Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

4 Writing the Materials and Methods (Methodology) Section
The Materials and Methods section briefly describes how you did your research. In other words, what did you do to answer your research question? If there were materials used for the research or materials experimented on you list them in this section. You also describe how you did the research or experiment. The key to a methodology is that another person must be able to replicate your research—follow the steps you take. For example if you used the internet to do a search it is not enough to say you “searched the internet.” A reader would need to know which search engine and what key words you used.
Open this section by describing the overall approach you took or the materials used. Then describe to the readers step-by-step the methods you used including any data analysis performed. See Fig. 2.5 below for an example of materials and methods section.
Writing tips:
- Explain procedures, materials, and equipment used
- Example: “We used an x-ray fluorescence spectrometer to analyze major and trace elements in the mystery mineral samples.”
- Order events chronologically, perhaps with subheadings (Field work, Lab Analysis, Statistical Models)
- Use past tense (you did X, Y, Z)
- Quantify measurements
- Include results in the methods! It’s easy to make this mistake!
- Example: “W e turned on the machine and loaded in our samples, then calibrated the instrument and pushed the start button and waited one hour. . . .”

Technical Writing @ SLCC Copyright © 2020 by Department of English, Linguistics, and Writing Studies at SLCC is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Your Methods

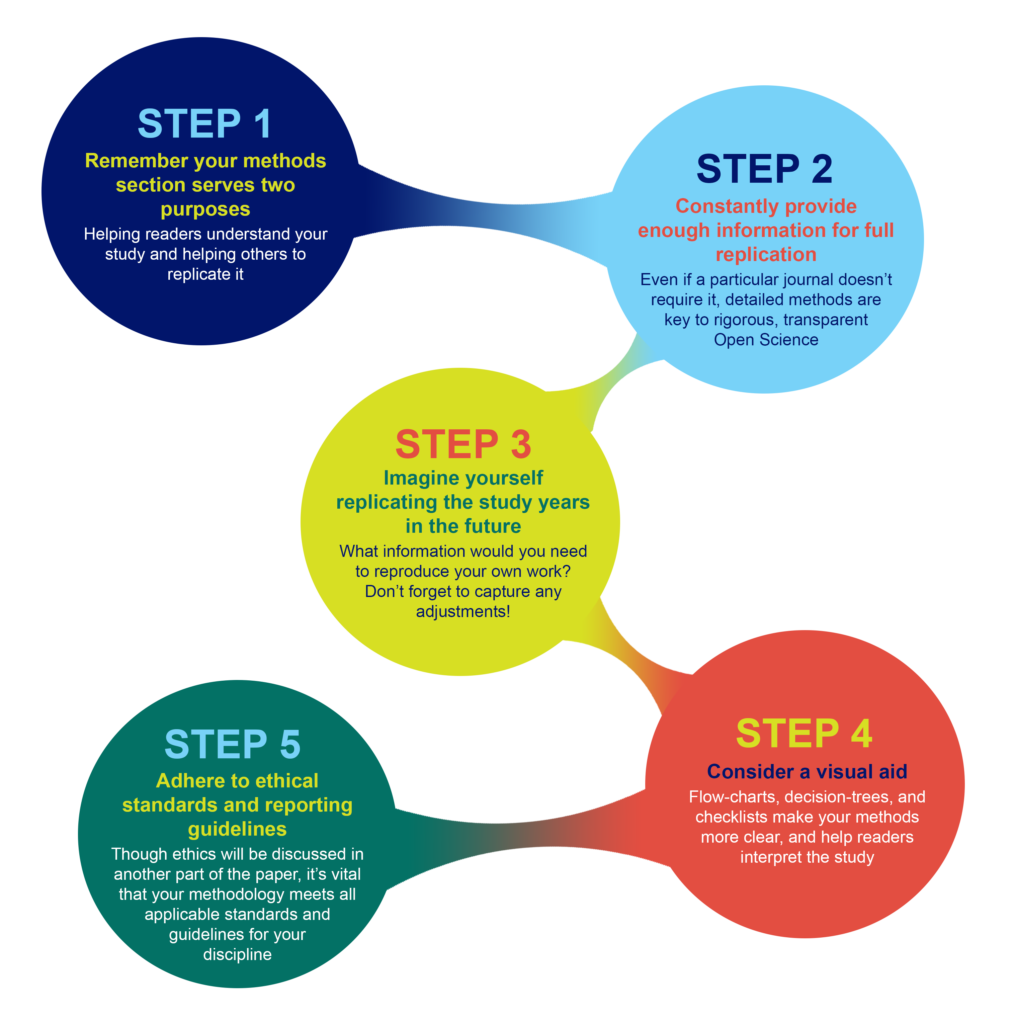
Ensure understanding, reproducibility and replicability
What should you include in your methods section, and how much detail is appropriate?
Why Methods Matter
The methods section was once the most likely part of a paper to be unfairly abbreviated, overly summarized, or even relegated to hard-to-find sections of a publisher’s website. While some journals may responsibly include more detailed elements of methods in supplementary sections, the movement for increased reproducibility and rigor in science has reinstated the importance of the methods section. Methods are now viewed as a key element in establishing the credibility of the research being reported, alongside the open availability of data and results.
A clear methods section impacts editorial evaluation and readers’ understanding, and is also the backbone of transparency and replicability.
For example, the Reproducibility Project: Cancer Biology project set out in 2013 to replicate experiments from 50 high profile cancer papers, but revised their target to 18 papers once they understood how much methodological detail was not contained in the original papers.
What to include in your methods section
What you include in your methods sections depends on what field you are in and what experiments you are performing. However, the general principle in place at the majority of journals is summarized well by the guidelines at PLOS ONE : “The Materials and Methods section should provide enough detail to allow suitably skilled investigators to fully replicate your study. ” The emphases here are deliberate: the methods should enable readers to understand your paper, and replicate your study. However, there is no need to go into the level of detail that a lay-person would require—the focus is on the reader who is also trained in your field, with the suitable skills and knowledge to attempt a replication.
A constant principle of rigorous science
A methods section that enables other researchers to understand and replicate your results is a constant principle of rigorous, transparent, and Open Science. Aim to be thorough, even if a particular journal doesn’t require the same level of detail . Reproducibility is all of our responsibility. You cannot create any problems by exceeding a minimum standard of information. If a journal still has word-limits—either for the overall article or specific sections—and requires some methodological details to be in a supplemental section, that is OK as long as the extra details are searchable and findable .
Imagine replicating your own work, years in the future
As part of PLOS’ presentation on Reproducibility and Open Publishing (part of UCSF’s Reproducibility Series ) we recommend planning the level of detail in your methods section by imagining you are writing for your future self, replicating your own work. When you consider that you might be at a different institution, with different account logins, applications, resources, and access levels—you can help yourself imagine the level of specificity that you yourself would require to redo the exact experiment. Consider:
- Which details would you need to be reminded of?
- Which cell line, or antibody, or software, or reagent did you use, and does it have a Research Resource ID (RRID) that you can cite?
- Which version of a questionnaire did you use in your survey?
- Exactly which visual stimulus did you show participants, and is it publicly available?
- What participants did you decide to exclude?
- What process did you adjust, during your work?
Tip: Be sure to capture any changes to your protocols
You yourself would want to know about any adjustments, if you ever replicate the work, so you can surmise that anyone else would want to as well. Even if a necessary adjustment you made was not ideal, transparency is the key to ensuring this is not regarded as an issue in the future. It is far better to transparently convey any non-optimal methods, or methodological constraints, than to conceal them, which could result in reproducibility or ethical issues downstream.
Visual aids for methods help when reading the whole paper
Consider whether a visual representation of your methods could be appropriate or aid understanding your process. A visual reference readers can easily return to, like a flow-diagram, decision-tree, or checklist, can help readers to better understand the complete article, not just the methods section.
Ethical Considerations
In addition to describing what you did, it is just as important to assure readers that you also followed all relevant ethical guidelines when conducting your research. While ethical standards and reporting guidelines are often presented in a separate section of a paper, ensure that your methods and protocols actually follow these guidelines. Read more about ethics .
Existing standards, checklists, guidelines, partners
While the level of detail contained in a methods section should be guided by the universal principles of rigorous science outlined above, various disciplines, fields, and projects have worked hard to design and develop consistent standards, guidelines, and tools to help with reporting all types of experiment. Below, you’ll find some of the key initiatives. Ensure you read the submission guidelines for the specific journal you are submitting to, in order to discover any further journal- or field-specific policies to follow, or initiatives/tools to utilize.
Tip: Keep your paper moving forward by providing the proper paperwork up front
Be sure to check the journal guidelines and provide the necessary documents with your manuscript submission. Collecting the necessary documentation can greatly slow the first round of peer review, or cause delays when you submit your revision.
Randomized Controlled Trials – CONSORT The Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) project covers various initiatives intended to prevent the problems of inadequate reporting of randomized controlled trials. The primary initiative is an evidence-based minimum set of recommendations for reporting randomized trials known as the CONSORT Statement .
Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses – PRISMA The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses ( PRISMA ) is an evidence-based minimum set of items focusing on the reporting of reviews evaluating randomized trials and other types of research.
Research using Animals – ARRIVE The Animal Research: Reporting of In Vivo Experiments ( ARRIVE ) guidelines encourage maximizing the information reported in research using animals thereby minimizing unnecessary studies. (Original study and proposal , and updated guidelines , in PLOS Biology .)
Laboratory Protocols Protocols.io has developed a platform specifically for the sharing and updating of laboratory protocols , which are assigned their own DOI and can be linked from methods sections of papers to enhance reproducibility. Contextualize your protocol and improve discovery with an accompanying Lab Protocol article in PLOS ONE .
Consistent reporting of Materials, Design, and Analysis – the MDAR checklist A cross-publisher group of editors and experts have developed, tested, and rolled out a checklist to help establish and harmonize reporting standards in the Life Sciences . The checklist , which is available for use by authors to compile their methods, and editors/reviewers to check methods, establishes a minimum set of requirements in transparent reporting and is adaptable to any discipline within the Life Sciences, by covering a breadth of potentially relevant methodological items and considerations. If you are in the Life Sciences and writing up your methods section, try working through the MDAR checklist and see whether it helps you include all relevant details into your methods, and whether it reminded you of anything you might have missed otherwise.
Summary Writing tips
The main challenge you may find when writing your methods is keeping it readable AND covering all the details needed for reproducibility and replicability. While this is difficult, do not compromise on rigorous standards for credibility!

- Keep in mind future replicability, alongside understanding and readability.
- Follow checklists, and field- and journal-specific guidelines.
- Consider a commitment to rigorous and transparent science a personal responsibility, and not just adhering to journal guidelines.
- Establish whether there are persistent identifiers for any research resources you use that can be specifically cited in your methods section.
- Deposit your laboratory protocols in Protocols.io, establishing a permanent link to them. You can update your protocols later if you improve on them, as can future scientists who follow your protocols.
- Consider visual aids like flow-diagrams, lists, to help with reading other sections of the paper.
- Be specific about all decisions made during the experiments that someone reproducing your work would need to know.

Don’t
- Summarize or abbreviate methods without giving full details in a discoverable supplemental section.
- Presume you will always be able to remember how you performed the experiments, or have access to private or institutional notebooks and resources.
- Attempt to hide constraints or non-optimal decisions you had to make–transparency is the key to ensuring the credibility of your research.
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
Materials and Methods: 7 Writing Tips
- Peer Review
- Research Process
Here are some tips for writing a good Materials and Methods section, which can lead to reproducibility of your results and credibility in the eyes of reviewers and readers.
Updated on January 2, 2011

One critical aspect of publishing research is describing the methods used in enough detail that the experiments can be reproduced by others. Some manuscripts are rejected because there is insufficient detail in the methods section.
In an editorial for the American Journal of Roentgenology , James Provenzale says, “ One of the more common reasons for rejection of a manuscript is that the reviewers cannot fully understand how the study was conducted. ” However, several journals have page limits or page charges, and the Materials and Methods section can take up valuable space.
For more tips on writing the Materials and Methods section of your manuscript, please see our downloadable white paper, Setting the Scene: Best Practices for Writing Materials and Methods .
What are the most important things to include, and how can you be sure that you're being concise AND sufficiently thorough? Here are seven tips for writing a good Materials and Methods section, which can lead to reproducibility of your results and credibility in the eyes of reviewers and readers. This list is not exhaustive; always remember to check the instructions for authors from your target journal for additional requirements or suggestions.
7 Tips for Writing an Effective Materials and Methods Section in Your Research Manuscript:
1. begin writing the materials and methods while you are performing your experiments..
Writing during the research process will prevent you from forgetting important details and save you time when you begin writing the full manuscript. You can also ask co-authors who performed specific experiments to write the corresponding parts of the Methods section.
2. Start with general information that applies to the entire manuscript and then move on to specific experimental details.
Examples of general information that you could begin with are characteristics of the study population, sources and genotypes of bacterial strains, or descriptions of samples or sample sites. Then, you could share more details about your experiment.
3. Match the order in which methods are described to the order of the results that were generated using those methods.
Also, be sure that each method you used is described, even if it is just a quick sentence (e.g., “Toxin assays were performed as described [reference]”). This practice is helpful for transparency, as well as reproducibility.
4. Always include citations for procedures that have been described previously.
If you made any modifications, be sure to list them.

5. Describe statistical tests as fully as possible.
Give as much information about the tests as possible; just mentioning a t -test is not sufficient for the reader to determine if the correct statistical analysis was performed.
6. Avoid discussing the pros and cons of certain methods or results of any kind.
Save evaluations for different methods for the Discussion section of your paper.
7. To save space, be concise, yet thorough, when listing the equipment you used.
You might consider listing all of your equipment purchased from a single company in one sentence. Or, you could create a flowchart figure of the steps in an important procedure.
Before you finish your manuscript, ask yourself the following questions about your Materials and Methods section to ensure that you have included all important information.
1. Is there sufficient detail so that the experiments can be reproduced?
2. Is there excess information that could be removed without affecting the interpretation of the results?
3. Are all the appropriate controls mentioned?
4. Are all appropriate citations included?
5. Is the source of each reagent listed?
Writing the Materials and Methods can be tedious, but a well-written section can enhance your chances of publication and strengthen your conclusions. If you have further questions, download our free white paper on writing the Materials and Methods section or send us an email . Best of luck with your research!

Ben Mudrak, PhD
See our "Privacy Policy"
We have a new app!
Take the Access library with you wherever you go—easy access to books, videos, images, podcasts, personalized features, and more.
Download the Access App here: iOS and Android . Learn more here!
- Remote Access
- Save figures into PowerPoint
- Download tables as PDFs

Chapter 5: Materials and Methods
- Download Chapter PDF
Disclaimer: These citations have been automatically generated based on the information we have and it may not be 100% accurate. Please consult the latest official manual style if you have any questions regarding the format accuracy.
Download citation file:
- Search Book
Jump to a Section
- ORGANIZATION
- SUMMARY OF GUIDELINES FOR THE MATERIALS AND METHODS SECTION
- EXERCISE 5.1: A CLEARLY WRITTEN METHODS SECTION
- EXERCISE 5.2: CONTENT AND ORGANIZATION IN THE METHODS SECTION
- Full Chapter
- Supplementary Content
For hypothesis-testing papers, the function of the Materials and Methods section (often referred to as the Methods section) is to tell the reader what experiments you did to answer the question posed in the Introduction. Similarly, for descriptive studies, the Methods section tells what experiments you did to obtain the message stated in the Introduction. For methods papers, the Methods section has two functions: it describes the new method in complete detail and also tells what experiments you did to test the new method. For all types of paper, the Methods section should include sufficient detail and references to permit a trained scientist to evaluate your work fully or to repeat the experiments exactly as you did them.
Hypothesis-Testing and Descriptive Papers
We saw that the first step in the story line of a hypothesis-testing or a descriptive paper is presented in the Introduction. This first step is either the question being asked or the structure being described. In either case, the second step in the story line is an overview of the experiments you did. This overview of the experiments gives the strategy of the experiments, the plan that connects the methods to each other and to the question or the message.
Where the overview of the experiments is presented depends on the type of research:
Methods Papers
For a Methods paper, the first step in the story line is a statement that you are presenting a new or improved material, method, or apparatus. The second step in the story line has two parts: a complete description of the new method, material, or apparatus; and a description of how this new method, material, or apparatus was tested. These two steps are described in the Methods section.
In this chapter, we will consider only Methods sections for hypothesis-testing papers.
Sign in or create a free Access profile below to access even more exclusive content.
With an Access profile, you can save and manage favorites from your personal dashboard, complete case quizzes, review Q&A, and take these feature on the go with our Access app.
Pop-up div Successfully Displayed
This div only appears when the trigger link is hovered over. Otherwise it is hidden from view.
Please Wait

Research Paper Writing: 5. Methods / Materials
- 1. Getting Started
- 2. Abstract
- 3. Introduction
- 4. Literature Review
- 5. Methods / Materials
- 6. Results / Analysis
- 7. Discussion
- 8. Conclusion
- 9. Reference
Methods / Materials Overview
These sections of the research paper should be concise. The audience reading the paper will always want to know what materials or methods that were used. The methods and materials may be under subheadings in the section or incorporated together. The main objective for these sections is to provide specialized materials, general procedures, and methods to judge the scientific value of the paper.
What to include in the sections
- Described separately
- Include the chemicals, biological, and any equipment
- Do not include common supplies, such as test tubes, pipette tips, beakers, etc. or standard lab equipment
- Single out sources like a specific type of equipment, enzyme, or a culture
- These should be mentioned in a separate paragraph with its own heading or highlighted in the procedure section if there is one
- Refer to solutions by name and describe
- Describes in detail how the analysis was conducted
- Be brief when presenting methods under the title devoted to a specific technique or groups of procedures
- Simplify and report what the procedure was
- Report the method by name
- Use third person passive voice, and avoid using first person
- Use normal text in these sections
- Avoid informal lists
- Use complete sentences
Example of a Methods Section
Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association Sixth Ed. 2010
- << Previous: 4. Literature Review
- Next: 6. Results / Analysis >>
- Last Updated: Nov 7, 2023 7:37 AM
- URL: https://wiu.libguides.com/researchpaperwriting
- SpringerLink shop
Materials and methods
The study’s methods are one of the most important parts used to judge the overall quality of the paper. In addition the Methods section should give readers enough information so that they can repeat the experiments. Reviewers should look for potential sources of bias in the way the study was designed and carried out, and for places where more explanation is needed.
The specific types of information in a Methods section will vary from field to field and from study to study. However, some general rules for Methods sections are:
- It should be clear from the Methods section how all of the data in the Results section were obtained.
- The study system should be clearly described. In medicine, for example, researchers need to specify the number of study subjects; how, when, and where the subjects were recruited, and that the study obtained appropriate ‘informed consent’ documents; and what criteria subjects had to meet to be included in the study.
- In most cases, the experiments should include appropriate controls or comparators. The conditions of the controls should be specified.
- The outcomes of the study should be defined, and the outcome measures should be objectively validated.
- The methods used to analyze the data must be statistically sound.
- For qualitative studies, an established qualitative research method (e.g. grounded theory is often used in sociology) must be used as appropriate for the study question.
- If the authors used a technique from a published study, they should include a citation and a summary of the procedure in the text. The method also needs to be appropriate to the present experiment.
- All materials and instruments should be identified, including the supplier’s name and location. For example, “Tests were conducted with a Vulcanizer 2.0 (XYZ Instruments, Mumbai, India).”
- The Methods section should not have information that belongs in another section (such as the Introduction or Results).
You may suggest if additional experiments would greatly improve the quality of the manuscript. Your suggestions should be in line with the study’s aims. Remember that almost any study could be strengthened by further experiments, so only suggest further work if you believe that the manuscript is not publishable without it.
Back │ Next
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write a Methods Section for a Psychology Paper
Tips and Examples of an APA Methods Section
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
Verywell / Brianna Gilmartin
The methods section of an APA format psychology paper provides the methods and procedures used in a research study or experiment . This part of an APA paper is critical because it allows other researchers to see exactly how you conducted your research.
Method refers to the procedure that was used in a research study. It included a precise description of how the experiments were performed and why particular procedures were selected. While the APA technically refers to this section as the 'method section,' it is also often known as a 'methods section.'
The methods section ensures the experiment's reproducibility and the assessment of alternative methods that might produce different results. It also allows researchers to replicate the experiment and judge the study's validity.
This article discusses how to write a methods section for a psychology paper, including important elements to include and tips that can help.
What to Include in a Method Section
So what exactly do you need to include when writing your method section? You should provide detailed information on the following:
- Research design
- Participants
- Participant behavior
The method section should provide enough information to allow other researchers to replicate your experiment or study.
Components of a Method Section
The method section should utilize subheadings to divide up different subsections. These subsections typically include participants, materials, design, and procedure.
Participants
In this part of the method section, you should describe the participants in your experiment, including who they were (and any unique features that set them apart from the general population), how many there were, and how they were selected. If you utilized random selection to choose your participants, it should be noted here.
For example: "We randomly selected 100 children from elementary schools near the University of Arizona."
At the very minimum, this part of your method section must convey:
- Basic demographic characteristics of your participants (such as sex, age, ethnicity, or religion)
- The population from which your participants were drawn
- Any restrictions on your pool of participants
- How many participants were assigned to each condition and how they were assigned to each group (i.e., randomly assignment , another selection method, etc.)
- Why participants took part in your research (i.e., the study was advertised at a college or hospital, they received some type of incentive, etc.)
Information about participants helps other researchers understand how your study was performed, how generalizable the result might be, and allows other researchers to replicate the experiment with other populations to see if they might obtain the same results.
In this part of the method section, you should describe the materials, measures, equipment, or stimuli used in the experiment. This may include:
- Testing instruments
- Technical equipment
- Any psychological assessments that were used
- Any special equipment that was used
For example: "Two stories from Sullivan et al.'s (1994) second-order false belief attribution tasks were used to assess children's understanding of second-order beliefs."
For standard equipment such as computers, televisions, and videos, you can simply name the device and not provide further explanation.
Specialized equipment should be given greater detail, especially if it is complex or created for a niche purpose. In some instances, such as if you created a special material or apparatus for your study, you might need to include an illustration of the item in the appendix of your paper.
In this part of your method section, describe the type of design used in the experiment. Specify the variables as well as the levels of these variables. Identify:
- The independent variables
- Dependent variables
- Control variables
- Any extraneous variables that might influence your results.
Also, explain whether your experiment uses a within-groups or between-groups design.
For example: "The experiment used a 3x2 between-subjects design. The independent variables were age and understanding of second-order beliefs."
The next part of your method section should detail the procedures used in your experiment. Your procedures should explain:
- What the participants did
- How data was collected
- The order in which steps occurred
For example: "An examiner interviewed children individually at their school in one session that lasted 20 minutes on average. The examiner explained to each child that he or she would be told two short stories and that some questions would be asked after each story. All sessions were videotaped so the data could later be coded."
Keep this subsection concise yet detailed. Explain what you did and how you did it, but do not overwhelm your readers with too much information.
Tips for How to Write a Methods Section
In addition to following the basic structure of an APA method section, there are also certain things you should remember when writing this section of your paper. Consider the following tips when writing this section:
- Use the past tense : Always write the method section in the past tense.
- Be descriptive : Provide enough detail that another researcher could replicate your experiment, but focus on brevity. Avoid unnecessary detail that is not relevant to the outcome of the experiment.
- Use an academic tone : Use formal language and avoid slang or colloquial expressions. Word choice is also important. Refer to the people in your experiment or study as "participants" rather than "subjects."
- Use APA format : Keep a style guide on hand as you write your method section. The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association is the official source for APA style.
- Make connections : Read through each section of your paper for agreement with other sections. If you mention procedures in the method section, these elements should be discussed in the results and discussion sections.
- Proofread : Check your paper for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors.. typos, grammar problems, and spelling errors. Although a spell checker is a handy tool, there are some errors only you can catch.
After writing a draft of your method section, be sure to get a second opinion. You can often become too close to your work to see errors or lack of clarity. Take a rough draft of your method section to your university's writing lab for additional assistance.
A Word From Verywell
The method section is one of the most important components of your APA format paper. The goal of your paper should be to clearly detail what you did in your experiment. Provide enough detail that another researcher could replicate your study if they wanted.
Finally, if you are writing your paper for a class or for a specific publication, be sure to keep in mind any specific instructions provided by your instructor or by the journal editor. Your instructor may have certain requirements that you need to follow while writing your method section.
Frequently Asked Questions
While the subsections can vary, the three components that should be included are sections on the participants, the materials, and the procedures.
- Describe who the participants were in the study and how they were selected.
- Define and describe the materials that were used including any equipment, tests, or assessments
- Describe how the data was collected
To write your methods section in APA format, describe your participants, materials, study design, and procedures. Keep this section succinct, and always write in the past tense. The main heading of this section should be labeled "Method" and it should be centered, bolded, and capitalized. Each subheading within this section should be bolded, left-aligned and in title case.
The purpose of the methods section is to describe what you did in your experiment. It should be brief, but include enough detail that someone could replicate your experiment based on this information. Your methods section should detail what you did to answer your research question. Describe how the study was conducted, the study design that was used and why it was chosen, and how you collected the data and analyzed the results.
Erdemir F. How to write a materials and methods section of a scientific article ? Turk J Urol . 2013;39(Suppl 1):10-5. doi:10.5152/tud.2013.047
Kallet RH. How to write the methods section of a research paper . Respir Care . 2004;49(10):1229-32. PMID: 15447808.
American Psychological Association. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). Washington DC: The American Psychological Association; 2019.
American Psychological Association. APA Style Journal Article Reporting Standards . Published 2020.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Writing the materials and methods
Affiliation.
- 1 Department of Biomedical Imaging, Biomedical Imaging and Interventional Journal, University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. [email protected]
- PMID: 19037549
When writing scientific papers to share their research findings with their peers, it is not enough for researchers to just communicate the results of their study; it is equally important to explain the process by which they arrived at their results, so that the study can be replicated to validate the observations. The materials and methods section is used to describe the experimental design and provide sufficient details so that a competent colleague can repeat the experiment. A good materials and methods section will enable readers to evaluate the research performed and replicate the study, if necessary.
- Biomedical Research
- Periodicals as Topic*
- Publications
- Research Design
- Writing / standards
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Methodology – Types, Examples and writing Guide
Research Methodology – Types, Examples and writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Methodology
Definition:
Research Methodology refers to the systematic and scientific approach used to conduct research, investigate problems, and gather data and information for a specific purpose. It involves the techniques and procedures used to identify, collect , analyze , and interpret data to answer research questions or solve research problems . Moreover, They are philosophical and theoretical frameworks that guide the research process.
Structure of Research Methodology
Research methodology formats can vary depending on the specific requirements of the research project, but the following is a basic example of a structure for a research methodology section:
I. Introduction
- Provide an overview of the research problem and the need for a research methodology section
- Outline the main research questions and objectives
II. Research Design
- Explain the research design chosen and why it is appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Discuss any alternative research designs considered and why they were not chosen
- Describe the research setting and participants (if applicable)
III. Data Collection Methods
- Describe the methods used to collect data (e.g., surveys, interviews, observations)
- Explain how the data collection methods were chosen and why they are appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Detail any procedures or instruments used for data collection
IV. Data Analysis Methods
- Describe the methods used to analyze the data (e.g., statistical analysis, content analysis )
- Explain how the data analysis methods were chosen and why they are appropriate for the research question(s) and objectives
- Detail any procedures or software used for data analysis
V. Ethical Considerations
- Discuss any ethical issues that may arise from the research and how they were addressed
- Explain how informed consent was obtained (if applicable)
- Detail any measures taken to ensure confidentiality and anonymity
VI. Limitations
- Identify any potential limitations of the research methodology and how they may impact the results and conclusions
VII. Conclusion
- Summarize the key aspects of the research methodology section
- Explain how the research methodology addresses the research question(s) and objectives
Research Methodology Types
Types of Research Methodology are as follows:
Quantitative Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection and analysis of numerical data using statistical methods. This type of research is often used to study cause-and-effect relationships and to make predictions.
Qualitative Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection and analysis of non-numerical data such as words, images, and observations. This type of research is often used to explore complex phenomena, to gain an in-depth understanding of a particular topic, and to generate hypotheses.
Mixed-Methods Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that combines elements of both quantitative and qualitative research. This approach can be particularly useful for studies that aim to explore complex phenomena and to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a particular topic.
Case Study Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves in-depth examination of a single case or a small number of cases. Case studies are often used in psychology, sociology, and anthropology to gain a detailed understanding of a particular individual or group.
Action Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves a collaborative process between researchers and practitioners to identify and solve real-world problems. Action research is often used in education, healthcare, and social work.
Experimental Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the manipulation of one or more independent variables to observe their effects on a dependent variable. Experimental research is often used to study cause-and-effect relationships and to make predictions.
Survey Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the collection of data from a sample of individuals using questionnaires or interviews. Survey research is often used to study attitudes, opinions, and behaviors.
Grounded Theory Research Methodology
This is a research methodology that involves the development of theories based on the data collected during the research process. Grounded theory is often used in sociology and anthropology to generate theories about social phenomena.
Research Methodology Example
An Example of Research Methodology could be the following:
Research Methodology for Investigating the Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Reducing Symptoms of Depression in Adults
Introduction:
The aim of this research is to investigate the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) in reducing symptoms of depression in adults. To achieve this objective, a randomized controlled trial (RCT) will be conducted using a mixed-methods approach.
Research Design:
The study will follow a pre-test and post-test design with two groups: an experimental group receiving CBT and a control group receiving no intervention. The study will also include a qualitative component, in which semi-structured interviews will be conducted with a subset of participants to explore their experiences of receiving CBT.
Participants:
Participants will be recruited from community mental health clinics in the local area. The sample will consist of 100 adults aged 18-65 years old who meet the diagnostic criteria for major depressive disorder. Participants will be randomly assigned to either the experimental group or the control group.
Intervention :
The experimental group will receive 12 weekly sessions of CBT, each lasting 60 minutes. The intervention will be delivered by licensed mental health professionals who have been trained in CBT. The control group will receive no intervention during the study period.
Data Collection:
Quantitative data will be collected through the use of standardized measures such as the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II) and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7). Data will be collected at baseline, immediately after the intervention, and at a 3-month follow-up. Qualitative data will be collected through semi-structured interviews with a subset of participants from the experimental group. The interviews will be conducted at the end of the intervention period, and will explore participants’ experiences of receiving CBT.
Data Analysis:
Quantitative data will be analyzed using descriptive statistics, t-tests, and mixed-model analyses of variance (ANOVA) to assess the effectiveness of the intervention. Qualitative data will be analyzed using thematic analysis to identify common themes and patterns in participants’ experiences of receiving CBT.
Ethical Considerations:
This study will comply with ethical guidelines for research involving human subjects. Participants will provide informed consent before participating in the study, and their privacy and confidentiality will be protected throughout the study. Any adverse events or reactions will be reported and managed appropriately.
Data Management:
All data collected will be kept confidential and stored securely using password-protected databases. Identifying information will be removed from qualitative data transcripts to ensure participants’ anonymity.
Limitations:
One potential limitation of this study is that it only focuses on one type of psychotherapy, CBT, and may not generalize to other types of therapy or interventions. Another limitation is that the study will only include participants from community mental health clinics, which may not be representative of the general population.
Conclusion:
This research aims to investigate the effectiveness of CBT in reducing symptoms of depression in adults. By using a randomized controlled trial and a mixed-methods approach, the study will provide valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying the relationship between CBT and depression. The results of this study will have important implications for the development of effective treatments for depression in clinical settings.
How to Write Research Methodology
Writing a research methodology involves explaining the methods and techniques you used to conduct research, collect data, and analyze results. It’s an essential section of any research paper or thesis, as it helps readers understand the validity and reliability of your findings. Here are the steps to write a research methodology:
- Start by explaining your research question: Begin the methodology section by restating your research question and explaining why it’s important. This helps readers understand the purpose of your research and the rationale behind your methods.
- Describe your research design: Explain the overall approach you used to conduct research. This could be a qualitative or quantitative research design, experimental or non-experimental, case study or survey, etc. Discuss the advantages and limitations of the chosen design.
- Discuss your sample: Describe the participants or subjects you included in your study. Include details such as their demographics, sampling method, sample size, and any exclusion criteria used.
- Describe your data collection methods : Explain how you collected data from your participants. This could include surveys, interviews, observations, questionnaires, or experiments. Include details on how you obtained informed consent, how you administered the tools, and how you minimized the risk of bias.
- Explain your data analysis techniques: Describe the methods you used to analyze the data you collected. This could include statistical analysis, content analysis, thematic analysis, or discourse analysis. Explain how you dealt with missing data, outliers, and any other issues that arose during the analysis.
- Discuss the validity and reliability of your research : Explain how you ensured the validity and reliability of your study. This could include measures such as triangulation, member checking, peer review, or inter-coder reliability.
- Acknowledge any limitations of your research: Discuss any limitations of your study, including any potential threats to validity or generalizability. This helps readers understand the scope of your findings and how they might apply to other contexts.
- Provide a summary: End the methodology section by summarizing the methods and techniques you used to conduct your research. This provides a clear overview of your research methodology and helps readers understand the process you followed to arrive at your findings.
When to Write Research Methodology
Research methodology is typically written after the research proposal has been approved and before the actual research is conducted. It should be written prior to data collection and analysis, as it provides a clear roadmap for the research project.
The research methodology is an important section of any research paper or thesis, as it describes the methods and procedures that will be used to conduct the research. It should include details about the research design, data collection methods, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations.
The methodology should be written in a clear and concise manner, and it should be based on established research practices and standards. It is important to provide enough detail so that the reader can understand how the research was conducted and evaluate the validity of the results.
Applications of Research Methodology
Here are some of the applications of research methodology:
- To identify the research problem: Research methodology is used to identify the research problem, which is the first step in conducting any research.
- To design the research: Research methodology helps in designing the research by selecting the appropriate research method, research design, and sampling technique.
- To collect data: Research methodology provides a systematic approach to collect data from primary and secondary sources.
- To analyze data: Research methodology helps in analyzing the collected data using various statistical and non-statistical techniques.
- To test hypotheses: Research methodology provides a framework for testing hypotheses and drawing conclusions based on the analysis of data.
- To generalize findings: Research methodology helps in generalizing the findings of the research to the target population.
- To develop theories : Research methodology is used to develop new theories and modify existing theories based on the findings of the research.
- To evaluate programs and policies : Research methodology is used to evaluate the effectiveness of programs and policies by collecting data and analyzing it.
- To improve decision-making: Research methodology helps in making informed decisions by providing reliable and valid data.
Purpose of Research Methodology
Research methodology serves several important purposes, including:
- To guide the research process: Research methodology provides a systematic framework for conducting research. It helps researchers to plan their research, define their research questions, and select appropriate methods and techniques for collecting and analyzing data.
- To ensure research quality: Research methodology helps researchers to ensure that their research is rigorous, reliable, and valid. It provides guidelines for minimizing bias and error in data collection and analysis, and for ensuring that research findings are accurate and trustworthy.
- To replicate research: Research methodology provides a clear and detailed account of the research process, making it possible for other researchers to replicate the study and verify its findings.
- To advance knowledge: Research methodology enables researchers to generate new knowledge and to contribute to the body of knowledge in their field. It provides a means for testing hypotheses, exploring new ideas, and discovering new insights.
- To inform decision-making: Research methodology provides evidence-based information that can inform policy and decision-making in a variety of fields, including medicine, public health, education, and business.
Advantages of Research Methodology
Research methodology has several advantages that make it a valuable tool for conducting research in various fields. Here are some of the key advantages of research methodology:
- Systematic and structured approach : Research methodology provides a systematic and structured approach to conducting research, which ensures that the research is conducted in a rigorous and comprehensive manner.
- Objectivity : Research methodology aims to ensure objectivity in the research process, which means that the research findings are based on evidence and not influenced by personal bias or subjective opinions.
- Replicability : Research methodology ensures that research can be replicated by other researchers, which is essential for validating research findings and ensuring their accuracy.
- Reliability : Research methodology aims to ensure that the research findings are reliable, which means that they are consistent and can be depended upon.
- Validity : Research methodology ensures that the research findings are valid, which means that they accurately reflect the research question or hypothesis being tested.
- Efficiency : Research methodology provides a structured and efficient way of conducting research, which helps to save time and resources.
- Flexibility : Research methodology allows researchers to choose the most appropriate research methods and techniques based on the research question, data availability, and other relevant factors.
- Scope for innovation: Research methodology provides scope for innovation and creativity in designing research studies and developing new research techniques.
Research Methodology Vs Research Methods
About the author.
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like


How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Help | Advanced Search
Condensed Matter > Soft Condensed Matter
Title: a snapshot review on soft-materials assembly design utilizing machine learning methods.
Abstract: Since the surge of data in materials science research and the advancement in machine learning methods, an increasing number of researchers are introducing machine learning techniques into the next generation of materials discovery, ranging from neural-network learned potentials to automated characterization techniques for experimental images. In this snapshot review, we first summarize the landscape of techniques for soft materials assembly design that do not employ machine learning or artificial intelligence and then discuss specific machine-learning and artificial-intelligence-based methods that enhance the design pipeline, such as high-throughput crystal-structure characterization and the inverse design of building blocks for materials assembly and properties. Additionally, we survey the landscape of current developments of scientific software, especially in the context of their compatibility with traditional molecular dynamics engines such as LAMMPS and HOOMD-blue.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
Training videos | Faqs

Limitations in Research – A Simplified Guide with Examples
Limitations are flaws and shortcomings of your study. It is very important that you discuss the limitations of your study in the discussion section of your research paper. In this blog, we provide tips for presenting study limitations in your paper along with some real-world examples.
1. Should I Report the Limitations of My Work?

Most studies will have some form of limitation. So be honest and don’t hide your limitations. You have to tell your readers how your limitations might influence the outcomes and conclusions of your research. In reality, your readers and reviewers will be impressed with your paper if you are upfront about your limitations.
2. Examples
Let’s look at some examples. We have selected a variety of examples from different research topics.
2.1. Limitations Example 1
Following example is from a Medical research paper.
✔ The authors talk about the limitations and emphasis the importance of reconfirming the findings in a much larger study Study design and small sample size are important limitations. This could have led to an overestimation of the effect. Future research should reconfirm these findings by conducting larger-scale studies. _ Limitation s _ How it might affect the results? _ How to fix the limitation?
The authors are saying that the main limitations of the study are the small sample size and weak study design. Then they explain how this might have affected their results. They are saying that it is possible that they are overestimating the actual effect they are measuring. Then finally they are telling the readers that more studies with larger sample sizes should be conducted to reconfirm the findings.
As you can see, the authors are clearly explaining three things here: (1) What is the limitation? (2) How it might affect the study outcomes? and (3) What should be done to address the limitation?
2.2. Limitations Example 2
Following example is from an Engineering research paper.
✔ The authors are acknowledging the limitations and warning readers against generalizing the research findings However, some study limitations should be acknowledged. The experiments do not fully consider the problems that can appear in real situations. Hence, caution should be taken with generalizing the findings and applying them to real-life situations. _ Acknowledging limitations _ Explaining the limitation _ How it might affect the results?
The authors acknowledge that their study has some limitations. Then they explain what the limitations are. They are saying that their experiments do not consider all problems that might occur in real-life situations. Then they explain how this might affect their research outcomes. They are saying that readers should be careful when generalizing the results to practical real-world situations, because there is a possibility that the methods might fail.
2.3. Limitations Example 3
It is important to remember not to end your paper with limitations. Finish your paper on a positive note by telling your readers about the benefits of your research and possible future directions. In the following example, right after listing the limitations, the authors proceed to talk about the positive aspects of the work.
✔ The authors finish their paper on a positive note by talking about the benefits of their work and possible future work With this limited study, it is not known whether this finding can be applied to all clinical scenarios. Notwithstanding these limitations, this study has proven that Ultrasound can potentially serve as a more efficient alternative to X-rays in diagnosis. Future directions include studying the effects of different ultrasound pulsing schemes on pain relief. Another interesting direction would be to consider applications in nonhuman primates. _ Limitations _ Benefits of the work _ Possible future directions
The authors are saying that their experiments were somewhat limited and are not sure if their findings apply to the wider clinical practice. Then the authors highlight the benefits of their research. The authors say that their study has proven that ultrasound can be used instead of X-rays for diagnosis of certain types of diseases. Then they are explaining how future research can extend this work further. The authors are suggesting that it will be interesting to explore if ultrasound can be used for the treatment of chronic pain. And they are also suggesting that future studies can explore treating certain types of animal diseases with ultrasound. This is a very good example of how to finish the discussion section of your paper on a positive note.
Limitations are a vital component of the discussion section of your research paper. Remember, every study has limitations. There is no such thing as a perfect study. One of the major mistakes beginner writers make is hiding the limitations in the paper. Don’t do this, reviewers will reject your paper. Explain clearly how your limitations might have impacted your results, and provide ideas to mitigate them in the future. For further reading, please refer to our blogs on handling negative results and advanced tactics to address study limitations.
If you have any questions, please drop a comment below, and we will answer as soon as possible. We also recommend you to refer to our other blogs on academic writing tools , academic writing resources , academic writing phrases and research paper examples which are relevant to the topic discussed in this blog.
Similar Posts

Materials and Methods Examples and Writing Tips
In this blog, we will go through many materials and methods examples and understand how to write a clear and concise method section for your research paper.

Writing a Medical Clinical Trial Research Paper – Example & Format
In this blog, we will teach you step-by-step how to write a clinical trial research paper for publication in a high quality scientific journal.

Research Paper Structure – Main Sections and Parts of a Research Paper
In this blog, we explain various topics and sub-topics to be included under each section of a research paper via word cloud diagrams.

A New Academic Writing Technique and Tool for Foreign Non-native English Speaking PhD students
In this blog, we explain various writing difficulties faced by international students and introduce the concept of ‘imitative learning’.

Writing a Questionnaire Survey Research Paper – Example & Format
In this blog, we will explain how to write a survey questionnaire paper and discuss all the important points to consider while writing the research paper.

Mastering Verb Tenses in Literature Reviews
In this blog, we will see what tense you should use in the literature review section of your research paper.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- 10 Share Facebook
- 0 Share Twitter
- 0 Share LinkedIn
- 0 Share Email
Land use transition and its effect on ecosystem service value with introducing “three wastes” factor in the industrial county, China
- Research Article
- Published: 08 May 2024
Cite this article

- Qizhuo Zhou 1 na1 ,
- Yuan Song 1 na1 ,
- Yong Zhang 2 ,
- Zongli Ping 2 ,
- Yanfeng Zheng 2 ,
- Hongyan Chen ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9916-6101 1 ,
- Peng Liu 3 ,
- Pizheng Hong 4 &
- Zhiyuan Zheng 5
Land use transition and its impact on ecosystem service value (ESV) are the foundation for optimizing the layout of territorial space and ecological civilization construction. With the acceleration of industrialization and urbanization, the area of construction land expands in China. To accurately estimate the ESV in industrial counties, the impact of construction land on the ecological environment should be fully considered. This paper took Gangcheng District, Jinan City, a steel base in the Shandong Province of China as an example, then the value coefficients of “three wastes” factors (waste gas, wastewater, and waste) were introduced, and an improved calculation method of ESV was put forward for industrial counties in combination with remote sensing and land use data. Finally, the land use transition and its ESV effect in typical industrial counties were analyzed using geo-informatic Tupu and grid method. The results showed that the most important land use transitions were from grassland and forestland to cultivated land, from cultivated land and forestland to construction land in 1990–2010, and from cultivated land transformed to forestland in 2010–2021. The types of land use transition were mainly repetitive and continuous. The ESV first decreased and then increased, with a slight overall decline for more than 30 years, showing a spatial distribution characteristic of “low in the south-central and high around.” Land use transition had the impact on ESV with the negative contribution rate of 68.28% in 1990–2000 and 73.16% in 2000–2010, mainly caused by the transition from forestland and grassland to cultivated land and construction land, and the positive contribution rate of 81.72% in 2010–2021, mainly caused by the transition from cultivated land to forestland. Compared with the ESV calculation method without introducing the “three wastes” factor and Xie Gaodi’s method, the improved method in this paper considered the inevitable impact of construction land on ESV in industrial counties and made the ESV calculated more accurate according to the regional nature. This paper cannot only enrich the theories and technical methods of land use transition and its effects, and provide a case reference for similar industrial counties, but also provide data and decision-making support for the spatial layout and ecological protection in the study area.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
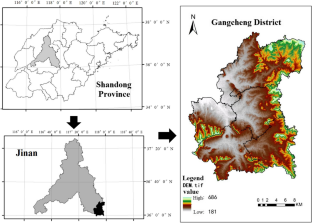
Data availability
The data sets used or analyzed in this study are from the China Statistical Yearbook, and the data sets used or analyzed in this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
Arowolo AO, Deng X, Olatunji OA, Obayelud AE (2018) Assessing changes in the value of ecosystem services in response to land-use/land-cover dynamics in Nigeria. Sci Total Environ 636:597–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.277
Article CAS Google Scholar
Bao D, Li J, Liu F, Hu JM (2021) Impact of land-use/land-cover change on ecosystem service values in Myanmar from 1995 to 2015. Acta Ecol Sin 41(17):6960–6969
Google Scholar
Birkhofer K, Diehl E, Andersson J et al (2015) Ecosystem services—current challenges and opportunities for ecological research. Front Ecol Evol 2(87):1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2014.00087
Article Google Scholar
Chen W, Zhao H, Li J, Zhu L, Wang Z, Zeng J (2020) Land use transitions and the associated impacts on ecosystem services in the middle reaches of the Yangtze river economic belt in China based on the geo-informatic TUPU method. Sci Total Environ 701:134690. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.134690
Costanza R, de Arge R, de Groot R, Farber S, Grasso M, Hannon B, Limburg K, Naeem S, Oneill RV, Paruelo J (1997) The value of the world’s ecosystem services and natural capital. Nature 387:253–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-8009(98)00020-2
Fei L, Shuwen Z, Jiuchun Y, Liping C, Haijuan Y, Kun B (2018) Effects of land use change on ecosystem services value in West Jilin since the reform and opening of China. Ecosystem Serv 31:12–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2018.03.009
Fengjiao Ma A, Eneji E, Liu J (2015) Assessment of ecosystem services and dis-services of an agro-ecosystem based on extended emergy framework: a case study of Luancheng county, North China. Ecol Eng 82:241–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.04.100
GOODCHILD MF (2022) Commentary: general principles and analytical frameworks in geography and GIScience. Annals of GIS 28:85–87. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475683.2022.2030943
Grimm NB, Foster D, Groffman P, Grove JM, Hopkinson CS, Nadelhoffer KJ, Nadelhoffer KJ, Peters DP (2008) The changing landscape: ecosystem responses to urbanization and pollution across climatic and societal gradients. Front Ecol Environ 6(5):264–272. https://doi.org/10.1890/070147
Guo P, Zhang F, Wang H (2022) The response of ecosystem service value to land use change in the middle and lower Yellow River: a case study of the Henan section. Ecol Ind 140:109019. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109019
Jiang W, Wu T, Fu B (2021) The value of ecosystem services in China: a systematic review for twenty years. Ecosyst Serv 52:101365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2021.101365
Kang Yu, Cheng C, Liu X, Zhang F, Li Z, Siqi Lu (2019) An ecosystem services value assessment of land-use change in Chengdu: based on a modification of scarcity factor. Phys Chem Earth A/B/C 110:157–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2019.01.003
Kusi KK, Khattabi A, Mhammdi N (2023) Analyzing the impact of land use change on ecosystem service value in the main watersheds of Morocco. Environ Dev Sustain 25(3):2688–2715. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-022-02162-4
Leviston Z, Walker I, Green M, Price J (2018) Linkages between ecosystem services and human wellbeing: a Nexus Webs approach. Ecol Indic 93:658–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2018.05.052
Li G, Fang C, Wang S (2016) Exploring spatio-temporal changes in ecosystem-service values and hotspots in China. Sci Total Environ 545–546:609–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.12.067
Li Y, Feng Y, Guo X et al (2017) Changes in coastal city ecosystem service values based on land use—A case study of Yingkou, China. Land Use Policy 65:287–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.04.021
Li Z, Jiang W, Wang W, Chen Z, Ling Z, Lv J (2020) Ecological risk assessment of the wetlands in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. Ecol Ind 117:106677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106677
Lin W, Xu D, Guo P et al (2019) Exploring variations of ecosystem service value in Hangzhou Bay Wetland Eastern China. Ecosystem Serv 37:100944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoser.2019.100944
Liu G, Zhang L, Zhang Q (2014) Spatial and temporal dynamics of land use and its influence on ecosystem service value in Yangtze river DELTA. Acta Ecologica Sinica 34:3311–3319. https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb201306121679
Liu J, Du J, Zhang C et al (2023) Ecosystem service assessment under ecological restoration programs: a systematic review of studies from China. Front Ecol Evol 11:1152907. https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2023.1152907
Long H, Liu Y, Hou X, Li T, Li Y (2014) Effects of land use transitions due to rapid urbanization on ecosystem services: implications for urban planning in the new developing area of China. Habitat Int 44:536–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2014.10.011
Long H, Yuan L, Yin Z, Wu X (2023) Spatiotemporal of ecosystem service values response to land use/cover change based on geo-informatic tupu – a case study in Tianjin China. Ecol Indic 154:110511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.110511
Lu X, Shi Y, Chen C, Yu M (2017) Monitoring cropland transition and its impact on ecosystem services value in developed regions of China: a case study of Jiangsu Province. Land Use Policy 69:25–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.08.035
Nijhum F, Westbrook C, Noble B, Belcher K, Lloyd-Smith P (2021) Evaluation of alternative land-use scenarios using an ecosystem services-based strategic environmental assessment approach. Land Use Policy 108:105540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2021.105540
Nuissl H, Siedentop S (2021) Urbanisation and land use change. Sustain Land Manag Eur Context 8:75–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-50841-8_5
Olushola AA, Xiangzheng D, Abiodun OO, Elijah OA (2018) Assessing changes in the value of ecosystem services in response to land-use/land-cover dynamics in Nigeria. Sci Total Environ 636:597–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.04.277
Peng K, Jiang W, Ling Z, Hou P, Deng Y (2021) Evaluating the potential impacts of land use changes on ecosystem service value under multiple scenarios in support of SDG reporting: a case study of the Wuhan urban agglomeration. J Clean Prod 307:127321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127321
Qinghua Y, Guoliang T, Gaohuarv L, Jingmin Y, Xin Y, Qingsheng L, Weiguo L, Shuguang W (2004) Tupu methods of spatial-temporal pattern on land use change. J Geogr Sci 14(2):131–142. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02837528
Qiu H, Baoqing Hu, Zhang Ze (2021) Impacts of land use change on ecosystem service value based on SDGs report—taking Guangxi as an example. Ecol Indic 133:108366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108366
Seto KC, Güneralp B, Hutyra LR (2012) Global forecasts of urban expansion to 2030 and direct impacts on biodiversity and carbon pools. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(40):16083–16088. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1211658109
Song W, Deng X (2017) Land-use/land-cover change and ecosystem service provision in China. Sci. Total Environment 576:705–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.07.078
Song W, Wu C (2021) Introduction to advancements of GIS in the new IT era. Ann GIS 27(1):1–4. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475683.2021.1890920
Wang C, Zhan J, Chu Xi, Liu W, Zhang F (2019) Variation in ecosystem services with rapid urbanization: a study of carbon sequestration in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region, China. Phys Chem Earth A/B/C 110:195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2018.09.001
Wang Y, Zhang Z, Chen X (2022) Spatiotemporal change in ecosystem service value in response to land use change in Guizhou Province, southwest China. Ecol Ind 144:109514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2022.109514
Wu Y, Huang Z, Han D, Qiu X, Pan Y (2023) Evolution of urban ecosystem service value and a scenario analysis based on land utilization changes: a case study of Hangzhou China. Sustainability 15(10):8274. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15108274
Xiao Yu, Huang M, Xie G, Zhen L (2022) Evaluating the impacts of land use change on ecosystem service values under multiple scenarios in the Hunshandake region of China. Sci Total Environ 850:158067. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158067
Xie G, Xiao Y, Zhen L, Lu C (2005) Study on ecosystem services value of food production in China. Chin J Eco-Agric 13(3):10–13
Xie G, Zhen L, Lu C, Xiao Y, Chen C (2008) Expert knowledge based valuation method of ecosystem services in China. J Nat Resour 23(5):911–919 ( http://www.jnr.ac.cn/EN/10.11849/zrzyxb.2008.05.019 )
Xie G, Zhang C, Zhang L, Chen W, Li S (2015) Improvement of the evaluation method for ecosystem service value based on per unit area. J Nat Resour 30(8):1243–1254 ( http://www.jnr.ac.cn/EN/10.11849/zrzyxb.2015.08.001 )
Xie H, He Y et al (2020) Warning of negative effects of land-use changes on ecological security based on GIS. Sci Total Environ 704:135427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135427
Xiong Y, Li H, Meichen Fu, Ma X, Wang L (2022) Evaluation of ecosystem service change patterns in a mining-based city: a case study of Wu’an City. Land 11(6):895. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11060895
Zhang H, Zhou C et al (2020) The connotation and inheritance of geo-information Tupu. J Geo-Inf Sci 4:653–661 ( https://www.dqxxkx.cn/EN/10.12082/dqxxkx.2020.200167 )
Zhao S, Yin M (2023) Change of urban and rural construction land and driving factors of arable land occupation. PLoS One 18(5):e0286248. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0286248
Zoderer BM, Tasser E, Erb K-H, Stanghellini PSL, Tappeiner U (2016) Identifying and mapping the tourists’ perception of cultural ecosystem services: a case study from an Alpine region. Land Use Policy 56:251–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.landusepol.2016.05.004
Download references
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program Project (grant number 2023YFD2303304) the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province of China (grant number ZR2023MD033) and the Key Research and Development Project of Shandong Province (grant number LJNY202103).
Author information
Qizhuo Zhou and Yuan Song are contributed equally to this work.
Authors and Affiliations
National Engineering Research Center for Efficient Utilization of Soil and Fertilizer, Department of Resources and Environment, Shandong Agricultural University, Taian, 271000, China
Qizhuo Zhou, Yuan Song & Hongyan Chen
Shandong Provincial Institute of Territorial Space Planning, Jinan, 250000, China
Yong Zhang, Zongli Ping & Yanfeng Zheng
Department of Agronomy, Shandong Agricultural University, Taian, 271000, China
Key Laboratory of Humic Acid Fertilizer of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Shandong Nongda Fertilizer Sci.&Tech. Co. Ltd, Feicheng, 271600, Shandong, Taian, China
Pizheng Hong
Northwest A&F University, Xianyang, 712000, China
Zhiyuan Zheng
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualization, data analysis, methodology, and writing—original draft preparation: Qizhuo Zhou, Yuan Song; writing—review and editing: Hongyan Chen; visualization and investigation: Yong Zhang, Zongli Ping; formal analysis and investigation: Yong Zhang, Yanfeng Zheng; funding acquisition: Hongyan Chen, Peng Liu; supervision: Pizheng Hong, Zhiyuan Zheng. All authors have read and approved this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Hongyan Chen .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval.
No ethical approval was necessary for this study.
Consent to participate
All participants in this study consent to participation.
Consent for publication
All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Zhihong Xu
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Zhou, Q., Song, Y., Zhang, Y. et al. Land use transition and its effect on ecosystem service value with introducing “three wastes” factor in the industrial county, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33569-3
Download citation
Received : 18 December 2023
Accepted : 30 April 2024
Published : 08 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-024-33569-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Land use transition
- Ecosystem services value
- Industrial county
- Ecological efficiency
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Social justice
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
Physicists arrange atoms in extremely close proximity
Press contact :, media download.
*Terms of Use:
Images for download on the MIT News office website are made available to non-commercial entities, press and the general public under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial No Derivatives license . You may not alter the images provided, other than to crop them to size. A credit line must be used when reproducing images; if one is not provided below, credit the images to "MIT."
Previous image Next image
Proximity is key for many quantum phenomena, as interactions between atoms are stronger when the particles are close. In many quantum simulators, scientists arrange atoms as close together as possible to explore exotic states of matter and build new quantum materials.
They typically do this by cooling the atoms to a stand-still, then using laser light to position the particles as close as 500 nanometers apart — a limit that is set by the wavelength of light. Now, MIT physicists have developed a technique that allows them to arrange atoms in much closer proximity, down to a mere 50 nanometers. For context, a red blood cell is about 1,000 nanometers wide.
The physicists demonstrated the new approach in experiments with dysprosium, which is the most magnetic atom in nature. They used the new approach to manipulate two layers of dysprosium atoms, and positioned the layers precisely 50 nanometers apart. At this extreme proximity, the magnetic interactions were 1,000 times stronger than if the layers were separated by 500 nanometers.
What’s more, the scientists were able to measure two new effects caused by the atoms’ proximity. Their enhanced magnetic forces caused “thermalization,” or the transfer of heat from one layer to another, as well as synchronized oscillations between layers. These effects petered out as the layers were spaced farther apart.
“We have gone from positioning atoms from 500 nanometers to 50 nanometers apart, and there is a lot you can do with this,” says Wolfgang Ketterle, the John D. MacArthur Professor of Physics at MIT. “At 50 nanometers, the behavior of atoms is so much different that we’re really entering a new regime here.”
Ketterle and his colleagues say the new approach can be applied to many other atoms to study quantum phenomena. For their part, the group plans to use the technique to manipulate atoms into configurations that could generate the first purely magnetic quantum gate — a key building block for a new type of quantum computer.
The team has published their results today in the journal Science . The study’s co-authors include lead author and physics graduate student Li Du, along with Pierre Barral, Michael Cantara, Julius de Hond, and Yu-Kun Lu — all members of the MIT-Harvard Center for Ultracold Atoms, the Department of Physics, and the Research Laboratory of Electronics at MIT.
Peaks and valleys
To manipulate and arrange atoms, physicists typically first cool a cloud of atoms to temperatures approaching absolute zero, then use a system of laser beams to corral the atoms into an optical trap.
Laser light is an electromagnetic wave with a specific wavelength (the distance between maxima of the electric field) and frequency. The wavelength limits the smallest pattern into which light can be shaped to typically 500 nanometers, the so-called optical resolution limit. Since atoms are attracted by laser light of certain frequencies, atoms will be positioned at the points of peak laser intensity. For this reason, existing techniques have been limited in how close they can position atomic particles, and could not be used to explore phenomena that happen at much shorter distances.
“Conventional techniques stop at 500 nanometers, limited not by the atoms but by the wavelength of light,” Ketterle explains. “We have found now a new trick with light where we can break through that limit.”
The team’s new approach, like current techniques, starts by cooling a cloud of atoms — in this case, to about 1 microkelvin, just a hair above absolute zero — at which point, the atoms come to a near-standstill. Physicists can then use lasers to move the frozen particles into desired configurations.
Then, Du and his collaborators worked with two laser beams, each with a different frequency, or color, and circular polarization, or direction of the laser’s electric field. When the two beams travel through a super-cooled cloud of atoms, the atoms can orient their spin in opposite directions, following either of the two lasers’ polarization. The result is that the beams produce two groups of the same atoms, only with opposite spins.
Each laser beam formed a standing wave, a periodic pattern of electric field intensity with a spatial period of 500 nanometers. Due to their different polarizations, each standing wave attracted and corralled one of two groups of atoms, depending on their spin. The lasers could be overlaid and tuned such that the distance between their respective peaks is as small as 50 nanometers, meaning that the atoms gravitating to each respective laser’s peaks would be separated by the same 50 nanometers.
But in order for this to happen, the lasers would have to be extremely stable and immune to all external noise, such as from shaking or even breathing on the experiment. The team realized they could stabilize both lasers by directing them through an optical fiber, which served to lock the light beams in place in relation to each other.
“The idea of sending both beams through the optical fiber meant the whole machine could shake violently, but the two laser beams stayed absolutely stable with respect to each others,” Du says.
Magnetic forces at close range
As a first test of their new technique, the team used atoms of dysprosium — a rare-earth metal that is one of the strongest magnetic elements in the periodic table, particularly at ultracold temperatures. However, at the scale of atoms, the element’s magnetic interactions are relatively weak at distances of even 500 nanometers. As with common refrigerator magnets, the magnetic attraction between atoms increases with proximity, and the scientists suspected that if their new technique could space dysprosium atoms as close as 50 nanometers apart, they might observe the emergence of otherwise weak interactions between the magnetic atoms.
“We could suddenly have magnetic interactions, which used to be almost neglible but now are really strong,” Ketterle says.
The team applied their technique to dysprosium, first super-cooling the atoms, then passing two lasers through to split the atoms into two spin groups, or layers. They then directed the lasers through an optical fiber to stabilize them, and found that indeed, the two layers of dysprosium atoms gravitated to their respective laser peaks, which in effect separated the layers of atoms by 50 nanometers — the closest distance that any ultracold atom experiment has been able to achieve.
At this extremely close proximity, the atoms’ natural magnetic interactions were significantly enhanced, and were 1,000 times stronger than if they were positioned 500 nanometers apart. The team observed that these interactions resulted in two novel quantum phenomena: collective oscillation, in which one layer’s vibrations caused the other layer to vibrate in sync; and thermalization, in which one layer transferred heat to the other, purely through magnetic fluctuations in the atoms.
“Until now, heat between atoms could only by exchanged when they were in the same physical space and could collide,” Du notes. “Now we have seen atomic layers, separated by vacuum, and they exchange heat via fluctuating magnetic fields.”
The team’s results introduce a new technique that can be used to position many types of atom in close proximity. They also show that atoms, placed close enough together, can exhibit interesting quantum phenomena, that could be harnessed to build new quantum materials, and potentially, magnetically-driven atomic systems for quantum computers.
“We are really bringing super-resolution methods to the field, and it will become a general tool for doing quantum simulations,” Ketterle says. “There are many variants possible, which we are working on.”
This research was funded, in part, by the National Science Foundation and the Department of Defense.
Share this news article on:
Related links.
- Wolfgang Ketterle
- MIT-Harvard Center for Ultracold Atoms
- Research Laboratory of Electronics
- Department of Physics
Related Topics
- Nanoscience and nanotechnology
- Quantum computing
- National Science Foundation (NSF)
- Department of Defense (DoD)
Related Articles
Physicists observe rare resonance in molecules for the first time
Physicists steer chemical reactions by magnetic fields and quantum interference

How ultracold, superdense atoms become invisible
Ultracold atoms reveal a new type of quantum magnetic behavior

New “refrigerator” super-cools molecules to nanokelvin temperatures
Previous item Next item
More MIT News
New treatment could reverse hair loss caused by an autoimmune skin disease
Read full story →

Study: Heavy snowfall and rain may contribute to some earthquakes

How AI might shape LGBTQIA+ advocacy

Two MIT PhD students awarded J-WAFS fellowships for their research on water

Exploring the mysterious alphabet of sperm whales

“Pathways to Invention” documentary debuts on PBS, streaming
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A reader would need to know which search engine and what key words you used. Open this section by describing the overall approach you took or the materials used. Then describe to the readers step-by-step the methods you used including any data analysis performed. See Fig. 2.5 below for an example of materials and methods section. Writing tips: Do:
The figures should be indicated within parentheses in their first mention in the "Materials and Methods" section. Headings and as a prevalent convention legends of the figures should be indicated at the end of the manuscript. If a different method is used in the study, this should be explained in detail.
The methods section of a research paper typically constitutes materials and methods; while writing this section, authors usually arrange the information under each category. The materials category describes the samples, materials, treatments, and instruments, while experimental design, sample preparation, data collection, and data analysis are ...
To structure your methods section, you can use the subheadings of "Participants," "Materials," and "Procedures.". These headings are not mandatory—aim to organize your methods section using subheadings that make sense for your specific study. Note that not all of these topics will necessarily be relevant for your study.
Materials and Methods examples. Sample 1: In preparing the catecholase extract, a potato was skinned, washed, and diced.30. g of the diced potato and 150 ml of distilled water were added to a kitchen blender and blended for approximately two minutes. The resulting solution was filtered through four layers of cheese cloth. The extract was stored in a clean, capped container.
The methods section should describe what was done to answer the research question, describe how it was done, justify the experimental design, and explain how the results were analyzed. Scientific writing is direct and orderly. Therefore, the methods section structure should: describe the materials used in the study, explain how the materials ...
2. Functions of the Materials and Methods Section. The M&M section of a paper has two main functions (): To allow readers to repeat the work and to convince them that the work has been done in an appropriate way.For hypothesis-testing papers, the most important function of the M&M section is to provide information on "what procedures were used to answer the main question(s) stated in the ...
Your Methods Section contextualizes the results of your study, giving editors, reviewers and readers alike the information they need to understand and interpret your work. Your methods are key to establishing the credibility of your study, along with your data and the results themselves. A complete methods section should provide enough detail for a skilled researcher to replicate your process ...
1. Begin writing the Materials and Methods while you are performing your experiments. 2. Start with general information that applies to the entire manuscript and then move on to specific experimental details. 3. Match the order in which methods are described to the order of the results that were generated using those methods.
For a Methods paper, the first step in the story line is a statement that you are presenting a new or improved material, method, or apparatus. The second step in the story line has two parts: a complete description of the new method, material, or apparatus; and a description of how this new method, material, or apparatus was tested.
We will look at some examples of materials and methods structure in different disciplines. 2.1. Materials & methods example #1 (Engineering paper) If you are writing an engineering sciences research paper in which you are introducing a new method, your materials and methods section would typically include the following information.
Methods / Materials Overview. These sections of the research paper should be concise. The audience reading the paper will always want to know what materials or methods that were used. The methods and materials may be under subheadings in the section or incorporated together. The main objective for these sections is to provide specialized ...
Research methods are specific procedures for collecting and analyzing data. Developing your research methods is an integral part of your research design. When planning your methods, there are two key decisions you will make. First, decide how you will collect data. Your methods depend on what type of data you need to answer your research question:
The Materials and methods section of a research paper is oftentimes the first and easiest part to write. It details the steps taken to answer a research hypothesis, the success of which determines whether or not the study can be replicated. Arranging the section in chronological order, writing succinctly, and consistently using the third-person ...
Materials and methods. The study's methods are one of the most important parts used to judge the overall quality of the paper. In addition the Methods section should give readers enough information so that they can repeat the experiments. Reviewers should look for potential sources of bias in the way the study was designed and carried out ...
and Methods' section should be in accordance with the related. ones in the 'Results' section. In other words, the sequence of. paragraphs, and subheadings in the 'Results' section should ...
Materials and Methods. The Methods and Materials section of a paper often seems the least interesting to read, or to write, but it serves several essential purposes. First, it demonstrates to readers that the research was designed appropriately and conducted competently. Scientists are skeptical readers.
4. Use subheadings: Dividing the Methods section in terms of the experiments helps the reader to follow the section better. You may write the specific objective of each experiment as a subheading. Alternatively, if applicable, the name of each experiment can also be used as subheading. 5.
The methodology section of your paper describes how your research was conducted. This information allows readers to check whether your approach is accurate and dependable. A good methodology can help increase the reader's trust in your findings. First, we will define and differentiate quantitative and qualitative research.
Abstract. The materials and methods (M&M) section is the heart of a scientific paper and is subject to initial screening of the editor to decide whether the manuscript should be sent for external review. If the M&M section of a scientific paper be considered as a recipe, its ingredients would be who, what, when, where, how, and why.
To write your methods section in APA format, describe your participants, materials, study design, and procedures. Keep this section succinct, and always write in the past tense. The main heading of this section should be labeled "Method" and it should be centered, bolded, and capitalized. Each subheading within this section should be bolded ...
When writing scientific papers to share their research findings with their peers, it is not enough for researchers to just communicate the results of their study; it is equally important to explain the process by which they arrived at their results, so that the study can be replicated to validate the observations. The materials and methods ...
The research methodology is an important section of any research paper or thesis, as it describes the methods and procedures that will be used to conduct the research. It should include details about the research design, data collection methods, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations.
Since the surge of data in materials science research and the advancement in machine learning methods, an increasing number of researchers are introducing machine learning techniques into the next generation of materials discovery, ranging from neural-network learned potentials to automated characterization techniques for experimental images. In this snapshot review, we first summarize the ...
This paper proposes a topology optimization method for the design of stretchable interconnect structures with stable resistance under large deformation. In the proposed method, an equal material method considering geometrically nonlinear and electromechanical coupling effects is developed to evaluate the resistance of a deformed structure.
Let's look at some examples. We have selected a variety of examples from different research topics. 2.1. Limitations Example 1. Following example is from a Medical research paper. The authors talk about the limitations and emphasis the importance of reconfirming the findings in a much larger study
This paper took Gangcheng District, Jinan City, a steel base in the Shandong Province of China as an example, then the value coefficients of "three wastes" factors (waste gas, wastewater, and waste) were introduced, and an improved calculation method of ESV was put forward for industrial counties in combination with remote sensing and land ...
Caption: MIT physicists developed a technique to arrange atoms (represented as spheres with arrows) in much closer proximity than previously possible, down to 50 nanometers. The group plans to use the method to manipulate atoms into configurations that could generate the first purely magnetic quantum gate — a key building block for a new type of quantum computer.