
Statistics Made Easy

Introduction to Hypothesis Testing
A statistical hypothesis is an assumption about a population parameter .
For example, we may assume that the mean height of a male in the U.S. is 70 inches.
The assumption about the height is the statistical hypothesis and the true mean height of a male in the U.S. is the population parameter .
A hypothesis test is a formal statistical test we use to reject or fail to reject a statistical hypothesis.
The Two Types of Statistical Hypotheses
To test whether a statistical hypothesis about a population parameter is true, we obtain a random sample from the population and perform a hypothesis test on the sample data.
There are two types of statistical hypotheses:
The null hypothesis , denoted as H 0 , is the hypothesis that the sample data occurs purely from chance.
The alternative hypothesis , denoted as H 1 or H a , is the hypothesis that the sample data is influenced by some non-random cause.
Hypothesis Tests
A hypothesis test consists of five steps:
1. State the hypotheses.
State the null and alternative hypotheses. These two hypotheses need to be mutually exclusive, so if one is true then the other must be false.
2. Determine a significance level to use for the hypothesis.
Decide on a significance level. Common choices are .01, .05, and .1.
3. Find the test statistic.
Find the test statistic and the corresponding p-value. Often we are analyzing a population mean or proportion and the general formula to find the test statistic is: (sample statistic – population parameter) / (standard deviation of statistic)
4. Reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Using the test statistic or the p-value, determine if you can reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis based on the significance level.
The p-value tells us the strength of evidence in support of a null hypothesis. If the p-value is less than the significance level, we reject the null hypothesis.
5. Interpret the results.
Interpret the results of the hypothesis test in the context of the question being asked.
The Two Types of Decision Errors
There are two types of decision errors that one can make when doing a hypothesis test:
Type I error: You reject the null hypothesis when it is actually true. The probability of committing a Type I error is equal to the significance level, often called alpha , and denoted as α.
Type II error: You fail to reject the null hypothesis when it is actually false. The probability of committing a Type II error is called the Power of the test or Beta , denoted as β.
One-Tailed and Two-Tailed Tests
A statistical hypothesis can be one-tailed or two-tailed.
A one-tailed hypothesis involves making a “greater than” or “less than ” statement.
For example, suppose we assume the mean height of a male in the U.S. is greater than or equal to 70 inches. The null hypothesis would be H0: µ ≥ 70 inches and the alternative hypothesis would be Ha: µ < 70 inches.
A two-tailed hypothesis involves making an “equal to” or “not equal to” statement.
For example, suppose we assume the mean height of a male in the U.S. is equal to 70 inches. The null hypothesis would be H0: µ = 70 inches and the alternative hypothesis would be Ha: µ ≠ 70 inches.
Note: The “equal” sign is always included in the null hypothesis, whether it is =, ≥, or ≤.
Related: What is a Directional Hypothesis?
Types of Hypothesis Tests
There are many different types of hypothesis tests you can perform depending on the type of data you’re working with and the goal of your analysis.
The following tutorials provide an explanation of the most common types of hypothesis tests:
Introduction to the One Sample t-test Introduction to the Two Sample t-test Introduction to the Paired Samples t-test Introduction to the One Proportion Z-Test Introduction to the Two Proportion Z-Test
Published by Zach
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
What is a Hypothesis Test?
A quick search for hypothesis tests online gives us several websites with short definitions. Here’s one from a quick definition from the Stat Trek:
A statistical hypothesis is an assumption about a population parameter. This assumption may or may not be true. Hypothesis testing refers to the formal procedures used by statisticians to accept or reject statistical hypotheses.
What is Hypothesis Testing? From Stat Trek
Most websites will have a similar definition or introduction, followed by a number of components, notation, key terminology, and examples.
The Basic Idea
Hypothesis tests show up in many areas of our everyday lives, but they are kind of sneaky. The basic structure of a hypothesis test is very much like a science project from elementary, middle, or high school. You have a problem, hypothesis, data collection, some computations, results or conclusions. What follows next are a few examples of what the hypothesis test and results would look like in journals or other publications, and how those results are presented to the public.
Some Examples of Hypothesis Tests
Example 1: agility testing in youth football (soccer)players; evaluating reliability, validity, and correlates of newly developed testing protocols.
Reactive agility (RAG)and change of direction speed (CODS) were analyzed in 13U and 15U youth soccer players. “Independent samples t-test indicated significant differences between U13 and U15 in S10 (t-test: 3.57, p < 0.001), S20M (t-test: 3.13, p < 0.001), 20Y (t-test: 4.89, p < 0.001), FS_RAG (t-test: 3.96, p < 0.001), and FS_CODS (t-test: 6.42, p < 0.001), with better performance in U15. Starters outperformed non-starters in most capacities among U13, but only in FS_RAG among U15 (t-test: 1.56, p < 0.05).”
Most of this might seem like gibberish for now, but essentially the two groups were analyzed and compared, with significant differences observed between the groups.
Source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31906269/
Example 2: Manual therapy in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome in diabetic patients: A randomized clinical trial
Thirty diabetic patients with carpal tunnel syndrome were split up into two groups. One received physiotherapy modality and the other received manual therapy. “Paired t-test revealed that all of the outcome measures had a significant change in the manual therapy group, whereas only the VAS and SSS changed significantly in the modality group at the end of 4 weeks. Independent t-test showed that the variables of SSS, FSS and MNT in the manual therapy group improved significantly greater than the modality group.”
Source: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30197774/
Example 3: Omega-3 fatty acids decreased irritability of patients with bipolar disorder in an add-on, open label study
“The initial mean was 63.51 (SD 34.17), indicating that on average, subjects were irritable for about six of the previous ten days. The mean for the last recorded percentage was less than half of the initial score: 30.27 (SD 34.03). The decrease was found to be statistically significant using a paired sample t-test (t = 4.36, 36 df, p < .001).”
Source: https://nutritionj.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1475-2891-4-6
Example 4: Evaluating the Efficacy of COVID-19 Vaccines
“We reduced all values of vaccine efficacy by 30% to reflect the waning of vaccine efficacy against each endpoint over time. We tested the null hypothesis that the vaccine efficacy is 0% versus the alternative hypothesis that the vaccine efficacy is greater than 0% at the nominal significance level of 2.5%.”
Source: https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.10.02.20205906v2.full
Example 5: Social Isolation During COVID-19 Pandemic. Perceived Stress and Containment Measures Compliance Among Polish and Italian Residents
“The Polish group had a higher stress level than the Italian group (mean PSS-10 total score 22,14 vs 17,01, respectively; p < 0.01). There was a greater prevalence of chronic diseases among Polish respondents. Italian subjects expressed more concern about their health, as well as about their future employment. Italian subjects did not comply with suggested restrictions as much as Polish subjects and were less eager to restrain from their usual activities (social, physical, and religious), which were more often perceived as “most needed matters” in Italian than in Polish residents.”
Source: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.673514/full
Example 6: A Comparative Analysis of Student Performance in an Online vs. Face-to-Face Environmental Science Course From 2009 to 2016
“The independent sample t-test showed no significant difference in student performance between online and F2F learners with respect to gender [t(145) = 1.42, p = 0.122].”
Source: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcomp.2019.00007/full
But what does it all mean?
That’s what comes next. The examples above span a variety of different types of hypothesis tests. Within this chapter we will take a look at some of the terminology, formulas, and concepts related to Hypothesis Testing for 1 Sample.
Key Terminology and Formulas
Hypothesis: This is a claim or statement about a population, usually focusing on a parameter such as a proportion (%), mean, standard deviation, or variance. We will be focusing primarily on the proportion and the mean.
Hypothesis Test: Also known as a Significance Test or Test of Significance , the hypothesis test is the collection of procedures we use to test a claim about a population.
Null Hypothesis: This is a statement that the population parameter (such as the proportion, mean, standard deviation, or variance) is equal to some value. In simpler terms, the Null Hypothesis is a statement that “nothing is different from what usually happens.” The Null Hypothesis is usually denoted by [latex]H_{0}[/latex], followed by other symbols and notation that describe how the parameter is the same as some value.
Alternative Hypothesis: This is a statement that the population parameter (such as the proportion, mean, standard deviation, or variance) is somehow different the value involved in the Null Hypothesis. For our examples, “somehow different” will involve the use of [latex] [/latex], or [latex]\neq[/latex]. In simpler terms, the Alternative Hypothesis is a statement that “something is different from what usually happens.” The Alternative Hypothesis is usually denoted by [latex]H_{1}[/latex], [latex]H_{A}[/latex], or [latex]H_{a}[/latex], followed by other symbols and notation that describe how the parameter is different from some value.
Significance Level: We previous learned about the significance level as the “left over” stuff from the confidence level. This is still true, but we will now focus more on the significance level as its own value, and we will use the symbol alpha, [latex]\alpha[/latex]. This looks like a lowercase “a,” or a drawing of a little fish. The significance level [latex]\alpha[/latex] is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is actually true (more on what this means in the next section). The common values are still similar to what we had previously, 1%, 5%, and 10%. We commonly write these as decimals instead, 0.01, 0.05, and 0.10.
Test Statistic: One of the key components of a hypothesis test is what we call a test statistic . This is a calculation, sort of like a z-score, that is specific to the type of test being conducted. The idea behind a test statistic, relating it back to science projects, would be like calculations from measurements that were taken. In this chapter we will address the test statistic for 1 proportion, 1 mean when we know [latex]\sigma[/latex], and 1 mean with [latex]\sigma[/latex] unknown. The formulas are listed in the table below:
Critical Region: The critical region , also known as the rejection region , is the area in the normal (or other) distribution in which we reject the null hypothesis. Think of the critical region like a target area that you are aiming for. If we are able to get a value in this region, it means we have evidence for the claim.
Critical Value: These are like special z-scores for us; the critical value (or values, sometimes there are two) separates the critical region from the rest of the distribution. This is the non-target part, or what we are not aiming for. If our value is in this region, we do not have evidence for the claim.
P-Value: This is a special value that we compute. If we assume the null hypothesis is true, the p-value represents the probability that a test statistic is at least as extreme as the one we computed from our sample data; for us the test statistics would be either [latex]z[/latex] or [latex]t[/latex].
Decision Rule for Hypothesis Testing: There are a few ways we can arrive at our decision with a hypothesis test. We can arrive at our conclusion by using confidence intervals, critical values (also known as traditional method), and using p-values. Relating this to a science project, the decision rule would be what we take into consideration to arrive at our conclusion. When we make our decision, the wording will sound a little strange. We’ll say things like “we have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis” or “there is insufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis.”
Decision Rule with Critical Values: If the test statistic is in the critical region, we have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis. We can also say we have sufficient evidence to support the claim. If the test statistic is not in the critical region, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. We can also say we do not have sufficient evidence to support the claim.
Decision Rule with P-Values: If the p-value is less than or equal to the significance level, we have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis. We can also say we have sufficient evidence to support the claim. If the p-value is greater than the significance level, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. We can also say we do not have sufficient evidence to support the claim.
More About Hypotheses
Writing the Null and Alternative Hypothesis can be tricky. Here are a few examples of claims followed by the respective hypotheses:
Basic Statistics Copyright © by Allyn Leon is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Choosing the Right Statistical Test | Types & Examples
Choosing the Right Statistical Test | Types & Examples
Published on January 28, 2020 by Rebecca Bevans . Revised on June 22, 2023.
Statistical tests are used in hypothesis testing . They can be used to:
- determine whether a predictor variable has a statistically significant relationship with an outcome variable.
- estimate the difference between two or more groups.
Statistical tests assume a null hypothesis of no relationship or no difference between groups. Then they determine whether the observed data fall outside of the range of values predicted by the null hypothesis.
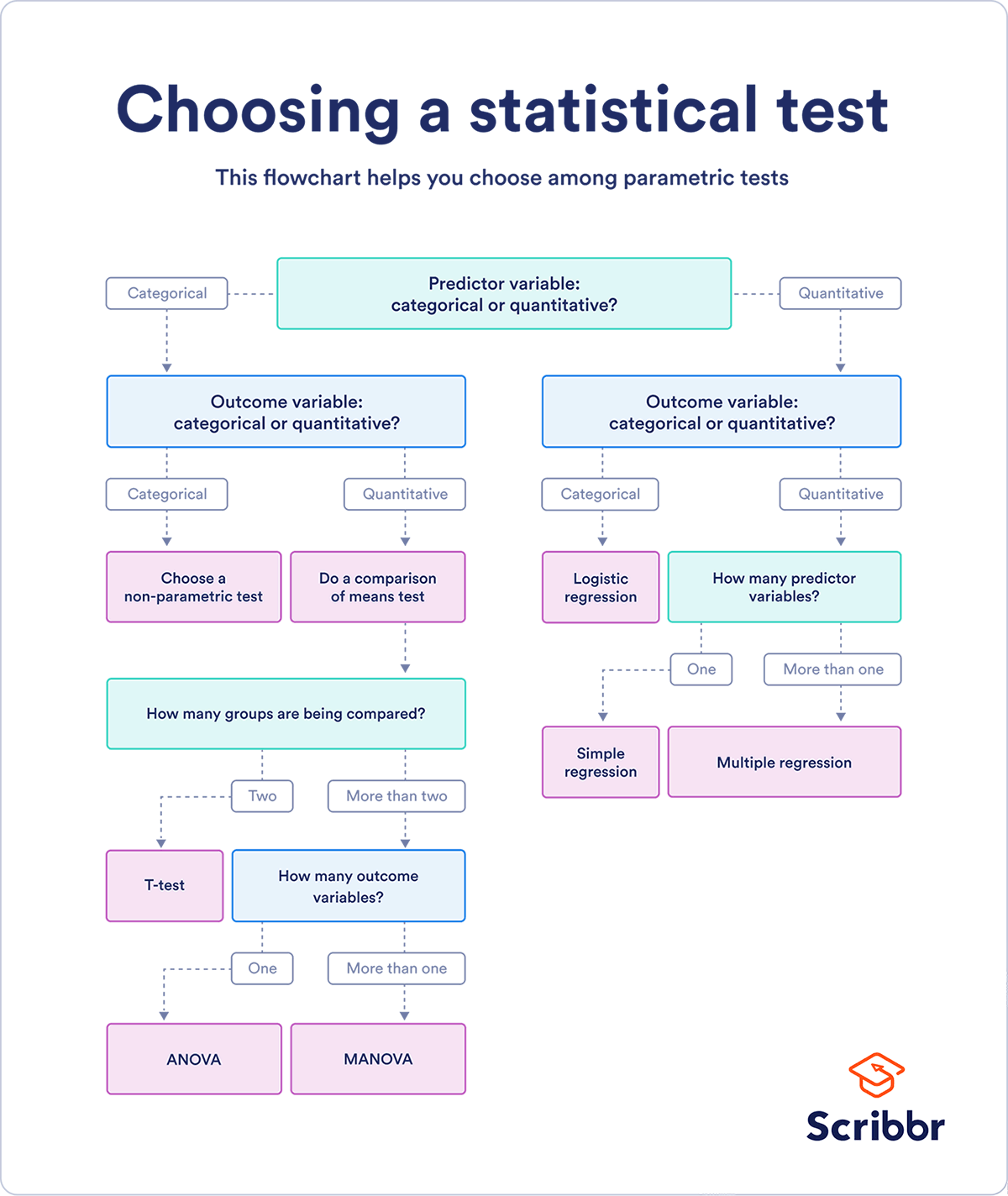
If you already know what types of variables you’re dealing with, you can use the flowchart to choose the right statistical test for your data.
Statistical tests flowchart
Table of contents
What does a statistical test do, when to perform a statistical test, choosing a parametric test: regression, comparison, or correlation, choosing a nonparametric test, flowchart: choosing a statistical test, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about statistical tests.
Statistical tests work by calculating a test statistic – a number that describes how much the relationship between variables in your test differs from the null hypothesis of no relationship.
It then calculates a p value (probability value). The p -value estimates how likely it is that you would see the difference described by the test statistic if the null hypothesis of no relationship were true.
If the value of the test statistic is more extreme than the statistic calculated from the null hypothesis, then you can infer a statistically significant relationship between the predictor and outcome variables.
If the value of the test statistic is less extreme than the one calculated from the null hypothesis, then you can infer no statistically significant relationship between the predictor and outcome variables.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
You can perform statistical tests on data that have been collected in a statistically valid manner – either through an experiment , or through observations made using probability sampling methods .
For a statistical test to be valid , your sample size needs to be large enough to approximate the true distribution of the population being studied.
To determine which statistical test to use, you need to know:
- whether your data meets certain assumptions.
- the types of variables that you’re dealing with.
Statistical assumptions
Statistical tests make some common assumptions about the data they are testing:
- Independence of observations (a.k.a. no autocorrelation): The observations/variables you include in your test are not related (for example, multiple measurements of a single test subject are not independent, while measurements of multiple different test subjects are independent).
- Homogeneity of variance : the variance within each group being compared is similar among all groups. If one group has much more variation than others, it will limit the test’s effectiveness.
- Normality of data : the data follows a normal distribution (a.k.a. a bell curve). This assumption applies only to quantitative data .
If your data do not meet the assumptions of normality or homogeneity of variance, you may be able to perform a nonparametric statistical test , which allows you to make comparisons without any assumptions about the data distribution.
If your data do not meet the assumption of independence of observations, you may be able to use a test that accounts for structure in your data (repeated-measures tests or tests that include blocking variables).
Types of variables
The types of variables you have usually determine what type of statistical test you can use.
Quantitative variables represent amounts of things (e.g. the number of trees in a forest). Types of quantitative variables include:
- Continuous (aka ratio variables): represent measures and can usually be divided into units smaller than one (e.g. 0.75 grams).
- Discrete (aka integer variables): represent counts and usually can’t be divided into units smaller than one (e.g. 1 tree).
Categorical variables represent groupings of things (e.g. the different tree species in a forest). Types of categorical variables include:
- Ordinal : represent data with an order (e.g. rankings).
- Nominal : represent group names (e.g. brands or species names).
- Binary : represent data with a yes/no or 1/0 outcome (e.g. win or lose).
Choose the test that fits the types of predictor and outcome variables you have collected (if you are doing an experiment , these are the independent and dependent variables ). Consult the tables below to see which test best matches your variables.
Parametric tests usually have stricter requirements than nonparametric tests, and are able to make stronger inferences from the data. They can only be conducted with data that adheres to the common assumptions of statistical tests.
The most common types of parametric test include regression tests, comparison tests, and correlation tests.
Regression tests
Regression tests look for cause-and-effect relationships . They can be used to estimate the effect of one or more continuous variables on another variable.
Comparison tests
Comparison tests look for differences among group means . They can be used to test the effect of a categorical variable on the mean value of some other characteristic.
T-tests are used when comparing the means of precisely two groups (e.g., the average heights of men and women). ANOVA and MANOVA tests are used when comparing the means of more than two groups (e.g., the average heights of children, teenagers, and adults).
Correlation tests
Correlation tests check whether variables are related without hypothesizing a cause-and-effect relationship.
These can be used to test whether two variables you want to use in (for example) a multiple regression test are autocorrelated.
Non-parametric tests don’t make as many assumptions about the data, and are useful when one or more of the common statistical assumptions are violated. However, the inferences they make aren’t as strong as with parametric tests.
This flowchart helps you choose among parametric tests. For nonparametric alternatives, check the table above.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Descriptive statistics
- Measures of central tendency
- Correlation coefficient
- Null hypothesis
Methodology
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Types of interviews
- Cohort study
- Thematic analysis
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Survivorship bias
- Availability heuristic
- Nonresponse bias
- Regression to the mean
Statistical tests commonly assume that:
- the data are normally distributed
- the groups that are being compared have similar variance
- the data are independent
If your data does not meet these assumptions you might still be able to use a nonparametric statistical test , which have fewer requirements but also make weaker inferences.
A test statistic is a number calculated by a statistical test . It describes how far your observed data is from the null hypothesis of no relationship between variables or no difference among sample groups.
The test statistic tells you how different two or more groups are from the overall population mean , or how different a linear slope is from the slope predicted by a null hypothesis . Different test statistics are used in different statistical tests.
Statistical significance is a term used by researchers to state that it is unlikely their observations could have occurred under the null hypothesis of a statistical test . Significance is usually denoted by a p -value , or probability value.
Statistical significance is arbitrary – it depends on the threshold, or alpha value, chosen by the researcher. The most common threshold is p < 0.05, which means that the data is likely to occur less than 5% of the time under the null hypothesis .
When the p -value falls below the chosen alpha value, then we say the result of the test is statistically significant.
Quantitative variables are any variables where the data represent amounts (e.g. height, weight, or age).
Categorical variables are any variables where the data represent groups. This includes rankings (e.g. finishing places in a race), classifications (e.g. brands of cereal), and binary outcomes (e.g. coin flips).
You need to know what type of variables you are working with to choose the right statistical test for your data and interpret your results .
Discrete and continuous variables are two types of quantitative variables :
- Discrete variables represent counts (e.g. the number of objects in a collection).
- Continuous variables represent measurable amounts (e.g. water volume or weight).
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bevans, R. (2023, June 22). Choosing the Right Statistical Test | Types & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved March 26, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/statistics/statistical-tests/
Is this article helpful?
Rebecca Bevans
Other students also liked, hypothesis testing | a step-by-step guide with easy examples, test statistics | definition, interpretation, and examples, normal distribution | examples, formulas, & uses, what is your plagiarism score.
Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing is a tool for making statistical inferences about the population data. It is an analysis tool that tests assumptions and determines how likely something is within a given standard of accuracy. Hypothesis testing provides a way to verify whether the results of an experiment are valid.
A null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis are set up before performing the hypothesis testing. This helps to arrive at a conclusion regarding the sample obtained from the population. In this article, we will learn more about hypothesis testing, its types, steps to perform the testing, and associated examples.
What is Hypothesis Testing in Statistics?
Hypothesis testing uses sample data from the population to draw useful conclusions regarding the population probability distribution . It tests an assumption made about the data using different types of hypothesis testing methodologies. The hypothesis testing results in either rejecting or not rejecting the null hypothesis.
Hypothesis Testing Definition
Hypothesis testing can be defined as a statistical tool that is used to identify if the results of an experiment are meaningful or not. It involves setting up a null hypothesis and an alternative hypothesis. These two hypotheses will always be mutually exclusive. This means that if the null hypothesis is true then the alternative hypothesis is false and vice versa. An example of hypothesis testing is setting up a test to check if a new medicine works on a disease in a more efficient manner.
Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis is a concise mathematical statement that is used to indicate that there is no difference between two possibilities. In other words, there is no difference between certain characteristics of data. This hypothesis assumes that the outcomes of an experiment are based on chance alone. It is denoted as \(H_{0}\). Hypothesis testing is used to conclude if the null hypothesis can be rejected or not. Suppose an experiment is conducted to check if girls are shorter than boys at the age of 5. The null hypothesis will say that they are the same height.
Alternative Hypothesis
The alternative hypothesis is an alternative to the null hypothesis. It is used to show that the observations of an experiment are due to some real effect. It indicates that there is a statistical significance between two possible outcomes and can be denoted as \(H_{1}\) or \(H_{a}\). For the above-mentioned example, the alternative hypothesis would be that girls are shorter than boys at the age of 5.
Hypothesis Testing P Value
In hypothesis testing, the p value is used to indicate whether the results obtained after conducting a test are statistically significant or not. It also indicates the probability of making an error in rejecting or not rejecting the null hypothesis.This value is always a number between 0 and 1. The p value is compared to an alpha level, \(\alpha\) or significance level. The alpha level can be defined as the acceptable risk of incorrectly rejecting the null hypothesis. The alpha level is usually chosen between 1% to 5%.
Hypothesis Testing Critical region
All sets of values that lead to rejecting the null hypothesis lie in the critical region. Furthermore, the value that separates the critical region from the non-critical region is known as the critical value.
Hypothesis Testing Formula
Depending upon the type of data available and the size, different types of hypothesis testing are used to determine whether the null hypothesis can be rejected or not. The hypothesis testing formula for some important test statistics are given below:
- z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\). \(\overline{x}\) is the sample mean, \(\mu\) is the population mean, \(\sigma\) is the population standard deviation and n is the size of the sample.
- t = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}\). s is the sample standard deviation.
- \(\chi ^{2} = \sum \frac{(O_{i}-E_{i})^{2}}{E_{i}}\). \(O_{i}\) is the observed value and \(E_{i}\) is the expected value.
We will learn more about these test statistics in the upcoming section.
Types of Hypothesis Testing
Selecting the correct test for performing hypothesis testing can be confusing. These tests are used to determine a test statistic on the basis of which the null hypothesis can either be rejected or not rejected. Some of the important tests used for hypothesis testing are given below.
Hypothesis Testing Z Test
A z test is a way of hypothesis testing that is used for a large sample size (n ≥ 30). It is used to determine whether there is a difference between the population mean and the sample mean when the population standard deviation is known. It can also be used to compare the mean of two samples. It is used to compute the z test statistic. The formulas are given as follows:
- One sample: z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\).
- Two samples: z = \(\frac{(\overline{x_{1}}-\overline{x_{2}})-(\mu_{1}-\mu_{2})}{\sqrt{\frac{\sigma_{1}^{2}}{n_{1}}+\frac{\sigma_{2}^{2}}{n_{2}}}}\).
Hypothesis Testing t Test
The t test is another method of hypothesis testing that is used for a small sample size (n < 30). It is also used to compare the sample mean and population mean. However, the population standard deviation is not known. Instead, the sample standard deviation is known. The mean of two samples can also be compared using the t test.
- One sample: t = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}\).
- Two samples: t = \(\frac{(\overline{x_{1}}-\overline{x_{2}})-(\mu_{1}-\mu_{2})}{\sqrt{\frac{s_{1}^{2}}{n_{1}}+\frac{s_{2}^{2}}{n_{2}}}}\).
Hypothesis Testing Chi Square
The Chi square test is a hypothesis testing method that is used to check whether the variables in a population are independent or not. It is used when the test statistic is chi-squared distributed.
One Tailed Hypothesis Testing
One tailed hypothesis testing is done when the rejection region is only in one direction. It can also be known as directional hypothesis testing because the effects can be tested in one direction only. This type of testing is further classified into the right tailed test and left tailed test.
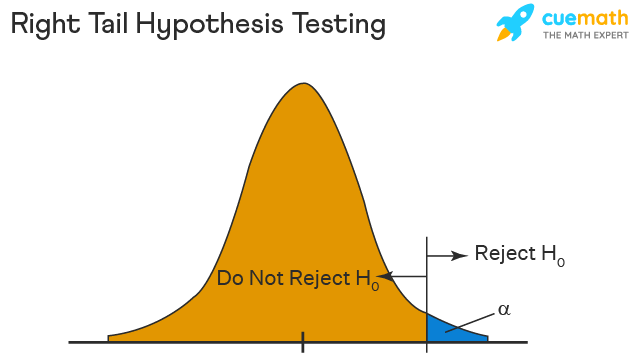
Right Tailed Hypothesis Testing
The right tail test is also known as the upper tail test. This test is used to check whether the population parameter is greater than some value. The null and alternative hypotheses for this test are given as follows:
\(H_{0}\): The population parameter is ≤ some value
\(H_{1}\): The population parameter is > some value.
If the test statistic has a greater value than the critical value then the null hypothesis is rejected
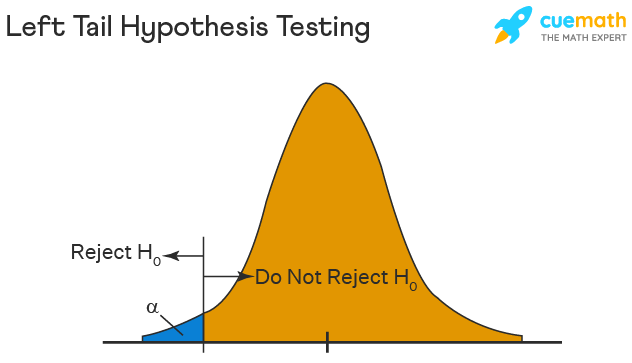
Left Tailed Hypothesis Testing
The left tail test is also known as the lower tail test. It is used to check whether the population parameter is less than some value. The hypotheses for this hypothesis testing can be written as follows:
\(H_{0}\): The population parameter is ≥ some value
\(H_{1}\): The population parameter is < some value.
The null hypothesis is rejected if the test statistic has a value lesser than the critical value.
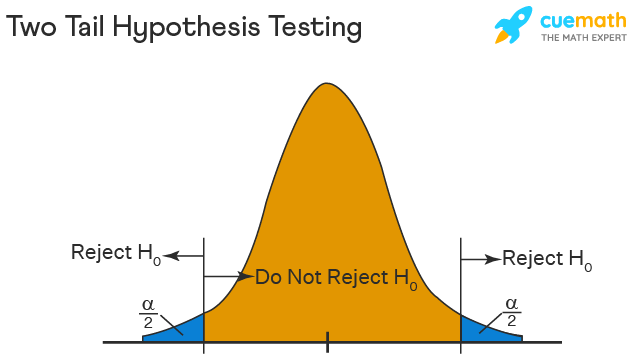
Two Tailed Hypothesis Testing
In this hypothesis testing method, the critical region lies on both sides of the sampling distribution. It is also known as a non - directional hypothesis testing method. The two-tailed test is used when it needs to be determined if the population parameter is assumed to be different than some value. The hypotheses can be set up as follows:
\(H_{0}\): the population parameter = some value
\(H_{1}\): the population parameter ≠ some value
The null hypothesis is rejected if the test statistic has a value that is not equal to the critical value.
Hypothesis Testing Steps
Hypothesis testing can be easily performed in five simple steps. The most important step is to correctly set up the hypotheses and identify the right method for hypothesis testing. The basic steps to perform hypothesis testing are as follows:
- Step 1: Set up the null hypothesis by correctly identifying whether it is the left-tailed, right-tailed, or two-tailed hypothesis testing.
- Step 2: Set up the alternative hypothesis.
- Step 3: Choose the correct significance level, \(\alpha\), and find the critical value.
- Step 4: Calculate the correct test statistic (z, t or \(\chi\)) and p-value.
- Step 5: Compare the test statistic with the critical value or compare the p-value with \(\alpha\) to arrive at a conclusion. In other words, decide if the null hypothesis is to be rejected or not.
Hypothesis Testing Example
The best way to solve a problem on hypothesis testing is by applying the 5 steps mentioned in the previous section. Suppose a researcher claims that the mean average weight of men is greater than 100kgs with a standard deviation of 15kgs. 30 men are chosen with an average weight of 112.5 Kgs. Using hypothesis testing, check if there is enough evidence to support the researcher's claim. The confidence interval is given as 95%.
Step 1: This is an example of a right-tailed test. Set up the null hypothesis as \(H_{0}\): \(\mu\) = 100.
Step 2: The alternative hypothesis is given by \(H_{1}\): \(\mu\) > 100.
Step 3: As this is a one-tailed test, \(\alpha\) = 100% - 95% = 5%. This can be used to determine the critical value.
1 - \(\alpha\) = 1 - 0.05 = 0.95
0.95 gives the required area under the curve. Now using a normal distribution table, the area 0.95 is at z = 1.645. A similar process can be followed for a t-test. The only additional requirement is to calculate the degrees of freedom given by n - 1.
Step 4: Calculate the z test statistic. This is because the sample size is 30. Furthermore, the sample and population means are known along with the standard deviation.
z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\).
\(\mu\) = 100, \(\overline{x}\) = 112.5, n = 30, \(\sigma\) = 15
z = \(\frac{112.5-100}{\frac{15}{\sqrt{30}}}\) = 4.56
Step 5: Conclusion. As 4.56 > 1.645 thus, the null hypothesis can be rejected.
Hypothesis Testing and Confidence Intervals
Confidence intervals form an important part of hypothesis testing. This is because the alpha level can be determined from a given confidence interval. Suppose a confidence interval is given as 95%. Subtract the confidence interval from 100%. This gives 100 - 95 = 5% or 0.05. This is the alpha value of a one-tailed hypothesis testing. To obtain the alpha value for a two-tailed hypothesis testing, divide this value by 2. This gives 0.05 / 2 = 0.025.
Related Articles:
- Probability and Statistics
- Data Handling
Important Notes on Hypothesis Testing
- Hypothesis testing is a technique that is used to verify whether the results of an experiment are statistically significant.
- It involves the setting up of a null hypothesis and an alternate hypothesis.
- There are three types of tests that can be conducted under hypothesis testing - z test, t test, and chi square test.
- Hypothesis testing can be classified as right tail, left tail, and two tail tests.
Examples on Hypothesis Testing
- Example 1: The average weight of a dumbbell in a gym is 90lbs. However, a physical trainer believes that the average weight might be higher. A random sample of 5 dumbbells with an average weight of 110lbs and a standard deviation of 18lbs. Using hypothesis testing check if the physical trainer's claim can be supported for a 95% confidence level. Solution: As the sample size is lesser than 30, the t-test is used. \(H_{0}\): \(\mu\) = 90, \(H_{1}\): \(\mu\) > 90 \(\overline{x}\) = 110, \(\mu\) = 90, n = 5, s = 18. \(\alpha\) = 0.05 Using the t-distribution table, the critical value is 2.132 t = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}\) t = 2.484 As 2.484 > 2.132, the null hypothesis is rejected. Answer: The average weight of the dumbbells may be greater than 90lbs
- Example 2: The average score on a test is 80 with a standard deviation of 10. With a new teaching curriculum introduced it is believed that this score will change. On random testing, the score of 38 students, the mean was found to be 88. With a 0.05 significance level, is there any evidence to support this claim? Solution: This is an example of two-tail hypothesis testing. The z test will be used. \(H_{0}\): \(\mu\) = 80, \(H_{1}\): \(\mu\) ≠ 80 \(\overline{x}\) = 88, \(\mu\) = 80, n = 36, \(\sigma\) = 10. \(\alpha\) = 0.05 / 2 = 0.025 The critical value using the normal distribution table is 1.96 z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\) z = \(\frac{88-80}{\frac{10}{\sqrt{36}}}\) = 4.8 As 4.8 > 1.96, the null hypothesis is rejected. Answer: There is a difference in the scores after the new curriculum was introduced.
- Example 3: The average score of a class is 90. However, a teacher believes that the average score might be lower. The scores of 6 students were randomly measured. The mean was 82 with a standard deviation of 18. With a 0.05 significance level use hypothesis testing to check if this claim is true. Solution: The t test will be used. \(H_{0}\): \(\mu\) = 90, \(H_{1}\): \(\mu\) < 90 \(\overline{x}\) = 110, \(\mu\) = 90, n = 6, s = 18 The critical value from the t table is -2.015 t = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{s}{\sqrt{n}}}\) t = \(\frac{82-90}{\frac{18}{\sqrt{6}}}\) t = -1.088 As -1.088 > -2.015, we fail to reject the null hypothesis. Answer: There is not enough evidence to support the claim.
go to slide go to slide go to slide

Book a Free Trial Class
FAQs on Hypothesis Testing
What is hypothesis testing.
Hypothesis testing in statistics is a tool that is used to make inferences about the population data. It is also used to check if the results of an experiment are valid.
What is the z Test in Hypothesis Testing?
The z test in hypothesis testing is used to find the z test statistic for normally distributed data . The z test is used when the standard deviation of the population is known and the sample size is greater than or equal to 30.
What is the t Test in Hypothesis Testing?
The t test in hypothesis testing is used when the data follows a student t distribution . It is used when the sample size is less than 30 and standard deviation of the population is not known.
What is the formula for z test in Hypothesis Testing?
The formula for a one sample z test in hypothesis testing is z = \(\frac{\overline{x}-\mu}{\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}}}\) and for two samples is z = \(\frac{(\overline{x_{1}}-\overline{x_{2}})-(\mu_{1}-\mu_{2})}{\sqrt{\frac{\sigma_{1}^{2}}{n_{1}}+\frac{\sigma_{2}^{2}}{n_{2}}}}\).
What is the p Value in Hypothesis Testing?
The p value helps to determine if the test results are statistically significant or not. In hypothesis testing, the null hypothesis can either be rejected or not rejected based on the comparison between the p value and the alpha level.
What is One Tail Hypothesis Testing?
When the rejection region is only on one side of the distribution curve then it is known as one tail hypothesis testing. The right tail test and the left tail test are two types of directional hypothesis testing.
What is the Alpha Level in Two Tail Hypothesis Testing?
To get the alpha level in a two tail hypothesis testing divide \(\alpha\) by 2. This is done as there are two rejection regions in the curve.
Hypothesis Testing Framework
Now that we've seen an example and explored some of the themes for hypothesis testing, let's specify the procedure that we will follow.
Hypothesis Testing Steps
The formal framework and steps for hypothesis testing are as follows:
- Identify and define the parameter of interest
- Define the competing hypotheses to test
- Set the evidence threshold, formally called the significance level
- Generate or use theory to specify the sampling distribution and check conditions
- Calculate the test statistic and p-value
- Evaluate your results and write a conclusion in the context of the problem.
We'll discuss each of these steps below.
Identify Parameter of Interest
First, I like to specify and define the parameter of interest. What is the population that we are interested in? What characteristic are we measuring?
By defining our population of interest, we can confirm that we are truly using sample data. If we find that we actually have population data, our inference procedures are not needed. We could proceed by summarizing our population data.
By identifying and defining the parameter of interest, we can confirm that we use appropriate methods to summarize our variable of interest. We can also focus on the specific process needed for our parameter of interest.
In our example from the last page, the parameter of interest would be the population mean time that a host has been on Airbnb for the population of all Chicago listings on Airbnb in March 2023. We could represent this parameter with the symbol $\mu$. It is best practice to fully define $\mu$ both with words and symbol.
Define the Hypotheses
For hypothesis testing, we need to decide between two competing theories. These theories must be statements about the parameter. Although we won't have the population data to definitively select the correct theory, we will use our sample data to determine how reasonable our "skeptic's theory" is.
The first hypothesis is called the null hypothesis, $H_0$. This can be thought of as the "status quo", the "skeptic's theory", or that nothing is happening.
Examples of null hypotheses include that the population proportion is equal to 0.5 ($p = 0.5$), the population median is equal to 12 ($M = 12$), or the population mean is equal to 14.5 ($\mu = 14.5$).
The second hypothesis is called the alternative hypothesis, $H_a$ or $H_1$. This can be thought of as the "researcher's hypothesis" or that something is happening. This is what we'd like to convince the skeptic to believe. In most cases, the desired outcome of the researcher is to conclude that the alternative hypothesis is reasonable to use moving forward.
Examples of alternative hypotheses include that the population proportion is greater than 0.5 ($p > 0.5$), the population median is less than 12 ($M < 12$), or the population mean is not equal to 14.5 ($\mu \neq 14.5$).
There are a few requirements for the hypotheses:
- the hypotheses must be about the same population parameter,
- the hypotheses must have the same null value (provided number to compare to),
- the null hypothesis must have the equality (the equals sign must be in the null hypothesis),
- the alternative hypothesis must not have the equality (the equals sign cannot be in the alternative hypothesis),
- there must be no overlap between the null and alternative hypothesis.
You may have previously seen null hypotheses that include more than an equality (e.g. $p \le 0.5$). As long as there is an equality in the null hypothesis, this is allowed. For our purposes, we will simplify this statement to ($p = 0.5$).
To summarize from above, possible hypotheses statements are:
$H_0: p = 0.5$ vs. $H_a: p > 0.5$
$H_0: M = 12$ vs. $H_a: M < 12$
$H_0: \mu = 14.5$ vs. $H_a: \mu \neq 14.5$
In our second example about Airbnb hosts, our hypotheses would be:
$H_0: \mu = 2100$ vs. $H_a: \mu > 2100$.
Set Threshold (Significance Level)
There is one more step to complete before looking at the data. This is to set the threshold needed to convince the skeptic. This threshold is defined as an $\alpha$ significance level. We'll define exactly what the $\alpha$ significance level means later. For now, smaller $\alpha$s correspond to more evidence being required to convince the skeptic.
A few common $\alpha$ levels include 0.1, 0.05, and 0.01.
For our Airbnb hosts example, we'll set the threshold as 0.02.
Determine the Sampling Distribution of the Sample Statistic
The first step (as outlined above) is the identify the parameter of interest. What is the best estimate of the parameter of interest? Typically, it will be the sample statistic that corresponds to the parameter. This sample statistic, along with other features of the distribution will prove especially helpful as we continue the hypothesis testing procedure.
However, we do have a decision at this step. We can choose to use simulations with a resampling approach or we can choose to rely on theory if we are using proportions or means. We then also need to confirm that our results and conclusions will be valid based on the available data.
Required Condition
The one required assumption, regardless of approach (resampling or theory), is that the sample is random and representative of the population of interest. In other words, we need our sample to be a reasonable sample of data from the population.
Using Simulations and Resampling
If we'd like to use a resampling approach, we have no (or minimal) additional assumptions to check. This is because we are relying on the available data instead of assumptions.
We do need to adjust our data to be consistent with the null hypothesis (or skeptic's claim). We can then rely on our resampling approach to estimate a plausible sampling distribution for our sample statistic.
Recall that we took this approach on the last page. Before simulating our estimated sampling distribution, we adjusted the mean of the data so that it matched with our skeptic's claim, shown in the code below.
We'll see a few more examples on the next page.
Using Theory
On the other hand, we could rely on theory in order to estimate the sampling distribution of our desired statistic. Recall that we had a few different options to rely on:
- the CLT for the sampling distribution of a sample mean
- the binomial distribution for the sampling distribution of a proportion (or count)
- the Normal approximation of a binomial distribution (using the CLT) for the sampling distribution of a proportion
If relying on the CLT to specify the underlying sampling distribution, you also need to confirm:
- having a random sample and
- having a sample size that is less than 10% of the population size if the sampling is done without replacement
- having a Normally distributed population for a quantitative variable OR
- having a large enough sample size (usually at least 25) for a quantitative variable
- having a large enough sample size for a categorical variable (defined by $np$ and $n(1-p)$ being at least 10)
If relying on the binomial distribution to specify the underlying sampling distribution, you need to confirm:
- having a set number of trials, $n$
- having the same probability of success, $p$ for each observation
After determining the appropriate theory to use, we should check our conditions and then specify the sampling distribution for our statistic.
For the Airbnb hosts example, we have what we've assumed to be a random sample. It is not taken with replacement, so we also need to assume that our sample size (700) is less than 10% of our population size. In other words, we need to assume that the population of Chicago Airbnbs in March 2023 was at least 7000. Since we do have our (presumed) population data available, we can confirm that there were at least 7000 Chicago Airbnbs in the population in 2023.
Additionally, we can confirm that normality of the sampling distribution applies for the CLT to apply. Our sample size is more than 25 and the parameter of interest is a mean, so this meets our necessary criteria for the normality condition to be valid.
With the conditions now met, we can estimate our sampling distribution. From the CLT, we know that the distribution for the sample mean should be $\bar{X} \sim N(\mu, \frac{\sigma}{\sqrt{n}})$.
Now, we face our next challenge -- what to plug in as the mean and standard error for this distribution. Since we are adopting the skeptic's point of view for the purpose of this approach, we can plug in the value of $\mu_0 = 2100$. We also know that the sample size $n$ is 700. But what should we plug in for the population standard deviation $\sigma$?
When we don't know the value of a parameter, we will generally plug in our best estimate for the parameter. In this case, that corresponds to plugging in $\hat{\sigma}$, or our sample standard deviation.
Now, our estimated sampling distribution based on the CLT is: $\bar{X} \sim N(2100, 41.4045)$.
If we compare to our corresponding skeptic's sampling distribution on the last page, we can confirm that the theoretical sampling distribution is similar to the simulated sampling distribution based on resampling.
Assumptions not met
What do we do if the necessary conditions aren't met for the sampling distribution? Because the simulation-based resampling approach has minimal assumptions, we should be able to use this approach to produce valid results as long as the provided data is representative of the population.
The theory-based approach has more conditions, and we may not be able to meet all of the necessary conditions. For example, if our parameter is something other than a mean or proportion, we may not have appropriate theory. Additionally, we may not have a large enough sample size.
- First, we could consider changing approaches to the simulation-based one.
- Second, we might look at how we could meet the necessary conditions better. In some cases, we may be able to redefine groups or make adjustments so that the setup of the test is closer to what is needed.
- As a last resort, we may be able to continue following the hypothesis testing steps. In this case, your calculations may not be valid or exact; however, you might be able to use them as an estimate or an approximation. It would be crucial to specify the violation and approximation in any conclusions or discussion of the test.
Calculate the evidence with statistics and p-values
Now, it's time to calculate how much evidence the sample contains to convince the skeptic to change their mind. As we saw above, we can convince the skeptic to change their mind by demonstrating that our sample is unlikely to occur if their theory is correct.
How do we do this? We do this by calculating a probability associated with our observed value for the statistic.
For example, for our situation, we want to convince the skeptic that the population mean is actually greater than 2100 days. We do that by calculating the probability that a sample mean would be as large or larger than what we observed in our actual sample, which was 2188 days. Why do we need the larger portion? We use the larger portion because a sample mean of 2200 days also provides evidence that the population mean is larger than 2100 days; it isn't limited to exactly what we observed in our sample. We call this specific probability the p-value.
That is, the p-value is the probability of observing a test statistic as extreme or more extreme (as determined by the alternative hypothesis), assuming the null hypothesis is true.
Our observed p-value for the Airbnb host example demonstrates that the probability of getting a sample mean host time of 2188 days (the value from our sample) or more is 1.46%, assuming that the true population mean is 2100 days.
Test statistic
Notice that the formal definition of a p-value mentions a test statistic . In most cases, this word can be replaced with "statistic" or "sample" for an equivalent statement.
Oftentimes, we'll see that our sample statistic can be used directly as the test statistic, as it was above. We could equivalently adjust our statistic to calculate a test statistic. This test statistic is often calculated as:
$\text{test statistic} = \frac{\text{estimate} - \text{hypothesized value}}{\text{standard error of estimate}}$
P-value Calculation Options
Note also that the p-value definition includes a probability associated with a test statistic being as extreme or more extreme (as determined by the alternative hypothesis . How do we determine the area that we consider when calculating the probability. This decision is determined by the inequality in the alternative hypothesis.
For example, when we were trying to convince the skeptic that the population mean is greater than 2100 days, we only considered those sample means that we at least as large as what we observed -- 2188 days or more.
If instead we were trying to convince the skeptic that the population mean is less than 2100 days ($H_a: \mu < 2100$), we would consider all sample means that were at most what we observed - 2188 days or less. In this case, our p-value would be quite large; it would be around 99.5%. This large p-value demonstrates that our sample does not support the alternative hypothesis. In fact, our sample would encourage us to choose the null hypothesis instead of the alternative hypothesis of $\mu < 2100$, as our sample directly contradicts the statement in the alternative hypothesis.
If we wanted to convince the skeptic that they were wrong and that the population mean is anything other than 2100 days ($H_a: \mu \neq 2100$), then we would want to calculate the probability that a sample mean is at least 88 days away from 2100 days. That is, we would calculate the probability corresponding to 2188 days or more or 2012 days or less. In this case, our p-value would be roughly twice the previously calculated p-value.
We could calculate all of those probabilities using our sampling distributions, either simulated or theoretical, that we generated in the previous step. If we chose to calculate a test statistic as defined in the previous section, we could also rely on standard normal distributions to calculate our p-value.
Evaluate your results and write conclusion in context of problem
Once you've gathered your evidence, it's now time to make your final conclusions and determine how you might proceed.
In traditional hypothesis testing, you often make a decision. Recall that you have your threshold (significance level $\alpha$) and your level of evidence (p-value). We can compare the two to determine if your p-value is less than or equal to your threshold. If it is, you have enough evidence to persuade your skeptic to change their mind. If it is larger than the threshold, you don't have quite enough evidence to convince the skeptic.
Common formal conclusions (if given in context) would be:
- I have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis (the skeptic's claim), and I have sufficient evidence to suggest that the alternative hypothesis is instead true.
- I do not have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis (the skeptic's claim), and so I do not have sufficient evidence to suggest the alternative hypothesis is true.
The only decision that we can make is to either reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis (we cannot "accept" the null hypothesis). Because we aren't actively evaluating the alternative hypothesis, we don't want to make definitive decisions based on that hypothesis. However, when it comes to making our conclusion for what to use going forward, we frame this on whether we could successfully convince someone of the alternative hypothesis.
A less formal conclusion might look something like:
Based on our sample of Chicago Airbnb listings, it seems as if the mean time since a host has been on Airbnb (for all Chicago Airbnb listings) is more than 5.75 years.
Significance Level Interpretation
We've now seen how the significance level $\alpha$ is used as a threshold for hypothesis testing. What exactly is the significance level?
The significance level $\alpha$ has two primary definitions. One is that the significance level is the maximum probability required to reject the null hypothesis; this is based on how the significance level functions within the hypothesis testing framework. The second definition is that this is the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when the null hypothesis is true; in other words, this is the probability of making a specific type of error called a Type I error.
Why do we have to be comfortable making a Type I error? There is always a chance that the skeptic was originally correct and we obtained a very unusual sample. We don't want to the skeptic to be so convinced of their theory that no evidence can convince them. In this case, we need the skeptic to be convinced as long as the evidence is strong enough . Typically, the probability threshold will be low, to reduce the number of errors made. This also means that a decent amount of evidence will be needed to convince the skeptic to abandon their position in favor of the alternative theory.

p-value Limitations and Misconceptions
In comparison to the $\alpha$ significance level, we also need to calculate the evidence against the null hypothesis with the p-value.
The p-value is the probability of getting a test statistic as extreme or more extreme (in the direction of the alternative hypothesis), assuming the null hypothesis is true.
Recently, p-values have gotten some bad press in terms of how they are used. However, that doesn't mean that p-values should be abandoned, as they still provide some helpful information. Below, we'll describe what p-values don't mean, and how they should or shouldn't be used to make decisions.
Factors that affect a p-value
What features affect the size of a p-value?
- the null value, or the value assumed under the null hypothesis
- the effect size (the difference between the null value under the null hypothesis and the true value of the parameter)
- the sample size
More evidence against the null hypothesis will be obtained if the effect size is larger and if the sample size is larger.
Misconceptions
We gave a definition for p-values above. What are some examples that p-values don't mean?
- A p-value is not the probability that the null hypothesis is correct
- A p-value is not the probability that the null hypothesis is incorrect
- A p-value is not the probability of getting your specific sample
- A p-value is not the probability that the alternative hypothesis is correct
- A p-value is not the probability that the alternative hypothesis is incorrect
- A p-value does not indicate the size of the effect
Our p-value is a way of measuring the evidence that your sample provides against the null hypothesis, assuming the null hypothesis is in fact correct.
Using the p-value to make a decision
Why is there bad press for a p-value? You may have heard about the standard $\alpha$ level of 0.05. That is, we would be comfortable with rejecting the null hypothesis once in 20 attempts when the null hypothesis is really true. Recall that we reject the null hypothesis when the p-value is less than or equal to the significance level.
Consider what would happen if you have two different p-values: 0.049 and 0.051.
In essence, these two p-values represent two very similar probabilities (4.9% vs. 5.1%) and very similar levels of evidence against the null hypothesis. However, when we make our decision based on our threshold, we would make two different decisions (reject and fail to reject, respectively). Should this decision really be so simplistic? I would argue that the difference shouldn't be so severe when the sample statistics are likely very similar. For this reason, I (and many other experts) strongly recommend using the p-value as a measure of evidence and including it with your conclusion.
Putting too much emphasis on the decision (and having a significant result) has created a culture of misusing p-values. For this reason, understanding your p-value itself is crucial.
Searching for p-values
The other concern with setting a definitive threshold of 0.05 is that some researchers will begin performing multiple tests until finding a p-value that is small enough. However, with a p-value of 0.05, we know that we will have a p-value less than 0.05 1 time out of every 20 times, even when the null hypothesis is true.
This means that if researchers start hunting for p-values that are small (sometimes called p-hacking), then they are likely to identify a small p-value every once in a while by chance alone. Researchers might then publish that result, even though the result is actually not informative. For this reason, it is recommended that researchers write a definitive analysis plan to prevent performing multiple tests in search of a result that occurs by chance alone.
Best Practices
With all of this in mind, what should we do when we have our p-value? How can we prevent or reduce misuse of a p-value?
- Report the p-value along with the conclusion
- Specify the effect size (the value of the statistic)
- Define an analysis plan before looking at the data
- Interpret the p-value clearly to specify what it indicates
- Consider using an alternate statistical approach, the confidence interval, discussed next, when appropriate
Tutorial Playlist
Statistics tutorial, everything you need to know about the probability density function in statistics, the best guide to understand central limit theorem, an in-depth guide to measures of central tendency : mean, median and mode, the ultimate guide to understand conditional probability.
A Comprehensive Look at Percentile in Statistics
The Best Guide to Understand Bayes Theorem
Everything you need to know about the normal distribution, an in-depth explanation of cumulative distribution function, a complete guide to chi-square test, a complete guide on hypothesis testing in statistics, understanding the fundamentals of arithmetic and geometric progression, the definitive guide to understand spearman’s rank correlation, a comprehensive guide to understand mean squared error, all you need to know about the empirical rule in statistics, the complete guide to skewness and kurtosis, a holistic look at bernoulli distribution, all you need to know about bias in statistics, a complete guide to get a grasp of time series analysis.
The Key Differences Between Z-Test Vs. T-Test
The Complete Guide to Understand Pearson's Correlation
A complete guide on the types of statistical studies, everything you need to know about poisson distribution, your best guide to understand correlation vs. regression, the most comprehensive guide for beginners on what is correlation, what is hypothesis testing in statistics types and examples.
Lesson 10 of 24 By Avijeet Biswal

Table of Contents
In today’s data-driven world , decisions are based on data all the time. Hypothesis plays a crucial role in that process, whether it may be making business decisions, in the health sector, academia, or in quality improvement. Without hypothesis & hypothesis tests, you risk drawing the wrong conclusions and making bad decisions. In this tutorial, you will look at Hypothesis Testing in Statistics.
What Is Hypothesis Testing in Statistics?
Hypothesis Testing is a type of statistical analysis in which you put your assumptions about a population parameter to the test. It is used to estimate the relationship between 2 statistical variables.
Let's discuss few examples of statistical hypothesis from real-life -
- A teacher assumes that 60% of his college's students come from lower-middle-class families.
- A doctor believes that 3D (Diet, Dose, and Discipline) is 90% effective for diabetic patients.
Now that you know about hypothesis testing, look at the two types of hypothesis testing in statistics.
Hypothesis Testing Formula
Z = ( x̅ – μ0 ) / (σ /√n)
- Here, x̅ is the sample mean,
- μ0 is the population mean,
- σ is the standard deviation,
- n is the sample size.
How Hypothesis Testing Works?
An analyst performs hypothesis testing on a statistical sample to present evidence of the plausibility of the null hypothesis. Measurements and analyses are conducted on a random sample of the population to test a theory. Analysts use a random population sample to test two hypotheses: the null and alternative hypotheses.
The null hypothesis is typically an equality hypothesis between population parameters; for example, a null hypothesis may claim that the population means return equals zero. The alternate hypothesis is essentially the inverse of the null hypothesis (e.g., the population means the return is not equal to zero). As a result, they are mutually exclusive, and only one can be correct. One of the two possibilities, however, will always be correct.
Your Dream Career is Just Around The Corner!
Null Hypothesis and Alternate Hypothesis
The Null Hypothesis is the assumption that the event will not occur. A null hypothesis has no bearing on the study's outcome unless it is rejected.
H0 is the symbol for it, and it is pronounced H-naught.
The Alternate Hypothesis is the logical opposite of the null hypothesis. The acceptance of the alternative hypothesis follows the rejection of the null hypothesis. H1 is the symbol for it.
Let's understand this with an example.
A sanitizer manufacturer claims that its product kills 95 percent of germs on average.
To put this company's claim to the test, create a null and alternate hypothesis.
H0 (Null Hypothesis): Average = 95%.
Alternative Hypothesis (H1): The average is less than 95%.
Another straightforward example to understand this concept is determining whether or not a coin is fair and balanced. The null hypothesis states that the probability of a show of heads is equal to the likelihood of a show of tails. In contrast, the alternate theory states that the probability of a show of heads and tails would be very different.
Become a Data Scientist with Hands-on Training!
Hypothesis Testing Calculation With Examples
Let's consider a hypothesis test for the average height of women in the United States. Suppose our null hypothesis is that the average height is 5'4". We gather a sample of 100 women and determine that their average height is 5'5". The standard deviation of population is 2.
To calculate the z-score, we would use the following formula:
z = ( x̅ – μ0 ) / (σ /√n)
z = (5'5" - 5'4") / (2" / √100)
z = 0.5 / (0.045)
We will reject the null hypothesis as the z-score of 11.11 is very large and conclude that there is evidence to suggest that the average height of women in the US is greater than 5'4".
Steps of Hypothesis Testing
Step 1: specify your null and alternate hypotheses.
It is critical to rephrase your original research hypothesis (the prediction that you wish to study) as a null (Ho) and alternative (Ha) hypothesis so that you can test it quantitatively. Your first hypothesis, which predicts a link between variables, is generally your alternate hypothesis. The null hypothesis predicts no link between the variables of interest.
Step 2: Gather Data
For a statistical test to be legitimate, sampling and data collection must be done in a way that is meant to test your hypothesis. You cannot draw statistical conclusions about the population you are interested in if your data is not representative.
Step 3: Conduct a Statistical Test
Other statistical tests are available, but they all compare within-group variance (how to spread out the data inside a category) against between-group variance (how different the categories are from one another). If the between-group variation is big enough that there is little or no overlap between groups, your statistical test will display a low p-value to represent this. This suggests that the disparities between these groups are unlikely to have occurred by accident. Alternatively, if there is a large within-group variance and a low between-group variance, your statistical test will show a high p-value. Any difference you find across groups is most likely attributable to chance. The variety of variables and the level of measurement of your obtained data will influence your statistical test selection.
Step 4: Determine Rejection Of Your Null Hypothesis
Your statistical test results must determine whether your null hypothesis should be rejected or not. In most circumstances, you will base your judgment on the p-value provided by the statistical test. In most circumstances, your preset level of significance for rejecting the null hypothesis will be 0.05 - that is, when there is less than a 5% likelihood that these data would be seen if the null hypothesis were true. In other circumstances, researchers use a lower level of significance, such as 0.01 (1%). This reduces the possibility of wrongly rejecting the null hypothesis.
Step 5: Present Your Results
The findings of hypothesis testing will be discussed in the results and discussion portions of your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. You should include a concise overview of the data and a summary of the findings of your statistical test in the results section. You can talk about whether your results confirmed your initial hypothesis or not in the conversation. Rejecting or failing to reject the null hypothesis is a formal term used in hypothesis testing. This is likely a must for your statistics assignments.
Types of Hypothesis Testing
To determine whether a discovery or relationship is statistically significant, hypothesis testing uses a z-test. It usually checks to see if two means are the same (the null hypothesis). Only when the population standard deviation is known and the sample size is 30 data points or more, can a z-test be applied.
A statistical test called a t-test is employed to compare the means of two groups. To determine whether two groups differ or if a procedure or treatment affects the population of interest, it is frequently used in hypothesis testing.
Chi-Square
You utilize a Chi-square test for hypothesis testing concerning whether your data is as predicted. To determine if the expected and observed results are well-fitted, the Chi-square test analyzes the differences between categorical variables from a random sample. The test's fundamental premise is that the observed values in your data should be compared to the predicted values that would be present if the null hypothesis were true.
Hypothesis Testing and Confidence Intervals
Both confidence intervals and hypothesis tests are inferential techniques that depend on approximating the sample distribution. Data from a sample is used to estimate a population parameter using confidence intervals. Data from a sample is used in hypothesis testing to examine a given hypothesis. We must have a postulated parameter to conduct hypothesis testing.
Bootstrap distributions and randomization distributions are created using comparable simulation techniques. The observed sample statistic is the focal point of a bootstrap distribution, whereas the null hypothesis value is the focal point of a randomization distribution.
A variety of feasible population parameter estimates are included in confidence ranges. In this lesson, we created just two-tailed confidence intervals. There is a direct connection between these two-tail confidence intervals and these two-tail hypothesis tests. The results of a two-tailed hypothesis test and two-tailed confidence intervals typically provide the same results. In other words, a hypothesis test at the 0.05 level will virtually always fail to reject the null hypothesis if the 95% confidence interval contains the predicted value. A hypothesis test at the 0.05 level will nearly certainly reject the null hypothesis if the 95% confidence interval does not include the hypothesized parameter.
Simple and Composite Hypothesis Testing
Depending on the population distribution, you can classify the statistical hypothesis into two types.
Simple Hypothesis: A simple hypothesis specifies an exact value for the parameter.
Composite Hypothesis: A composite hypothesis specifies a range of values.
A company is claiming that their average sales for this quarter are 1000 units. This is an example of a simple hypothesis.
Suppose the company claims that the sales are in the range of 900 to 1000 units. Then this is a case of a composite hypothesis.
One-Tailed and Two-Tailed Hypothesis Testing
The One-Tailed test, also called a directional test, considers a critical region of data that would result in the null hypothesis being rejected if the test sample falls into it, inevitably meaning the acceptance of the alternate hypothesis.
In a one-tailed test, the critical distribution area is one-sided, meaning the test sample is either greater or lesser than a specific value.
In two tails, the test sample is checked to be greater or less than a range of values in a Two-Tailed test, implying that the critical distribution area is two-sided.
If the sample falls within this range, the alternate hypothesis will be accepted, and the null hypothesis will be rejected.
Become a Data Scientist With Real-World Experience
Right Tailed Hypothesis Testing
If the larger than (>) sign appears in your hypothesis statement, you are using a right-tailed test, also known as an upper test. Or, to put it another way, the disparity is to the right. For instance, you can contrast the battery life before and after a change in production. Your hypothesis statements can be the following if you want to know if the battery life is longer than the original (let's say 90 hours):
- The null hypothesis is (H0 <= 90) or less change.
- A possibility is that battery life has risen (H1) > 90.
The crucial point in this situation is that the alternate hypothesis (H1), not the null hypothesis, decides whether you get a right-tailed test.
Left Tailed Hypothesis Testing
Alternative hypotheses that assert the true value of a parameter is lower than the null hypothesis are tested with a left-tailed test; they are indicated by the asterisk "<".
Suppose H0: mean = 50 and H1: mean not equal to 50
According to the H1, the mean can be greater than or less than 50. This is an example of a Two-tailed test.
In a similar manner, if H0: mean >=50, then H1: mean <50
Here the mean is less than 50. It is called a One-tailed test.
Type 1 and Type 2 Error
A hypothesis test can result in two types of errors.
Type 1 Error: A Type-I error occurs when sample results reject the null hypothesis despite being true.
Type 2 Error: A Type-II error occurs when the null hypothesis is not rejected when it is false, unlike a Type-I error.
Suppose a teacher evaluates the examination paper to decide whether a student passes or fails.
H0: Student has passed
H1: Student has failed
Type I error will be the teacher failing the student [rejects H0] although the student scored the passing marks [H0 was true].
Type II error will be the case where the teacher passes the student [do not reject H0] although the student did not score the passing marks [H1 is true].
Level of Significance
The alpha value is a criterion for determining whether a test statistic is statistically significant. In a statistical test, Alpha represents an acceptable probability of a Type I error. Because alpha is a probability, it can be anywhere between 0 and 1. In practice, the most commonly used alpha values are 0.01, 0.05, and 0.1, which represent a 1%, 5%, and 10% chance of a Type I error, respectively (i.e. rejecting the null hypothesis when it is in fact correct).
Future-Proof Your AI/ML Career: Top Dos and Don'ts
A p-value is a metric that expresses the likelihood that an observed difference could have occurred by chance. As the p-value decreases the statistical significance of the observed difference increases. If the p-value is too low, you reject the null hypothesis.
Here you have taken an example in which you are trying to test whether the new advertising campaign has increased the product's sales. The p-value is the likelihood that the null hypothesis, which states that there is no change in the sales due to the new advertising campaign, is true. If the p-value is .30, then there is a 30% chance that there is no increase or decrease in the product's sales. If the p-value is 0.03, then there is a 3% probability that there is no increase or decrease in the sales value due to the new advertising campaign. As you can see, the lower the p-value, the chances of the alternate hypothesis being true increases, which means that the new advertising campaign causes an increase or decrease in sales.
Why is Hypothesis Testing Important in Research Methodology?
Hypothesis testing is crucial in research methodology for several reasons:
- Provides evidence-based conclusions: It allows researchers to make objective conclusions based on empirical data, providing evidence to support or refute their research hypotheses.
- Supports decision-making: It helps make informed decisions, such as accepting or rejecting a new treatment, implementing policy changes, or adopting new practices.
- Adds rigor and validity: It adds scientific rigor to research using statistical methods to analyze data, ensuring that conclusions are based on sound statistical evidence.
- Contributes to the advancement of knowledge: By testing hypotheses, researchers contribute to the growth of knowledge in their respective fields by confirming existing theories or discovering new patterns and relationships.
Limitations of Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing has some limitations that researchers should be aware of:
- It cannot prove or establish the truth: Hypothesis testing provides evidence to support or reject a hypothesis, but it cannot confirm the absolute truth of the research question.
- Results are sample-specific: Hypothesis testing is based on analyzing a sample from a population, and the conclusions drawn are specific to that particular sample.
- Possible errors: During hypothesis testing, there is a chance of committing type I error (rejecting a true null hypothesis) or type II error (failing to reject a false null hypothesis).
- Assumptions and requirements: Different tests have specific assumptions and requirements that must be met to accurately interpret results.
After reading this tutorial, you would have a much better understanding of hypothesis testing, one of the most important concepts in the field of Data Science . The majority of hypotheses are based on speculation about observed behavior, natural phenomena, or established theories.
If you are interested in statistics of data science and skills needed for such a career, you ought to explore Simplilearn’s Post Graduate Program in Data Science.
If you have any questions regarding this ‘Hypothesis Testing In Statistics’ tutorial, do share them in the comment section. Our subject matter expert will respond to your queries. Happy learning!
1. What is hypothesis testing in statistics with example?
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method used to determine if there is enough evidence in a sample data to draw conclusions about a population. It involves formulating two competing hypotheses, the null hypothesis (H0) and the alternative hypothesis (Ha), and then collecting data to assess the evidence. An example: testing if a new drug improves patient recovery (Ha) compared to the standard treatment (H0) based on collected patient data.
2. What is hypothesis testing and its types?
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method used to make inferences about a population based on sample data. It involves formulating two hypotheses: the null hypothesis (H0), which represents the default assumption, and the alternative hypothesis (Ha), which contradicts H0. The goal is to assess the evidence and determine whether there is enough statistical significance to reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis.
Types of hypothesis testing:
- One-sample test: Used to compare a sample to a known value or a hypothesized value.
- Two-sample test: Compares two independent samples to assess if there is a significant difference between their means or distributions.
- Paired-sample test: Compares two related samples, such as pre-test and post-test data, to evaluate changes within the same subjects over time or under different conditions.
- Chi-square test: Used to analyze categorical data and determine if there is a significant association between variables.
- ANOVA (Analysis of Variance): Compares means across multiple groups to check if there is a significant difference between them.
3. What are the steps of hypothesis testing?
The steps of hypothesis testing are as follows:
- Formulate the hypotheses: State the null hypothesis (H0) and the alternative hypothesis (Ha) based on the research question.
- Set the significance level: Determine the acceptable level of error (alpha) for making a decision.
- Collect and analyze data: Gather and process the sample data.
- Compute test statistic: Calculate the appropriate statistical test to assess the evidence.
- Make a decision: Compare the test statistic with critical values or p-values and determine whether to reject H0 in favor of Ha or not.
- Draw conclusions: Interpret the results and communicate the findings in the context of the research question.
4. What are the 2 types of hypothesis testing?
- One-tailed (or one-sided) test: Tests for the significance of an effect in only one direction, either positive or negative.
- Two-tailed (or two-sided) test: Tests for the significance of an effect in both directions, allowing for the possibility of a positive or negative effect.
The choice between one-tailed and two-tailed tests depends on the specific research question and the directionality of the expected effect.
5. What are the 3 major types of hypothesis?
The three major types of hypotheses are:
- Null Hypothesis (H0): Represents the default assumption, stating that there is no significant effect or relationship in the data.
- Alternative Hypothesis (Ha): Contradicts the null hypothesis and proposes a specific effect or relationship that researchers want to investigate.
- Nondirectional Hypothesis: An alternative hypothesis that doesn't specify the direction of the effect, leaving it open for both positive and negative possibilities.
Find our Data Analyst Online Bootcamp in top cities:
About the author.
Avijeet is a Senior Research Analyst at Simplilearn. Passionate about Data Analytics, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning, Avijeet is also interested in politics, cricket, and football.
Recommended Resources
Free eBook: Top Programming Languages For A Data Scientist
Normality Test in Minitab: Minitab with Statistics
The Triple Threat: AI Ethics, Bias, and Deepfakes in Cybersecurity
Machine Learning Career Guide: A Playbook to Becoming a Machine Learning Engineer
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
User Preferences
Content preview.
Arcu felis bibendum ut tristique et egestas quis:
- Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris
- Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate
- Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident
Keyboard Shortcuts
5.1 - introduction to hypothesis testing.
Previously we used confidence intervals to estimate unknown population parameters. We compared confidence intervals to specified parameter values and when the specific value was contained in the interval, we concluded that there was not sufficient evidence of a difference between the population parameter and the specified value. In other words, any values within the confidence intervals were reasonable estimates of the population parameter and any values outside of the confidence intervals were not reasonable estimates. Here, we are going to look at a more formal method for testing whether a given value is a reasonable value of a population parameter. To do this we need to have a hypothesized value of the population parameter.
In this lesson we will compare data from a sample to a hypothesized parameter. In each case, we will compute the probability that a population with the specified parameter would produce a sample statistic as extreme or more extreme to the one we observed in our sample. This probability is known as the p-value and it is used to evaluate statistical significance.
A test is considered to be statistically significant when the p-value is less than or equal to the level of significance, also known as the alpha (\(\alpha\)) level. For this class, unless otherwise specified, \(\alpha=0.05\); this is the most frequently used alpha level in many fields.
Sample statistics vary from the population parameter randomly. When results are statistically significant, we are concluding that the difference observed between our sample statistic and the hypothesized parameter is unlikely due to random sampling variation.

Snapsolve any problem by taking a picture. Try it in the Numerade app?
U-statistics Based Tests for Marginal Hazard Rate Orderings of Two Dependent Variables
- Original Article
- Published: 26 March 2024
- Volume 18 , article number 19 , ( 2024 )
Cite this article
- Leena Kulkarni 1 ,
- Sangita Kulathinal 2 &
- Isha Dewan 3
We aim to compare marginal distributions of a bivariate random vector ( X , Y ) with reference to their hazard rates, \((h_F(t), h_G(t))\) . In many applications, it is likely that the marginal hazard rates are ordered, e.g., \(h_F(t) \le h_G(t)\) . We consider two U -statistics based tests for testing equality of the marginal hazards against the alternative that they are ordered. Further, we compare these tests with the existing W and S tests when X and Y are assumed to be independent. The two proposed statistics are also extended to cover situations when the pair ( X , Y ) is subjected to independent univariate censoring. We provide extensive simulation studies based on copulae where the power performance of these tests is assessed. The marginal distributions considered are Weibull, linear failure rate, Gompertz and three other families of distributions based on copulae. We apply the tests to two real data examples.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Bagai I, Kochar SC (1986) On tail-ordering and comparison of failure rates. Commun Stat Theory Methods 15(4):1377–1388. https://doi.org/10.1080/03610928608829189
MathSciNet Google Scholar
Cai J, Kim J (2003) Nonparametric quantile estimation with correlated failure time data. Lifetime Data Anal 9:357–371
Callaert H, Veraverbeke N (1981) The order of the normal approximation for a studentized U-Statistic. Ann Stat 9(1):194–200
Cheng KF (1985) Tests for the equality of failure rates. Biometrika 72(1):211–215
Chikkagoudar MS, Shuster JS (1974) Comparison of failure rates using rank tests. J Am Stat Assoc 69:411–413
Frees EW, Carriere JF, Valdez EA (1996) Annuity valuation with dependent mortality. J Risk Insur 63(2):229–261
Google Scholar
Hofert M, Kojadinovic I, Maechler M, Yan J (2023) copula: multivariate Dependence with copulas. R package version 1.1-2, https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=copula
Hoeffding W (1948) A class of statistics with asymptotically normal distribution. Ann Math Stat 19:293–325
Huang H, Zhao Y (2018) Empirical likelihood for the bivariate survival function under univariate censoring. J Stat Plan Inference 194:32–46
Huster WJ, Brookmeyer R, Self SG (1989) Modelling paired survival data with covariates. Biometrics 45(1):145–156
Kalbfleisch JD, Prentice RL (2002) The statistical analysis of failure time data, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Kochar SC (1978) Distribution-free comparisons of two probability distributions with reference to their hazard rates. PhD thesis
Kochar SC (1979) Distribution-free comparison of two probability distributions with reference to their hazard rates. Biometrika 66(3):437–41
Kochar SC (1981) A new distribution-free test for the equality of two failure rates. Biometrika 68(2):423–426
Kulathinal S, Dewan I (2023) Weighted U-statistics for likelihood-ratio ordering of bivariate data. Stat Pap 64:705–735. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00362-022-01332-w
Le CT, Lindgren BR (1996) Duration of ventilating tubes: a test for comparing two clustered samples of censored data. Biometrics 52(1):328–334
Lee AJ (2020) U-statistics: theory and practice. CRC Press, Cambridge
Lehmann EL (1951) Consistency and unbiasedness of certain nonparametric tests. Ann Math Stat 22:165–179
Lai CD, Xie M (2006) Stochastic ageing and dependence for reliability. Springer, New York
Li R, Cheng Y, Chen Q, Fine J (2017) Quantile association for bivariate survival data. Biometrics 73:506–516. https://doi.org/10.1111/biom.12584
Luciano E, Spreeuw J, Vigna E (2008) Modelling stochastic mortality for dependent lives. Insur Math Econ 43:234–244
Nelsen RB (1999) An introduction to copulas. Springer, New York
R Core Team (2022) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Shaked M, Shanthikumar JG (2007) Stochastic orders. Springer, New York
Therneau T (2023) A package for survival analysis in R. https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/survival/index.html
Download references
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank the Society of Actuaries, through the courtesy of Edward (Jed) Frees and Emiliano A. Valdez, for providing the Canadian data used in this paper. The authors would like to thank the referees and the editor for their constructive comments that have led to the improved version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Statistics, SVKM’s NMIMS Deemed-to-be University, Vile-Parle (West), Mumbai, Maharashtra, 400056, India
Leena Kulkarni
Department of Mathematics and Statistics, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland
Sangita Kulathinal
Theoretical Statistics and Mathematics Unit, Indian Statistical Institute, New Delhi, India
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Leena Kulkarni .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
LK’s work was carried out while she was a visiting scientist at the Indian Statistical Institute, New Delhi, India.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file 1 (pdf 135 KB)
Symmetric kernel and asymptotic distribution of \(u_{fc}\) ( 10 ).
The symmetric version of the kernel ( 9 ) is obtained by averaging over 6 combinations, as defined below.
In order to obtain the asymptotic variance of \(U_{fc}\) , we first define and derive \(\psi _{fc}(z_i)\) as follows.
If \(E[\psi _{fc}(Z_i)]^2 < \infty \) and \(\sigma _{1c}^2>0,\) then \(\sqrt{n} (U_{fc}-E(U_{fc})) \xrightarrow {d} N(0, 9\sigma _{1c}^2) \ as \ n \rightarrow \infty .\) Under the null hypothesis, \(E(U_{fc}) = 0.\)
Otitis media data. Ratio of the Kaplan-Meier estimates of the survival functions of survival times of the surgically inserted ventilating tubes in the left ear ( X ) to that in the right ear ( Y ). Black and red colour show the estimated ratios for the control and the treatment groups, respectively
Insurance data. Ratio of estimates of survival functions of ages of a couple at contract initiation for the entire data (ALL) and a randomly selected sample of size 500 (Sample), for \(20\%\) censoring imposed on the complete data and on the selected sample (ALL 20% and Sample 20%)
When \(\sigma _{1c}^2 = Var[\Psi _{fc}(Z_i)] >0\) , \(\sqrt{n}(U_{fc} - E(U_{fc})) \xrightarrow {d} N(0,9\sigma _{1c}^2) \ as \ n \rightarrow \infty \) . Also, \(E(U_{fc}) = 0\) under \(H_{0f}.\)
W and S Tests
We review tests W and S (Kochar [ 13 , 14 ]), and provide computational details here. Let \(X_1, X_2,...X_n\) and \(Y_1, Y_2,..., Y_m\) be independent random samples from the two distributions F and, G respectively. Let \(X_{(1)}, X_{(2)},...,X_{(n)}\) be the order statistics of the X-sample and \(Y_{(1)}, Y_{(2)},...,Y_{(m)}\) be the order statistics of the Y-sample. The U-statistic W in terms of rank representation, is defined as
where \(R_{(i)}, i= 1,2,...,n\) and \(S_{(j)},j=1,2,...,m\) are the ranks of \(X_{(i)}\) and \(Y_{(j)},\) respectively, in the combined sample of X and Y observations. Detailed proof of the above representation is available in Kochar [ 12 ].
To compare the performance of the proposed tests with the W test, we take \(n=m.\) Hence, under \(H_0, E(W)=0,\) and
Asymptotically as \(n \rightarrow \infty \) , \(\sqrt{2n} ~ W \sim N(0, 128/105).\)
Let \(Y_{(1)}, Y_{(2)},...,Y_{(m)}\) be the order statistics of the Y-sample, and let \(\tilde{S}_{(j)}\) denote the rank of the \(Y_{(j)}\) in the combined increasing arrangement of \(X's\) and \(Y's\) . Then the S-statistic can be expressed as
where \(a_j = \frac{1}{2}+log\{1-j/(m+1)\}.\) Under \(H_0\) and when \(n=m\) ,
where the matrix \(\Omega =((w_{ij})) (i,j = 1,2,...,n),\) has \(w_{ij}=i(m+1-j)=w_{ji}\) for \(i\le j\) and \(a' = (a_1, a_2,...,a_n).\) Then, asymptotically, as \(n \rightarrow \infty \) , \((S-E(S))/\sqrt{V(S)} \sim N(0,1).\)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Kulkarni, L., Kulathinal, S. & Dewan, I. U-statistics Based Tests for Marginal Hazard Rate Orderings of Two Dependent Variables. J Stat Theory Pract 18 , 19 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42519-024-00372-9
Download citation
Accepted : 22 February 2024
Published : 26 March 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s42519-024-00372-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Hazard rate ordering
- U -statistics
- Bivariate distributions
- Censored data
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

9.E: Hypothesis Testing with One Sample (Exercises)
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 1146

These are homework exercises to accompany the Textmap created for "Introductory Statistics" by OpenStax.
9.1: Introduction
9.2: null and alternative hypotheses.
Some of the following statements refer to the null hypothesis, some to the alternate hypothesis.
State the null hypothesis, \(H_{0}\), and the alternative hypothesis. \(H_{a}\), in terms of the appropriate parameter \((\mu \text{or} p)\).
- The mean number of years Americans work before retiring is 34.
- At most 60% of Americans vote in presidential elections.
- The mean starting salary for San Jose State University graduates is at least $100,000 per year.
- Twenty-nine percent of high school seniors get drunk each month.
- Fewer than 5% of adults ride the bus to work in Los Angeles.
- The mean number of cars a person owns in her lifetime is not more than ten.
- About half of Americans prefer to live away from cities, given the choice.
- Europeans have a mean paid vacation each year of six weeks.
- The chance of developing breast cancer is under 11% for women.
- Private universities' mean tuition cost is more than $20,000 per year.
- \(H_{0}: \mu = 34; H_{a}: \mu \neq 34\)
- \(H_{0}: p \leq 0.60; H_{a}: p > 0.60\)
- \(H_{0}: \mu \geq 100,000; H_{a}: \mu < 100,000\)
- \(H_{0}: p = 0.29; H_{a}: p \neq 0.29\)
- \(H_{0}: p = 0.05; H_{a}: p < 0.05\)
- \(H_{0}: \mu \leq 10; H_{a}: \mu > 10\)
- \(H_{0}: p = 0.50; H_{a}: p \neq 0.50\)
- \(H_{0}: \mu = 6; H_{a}: \mu \neq 6\)
- \(H_{0}: p ≥ 0.11; H_{a}: p < 0.11\)
- \(H_{0}: \mu \leq 20,000; H_{a}: \mu > 20,000\)
Over the past few decades, public health officials have examined the link between weight concerns and teen girls' smoking. Researchers surveyed a group of 273 randomly selected teen girls living in Massachusetts (between 12 and 15 years old). After four years the girls were surveyed again. Sixty-three said they smoked to stay thin. Is there good evidence that more than thirty percent of the teen girls smoke to stay thin? The alternative hypothesis is:
- \(p < 0.30\)
- \(p \leq 0.30\)
- \(p \geq 0.30\)
- \(p > 0.30\)
A statistics instructor believes that fewer than 20% of Evergreen Valley College (EVC) students attended the opening night midnight showing of the latest Harry Potter movie. She surveys 84 of her students and finds that 11 attended the midnight showing. An appropriate alternative hypothesis is:
- \(p = 0.20\)
- \(p > 0.20\)
- \(p < 0.20\)
- \(p \leq 0.20\)
Previously, an organization reported that teenagers spent 4.5 hours per week, on average, on the phone. The organization thinks that, currently, the mean is higher. Fifteen randomly chosen teenagers were asked how many hours per week they spend on the phone. The sample mean was 4.75 hours with a sample standard deviation of 2.0. Conduct a hypothesis test. The null and alternative hypotheses are:
- \(H_{0}: \bar{x} = 4.5, H_{a}: \bar{x} > 4.5\)
- \(H_{0}: \mu \geq 4.5, H_{a}: \mu < 4.5\)
- \(H_{0}: \mu = 4.75, H_{a}: \mu > 4.75\)
- \(H_{0}: \mu = 4.5, H_{a}: \mu > 4.5\)
9.3: Outcomes and the Type I and Type II Errors
State the Type I and Type II errors in complete sentences given the following statements.
- The mean number of cars a person owns in his or her lifetime is not more than ten.
- Private universities mean tuition cost is more than $20,000 per year.
- Type I error: We conclude that the mean is not 34 years, when it really is 34 years. Type II error: We conclude that the mean is 34 years, when in fact it really is not 34 years.
- Type I error: We conclude that more than 60% of Americans vote in presidential elections, when the actual percentage is at most 60%.Type II error: We conclude that at most 60% of Americans vote in presidential elections when, in fact, more than 60% do.
- Type I error: We conclude that the mean starting salary is less than $100,000, when it really is at least $100,000. Type II error: We conclude that the mean starting salary is at least $100,000 when, in fact, it is less than $100,000.
- Type I error: We conclude that the proportion of high school seniors who get drunk each month is not 29%, when it really is 29%. Type II error: We conclude that the proportion of high school seniors who get drunk each month is 29% when, in fact, it is not 29%.
- Type I error: We conclude that fewer than 5% of adults ride the bus to work in Los Angeles, when the percentage that do is really 5% or more. Type II error: We conclude that 5% or more adults ride the bus to work in Los Angeles when, in fact, fewer that 5% do.
- Type I error: We conclude that the mean number of cars a person owns in his or her lifetime is more than 10, when in reality it is not more than 10. Type II error: We conclude that the mean number of cars a person owns in his or her lifetime is not more than 10 when, in fact, it is more than 10.
- Type I error: We conclude that the proportion of Americans who prefer to live away from cities is not about half, though the actual proportion is about half. Type II error: We conclude that the proportion of Americans who prefer to live away from cities is half when, in fact, it is not half.
- Type I error: We conclude that the duration of paid vacations each year for Europeans is not six weeks, when in fact it is six weeks. Type II error: We conclude that the duration of paid vacations each year for Europeans is six weeks when, in fact, it is not.
- Type I error: We conclude that the proportion is less than 11%, when it is really at least 11%. Type II error: We conclude that the proportion of women who develop breast cancer is at least 11%, when in fact it is less than 11%.
- Type I error: We conclude that the average tuition cost at private universities is more than $20,000, though in reality it is at most $20,000. Type II error: We conclude that the average tuition cost at private universities is at most $20,000 when, in fact, it is more than $20,000.
For statements a-j in Exercise 9.109 , answer the following in complete sentences.
- State a consequence of committing a Type I error.
- State a consequence of committing a Type II error.
When a new drug is created, the pharmaceutical company must subject it to testing before receiving the necessary permission from the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to market the drug. Suppose the null hypothesis is “the drug is unsafe.” What is the Type II Error?
- To conclude the drug is safe when in, fact, it is unsafe.
- Not to conclude the drug is safe when, in fact, it is safe.
- To conclude the drug is safe when, in fact, it is safe.
- Not to conclude the drug is unsafe when, in fact, it is unsafe.
A statistics instructor believes that fewer than 20% of Evergreen Valley College (EVC) students attended the opening midnight showing of the latest Harry Potter movie. She surveys 84 of her students and finds that 11 of them attended the midnight showing. The Type I error is to conclude that the percent of EVC students who attended is ________.
- at least 20%, when in fact, it is less than 20%.
- 20%, when in fact, it is 20%.
- less than 20%, when in fact, it is at least 20%.
- less than 20%, when in fact, it is less than 20%.
It is believed that Lake Tahoe Community College (LTCC) Intermediate Algebra students get less than seven hours of sleep per night, on average. A survey of 22 LTCC Intermediate Algebra students generated a mean of 7.24 hours with a standard deviation of 1.93 hours. At a level of significance of 5%, do LTCC Intermediate Algebra students get less than seven hours of sleep per night, on average?
The Type II error is not to reject that the mean number of hours of sleep LTCC students get per night is at least seven when, in fact, the mean number of hours
- is more than seven hours.
- is at most seven hours.
- is at least seven hours.
- is less than seven hours.
Previously, an organization reported that teenagers spent 4.5 hours per week, on average, on the phone. The organization thinks that, currently, the mean is higher. Fifteen randomly chosen teenagers were asked how many hours per week they spend on the phone. The sample mean was 4.75 hours with a sample standard deviation of 2.0. Conduct a hypothesis test, the Type I error is:
- to conclude that the current mean hours per week is higher than 4.5, when in fact, it is higher
- to conclude that the current mean hours per week is higher than 4.5, when in fact, it is the same
- to conclude that the mean hours per week currently is 4.5, when in fact, it is higher
- to conclude that the mean hours per week currently is no higher than 4.5, when in fact, it is not higher
9.4: Distribution Needed for Hypothesis Testing
It is believed that Lake Tahoe Community College (LTCC) Intermediate Algebra students get less than seven hours of sleep per night, on average. A survey of 22 LTCC Intermediate Algebra students generated a mean of 7.24 hours with a standard deviation of 1.93 hours. At a level of significance of 5%, do LTCC Intermediate Algebra students get less than seven hours of sleep per night, on average? The distribution to be used for this test is \(\bar{X} \sim\) ________________
- \(N\left(7.24, \frac{1.93}{\sqrt{22}}\right)\)
- \(N\left(7.24, 1.93\right)\)
9.5: Rare Events, the Sample, Decision and Conclusion
The National Institute of Mental Health published an article stating that in any one-year period, approximately 9.5 percent of American adults suffer from depression or a depressive illness. Suppose that in a survey of 100 people in a certain town, seven of them suffered from depression or a depressive illness. Conduct a hypothesis test to determine if the true proportion of people in that town suffering from depression or a depressive illness is lower than the percent in the general adult American population.
- Is this a test of one mean or proportion?
- State the null and alternative hypotheses. \(H_{0}\) : ____________________ \(H_{a}\) : ____________________
- Is this a right-tailed, left-tailed, or two-tailed test?
- What symbol represents the random variable for this test?
- In words, define the random variable for this test.
- \(x =\) ________________
- \(n =\) ________________
- \(p′ =\) _____________
- Calculate \(\sigma_{x} =\) __________. Show the formula set-up.
- State the distribution to use for the hypothesis test.
- Find the \(p\text{-value}\).
- Reason for the decision:
- Conclusion (write out in a complete sentence):
9.6: Additional Information and Full Hypothesis Test Examples
For each of the word problems, use a solution sheet to do the hypothesis test. The solution sheet is found in [link] . Please feel free to make copies of the solution sheets. For the online version of the book, it is suggested that you copy the .doc or the .pdf files.
If you are using a Student's \(t\) - distribution for one of the following homework problems, you may assume that the underlying population is normally distributed. (In general, you must first prove that assumption, however.)
A particular brand of tires claims that its deluxe tire averages at least 50,000 miles before it needs to be replaced. From past studies of this tire, the standard deviation is known to be 8,000. A survey of owners of that tire design is conducted. From the 28 tires surveyed, the mean lifespan was 46,500 miles with a standard deviation of 9,800 miles. Using \(\alpha = 0.05\), is the data highly inconsistent with the claim?
- \(H_{0}: \mu \geq 50,000\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu < 50,000\)
- Let \(\bar{X} =\) the average lifespan of a brand of tires.
- normal distribution
- \(z = -2.315\)
- \(p\text{-value} = 0.0103\)
- Check student’s solution.
- alpha: 0.05
- Decision: Reject the null hypothesis.
- Reason for decision: The \(p\text{-value}\) is less than 0.05.
- Conclusion: There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the mean lifespan of the tires is less than 50,000 miles.
- \((43,537, 49,463)\)
From generation to generation, the mean age when smokers first start to smoke varies. However, the standard deviation of that age remains constant of around 2.1 years. A survey of 40 smokers of this generation was done to see if the mean starting age is at least 19. The sample mean was 18.1 with a sample standard deviation of 1.3. Do the data support the claim at the 5% level?
The cost of a daily newspaper varies from city to city. However, the variation among prices remains steady with a standard deviation of 20¢. A study was done to test the claim that the mean cost of a daily newspaper is $1.00. Twelve costs yield a mean cost of 95¢ with a standard deviation of 18¢. Do the data support the claim at the 1% level?
- \(H_{0}: \mu = $1.00\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu \neq $1.00\)
- Let \(\bar{X} =\) the average cost of a daily newspaper.
- \(z = –0.866\)
- \(p\text{-value} = 0.3865\)
- \(\alpha: 0.01\)
- Decision: Do not reject the null hypothesis.
- Reason for decision: The \(p\text{-value}\) is greater than 0.01.
- Conclusion: There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that the mean cost of daily papers is $1. The mean cost could be $1.
- \(($0.84, $1.06)\)
An article in the San Jose Mercury News stated that students in the California state university system take 4.5 years, on average, to finish their undergraduate degrees. Suppose you believe that the mean time is longer. You conduct a survey of 49 students and obtain a sample mean of 5.1 with a sample standard deviation of 1.2. Do the data support your claim at the 1% level?
The mean number of sick days an employee takes per year is believed to be about ten. Members of a personnel department do not believe this figure. They randomly survey eight employees. The number of sick days they took for the past year are as follows: 12; 4; 15; 3; 11; 8; 6; 8. Let \(x =\) the number of sick days they took for the past year. Should the personnel team believe that the mean number is ten?
- \(H_{0}: \mu = 10\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu \neq 10\)
- Let \(\bar{X}\) the mean number of sick days an employee takes per year.
- Student’s t -distribution
- \(t = –1.12\)
- \(p\text{-value} = 0.300\)
- \(\alpha: 0.05\)
- Reason for decision: The \(p\text{-value}\) is greater than 0.05.
- Conclusion: At the 5% significance level, there is insufficient evidence to conclude that the mean number of sick days is not ten.
- \((4.9443, 11.806)\)
In 1955, Life Magazine reported that the 25 year-old mother of three worked, on average, an 80 hour week. Recently, many groups have been studying whether or not the women's movement has, in fact, resulted in an increase in the average work week for women (combining employment and at-home work). Suppose a study was done to determine if the mean work week has increased. 81 women were surveyed with the following results. The sample mean was 83; the sample standard deviation was ten. Does it appear that the mean work week has increased for women at the 5% level?
Your statistics instructor claims that 60 percent of the students who take her Elementary Statistics class go through life feeling more enriched. For some reason that she can't quite figure out, most people don't believe her. You decide to check this out on your own. You randomly survey 64 of her past Elementary Statistics students and find that 34 feel more enriched as a result of her class. Now, what do you think?
- \(H_{0}: p \geq 0.6\)
- \(H_{a}: p < 0.6\)
- Let \(P′ =\) the proportion of students who feel more enriched as a result of taking Elementary Statistics.
- normal for a single proportion
- \(p\text{-value} = 0.1308\)
- Conclusion: There is insufficient evidence to conclude that less than 60 percent of her students feel more enriched.
The “plus-4s” confidence interval is \((0.411, 0.648)\)
A Nissan Motor Corporation advertisement read, “The average man’s I.Q. is 107. The average brown trout’s I.Q. is 4. So why can’t man catch brown trout?” Suppose you believe that the brown trout’s mean I.Q. is greater than four. You catch 12 brown trout. A fish psychologist determines the I.Q.s as follows: 5; 4; 7; 3; 6; 4; 5; 3; 6; 3; 8; 5. Conduct a hypothesis test of your belief.
Refer to Exercise 9.119 . Conduct a hypothesis test to see if your decision and conclusion would change if your belief were that the brown trout’s mean I.Q. is not four.
- \(H_{0}: \mu = 4\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu \neq 4\)
- Let \(\bar{X}\) the average I.Q. of a set of brown trout.
- two-tailed Student's t-test
- \(t = 1.95\)
- \(p\text{-value} = 0.076\)
- Reason for decision: The \(p\text{-value}\) is greater than 0.05
- Conclusion: There is insufficient evidence to conclude that the average IQ of brown trout is not four.
- \((3.8865,5.9468)\)
According to an article in Newsweek , the natural ratio of girls to boys is 100:105. In China, the birth ratio is 100: 114 (46.7% girls). Suppose you don’t believe the reported figures of the percent of girls born in China. You conduct a study. In this study, you count the number of girls and boys born in 150 randomly chosen recent births. There are 60 girls and 90 boys born of the 150. Based on your study, do you believe that the percent of girls born in China is 46.7?
A poll done for Newsweek found that 13% of Americans have seen or sensed the presence of an angel. A contingent doubts that the percent is really that high. It conducts its own survey. Out of 76 Americans surveyed, only two had seen or sensed the presence of an angel. As a result of the contingent’s survey, would you agree with the Newsweek poll? In complete sentences, also give three reasons why the two polls might give different results.
- \(H_{a}: p < 0.13\)
- Let \(P′ =\) the proportion of Americans who have seen or sensed angels
- –2.688
- \(p\text{-value} = 0.0036\)
- Reason for decision: The \(p\text{-value}\)e is less than 0.05.
- Conclusion: There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the percentage of Americans who have seen or sensed an angel is less than 13%.
The“plus-4s” confidence interval is (0.0022, 0.0978)
The mean work week for engineers in a start-up company is believed to be about 60 hours. A newly hired engineer hopes that it’s shorter. She asks ten engineering friends in start-ups for the lengths of their mean work weeks. Based on the results that follow, should she count on the mean work week to be shorter than 60 hours?
Data (length of mean work week): 70; 45; 55; 60; 65; 55; 55; 60; 50; 55.
Use the “Lap time” data for Lap 4 (see [link] ) to test the claim that Terri finishes Lap 4, on average, in less than 129 seconds. Use all twenty races given.
- \(H_{0}: \mu \geq 129\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu < 129\)
- Let \(\bar{X} =\) the average time in seconds that Terri finishes Lap 4.
- Student's t -distribution
- \(t = 1.209\)
- Conclusion: There is insufficient evidence to conclude that Terri’s mean lap time is less than 129 seconds.
- \((128.63, 130.37)\)
Use the “Initial Public Offering” data (see [link] ) to test the claim that the mean offer price was $18 per share. Do not use all the data. Use your random number generator to randomly survey 15 prices.
The following questions were written by past students. They are excellent problems!
"Asian Family Reunion," by Chau Nguyen
Every two years it comes around.
We all get together from different towns.
In my honest opinion,
It's not a typical family reunion.
Not forty, or fifty, or sixty,
But how about seventy companions!
The kids would play, scream, and shout
One minute they're happy, another they'll pout.
The teenagers would look, stare, and compare
From how they look to what they wear.
The men would chat about their business
That they make more, but never less.
Money is always their subject
And there's always talk of more new projects.
The women get tired from all of the chats
They head to the kitchen to set out the mats.
Some would sit and some would stand
Eating and talking with plates in their hands.
Then come the games and the songs
And suddenly, everyone gets along!
With all that laughter, it's sad to say
That it always ends in the same old way.
They hug and kiss and say "good-bye"
And then they all begin to cry!
I say that 60 percent shed their tears
But my mom counted 35 people this year.
She said that boys and men will always have their pride,
So we won't ever see them cry.
I myself don't think she's correct,
So could you please try this problem to see if you object?
- \(H_{0}: p = 0.60\)
- \(H_{a}: p < 0.60\)
- Let \(P′ =\) the proportion of family members who shed tears at a reunion.
- –1.71
- Reason for decision: \(p\text{-value} < \alpha\)
- Conclusion: At the 5% significance level, there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the proportion of family members who shed tears at a reunion is less than 0.60. However, the test is weak because the \(p\text{-value}\) and alpha are quite close, so other tests should be done.
- We are 95% confident that between 38.29% and 61.71% of family members will shed tears at a family reunion. \((0.3829, 0.6171)\). The“plus-4s” confidence interval (see chapter 8) is \((0.3861, 0.6139)\)
Note that here the “large-sample” \(1 - \text{PropZTest}\) provides the approximate \(p\text{-value}\) of 0.0438. Whenever a \(p\text{-value}\) based on a normal approximation is close to the level of significance, the exact \(p\text{-value}\) based on binomial probabilities should be calculated whenever possible. This is beyond the scope of this course.
"The Problem with Angels," by Cyndy Dowling
Although this problem is wholly mine,
The catalyst came from the magazine, Time.
On the magazine cover I did find
The realm of angels tickling my mind.
Inside, 69% I found to be
In angels, Americans do believe.
Then, it was time to rise to the task,
Ninety-five high school and college students I did ask.
Viewing all as one group,
Random sampling to get the scoop.
So, I asked each to be true,
"Do you believe in angels?" Tell me, do!
Hypothesizing at the start,
Totally believing in my heart
That the proportion who said yes
Would be equal on this test.
Lo and behold, seventy-three did arrive,
Out of the sample of ninety-five.
Now your job has just begun,
Solve this problem and have some fun.
"Blowing Bubbles," by Sondra Prull
Studying stats just made me tense,
I had to find some sane defense.
Some light and lifting simple play
To float my math anxiety away.
Blowing bubbles lifts me high
Takes my troubles to the sky.
POIK! They're gone, with all my stress
Bubble therapy is the best.
The label said each time I blew
The average number of bubbles would be at least 22.
I blew and blew and this I found
From 64 blows, they all are round!
But the number of bubbles in 64 blows
Varied widely, this I know.
20 per blow became the mean
They deviated by 6, and not 16.
From counting bubbles, I sure did relax
But now I give to you your task.
Was 22 a reasonable guess?
Find the answer and pass this test!
- \(H_{0}: \mu \geq 22\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu < 22\)
- Let \(\bar{X} =\) the mean number of bubbles per blow.
- –2.667
- \(p\text{-value} = 0.00486\)
- Conclusion: There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the mean number of bubbles per blow is less than 22.
- \((18.501, 21.499)\)
"Dalmatian Darnation," by Kathy Sparling
A greedy dog breeder named Spreckles
Bred puppies with numerous freckles
The Dalmatians he sought
Possessed spot upon spot
The more spots, he thought, the more shekels.
His competitors did not agree
That freckles would increase the fee.
They said, “Spots are quite nice
But they don't affect price;
One should breed for improved pedigree.”
The breeders decided to prove
This strategy was a wrong move.
Breeding only for spots
Would wreak havoc, they thought.
His theory they want to disprove.
They proposed a contest to Spreckles
Comparing dog prices to freckles.
In records they looked up
One hundred one pups:
Dalmatians that fetched the most shekels.
They asked Mr. Spreckles to name
An average spot count he'd claim
To bring in big bucks.
Said Spreckles, “Well, shucks,
It's for one hundred one that I aim.”
Said an amateur statistician
Who wanted to help with this mission.
“Twenty-one for the sample
Standard deviation's ample:
They examined one hundred and one
Dalmatians that fetched a good sum.
They counted each spot,
Mark, freckle and dot
And tallied up every one.
Instead of one hundred one spots
They averaged ninety six dots
Can they muzzle Spreckles’
Obsession with freckles
Based on all the dog data they've got?
"Macaroni and Cheese, please!!" by Nedda Misherghi and Rachelle Hall
As a poor starving student I don't have much money to spend for even the bare necessities. So my favorite and main staple food is macaroni and cheese. It's high in taste and low in cost and nutritional value.
One day, as I sat down to determine the meaning of life, I got a serious craving for this, oh, so important, food of my life. So I went down the street to Greatway to get a box of macaroni and cheese, but it was SO expensive! $2.02 !!! Can you believe it? It made me stop and think. The world is changing fast. I had thought that the mean cost of a box (the normal size, not some super-gigantic-family-value-pack) was at most $1, but now I wasn't so sure. However, I was determined to find out. I went to 53 of the closest grocery stores and surveyed the prices of macaroni and cheese. Here are the data I wrote in my notebook:
Price per box of Mac and Cheese:
- 5 stores @ $2.02
- 15 stores @ $0.25
- 3 stores @ $1.29
- 6 stores @ $0.35
- 4 stores @ $2.27
- 7 stores @ $1.50
- 5 stores @ $1.89
- 8 stores @ 0.75.
I could see that the cost varied but I had to sit down to figure out whether or not I was right. If it does turn out that this mouth-watering dish is at most $1, then I'll throw a big cheesy party in our next statistics lab, with enough macaroni and cheese for just me. (After all, as a poor starving student I can't be expected to feed our class of animals!)
- \(H_{0}: \mu \leq 1\)
- \(H_{a}: \mu > 1\)
- Let \(\bar{X} =\) the mean cost in dollars of macaroni and cheese in a certain town.
- Student's \(t\)-distribution
- \(t = 0.340\)
- \(p\text{-value} = 0.36756\)
- Conclusion: The mean cost could be $1, or less. At the 5% significance level, there is insufficient evidence to conclude that the mean price of a box of macaroni and cheese is more than $1.
- \((0.8291, 1.241)\)
"William Shakespeare: The Tragedy of Hamlet, Prince of Denmark," by Jacqueline Ghodsi
THE CHARACTERS (in order of appearance):
- HAMLET, Prince of Denmark and student of Statistics
- POLONIUS, Hamlet’s tutor
- HOROTIO, friend to Hamlet and fellow student
Scene: The great library of the castle, in which Hamlet does his lessons
(The day is fair, but the face of Hamlet is clouded. He paces the large room. His tutor, Polonius, is reprimanding Hamlet regarding the latter’s recent experience. Horatio is seated at the large table at right stage.)
POLONIUS: My Lord, how cans’t thou admit that thou hast seen a ghost! It is but a figment of your imagination!
HAMLET: I beg to differ; I know of a certainty that five-and-seventy in one hundred of us, condemned to the whips and scorns of time as we are, have gazed upon a spirit of health, or goblin damn’d, be their intents wicked or charitable.
POLONIUS If thou doest insist upon thy wretched vision then let me invest your time; be true to thy work and speak to me through the reason of the null and alternate hypotheses. (He turns to Horatio.) Did not Hamlet himself say, “What piece of work is man, how noble in reason, how infinite in faculties? Then let not this foolishness persist. Go, Horatio, make a survey of three-and-sixty and discover what the true proportion be. For my part, I will never succumb to this fantasy, but deem man to be devoid of all reason should thy proposal of at least five-and-seventy in one hundred hold true.
HORATIO (to Hamlet): What should we do, my Lord?
HAMLET: Go to thy purpose, Horatio.
HORATIO: To what end, my Lord?
HAMLET: That you must teach me. But let me conjure you by the rights of our fellowship, by the consonance of our youth, but the obligation of our ever-preserved love, be even and direct with me, whether I am right or no.
(Horatio exits, followed by Polonius, leaving Hamlet to ponder alone.)
(The next day, Hamlet awaits anxiously the presence of his friend, Horatio. Polonius enters and places some books upon the table just a moment before Horatio enters.)
POLONIUS: So, Horatio, what is it thou didst reveal through thy deliberations?
HORATIO: In a random survey, for which purpose thou thyself sent me forth, I did discover that one-and-forty believe fervently that the spirits of the dead walk with us. Before my God, I might not this believe, without the sensible and true avouch of mine own eyes.
POLONIUS: Give thine own thoughts no tongue, Horatio. (Polonius turns to Hamlet.) But look to’t I charge you, my Lord. Come Horatio, let us go together, for this is not our test. (Horatio and Polonius leave together.)
HAMLET: To reject, or not reject, that is the question: whether ‘tis nobler in the mind to suffer the slings and arrows of outrageous statistics, or to take arms against a sea of data, and, by opposing, end them. (Hamlet resignedly attends to his task.)
(Curtain falls)
"Untitled," by Stephen Chen
I've often wondered how software is released and sold to the public. Ironically, I work for a company that sells products with known problems. Unfortunately, most of the problems are difficult to create, which makes them difficult to fix. I usually use the test program X, which tests the product, to try to create a specific problem. When the test program is run to make an error occur, the likelihood of generating an error is 1%.
So, armed with this knowledge, I wrote a new test program Y that will generate the same error that test program X creates, but more often. To find out if my test program is better than the original, so that I can convince the management that I'm right, I ran my test program to find out how often I can generate the same error. When I ran my test program 50 times, I generated the error twice. While this may not seem much better, I think that I can convince the management to use my test program instead of the original test program. Am I right?
- \(H_{0}: p = 0.01\)
- \(H_{a}: p > 0.01\)
- Let \(P′ =\) the proportion of errors generated
- Normal for a single proportion
- Decision: Reject the null hypothesis
- Conclusion: At the 5% significance level, there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the proportion of errors generated is more than 0.01.
The“plus-4s” confidence interval is \((0.004, 0.144)\).
"Japanese Girls’ Names"
by Kumi Furuichi
It used to be very typical for Japanese girls’ names to end with “ko.” (The trend might have started around my grandmothers’ generation and its peak might have been around my mother’s generation.) “Ko” means “child” in Chinese characters. Parents would name their daughters with “ko” attaching to other Chinese characters which have meanings that they want their daughters to become, such as Sachiko—happy child, Yoshiko—a good child, Yasuko—a healthy child, and so on.
However, I noticed recently that only two out of nine of my Japanese girlfriends at this school have names which end with “ko.” More and more, parents seem to have become creative, modernized, and, sometimes, westernized in naming their children.
I have a feeling that, while 70 percent or more of my mother’s generation would have names with “ko” at the end, the proportion has dropped among my peers. I wrote down all my Japanese friends’, ex-classmates’, co-workers, and acquaintances’ names that I could remember. Following are the names. (Some are repeats.) Test to see if the proportion has dropped for this generation.
Ai, Akemi, Akiko, Ayumi, Chiaki, Chie, Eiko, Eri, Eriko, Fumiko, Harumi, Hitomi, Hiroko, Hiroko, Hidemi, Hisako, Hinako, Izumi, Izumi, Junko, Junko, Kana, Kanako, Kanayo, Kayo, Kayoko, Kazumi, Keiko, Keiko, Kei, Kumi, Kumiko, Kyoko, Kyoko, Madoka, Maho, Mai, Maiko, Maki, Miki, Miki, Mikiko, Mina, Minako, Miyako, Momoko, Nana, Naoko, Naoko, Naoko, Noriko, Rieko, Rika, Rika, Rumiko, Rei, Reiko, Reiko, Sachiko, Sachiko, Sachiyo, Saki, Sayaka, Sayoko, Sayuri, Seiko, Shiho, Shizuka, Sumiko, Takako, Takako, Tomoe, Tomoe, Tomoko, Touko, Yasuko, Yasuko, Yasuyo, Yoko, Yoko, Yoko, Yoshiko, Yoshiko, Yoshiko, Yuka, Yuki, Yuki, Yukiko, Yuko, Yuko.
"Phillip’s Wish," by Suzanne Osorio
My nephew likes to play
Chasing the girls makes his day.
He asked his mother
If it is okay
To get his ear pierced.
She said, “No way!”
To poke a hole through your ear,
Is not what I want for you, dear.
He argued his point quite well,
Says even my macho pal, Mel,
Has gotten this done.
It’s all just for fun.
C’mon please, mom, please, what the hell.
Again Phillip complained to his mother,
Saying half his friends (including their brothers)
Are piercing their ears
And they have no fears
He wants to be like the others.
She said, “I think it’s much less.
We must do a hypothesis test.
And if you are right,
I won’t put up a fight.
But, if not, then my case will rest.”
We proceeded to call fifty guys
To see whose prediction would fly.
Nineteen of the fifty
Said piercing was nifty
And earrings they’d occasionally buy.
Then there’s the other thirty-one,
Who said they’d never have this done.
So now this poem’s finished.
Will his hopes be diminished,
Or will my nephew have his fun?
- \(H_{0}: p = 0.50\)
- \(H_{a}: p < 0.50\)
- Let \(P′ =\) the proportion of friends that has a pierced ear.
- –1.70
- \(p\text{-value} = 0.0448\)
- Reason for decision: The \(p\text{-value}\) is less than 0.05. (However, they are very close.)
- Conclusion: There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that less than 50% of his friends have pierced ears.
- Confidence Interval: \((0.245, 0.515)\): The “plus-4s” confidence interval is \((0.259, 0.519)\).
"The Craven," by Mark Salangsang
Once upon a morning dreary
In stats class I was weak and weary.
Pondering over last night’s homework
Whose answers were now on the board
This I did and nothing more.
While I nodded nearly napping
Suddenly, there came a tapping.
As someone gently rapping,
Rapping my head as I snore.
Quoth the teacher, “Sleep no more.”
“In every class you fall asleep,”
The teacher said, his voice was deep.
“So a tally I’ve begun to keep
Of every class you nap and snore.
The percentage being forty-four.”
“My dear teacher I must confess,
While sleeping is what I do best.
The percentage, I think, must be less,
A percentage less than forty-four.”
This I said and nothing more.
“We’ll see,” he said and walked away,
And fifty classes from that day
He counted till the month of May
The classes in which I napped and snored.
The number he found was twenty-four.
At a significance level of 0.05,
Please tell me am I still alive?
Or did my grade just take a dive
Plunging down beneath the floor?
Upon thee I hereby implore.
Toastmasters International cites a report by Gallop Poll that 40% of Americans fear public speaking. A student believes that less than 40% of students at her school fear public speaking. She randomly surveys 361 schoolmates and finds that 135 report they fear public speaking. Conduct a hypothesis test to determine if the percent at her school is less than 40%.
- \(H_{0}: p = 0.40\)
- \(H_{a}: p < 0.40\)
- Let \(P′ =\) the proportion of schoolmates who fear public speaking.
- –1.01
- \(p\text{-value} = 0.1563\)
- Conclusion: There is insufficient evidence to support the claim that less than 40% of students at the school fear public speaking.
- Confidence Interval: \((0.3241, 0.4240)\): The “plus-4s” confidence interval is \((0.3257, 0.4250)\).
Sixty-eight percent of online courses taught at community colleges nationwide were taught by full-time faculty. To test if 68% also represents California’s percent for full-time faculty teaching the online classes, Long Beach City College (LBCC) in California, was randomly selected for comparison. In the same year, 34 of the 44 online courses LBCC offered were taught by full-time faculty. Conduct a hypothesis test to determine if 68% represents California. NOTE: For more accurate results, use more California community colleges and this past year's data.
According to an article in Bloomberg Businessweek , New York City's most recent adult smoking rate is 14%. Suppose that a survey is conducted to determine this year’s rate. Nine out of 70 randomly chosen N.Y. City residents reply that they smoke. Conduct a hypothesis test to determine if the rate is still 14% or if it has decreased.
- \(H_{0}: p = 0.14\)
- \(H_{a}: p < 0.14\)
- Let \(P′ =\) the proportion of NYC residents that smoke.
- –0.2756
- \(p\text{-value} = 0.3914\)
- At the 5% significance level, there is insufficient evidence to conclude that the proportion of NYC residents who smoke is less than 0.14.
- Confidence Interval: \((0.0502, 0.2070)\): The “plus-4s” confidence interval (see chapter 8) is \((0.0676, 0.2297)\).
The mean age of De Anza College students in a previous term was 26.6 years old. An instructor thinks the mean age for online students is older than 26.6. She randomly surveys 56 online students and finds that the sample mean is 29.4 with a standard deviation of 2.1. Conduct a hypothesis test.
Registered nurses earned an average annual salary of $69,110. For that same year, a survey was conducted of 41 California registered nurses to determine if the annual salary is higher than $69,110 for California nurses. The sample average was $71,121 with a sample standard deviation of $7,489. Conduct a hypothesis test.
- \(H_{0}: \mu = 69,110\)
- \(H_{0}: \mu > 69,110\)
- Let \(\bar{X} =\) the mean salary in dollars for California registered nurses.
- \(t = 1.719\)
- \(p\text{-value}: 0.0466\)
- Conclusion: At the 5% significance level, there is sufficient evidence to conclude that the mean salary of California registered nurses exceeds $69,110.
- \(($68,757, $73,485)\)
La Leche League International reports that the mean age of weaning a child from breastfeeding is age four to five worldwide. In America, most nursing mothers wean their children much earlier. Suppose a random survey is conducted of 21 U.S. mothers who recently weaned their children. The mean weaning age was nine months (3/4 year) with a standard deviation of 4 months. Conduct a hypothesis test to determine if the mean weaning age in the U.S. is less than four years old.
Over the past few decades, public health officials have examined the link between weight concerns and teen girls' smoking. Researchers surveyed a group of 273 randomly selected teen girls living in Massachusetts (between 12 and 15 years old). After four years the girls were surveyed again. Sixty-three said they smoked to stay thin. Is there good evidence that more than thirty percent of the teen girls smoke to stay thin?
After conducting the test, your decision and conclusion are
- Reject \(H_{0}\): There is sufficient evidence to conclude that more than 30% of teen girls smoke to stay thin.
- Do not reject \(H_{0}\): There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that less than 30% of teen girls smoke to stay thin.
- Do not reject \(H_{0}\): There is not sufficient evidence to conclude that more than 30% of teen girls smoke to stay thin.
- Reject \(H_{0}\): There is sufficient evidence to conclude that less than 30% of teen girls smoke to stay thin.
A statistics instructor believes that fewer than 20% of Evergreen Valley College (EVC) students attended the opening night midnight showing of the latest Harry Potter movie. She surveys 84 of her students and finds that 11 of them attended the midnight showing.
At a 1% level of significance, an appropriate conclusion is:
- There is insufficient evidence to conclude that the percent of EVC students who attended the midnight showing of Harry Potter is less than 20%.
- There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the percent of EVC students who attended the midnight showing of Harry Potter is more than 20%.
- There is sufficient evidence to conclude that the percent of EVC students who attended the midnight showing of Harry Potter is less than 20%.
- There is insufficient evidence to conclude that the percent of EVC students who attended the midnight showing of Harry Potter is at least 20%.
Previously, an organization reported that teenagers spent 4.5 hours per week, on average, on the phone. The organization thinks that, currently, the mean is higher. Fifteen randomly chosen teenagers were asked how many hours per week they spend on the phone. The sample mean was 4.75 hours with a sample standard deviation of 2.0. Conduct a hypothesis test.
At a significance level of \(a = 0.05\), what is the correct conclusion?
- There is enough evidence to conclude that the mean number of hours is more than 4.75
- There is enough evidence to conclude that the mean number of hours is more than 4.5
- There is not enough evidence to conclude that the mean number of hours is more than 4.5
- There is not enough evidence to conclude that the mean number of hours is more than 4.75
Instructions: For the following ten exercises,
Hypothesis testing: For the following ten exercises, answer each question.
State the null and alternate hypothesis.
State the \(p\text{-value}\).
State \(\alpha\).
What is your decision?
Write a conclusion.
Answer any other questions asked in the problem.
According to the Center for Disease Control website, in 2011 at least 18% of high school students have smoked a cigarette. An Introduction to Statistics class in Davies County, KY conducted a hypothesis test at the local high school (a medium sized–approximately 1,200 students–small city demographic) to determine if the local high school’s percentage was lower. One hundred fifty students were chosen at random and surveyed. Of the 150 students surveyed, 82 have smoked. Use a significance level of 0.05 and using appropriate statistical evidence, conduct a hypothesis test and state the conclusions.
A recent survey in the N.Y. Times Almanac indicated that 48.8% of families own stock. A broker wanted to determine if this survey could be valid. He surveyed a random sample of 250 families and found that 142 owned some type of stock. At the 0.05 significance level, can the survey be considered to be accurate?
- \(H_{0}: p = 0.488\) \(H_{a}: p \neq 0.488\)
- \(p\text{-value} = 0.0114\)
- \(\alpha = 0.05\)
- Reject the null hypothesis.
- At the 5% level of significance, there is enough evidence to conclude that 48.8% of families own stocks.
- The survey does not appear to be accurate.
Driver error can be listed as the cause of approximately 54% of all fatal auto accidents, according to the American Automobile Association. Thirty randomly selected fatal accidents are examined, and it is determined that 14 were caused by driver error. Using \(\alpha = 0.05\), is the AAA proportion accurate?
The US Department of Energy reported that 51.7% of homes were heated by natural gas. A random sample of 221 homes in Kentucky found that 115 were heated by natural gas. Does the evidence support the claim for Kentucky at the \(\alpha = 0.05\) level in Kentucky? Are the results applicable across the country? Why?
- \(H_{0}: p = 0.517\) \(H_{0}: p \neq 0.517\)
- \(p\text{-value} = 0.9203\).
- \(\alpha = 0.05\).
- Do not reject the null hypothesis.
- At the 5% significance level, there is not enough evidence to conclude that the proportion of homes in Kentucky that are heated by natural gas is 0.517.
- However, we cannot generalize this result to the entire nation. First, the sample’s population is only the state of Kentucky. Second, it is reasonable to assume that homes in the extreme north and south will have extreme high usage and low usage, respectively. We would need to expand our sample base to include these possibilities if we wanted to generalize this claim to the entire nation.
For Americans using library services, the American Library Association claims that at most 67% of patrons borrow books. The library director in Owensboro, Kentucky feels this is not true, so she asked a local college statistic class to conduct a survey. The class randomly selected 100 patrons and found that 82 borrowed books. Did the class demonstrate that the percentage was higher in Owensboro, KY? Use \(\alpha = 0.01\) level of significance. What is the possible proportion of patrons that do borrow books from the Owensboro Library?
The Weather Underground reported that the mean amount of summer rainfall for the northeastern US is at least 11.52 inches. Ten cities in the northeast are randomly selected and the mean rainfall amount is calculated to be 7.42 inches with a standard deviation of 1.3 inches. At the \(\alpha = 0.05 level\), can it be concluded that the mean rainfall was below the reported average? What if \(\alpha = 0.01\)? Assume the amount of summer rainfall follows a normal distribution.
- \(H_{0}: \mu \geq 11.52\) \(H_{a}: \mu < 11.52\)
- \(p\text{-value} = 0.000002\) which is almost 0.
- At the 5% significance level, there is enough evidence to conclude that the mean amount of summer rain in the northeaster US is less than 11.52 inches, on average.
- We would make the same conclusion if alpha was 1% because the \(p\text{-value}\) is almost 0.
A survey in the N.Y. Times Almanac finds the mean commute time (one way) is 25.4 minutes for the 15 largest US cities. The Austin, TX chamber of commerce feels that Austin’s commute time is less and wants to publicize this fact. The mean for 25 randomly selected commuters is 22.1 minutes with a standard deviation of 5.3 minutes. At the \(\alpha = 0.10\) level, is the Austin, TX commute significantly less than the mean commute time for the 15 largest US cities?
A report by the Gallup Poll found that a woman visits her doctor, on average, at most 5.8 times each year. A random sample of 20 women results in these yearly visit totals
3; 2; 1; 3; 7; 2; 9; 4; 6; 6; 8; 0; 5; 6; 4; 2; 1; 3; 4; 1
At the \(\alpha = 0.05\) level can it be concluded that the sample mean is higher than 5.8 visits per year?
- \(H_{0}: \mu \leq 5.8\) \(H_{a}: \mu > 5.8\)
- \(p\text{-value} = 0.9987\)
- At the 5% level of significance, there is not enough evidence to conclude that a woman visits her doctor, on average, more than 5.8 times a year.
According to the N.Y. Times Almanac the mean family size in the U.S. is 3.18. A sample of a college math class resulted in the following family sizes:
5; 4; 5; 4; 4; 3; 6; 4; 3; 3; 5; 5; 6; 3; 3; 2; 7; 4; 5; 2; 2; 2; 3; 2
At \(\alpha = 0.05\) level, is the class’ mean family size greater than the national average? Does the Almanac result remain valid? Why?
The student academic group on a college campus claims that freshman students study at least 2.5 hours per day, on average. One Introduction to Statistics class was skeptical. The class took a random sample of 30 freshman students and found a mean study time of 137 minutes with a standard deviation of 45 minutes. At α = 0.01 level, is the student academic group’s claim correct?
- \(H_{0}: \mu \geq 150\) \(H_{0}: \mu < 150\)
- \(p\text{-value} = 0.0622\)
- \(\alpha = 0.01\)
- At the 1% significance level, there is not enough evidence to conclude that freshmen students study less than 2.5 hours per day, on average.
- The student academic group’s claim appears to be correct.
9.7: Hypothesis Testing of a Single Mean and Single Proportion
Help | Advanced Search
Quantum Physics
Title: sample complexity of quantum hypothesis testing.
Abstract: Quantum hypothesis testing has been traditionally studied from the information-theoretic perspective, wherein one is interested in the optimal decay rate of error probabilities as a function of the number of samples of an unknown state. In this paper, we study the sample complexity of quantum hypothesis testing, wherein the goal is to determine the minimum number of samples needed to reach a desired error probability. By making use of the wealth of knowledge that already exists in the literature on quantum hypothesis testing, we characterize the sample complexity of binary quantum hypothesis testing in the symmetric and asymmetric settings, and we provide bounds on the sample complexity of multiple quantum hypothesis testing. In more detail, we prove that the sample complexity of symmetric binary quantum hypothesis testing depends logarithmically on the inverse error probability and inversely on the negative logarithm of the fidelity. As a counterpart of the quantum Stein's lemma, we also find that the sample complexity of asymmetric binary quantum hypothesis testing depends logarithmically on the inverse type~II error probability and inversely on the quantum relative entropy. Finally, we provide lower and upper bounds on the sample complexity of multiple quantum hypothesis testing, with it remaining an intriguing open question to improve these bounds.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- INSPIRE HEP
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Table of contents. Step 1: State your null and alternate hypothesis. Step 2: Collect data. Step 3: Perform a statistical test. Step 4: Decide whether to reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis. Step 5: Present your findings. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about hypothesis testing.
A test statistic assesses how consistent your sample data are with the null hypothesis in a hypothesis test. Test statistic calculations take your sample data and boil them down to a single number that quantifies how much your sample diverges from the null hypothesis. As a test statistic value becomes more extreme, it indicates larger ...
If the engineer used the P -value approach to conduct his hypothesis test, he would determine the area under a tn - 1 = t24 curve and to the right of the test statistic t * = 1.22: In the output above, Minitab reports that the P -value is 0.117. Since the P -value, 0.117, is greater than α = 0.05, the engineer fails to reject the null hypothesis.
Hypothesis testing is a crucial procedure to perform when you want to make inferences about a population using a random sample. These inferences include estimating population properties such as the mean, differences between means, proportions, and the relationships between variables. This post provides an overview of statistical hypothesis testing.
A sample of 30 patients who have tried the raw cornstarch diet have a mean glucose level of 140. Test the hypothesis that the raw cornstarch had an effect. Step 1: State the null hypothesis: H 0 :μ=100. Step 2: State the alternate hypothesis: H 1 :≠100. Step 3: State your alpha level. We'll use 0.05 for this example.
Start Unit test. Significance tests give us a formal process for using sample data to evaluate the likelihood of some claim about a population value. Learn how to conduct significance tests and calculate p-values to see how likely a sample result is to occur by random chance. You'll also see how we use p-values to make conclusions about hypotheses.
The Two Types of Statistical Hypotheses. To test whether a statistical hypothesis about a population parameter is true, we obtain a random sample from the population and perform a hypothesis test on the sample data. There are two types of statistical hypotheses: The null hypothesis, denoted as H 0, is the hypothesis that the sample data occurs ...
A hypothesis, in statistics, is a statement about a population parameter, where this statement typically is represented by some specific numerical value. In testing a hypothesis, we use a method where we gather data in an effort to gather evidence about the hypothesis. ... Calculate the test statistic: Gather sample data and calculate a test ...
State and check the assumptions for a hypothesis test. A random sample of size n is taken. The population standard derivation is known. The sample size is at least 30 or the population of the random variable is normally distributed. Find the sample statistic, test statistic, and p-value. Conclusion; Interpretation; Solution. 1. x = life of battery
hypothesis testing. S.3 Hypothesis Testing. In reviewing hypothesis tests, we start first with the general idea. Then, we keep returning to the basic procedures of hypothesis testing, each time adding a little more detail. The general idea of hypothesis testing involves: Making an initial assumption. Collecting evidence (data).
A statistical hypothesis test is a method of statistical inference used to decide whether the data sufficiently support a particular hypothesis. A statistical hypothesis test typically involves a calculation of a test statistic. Then a decision is made, either by comparing the test statistic to a critical value or equivalently by evaluating a p ...
Test Statistic: One of the key components of a hypothesis test is what we call a test statistic. This is a calculation, sort of like a z-score, that is specific to the type of test being conducted. The idea behind a test statistic, relating it back to science projects, would be like calculations from measurements that were taken.
When to perform a statistical test. You can perform statistical tests on data that have been collected in a statistically valid manner - either through an experiment, or through observations made using probability sampling methods.. For a statistical test to be valid, your sample size needs to be large enough to approximate the true distribution of the population being studied.
The z test in hypothesis testing is used to find the z test statistic for normally distributed data. The z test is used when the standard deviation of the population is known and the sample size is greater than or equal to 30.
That is, the p-value is the probability of observing a test statistic as extreme or more extreme (as determined by the alternative hypothesis), assuming the null hypothesis is true. Our observed p-value for the Airbnb host example demonstrates that the probability of getting a sample mean host time of 2188 days (the value from our sample) or ...
In this video there was no critical value set for this experiment. In the last seconds of the video, Sal briefly mentions a p-value of 5% (0.05), which would have a critical of value of z = (+/-) 1.96. Since the experiment produced a z-score of 3, which is more extreme than 1.96, we reject the null hypothesis.
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method used to make inferences about a population based on sample data. It involves formulating two hypotheses: the null hypothesis (H0), which represents the default assumption, and the alternative hypothesis (Ha), which contradicts H0.
where μ denotes the mean distance between the holes. Step 2. The sample is small and the population standard deviation is unknown. Thus the test statistic is. T = x¯ −μ0 s/ n−−√. and has the Student t -distribution with n − 1 = 4 − 1 = 3 degrees of freedom. Step 3. From the data we compute x¯ = 0.02075 and s = 0.00171.
The following screen shots display the summary statistics from the hypothesis test. Figure 9.6.13. ... the sample data indicates that we should reject the null hypothesis. In conclusion, the sample data support the claim that the proportion of sexual assaults in Daviess County, Kentucky is different from the national average proportion. ...
A test is considered to be statistically significant when the p-value is less than or equal to the level of significance, also known as the alpha ( α) level. For this class, unless otherwise specified, α = 0.05; this is the most frequently used alpha level in many fields. Sample statistics vary from the population parameter randomly.
Simple hypothesis testing. Niels has a Magic 8 -Ball, which is a toy used for fortune-telling or seeking advice. To consult the ball, you ask the ball a question and shake it. One of 5 different possible answers then appears at random in the ball. Niels sensed that the ball answers " Ask again later " too frequently.
Title: The Sample Complexity of Simple Binary Hypothesis Testing Authors: Ankit Pensia , Varun Jog , Po-Ling Loh View a PDF of the paper titled The Sample Complexity of Simple Binary Hypothesis Testing, by Ankit Pensia and 2 other authors
Alright, so in the given question we are going to conduct a hypothesis test. So, our null hypothesis here is that the population average is 150 while the alternative hypothesis is that population average is greater than 150, right. So, this is a right tailed hypothesis test, right. Now the size of the sample here is it is 20 alright and the ...
We note that \(\Delta _f(F,G) \le \Delta ^*_f(F,G)\).. Remark 2. X and Y independent.. Kochar [] proposed a test W based on a U-statistic, and Kochar [] proposed another test S based on a linear ordered rank statistics.These tests can be applied when the two samples are of equal sizes (\(n = m\), n and m are sizes of samples from F and G, respectively).We give the definitions of W and S tests ...
An Introduction to Statistics class in Davies County, KY conducted a hypothesis test at the local high school (a medium sized-approximately 1,200 students-small city demographic) to determine if the local high school's percentage was lower. One hundred fifty students were chosen at random and surveyed.
Statistics and Probability questions and answers; A hypothesis test with a sample of n=15 participants produces a t statistic of t=+2.72. Assuming a one-tailed test with the critical region in the right-hand tail, what is the correct decision?Select one:a. The researcher can reject the null hypothesis with α=.05 but not with α=.01.b.
View a PDF of the paper titled Sample complexity of quantum hypothesis testing, by Hao-Chung Cheng and 5 other authors ... Information Theory (cs.IT); Machine Learning (cs.LG); Statistics Theory (math.ST) Cite as: ... 26 Mar 2024 16:57:01 UTC (164 KB) Full-text links: Access Paper: View a PDF of the paper titled Sample complexity of quantum ...