature.
- Position your own research in the context of the existing literature.
- Show how your research will contribute to the field.
How To Write A Literature Review Example
Writing a literature review involves a systematic and organized approach. Follow the research paper format stated by your organization. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you write an effective literature review:
Step 1: Define The Scope And Purpose
- Clearly define the research question, thesis statement, or topic you want to address in your literature review.
- Determine the scope of your review by setting boundaries for the time period, geographic location, and specific aspects of the topic you want to cover.
- Identify the purpose of your literature review, such as providing an overview, identifying gaps in existing research, or evaluating the current state of knowledge.
Step 2: Conduct A Comprehensive Literature Search
- Use academic databases, library catalogues, and search engines to find relevant literature. Common databases include PubMed , Google Scholar , and specialized databases related to your field.
- Use a combination of keywords and controlled vocabulary to refine your search.
- Keep track of the sources you find, including bibliographic information, abstracts, and key findings.
- Read professionally written examples of literature review for better understanding.
Step 3: Evaluate And Select Sources
- Critically evaluate the quality and relevance of each source. Consider the credibility of the author, the publication venue, and the methodology used in the studies.
- Organize the selected sources into themes or categories based on commonalities and differences.
- Identify key theories, concepts, or methodologies that are central to your topic.
- For example, in a finance thesis , add sources that are only relevant to the specific topic of finance that you wish to explore.
Step 4: Synthesize Information
- Summarize the main findings and arguments of each source, highlighting key themes and trends.
- Identify areas of agreement and disagreement among the sources.
- Organize the information in a logical and coherent manner. You can use a chronological, thematic, or methodological approach, depending on the nature of your literature review.
Step 5: Write And Revise
- Start with an introduction that provides context for your literature review and clearly states the research question or purpose.
- Organize the body of your literature review based on the themes or categories you identified during the synthesis.
- Discuss each source in relation to your research question, highlighting key findings and their implications.
- Conclude by summarizing the main contributions of the literature to your research question and identifying any gaps or areas for future research.
- Revise and edit your literature review for clarity, coherence, and conciseness.
APA Literature Review Example
Whether you are writing a literature review in APA or MLA , follow the guidelines provided on the websites. Here is a comprehensive example of a literature review in APA that will provide a better understanding of how to write a literature review.
Literature Review: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health in Adolescents
Social media has become an integral part of the lives of adolescents, with platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and Snapchat dominating their online experiences. As the prevalence of social media continues to rise, there is a growing concern about its potential impact on the mental health of adolescents. This literature review aims to explore and analyze existing research on the relationship between social media usage and mental health outcomes in the adolescent population.
Social Media Usage Patterns
Several studies have investigated the patterns of social media usage among adolescents. Smith et al. (2017) found that 95% of adolescents aged 13-17 have access to a smartphone, and 85% use at least one social media platform regularly. Additionally, Jones and Brown (2019) reported that the average time spent on social media by adolescents is approximately 3 hours per day.
Cyberbullying and Mental Health
One of the negative consequences associated with social media use is the prevalence of cyberbullying. Patchin and Hinduja (2018) highlighted that adolescents who experience cyberbullying are more likely to report symptoms of depression and anxiety. This finding is consistent with a longitudinal study by Williams et al. (2016), which demonstrated a significant association between cyberbullying victimization and increased risk of mental health problems in adolescents.
Social Comparison and Body Image
Social media platforms often facilitate social comparison, which has been linked to body image dissatisfaction and low self-esteem among adolescents. Fardouly et al. (2020) conducted a meta-analysis of 15 studies and found a moderate effect size, indicating a strong association between social media use and negative body image. Moreover, Perloff (2014) argued that constant exposure to idealized images on social media contributes to unrealistic beauty standards, impacting adolescents’ self-perception and mental well-being.
Fear of Missing Out (FOMO) and Anxiety
The Fear of Missing Out (FOMO) is a psychological phenomenon associated with anxiety and stress related to the fear of not being included or missing out on experiences others are having. Primack et al. (2017) conducted a cross-sectional analysis and discovered a positive correlation between higher social media use, FOMO, and increased levels of anxiety among adolescents. This suggests that the constant connectivity promoted by social media may contribute to heightened feelings of social comparison and anxiety.
Positive Aspects of Social Media Use
While there is a substantial body of literature examining the negative impacts of social media on adolescent mental health, some studies suggest positive aspects as well. Moreno et al. (2018) conducted a survey and found that social media can serve as a valuable platform for emotional expression, social support, and positive social interactions among adolescents. Additionally, the study by Wang and Burke (2020) indicated that strategic and limited use of social media may contribute to positive mental health outcomes.
The existing literature provides a deep understanding of the complex relationship between social media use and mental health outcomes in adolescents. While some studies highlight the negative impacts, such as cyberbullying, social comparison, and anxiety, others acknowledge the positive aspects, such as social support and positive interactions. Future research should focus on the development of effective interventions and guidelines to promote healthy social media use among adolescents.
Types Of Literature Review
There are several types of literature reviews, each serving different purposes and objectives. Here are some common types:
Narrative Or Traditional Literature Review
- Provides a comprehensive overview of the existing literature on a particular topic.
- Summarizes and synthesizes information from various sources without a specific methodological approach.
Systematic Literature Review
- Follows a systematic and structured approach to identify, analyze, and synthesize relevant literature.
- Involves a clearly defined research question and a detailed search strategy.
- Aims to minimize bias and subjectivity in the selection and analysis of studies.
Systematic Literature Review Example
Conducted in accordance with PRISMA guidelines, this systematic literature review focuses on the efficacy of cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) for anxiety disorders in pediatric populations. A comprehensive search across databases identified 25 relevant studies meeting the inclusion criteria. Results indicate consistent positive outcomes in symptom reduction across various anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety and social anxiety (Jones et al., 2020; Smith & Brown, 2019). However, methodological variations in CBT delivery and outcome measures highlight the need for standardized protocols. This review underscores the robust evidence supporting CBT’s effectiveness in treating pediatric anxiety, while advocating for more uniform research methodologies to enhance comparability and generalizability (Johnson et al., 2018).
Meta-Analysis
- A specialized form of systematic review that involves statistical analysis of quantitative data from multiple studies.
- Combines results from different studies to derive overall conclusions or effect sizes.
- Requires homogeneity in study design and outcome measures for accurate analysis.
Meta-Synthesis
- Meta-synthesis is a qualitative approach that synthesizes findings from multiple qualitative studies.
- Involves the interpretation and integration of themes, concepts, or qualitative data across different studies.
Scoping Review
- A preliminary literature review on a broad topic to identify key concepts, gaps, and research areas.
- Provides an overview without necessarily synthesizing the evidence.
Scoping Literature Review Example
This scoping review investigates the breadth of literature on the impact of mindfulness interventions on stress reduction. Initial searches in databases such as PubMed and PsycINFO yielded 80 relevant articles. Key themes emerged, including diverse intervention formats (e.g., mindfulness-based stress reduction, mindfulness apps), target populations (e.g., healthcare professionals, students), and outcome measures (e.g., self-reported stress levels, physiological markers). Noteworthy is the limited exploration of long-term effects and variations in intervention delivery. The review provides a foundation for future research directions, emphasizing the need for standardized methodologies and comprehensive assessments to advance our understanding of mindfulness interventions’ effectiveness in stress reduction (Smith et al., 2021; Brown & Jones, 2020).
Critical Review
- Evaluates and critiques the strengths and weaknesses of existing literature.
- Focuses on the methodology, theoretical framework, and overall quality of the studies reviewed.
Integrative Review
- Aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of a topic by integrating findings from different types of studies (quantitative, qualitative, or both).
- May include a range of research designs and methodologies.
Rapid Review
- Conducted within a shorter timeframe, often for decision-making purposes.
- Involves a streamlined review process with limitations in terms of depth and comprehensiveness.
Umbrella Review
- A review of existing systematic reviews and meta-analyses on a specific topic.
- Provides a higher level of evidence synthesis by examining the findings of multiple reviews.
Mixed Methods Review
Incorporates both quantitative and qualitative research studies to gain a comprehensive understanding of a research question.
The literature review we write have:
- Precision and Clarity
- Zero Plagiarism
- High-level Encryption
- Authentic Sources
Tips For Writing A Good Literature Review
Here are a few additional tips for writing a good literature review in a dissertation or thesis :
Tip 1: Start Early
Do not wait until the last minute to start writing your literature review. It takes time to do a good job.
Tip 2: Read Widely
Do not just read the most recent articles on your topic. Be sure to read older articles as well.
Tip 3: Take Breaks
Do not try to write your literature review all at once. Take breaks to avoid getting burned out.
Tip 4: Get Feedback
Ask your professor or a classmate to read your literature review and give you feedback.
Common Mistakes To Avoid When Writing A Literature Review
While literature review examples can provide valuable guidance, it is equally important to be aware of common pitfalls that can undermine the effectiveness of your literature review.
- Lack of Focus: A literature review should have a clear focus and not attempt to cover an entire field. Define the boundaries of your review and concentrate on the most relevant and recent literature.
- Overreliance on Secondary Sources: While reviews of existing reviews can be informative, relying solely on secondary sources, such as newspapers , may lead to a lack of depth in your analysis. Strive to include primary research studies to strengthen the credibility of your literature review.
- Failure to Synthesize: Merely summarizing individual studies without synthesizing their findings can result in a disjointed and unconvincing literature review. Connect the dots between different sources to provide a cohesive narrative.
- Ignoring Contradictory Evidence: A robust literature review acknowledges and addresses conflicting findings in the existing literature. Ignoring contradictory evidence can weaken the overall credibility of your review.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a literature review.
A literature review is a critical analysis of existing research and scholarly works on a specific topic. It involves summarizing, evaluating, and synthesizing relevant literature to identify gaps, patterns, and trends. The review provides a foundation for understanding the current state of knowledge and informs future research directions.
How to write a literature review example?
To write a literature review, define your purpose, conduct a comprehensive search, critically evaluate sources, organize them thematically, and synthesize key findings. Structure your review with an introduction, thematic sections, and a conclusion. Properly cite sources, seek feedback, and revise. Maintain clarity, coherence, and adherence to citation styles throughout.
How to start a literature review example?
Begin your literature review with a concise introduction, providing context for the topic and clearly stating its importance. Define the scope and purpose, indicating the key themes or questions to be addressed. Engage readers by highlighting the relevance and significance of the reviewed literature to the broader research field.
How to write a literature review introduction example?
In this literature review, we explore the evolving landscape of artificial intelligence in healthcare. As advancements accelerate, understanding the implications of patient care and ethical considerations is crucial. This review aims to synthesize existing literature, identifying key trends, challenges, and opportunities in the intersection of artificial intelligence and healthcare delivery.
How to conclude a literature review example?
In conclusion, this literature review reveals the multifaceted nature of social media’s impact on mental health. While negative outcomes are associated with social comparison and excessive use, positive effects include social support. Thorough research is essential, considering individual differences and evolving social media dynamics, for a comprehensive understanding of its influence.
How to critique a literature review example?
This literature review demonstrates a comprehensive analysis of existing research on climate change adaptation strategies. Strengths include a clear organization and synthesis of findings. However, potential limitations include an emphasis on studies from specific regions, possibly affecting the generalizability of the conclusions. Further exploration of diverse geographic contexts could enhance the review’s robustness.
What is a preliminary literature review?
A preliminary literature review is an initial exploration of existing research on a specific topic. It helps researchers identify key concepts, relevant studies, and gaps in the literature before conducting an in-depth review. This phase informs the development of research questions and refines the focus for a more comprehensive literature review.
You May Also Like
Learn everything about meta synthesis literature review in this comprehensive guide. From definition and process to its types and challenges.
The answer to the question, “Can literature review include newspaper articles?” is provided in this comprehensive guide. Read more.
This blog discusses the difference between R and P. Read it to get into the world of statistics and programming.
Ready to place an order?
USEFUL LINKS
Learning resources, company details.
- How It Works
Automated page speed optimizations for fast site performance

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
7 Writing a Literature Review
Hundreds of original investigation research articles on health science topics are published each year. It is becoming harder and harder to keep on top of all new findings in a topic area and – more importantly – to work out how they all fit together to determine our current understanding of a topic. This is where literature reviews come in.
In this chapter, we explain what a literature review is and outline the stages involved in writing one. We also provide practical tips on how to communicate the results of a review of current literature on a topic in the format of a literature review.
7.1 What is a literature review?

Literature reviews provide a synthesis and evaluation of the existing literature on a particular topic with the aim of gaining a new, deeper understanding of the topic.
Published literature reviews are typically written by scientists who are experts in that particular area of science. Usually, they will be widely published as authors of their own original work, making them highly qualified to author a literature review.
However, literature reviews are still subject to peer review before being published. Literature reviews provide an important bridge between the expert scientific community and many other communities, such as science journalists, teachers, and medical and allied health professionals. When the most up-to-date knowledge reaches such audiences, it is more likely that this information will find its way to the general public. When this happens, – the ultimate good of science can be realised.
A literature review is structured differently from an original research article. It is developed based on themes, rather than stages of the scientific method.
In the article Ten simple rules for writing a literature review , Marco Pautasso explains the importance of literature reviews:
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications. For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively. Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every single new paper relevant to their interests. Thus, it is both advantageous and necessary to rely on regular summaries of the recent literature. Although recognition for scientists mainly comes from primary research, timely literature reviews can lead to new synthetic insights and are often widely read. For such summaries to be useful, however, they need to be compiled in a professional way (Pautasso, 2013, para. 1).
An example of a literature review is shown in Figure 7.1.
Video 7.1: What is a literature review? [2 mins, 11 secs]
Watch this video created by Steely Library at Northern Kentucky Library called ‘ What is a literature review? Note: Closed captions are available by clicking on the CC button below.
Examples of published literature reviews
- Strength training alone, exercise therapy alone, and exercise therapy with passive manual mobilisation each reduce pain and disability in people with knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review
- Traveler’s diarrhea: a clinical review
- Cultural concepts of distress and psychiatric disorders: literature review and research recommendations for global mental health epidemiology
7.2 Steps of writing a literature review
Writing a literature review is a very challenging task. Figure 7.2 summarises the steps of writing a literature review. Depending on why you are writing your literature review, you may be given a topic area, or may choose a topic that particularly interests you or is related to a research project that you wish to undertake.
Chapter 6 provides instructions on finding scientific literature that would form the basis for your literature review.
Once you have your topic and have accessed the literature, the next stages (analysis, synthesis and evaluation) are challenging. Next, we look at these important cognitive skills student scientists will need to develop and employ to successfully write a literature review, and provide some guidance for navigating these stages.
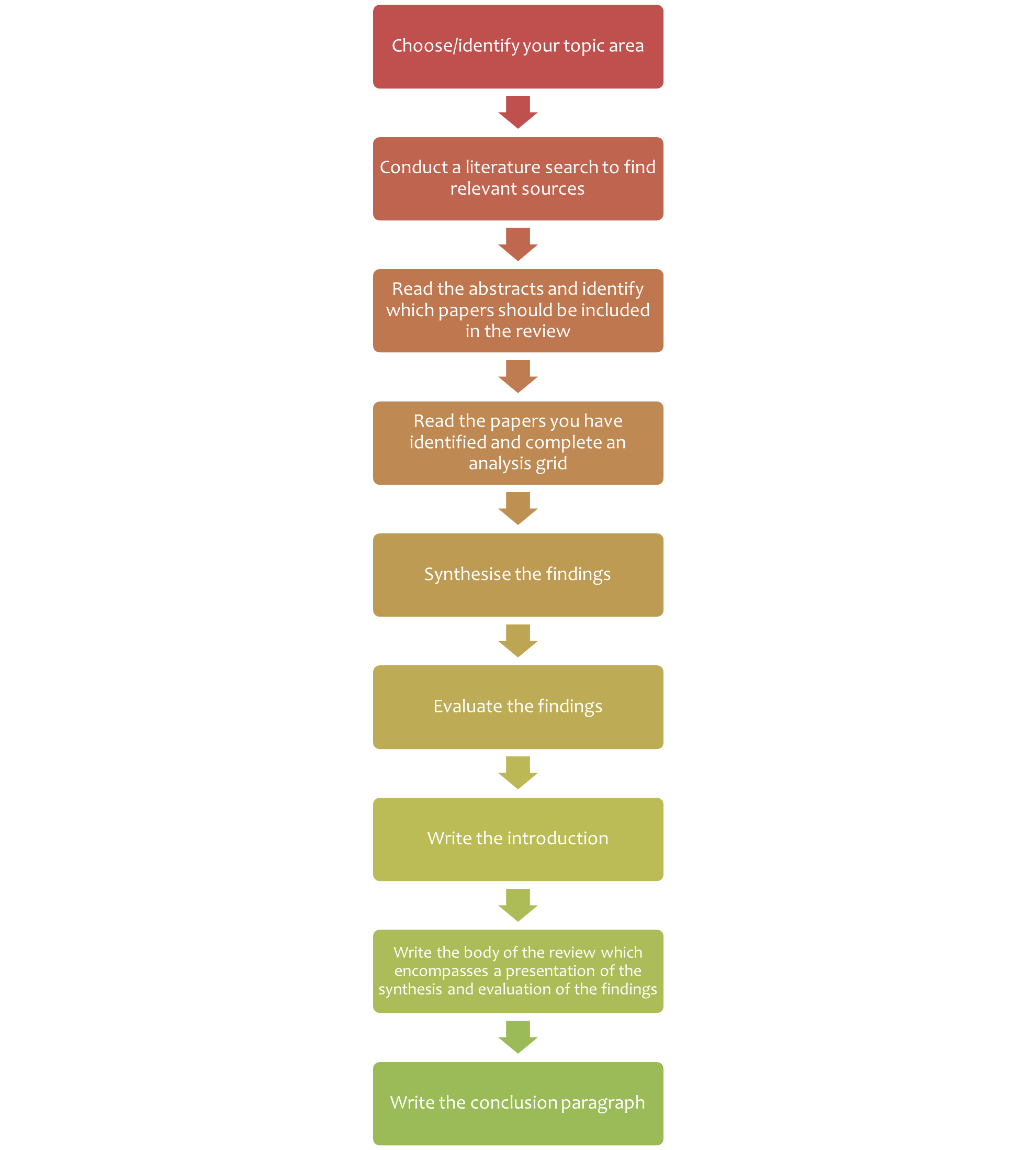
Analysis, synthesis and evaluation
Analysis, synthesis and evaluation are three essential skills required by scientists and you will need to develop these skills if you are to write a good literature review ( Figure 7.3 ). These important cognitive skills are discussed in more detail in Chapter 9.
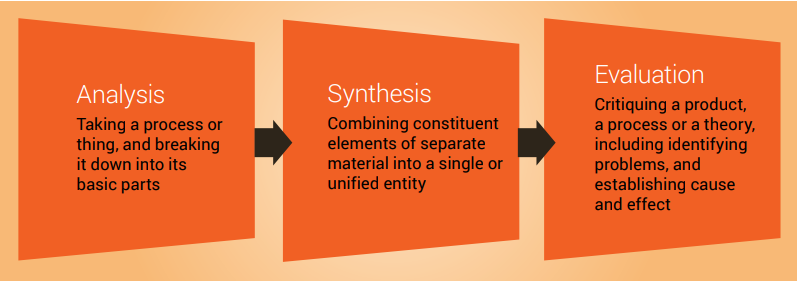
The first step in writing a literature review is to analyse the original investigation research papers that you have gathered related to your topic.
Analysis requires examining the papers methodically and in detail, so you can understand and interpret aspects of the study described in each research article.
An analysis grid is a simple tool you can use to help with the careful examination and breakdown of each paper. This tool will allow you to create a concise summary of each research paper; see Table 7.1 for an example of an analysis grid. When filling in the grid, the aim is to draw out key aspects of each research paper. Use a different row for each paper, and a different column for each aspect of the paper ( Tables 7.2 and 7.3 show how completed analysis grid may look).
Before completing your own grid, look at these examples and note the types of information that have been included, as well as the level of detail. Completing an analysis grid with a sufficient level of detail will help you to complete the synthesis and evaluation stages effectively. This grid will allow you to more easily observe similarities and differences across the findings of the research papers and to identify possible explanations (e.g., differences in methodologies employed) for observed differences between the findings of different research papers.
Table 7.1: Example of an analysis grid
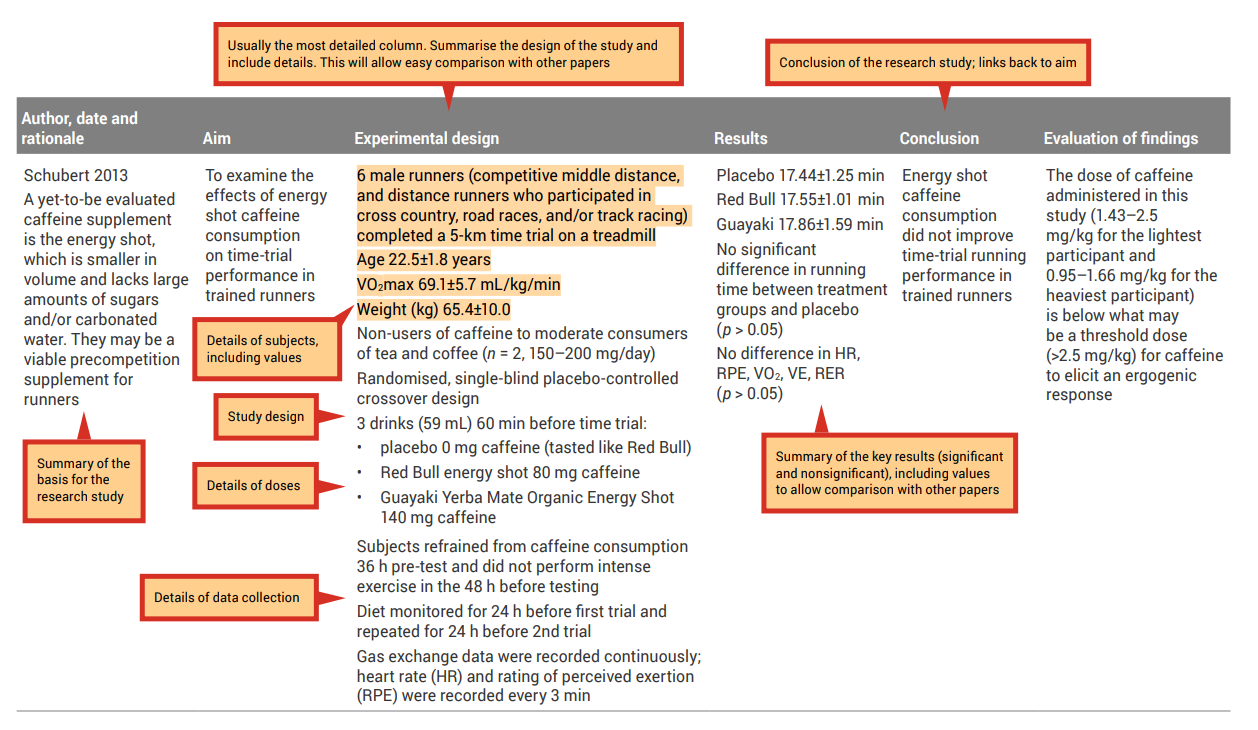
Table 7.3: Sample filled-in analysis grid for research article by Ping and colleagues
Source: Ping, WC, Keong, CC & Bandyopadhyay, A 2010, ‘Effects of acute supplementation of caffeine on cardiorespiratory responses during endurance running in a hot and humid climate’, Indian Journal of Medical Research, vol. 132, pp. 36–41. Used under a CC-BY-NC-SA licence.
Step two of writing a literature review is synthesis.
Synthesis describes combining separate components or elements to form a connected whole.
You will use the results of your analysis to find themes to build your literature review around. Each of the themes identified will become a subheading within the body of your literature review.
A good place to start when identifying themes is with the dependent variables (results/findings) that were investigated in the research studies.
Because all of the research articles you are incorporating into your literature review are related to your topic, it is likely that they have similar study designs and have measured similar dependent variables. Review the ‘Results’ column of your analysis grid. You may like to collate the common themes in a synthesis grid (see, for example Table 7.4 ).
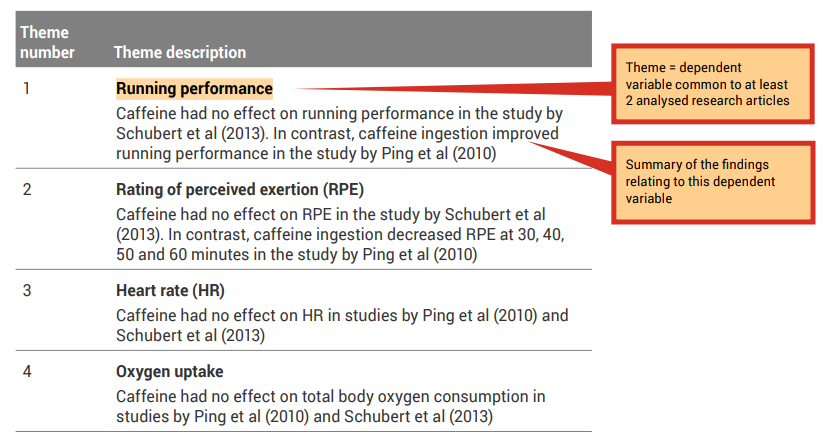
Step three of writing a literature review is evaluation, which can only be done after carefully analysing your research papers and synthesising the common themes (findings).
During the evaluation stage, you are making judgements on the themes presented in the research articles that you have read. This includes providing physiological explanations for the findings. It may be useful to refer to the discussion section of published original investigation research papers, or another literature review, where the authors may mention tested or hypothetical physiological mechanisms that may explain their findings.
When the findings of the investigations related to a particular theme are inconsistent (e.g., one study shows that caffeine effects performance and another study shows that caffeine had no effect on performance) you should attempt to provide explanations of why the results differ, including physiological explanations. A good place to start is by comparing the methodologies to determine if there are any differences that may explain the differences in the findings (see the ‘Experimental design’ column of your analysis grid). An example of evaluation is shown in the examples that follow in this section, under ‘Running performance’ and ‘RPE ratings’.
When the findings of the papers related to a particular theme are consistent (e.g., caffeine had no effect on oxygen uptake in both studies) an evaluation should include an explanation of why the results are similar. Once again, include physiological explanations. It is still a good idea to compare methodologies as a background to the evaluation. An example of evaluation is shown in the following under ‘Oxygen consumption’.
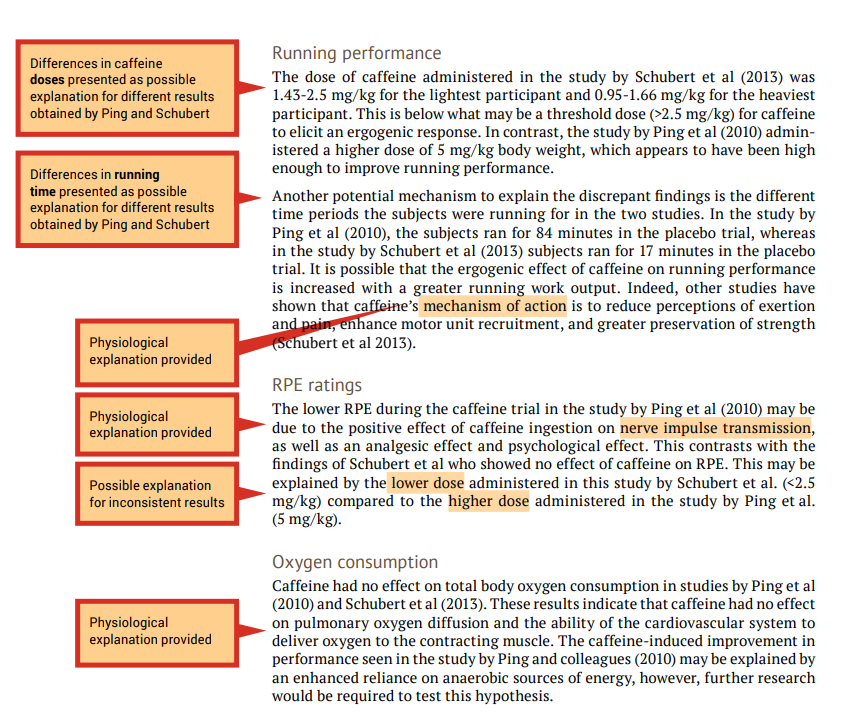
7.3 Writing your literature review
Once you have completed the analysis, and synthesis grids and written your evaluation of the research papers , you can combine synthesis and evaluation information to create a paragraph for a literature review ( Figure 7.4 ).
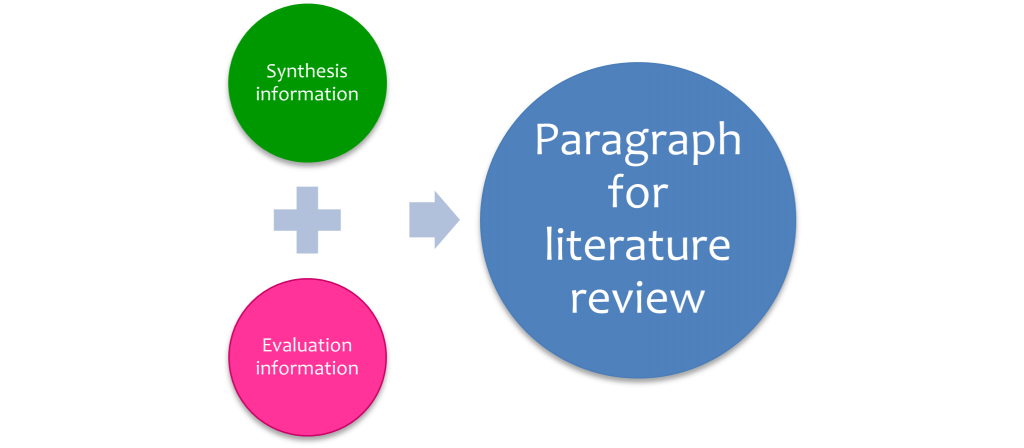
The following paragraphs are an example of combining the outcome of the synthesis and evaluation stages to produce a paragraph for a literature review.
Note that this is an example using only two papers – most literature reviews would be presenting information on many more papers than this ( (e.g., 106 papers in the review article by Bain and colleagues discussed later in this chapter). However, the same principle applies regardless of the number of papers reviewed.

The next part of this chapter looks at the each section of a literature review and explains how to write them by referring to a review article that was published in Frontiers in Physiology and shown in Figure 7.1. Each section from the published article is annotated to highlight important features of the format of the review article, and identifies the synthesis and evaluation information.
In the examination of each review article section we will point out examples of how the authors have presented certain information and where they display application of important cognitive processes; we will use the colour code shown below:

This should be one paragraph that accurately reflects the contents of the review article.
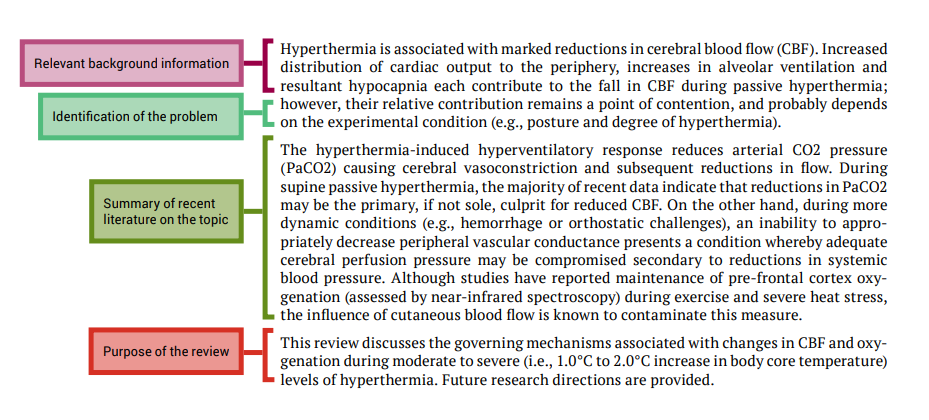
Introduction
The introduction should establish the context and importance of the review

Body of literature review
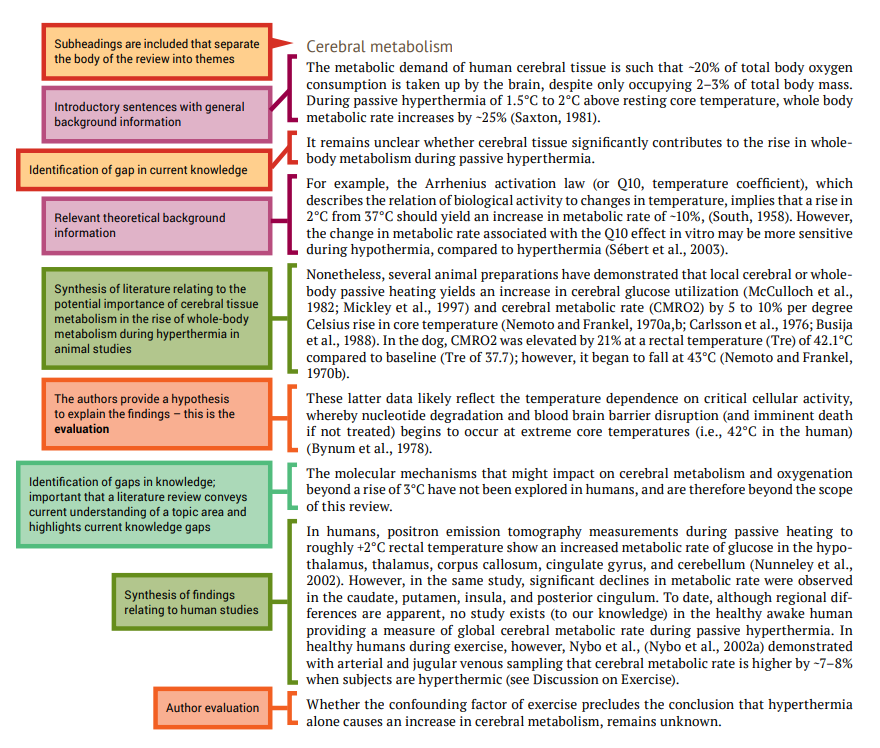
The reference section provides a list of the references that you cited in the body of your review article. The format will depend on the journal of publication as each journal has their own specific referencing format.
It is important to accurately cite references in research papers to acknowledge your sources and ensure credit is appropriately given to authors of work you have referred to. An accurate and comprehensive reference list also shows your readers that you are well-read in your topic area and are aware of the key papers that provide the context to your research.
It is important to keep track of your resources and to reference them consistently in the format required by the publication in which your work will appear. Most scientists will use reference management software to store details of all of the journal articles (and other sources) they use while writing their review article. This software also automates the process of adding in-text references and creating a reference list. In the review article by Bain et al. (2014) used as an example in this chapter, the reference list contains 106 items, so you can imagine how much help referencing software would be. Chapter 5 shows you how to use EndNote, one example of reference management software.
Click the drop down below to review the terms learned from this chapter.
Copyright note:
- The quotation from Pautasso, M 2013, ‘Ten simple rules for writing a literature review’, PLoS Computational Biology is use under a CC-BY licence.
- Content from the annotated article and tables are based on Schubert, MM, Astorino, TA & Azevedo, JJL 2013, ‘The effects of caffeinated ‘energy shots’ on time trial performance’, Nutrients, vol. 5, no. 6, pp. 2062–2075 (used under a CC-BY 3.0 licence ) and P ing, WC, Keong , CC & Bandyopadhyay, A 2010, ‘Effects of acute supplementation of caffeine on cardiorespiratory responses during endurance running in a hot and humid climate’, Indian Journal of Medical Research, vol. 132, pp. 36–41 (used under a CC-BY-NC-SA 4.0 licence ).
Bain, A.R., Morrison, S.A., & Ainslie, P.N. (2014). Cerebral oxygenation and hyperthermia. Frontiers in Physiology, 5 , 92.
Pautasso, M. (2013). Ten simple rules for writing a literature review. PLoS Computational Biology, 9 (7), e1003149.
How To Do Science Copyright © 2022 by University of Southern Queensland is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
How To Structure Your Literature Review
3 options to help structure your chapter.
By: Amy Rommelspacher (PhD) | Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | November 2020 (Updated May 2023)
Writing the literature review chapter can seem pretty daunting when you’re piecing together your dissertation or thesis. As we’ve discussed before , a good literature review needs to achieve a few very important objectives – it should:
- Demonstrate your knowledge of the research topic
- Identify the gaps in the literature and show how your research links to these
- Provide the foundation for your conceptual framework (if you have one)
- Inform your own methodology and research design
To achieve this, your literature review needs a well-thought-out structure . Get the structure of your literature review chapter wrong and you’ll struggle to achieve these objectives. Don’t worry though – in this post, we’ll look at how to structure your literature review for maximum impact (and marks!).

But wait – is this the right time?
Deciding on the structure of your literature review should come towards the end of the literature review process – after you have collected and digested the literature, but before you start writing the chapter.
In other words, you need to first develop a rich understanding of the literature before you even attempt to map out a structure. There’s no use trying to develop a structure before you’ve fully wrapped your head around the existing research.
Equally importantly, you need to have a structure in place before you start writing , or your literature review will most likely end up a rambling, disjointed mess.
Importantly, don’t feel that once you’ve defined a structure you can’t iterate on it. It’s perfectly natural to adjust as you engage in the writing process. As we’ve discussed before , writing is a way of developing your thinking, so it’s quite common for your thinking to change – and therefore, for your chapter structure to change – as you write.
Need a helping hand?
Like any other chapter in your thesis or dissertation, your literature review needs to have a clear, logical structure. At a minimum, it should have three essential components – an introduction , a body and a conclusion .
Let’s take a closer look at each of these.
1: The Introduction Section
Just like any good introduction, the introduction section of your literature review should introduce the purpose and layout (organisation) of the chapter. In other words, your introduction needs to give the reader a taste of what’s to come, and how you’re going to lay that out. Essentially, you should provide the reader with a high-level roadmap of your chapter to give them a taste of the journey that lies ahead.
Here’s an example of the layout visualised in a literature review introduction:
Your introduction should also outline your topic (including any tricky terminology or jargon) and provide an explanation of the scope of your literature review – in other words, what you will and won’t be covering (the delimitations ). This helps ringfence your review and achieve a clear focus . The clearer and narrower your focus, the deeper you can dive into the topic (which is typically where the magic lies).
Depending on the nature of your project, you could also present your stance or point of view at this stage. In other words, after grappling with the literature you’ll have an opinion about what the trends and concerns are in the field as well as what’s lacking. The introduction section can then present these ideas so that it is clear to examiners that you’re aware of how your research connects with existing knowledge .

2: The Body Section
The body of your literature review is the centre of your work. This is where you’ll present, analyse, evaluate and synthesise the existing research. In other words, this is where you’re going to earn (or lose) the most marks. Therefore, it’s important to carefully think about how you will organise your discussion to present it in a clear way.
The body of your literature review should do just as the description of this chapter suggests. It should “review” the literature – in other words, identify, analyse, and synthesise it. So, when thinking about structuring your literature review, you need to think about which structural approach will provide the best “review” for your specific type of research and objectives (we’ll get to this shortly).
There are (broadly speaking) three options for organising your literature review.

Option 1: Chronological (according to date)
Organising the literature chronologically is one of the simplest ways to structure your literature review. You start with what was published first and work your way through the literature until you reach the work published most recently. Pretty straightforward.
The benefit of this option is that it makes it easy to discuss the developments and debates in the field as they emerged over time. Organising your literature chronologically also allows you to highlight how specific articles or pieces of work might have changed the course of the field – in other words, which research has had the most impact . Therefore, this approach is very useful when your research is aimed at understanding how the topic has unfolded over time and is often used by scholars in the field of history. That said, this approach can be utilised by anyone that wants to explore change over time .

For example , if a student of politics is investigating how the understanding of democracy has evolved over time, they could use the chronological approach to provide a narrative that demonstrates how this understanding has changed through the ages.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself to help you structure your literature review chronologically.
- What is the earliest literature published relating to this topic?
- How has the field changed over time? Why?
- What are the most recent discoveries/theories?
In some ways, chronology plays a part whichever way you decide to structure your literature review, because you will always, to a certain extent, be analysing how the literature has developed. However, with the chronological approach, the emphasis is very firmly on how the discussion has evolved over time , as opposed to how all the literature links together (which we’ll discuss next ).
Option 2: Thematic (grouped by theme)
The thematic approach to structuring a literature review means organising your literature by theme or category – for example, by independent variables (i.e. factors that have an impact on a specific outcome).
As you’ve been collecting and synthesising literature , you’ll likely have started seeing some themes or patterns emerging. You can then use these themes or patterns as a structure for your body discussion. The thematic approach is the most common approach and is useful for structuring literature reviews in most fields.
For example, if you were researching which factors contributed towards people trusting an organisation, you might find themes such as consumers’ perceptions of an organisation’s competence, benevolence and integrity. Structuring your literature review thematically would mean structuring your literature review’s body section to discuss each of these themes, one section at a time.

Here are some questions to ask yourself when structuring your literature review by themes:
- Are there any patterns that have come to light in the literature?
- What are the central themes and categories used by the researchers?
- Do I have enough evidence of these themes?
PS – you can see an example of a thematically structured literature review in our literature review sample walkthrough video here.
Option 3: Methodological
The methodological option is a way of structuring your literature review by the research methodologies used . In other words, organising your discussion based on the angle from which each piece of research was approached – for example, qualitative , quantitative or mixed methodologies.
Structuring your literature review by methodology can be useful if you are drawing research from a variety of disciplines and are critiquing different methodologies. The point of this approach is to question how existing research has been conducted, as opposed to what the conclusions and/or findings the research were.

For example, a sociologist might centre their research around critiquing specific fieldwork practices. Their literature review will then be a summary of the fieldwork methodologies used by different studies.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself when structuring your literature review according to methodology:
- Which methodologies have been utilised in this field?
- Which methodology is the most popular (and why)?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the various methodologies?
- How can the existing methodologies inform my own methodology?
3: The Conclusion Section
Once you’ve completed the body section of your literature review using one of the structural approaches we discussed above, you’ll need to “wrap up” your literature review and pull all the pieces together to set the direction for the rest of your dissertation or thesis.
The conclusion is where you’ll present the key findings of your literature review. In this section, you should emphasise the research that is especially important to your research questions and highlight the gaps that exist in the literature. Based on this, you need to make it clear what you will add to the literature – in other words, justify your own research by showing how it will help fill one or more of the gaps you just identified.
Last but not least, if it’s your intention to develop a conceptual framework for your dissertation or thesis, the conclusion section is a good place to present this.

Example: Thematically Structured Review
In the video below, we unpack a literature review chapter so that you can see an example of a thematically structure review in practice.
Let’s Recap
In this article, we’ve discussed how to structure your literature review for maximum impact. Here’s a quick recap of what you need to keep in mind when deciding on your literature review structure:
- Just like other chapters, your literature review needs a clear introduction , body and conclusion .
- The introduction section should provide an overview of what you will discuss in your literature review.
- The body section of your literature review can be organised by chronology , theme or methodology . The right structural approach depends on what you’re trying to achieve with your research.
- The conclusion section should draw together the key findings of your literature review and link them to your research questions.
If you’re ready to get started, be sure to download our free literature review template to fast-track your chapter outline.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling Udemy Course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

27 Comments
Great work. This is exactly what I was looking for and helps a lot together with your previous post on literature review. One last thing is missing: a link to a great literature chapter of an journal article (maybe with comments of the different sections in this review chapter). Do you know any great literature review chapters?
I agree with you Marin… A great piece
I agree with Marin. This would be quite helpful if you annotate a nicely structured literature from previously published research articles.
Awesome article for my research.
I thank you immensely for this wonderful guide
It is indeed thought and supportive work for the futurist researcher and students
Very educative and good time to get guide. Thank you
Great work, very insightful. Thank you.
Thanks for this wonderful presentation. My question is that do I put all the variables into a single conceptual framework or each hypothesis will have it own conceptual framework?
Thank you very much, very helpful
This is very educative and precise . Thank you very much for dropping this kind of write up .
Pheeww, so damn helpful, thank you for this informative piece.
I’m doing a research project topic ; stool analysis for parasitic worm (enteric) worm, how do I structure it, thanks.
comprehensive explanation. Help us by pasting the URL of some good “literature review” for better understanding.
great piece. thanks for the awesome explanation. it is really worth sharing. I have a little question, if anyone can help me out, which of the options in the body of literature can be best fit if you are writing an architectural thesis that deals with design?
I am doing a research on nanofluids how can l structure it?
Beautifully clear.nThank you!
Lucid! Thankyou!
Brilliant work, well understood, many thanks
I like how this was so clear with simple language 😊😊 thank you so much 😊 for these information 😊
Insightful. I was struggling to come up with a sensible literature review but this has been really helpful. Thank you!
You have given thought-provoking information about the review of the literature.
Thank you. It has made my own research better and to impart your work to students I teach
I learnt a lot from this teaching. It’s a great piece.
I am doing research on EFL teacher motivation for his/her job. How Can I structure it? Is there any detailed template, additional to this?
You are so cool! I do not think I’ve read through something like this before. So nice to find somebody with some genuine thoughts on this issue. Seriously.. thank you for starting this up. This site is one thing that is required on the internet, someone with a little originality!
I’m asked to do conceptual, theoretical and empirical literature, and i just don’t know how to structure it
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 5. The Literature Review
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
A literature review surveys prior research published in books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated. Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have used in researching a particular topic and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within existing scholarship about the topic.
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . Fourth edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE, 2014.
Importance of a Good Literature Review
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories . A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that informs how you are planning to investigate a research problem. The analytical features of a literature review might:
- Give a new interpretation of old material or combine new with old interpretations,
- Trace the intellectual progression of the field, including major debates,
- Depending on the situation, evaluate the sources and advise the reader on the most pertinent or relevant research, or
- Usually in the conclusion of a literature review, identify where gaps exist in how a problem has been researched to date.
Given this, the purpose of a literature review is to:
- Place each work in the context of its contribution to understanding the research problem being studied.
- Describe the relationship of each work to the others under consideration.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies.
- Identify areas of prior scholarship to prevent duplication of effort.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important].
Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2011; Knopf, Jeffrey W. "Doing a Literature Review." PS: Political Science and Politics 39 (January 2006): 127-132; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012.
Types of Literature Reviews
It is important to think of knowledge in a given field as consisting of three layers. First, there are the primary studies that researchers conduct and publish. Second are the reviews of those studies that summarize and offer new interpretations built from and often extending beyond the primary studies. Third, there are the perceptions, conclusions, opinion, and interpretations that are shared informally among scholars that become part of the body of epistemological traditions within the field.
In composing a literature review, it is important to note that it is often this third layer of knowledge that is cited as "true" even though it often has only a loose relationship to the primary studies and secondary literature reviews. Given this, while literature reviews are designed to provide an overview and synthesis of pertinent sources you have explored, there are a number of approaches you could adopt depending upon the type of analysis underpinning your study.
Argumentative Review This form examines literature selectively in order to support or refute an argument, deeply embedded assumption, or philosophical problem already established in the literature. The purpose is to develop a body of literature that establishes a contrarian viewpoint. Given the value-laden nature of some social science research [e.g., educational reform; immigration control], argumentative approaches to analyzing the literature can be a legitimate and important form of discourse. However, note that they can also introduce problems of bias when they are used to make summary claims of the sort found in systematic reviews [see below].
Integrative Review Considered a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated. The body of literature includes all studies that address related or identical hypotheses or research problems. A well-done integrative review meets the same standards as primary research in regard to clarity, rigor, and replication. This is the most common form of review in the social sciences.
Historical Review Few things rest in isolation from historical precedent. Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period of time, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, phenomena emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and to identify the likely directions for future research.
Methodological Review A review does not always focus on what someone said [findings], but how they came about saying what they say [method of analysis]. Reviewing methods of analysis provides a framework of understanding at different levels [i.e. those of theory, substantive fields, research approaches, and data collection and analysis techniques], how researchers draw upon a wide variety of knowledge ranging from the conceptual level to practical documents for use in fieldwork in the areas of ontological and epistemological consideration, quantitative and qualitative integration, sampling, interviewing, data collection, and data analysis. This approach helps highlight ethical issues which you should be aware of and consider as you go through your own study.
Systematic Review This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research, and to collect, report, and analyze data from the studies that are included in the review. The goal is to deliberately document, critically evaluate, and summarize scientifically all of the research about a clearly defined research problem . Typically it focuses on a very specific empirical question, often posed in a cause-and-effect form, such as "To what extent does A contribute to B?" This type of literature review is primarily applied to examining prior research studies in clinical medicine and allied health fields, but it is increasingly being used in the social sciences.
Theoretical Review The purpose of this form is to examine the corpus of theory that has accumulated in regard to an issue, concept, theory, phenomena. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories already exist, the relationships between them, to what degree the existing theories have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested. Often this form is used to help establish a lack of appropriate theories or reveal that current theories are inadequate for explaining new or emerging research problems. The unit of analysis can focus on a theoretical concept or a whole theory or framework.
NOTE : Most often the literature review will incorporate some combination of types. For example, a review that examines literature supporting or refuting an argument, assumption, or philosophical problem related to the research problem will also need to include writing supported by sources that establish the history of these arguments in the literature.
Baumeister, Roy F. and Mark R. Leary. "Writing Narrative Literature Reviews." Review of General Psychology 1 (September 1997): 311-320; Mark R. Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Kennedy, Mary M. "Defining a Literature." Educational Researcher 36 (April 2007): 139-147; Petticrew, Mark and Helen Roberts. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers, 2006; Torracro, Richard. "Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples." Human Resource Development Review 4 (September 2005): 356-367; Rocco, Tonette S. and Maria S. Plakhotnik. "Literature Reviews, Conceptual Frameworks, and Theoretical Frameworks: Terms, Functions, and Distinctions." Human Ressource Development Review 8 (March 2008): 120-130; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Thinking About Your Literature Review
The structure of a literature review should include the following in support of understanding the research problem :
- An overview of the subject, issue, or theory under consideration, along with the objectives of the literature review,
- Division of works under review into themes or categories [e.g. works that support a particular position, those against, and those offering alternative approaches entirely],
- An explanation of how each work is similar to and how it varies from the others,
- Conclusions as to which pieces are best considered in their argument, are most convincing of their opinions, and make the greatest contribution to the understanding and development of their area of research.
The critical evaluation of each work should consider :
- Provenance -- what are the author's credentials? Are the author's arguments supported by evidence [e.g. primary historical material, case studies, narratives, statistics, recent scientific findings]?
- Methodology -- were the techniques used to identify, gather, and analyze the data appropriate to addressing the research problem? Was the sample size appropriate? Were the results effectively interpreted and reported?
- Objectivity -- is the author's perspective even-handed or prejudicial? Is contrary data considered or is certain pertinent information ignored to prove the author's point?
- Persuasiveness -- which of the author's theses are most convincing or least convincing?
- Validity -- are the author's arguments and conclusions convincing? Does the work ultimately contribute in any significant way to an understanding of the subject?
II. Development of the Literature Review
Four Basic Stages of Writing 1. Problem formulation -- which topic or field is being examined and what are its component issues? 2. Literature search -- finding materials relevant to the subject being explored. 3. Data evaluation -- determining which literature makes a significant contribution to the understanding of the topic. 4. Analysis and interpretation -- discussing the findings and conclusions of pertinent literature.
Consider the following issues before writing the literature review: Clarify If your assignment is not specific about what form your literature review should take, seek clarification from your professor by asking these questions: 1. Roughly how many sources would be appropriate to include? 2. What types of sources should I review (books, journal articles, websites; scholarly versus popular sources)? 3. Should I summarize, synthesize, or critique sources by discussing a common theme or issue? 4. Should I evaluate the sources in any way beyond evaluating how they relate to understanding the research problem? 5. Should I provide subheadings and other background information, such as definitions and/or a history? Find Models Use the exercise of reviewing the literature to examine how authors in your discipline or area of interest have composed their literature review sections. Read them to get a sense of the types of themes you might want to look for in your own research or to identify ways to organize your final review. The bibliography or reference section of sources you've already read, such as required readings in the course syllabus, are also excellent entry points into your own research. Narrow the Topic The narrower your topic, the easier it will be to limit the number of sources you need to read in order to obtain a good survey of relevant resources. Your professor will probably not expect you to read everything that's available about the topic, but you'll make the act of reviewing easier if you first limit scope of the research problem. A good strategy is to begin by searching the USC Libraries Catalog for recent books about the topic and review the table of contents for chapters that focuses on specific issues. You can also review the indexes of books to find references to specific issues that can serve as the focus of your research. For example, a book surveying the history of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict may include a chapter on the role Egypt has played in mediating the conflict, or look in the index for the pages where Egypt is mentioned in the text. Consider Whether Your Sources are Current Some disciplines require that you use information that is as current as possible. This is particularly true in disciplines in medicine and the sciences where research conducted becomes obsolete very quickly as new discoveries are made. However, when writing a review in the social sciences, a survey of the history of the literature may be required. In other words, a complete understanding the research problem requires you to deliberately examine how knowledge and perspectives have changed over time. Sort through other current bibliographies or literature reviews in the field to get a sense of what your discipline expects. You can also use this method to explore what is considered by scholars to be a "hot topic" and what is not.
III. Ways to Organize Your Literature Review
Chronology of Events If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials according to when they were published. This approach should only be followed if a clear path of research building on previous research can be identified and that these trends follow a clear chronological order of development. For example, a literature review that focuses on continuing research about the emergence of German economic power after the fall of the Soviet Union. By Publication Order your sources by publication chronology, then, only if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on environmental studies of brown fields if the progression revealed, for example, a change in the soil collection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies. Thematic [“conceptual categories”] A thematic literature review is the most common approach to summarizing prior research in the social and behavioral sciences. Thematic reviews are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time, although the progression of time may still be incorporated into a thematic review. For example, a review of the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics could focus on the development of online political satire. While the study focuses on one topic, the Internet’s impact on American presidential politics, it would still be organized chronologically reflecting technological developments in media. The difference in this example between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: themes related to the role of the Internet in presidential politics. Note that more authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point being made. Methodological A methodological approach focuses on the methods utilized by the researcher. For the Internet in American presidential politics project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of American presidents on American, British, and French websites. Or the review might focus on the fundraising impact of the Internet on a particular political party. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Other Sections of Your Literature Review Once you've decided on the organizational method for your literature review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out because they arise from your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period; a thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue. However, sometimes you may need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. However, only include what is necessary for the reader to locate your study within the larger scholarship about the research problem.
Here are examples of other sections, usually in the form of a single paragraph, you may need to include depending on the type of review you write:
- Current Situation : Information necessary to understand the current topic or focus of the literature review.
- Sources Used : Describes the methods and resources [e.g., databases] you used to identify the literature you reviewed.
- History : The chronological progression of the field, the research literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
- Selection Methods : Criteria you used to select (and perhaps exclude) sources in your literature review. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed [i.e., scholarly] sources.
- Standards : Description of the way in which you present your information.
- Questions for Further Research : What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
IV. Writing Your Literature Review
Once you've settled on how to organize your literature review, you're ready to write each section. When writing your review, keep in mind these issues.
Use Evidence A literature review section is, in this sense, just like any other academic research paper. Your interpretation of the available sources must be backed up with evidence [citations] that demonstrates that what you are saying is valid. Be Selective Select only the most important points in each source to highlight in the review. The type of information you choose to mention should relate directly to the research problem, whether it is thematic, methodological, or chronological. Related items that provide additional information, but that are not key to understanding the research problem, can be included in a list of further readings . Use Quotes Sparingly Some short quotes are appropriate if you want to emphasize a point, or if what an author stated cannot be easily paraphrased. Sometimes you may need to quote certain terminology that was coined by the author, is not common knowledge, or taken directly from the study. Do not use extensive quotes as a substitute for using your own words in reviewing the literature. Summarize and Synthesize Remember to summarize and synthesize your sources within each thematic paragraph as well as throughout the review. Recapitulate important features of a research study, but then synthesize it by rephrasing the study's significance and relating it to your own work and the work of others. Keep Your Own Voice While the literature review presents others' ideas, your voice [the writer's] should remain front and center. For example, weave references to other sources into what you are writing but maintain your own voice by starting and ending the paragraph with your own ideas and wording. Use Caution When Paraphrasing When paraphrasing a source that is not your own, be sure to represent the author's information or opinions accurately and in your own words. Even when paraphrasing an author’s work, you still must provide a citation to that work.
V. Common Mistakes to Avoid
These are the most common mistakes made in reviewing social science research literature.
- Sources in your literature review do not clearly relate to the research problem;
- You do not take sufficient time to define and identify the most relevant sources to use in the literature review related to the research problem;
- Relies exclusively on secondary analytical sources rather than including relevant primary research studies or data;
- Uncritically accepts another researcher's findings and interpretations as valid, rather than examining critically all aspects of the research design and analysis;
- Does not describe the search procedures that were used in identifying the literature to review;
- Reports isolated statistical results rather than synthesizing them in chi-squared or meta-analytic methods; and,
- Only includes research that validates assumptions and does not consider contrary findings and alternative interpretations found in the literature.
Cook, Kathleen E. and Elise Murowchick. “Do Literature Review Skills Transfer from One Course to Another?” Psychology Learning and Teaching 13 (March 2014): 3-11; Fink, Arlene. Conducting Research Literature Reviews: From the Internet to Paper . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2005; Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1998; Jesson, Jill. Doing Your Literature Review: Traditional and Systematic Techniques . London: SAGE, 2011; Literature Review Handout. Online Writing Center. Liberty University; Literature Reviews. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2016; Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-Step Guide for Students . 2nd ed. Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2012; Randolph, Justus J. “A Guide to Writing the Dissertation Literature Review." Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation. vol. 14, June 2009; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016; Taylor, Dena. The Literature Review: A Few Tips On Conducting It. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Writing a Literature Review. Academic Skills Centre. University of Canberra.
Writing Tip
Break Out of Your Disciplinary Box!
Thinking interdisciplinarily about a research problem can be a rewarding exercise in applying new ideas, theories, or concepts to an old problem. For example, what might cultural anthropologists say about the continuing conflict in the Middle East? In what ways might geographers view the need for better distribution of social service agencies in large cities than how social workers might study the issue? You don’t want to substitute a thorough review of core research literature in your discipline for studies conducted in other fields of study. However, particularly in the social sciences, thinking about research problems from multiple vectors is a key strategy for finding new solutions to a problem or gaining a new perspective. Consult with a librarian about identifying research databases in other disciplines; almost every field of study has at least one comprehensive database devoted to indexing its research literature.
Frodeman, Robert. The Oxford Handbook of Interdisciplinarity . New York: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Another Writing Tip
Don't Just Review for Content!
While conducting a review of the literature, maximize the time you devote to writing this part of your paper by thinking broadly about what you should be looking for and evaluating. Review not just what scholars are saying, but how are they saying it. Some questions to ask:
- How are they organizing their ideas?
- What methods have they used to study the problem?
- What theories have been used to explain, predict, or understand their research problem?
- What sources have they cited to support their conclusions?
- How have they used non-textual elements [e.g., charts, graphs, figures, etc.] to illustrate key points?
When you begin to write your literature review section, you'll be glad you dug deeper into how the research was designed and constructed because it establishes a means for developing more substantial analysis and interpretation of the research problem.
Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Social Science Research Imagination . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 1 998.
Yet Another Writing Tip
When Do I Know I Can Stop Looking and Move On?
Here are several strategies you can utilize to assess whether you've thoroughly reviewed the literature:
- Look for repeating patterns in the research findings . If the same thing is being said, just by different people, then this likely demonstrates that the research problem has hit a conceptual dead end. At this point consider: Does your study extend current research? Does it forge a new path? Or, does is merely add more of the same thing being said?
- Look at sources the authors cite to in their work . If you begin to see the same researchers cited again and again, then this is often an indication that no new ideas have been generated to address the research problem.
- Search Google Scholar to identify who has subsequently cited leading scholars already identified in your literature review [see next sub-tab]. This is called citation tracking and there are a number of sources that can help you identify who has cited whom, particularly scholars from outside of your discipline. Here again, if the same authors are being cited again and again, this may indicate no new literature has been written on the topic.
Onwuegbuzie, Anthony J. and Rebecca Frels. Seven Steps to a Comprehensive Literature Review: A Multimodal and Cultural Approach . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2016; Sutton, Anthea. Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review . Los Angeles, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
- << Previous: Theoretical Framework
- Next: Citation Tracking >>
- Last Updated: Apr 5, 2024 1:38 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Ask Yale Library
My Library Accounts
Find, Request, and Use
Help and Research Support
Visit and Study
Explore Collections
Political Science Subject Guide: Literature Reviews
- Political Science
- Books & Dissertations
- Articles & Databases
- Literature Reviews
- Senior Essay Resources
- Country Information
More Literature Review Writing Tips
- Thesis Whisperer- Bedraggled Daisy Lay advice on writing theses and dissertations. This article demonstrates in more detail one aspect of our discussion
Books on the Literature Review
What is a literature review?
"A literature review is an account of what has been published on a topic by accredited scholars and researchers. [...] In writing the literature review, your purpose is to convey to your reader what knowledge and ideas have been established on a topic, and what their strengths and weaknesses are. As a piece of writing, the literature review must be defined by a guiding concept (e.g., your research objective, the problem or issue you are discussing, or your argumentative thesis). It is not just a descriptive list of the material available, or a set of summaries."
(from "The Literature Review: A Few Tips on Writing It," http://www.writing.utoronto.ca/advice/specific-types-of-writing/literature-review )
Strategies for conducting your own literature review
1. Use this guide as a starting point. Begin your search with the resources linked from the political science subject guide. These library catalogs and databases will help you identify what's been published on your topic.
2. What came first? Try bibliographic tracing. As you're finding sources, pay attention to what and whom these authors cite. Their footnotes and bibliographies will point you in the direction of additional scholarship on your topic.
3. What comes next? Look for reviews and citation reports. What did scholars think about that book when it was published in 2003? Has anyone cited that article since 1971? Reviews and citation analysis tools can help you determine if you've found the seminal works on your topic--so that you can be confident that you haven't missed anything important, and that you've kept up with the debates in your field. You'll find book reviews in JSTOR and other databases. Google Scholar has some citation metrics; you can use Web of Science ( Social Sciences Citation Index ) for more robust citation reports.
4. Stay current. Get familiar with the top journals in your field, and set up alerts for new articles. If you don't know where to begin, APSA and other scholarly associations often maintain lists of journals, broken out by subfield . In many databases (and in Google Scholar), you can also set up search alerts, which will notify you when additional items have been added that meet your search criteria.
5. Stay organized. A citation management tool--e.g., RefWorks, Endnote, Zotero, Mendeley--will help you store your citations, generate a bibliography, and cite your sources while you write. Some of these tools are also useful for file storage, if you'd like to keep PDFs of the articles you've found. To get started with citation management tools, check out this guide .
How to find existing literature reviews
1. Consult Annual Reviews. The Annual Review of Political Science consists of thorough literature review essays in all areas of political science, written by noted scholars. The library also subscribes to Annual Reviews in economics, law and social science, sociology, and many other disciplines.
2. Turn to handbooks, bibliographies, and other reference sources. Resources like Oxford Bibliographies Online and assorted handbooks ( Oxford Handbook of Comparative Politics , Oxford Handbook of American Elections and Political Behavior , etc.) are great ways to get a substantive introduction to a topic, subject area, debate, or issue. Not exactly literature reviews, but they do provide significant reference to and commentary on the relevant literature--like a heavily footnoted encyclopedia for specialists in a discipline.
3. Search databases and Google Scholar. Use the recommended databases in the "Articles & Databases" tab of this guide and try a search that includes the phrase "literature review."
4. Search in journals for literature review articles. Once you've identified the important journals in your field as suggested in the section above, you can target these journals and search for review articles.
5. Find book reviews. These reviews can often contain useful contextual information about the concerns and debates of a field. Worldwide Political Science Abstracts is a good source for book reviews, as is JSTOR . To get to book reviews in JSTOR, select the advanced search option, use the title of the book as your search phrase, and narrow by item type: reviews. You can also narrow your search further by discipline.
6. Cast a wide net--don't forget dissertations. Dissertations and theses often include literature review sections. While these aren't necessarily authoritative, definitive literature reviews (you'll want to check in Annual Reviews for those), they can provide helpful suggestions for sources to consider.
- << Previous: News
- Next: Senior Essay Resources >>
- Last Updated: Jan 9, 2024 12:55 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/politicalscience
Site Navigation
P.O. BOX 208240 New Haven, CT 06250-8240 (203) 432-1775
Yale's Libraries
Bass Library
Beinecke Rare Book and Manuscript Library
Classics Library
Cushing/Whitney Medical Library
Divinity Library
East Asia Library
Gilmore Music Library
Haas Family Arts Library
Lewis Walpole Library
Lillian Goldman Law Library
Marx Science and Social Science Library
Sterling Memorial Library
Yale Center for British Art
SUBSCRIBE TO OUR NEWSLETTER
@YALELIBRARY

Yale Library Instagram
Accessibility Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Giving Privacy and Data Use Contact Our Web Team
© 2022 Yale University Library • All Rights Reserved
Press ESC to close
A Comprehensive Chronological Literature Review: Examples and Best Practices
- backlinkworks
- Writing Articles & Reviews
- September 17, 2023

Introduction
A literature review is an essential component of any research project, providing an overview of the existing scholarly works on a particular topic. IT helps researchers identify the gaps in knowledge and explore avenues for further study. One popular approach to organizing a literature review is by following a chronological order, which enables a comprehensive understanding of how research has evolved over time. In this article, we will dive into the best practices and explore some examples of a chronological literature review.
Understanding Chronological Literature Review
A chronological literature review entails organizing and discussing the existing research literature on a topic, starting from the earliest published works and progressing to the most recent ones. This approach allows researchers to trace the development of knowledge on a specific subject, highlighting key milestones, major theories, and shifts in perspectives. By presenting an overview of the sequence of studies, a chronological literature review facilitates the identification of patterns, controversies, and areas where further research is needed. IT ensures that researchers are up-to-date with the latest findings while acknowledging the contributions of earlier works.
Best Practices for Conducting a Chronological Literature Review
To ensure a comprehensive and effective chronological literature review, researchers should follow these best practices:
1. Thorough Planning
Before diving into the literature review, IT is crucial to plan and outline the expected structure and scope of the review. Identify the key themes, theories, and concepts to guide your search and organization of the literature. This step will help you stay focused and avoid getting overwhelmed by the extensive body of existing research.
2. Extensive Literature Search
Conduct a systematic and thorough search of electronic databases, libraries, and reputable scholarly platforms. Include a wide range of sources such as academic journals, books, conference papers, theses/dissertations, and relevant grey literature. By utilizing various sources, you can gather a diverse range of perspectives and ensure the inclusivity of different scholarly contributions.
3. Organization and Synthesis
Categorize the literature according to themes, methodologies, or key concepts to provide a coherent narrative. This allows you to identify themes that emerge across different studies and trace their development over time. Summarize the key findings, methodologies, and theories employed in each study while highlighting connections, gaps, and areas of disagreement.
4. Analysis and Interpretation
Analyze and critically evaluate the literature to identify strengths, weaknesses, and limitations of the existing research. Compare and contrast the methodologies, theories, and findings of each study to reveal patterns, inconsistencies, or gaps in the knowledge. Formulate your interpretation based on the collective evidence presented in the literature.
5. Integration with Current Research
Relate the findings of the literature review to your research objectives and questions. Discuss how the existing knowledge can contribute to your study, highlight areas where further research is needed, and propose potential directions for new investigations. By integrating the literature with your own research, you position your study within the broader scholarly context.
Examples of Chronological Literature Reviews
To illustrate the application of a chronological literature review, let’s explore two examples from different disciplines.
Example 1: The Evolution of Artificial Intelligence Research
In this example, the researcher starts by discussing the early theories and experiments in the field of artificial intelligence (AI), such as the Dartmouth Conference in 1956. The review then progresses through the decades, highlighting key developments, breakthroughs, and controversies in AI research. The aim is to provide readers with a clear understanding of the evolving landscape of AI, from early symbolic systems to machine learning and neural networks. By presenting the historical context and the influential researchers, this review aids in comprehending the current state of AI research and potential future directions.
Example 2: Changing Perspectives on Climate Change
In this example, the chronological literature review traces the evolution of climate change studies over the past century. IT begins by discussing early debates on the existence of global warming and the first climate models. The review then progresses through the decades, highlighting significant events, political developments, and scientific breakthroughs that have shaped the understanding of climate change. By analyzing the changing perspectives, controversies, and the role of scientific consensus, this review provides a comprehensive view of the challenges and advancements in the field of climate change research.
A chronological literature review is a valuable tool for researchers to understand the progression of knowledge on a specific topic. By organizing and analyzing existing research in a chronological order, researchers can identify patterns, gaps, and contributions that have shaped their field of study. Following best practices like thorough planning, extensive literature search, organization and synthesis, analysis and interpretation, and integration with current research ensures the effectiveness of a chronological literature review. Examples from different disciplines highlight the benefits of this approach and its application in various research areas.
What is the purpose of a literature review?
A literature review serves the purpose of summarizing and critically evaluating the existing scholarly works on a specific topic. IT helps identify gaps in knowledge, highlight key findings and theories, and provide a foundation for further research.
Why is a chronological literature review beneficial?
A chronological literature review allows researchers to understand the historical development and evolution of research on a particular topic. IT provides a comprehensive overview and helps identify patterns, controversies, and areas for further investigation.
How do I organize a chronological literature review?
To organize a chronological literature review, categorize the literature according to themes, theories, or key concepts. Summarize key findings, methodologies, and theories employed in each study while highlighting connections, gaps, and disagreements.
How do I conduct a literature search for a chronological review?
To conduct a literature search for a chronological review, utilize electronic databases, libraries, and reputable scholarly platforms. Include academic journals, books, conference papers, theses/dissertations, and relevant grey literature to ensure a diverse range of perspectives.
Why is IT important to integrate the literature review with my own research?
Integrating the literature review with your own research allows you to position your study within the broader scholarly context. IT helps identify how the existing literature can contribute to your research objectives and questions and provides directions for future investigations.
A Comprehensive Guide to Microsoft Office 2007: Everything You Need to Know
Choosing the perfect business website theme for your brand.

Recent Posts
- Driving Organic Growth: How a Digital SEO Agency Can Drive Traffic to Your Website
- Mastering Local SEO for Web Agencies: Reaching Your Target Market
- The Ultimate Guide to Unlocking Powerful Backlinks for Your Website
- SEO vs. Paid Advertising: Finding the Right Balance for Your Web Marketing Strategy
- Discover the Secret Weapon for Local SEO Success: Local Link Building Services
Popular Posts

Shocking Secret Revealed: How Article PHP ID Can Transform Your Website!

Uncovering the Top Secret Tricks for Mastering SPIP PHP – You Won’t Believe What You’re Missing Out On!

Discover the Shocking Truth About Your Website’s Ranking – You Won’t Believe What This Checker Reveals!

10 Tips for Creating a Stunning WordPress Theme

How to Use HTTrack to Mirror a WordPress Website
Explore topics.
- Backlinks (2,425)
- Blog (2,744)
- Computers (5,318)
- Digital Marketing (7,741)
- Internet (6,340)
- Website (4,705)
- Wordpress (4,705)
- Writing Articles & Reviews (4,208)
- Library Guides
- Literature Reviews
- Searching the Literature
Literature Reviews: Searching the Literature
Starting to research your topic.
Before you can searching for the existing literature, you need to make sure you know what is meant by "the literature," which is usually defined as a collection of all the scholarly writings on a topic . The literature can include peer reviewed articles, books/ebooks, conference proceedings, theses/dissertations, documents published by governmental agencies and non-profit organizations, and other forms of gray literature.
STRATEGIES TO START YOUR RESEARCH
- You can learn how to search the OSU Library using this video playlist.
- Talk with knowledgeable collaborators , colleagues, professors, friends, etc. They may have suggest important authors, journals or documents on your topic.
- Look over popular interest sources (with caution!), like Wikipedia.
- Look at the most highly cited documents on your topic . Many scholarly databases have the ability to sort results by "Cited Highest." See the Searching Tips tab for instructions on how implement this.
Selecting Databases to Search
- Library Subject Specialists are available to help throughout the literature review process, including recommending which scholarly databases to search based on your topic.
BACKGROUND INFORMATION & REFERENCE
- Very Short Introductions Very Short Introductions are published by Oxford University Press and offer concise and original introductions to a wide range of subjects. This collection includes over 600 e-books on topics in arts and humanities, history, law, literature, medicine and health, religion, science and mathematics, and social sciences.
- Oxford Reference Online: Premium Access to more than 170 full-text Oxford dictionaries and reference works. There are over 1.5 million dictionary definitions with the dictionary updated continuously.
- Gale eBooks A database of encyclopedias, reference sources, and full-text eBooks that cover multiple disciplines.
- Statista Statista consolidates statistical data on over 80,000 topics from more than 22,500 sources. It includes insights and facts across 600 industries and 50+ countries.
Using Library Search to Find Reference Materials
- Perform a search from the library's home page and then click the the "Reference Resources" option under the Limit To heading
- Or, using the same search tool, combine your search terms with the following: encyclopedias OR dictionaries OR handbooks OR companion
SUBSCRIPTION MULTI-DISCIPLINARY SEARCH DATABASES (REQUIRES OSU LOGIN)
- OSU Library Search more... less... Consider adding terms like "literature review" OR "review of the literature" OR "review of literature" OR "systematic review"
- Scopus Scopus is the largest abstract and citation database of peer-reviewed literature: scientific journals, books and conference proceedings. Delivering a comprehensive overview of the world's research output in the fields of science, technology, medicine, social sciences, and arts and humanities, Scopus features smart tools to track, analyze and visualize research. more... less... To learn more about logging into Scopus, see this guide .
- Use the "Review article" filter under Document Type to find articles that summarize the current state of understanding on a topic
- SciVal Quick and easy access to the research performance of 8500 research institutions and 220 countries worldwide. SciVal requires a one-time registration from on campus.
This multi-disciplinary database offers full text for nearly 2,000 scholarly journals, including more than 1,500 peer-reviewed titles. Covering virtually every area of academic study, Academic Search Premier offers full text information dating as far back as 1985. This database is updated on a daily basis.
- ProQuest Research Library ProQuest Research Library provides one-stop access to thousands of full-text periodicals from one of the broadest, most inclusive general reference databases ProQuest has to offer. Search from a highly-respected, diversified mix of scholarly journals, professional and trade publications, and magazines covering over 150 subjects and topics.
- JSTOR Full-text access for over 17 million journal articles, books, documents, and research reports in a variety of disciplines.
- Compendex Compendex has over 27.5 million records from 85 countries across 190 engineering disciplines. There is also a comprehensive, historical view of engineering innovations between 1884-1969 in the Engineering Index Backfile. more... less... To learn more about searching in Compendex, see this guide .
ADDITIONAL MULTI-DISCIPLINARY SEARCH DATABASES ("FREE" STATUS MAY VARY)
- PubMed More than 34 million citations for biomedical literature from MEDLINE, life science journals, and eBooks, with some full-text linked.
BROWSER PLUGINS
Developing & Executing Your Search Strategy
Search strategy.
A search strategy translates your research question into search terms. See an example below.
Look over the searching techniques on the Searching Tips tab to learn how to combine your search terms.
EXECUTING YOUR SEARCH STRATEGY IN A SCHOLARLY DATABASE
The screenshots below shows how you can enter your search terms into two different databases, Scopus (top) and ProQuest (bottom). Searches can be built using multiple search boxes (as shown below).

You can also build your search using a single search box (as shown below).

How Much Literature is Enough?
Remember: a comprehensive literature review (like for a dissertation) will require more sources than a selective literature review (like for a course assignment).
THINGS TO CONSIDER
Searching for, reading and understanding the existing literature is more of an art than a science. The more you do, the more you'll understand the current state of research and therefore know if you've found enough literature.
New literature is being published daily. You must stop searching at some point.
Consider the volume of research on your topic. A larger volume equates to more searching. For example:
Type II diabetes = large amount of literature
Multiple Myeloma [rare cancer] = smaller amount of literature
Evaluate the resources available to you
Time: How much time do you have to complete this review?
Collaborators: Do you have collaborators or colleagues helping to complete the review?
Reflect on your Research Question
Continually revisit your Research Question and objectives — ensure the literature you've collected directly address your research goals.
Attribution
Thanks to Librarian Jamie Niehof at the University of Michigan for providing permission to reuse and remix this Literature Reviews guide.
Grey Literature

Grey Literature is research information that is public (not behind paywalls).
It can include government reports, web content, documents from professional organizations, and conference abstracts. It might be relevant for your literature review.
Avoiding Bias
Selection bias.
This occurs when you don't do a thorough search of the existing literature . Your review doesn't need to find every document ever published, but should not be misleading. It will be misleading if you leave out whole categories of studies or only look at a haphazard section of studies.
Ways to avoid selection bias:
- search multiple scholarly databases (each contain different documents)
- search for grey literature
- search on multiple days (new research is being published daily)
- search using a variety of different search terms
Searching using AI
AI-assisted literature searching applies artificial intelligence and machine learning to the act of searching the literature, possibly finding connections that you wouldn't normally find. The tools below are a starting point.

Raxter — https://raxter.io
Research Rabbit — researchrabbit. ai
Iris — https://iris.ai
Scite (paid app | instructions ) — https://scite.ai
- Last Updated: Apr 4, 2024 4:51 PM
- URL: https://info.library.okstate.edu/literaturereviews

COMMENTS
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
15 Literature Review Examples. Literature reviews are a necessary step in a research process and often required when writing your research proposal. They involve gathering, analyzing, and evaluating existing knowledge about a topic in order to find gaps in the literature where future studies will be needed. Ideally, once you have completed your ...
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship ...
Steps for Conducting a Lit Review; Finding "The Literature" Organizing/Writing; APA Style This link opens in a new window; Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window; MLA Style This link opens in a new window; Sample Literature Reviews. Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts; Have an exemplary literature review? Get Help!
A literature review usually becomes chapter 1 in dissertations and theses, allowing to explore the current knowledge on the topic. It evaluates academic and professional articles, journal publications, books, and web-based resources. A literature review is an indispensable part of a research paper. It serves many purposes, some of which are not ...
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays).
Step 1: Find the relevant literature. Naturally, the first step in the literature review journey is to hunt down the existing research that's relevant to your topic. While you probably already have a decent base of this from your research proposal, you need to expand on this substantially in the dissertation or thesis itself.. Essentially, you need to be looking for any existing literature ...
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
Types of Literature Review are as follows: Narrative literature review: This type of review involves a comprehensive summary and critical analysis of the available literature on a particular topic or research question. It is often used as an introductory section of a research paper. Systematic literature review: This is a rigorous and ...
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review. As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications.
How to write a literature review in 6 steps. How do you write a good literature review? This step-by-step guide on how to write an excellent literature review covers all aspects of planning and writing literature reviews for academic papers and theses.
If you're working on a dissertation or thesis and are looking for an example of a strong literature review chapter, you've come to the right place.. In this video, we walk you through an A-grade literature review from a dissertation that earned full distinction.We start off by discussing the five core sections of a literature review chapter by unpacking our free literature review template.
29 Jul 2021. A literature review is an account of the scholarly works published on a topic. It is different from an annotated bibliography - and far more interesting at that. Instead of being just a list of summaries, a literature review synthesizes the information from all available sources in an overall relationship to your guiding concept.
The purpose of a literature review. The four main objectives of a literature review are:. Studying the references of your research area; Summarizing the main arguments; Identifying current gaps, stances, and issues; Presenting all of the above in a text; Ultimately, the main goal of a literature review is to provide the researcher with sufficient knowledge about the topic in question so that ...
A literature review is a comprehensive summary and analysis of previously published research on a particular topic. Literature reviews should give the reader an overview of the important theories and themes that have previously been discussed on the topic, as well as any important researchers who have contributed to the discourse. This review ...
Here are a few additional tips for writing a good literature review in a dissertation or thesis: Tip 1: Start Early. Do not wait until the last minute to start writing your literature review. It takes time to do a good job. Tip 2: Read Widely. Do not just read the most recent articles on your topic.
7.2 Steps of writing a literature review. Writing a literature review is a very challenging task. Figure 7.2 summarises the steps of writing a literature review. Depending on why you are writing your literature review, you may be given a topic area, or may choose a topic that particularly interests you or is related to a research project that ...
Demonstrate your knowledge of the research topic. Identify the gaps in the literature and show how your research links to these. Provide the foundation for your conceptual framework (if you have one) Inform your own methodology and research design. To achieve this, your literature review needs a well-thought-out structure.
A literature review may consist of simply a summary of key sources, but in the social sciences, a literature review usually has an organizational pattern and combines both summary and synthesis, often within specific conceptual categories.A summary is a recap of the important information of the source, but a synthesis is a re-organization, or a reshuffling, of that information in a way that ...
An example outline for a Literature Review might look like this: Introduction. Background information on the topic & definitions; Purpose of the literature review; Scope and limitations of the review (what is included /excluded) Body. Historical background ; Overview of the existing research on the topic; Principle question being asked
the initial steps we take to prepare for the review. carrying out the work. writing and revising the review. Let's now get familiar with the preparatory steps: 3.1. Identifying the Search topic (s) This may appear obvious at first glance, but there's no literature review without clearly defining what we want to cover.
Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review by Andrew Booth; Anthea Sutton; Diana Papaioannou Showing you how to take a structured and organized approach to a wide range of literature review types, this book helps you to choose which approach is right for your research. Packed with constructive tools, examples, case studies and hands-on exercises, the book covers the full range of ...
A literature review is a compilation of current knowledge on a particular topic derived from the critical evaluation of different scholarly sources such as books, articles, and publications, which is then presented in an organized manner to relate to a specific research problem being investigated. It highlights the methods, relevant theories, and gaps in existing research on a particular ...
A chronological literature review entails organizing and discussing the existing research literature on a topic, starting from the earliest published works and progressing to the most recent ones. This approach allows researchers to trace the development of knowledge on a specific subject, highlighting key milestones, major theories, and shifts ...
Elicit is a research assistant using language models like GPT-3 to automate parts of researchers' workflows. Currently, the main workflow in Elicit is Literature Review. If you ask a question, Elicit will show relevant papers and summaries of key information about those papers in an easy-to-use table. Perplexity.