

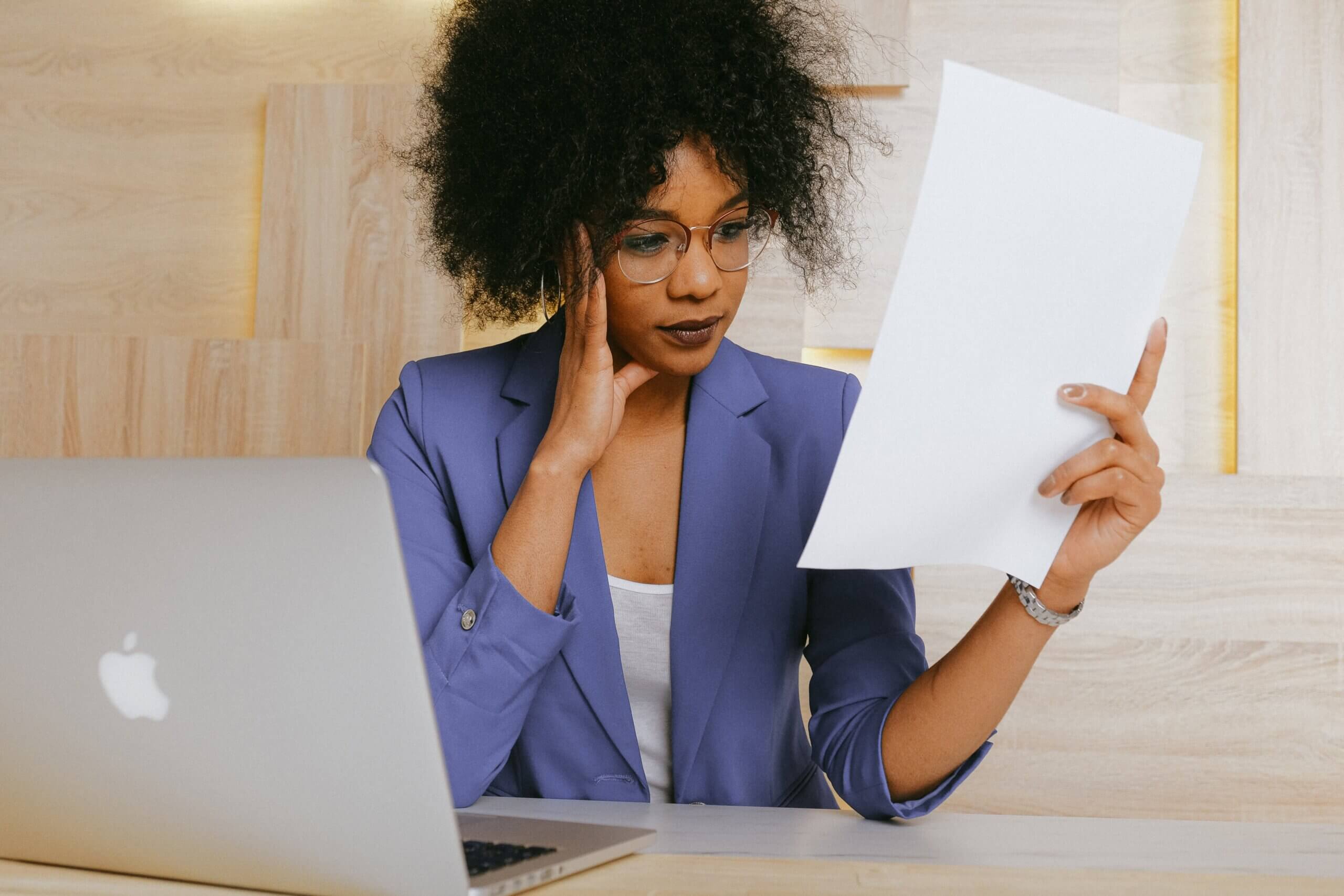
50 Useful Academic Words & Phrases for Research
Like all good writing, writing an academic paper takes a certain level of skill to express your ideas and arguments in a way that is natural and that meets a level of academic sophistication. The terms, expressions, and phrases you use in your research paper must be of an appropriate level to be submitted to academic journals.
Therefore, authors need to know which verbs , nouns , and phrases to apply to create a paper that is not only easy to understand, but which conveys an understanding of academic conventions. Using the correct terminology and usage shows journal editors and fellow researchers that you are a competent writer and thinker, while using non-academic language might make them question your writing ability, as well as your critical reasoning skills.
What are academic words and phrases?
One way to understand what constitutes good academic writing is to read a lot of published research to find patterns of usage in different contexts. However, it may take an author countless hours of reading and might not be the most helpful advice when faced with an upcoming deadline on a manuscript draft.
Briefly, “academic” language includes terms, phrases, expressions, transitions, and sometimes symbols and abbreviations that help the pieces of an academic text fit together. When writing an academic text–whether it is a book report, annotated bibliography, research paper, research poster, lab report, research proposal, thesis, or manuscript for publication–authors must follow academic writing conventions. You can often find handy academic writing tips and guidelines by consulting the style manual of the text you are writing (i.e., APA Style , MLA Style , or Chicago Style ).
However, sometimes it can be helpful to have a list of academic words and expressions like the ones in this article to use as a “cheat sheet” for substituting the better term in a given context.
How to Choose the Best Academic Terms
You can think of writing “academically” as writing in a way that conveys one’s meaning effectively but concisely. For instance, while the term “take a look at” is a perfectly fine way to express an action in everyday English, a term like “analyze” would certainly be more suitable in most academic contexts. It takes up fewer words on the page and is used much more often in published academic papers.
You can use one handy guideline when choosing the most academic term: When faced with a choice between two different terms, use the Latinate version of the term. Here is a brief list of common verbs versus their academic counterparts:
Although this can be a useful tip to help academic authors, it can be difficult to memorize dozens of Latinate verbs. Using an AI paraphrasing tool or proofreading tool can help you instantly find more appropriate academic terms, so consider using such revision tools while you draft to improve your writing.
Top 50 Words and Phrases for Different Sections in a Research Paper
The “Latinate verb rule” is just one tool in your arsenal of academic writing, and there are many more out there. But to make the process of finding academic language a bit easier for you, we have compiled a list of 50 vital academic words and phrases, divided into specific categories and use cases, each with an explanation and contextual example.
Best Words and Phrases to use in an Introduction section
1. historically.
An adverb used to indicate a time perspective, especially when describing the background of a given topic.
2. In recent years
A temporal marker emphasizing recent developments, often used at the very beginning of your Introduction section.
3. It is widely acknowledged that
A “form phrase” indicating a broad consensus among researchers and/or the general public. Often used in the literature review section to build upon a foundation of established scientific knowledge.
4. There has been growing interest in
Highlights increasing attention to a topic and tells the reader why your study might be important to this field of research.
5. Preliminary observations indicate
Shares early insights or findings while hedging on making any definitive conclusions. Modal verbs like may , might , and could are often used with this expression.
6. This study aims to
Describes the goal of the research and is a form phrase very often used in the research objective or even the hypothesis of a research paper .
7. Despite its significance
Highlights the importance of a matter that might be overlooked. It is also frequently used in the rationale of the study section to show how your study’s aim and scope build on previous studies.
8. While numerous studies have focused on
Indicates the existing body of work on a topic while pointing to the shortcomings of certain aspects of that research. Helps focus the reader on the question, “What is missing from our knowledge of this topic?” This is often used alongside the statement of the problem in research papers.
9. The purpose of this research is
A form phrase that directly states the aim of the study.
10. The question arises (about/whether)
Poses a query or research problem statement for the reader to acknowledge.
Best Words and Phrases for Clarifying Information
11. in other words.
Introduces a synopsis or the rephrasing of a statement for clarity. This is often used in the Discussion section statement to explain the implications of the study .
12. That is to say
Provides clarification, similar to “in other words.”
13. To put it simply
Simplifies a complex idea, often for a more general readership.
14. To clarify
Specifically indicates to the reader a direct elaboration of a previous point.
15. More specifically
Narrows down a general statement from a broader one. Often used in the Discussion section to clarify the meaning of a specific result.
16. To elaborate
Expands on a point made previously.
17. In detail
Indicates a deeper dive into information.
Points out specifics. Similar meaning to “specifically” or “especially.”
19. This means that
Explains implications and/or interprets the meaning of the Results section .
20. Moreover
Expands a prior point to a broader one that shows the greater context or wider argument.
Best Words and Phrases for Giving Examples
21. for instance.
Provides a specific case that fits into the point being made.
22. As an illustration
Demonstrates a point in full or in part.
23. To illustrate
Shows a clear picture of the point being made.
24. For example
Presents a particular instance. Same meaning as “for instance.”
25. Such as
Lists specifics that comprise a broader category or assertion being made.
26. Including
Offers examples as part of a larger list.
27. Notably
Adverb highlighting an important example. Similar meaning to “especially.”
28. Especially
Adverb that emphasizes a significant instance.
29. In particular
Draws attention to a specific point.
30. To name a few
Indicates examples than previously mentioned are about to be named.
Best Words and Phrases for Comparing and Contrasting
31. however.
Introduces a contrasting idea.
32. On the other hand
Highlights an alternative view or fact.
33. Conversely
Indicates an opposing or reversed idea to the one just mentioned.
34. Similarly
Shows likeness or parallels between two ideas, objects, or situations.
35. Likewise
Indicates agreement with a previous point.
36. In contrast
Draws a distinction between two points.
37. Nevertheless
Introduces a contrasting point, despite what has been said.
38. Whereas
Compares two distinct entities or ideas.
Indicates a contrast between two points.
Signals an unexpected contrast.
Best Words and Phrases to use in a Conclusion section
41. in conclusion.
Signifies the beginning of the closing argument.
42. To sum up
Offers a brief summary.
43. In summary
Signals a concise recap.
44. Ultimately
Reflects the final or main point.
45. Overall
Gives a general concluding statement.
Indicates a resulting conclusion.
Demonstrates a logical conclusion.
48. Therefore
Connects a cause and its effect.
49. It can be concluded that
Clearly states a conclusion derived from the data.
50. Taking everything into consideration
Reflects on all the discussed points before concluding.
Edit Your Research Terms and Phrases Before Submission
Using these phrases in the proper places in your research papers can enhance the clarity, flow, and persuasiveness of your writing, especially in the Introduction section and Discussion section, which together make up the majority of your paper’s text in most academic domains.
However, it's vital to ensure each phrase is contextually appropriate to avoid redundancy or misinterpretation. As mentioned at the top of this article, the best way to do this is to 1) use an AI text editor , free AI paraphrasing tool or AI proofreading tool while you draft to enhance your writing, and 2) consult a professional proofreading service like Wordvice, which has human editors well versed in the terminology and conventions of the specific subject area of your academic documents.
For more detailed information on using AI tools to write a research paper and the best AI tools for research , check out the Wordvice AI Blog .
- Daily Crossword
- Word Puzzle
- Word Finder
- Word of the Day
Synonym of the Day
- Word of the Year
- Language stories
- All featured
- Gender and sexuality
- All pop culture
- Grammar Coach ™
- Writing hub
- Grammar essentials
- Commonly confused
- All writing tips
- Pop culture
- Writing tips
Advertisement
- research paper
noun as in position paper
Weak matches
- policy report
- statement of belief
- statement of principles
noun as in term paper
Discover More
Related words.
Words related to research paper are not direct synonyms, but are associated with the word research paper . Browse related words to learn more about word associations.
noun as in paper stating beliefs
noun as in long student essay
Start each day with the Synonym of the Day in your inbox!
By clicking "Sign Up", you are accepting Dictionary.com Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policies.
On this page you'll find 16 synonyms, antonyms, and words related to research paper, such as: manifesto, outline, plank, platform, policy report, and prospectus.
From Roget's 21st Century Thesaurus, Third Edition Copyright © 2013 by the Philip Lief Group.
bottom_desktop desktop:[300x250]
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
Glossary of research terms.
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
This glossary is intended to assist you in understanding commonly used terms and concepts when reading, interpreting, and evaluating scholarly research. Also included are common words and phrases defined within the context of how they apply to research in the social and behavioral sciences.
- Acculturation -- refers to the process of adapting to another culture, particularly in reference to blending in with the majority population [e.g., an immigrant adopting American customs]. However, acculturation also implies that both cultures add something to one another, but still remain distinct groups unto themselves.
- Accuracy -- a term used in survey research to refer to the match between the target population and the sample.
- Affective Measures -- procedures or devices used to obtain quantified descriptions of an individual's feelings, emotional states, or dispositions.
- Aggregate -- a total created from smaller units. For instance, the population of a county is an aggregate of the populations of the cities, rural areas, etc. that comprise the county. As a verb, it refers to total data from smaller units into a large unit.
- Anonymity -- a research condition in which no one, including the researcher, knows the identities of research participants.
- Baseline -- a control measurement carried out before an experimental treatment.
- Behaviorism -- school of psychological thought concerned with the observable, tangible, objective facts of behavior, rather than with subjective phenomena such as thoughts, emotions, or impulses. Contemporary behaviorism also emphasizes the study of mental states such as feelings and fantasies to the extent that they can be directly observed and measured.
- Beliefs -- ideas, doctrines, tenets, etc. that are accepted as true on grounds which are not immediately susceptible to rigorous proof.
- Benchmarking -- systematically measuring and comparing the operations and outcomes of organizations, systems, processes, etc., against agreed upon "best-in-class" frames of reference.
- Bias -- a loss of balance and accuracy in the use of research methods. It can appear in research via the sampling frame, random sampling, or non-response. It can also occur at other stages in research, such as while interviewing, in the design of questions, or in the way data are analyzed and presented. Bias means that the research findings will not be representative of, or generalizable to, a wider population.
- Case Study -- the collection and presentation of detailed information about a particular participant or small group, frequently including data derived from the subjects themselves.
- Causal Hypothesis -- a statement hypothesizing that the independent variable affects the dependent variable in some way.
- Causal Relationship -- the relationship established that shows that an independent variable, and nothing else, causes a change in a dependent variable. It also establishes how much of a change is shown in the dependent variable.
- Causality -- the relation between cause and effect.
- Central Tendency -- any way of describing or characterizing typical, average, or common values in some distribution.
- Chi-square Analysis -- a common non-parametric statistical test which compares an expected proportion or ratio to an actual proportion or ratio.
- Claim -- a statement, similar to a hypothesis, which is made in response to the research question and that is affirmed with evidence based on research.
- Classification -- ordering of related phenomena into categories, groups, or systems according to characteristics or attributes.
- Cluster Analysis -- a method of statistical analysis where data that share a common trait are grouped together. The data is collected in a way that allows the data collector to group data according to certain characteristics.
- Cohort Analysis -- group by group analytic treatment of individuals having a statistical factor in common to each group. Group members share a particular characteristic [e.g., born in a given year] or a common experience [e.g., entering a college at a given time].
- Confidentiality -- a research condition in which no one except the researcher(s) knows the identities of the participants in a study. It refers to the treatment of information that a participant has disclosed to the researcher in a relationship of trust and with the expectation that it will not be revealed to others in ways that violate the original consent agreement, unless permission is granted by the participant.
- Confirmability Objectivity -- the findings of the study could be confirmed by another person conducting the same study.
- Construct -- refers to any of the following: something that exists theoretically but is not directly observable; a concept developed [constructed] for describing relations among phenomena or for other research purposes; or, a theoretical definition in which concepts are defined in terms of other concepts. For example, intelligence cannot be directly observed or measured; it is a construct.
- Construct Validity -- seeks an agreement between a theoretical concept and a specific measuring device, such as observation.
- Constructivism -- the idea that reality is socially constructed. It is the view that reality cannot be understood outside of the way humans interact and that the idea that knowledge is constructed, not discovered. Constructivists believe that learning is more active and self-directed than either behaviorism or cognitive theory would postulate.
- Content Analysis -- the systematic, objective, and quantitative description of the manifest or latent content of print or nonprint communications.
- Context Sensitivity -- awareness by a qualitative researcher of factors such as values and beliefs that influence cultural behaviors.
- Control Group -- the group in an experimental design that receives either no treatment or a different treatment from the experimental group. This group can thus be compared to the experimental group.
- Controlled Experiment -- an experimental design with two or more randomly selected groups [an experimental group and control group] in which the researcher controls or introduces the independent variable and measures the dependent variable at least two times [pre- and post-test measurements].
- Correlation -- a common statistical analysis, usually abbreviated as r, that measures the degree of relationship between pairs of interval variables in a sample. The range of correlation is from -1.00 to zero to +1.00. Also, a non-cause and effect relationship between two variables.
- Covariate -- a product of the correlation of two related variables times their standard deviations. Used in true experiments to measure the difference of treatment between them.
- Credibility -- a researcher's ability to demonstrate that the object of a study is accurately identified and described based on the way in which the study was conducted.
- Critical Theory -- an evaluative approach to social science research, associated with Germany's neo-Marxist “Frankfurt School,” that aims to criticize as well as analyze society, opposing the political orthodoxy of modern communism. Its goal is to promote human emancipatory forces and to expose ideas and systems that impede them.
- Data -- factual information [as measurements or statistics] used as a basis for reasoning, discussion, or calculation.
- Data Mining -- the process of analyzing data from different perspectives and summarizing it into useful information, often to discover patterns and/or systematic relationships among variables.
- Data Quality -- this is the degree to which the collected data [results of measurement or observation] meet the standards of quality to be considered valid [trustworthy] and reliable [dependable].
- Deductive -- a form of reasoning in which conclusions are formulated about particulars from general or universal premises.
- Dependability -- being able to account for changes in the design of the study and the changing conditions surrounding what was studied.
- Dependent Variable -- a variable that varies due, at least in part, to the impact of the independent variable. In other words, its value “depends” on the value of the independent variable. For example, in the variables “gender” and “academic major,” academic major is the dependent variable, meaning that your major cannot determine whether you are male or female, but your gender might indirectly lead you to favor one major over another.
- Deviation -- the distance between the mean and a particular data point in a given distribution.
- Discourse Community -- a community of scholars and researchers in a given field who respond to and communicate to each other through published articles in the community's journals and presentations at conventions. All members of the discourse community adhere to certain conventions for the presentation of their theories and research.
- Discrete Variable -- a variable that is measured solely in whole units, such as, gender and number of siblings.
- Distribution -- the range of values of a particular variable.
- Effect Size -- the amount of change in a dependent variable that can be attributed to manipulations of the independent variable. A large effect size exists when the value of the dependent variable is strongly influenced by the independent variable. It is the mean difference on a variable between experimental and control groups divided by the standard deviation on that variable of the pooled groups or of the control group alone.
- Emancipatory Research -- research is conducted on and with people from marginalized groups or communities. It is led by a researcher or research team who is either an indigenous or external insider; is interpreted within intellectual frameworks of that group; and, is conducted largely for the purpose of empowering members of that community and improving services for them. It also engages members of the community as co-constructors or validators of knowledge.
- Empirical Research -- the process of developing systematized knowledge gained from observations that are formulated to support insights and generalizations about the phenomena being researched.
- Epistemology -- concerns knowledge construction; asks what constitutes knowledge and how knowledge is validated.
- Ethnography -- method to study groups and/or cultures over a period of time. The goal of this type of research is to comprehend the particular group/culture through immersion into the culture or group. Research is completed through various methods but, since the researcher is immersed within the group for an extended period of time, more detailed information is usually collected during the research.
- Expectancy Effect -- any unconscious or conscious cues that convey to the participant in a study how the researcher wants them to respond. Expecting someone to behave in a particular way has been shown to promote the expected behavior. Expectancy effects can be minimized by using standardized interactions with subjects, automated data-gathering methods, and double blind protocols.
- External Validity -- the extent to which the results of a study are generalizable or transferable.
- Factor Analysis -- a statistical test that explores relationships among data. The test explores which variables in a data set are most related to each other. In a carefully constructed survey, for example, factor analysis can yield information on patterns of responses, not simply data on a single response. Larger tendencies may then be interpreted, indicating behavior trends rather than simply responses to specific questions.
- Field Studies -- academic or other investigative studies undertaken in a natural setting, rather than in laboratories, classrooms, or other structured environments.
- Focus Groups -- small, roundtable discussion groups charged with examining specific topics or problems, including possible options or solutions. Focus groups usually consist of 4-12 participants, guided by moderators to keep the discussion flowing and to collect and report the results.
- Framework -- the structure and support that may be used as both the launching point and the on-going guidelines for investigating a research problem.
- Generalizability -- the extent to which research findings and conclusions conducted on a specific study to groups or situations can be applied to the population at large.
- Grey Literature -- research produced by organizations outside of commercial and academic publishing that publish materials, such as, working papers, research reports, and briefing papers.
- Grounded Theory -- practice of developing other theories that emerge from observing a group. Theories are grounded in the group's observable experiences, but researchers add their own insight into why those experiences exist.
- Group Behavior -- behaviors of a group as a whole, as well as the behavior of an individual as influenced by his or her membership in a group.
- Hypothesis -- a tentative explanation based on theory to predict a causal relationship between variables.
- Independent Variable -- the conditions of an experiment that are systematically manipulated by the researcher. A variable that is not impacted by the dependent variable, and that itself impacts the dependent variable. In the earlier example of "gender" and "academic major," (see Dependent Variable) gender is the independent variable.
- Individualism -- a theory or policy having primary regard for the liberty, rights, or independent actions of individuals.
- Inductive -- a form of reasoning in which a generalized conclusion is formulated from particular instances.
- Inductive Analysis -- a form of analysis based on inductive reasoning; a researcher using inductive analysis starts with answers, but formulates questions throughout the research process.
- Insiderness -- a concept in qualitative research that refers to the degree to which a researcher has access to and an understanding of persons, places, or things within a group or community based on being a member of that group or community.
- Internal Consistency -- the extent to which all questions or items assess the same characteristic, skill, or quality.
- Internal Validity -- the rigor with which the study was conducted [e.g., the study's design, the care taken to conduct measurements, and decisions concerning what was and was not measured]. It is also the extent to which the designers of a study have taken into account alternative explanations for any causal relationships they explore. In studies that do not explore causal relationships, only the first of these definitions should be considered when assessing internal validity.
- Life History -- a record of an event/events in a respondent's life told [written down, but increasingly audio or video recorded] by the respondent from his/her own perspective in his/her own words. A life history is different from a "research story" in that it covers a longer time span, perhaps a complete life, or a significant period in a life.
- Margin of Error -- the permittable or acceptable deviation from the target or a specific value. The allowance for slight error or miscalculation or changing circumstances in a study.
- Measurement -- process of obtaining a numerical description of the extent to which persons, organizations, or things possess specified characteristics.
- Meta-Analysis -- an analysis combining the results of several studies that address a set of related hypotheses.
- Methodology -- a theory or analysis of how research does and should proceed.
- Methods -- systematic approaches to the conduct of an operation or process. It includes steps of procedure, application of techniques, systems of reasoning or analysis, and the modes of inquiry employed by a discipline.
- Mixed-Methods -- a research approach that uses two or more methods from both the quantitative and qualitative research categories. It is also referred to as blended methods, combined methods, or methodological triangulation.
- Modeling -- the creation of a physical or computer analogy to understand a particular phenomenon. Modeling helps in estimating the relative magnitude of various factors involved in a phenomenon. A successful model can be shown to account for unexpected behavior that has been observed, to predict certain behaviors, which can then be tested experimentally, and to demonstrate that a given theory cannot account for certain phenomenon.
- Models -- representations of objects, principles, processes, or ideas often used for imitation or emulation.
- Naturalistic Observation -- observation of behaviors and events in natural settings without experimental manipulation or other forms of interference.
- Norm -- the norm in statistics is the average or usual performance. For example, students usually complete their high school graduation requirements when they are 18 years old. Even though some students graduate when they are younger or older, the norm is that any given student will graduate when he or she is 18 years old.
- Null Hypothesis -- the proposition, to be tested statistically, that the experimental intervention has "no effect," meaning that the treatment and control groups will not differ as a result of the intervention. Investigators usually hope that the data will demonstrate some effect from the intervention, thus allowing the investigator to reject the null hypothesis.
- Ontology -- a discipline of philosophy that explores the science of what is, the kinds and structures of objects, properties, events, processes, and relations in every area of reality.
- Panel Study -- a longitudinal study in which a group of individuals is interviewed at intervals over a period of time.
- Participant -- individuals whose physiological and/or behavioral characteristics and responses are the object of study in a research project.
- Peer-Review -- the process in which the author of a book, article, or other type of publication submits his or her work to experts in the field for critical evaluation, usually prior to publication. This is standard procedure in publishing scholarly research.
- Phenomenology -- a qualitative research approach concerned with understanding certain group behaviors from that group's point of view.
- Philosophy -- critical examination of the grounds for fundamental beliefs and analysis of the basic concepts, doctrines, or practices that express such beliefs.
- Phonology -- the study of the ways in which speech sounds form systems and patterns in language.
- Policy -- governing principles that serve as guidelines or rules for decision making and action in a given area.
- Policy Analysis -- systematic study of the nature, rationale, cost, impact, effectiveness, implications, etc., of existing or alternative policies, using the theories and methodologies of relevant social science disciplines.
- Population -- the target group under investigation. The population is the entire set under consideration. Samples are drawn from populations.
- Position Papers -- statements of official or organizational viewpoints, often recommending a particular course of action or response to a situation.
- Positivism -- a doctrine in the philosophy of science, positivism argues that science can only deal with observable entities known directly to experience. The positivist aims to construct general laws, or theories, which express relationships between phenomena. Observation and experiment is used to show whether the phenomena fit the theory.
- Predictive Measurement -- use of tests, inventories, or other measures to determine or estimate future events, conditions, outcomes, or trends.
- Principal Investigator -- the scientist or scholar with primary responsibility for the design and conduct of a research project.
- Probability -- the chance that a phenomenon will occur randomly. As a statistical measure, it is shown as p [the "p" factor].
- Questionnaire -- structured sets of questions on specified subjects that are used to gather information, attitudes, or opinions.
- Random Sampling -- a process used in research to draw a sample of a population strictly by chance, yielding no discernible pattern beyond chance. Random sampling can be accomplished by first numbering the population, then selecting the sample according to a table of random numbers or using a random-number computer generator. The sample is said to be random because there is no regular or discernible pattern or order. Random sample selection is used under the assumption that sufficiently large samples assigned randomly will exhibit a distribution comparable to that of the population from which the sample is drawn. The random assignment of participants increases the probability that differences observed between participant groups are the result of the experimental intervention.
- Reliability -- the degree to which a measure yields consistent results. If the measuring instrument [e.g., survey] is reliable, then administering it to similar groups would yield similar results. Reliability is a prerequisite for validity. An unreliable indicator cannot produce trustworthy results.
- Representative Sample -- sample in which the participants closely match the characteristics of the population, and thus, all segments of the population are represented in the sample. A representative sample allows results to be generalized from the sample to the population.
- Rigor -- degree to which research methods are scrupulously and meticulously carried out in order to recognize important influences occurring in an experimental study.
- Sample -- the population researched in a particular study. Usually, attempts are made to select a "sample population" that is considered representative of groups of people to whom results will be generalized or transferred. In studies that use inferential statistics to analyze results or which are designed to be generalizable, sample size is critical, generally the larger the number in the sample, the higher the likelihood of a representative distribution of the population.
- Sampling Error -- the degree to which the results from the sample deviate from those that would be obtained from the entire population, because of random error in the selection of respondent and the corresponding reduction in reliability.
- Saturation -- a situation in which data analysis begins to reveal repetition and redundancy and when new data tend to confirm existing findings rather than expand upon them.
- Semantics -- the relationship between symbols and meaning in a linguistic system. Also, the cuing system that connects what is written in the text to what is stored in the reader's prior knowledge.
- Social Theories -- theories about the structure, organization, and functioning of human societies.
- Sociolinguistics -- the study of language in society and, more specifically, the study of language varieties, their functions, and their speakers.
- Standard Deviation -- a measure of variation that indicates the typical distance between the scores of a distribution and the mean; it is determined by taking the square root of the average of the squared deviations in a given distribution. It can be used to indicate the proportion of data within certain ranges of scale values when the distribution conforms closely to the normal curve.
- Statistical Analysis -- application of statistical processes and theory to the compilation, presentation, discussion, and interpretation of numerical data.
- Statistical Bias -- characteristics of an experimental or sampling design, or the mathematical treatment of data, that systematically affects the results of a study so as to produce incorrect, unjustified, or inappropriate inferences or conclusions.
- Statistical Significance -- the probability that the difference between the outcomes of the control and experimental group are great enough that it is unlikely due solely to chance. The probability that the null hypothesis can be rejected at a predetermined significance level [0.05 or 0.01].
- Statistical Tests -- researchers use statistical tests to make quantitative decisions about whether a study's data indicate a significant effect from the intervention and allow the researcher to reject the null hypothesis. That is, statistical tests show whether the differences between the outcomes of the control and experimental groups are great enough to be statistically significant. If differences are found to be statistically significant, it means that the probability [likelihood] that these differences occurred solely due to chance is relatively low. Most researchers agree that a significance value of .05 or less [i.e., there is a 95% probability that the differences are real] sufficiently determines significance.
- Subcultures -- ethnic, regional, economic, or social groups exhibiting characteristic patterns of behavior sufficient to distinguish them from the larger society to which they belong.
- Testing -- the act of gathering and processing information about individuals' ability, skill, understanding, or knowledge under controlled conditions.
- Theory -- a general explanation about a specific behavior or set of events that is based on known principles and serves to organize related events in a meaningful way. A theory is not as specific as a hypothesis.
- Treatment -- the stimulus given to a dependent variable.
- Trend Samples -- method of sampling different groups of people at different points in time from the same population.
- Triangulation -- a multi-method or pluralistic approach, using different methods in order to focus on the research topic from different viewpoints and to produce a multi-faceted set of data. Also used to check the validity of findings from any one method.
- Unit of Analysis -- the basic observable entity or phenomenon being analyzed by a study and for which data are collected in the form of variables.
- Validity -- the degree to which a study accurately reflects or assesses the specific concept that the researcher is attempting to measure. A method can be reliable, consistently measuring the same thing, but not valid.
- Variable -- any characteristic or trait that can vary from one person to another [race, gender, academic major] or for one person over time [age, political beliefs].
- Weighted Scores -- scores in which the components are modified by different multipliers to reflect their relative importance.
- White Paper -- an authoritative report that often states the position or philosophy about a social, political, or other subject, or a general explanation of an architecture, framework, or product technology written by a group of researchers. A white paper seeks to contain unbiased information and analysis regarding a business or policy problem that the researchers may be facing.
Elliot, Mark, Fairweather, Ian, Olsen, Wendy Kay, and Pampaka, Maria. A Dictionary of Social Research Methods. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press, 2016; Free Social Science Dictionary. Socialsciencedictionary.com [2008]. Glossary. Institutional Review Board. Colorado College; Glossary of Key Terms. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Glossary A-Z. Education.com; Glossary of Research Terms. Research Mindedness Virtual Learning Resource. Centre for Human Servive Technology. University of Southampton; Miller, Robert L. and Brewer, John D. The A-Z of Social Research: A Dictionary of Key Social Science Research Concepts London: SAGE, 2003; Jupp, Victor. The SAGE Dictionary of Social and Cultural Research Methods . London: Sage, 2006.
- << Previous: Independent and Dependent Variables
- Next: 1. Choosing a Research Problem >>
- Last Updated: Apr 9, 2024 1:19 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
Effective Transition Words for Research Papers
What are transition words in academic writing?
A transition is a change from one idea to another idea in writing or speaking and can be achieved using transition terms or phrases. These transitions are usually placed at the beginning of sentences, independent clauses, and paragraphs and thus establish a specific relationship between ideas or groups of ideas. Transitions are used to enhance cohesion in your paper and make its logical development clearer to readers.
Types of Transition Words
Transitions accomplish many different objectives. We can divide all transitions into four basic categories:
- Additive transitions signal to the reader that you are adding or referencing information
- Adversative transitions indicate conflict or disagreement between pieces of information
- Causal transitions point to consequences and show cause-and-effect relationships
- Sequential transitions clarify the order and sequence of information and the overall structure of the paper
Additive Transitions
These terms signal that new information is being added (between both sentences and paragraphs), introduce or highlight information, refer to something that was just mentioned, add a similar situation, or identify certain information as important.
Adversative Transitions
These terms and phrases distinguish facts, arguments, and other information, whether by contrasting and showing differences; by conceding points or making counterarguments; by dismissing the importance of a fact or argument; or replacing and suggesting alternatives.
Causal Transitions
These terms and phrases signal the reasons, conditions, purposes, circumstances, and cause-and-effect relationships. These transitions often come after an important point in the research paper has been established or to explore hypothetical relationships or circumstances.
Sequential Transitions
These transition terms and phrases organize your paper by numerical sequence; by showing continuation in thought or action; by referring to previously-mentioned information; by indicating digressions; and, finally, by concluding and summing up your paper. Sequential transitions are essential to creating structure and helping the reader understand the logical development through your paper’s methods, results, and analysis.
How to Choose Transitions in Academic Writing
Transitions are commonplace elements in writing, but they are also powerful tools that can be abused or misapplied if one isn’t careful. Here are some ways to ensure you are using transitions effectively.
- Check for overused, awkward, or absent transitions during the paper editing process. Don’t spend too much time trying to find the “perfect” transition while writing the paper.
- When you find a suitable place where a transition could connect ideas, establish relationships, and make it easier for the reader to understand your point, use the list to find a suitable transition term or phrase.
- Similarly, if you have repeated some terms again and again, find a substitute transition from the list and use that instead. This will help vary your writing and enhance the communication of ideas.
- Read the beginning of each paragraph. Did you include a transition? If not, look at the information in that paragraph and the preceding paragraph and ask yourself: “How does this information connect?” Then locate the best transition from the list.
- Check the structure of your paper—are your ideas clearly laid out in order? You should be able to locate sequence terms such as “first,” “second,” “following this,” “another,” “in addition,” “finally,” “in conclusion,” etc. These terms will help outline your paper for the reader.
For more helpful information on academic writing and the journal publication process, visit Wordvice’s Academic Resources Page. And be sure to check out Wordvice’s professional English editing services if you are looking for paper editing and proofreading after composing your academic document.
Wordvice Tools
- Wordvice APA Citation Generator
- Wordvice MLA Citation Generator
- Wordvice Chicago Citation Generator
- Wordvice Vancouver Citation Generator
- Wordvice Plagiarism Checker
- Editing & Proofreading Guide
Wordvice Resources
- How to Write the Best Journal Submissions Cover Letter
- 100+ Strong Verbs That Will Make Your Research Writing Amazing
- How to Write an Abstract
- Which Tense to Use in Your Abstract
- Active and Passive Voice in Research Papers
- Common Phrases Used in Academic Writing
Other Resources Around the Web
- MSU Writing Center. Transition Words.
- UW-Madison Writing Center. Transition Words and Phrases.

Your Guide to Understanding Common Research Terms
Share this:.
Demystifying Clinical Trials -- Part 2
The clinical research world can sometimes seem confusing. Research teams have many people in different roles, and they may use words that are unfamiliar to people outside of research work.
The guide below defines some commonly used words and phrases. Let us know in the comments below or on our Facebook , Twitter , or Instagram pages if you’d like definitions of other words or parts of the research process!
Accrual – the number of subjects who have completed or are actively in the process of completing a study. The accrual goal is how many subjects are needed to finish the study (2).
Adverse event (AE) – a negative symptom or experience encountered by an subject during the course of a clinical trial. Adverse events can be expected or unexpected.
Assent – a minor child’s affirmative agreement to participate in a clinical trial. Failure to object may not be taken as assent.
Clinical research coordinator – a study team member who manages the day-to-day study tasks as directed by the principal investigator. (3)
Consent form – a document explaining all relevant study information to assist the study subject in understanding the expectations and requirements of participating in the trial. This document is presented to and signed by the study subject.
Control arm/group – a comparison group of study subjects who are not treated with the investigational agent. The subjects in this group have the same disease or condition under study, but receive either a different treatment, no treatment, or a placebo.
Data – the objective information gathered during a research study that is used to determine the results of the study.
De-identification – the process of removing identifiers (personal names, dates, social security numbers, etc.) that directly or indirectly point to a person, and removing those identifiers from the data. De-identification of protected health information is essential for protecting patient privacy (4).
Enroll/Enrollment – the process of an eligible participant signing a consent form and voluntarily agreeing to participate in a research study (2).
Ethics committee – an independent group of both medical and non-medical professionals who are responsible for verifying the integrity of a study and ensuring the safety, integrity, and human rights of the study participants.
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) – the agency within the Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS) that enforces public health laws related to research conduct.
Greater than minimal risk – the research involves more than minimal risk to subjects (2).
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) – required the Department of Health & Human Services to develop regulations protecting the privacy and security of certain health information (5). The HIPAA Privacy Rule established the conditions under which health information may be used or disclosed by approved entities for research purposes (6).
Hypothesis – a specific, clear, and testable proposition or prediction about the possible outcome of a scientific research study (7).
Informed consent – the process of discussing a clinical trial that goes beyond signing the consent form. The discussion should provide sufficient information so that a subject can make an informed decision about whether or not to enroll in a study, or continue participation in a study. Informed consent is a voluntary agreement to participate in research, and should be an ongoing conversation throughout a subject’s entire time in the study (8).
Investigational New Drug Application (IND) – the process through which an investigator requests the FDA to allow human testing of a new drug.
Institutional Review Board (IRB) – an independent group of professionals designated to review and approve the clinical protocol, informed consent forms, study advertisements, and patient brochures to ensure that the study is safe for human participation. It is also the IRB’s responsibility to ensure that the study adheres to the FDA’s regulations.
Minimal risk – the probability that harm or discomfort anticipated in the research study are not greater than those encountered in daily life or during routine physical examinations (2).
National Institutes of Health (NIH) – agency within DHHS that provides funding for research, conducts studies, and funds multi-site national studies.
Protected Health Information (PHI) – individually identifiable health information. HIPAA provides federal protections for personal health information and gives patients more control over their health information. It also sets boundaries for how entities and institutions can use and release health records (9).
Placebo – an inactive substance designed to resemble the drug being tested. It is used as a control to rule out any psychological effects testing may present. Most advanced clinical trials include a control group that is unknowingly taking a placebo.
Principal Investigator – the primary individual responsible for conducting a clinical trial and adhering to federal regulations, institutional policies, and IRB regulations (2).
Protocol – a detailed plan that sets out the objectives, study design, and methodology for a clinical trial. A study protocol must be approved by an IRB before research may begin on human subjects.
Randomization – study participants are assigned to groups in such a way that each participant has an equal chance of being assigned to each treatment or control group. Since randomization ensures that no specific criteria are used to assign any patients to a particular group, all the groups will be equally comparable.
Research – systematic investigation designed to develop or contribute to generalizable knowledge.
Standard treatment/Standard of care – the currently accepted treatment or intervention considered to be effective in the treatment of a specific disease or condition.
Statistical significance – the probability that an event or difference was occurred by chance alone. In clinical trials, the level of statistical significance depends on the number or participants studied and the observations made, as well as the magnitude of differences observed.
Subject/Participant – a patient or healthy individual participating in a research study.
Treatment arm/group – a group of study subjects who are treated with the investigational agent.
Visit schedule/Test schedule – the number, frequency, and type of exams, tests, and procedures that research subjects will be expected to undergo during the study. Some visits may be the same as normal clinical care visits, while others may be required just for the purpose of collecting data for the research study.
Definitions taken from https://www.centerwatch.com/health-resources/glossary/ unless otherwise cited.
(2) https://www.mayo.edu/research/institutional-review-board/definition-terms
(3) https://acrpnet.org/2018/08/14/the-anatomy-of-a-great-clinical-research-coordinator/
(4) https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5977668/
(5) https://www.hhs.gov/hipaa/for-professionals/privacy/index.html
(6) https://www.hhs.gov/hipaa/for-professionals/special-topics/research/index.html
(7) https://methods.sagepub.com/Reference//encyclopedia-of-survey-research-methods/n472.xml
(8) https://oprs.usc.edu/files/2017/04/Informed-Consent-Booklet-4.4.13.pdf
(9) https://www.hhs.gov/hipaa/for-individuals/faq/187/what-does-the-hipaa-privacy-rule-do/index.html
The Todd and Karen Wanek Family Program for Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) is a collaborative network of specialists bonded by the vision of finding solutions for individuals affected by congenital heart defects including HLHS. The specialized team is addressing the various aspects of these defects by using research and clinical strategies ranging from basic science to diagnostic imaging to regenerative therapies. Email the program at [email protected] to learn more.
- Copy link to clipboard
- Report newsfeed post
Interested in more newsfeed posts like this? Go to the HLHS blog.

Connect with thousands of patients and caregivers for support and answers.
- Hosted and moderated by Mayo Clinic.
- Safe and secure.
Already have an account? Sign In
Synonyms of research
- as in investigation
- as in to explore
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
Thesaurus Definition of research
(Entry 1 of 2)
Synonyms & Similar Words
- investigation
- exploration
- examination
- inquisition
- disquisition
- questionnaire
- interrogation
- reinvestigation
- soul - searching
- cross - examination
- questionary
- self - examination
- self - reflection
- self - exploration
- going - over
- self - scrutiny
- self - questioning
Thesaurus Definition of research (Entry 2 of 2)
- investigate
- look (into)
- inquire (into)
- delve (into)
- check up on
- skim (through)
- thumb (through)
- reinvestigate
Thesaurus Entries Near research
Cite this entry.
“Research.” Merriam-Webster.com Thesaurus , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/thesaurus/research. Accessed 10 Apr. 2024.
More from Merriam-Webster on research
Nglish: Translation of research for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of research for Arabic Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about research
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
Your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, more commonly mispronounced words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), absent letters that are heard anyway, popular in wordplay, the words of the week - apr. 5, 12 bird names that sound like compliments, 10 scrabble words without any vowels, 12 more bird names that sound like insults (and sometimes are), 8 uncommon words related to love, games & quizzes.

- Visit the University of Nebraska–Lincoln
- Apply to the University of Nebraska–Lincoln
- Give to the University of Nebraska–Lincoln
Search Form
Key research terms.
bias: any influence that may distort the results of a research study and lead to error; the loss of balance and accuracy in the use of research methods.
case study: presentation of data about selected settings, persons, groups or events. Data can have been gathered using variety of different research methods (e.g., questionnaire, observation, historical or literary analysis). Is chiefly descriptive and analytical, usually based on qualitative data, though statistics such as survey findings may be included.
causal relationship: relationship between variables where movements in one or more variable(s) are held to cause changes in the other (s).
coded data: data are put into groups or categories, such as age groups, and each category is given a code number. Data are usually coded for convenience, speed, and handling to enable statistical analysis. construct: a mental state that can’t be directly observed or manipulated, such as love, intelligence, hunger, feeling warm, and aggression; a concept developed (constructed) for describing relations among or between phenomena or for other research purposes.
construct validity: the degree to which the study actually measures and manipulates the elements that the researcher claims to be measuring and manipulating. If the operational definitions of the constructs are poor, the study will not have good construct validity. For example, a test claiming to measure “aggressiveness” would not have construct validity if it really measured assertiveness.
internal validity: the degree to which the study demonstrates that a particular factor caused a change in behavior. If a study lacks internal validity, the researcher may falsely believe that a factor causes an effect when it really doesn’t. Most studies involving humans do not have internal validity because they can’t rule out the possibility that some other factor may have been responsible for the effect.
controls: processes used to make uniform or constant the conditions for carrying out an investigation.
control group: in experimental research, the group or item which does not receive the treatment or intervention under investigation and is used to compare outcomes with the one that does. correlation: the extent to which two or more factors vary in relationship to one another; the extent of association between two or more variables. Correlation does not equal causation. For example, might suggest relationship between academic success and self-esteem, but cannot prove that a change in first variable causes a change in second variable. correlation coefficient: a measure of the degree of relationship between two variables. It usually lies between +1 (showing a perfect positive relationship), 0 (showing no relationship), to -1.0 (showing a perfect negative relationship). dependent variable: variable thought to be determined or influenced by others.
experiment: a special type of study (not all studies are experiments!) that allows researchers to determine the cause of an effect; usually involves randomly assigning participants to groups.
external validity: the degree to which the results of the study can be generalized to other places, people, or times.
hypothesis: a proposition which research sets out to prove or disprove: “experimental” where the hypothesis is a positive statement, or “null” where statement contains a negative.
independent variable: a variable that researcher believes precedes, influences or predicts the dependent variable.
informed consent: giving potential participants information about the study, especially in terms of factors that might lead them to refuse to be in the study, before they decide whether to participate. Institutional Review Board (IRB): a committee of at least five members--one of whom must be a nonscientist--that review proposed research and monitor approved research in an effort to protect human research participants.
literature review: often the first step in the research process, it is a review of the literature on and around the subject of inquiry. Its main purposes are to avoid duplication, to identify gaps in research and to place the researcher’s approach within the work and approaches of others.
primary/secondary sources: primary sources are original firsthand records or materials relating to an event or happening. They may include, for example, official minutes of meetings, diaries, verbatim transcripts of interviews, completed questionnaires or records of the results of experiments. Secondary sources are accounts bases upon these, which usually offer an interpretation, commentary, analysis, or restatement of the primary sources. They can include, for example, books, journal articles, and conference papers.
qualitative data: information gathered in narrative, non-numerical form (e.g., transcript of an interview). Qualitative research used for exploratory (hypothesis-generating) purposes or explaining puzzling quantitative results, while quantitative methods are used to test hypotheses.
quantitative data: information gathered in numerical form. reliability: extent to which the same result will be repeated/achieved by using the same measure.
statistical significance: tests used to estimate the likelihood that the finding in a sample is true of the population from which the sample is derived and not due to chance.
simple experiment: used to establish cause and effect, so this type often used to determine effect of treatment. Participants randomly assigned to either control group with no treatment, while the experimental group receives treatment.
validity: extent to which research findings can be said to be accurate and reliable; degree to which conclusions are justified. Internal validity is extent to which researchers can show that they have evidence for the statements they make; external validity refers to a study’s generalizability.
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

6 Commonly Confused Research Terms

While writing your research paper, you would come across elements that are the building blocks of a research paper. However, these often technical and confusing terms in research papers may trip up early career researchers. They may find some terms or elements overlapping and may struggle to differentiate between them. Through this article, we aim to clear the deck for successful research writing by helping you understand commonly confused research terms.
1. Citations and references
One set of confusing terms in research is citations and references You All sources used in a paper must always be mentioned within or at the end of the research paper. Text taken verbatim from any source must have all the details of the source within the paper and alongside the text. In research paper terms, this is a citation. References, on the other hand, are the listed versions of all the sources – books, articles, documents, videos, interviews – that were consumed as a part of research and used for writing the research paper.
2. Aim and objectives
These research paper terms might have similar meanings but when these terms are used in research, they should be considered separate. You may think of aims as the ultimate destination and objectives as the route you take to reach your destination. Here’s something to help understand these confusing terms in research. Aims refer to the outcome of the study – anything that you found out, could prove, or could conclude through your research. On the other hand, objectives are the ways in which you’re going to attain your research aims. Aims are broad in nature, while objectives are very specific and focused. Some types of manuscripts only require you to state an aim, others only objectives, and some require both.
3. Research methods and research methodology
Yes, these research paper terms are not interchangeable. Research methodology refers to the principles that guide you to pick the suitable methods for your research paper. For example, it helps you decide what kind of data analysis would help you achieve your aim – qualitative or quantitative. Research methods are the actual methods used to perform the experiments required to successfully complete your research paper. Depending on your research methodology, the research methods may vary including, but not limited to, observation, surveys, interviews, and laboratory experiments. So, be very careful when working with these two confusing terms in research and writing these sections.
4. Background of a study and introduction
It’s essential to understand these research paper terms to impress your readers – journal editors, fellow researchers, and your target audience. The background of a study is the missing piece of the existing literature’s puzzle. Its purpose is to state the significance of your study and the position of your research paper within the existing literature. It is not lengthy and helps the reader understand your topic of research with a wider perspective. Meanwhile, the introduction of a research paper is the opening section of your paper. It’s meant to set the context for the rest of the paper, establish the purpose of the study, and state the research question. So be sure not to mix up these confusing terms in research.

5. Implications and limitations
Another set of research paper terms that researchers often get confused about is implications and limitations. The ways in which your research findings can be helpful and may be applied are called implications, whereas the shortcomings or the way in which your research findings cannot be applied in real life are the limitations. Stating these two distinct research terms gives a holistic view of the applicability and scope of your research findings, and thus, having clarity on the meaning of these confusing terms in research is crucial.
6. Footnotes and endnotes
The last pair of research paper terms is footnotes and endnotes. Despite their self-explanatory names, this pair of confusing terms in research is a common source of error. Footnotes and endnotes are a way of providing additional information in your research paper. At times, authors may want to elaborate something they have written, but since adding an explanation within the main text may obstruct the flow, this information is added either at the bottom of the page or at the end of the research paper. Depending on the positioning, these additional notes are categorized as footnotes or endnotes when talking about research paper terms. As the names suggest, footnotes are mentioned at the bottom of the page, while endnotes are mentioned at the end of the research paper. Since both have the same function, it’s only a matter of choice which one you prefer to use. While footnotes make it convenient for the reader, having endnotes makes your paper clutter-free.
I hope reading this article helped you distinguish between these confusing terms in research. Moreover, as you gain experience by reading more research papers and writing more papers, you will get better at understanding these research paper terms and other nuances.
Related Posts

Top 10 High Impact Factor Journals

Is There a Reproducibility Crisis in Science?
How to Research a Term Paper
#scribendiinc
The term paper researching process
So, you wrote a great college admissions essay and were accepted at the university or college of your dreams. Now, you've been assigned your first term paper, and you don't know where to start!
The research process is an exploratory quest, a hunt for information that can be both exciting and rewarding. The word itself is derived from the French rechercher, which literally means "to investigate thoroughly." So, when embarking on writing a term paper or research paper, think of yourself as a detective. You will not only search for information but also delve into the whys and wherefores behind the subject material, seeking to provide elucidation through your term paper.
Select a topic for your term paper
Let's start at the beginning. The first step in the essay writing process is to decide on a worthy topic, choosing one that is interesting to you. Make a list of keywords—these are important words or phrases that encapsulate the essence of your topic. Good keywords will specifically describe your topic, but consider using closely related words, as well. Use these keywords when searching print or electronic sources that you can use in your term paper.
Research your term paper topic
General-purpose reference books, such as encyclopedias and fact books, provide comprehensive summaries and suggestions for sub-topics, as well as related terminology. Although these books are not generally considered suitable sources to cite in a term paper, the bibliographies they contain can be very helpful. This initial reading may help you to narrow your interest, stimulate additional questions, and focus your research. We recommend the following general resources, as they are more global in scope: The Oxford Companion to Politics of the World , CQ Researcher , the Political Handbook of the World, the Index to International Public Opinion, and World Opinion Update . These publications deal with particular topics, give summaries of various governments, or take other specialized approaches, which are generally considered acceptable sources to cite in a term paper.
The next step is to either narrow your topic (so you can deal with the amount of information) or to broaden it so you have enough to write about. You might have to pick a particular sub-topic and make that your area of interest, or combine certain aspects of a topic to create a narrower one. Decide the direction you want the research for your term paper to take. What are the most interesting aspects of the topic, and what do you want to learn? Be careful not to be too general. This term paper researching process will keep you from getting lost or sidetracked when searching for information.
Find suitable sources for your term paper
At this point, decide on the most likely sources of information—books, journal articles, newspapers, online databases, CD-ROM databases, interviews, etc. Dig around in the library and locate sources for your term paper. Use your library's computer access system to find books on your subject. Some topics may be so current that few, if any, books are available. If this is the case, research scholarly journals for up-to-date information and analyses. You should consult journals even for non-contemporary topics, since scholars may have unearthed new information or produced new analyses. You may also find valuable information published in the reports of a government agency, in hearings or reports of a government committee, or in the transcripts of the proceedings of a government body. The United Nations and a number of other international organizations also publish proceedings and reports.
Don't forget that when you locate the sources you want to use for your term paper, you should be trying to find answers to the questions you posed previously. Also, don't forget to make use of the reference librarian, who can help you to locate and use sources efficiently.
Get organized early! Keep track of your sources
It is very helpful to make notes about your sources on index cards or in an Excel spreadsheet . Such notes should include bibliographic information, page numbers for quotations, and source locations. This way, you can easily find the source of an idea, quote, reference, etc. Number these cards so you can link them to your term paper notes: this will make the references section of your report a snap to complete.
Remember—thoroughly peruse all the information you have gathered, making copious notes as you go. This preliminary research should answer basic factual questions, as well as interpretive ones, and should help you to refocus. Give yourself a reasonable amount of time to absorb all the information you've read.
Writing a research or term paper
In our follow-up article about writing a research paper , we explain the next steps in the term paper writing process. The article discusses your thesis statement, body of your paper, and your reference page. If you would like to learn more about essay writing, check out Scribendi's article 12 Ways to Quickly Improve Your Academic Essay Writing Skills .
Image source: Samuel Zeller/Unsplash.com
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

Essay Writing Help


How to Improve Essay Writing Skills

How to Write a Great Thesis Statement
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).

- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Term Paper – Format, Examples and Writing Guide
Term Paper – Format, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Definition:
Term paper is a type of academic writing assignment that is typically assigned to students at the end of a semester or term. It is usually a research-based paper that is meant to demonstrate the student’s understanding of a particular topic, as well as their ability to analyze and synthesize information from various sources.
Term papers are usually longer than other types of academic writing assignments and can range anywhere from 5 to 20 pages or more, depending on the level of study and the specific requirements of the assignment. They often require extensive research and the use of a variety of sources, including books, articles, and other academic publications.
Term Paper Format
The format of a term paper may vary depending on the specific requirements of your professor or institution. However, a typical term paper usually consists of the following sections:
- Title page: This should include the title of your paper, your name, the course name and number, your instructor’s name, and the date.
- Abstract : This is a brief summary of your paper, usually no more than 250 words. It should provide an overview of your topic, the research question or hypothesis, your methodology, and your main findings or conclusions.
- Introduction : This section should introduce your topic and provide background information on the subject. You should also state your research question or hypothesis and explain the importance of your research.
- Literature review : This section should review the existing literature on your topic. You should summarize the key findings and arguments made by other scholars and identify any gaps in the literature that your research aims to address.
- Methodology: This section should describe the methods you used to collect and analyze your data. You should explain your research design, sampling strategy, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques.
- Results : This section should present your findings. You can use tables, graphs, and charts to illustrate your data.
- Discussion : This section should interpret your findings and explain what they mean in relation to your research question or hypothesis. You should also discuss any limitations of your study and suggest areas for future research.
- Conclusion : This section should summarize your main findings and conclusions. You should also restate the importance of your research and its implications for the field.
- References : This section should list all the sources you cited in your paper using a specific citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago).
- Appendices : This section should include any additional materials that are relevant to your study but not essential to your main argument (e.g., survey questions, interview transcripts).
Structure of Term Paper
Here’s an example structure for a term paper:
I. Introduction
A. Background information on the topic
B. Thesis statement
II. Literature Review
A. Overview of current literature on the topic
B. Discussion of key themes and findings from literature
C. Identification of gaps in current literature
III. Methodology
A. Description of research design
B. Discussion of data collection methods
C. Explanation of data analysis techniques
IV. Results
A. Presentation of findings
B. Analysis and interpretation of results
C. Comparison of results with previous studies
V. Discussion
A. Summary of key findings
B. Explanation of how results address the research questions
C. Implications of results for the field
VI. Conclusion
A. Recap of key points
B. Significance of findings
C. Future directions for research
VII. References
A. List of sources cited in the paper
How to Write Term Paper
Here are some steps to help you write a term paper:
- Choose a topic: Choose a topic that interests you and is relevant to your course. If your professor has assigned a topic, make sure you understand it and clarify any doubts before you start.
- Research : Conduct research on your topic by gathering information from various sources such as books, academic journals, and online resources. Take notes and organize your information systematically.
- Create an outline : Create an outline of your term paper by arranging your ideas and information in a logical sequence. Your outline should include an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
- Write a thesis statement: Write a clear and concise thesis statement that states the main idea of your paper. Your thesis statement should be included in your introduction.
- Write the introduction: The introduction should grab the reader’s attention, provide background information on your topic, and introduce your thesis statement.
- Write the body : The body of your paper should provide supporting evidence for your thesis statement. Use your research to provide details and examples to support your argument. Make sure to organize your ideas logically and use transition words to connect paragraphs.
- Write the conclusion : The conclusion should summarize your main points and restate your thesis statement. Avoid introducing new information in the conclusion.
- Edit and proofread: Edit and proofread your term paper carefully to ensure that it is free of errors and flows smoothly. Check for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors.
- Format and cite your sources: Follow the formatting guidelines provided by your professor and cite your sources properly using the appropriate citation style.
- Submit your paper : Submit your paper on time and according to the instructions provided by your professor.
Term Paper Example
Here’s an example of a term paper:
Title : The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity
As the world becomes more digitally interconnected, cybersecurity threats are increasing in frequency and sophistication. Traditional security measures are no longer enough to protect against these threats. This paper explores the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in cybersecurity, including how AI can be used to detect and respond to threats in real-time, the challenges of implementing AI in cybersecurity, and the potential ethical implications of AI-powered security systems. The paper concludes with recommendations for organizations looking to integrate AI into their cybersecurity strategies.
Introduction :
The increasing number of cybersecurity threats in recent years has led to a growing interest in the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) to improve cybersecurity. AI has the ability to analyze vast amounts of data and identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate a security breach. Additionally, AI can automate responses to threats, allowing for faster and more effective mitigation of security incidents. However, there are also challenges associated with implementing AI in cybersecurity, such as the need for large amounts of high-quality data, the potential for AI systems to make mistakes, and the ethical considerations surrounding the use of AI in security.
Literature Review:
This section of the paper reviews existing research on the use of AI in cybersecurity. It begins by discussing the types of AI techniques used in cybersecurity, including machine learning, natural language processing, and neural networks. The literature review then explores the advantages of using AI in cybersecurity, such as its ability to detect previously unknown threats and its potential to reduce the workload of security analysts. However, the review also highlights some of the challenges associated with implementing AI in cybersecurity, such as the need for high-quality training data and the potential for AI systems to be fooled by sophisticated attacks.
Methodology :
To better understand the challenges and opportunities associated with using AI in cybersecurity, this paper conducted a survey of cybersecurity professionals working in a variety of industries. The survey included questions about the types of AI techniques used in their organizations, the challenges they faced when implementing AI in cybersecurity, and their perceptions of the ethical implications of using AI in security.
The results of the survey showed that while many organizations are interested in using AI in cybersecurity, they face several challenges when implementing these systems. These challenges include the need for high-quality training data, the potential for AI systems to be fooled by sophisticated attacks, and the difficulty of integrating AI with existing security systems. Additionally, many respondents expressed concerns about the ethical implications of using AI in security, such as the potential for AI to be biased or to make decisions that are harmful to individuals or society as a whole.
Discussion :
Based on the results of the survey and the existing literature, this paper discusses the potential benefits and risks of using AI in cybersecurity. It also provides recommendations for organizations looking to integrate AI into their security strategies, such as the need to prioritize data quality and to ensure that AI systems are transparent and accountable.
Conclusion :
While there are challenges associated with implementing AI in cybersecurity, the potential benefits of using these systems are significant. AI can help organizations detect and respond to threats more quickly and effectively, reducing the risk of security breaches. However, it is important for organizations to be aware of the potential ethical implications of using AI in security and to take steps to ensure that these systems are transparent and accountable.
References:
- Alkhaldi, S., Al-Daraiseh, A., & Lutfiyya, H. (2019). A Survey on Artificial Intelligence Techniques in Cyber Security. Journal of Information Security, 10(03), 191-207.
- Gartner. (2019). Gartner Top 10 Strategic Technology Trends for 2020. Retrieved from https://www.gartner.com/smarterwithgartner/gartner-top-10-strategic-technology-trends-for-2020/
- Kshetri, N. (2018). Blockchain’s roles in meeting key supply chain management objectives. International Journal of Information Management, 39, 80-89.
- Lipton, Z. C. (2018). The mythos of model interpretability. arXiv preprint arXiv:1606.03490.
- Schneier, B. (2019). Click Here to Kill Everybody: Security and Survival in a Hyper-Connected World. WW Norton & Company.
- Wahab, M. A., Rahman, M. S., & Islam, M. R. (2020). A Survey on AI Techniques in Cybersecurity. International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, 11(2), 22-27.
When to Write Term Paper
A term paper is usually a lengthy research paper that is assigned to students at the end of a term or semester. There are several situations when writing a term paper may be required, including:
- As a course requirement: In most cases, a term paper is required as part of the coursework for a particular course. It may be assigned by the instructor as a way of assessing the student’s understanding of the course material.
- To explore a specific topic : A term paper can be an excellent opportunity for students to explore a specific topic of interest in-depth. It allows them to conduct extensive research on the topic and develop their understanding of it.
- To develop critical thinking skills : Writing a term paper requires students to engage in critical thinking and analysis. It helps them to develop their ability to evaluate and interpret information, as well as to present their ideas in a clear and coherent manner.
- To prepare for future academic or professional pursuits: Writing a term paper can be an excellent way for students to prepare for future academic or professional pursuits. It can help them to develop the research and writing skills necessary for success in higher education or in a professional career.
Purpose of Term Paper
The main purposes of a term paper are:
- Demonstrate mastery of a subject: A term paper provides an opportunity for students to showcase their knowledge and understanding of a particular subject. It requires students to research and analyze the topic, and then present their findings in a clear and organized manner.
- Develop critical thinking skills: Writing a term paper requires students to think critically about their subject matter, analyzing various sources and viewpoints, and evaluating evidence to support their arguments.
- Improve writing skills : Writing a term paper helps students improve their writing skills, including organization, clarity, and coherence. It also requires them to follow specific formatting and citation guidelines, which can be valuable skills for future academic and professional endeavors.
- Contribute to academic discourse : A well-written term paper can contribute to academic discourse by presenting new insights, ideas, and arguments that add to the existing body of knowledge on a particular topic.
- Prepare for future research : Writing a term paper can help prepare students for future research, by teaching them how to conduct a literature review, evaluate sources, and formulate research questions and hypotheses. It can also help them develop research skills that they can apply in future academic or professional endeavors.
Advantages of Term Paper
There are several advantages of writing a term paper, including:
- In-depth exploration: Writing a term paper allows you to delve deeper into a specific topic, allowing you to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
- Improved writing skills: Writing a term paper involves extensive research, critical thinking, and the organization of ideas into a cohesive written document. As a result, writing a term paper can improve your writing skills significantly.
- Demonstration of knowledge: A well-written term paper demonstrates your knowledge and understanding of the subject matter, which can be beneficial for academic or professional purposes.
- Development of research skills : Writing a term paper requires conducting thorough research, analyzing data, and synthesizing information from various sources. This process can help you develop essential research skills that can be applied in many other areas.
- Enhancement of critical thinking : Writing a term paper encourages you to think critically, evaluate information, and develop well-supported arguments. These skills can be useful in many areas of life, including personal and professional decision-making.
- Preparation for further academic work : Writing a term paper is excellent preparation for more extensive academic projects, such as a thesis or dissertation.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

What is Art – Definition, Types, Examples

What is Anthropology – Definition and Overview

What is Literature – Definition, Types, Examples

Economist – Definition, Types, Work Area

Anthropologist – Definition, Types, Work Area

What is History – Definitions, Periods, Methods

- SMU Libraries
- Scholarship & Research
- Teaching & Learning
- Bridwell Library
- Business Library
- DeGolyer Library
- Fondren Library
- Hamon Arts Library
- Underwood Law Library
- Fort Burgwin Library
- Exhibits & Digital Collections
- SMU Scholar
- Special Collections & Archives
- Connect With Us
- Research Guides by Subject
- How Do I . . . ? Guides
- Find Your Librarian
- Writing Support
Types of Research Papers: Overview
A research paper is simply a piece of writing that uses outside sources. There are different types of research papers with varying purposes and expectations for sourcing.
While this guide explains those differences broadly, ask your professor about specific disciplinary conventions.
Need More Help?
Chat
Schedule Appointment
Related Guides
- Literature Reviews
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Starting Your Research
Research and Writing Lab
Need last minute help but didn't book an appointment? Every week we offer online drop-in labs.
Tuesdays 3:00pm - 4:30pm via Zoom @ https://smu.zoom.us/j/92637892352 and in-person, Fondren Red 1st floor (near elevators)
- Last Updated: Apr 9, 2024 12:04 PM
- URL: https://guides.smu.edu/researchpapertypes
× All floors of the JFK Library are open for summer quarter. For details see Library Access
Research Guides
Eastern Washington University Libraries
APA Style 7th Edition Tutorials for Students in Psychology and Social Work
What is apa style.
- The Importance of Citing
Why is APA Style needed?
How do i get started with apa style, let us practice what we have learned, attribution and acknowledgement.
- Basics of APA Style Tutorial
- Reference Entry Elements
- Reference Examples
- Reference List
- In-Text Citations
- Student Paper Format
- Managing References - Zotero
Origination of APA Style
- Where did APA Style come from?
Commonly Used APA Related Terms
Abstract : Abstract is a brief synopses of article. It provides a brief but comprehensive summary of the article.
Citing : In the context of academic writing, citing is the act of acknowledging the sources of information you have used when writing your work.
Citation: A citation gives credit to a source, and contains publication information such as author(s), title and date.
DOI (digital object identifier): It is a unique alphanumeric string assigned to a digital object, mainly a scholarly article, to provide a persistent link to its location on the internet.
In-Text Citation : It is a brief note that appears within the body of the paper and briefly identifies the cited work by its author and date of publication. An in-text citation should always match the corresponding entry in the reference list at the end of paper.
Paraphrasing : A paraphrase restates another’s idea (or your own previously published idea) in your own words.
Plagiarism : It is the act of presenting the words, ideas, or images of another as your own; it denies creators of content the credit they are due.
Quoting : It is the act of reproducing the exact wording used by the original author. Direct quotations appear within quotation marks and end with a citation.
Reference : It contains details about one cited work, generally including four elements: author, date, title, and source.
Reference List : It identifies all the sources you cited in the text of your paper. It generally is at the end of the paper and definitely on a new page after the text of your paper.
APA Style is the most common writing style used in college and career. Its purpose is to promote excellence in communication by helping writers create clear, precise, and inclusive sentences with a straightforward scholarly tone. It addresses areas of writing such as how to
- format a paper so it looks professional;
- credit other people’s words and ideas via citations and references to avoid plagiarism; and
- describe other people with dignity and respect using inclusive, bias-free language.
APA Style is primarily used in the behavioral sciences, which are subjects related to people, such as psychology, education, and nursing. It is also used by students in business, engineering, communications, and other classes. Students use it to write academic essays and research papers in college, and professionals use it to conduct, report, and publish scientific research.
In addition, APA Style provides you with a powerful tool that will hep you avoid deliberate or unintentional plagiarism. Please review the Avoiding Plagiarism Guide created by the APA experts to understand what two common types of plagiarism are and how to avoid them.
Why is learning citations important? Citations help readers understand where the information used in your paper comes from, enabling them to trace the path of that information. When readers wish to explore a specific point or reference cited in the text, citations make it easier by providing information about your sources in a standardized format.
Besides showing readers where you obtained information, using citations also has a strong ethical purpose. In academic writing, it is important to credit ideas that are not your own. Citations allow you to integrate the ideas of others with your own thoughts in a fair and honest way.
The reference formats for APA Style manuals are as follows:
APA Style provides a foundation for effective scholarly communication because it helps authors present their ideas in a clear and concise, and organized manner. Uniformity and consistency enable readers to (a) focus on the ideas being presented rather than formatting and (b) scan works quickly for key points, findings, and sources. When style works best, ideas flow logically, sources are credited appropriately, and papers are organized predictably and consistently.
Students are encouraged to first learn about APA Style by reading works written in APA Style. A couple of guides created by APA experts from the American Psychological Association can help you with that:
Anatomy of a Journal Article https://apastyle.apa.org/instructional-aids/anatomy-journal-article.pdf
Scholarly journal articles share a common anatomy or structure. Each part of an article serves a specific purpose. The handout of Anatomy of a Journal Article explains how journal articles are structured and how to become more efficient at reading and understanding them. Understanding the structure of a scholarly article and the purpose of each part helps you grasp a strategy called targeted reading. Targeted reading means to read specific sections of research articles first to determine if the article seems useful for your research topic. This way you will save time, find useful article faster, and choose which articles to read in full.
Reading and Understanding Abstracts https://apastyle.apa.org/instructional-aids/reading-abstracts.pdf
Abstracts are short summaries of scientific research articles. The handout of Reading & Understanding Abstracts explains the definition and purpose of abstracts and the benefits of reading them, including analysis of a sample abstract. The skill of reading and understanding abstracts of scholarly articles not only saves time but also helps you conduct better research and write more effectively.
APA Style Writing Principles https://apastyle.apa.org/instructional-aids/writing-principles.pdf
The poster created by APA experts shows the three main principles of APA Style: clarity, precision, and inclusion and lists steps on how to achieve them. As a student writer, you always should write your academic paper with clarity, precision, and inclusion.
Research Article Activity https://apastyle.apa.org/instructional-aids/apa-style-research-activity.pdf
Reading research articles is not an easy task for you as a student. The Research Article Activity designed by APA Style experts aims to make it easy to read and understand a scholarly article. This activity worksheet helps you find, cite, analyze, and summarize a research article. Completing this activity breaks down a lengthy research article into easily understandable chunks. This way helps you better understand the study in the article before you write about it.
The information in this Guide is courtesy of the official APA Style website by the American Psychological Association.
Source Credit: Information on this LibGuide comes from APA Style website https://apastyle.apa.org/ This website has a wealth of free and authoritative resources designed to help anyone new to APA Style.
- Next: Basics of APA Style Tutorial >>
- Last Updated: Apr 6, 2024 12:06 PM
- URL: https://research.ewu.edu/APAStyleTutorial
Retirement planning – a systematic review of literature and future research directions
- Published: 28 October 2023
Cite this article
- Kavita Karan Ingale ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3570-4211 1 &
- Ratna Achuta Paluri 2
508 Accesses
Explore all metrics
Rising life expectancy and an aging population across nations are leading to an increased need for long-term financial savings and a focus on the financial well-being of retired individuals amidst changing policy framework. This study is a systematic review based on a scientific way of producing high-quality evidence based on 191 articles from the Scopus and Web of Science databases. It adopts the Theory, Context, Characteristics, and Method (TCCM) framework to analyze literature. This study provides collective insights into financial decision-making for retirement savings and identifies constructs for operationalizing and measuring financial behavior for retirement planning. Further, it indicates the need for an interdisciplinary approach. Though cognitive areas were studied extensively, the non-cognitive areas received little attention. Qualitative research design is gaining prominence in research over other methods, with the sparse application of mixed methods design. The study’s TCCM framework explicates several areas for further research. Furthermore, it guides the practice and policy by integrating empirical evidence and concomitant findings. Coherent synthesis of the extant literature reconciles the highly fragmented field of retirement planning. No research reports prospective areas for further analysis based on the TCCM framework on retirement planning, which highlights the uniqueness of the study.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price excludes VAT (USA) Tax calculation will be finalised during checkout.
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

A Research Proposal to Examine Psychological Factors Influence on Financial Planning for Retirement in China
Domains and determinants of retirement timing: A systematic review of longitudinal studies
Micky Scharn, Ranu Sewdas, … Allard J. van der Beek

Reinventing Retirement
Deanna L. Sharpe
Data Availability
The research data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgment.
Elderly population is defined as a population aged 65 years and over.
Defined benefit plan guarantees benefits to the employee, while defined contribution plan requires employees to decide on their own investment and bear the financial risks identified with it.
“The old-age dependency ratio is defined as the number of individuals aged 65 and over per 100 people of working age defined as those at ages 20 to 64”(OECD 2023 ).
Adams GA, Rau BL (2011) Putting off tomorrow to do what you want today: planning for Retirement. Am Psychol 66(3):180–192. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0022131
Article Google Scholar
Aegon Cfor, Longevity, Retirement ICR (2016) The Aegon Retirement Readiness Survey 2016. In The Aegon Retirement Readiness Survey 2016 . https://www.aegon.com/contentassets/c6a4b1cdded34f1b85a4f21d4c66e5d3/2016-aegon-retirement-readiness-report-india.pdf
Agarwalla SK, Barua SK, Jacob J, Varma JR (2015) Financial Literacy among Working Young in Urban India. World Development , 67 (2013), 101–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2014.10.004
Ajzen I (1991) The theory of Planned Behavior. Organ Behav Hum Decis Process 50:179–211. https://doi.org/10.47985/dcidj.475
Anderson A, Baker F, Robinson DT (2017) Precautionary savings, retirement planning, and misperceptions of financial literacy. J Financ Econ 126(2):383–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfineco.2017.07.008
Atkinson A, Messy FA (2011) Assessing financial literacy in 12 countries: an OECD/INFE international pilot exercise. J Pension Econ Finance 10(4):657–665. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1474747211000539`
Aydin AE, Akben Selcuk E (2019) An investigation of financial literacy, money ethics, and time preferences among college students: a structural equation model. Int J Bank Mark 37(3):880–900. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJBM-05-2018-0120
Bapat D (2020) Antecedents to responsible financial management behavior among young adults: the moderating role of financial risk tolerance. Int J Bank Mark 38(5):1177–1194. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJBM-10-2019-0356
Beckett A, Hewer P, Howcroft B (2000) An exposition of consumer behaviour in the financial services industry. Int J Bank Mark 18(1):15–26. https://doi.org/10.1108/02652320010315325
Białowolski P (2019) Economic sentiment as a driver for household financial behavior. J Behav Experimental Econ 80(August 2017):59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socec.2019.03.006
Binswanger J, Carman KG (2012) How real people make long-term decisions: the case of retirement preparation. J Economic Behav Organ 81(1):39–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jebo.2011.08.010
Brounen D, Koedijk KG, Pownall RAJ (2016) Household financial planning and savings behavior. J Int Money Finance 69:95–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jimonfin.2016.06.011
Brown R, Jones M (2015) Mapping and exploring the topography of contemporary financial accounting research. Br Acc Rev 47(3):237–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bar.2014.08.006
Brown S, Gray D (2016) Household finances and well-being in Australia: an empirical analysis of comparison effects. J Econ Psychol 53:17–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2015.12.006
Brown S, Taylor K (2014) Household finances and the big five personality traits. J Econ Psychol 45:197–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2014.10.006
Brown S, Taylor K (2016) Early influences on saving behaviour: analysis of British panel data. J Bank Finance 62:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbankfin.2015.09.011
Brüggen EC, Post T, Schmitz K (2019) Interactivity in online pension planners enhances engagement with retirement planning – but not for everyone. J Serv Mark 33(4):488–501. https://doi.org/10.1108/JSM-02-2018-0082
Bruggen E, Post T, Katharina S (2019) Interactivity in online pension planners enhances engagement with retirement planning but not for everyone. J Serv Mark 33(4):488–501
Calcagno R, Monticone C (2015) Financial literacy and the demand for financial advice. J Bank Finance 50:363–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbankfin.2014.03.013
Campbell JY (2006) Household finance. J Finance 61(4):1553–1604. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-6261.2006.00883.x
Choudhury K (2015) Service quality and customers’ behavioural intentions: class and mass banking and implications for the consumer and society. Asia Pac J Mark Logistics 27(5):735–757
Chowdhry N, Jung J, Dholakia U (2018) Association for consumer research. Adv Consum Res 42:42–46
Google Scholar
Clark GL, Knox-Hayes J, Strauss K (2009) Financial sophistication, salience, and the scale of deliberation in UK retirement planning. Environ Plann A 41(10):2496–2515. https://doi.org/10.1068/a41265
Clark R, Lusardi A, Mitchell OS (2017) Employee Financial Literacy and Retirement Plan Behavior: a case study. Econ Inq 55(1):248–259. https://doi.org/10.1111/ecin.12389
Collins JM, Urban C (2016) The role of information on Retirement Planning: evidence from a field study. Econ Inq 54(4):1860–1872. https://doi.org/10.1111/ecin.12349
Creswell J (2009) Research Design Qualitative Quantitative and Mixed Methods Approaches. In Sage Publishing: Vol. Third edit . https://doi.org/10.1002/tl.20234
Csorba L (2020) The determining factors of financial culture, financial literacy, and financial behavior. Public Finance Q 65:67–83. https://doi.org/10.35551/PFQ_2020_1_6
Davidoff T, Gerhard P, Post T (2017) Reverse mortgages: what homeowners (don’t) know and how it matters. J Economic Behav Organ 133:151–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jebo.2016.11.007
Davis FD (1989) Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Quarterly: Management Information Systems 13(3):319–339. https://doi.org/10.2307/249008
Devlin J (2001) Consumer evaluation and competitive advantage in retail financial services - a research agenda. Eur J Mark 35(5/6):639–660
Dholakia U, Tam L, Yoon S, Wong N (2016) The ant and the grasshopper: understanding personal saving orientation of consumers. J Consum Res 43(1):134–155. https://doi.org/10.1093/jcr/ucw004
Dolls M, Doerrenberg P, Peichl A, Stichnoth H (2018) Do retirement savings increase in response to information about retirement and expected pensions? J Public Econ 158(July 2017):168–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpubeco.2017.12.014
Dragos SL, Dragos CM, Muresan GM (2020) From intention to the decision in purchasing life insurance and private pensions: different effects of knowledge and behavioural factors. J Behav Experimental Econ 87(March):101555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socec.2020.101555
Drever AI, Odders-white E, Kalish CW, Hoagland EM, Nelms EN, Drever AI, Odders-white E, Charles W, Else-quest NM, Hoagland EM, Nelms EN (2015) Foundations of Financial Weil-Being: Insights into the Role of Executive Function, Financial Socialization, and Experience-Based Learning in Childhood and Youth Source : The Journal of Consumer Affairs, Vol. 49, No. 1, Special Issue on Starting Ea. The Journal of Consumer Affairs , 49 (1)
Duflo E, Saez E (2002) Participation and investment decisions in a retirement plan: the influence of colleagues’ choices. J Public Econ 85(1):121–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0047-2727(01)00098-6
Duxbury D, Summers B, Hudson R, Keasey K (2013) How people evaluate defined contribution, annuity-based pension arrangements: a behavioral exploration. J Econ Psychol 34:256–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2012.10.008
Earl J, Bednall T, Muratore A (2015) A matter of time: why some people plan for retirement and others do not. Work Aging and Retirement 1(2):181–189. https://doi.org/10.1093/workar/wau005
Employees Benefits Research Institute (2020) EBRI Retirement Confidence Survey Report (Issue 202)
Engel JF, Kollat DT, Blackwell RD (1968) A model of consumer motivation and behavior. In: Research in consumer behavior. Holt, Rinehart and Winston, Inc., New York, pp 3–20
Erasmus A, Boshoff E, Rousseau G (2001) Consumer decision-making models within the discipline of consumer science: a critical approach. J Family Ecol Consumer Sci /Tydskrif Vir Gesinsekologie En Verbruikerswetenskappe 29(1):82–90. https://doi.org/10.4314/jfecs.v29i1.52799
Farrell L, Fry TRL, Risse L (2016) The significance of financial self-efficacy in explaining women’s personal finance behaviour. J Econ Psychol 54:85–99
Fernandes D, Lynch JG, Netemeyer RG (2014) Financial literacy, financial education, and downstream financial behaviors. Manage Sci 60(8):1861–1883. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.2013.1849
Filbec G, Ricciardi V, Evensky H, Fan S, Holzhauer H, Spieler A (2017) Behavioral finance: a panel discussion. J Behav Experimental Finance 15:52–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbef.2015.07.003
Fishbein M (1979) A theory of reasoned action: some applications and implications. Nebraska Symposium on Motivation 27:65–116
Fisher PJ, Montalto CP (2010) Effect of saving motives and horizon on saving behaviors. J Econ Psychol 31(1):92–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2009.11.002
Flores SAM, Vieira KM (2014) Propensity toward indebtedness: an analysis using behavioral factors. J Behav Exp Finance 3:1–10
Foxall GR, Pallister JG (1998) Measuring purchase decision involvement for financial services: comparison of the Zaichkowsky and Mittal scales. Int J Bank Mark 16(5):180–194. https://doi.org/10.1108/02652329810228181
Friedman M (1957) Introduction to “A theory of the consumption function”. In: A theory of the consumption function. Princeton University Press, pp 1–6
Frydman C, Camerer CF (2016) The psychology and neuroscience of financial decision making. Trends Cogn Sci 20(9):661–675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2016.07.003
Gardarsdóttir RB, Dittmar H (2012) The relationship of materialism to debt and financial well-being: the case of Iceland’s perceived prosperity. J Econ Psychol 33(3):471–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2011.12.008
Gathergood J (2012) Self-control, financial literacy and consumer over-indebtedness. J Econ Psychol 33(3):590–602
Gerhard P, Gladstone JJ, Hoffmann AOI (2018) Psychological characteristics and household savings behavior: the importance of accounting for latent heterogeneity. J Economic Behav Organ 148:66–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jebo.2018.02.013
Gibbs PT (2009) Time, temporality, and
Goedde-Menke M, Lehmensiek-Starke M, Nolte S (2014) An empirical test of competing hypotheses for the annuity puzzle. J Econ Psychol 43:75–91
Gough O, Nurullah M (2009) Understanding what drives the purchase decision in pension and investment products. J Financial Serv Mark 14(2):152–172. https://doi.org/10.1057/fsm.2009.14
Griffin B, Loe D, Hesketh B (2012) Using Proactivity, Time Discounting, and the theory of Planned Behavior to identify predictors of Retirement Planning. Educ Gerontol 38(12):877–889. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601277.2012.660857
Gritten A (2011) New insights into consumer confidence in financial services. Int J Bank Mark 29(2):90–106. https://doi.org/10.1108/02652321111107602
Grohmann A (2018) Financial literacy and financial behavior: Evidence from the emerging Asian middle class. Pacific Basin Finance Journal , 48 (November 2017), 129–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pacfin.2018.01.007
Grohmann A, Kouwenberg R, Menkhoff L (2015) Childhood roots of financial literacy. J Econ Psychol 51:114–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2015.09.002
Hair JF, Sarstedt M, Ringle CM, Mena JA (2012) An assessment of the use of partial least squares structural equation modeling in marketing research . 414–433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-011-0261-6
Hanna SD, Kim KT, Chen SCC (2016) Retirement savings. In: Handbook of consumer finance research, pp 33–43
Harrison T, Waite K, White P (2006) Analysis by paralysis: the pension purchase decision process. Int J Bank Mark 24(1):5–23. https://doi.org/10.1108/02652320610642317
Hastings J, Mitchell O (2011) How financial literact and impatience shape retirement wealth and investment behaviors. Pengaruh Harga Diskon Dan Persepsi Produk Terhadap Nilai Belanja Serta Perilaku Pembelian Konsumen, NBER Working paper, 1–28
Hauff J, Carlander A, Amelie G, Tommy G, Holmen M (2016) Breaking the ice of low financial involvement: does narrative information format from a trusted sender increase savings in mutual funds? Int J Bank Mark 34(2):151–170
Hentzen JK, Hoffmann A, Dolan R, Pala E (2021) Artificial intelligence in customer-facing financial services: a systematic literature review and agenda for future research. Int J Bank Mark. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJBM-09-2021-0417
Hershey DA, Mowen JC (2000) Psychological determinants of financial preparedness for retirement. Gerontologist 40(6):687–697. https://doi.org/10.1093/geront/40.6.687
Hershey DA, Henkens K, Van Dalen HP (2007) Mapping the minds of retirement planners: a cross-cultural perspective. J Cross-Cult Psychol 38(3):361–382. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022022107300280
Hershey DA, Jacobs-Lawson JM, McArdle JJ, Hamagami F (2007b) Psychological foundations of financial planning for retirement. J Adult Dev 14(1–2):26–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10804-007-9028-1
Hershey DA, Jacobs-Lawson JM, McArdle JJ, Hamagami F (2008) Psychological foundations of financial planning for retirement. J Adult Dev 14(1–2):26–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10804-007-9028-1
Hershfield H, Goldstein D, Sharpe W, Fox J, Yeykelis L, Carstensen L, Bailenson J (2011) Increasing saving behavior through age-progressed renderings of the future self. J Mark Res 48:23–37
Hoffmann AOI, Broekhuizen TLJ (2009) Susceptibility to and impact of interpersonal influence in an investment context. J Acad Mark Sci 37:488–503
Hoffmann AOI, Broekhuizen TLJ (2010) Understanding investors’ decisions to purchase innovative products: drivers of adoption timing and range. Int J Res Mark 27(4):342–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijresmar.2010.08.002
Hoffmann AOI, Plotkina D (2020a) Positive framing when assessing the personal resources to manage one’s finances increases consumers’ retirement self-efficacy and improves retirement goal clarity. Psychol Mark 38(12):2286–2304. https://doi.org/10.1002/mar.21563
Hoffmann AOI, Plotkina D (2020b) Why and when does financial information affect retirement planning intentions and which consumers are more likely to act on them? Journal of Business Research , 117 (September 2019), 411–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.06.023
Hoffmann AOI, Plotkina D (2021) Let your past define your future. How recalling successful financial experiences can increase beliefs of self-efficacy in financial planning. J Consum Aff 55(3):847–871. https://doi.org/10.1111/joca.12378
Hoffmann AOI, Risse L (2020) Do good things come in pairs? How personality traits help explain individuals’ simultaneous pursuit of a healthy lifestyle and financially responsible behavior. J Consum Aff 54(3):1082–1120. https://doi.org/10.1111/joca.12317
Hsiao YJ, Tsai WC (2018) Financial literacy and participation in the derivatives markets. J Bank Finance 88:15–29
Huhmann BA, McQuitty S (2009) A model of consumer financial numeracy. Int J Bank Mark 27(4):270–293. https://doi.org/10.1108/02652320910968359
Huston SJ (2010) Measuring financial literacy. J Consum Aff 44(2):296–316. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6606.2010.01170.x
Ijevleva K, Arefjevs I (2014) Analysis of the Aggregate Financial Behaviour of customers using the Transtheoretical Model of Change. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 156(April):435–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.11.217
Ingale KK, Paluri RA (2020) Financial literacy and financial behavior: a bibliometric analysis. Rev Behav Finance. https://doi.org/10.1108/RBF-06-2020-0141
Jacobs-Lawson J, Hershey D (2005) Influence of future time perspective, financial knowledge, and financial risk tolerance on retirement savings behavior. Financial Serv Rev 14:331–344. https://doi.org/10.1088/1751-8113/44/8/085201
Jappelli T, Padula M (2013) Investment in financial literacy and saving decisions. J Bank Finance 37(8):2779–2792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbankfin.2013.03.019
Kadoya Y, Rahim Khan MS (2020) Financial literacy in Japan: new evidence using financial knowledge, behavior, and attitude. Sustain (Switzerland) 12(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12093683
Kamil NSSN, Musa R, Sahak SZ (2014) Examining the Role of Financial Intelligence Quotient (FiQ) in explaining credit card usage behavior: a conceptual Framework. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 130:568–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.04.066
Kerry MJ (2018) Psychological antecedents of retirement planning: a systematic review. Front Psychol 9(OCT). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01870
Kerry MJ, Embretson SE (2018) An experimental evaluation of competing age predictions of future time perspective between workplace and retirement domains. Front Psychol 8(JAN):1–9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.02316
Kiliyanni AL, Sivaraman S (2016) The perception-reality gap in financial literacy: evidence from the most literate state in India. Int Rev Econ Educ 23:47–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iree.2016.07.001
Kimiyaghalam F, Mansori S, Safari M, Yap S (2017) Parents’ influence on retirement planning in Malaysia. Family Consumer Sci Res J 45(3):315–325
Klapper L, Lusardi A, Panos GA (2013) Financial literacy and its consequences: evidence from Russia during the financial crisis. J Bank Finance 37(10):3904–3923
Koehler DJ, Langstaff J, Liu WQ (2015) A simulated financial savings task for studying consumption and retirement decision-making. J Econ Psychol 46:89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2014.12.004
Kramer MM (2016) Financial literacy, confidence, and financial advice seeking. Journal of Economic Behavior and Organization , 131 (June 2015), 198–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jebo.2016.08.016
Kumar S, Tomar S, Verma D (2019) Women’s financial planning for retirement: systematic literature review and future research agenda. Int J Bank Mark 37(1):120–141. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJBM-08-2017-0165
Kwon KN, Lee J (2009) The effects of reference point, knowledge, and risk propensity on the evaluation of financial products. J Bus Res 62(7):719–725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2008.07.002
Landerretche OM, Martínez C (2013) Voluntary savings, financial behavior, and pension finance literacy: evidence from Chile. J Pension Econ Finance 12(3):251–297. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1474747212000340
Lee T (2017) (David). Clear, conspicuous, and improving: US corporate websites for critical financial literacy in retirement. International Journal of Bank Marketing , 35 (5), 761–780. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJBM-01-2016-0010
Liang C-J, Wang Wen‐Hung, Farquhar JD (2009) (2009). The influence of customer perceptions on financial performance in financial services. International Journal of Bank Marketing , 27 (2), 129–149
Liberman N, Trope Y (2003) Construal level theory of intertemporal judgment and decision. In: Loewenstein G, Read D, Baumeister R (eds) Time and decision: economic and psychological perspectives on intertemporal choice, pp 245–276
Lim KL, Soutar GN, Lee JA (2013) Factors affecting investment intentions: a consumer behaviour perspective. J Financ Serv Mark 18:301–315
Lin C, Hsiao YJ, Yeh CY (2017) Financial literacy, financial advisors, and information sources on demand for life insurance. Pac Basin Finance J 43(March):218–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pacfin.2017.04.002
Lown JM (2011) Development and validation of a Financial Self-Efficacy Scale. J Financial Couns Plann 22(2):54–63
Lusardi A, Mitchell OS (2007) Baby Boomer retirement security: the roles of planning, financial literacy, and housing wealth. J Monet Econ 54(1):205–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmoneco.2006.12.001
Maloney M, McCarthy A (2017) Understanding pension communications at the organizational level: insights from bounded rationality theory & implications for HRM. Hum Resource Manage Rev 27(2):338–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrmr.2016.08.001
Marjanovic Z, Fiksenbaum L, Greenglass E (2018) Financial threat correlates with acute economic hardship and behavioral intentions that can improve one’s personal finances and health. J Behav Experimental Econ 77(April):151–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socec.2018.09.012
Marques S, Mariano J, Lima ML, Abrams D (2018) Are you talking to the future me? The moderator role of future self-relevance on the effects of aging salience in retirement savings. J Appl Soc Psychol 48(7):360–368. https://doi.org/10.1111/jasp.12516
McKechnie S (1992) Consumer buying behaviour in financial services: an overview. Int J Bank Mark 10(5):5–39. https://doi.org/10.1108/02652329210016803
Milner T, Rosenstreich D (2013a) A review of consumer decision-making models and development of a new model for financial services. J Financial Serv Mark 18(2):106–120. https://doi.org/10.1057/fsm.2013.7
Milner T, Rosenstreich D (2013b) Insights into mature consumers of financial services. J Consumer Mark 30(3):248–257. https://doi.org/10.1108/07363761311328919
Mitchell OS, Mukherjee A (2017) Assessing the demand for micro pensions among India’s poor. J Econ Ageing 9:30–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeoa.2016.05.004
Mitchell O, Utkus S (2003) Lessons from Behavioral Finance for Retirement Plan Design (PRC WP 2003-6). http://prc.wharton.upenn.edu/prc/prc.html
Modigliani F, Brumberg RH (1954) Utility analysis and the consumption function: an interpretation of cross-section data. In: Kurihara KK (ed) Post-Keynesian economics. Rutgers University Press, New Brunswick, pp 388–436
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Altman D, Antes G, Atkins D, Barbour V, Barrowman N, Berlin JA, Clark J, Clarke M, Cook D, D’Amico R, Deeks JJ, Devereaux PJ, Dickersin K, Egger M, Ernst E, …, Tugwell P (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med 6(7). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097
Monti M, Pelligra V, Martignon L, Berg N (2014) Retail investors and financial advisors: new evidence on trust and advice taking heuristics. J Bus Res 67(8):1749–1757. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2014.02.022
Mouna A, Anis J (2017) Financial literacy in Tunisia: its determinants and its implications on investment behavior. Res Int Bus Finance 39:568–577
Mullainathan S, Thaler R (2000) Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Economics Working Paper Series . September
Nga KH, Yeoh KK (2018) An exploratory model on retirement savings behaviour: a Malaysian study. Int J Bus Soc 19(3):637–659
OECD (2023) Old-age dependency ratio (indicator). https://doi.org/10.1787/e0255c98-en . Accessed 13 Oct 2023
Onwuegbuzie AJ, Collins KM (2007) A typology of mixed methods sampling designs in social science research. Qualitative Rep 12(2):474–498
Pallister JG, Wang HC, Foxall GR (2007) An application of the style/involvement model to financial services. Technovation 27(1–2):78–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.technovation.2005.10.001
Pan L, Pezzuti T, Lu W, Pechmann C (2019) Hyperopia and frugality: different motivational drivers and yet similar effects on consumer spending. J Bus Res 95(August 2018):347–356
Parise G, Peijnenburg K (2017) Understanding the Determinants of Financial Outcomes and Choices: The Role of Noncognitive Abilities. BIS Working Papers
Paul J, Rosado-Serrano A (2019) Gradual internationalization vs Born-Global/International new venture models: a review and research agenda. Int Mark Rev 36(6):830–858. https://doi.org/10.1108/IMR-10-2018-0280
Paul J, Criado AR (2020) The art of writing literature review: what do we know and what do we need to know? Int Bus Rev 29(4):101717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibusrev.2020.101717
Paul J, Khatri P, Kaur Duggal H (2023) Frameworks for developing impactful systematic literature reviews and theory building: what, why and how? J Decis Syst 00(00):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/12460125.2023.2197700
Petkoska J, Earl JK (2009) Understanding the influence of demographic and psychological variables on Retirement Planning. Psychol Aging 24(1):245–251. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0014096
Piotrowska M (2019) The importance of personality characteristics and behavioral constraints for retirement saving. Econ Anal Policy 64:194–220
Plath DA, Stevenson TH (2005) Financial services consumption behavior across Hispanic American consumers. J Bus Res 58(8):1089–1099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2004.03.003
Poterba JM (2015) Saver heterogeneity and the challenge of assessing retirement saving adequacy. Natl Tax J 68(2):377–388. https://doi.org/10.17310/ntj.2015.2.06
Potrich ACG, Vieira KM, Kirch G (2018) How well do women do when it comes to financial literacy? Proposition of an indicator and analysis of gender differences. J Behav Experimental Finance 17:28–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbef.2017.12.005
Rai D, Lin CW (2019) (Wilson). The influence of implicit self-theories on consumer financial decision making. Journal of Business Research , 95 (August 2018), 316–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2018.08.016
Ramalho TB, Forte D (2019) Financial literacy in Brazil – do knowledge and self-confidence relate with behavior? RAUSP Manage J 54(1):77–95. https://doi.org/10.1108/RAUSP-04-2018-0008
Rana J, Paul J (2017) Consumer behavior and purchase intention for organic food: a review and research agenda. J Retailing Consumer Serv 38(June):157–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2017.06.004
Ranyard R, McNair S, Nicolini G, Duxbury D (2020) An item response theory approach to constructing and evaluating brief and in-depth financial literacy scales. J Consum Aff 54(3):1121–1156. https://doi.org/10.1111/joca.12322
RBI Household Finance Committee (2017) Indian household finance. Reserve Bank of India, Mumbai
Ruefenacht M, Schlager T, Maas P, Puustinen P (2015) Drivers of long-term savings behavior from consumer’s perspective. Electron Libr 34(1):1–5
Scholz JK, Seshadri A, Khitatrakun S (2006) Are Americans saving “optimally” for retirement? J Polit Econ 114(4):607–643
Schuabb T, França LH, Amorim SM (2019) Retirement savings model tested with Brazilian private health care workers. Front Psychol 10(JULY):1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01701
Schuhen M, Schurkmann S (2014) International Review of Economics Education. Int Rev Econ Educ 16:1–11
Segel-Karpas D, Werner P (2014) Perceived financial retirement preparedness and its correlates: a national study in Israel. Int J Aging Hum Dev 79(4):279–301. https://doi.org/10.1177/0091415015574177
Seth H, Talwar S, Bhatia A, Saxena A, Dhir A (2020) Consumer resistance and inertia of retail investors: Development of the resistance adoption inertia continuance (RAIC) framework. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services , 55 (August 2019), 102071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jretconser.2020.102071
Sewell M (2008) Behavioural finance. Economist 389(8604):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1057/9780230280786_5
Shefrin HM, Thaler RH (1988) The behavioral life‐cycle hypothesis. Econ Inq 26(4):609–643
Shim S, Serido J, Tang C (2012) The ant and the grasshopper revisited: the present psychological benefits of saving and future oriented financial behavior. J Econ Psychol 33(1):155–165
Simon HA (1978) Information-processing theory of human problem solving. In: Handbook of learning and cognitive processes, vol 5, pp 271–295
Sivaramakrishnan S, Srivastava M, Rastogi A (2017) Attitudinal factors, financial literacy, and stock market participation. Int J Bank Mark 34(1):1–5
Snyder H (2019) Literature review as a research methodology: an overview and guidelines. J Bus Res 104(August):333–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2019.07.039
Stawski RS, Hershey DA, Jacobs-Lawson JM (2007) Goal clarity and financial planning activities as determinants of retirement savings contributions. Int J Aging Hum Dev 64(1):13–32. https://doi.org/10.2190/13GK-5H72-H324-16P2
Steinert JI, Zenker J, Filipiak U, Movsisyan A, Cluver LD, Shenderovich Y (2018) Do saving promotion interventions increase household savings, consumption, and investments in Sub-saharan Africa? A systematic review and meta-analysis. World Dev 104:238–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.worlddev.2017.11.018
Steinhart Y, Mazursky D (2010) Purchase availability and involvement antecedents among financial products. Int J Bank Mark 28(2):113–135. https://doi.org/10.1108/02652321011018314
Strömbäck C, Lind T, Skagerlund K, Västfjäll D, Tinghög G (2017) Does self-control predict financial behavior and financial well-being? J Behav Experimental Finance 14:30–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbef.2017.04.002
Strömbäck C, Skagerlund K, Västfjäll D, Tinghög G (2020) Subjective self-control but not objective measures of executive functions predict financial behavior and well-being. Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Finance , 27 . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbef.2020.100339
Tam L, Dholakia U (2014) Saving in cycles: how to get people to save more money. Psychol Sci 25(2):531–537. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797613512129
Tang N, Baker A (2016) Self-esteem, financial knowledge and financial behavior. J Econ Psychol 54:164–176
Tate M, Evermann J, Gable G (2015) An integrated framework for theories of individual attitudes toward technology. Inform Manage 52(6):710–727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2015.06.005
Taylor MP, Jenkins SP, Sacker A (2011) Financial capability and psychological health. J Econ Psychol 32(5):710–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2011.05.006
Tennyson S, Yang HK (2014) The role of life experience in long-term care insurance decisions. Journal of Economic Psychology , 42 (2014), 175–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2014.04.002
Thaler BRH (1994) Psychology and savings policies. Am Econ Rev 84(2):175–179. http://www.jstor.org/stable/3132220
Thaler R (1980) Toward a positive theory of consumer choice. J Econ Behav Organ 1:39–60
Thaler RH (2005) Advances in behavioral finance. Adv Behav Finance 2:1–694. https://doi.org/10.2307/2329257
Thaler R, Shefrin H (1981) An economic theory of self-control. J Polit Econ 89(2):392–406
Tomar S, Kent Baker H, Kumar S, Hoffmann AOI (2021) Psychological determinants of retirement financial planning behavior. Journal of Business Research , 133 (November 2020), 432–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2021.05.007
Topa G, Moriano JA, Depolo M, Alcover CM, Morales JF (2009) Antecedents and consequences of retirement planning and decision-making: a meta-analysis and model. J Vocat Behav 75(1):38–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvb.2009.03.002
Topa G, Moriano JA, Depolo M, Alcover CM, Moreno A (2011) Retirement and wealth relationships: Meta-analysis and SEM. Res Aging 33(5):501–528. https://doi.org/10.1177/0164027511410549
Tranfield D, Denyer D, Smart P (2003) Towards a methodology for developing evidence-informed management knowledge by means of systematic review. Br J Manag 14(3):207–222. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8551.00375
Ülkümen G, Cheema A (2011) Framing goals to influence personal savings: the role of specificity and construal level. J Mark Res 48(6):958–969. https://doi.org/10.1509/jmr.09.0516
United Nations, Department of Economic and Social, Affairs PD (2020) (2019). World Population Ageing 2019. In United Nations . http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/ 978-94-007-5204-7_6
Utkarsh, Pandey A, Ashta A, Spiegelman E, Sutan A (2020) Catch them young: impact of financial Socialization, financial literacy and attitude towards money on the financial well-being of young adults. Int J Consumer Stud 44(6):531–541. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijcs.12583
Valente TW, Paredes P, Poppe P (1998) Matching the message to the process: the relative ordering of knowledge, attitudes, and practices in behavior change research. Hum Commun Res 24(3):366–385
Van Rooij M, Teppa F (2014) Personal traits and individual choices: taking action in economic and non-economic decisions. J Econ Behav Organ 100:33–43
van Rooij M, Lusardi A, Alessie R (2011) Financial literacy and stock market participation. J Financ Econ 101(2):449–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfineco.2011.03.006
Van Rooij MCJ, Lusardi A, Alessie RJM (2011a) Financial literacy and retirement planning in the Netherlands. J Econ Psychol 32(4):593–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2011.02.004
van Schie RJG, Dellaert BGC, Donkers B (2015) Promoting later planned retirement: construal level intervention impact reverses with age. J Econ Psychol 50:124–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2015.06.010
Venkatesh V, Morris M, Davis G, Davis F (2003) Factors influencing the Use of M-Banking by academics: Case Study sms-based M-Banking. MIS Q 27(3):425–478
Vitt LA (2004) Consumers’ financial decisions and the psychology of values. J Financial Service Professionals 58(November):68–77. http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true &db=bth&AN=14888952&site=ehost-live
Wang L, Lu W, Malhotra NK (2011) Demographics, attitude, personality, and credit card features correlate with credit card debt: a view from China. J Econ Psychol 32(1):179–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joep.2010.11.006
World Economic Forum (2019) Investing in (and for) our future. Issue June. www.weforum.org
Xia T, Wang Z, Li K (2014) Financial literacy overconfidence and stock market participation. Soc Indic Res 119(3):1233–1245. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-013-0555-9
Xiao JJ, Chen C, Chen F (2014) Consumer financial capability and financial satisfaction. Soc Indic Res 118(1):415–432. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11205-013-0414-8
Yeung DY, Zhou X (2017) Planning for retirement: longitudinal effect on retirement resources and post-retirement well-being. Front Psychol 8:1300
Zhou R, Pham MT (2004) Promotion and prevention across mental accounts: when financial products dictate consumers’ investment goals. J Consum Res 31(1):125–135. https://doi.org/10.1086/383429
Download references
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to acknowledge the academicians and researchers who guided the search of the article and would like to thank the experts for the valuable inputs to refine the work.
There is no funding received for this research.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Symbiosis International (Deemed University), Pune, India
Kavita Karan Ingale
Symbiosis Institute of Operations Management, Symbiosis International (Deemed) University, Pune, India
Ratna Achuta Paluri
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Both authors contributed to the conceptualization, research design, methodology, analysis of the data,writing of the manuscript and its revision.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Kavita Karan Ingale .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Ingale, K.K., Paluri, R.A. Retirement planning – a systematic review of literature and future research directions. Manag Rev Q (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-023-00377-x
Download citation
Received : 14 December 2022
Accepted : 04 October 2023
Published : 28 October 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11301-023-00377-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Retirement planning
- Systematic literature review
- Financial behavior
- Household finance
- Long-term savings
- Pension plan
- Financial literacy
- TCCM framework
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
This paper is in the following e-collection/theme issue:
Published on 10.4.2024 in Vol 26 (2024)
Effectiveness of a Web-Based Individual Coping and Alcohol Intervention Program for Children of Parents With Alcohol Use Problems: Randomized Controlled Trial
Authors of this article:

Original Paper
- Håkan Wall 1 , PhD ;
- Helena Hansson 2 , PhD ;
- Ulla Zetterlind 3 , PhD ;
- Pia Kvillemo 1 , PhD ;
- Tobias H Elgán 1 , PhD
1 Stockholm Prevents Alcohol and Drug Problems, Centre for Psychiatry Research, Department of Clinical Neuroscience, Karolinska Institutet, & Stockholm Health Care Services, Stockholm, Sweden
2 School of Social Work, Faculty of Social Sciences, Lund University, Lund, Sweden
3 Clinical Health Promotion Centre, Department of Health Sciences, Lund University, Lund, Sweden
Corresponding Author:
Tobias H Elgán, PhD
Stockholm Prevents Alcohol and Drug Problems, Centre for Psychiatry Research
Department of Clinical Neuroscience
Karolinska Institutet, & Stockholm Health Care Services
Norra Stationsgatan 69
Stockholm, 11364
Phone: 46 700011003
Email: [email protected]
Background: Children whose parents have alcohol use problems are at an increased risk of several negative consequences, such as poor school performance, an earlier onset of substance use, and poor mental health. Many would benefit from support programs, but the figures reveal that only a small proportion is reached by existing support. Digital interventions can provide readily accessible support and potentially reach a large number of children. Research on digital interventions aimed at this target group is scarce. We have developed a novel digital therapist-assisted self-management intervention targeting adolescents whose parents had alcohol use problems. This program aims to strengthen coping behaviors, improve mental health, and decrease alcohol consumption in adolescents.
Objective: This study aims to examine the effectiveness of a novel web-based therapist-assisted self-management intervention for adolescents whose parents have alcohol use problems.
Methods: Participants were recruited on the internet from social media and websites containing health-related information about adolescents. Possible participants were screened using the short version of the Children of Alcoholics Screening Test-6. Eligible participants were randomly allocated to either the intervention group (n=101) or the waitlist control group (n=103), and they were unblinded to the condition. The assessments, all self-assessed, consisted of a baseline and 2 follow-ups after 2 and 6 months. The primary outcome was the Coping With Parents Abuse Questionnaire (CPAQ), and secondary outcomes were the Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale, Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT-C), and Ladder of Life (LoL).
Results: For the primary outcome, CPAQ, a small but inconclusive treatment effect was observed (Cohen d =–0.05 at both follow-up time points). The intervention group scored 38% and 46% lower than the control group on the continuous part of the AUDIT-C at the 2- and 6-month follow-up, respectively. All other between-group comparisons were inconclusive at either follow-up time point. Adherence was low, as only 24% (24/101) of the participants in the intervention group completed the intervention.
Conclusions: The findings were inconclusive for the primary outcome but demonstrate that a digital therapist-assisted self-management intervention may contribute to a reduction in alcohol consumption. These results highlight the potential for digital interventions to reach a vulnerable, hard-to-reach group of adolescents but underscore the need to develop more engaging support interventions to increase adherence.
Trial Registration: ISRCTN Registry ISRCTN41545712; https://www.isrctn.com/ISRCTN41545712?q=ISRCTN41545712
International Registered Report Identifier (IRRID): RR2-10.1186/1471-2458-12-35
Introduction
Children who grow up with parents who have substance use problems or disorders face extraordinary challenges. Approximately 20% of all children have parents with alcohol problems [ 1 - 5 ], while approximately 5% have parents with alcohol use disorders [ 4 , 6 , 7 ]. Children growing up with parental substance abuse are at an increased risk of several negative outcomes, such as psychiatric morbidity [ 8 - 12 ]; poor intellectual, cognitive, and academic achievement [ 13 - 15 ]; domestic physical abuse [ 16 ]; and early drinking onset and the development of substance use problems [ 9 , 17 , 18 ]. Thus, children exposed to parental substance abuse comprise a target group for selective interventions and prevention strategies [ 19 - 22 ].
In Sweden, municipalities account for most of the support offered to these children. An annual survey by the junior association of the Swedish branch of Movendi International (ie, an international temperance movement) reported that 97% of all municipalities provided support resources [ 23 ]. However, estimates from the same survey showed that approximately 2% of the children in the target group received support. Hence, an overwhelming majority never receives support, mainly because of difficulties in identifying and attracting them to intervention programs [ 22 , 24 ].
The internet has become an appealing way to reach and support a large number of people [ 25 , 26 ]. Web-based interventions seem particularly attractive to adolescents, as they generally use digital technology and social media. Furthermore, research has shown that adolescents regard the internet as inviting because it is a readily accessible, anonymous way of seeking help [ 27 ]. Web-based interventions can reduce the stigma associated with face-to-face consultations in health care settings [ 28 ], and young people appreciate the flexibility of completing web-based sessions to fit their own schedules [ 29 ]. The positive effects of web-based interventions have been detected across a broad range of conditions. A recent review by Hedman-Lagerlöf et al [ 30 ] concluded that therapist-supported internet-based cognitive behavioral therapy for adults yielded similar effects as face-to-face therapy. To date, most web-based interventions have been designed for adults. Although the number of web-based interventions targeting children or adolescents is increasing [ 25 , 31 - 33 ], the number of digital interventions aimed at children of substance-abusing parents is still scarce [ 22 , 34 - 38 ]. Those described in the literature, however, all have in common that they are quite extensive, with a duration over several weeks, and a brief digital intervention could complement these more extended interventions. For instance, our research group initiated a study on a web-based group chat for 15- to 25-year-old individuals who have parents with mental illness or substance use problems [ 35 ]. The duration of the program is 8 weeks, and it is a translated version of a program from the Netherlands [ 34 ], which has been shown to have inconclusive treatment effects [ 39 ]. In Sweden, 2 other programs with inconclusive treatment effects have been tested that target significant others and their children [ 37 , 38 ]. Finally, a digital intervention developed in Australia for 18- to 25-year-old individuals with parents with mental illness or substance use disorder [ 36 ] was tested in a pilot study demonstrating positive findings [ 40 ].
To meet the need for a brief, web-based intervention that targets adolescents having parents with alcohol problems and build on the evidence base of digital interventions targeting this vulnerable group, we developed a novel internet-delivered therapist-assisted self-management intervention called “Alcohol and Coping.” Our program originated from a manual-based face-to-face intervention called the “Individual Coping and Alcohol Intervention Program” (ICAIP) [ 41 , 42 ]. Previous studies on both the ICAIP, which aimed at college students having parents with alcohol problems, and a coping skills intervention program, which aimed at spouses of partners with alcohol dependency [ 43 ], have demonstrated positive effects regarding decreased alcohol consumption and improved mental health and coping behaviors [ 41 - 44 ]. Furthermore, the results from these studies underscore the importance of improving coping skills [ 42 , 44 ]. Among college students, those who received a combination of coping skills and an alcohol intervention program had better long-term outcomes [ 42 ].
The aim of this study was to test the effectiveness of Alcohol and Coping among a sample of adolescents aged 15-19 years with at least 1 parent with alcohol use problems. We hypothesized that the intervention group would be superior to the control group in improving coping skills. Secondary research questions concerned the participants’ improvement in (1) depression, (2) alcohol consumption, and (3) quality of life.
This study was a parallel-group randomized controlled trial in which participants were randomized to either the intervention or waitlist control group in a 1:1 allocation ratio. The trial design is illustrated in Figure 1 .

Recruitment and Screening
The participants were recruited from August 2012 to December 2013 through advertisements on social media (Facebook). The advertisements targeted individuals aged 15-19 years with Facebook accounts. Participants were recruited on the internet through advertisements on websites containing health-related information about adolescents. The advertisements included the text, “Do your parents drink too much? Participate in a study.” The advertisement contained an invitation to perform a web-based, self-assessed screening procedure. In addition to questions about age and sex, participants were screened for having parents with alcohol problems using the short version of the Children of Alcoholics Screening Test-6 (CAST-6), developed from a 30-item original version [ 45 ]. The CAST-6 is a 6-item true-false measure designed to assess whether participants perceive their parents’ alcohol consumption to be problematic. The CAST-6 has demonstrated high internal consistency ( r =0.92-0.94), test-retest reliability ( r =0.94), and high validity as compared to the 30-item version ( r =0.93) using the recommended threshold score of 3 or higher [ 45 , 46 ]. We previously translated the CAST-6 into Swedish and validated the translated version among 1450 adolescents, showing good internal consistency (α=.88), excellent test-retest reliability (intraclass correlation coefficient=0.93), and loading into 1 latent factor [ 47 ]. Additional inclusion criteria included having access to a computer and the internet and being sufficiently fluent in Swedish. Participants were excluded from the study and were referred to appropriate care if there were indications of either suicidal or self-inflicted harmful behaviors. Individuals eligible for inclusion received further information about the study and were asked to provide consent to participate by providing an email address.
Data Collection and Measures
All assessments were administered through email invitations containing a hyperlink to the web-based self-reported assessments. Up to 3 reminders were sent through email at 5, 10, and 15 days after the first invitation. A baseline assessment (t 0 ) was collected before randomization, and follow-up assessments were conducted at 2 and 6 months (t 1 and t 2 , respectively) after the initial assessment.
Participants were asked for age, sex, whether they lived with a parent (mother and father, mother or father, mother or father and stepparent, or alternate between mother and father), where their parents were born (Sweden or a Nordic country excluding Sweden or outside of the Nordic countries), parental status (employed, student, on parental leave, or unemployed), and any previous or present participation in support activities for children having parents with alcohol use problems. The primary outcome was coping, measured using the Coping With Parents Abuse Questionnaire (CPAQ) based on the Coping Behavior Scale developed by Orford et al [ 48 ]. Secondary outcomes were the Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale (CES-DC) [ 49 ], the 3-question Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT-C) [ 50 ], and the Ladder of Life (LoL), which measures the overall quality of life by asking about the participants’ past, present, and future ratings of their overall life satisfaction [ 50 ]. CPAQ has been shown to be reliable [ 41 , 42 ]. For this study, this scale was factor-analyzed to reduce the number of questions from 37 to 20. The resulting scale measures 6 coping typologies (discord, emotion, control, relationship, avoidance, and taking specific action) using a 4-point Likert scale, with a threshold score above 50 points (out of 80) indicating dysfunctional coping behavior. The CES-DC measures depressive symptoms during the past week using a 4-point Likert scale, where a higher total score indicates more depressive symptoms [ 49 ]. A cutoff score of ≥16 indicates symptoms of moderate depression, while a score of ≥30 indicates symptoms of severe depression [ 51 , 52 ]. The scale measures 4 dimensions of depression: depressed mood, tiredness, inability to concentrate, and feelings of being outside and lonely, and has positively stated items [ 52 ]. Additionally, this scale is a general measure of childhood psychopathology [ 53 ] and has been demonstrated to be reliable and valid among Swedish adolescents [ 52 ]. Alcohol consumption was measured using a modified AUDIT-C, which assesses the frequency of drinking, quantity consumed on a typical occasion, and frequency of heavy episodic drinking (ie, binge drinking) [ 50 ] using a 30-day perspective (as opposed to the original 12-month perspective). These questions have previously been translated into Swedish [ 54 ], and a score of ≥4 and ≥5 points for women and men, respectively, was used as a cutoff for risky drinking. This scale has been demonstrated to be reliable and valid for Swedish adolescents [ 55 ]. Furthermore, 2 questions were added concerning whether the participants had ever consumed alcohol to the point of intoxication and their age at the onset of drinking and intoxication. The original version of the LoL was designed for adults and asked the respondents to reflect on their, present, and future life status from a 5-year perspective on a 10-point Visual Analogue Scale representing life status from “worst” to “best” possible life imaginable [ 56 ]. A modified version for children, using a time frame of 1 year, has been used previously in Sweden [ 57 ] and was used in this study.
Randomization
After completing the baseline assessment, each participant was allocated to either the intervention or the control group. An external researcher generated an unrestricted random allocation sequence using random allocation software [ 58 ]. Neither the participants nor the researchers involved in the study were blinded to group allocation.
Based on the order in which participants were included in the study, they were allocated to 1 of the 2 study groups and informed of their allocation by email. Additionally, those who were randomized to the intervention group received a hyperlink to the Alcohol and Coping program, whereas the control group participants received information that they would gain access to Alcohol and Coping after the last follow-up assessment (ie, the waitlist control group). All participants were informed about other information and support available through web pages, notably drugsmart [ 59 ], which contains general information and facts about alcohol and drugs, in addition to more specific information about having substance-abusing parents. Telephone numbers and contact information for other organizations and primary health care facilities were also provided.
The Intervention
As noted previously, Alcohol and Coping is derived from the aforementioned manual-based face-to-face ICAIP intervention program [ 41 , 42 ]. The ICAIP consists of a combination of an alcohol intervention program, which is based on the short version of the Brief Alcohol Screening and Intervention for College Students program [ 60 ], and a coping intervention program developed for the purpose of the ICAIP [ 41 , 42 ]. Like the original ICAIP intervention, Alcohol and Coping builds on psychoeducational principles and includes components such as film-based lectures, various exercises, and both automated and therapist-assisted feedback. Briefly, once the participants logged into the Alcohol and Coping platform, they were introduced to the program, which followed the pattern of a board game ( Figure 2 ). Following the introduction, participants took part in 3 film-based lectures (between 8 and 15 minutes each, Figure 3 ) concerning alcohol problems within the family. The respective lectures included information about (1) dependency in general as well as the genetic and environmental risks for developing dependency, (2) family patterns and how the family adapts to the one having alcohol problems, and (3) attitudes toward alcohol and how they influence drinking and the physiological effects of alcohol. After completing the lectures, the participants were asked to answer 2 questions about their own alcohol consumption (ie, how often they drink and how often they drink to intoxication), followed by an automatic feedback message that depended on their answers. It was then suggested that the participants log out of the intervention for a 1- to 2-day break. The reason for this break was to give the participants a chance to digest all information and impressions. When they logged back into the intervention, they were asked to answer 20 questions about their coping strategies, which were also followed by automatic feedback. This feedback comprised a library covering all the prewritten feedback messages, each of which was tailored to the participants’ specific answers. The participants then participated in a 5-minute–long film-based lecture on emotion and problem-focused coping in relation to family alcohol problems ( Figure 3 ). This was followed by 4 exercises where the participants read through vignette-like stories from 4 fictional persons describing their everyday lives related to coping and alcohol problems in the family. The stories are presented by film-based introductions that are each 1-2 minutes long. Participants were then requested to respond to each story by describing how the fictive person could have coped with their situation. As a final exercise, participants were asked to reflect on their own family situation and how they cope with situations. The participants then had to take a break for a few days.
During the break, a therapist composed individual feedback that covered reflections and confirmation of the participant’s exercises and answers to questions and included suggestions on well-suited coping strategies. Additionally, the therapist encouraged the participants to talk to others in their surroundings, such as friends, teachers, or coaches, and seek further support elsewhere, such as from municipal social services, youth health care centers, or other organizations. Finally, the therapist reflected on the participants’ alcohol consumption patterns and reminded them of increased genetic and environmental risks. Those who revealed patterns of risky alcohol use were encouraged to look at 2 additional film-based lectures with more information about alcohol and intoxication (4 minutes) and alcohol use and dependency (5 minutes). Participants received this feedback once they logged back into the program, but they also had the opportunity to receive feedback through email. The total estimated effective time for completing the program was about 1 hour, but as described above, there was 1 required break when the individualized feedback was written. To keep track of the dose each participant received, each of the 15 components in the program ( Figure 1 ) is equal to completing 6.7% (1/15) of the program in total.

Sample Size
The trial was designed to detect a medium or large effect size corresponding to a standardized mean difference (Cohen d >0.5) [ 61 ]. An a priori calculation of the estimated sample size, using the software G*Power (G*Power Team) [ 62 ], revealed that a total of 128 participants (64 in each group) were required to enroll in the trial (power=0.80; α=.05; 2-tailed). However, to account for an estimated attrition rate of approximately 30% [ 34 ], it was necessary to enroll a minimum of 128/(1 – 0.3) = 183 participants in the trial. After a total of 204 individuals had been recruited and randomized into 2 study arms, recruitment was ended.
Statistical Analysis
Data were analyzed according to the intention-to-treat (ITT) principle, and all randomized participants were included, irrespective of whether they participated in the trial. The 4 research variables were depression (CES-DC), coping (CPAQ), alcohol use (AUDIT-C), and life status (LoL).
Data analysis consisted of comparing outcome measurements at t 1 and t 2 . The baseline measurement t 0 value was added as an adjustment variable in all models. The resulting data from CPAQ, CES-DC, and LoL were normally distributed and analyzed using linear mixed models. The resulting AUDIT-C scores were nonnormally distributed, with an excess of 0 values, and were analyzed using a 2-part model for longitudinal data. This model is sufficiently flexible to account for numerous 0 reports. This was achieved by combining a logistic generalized linear mixed model (GLMM) for the 0 parts and a skewed continuous GLMM for the non-0 alcohol consumption parts. R-package brms (Bayesian regression models using Stan; R Foundation for Statistical Computing) [ 63 ], a higher-level interface for the probabilistic programming language Stan [ 64 ], and a custom brms family for a marginalized 2-part lognormal distribution were used to fit the model [ 65 ]. The logistic part of the model represents the subject-specific effects on the odds of reporting no drinking. The continuous part was modeled using a gamma GLMM with a log link. The exponentiated treatment effect represents the subject-specific ratio of the total AUDIT-C scores between the treatment and waitlist control groups for those who reported drinking during the specific follow-up period.
Handling of Missing Data
GLMMs include all available data and provide unbiased ITT estimates under the assumption that data are missing at random, meaning that the missing data can be explained by existing data. However, it is impossible to determine whether the data are missing at random or whether the missing data are due to unobserved factors [ 66 ]. Therefore, we also assumed that data were not missing at random, and subsequent sensitivity analyses were performed [ 66 ]. We used the pattern mixture method, which assumes not missing at random, to compare those who completed the follow-up at 6 months (t 2 ) with those who did not (but completed the 2-month follow-up). The overall effect of this model is a combination of the effects of each subgroup. We also tested the robustness of the results by performing ANCOVAs at the 2-month follow-up, both using complete cases and with missing values imputed using multilevel multiple imputation.
The effect of the program was estimated using Cohen d , where a value of approximately 0.2 indicates a small effect size and values of approximately 0.5 and 0.8 indicate medium and large effect sizes, respectively [ 61 ].
Ethical Considerations
All procedures were performed in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional or national research committees, the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments, and comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all the participants included in the study. This study was approved by the Swedish Ethical Review Authority (formerly the Regional Ethical Review Board in Stockholm, No. 2011/1648-31/5).
To enhance the response rates, participants received a cinema gift certificate corresponding to approximately EUR 11 (US $12) as compensation for completing each assessment. If a participant completed all assessments, an additional gift certificate was provided. The participants could subsequently receive 4 cinema gift certificates totaling EUR 44 (US $48).
The trial profile is depicted in Figure 1 and reveals that 2722 individuals who were aged between 15 and 19 years performed the screening procedure. A total of 1448 individuals did not fulfill the inclusion criteria and were excluded, leaving 1274 eligible participants. Another 1070 individuals were excluded because they did not provide informed consent or complete the baseline assessment, leaving 204 participants who were allocated to 1 of the 2 study groups. A total of 140 (69%) and 131 (64%) participants completed t 1 and t 2 assessments, respectively. Of the participants in the intervention group (n=101), 63% (n=64) registered an account on the Alcohol and Coping website, 35% (n=35) completed the alcohol intervention section, and 24% (n=24) completed both the alcohol and coping intervention sections.
Sample Characteristics
The mean age of the sample was 17.0 (SD 1.23) years, and the vast majority were female, with both parents born in Sweden and currently working ( Table 1 ). Approximately one-third of the participants reported living with both parents. The mean score on the CAST-6 was 5.33 (SD 0.87) out of a total of 6, and the majority of the sample (147/204, 72.1%) perceived their father to have alcohol problems. Approximately 12% (25/204) had never consumed alcohol, whereas approximately 70% (144/204) had consumed alcohol at a level of intoxication. The mean age at onset was 13.7 (SD 2.07) years and the age at first intoxication was 14.8 (SD 1.56) years. The proportion of participants with symptoms of at least moderate depression was 77.5% (158/204), of whom 55.1% (87/158) had symptoms of severe depression and 42.6% (87/204) had symptoms of dysfunctional coping behaviors. The percentage of participants who consumed alcohol at a risky level was 39.7% (81/204). Table 1 provides complete information regarding the study sample.
a Significance levels calculated by Pearson chi-square statistics for categorical variables and 2-tailed t tests for continuous variables.
Treatment Effects
For the primary outcome, coping behavior (CPAQ), we found a small but inconclusive treatment effect in favor of treatment at both 2 (t 1 ) and 6 (t 2 ) months (Cohen d =–0.05 at both t 1 and t 2 ). For the secondary outcome, alcohol use (AUDIT-C), we found a treatment effect in that the intervention group scored 38% less than the control group on the continuous part (ie, drinking when it occurred) at t 1 and 46% less at t 2 . Regarding depression (CES-DC) and life status (LoL), all between-group comparisons of treatment effects were inconclusive at both follow-up time points ( Table 2 ).
a CPAQ: Coping With Parents Abuse Questionnaire.
b CES-DC: Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale.
c LoL: Ladder of Life.
d AUDIT-C: Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test.
e N/A: not applicable.
Missing Data
In contrast to the ITT analyses, the sensitivity analyses showed that the treatment group, averaged over the levels of dropout, scored higher (ie, a negative effect) on the main outcome, coping behavior (CPAQ), at t 1 (2.44; P =.20). However, the results remain inconclusive.
Dose-Response Effects
We did not find any evidence for greater involvement in the program being linked to improved outcomes with regard to coping behavior.
We did not find any support for the primary hypothesis: the intervention was not superior to the control condition with regard to coping behavior. Inconclusive results with small effect sizes were observed at both follow-up time points. However, for the secondary outcomes, we found that those in the intervention group who drank alcohol drank approximately 40%-50% less than those in the control group at both follow-ups. These results corroborate previous findings on the precursor face-to-face ICAIP intervention program, demonstrating that participants who received a combined alcohol and coping intervention reported superior outcomes with regard to alcohol-related outcomes compared to participants in the other 2 study arms, who received only a coping or alcohol intervention [ 41 , 42 ]. In contrast to this study, Hansson et al [ 42 ] found that all groups improved their coping skills, although the between-group comparisons were inconclusive and the improvements were maintained over time. These differences could be explained by the different settings in which the precursor program was provided (ie, face-to-face to young adults in a university setting), whereas this study targeted young people (15-19 years of age) through a web-based digital intervention. Additionally, the poor adherence in this study may explain the absence of primary results favoring the intervention group. In a recent study, parents without alcohol problems were recruited to participate in a randomized trial evaluating the web-based SPARE (Supportive Parenting and Reinforcement) program to improve children’s mental health and reduce coparents’ alcohol use. In line with our study, the authors did not find the primary outcome of the SPARE program to be superior to that of the active control group (which received written psychoeducation); however, both groups reported decreased coparental alcohol consumption [ 38 ].
Considering that approximately 3600 children in 2022 participated in various forms of support provided by Swedish municipalities [ 23 ], our recruitment activities reached a large number of eligible individuals, pointing to the potential of finding these children on these platforms. There were unexpectedly high levels of depression among the participants in this study. Although the intervention did not target depressive symptoms per se , there was a trend for the intervention group to have decreased depression levels compared to the control group. A large proportion of participants had symptoms of severe depression, which may have aggravated their capacity for improvement at follow-up [ 28 , 67 ]. Targeting dysfunctional coping patterns could affect an individual’s perceived mental health, and studies have shown that healthy coping strategies positively affect depression and anxiety in a positive way [ 68 ]. Using dysfunctional coping strategies, such as negative self-talk and alcohol consumption, can lead to depressive symptoms [ 69 ]. Targeting these symptoms in the context of healthy and unhealthy coping strategies may be a viable route to fostering appropriate coping strategies that work in the long run. Given that the young people who were reached by the intervention in this study displayed high levels of depression, future interventions for this group should include programs targeting depressive symptoms.
Almost 37% (37/101) of the intervention group did not log into the intervention at all, and only 24% (24/101) of the intervention group participants completed all parts of the program. The fact that a high proportion of the participants had symptoms of severe depression could explain the low adherence. Another reason could be that the initial film-based lectures were too long to maintain the participants’ attention, as the lectures ranged from 8-15 minutes. Yet a final reason could be that we had a 1- to 2-day break built into the intervention, and for unknown reasons, some participants did not log back into the intervention. However, we did not find a dose-response relationship indicating favorable outcomes for those who completed more of the program content. High levels of attrition are not uncommon in self-directed programs such as the one in this study; for example, in a study on a smoking cessation intervention, 37% of the participants never logged into the platform [ 70 ], and in a self-directed intervention for problem gamblers, a majority dropped out after 1 week and none completed the entire program [ 71 ]. Increased intervention adherence is a priority when developing new digital interventions, particularly for young people. One method is to use more persuasive technologies, such as primary tasks, dialogue, and social support [ 72 ]. Considering children whose parents have mental disorders, Grové and Reupert [ 73 ] suggested that digital interventions should include components such as providing information about parental mental illness, access to health care, genetic risk, and suggestions for how children might initiate conversations with parents who have the illness. These suggestions should be considered in future studies on interventions for youths whose parents have substance use problems. Representatives of the target group and other relevant stakeholders should also be involved in coproducing new interventions to increase the probability of developing more engaging programs [ 74 ]. Moreover, one cannot expect study participants to return to the program more than once, and for the sake of adherence, briefer interventions should not encourage participants to log-out for a break. To keep adherence at an acceptable level, similar future interventions for this target group should also consider having symptoms of severe depression as an exclusion criterion [ 28 , 67 ]. Further, to improve adherence, strategies of coproduction could be used where all stakeholders, including the target group, are involved in intervention development [ 75 ]. Other important factors identified to improve adherence to digital interventions are to make the content relatable, useful, and even more interactive [ 76 ]. Those participants who have symptoms of severe depression should be referred to other appropriate health care. Finally, it is probably beneficial to develop shorter psychoeducative film-based lectures than ours, lasting up to 15 minutes. Future self-directed digital interventions targeting this population should, therefore, focus on a very brief and focused intervention, which, based on theory, has the potential to foster healthy coping behaviors that can lead to an increased quality of life and improved mental health for this group of young people.
Another concern for future projects would be to use a data-driven approach during the program development phase, where A/B testing can be used to test different setups of the program to highlight which setup works best. Another aspect that must be considered is the fast-changing world of technology, where young people are exposed to an infinite number of different apps that grab their attention, which also calls for interventions to be short and to the point. Furthermore, if the program is to spread and become generally available, one must consider that keeping the program alive for a longer period will require funding and staffing for both product management and technical support.
Strengths and Limitations
This study had several strengths. First, Alcohol and Coping is a web-based intervention program, and it appears as if the internet is a particularly promising way to provide support to adolescents growing up with parents with alcohol problems because it offers an anonymous means of communicating and makes intervention programs readily accessible [ 25 ]. Our recruitment strategies reached a considerable number of interested and eligible individuals, demonstrating the potential for recruiting through social media and other web platforms. Additionally, this program is one of the first brief web-based interventions aimed at adolescents with parents with alcohol-related problems. We used the CAST-6, which has been validated among Swedish adolescents [ 47 ], to screen eligible participants. Another strength is that the intervention program involved personalized, tailored feedback in the form of prewritten automatic messages and therapist-written personalized feedback, both of which have proven to be important components of web-based interventions aimed at adolescents [ 77 , 78 ]. Finally, this study evaluated the effectiveness of the Alcohol and Coping program using a randomized controlled trial design, which is considered the strongest experimental design with regard to allocation bias.
This study had some limitations. First, the design with a passive waitlist control group and an active intervention group, both unblinded to study allocation, may have resulted in biased estimates of treatment effects. Intervention adherence was low, and most of the study participants had symptoms of depression, where 55% (87/158) had symptoms of severe depression. This may have contributed to the small and overall inconclusive effects on the primary outcomes of this study. Many digital interventions have problems with low adherence, and in a review by Välimäki et al [ 79 ], some studies reported adherence rates as low as 10%. A vast proportion of the study participants were women, making the findings difficult to generalize to men. However, another limitation concerns selection bias and external validity. We recruited study participants through social media and other relevant websites containing health-related information, including information about parents with alcohol-related problems. It is, therefore, possible that the study population can be classified as “information-seeking” adolescents, who may have different personality traits relative to other adolescents in the same home situation. Additionally, as an inclusion criterion was having ready access to computers and the internet, it is possible that participants belonging to a lower socioeconomic class were underrepresented in the study. It should also be noted that the data presented here were collected approximately 10 years ago. However, we believe our findings make an important contribution to the field since, like our intervention, many recent web-based interventions use strategies of psychoeducation, films, exercises, questions, and feedback. Further, the number of web-based interventions for this target group remains scarce in the literature, which underscores the need for future research. Finally, the study was powered to detect a medium effect size. However, given the small effect sizes detected in this study, it is plausible that too few participants were recruited to detect differences between the groups.
Implications for Practice
Although growing up with parents who have alcohol problems per se is not sufficient for developing psychosocial disorders, many children need support to manage their situation. Therefore, it is difficult to recruit children to support these groups. In Sweden, not even 2% of all children growing up with parental alcohol problems attend face-to-face support groups provided by municipalities.
Offering support through web-based intervention programs seems particularly attractive to adolescents whose parents have alcohol-related problems. To date, evidence for such programs is scarce, and there is an urgent need to develop and evaluate digital interventions targeting this group of adolescents. This study makes important contributions to this novel field of research. The results provide insight into effective strategies for delivering intervention programs to children of parents with substance abuse issues, highlighting the potential for digital interventions to reach a vulnerable, hard-to-reach group of adolescents. Our findings underscore the need to develop more engaging interventions in coproduction with the target group.
Conclusions
We found that a digital therapist-assisted self-management intervention for adolescents whose parents have alcohol use problems contributed to a reduction in the adolescents’ own alcohol consumption. This result highlights the potential for digital interventions to reach a large, vulnerable, and hard-to-reach group of adolescents with support efforts. Findings were inconclusive for all other outcomes, which may be attributable to low adherence. This points to the need for future research on developing more engaging digital interventions to increase adherence among adolescents.
Acknowledgments
This work was undertaken on behalf of the Swedish Council for Information on Alcohol and Other Drugs (CAN) and was supported by grants from the Swedish National Institute of Public Health and the Swedish Council for Working Life and Social Research.
Conflicts of Interest
HH and UZ developed the study interventions. However, the parties did not derive direct financial income from these interventions. HW, PK, and THE declare no conflicts of interest.
CONSORT-eHEALTH checklist (V 1.6.1).
- Haugland SH, Elgán TH. Prevalence of parental alcohol problems among a general population sample of 28,047 Norwegian adults: evidence for a socioeconomic gradient. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(10):5412. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Elgán TH, Leifman H. Prevalence of adolescents who perceive their parents to have alcohol problems: a Swedish national survey using a web panel. Scand J Public Health. 2013;41(7):680-683. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Laslett AM, Ferris J, Dietze P, Room R. Social demography of alcohol-related harm to children in Australia. Addiction. 2012;107(6):1082-1089. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Manning V, Best DW, Faulkner N, Titherington E. New estimates of the number of children living with substance misusing parents: results from UK national household surveys. BMC Public Health. 2009;9:377. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Grant BF. Estimates of US children exposed to alcohol abuse and dependence in the family. Am J Public Health. 2000;90(1):112-115. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Raninen J, Elgán TH, Sundin E, Ramstedt M. Prevalence of children whose parents have a substance use disorder: findings from a Swedish general population survey. Scand J Public Health. 2016;44(1):14-17. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Christoffersen MN, Soothill K. The long-term consequences of parental alcohol abuse: a cohort study of children in Denmark. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2003;25(2):107-116. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Martikainen PN, Korhonen K, Moustgaard H, Aaltonen M, Remes H. Substance abuse in parents and subsequent risk of offspring psychiatric morbidity in late adolescence and early adulthood: a longitudinal analysis of siblings and their parents. Soc Sci Med. 2018;217:106-111. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Jääskeläinen M, Holmila M, Notkola IL, Raitasalo K. Mental disorders and harmful substance use in children of substance abusing parents: a longitudinal register-based study on a complete birth cohort born in 1991. Drug Alcohol Rev. 2016;35(6):728-740. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Velleman R, Templeton LJ. Impact of parents' substance misuse on children: an update. BJPsych Adv. Apr 11, 2018;22(2):108-117. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ohannessian CM, Hesselbrock VM, Kramer J, Bucholz KK, Schuckit MA, Kuperman S, et al. Parental substance use consequences and adolescent psychopathology. J Stud Alcohol. 2004;65(6):725-730. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Johnson JL, Leff M. Children of substance abusers: overview of research findings. Pediatrics. 1999;103(5 Pt 2):1085-1099. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Berg L, Bäck K, Vinnerljung B, Hjern A. Parental alcohol-related disorders and school performance in 16-year-olds-a Swedish national cohort study. Addiction. 2016;111(10):1795-1803. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Casas-Gil MJ, Navarro-Guzman JI. School characteristics among children of alcoholic parents. Psychol Rep. 2002;90(1):341-348. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- McGrath CE, Watson AL, Chassin L. Academic achievement in adolescent children of alcoholics. J Stud Alcohol. 1999;60(1):18-26. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Velleman R, Templeton L, Reuber D, Klein M, Moesgen D. Domestic abuse experienced by young people living in families with alcohol problems: results from a cross‐european study. Child Abuse Rev. Nov 24, 2008;17(6):387-409. [ CrossRef ]
- Rothman EF, Edwards EM, Heeren T, Hingson RW. Adverse childhood experiences predict earlier age of drinking onset: results from a representative US sample of current or former drinkers. Pediatrics. 2008;122(2):e298-e304. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Anda RF, Whitfield CL, Felitti VJ, Chapman D, Edwards VJ, Dube SR, et al. Adverse childhood experiences, alcoholic parents, and later risk of alcoholism and depression. Psychiatr Serv. 2002;53(8):1001-1009. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Straussner SLA, Fewell CH. A review of recent literature on the impact of parental substance use disorders on children and the provision of effective services. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2018;31(4):363-367. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Calhoun S, Conner E, Miller M, Messina N. Improving the outcomes of children affected by parental substance abuse: a review of randomized controlled trials. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 2015;6:15-24. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Emshoff JG, Price AW. Prevention and intervention strategies with children of alcoholics. Pediatrics. 1999;103(5 Pt 2):1112-1121. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Cuijpers P. Prevention programmes for children of problem drinkers: a review. Drugs Educ Prev Policy. 2009;12(6):465-475. [ CrossRef ]
- Wannberg H. Plats för barnen—Om kommunernas stöd till barn som växer upp med missbrukande föräldrar [Make room for the children—municipalities and their support for children who grow up with parents with substance abuse]. Stockholm, Sweden. Junis, IOGT-NTO's ungdomsförbund; 2023.
- Elgán TH, Leifman H. Children of substance abusing parents: a national survey on policy and practice in Swedish schools. Health Policy. 2011;101(1):29-36. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- de Sousa D, Fogel A, Azevedo J, Padrão P. The effectiveness of web-based interventions to promote health behaviour change in adolescents: a systematic review. Nutrients. 2022;14(6):1258. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Andersson G. Internet-delivered psychological treatments. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2016;12:157-179. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- King R, Bambling M, Lloyd C, Gomurra R, Smith S, Reid W, et al. Online counselling: the motives and experiences of young people who choose the internet instead of face to face or telephone counselling. Couns Psychother Res. 2007;6(3):169-174. [ CrossRef ]
- Borghouts J, Eikey E, Mark G, De Leon C, Schueller SM, Schneider M, et al. Barriers to and facilitators of user engagement with digital mental health interventions: systematic review. J Med Internet Res. 2021;23(3):e24387. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Boggs JM, Beck A, Felder JN, Dimidjian S, Metcalf CA, Segal ZV. Web-based intervention in mindfulness meditation for reducing residual depressive symptoms and relapse prophylaxis: a qualitative study. J Med Internet Res. 2014;16(3):e87. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hedman-Lagerlöf E, Carlbring P, Svärdman F, Riper H, Cuijpers P, Andersson G. Therapist-supported internet-based cognitive behaviour therapy yields similar effects as face-to-face therapy for psychiatric and somatic disorders: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. World Psychiatry. 2023;22(2):305-314. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Lehtimaki S, Martic J, Wahl B, Foster KT, Schwalbe N. Evidence on digital mental health interventions for adolescents and young people: systematic overview. JMIR Ment Health. 2021;8(4):e25847. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Li J, Theng YL, Foo S. Game-based digital interventions for depression therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2014;17(8):519-527. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Pennant ME, Loucas CE, Whittington C, Creswell C, Fonagy P, Fuggle P, et al. Computerised therapies for anxiety and depression in children and young people: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Behav Res Ther. 2015;67:1-18. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Woolderink M, Smit F, van der Zanden R, Beecham J, Knapp M, Paulus A, et al. Design of an internet-based health economic evaluation of a preventive group-intervention for children of parents with mental illness or substance use disorders. BMC Public Health. 2010;10:470. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Elgán TH, Kartengren N, Strandberg AK, Ingemarson M, Hansson H, Zetterlind U, et al. A web-based group course intervention for 15-25-year-olds whose parents have substance use problems or mental illness: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. BMC Public Health. 2016;16(1):1011. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Maybery D, Reupert A, Bartholomew C, Cuff R, Duncan Z, Foster K, et al. A web-based intervention for young adults whose parents have a mental illness or substance use concern: protocol for a randomized controlled trial. JMIR Res Protoc. 2020;9(6):e15626. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- EÉk N, Romberg K, Siljeholm O, Johansson M, Andreasson S, Lundgren T, et al. Efficacy of an internet-based community reinforcement and family training program to increase treatment engagement for AUD and to improve psychiatric health for CSOs: a randomized controlled trial. Alcohol Alcohol. 2020;55(2):187-195. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Siljeholm O, Lindner P, Johansson M, Hammarberg A. An online self-directed program combining Community Reinforcement Approach and Family Training and parenting training for concerned significant others sharing a child with a person with problematic alcohol consumption: a randomized controlled trial. Addict Sci Clin Pract. 2022;17(1):49. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Woolderink M. Mind the gap: evaluation of an online preventive programme for adolescents with mentally ill or addicted parents. Maastricht University. 2016. URL: https://cris.maastrichtuniversity.nl/ws/portalfiles/portal/7281149/c5531.pdf [accessed 2024-03-14]
- Maybery D, Reupert A, Bartholomew C, Cuff R, Duncan Z, McAuliffe C, et al. An online intervention for 18-25-year-old youth whose parents have a mental illness and/or substance use disorder: a pilot randomized controlled trial. Early Interv Psychiatry. 2022;16(11):1249-1258. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hansson H, Rundberg J, Zetterlind U, Johnsson KO, Berglund M. An intervention program for university students who have parents with alcohol problems: a randomized controlled trial. Alcohol Alcohol. 2006;41(6):655-663. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hansson H, Rundberg J, Zetterlind U, Johnsson KO, Berglund M. Two-year outcome of an intervention program for university students who have parents with alcohol problems: a randomized controlled trial. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2007;31(11):1927-1933. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Zetterlind U, Hansson H, Aberg-Orbeck K, Berglund M. Effects of coping skills training, group support, and information for spouses of alcoholics: a controlled randomized study. Nord J Psychiatry. 2001;55(4):257-262. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hansson H, Zetterlind U, Aberg-Orbeck K, Berglund M. Two-year outcome of coping skills training, group support and information for spouses of alcoholics: a randomized controlled trial. Alcohol Alcohol. 2004;39(2):135-140. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hodgins DC, Maticka-Tyndale E, El-Guebaly N, West M. The CAST-6: development of a short-form of the Children of Alcoholics Screening Test. Addict Behav. 1993;18(3):337-345. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hodgins DC, Shimp L. Identifying adult children of alcoholics: methodological review and a comparison of the CAST-6 with other methods. Addiction. 1995;90(2):255-267. [ Medline ]
- Elgán TH, Berman AH, Jayaram-Lindström N, Hammarberg A, Jalling C, Källmén H. Psychometric properties of the short version of the children of alcoholics screening test (CAST-6) among Swedish adolescents. Nord J Psychiatry. 2021;75(2):155-158. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Orford J, Guthrie S, Nicholls P, Oppenheimer E, Egert S, Hensman C. Self-reported coping behavior of wives of alcoholics and its association with drinking outcome. J Stud Alcohol. 1975;36(9):1254-1267. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Schoenbach VJ, Kaplan BH, Grimson RC, Wagner EH. Use of a symptom scale to study the prevalence of a depressive syndrome in young adolescents. Am J Epidemiol. 1982;116(5):791-800. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Bush K, Kivlahan DR, McDonell MB, Fihn SD, Bradley KA. The AUDIT alcohol consumption questions (AUDIT-C): an effective brief screening test for problem drinking. Ambulatory Care Quality Improvement Project (ACQUIP). Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test. Arch Intern Med. 1998;158(16):1789-1795. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Myers JK, Weissman MM. Use of a self-report symptom scale to detect depression in a community sample. Am J Psychiatry. 1980;137(9):1081-1084. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Olsson G, von Knorring AL. Depression among Swedish adolescents measured by the self-rating scale Center for Epidemiology Studies-Depression Child (CES-DC). Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1997;6(2):81-87. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Fendrich M, Weissman MM, Warner V. Screening for depressive disorder in children and adolescents: validating the Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale for Children. Am J Epidemiol. 1990;131(3):538-551. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Bergman H, Källmen H, Rydberg U, Sandahl C. Tio frågor om alkohol identifierar beroendeproblem. Psykometrisk prövning på psykiatrisk akutmottagning [Ten questions about alcohol as identifier of addiction problems. Psychometric tests at an emergency psychiatric department]. Läkartidningen. 1998;95(43):4731-4735. [ FREE Full text ]
- Källmén H, Berman AH, Jayaram-Lindström N, Hammarberg A, Elgán TH. Psychometric properties of the AUDIT, AUDIT-C, CRAFFT and ASSIST-Y among Swedish adolescents. Eur Addict Res. 2019;25(2):68-77. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Andrews FM, Withey SB. Developing measures of perceived life quality: results from several national surveys. Soc Indic Res. 1974;1(1):1-26. [ CrossRef ]
- Nagy E. Barns känsla av sammanhang—En valideringsstudie av BarnKASAM i årskurserna 1-6 (ålder 7-12 år) [Children's sense of coherence—a study validating SOC for children in grades 1-6 (7-12 years old)]. Lunds Universitet [Lund University]. 2004. URL: https://lup.lub.lu.se/luur/download?func=downloadFile&recordOId=1358959&fileOId=1358960 [accessed 2024-03-14]
- Saghaei M. Random allocation software for parallel group randomized trials. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2004;4:26. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- drugsmart. URL: https://www.drugsmart.se/ [accessed 2024-03-19]
- Dimeff LA, Baer JS, Kivlahan DR, Marlatt GA. Brief Alcohol Screening and Intervention for College Students: A Harm Reduction Approach. New York. The Guilford Press; 1999.
- Cohen J. A power primer. Psychol Bull. 1992;112(1):155-159. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Faul F, Erdfelder E, Lang A, Buchner A. G*Power 3: a flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav Res Methods. 2007;39(2):175-191. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Bürkner PC. brms: an R package for bayesian multilevel models using stan. J Stat Soft. 2017;80(1):1-28. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ]
- Carpenter B, Gelman A, Hoffman MD, Lee D, Goodrich B, Betancourt M, et al. Stan: a probabilistic programming language. J Stat Softw. 2017;76(1):1-32. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Magnusson K, Nilsson A, Carlbring P. Modeling longitudinal gambling data: challenges and opportunities. PsyArxiv. Preprint posted online on September 12, 2019. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ]
- Coertjens L, Donche V, De Maeyer S, Vanthournout G, Van Petegem P. To what degree does the missing-data technique influence the estimated growth in learning strategies over time? A tutorial example of sensitivity analysis for longitudinal data. PLoS One. 2017;12(9):e0182615. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kunas SL, Lautenbacher LM, Lueken PU, Hilbert K. Psychological predictors of cognitive-behavioral therapy outcomes for anxiety and depressive disorders in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Affect Disord. 2021;278:614-626. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Stallman HM, Lipson SK, Zhou S, Eisenberg D. How do university students cope? An exploration of the health theory of coping in a US sample. J Am Coll Health. 2022;70(4):1179-1185. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Stallman HM, Beaudequin D, Hermens DF, Eisenberg D. Modelling the relationship between healthy and unhealthy coping strategies to understand overwhelming distress: a Bayesian network approach. J Affect Disord Rep. 2021;3:100054. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ]
- McClure JB, Shortreed SM, Bogart A, Derry H, Riggs K, St John J, et al. The effect of program design on engagement with an internet-based smoking intervention: randomized factorial trial. J Med Internet Res. 2013;15(3):e69. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Humphrey G, Bullen C. Smartphone-based problem gambling evaluation and technology testing initiative ('SPGeTTI'): final report reference 354913/00 for the Ministry of Health. National Institute for Health Innovation (NIHI), Auckland UniServices Ltd, The Univerisy of Auckland. 2019. URL: https://www.health.govt.nz/system/files/documents/publications/20190424-spgetti-354913-00-final-report.pdf [accessed 2024-03-14]
- Kelders SM, Kok RN, Ossebaard HC, Van Gemert-Pijnen JEWC. Persuasive system design does matter: a systematic review of adherence to web-based interventions. J Med Internet Res. 2012;14(6):e152. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Grové C, Reupert A. Moving the field forward: developing online interventions for children of parents with a mental illness. Child Youth Serv Rev. 2017;82:354-358. [ CrossRef ]
- Moffat BM, Haines-Saah RJ, Johnson JL. From didactic to dialogue: assessing the use of an innovative classroom resource to support decision-making about cannabis use. Drugs Educ Prev Policy. 2016;24(1):85-95. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bevan Jones R, Stallard P, Agha SS, Rice S, Werner-Seidler A, Stasiak K, et al. Practitioner review: co-design of digital mental health technologies with children and young people. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2020;61(8):928-940. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Garrido S, Millington C, Cheers D, Boydell K, Schubert E, Meade T, et al. What works and what doesn't work? A systematic review of digital mental health interventions for depression and anxiety in young people. Front Psychiatry. 2019;10:759. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Crutzen R, de Nooijer J, Brouwer W, Oenema A, Brug J, de Vries NK. Strategies to facilitate exposure to internet-delivered health behavior change interventions aimed at adolescents or young adults: a systematic review. Health Educ Behav. 2011;38(1):49-62. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Milward J, Drummond C, Fincham-Campbell S, Deluca P. What makes online substance-use interventions engaging? A systematic review and narrative synthesis. Digit Health. 2018;4:2055207617743354. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Välimäki M, Anttila K, Anttila M, Lahti M. Web-based interventions supporting adolescents and young people with depressive symptoms: systematic review and meta-analysis. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2017;5(12):e180. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
Abbreviations
Edited by YH Lin; submitted 24.08.23; peer-reviewed by X Zhang, C Asuzu, D Liu; comments to author 28.01.24; revised version received 08.02.24; accepted 27.02.24; published 10.04.24.
©Håkan Wall, Helena Hansson, Ulla Zetterlind, Pia Kvillemo, Tobias H Elgán. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (https://www.jmir.org), 10.04.2024.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work, first published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research, is properly cited. The complete bibliographic information, a link to the original publication on https://www.jmir.org/, as well as this copyright and license information must be included.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
Research Methods | Definitions, Types, Examples
Research methods are specific procedures for collecting and analyzing data. Developing your research methods is an integral part of your research design . When planning your methods, there are two key decisions you will make.
First, decide how you will collect data . Your methods depend on what type of data you need to answer your research question :
- Qualitative vs. quantitative : Will your data take the form of words or numbers?
- Primary vs. secondary : Will you collect original data yourself, or will you use data that has already been collected by someone else?
- Descriptive vs. experimental : Will you take measurements of something as it is, or will you perform an experiment?
Second, decide how you will analyze the data .
- For quantitative data, you can use statistical analysis methods to test relationships between variables.
- For qualitative data, you can use methods such as thematic analysis to interpret patterns and meanings in the data.
Table of contents
Methods for collecting data, examples of data collection methods, methods for analyzing data, examples of data analysis methods, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research methods.
Data is the information that you collect for the purposes of answering your research question . The type of data you need depends on the aims of your research.
Qualitative vs. quantitative data
Your choice of qualitative or quantitative data collection depends on the type of knowledge you want to develop.
For questions about ideas, experiences and meanings, or to study something that can’t be described numerically, collect qualitative data .
If you want to develop a more mechanistic understanding of a topic, or your research involves hypothesis testing , collect quantitative data .
You can also take a mixed methods approach , where you use both qualitative and quantitative research methods.
Primary vs. secondary research
Primary research is any original data that you collect yourself for the purposes of answering your research question (e.g. through surveys , observations and experiments ). Secondary research is data that has already been collected by other researchers (e.g. in a government census or previous scientific studies).
If you are exploring a novel research question, you’ll probably need to collect primary data . But if you want to synthesize existing knowledge, analyze historical trends, or identify patterns on a large scale, secondary data might be a better choice.
Descriptive vs. experimental data
In descriptive research , you collect data about your study subject without intervening. The validity of your research will depend on your sampling method .
In experimental research , you systematically intervene in a process and measure the outcome. The validity of your research will depend on your experimental design .
To conduct an experiment, you need to be able to vary your independent variable , precisely measure your dependent variable, and control for confounding variables . If it’s practically and ethically possible, this method is the best choice for answering questions about cause and effect.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Your data analysis methods will depend on the type of data you collect and how you prepare it for analysis.
Data can often be analyzed both quantitatively and qualitatively. For example, survey responses could be analyzed qualitatively by studying the meanings of responses or quantitatively by studying the frequencies of responses.
Qualitative analysis methods
Qualitative analysis is used to understand words, ideas, and experiences. You can use it to interpret data that was collected:
- From open-ended surveys and interviews , literature reviews , case studies , ethnographies , and other sources that use text rather than numbers.
- Using non-probability sampling methods .
Qualitative analysis tends to be quite flexible and relies on the researcher’s judgement, so you have to reflect carefully on your choices and assumptions and be careful to avoid research bias .
Quantitative analysis methods
Quantitative analysis uses numbers and statistics to understand frequencies, averages and correlations (in descriptive studies) or cause-and-effect relationships (in experiments).
You can use quantitative analysis to interpret data that was collected either:
- During an experiment .
- Using probability sampling methods .
Because the data is collected and analyzed in a statistically valid way, the results of quantitative analysis can be easily standardized and shared among researchers.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Chi square test of independence
- Statistical power
- Descriptive statistics
- Degrees of freedom
- Pearson correlation
- Null hypothesis
- Double-blind study
- Case-control study
- Research ethics
- Data collection
- Hypothesis testing
- Structured interviews
Research bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Unconscious bias
- Recall bias
- Halo effect
- Self-serving bias
- Information bias
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to systematically measure variables and test hypotheses . Qualitative methods allow you to explore concepts and experiences in more detail.
In mixed methods research , you use both qualitative and quantitative data collection and analysis methods to answer your research question .
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population . Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research. For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
In statistics, sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population.
The research methods you use depend on the type of data you need to answer your research question .
- If you want to measure something or test a hypothesis , use quantitative methods . If you want to explore ideas, thoughts and meanings, use qualitative methods .
- If you want to analyze a large amount of readily-available data, use secondary data. If you want data specific to your purposes with control over how it is generated, collect primary data.
- If you want to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables , use experimental methods. If you want to understand the characteristics of a research subject, use descriptive methods.
Methodology refers to the overarching strategy and rationale of your research project . It involves studying the methods used in your field and the theories or principles behind them, in order to develop an approach that matches your objectives.
Methods are the specific tools and procedures you use to collect and analyze data (for example, experiments, surveys , and statistical tests ).
In shorter scientific papers, where the aim is to report the findings of a specific study, you might simply describe what you did in a methods section .
In a longer or more complex research project, such as a thesis or dissertation , you will probably include a methodology section , where you explain your approach to answering the research questions and cite relevant sources to support your choice of methods.
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples.
- What Is a Research Design | Types, Guide & Examples
- Data Collection | Definition, Methods & Examples
More interesting articles
- Between-Subjects Design | Examples, Pros, & Cons
- Cluster Sampling | A Simple Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- Confounding Variables | Definition, Examples & Controls
- Construct Validity | Definition, Types, & Examples
- Content Analysis | Guide, Methods & Examples
- Control Groups and Treatment Groups | Uses & Examples
- Control Variables | What Are They & Why Do They Matter?
- Correlation vs. Causation | Difference, Designs & Examples
- Correlational Research | When & How to Use
- Critical Discourse Analysis | Definition, Guide & Examples
- Cross-Sectional Study | Definition, Uses & Examples
- Descriptive Research | Definition, Types, Methods & Examples
- Ethical Considerations in Research | Types & Examples
- Explanatory and Response Variables | Definitions & Examples
- Explanatory Research | Definition, Guide, & Examples
- Exploratory Research | Definition, Guide, & Examples
- External Validity | Definition, Types, Threats & Examples
- Extraneous Variables | Examples, Types & Controls
- Guide to Experimental Design | Overview, Steps, & Examples
- How Do You Incorporate an Interview into a Dissertation? | Tips
- How to Do Thematic Analysis | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
- How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples
- Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria | Examples & Definition
- Independent vs. Dependent Variables | Definition & Examples
- Inductive Reasoning | Types, Examples, Explanation
- Inductive vs. Deductive Research Approach | Steps & Examples
- Internal Validity in Research | Definition, Threats, & Examples
- Internal vs. External Validity | Understanding Differences & Threats
- Longitudinal Study | Definition, Approaches & Examples
- Mediator vs. Moderator Variables | Differences & Examples
- Mixed Methods Research | Definition, Guide & Examples
- Multistage Sampling | Introductory Guide & Examples
- Naturalistic Observation | Definition, Guide & Examples
- Operationalization | A Guide with Examples, Pros & Cons
- Population vs. Sample | Definitions, Differences & Examples
- Primary Research | Definition, Types, & Examples
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research | Differences, Examples & Methods
- Quasi-Experimental Design | Definition, Types & Examples
- Questionnaire Design | Methods, Question Types & Examples
- Random Assignment in Experiments | Introduction & Examples
- Random vs. Systematic Error | Definition & Examples
- Reliability vs. Validity in Research | Difference, Types and Examples
- Reproducibility vs Replicability | Difference & Examples
- Reproducibility vs. Replicability | Difference & Examples
- Sampling Methods | Types, Techniques & Examples
- Semi-Structured Interview | Definition, Guide & Examples
- Simple Random Sampling | Definition, Steps & Examples
- Single, Double, & Triple Blind Study | Definition & Examples
- Stratified Sampling | Definition, Guide & Examples
- Structured Interview | Definition, Guide & Examples
- Survey Research | Definition, Examples & Methods
- Systematic Review | Definition, Example, & Guide
- Systematic Sampling | A Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- Textual Analysis | Guide, 3 Approaches & Examples
- The 4 Types of Reliability in Research | Definitions & Examples
- The 4 Types of Validity in Research | Definitions & Examples
- Transcribing an Interview | 5 Steps & Transcription Software
- Triangulation in Research | Guide, Types, Examples
- Types of Interviews in Research | Guide & Examples
- Types of Research Designs Compared | Guide & Examples
- Types of Variables in Research & Statistics | Examples
- Unstructured Interview | Definition, Guide & Examples
- What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
- What Is a Case-Control Study? | Definition & Examples
- What Is a Cohort Study? | Definition & Examples
- What Is a Conceptual Framework? | Tips & Examples
- What Is a Controlled Experiment? | Definitions & Examples
- What Is a Double-Barreled Question?
- What Is a Focus Group? | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
- What Is a Likert Scale? | Guide & Examples
- What Is a Prospective Cohort Study? | Definition & Examples
- What Is a Retrospective Cohort Study? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples
- What Is an Observational Study? | Guide & Examples
- What Is Concurrent Validity? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Content Validity? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Convenience Sampling? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Convergent Validity? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Criterion Validity? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Data Cleansing? | Definition, Guide & Examples
- What Is Deductive Reasoning? | Explanation & Examples
- What Is Discriminant Validity? | Definition & Example
- What Is Ecological Validity? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Ethnography? | Definition, Guide & Examples
- What Is Face Validity? | Guide, Definition & Examples
- What Is Non-Probability Sampling? | Types & Examples
- What Is Participant Observation? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Peer Review? | Types & Examples
- What Is Predictive Validity? | Examples & Definition
- What Is Probability Sampling? | Types & Examples
- What Is Purposive Sampling? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Qualitative Observation? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
- What Is Quantitative Observation? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Quantitative Research? | Definition, Uses & Methods
What is your plagiarism score?
Read our research on: Gun Policy | International Conflict | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
How common is religious fasting in the united states.

Muslims are currently observing Ramadan , a holy month when people fast by abstaining from certain activities, including eating and drinking, during the day. Many Christians, Jews and adherents of other religions also practice some form of fasting at certain times of the year. Many Catholics, for example, recently fasted for Lent by abstaining from meat on Fridays, among other things.
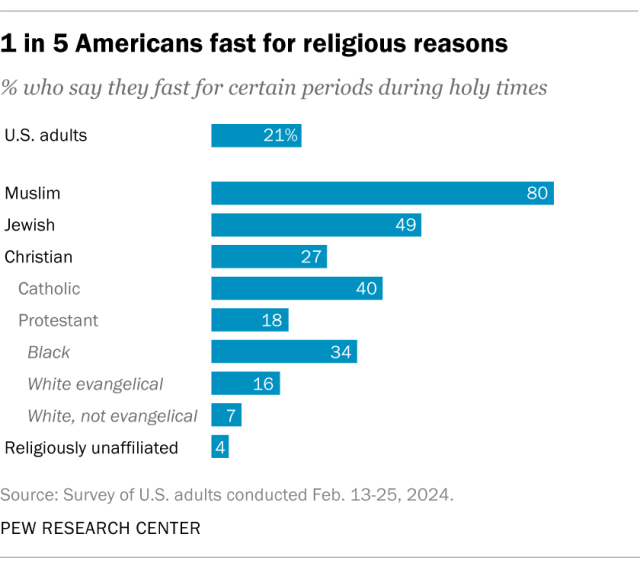
In the United States, 21% of adults overall say they fast for certain periods during holy times, according to a Pew Research Center survey from February. Muslim Americans are by far the most likely to say they fast for religious reasons, followed by Jewish Americans, Catholics and Black Protestants.
While the February survey includes people of all religious backgrounds, we do not have large enough samples to report on the fasting habits of smaller groups, such as Hindus, Buddhists or Orthodox Christians.
Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to see how many U.S. adults fast for religious reasons and what percentage of people in various religious groups take part in fasting.
For this analysis, we surveyed 12,693 respondents from Feb. 13 to 25, 2024. Most of the respondents (10,642) are members of the American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel recruited through national random sampling of residential addresses, which gives nearly all U.S. adults a chance of selection.
The remaining respondents (2,051) are members of three other panels; the Ipsos KnowledgePanel, the NORC Amerispeak Panel and the SSRS Opinion Panel. All three are national survey panels recruited through random sampling (not “opt-in” polls). We used these additional panels to ensure that the survey would have enough Jewish and Muslim respondents to be able to report on their views.
The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education, religious affiliation and other categories.
For more information, refer to the ATP’s methodology and the methodology for this analysis. Read the questions used in this analysis .
Eight-in-ten Muslim Americans say they fast, according to the February survey. We did not ask whether Muslims are fasting specifically for Ramadan , which runs from early March through early April this year. However, a 2017 Center survey found that 80% of Muslims fast for Ramadan, making it a far more common practice than other Islamic traditions like praying five times a day (42%) or attending mosque weekly (43%).
About half of Jewish Americans (49%) say they fast for certain periods during holy times, according to the February survey. And in a 2019-2020 Center survey , 56% of Jewish adults said they fasted for all or part of the previous Yom Kippur.
Yom Kippur is a day of atonement for sins . The fast traditionally entails not eating or drinking for approximately 25 hours, from sunset on the eve of Yom Kippur until after sunset the following day. Some Jews also fast at other times of the year, such as Tishah b’Av , which primarily commemorates the destruction of the first and second ancient Jewish temples in Jerusalem.
Four-in-ten U.S. Catholics fast, according to the February survey. We didn’t ask respondents about when they fast specifically, but many Catholics around the world fast during Lent, the 40-day period leading up to Easter. Lenten sacrifices often include abstaining from eating meat on Fridays and giving up something one typically enjoys – like a favorite food, drink or pastime. The U.S. Conference of Catholic Bishops says Lent calls for giving up luxuries and practicing self-discipline. In 2015, we found that 47% of Catholics said they gave up something or did something extra for Lent in the previous year.
Protestants also sometimes fast, with Black Protestants most likely to do so (34%). Fewer White evangelical Protestants (16%) or White nonevangelical Protestants (7%) fast. Some Protestants fast for Lent, while individual Protestant churches or religious leaders sometimes call for short periods of abstention from food – or food and drink – to focus practitioners on spiritual activities such as prayer, charity or seeking guidance from God .
Many other religions , including Buddhism and Hinduism, also have traditions that involve fasting. Various religions teach that fasting improves self-control, increases spiritual awareness or fosters empathy for the less fortunate , among other things.
Note: For more information, refer to the ATP’s methodology and the methodology for this analysis. Read the questions used in this analysis .

Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivered Saturday mornings
Christians, religiously unaffiliated differ on whether most things in society can be divided into good, evil
Few americans blame god or say faith has been shaken amid pandemic, other tragedies, in their own words, how americans explain why bad things happen, most indians, including most hindus, do not practice yoga, about a quarter of religiously affiliated teens in u.s. public schools say they pray before lunch, most popular.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Skip to Content

- Undergraduate Programs
- Graduate Programs
- Faculty & Research
Other ways to search:
- Events Calendar
Facts Ignored: The Truth is Flexible When Falsehoods Support Political Beliefs
You are here.
This paper presents results from a series of online surveys—conducted among American voters during and after the (President Donald) Trump administration—that show how voters (both Republican and Democratic) provide explicit moral justification for politicians’ statements that flagrantly violate the norm of fact-grounding. Such justification is inconsistent with prevailing theory, whereby partisan voters’ tendency (due either to laziness or bias) to mistake misinformation for fact is the only factor responsible for their positive response to misinformation purveyed by partisan standard bearers. The studies presented in this paper provide consistent evidence of such factual flexibility. Yet they also provide consistent evidence of moral flexibility, whereby voters justify demagogic fact-flouting as an effective way of proclaiming a deeply resonant political “truth.” A key implication is that political misinformation cannot be fully eliminated by getting voters to distinguish fact from fiction; voters’ moral orientations may be such that they prefer fact-flouting. More general lessons pertain to the role of democratic norms in liberal democracies and to how moral orientations relate to perceived interests.
Why do people support politicians who make blatantly false statements?
A forthcoming study dug into this phenomenon and found that people knowingly support falsehoods when it aligns with their personal politics.
The research, led by Minjae Kim of Rice University’s Jones Graduate School of Business and co-authored by Oliver Hahl of Carnegie Mellon University’s Tepper School of Business and Ezra W. Zuckerman Sivan of Massachusetts Institute of Technology’s Sloan School of Management, sought to discern why people support politicians who disseminate information that is not truthful.
Read the full article here.
- Share via Twitter
- Share via Facebook
- Share via Google Plus
- Share via LinkedIn
- Share via E-mail
- Leeds Faculty Directory
- Faculty in the News
- Select Faculty Publications
- Frascona Teaching Excellence Award
Frank Sinatra Research Paper
Frank Sinatra Glorious Life There are many celebrities in the world. Many people try to become famous, but are unsuccessful. On the other hand, a good celebrity is Frank Sinatra. One celebrity that has won Grammys in the music industry is Frank Sinatra. Frank Sinatra was a talented musician from the 1940’s through the 1990’s. First, Frank Sinatra’s early life influenced his career. To begin, Sinatra was born December 12, 1915. Frank Sinatra was born to Silician parents in Hoboken, New Jersey (Biography.com). Sinatra’s mother influenced his personality and character. To continue, Sinatra was not too good at school. Frank Sinatra was a poor student in school, making him not enjoy it or feel successful in it (“Frank”). Sinatra decided to join …show more content…
He then started singing at local nightclubs, showing off his skills. Sinatra caught the attention of bandleader Harry Jones after he started singing on the radio (Biography.com). Second, Frank Sinatra had a successful career. Initially, Sinatra had many hit songs by himself. He found a new vocal outlet when he received a recording contract with Capitol Records. Between 1943 and 1946 Sinatra’s solo career blossomed as the singer, and Sinatra charted a bunch of hit singles. Additionally, Sinatra made many songs with others. Sinatra made his first recording with Harry James. Tommy Dorsey heard Sinatra sing and invited him to his band. Sinatra stayed with the band for two years before he became a soloist. Finally, Sinatra had a successful acting career. Sinatra made his acting debut in 1943 with films like “Reveille with Beverly” and “Higher and Higher”. In 1945 he won a Special Academy award. Sinatra’s popularity decreased in postwar years, leading to a loss of his recording and film contracts in early 1950, but made a triumphant return in 1953 by winning an Oscar (Biography.com). Third, Frank Sinatra has many achievements and awards. To start, Sinatra has many song
More about Frank Sinatra Research Paper

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Provides clarification, similar to "in other words.". Example The reaction is exothermic; that is to say, it releases heat. 13. To put it simply. Simplifies a complex idea, often for a more general readership. Example The universe is vast; to put it simply, it is larger than anything we can truly imagine. 14.
Synonyms for Research Paper (other words and phrases for Research Paper). Synonyms for Research paper. 330 other terms for research paper- words and phrases with similar meaning. Lists. synonyms. antonyms. definitions. sentences. thesaurus. words. phrases. Parts of speech. nouns. Tags. answer. reaction. reply. suggest new.
Wordvice provides high-quality English proofreading and editing services.We have helped thousands of researchers, students, writers, and businesses maximize the impact of their writing. Here are 100+ active verbs to make your research writing more engaging. Includes additional tops to improve word and phrase choices.
Find 14 different ways to say RESEARCH PAPER, along with antonyms, related words, and example sentences at Thesaurus.com.
Synonyms for research paper include term paper, report, study, monograph, theme, discourse, paper, article, review and essay. Find more similar words at wordhippo.com!
Definition: Research Paper is a written document that presents the author's original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue. It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new ...
Most related words/phrases with sentence examples define Research paper meaning and usage. Thesaurus for Research paper. Related terms for research paper- synonyms, antonyms and sentences with research paper. Lists. synonyms. antonyms. definitions. sentences. thesaurus. Parts of speech. nouns. Synonyms Similar meaning.
Research Papers synonyms - 180 Words and Phrases for Research Papers. research notes. scientific works. academic papers. academic sources. academic text books. academic texts. academic writings.
Choose a research paper topic. There are many ways to generate an idea for a research paper, from brainstorming with pen and paper to talking it through with a fellow student or professor.. You can try free writing, which involves taking a broad topic and writing continuously for two or three minutes to identify absolutely anything relevant that could be interesting.
Grey Literature-- research produced by organizations outside of commercial and academic publishing that publish materials, such as, working papers, research reports, and briefing papers. Grounded Theory-- practice of developing other theories that emerge from observing a group. Theories are grounded in the group's observable experiences, but ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
In other words, the fall of the Empire was caused by over-expansion." Adversative Transitions These terms and phrases distinguish facts, arguments, and other information, whether by contrasting and showing differences; by conceding points or making counterarguments; by dismissing the importance of a fact or argument; or replacing and ...
Accrual - the number of subjects who have completed or are actively in the process of completing a study. The accrual goal is how many subjects are needed to finish the study (2). Adverse event (AE) - a negative symptom or experience encountered by an subject during the course of a clinical trial. Adverse events can be expected or unexpected.
Formatting an APA paper. The main guidelines for formatting a paper in APA Style are as follows: Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman or 11 pt Arial. Set 1 inch page margins. Apply double line spacing. If submitting for publication, insert a APA running head on every page. Indent every new paragraph ½ inch.
Synonyms for RESEARCH: investigation, inquiry, study, exploration, examination, probing, probe, inspection, inquisition, delving
hypothesis: a proposition which research sets out to prove or disprove: "experimental" where the hypothesis is a positive statement, or "null" where statement contains a negative. independent variable: a variable that researcher believes precedes, influences or predicts the dependent variable. informed consent: giving potential ...
It's meant to set the context for the rest of the paper, establish the purpose of the study, and state the research question. So be sure not to mix up these confusing terms in research. 5. Implications and limitations. Another set of research paper terms that researchers often get confused about is implications and limitations.
At this point, decide on the most likely sources of information—books, journal articles, newspapers, online databases, CD-ROM databases, interviews, etc. Dig around in the library and locate sources for your term paper. Use your library's computer access system to find books on your subject. Some topics may be so current that few, if any ...
Term Paper. Definition: Term paper is a type of academic writing assignment that is typically assigned to students at the end of a semester or term. It is usually a research-based paper that is meant to demonstrate the student's understanding of a particular topic, as well as their ability to analyze and synthesize information from various sources.. Term papers are usually longer than other ...
A key term is a term that holds significant importance or plays a crucial role within the context of a research paper. It is a term that encapsulates a core concept, idea, or variable that is central to the study. Key terms are often essential for understanding the research objectives, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
A research paper is simply a piece of writing that uses outside sources. There are different types of research papers with varying purposes and expectations for sourcing. While this guide explains those differences broadly, ask your professor about specific disciplinary conventions. To argue for a single claim or thesis through evidence and ...
credit other people's words and ideas via citations and references to avoid plagiarism; and describe other people with dignity and respect using inclusive, bias-free language. APA Style is primarily used in the behavioral sciences, which are subjects related to people, such as psychology, education, and nursing.
Rising life expectancy and an aging population across nations are leading to an increased need for long-term financial savings and a focus on the financial well-being of retired individuals amidst changing policy framework. This study is a systematic review based on a scientific way of producing high-quality evidence based on 191 articles from the Scopus and Web of Science databases. It adopts ...
This paper is in the following e-collection/theme issue: Web-based and Mobile Health Interventions (2944) Registered Report (472) Alcohol Abuse, Alcoholism Prevention and Recovery (279) Formative Evaluation of Digital Health Interventions (2052) Substance Abuse (351) Prevention and Health Promotion (787) Interventions and Support for Informal Caregivers of People with Mental Illness (85)
Romeo And Juliet Research Paper. 793 Words4 Pages. Romeo and Juliet are an awful example of true love. Star-crossed lovers don't show any signs of true love. Romeo and Juliet don't respect each other, can make rational decisions, and they don't fully care for each other. Romeo and Juliet didn't fully respect each other.
Ben Wallace Research Paper. 1100 Words5 Pages. "B-B-B-B-B BEN WALLACE!" screams the commentator as Ben Wallace comes running down in between two lines of his Detroit Pistons teammates, body checking every single one of them making them fall backwards because of his pure strength. When people think of a villain, they think of cool costumes ...
Research methods are specific procedures for collecting and analyzing data. Developing your research methods is an integral part of your research design. When planning your methods, there are two key decisions you will make. First, decide how you will collect data. Your methods depend on what type of data you need to answer your research question:
Many Catholics, for example, recently fasted for Lent by abstaining from meat on Fridays, among other things. In the United States, 21% of adults overall say they fast for certain periods during holy times, according to a Pew Research Center survey from February. Muslim Americans are by far the most likely to say they fast for religious reasons ...
Abstract. This paper presents results from a series of online surveys—conducted among American voters during and after the (President Donald) Trump administration—that show how voters (both Republican and Democratic) provide explicit moral justification for politicians' statements that flagrantly violate the norm of fact-grounding.
557 Words3 Pages. Frank Sinatra Glorious Life There are many celebrities in the world. Many people try to become famous, but are unsuccessful. On the other hand, a good celebrity is Frank Sinatra. One celebrity that has won Grammys in the music industry is Frank Sinatra. Frank Sinatra was a talented musician from the 1940's through the 1990's.