
Top PhD in Nursing Programs
What is a ph.d. in nursing.
- Ph.D. in Nursing vs DNP
- Types of Programs
- Top Programs
- Program Overview
- Is a Nursing Ph.D. For Me?
The Ph.D. in Nursing degree opens career opportunities for nurses as researchers, forging new and cutting-edge nursing practices for future generations. This article explores this terminal nursing degree, how to get it, and the top Ph.D. in Nursing programs.

A Ph.D. in Nursing is the highest degree awarded to nurses and one of two terminal nursing degrees. Ph.D. stands for Doctor of Philosophy, and Ph.D. in Nursing programs focus on evidence-based research.
Throughout their 4-6 year study, nursing Ph.D. students learn how to conduct, analyze, and publish nursing research. The degree culminates in students conducting an independent research project and writing a dissertation on it.
Ph.D. in Nursing and DNP Differences
A Ph.D. in Nursing and a Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) are both terminal nursing degrees. However, comparing a DNP vs. a Ph.D. in Nursing reveals distinct differences. Notably, the Ph.D. in Nursing prepares you for a science, academic, or research-focused career as opposed to a clinical one.
Key Ph.D. in Nursing vs. DNP Differences
>> Related: Top Online DNP Programs
Types of Ph.D. in Nursing Programs
The United States is home to over 135 Ph.D. in Nursing programs, which you can attend in multiple formats at nearly every educational level. The types of Ph.D. in nursing programs include the following:
- BSN to Ph.D. in Nursing: These Ph.D. in nursing programs allow nurses with a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) degree to pursue a career in nursing research without first attending an MSN program.
- MSN to Ph.D. in Nursing: Designed for Master of Science in Nursing (MSN) trained nurses, these programs typically include core courses for the doctoral program, electives, and dissertation study.
- DNP/Ph.D. Dual Degree: These rigorous programs allow students to concurrently attain expertise in scientific inquiry and faculty practice and hone the practical skills of expert nurse clinicians.
>> Show Me DNP Programs
Online Ph.D. in Nursing Programs
Are Ph.D. in Nursing programs available online? The answer is yes; you can find several online options to pursue this degree. Since a Ph.D. in Nursing focuses on scientific inquiry, it doesn't have the same onsite practical hours as other nursing degrees.
Program dependant, you may still need to show up on campus a few times each year. However, for the most part, all you need to earn a Ph.D. in nursing is Wi-Fi, good study habits, and determination.
Top Ph.D. in Nursing Programs
Each Ph.D. in Nursing program is unique, offering its own benefits and features. We assembled the top five Ph.D. in Nursing programs nationwide following Nurse.org's proprietary ranking algorithm , which considers and ranks schools based on factors like:
- Tuition costs
- Program length
- Nursing school accreditation
- Admission requirements
- The variety of available programs
- Additional program accolades
1. University of Pennsylvania
- Program Cost: $46,934 per academic year
- Program Length: 4-6 years
- Application Due Date: Dec. 1st
The University of Pennsylvania boasts one of the top Ph.D. in nursing programs nationwide. To offset the expensive tuition, the university offers full-time students stipends during their first four years. In exchange, students may work as Teaching Assistants within UPenn's School of Nursing for up to 16 hours a week.
Contact UPenn about this program:
- Phone: (215) 898-4271
- Email: [email protected]
Source: University of Pennsylvania
2. Duke University
- Program Cost: Fully funded (up to 5 years)
- Application Due Date: November 30th
In 2023, U.S. News & World Report named Duke University the second-best graduate school for nursing. Duke's Ph.D. in Nursing program prepares nurses to become stalwart scholars. Graduates will build nursing science by leading multidisciplinary research that determines the relationship between chronic illness and care systems.
Contact Duke University about this program:
- Phone: (919) 684-3786
- Email: Contact Request Form
Source: Duke University
3. Duquesne University
- Program Cost: $1,765 per credit
- Program Length: 3-4 years
- Application Due Date: February 1st
As the first fully online Ph.D. in Nursing program, Duquesne offers a highly flexible education option to many students nationwide. Additionally, students attending the program may get to study abroad at the Duquesne campus in Dublin, Ireland. The 56-credit program culminates in a dissertation proposal and final defense in which students orally defend their research thesis to the dissertation committee.
Contact Duquesne University about this program:
- Phone: (412) 396-6219
- Email: [email protected]
Source: Duquesne University
4. Columbia University
- Program Cost: Fully funded (up to 3 years)
- Application Due Date: November 15th
Ph.D. in Nursing student at Columbia choose one of three major areas to study, which include Theoretical Foundations of Nursing Science, Analytical Foundations of Nursing Science, and Electives and Applications. The programming heavily focuses on publication, grantsmanship, presentation, and networking. In addition to their coursework, students participate in research experience and training.
Contact Columbia University about this program:
- Phone: (212) 305-5756
- Email: [email protected]
Source: Columbia University
5. Rush University
- Program Cost: $1,344 per credit hour
- Program Length: 3-5 years
- Application Due Date: March 4th
Rush University's Ph.D. in Nursing is fully online except for an on-campus orientation and summer intensive learning sessions. The program focuses on preparing nurses and non-nurses with graduate degrees to become leaders in clinical research and educators who influence healthcare policy. While many students keep working throughout the program, they often must take fewer hours while completing their dissertation.
Contact Rush University about this program:
- Phone : (312) 942-7100
- Email: [email protected]
Source: Rush University
What to Expect in a Ph.D. in Nursing Program
Nursing Ph.D. degrees focus on scholarship and nursing research. By the end of the course, you'll be able to conduct and publish evidence-based research that can alter the face of nursing practice and healthcare policy for future generations.
Generally, these educational pathways combine graduate study and research activities and do not include clinical rotations. Instead, you will be required to complete a long-form research paper called a dissertation. To write your dissertation, you'll complete independent research based on a significant and relevant scientific inquiry in the nursing field.
>> Related: The Best Nursing Research Topics
What Can You Do With a Ph.D. in Nursing?
Ph.D. in Nursing programs prepare graduates to pursue careers in research and teaching, advanced clinical practice, health care administration, and policy. Following graduation, your future may hold a career as a nurse scientist, as an administrator, as a nurse educator, or in establishing health policy.
Ph.D. in Nursing Salary
Healthcare workers who hold a Ph.D. in nursing earn an average annual salary of $100,00 or $60.45 per hour , according to Payscale . However, your nursing salary will vary depending on your career, employer, location, experience, and other relevant factors.
How Much Does a Ph.D. in Nursing Degree Cost?
Ph.D. in nursing programs range from $400 to over $2,300 per credit hour at more distinguished institutions. However, several universities will fund your Ph.D. tuition itself or through a federal research grant. Most often, these funding opportunities are only available to full-time students, while part-timers must pay the full tuition costs.
How Long Do PhD in Nursing Programs Take?
Most Ph.D. in nursing programs take between 4-6 years to complete. Your educational timeline will vary based on your previous education and whether you attend full or part-time.
What Will You Learn in a PhD in Nursing Program?
Since all Ph.D. degrees in nursing emphasize healthcare research, their curriculums will all share certain core elements, which include:
- The philosophical and historical foundations of nursing knowledge
- Review of existing and evolving nursing theory
- Methods and process of developing theory
- Research methodology and data management
- Academic, research, practice, and policy development
Your graduate nursing program will consist of several key milestones to reinforce your education. These include:
- Leadership strategies related to nursing, healthcare, and research
- Mentorship and working alongside faculty on their individual research programs
- Immersion experiences are designed to encourage leadership and scholarship.
- Each student will be required to complete a dissertation.
Ph.D. in Nursing Program Requirements
Each university sets its own entry standards, which vary based on the type of program . However, general Ph.D. in nursing admission requirements include the following:
- BSN, MSN, or non-nursing graduate degree
- Personal research statement
- A minimum GPA of 3.0
- Admissions interview
- Writing sample
- Resume or curriculum vitae
- Letters of recommendation
- Unencumbered RN license
- Official post-secondary school transcripts
- TOEFL or IELTS scores
Is a Ph.D. in Nursing Degree Right for Me?
Your professional goals play a massive role in deciding whether to pursue a Ph.D. in nursing. If you're interested in scientific and academic nursing research, healthcare policy, or becoming a nurse educator, a Ph.D. in nursing is an excellent option. Remember, it will not qualify you for APRN positions, so if you have clinical aspirations, a DNP is the right doctoral nursing option.
Next Steps to Enroll in a PhD in Nursing Degree Program
Ready to start your educational journey toward earning a Ph.D. in Nursing? You can start working toward those goals today with these simple steps:
- Research Universities: Find a program that suits you based on your budget, attendance needs (e.g., part vs. full-time and in-person vs. online), and interests.
- Plan Applications: Understand the program requirements and application deadlines for each school you're applying to. Then, make a plan to collect and submit all the necessary materials and documentation on time.
- Prepare Properly: If a university considers you for Ph.D. candidacy, you'll attend an admissions interview. Planning and practicing this interview and paying close attention to why you chose the program and your research interests will optimize your chances of admission.

Plus, get exclusive access to discounts for nurses, stay informed on the latest nurse news, and learn how to take the next steps in your career.
By clicking “Join Now”, you agree to receive email newsletters and special offers from Nurse.org. We will not sell or distribute your email address to any third party, and you may unsubscribe at any time by using the unsubscribe link, found at the bottom of every email.
An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.

- Research Initiatives
- Meet Our Researchers
- Meet Our Program Officers
- RESEARCH LENSES
- Health Equity
- Social Determinants of Health
- Population and Community Health
- Prevention and Health Promotion
- Systems and Models of Care
- Funding Opportunities
- Small Business Funding
- Grant Applicant Resources
- Training Grants
- Featured Research
- Strategic Plan
- Budget and Legislation
- Connect With Us
- Jobs at NINR

NINR Job Opportunities
NINR offers exciting career opportunities for a broad range of forward-thinking scientists, researchers, leaders, and other professionals who are interested in supporting our mission: to lead nursing research to solve pressing health challenges and inform practice and policy-optimizing health and advancing health equity into the future. NINR also offers training opportunities for students and professionals from postbac through posdoc levels.

Join our team!
NINR recruits for open positions frequently throughout the year. Current and upcoming opportunities are listed below. Sign up for email updates to receive information about job opportunities and other updates from NINR.
For federal resume tips, frequently asked questions, and more visit the NIH Office of Human Resources .
NINR’s scientific strategy builds on the strengths of nursing research, spans the intersection of health care and public health, and encompasses the clinical and community settings where nurses engage in prevention, treatment, and care – focusing on people in the context of their lives and the conditions in which they are born live, work, play, and age. These settings include hospitals and clinics, schools and workplaces, homes and long-term facilities, justice settings, and throughout the community.
Doctoral Degrees
Top Careers for RNs with a Doctorate in Nursing
Home » PhD and DNP Degrees » Top Careers for RNs with a Doctorate in Nursing
Nursing is a calling for most RNs , and many want to continue their education to further their careers and take an even greater leadership role in the field. A doctorate in nursing is the terminal degree for nurses who want to expand their current roles, move into management and leadership positions, conduct clinical research or pursue employment in higher education.
A number of career possibilities exist for nurses with a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) in Nursing or a Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP).
Here are some of the top jobs that are available for nurses with a doctorate in nursing.
Nurse faculty
A career in nursing education is a great option for nurses who want to prepare future nurses and are interested in nursing research. The shortage of qualified nursing faculty has been well documented by nursing organizations and in professional research.
A survey released by the American Association of Colleges of Nursing in October 2018 found a total of 1,715 vacant faculty positions at 872 nursing schools, with a national vacancy rate of 7.9%. More than 90% of those vacancies were for faculty positions requiring or preferring a doctoral degree, the survey found.
A PhD in Nursing is a research-focused degree and is generally the most common doctoral degree for nurse faculty, although some nurse educators hold a DNP in nursing. The average salary for nursing instructors and teachers in higher education was $81,300 in 2018, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, while those on the higher end of the pay scale can make $130,000 or more.
While salaries for nurse educators may not go as high as some occupations with advanced nursing degrees, faculty members typically work shorter hours and may face less stress than most practicing nurses.
Nurse anesthetist
One of the more lucrative career options for advanced practice registered nurses with a doctoral degree is that of nurse anesthetist. Certified registered nurse anesthetists (CRNAs) administer anesthesia to patients for surgical and other medical procedures and are the sole anesthesia providers in nearly all rural hospitals, according to the AACN.
The average annual salary for nurse anesthetists was nearly $175,000 in 2018. In several states, such as Montana, California, Iowa, Oregon and Wisconsin, average annual wages for CRNAs top $200,000, according to BLS.
The most common doctoral degrees for nurse anesthetists are the DNP or Doctor of Nurse Anesthesia Practice (DNAP). By 2025, the Council on Accreditation of Nurse Anesthesia Educational Programs , which accredits nurse anesthesia programs in the U.S. and Puerto Rico, will require all new CRNAs to have doctoral degrees.
Nurse practitioner
A doctorate in nursing also is very valuable to those who are looking to become nurse practitioners . NPs are “clinicians who assess, diagnose and treat acute chronic illnesses, as well as counsel, coordinate care and educate patients regarding their illnesses,” according to the website of the American Association of Nurse Practitioners .
NPs work in a variety of settings , including private practice, hospital outpatient clinics, inpatient hospital units, emergency rooms, urgent care facilities, community health centers and Federally Qualified Health Centers.
Working as a nurse practitioner comes with many benefits. NPs have greater authority in diagnosing and treating patients and prescribing medications, and many states now allow nurse practitioners to practice independently without physician oversight.
Nurse practitioners also make significantly higher salaries than other nurses, with average annual earnings of about $110,000. While a doctorate in nursing is not required to become a nurse practitioner, the AACN supports moving the standard preparation level for advanced nursing practice from a master’s to a doctoral degree. A growing number of students that are considering careers as NPs are enrolling in DNP programs.
Nurse leader
Nurses who want to move into top management and leadership roles in hospitals, nursing homes and other health systems can benefit from a doctorate in nursing.
Some of those positions include CNO, chief nurse executive, director of nursing, nursing administrator, nurse manager and health system president or CEO. A 2019 survey of nurse leaders conducted by the American Organization for Nursing Leadership found that most nursing leaders’ annual salaries ranged from $90,000 to $169,000, with those at the top end of the pay scale earning more than $250,000 a year.
While a doctorate in nursing may not be required for all of these positions, it can certainly help improve a nurse’s chances of moving into leadership or management roles.
Nurse scientist/researcher
Nurse scientists or nurse researchers are dedicated to the study of nursing research. They conduct scientific studies, collect data and present their findings, often partnering with researchers from other fields, such as medicine, pharmacy and nutrition to address complex healthcare questions or problems, according to an article .
While nurse researchers often work as faculty at colleges and universities, they also can work at hospitals, research laboratories or other healthcare facilities. Many of these jobs require a PhD in Nursing or DNP degree. The average salary for a nurse scientist is about $95,000.
Nurse informatics
For nurses with an interest in information technology and analytics, a career in nurse informatics may be a good option. Nursing informatics is “a specialty that integrates nursing science, computer science and information science to manage and communicate data, information, knowledge and wisdom in nursing practice,” according to the Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society .
A doctorate in nursing is not required for all nurse informatics roles, but it could be beneficial when applying for higher-level positions such as chief nurse informatics officer. Salaries vary for nursing informatics roles depending upon skill level and geographic area, but the average salary for a chief nursing informatics officer is $109,072, with those in some areas of the country making upward of $200,000.
While these are some of the potential roles for nurses with doctoral degrees, many other career options are available. Some of the other roles that can benefit from an advanced nursing degree include clinical nurse specialist, certified nurse-midwife (CNM) and public health and public policy nurses.
Nursing Education
Search Programs
Search hundreds of nursing programs in just a few steps.
Related Articles


Home / Getting Your Ph.D. in Nursing
Getting Your Ph.D. in Nursing
Becoming a ph.d. nurse, what does a ph.d. nurse do, ph.d. nurse salary & employment, ph.d. vs. dnp in nursing, helpful organizations, societies, and agencies, what is a ph.d. nurse.
A Ph.D. nurse is one who has completed a Doctor of Philosophy in Nursing degree. A Ph.D., or doctoral degree, is the highest level of education a nurse can achieve. Different from a Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) degree, which focuses on advanced clinical practice, a Ph.D. in Nursing program is a research and science-focused degree that prepares nurses for careers conducting important medical research that will advance the entire nursing profession and for teaching nursing at the college level.

In order to become a Ph.D. nurse, of course, nurses must complete a Ph.D. in nursing program, which generally takes 4 to 6 years to finish. An aspiring Ph.D. nurse must have a strong interest in conducting medical research and/or teaching future nurses. Strong leadership skills are also important, as many Ph.D. nurses go on to supervise and mentor other nurses, whether they work in scientific research, management, or teaching capacity.
What Are the Educational Requirements For a Ph.D. Nurse Program?
A Ph.D. in Nursing program is known as a terminal degree, meaning it is the highest level of education for the nursing profession (in addition to the DNP degree, another separate nursing doctorate program track). Prior to entering a Ph.D. program, nurses must complete a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) degree and pass the NCLEX-RN exam. In some cases, applicants to a Ph.D. in Nursing program must also complete a Master of Science in Nursing (MSN) degree, which provides advanced education in nursing practice with courses in pharmacology, pathophysiology, and clinical practice.
Educational Prerequisites
Specific requirements to complete a Ph.D. in Nursing program will vary slightly from school to school. Schools offer Ph.D. in Nursing programs in traditional classroom formats, as well as online and hybrid styles that combine in-person study with online coursework. In addition to a variety of formats for Ph.D. in Nursing programs, students can also sometimes opt to take these programs on a full-time or part-time basis to suit their personal schedules.
The curriculum for a Ph.D. in Nursing program is research-focused, with coursework in advanced scientific research principles, data analysis, and statistical measurement. Ph.D. programs generally culminate in a dissertation and original research project. As an example of Ph.D. curriculum, below is a selection of courses offered by the Medical University of South Carolina as part of their online Ph.D. in Nursing Science program:
- Advanced Quantitative Research Methods
- Qualitative Research Methods
- Advanced Statistical Methods for Nursing Research
- Advanced Study Design and Methods
- Advanced Health Policy & Advocacy
- Research Team Leadership
A Ph.D. nurse conducts scientific research that advances the nursing profession. The knowledge that Ph.D. nurses gather and present as a part of their scientific research powers positive change in the quality of patient care and outcomes in the entire nursing field. In addition to their role as nurse scientists, Ph.D. nurses also teach and mentor nurses at the college/university level, working to shape the next generation of nurses.
What Are the Roles and Duties of a Ph.D. Nurse?
The majority of Ph.D. nurses pursue careers in either the research or teaching fields, so their day-to-day duties will vary depending on which career track they have chosen.
For a nurse researcher , typical duties may include:
- Identify research questions, and design and conduct scientific research in partnership with other scientists from various fields
- Collect and analyze scientific data and publish reports detailing findings
- Write proposals and apply for grants to help fund their research
- Establish and maintain quality assurance programs to ensure the validity of their data findings
- Train and supervise laboratory staff and other nurses or scientists
For a Ph.D. nurse educator who has chosen to pursue a faculty position, typical duties may include:
- Plan, prepare, and revise curriculum and study materials for nursing courses
- Deliver lectures to undergraduate and graduate level nursing students
- Supervise students' laboratory and clinical work
- Grade students' classwork, laboratory, and clinical performance
- Mentor and advise students regarding their future work in the nursing industry
For faculty members who pursue department chair or administration roles, additional duties may include:
- Hire, supervise and conduct performance reviews of faculty members
- Assist with the scheduling of classes and professors
- Oversee department curriculum and provide quality control as to the content and materials of given nursing courses
Workplace Settings
A Ph.D. nurse can work in a variety of settings, depending on the career path he or she has chosen. A Ph.D. nurse may find employment at a hospital, medical laboratory, research facility, or university as a research scientist, or may work at a nursing school, college, or university as a faculty member or department chair. In some cases, a Ph.D. nurse may also work as a public health nurse in a government setting, helping to develop research-based solutions to public health issues.
Salaries for Ph.D. nurses vary based on the type of employment a nurse seeks after graduation. Nurse researchers, a primary career path for Ph.D. nurses, can expect a median salary of $90,000 according to Payscale.com. For Ph.D. nurses who pursue a teaching position, the median annual wage for post-secondary nursing instructors is $77,440 according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics as of May 2021. Geographical location, career length, and experience level are all factors that can influence a Ph.D. nurse's annual salary.
The nursing profession as a whole has a particularly bright employment outlook, with the employment of registered nurses projected to grow 9 percent from 2020 to 2030 according to the BLS. In addition, a large number of healthcare facilities are looking for nursing professionals with higher degrees, which means the demand for Ph.D. and DNP level nurses will continue to grow. In fact, the Institute of Medicine 's 2015 "The Future of Nursing Report" emphasized the need for more Ph.D. level nurses.
As there are two doctorate-level nursing program types to choose from, there may be some confusion as to the differences between a Ph.D. nursing program and a Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) degree. The primary difference between the two programs relates to nurses' career aspirations. A DNP program trains nurses to perform the highest level of nursing practice and to translate research into high-quality patient care, while a Ph.D. program prepares nurses to conduct cutting-edge research that will advance the science of nursing and patient care. In addition to research positions, a Ph.D. program prepares nurses for leadership and teaching positions at hospitals and colleges/universities. To simplify, a DNP is a nursing practice doctorate degree, while a Ph.D. is a research and teaching doctorate.
Other key differences between DNP and Ph.D. programs are curriculum and program length. A typical DNP program includes courses on advanced nursing practice, leadership, and management topics and requires patient care clinical hours as well as a final capstone project. A Ph.D. program includes coursework on research methodologies, data analysis, and healthcare leadership and policy, and requires students to complete original research and a dissertation. In general, a Ph.D. program takes longer to complete than a DNP program, with Ph.D. programs taking an average of 4 to 6 years to complete and a DNP program taking 3 to 4 years, but can be completed in as little as 2 years depending on the school and program chosen.
- American Association of Colleges of Nursing
- American Nurses Association
- International Association of Clinical Research Nurses
- National Institute of Nursing Research
Skip to content
Our Culture
Diversity, equity, and inclusion.
Learn about our commitment to social justice and health equality and anti-racism.
Academic Programs
Admissions at a glance.
Learn more about Admissions at Columbia Nursing, including important dates and deadlines, and how to apply to all of our programs.
Research Centers and Programs
Research areas of focus.
Explore the research areas of focus conducted by our faculty, postdocs, and students.
Patient Care
Primary care services.
The ColumbiaDoctors Primary Care Nurse Practitioner Group, combines evidence-based practice with a personalized approach to provide quality care.
Global Health
Global opportunities for students.
Global opportunities for clinical practicum and research may be available for MDE and doctoral students at Columbia Nursing.
Doctor of Philosophy
Doctor of philosophy (phd), ignite your future with a columbia nursing phd.
The Columbia University School of Nursing PhD program is a full-time, research-intensive curriculum that prepares nurses for careers as nurse scientists who will conduct research across a broad range of populations and health conditions. Importantly, much of our research is focused on health disparity populations with the long-term goal of informing health policy and clinical practice across the lifespan.
Columbia Nursing provides three years (eight semesters) of funding for tuition, related fees, health insurance, and a stipend for full-time PhD students.
Program Design
Our PhD program provides students with an understanding of the philosophical and theoretical underpinnings of nursing science and a strong foundation in research methods (design, statistics, measurement, quantitative and qualitative methods) for clinical, translational and health services research. All students are mentored by research advisors with active programs of research as they move toward independent research and assume the roles of doctorally prepared nurse scientists.
As a Columbia Nursing PhD student, you will learn to:
- Design, conduct, and report multidisciplinary research studies that increase knowledge to improve the health and well-being of patients and families across the lifespan
- Advance the state of the science in a substantive area of research through application of innovative and rigorous methods
- Promote health and well-being for individuals and families in the context of their communities
- Provide leadership in improving the health care delivery system at local, national, and international levels
- Collaborate with other professionals to evaluate and develop policies for delivery of health service
- Translate evidence accumulated through research into practice and policy at multiple levels
As part of Columbia University Irving Medical Center (CUIMC), Columbia Nursing enjoys a unique collaboration with the College of Physicians and Surgeons, the Mailman School of Public Health, and the College of Dental Medicine. CUIMC provides myriad opportunities for interprofessional collaboration in research .
The PhD curriculum builds on the foundation of nursing science by bringing together practice, policy, translational research, and leadership. The core courses provide the knowledge and skills necessary to conduct relevant and well-designed research studies. Electives strengthen an area of clinical interest or intensify understanding of a specific research or analytic method.
Both post-master's and post-BSN students admitted to the program will complete a minimum of 57 credits. The curriculum plan is designed to make it possible to complete the program in three years for those students with clearly defined plans for their dissertation research.
PhD courses are offered in three major areas:
- Theoretical foundations of nursing science
- Analytical foundations of nursing science
- Electives and application
Students must be registered as full-time for the duration of the program (typically three to four years). The minimum number of semester credits in required coursework is 37 (four semesters) for eligibility to progress to the qualifying exam. Six of the 37 credits required to be completed prior to the qualifying examination are elective courses tailored to the student’s dissertation topic and/or dissertation methods. The PhD program requires nine credits of elective courses. A minimum of 57 total credits is required for program completion.
Concurrent with Coursework
- Research Experience (participating in faculty research projects and/or a research practicum)
- Research Faculty Training
Request a Sample Academic Program Plan
Qualifying Examination
The qualifying examination helped me to combine the content I learned in my courses and my research interests so I could further articulate my research question. Performing a scoping review on my topic of interest immersed me in the current literature and was crucial to the development of my dissertation. This experience prepared me to successfully work independently through the rest of my Ph.D.
Kylie Dougherty, BSN, RN, M.Phil.
In addition to coursework, students must successfully complete a qualifying examination with written and oral components. The Master of Philosophy (MPhil) is awarded after successful completion of the qualifying examination and the student enters doctoral candidacy status.
Dissertation
Students are expected to successfully defend a dissertation reporting original research. Four dissertation credits are required each semester during the dissertation phase of study.
Scholarship Expectations
My advisor and the Columbia Nursing faculty provided me exceptional guidance throughout the PhD program to extend my learning beyond the classroom with the goal of becoming an independent nurse scientist. I learned valuable skills and knowledge to successfully obtain a NIH-funded predoctoral training award, present research findings at local, regional, and national conferences, and publish manuscripts in peer-reviewed journals with good impact factors.
Joseph Belloir, MSN, RN, PMHNP-BC
- Publication: At least one manuscript published in an appropriate peer-reviewed journal.
- Grantsmanship: At least one grant application submitted to an appropriate funding agency or organization.
- Presentation: At least one abstract submitted for presentation as a poster or oral presentation at an appropriate professional meeting.
- Networking: Student will attend at least one regional or national research meeting.
Preparation for Postdoctoral Fellowship: Research Career Next Step
The coursework and research mentoring at Columbia Nursing helped prepare me for the next steps in my education and career post-PhD. In addition to structured coursework and educational seminars, the school provided beneficial informal support and resources. Feedback sessions with both peers and faculty were very helpful in preparing me to present posters and presentations at research conferences. The school also provided funds for travel to conferences where I presented my research. The grant writing workshop and mock reviews of grant applications provided me with tools and feedback needed to successfully apply for additional funding for my research. Finally, interdisciplinary research collaborations with faculty provided me with opportunities to work with researchers from several disciplines to complete my dissertation.
Melissa Beauchemin, PhD '19, MS '10, RN
PhD Student Handbook
The Columbia Nursing PhD student handbook provides information to aid doctoral students in planning coursework and proceeding through all phases of the program.
Request a PhD Student Handbook

What is it like to be a PhD student at Columbia Nursing?
Required courses (excluding electives).
Building upon the foundations provided in the quantitative and qualitative research method courses, in this course students examine advanced methods and frameworks frequently used in studying health policy, health services research problems and comparative effectiveness research. In addition to a critical review of the methods, the course examines the relationship among science, policy and healthcare delivery, and identifies critical questions shaping the future policy research agenda.
Interdisciplinary research is an approach to advancing scientific knowledge in which researchers from different disciplines work at the borders of those disciplines in order to address complex questions and problems. Successful interdisciplinary efforts require mastery of specific competencies. This seminar will introduce students to competencies in interdisciplinary research through a combination of readings, case studies, and lectures in each necessary aspect, chosen from fields essential to successful interdisciplinary research. It is intended to assist learners to understand why and how different professional disciplines must work together to generate and disseminate knowledge. We will examine: different conceptualizations of interdisciplinary; barriers to and facilitators of interdisciplinary research; approaches, benefits, and limitations of collaboration and team science; methods for measuring interdisciplinary collaboration; the intersection of translational and interdisciplinary scientific strategies; and individual researchers' experiences with and evaluations of their own interdisciplinary scientific projects. Learners will develop a set of skills to be effective members and leaders of interdisciplinary research teams.
The student works with a faculty member or other scientist who is conducting a research project. The specific nature of the experience depends on the nature and stage of the research, but might include search and review of relevant literature, data collection, data analysis and/or grant preparation.
This course is intended for PhD students who are engaged in relevant scholarly activities that are associated with dissertation research.
This foundational course will examine the philosophy of nursing knowledge including foundations of nursing theory, concept development, and its application to research. Students will explore approaches to the analysis and development of concepts and the application of nursing concepts and frameworks to clinical practice and research. Ideas, assumptions, events, people, and writings are examined for their influence, inter-relationships, and significance to nursing. Types of reasoning will be evaluated within the context of nursing and health. Major theories, frameworks, and concepts of nursing and health and their implication for research will be discussed. The focus of the course will be on development of critical thinking skills in analyzing key elements of philosophies, concepts, and conceptual frameworks.
In this foundational course students will study the links between theory and the psychosocial and biophysical measures used in nursing research. Students will employ the principles of classical test theory and item response theory to evaluate the reliability and validity of measurement. Application of computational techniques will be covered in the lab portion of the course. Course topics include types and uses of measures, item/scale development and validation, survey methods, reporting for publication, and the relationships between measurement and research ethics, cultural competency, and health disparities.
This course provides a foundation for quantitative research methods and design. Research process topics examined include: appraisal of the quality of existing evidence; identification of gaps in the literature; formulation of researchable questions and testable hypotheses; types of research variables; sampling designs and power analyses; and the uses, strengths, and weaknesses of various experimental and quasi-experimental research designs.
This course provides an in-depth examination of qualitative study designs and methods through a combination of theoretical discussion and hands-on practical experience. Topics include paradigm distinctions, theoretical perspectives, designs and methods, critique of research reports, and ethical issues in qualitative research.
The course is intended for PhD students who are engaged in relevant scholarly activities that are not associated with the required course sequence. Such activities must accrue more than 20 hours/week.
This course is intended to provide a hands-on introduction to delivering data visualizations to serve as a critical lens through which individual and population level health can be examined. The proposed course will combine concepts and theory in data visualization and exploration and practice to enable the student to gain the necessary knowledge to use graphics and statistics to explore the data, find and construct a narrative, and share findings in ways colleagues and decision-makes can readily understand and act upon.
This course is designed to provide the tools for the doctorally prepared nurse to evaluate, translate and integrate published research results into clinical practice. During the course, students will learn how to conceptualize clinical practice problems and transform them into answerable clinical research questions, how to search for the best clinical evidence, and how to assess clinical evidence using basic epidemiological, biostatistical and scientific principles. The course will culminate in a systematic review or meta-analysis of a body of research relevant to advanced practice nursing.
Total Credits:
What do you do with a PhD in nursing?

- North America

This site uses cookies to keep track of your information. Learn more here . Accept and close .

Data Spotlight: Trends in Nursing PhD Programs
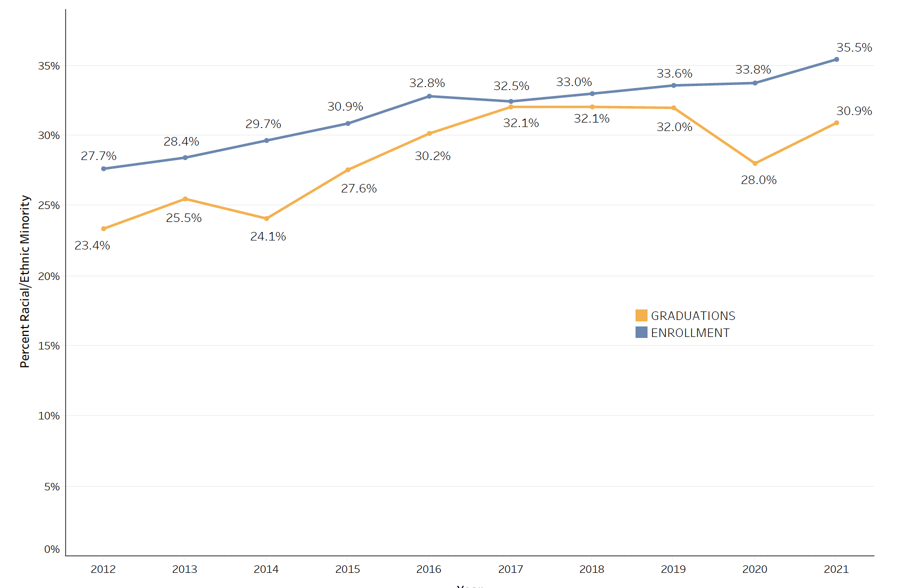
Generating strong interest in the PhD in nursing (and similar research-focused doctorates) is a priority for the profession. Although less than 1% of today’s nursing workforce has earned a PhD (NCSBN, 2021), these individuals are in high demand with the need for nurse scientists, faculty, and leaders on the rise. Despite this great need, AACN has seen a steady decline in enrollment in PhD programs over the last 10 years. Since 2012 enrollments have declined 12%, from 5,110 to 4,476 students, even though graduations have increased 20% from 611 to 733 graduates ( Figure 1 ). During this period, the number of research-focused doctoral nursing programs has increased 14%, from 131 to 149. As seen in Figure 2 , these programs are now available in almost every state in the U.S. The regional distribution of students enrolled reflects the distribution of programs, which are more heavily concentrated in the South and North Atlantic ( Figure 3 ). In 2021, the largest number of graduates were in the South and Midwest, respectively ( Figure 4 ). The data on racial and ethnic diversity within the PhD student population shows a growing level of representation. Over the last 10 years, the percentage of students and graduates from underrepresented racial/ethnic groups has increased by 8% ( Figure 5 ). Notably, the percentage of African American students has increased 5% from 2012 to 2021, and the percentage of graduates has increased 1.5%. AACN is committed to working with practice partners and other stakeholders to advocate for more resources for PhD programs and support to create a more diverse community of nurse scholars. Released in April 2022, our position statement on The Research-Focused Doctoral Program in Nursing: Pathways to Excellence presents a new vision for the PhD in nursing and program graduates, which will help spark strong interest among students in careers as nurse researchers.
Figure 1: Research-Focused Doctoral Enrollments and Graduations, 2012-2021
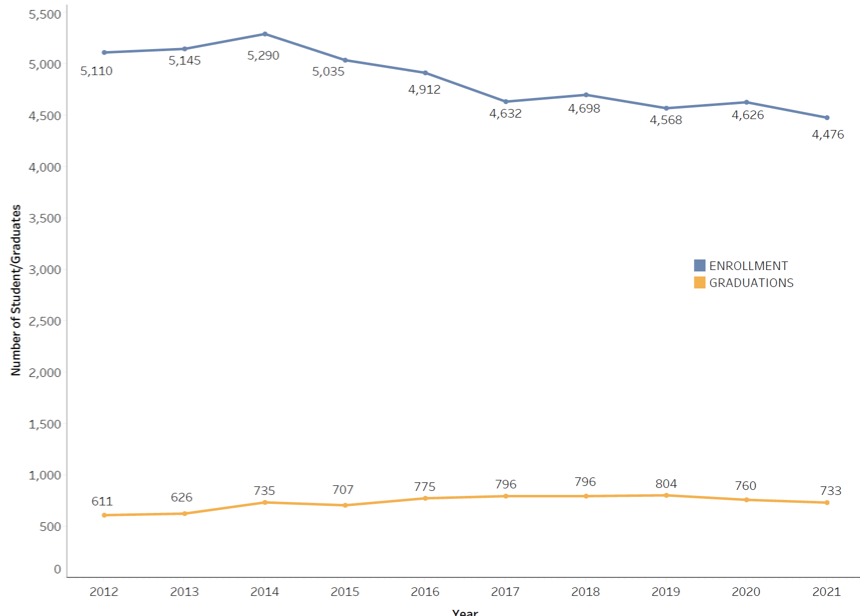
Figure 2: Fall 2021 Number of Research-Focused Doctoral Programs by State
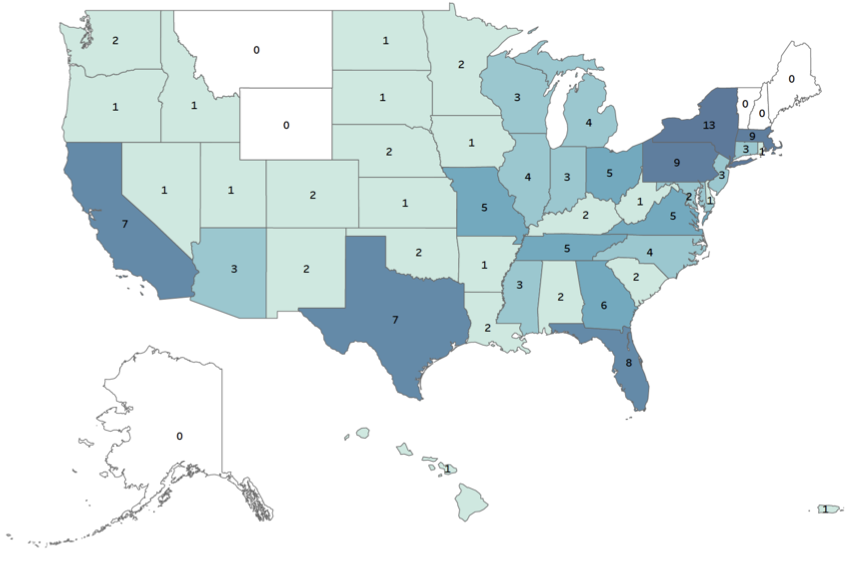
Figure 3: 2021 Research-Focused Doctoral Enrollment by Region
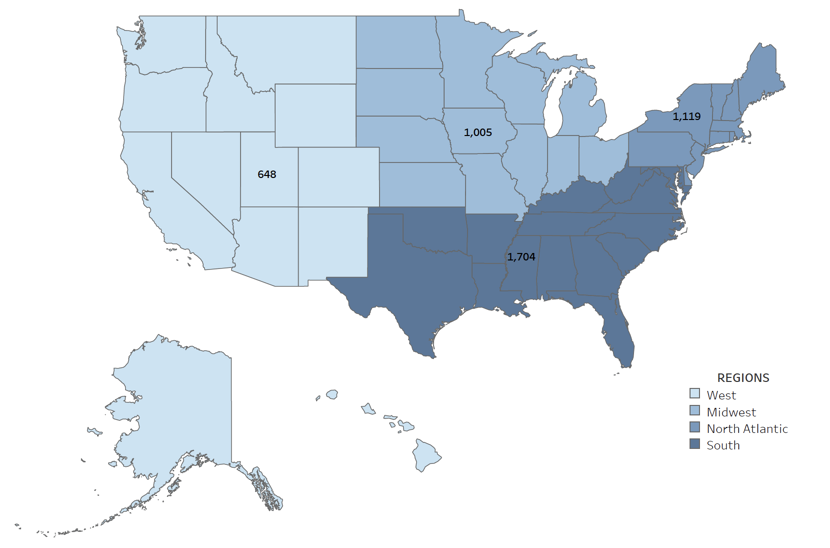
Figure 4: 2021 Research-Focused Doctoral Graduations by Region
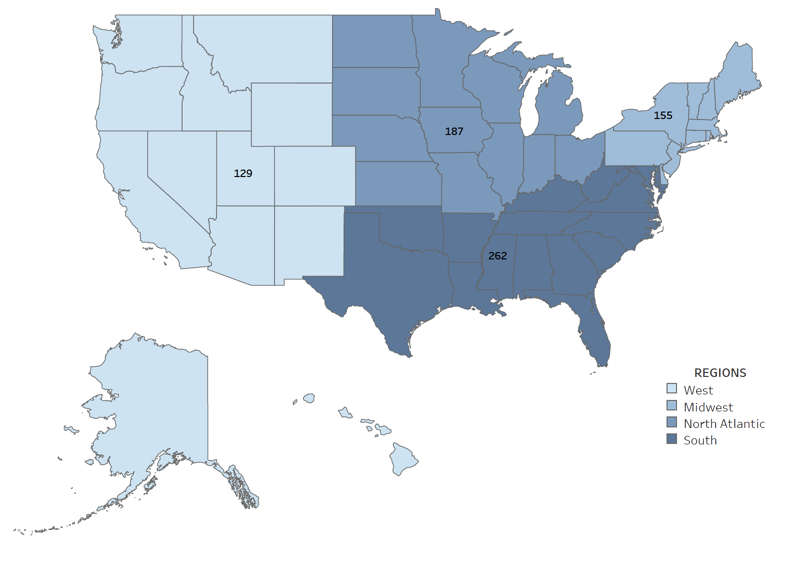
Figure 5: Percent of Racial/Ethnic Minority Students and Graduates, Research-Focused Doctoral 2012-2021
News Categories
- Accreditation Expand/Collapse
- Certification Expand/Collapse
- Diversity, Equity, & Inclusion Expand/Collapse
- Education Expand/Collapse
- Enrollment Expand/Collapse
- Essentials Expand/Collapse
- Grant Initiatives Expand/Collapse
- Foundation Expand/Collapse
- Funding Opportunities Expand/Collapse
- Membership Announcements Expand/Collapse
- Member Resolutions Expand/Collapse
- Syllabus Expand/Collapse
- Faculty Link Expand/Collapse
- GNSA Bulletin Expand/Collapse
- Diversity Digest Expand/Collapse
- ELNEC Connections Expand/Collapse
- Policy & Advocacy Expand/Collapse
- Population Health Expand/Collapse
- Press Release Expand/Collapse
- Professional Development Expand/Collapse
- Research & Data Expand/Collapse
- Rounds with Leadership Expand/Collapse
- Scholarships Expand/Collapse
- Student News Expand/Collapse
- Well-being Expand/Collapse
- Connect with us:
- X (Twitter)
Is earning a Ph.D. in nursing worth it? MCN faculty say yes.
- Author By Bryanna Tidmarsh
- March 26, 2021

It’s a story every nurse knows: the need for nurses is growing. Worldwide, health care faces growing nursing provider and educator shortages. One of the most important ways nurses can address this dire need is by earning a Ph.D. in nursing.
Only 13% of nurses in the United States currently hold a graduate degree. Fewer than 1 percent hold a doctorate. That means that just 13 percent of the nursing workforce is eligible to become nursing faculty at all, and less than 1 percent is eligible to teach at the highest level.
A Ph.D. prepares nurses to be experts in their field and to pursue a research-focused career. We need more PhD-prepared nurses now more than ever: to educate future nurses, to lead nursing teams, and to develop research that improves best practices. MCN’s Ph.D. in nursing aims to uplift nurses in their profession, preparing them to take on leadership roles and perform cutting edge research that shapes the health care landscape.
Who should consider a Ph.D. in nursing?
In short: everyone. Nursing is one of many fields in health care that are moving towards requiring masters and doctorate-level education.
Designed for those who want to focus on education and research, the doctorate of philosophy degree prepares nurse researchers with expertise in vulnerable populations. Many graduates of MCN’s Ph.D. program return to teach and conduct research, such as Dr. John Blakeman ‘20.
Take it from Blakeman: “With a PhD, we are expected to affect the whole nursing profession: how we shape practice and policy and education.”
Is research not for you? Consider earning a doctorate in nursing practice via MCN’s DNP program .
What can I do with a Ph.D. in nursing?
The PhD-prepared nurse serves the public by designing and conducting research on relevant clinical, educational, health systems, and/or health policy topics. Following graduation, a nurse with a PhD may pursue a research career in the academic, business, government, or industrial setting. Nurses with a PhD may also serve as educators and/or administrators and develop or consult on health care policy in a variety of settings.
Become a nurse educator —in a university or on the hospital floor.
As the field works to usher in more nurses, it lacks sufficient nurses who are trained to teach them. With a Ph.D. in nursing, you will be prepared to educate nursing students or take on an education role within a health care setting, helping to train current nurses in new research and best practices. with the latest research in best practices.
With a Ph.D. in nursing, you will be prepared to review health care policy, test it, and make recommendations for federal or state regulations. An example would be to study the need for annual flu vaccinations for health care staff and whether or not requirements are evidence-based. With a Ph.D. in nursing, you will be prepared to evaluate symptoms of health issues, such as: fatigue prior to heart attacks, exercise needs of rural post-menopausal women, or pain assessment of older adults. A PhD-prepared nurse could also work with a coroner to analyze older adult falls and community recommendations to prevent future falls.
Become a nurse researcher —a critical role to keeping health care facilities up-to-date with the latest research in best practices.
Advance your career. The Ph.D. opens up career opportunities such as serving as a nurse researcher, administrator, policymaker, leader, or educator.
“With a PhD in nursing, you are better positioned to be a leader in the area of nursing education or be hired as a full-time faculty member,” says Dr. Seon Yoon Chung, Associate Dean for Academics. “The Ph.D. allows one to be part of advancing the science of nursing education by generating and applying evidence and promoting evidence-based teaching.”
In what settings will a Ph.D. in nursing be applicable?
No matter what nursing role you’re in, the knowledge and skills you gain in the Ph.D. program is applicable, including in practice, in teaching, in your research, and in administrative roles. Nurses often encounter tough questions, whether from patients, our community members, our families, or even our own interests in learning how to improve nursing practice. A Ph.D. program gives you the space to pursue topics that interest you, and it provides you with the knowledge and skills necessary to answer these questions in ways that are systematic, valid, and reliable.
One growing need for Ph.D.-prepared nurses is the rising impact big data has in health care practice. “We are now living in the era of artificial intelligence and big data. Soon, it will be necessary to know how to deal with data—that is, generate and/or use existing data to inform your practice, teaching, research, administration,” says Chung.
She emphasizes the ways in which core competencies gained from MCN’s Ph.D. program are transferable to the real world. “The Ph.D. prepares you to be friends with data and information and understand how data-driven decisions are made. To be a leader who transforms health care and improves individual and population health, knowledge and skills acquired in a rigorous PhD program will be critical.”
How can I balance a Ph.D. program while working full-time and/or honoring my commitments to my family?
MCN’s Ph.D. program can be completed part-time, making it conducive for those balancing work, family, research, and education.
“The faculty all understood that we had full-time jobs. Most of us were either teaching, working as a nurse on the floor, or working as a clinical nurse. The faculty were able to maintain the appropriate amount of rigor and expectations while also granting students grace,” says Blakeman.
“The decision to complete a Ph.D. program is a commitment to yourself and your discipline,” affirms Melissa Moody, MCN’s academic advisor for post-licensure programs. “You may be balancing this new and exciting endeavor among many other obligations. The key to your success will be early planning, staying organized, managing your time well, maintaining open communication with faculty and staff, and staying the course—one day at a time.”
She adds, “MCN faculty and staff are here to guide and support you on the path. We share a common goal: we want to see you succeed.”
MCN’s PhD program offers a professional, efficient, supportive environment. With both online and in-person requirements, the coursework is designed to work around nurses’ busy schedules with work and family. In MCN’s program, the coursework and research projects are customized around the needs and interests of our Ph.D. students.
Students also benefit from the expertise of MCN’s faculty. From advisement to knowledge of current research in the field, our faculty provides individualized attention for each student in the program.
Dr. Kim Astroth notes how important it is to MCN faculty that they give their students the time and attention. “It’s what sets MCN apart,” says Astroth. “Our faculty are attentive, flexible, and giving, working to empower our students. And our students are prepared to create high quality work as a result.”
Blakeman agrees. “I wasn’t just one number in a large group of people,” he says. “The faculty really knew us and cared about our personal lives—and so did our classmates. There was a close sense of community.”
So, is the Ph.D. in nursing worth it?
A Ph.D. program gives nurses the opportunity to pursue their research and make a difference in the health care landscape. MCN’s Ph.D. program is flexible in order to serve the needs of working nurses with busy lives while still providing the rigorous training necessary to becoming an expert. Nurses with Ph.D.s are prepared to make a huge difference in their communities, in their workplaces, and in the larger landscape of health care.
“A Ph.D. opens doors to a wide variety of practice areas,” says Associate Dean of Research Mary Dyck. “I’ve had the opportunity to chair a board of directors at a retirement community where I impacted the care for all of the residents. I’ve testified as a legal expert on quality of care. And I’ve worked with students as they’ve implemented major projects in health care institutions in the area. The Ph.D. allows nurses to have a much broader impact on the quality of care.”
Ph.D.-prepared nurses help shape health care policy and practice, and they are crucial to addressing the nursing shortage. We need nurse leaders to rise to the challenge and meet this call.
At MCN, we ask: why not you?
MCN is providing leadership in nursing. Learn more.
Our undergraduate programs
- Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN)
- Accelerated BSN
- Online RN-to-BSN
Our graduate programs
- BSN to DNP: Family Nurse Practitioner
- BSN to DNP: Leadership & Management
- Ph.D. in nursing
- Online Doctor of Nursing Practice
Related Articles
- Privacy Statement
- Appropriate Use Policy
- Accessibility Resources
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Florence Nightingale J Nurs
- v.30(2); 2022 Jun

Expected Roles of PhD Graduated Nurses: A Scoping Review
Reza negarandeh.
1 Nursing and Midwifery Care Research Center, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
Sahar Khoshkesht
2 Department of Medical-Surgical Nursing, School of Nursing & Midwifery, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran

The aim of this study was to investigate the expected roles of the Doctor of Philosophy graduated nurses and their challenges. This study was conducted as a scoping review based on Arksey and O'Malley’s approach. After a search in valid databases such as Google Scholar, Information Sciences Institute, Science Direct, Ovid, PubMed, and Scientific Information Database between 2000 and 2019 and review the websites of some well-known universities and the contents of some of the global nursing websites such as the American Association of Colleges of Nursing, National League for Nursing (NLN), International Network for Doctoral Education in Nursing (IDEN), as well as reports such as Institute of Medicine. All data were collected, summarized, and then described narratively. There was much evidence that the Doctor of Philosophy programs had failed to prepare graduated nurses for the related roles and responsibilities. The expected roles of the Doctor of Philosophy graduated nurses in this study summarized in five domains of education, clinical practice, research, leadership and management, and policy-making along with worldwide challenges, especially those highlighted in Iran. It seems that besides clarifications of the expected roles of the Doctor of Philosophy graduated nurses, there should be more thought about the contents of the programs along with roles responsibilities, as well as the establishment of better communications between universities and workplaces.
Introduction
The Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) refers to the philosophy and scientific diligence in knowledge which is also regarded as the highest academic degree in all disciplines. The term “doctorate” is rooted in the Latin word “docere” which means teaching ( Winter et al., 2000 ) and it is also characterized by an advanced level of education and research that is employed to create new knowledge ( Ellis, 2005 ). The graduates of disciplines such as medicine labeled as “MD,” pharmacy called “Pharm.D,” veterinary named as “DVSc,” and dentistry termed as “DT” are also mentioned as doctorate which is a degree equivalent to a bachelor’s and master’s in other sciences.
History showed that PhD education was established in Europe and Germany. Then, it was brought to the United States in the 1860s. Yale University was the first academic center to award a PhD degree in 1861. Then, Oxford University in the United Kingdom began to accept students in PhD programs in 1920 ( Carpenter & Hudacek, 1996 ).
In general, the goal of a PhD program is to educate scholars and scientists to develop disciplines and to create new knowledge in which there is an emphasis on preparing students to assume expected roles after completion of the courses ( Fiedler et al., 2015 ). The global competition for doctoral study is growing. Moreover, PhD graduates play an important role in the development of communities because of having specific skills in research methods and abilities to create, implement, and publish knowledge and innovation ( Auriol, 2010 ).
The concept of PhD in nursing is not new. In the past, most nurses could also obtain their doctoral degrees in disciplines such as physiology, education, or social sciences. Doctorate of Education (EdD) was created between 1900 and 1940 and the first EdD in nursing was awarded in 1933 at Columbia University. In the 1950s, the University of Pittsburgh emphasized the importance of clinical research for the development of a body of knowledge and nursing profession in the PhD program. Then Boston University launched the Doctorate of Nursing Science (DNSc) ( Robb, 2005 ). Later, different types of nursing doctorates were developed including Doctorate of Science in Nursing, Nursing Doctorate, Doctor of Philosophy in Nursing (PhD), and Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP) ( Meleis, 1988 ; Rosseter, 2017 ). The history of PhD degrees development in nursing in some countries across the world such as the United States (1933), the United Kingdom (1970), Sweden (1986), Australia (1987), South Korea (1988), Brazil (1990), Canada (1991), Venezuela (1998), and China (2003) is reflecting the historical record and the importance of developing PhD studies in nursing worldwide.
Historically, the first PhD program in nursing in Iran was held by Tabriz University of Medical Sciences in 1995. Then, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, and Isfahan University of Medical Sciences started accepting PhD students in nursing. Currently, a total number of 17 universities of medical sciences in Iran have permission to train PhD students in this domain.
In general, two models of PhD programs in nursing are known worldwide. In the research-based/oriented European model, students only focus on the implementation of research projects. This model is being used in European countries, North Africa, Egypt, Japan, Australia, and New Zealand. But in the North American model or the Pan-American model, students first take courses that are related to the subject of the dissertation and, after successfully passing the relevant exams; they concentrate on doing their dissertations. This model is being implemented in countries such as Brazil, Canada, the United States, Venezuela, South Korea, the Philippines, Taiwan, Thailand, and Iran ( Ketefian et al., 2001 ).
In recent years, scientific research studies have put more stress on the professional development of nursing and they have particularly focused on the unique characteristics of nursing. Unlike other disciplines that start with general studies and then make progress toward specializations in the postgraduate programs, nursing is a profession that requires a general perspective in the PhD program ( Rosseter, 2017 ). Nursing programs traditionally present courses in the fields of nursing history and philosophy and development of healthcare techniques as well as socio-economic, political, and ethical issues. Data management and research methods are also included as the most important areas in doctoral education in nursing ( American Association of Colleges of Nursing [AACN], 2018 ).
Undoubtedly, the purpose of PhD programs in the development of nursing sciences is through research. In this respect, graduates are trained in research-based disciplines to contribute to a collection of unique knowledge in nursing and they are expected to accept leadership positions in their fields. As noted, the nursing process has been toward increasing PhD programs. Having doctoral degrees, as the most known and highest degree of science, has also clarified the value of PhD in nursing. Although the American Association of Colleges of Nursing (AACN) announced in 2004, there are mainly two types of nursing doctorate including PhD and DNP in Nursing; but most of the nursing leaders who recognize and accept PhD as a degree at the postgraduate level are strongly advocating the removal of other specialized programs such as DNP named as PhD in Nursing. Moreover, the AACN has differentiated PhD graduates as knowledge developers and DNP and DNSc ones as experts in using the new knowledge ( AACN, 2002 ; Rosseter, 2017 ).
Growing knowledge and increasing complexity of health systems increase the need for advanced and qualified nursing. Therefore, nursing education and the training of Ph.D. students are very important ( Patelarou et al., 2009 ). According to the Institute of Medicine (2011) , “The Future of Nursing: Leading Change, Advancing Health,” nurses could play a very important role in reforming and redesigning health systems that need improving the levels of knowledge and attitudes. Based on the recommendations in this report, there is an emphasis on increasing levels of nursing education, doubling the number of PhD graduates in nursing by 2020, and using the full extent of nurse education and training; therefore, nurses should be responsive to changing needs of health care systems. However; there is much more evidence that PhD programs in nursing have failed to prepare graduates for relevant roles and responsibilities ( Booth et al., 2016 ). Generally, the relationship between doctoral education and expectations and roles is vague and there are sometimes no defined roles and responsibilities for nursing graduates in health systems ( Agger et al., 2014 ; Bullin, 2018 ). Even if the roles and responsibilities have been defined, they have not been properly addressed in practice. Considering the increasing importance and the need for training nurses with PhD degrees as the source of changes in healthcare systems, as well as the controversies in preparation of graduates that exposed them to the confusion of their roles, there is the need to discuss the role of PhD graduate students. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the expected role of PhD graduate nurses.
Research Questions
1. What are the roles and responsibilities of PhD graduate nurses? 2. Is there compatibility between the expected roles, curriculum, clinical environment, and organizations that provide job opportunities? 3. What are the worldwide PhD graduate nurses challenges; especially those highlighted in Iran?
Study Design
This study was a scoping review based on Arksey and O’Malley approach (2005).
Study Process
The five-stage approach of Arksey and O’Malley (2005) includes identifying the research question, identifying relevant studies, study selection, charting the data, collating, summarizing, and reporting. A summary of the stages is shown in the below flowchart ( Figure 1 ).

Flowchart of the Process of Study Based on Arksey and O’Malley’s Five-Stage Approach.
Search Process and Study Identification
Regarding the importance of the subject in the field of nursing and the lack of sufficient evidence in this domain, the main research question was about the expected roles of PhD graduated nurses and their challenges. Accordingly, various keywords such as doctorate in nursing OR PhD in nursing AND roles of PhD nurses AND scope of practice of PhD nurses were searched in valid databases such as Google Scholar, Information Sciences Institute, Ovid, PubMed, and Scientific Information Database in the related studies published between 2000 and 2019.
Eligibility of Resources
More than 414 articles were extracted. After removing duplicate items, examining the relevancy of titles, and reviewing the relevance of the subject, the validity of the source, and accessibility to the article, finally, the 23 articles were examined. Also, seven articles and two books were added after reference lists review. Since the purpose of a scoping review is a brief analysis around key concepts in the research subject and finding main sources and types of evidence without considering the quality of the studies ( Tricco et al., 2016 ), the studies were selected only based on the proximity to the subject and scope of the investigation. Exclusion criteria included irrelevant, duplicate, and non-English articles. However, lectures, summaries, studies related to other disciplines, and studies just related to DNP were excluded from the final review. In addition, the websites of some well-known universities and the contents of some of the global nursing websites such as AACN, NLN, IDEN, as well as reports such as IOM were reviewed. All data were collected, summarized, and then described narratively and discussed.
Goals of PhD in Nursing
By exploring PhD programs in nursing across the world, it becomes clear that the educational goals of training PhD graduates are different due to discrepancies in defined roles and responsibilities. The following cases are examples of such differences.
The University of Virginia in the United States which accepts students through two PhD and DNP programs aims to educate clinical professionals, nursing scholars, and researchers to develop nursing knowledge in the 21 century ( The University of Virginia, 2018 ), while the John Hopkins University, in the United States, emphasized the empowerment of students in development and direction of research toward improving provision of healthcare services ( The Johns Hopkins University School of Nursing, 2018 ). Accordingly, the general purpose of this university is to educate nursing scholars to develop and conduct research studies and finally progress the nursing discipline and deliver better healthcare services ( The Johns Hopkins University School of Nursing, 2018 )
The University of Alberta in Canada also expects the following roles from nursing graduates including nursing progress, knowledge mobilization, research development, and change in leadership ( The University of Alberta, 2018 ). Also, the objective of nursing education in China, which has been working on nursing education since 2003, is to educate future nurses in the domains of research and management ( Wang et al., 2016 ).
In general, the major objectives of establishing the nursing discipline in Iran include training specialized staff to provide the required workforce in the areas of research, education, technology, management, and services. Therefore, graduates can play roles in the domains of education, research, care, counseling, management, and prevention in communities. Accordingly, the positions considered for nurses can extend from hospitals to private centers, welfare and rehabilitation centers, research centers and institutes, planning centers related to nursing, growth centers, and knowledge-based companies as well as the community. However; the goals, visions, roles, and responsibilities of PhD graduated nurses in Iran have undergone changes in three periods since 1994. The focus of the first PhD programs in nursing was on improving the quality of education and research in order to achieve professional independence to supply the required human resource and also to promote nursing ( The Iranian Curriculum of PhD in Nursing, 1995 ). In 2003, following the graduation of only ten students, the curriculum of PhD programs in nursing was revised and training of high-quality students in terms of research gained more weight ( The Iranian Curriculum of PhD in Nursing, 2005 ). In the last period and following the approval of the curriculum for PhD programs in nursing which had been implemented since 2017, the main goal was training specialized nursing staff to provide the required human resources in the field of research, education, technology, management, and nursing services as well as participation in policy-making in the health system. By adding six non-core units to the curriculum, a clinical perspective was formed ( The Iranian Curriculum of PhD in Nursing, 2017 ). Moreover, 24 professional responsibilities were considered for graduates. But there are not enough infrastructures to prepare nurses for gaining enough knowledge and skills during the years of education.
It seems that the shift in the locus of attention to the nursing PhD programs in Iran and some other countries from education to research and then clinical practice, as evident in curriculum changes, along with inappropriate consideration of specialized roles and responsibilities in PhD programs that distinguish graduates of PhD nursing from other nursing groups can be a reason for the role confusion among PhD graduates.
PhD in Nursing Careers
Based on the IOM (2011) reports as well as AACN (2018) , the nursing profession requires much more nurses at the doctoral level to deal with the difficulty of the lack of nursing faculty members and scholars. The Doctor of Philosophy programs in nursing is held with the purpose of preparing graduates to accept careers in health, education, research, and clinical practice.
Most nurses with PhD degrees have a normal transition to achieve an academic career; however, there are other alternatives for nurses at this level. For example, PhD graduated nurses are often recruited by large consulting companies to work with other individuals in terms of designing solutions related to problems in providing healthcare services. Some other nurses are employed by big hospitals to manage different wards. Moreover, a group of such nurses is hired for the management of complicated healthcare systems at an executive level. In other places, these nurses could carry out research and also formulate and develop national and international healthcare policies. No need to say that PhD studies can meet individuals with a wide range of appropriate job opportunities.
Roles, Expectations, and Challenges
Within the nursing profession, graduate students are trained to develop new nursing knowledge and to prepare future nurses in the fields of research, education, clinical practice, leadership, and health-related policies. However, one of the major challenges of nursing education is the lack of clarity in the roles and responsibilities of graduated nurses, especially those involved in PhD programs ( Bunkers, 2002 ).
In the study by Cheraghi et al. (2014) , clinical nurses’ perceptions and expectations about the roles and responsibilities of nursing doctorates were addressed. This study suggested that although nurses were good perceptions of PhD in nursing and believed that PhD nurses had been prepared to do research and to utilize theoretical knowledge in practice and they could also make use of their own specific conditions to improve current nursing status, PhD nurses, in reality, in the clinical setting cannot analyze issues related to healthcare systems and establish strategies to address nursing challenges.
Also, McKenna et al. (2014) highlighted the inadequate competency of PhD graduated nurses in confronting existing challenges in health systems. They acknowledged that although PhD graduates were expected to deal with nursing problems via knowledge and in-depth insights, in practice, such individuals had failed to play their roles in reforming the health system.
On the other hand, Sahebi et al. (2017) reviewing the challenges of the nursing doctoral curriculum in Iran conceded that with regard to the dynamism nature of needs of the health system and the development of nursing education, the nursing curriculum was faced with challenges and needed some changes. One of the most important findings of this study was that the nursing doctoral curriculum could not meet the needs of the community, health care system, the nursing profession, and even faculty members and PhD students. In the study by Zamanzadeh et al. (2014) investigating students’ attitudes toward the quality of PhD programs in nursing, the lowest score was associated with “no consistency between the curriculum of PhD programs and the nursing profession as well as its missions and obligations.”
Following the changes that occurred in the curriculum approved by the Ministry of Health and Medical Education in 2017, it seemed that no adaptation was expected in this domain via adding six non-core units whose method of implementation was not defined clearly. The confusion and challenges faced by PhD students in relation to the expected roles of passing these six units also increased. In a study by Feizalahzadeh and Hassani (2012) , the participants showed that if nurses with PhD degrees were to be employed in clinical practice, necessary and sufficient infrastructure and organizational positions, as well as salaries, are required.
Expectations from PhD graduated nurses are miscellaneous and multifaceted. So, it is expected that individuals demonstrate their best performance in different domains and positions; while there is no proper and practical preparation in the clinical, care, decision-making, policy-making, and education fields. There actually seems to be a contradiction in what universities are producing and what employers expect from the graduated nurses. The following is a summary of the expected roles of PhD graduated nurses in five domains of education, clinical practice, research, leadership and management, and policy-making along with worldwide challenges, especially those highlighted in Iran.
Before the mid-19th century, the main focus of PhD programs was on teaching and higher education, aimed at training faculty members ( Glanville & Houde, 2004 ). Nonetheless, with the expansion of PhD programs in nursing and admitting more students, teaching became a secondary activity and concentration was directed to research programs ( AACN, 2016 ). One of the tasks of schools in this domain is to train experts, that is, future students and nurses, in terms of theoretical and clinical education ( Oermann et al., 2016 ). It is also one of the professional responsibilities and roles of PhD graduated nurses in Iran. Thus, nursing education has great importance in the development of the nursing profession and preparation of future nurses to accept today’s advanced roles and to take on responsibilities for providing safe and high-quality nursing services ( Burton et al., 2009 ).
Nursing graduates are expected to be able to prepare for the quality training of future nurses, but this readiness is low or not at all ( Bullin, 2018 ). Previous studies have shown that insufficient preparation among graduates to assume the role of lecturers and faculty members could reduce job satisfaction and have a negative impact on their performance in the educational role ( Whitehead, 2015 ). In the study by Moghadam et al. (2017) , it has been reported that PhD nursing students and graduates were not ready for nursing education. PhD graduated nurses further acknowledged that organizational expectations were much beyond their abilities, clinical competencies were low, and uncertainties and obligations could lead to identity threats in PhD students. Also, McNelis et al. (2019) showed that there is a vague process for preparing graduates for teaching in both PhD and DNP curricula. so, should prepare graduates for faculty roles by including coursework on teaching.
Currently, the presence of Iranian PhD graduated nurses in clinical practice is defined as lecturers in undergraduate and postgraduate courses in clinical settings ( Cheraghi, et al., 2014 ). But based on the contents of the PhD programs, students are not completely prepared for clinical education. So, assuming the role of clinical instructors by PhD graduated nurses is neither acceptable nor cost-effective. Perhaps, teaching-specialized clinical education can be assigned to experts of the related field and the educational role of nursing doctorates can be limited to teaching how to acquire knowledge and research and how to enhance the body of nursing knowledge. It has been highlighted in most PhD programs worldwide, and PhD nursing students are prepared in that domain.
Clinical Practice
As stated, the nursing discipline is inherently clinical and one of the goals to train future nurses is helping in terms of provision of safe and high-quality services and consequently improvement of community health ( Edwards et al., 2018 ). By assessing the roles for PhD graduates in clinical practice, it can be realized that the expected clinical role is promoting health in communities at higher executive and managerial levels, and no direct clinical role for such graduates in the care domain has been taken into consideration. In contrast, in Iran, planning, implementation, and evaluation of nursing services, working with healthcare teams, as well as patient follow-up after discharge, have been considered as responsibilities of PhD graduated nurses, while the defined positions for playing these roles have been not considered ( The Iranian Curriculum of PhD in Nursing, 2017 ). Additionally, the lack of well-defined and purposeful program have faced students with more confusion. There is no doubt about the role that nurses can play in clinical practice, but if nurses with PhD degrees have the same responsibilities assumed by other nursing groups, what is the need to spend money, time, and manpower to train nursing doctorates.
Certainly, DNP has a different definition of PhD. Accordingly, there are different programs, goals, missions, and job positions ( Oermann et al., 2016 ). The launch of the DNP program alongside PhD in nursing as a separate discipline considering educational infrastructure, manpower, working environment, community acceptance, and … can be debated; however, the problem is to what extent the integration of these two programs will be practical.
Research and Investigation
The goal of the PhD programs is to prepare nursing students to produce new knowledge, develop the profession, and improve the quality of healthcare and health policies that are possible in the light of research studies. Therefore, one of the expected roles of PhD students in nursing is the ability to carry out applied research ( Henly et al., 2015 ). Now, in the PhD Programs in Nursing in Iran (2017), students are required to fulfill a final research dissertation. In fact, one of the prominent roles of PhD graduated nurses is setting up and conducting proper and high-quality research. Thus, PhD students can identify concepts and structures of their interest, study their relationships, develop predicted models, and finally test them. The result can be the production of new knowledge for the nursing profession. However, AACN (2013) and Quality Assurance Agency for Higher Education ( The Quality Assurance Agency for Higher Education [QAAHE], 2011 ) in the United Kingdom have expressed concerns about the quality of PhD theses.
It seems that attention to the quantity of the dissertations, limited research areas, and lack of interest in fundamental subjects, along with the prolongation of the research period, can all reduce the quality of research in PhD programs in nursing.
Leadership and Policy-Making
Although the tasks of governments or nursing leaders appointed to state affairs are policy-making, the presence of nurses in policy-making can improve nursing performance and consequently increase the quality of care services ( Sullivan & Garland, 2010 ).
More than any other efforts up to the present, the IOM report (2011) has encouraged nurses to make changes in policies. According to this report, nurses have been called on to enhance their leadership capacities in order to design, implement, and support health policies that affect community health.
In recent years, Iranian nurses have tried to increase their participation in policy-making in nursing affairs although the status of nurses in the domain of policy-making is not still clear enough ( Ministry of Health Policy Making Council, 2014 ).
It is also obvious that PhD graduated nurses have the most important role in shaping leadership. In the curriculum ( The Iranian Curriculum of PhD in Nursing, 2017 ), there are at least eight to ten leadership responsibilities that have been listed for PhD graduated nurses. It is also believed that the endpoint of the nursing profession is a leadership position to provide nursing services or train nurses. Accordingly, the PhD degree puts more emphasis on the leadership position of nurses, particularly in clinical practice. Moreover, it is claimed that nursing managers should benefit from the cooperation of PhD nurses in decision-making processes ( Brar et al., 2010 ).
In regard to the preparation of PhD graduated nurses to assume leadership and policy-making roles, there are still ambiguities. Recently, two units of policy-making have been included in the nursing syllabus, but they have not been enough and also failed to prepare nurses for such situations. Therefore, it seems necessary to change the goals and the plans of PhD programs in nursing in order to prepare nurses to take on leadership and policy-making roles in the future.
On the other hand, due to the lack of a precise definition for organizational positions in leadership and policy-making groups in the Ministry of Health or at hospitals, graduates have no idea of employment in such organizations. Moreover, the terms “cooperation” or “participation” have been used in the responsibilities listed in the curriculum and independent roles have not been considered for PhD graduated nurses.
Study Limitations
One of the limitations of this study was the difficulty of fully accessing up-to-date and reliable sources. However, the best and most reliable sources were selected and retrieved according to the situation and needs.
Conclusion and Recommendations
The Doctor of Philosophy graduated nurses are expected to play the roles of agents for the development of the body of knowledge and nursing profession, as well as for educators, researchers, leaders, policy-makers, and professional consultants. Nevertheless, one of the major challenges facing nursing education is ambiguity in defining the roles of nursing graduates particularly those with PhD degrees (Bunkers, 2001). The definition of nursing roles can be challenging because studies in many countries have indicated disruptions in roles as well as overlaps ( Chiarella & McInnes, 2010 )
There is much evidence that PhD programs in nursing do not prepare graduates for their roles and responsibilities ( Booth et al., 2016 ). In general, the relationships between doctoral education, expectations, and career roles for PhD graduated nurses have not been well defined ( Agger et al., 2014 ; Bullin, 2018 ). Therefore, for possessing graduates with multiple abilities and multiple tasks, there is a need for the enrichment of the curriculum, defining clear roles, and proper preparation to achieve these roles ( Adib-Hajbaghery & Hosieni, 2018 ).
It seems that PhD programs lasting for 4–5 years have failed to create the competency required to provide these complex, broad, and sometimes cooperating roles with other medical and nursing staff. On the other hand, the working environment is not ready to accept these graduates.
As a whole, all the expected roles of PhD graduated nurses need further clarifications and there is a need to think about the consistency between curriculums and roles, as well as the establishment of better relationships between academic settings and educational programs and organizations providing job opportunities.
Educational planning to achieve the competency to accept the roles needed for the market in order to meet the needs of communities and the nursing profession is worthwhile because the type of investments in an educational system will be equal to its outputs. Therefore, the type of perspectives to educational programs can direct human resource policy. Therefore, the results of this study, while reporting the situation in Iran, should be considered as a basis for expanding awareness of the challenges in this field, and the authorities should find a solution in the field with proper planning.
This article provides an overview of the expected role of nursing PhD graduates around the world with a special focus on nursing PhD graduates in Iran and discusses its challenges. Obviously, because of cultural differences and the educational and care structure of each country, roles and expectations will be different. Therefore, it is suggested that this issue be discussed in several countries and a solution be found to its challenges.
Peer Review: Externally peer-reviewed.
Author Contributions: Concept – S.K., R.N.; Design S.K., R.N.; Supervision – R.N.; Resources – S.K., R.N.; Materials – S.K., R.N.; Data Collection and/or Processing – S.K.; Analysis and/or Interpretation – S.K., R.N.; Literature Search – S.K., R.N.; Writing Manuscript – S.K.; Critical Review – R.N.
Declaration of Interests: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Funding: The authors declared that this study has received no financial support.
- Adib-Hajbaghery M., Hosieni F. (2018). Comparison of expected potentials of PhD nursing students in Iran and top universities of the world . Iran Journal of Nursing , 31 ( 113 ), 30–41. 10.29252/ijn.31.113.30) [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Agger C. A., Oermann M. H., Lynn M. R. (2014). Hiring and incorporating doctor of nursing practice–prepared nurse faculty into academic nursing programs . Journal of Nursing Education , 53 ( 8 ), 439–446. 10.3928/01484834-20140724-03) [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- American Association of Colleges of Nursing (AACN). 2018. Nursing education programs/phd education . Retrieved from http://www.aacnnursing.org/Nursing-Education-Programs/PhD- Education. [ Google Scholar ]
- American Association of Colleges of Nursing (AACN). (2002). Indicators of quality in research-focused doctoral programs in nursing . Journal of Professional Nursing , 18 ( 5 ), 289–294. 10.1053/jpnu.2002.129230) [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- American Association of Colleges of Nursing (AACN). (2013). PhD summit . Retrieved from http://www.aacn.nche.edu/events/2013/09/19/phd-summit. [ Google Scholar ]
- American Association of Colleges of Nursing (AACN). (2016). Advancing health care transformation: A new era for academic nursing . Retrieved from http://www.aacnnursing.org/ Portals/42/Publications/Futures-Task-Force-Final-Report.pdf. [ Google Scholar ]
- Arksey H., O'Malley L. (2005). Scoping studies: Towards a methodological framework . International Journal of Social Research Methodology , 8 ( 1 ), 19–32. 10.1080/1364557032000119616) [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Auriol L.(2010). Careers of doctorate holders: Employment and mobility patterns, OECD science, technology and industry working papers , 4 , p. 29. Paris: OECD Publishing. Retrieved from 10.1787/5kmh8phxvvf5-en. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Booth T. L., Emerson C. J., Hackney M. G., Souter S. (2016). Preparation of academic nurse educators . Nurse Education in Practice , 19 , 54–57. 10.1016/j.nepr.2016.04.006) [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brar K., Boschma G., McCuaig F. (2010). The development of nurse practitioner preparation beyond the master’s level: What is the debate about? International Journal of Nursing Education Scholarship , 7 ( 1 ), Article 9. 10.2202/1548-923X.1928) [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bullin C. 2018). To what extent has doctoral (PhD) education supported academic nurse educators in their teaching roles: An integrative review . BMC Nursing , 17 ( 1 ), 6. 10.1186/s12912-018-0273-3) [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bunkers S. S. 2001). Doctoral education in nursing: Seeking clarity . Nursing Science Quarterly , 15 ( 3 ), 201–208. 10.1177/08918402015003005) [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Burton C. R., Duxbury J., French B., Monks R., Carter B. (2009). Re-visioning the doctoral research degree in nursing in the United Kingdom . Nurse Education Today , 29 ( 4 ), 423–431. 10.1016/j.nedt.2008.10.002) [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Carpenter D. R., Hudacek S. (1996). On doctoral education in nursing: The voice of the student . Jones & Bartlett Publishers Learning. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cheraghi M. A., Jasper M., Vaismoradi M. (2014). Clinical nurses’ perceptions and expectations of the role of doctorally-prepared nurses: A qualitative study in Iran . Nurse Education in Practice , 14 ( 1 ), 18–23. 10.1016/j.nepr.2013.06.007) [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chiarella M., McInnes E. (2010). Who to turn to? ‘Knowing the ropes’ in an underbounded health care system . Contemporary Nurse , 36 ( 1–2 ), 10–20. 10.5172/conu.2010.36.1-2.010) [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Edwards N. E., Coddington J., Erler C., Kirkpatrick J. (2018). The impact of the role of doctor of nursing practice nurses on healthcare and leadership . Medical Research Archives , 6 ( 4 ). 10.18103/mra.v6i4.1734) [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ellis L. B. 2005). Professional doctorates for nurses: Mapping provision and perceptions . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 50 ( 4 ), 440–448. 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2005.03410.x) [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Feizalahzadeh H., Hassani P. (2012). Challenges and opportunities of doctorate of nursing graduates in clinical settings . Journal of Health Promotion Management , 1 ( 1 ), 74–84. Retrived from http://jhpm.ir/article-1-30-en.html . [ Google Scholar ]
- Fiedler R., Degenhardt M., Engstrom J. L. (2015). Systematic preparation for teaching in a nursing Doctor of Philosophy program . Journal of Professional Nursing , 31 ( 4 ), 305–310. 10.1016/j.profnurs.2015.02.009) [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Glanville I., Houde S. (2004). The scholarship of teaching: Implications for nursing faculty . Journal of Professional Nursing , 20 ( 1 ), 7–14. 10.1016/j.profnurs.2003.12.002) [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Henly S. J., McCarthy D. O., Wyman J. F., Heitkemper M. M., Redeker N. S., Titler M. G., McCarthy A. M., Stone P. W., Moore S. M., Alt-White A. C., Conley Y. P., Dunbar-Jacob J., Stone P. W., Moore S. M., Alt-White A. C., Conley Y. P., Dunbar-Jacob J. (2015). Emerging areas of science: Recommendations for nursing science education from the council for the advancement of nursing science idea festival . Nursing Outlook , 63 ( 4 ), 398–407. 10.1016/j.outlook.2015.04.007) [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Institute of Medicine (IOM). (2011). The future of nursing: Leading change, advancing health . Washington, DC: National Academies Press. Retrieved from www.iom.edu/nursing . [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ketefian S., Neves E., Gutierrez M. (2001). Nursing doctoral education in the Americas . Online Journal of Issues in Nursing , 5 ( 2 ), 8. Retrived from www.nursingworld.org//MainMenuCategories/ANAMarketplace/ANAPeriodicals/OJIN/TableofContents/Volume62001/No2May01/ArticlePreviousTopic/DoctoralEducationAmericas.aspx . [ Google Scholar ]
- McKenna H., Keeney S., Kim M. J., Park C. G. (2014). Quality of doctoral nursing education in the United Kingdom: Exploring the views of doctoral students and staff based on a cross-sectional questionnaire survey . Journal of Advanced Nursing , 70 ( 7 ), 1639–1652. 10.1111/jan.12326) [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McNelis A. M., Dreifuerst K. T., Schwindt R. (2019). Doctoral education and preparation for nursing faculty roles . Nurse Educator , 44 ( 4 ), 202–206. 10.1097/NNE.0000000000000597) [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Meleis A. I. 1988). Doctoral education in nursing: Its present and its future . Journal of Professional Nursing , 4 ( 6 ), 436–446. 10.1016/S8755-7223(88)80095-4) [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ministry of Health Policy Making Council. (2014). The thirty joint programs of the nursing deputy of the health ministry and Iranian nursing organization . Retrieved from http://www.dn.behdasht.gov.ir/ . [ Google Scholar ]
- Moghadam Y. H., Atashzadeh-Shoorideh F., Abbaszadeh A., Feizi A. (2017). Challenges of PhD graduated nurses for role acceptance as a clinical educator: A qualitative study . Journal of Caring Sciences , 6 ( 2 ), 153–161. 10.15171/jcs.2017.015) [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Oermann M. H., Lynn M. R., Agger C. A. (2016). Hiring intentions of Directors of Nursing Programs related to DNP- and PhD-prepared faculty and roles of faculty . Journal of Professional Nursing , 32 ( 3 ), 173–179. 10.1016/j.profnurs.2015.06.010) [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Patelarou E., Vardavas C. I., Ntzilepi P., Sourtzi P. (2009). Nursing education and practice in a changing environment: The case of Greece . Nurse Education Today , 29 ( 8 ), 840–844. 10.1016/j.nedt.2009.04.005) [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Robb W. J. W. 2005). PhD, DNSc, ND: The ABCs of nursing doctoral degrees . Dimensions of Critical Care Nursing , 24 ( 2 ), 89–96. 10.1097/00003465-200503000-00010) [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rosseter R. 2017). The Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP): Fact sheet . Retrieved from https://www.aacnnursing.org/Portals/42/News/Factsheets/DNP-Factsheet.pdf. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sahebi H. M., Khadivi A., Soheili A., Moghbeli G., Khaje G. M., Valizadeh L. (2017). The challenges of nursing doctoral curriculum in Iran: A critical look based on Delphi technique . Nursing and Midwifery Journal , 15 ( 6 ), 424–439. Retrived from https://www.sid.ir/en/journal/ViewPaper.aspx?id=542702 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Sullivan E. J., Garland G. (2010). Practical leadership and management in nursing . US: Pearson Education. [ Google Scholar ]
- The Iranian Curriculum of PhD in Nursing. (1995). Retrived from http://mbs.behdasht.gov.ir/uploads/phd_parastari95.pdf . [ Google Scholar ]
- The Iranian Curriculum of PhD in Nursing. (2005) Retrived from http://mbs.behdasht.gov.ir/uploads/phd_parastari95.pdf . [ Google Scholar ]
- The Iranian Curriculum of PhD in Nursing. (2017). Retrived from http://mbs.behdasht.gov.ir/uploads/phd_parastari95.pdf . [ Google Scholar ]
- The Johns Hopkins University School of Nursing. (2018). Doctor of philosophy academic manual . Retrieved from http://nursing.jhu.edu/faculty_research/faculty/hand book/2014-2015. [ Google Scholar ]
- The Johns Hopkins University School of Nursing. (2018). Doctor of philosophy academic manual . Retrieved from http://nursing.jhu.edu/academics/resources/ policies/index.html. [ Google Scholar ]
- The Quality Assurance Agency for Higher Education (QAAHE). (2011). Doctoral degree characteristics . Retrieved from http://www.qaa.ac.uk/Publications/InformationAndGuidance/Documents/Doctoral_Characteristics.pdf . [ Google Scholar ]
- The University of Alberta. (2018). PhD program . Retrieved from https://www.ualberta.ca/nursing/programs/graduate-programs-and-admissions/doctoral- program/index.html. [ Google Scholar ]
- The University of Virginia. (2018). Doctor of philosophy in nursing . Retrieved from https://www.nursing.virginia.edu/academics/phd/ . [ Google Scholar ]
- Tricco A. C., Lillie E., Zarin W., O’Brien K., Colquhoun H., Kastner M., Levac D., Ng C., Sharpe J. P., Wilson K., Kenny M., Warren R., Wilson C., Stelfox H. T., Straus S. E., Ng C., Sharpe J. P., Wilson K., Kenny M., Warren R., et al. (2016). A scoping review on the conduct and reporting of scoping reviews . BMC Medical Research Methodology , 16 ( 1 ), 15. 10.1186/s12874-016-0116-4) [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang C. C., Whitehead L., Bayes S. (2016). Nursing education in China: Meeting the global demand for quality healthcare . International Journal of Nursing Sciences , 3 ( 1 ), 131–136. 10.1016/j.ijnss.2016.02.009) [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Whitehead P. S. 2015). Role ambiguity, role strain, job dissatisfaction, and difficulty transitioning into academia among nursing faculty [Doctoral Dissertation]. New Orleans: Walden University. Retrieved from https://search.proquest.com/openview/82b38976dfcf155c6fb3beedc55ee003/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=18750&diss=y . [ Google Scholar ]
- Winter R., Griffiths M., Green K. (2000). The academic qualities of practice: What are the criteria for a practice-based PhD? Studies in Higher Education , 25 ( 1 ), 25–37. 10.1080/030750700115993) [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zamanzadeh V., Jasemi M., Mansoori A., Khodabandeh F., Alsadat Hoseini F. (2014). Doctoral nursing students’ perspectives towards educational quality of PhD course . Iran Journal of Nursing , 27 ( 89 ), 30–39. 10.29252/ijn.27.89.30) [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]

Visit U of I
Learn about the many reasons the University of Idaho could be a perfect fit for you. Schedule Your Visit
- Discover a Career
- Find a Major
- Experience U of I Life
More Resources
- Admitted Students
- International Students
Take Action
- Find Financial Aid
- View Deadlines
- Find Your Rep

Helping to ensure U of I is a safe and engaging place for students to learn and be successful. Read about Title IX
Get Involved
- Clubs & Volunteer Opportunities
Campus Recreation
- Student Government
- Sustainability Center
- Academic Assistance
- Safety & Security
- Career Services
- Health & Wellness Services
- Register for Classes
- Dates & Deadlines
- Financial Aid
- U of I Library

Homecoming Oct. 14 - 21
Join other Vandal families for a week of celebration and Vandal traditions. View Calendar
Stay Connected
- Upcoming Events
- Here We Have Idaho Magazine
- Support Services
- About Moscow
- Commencement
- Dads' Weekend
- Moms' Weekend

- U of I Retirees Association
UIRA has a membership of nearly 500 from every part of the University. Learn about UIRA
- Submit Class Notes
- Make a Gift
- View Events
- Vandal Pride Products
- Vandal Voyagers Program
- Alumni Chapters
- University Magazine
- Alumni Newsletter

Gym memberships and wellness class passes are available for faculty, staff and their spouses. Get Healthy
Common Tools
- Administrative Procedures Manual (APM)
- Class Schedule
- ITS Tech Support
- Academic Dates & Deadlines
- Daily Register
- Faculty Senate
- Staff Council
Application Management
Office of admissions.
Physical Address: University of Idaho Bruce M. Pitman Center 709 Deakin Street Rm 117 Moscow, ID 83844
Mailing Address: University of Idaho 875 Perimeter Drive MS 4264 Moscow, ID 83844-4264
Phone: 208-885-6326
Fax: 208-885-9119
Email: [email protected]
Web: Office of Admissions
Physical Address: University of Idaho Boise 322 E. Front St Boise, ID 83702
Email: [email protected]
Web: Boise Center
Coeur d'Alene
Physical Address: University of Idaho Coeur d'Alene 1031 N Academic Way Suite 242 Coeur d'Alene, ID 83814
Web: Coeur d'Alene Center
Idaho Falls
Physical Address: University of Idaho Idaho Fall 1776 Science Center Dr. Suite 306 Idaho Falls, ID 83840
Web: Idaho Falls Center

CREEES Professional Resources Forum
Center for Russian, East European and Eurasian Studies at The University of Texas at Austin
Academic Job: Postdoctoral research positions, HSE (Moscow)
Deadline to apply: february 15, 2018, the job involves:.
- Working under the supervision of Oleg Budnitskii, the Center’s Director, and Michael David-Fox, the Academic advisor at the International Center for the History and Sociology of World War II and Its Consequences
- Participants are encouraged to pursue their own research that is thematically related to the Center’s research project on the history of World War II and wartime Stalinism, as well as on other topics dealing with Soviet history and culture more broadly
- Writing research papers for international peer-reviewed journals
- Providing consultations on writing scholarly papers in English to Russian colleagues and students
- Participation in organization of the events and other contribution to the Center’s development
- Public presentations of candidate’s own research to the researchers in the field and the broader academic community
- Some teaching is encouraged, though not required.
Requirements:
- PhD from an international research university in the field of Soviet or Modern European History or other related fields,
- Publication record in English or potential for producing high-quality research publications,
- Ability to work in a team,
- Fluent English
General conditions for Post-Doctoral Research positions can be found here . Appointments will be normally made for one year. They assume internationally competitive compensation and other benefits including medical insurance.
A CV and research statement should be submitted via online application form and two letters of recommendation should be submitted be the referees directly to [email protected] by February 15, 2018. Please note that direct applications to the hiring laboratory may not be reviewed.
Social Widgets powered by AB-WebLog.com .
Finance Graduate Jobs in Moscow, Russia

About iAgora
With up to 1.000 new internships/day, iAgora is the most active pool of internships in Europe. Students and universities across Europe use our platform to find internships abroad and at home, VIE, graduate jobs and graduate programmes. We want to improve lives and help the planet through more meaningful internships.
© 2024 iAgora Europa, SLU
Articles About iAgora Advertise on iAgora Terms of use Privacy Policy Contact Us
All job opportunities All Companies Graduate Jobs Internships Marketing offers CV guides Leonardo Grants Publish job offers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Tenure Track Faculty - Undergraduate Nursing. PACE UNIVERSITY. 4.2. 861 Bedford Rd, Pleasantville, NY 10570. $100,000 - $110,000 a year - Full-time, Tenure track. Responded to 75% or more applications in the past 30 days, typically within 3 days.
1 month ago. Today's top 8,000+ Phd Nursing jobs in United States. Leverage your professional network, and get hired. New Phd Nursing jobs added daily.
The Ph.D. in Nursing degree opens career opportunities for nurses as researchers, forging new and cutting-edge nursing practices for future generations. ... Your graduate nursing program will consist of several key milestones to reinforce your education. These include: Leadership strategies related to nursing, healthcare, and research;
This program will provide you with the knowledge and skills in theoretical, methodological, and analytical approaches that will enable you to conduct research to discover and apply knowledge in nursing science and health care. Most full-time Johns Hopkins Nursing PhD students are 100% funded with a stipend for the first three years of study.
NINR Job Opportunities. NINR offers exciting career opportunities for a broad range of forward-thinking scientists, researchers, leaders, and other professionals who are interested in supporting our mission: to lead nursing research to solve pressing health challenges and inform practice and policy-optimizing health and advancing health equity ...
Top Careers for RNs with a Doctorate in Nursing. Nursing is a calling for most RNs, and many want to continue their education to further their careers and take an even greater leadership role in the field.A doctorate in nursing is the terminal degree for nurses who want to expand their current roles, move into management and leadership positions, conduct clinical research or pursue employment ...
Ph.D. Nurse Salary & Employment. Salaries for Ph.D. nurses vary based on the type of employment a nurse seeks after graduation. Nurse researchers, a primary career path for Ph.D. nurses, can expect a median salary of $90,000 according to Payscale.com. For Ph.D. nurses who pursue a teaching position, the median annual wage for post-secondary ...
PHD. Advance the theoretical foundation of nursing practice and healthcare delivery with a Johns Hopkins PhD in nursing. With access to world-renowned faculty, cutting-edge facilities, and opportunities for interdisciplinary collaboration with noted researchers throughout Johns Hopkins, you'll build the skills to develop and implement a scientific research program.
Application Deadline: November 15, 2023. Decisions Posted: Early 2024. Program Start Date: September 2024. The Columbia University School of Nursing PhD program is a full-time, research-intensive curriculum that prepares nurses for careers as nurse scientists who will conduct research across a broad range of populations and health conditions.
A nurse who has attained a PhD can practically work anywhere that research, education, or program evaluation takes place. The important thing to remember is that graduation from a reputable PhD program ensures that a nurse has received proper research training. Tiffany M. Montgomery, MSN, RNC-OB, C-EFM, a women's health nurse since 2005 ...
Generating strong interest in the PhD in nursing (and similar research-focused doctorates) is a priority for the profession. Although less than 1% of today's nursing workforce has earned a PhD (NCSBN, 2021), these individuals are in high demand with the need for nurse scientists, faculty, and leaders on the rise. Despite this great need, AACN has seen a steady decline in enrollment in PhD ...
Advance your career. The Ph.D. opens up career opportunities such as serving as a nurse researcher, administrator, policymaker, leader, or educator. "With a PhD in nursing, you are better positioned to be a leader in the area of nursing education or be hired as a full-time faculty member," says Dr. Seon Yoon Chung, Associate Dean for Academics.
Experience the Possibilities… Overview Join the Johns Hopkins community as an academic leader at the School of Nursing. Our faculty members are committed to excellence in research, teaching, practice, and service, and are recognized nationally and internationally as experts in their disciplines. The School is top ranked for its nursing graduate program and for its DNP program by U.S. News
Therefore, one of the expected roles of PhD students in nursing is the ability to carry out applied research ( Henly et al., 2015 ). Now, in the PhD Programs in Nursing in Iran (2017), students are required to fulfill a final research dissertation. In fact, one of the prominent roles of PhD graduated nurses is setting up and conducting proper ...
Physical Address: University of Idaho Bruce M. Pitman Center 709 Deakin Street Rm 117 Moscow, ID 83844. Mailing Address: University of Idaho 875 Perimeter Drive MS 4264
Statement of career objectives/research goals. It should be 2-3 pages double spaced and include: ... Please check back for future opportunities. ... A PhD in nursing, public health, psychology, behavioral sciences or health related field is required. All applicants must have experience or interest in sexual health, HIV, and/or violence research ...
The job involves: Working under the supervision of Oleg Budnitskii, the Center's Director, and Michael David-Fox, the Academic advisor at the International Center for the History and Sociology of World War II and Its Consequences ... PhD from an international research university in the field of Soviet or Modern European History or other ...
Part time Full time. Graduate Development Program Trainee. Employment Type: Unspecified. Contractor. Employee Graduate Development Program Trainee. Internship. Temporary Employee. Search through a wide range of accurate filters to find the perfect job for you, find an opportunity that fits with your skills, experience, and education.
Funding Opportunities April 2024. Funding Opportunities March 2024. Post-Doctoral. As a research intensive university, Johns Hopkins is committed to having faculty and students engage in discovery of knowledge, inventing new technologies, and applying knowledge in the community and abroad. The School of Nursing offers a variety of post-doctoral ...
04/04/2024: 112.239 internships and jobs in 148 countries | Personalised work abroad recommendations for students and graduates | Finance Graduate Jobs in Moscow, Russia | Sign-up free.