
Get Access To 1000+ Research Topic Ideas
If you’re trying to find a suitable research topic for your dissertation, thesis or research project, this is for you. Simply put, this mega list of research topic ideas will help stimulate your thinking and fast-track the topic ideation process.
The list provides 1000+ topic ideas across 25 research areas, including:
- Accounting & finance
- Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning
- Biotech and genetic engineering
- Blockchain and crypto
- Business, management and leadership
- Communication
- Cybersecurity
- Data science and analytics
- Education and training
- Engineering
- Environmental science and climate change
- Law and public policy
- Materials science
- Mental health
- Neuroscience
- Political science
- Psychology and sociology
- Public administration
- Public health and epidemiology
- Robotics and automation
Simply put, this is the largest single source of research topic inspiration you’ll find. Plus, you’ll get free access to our popular webinar , Research Topic Ideation 101, as well as our tried and trusted research proposal template .
PS – You can also download our free dissertation template below 🙂


Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, 113 great research paper topics.
General Education

One of the hardest parts of writing a research paper can be just finding a good topic to write about. Fortunately we've done the hard work for you and have compiled a list of 113 interesting research paper topics. They've been organized into ten categories and cover a wide range of subjects so you can easily find the best topic for you.
In addition to the list of good research topics, we've included advice on what makes a good research paper topic and how you can use your topic to start writing a great paper.
What Makes a Good Research Paper Topic?
Not all research paper topics are created equal, and you want to make sure you choose a great topic before you start writing. Below are the three most important factors to consider to make sure you choose the best research paper topics.
#1: It's Something You're Interested In
A paper is always easier to write if you're interested in the topic, and you'll be more motivated to do in-depth research and write a paper that really covers the entire subject. Even if a certain research paper topic is getting a lot of buzz right now or other people seem interested in writing about it, don't feel tempted to make it your topic unless you genuinely have some sort of interest in it as well.
#2: There's Enough Information to Write a Paper
Even if you come up with the absolute best research paper topic and you're so excited to write about it, you won't be able to produce a good paper if there isn't enough research about the topic. This can happen for very specific or specialized topics, as well as topics that are too new to have enough research done on them at the moment. Easy research paper topics will always be topics with enough information to write a full-length paper.
Trying to write a research paper on a topic that doesn't have much research on it is incredibly hard, so before you decide on a topic, do a bit of preliminary searching and make sure you'll have all the information you need to write your paper.
#3: It Fits Your Teacher's Guidelines
Don't get so carried away looking at lists of research paper topics that you forget any requirements or restrictions your teacher may have put on research topic ideas. If you're writing a research paper on a health-related topic, deciding to write about the impact of rap on the music scene probably won't be allowed, but there may be some sort of leeway. For example, if you're really interested in current events but your teacher wants you to write a research paper on a history topic, you may be able to choose a topic that fits both categories, like exploring the relationship between the US and North Korea. No matter what, always get your research paper topic approved by your teacher first before you begin writing.
113 Good Research Paper Topics
Below are 113 good research topics to help you get you started on your paper. We've organized them into ten categories to make it easier to find the type of research paper topics you're looking for.
Arts/Culture
- Discuss the main differences in art from the Italian Renaissance and the Northern Renaissance .
- Analyze the impact a famous artist had on the world.
- How is sexism portrayed in different types of media (music, film, video games, etc.)? Has the amount/type of sexism changed over the years?
- How has the music of slaves brought over from Africa shaped modern American music?
- How has rap music evolved in the past decade?
- How has the portrayal of minorities in the media changed?

Current Events
- What have been the impacts of China's one child policy?
- How have the goals of feminists changed over the decades?
- How has the Trump presidency changed international relations?
- Analyze the history of the relationship between the United States and North Korea.
- What factors contributed to the current decline in the rate of unemployment?
- What have been the impacts of states which have increased their minimum wage?
- How do US immigration laws compare to immigration laws of other countries?
- How have the US's immigration laws changed in the past few years/decades?
- How has the Black Lives Matter movement affected discussions and view about racism in the US?
- What impact has the Affordable Care Act had on healthcare in the US?
- What factors contributed to the UK deciding to leave the EU (Brexit)?
- What factors contributed to China becoming an economic power?
- Discuss the history of Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies (some of which tokenize the S&P 500 Index on the blockchain) .
- Do students in schools that eliminate grades do better in college and their careers?
- Do students from wealthier backgrounds score higher on standardized tests?
- Do students who receive free meals at school get higher grades compared to when they weren't receiving a free meal?
- Do students who attend charter schools score higher on standardized tests than students in public schools?
- Do students learn better in same-sex classrooms?
- How does giving each student access to an iPad or laptop affect their studies?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Montessori Method ?
- Do children who attend preschool do better in school later on?
- What was the impact of the No Child Left Behind act?
- How does the US education system compare to education systems in other countries?
- What impact does mandatory physical education classes have on students' health?
- Which methods are most effective at reducing bullying in schools?
- Do homeschoolers who attend college do as well as students who attended traditional schools?
- Does offering tenure increase or decrease quality of teaching?
- How does college debt affect future life choices of students?
- Should graduate students be able to form unions?

- What are different ways to lower gun-related deaths in the US?
- How and why have divorce rates changed over time?
- Is affirmative action still necessary in education and/or the workplace?
- Should physician-assisted suicide be legal?
- How has stem cell research impacted the medical field?
- How can human trafficking be reduced in the United States/world?
- Should people be able to donate organs in exchange for money?
- Which types of juvenile punishment have proven most effective at preventing future crimes?
- Has the increase in US airport security made passengers safer?
- Analyze the immigration policies of certain countries and how they are similar and different from one another.
- Several states have legalized recreational marijuana. What positive and negative impacts have they experienced as a result?
- Do tariffs increase the number of domestic jobs?
- Which prison reforms have proven most effective?
- Should governments be able to censor certain information on the internet?
- Which methods/programs have been most effective at reducing teen pregnancy?
- What are the benefits and drawbacks of the Keto diet?
- How effective are different exercise regimes for losing weight and maintaining weight loss?
- How do the healthcare plans of various countries differ from each other?
- What are the most effective ways to treat depression ?
- What are the pros and cons of genetically modified foods?
- Which methods are most effective for improving memory?
- What can be done to lower healthcare costs in the US?
- What factors contributed to the current opioid crisis?
- Analyze the history and impact of the HIV/AIDS epidemic .
- Are low-carbohydrate or low-fat diets more effective for weight loss?
- How much exercise should the average adult be getting each week?
- Which methods are most effective to get parents to vaccinate their children?
- What are the pros and cons of clean needle programs?
- How does stress affect the body?
- Discuss the history of the conflict between Israel and the Palestinians.
- What were the causes and effects of the Salem Witch Trials?
- Who was responsible for the Iran-Contra situation?
- How has New Orleans and the government's response to natural disasters changed since Hurricane Katrina?
- What events led to the fall of the Roman Empire?
- What were the impacts of British rule in India ?
- Was the atomic bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki necessary?
- What were the successes and failures of the women's suffrage movement in the United States?
- What were the causes of the Civil War?
- How did Abraham Lincoln's assassination impact the country and reconstruction after the Civil War?
- Which factors contributed to the colonies winning the American Revolution?
- What caused Hitler's rise to power?
- Discuss how a specific invention impacted history.
- What led to Cleopatra's fall as ruler of Egypt?
- How has Japan changed and evolved over the centuries?
- What were the causes of the Rwandan genocide ?

- Why did Martin Luther decide to split with the Catholic Church?
- Analyze the history and impact of a well-known cult (Jonestown, Manson family, etc.)
- How did the sexual abuse scandal impact how people view the Catholic Church?
- How has the Catholic church's power changed over the past decades/centuries?
- What are the causes behind the rise in atheism/ agnosticism in the United States?
- What were the influences in Siddhartha's life resulted in him becoming the Buddha?
- How has media portrayal of Islam/Muslims changed since September 11th?
Science/Environment
- How has the earth's climate changed in the past few decades?
- How has the use and elimination of DDT affected bird populations in the US?
- Analyze how the number and severity of natural disasters have increased in the past few decades.
- Analyze deforestation rates in a certain area or globally over a period of time.
- How have past oil spills changed regulations and cleanup methods?
- How has the Flint water crisis changed water regulation safety?
- What are the pros and cons of fracking?
- What impact has the Paris Climate Agreement had so far?
- What have NASA's biggest successes and failures been?
- How can we improve access to clean water around the world?
- Does ecotourism actually have a positive impact on the environment?
- Should the US rely on nuclear energy more?
- What can be done to save amphibian species currently at risk of extinction?
- What impact has climate change had on coral reefs?
- How are black holes created?
- Are teens who spend more time on social media more likely to suffer anxiety and/or depression?
- How will the loss of net neutrality affect internet users?
- Analyze the history and progress of self-driving vehicles.
- How has the use of drones changed surveillance and warfare methods?
- Has social media made people more or less connected?
- What progress has currently been made with artificial intelligence ?
- Do smartphones increase or decrease workplace productivity?
- What are the most effective ways to use technology in the classroom?
- How is Google search affecting our intelligence?
- When is the best age for a child to begin owning a smartphone?
- Has frequent texting reduced teen literacy rates?

How to Write a Great Research Paper
Even great research paper topics won't give you a great research paper if you don't hone your topic before and during the writing process. Follow these three tips to turn good research paper topics into great papers.
#1: Figure Out Your Thesis Early
Before you start writing a single word of your paper, you first need to know what your thesis will be. Your thesis is a statement that explains what you intend to prove/show in your paper. Every sentence in your research paper will relate back to your thesis, so you don't want to start writing without it!
As some examples, if you're writing a research paper on if students learn better in same-sex classrooms, your thesis might be "Research has shown that elementary-age students in same-sex classrooms score higher on standardized tests and report feeling more comfortable in the classroom."
If you're writing a paper on the causes of the Civil War, your thesis might be "While the dispute between the North and South over slavery is the most well-known cause of the Civil War, other key causes include differences in the economies of the North and South, states' rights, and territorial expansion."
#2: Back Every Statement Up With Research
Remember, this is a research paper you're writing, so you'll need to use lots of research to make your points. Every statement you give must be backed up with research, properly cited the way your teacher requested. You're allowed to include opinions of your own, but they must also be supported by the research you give.
#3: Do Your Research Before You Begin Writing
You don't want to start writing your research paper and then learn that there isn't enough research to back up the points you're making, or, even worse, that the research contradicts the points you're trying to make!
Get most of your research on your good research topics done before you begin writing. Then use the research you've collected to create a rough outline of what your paper will cover and the key points you're going to make. This will help keep your paper clear and organized, and it'll ensure you have enough research to produce a strong paper.
What's Next?
Are you also learning about dynamic equilibrium in your science class? We break this sometimes tricky concept down so it's easy to understand in our complete guide to dynamic equilibrium .
Thinking about becoming a nurse practitioner? Nurse practitioners have one of the fastest growing careers in the country, and we have all the information you need to know about what to expect from nurse practitioner school .
Want to know the fastest and easiest ways to convert between Fahrenheit and Celsius? We've got you covered! Check out our guide to the best ways to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit (or vice versa).
These recommendations are based solely on our knowledge and experience. If you purchase an item through one of our links, PrepScholar may receive a commission.

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Trends and hot topics in linguistics studies from 2011 to 2021: a bibliometric analysis of highly cited papers.

- School of Foreign Languages, Central China Normal University, Wuhan, China
High citations most often characterize quality research that reflects the foci of the discipline. This study aims to spotlight the most recent hot topics and the trends looming from the highly cited papers (HCPs) in Web of Science category of linguistics and language & linguistics with bibliometric analysis. The bibliometric information of the 143 HCPs based on Essential Citation Indicators was retrieved and used to identify and analyze influential contributors at the levels of journals, authors, and countries. The most frequently explored topics were identified by corpus analysis and manual checking. The retrieved topics can be grouped into five general categories: multilingual-related , language teaching , and learning related , psycho/pathological/cognitive linguistics-related , methods and tools-related , and others . Topics such as bi/multilingual(ism) , translanguaging , language/writing development , models , emotions , foreign language enjoyment (FLE) , cognition , anxiety are among the most frequently explored. Multilingual and positive trends are discerned from the investigated HCPs. The findings inform linguistic researchers of the publication characteristics of the HCPs in the linguistics field and help them pinpoint the research trends and directions to exert their efforts in future studies.
1. Introduction
Citations, as a rule, exhibit a skewed distributional pattern over the academic publications: a few papers accumulate an overwhelming large citations while the majority are rarely, if ever, cited. Correspondingly, the highly cited papers (HCPs) receive the greatest amount of attention in the academia as citations are commonly regarded as a strong indicator of research excellence. For academic professionals, following HCPs is an efficient way to stay current with the developments in a field and to make better informed decisions regarding potential research topics and directions to exert their efforts. For academic institutions, government and private agencies, and generally the science policy makers, they keep a close eye on and take advantage of this visible indicator, citations, to make more informed decisions on research funding allocation and science policy formulation. Under the backdrop of ever-growing academic outputs, there is noticeable attention shift from publication quantity to publication quality. Many countries are developing research policies to identify “excellent” universities, research groups, and researchers ( Danell, 2011 ). In a word, HCPs showcase high-quality research, encompass significant themes, and constitute a critical reference point in a research field as they are “gold bullion of science” ( Smith, 2007 ).
2. Literature review
Bibliometrics, a term coined by Pritchard (1969) , refers to the application of mathematical methods to the analysis of academic publications. Essentially this is a quantitative method to depict publication patterns within a given field based on a body of literature. There are many bibliometric studies on natural and social sciences in general ( Hsu and Ho, 2014 ; Zhu and Lei, 2022 ) and on various specific disciplines such as management sciences ( Liao et al., 2018 ), biomass research ( Chen and Ho, 2015 ), computer sciences ( Xie and Willett, 2013 ), and sport sciences ( Mancebo et al., 2013 ; Ríos et al., 2013 ), etc. In these studies, researchers tracked developments, weighed research impacts, and highlighted emerging scientific fronts with bibliometric methods. In the field of linguistics, bibliometric studies all occurred in the past few years ( van Doorslaer and Gambier, 2015 ; Lei and Liao, 2017 ; Gong et al., 2018 ; Lei and Liu, 2018 , 2019 ). These bibliometric studies mostly examined a sub-area of linguistics, such as corpus linguistics ( Liao and Lei, 2017 ), translation studies ( van Doorslaer and Gambier, 2015 ), the teaching of Chinese as a second/foreign language ( Gong et al., 2018 ), academic journals like System ( Lei and Liu, 2018 ) or Porta Linguarum ( Sabiote and Rodríguez, 2015 ), etc. Although Lei and Liu (2019) took the entire discipline of linguistics under investigation, their research is exclusively focused on applied linguistics and restricted in a limited number of journals (42 journals in total), leaving publications in other linguistics disciplines and qualified journals unexamined.
Over the recent years, a number of studies have been concerned with “excellent” papers or HCPs. For example, Small (2004) surveyed the HCPs authors’ opinions on why their papers are highly cited. The strong interest, the novelty, the utility, and the high importance of the work were among the most frequently mentioned. Most authors also considered that their selected HCPs are indeed based on their most important work in their academic career. Aksnes (2003) investigated the characteristics of HCPs and found that they were generally authored by a large number of scientists, often involving international collaboration. Some researchers even attempted to predict the HCPs by building mathematical models, implying “the first mover advantage in scientific publication” ( Newman, 2008 , 2014 ). In other words, papers published earlier in a field generally are more likely to accumulate more citations than those published later. Although many papers addressed HCPs from different perspectives, they held a common belief that HCPs are very different from less or zero cited papers and thus deserve utmost attention in academic research ( Aksnes, 2003 ; Blessinger and Hrycaj, 2010 ; Yan et al., 2022 ).
Although an increased focus on research quality can be observed in different fields, opinions diverge on the range and the inclusion criterion of excellent papers. Are they ‘highly cited’, ‘top cited’, or ‘most frequently cited’ papers? Aksnes (2003) noted two different approaches to define a highly cited article, involving absolute or relative thresholds, respectively. An absolute threshold stipulates a minimum number of citations for identifying excellent papers while a relative threshold employs the percentile rank classes, for example, the top 10% most highly cited papers in a discipline or in a publication year or in a publication set. It is important to note that citations differ significantly in different fields and disciplines. A HCP in natural sciences generally accumulates more citations than its counterpart in social sciences. Thus, it is necessary to investigate HCPs from different fields separately or adopt different inclusion criterion to ensure a valid comparison.
The present study has been motivated by two considerations. First, the sizable number of publications of varied qualities in a scientific field makes it difficult or even impossible to conduct any reliable and effective literature research. Focusing on the quality publications, the HCPs in particular, might lend more credibility to the findings on trends. Second, HCPs can serve as a great platform to discover potentially important information for the development of a discipline and understand the past, present, and future of the scientific structure. Therefore, the present study aims to investigate the hot topics and publication trends in the Web of Science category of linguistics or language & linguistics (shortened as linguistics in later references) with bibliometric methods. The study aims to answer the following three questions:
1. Who are the most productive and impactful contributors of the HCPs in WoS category of linguistics or language & linguistics in terms of publication venues, authors, and countries?
2. What are the most frequently explored topics in HCPs?
3. What are the general research trends revealed from the HCPs?
3. Materials and methods
Different from previous studies which used an arbitrary inclusion threshold (e.g., Blessinger and Hrycaj, 2010 ; Hsu and Ho, 2014 ), we rely on Essential Science Indicator (ESI) to identify the HCPs. Developed by Clarivate, a leading company in the areas of bibliometrics and scientometrics, ESI reveals emerging science trends as well as influential individuals, institutions, papers, journals, and countries in any scientific fields of inquiry by drawing on the complete WoS databases. ESI has been chosen for the following three reasons. First, ESI adopts a stricter inclusion criterion for HCPs identification. That is, a paper is selected as a HCP only when its citations exceed the top 1% citation threshold in each of the 22 ESI subject categories. Second, ESI is widely used and recognized for its reliability and authority in identifying the top-charting work, generating “excellent” metrics including hot and highly cited papers. Third, ESI automatically updates its database to generate the most recent HCPs, especially suitable for trend studies for a specified timeframe.
3.1. Data source
The data retrieval was completed at the portal of our university library on June 20, 2022. The methods to retrieve the data are described in Table 1 . The bibliometric indicators regarding the important contributors at journal/author/country levels were obtained. Specifically, after the research was completed, we clicked the “Analyze Results” bar on the result page for the detailed descriptive analysis of the retrieved bibliometric data.
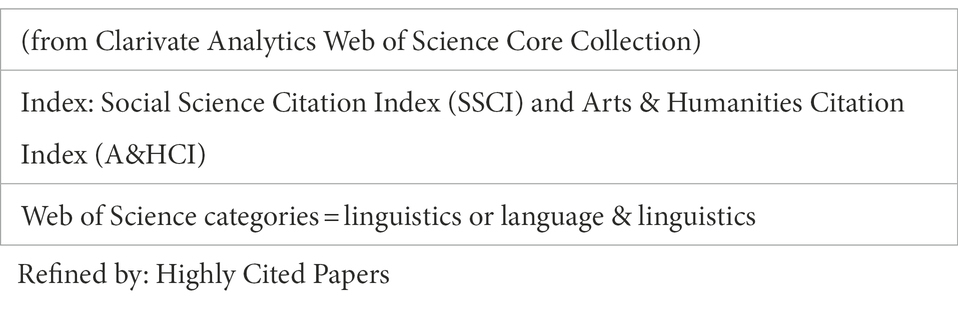
Table 1 . Retrieval strategies.
Several points should be noted about the search strategies. First, we searched the bibliometric data from two sub-databases of WoS core collection: Social Science Citation Index (SSCI) and Arts & Humanities Citation Index (A&HCI). There is no need to include the sub-database of Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-EXPANDED) because publications in the linguistics field are almost exclusively indexed in SSCI and A&HCI journals. WoS core collection was chosen as the data source because it boasts one of the most comprehensive and authoritative databases of bibliometric information in the world. Many previous studies utilized WoS to retrieve bibliometric data. van Oorschot et al. (2018) and Ruggeri et al. (2019) even indicated that WoS meets the highest standards in terms of impact factor and citation counts and hence guarantees the validity of any bibliometric analysis. Second, we do not restrict the document types as HCPs selection informed by ESI only considers articles and reviews. Third, we do not set the date range as the dataset of ESI-HCPs is automatically updated regularly to include the most recent 10 years of publications.
The aforementioned query obtained a total of 143 HCPs published in 48 journals contributed by 352 authors of 226 institutions. We then downloaded the raw bibliometric parameters of the 143 HCPs for follow-up analysis including publication years, authors, publication titles, countries, affiliations, abstracts, citation reports, etc. A complete list of the 143 HCPs can be found in the Supplementary Material . We collected the most recent impact factor (IF) of each journal from the 2022 Journal Citation Reports (JCR).
3.2. Data analysis
3.2.1. citation analysis.
A citation threshold is the minimum number of citations obtained by ranking papers in a research field in descending order by citation counts and then selecting the top fraction or percentage of papers. In ESI, the highly cited threshold reveals the minimum number of citations received by the top 1% of papers from each of the 10 database years. In other words, a paper has to meet the minimum citation threshold that varies by research fields and by years to enter the HCP list. Of the 22 research fields in ESI, Social Science, General is a broad field covering a number of WoS categories including linguistics and language & linguistics . We checked the ESI official website to obtain the yearly highly cited thresholds in the research field of Social Science , General as shown in Figure 1 ( https://esi.clarivate.com/ThresholdsAction.action ). As we can see, the longer a paper has been published, the more citations it has to receive to meet the threshold. We then divided the raw citation numbers of HCPs with the Highly Cited Thresholds in the corresponding year to obtain the normalized citations for each HCP.
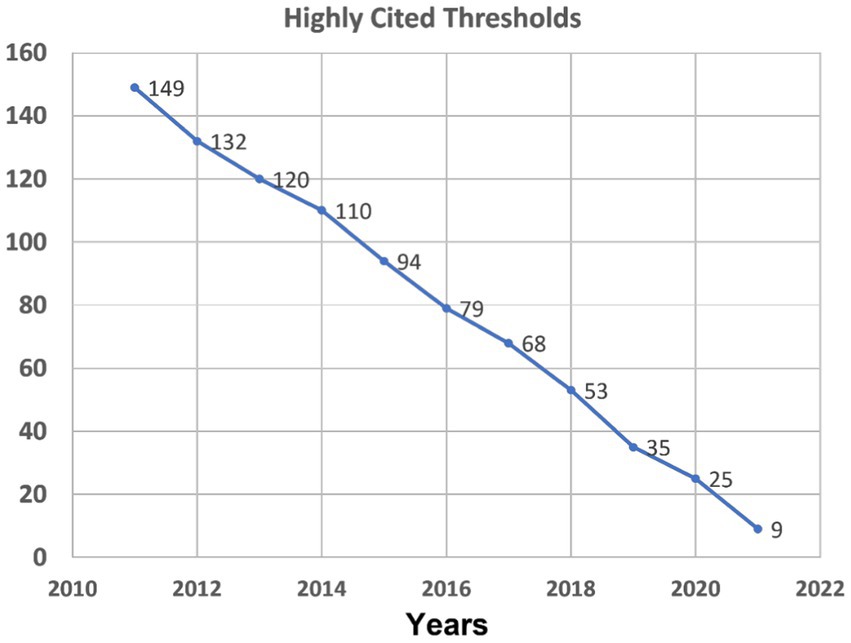
Figure 1 . Highly cited thresholds in the research field of Social Sciences, General.
3.2.2. Corpus analysis and manual checking
To determine the most frequently explored topics in these HCPs, we used both corpus-based analysis of word frequency and manual checking. Specifically, the more frequently a word or phrase occurs in a specifically designed corpus, the more likely it constitutes a research topic. In this study, we built an Abstract corpus with all the abstracts of the 143 HCPs, totaling 24,800 tokens. The procedures to retrieve the research topics in the Abstract corpus were as follows. First, the 143 pieces of abstracts were saved as separate.txt files in one folder. Second, AntConc ( Anthony, 2022 ), a corpus analysis tool for concordancing and text analysis, was employed to extract lists of n-grams (2–4) in decreasing order of frequency. We also generated a list of individual nouns because sometimes individual nouns can also constitute research topics. Considering our small corpus data, we adopted both frequency (3) and range criteria (3) for topic candidacy. That is, a candidate n-gram must occur at least 3 times and in at least 3 different abstract files. The frequency threshold guarantees the importance of the candidate topics while the range threshold guarantees that the topics are not overly crowded in a few number of publications. In this process, we actually tested the frequency and range thresholds several rounds for the inclusion of all the potential topics. In total, we obtained 531 nouns, 1,330 2-grams, 331 3-grams, and 81 4-grams. Third, because most of the retrieved n-grams cannot function as meaningful research topics, we manually checked all the candidate items and discussed extensively to decide their roles as potential research topics until full agreements were reached. Finally, we read all the abstracts of the 143 HCPs to further validate their roles as research topics. In the end, we got 118 topic items in total.
4.1. Main publication venues of HCPs
Of the 48 journals which published the 143 HCPs, 17 journals have contributed at least 3 HCPs ( Table 2 ), around 71.33% of the total examined HCPs (102/143), indicating that HCPs tend to be highly concentrated in a limited number of journals. The three largest publication outlets of HCPs are Bilingualism Language and Cognition (16), International Journal of Bilingual Education and Bilingualism (11), and Modern Language Journal (10). Because each journal varies greatly in the number of papers published per year and the number of HCPs is associated with journal circulations, we divided the total number of papers (TP) in the examined years (2011–2021) with the number of the HCPs to acquire the HCP percentage for each journal (HCPs/TP). The three journals with the highest HCPs/TP percentage are Annual Review of Applied Linguistics (2.26), Modern Language Journal (2.08), and Bilingualism Language and Cognition (1.74), indicating that papers published in these journals have a higher probability to enter the HCPs list.
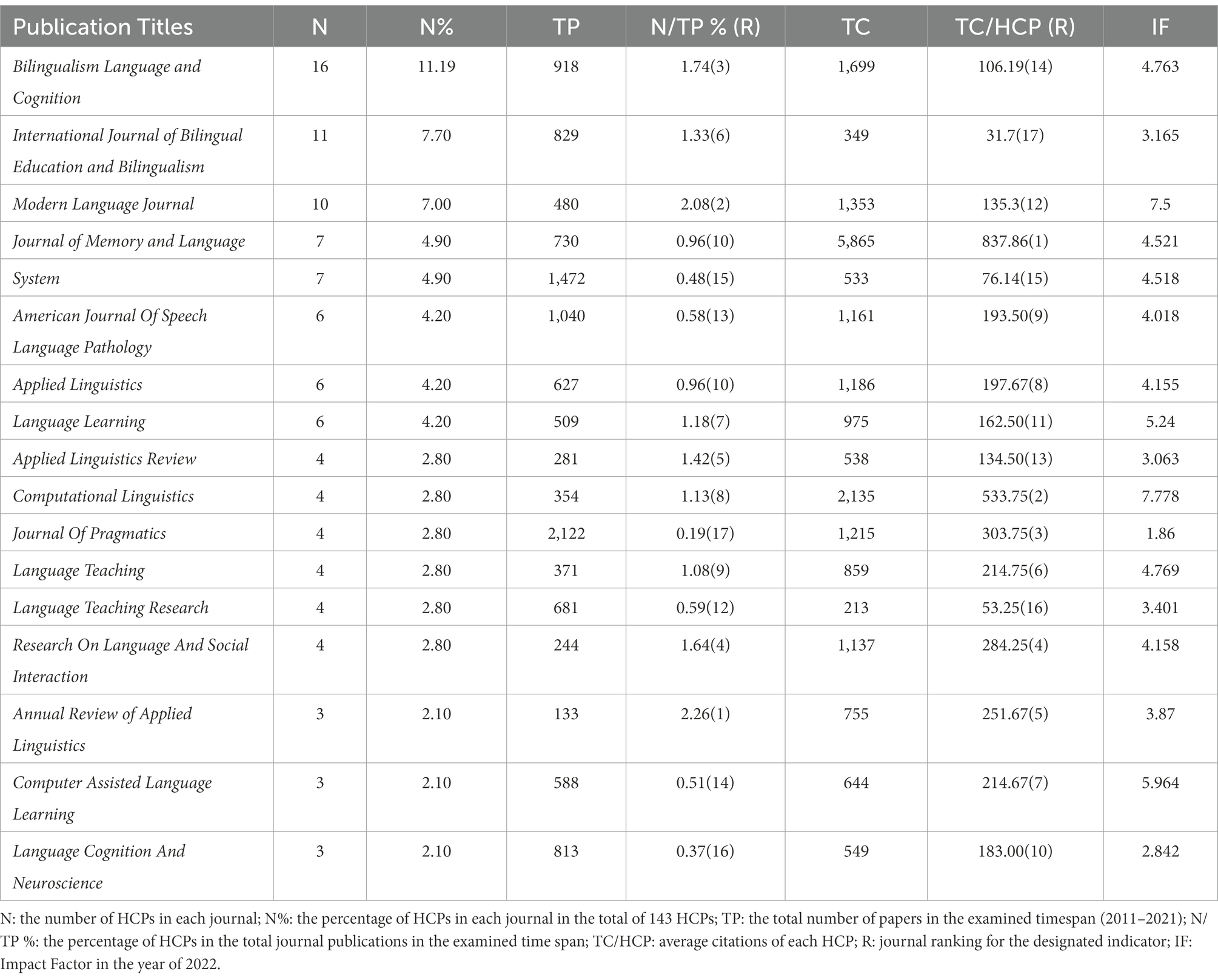
Table 2 . Top 17 publication venues of HCPs.
In terms of the general impact of the HCPs from each journal, we divided the number of HCPs with their total citations (TC) to obtain the average citations for each HCP (TC/HCP). The three journals with the highest TC/HCP are Journal of Memory and Language (837.86), Computational Linguistics (533.75), and Journal of Pragmatics (303.75). It indicates that even in the same WoS category, HCPs in different journals have strikingly different capability to accumulate citations. For example, the TC/HCP in System is as low as 31.73, which is even less than 4% of the highest TC/HCP in Journal of Memory and Language .
In regards to the latest journal impact factor (IF) in 2022, the top four journals with the highest IF are Computational Linguistics (7.778) , Modern Language Journal (7.5), Computer Assisted Language Learning (5.964), and Language Learning (5.24). According to the Journal Citation Reports (JCR) quantile rankings in WoS category of linguistics , all the journals on the list belong to the Q 1 (the top 25%), indicating that contributors are more likely to be attracted to contribute and cite papers in these prestigious high impact journals.
4.2. Authors of HCPs
A total of 352 authors had their names listed in the 143 HCPs, of whom 33 authors appeared in at least 2 HCPs as shown in Table 3 . We also provided in Table 3 other indicators to evaluate the authors’ productivity and impact including the total number of citations (TC), the number of citations per HCP, and the number of First author or Corresponding author HCPs (FA/CA). The reason we include the FA/CA indicator is that first authors and corresponding authors are usually considered to contribute the most and should receive greater proportion of credit in academic publications ( Marui et al., 2004 ; Dance, 2012 ).
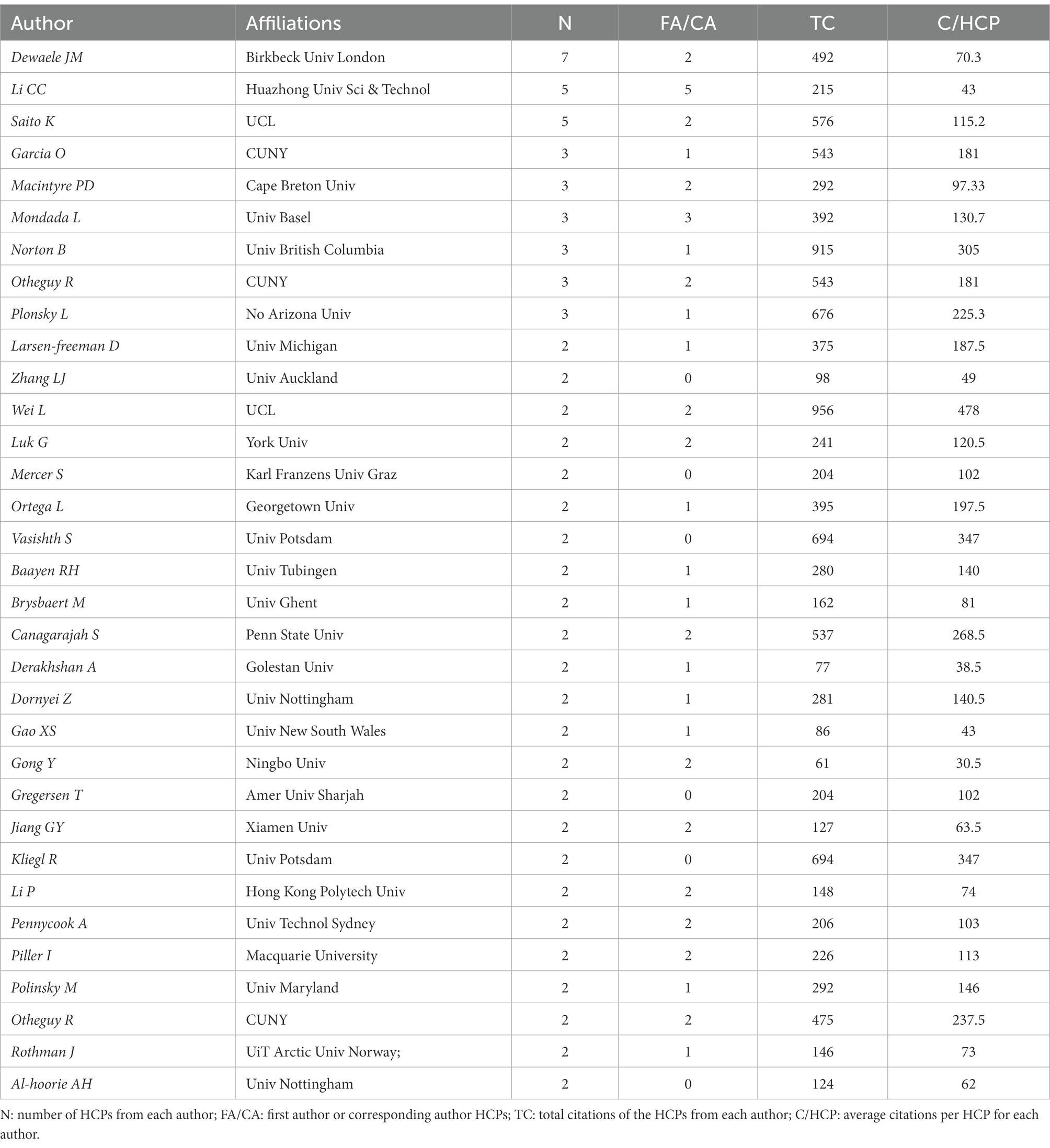
Table 3 . Authors with at least 2 HCPs.
In terms of the number of HCPs, Dewaele JM from Birkbeck Univ London tops the list with 7 HCPs with total citations of 492 (TC = 492), followed by Li C from Huazhong Univ Sci & Technol (#HCPs = 5; TC = 215) and Saito K from UCL (#HCPs = 5; TC = 576). It is to be noted that both Li C and Saito K have close academic collaborations with Dewaele JM . For example, 3 of the 5 HCPs by Li C are co-authored with Dewaele JM . The topics in their co-authored HCPs are mostly about foreign language learning emotions such as boredom , anxiety , enjoyment , the measurement , and positive psychology .
In regards to TC, Li, W . from UCL stands out as the most influential scholar among all the listed authors with total citations of 956 from 2 HCPs, followed by Norton B from Univ British Columbia (TC = 915) and Vasishth S from Univ Potsdam (TC = 694). The average citations per HCP from them are also the highest among the listed authors (478, 305, 347, respectively). It is important to note that Li, W.’ s 2 HCPs are his groundbreaking works on translanguaging which almost become must-reads for anyone who engages in translanguaging research ( Li, 2011 , 2018 ). Besides, Li, W. single authors his 2 HCPs, which is extremely rare as HCPs are often the results from multiple researchers. Norton B ’s HCPs are exploring some core issues in applied linguistics such as identity and investment , language learning , and social change that are considered the foundational work in its field ( Norton and Toohey, 2011 ; Darvin and Norton, 2015 ).
From the perspective of FA/CA papers, Li C from Huazhong Univ Sci and Technol is prominent because she is the first author of all her 5 HCPs. Her research on language learning emotions in the Chinese context is gaining widespread recognition ( Li et al., 2018 , 2019 , 2021 ; Li, 2019 , 2021 ). However, as a newly emerging researcher, most of her HCPs are published in the very recent years and hence accumulate relatively fewer citations (TC = 215). Mondada L from Univ Basel follows closely and single authors her 3 HCPs. Her work is mostly devoted to conversation analysis , multimodality , and social interaction ( Mondada, 2016 , 2018 , 2019 ).
We need to mention the following points regarding the productive authors of HCPs. First, when we calculated the number of HCPs from each author, only the papers published in the journals indexed in the investigated WoS categories were taken in account ( linguistics; language & linguistics ), which came as a compromise to protect the linguistics oriented nature of the HCPs. For example, Brysbaert M from Ghent University claimed a total of 8 HCPs at the time of the data retrieval, of which 6 HCPs were published in WoS category of psychology and more psychologically oriented, hence not included in our study. Besides, all the authors on the author list were treated equally when we calculated the number of HCPs, disregarding the author ordering. That implies that some influential authors may not be able to enter the list as their publications are comparatively fewer. Second, as some authors reported different affiliations at their different career stages, we only provide their most recent affiliation for convenience. Third, it is highly competitive to have one’s work selected as HCPs. The fact that a majority of the HCPs authors do not appear in our productive author list does not diminish their great contributions to this field. The rankings in Table 3 does not necessarily reflect the recognition authors have earned in academia at large.
4.3. Productive countries of HCPs
In total, the 143 HCPs originated from 33 countries. The most productive countries that contributed at least three HCPs are listed in Table 4 . The USA took an overwhelming lead with 59 HCPs, followed distantly by England with 31 HCPs. They also boasted the highest total citations (TC = 15,770; TC = 9,840), manifesting their high productivity and strong influence as traditional powerhouses in linguistics research. In regards to the average citations per HCP, Germany , England and the USA were the top three countries (TC/HCP = 281.67, 281.14, and 267.29, respectively). Although China held the third position with 19 HCPs published, its TC/HCP is the third from the bottom (TC/HCP = 66.84). One of the important reasons is that 13 out of the 19 HCPs contributed by scholars in China are published in the year of 2020 or 2021. The newly published HCPs may need more time to accumulate citations. Besides, 18 out of the 19 HCPs in China are first author and/or corresponding authors, indicating that scholars in China are becoming more independent and gaining more voice in English linguistics research.
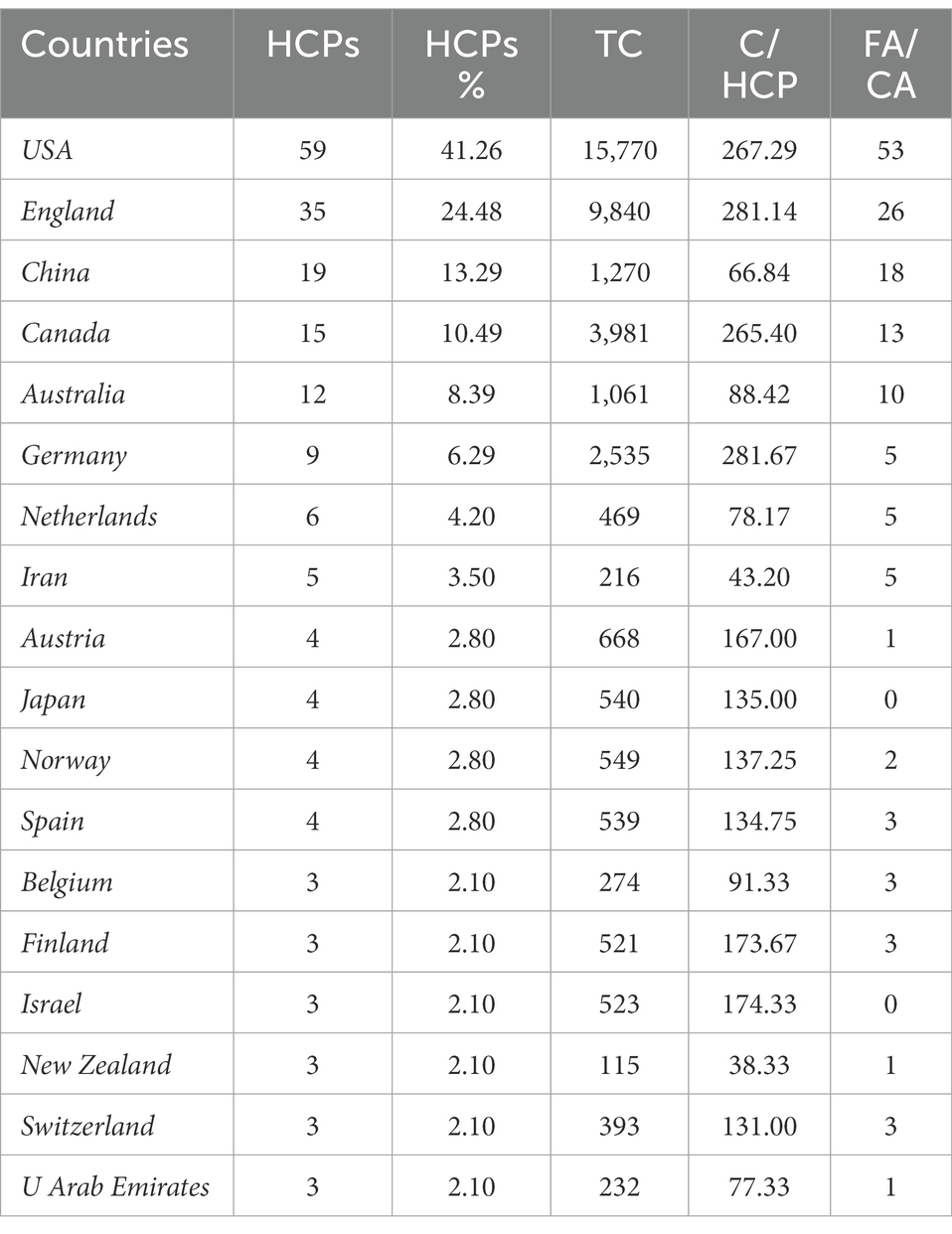
Table 4 . Top 18 countries with at least 3 HCPs.
Two points should be noted here as to the productive countries. First, we calculated the HCP contributions from the country level instead of the region level. In other words, HCP contributions from different regions of the same country will be combined in the calculation. For example, HCPs from Scotland were added to the HCPs from England . HCPs from Hong Kong , Macau , and Taiwan are put together with the HCPs from Mainland China . In this way, a clear picture of the HCPs on the country level can be painted. Second, we manually checked the address information of the first author and corresponding author for each HCP. There are some cases where the first author or the corresponding author may report affiliations from more than one country. In this case, every country in their address list will be treated equally in the FA/CA calculation. In other word, a HCP may be classified into more than one country because of the different country backgrounds of the first and/or the corresponding author.
4.4. Top 20 HCPs
The top 20 HCPs with the highest normed citations are listed in decreasing order in Table 5 . The top cited publications can guide us to better understand the development and research topics in recent years.
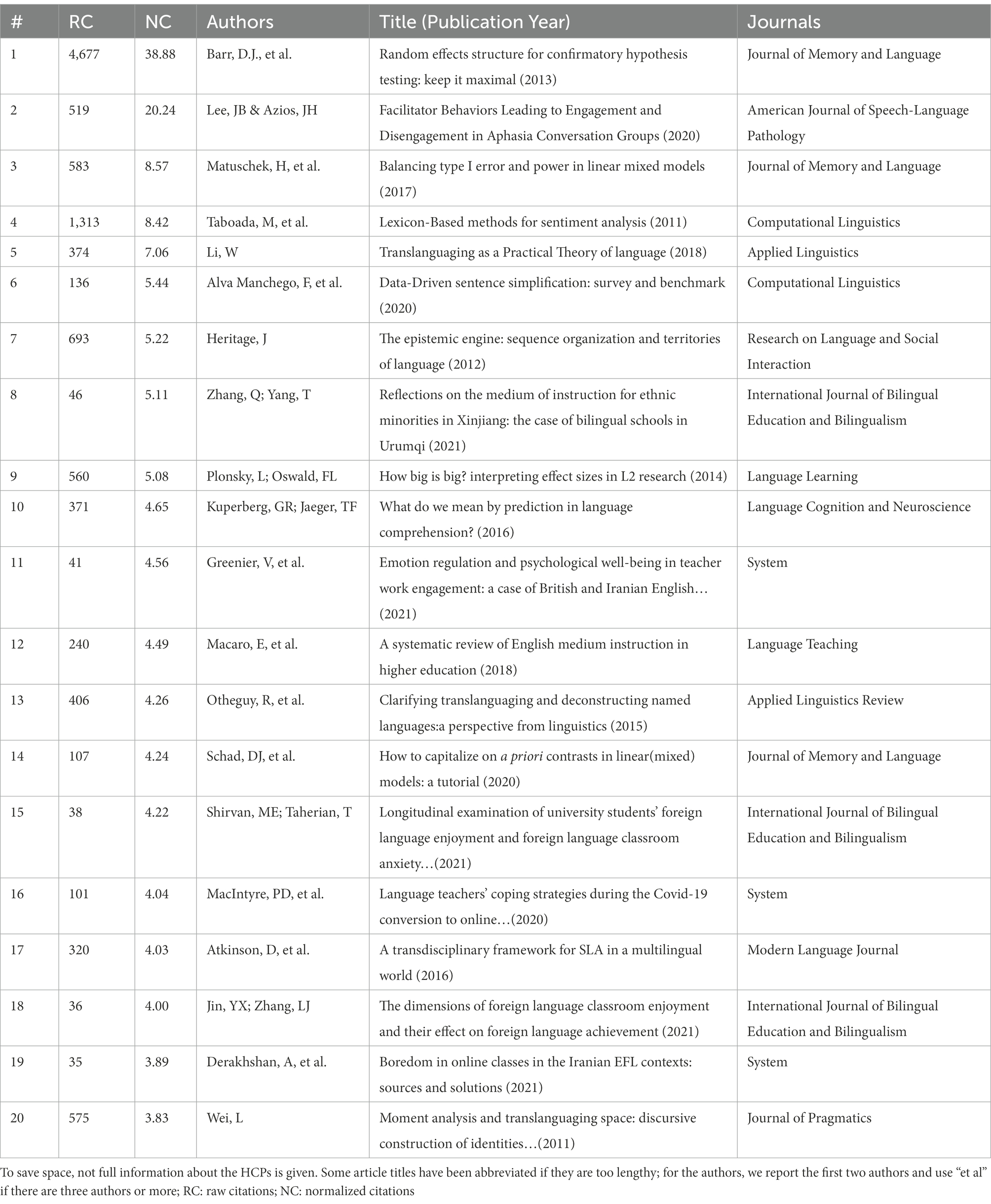
Table 5 . Top 20 HCPs.
By reading the titles and the abstracts of these top HCPs, we categorized the topics of the 20 HCPs into the following five groups: (i) statistical and analytical methods in (psycho)linguistics such as sentimental analysis, sentence simplification techniques, effect sizes, linear mixed models (#1, 3, 4, 6, 9, 14), (ii) language learning/teaching emotions such enjoyment, anxiety, boredom, stress (#11, 15, 16, 18, 19), (iii) translanguaging or multilinguilism (#5, 13, 20, 17), (iv) language perception (#2, 7, 10), (v) medium of instruction (#8, 12). It is no surprise that 6 out of the top 20 HCPs are about statistical methods in linguistics because language researchers aspire to employ statistics to make their research more scientific. Besides, we noticed that the papers on language teaching/learning emotions on the list are all published in the year of 2020 and 2021, indicating that these emerging topics may deserve more attention in future research. We also noticed two Covid-19 related articles (#16, 19) explored the emotions teachers and students experience during the pandemic, a timely response to the urgent need of the language learning and teaching community.
It is of special interest to note that papers from the journals indexed in multiple JCR categories seem to accumulate more citations. For example, Journal of Memory and Language , American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology , and Computational Linguistics are indexed both in SSCI and SCIE and contribute the top 4 HCPs, manifesting the advantage of these hybrid journals in amassing citations compared to the conventional language journals. Besides, different to findings from Yan et al. (2022) that most of the top HCPs in the field of radiology are reviews in document types, 19 out of the top 20 HCPs are research articles instead of reviews except Macaro et al. (2018) .
4.5. Most frequently explored topics of HCPs
After obtaining the corpus based topic items, we read all the titles and abstracts of the 143 HCPs to further validate their roles as research topics. Table 6 presents the top research topics with the observed frequency of 5 or above. We grouped these topics into five broad categories: bilingual-related, language learning/teaching-related, psycho/pathological/cognitive linguistics-related, methods and tools-related, and others . The observed frequency count for each topic in the abstract corpus were included in the brackets. We found that about 34 of the 143 HCPs are exploring bilingual related issues, the largest share among all the categorized topics, testifying its academic popularity in the examined timespan. Besides, 30 of the 143 HCPs are investigating language learning/teaching-related issues, with topics ranging from learners (e.g., EFL learners, individual difference) to multiple learning variables (e.g., learning strategy, motivation, agency). The findings here will be validated by the analysis of the keywords.
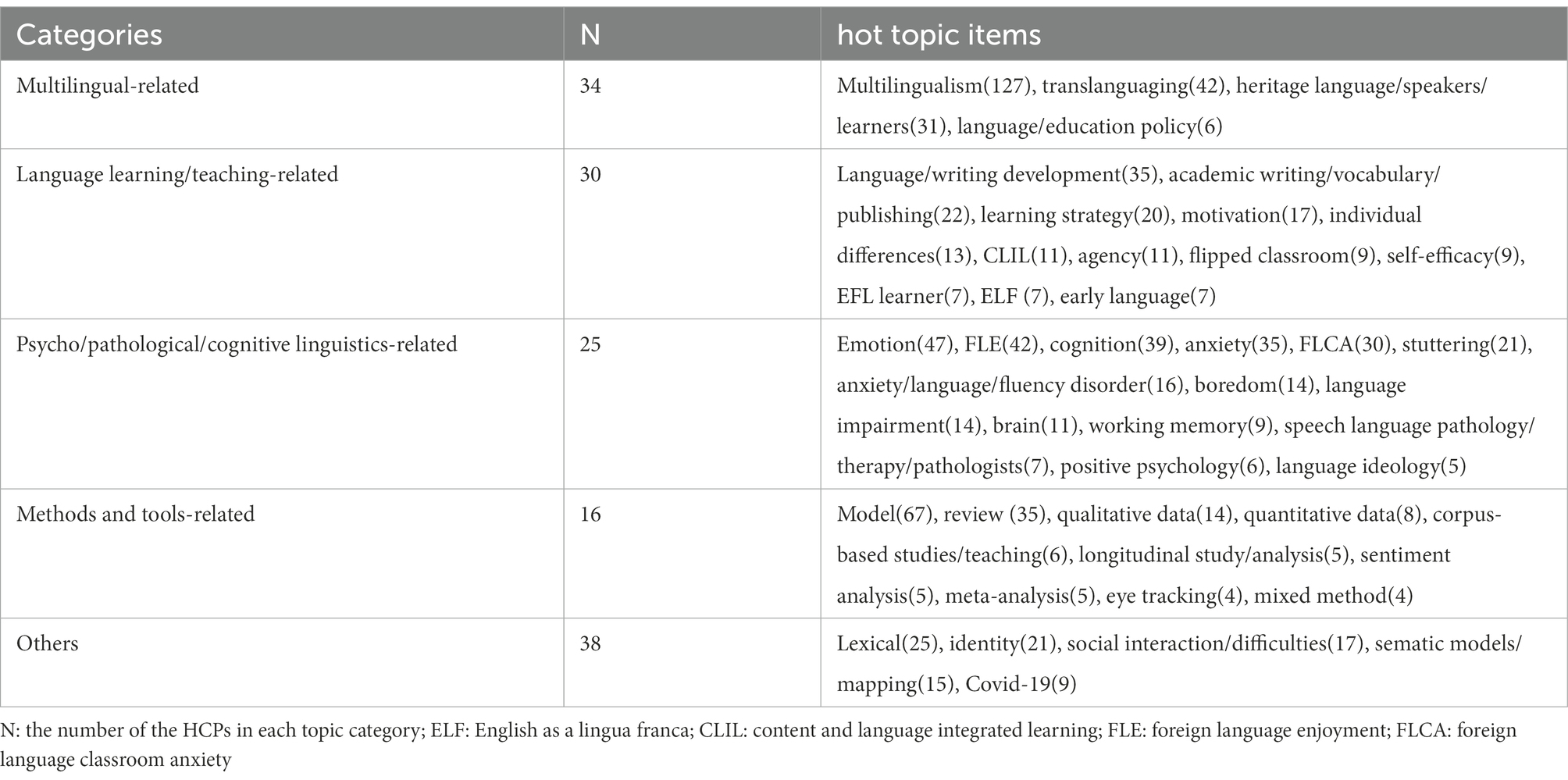
Table 6 . Categorization of the most explored research topics.
Several points should be mentioned regarding the topic candidacy. First, for similar topic expressions, we used a cover term and added the frequency counts. For example, multilingualism is a cover term for bilinguals, bilingualism, plurilingualism, and multilingualism . Second, for nouns of singular and plural forms (e.g., emotion and emotions ) or for items with different spellings (e.g., meta analysis and meta analyses ), we combined the frequency counts. Third, we found that some longer items (3 grams and 4 grams) could be subsumed to short ones (2 grams or monogram) without loss of essential meaning (e.g., working memory from working memory capacity ). In this case, the shorter ones were kept for their higher frequency. Fourth, some highly frequent terms were discarded because they were too general to be valuable topics in language research, for example, applied linguistics , language use , second language .
5. Discussion and implications
Based on 143 highly cited papers collected from the WoS categories of linguistics , the present study attempts to present a bird’s eye view of the publication landscape and the most updated research themes reflected from the HCPs in the linguistics field. Specifically, we investigated the important contributors of HCPs in terms of journals, authors and countries. Besides, we spotlighted the research topics by corpus-based analysis of the abstracts and a detailed analysis of the top HCPs. The study has produced several findings that bear important implications.
The first finding is that the HCPs are highly concentrated in a limited journals and countries. In regards to journals, those in the spheres of bilingualism and applied linguistics (e.g., language teaching and learning) are likely to accumulate more citations and hence to produce more HCPs. Journals that focus on bilingualism from a linguistic, psycholinguistic, and neuroscientific perspective are the most frequent outlets of HCPs as evidenced by the top two productive journals of HCPs, Bilingualism Language and Cognition and International Journal of Bilingual Education and Bilingualism . This can be explained by the multidisciplinary nature of bilingual-related research and the development of cognitive measurement techniques. The merits of analyzing publication venues of HCPs are two folds. One the one hand, it can point out which sources of high-quality publications in this field can be inquired for readers as most of the significant and cutting-edge achievements are concentrated in these prestigious journals. On the other hand, it also provides essential guidance or channels for authors or contributors to submit their works for higher visibility.
In terms of country distributions, the traditional powerhouses in linguistics research such as the USA and England are undoubtedly leading the HCP publications in both the number and the citations of the HCPs. However, developing countries are also becoming increasing prominent such as China and Iran , which could be traceable in the funding and support of national language policies and development policies as reported in recent studies ( Ping et al., 2009 ; Lei and Liu, 2019 ). Take China as an example. Along with economic development, China has given more impetus to academic outputs with increased investment in scientific research ( Lei and Liao, 2017 ). Therefore, researchers in China are highly motivated to publish papers in high-quality journals to win recognition in international academia and to deal with the publish or perish pressure ( Lee, 2014 ). These factors may explain the rise of China as a new emerging research powerhouse in both natural and social sciences, including English linguistics research.
The second finding is the multilingual trend in linguistics research. The dominant clustering of topics regarding multilingualism can be understood as a timely response to the multilingual research fever ( May, 2014 ). 34 out of the 143 HCPs have such words as bilingualism, bilingual, multilingualism , translanguaging , etc., in their titles, reflecting a strong multilingual tendency of the HCPs. Multilingual-related HCPs mainly involve three aspects: multilingualism from the perspectives of psycholinguistics and cognition (e.g., Luk et al., 2011 ; Leivada et al., 2020 ); multilingual teaching (e.g., Schissel et al., 2018 ; Ortega, 2019 ; Archila et al., 2021 ); language policies related to multilingualism (e.g., Shen and Gao, 2018 ). As a pedagogical process initially used to describe the bilingual classroom practice and also a frequently explored topic in HCPs, translanguaging is developed into an applied linguistics theory since Li’s Translanguaging as a Practical Theory of Language ( Li, 2018 ). The most common collocates of translanguaging in the Abstract corpus are pedagogy/pedagogies, practices, space/spaces . There are two main reasons for this multilingual turn. First, the rapid development of globalization, immigration, and overseas study programs greatly stimulate the use and research of multiple languages in different linguistic contexts. Second, in many non-English countries, courses are delivered through languages (mostly English) besides their mother tongue ( Clark, 2017 ). Students are required to use multiple languages as resources to learn and understand subjects and ideas. The burgeoning body of English Medium Instruction literature in higher education is in line with the rising interest in multilingualism. Due to the innate multidisciplinary nature, it is to be expected that, multilingualism, the topic du jour, is bound to attract more attention in the future.
The third finding is the application of Positive Psychology (PP) in second language acquisition (SLA), that is, the positive trend in linguistic research. In our analysis, 20 out of 143 HCPs have words or phrases such as emotions, enjoyment, boredom, anxiety , and positive psychology in their titles, which might signal a shift of interest in the psychology of language learners and teachers in different linguistic environments. Our study shows Foreign language enjoyment (FLE) is the most frequently explored emotion, followed by foreign language classroom anxiety (FLCA), the learners’ metaphorical left and right feet on their journey to acquiring the foreign language ( Dewaele and MacIntyre, 2016 ). In fact, the topics of PP are not entirely new to SLA. For example, studies of language motivations, affections, and good language learners all provide roots for the emergence of PP in SLA ( Naiman, 1978 ; Gardner, 2010 ). In recent years, both research and teaching applications of PP in SLA are building rapidly, with a diversity of topics already being explored such as positive education and PP interventions. It is to be noted that SLA also feeds back on PP theories and concepts besides drawing inspirations from it, which makes it “an area rich for interdisciplinary cross-fertilization of ideas” ( Macintyre et al., 2019 ).
It should be noted that subjectivity is involved when we decide and categorize the candidate topic items based on the Abstract corpus. However, the frequency and range criteria guarantee that these items are actually more explored in multiple HCPs, thus indicating topic values for further investigation. Some high frequent n-grams are abandoned because they are too general or not meaningful topics. For example, applied linguistics is too broad to be included as most of the HCPs concern issues in this research line instead of theoretical linguistics. By meaningful topics, we mean that the topics can help journal editors and readers quickly locate their interested fields ( Lei and Liu, 2019 ), as the author keywords such as bilingualism , emotions , and individual differences . The examination of the few 3/4-grams and monograms (mostly nouns) revealed that most of them were either not meaningful topics or they could be subsumed in the 2-grams. Besides, there is inevitably some overlapping in the topic categorizations. For example, some topics in the language teaching and learning category are situated and discussed within the context of multilingualism. The merits of topic categorizations are two folds: to better monitor the overlapping between the Abstract corpus-based topic items and the keywords; to roughly delineate the research strands in the HCPs for future research.
It should also be noted that all the results were based on the retrieved HCPs only. The study did not aim to paint a comprehensive and full picture of the whole landscape of linguistic research. Rather, it specifically focused on the most popular literature in a specified timeframe, thus generating the snapshots or trends in linguistic research. One of the important merits of this methodology is that some newly emerging but highly cited researchers can be spotlighted and gain more academic attention because only the metrics of HCPs are considered in calculation. On the contrary, the exclusion of some other highly cited researchers in general such as Rod Ellis and Ken Hyland just indicates that their highly cited publications are not within our investigated timeframe and cannot be interpreted as their diminishing academic influence in the field. Besides, the study does not consider the issue of collaborators or collaborations in calculating the number of HCPs for two reasons. First, although some researchers are regular collaborators such as Li CC and Dewaele JM, their individual contribution can never be undermined. Second, the study also provides additional information about the number of the FA/CA HCPs from each listed author, which may aid readers in locating their interested research.
We acknowledge that our study has some limitations that should be addressed in future research. First, our study focuses on the HCPs extracted from WoS SSCI and A&HCI journals, the alleged most celebrated papers in this field. Future studies may consider including data from other databases such as Scopus to verify the findings of the present study. Second, our Abstract corpus-based method for topic extraction involved human judgement. Although the final list was the result of several rounds of discussions among the authors, it is difficult or even impossible to avoid subjectivity and some worthy topics may be unconsciously missed. Therefore, future research may consider employing automatic algorithms to extract topics. For example, a dependency-based machine learning approach can be used to identify research topics ( Zhu and Lei, 2021 ).
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/ supplementary material .
Author contributions
SY: conceptualization and methodology. SY and LZ: writing-review and editing and writing-original draft. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
This work was supported by Humanities and Social Sciences Youth Fund of China MOE under the grant 20YJC740076 and 18YJC740141.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1052586/full#supplementary-material
Aksnes, D. W. (2003). Characteristics of highly cited papers. Res. Eval. 12, 159–170. doi: 10.3152/147154403781776645
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Anthony, L. (2022). AntConc (version 4.0.5) Tokyo, Japan: Waseda University. Available at: https://www.laurenceanthony.net/software (Accessed June 20, 2022).
Google Scholar
Archila, P. A., Molina, J., and Truscott de Mejía, A.-M. (2021). Fostering bilingual scientific writing through a systematic and purposeful code-switching pedagogical strategy. Int. J. Biling. Educ. Biling. 24, 785–803. doi: 10.1080/13670050.2018.1516189
Blessinger, K., and Hrycaj, P. (2010). Highly cited articles in library and information science: an analysis of content and authorship trends. Libr. Inf. Sci. Res. 32, 156–162. doi: 10.1016/j.lisr.2009.12.007
Chen, H., and Ho, Y. S. (2015). Highly cited articles in biomass research: a bibliometric analysis. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 49, 12–20. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.04.060
Clark, S. (2017). Translanguaging in higher education: beyond monolingual ideologies. Int. J. Biling. Educ. Biling. 22, 1048–1051. doi: 10.1080/13670050.2017.1322568
Dance, A. (2012). Authorship: Who’s on first? Nature 489, 591–593. doi: 10.1038/nj7417-591a
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Danell, R. (2011). Can the quality of scientific work be predicted using information on the author’s track record? J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 62, 50–60. doi: 10.1002/asi.21454
Darvin, R., and Norton, B. (2015). Identity and a model of Investment in Applied Linguistics. Annu. Rev. Appl. Linguist. 35, 36–56. doi: 10.1017/S0267190514000191
Dewaele, J.-M., and MacIntyre, P. D. (2016). “Foreign language enjoyment and foreign language classroom anxiety: the right and left feet of the language learner” in Positive psychology in SLA . eds. D. M. Peter, G. Tammy, and M. Sarah (Bristol, Blue Ridge Summit: Multilingual Matters), 215–236.
Gardner, R. (2010). Motivation and second language acquisition: The socio-educational model . New York: Peter Lang.
Gong, Y., Lyu, B., and Gao, X. (2018). Research on teaching Chinese as a second or foreign language in and outside mainland China: a bibliometric analysis. Asia Pac. Educ. Res. 27, 277–289. doi: 10.1007/s40299-018-0385-2
Hsu, Y., and Ho, Y. S. (2014). Highly cited articles in health care sciences and services field in science citation index Expanded. Methods Inf. Med. 53, 446–458. doi: 10.3414/ME14-01-0022
Lee, I. (2014). Publish or perish: the myth and reality of academic publishing. Lang. Teach. 47, 250–261. doi: 10.1017/S0261444811000504
Lei, L., and Liao, S. (2017). Publications in linguistics journals from mainland China, Hong Kong, Taiwan, and Macau (2003–2012): a bibliometric analysis. J. Quant. Ling. 24, 54–64. doi: 10.1080/09296174.2016.1260274
Lei, L., and Liu, D. (2018). The research trends and contributions of System’s publications over the past four decades (1973–2017): a bibliometric analysis. System 80, 1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.system.2018.10.003
Lei, L., and Liu, D. (2019). Research trends in applied linguistics from 2005 to 2016: a bibliometric analysis and its implications. Appl. Linguis. 40, 540–561. doi: 10.1093/applin/amy003
Leivada, E., Westergaard, M., Duabeitia, J. A., and Rothman, J. (2020). On the phantom-like appearance of bilingualism effects on neurocognition: (how) should we proceed? Biling. Lang. Congn. 24, 197–210. doi: 10.1017/S1366728920000358
Li, W. (2011). Moment analysis and translanguaging space: discursive construction of identities by multilingual Chinese youth in Britain. Energy Fuel 43, 1222–1235. doi: 10.1016/j.pragma.2010.07.035
Li, W. (2018). Translanguaging as a practical theory of language. Appl. Linguis. 39, 9–30. doi: 10.1093/applin/amx039
Li, C. (2019). A positive psychology perspective on Chinese EFL students’ trait emotional intelligence, foreign language enjoyment and EFL learning achievement. J. Multiling. Multicult. Dev. 41, 246–263. doi: 10.1080/01434632.2019.1614187
Li, C. (2021). A control-value theory approach to boredom in English classes among university students in China. Mod. Lang. J. 105, 317–334. doi: 10.1111/modl.12693
Li, C., Dewaele, J. M., and Hu, Y. (2021). Foreign language learning boredom: conceptualization and measurement. Appl. Ling. Rev. doi: 10.1515/applirev-2020-0124
Li, C., Dewaele, J. M., and Jiang, G. (2019). The complex relationship between classroom emotions and EFL achievement in China. Appl. Ling. Rev. 11, 485–510. doi: 10.1515/applirev-2018-0043
Li, C., Jiang, G., and Jean-Marc, D. (2018). Understanding Chinese high school students’ foreign language enjoyment: validation of the Chinese version of the foreign language enjoyment scale. System 76, 183–196. doi: 10.1016/j.system.2018.06.004
Liao, S., and Lei, L. (2017). What we talk about when we talk about corpus: a bibliometric analysis of corpus-related research in linguistics (2000-2015). Glottometrics 38, 1–20.
Liao, H., Tang, M., Li, Z., and Lev, B. (2018). Bibliometric analysis for highly cited papers in operations research and management science from 2008 to 2017 based on essential science indicators. Omega 88, 223–236. doi: 10.1016/j.omega.2018.11.005
Luk, G., Sa, E. D., and Bialystok, E. (2011). Is there a relation between onset age of bilingualism and enhancement of cognitive control? Biling. Lang. Cogn. 14, 588–595. doi: 10.1017/S1366728911000010
Macaro, E., Curle, S., Pun, J., and Dearden, J. (2018). A systematic review of English medium instruction in higher education. Lang. Teach. 51, 36–76. doi: 10.1017/S0261444817000350
Macintyre, P., Gregersen, T., and Mercer, S. (2019). Setting an agenda for positive psychology in SLA: theory, practice, and research. Mod. Lang. J. 103, 262–274. doi: 10.1111/modl.12544
Mancebo, F. P., Sapena, A. F., Herrera, M. V., González, L., Toca, H., and Benavent, R. A. (2013). Scientific literature analysis of judo in web of science. Arch. Budo 9, 81–91. doi: 10.12659/AOB.883883
Marui, M., Bozikov, J., Katavi, V., Hren, D., Kljakovi-Gapi, M., and Marui, A. (2004). Authorship in a small medical journal: a study of contributorship statements by corresponding authors. Sci. Eng. Ethics 10, 493–502. doi: 10.1007/s11948-004-0007-7
May, S. (2014). The multilingual turn: Implications for SLA, TESOL and bilingual education . New York: Routledge.
Mondada, L. (2016). Challenges of multimodality: language and the body in social interaction. J. Socioling. 20, 336–366. doi: 10.1111/josl.1_12177
Mondada, L. (2018). Multiple temporalities of language and body in interaction: challenges for transcribing multimodality. Res. Lang. Soc. Interact. 51, 85–106. doi: 10.1080/08351813.2018.1413878
Mondada, L. (2019). Contemporary issues in conversation analysis: embodiment and materiality, multimodality and multisensoriality in social interaction. J. Pragmat. 145, 47–62. doi: 10.1016/j.pragma.2019.01.016
Naiman, N. (1978). The good language learner . Clevedon, UK: Multilingual Matters.
Newman, M. (2008). The first-mover advantage in scientific publication. Eplasty 86, 68001–68006. doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/86/68001
Newman, M. (2014). Prediction of highly cited papers. Eplasty 105:28002. doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/105/28002
Norton, B., and Toohey, K. (2011). Identity, language learning, and social change. Lang. Teach. 44, 412–446. doi: 10.1017/S0261444811000309
Ortega, L. (2019). SLA and the study of equitable multilingualism. Mod. Lang. J. 103, 23–38. doi: 10.1111/modl.12525
Ping, Z., Thijs, B., and Glnzel, W. (2009). Is China also becoming a giant in social sciences? Scientometrics 79, 593–621. doi: 10.1007/s11192-007-2068-x
Pritchard, A. (1969). Statistical bibliography or bibliometrics. J. Doc. 25, 348–349.
Ríos, L. J. C., Tamao, I. M., and Olmos, J. (2013). Bibliometric study (1922-2009) on rugby articles in research journals. South Afr. J. Res. Sport Phys. Educ. Rec. 17, 313–109. doi: 10.3176/tr.2013.3.06
Ruggeri, G., Orsi, L., and Corsi, S. (2019). A bibliometric analysis of the scientific literature on Fairtrade labelling. Int. IJC 43, 134–152. doi: 10.1111/ijcs.12492
Sabiote, C. R., and Rodríguez, J. A. (2015). Bibliometric study and methodological quality indicators of the journal porta Linguarum during six year period 2008-2013. Porta Ling. 24, 135–150. doi: 10.30827/Digibug.53866
Schissel, J. L., De Korne, H., and López-Gopar, M. E. (2018). Grappling with translanguaging for teaching and assessment in culturally and linguistically diverse contexts: teacher perspectives from Oaxaca, Mexico. Int. J. Biling. Educ. Biling. 24, 340–356. doi: 10.1080/13670050.2018.1463965
Shen, Q., and Gao, X. (2018). Multilingualism and policy making in greater China: ideological and implementational spaces. Lang. Policy 18, 1–16. doi: 10.1007/s10993-018-9473-7
Small, H. (2004). Why authors think their papers are highly cited. Scientometrics 60, 305–316. doi: 10.1023/B:SCIE.0000034376.55800.18
Smith, D. R. (2007). The New Zealand timber economy, 1840–1935. N. Z. Med. J. 120, U2871–U2313. doi: 10.1016/0305-7488(90)90044-C
van Doorslaer, L., and Gambier, Y. (2015). Measuring relationships in translation studies. On affiliations and keyword frequencies in the translation studies bibliography. Perspectives 23, 305–319. doi: 10.1080/0907676X.2015.1026360
van Oorschot, J. A. W. H., Hofman, E., and Halman, J. (2018). A bibliometric review of the innovation adoption literature. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 134, 1–21. doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2018.04.032
Xie, Z., and Willett, P. (2013). The development of computer science research in the People’s republic of China 2000–2009: a bibliometric study. Inf. Dev. 29, 251–264. doi: 10.1177/0266666912458515
Yan, S., Zhang, H., and Wang, J. (2022). Trends and hot topics in radiology, nuclear medicine and medical imaging from 2011–2021: a bibliometric analysis of highly cited papers. Jpn. J. Radiol. 40, 847–856. doi: 10.1007/s11604-022-01268-z
Zhu, H., and Lei, L. (2021). A dependency-based machine learning approach to the identification of research topics: a case in COVID-19 studies. Lib. Hi Tech 40, 495–515. doi: 10.1108/LHT-01-2021-0051
Zhu, H., and Lei, L. (2022). The research trends of text classification studies (2000–2020): a bibliometric analysis. SAGE Open 12, 215824402210899–215824402210816. doi: 10.1177%2F21582440221089963
Keywords: bibliometric analysis, linguistics, highly cited papers, corpus analysis, research trends
Citation: Yan S and Zhang L (2023) Trends and hot topics in linguistics studies from 2011 to 2021: A bibliometric analysis of highly cited papers. Front. Psychol . 13:1052586. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1052586
Received: 24 September 2022; Accepted: 23 December 2022; Published: 11 January 2023.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2023 Yan and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Le Zhang, ✉ [email protected]
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Topics – Ideas and Examples
Research Topics – Ideas and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Topic
Definition:
Research topic is a specific subject or area of interest that a researcher wants to investigate or explore in-depth through research. It is the overarching theme or question that guides a research project and helps to focus the research activities towards a clear objective.
How to Choose Research Topic
You can Choose a Research Topic by following the below guide:
Identify your Interests
One of the most important factors to consider when choosing a research topic is your personal interest. This is because you will be spending a considerable amount of time researching and writing about the topic, so it’s essential that you are genuinely interested and passionate about it. Start by brainstorming a list of potential research topics based on your interests, hobbies, or areas of expertise. You can also consider the courses that you’ve enjoyed the most or the topics that have stood out to you in your readings.
Review the Literature
Before deciding on a research topic, you need to understand what has already been written about it. Conducting a preliminary review of the existing literature in your field can help you identify gaps in knowledge, inconsistencies in findings, or unanswered questions that you can explore further. You can do this by reading academic articles, books, and other relevant sources in your field. Make notes of the themes or topics that emerge and use this information to guide your research question.
Consult with your Advisor
Your academic advisor or a mentor in your field can provide you with valuable insights and guidance on choosing a research topic. They can help you identify areas of interest, suggest potential research questions, and provide feedback on the feasibility of your research proposal. They can also direct you towards relevant literature and resources that can help you develop your research further.
Consider the Scope and Feasibility
The research topic you choose should be manageable within the time and resource constraints of your project. Be mindful of the scope of your research and ensure that you are not trying to tackle a topic that is too broad or too narrow. If your topic is too broad, you may find it challenging to conduct a comprehensive analysis, while if it’s too narrow, you may struggle to find enough material to support your research.
Brainstorm with Peers
Discussing potential research topics with your peers or colleagues can help you generate new ideas and perspectives. They may have insights or expertise that you haven’t considered, and their feedback can help you refine your research question. You can also join academic groups or attend conferences in your field to network with other researchers and get inspiration for your research.
Consider the Relevance
Choose a research topic that is relevant to your field of study and has the potential to contribute to the existing knowledge. You can consider the latest trends and emerging issues in your field to identify topics that are both relevant and interesting. Conducting research on a topic that is timely and relevant can also increase the likelihood of getting published or presenting your research at conferences.
Keep an Open Mind
While it’s essential to choose a research topic that aligns with your interests and expertise, you should also be open to exploring new ideas or topics that may be outside of your comfort zone. Consider researching a topic that challenges your assumptions or introduces new perspectives that you haven’t considered before. You may discover new insights or perspectives that can enrich your research and contribute to your growth as a researcher.
Components of Research Topic
A research topic typically consists of several components that help to define and clarify the subject matter of the research project. These components include:
- Research problem or question: This is the central issue or inquiry that the research seeks to address. It should be well-defined and focused, with clear boundaries that limit the scope of the research.
- Background and context: This component provides the necessary background information and context for the research topic. It explains why the research problem or question is important, relevant, and timely. It may also include a literature review that summarizes the existing research on the topic.
- Objectives or goals : This component outlines the specific objectives or goals that the research seeks to achieve. It should be clear and concise, and should align with the research problem or question.
- Methodology : This component describes the research methods and techniques that will be used to collect and analyze data. It should be detailed enough to provide a clear understanding of how the research will be conducted, including the sampling method, data collection tools, and statistical analyses.
- Significance or contribution : This component explains the significance or contribution of the research topic. It should demonstrate how the research will add to the existing knowledge in the field, and how it will benefit practitioners, policymakers, or society at large.
- Limitations: This component outlines the limitations of the research, including any potential biases, assumptions, or constraints. It should be transparent and honest about the potential shortcomings of the research, and how these limitations will be addressed.
- Expected outcomes or findings : This component provides an overview of the expected outcomes or findings of the research project. It should be realistic and based on the research objectives and methodology.
Purpose of Research Topic
The purpose of a research topic is to identify a specific area of inquiry that the researcher wants to explore and investigate. A research topic is typically a broad area of interest that requires further exploration and refinement through the research process. It provides a clear focus and direction for the research project, and helps to define the research questions and objectives. A well-defined research topic also helps to ensure that the research is relevant and useful, and can contribute to the existing body of knowledge in the field. Ultimately, the purpose of a research topic is to generate new insights, knowledge, and understanding about a particular phenomenon, issue, or problem.
Characteristics of Research Topic
some common characteristics of a well-defined research topic include:
- Relevance : A research topic should be relevant and significant to the field of study and address a current issue, problem, or gap in knowledge.
- Specificity : A research topic should be specific enough to allow for a focused investigation and clear understanding of the research question.
- Feasibility : A research topic should be feasible, meaning it should be possible to carry out the research within the given constraints of time, resources, and expertise.
- Novelty : A research topic should add to the existing body of knowledge by introducing new ideas, concepts, or theories.
- Clarity : A research topic should be clearly articulated and easy to understand, both for the researcher and for potential readers of the research.
- Importance : A research topic should be important and have practical implications for the field or society as a whole.
- Significance : A research topic should be significant and have the potential to generate new insights and understanding in the field.
Examples of Research Topics
Here are some examples of research topics that are currently relevant and in-demand in various fields:
- The impact of social media on mental health: With the rise of social media use, this topic has gained significant attention in recent years. Researchers could investigate how social media affects self-esteem, body image, and other mental health concerns.
- The use of artificial intelligence in healthcare: As healthcare becomes increasingly digitalized, researchers could explore the use of AI algorithms to predict and prevent disease, optimize treatment plans, and improve patient outcomes.
- Renewable energy and sustainable development: As the world seeks to reduce its carbon footprint, researchers could investigate the potential of renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power, and how these technologies can be integrated into existing infrastructure.
- The impact of workplace diversity and inclusion on employee productivity: With an increasing focus on diversity and inclusion in the workplace, researchers could investigate how these factors affect employee morale, productivity, and retention.
- Cybersecurity and data privacy: As data breaches and cyber attacks become more common, researchers could explore new methods of protecting sensitive information and preventing malicious attacks.
- T he impact of mindfulness and meditation on stress reduction: As stress-related health issues become more prevalent, researchers could investigate the effectiveness of mindfulness and meditation practices on reducing stress and improving overall well-being.
Research Topics Ideas
Here are some Research Topics Ideas from different fields:
- The impact of social media on mental health and well-being.
- The effectiveness of various teaching methods in improving academic performance in high schools.
- The role of AI and machine learning in healthcare: current applications and future potentials.
- The impact of climate change on wildlife habitats and conservation efforts.
- The effects of video game violence on aggressive behavior in young adults.
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based stress reduction techniques in reducing anxiety and depression.
- The impact of technology on human relationships and social interactions.
- The role of exercise in promoting physical and mental health in older adults.
- The causes and consequences of income inequality in developed and developing countries.
- The effects of cultural diversity in the workplace on job satisfaction and productivity.
- The impact of remote work on employee productivity and work-life balance.
- The relationship between sleep patterns and cognitive functioning.
- The effectiveness of online learning versus traditional classroom learning.
- The role of government policies in promoting renewable energy adoption.
- The effects of childhood trauma on mental health in adulthood.
- The impact of social media on political participation and civic engagement.
- The effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy in treating anxiety disorders.
- The relationship between nutrition and cognitive functioning.
- The impact of gentrification on urban communities.
- The effects of music on mood and emotional regulation.
- The impact of microplastics on marine ecosystems and food webs.
- The role of artificial intelligence in detecting and preventing cyberattacks.
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions in managing chronic pain.
- The relationship between personality traits and job satisfaction.
- The effects of social isolation on mental and physical health in older adults.
- The impact of cultural and linguistic diversity on healthcare access and outcomes.
- The effectiveness of psychotherapy in treating depression and anxiety in adolescents.
- The relationship between exercise and cognitive aging.
- The effects of social media on body image and self-esteem.
- The role of corporate social responsibility in promoting sustainable business practices.
- The impact of mindfulness meditation on attention and focus in children.
- The relationship between political polarization and media consumption habits.
- The effects of urbanization on mental health and well-being.
- The role of social support in managing chronic illness.
- The impact of social media on romantic relationships and dating behaviors.
- The effectiveness of behavioral interventions in promoting physical activity in sedentary adults.
- The relationship between sleep quality and immune function.
- The effects of workplace diversity and inclusion programs on employee retention.
- The impact of climate change on global food security.
- The role of music therapy in improving communication and social skills in individuals with autism spectrum disorder.
- The impact of cultural values on the development of mental health stigma.
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based stress reduction techniques in reducing burnout in healthcare professionals.
- The relationship between social media use and body dissatisfaction among adolescents.
- The effects of nature exposure on cognitive functioning and well-being.
- The role of peer mentoring in promoting academic success in underrepresented student populations.
- The impact of neighborhood characteristics on physical activity and obesity.
- The effectiveness of cognitive rehabilitation interventions in improving cognitive functioning in individuals with traumatic brain injury.
- The relationship between organizational culture and employee job satisfaction.
- The effects of cultural immersion experiences on intercultural competence development.
- The role of assistive technology in promoting independence and quality of life for individuals with disabilities.
- The impact of workplace design on employee productivity and well-being.
- The impact of digital technologies on the music industry and artist revenues.
- The effectiveness of cognitive behavioral therapy in treating insomnia.
- The relationship between social media use and body weight perception among young adults.
- The effects of green spaces on mental health and well-being in urban areas.
- The role of mindfulness-based interventions in reducing substance use disorders.
- The impact of workplace bullying on employee turnover and job satisfaction.
- The effectiveness of animal-assisted therapy in treating mental health disorders.
- The relationship between teacher-student relationships and academic achievement.
- The effects of social support on resilience in individuals experiencing adversity.
- The role of cognitive aging in driving safety and mobility.
- The effectiveness of psychotherapy in treating post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
- The relationship between social media use and sleep quality.
- The effects of cultural competency training on healthcare providers’ attitudes and behaviors towards diverse patient populations.
- The role of exercise in preventing chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
- The impact of the gig economy on job security and worker rights.
- The effectiveness of art therapy in promoting emotional regulation and coping skills in children and adolescents.
- The relationship between parenting styles and child academic achievement.
- The effects of social comparison on well-being and self-esteem.
- The role of nutrition in promoting healthy aging and longevity.
- The impact of gender diversity in leadership on organizational performance.
- The effectiveness of family-based interventions in treating eating disorders.
- The relationship between social media use and perceived loneliness among older adults.
- The effects of mindfulness-based interventions on pain management in chronic pain patients.
- The role of physical activity in preventing and treating depression.
- The impact of cultural differences on communication and conflict resolution in international business.
- The effectiveness of eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) in treating anxiety disorders.
- The relationship between student engagement and academic success in higher education.
- The effects of discrimination on mental health outcomes in minority populations.
- The role of virtual reality in enhancing learning experiences.
- The impact of social media influencers on consumer behavior and brand loyalty.
- The effectiveness of acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT) in treating chronic pain.
- The relationship between social media use and body image dissatisfaction among men.
- The effects of exposure to nature on cognitive functioning and creativity.
- The role of spirituality in coping with illness and disability.
- The impact of automation on employment and job displacement.
- The effectiveness of dialectical behavior therapy (DBT) in treating borderline personality disorder.
- The relationship between teacher-student relationships and school attendance.
- The effects of mindfulness-based interventions on workplace stress and burnout.
- The role of exercise in promoting cognitive functioning and brain health in older adults.
- The impact of diversity and inclusion initiatives on organizational innovation and creativity.
- The effectiveness of cognitive remediation therapy in treating schizophrenia.
- The relationship between social media use and body dissatisfaction among women.
- The effects of exposure to natural light on mood and sleep quality.
- The role of spirituality in enhancing well-being and resilience in military personnel.
- The impact of artificial intelligence on job training and skill development.
- The effectiveness of interpersonal therapy (IPT) in treating depression.
- The relationship between parental involvement and academic achievement among low-income students.
- The effects of mindfulness-based interventions on emotional regulation and coping skills in trauma survivors.
- The role of nutrition in preventing and treating mental health disorders.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples


Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

U.S. DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE
Northeast area.

Hot Research Topics 2011
Hot Topics Home 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006
Agricultural Research Service Information Staff's Image Gallery - a complimentary source of high quality digital photographs

Insect Pests

Chesapeake Bay

Water Quality

Food Safety/Security

Crop Diversity

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Trending Articles
- Depleting myeloid-biased haematopoietic stem cells rejuvenates aged immunity. Ross JB, et al. Nature. 2024. PMID: 38538791
- Embracing cancer complexity: Hallmarks of systemic disease. Swanton C, et al. Cell. 2024. PMID: 38552609 Review.
- Formation of memory assemblies through the DNA-sensing TLR9 pathway. Jovasevic V, et al. Nature. 2024. PMID: 38538785
- Transketolase promotes MAFLD by limiting inosine-induced mitochondrial activity. Tong L, et al. Cell Metab. 2024. PMID: 38547864
- Oxygen imaging of hypoxic pockets in the mouse cerebral cortex. Beinlich FRM, et al. Science. 2024. PMID: 38547288
Latest Literature
- Ann Rheum Dis (1)
- Arch Phys Med Rehabil (2)
- J Am Coll Cardiol (1)
- J Ethnopharmacol (4)
- J Neurosci (7)
- Nat Commun (22)
- Oncogene (1)
- Sci Rep (70)
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Psychol
Trends and hot topics in linguistics studies from 2011 to 2021: A bibliometric analysis of highly cited papers
Associated data.
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/ supplementary material .
High citations most often characterize quality research that reflects the foci of the discipline. This study aims to spotlight the most recent hot topics and the trends looming from the highly cited papers (HCPs) in Web of Science category of linguistics and language & linguistics with bibliometric analysis. The bibliometric information of the 143 HCPs based on Essential Citation Indicators was retrieved and used to identify and analyze influential contributors at the levels of journals, authors, and countries. The most frequently explored topics were identified by corpus analysis and manual checking. The retrieved topics can be grouped into five general categories: multilingual-related , language teaching , and learning related , psycho/pathological/cognitive linguistics-related , methods and tools-related , and others . Topics such as bi/multilingual(ism) , translanguaging , language/writing development , models , emotions , foreign language enjoyment (FLE) , cognition , anxiety are among the most frequently explored. Multilingual and positive trends are discerned from the investigated HCPs. The findings inform linguistic researchers of the publication characteristics of the HCPs in the linguistics field and help them pinpoint the research trends and directions to exert their efforts in future studies.
1. Introduction
Citations, as a rule, exhibit a skewed distributional pattern over the academic publications: a few papers accumulate an overwhelming large citations while the majority are rarely, if ever, cited. Correspondingly, the highly cited papers (HCPs) receive the greatest amount of attention in the academia as citations are commonly regarded as a strong indicator of research excellence. For academic professionals, following HCPs is an efficient way to stay current with the developments in a field and to make better informed decisions regarding potential research topics and directions to exert their efforts. For academic institutions, government and private agencies, and generally the science policy makers, they keep a close eye on and take advantage of this visible indicator, citations, to make more informed decisions on research funding allocation and science policy formulation. Under the backdrop of ever-growing academic outputs, there is noticeable attention shift from publication quantity to publication quality. Many countries are developing research policies to identify “excellent” universities, research groups, and researchers ( Danell, 2011 ). In a word, HCPs showcase high-quality research, encompass significant themes, and constitute a critical reference point in a research field as they are “gold bullion of science” ( Smith, 2007 ).
2. Literature review
Bibliometrics, a term coined by Pritchard (1969) , refers to the application of mathematical methods to the analysis of academic publications. Essentially this is a quantitative method to depict publication patterns within a given field based on a body of literature. There are many bibliometric studies on natural and social sciences in general ( Hsu and Ho, 2014 ; Zhu and Lei, 2022 ) and on various specific disciplines such as management sciences ( Liao et al., 2018 ), biomass research ( Chen and Ho, 2015 ), computer sciences ( Xie and Willett, 2013 ), and sport sciences ( Mancebo et al., 2013 ; Ríos et al., 2013 ), etc. In these studies, researchers tracked developments, weighed research impacts, and highlighted emerging scientific fronts with bibliometric methods. In the field of linguistics, bibliometric studies all occurred in the past few years ( van Doorslaer and Gambier, 2015 ; Lei and Liao, 2017 ; Gong et al., 2018 ; Lei and Liu, 2018 , 2019 ). These bibliometric studies mostly examined a sub-area of linguistics, such as corpus linguistics ( Liao and Lei, 2017 ), translation studies ( van Doorslaer and Gambier, 2015 ), the teaching of Chinese as a second/foreign language ( Gong et al., 2018 ), academic journals like System ( Lei and Liu, 2018 ) or Porta Linguarum ( Sabiote and Rodríguez, 2015 ), etc. Although Lei and Liu (2019) took the entire discipline of linguistics under investigation, their research is exclusively focused on applied linguistics and restricted in a limited number of journals (42 journals in total), leaving publications in other linguistics disciplines and qualified journals unexamined.
Over the recent years, a number of studies have been concerned with “excellent” papers or HCPs. For example, Small (2004) surveyed the HCPs authors’ opinions on why their papers are highly cited. The strong interest, the novelty, the utility, and the high importance of the work were among the most frequently mentioned. Most authors also considered that their selected HCPs are indeed based on their most important work in their academic career. Aksnes (2003) investigated the characteristics of HCPs and found that they were generally authored by a large number of scientists, often involving international collaboration. Some researchers even attempted to predict the HCPs by building mathematical models, implying “the first mover advantage in scientific publication” ( Newman, 2008 , 2014 ). In other words, papers published earlier in a field generally are more likely to accumulate more citations than those published later. Although many papers addressed HCPs from different perspectives, they held a common belief that HCPs are very different from less or zero cited papers and thus deserve utmost attention in academic research ( Aksnes, 2003 ; Blessinger and Hrycaj, 2010 ; Yan et al., 2022 ).
Although an increased focus on research quality can be observed in different fields, opinions diverge on the range and the inclusion criterion of excellent papers. Are they ‘highly cited’, ‘top cited’, or ‘most frequently cited’ papers? Aksnes (2003) noted two different approaches to define a highly cited article, involving absolute or relative thresholds, respectively. An absolute threshold stipulates a minimum number of citations for identifying excellent papers while a relative threshold employs the percentile rank classes, for example, the top 10% most highly cited papers in a discipline or in a publication year or in a publication set. It is important to note that citations differ significantly in different fields and disciplines. A HCP in natural sciences generally accumulates more citations than its counterpart in social sciences. Thus, it is necessary to investigate HCPs from different fields separately or adopt different inclusion criterion to ensure a valid comparison.
The present study has been motivated by two considerations. First, the sizable number of publications of varied qualities in a scientific field makes it difficult or even impossible to conduct any reliable and effective literature research. Focusing on the quality publications, the HCPs in particular, might lend more credibility to the findings on trends. Second, HCPs can serve as a great platform to discover potentially important information for the development of a discipline and understand the past, present, and future of the scientific structure. Therefore, the present study aims to investigate the hot topics and publication trends in the Web of Science category of linguistics or language & linguistics (shortened as linguistics in later references) with bibliometric methods. The study aims to answer the following three questions:
- Who are the most productive and impactful contributors of the HCPs in WoS category of linguistics or language & linguistics in terms of publication venues, authors, and countries?
- What are the most frequently explored topics in HCPs?
- What are the general research trends revealed from the HCPs?
3. Materials and methods
Different from previous studies which used an arbitrary inclusion threshold (e.g., Blessinger and Hrycaj, 2010 ; Hsu and Ho, 2014 ), we rely on Essential Science Indicator (ESI) to identify the HCPs. Developed by Clarivate, a leading company in the areas of bibliometrics and scientometrics, ESI reveals emerging science trends as well as influential individuals, institutions, papers, journals, and countries in any scientific fields of inquiry by drawing on the complete WoS databases. ESI has been chosen for the following three reasons. First, ESI adopts a stricter inclusion criterion for HCPs identification. That is, a paper is selected as a HCP only when its citations exceed the top 1% citation threshold in each of the 22 ESI subject categories. Second, ESI is widely used and recognized for its reliability and authority in identifying the top-charting work, generating “excellent” metrics including hot and highly cited papers. Third, ESI automatically updates its database to generate the most recent HCPs, especially suitable for trend studies for a specified timeframe.
3.1. Data source
The data retrieval was completed at the portal of our university library on June 20, 2022. The methods to retrieve the data are described in Table 1 . The bibliometric indicators regarding the important contributors at journal/author/country levels were obtained. Specifically, after the research was completed, we clicked the “Analyze Results” bar on the result page for the detailed descriptive analysis of the retrieved bibliometric data.
Retrieval strategies.
Several points should be noted about the search strategies. First, we searched the bibliometric data from two sub-databases of WoS core collection: Social Science Citation Index (SSCI) and Arts & Humanities Citation Index (A&HCI). There is no need to include the sub-database of Science Citation Index Expanded (SCI-EXPANDED) because publications in the linguistics field are almost exclusively indexed in SSCI and A&HCI journals. WoS core collection was chosen as the data source because it boasts one of the most comprehensive and authoritative databases of bibliometric information in the world. Many previous studies utilized WoS to retrieve bibliometric data. van Oorschot et al. (2018) and Ruggeri et al. (2019) even indicated that WoS meets the highest standards in terms of impact factor and citation counts and hence guarantees the validity of any bibliometric analysis. Second, we do not restrict the document types as HCPs selection informed by ESI only considers articles and reviews. Third, we do not set the date range as the dataset of ESI-HCPs is automatically updated regularly to include the most recent 10 years of publications.
The aforementioned query obtained a total of 143 HCPs published in 48 journals contributed by 352 authors of 226 institutions. We then downloaded the raw bibliometric parameters of the 143 HCPs for follow-up analysis including publication years, authors, publication titles, countries, affiliations, abstracts, citation reports, etc. A complete list of the 143 HCPs can be found in the Supplementary Material . We collected the most recent impact factor (IF) of each journal from the 2022 Journal Citation Reports (JCR).
3.2. Data analysis
3.2.1. citation analysis.
A citation threshold is the minimum number of citations obtained by ranking papers in a research field in descending order by citation counts and then selecting the top fraction or percentage of papers. In ESI, the highly cited threshold reveals the minimum number of citations received by the top 1% of papers from each of the 10 database years. In other words, a paper has to meet the minimum citation threshold that varies by research fields and by years to enter the HCP list. Of the 22 research fields in ESI, Social Science, General is a broad field covering a number of WoS categories including linguistics and language & linguistics . We checked the ESI official website to obtain the yearly highly cited thresholds in the research field of Social Science , General as shown in Figure 1 ( https://esi.clarivate.com/ThresholdsAction.action ). As we can see, the longer a paper has been published, the more citations it has to receive to meet the threshold. We then divided the raw citation numbers of HCPs with the Highly Cited Thresholds in the corresponding year to obtain the normalized citations for each HCP.

Highly cited thresholds in the research field of Social Sciences, General.
3.2.2. Corpus analysis and manual checking
To determine the most frequently explored topics in these HCPs, we used both corpus-based analysis of word frequency and manual checking. Specifically, the more frequently a word or phrase occurs in a specifically designed corpus, the more likely it constitutes a research topic. In this study, we built an Abstract corpus with all the abstracts of the 143 HCPs, totaling 24,800 tokens. The procedures to retrieve the research topics in the Abstract corpus were as follows. First, the 143 pieces of abstracts were saved as separate .txt files in one folder. Second, AntConc ( Anthony, 2022 ), a corpus analysis tool for concordancing and text analysis, was employed to extract lists of n-grams (2–4) in decreasing order of frequency. We also generated a list of individual nouns because sometimes individual nouns can also constitute research topics. Considering our small corpus data, we adopted both frequency (3) and range criteria (3) for topic candidacy. That is, a candidate n-gram must occur at least 3 times and in at least 3 different abstract files. The frequency threshold guarantees the importance of the candidate topics while the range threshold guarantees that the topics are not overly crowded in a few number of publications. In this process, we actually tested the frequency and range thresholds several rounds for the inclusion of all the potential topics. In total, we obtained 531 nouns, 1,330 2-grams, 331 3-grams, and 81 4-grams. Third, because most of the retrieved n-grams cannot function as meaningful research topics, we manually checked all the candidate items and discussed extensively to decide their roles as potential research topics until full agreements were reached. Finally, we read all the abstracts of the 143 HCPs to further validate their roles as research topics. In the end, we got 118 topic items in total.
4.1. Main publication venues of HCPs
Of the 48 journals which published the 143 HCPs, 17 journals have contributed at least 3 HCPs ( Table 2 ), around 71.33% of the total examined HCPs (102/143), indicating that HCPs tend to be highly concentrated in a limited number of journals. The three largest publication outlets of HCPs are Bilingualism Language and Cognition (16), International Journal of Bilingual Education and Bilingualism (11), and Modern Language Journal (10). Because each journal varies greatly in the number of papers published per year and the number of HCPs is associated with journal circulations, we divided the total number of papers (TP) in the examined years (2011–2021) with the number of the HCPs to acquire the HCP percentage for each journal (HCPs/TP). The three journals with the highest HCPs/TP percentage are Annual Review of Applied Linguistics (2.26), Modern Language Journal (2.08), and Bilingualism Language and Cognition (1.74), indicating that papers published in these journals have a higher probability to enter the HCPs list.
Top 17 publication venues of HCPs.
N: the number of HCPs in each journal; N%: the percentage of HCPs in each journal in the total of 143 HCPs; TP: the total number of papers in the examined timespan (2011–2021); N/TP %: the percentage of HCPs in the total journal publications in the examined time span; TC/HCP: average citations of each HCP; R: journal ranking for the designated indicator; IF: Impact Factor in the year of 2022.
In terms of the general impact of the HCPs from each journal, we divided the number of HCPs with their total citations (TC) to obtain the average citations for each HCP (TC/HCP). The three journals with the highest TC/HCP are Journal of Memory and Language (837.86), Computational Linguistics (533.75), and Journal of Pragmatics (303.75). It indicates that even in the same WoS category, HCPs in different journals have strikingly different capability to accumulate citations. For example, the TC/HCP in System is as low as 31.73, which is even less than 4% of the highest TC/HCP in Journal of Memory and Language .
In regards to the latest journal impact factor (IF) in 2022, the top four journals with the highest IF are Computational Linguistics (7.778) , Modern Language Journal (7.5), Computer Assisted Language Learning (5.964), and Language Learning (5.24). According to the Journal Citation Reports (JCR) quantile rankings in WoS category of linguistics , all the journals on the list belong to the Q 1 (the top 25%), indicating that contributors are more likely to be attracted to contribute and cite papers in these prestigious high impact journals.
4.2. Authors of HCPs
A total of 352 authors had their names listed in the 143 HCPs, of whom 33 authors appeared in at least 2 HCPs as shown in Table 3 . We also provided in Table 3 other indicators to evaluate the authors’ productivity and impact including the total number of citations (TC), the number of citations per HCP, and the number of First author or Corresponding author HCPs (FA/CA). The reason we include the FA/CA indicator is that first authors and corresponding authors are usually considered to contribute the most and should receive greater proportion of credit in academic publications ( Marui et al., 2004 ; Dance, 2012 ).
Authors with at least 2 HCPs.
N: number of HCPs from each author; FA/CA: first author or corresponding author HCPs; TC: total citations of the HCPs from each author; C/HCP: average citations per HCP for each author.
In terms of the number of HCPs, Dewaele JM from Birkbeck Univ London tops the list with 7 HCPs with total citations of 492 (TC = 492), followed by Li C from Huazhong Univ Sci & Technol (#HCPs = 5; TC = 215) and Saito K from UCL (#HCPs = 5; TC = 576). It is to be noted that both Li C and Saito K have close academic collaborations with Dewaele JM . For example, 3 of the 5 HCPs by Li C are co-authored with Dewaele JM . The topics in their co-authored HCPs are mostly about foreign language learning emotions such as boredom , anxiety , enjoyment , the measurement , and positive psychology .
In regards to TC, Li, W . from UCL stands out as the most influential scholar among all the listed authors with total citations of 956 from 2 HCPs, followed by Norton B from Univ British Columbia (TC = 915) and Vasishth S from Univ Potsdam (TC = 694). The average citations per HCP from them are also the highest among the listed authors (478, 305, 347, respectively). It is important to note that Li, W.’ s 2 HCPs are his groundbreaking works on translanguaging which almost become must-reads for anyone who engages in translanguaging research ( Li, 2011 , 2018 ). Besides, Li, W. single authors his 2 HCPs, which is extremely rare as HCPs are often the results from multiple researchers. Norton B ’s HCPs are exploring some core issues in applied linguistics such as identity and investment , language learning , and social change that are considered the foundational work in its field ( Norton and Toohey, 2011 ; Darvin and Norton, 2015 ).
From the perspective of FA/CA papers, Li C from Huazhong Univ Sci and Technol is prominent because she is the first author of all her 5 HCPs. Her research on language learning emotions in the Chinese context is gaining widespread recognition ( Li et al., 2018 , 2019 , 2021 ; Li, 2019 , 2021 ). However, as a newly emerging researcher, most of her HCPs are published in the very recent years and hence accumulate relatively fewer citations (TC = 215). Mondada L from Univ Basel follows closely and single authors her 3 HCPs. Her work is mostly devoted to conversation analysis , multimodality , and social interaction ( Mondada, 2016 , 2018 , 2019 ).
We need to mention the following points regarding the productive authors of HCPs. First, when we calculated the number of HCPs from each author, only the papers published in the journals indexed in the investigated WoS categories were taken in account ( linguistics; language & linguistics ), which came as a compromise to protect the linguistics oriented nature of the HCPs. For example, Brysbaert M from Ghent University claimed a total of 8 HCPs at the time of the data retrieval, of which 6 HCPs were published in WoS category of psychology and more psychologically oriented, hence not included in our study. Besides, all the authors on the author list were treated equally when we calculated the number of HCPs, disregarding the author ordering. That implies that some influential authors may not be able to enter the list as their publications are comparatively fewer. Second, as some authors reported different affiliations at their different career stages, we only provide their most recent affiliation for convenience. Third, it is highly competitive to have one’s work selected as HCPs. The fact that a majority of the HCPs authors do not appear in our productive author list does not diminish their great contributions to this field. The rankings in Table 3 does not necessarily reflect the recognition authors have earned in academia at large.
4.3. Productive countries of HCPs
In total, the 143 HCPs originated from 33 countries. The most productive countries that contributed at least three HCPs are listed in Table 4 . The USA took an overwhelming lead with 59 HCPs, followed distantly by England with 31 HCPs. They also boasted the highest total citations (TC = 15,770; TC = 9,840), manifesting their high productivity and strong influence as traditional powerhouses in linguistics research. In regards to the average citations per HCP, Germany , England and the USA were the top three countries (TC/HCP = 281.67, 281.14, and 267.29, respectively). Although China held the third position with 19 HCPs published, its TC/HCP is the third from the bottom (TC/HCP = 66.84). One of the important reasons is that 13 out of the 19 HCPs contributed by scholars in China are published in the year of 2020 or 2021. The newly published HCPs may need more time to accumulate citations. Besides, 18 out of the 19 HCPs in China are first author and/or corresponding authors, indicating that scholars in China are becoming more independent and gaining more voice in English linguistics research.
Top 18 countries with at least 3 HCPs.
Two points should be noted here as to the productive countries. First, we calculated the HCP contributions from the country level instead of the region level. In other words, HCP contributions from different regions of the same country will be combined in the calculation. For example, HCPs from Scotland were added to the HCPs from England . HCPs from Hong Kong , Macau , and Taiwan are put together with the HCPs from Mainland China . In this way, a clear picture of the HCPs on the country level can be painted. Second, we manually checked the address information of the first author and corresponding author for each HCP. There are some cases where the first author or the corresponding author may report affiliations from more than one country. In this case, every country in their address list will be treated equally in the FA/CA calculation. In other word, a HCP may be classified into more than one country because of the different country backgrounds of the first and/or the corresponding author.
4.4. Top 20 HCPs
The top 20 HCPs with the highest normed citations are listed in decreasing order in Table 5 . The top cited publications can guide us to better understand the development and research topics in recent years.
Top 20 HCPs.
To save space, not full information about the HCPs is given. Some article titles have been abbreviated if they are too lengthy; for the authors, we report the first two authors and use “et al” if there are three authors or more; RC: raw citations; NC: normalized citations
By reading the titles and the abstracts of these top HCPs, we categorized the topics of the 20 HCPs into the following five groups: (i) statistical and analytical methods in (psycho)linguistics such as sentimental analysis, sentence simplification techniques, effect sizes, linear mixed models (#1, 3, 4, 6, 9, 14), (ii) language learning/teaching emotions such enjoyment, anxiety, boredom, stress (#11, 15, 16, 18, 19), (iii) translanguaging or multilinguilism (#5, 13, 20, 17), (iv) language perception (#2, 7, 10), (v) medium of instruction (#8, 12). It is no surprise that 6 out of the top 20 HCPs are about statistical methods in linguistics because language researchers aspire to employ statistics to make their research more scientific. Besides, we noticed that the papers on language teaching/learning emotions on the list are all published in the year of 2020 and 2021, indicating that these emerging topics may deserve more attention in future research. We also noticed two Covid-19 related articles (#16, 19) explored the emotions teachers and students experience during the pandemic, a timely response to the urgent need of the language learning and teaching community.
It is of special interest to note that papers from the journals indexed in multiple JCR categories seem to accumulate more citations. For example, Journal of Memory and Language , American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology , and Computational Linguistics are indexed both in SSCI and SCIE and contribute the top 4 HCPs, manifesting the advantage of these hybrid journals in amassing citations compared to the conventional language journals. Besides, different to findings from Yan et al. (2022) that most of the top HCPs in the field of radiology are reviews in document types, 19 out of the top 20 HCPs are research articles instead of reviews except Macaro et al. (2018) .
4.5. Most frequently explored topics of HCPs
After obtaining the corpus based topic items, we read all the titles and abstracts of the 143 HCPs to further validate their roles as research topics. Table 6 presents the top research topics with the observed frequency of 5 or above. We grouped these topics into five broad categories: bilingual-related, language learning/teaching-related, psycho/pathological/cognitive linguistics-related, methods and tools-related, and others . The observed frequency count for each topic in the abstract corpus were included in the brackets. We found that about 34 of the 143 HCPs are exploring bilingual related issues, the largest share among all the categorized topics, testifying its academic popularity in the examined timespan. Besides, 30 of the 143 HCPs are investigating language learning/teaching-related issues, with topics ranging from learners (e.g., EFL learners, individual difference) to multiple learning variables (e.g., learning strategy, motivation, agency). The findings here will be validated by the analysis of the keywords.
Categorization of the most explored research topics.
N: the number of the HCPs in each topic category; ELF: English as a lingua franca; CLIL: content and language integrated learning; FLE: foreign language enjoyment; FLCA: foreign language classroom anxiety
Several points should be mentioned regarding the topic candidacy. First, for similar topic expressions, we used a cover term and added the frequency counts. For example, multilingualism is a cover term for bilinguals, bilingualism, plurilingualism, and multilingualism . Second, for nouns of singular and plural forms (e.g., emotion and emotions ) or for items with different spellings (e.g., meta analysis and meta analyses ), we combined the frequency counts. Third, we found that some longer items (3 grams and 4 grams) could be subsumed to short ones (2 grams or monogram) without loss of essential meaning (e.g., working memory from working memory capacity ). In this case, the shorter ones were kept for their higher frequency. Fourth, some highly frequent terms were discarded because they were too general to be valuable topics in language research, for example, applied linguistics , language use , second language .
5. Discussion and implications
Based on 143 highly cited papers collected from the WoS categories of linguistics , the present study attempts to present a bird’s eye view of the publication landscape and the most updated research themes reflected from the HCPs in the linguistics field. Specifically, we investigated the important contributors of HCPs in terms of journals, authors and countries. Besides, we spotlighted the research topics by corpus-based analysis of the abstracts and a detailed analysis of the top HCPs. The study has produced several findings that bear important implications.
The first finding is that the HCPs are highly concentrated in a limited journals and countries. In regards to journals, those in the spheres of bilingualism and applied linguistics (e.g., language teaching and learning) are likely to accumulate more citations and hence to produce more HCPs. Journals that focus on bilingualism from a linguistic, psycholinguistic, and neuroscientific perspective are the most frequent outlets of HCPs as evidenced by the top two productive journals of HCPs, Bilingualism Language and Cognition and International Journal of Bilingual Education and Bilingualism . This can be explained by the multidisciplinary nature of bilingual-related research and the development of cognitive measurement techniques. The merits of analyzing publication venues of HCPs are two folds. One the one hand, it can point out which sources of high-quality publications in this field can be inquired for readers as most of the significant and cutting-edge achievements are concentrated in these prestigious journals. On the other hand, it also provides essential guidance or channels for authors or contributors to submit their works for higher visibility.
In terms of country distributions, the traditional powerhouses in linguistics research such as the USA and England are undoubtedly leading the HCP publications in both the number and the citations of the HCPs. However, developing countries are also becoming increasing prominent such as China and Iran , which could be traceable in the funding and support of national language policies and development policies as reported in recent studies ( Ping et al., 2009 ; Lei and Liu, 2019 ). Take China as an example. Along with economic development, China has given more impetus to academic outputs with increased investment in scientific research ( Lei and Liao, 2017 ). Therefore, researchers in China are highly motivated to publish papers in high-quality journals to win recognition in international academia and to deal with the publish or perish pressure ( Lee, 2014 ). These factors may explain the rise of China as a new emerging research powerhouse in both natural and social sciences, including English linguistics research.
The second finding is the multilingual trend in linguistics research. The dominant clustering of topics regarding multilingualism can be understood as a timely response to the multilingual research fever ( May, 2014 ). 34 out of the 143 HCPs have such words as bilingualism, bilingual, multilingualism , translanguaging , etc., in their titles, reflecting a strong multilingual tendency of the HCPs. Multilingual-related HCPs mainly involve three aspects: multilingualism from the perspectives of psycholinguistics and cognition (e.g., Luk et al., 2011 ; Leivada et al., 2020 ); multilingual teaching (e.g., Schissel et al., 2018 ; Ortega, 2019 ; Archila et al., 2021 ); language policies related to multilingualism (e.g., Shen and Gao, 2018 ). As a pedagogical process initially used to describe the bilingual classroom practice and also a frequently explored topic in HCPs, translanguaging is developed into an applied linguistics theory since Li’s Translanguaging as a Practical Theory of Language ( Li, 2018 ). The most common collocates of translanguaging in the Abstract corpus are pedagogy/pedagogies, practices, space/spaces . There are two main reasons for this multilingual turn. First, the rapid development of globalization, immigration, and overseas study programs greatly stimulate the use and research of multiple languages in different linguistic contexts. Second, in many non-English countries, courses are delivered through languages (mostly English) besides their mother tongue ( Clark, 2017 ). Students are required to use multiple languages as resources to learn and understand subjects and ideas. The burgeoning body of English Medium Instruction literature in higher education is in line with the rising interest in multilingualism. Due to the innate multidisciplinary nature, it is to be expected that, multilingualism, the topic du jour, is bound to attract more attention in the future.
The third finding is the application of Positive Psychology (PP) in second language acquisition (SLA), that is, the positive trend in linguistic research. In our analysis, 20 out of 143 HCPs have words or phrases such as emotions, enjoyment, boredom, anxiety , and positive psychology in their titles, which might signal a shift of interest in the psychology of language learners and teachers in different linguistic environments. Our study shows Foreign language enjoyment (FLE) is the most frequently explored emotion, followed by foreign language classroom anxiety (FLCA), the learners’ metaphorical left and right feet on their journey to acquiring the foreign language ( Dewaele and MacIntyre, 2016 ). In fact, the topics of PP are not entirely new to SLA. For example, studies of language motivations, affections, and good language learners all provide roots for the emergence of PP in SLA ( Naiman, 1978 ; Gardner, 2010 ). In recent years, both research and teaching applications of PP in SLA are building rapidly, with a diversity of topics already being explored such as positive education and PP interventions. It is to be noted that SLA also feeds back on PP theories and concepts besides drawing inspirations from it, which makes it “an area rich for interdisciplinary cross-fertilization of ideas” ( Macintyre et al., 2019 ).
It should be noted that subjectivity is involved when we decide and categorize the candidate topic items based on the Abstract corpus. However, the frequency and range criteria guarantee that these items are actually more explored in multiple HCPs, thus indicating topic values for further investigation. Some high frequent n-grams are abandoned because they are too general or not meaningful topics. For example, applied linguistics is too broad to be included as most of the HCPs concern issues in this research line instead of theoretical linguistics. By meaningful topics, we mean that the topics can help journal editors and readers quickly locate their interested fields ( Lei and Liu, 2019 ), as the author keywords such as bilingualism , emotions , and individual differences . The examination of the few 3/4-grams and monograms (mostly nouns) revealed that most of them were either not meaningful topics or they could be subsumed in the 2-grams. Besides, there is inevitably some overlapping in the topic categorizations. For example, some topics in the language teaching and learning category are situated and discussed within the context of multilingualism. The merits of topic categorizations are two folds: to better monitor the overlapping between the Abstract corpus-based topic items and the keywords; to roughly delineate the research strands in the HCPs for future research.
It should also be noted that all the results were based on the retrieved HCPs only. The study did not aim to paint a comprehensive and full picture of the whole landscape of linguistic research. Rather, it specifically focused on the most popular literature in a specified timeframe, thus generating the snapshots or trends in linguistic research. One of the important merits of this methodology is that some newly emerging but highly cited researchers can be spotlighted and gain more academic attention because only the metrics of HCPs are considered in calculation. On the contrary, the exclusion of some other highly cited researchers in general such as Rod Ellis and Ken Hyland just indicates that their highly cited publications are not within our investigated timeframe and cannot be interpreted as their diminishing academic influence in the field. Besides, the study does not consider the issue of collaborators or collaborations in calculating the number of HCPs for two reasons. First, although some researchers are regular collaborators such as Li CC and Dewaele JM, their individual contribution can never be undermined. Second, the study also provides additional information about the number of the FA/CA HCPs from each listed author, which may aid readers in locating their interested research.
We acknowledge that our study has some limitations that should be addressed in future research. First, our study focuses on the HCPs extracted from WoS SSCI and A&HCI journals, the alleged most celebrated papers in this field. Future studies may consider including data from other databases such as Scopus to verify the findings of the present study. Second, our Abstract corpus-based method for topic extraction involved human judgement. Although the final list was the result of several rounds of discussions among the authors, it is difficult or even impossible to avoid subjectivity and some worthy topics may be unconsciously missed. Therefore, future research may consider employing automatic algorithms to extract topics. For example, a dependency-based machine learning approach can be used to identify research topics ( Zhu and Lei, 2021 ).
Data availability statement
Author contributions.
SY: conceptualization and methodology. SY and LZ: writing-review and editing and writing-original draft. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
This work was supported by Humanities and Social Sciences Youth Fund of China MOE under the grant 20YJC740076 and 18YJC740141.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1052586/full#supplementary-material
- Aksnes D. W. (2003). Characteristics of highly cited papers . Res. Eval. 12 , 159–170. doi: 10.3152/147154403781776645 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Anthony L. (2022). AntConc (version 4.0.5) Tokyo, Japan: Waseda University. Available at: https://www.laurenceanthony.net/software (Accessed June 20, 2022).
- Archila P. A., Molina J., Truscott de Mejía A.-M. (2021). Fostering bilingual scientific writing through a systematic and purposeful code-switching pedagogical strategy . Int. J. Biling. Educ. Biling. 24 , 785–803. doi: 10.1080/13670050.2018.1516189 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Blessinger K., Hrycaj P. (2010). Highly cited articles in library and information science: an analysis of content and authorship trends . Libr. Inf. Sci. Res. 32 , 156–162. doi: 10.1016/j.lisr.2009.12.007 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chen H., Ho Y. S. (2015). Highly cited articles in biomass research: a bibliometric analysis . Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 49 , 12–20. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.04.060 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Clark S. (2017). Translanguaging in higher education: beyond monolingual ideologies . Int. J. Biling. Educ. Biling. 22 , 1048–1051. doi: 10.1080/13670050.2017.1322568 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dance A. (2012). Authorship: Who’s on first? Nature 489 , 591–593. doi: 10.1038/nj7417-591a, PMID: [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Danell R. (2011). Can the quality of scientific work be predicted using information on the author’s track record? J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 62 , 50–60. doi: 10.1002/asi.21454 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Darvin R., Norton B. (2015). Identity and a model of Investment in Applied Linguistics . Annu. Rev. Appl. Linguist. 35 , 36–56. doi: 10.1017/S0267190514000191 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dewaele J.-M., MacIntyre P. D. (2016). “ Foreign language enjoyment and foreign language classroom anxiety: the right and left feet of the language learner ” in Positive psychology in SLA . eds. Peter D. M., Tammy G., Sarah M. (Bristol, Blue Ridge Summit: Multilingual Matters; ), 215–236. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gardner R. (2010). Motivation and second language acquisition: The socio-educational model . New York: Peter Lang. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gong Y., Lyu B., Gao X. (2018). Research on teaching Chinese as a second or foreign language in and outside mainland China: a bibliometric analysis . Asia Pac. Educ. Res. 27 , 277–289. doi: 10.1007/s40299-018-0385-2 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hsu Y., Ho Y. S. (2014). Highly cited articles in health care sciences and services field in science citation index Expanded . Methods Inf. Med. 53 , 446–458. doi: 10.3414/ME14-01-0022, PMID: [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lee I. (2014). Publish or perish: the myth and reality of academic publishing . Lang. Teach. 47 , 250–261. doi: 10.1017/S0261444811000504 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lei L., Liao S. (2017). Publications in linguistics journals from mainland China, Hong Kong, Taiwan, and Macau (2003–2012): a bibliometric analysis . J. Quant. Ling. 24 , 54–64. doi: 10.1080/09296174.2016.1260274 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lei L., Liu D. (2018). The research trends and contributions of System’s publications over the past four decades (1973–2017): a bibliometric analysis . System 80 , 1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.system.2018.10.003 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lei L., Liu D. (2019). Research trends in applied linguistics from 2005 to 2016: a bibliometric analysis and its implications . Appl. Linguis. 40 , 540–561. doi: 10.1093/applin/amy003 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Leivada E., Westergaard M., Duabeitia J. A., Rothman J. (2020). On the phantom-like appearance of bilingualism effects on neurocognition: (how) should we proceed? Biling. Lang. Congn. 24 , 197–210. doi: 10.1017/S1366728920000358 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Li W. (2011). Moment analysis and translanguaging space: discursive construction of identities by multilingual Chinese youth in Britain . Energy Fuel 43 , 1222–1235. doi: 10.1016/j.pragma.2010.07.035 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Li W. (2018). Translanguaging as a practical theory of language . Appl. Linguis. 39 , 9–30. doi: 10.1093/applin/amx039 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Li C. (2019). A positive psychology perspective on Chinese EFL students’ trait emotional intelligence, foreign language enjoyment and EFL learning achievement . J. Multiling. Multicult. Dev. 41 , 246–263. doi: 10.1080/01434632.2019.1614187 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Li C. (2021). A control-value theory approach to boredom in English classes among university students in China . Mod. Lang. J. 105 , 317–334. doi: 10.1111/modl.12693 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Li C., Dewaele J. M., Hu Y. (2021). Foreign language learning boredom: conceptualization and measurement . Appl. Ling. Rev. doi: 10.1515/applirev-2020-0124 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Li C., Dewaele J. M., Jiang G. (2019). The complex relationship between classroom emotions and EFL achievement in China . Appl. Ling. Rev. 11 , 485–510. doi: 10.1515/applirev-2018-0043 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Li C., Jiang G., Jean-Marc D. (2018). Understanding Chinese high school students’ foreign language enjoyment: validation of the Chinese version of the foreign language enjoyment scale . System 76 , 183–196. doi: 10.1016/j.system.2018.06.004 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Liao S., Lei L. (2017). What we talk about when we talk about corpus: a bibliometric analysis of corpus-related research in linguistics (2000-2015) . Glottometrics 38 , 1–20. [ Google Scholar ]
- Liao H., Tang M., Li Z., Lev B. (2018). Bibliometric analysis for highly cited papers in operations research and management science from 2008 to 2017 based on essential science indicators . Omega 88 , 223–236. doi: 10.1016/j.omega.2018.11.005 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Luk G., Sa E. D., Bialystok E. (2011). Is there a relation between onset age of bilingualism and enhancement of cognitive control? Biling. Lang. Cogn. 14 , 588–595. doi: 10.1017/S1366728911000010 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Macaro E., Curle S., Pun J., Dearden J. (2018). A systematic review of English medium instruction in higher education . Lang. Teach. 51 , 36–76. doi: 10.1017/S0261444817000350 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Macintyre P., Gregersen T., Mercer S. (2019). Setting an agenda for positive psychology in SLA: theory, practice, and research . Mod. Lang. J. 103 , 262–274. doi: 10.1111/modl.12544 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mancebo F. P., Sapena A. F., Herrera M. V., González L., Toca H., Benavent R. A. (2013). Scientific literature analysis of judo in web of science . Arch. Budo 9 , 81–91. doi: 10.12659/AOB.883883 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Marui M., Bozikov J., Katavi V., Hren D., Kljakovi-Gapi M., Marui A. (2004). Authorship in a small medical journal: a study of contributorship statements by corresponding authors . Sci. Eng. Ethics 10 , 493–502. doi: 10.1007/s11948-004-0007-7, PMID: [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- May S. (2014). The multilingual turn: Implications for SLA, TESOL and bilingual education . New York: Routledge. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mondada L. (2016). Challenges of multimodality: language and the body in social interaction . J. Socioling. 20 , 336–366. doi: 10.1111/josl.1_12177 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mondada L. (2018). Multiple temporalities of language and body in interaction: challenges for transcribing multimodality . Res. Lang. Soc. Interact. 51 , 85–106. doi: 10.1080/08351813.2018.1413878 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mondada L. (2019). Contemporary issues in conversation analysis: embodiment and materiality, multimodality and multisensoriality in social interaction . J. Pragmat. 145 , 47–62. doi: 10.1016/j.pragma.2019.01.016 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Naiman N. (1978). The good language learner . Clevedon, UK: Multilingual Matters. [ Google Scholar ]
- Newman M. (2008). The first-mover advantage in scientific publication . Eplasty 86 , 68001–68006. doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/86/68001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Newman M. (2014). Prediction of highly cited papers . Eplasty 105 :28002. doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/105/28002 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Norton B., Toohey K. (2011). Identity, language learning, and social change . Lang. Teach. 44 , 412–446. doi: 10.1017/S0261444811000309 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ortega L. (2019). SLA and the study of equitable multilingualism . Mod. Lang. J. 103 , 23–38. doi: 10.1111/modl.12525 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ping Z., Thijs B., Glnzel W. (2009). Is China also becoming a giant in social sciences? Scientometrics 79 , 593–621. doi: 10.1007/s11192-007-2068-x [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pritchard A. (1969). Statistical bibliography or bibliometrics . J. Doc. 25 , 348–349. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ríos L. J. C., Tamao I. M., Olmos J. (2013). Bibliometric study (1922-2009) on rugby articles in research journals . South Afr. J. Res. Sport Phys. Educ. Rec. 17 , 313–109. doi: 10.3176/tr.2013.3.06 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ruggeri G., Orsi L., Corsi S. (2019). A bibliometric analysis of the scientific literature on Fairtrade labelling . Int. IJC 43 , 134–152. doi: 10.1111/ijcs.12492 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sabiote C. R., Rodríguez J. A. (2015). Bibliometric study and methodological quality indicators of the journal porta Linguarum during six year period 2008-2013 . Porta Ling. 24 , 135–150. doi: 10.30827/Digibug.53866 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Schissel J. L., De Korne H., López-Gopar M. E. (2018). Grappling with translanguaging for teaching and assessment in culturally and linguistically diverse contexts: teacher perspectives from Oaxaca, Mexico . Int. J. Biling. Educ. Biling. 24 , 340–356. doi: 10.1080/13670050.2018.1463965 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shen Q., Gao X. (2018). Multilingualism and policy making in greater China: ideological and implementational spaces . Lang. Policy 18 , 1–16. doi: 10.1007/s10993-018-9473-7 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Small H. (2004). Why authors think their papers are highly cited . Scientometrics 60 , 305–316. doi: 10.1023/B:SCIE.0000034376.55800.18 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith D. R. (2007). The New Zealand timber economy, 1840–1935 . N. Z. Med. J. 120 , U2871–U2313. doi: 10.1016/0305-7488(90)90044-C, PMID: [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- van Doorslaer L., Gambier Y. (2015). Measuring relationships in translation studies. On affiliations and keyword frequencies in the translation studies bibliography . Perspectives 23 , 305–319. doi: 10.1080/0907676X.2015.1026360 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- van Oorschot J. A. W. H., Hofman E., Halman J. (2018). A bibliometric review of the innovation adoption literature . Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 134 , 1–21. doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2018.04.032 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Xie Z., Willett P. (2013). The development of computer science research in the People’s republic of China 2000–2009: a bibliometric study . Inf. Dev. 29 , 251–264. doi: 10.1177/0266666912458515 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yan S., Zhang H., Wang J. (2022). Trends and hot topics in radiology, nuclear medicine and medical imaging from 2011–2021: a bibliometric analysis of highly cited papers . Jpn. J. Radiol. 40 , 847–856. doi: 10.1007/s11604-022-01268-z, PMID: [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhu H., Lei L. (2021). A dependency-based machine learning approach to the identification of research topics: a case in COVID-19 studies . Lib. Hi Tech 40 , 495–515. doi: 10.1108/LHT-01-2021-0051 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhu H., Lei L. (2022). The research trends of text classification studies (2000–2020): a bibliometric analysis . SAGE Open 12 , 215824402210899–215824402210816. doi: 10.1177%2F21582440221089963 [ Google Scholar ]
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Research: Leaders Undervalue Creative Work from AI-Managed Teams
- Shane Schweitzer
- David De Cremer

Beware the unintended consequences of using algorithmic tools for management.
Because of AI’s ability to learn from vast amounts of data and maximize efficiency, companies have predicted that humans working with it will be able to free up their time and expand their creative efforts, thereby driving greater innovation. But, despite the enthusiasm of tech gurus and companies alike, is this really how adopting AI tools will play out? A series of experiments that how algorithmic tools changed the consideration and resources workers were given for creative and innovative work suggest that these tools — specifically, the algorithmic tools that oversee employee productivity — could actually undercut employees’ ability to do this work, and that companies that deploy these tools haphazardly could find their optimism souring.
How will creative work be impacted by artificial intelligence (AI)? With AI’s immense and growing capabilities — it can do everything from structuring work schedules, managing administrative tasks , and giving advice to decision-makers — industry thought leaders are understandably optimistic about its potential. Much of this optimism hinges on the claim that, because of AI’s ability to learn from vast amounts of data and maximize efficiency, humans working with it will be able to free up their time and expand their creative efforts, thereby driving greater innovation. Numerous analyses and corporate reports have been written in favor of this claim.
- SS Shane Schweitzer is an Assistant Professor of Management and Organizational Development at the D’Amore-McKim School of Business.
- David De Cremer is a professor of management and technology at Northeastern University and the Dunton Family Dean of its D’Amore-McKim School of Business. His website is daviddecremer.com .
Partner Center
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Social justice
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
MIT economics to launch new predoctoral fellowship program
Press contact :.

Previous image Next image
The MIT Department of Economics is launching a new program this year that will pair faculty with predoctoral fellows.
“MIT economics right now is historically strong,” says Jon Gruber, the Ford Professor of Economics and department head of MIT economics. “To remain in that position involves having the resources to stay on the cutting edge of the research frontier, and that requires the use of predocs.”
The nature of economic research has changed enormously, adds Gruber, due to factors like the use of large datasets, innovations in experiment design, and comprehensive data analysis, all of which require the support of predocs. This new research model empowers economists to address national and global challenges in profound and much more effective ways.
The new predoc program is made possible by an ongoing major fundraising initiative in the department.
Gruber gave credit to Glenn Ellison, the Gregory K. Palm (1970) Professor of Economics and former department chair, for working closely with Roger Altman, MIT Corporation member and the former head and current member of the visiting committee, to craft a vision for the future of the department that will ultimately include up to 24 predocs that would work for economics faculty at MIT.
“It’s a great vision. They put a lot of work into it,” Gruber says.
With significant support from the Altman Family Fund, Gruber explains, the predoc program will be able to ramp up, providing predocs to the department’s junior faculty. He expects six predocs to start in the department this fall.
“We’ll have a wide range of junior faculty who will be using these predocs for a bunch of really interesting and important questions that are very data- and research-intensive,” Gruber says.
Tobias Salz, the Castle Krob Career Development Associate Professor of Economics, is one of the faculty members already benefiting from a pilot of the new program. He’s working on a large project on the search engine market.
“I am working with a predoctoral research fellow who has been instrumental in many parts of the project, including the design of an experiment and data analysis,” says Salz. “Initially, I was only able to hire him for one year, but with the new funding I am able to extend his contract. The predoctoral program has therefore helped ensure continuity on this project, which has made a big difference.”
Nina Roussille, assistant professor of economics, says her work will greatly benefit from collaborating with a predoc. Several of her projects either require the analysis of large, administrative datasets or the implementation of large-scale experiments.
“This kind of work will be greatly enhanced and streamlined with the help of a predoc to construct, clean, and analyze the data, as well as to set up the experiments and study their effects. This will free up some of my time to participate in more projects and allow me to focus my efforts on high-yield tasks, such as data analysis and paper writing,” says Roussille.
Roussille adds that she’s excited about the opportunity to mentor a young economist on the path to a PhD.
“They’ll greatly benefit from the vibrant research environment of the MIT economics department,” she said.
Gruber sees the program as mutually beneficial for both the predocs and the faculty.
“The advantage for the predoc is they get research experience and they get to know a faculty member,” adds Gruber. “The advantage for the faculty is they get to work with someone who wants to excel and make an impression with the person they research for.”
Beyond establishing the predoc program, this current fundraising initiative prioritizes building resources for faculty research in the Department of Economics. In addition to the gift from the Altman Family Fund to establish the predoctoral fellowship program, this fundraising initiative has secured several other significant contributions, including:
- the creation of the Daniel (1972) and Gail Rubinfeld Professorship Fund, through the support of Dan Rubinfeld, PhD ’72;
- the Thapanee Sirivadhanabhakdi Techajareonvikul (1999) Professorship Fund, established by economics undergraduate alumna and her husband, Aswin Techajareonvkul MBA ’02;
- another endowed professorship in the department, through the support of an anonymous donor;
- the creation of the Locher Economics Fund, which will provide discretionary resources to support faculty research for the department, through the support of Kurt ’88, SM ’89, and Anne Stark Locher; and
- a gift to create the Dr. James A. Berkovec (1977) Memorial Faculty Research Fund in Economics, established by Ben Golub, ’78, SM ’82, PhD ’84.
To date, almost $30 million has been secured for these purposes, and efforts are ongoing.
Share this news article on:
Related links.
- Department of Economics
Related Topics
- Awards, honors and fellowships
- MIT Corporation
- School of Humanities Arts and Social Sciences
Related Articles

MIT scholars awarded seed grants to probe the social implications of generative AI

QS ranks MIT the world’s No. 1 university for 2023-24

Nine from MIT named 2023 Sloan Research Fellows
Previous item Next item
More MIT News
Programming functional fabrics
Read full story →

Most work is new work, long-term study of U.S. census data shows
Does technology help or hurt employment?
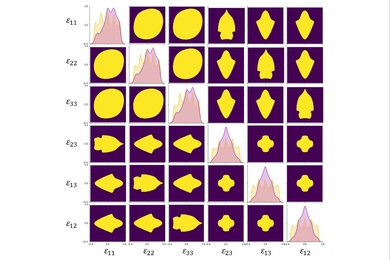
A first-ever complete map for elastic strain engineering

“Life is short, so aim high”

Shining a light on oil fields to make them more sustainable
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram
- See us on facebook
- See us on twitter
- See us on youtube
- See us on linkedin
- See us on instagram
Pilot study shows ketogenic diet improves severe mental illness
A small clinical trial led by Stanford Medicine found that the metabolic effects of a ketogenic diet may help stabilize the brain.
April 1, 2024 - By Nina Bai

A study led by researchers at Stanford Medicine showed that diet can help those with serious mental illness. nishihata
For people living with serious mental illness like schizophrenia or bipolar disorder, standard treatment with antipsychotic medications can be a double-edged sword. While these drugs help regulate brain chemistry, they often cause metabolic side effects such as insulin resistance and obesity, which are distressing enough that many patients stop taking the medications.
Now, a pilot study led by Stanford Medicine researchers has found that a ketogenic diet not only restores metabolic health in these patients as they continue their medications, but it further improves their psychiatric conditions. The results, published March 27 in Psychiatry Research , suggest that a dietary intervention can be a powerful aid in treating mental illness.
“It’s very promising and very encouraging that you can take back control of your illness in some way, aside from the usual standard of care,” said Shebani Sethi , MD, associate professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences and the first author of the new paper.
Making the connection
Sethi, who is board certified in obesity and psychiatry, remembers when she first noticed the connection. As a medical student working in an obesity clinic, she saw a patient with treatment-resistant schizophrenia whose auditory hallucinations quieted on a ketogenic diet.
That prompted her to dig into the medical literature. There were only a few, decades-old case reports on using the ketogenic diet to treat schizophrenia, but there was a long track record of success in using ketogenic diets to treat epileptic seizures.
“The ketogenic diet has been proven to be effective for treatment-resistant epileptic seizures by reducing the excitability of neurons in the brain,” Sethi said. “We thought it would be worth exploring this treatment in psychiatric conditions.”
A few years later, Sethi coined the term metabolic psychiatry, a new field that approaches mental health from an energy conversion perspective.

Shebani Sethi
In the four-month pilot trial, Sethi’s team followed 21 adult participants who were diagnosed with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder, taking antipsychotic medications, and had a metabolic abnormality — such as weight gain, insulin resistance, hypertriglyceridemia, dyslipidemia or impaired glucose tolerance. The participants were instructed to follow a ketogenic diet, with approximately 10% of the calories from carbohydrates, 30% from protein and 60% from fat. They were not told to count calories.
“The focus of eating is on whole non-processed foods including protein and non-starchy vegetables, and not restricting fats,” said Sethi, who shared keto-friendly meal ideas with the participants. They were also given keto cookbooks and access to a health coach.
The research team tracked how well the participants followed the diet through weekly measures of blood ketone levels. (Ketones are acids produced when the body breaks down fat — instead of glucose — for energy.) By the end of the trial, 14 patients had been fully adherent, six were semi-adherent and only one was non-adherent.
The participants underwent a variety of psychiatric and metabolic assessments throughout the trial.
Before the trial, 29% of the participants met the criteria for metabolic syndrome, defined as having at least three of five conditions: abdominal obesity, elevated triglycerides, low HDL cholesterol, elevated blood pressure and elevated fasting glucose levels. After four months on a ketogenic diet, none of the participants had metabolic syndrome.
On average, the participants lost 10% of their body weight; reduced their waist circumference by 11% percent; and had lower blood pressure, body mass index, triglycerides, blood sugar levels and insulin resistance.
“We’re seeing huge changes,” Sethi said. “Even if you’re on antipsychotic drugs, we can still reverse the obesity, the metabolic syndrome, the insulin resistance. I think that’s very encouraging for patients.”
The participants reported improvements in their energy, sleep, mood and quality of life.
The psychiatric benefits were also striking. On average, the participants improved 31% on a psychiatrist rating of mental illness known as the clinical global impressions scale, with three-quarters of the group showing clinically meaningful improvement. Overall, the participants also reported better sleep and greater life satisfaction.
“The participants reported improvements in their energy, sleep, mood and quality of life,” Sethi said. “They feel healthier and more hopeful.”
The researchers were impressed that most of the participants stuck with the diet. “We saw more benefit with the adherent group compared with the semi-adherent group, indicating a potential dose-response relationship,” Sethi said.
Alternative fuel for the brain
There is increasing evidence that psychiatric diseases such as schizophrenia and bipolar disorder stem from metabolic deficits in the brain, which affect the excitability of neurons, Sethi said.
The researchers hypothesize that just as a ketogenic diet improves the rest of the body’s metabolism, it also improves the brain’s metabolism.
“Anything that improves metabolic health in general is probably going to improve brain health anyway,” Sethi said. “But the ketogenic diet can provide ketones as an alternative fuel to glucose for a brain with energy dysfunction.”
Likely there are multiple mechanisms at work, she added, and the main purpose of the small pilot trial is to help researchers detect signals that will guide the design of larger, more robust studies.
As a physician, Sethi cares for many patients with both serious mental illness and obesity or metabolic syndrome, but few studies have focused on this undertreated population.
She is the founder and director of the metabolic psychiatry clinic at Stanford Medicine.
“Many of my patients suffer from both illnesses, so my desire was to see if metabolic interventions could help them,” she said. “They are seeking more help. They are looking to just feel better.”
Researchers from the University of Michigan; the University of California, San Francisco; and Duke University contributed to the study.
The study was supported by Baszucki Group Research Fund, Keun Lau Fund and the Obesity Treatment Foundation.

About Stanford Medicine
Stanford Medicine is an integrated academic health system comprising the Stanford School of Medicine and adult and pediatric health care delivery systems. Together, they harness the full potential of biomedicine through collaborative research, education and clinical care for patients. For more information, please visit med.stanford.edu .
Artificial intelligence
Exploring ways AI is applied to health care

Read our research on: Abortion | Podcasts | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
June 2011 political survey, public wants changes in entitlements, not changes in benefits.
Overview As policymakers at the state and national level struggle with rising entitlement costs, overwhelming numbers of Americans agree that, over the years, Social Security, Medicare and Medicaid have been good for the country. But these cherished programs receive negative marks for current performance, and their finances are widely viewed as troubled. Reflecting these concerns, […]
Majority Sees U.S. Leadership in Space as Essential
Overview On the eve of the final mission of the U.S. space shuttle program, most Americans say the United States must be at the forefront of future space exploration. Fifty years after the first American manned space flight, nearly six-in-ten (58%) say it is essential that the United States continue to be a world leader […]
Four Years After Walter Reed, Government Still Faulted for Troop Support
Overview As President Obama begins to draw down U.S. forces in Afghanistan, most Americans continue to say that government support for troops returning from war is falling short. The public remains divided over whether the American people give enough support to soldiers who have served in Iraq and Afghanistan. Opinions on this tilt more negative, […]
Pessimism About National Economy Rises, Personal Financial Views Hold Steady
Overview With a growing number of Americans saying they have been hearing “mostly bad” economic news, opinions about the current state of the national economy remain grim. Positive expectations regarding future economic conditions, which remained high even during the depths of the recession, have declined and now stand at their lowest point since mid-2008. Yet […]
Record Number Favors Removing U.S. Troops from Afghanistan
Overview As President Obama prepares to announce his policy for drawing down U.S. forces in Afghanistan, the percentage of Americans who favor removing the troops as soon as possible has reached an all-time high in Pew Research Center surveys. For the first time, a majority (56%) says that U.S. troops should be brought home as […]
Download This Dataset
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
- Environment
Sea levels are rising but parts of Florida are also sinking, research shows
- Alex Harris Miami Herald staff writer
MIAMI — In South Florida, sea levels have already risen several inches since the start of the century and could be around 6 feet higher by 2100. But another factor could be making those sunny day floods in South Florida worse: We’re sinking.
Well, only a little bit. And only in some places. That’s according to new and old research on the phenomena of sinking land — also known as subsidence — along the entire U.S. coast.
New research published in the journal Nature on March 6 showed the potential risk of a one-two combo of sinking land and rising seas to cities along the coast, and Miami topped the list as a location that could see quite a bit of flooded property by mid-century.
The paper, led by researchers at Virginia Tech, suggested that Miami could have around 80,000 properties flooding by mid-century, a multibillion-dollar risk, due to the combination of sinking land and rising seas.
Associate Professor Manoochehr Shirzaei at Virginia Tech’s Earth Observation and Innovation Lab, co-author of the study, said he believes cities aren’t taking the slipping elevation of their coastal land as seriously as they take sea level rise.
“The coastal hazard through 2050 is more likely driven by land subsidence than sea level rise, and this has to come across very clearly in every sea rise strategy,” he said. “I’m confident in this moment in most places, this is not the case.”
Subsidence is caused by several things, from glaciers moving or melting in the North Pole to overpumping oil, gas and groundwater, or, in South Florida’s case, compacting soil.
While the nationwide maps make clear that the real problem area for subsidence is in the Gulf Coast, specifically in places like Louisiana, Shirzaei said South Florida should still be paying attention to the future risk.
Specifically, he said, on the glitzy, expensive island communities that ring the coast of the Sunshine State.
“You do have some of the famous barrier islands. All of them are sinking,” he said.
How South Florida stacks up
Local research into subsidence in South Florida has found that yes, indeed, there are spots along the coast that are lower than they were decades ago. That’s especially true on barrier islands, said Shimon Wdowinski, a geophysics professor at Florida International University who has published several papers on subsidence.
But it’s only a minuscule amount.
His 2020 paper compared Miami Beach to Norfolk, Virginia, and found that Miami Beach experienced very little subsidence overall. It also happens in small patches, typically around new construction. In that paper, he noted that the Champlain Towers condominium building in Surfside sank at a rank of 2 millimeters a year from 1993 to 1997 — about the width of two credit cards stacked on top of each other.
His research, released before the tragic 2021 collapse, initially led some to believe that sinking earth could have played a role in the disaster, but the investigation has so far not pointed to land change as a culprit.
Keep up with Tampa Bay’s top headlines
Subscribe to our free DayStarter newsletter
You’re all signed up!
Want more of our free, weekly newsletters in your inbox? Let’s get started.
Wdowinski said that his research suggests that land subsidence is mostly localized to the space of a single building in South Florida, and it’s by design. Heavy buildings compact the soil, so good engineers design buildings with the knowledge that they will slowly settle over a long period of time.
And that’s not just because of South Florida’s dirt. It can be what’s underneath, too. When barrier islands like Miami Beach were first built or expanded, it was common practice to mow down trees and mangroves and use those cuttings to expand the island. Decades later, those trees have rotted, sinking the earth down a bit.
“In southeast Florida, we have mostly localized subsidence, which is associated with construction of new buildings,” Wdowinski said. “The weight of the building is actually pushing down, and if you have the proper foundation it should be fine.”
The problem comes when one side of the building sinks faster or further than another side, potentially straining the building’s foundation or the pipes underneath.
That is, unless the seas are rising.
South Florida is already a low-lying place, so millimeters matter here. Continued subsidence, paired with rising seas, rising groundwater levels and more intense rainstorms could leave South Florida at risk of more frequent and more intense floods.
That’s why Wdowinski is pursuing more grants and more research into the phenomenon all across the state. While he’s confident that sinking is a bigger problem on the Gulf Coast — including Florida’s west coast — he noted that all information is important when it comes to planning for climate change.
“It’s a factor. It’s not the most important one. But still, if we can get a better grip on that it would be helpful,” he said.
©2024 Miami Herald. Visit miamiherald.com . Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.
Alex Harris covers climate change for the Miami Herald, including how South Florida communities are adapting to the warming world. She attended the University of Florida.
MORE FOR YOU
- Advertisement
ONLY AVAILABLE FOR SUBSCRIBERS
The Tampa Bay Times e-Newspaper is a digital replica of the printed paper seven days a week that is available to read on desktop, mobile, and our app for subscribers only. To enjoy the e-Newspaper every day, please subscribe.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The list provides 1000+ topic ideas across 25 research areas, including: Accounting & finance. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. Biotech and genetic engineering. Blockchain and crypto. Business, management and leadership. Communication. Cybersecurity. Data science and analytics.
55 Research Paper Topics to Jump-Start Your Paper. Matt Ellis. Updated on October 9, 2023 Students. Coming up with research paper topics is the first step in writing most papers. While it may seem easy compared to the actual writing, choosing the right research paper topic is nonetheless one of the most important steps.
113 Great Research Paper Topics. One of the hardest parts of writing a research paper can be just finding a good topic to write about. Fortunately we've done the hard work for you and have compiled a list of 113 interesting research paper topics. They've been organized into ten categories and cover a wide range of subjects so you can easily ...
Major Breaking News Stories. Starting shortly after New Year's Day, 2011 proved a year of major breaking stories - both foreign and domestic - that captured the public's attention for weeks at a time. A Jan. 8 shooting rampage in Tucson, Ariz., left six dead and 13 injured, including Giffords. For the next three weeks, Americans said ...
Research Topics . All Publications Methods Short Reads Tools & Resources Experts About. ... About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other ...
9% of social network site users, or 4% of adults, have started or joined a health-related group on a social networking site. The social life of health information is robust. The online conversation about health is being driven forward by two forces: 1) the availability of social tools and 2) the motivation, especially among people living with ...
research. e dominant cl ustering of topics rega rding multilingualism can be understood as a timely response to the multilingual research fever ( Ma y, 2014 ). 34 o ut of the 143 HCPs
Trends and hot topics in radiology, nuclear medicine and medical imaging from 2011-2021: a bibliometric analysis of highly cited papers. Sheng Yan, 1 Huiting Zhang, 2 and Jun Wang 3 ... Table Table5 5 presents the top 33 research topics above the observed frequency of 38. The observed frequency count for each topic in the abstract corpus is ...
Many countries are developing research policies to identify "excellent" universities, research groups, and researchers (Danell, 2011). In a word, HCPs showcase high-quality research, encompass significant themes, and constitute a critical reference point in a research field as they are "gold bullion of science" ( Smith, 2007 ).
Naidoo (2011), stated that research is a systematic investigation of nature and the society to validate and refine existing information and generate new knowledge. Research refers to the ...
Finding a great idea. The 3 Cs: Curiosity to investigate and question situations. Critical thinking skills to refine your curiosity into a clearly stated idea. Courage to have "bad ideas". Broadly define the area of research. Are not the same as the title of your research study. Need further work to become feasible research projects.
A research topic typically consists of several components that help to define and clarify the subject matter of the research project. These components include: Research problem or question: This is the central issue or inquiry that the research seeks to address. It should be well-defined and focused, with clear boundaries that limit the scope ...
Hot Research Topics 2011. Hot Topics Home 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 ... Agricultural Research magazine, Feburary 2011 Complete Article. Insect Pests. Innovative Ways To Fight Insect Pests - If left uncontrolled, insect pests would eat or ruin about half of all crops grown in the United States. Insects and ticks that bite livestock cause ...
2011 Research Topics list is intended to guide research projects for Professional Military Education (PME) students, JSOU fac-ulty, research fellows, and others writing about special operations during this academic year. Research is one of the cornerstones of JSOU's aca-demic mission as we strive to produce publications to meet joint Special
Alex P. Schmid, 50 Un- and Under-researched Topics in the Field of (Counter-) Terrorism Studies, Perspectives on Terrorism, Vol. 5, No. 1 (March 2011), pp. 76-78
KEY WORDS: research participation, human subjects, child abuse, distress, benefit, ethics, trauma Received: August 3, 2010; revised: January 3, 2011 A sensitive topic in research has been defined as a topic that poses a potential threat for those involved, causing data collection, holding, or dissemination to be problematic for partici-
PEJ's The Year in the News is derived from an analysis of close to 46,000 stories produced from January 1-December 11, 2011 that were examined as part of the group's ongoing content analysis of 52 different traditional news outlets from the main five media sectors, its News Coverage Index. The report also includes an analysis of the year in ...
PubMed is a comprehensive database of biomedical literature from various sources, including MEDLINE, life science journals, and online books. You can search for citations, access full text content, and explore topics related to health, medicine, and biology. PubMed also provides advanced search options and tools for researchers and clinicians.
High citations most often characterize quality research that reflects the foci of the discipline. This study aims to spotlight the most recent hot topics and the trends looming from the highly cited papers (HCPs) in Web of Science category of linguistics and language & linguistics with bibliometric analysis. The bibliometric information of the 143 HCPs based on Essential Citation Indicators ...
The interactive, conversational, analytical, and generative features of GenAI offer support for creativity, problem-solving, and processing and digestion of large bodies of information. Therefore ...
Mental health. Mental health is a state of mind characterized by emotional well-being, good behavioral adjustment, relative freedom from anxiety and disabling symptoms, and a capacity to establish constructive relationships and cope with the ordinary demands and stresses of life. Adapted from APA Dictionary of Psychology.
Summary. Because of AI's ability to learn from vast amounts of data and maximize efficiency, companies have predicted that humans working with it will be able to free up their time and expand ...
Study participants born in the 1970s had 6.6% larger brain volumes and almost 15% larger brain surface area than those born in the 1930s. The researchers hypothesize the increased brain size may lead to an increased brain reserve, potentially reducing the overall risk of age-related dementias. The findings were published in JAMA Neurology.
A new program in the MIT Department of Economics will support predoctoral research fellows working with the department's junior faculty. Thanks to the new program, predoc Wonjoon Choi (right) will be able to extend his contract with Tobias Salz (left), the Castle Krob Career Development Associate Professor of Economics.
The research team tracked how well the participants followed the diet through weekly measures of blood ketone levels. (Ketones are acids produced when the body breaks down fat — instead of glucose — for energy.) By the end of the trial, 14 patients had been fully adherent, six were semi-adherent and only one was non-adherent.
The Pew Internet Project and California HealthCare Foundation have added eight new topics to our national survey measuring internet users' interest in health information: 29% of internet users look online for information about food safety or recalls. 24% of internet users look online for information about drug safety or recalls.
Overview On the eve of the final mission of the U.S. space shuttle program, most Americans say the United States must be at the forefront of future space exploration. Fifty years after the first American manned space flight, nearly six-in-ten (58%) say it is essential that the United States continue to be a world leader […] report | Jun 29, 2011.
MIAMI — In South Florida, sea levels have already risen several inches since the start of the century and could be around 6 feet higher by 2100. But another factor could be making those sunny ...
As a result, NIA is delighted to share our updated payline news. The law sets the total NIA budget allocation at more than $4.5 billion. The budget designates a generous $100 million increase for Alzheimer's disease and related dementias (AD/ADRD) research, including $90 million for NIA and $10 million for the National Institute of ...