share this!
August 16, 2021

Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in
by Sara M Moniuszko

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide-range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas over workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework .
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy work loads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace, says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework causes, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high-achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school ," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely, but to be more mindful of the type of work students go home with, suggests Kang, who was a high-school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework, I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.
The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the last two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic, making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized... sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking assignments up can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
©2021 USA Today Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.
Explore further
Feedback to editors
Heat from El Niño can warm oceans off West Antarctica—and melt floating ice shelves from below
55 minutes ago
Peregrine falcons expose lasting harms of flame retardant use

The hidden role of the Milky Way in ancient Egyptian mythology
Unraveling the iconography of the Etruscan lamp of Cortona, Italy
2 hours ago

Archaeological study suggests cultural diversity increases biodiversity of ecosystems
How whales struggle to navigate in a sea of noise pollution

New technique lets scientists create resistance-free electron channels

Machine learning method reveals chromosome locations in individual cell nucleus
3 hours ago

The 'Iron Pipeline': Is Interstate 95 the connection for moving guns up and down the East Coast?

Impact of climate change on marine life shown to be much bigger than previously known
Relevant physicsforums posts, motivating high school physics students with popcorn physics.
Apr 3, 2024
How is Physics taught without Calculus?
Mar 29, 2024
Why are Physicists so informal with mathematics?
Mar 24, 2024
The changing physics curriculum in 1961
Suggestions for using math puzzles to stimulate my math students.
Mar 21, 2024
The New California Math Framework: Another Step Backwards?
Mar 14, 2024
More from STEM Educators and Teaching
Related Stories

Smartphones are lowering student's grades, study finds
Aug 18, 2020

Doing homework is associated with change in students' personality
Oct 6, 2017

Scholar suggests ways to craft more effective homework assignments
Oct 1, 2015

Should parents help their kids with homework?
Aug 29, 2019

How much math, science homework is too much?
Mar 23, 2015

Anxiety, depression, burnout rising as college students prepare to return to campus
Jul 26, 2021
Recommended for you

Earth, the sun and a bike wheel: Why your high-school textbook was wrong about the shape of Earth's orbit
Apr 8, 2024

Touchibo, a robot that fosters inclusion in education through touch
Apr 5, 2024

More than money, family and community bonds prep teens for college success: Study
Research reveals significant effects of onscreen instructors during video classes in aiding student learning
Mar 25, 2024

Prestigious journals make it hard for scientists who don't speak English to get published, study finds
Mar 23, 2024

Using Twitter/X to promote research findings found to have little impact on number of citations
Mar 22, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Student Opinion
Should We Get Rid of Homework?
Some educators are pushing to get rid of homework. Would that be a good thing?

By Jeremy Engle and Michael Gonchar
Do you like doing homework? Do you think it has benefited you educationally?
Has homework ever helped you practice a difficult skill — in math, for example — until you mastered it? Has it helped you learn new concepts in history or science? Has it helped to teach you life skills, such as independence and responsibility? Or, have you had a more negative experience with homework? Does it stress you out, numb your brain from busywork or actually make you fall behind in your classes?
Should we get rid of homework?
In “ The Movement to End Homework Is Wrong, ” published in July, the Times Opinion writer Jay Caspian Kang argues that homework may be imperfect, but it still serves an important purpose in school. The essay begins:
Do students really need to do their homework? As a parent and a former teacher, I have been pondering this question for quite a long time. The teacher side of me can acknowledge that there were assignments I gave out to my students that probably had little to no academic value. But I also imagine that some of my students never would have done their basic reading if they hadn’t been trained to complete expected assignments, which would have made the task of teaching an English class nearly impossible. As a parent, I would rather my daughter not get stuck doing the sort of pointless homework I would occasionally assign, but I also think there’s a lot of value in saying, “Hey, a lot of work you’re going to end up doing in your life is pointless, so why not just get used to it?” I certainly am not the only person wondering about the value of homework. Recently, the sociologist Jessica McCrory Calarco and the mathematics education scholars Ilana Horn and Grace Chen published a paper, “ You Need to Be More Responsible: The Myth of Meritocracy and Teachers’ Accounts of Homework Inequalities .” They argued that while there’s some evidence that homework might help students learn, it also exacerbates inequalities and reinforces what they call the “meritocratic” narrative that says kids who do well in school do so because of “individual competence, effort and responsibility.” The authors believe this meritocratic narrative is a myth and that homework — math homework in particular — further entrenches the myth in the minds of teachers and their students. Calarco, Horn and Chen write, “Research has highlighted inequalities in students’ homework production and linked those inequalities to differences in students’ home lives and in the support students’ families can provide.”
Mr. Kang argues:
But there’s a defense of homework that doesn’t really have much to do with class mobility, equality or any sense of reinforcing the notion of meritocracy. It’s one that became quite clear to me when I was a teacher: Kids need to learn how to practice things. Homework, in many cases, is the only ritualized thing they have to do every day. Even if we could perfectly equalize opportunity in school and empower all students not to be encumbered by the weight of their socioeconomic status or ethnicity, I’m not sure what good it would do if the kids didn’t know how to do something relentlessly, over and over again, until they perfected it. Most teachers know that type of progress is very difficult to achieve inside the classroom, regardless of a student’s background, which is why, I imagine, Calarco, Horn and Chen found that most teachers weren’t thinking in a structural inequalities frame. Holistic ideas of education, in which learning is emphasized and students can explore concepts and ideas, are largely for the types of kids who don’t need to worry about class mobility. A defense of rote practice through homework might seem revanchist at this moment, but if we truly believe that schools should teach children lessons that fall outside the meritocracy, I can’t think of one that matters more than the simple satisfaction of mastering something that you were once bad at. That takes homework and the acknowledgment that sometimes a student can get a question wrong and, with proper instruction, eventually get it right.
Students, read the entire article, then tell us:
Should we get rid of homework? Why, or why not?
Is homework an outdated, ineffective or counterproductive tool for learning? Do you agree with the authors of the paper that homework is harmful and worsens inequalities that exist between students’ home circumstances?
Or do you agree with Mr. Kang that homework still has real educational value?
When you get home after school, how much homework will you do? Do you think the amount is appropriate, too much or too little? Is homework, including the projects and writing assignments you do at home, an important part of your learning experience? Or, in your opinion, is it not a good use of time? Explain.
In these letters to the editor , one reader makes a distinction between elementary school and high school:
Homework’s value is unclear for younger students. But by high school and college, homework is absolutely essential for any student who wishes to excel. There simply isn’t time to digest Dostoyevsky if you only ever read him in class.
What do you think? How much does grade level matter when discussing the value of homework?
Is there a way to make homework more effective?
If you were a teacher, would you assign homework? What kind of assignments would you give and why?
Want more writing prompts? You can find all of our questions in our Student Opinion column . Teachers, check out this guide to learn how you can incorporate them into your classroom.
Students 13 and older in the United States and Britain, and 16 and older elsewhere, are invited to comment. All comments are moderated by the Learning Network staff, but please keep in mind that once your comment is accepted, it will be made public.
Jeremy Engle joined The Learning Network as a staff editor in 2018 after spending more than 20 years as a classroom humanities and documentary-making teacher, professional developer and curriculum designer working with students and teachers across the country. More about Jeremy Engle
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

News and Media
- News & Media Home
- Research Stories
- School's In
- In the Media
You are here
More than two hours of homework may be counterproductive, research suggests.

A Stanford education researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter. "Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good," wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education . The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students' views on homework. Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year. Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night. "The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students' advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being," Pope wrote. Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school. Their study found that too much homework is associated with: • Greater stress : 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor. • Reductions in health : In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems. • Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits : Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were "not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills," according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy. A balancing act The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills. Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as "pointless" or "mindless" in order to keep their grades up. "This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points," said Pope, who is also a co-founder of Challenge Success , a nonprofit organization affiliated with the GSE that conducts research and works with schools and parents to improve students' educational experiences.. Pope said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said. "Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development," wrote Pope. High-performing paradox In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. "Young people are spending more time alone," they wrote, "which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities." Student perspectives The researchers say that while their open-ended or "self-reporting" methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for "typical adolescent complaining" – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe. The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Clifton B. Parker is a writer at the Stanford News Service .
More Stories

⟵ Go to all Research Stories
Get the Educator
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
Improving lives through learning
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .

Search form
- Find Stories
- For Journalists
Stanford research shows pitfalls of homework
A Stanford researcher found that students in high-achieving communities who spend too much time on homework experience more stress, physical health problems, a lack of balance and even alienation from society. More than two hours of homework a night may be counterproductive, according to the study.

Education scholar Denise Pope has found that too much homework has negative effects on student well-being and behavioral engagement. (Image credit: L.A. Cicero)
A Stanford researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter.
“Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good,” wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education .
The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students’ views on homework.
Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year.
Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night.
“The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students’ advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being,” Pope wrote.
Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school.
Their study found that too much homework is associated with:
• Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor.
• Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems.
• Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits: Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were “not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills,” according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy.
A balancing act
The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills.
Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as “pointless” or “mindless” in order to keep their grades up.
“This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points,” Pope said.
She said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said.
“Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development,” wrote Pope.
High-performing paradox
In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. “Young people are spending more time alone,” they wrote, “which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities.”
Student perspectives
The researchers say that while their open-ended or “self-reporting” methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for “typical adolescent complaining” – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe.
The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
The Truth About Homework Stress: What Parents & Students Need to Know
- Fact Checked
Written by:
published on:
- December 21, 2023
Updated on:
- January 9, 2024
Looking for a therapist?
Homework is generally given out to ensure that students take time to review and remember the days lessons. It can help improve on a student’s general performance and enhance traits like self-discipline and independent problem solving.
Parents are able to see what their children are doing in school, while also helping teachers determine how well the lesson material is being learned. Homework is quite beneficial when used the right way and can improve student performance.
This well intentioned practice can turn sour if it’s not handled the right way. Studies show that if a student is inundated with too much homework, not only do they get lower scores, but they are more likely to get stressed.
The age at which homework stress is affecting students is getting lower, some even as low as kindergarten. Makes you wonder what could a five year old possibly need to review as homework?
One of the speculated reasons for this stress is that the complexity of what a student is expected to learn is increasing, while the breaks for working out excess energy are reduced. Students are getting significantly more homework than recommended by the education leaders, some even nearly three times more.
To make matters worse, teachers may give homework that is both time consuming and will keep students busy while being totally non-productive.
Remedial work like telling students to copy notes word for word from their text books will do nothing to improve their grades or help them progress. It just adds unnecessary stress.
Explore emotional well-being with BetterHelp – your partner in affordable online therapy. With 30,000+ licensed therapists and plans starting from only $65 per week, BetterHelp makes self-care accessible to all. Complete the questionnaire to match with the right therapist.
Effects of homework stress at home
Both parents and students tend to get stressed out at the beginning of a new school year due to the impending arrival of homework.
Nightly battles centered on finishing assignments are a household routine in houses with students.
Research has found that too much homework can negatively affect children. In creating a lack of balance between play time and time spent doing homework, a child can get headaches, sleep deprivation or even ulcers.
And homework stress doesn’t just impact grade schoolers. College students are also affected, and the stress is affecting their academic performance.
Even the parent’s confidence in their abilities to help their children with homework suffers due increasing stress levels in the household.
Fights and conflict over homework are more likely in families where parents do not have at least a college degree. When the child needs assistance, they have to turn to their older siblings who might already be bombarded with their own homework.
Parents who have a college degree feel more confident in approaching the school and discussing the appropriate amount of school work.
“It seems that homework being assigned discriminates against parents who don’t have college degree, parents who have English as their second language and against parents who are poor.” Said Stephanie Donaldson Pressman, the contributing editor of the study and clinical director of the New England Center for Pediatric Psychology.
With all the stress associated with homework, it’s not surprising that some parents have opted not to let their children do homework. Parents that have instituted a no-homework policy have stated that it has taken a lot of the stress out of their evenings.
The recommended amount homework
The standard endorsed by the National Education Association is called the “10 minute rule”; 10 minutes per grade level per night. This recommendation was made after a number of studies were done on the effects of too much homework on families.
The 10 minute rule basically means 10 minutes of homework in the first grade, 20 minute for the second grade all the way up to 120 minutes for senior year in high school. Note that no homework is endorsed in classes under the first grade.
Parents reported first graders were spending around half an hour on homework each night, and kindergarteners spent 25 minutes a night on assignments according to a study carried out by Brown University.
Making a five year old sit still for half an hour is very difficult as they are at the age where they just want to move around and play.
A child who is exposed to 4-5 hours of homework after school is less likely to find the time to go out and play with their friends, which leads to accumulation of stress energy in the body.
Their social life also suffers because between the time spent at school and doing homework, a child will hardly have the time to pursue hobbies. They may also develop a negative attitude towards learning.
The research highlighted that 56% of students consider homework a primary source of stress.
And if you’re curious how the U.S stacks up against other countries in regards to how much time children spend on homework, it’s pretty high on the list .
Signs to look out for on a student that has homework stress
Since not every student is affected by homework stress in the same way, it’s important to be aware of some of the signs your child might be mentally drained from too much homework.
Here are some common signs of homework stress:
- Sleep disturbances
- Frequent stomachaches and headaches
- Decreased appetite or changed eating habits
- New or recurring fears
- Not able to relax
- Regressing to behavior they had when younger
- Bursts of anger crying or whining
- Becoming withdrawn while others may become clingy
- Drastic changes in academic performance
- Having trouble concentrating or completing homework
- Constantly complains about their ability to do homework
If you’re a parent and notice any of these signs in your child, step in to find out what’s going on and if homework is the source of their stress.
If you’re a student, pay attention if you start experiencing any of these symptoms as a result of your homework load. Don’t be afraid to ask your teacher or parents for help if the stress of homework becomes too much for you.
What parents do wrong when it comes to homework stress
Most parents push their children to do more and be more, without considering the damage being done by this kind of pressure.
Some think that homework brought home is always something the children can deal with on their own. If the child cannot handle their homework then these parents get angry and make the child feel stupid.
This may lead to more arguing and increased dislike of homework in the household. Ultimately the child develops an even worse attitude towards homework.
Another common mistake parents make is never questioning the amount of homework their children get, or how much time they spend on it. It’s easy to just assume whatever the teacher assigned is adequate, but as we mentioned earlier, that’s not always the case.
Be proactive and involved with your child’s homework. If you notice they’re spending hours every night on homework, ask them about it. Just because they don’t complain doesn’t mean there isn’t a problem.
How can parents help?
- While every parent wants their child to become successful and achieve the very best, it’s important to pull back on the mounting pressure and remember that they’re still just kids. They need time out to release their stress and connect with other children.
- Many children may be afraid to admit that they’re overwhelmed by homework because they might be misconstrued as failures. The best thing a parent can do is make home a safe place for children to express themselves freely. You can do this by lending a listening ear and not judging your kids.
- Parents can also take the initiative to let the school know that they’re unhappy with the amount of homework being given. Even if you don’t feel comfortable complaining, you can approach the school through the parent-teacher association available and request your representative to plead your case.
- It may not be all the subjects that are causing your child to get stressed. Parents should find out if there is a specific subject of homework that is causing stress. You could also consult with other parents to see what they can do to fix the situation. It may be the amount or the content that causes stress, so the first step is identifying the problem.
- Work with your child to create a schedule for getting homework done on time. You can set a specific period of time for homework, and schedule time for other activities too. Strike a balance between work and play.
- Understanding that your child is stressed about homework doesn’t mean you have to allow them not to try. Let them sit down and work on it as much as they’re able to, and recruit help from the older siblings or a neighbor if possible.
- Check out these resources to help your child with their homework .
The main idea here is to not abolish homework completely, but to review the amount and quality of homework being given out. Stress, depression and lower grades are the last things parents want for their children.
The schools and parents need to work together to find a solution to this obvious problem.
Take the stress test!
Join the Find-a-therapist community and get access to our free stress assessment!
Additional Resources
Online therapy.
Discover a path to emotional well-being with BetterHelp – your partner in convenient and affordable online therapy. With a vast network of 30,000+ licensed therapists, they’re committed to helping you find the one to support your needs. Take advantage of their Free Online Assessment, and connect with a therapist who truly understands you. Begin your journey today.
Relationship Counceling
Whether you’re facing communication challenges, trust issues, or simply seeking to strengthen your connection, ReGain’ s experienced therapists are here to guide you and your partner toward a healthier, happier connection from the comfort of your own space. Get started.
Therapist Directory
Discover the perfect therapist who aligns with your goals and preferences, allowing you to take charge of your mental health. Whether you’re searching for a specialist based on your unique needs, experience level, insurance coverage, budget, or location, our user-friendly platform has you covered. Search here.
About the author
You might also be interested in
Therapist vs. Psychologist: Recognizing the Differences
Top Magnesium Side Effects to Look Out For
Does Green Tea Relieve Stress?
Disclaimers
Online Therapy, Your Way
Follow us on social media
We may receive a commission if you click on and become a paying customer of a therapy service that we mention.
The information contained in Find A Therapist is general in nature and is not medical advice. Please seek immediate in-person help if you are in a crisis situation.
Therapy Categories
More information
If you are in a life threatening situation – don’t use this site. Call +1 (800) 273-8255 or check these resources to get immediate help.
Are You Down With or Done With Homework?
- Posted January 17, 2012
- By Lory Hough

The debate over how much schoolwork students should be doing at home has flared again, with one side saying it's too much, the other side saying in our competitive world, it's just not enough.
It was a move that doesn't happen very often in American public schools: The principal got rid of homework.
This past September, Stephanie Brant, principal of Gaithersburg Elementary School in Gaithersburg, Md., decided that instead of teachers sending kids home with math worksheets and spelling flash cards, students would instead go home and read. Every day for 30 minutes, more if they had time or the inclination, with parents or on their own.
"I knew this would be a big shift for my community," she says. But she also strongly believed it was a necessary one. Twenty-first-century learners, especially those in elementary school, need to think critically and understand their own learning — not spend night after night doing rote homework drills.
Brant's move may not be common, but she isn't alone in her questioning. The value of doing schoolwork at home has gone in and out of fashion in the United States among educators, policymakers, the media, and, more recently, parents. As far back as the late 1800s, with the rise of the Progressive Era, doctors such as Joseph Mayer Rice began pushing for a limit on what he called "mechanical homework," saying it caused childhood nervous conditions and eyestrain. Around that time, the then-influential Ladies Home Journal began publishing a series of anti-homework articles, stating that five hours of brain work a day was "the most we should ask of our children," and that homework was an intrusion on family life. In response, states like California passed laws abolishing homework for students under a certain age.
But, as is often the case with education, the tide eventually turned. After the Russians launched the Sputnik satellite in 1957, a space race emerged, and, writes Brian Gill in the journal Theory Into Practice, "The homework problem was reconceived as part of a national crisis; the U.S. was losing the Cold War because Russian children were smarter." Many earlier laws limiting homework were abolished, and the longterm trend toward less homework came to an end.
The debate re-emerged a decade later when parents of the late '60s and '70s argued that children should be free to play and explore — similar anti-homework wellness arguments echoed nearly a century earlier. By the early-1980s, however, the pendulum swung again with the publication of A Nation at Risk , which blamed poor education for a "rising tide of mediocrity." Students needed to work harder, the report said, and one way to do this was more homework.
For the most part, this pro-homework sentiment is still going strong today, in part because of mandatory testing and continued economic concerns about the nation's competitiveness. Many believe that today's students are falling behind their peers in places like Korea and Finland and are paying more attention to Angry Birds than to ancient Babylonia.
But there are also a growing number of Stephanie Brants out there, educators and parents who believe that students are stressed and missing out on valuable family time. Students, they say, particularly younger students who have seen a rise in the amount of take-home work and already put in a six- to nine-hour "work" day, need less, not more homework.
Who is right? Are students not working hard enough or is homework not working for them? Here's where the story gets a little tricky: It depends on whom you ask and what research you're looking at. As Cathy Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework , points out, "Homework has generated enough research so that a study can be found to support almost any position, as long as conflicting studies are ignored." Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth and a strong believer in eliminating all homework, writes that, "The fact that there isn't anything close to unanimity among experts belies the widespread assumption that homework helps." At best, he says, homework shows only an association, not a causal relationship, with academic achievement. In other words, it's hard to tease out how homework is really affecting test scores and grades. Did one teacher give better homework than another? Was one teacher more effective in the classroom? Do certain students test better or just try harder?
"It is difficult to separate where the effect of classroom teaching ends," Vatterott writes, "and the effect of homework begins."
Putting research aside, however, much of the current debate over homework is focused less on how homework affects academic achievement and more on time. Parents in particular have been saying that the amount of time children spend in school, especially with afterschool programs, combined with the amount of homework given — as early as kindergarten — is leaving students with little time to run around, eat dinner with their families, or even get enough sleep.
Certainly, for some parents, homework is a way to stay connected to their children's learning. But for others, homework creates a tug-of-war between parents and children, says Liz Goodenough, M.A.T.'71, creator of a documentary called Where Do the Children Play?
"Ideally homework should be about taking something home, spending a few curious and interesting moments in which children might engage with parents, and then getting that project back to school — an organizational triumph," she says. "A nag-free activity could engage family time: Ask a parent about his or her own childhood. Interview siblings."

Instead, as the authors of The Case Against Homework write, "Homework overload is turning many of us into the types of parents we never wanted to be: nags, bribers, and taskmasters."
Leslie Butchko saw it happen a few years ago when her son started sixth grade in the Santa Monica-Malibu (Calif.) United School District. She remembers him getting two to four hours of homework a night, plus weekend and vacation projects. He was overwhelmed and struggled to finish assignments, especially on nights when he also had an extracurricular activity.
"Ultimately, we felt compelled to have Bobby quit karate — he's a black belt — to allow more time for homework," she says. And then, with all of their attention focused on Bobby's homework, she and her husband started sending their youngest to his room so that Bobby could focus. "One day, my younger son gave us 15-minute coupons as a present for us to use to send him to play in the back room. … It was then that we realized there had to be something wrong with the amount of homework we were facing."
Butchko joined forces with another mother who was having similar struggles and ultimately helped get the homework policy in her district changed, limiting homework on weekends and holidays, setting time guidelines for daily homework, and broadening the definition of homework to include projects and studying for tests. As she told the school board at one meeting when the policy was first being discussed, "In closing, I just want to say that I had more free time at Harvard Law School than my son has in middle school, and that is not in the best interests of our children."
One barrier that Butchko had to overcome initially was convincing many teachers and parents that more homework doesn't necessarily equal rigor.
"Most of the parents that were against the homework policy felt that students need a large quantity of homework to prepare them for the rigorous AP classes in high school and to get them into Harvard," she says.
Stephanie Conklin, Ed.M.'06, sees this at Another Course to College, the Boston pilot school where she teaches math. "When a student is not completing [his or her] homework, parents usually are frustrated by this and agree with me that homework is an important part of their child's learning," she says.
As Timothy Jarman, Ed.M.'10, a ninth-grade English teacher at Eugene Ashley High School in Wilmington, N.C., says, "Parents think it is strange when their children are not assigned a substantial amount of homework."
That's because, writes Vatterott, in her chapter, "The Cult(ure) of Homework," the concept of homework "has become so engrained in U.S. culture that the word homework is part of the common vernacular."
These days, nightly homework is a given in American schools, writes Kohn.
"Homework isn't limited to those occasions when it seems appropriate and important. Most teachers and administrators aren't saying, 'It may be useful to do this particular project at home,'" he writes. "Rather, the point of departure seems to be, 'We've decided ahead of time that children will have to do something every night (or several times a week). … This commitment to the idea of homework in the abstract is accepted by the overwhelming majority of schools — public and private, elementary and secondary."
Brant had to confront this when she cut homework at Gaithersburg Elementary.
"A lot of my parents have this idea that homework is part of life. This is what I had to do when I was young," she says, and so, too, will our kids. "So I had to shift their thinking." She did this slowly, first by asking her teachers last year to really think about what they were sending home. And this year, in addition to forming a parent advisory group around the issue, she also holds events to answer questions.
Still, not everyone is convinced that homework as a given is a bad thing. "Any pursuit of excellence, be it in sports, the arts, or academics, requires hard work. That our culture finds it okay for kids to spend hours a day in a sport but not equal time on academics is part of the problem," wrote one pro-homework parent on the blog for the documentary Race to Nowhere , which looks at the stress American students are under. "Homework has always been an issue for parents and children. It is now and it was 20 years ago. I think when people decide to have children that it is their responsibility to educate them," wrote another.
And part of educating them, some believe, is helping them develop skills they will eventually need in adulthood. "Homework can help students develop study skills that will be of value even after they leave school," reads a publication on the U.S. Department of Education website called Homework Tips for Parents. "It can teach them that learning takes place anywhere, not just in the classroom. … It can foster positive character traits such as independence and responsibility. Homework can teach children how to manage time."
Annie Brown, Ed.M.'01, feels this is particularly critical at less affluent schools like the ones she has worked at in Boston, Cambridge, Mass., and Los Angeles as a literacy coach.
"It feels important that my students do homework because they will ultimately be competing for college placement and jobs with students who have done homework and have developed a work ethic," she says. "Also it will get them ready for independently taking responsibility for their learning, which will need to happen for them to go to college."
The problem with this thinking, writes Vatterott, is that homework becomes a way to practice being a worker.
"Which begs the question," she writes. "Is our job as educators to produce learners or workers?"
Slate magazine editor Emily Bazelon, in a piece about homework, says this makes no sense for younger kids.
"Why should we think that practicing homework in first grade will make you better at doing it in middle school?" she writes. "Doesn't the opposite seem equally plausible: that it's counterproductive to ask children to sit down and work at night before they're developmentally ready because you'll just make them tired and cross?"
Kohn writes in the American School Board Journal that this "premature exposure" to practices like homework (and sit-and-listen lessons and tests) "are clearly a bad match for younger children and of questionable value at any age." He calls it BGUTI: Better Get Used to It. "The logic here is that we have to prepare you for the bad things that are going to be done to you later … by doing them to you now."
According to a recent University of Michigan study, daily homework for six- to eight-year-olds increased on average from about 8 minutes in 1981 to 22 minutes in 2003. A review of research by Duke University Professor Harris Cooper found that for elementary school students, "the average correlation between time spent on homework and achievement … hovered around zero."
So should homework be eliminated? Of course not, say many Ed School graduates who are teaching. Not only would students not have time for essays and long projects, but also teachers would not be able to get all students to grade level or to cover critical material, says Brett Pangburn, Ed.M.'06, a sixth-grade English teacher at Excel Academy Charter School in Boston. Still, he says, homework has to be relevant.
"Kids need to practice the skills being taught in class, especially where, like the kids I teach at Excel, they are behind and need to catch up," he says. "Our results at Excel have demonstrated that kids can catch up and view themselves as in control of their academic futures, but this requires hard work, and homework is a part of it."
Ed School Professor Howard Gardner basically agrees.
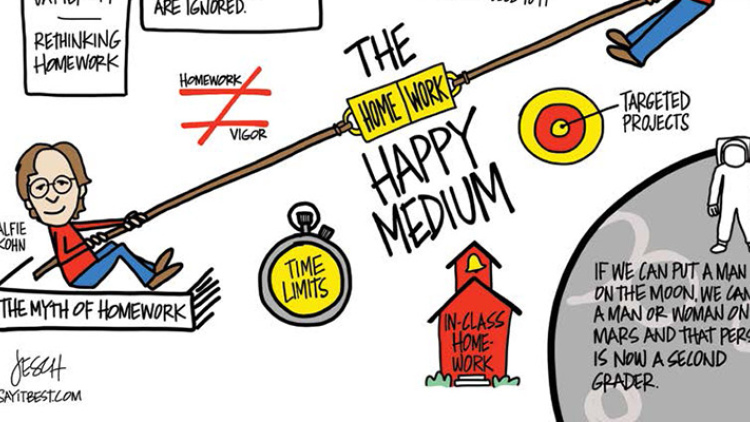
"America and Americans lurch between too little homework in many of our schools to an excess of homework in our most competitive environments — Li'l Abner vs. Tiger Mother," he says. "Neither approach makes sense. Homework should build on what happens in class, consolidating skills and helping students to answer new questions."
So how can schools come to a happy medium, a way that allows teachers to cover everything they need while not overwhelming students? Conklin says she often gives online math assignments that act as labs and students have two or three days to complete them, including some in-class time. Students at Pangburn's school have a 50-minute silent period during regular school hours where homework can be started, and where teachers pull individual or small groups of students aside for tutoring, often on that night's homework. Afterschool homework clubs can help.
Some schools and districts have adapted time limits rather than nix homework completely, with the 10-minute per grade rule being the standard — 10 minutes a night for first-graders, 30 minutes for third-graders, and so on. (This remedy, however, is often met with mixed results since not all students work at the same pace.) Other schools offer an extended day that allows teachers to cover more material in school, in turn requiring fewer take-home assignments. And for others, like Stephanie Brant's elementary school in Maryland, more reading with a few targeted project assignments has been the answer.
"The routine of reading is so much more important than the routine of homework," she says. "Let's have kids reflect. You can still have the routine and you can still have your workspace, but now it's for reading. I often say to parents, if we can put a man on the moon, we can put a man or woman on Mars and that person is now a second-grader. We don't know what skills that person will need. At the end of the day, we have to feel confident that we're giving them something they can use on Mars."
Read a January 2014 update.
Homework Policy Still Going Strong
Ed. Magazine
The magazine of the Harvard Graduate School of Education
Related Articles

Commencement Marshal Sarah Fiarman: The Principal of the Matter

Making Math “Almost Fun”
Alum develops curriculum to entice reluctant math learners
“Don’t Worry — You’ll Figure It Out”
US South Carolina
Recently viewed courses
Recently viewed.
Find Your Dream School
This site uses various technologies, as described in our Privacy Policy, for personalization, measuring website use/performance, and targeted advertising, which may include storing and sharing information about your site visit with third parties. By continuing to use this website you consent to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
COVID-19 Update: To help students through this crisis, The Princeton Review will continue our "Enroll with Confidence" refund policies. For full details, please click here.
Enter your email to unlock an extra $25 off an SAT or ACT program!
By submitting my email address. i certify that i am 13 years of age or older, agree to recieve marketing email messages from the princeton review, and agree to terms of use., how to manage homework stress.
Feeling overwhelmed by your nightly homework grind? You’re not alone. Our Student Life in America survey results show that teens spend a third of their study time feeling worried, stressed, or stuck. If you’re spending close to four hours a night on your homework (the national average), that’s over an hour spent spent feeling panicky and still not getting your work done. Homework anxiety can become a self-fulfilling prophecy: If you’re already convinced that calculus is unconquerable, that anxiety can actually block your ability to learn the material.

Whether your anxiety is related to handling your workload (we know you’re getting more homework than ever!), mastering a particular subject like statistics, or getting great grades for your college application, stress doesn’t have to go hand-in-hand with studying .
In fact, a study by Stanford University School of Medicine and published in The Journal of Neuroscience shows that a student’s fear of math (and, yes, this fear is completely real and can be detectable in scans of the brain) can be eased by a one-on-one math tutoring program. At The Princeton Review this wasn’t news to us! Our online tutors are on-call 24/7 for students working on everything from AP Chemistry to Pre-Calc. Here’s a roundup of what our students have to say about managing homework stress by working one-one-one with our expert tutors .
1. Work the Best Way for YOU
From the way you decorate your room to the way you like to study, you have a style all your own:
"I cannot thank Christopher enough! I felt so anxious and stressed trying to work on my personal statement, and he made every effort to help me realize my strengths and focus on writing in a way that honored my personality. I wanted to give up, but he was patient with me and it made the difference."
"[My] tutor was 1000000000000% great . . . He made me feel important and fixed all of my mistakes and adapted to my learning style . . . I have so much confidence for my midterms that I was so stressed out about."
"I liked how the tutor asked me how was I starting the problem and allowed me to share what I was doing and what I had. The tutor was able to guide me from there and break down the steps and I got the answer all on my own and the tutor double checked it... saved me from tears and stress."
2. Study Smarter, Not Harder
If you’ve read the chapter in your history textbook twice and aren’t retaining the material, don’t assume the third time will be the charm. Our tutors will help you break the pattern, and learn ways to study more efficiently:
"[My] tutor has given me an easier, less stressful way of seeing math problems. It is like my eyes have opened up."
"I was so lost in this part of math but within minutes the tutor had me at ease and I get it now. I wasn't even with her maybe 30 minutes or so, and she helped me figure out what I have been stressing over for the past almost two days."
"I can not stress how helpful it is to have a live tutor available. Math was never and still isn't my favorite subject, but I know I need to take it. Being able to talk to someone and have them walk you through the steps on how to solve a problem is a huge weight lifted off of my shoulder."
3. Get Help in a Pinch
Because sometimes you need a hand RIGHT NOW:
"I was lost and stressed because I have a test tomorrow and did not understand the problems. I fully get it now!"
"My tutor was great. I was freaking out and stressed out about the entire assignment, but she really helped me to pull it together. I am excited to turn my paper in tomorrow."
"This was so helpful to have a live person to validate my understanding of the formulas I need to use before actually submitting my homework and getting it incorrect. My stress level reduced greatly with a project deadline due date."
4. Benefit from a Calming Presence
From PhDs and Ivy Leaguers to doctors and teachers, our tutors are experts in their fields, and they know how to keep your anxiety at bay:
"I really like that the tutors are real people and some of them help lighten the stress by making jokes or having quirky/witty things to say. That helps when you think you're messing up! Gives you a reprieve from your brain jumbling everything together!"
"He seemed understanding and empathetic to my situation. That means a lot to a new student who is under stress."
"She was very thorough in explaining her suggestions as well as asking questions and leaving the changes up to me, which I really appreciated. She was very encouraging and motivating which helped with keeping me positive about my paper and knowing that I am not alone in my struggles. She definitely eased my worries and stress. She was wonderful!"
5. Practice Makes Perfect
The Stanford study shows that repeated exposure to math problems through one-on-one tutoring helped students relieve their math anxiety (the authors’ analogy was how a fear of spiders can be treated with repeated exposure to spiders in a safe environment). Find a tutor you love, and come back to keep practicing:
"Love this site once again. It’s so helpful and this is the first time in years when I don’t stress about my frustration with HW because I know this site will always be here to help me."
"I've been using this service since I was in seventh grade and now I am a Freshman in High School. School has just started and I am already using this site again! :) This site is so dependable. I love it so much and it’s a lot easier than having an actual teacher sitting there hovering over you, waiting for you to finish the problem."
"I can always rely on this site to help me when I'm confused, and it always makes me feel more confident in the work I'm doing in school."
Stuck on homework?
Try an online tutoring session with one of our experts, and get homework help in 40+ subjects.
Try a Free Session
- Tutoring
- College
- Applying to College

Explore Colleges For You
Connect with our featured colleges to find schools that both match your interests and are looking for students like you.

Career Quiz
Take our short quiz to learn which is the right career for you.

Get Started on Athletic Scholarships & Recruiting!
Join athletes who were discovered, recruited & often received scholarships after connecting with NCSA's 42,000 strong network of coaches.

Best 389 Colleges
165,000 students rate everything from their professors to their campus social scene.
SAT Prep Courses
1400+ course, act prep courses, free sat practice test & events, 1-800-2review, free digital sat prep try our self-paced plus program - for free, get a 14 day trial.
Free MCAT Practice Test
Thank you! Look for the MCAT Review Guide in your inbox.
I already know my score.
Enrollment Advisor
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 1
1-877-LEARN-30
Mon-Fri 9AM-10PM ET
Sat-Sun 9AM-8PM ET
Student Support
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 2
Mon-Fri 9AM-9PM ET
Sat-Sun 8:30AM-5PM ET
Partnerships
- Teach or Tutor for Us
College Readiness
International
Advertising
Affiliate/Other
- Enrollment Terms & Conditions
- Accessibility
- Cigna Medical Transparency in Coverage
Register Book
Local Offices: Mon-Fri 9AM-6PM
- SAT Subject Tests
Academic Subjects
- Social Studies
Find the Right College
- College Rankings
- College Advice
- Applying to College
- Financial Aid
School & District Partnerships
- Professional Development
- Advice Articles
- Private Tutoring
- Mobile Apps
- Local Offices
- International Offices
- Work for Us
- Affiliate Program
- Partner with Us
- Advertise with Us
- International Partnerships
- Our Guarantees
- Accessibility – Canada
Privacy Policy | CA Privacy Notice | Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information | Your Opt-Out Rights | Terms of Use | Site Map
©2024 TPR Education IP Holdings, LLC. All Rights Reserved. The Princeton Review is not affiliated with Princeton University
TPR Education, LLC (doing business as “The Princeton Review”) is controlled by Primavera Holdings Limited, a firm owned by Chinese nationals with a principal place of business in Hong Kong, China.

Get Free Profile Evaluation

10 Effective Tips on How to Reduce Homework Stress

Wondering how to reduce homework stress? You're not alone, as students of all ages and grades often grapple with this issue.

The pressure to get good grades, finish homework on time, and keep up with different tasks can make you lose sleep, feel anxious, and even make you sick. This blog post is here to help you handle all that stress.
We're going to explore ways to reduce homework stress, why taking notes can help, and answer some common questions about dealing with homework stress. So, let's get started on making schoolwork less stressful!
10 Ways to Deal With Homework Stress
Understanding how to deal with homework stress is key. Here are ten tried-and-true methods to help you cope effectively.
The first line of defense against homework stress is a well-thought-out plan. A homework schedule serves as your blueprint for academic success. It helps ensure that you're not cramming at the last minute and makes it easier to study .
Use digital tools like Google Calendar or traditional planners to map out your study plan. The act of planning itself can alleviate stress by giving you a sense of control over your tasks.
1. Prioritize Tasks
Not all assignments are created equal. Some carry more weight in your grades, while others are crucial for mastering the subject matter. As a result, it’s important to prioritize these tasks to focus your energy where it counts the most.
Use the Eisenhower Box technique to categorize tasks into urgent-important, important-not urgent, urgent-not important, and neither. This will help you allocate your time and resources more efficiently.
2. Take Short Breaks
It's a common misconception that working for extended periods without a break is a sign of dedication. In reality, it's a recipe for burnout. Short breaks can rejuvenate your mind, improving focus and productivity.
Techniques like the Pomodoro Technique , which involves 25-minute work intervals followed by five-minute breaks, can be particularly effective.
3. Exercise Regularly
Physical activity is not just good for your body; it's excellent for your mind too. Exercise releases endorphins, which are natural stress relievers. Even a brisk 15-minute walk can significantly reduce stress and improve your mood. Incorporate regular exercise into your routine to keep stress at bay.

4. Reach Out for Help
There's no shame in seeking assistance when you're grappling with a tough issue. Whether it's from a teacher, a peer, or an online educational platform, outside viewpoints can offer invaluable guidance. Overall, there are a ton of advantages of tutoring .
In fact, our tutoring services specialize in providing personalized, one-on-one support to help you overcome academic challenges. By turning to our team of experts, you not only save time but also alleviate the stress that comes with feeling stuck.
5. Use Technology Wisely
In this digital age, technology can be a double-edged sword. While it can be a source of distraction, it can also be a valuable ally in your academic journey.
Educational platforms, both apps and websites, provide a wide array of resources to aid your learning journey. For instance, you can find apps that help you solve complex math equations or websites that assist you in refining your grammar. While these tools can be incredibly beneficial, it's important to strike a balance and not become too dependent on them.
For example, you might use a math app to understand the steps of solving a quadratic equation but try to practice solving some on your own afterward. Similarly, a grammar checker can help you identify errors in your writing, but you should also make an effort to understand the rules behind those corrections.

6. Create a Study Environment
Your study environment plays a pivotal role in your academic performance. A clutter-free, quiet space can significantly enhance your focus and efficiency. Invest time in creating a study sanctuary equipped with all the supplies you'll need. This preparation can go a long way in reducing stress.
7. Practice Mindfulness
Mindfulness techniques, such as meditation and deep-breathing exercises, can help you become more aware of your thoughts and feelings. This heightened awareness makes it easier to control your stress levels. Even a few minutes of mindfulness practice can make a world of difference.

8. Stay Organized
Being organized goes beyond just maintaining a clean study area; it also involves systematically managing your study materials. Utilize physical folders and binders or opt for digital solutions like note-taking apps to keep your notes, assignments, and resources well-arranged.
For example, apps like Evernote and Microsoft OneNote can be excellent tools for getting organized. They allow you to create different notebooks for various subjects, attach files, and even collaborate with others. Having a well-organized system helps you locate what you need effortlessly, saving you time and reducing stress.
9. Learn From Your Mistakes
Mistakes are a natural part of the learning process. They signal areas where you might need more practice or a different approach. Instead of getting frustrated, take a moment to understand why you made a mistake. Was it a lack of understanding, a misinterpretation, or simply a slip-up?
Once you identify the root cause, you can work on strengthening that particular skill or concept. Over time, you'll notice that your homework becomes less stressful because you're not just completing it; you're also learning from it. So, don't fear mistakes – embrace them as your homework allies.
10. Reward Yourself
Positive reinforcement can be a powerful motivator. Treat yourself to small rewards after completing challenging tasks or reaching milestones. Whether it's a favorite snack, a short gaming session, or a walk in the park, these rewards can make the study process less daunting.
Why Are Note-Taking Techniques Important?

Note-taking is often misunderstood as a mere transcription activity where students jot down whatever the teacher is saying. However, this couldn't be further from the truth. Effective note-taking is an intricate skill that serves multiple functions, from aiding in comprehension to serving as a reliable study aid for future exams.
It's not just about capturing information; it's about processing that information in a way that makes it easier to understand, remember, and apply.
The Science Behind Effective Note-Taking
When you engage in effective note-taking, you're actually participating in "active learning." This means you're not just passively absorbing information but actively processing it. This active engagement triggers cognitive functions that help in better retention and understanding.
According to research , students who take notes perform better in exams compared to those who don't. The act of writing or typing out notes forces you to think critically about the material, thereby enhancing your understanding and ability to recall it later.
FAQs: How to Reduce Homework Stress
Discover practical tips and strategies to ease the burden of homework and make your academic journey less stressful.
1. How Can I Relieve Stress From Homework?
Stress relief comes in many forms. Techniques like deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and even short physical exercises can help. Consider incorporating these into your study routine.
2. What Causes Homework Stress?
Homework stress can arise from various factors, including tight deadlines, high academic expectations, and a lack of understanding of the subject matter. Identifying the root cause can help you address it more effectively.
3. How Can I Help My Child With Homework Anxiety?
Supporting your child emotionally is crucial. Create a conducive study environment, establish a regular study routine, and consider seeking professional help like tutors or counselors if the anxiety persists.
Final Thoughts
Homework stress may seem like a hurdle, but it's one you can clear. Learning how to reduce homework stress is essential. With the right approaches and a positive mindset, you can not only handle this stress but also excel in your studies.
Keep in mind that achieving academic success is more of a long-term race than a quick dash. By arming yourself with these proven strategies, you can make your educational journey much less stressful.

Book Your Free Assessment Today

Mastering the Art of Homework: Expert Tips for a Stress-Free Study Session
2023-05-09 | By Orcam Staff
.webp)
As students, parents, and teachers alike can attest, homework is a ubiquitous feature of modern education. But as much as homework is a fact of life for many students, the question of whether it causes stress remains a hotly debated topic. The importance of this topic cannot be overstated, as research has consistently shown that homework-related stress can have negative impacts on student mental health, academic performance, and overall well-being.
In this article, we will explore the underlying causes of homework-related stress, its effects on students, and evidence-based strategies to alleviate homework-related stress and improve student well-being. By the end of this article, readers will have a clearer understanding of the issue at hand and practical tools to help manage the stress that homework can sometimes bring.
Homework is a common aspect of education that can cause stress for many students, parents, and teachers. The question of whether homework causes stress is a controversial topic. However, it is crucial to address this issue as research has consistently shown that homework-related stress can negatively impact students' mental health, academic performance, and overall well-being. One effective solution to alleviate homework-related stress is to learn how to make homework less frustrating.
This article aims to explore the underlying causes of homework-related stress, its effects on students, and evidence-based strategies to improve student well-being. By the end of this article, readers will have gained a better understanding of the issue and practical tools to manage the stress that homework can bring.
Homework and Stress: Understanding the Causes and Effects
Homework policies: a contributing factor to student stress.
Homework can be a significant source of stress for students, leading to a range of negative effects on their mental health, academic performance, and overall well-being. Research has shown that homework policies that assign excessive amounts of homework or place unrealistic expectations on students can contribute to feelings of anxiety and stress.
Study Habits: The Key to Managing Homework-Related Stress
Some of the key causes of homework-related stress include academic pressure, lack of effective time management skills, and poor study habits. When students feel overwhelmed by their workload, it can lead to anxiety and feelings of being unable to cope. This can ultimately impact their academic performance and overall well-being.
Negative Impact of Academic Pressure on Student Mental Health and Well-Being
It's important to recognize that homework itself is not inherently stressful. Rather, it is the amount and type of homework assigned, as well as the expectations placed on students, that can contribute to stress. By implementing effective homework alternatives and strategies, such as project-based learning or flipped classrooms, educators can help alleviate homework-related stress and improve student engagement and performance.
Time Management: A Crucial Skill to Alleviate Homework Stress
To reduce homework stress, students can try to implement effective time management techniques, such as breaking down assignments into manageable tasks and creating a study schedule that prioritizes important assignments. They can also explore homework alternatives, such as online resources and study groups, that can help them better understand the material and complete their assignments more efficiently.
Overall, by understanding the causes and effects of homework-related stress, students, parents, and educators can work together to create a more supportive and less stressful learning environment.
Many students know all too well the feelings of anxiety, frustration, and even hopelessness that can come with excessive homework. But why exactly does homework cause stress? The answer lies in a number of factors, from the policies governing homework to the individual habits and well-being of each student.
The link between homework policies and student stress
One major source of homework-related stress is the policies and expectations surrounding homework. While homework is meant to help reinforce learning and promote academic success, too much homework or overly strict homework policies can lead to anxiety and burnout. When students feel overwhelmed by the sheer volume of homework, they may experience anxiety or even feelings of helplessness, leading to a vicious cycle of stress and poor academic performance.
The Role of study habits in Managing homework-related stress
But homework-related stress is not solely the result of external factors. Study habits and time management can play a significant role in how students experience homework-related stress. Students who struggle with effective study habits or who have difficulty managing their time may find themselves feeling overwhelmed by homework and unable to cope with the associated stress.
The Impact of academic pressure on student mental health and Well-being
Academic pressure is also a major contributor to homework-related stress. Whether from parents, teachers, or self-imposed expectations, students may feel intense pressure to perform well academically. This pressure can lead to a range of negative consequences, from burnout to anxiety and depression.
The relationship between homework, time management, and student stress
So, does homework cause anxiety or stress? The answer is yes, and the effects can be significant. When students experience high levels of stress related to homework, they may struggle to concentrate, retain information, and perform well academically. Over time, this can take a toll on their mental health and well-being.
In the next section, we will explore evidence-based strategies for managing homework-related stress, including homework alternatives and techniques for reducing anxiety and improving time management. By implementing these strategies, students can reduce the impact of homework-related stress on their lives and enjoy greater academic success and overall well-being.
The Psychology of Homework and Stress
Homework is a complex issue that goes beyond just completing assignments. The psychological impact of homework on students cannot be ignored. In this section, we will explore the educational psychology theories related to homework and stress.
Overview of Educational Psychology Theories Related to Homework and Stress a. Self-Determination Theory b. Control-Value Theory c. Cognitive Load Theory
Impact of Homework on Student Motivation and Engagement a. How homework can positively or negatively impact student motivation b. How different types of homework assignments affect student engagement
Homework Anxiety and Its Effects on Student Mental Health and Academic Performance a. How homework anxiety can lead to stress and negatively affect student mental health b. The relationship between homework anxiety and academic performance

Strategies to Alleviate Homework-Related Stress and Improve Student Well-being
After discussing the underlying causes and effects of homework-related stress, it's important to explore strategies that can help alleviate stress and promote student well-being. Here are some evidence-based strategies:
Alternatives to Traditional Homework Assignments
While homework has long been a staple of the education system, it may not always be the most effective way for students to learn. Here are some alternatives to traditional homework assignments:
Project-Based Learning:
Instead of assigning daily homework, teachers can assign longer-term projects that allow students to explore a topic in-depth and demonstrate their understanding in creative ways.
Collaborative Learning:
Group assignments can help students learn from one another and work together to achieve a common goal.
Flipped Classroom:
In this approach, students watch lectures or read materials at home and use class time to work on assignments or projects, allowing for more individualized support from the teacher.
Time-Management Strategies to Reduce Homework-Related Stress
Effective time management can help students better balance their academic workload and reduce homework-related stress. Here are some strategies students can use:
Prioritize Tasks:
Help students prioritize tasks by breaking down large assignments into smaller tasks and prioritizing tasks based on deadlines and importance.
Use a Planner:
Encourage students to use a planner to keep track of assignments, deadlines, and extracurricular activities.
Take Breaks:
Encourage students to take breaks and engage in physical activity or other hobbies to help reduce stress and increase focus.
Tips for Students on How to Make School Less Stressful
In addition to effective time management, there are other strategies students can use to make school less stressful:
Practice Mindfulness:
Encourage students to practice mindfulness exercises such as deep breathing or meditation to help reduce stress and increase focus.
Get Enough Sleep:
Getting enough sleep is crucial for student well-being and academic success. Encourage students to prioritize a consistent sleep schedule.
Seek Support:
Encourage students to seek support from friends, family, or mental health professionals if they are feeling overwhelmed or anxious.
Strategies for Parents and Teachers to Support Students' Well-being and Academic Success
Parents and teachers can play a crucial role in supporting student well-being and academic success. Here are some strategies they can use:
Communicate:
Encourage open communication between parents, teachers, and students to ensure everyone is aware of expectations and concerns.
Prioritize Playtime:
Encourage parents to prioritize playtime and physical activity outside of school hours to help reduce stress and promote well-being.
Provide Support:
Teachers can provide additional support to students who are struggling with homework by offering extra help sessions or alternative assignments.
By implementing these strategies, we can work towards reducing homework-related stress and promoting student well-being and academic success.
In conclusion, this article has explored the underlying causes and effects of homework-related stress on students, as well as evidence-based strategies to alleviate this stress and improve student well-being. It has been established that homework policies, study habits, academic pressure, and time management all play a significant role in contributing to homework-related stress. Moreover, it has been highlighted that homework-related stress can have a negative impact on student mental health, academic performance, and overall well-being.
To alleviate this stress and promote student well-being, there are various strategies that can be employed, such as alternatives to traditional homework assignments, time-management strategies, and tips for making school less stressful. Additionally, parents and teachers can play an important role in supporting students' well-being and academic success.
In conclusion, it is important for students, parents, and teachers to prioritize student well-being and to seek out additional resources on this topic. By taking steps to reduce homework-related stress, we can help ensure that students are better able to thrive academically, mentally, and emotionally.
Key Takeaways:
Homework can cause stress in students, which can negatively impact their mental health and academic performance.
Homework-related stress can stem from a variety of factors, including academic pressure, time management, and ineffective homework policies.
Alternatives to traditional homework assignments and time-management strategies can help reduce homework-related stress.
It's important for parents and teachers to prioritize student well-being and to seek out additional resources to support students in managing homework-related stress.
Select Your Country/ Region
North America
United States
United Kingdom
Deutschland
Middle East
Asia Pacific
Other Countries and Regions
Latinoamérica

How to Reduce Homework Stress
If homework is a source of frustration and stress in your home, it doesn’t have to be that way! Read on to learn effective strategies to reduce your child’s homework stress.

Author Katie Wickliff
Published March 2024

If homework is a source of frustration and stress in your home, it doesn’t have to be that way! Read on to learn effective strategies to reduce your child’s homework stress.
- Key takeaways
- Homework stress can be a significant problem for children and their families
- An appropriate amount of quality homework can be beneficial for students
- Parents can help reduce homework stress in several key ways
Table of contents
- Homework stress effects
- How to reduce homework stress
As a parent who has felt the frustration of watching my child be reduced to tears because of her homework each night, I’ve often wondered: do these math worksheets and reading trackers really make a difference to a child’s academic success? Or does homework cause stress without having a positive impact on learning?
If your child experiences a significant amount of homework stress, you may feel at a loss to help. However, there are several things you can do at home to minimize the negative effects of this stress on your child–and you! We’ve put together a list of research-based practices that can help your child better handle their homework load.
The Effects of Homework Stress on Students
Does homework cause stress? Short answer: Yes. It’s been well documented that too much homework can cause stress and anxiety for students–and their parents. However, do the benefits of homework outweigh the costs? Is homework “worth” the frustration and exhaustion that our children experience?
Findings on the benefits of homework at the elementary school level are mixed, with studies showing that homework appears to have more positive effects under certain conditions for certain groups of students.
After examining decades of studies on the relationship between homework and academic achievement, leading homework researcher Harris M. Cooper has proposed the “10-minute rule,” suggesting that homework be limited to 10 minutes per grade level. For example, children in 3rd grade should do no more than 30 minutes of homework daily, while a 1st grader should do no more than 10 minutes of homework. The National Parent Teacher Association and the National Education Association both endorse this guideline as a general rule of thumb.
Because of these research findings, Doodle believes that an appropriate amount of quality homework can help students feel more positive about learning and can provide parents with a critical connection to their child’s school experience . But to keep learning positive, we need to reduce the amount of stress both students and parents feel about homework.
1. Routine, Routine, Routine
Creating an after-school routine and sticking to it helps children feel organized, but with sports, tutoring, or music lessons, many children have varying weekday schedules. As a former classroom teacher and private tutor, I suggest that families post a weekly schedule somewhere visible and communicate that schedule with their child.
At our house, we have a dry-erase calendar posted on the wall. Every Sunday evening, I write both of my children’s schedules for the following week–including homework time. We go through the calendar together, and they reference it often throughout the week. I can tell both my son and daughter feel better when they know when they’ll get their homework done.
2. Create a Homework Space
Ideally, your child should have a dedicated homework space. It doesn’t matter if that space is a desk, a dining room table, or a kitchen countertop. What does matter is that the homework area is tidy, because an unorganized homework area is very distracting.
3. Start Homework Early
Encourage your child to start their homework as early as possible. Help them review their assignments, make a plan for what needs to be completed, and then dive in. Naturally, children are more tired later in the evening which can lead to more stress.
4. Encourage Breaks
If you can see your child becoming frustrated or overwhelmed by their homework, encourage them to take a breather and come back to it later. As a teacher and tutor, I called this a “brain break” and believe these breaks are essential. Taking a short break will give your child a chance to step away from a frustrating problem or assignment.
5. It’s Okay to Ask for Help
Sometimes, homework can become just too stressful and overwhelming. In that case, it really is okay to stop. Children can learn to advocate for themselves by making a list of questions for their teacher and asking for help the next day. Depending on their age, you might need to help role-play how to approach their teacher with their frustrations.
Additionally, parents should never feel afraid to contact their child’s teacher to talk about homework issues. When I was teaching elementary school, I always wanted parents to feel comfortable reaching out about any issues, including homework stress.
6. Get Plenty of Rest
Sleep is critical to a child’s overall wellbeing , which includes their academic performance. Tired kids can’t concentrate as well, which can lead to feeling more overwhelmed about homework assignments. According to the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, kids aged 6-12 should get at least 9 hours of sleep each night.
7. Consider a Homework Group
Organizing a homework group a few times a week is another way for your child to view homework more positively. Working as a group encourages collaboration, while discussions can solidify concepts learned in class.
8. Encourage Positivity
No matter what your school experience was like, it’s important to model a growth mindset for your child. A growth mindset is the belief that your abilities can develop and improve over time. So if your child says something like “ I can’t do this! ” first acknowledge their frustration. Then, encourage them to say, “ I may not understand this yet, but I will figure it out. ” Speaking positively about tough experiences takes practice, but it will go a long way in reducing homework stress for your child.
9. Develop Skills With Fun Games
Feeling stressed about homework is no fun. Completing worksheets and memorizing facts is necessary, but playing games is a great way to inject some excitement into learning. Doodle’s interactive math app is filled with interactive exercises, engaging math games, and unique rewards that help kids develop their skills while having fun.
Lower Math Anxiety with DoodleMath
Does your child struggle with math anxiety? DoodleMath is an award-winning math app f illed with fun, interactive math questions aligned to state standards. Doodle creates a unique work program tailored to each child’s skill level to boost confidence and reduce math anxiety. Try it free today!

FAQs About Homework Stress
Many studies have shown that homework and stress often go hand-in-hand, often because many children feel pressure to perform perfectly or they have trouble managing their emotions–they get overwhelmed or flooded easily.
You can help your child reduce homework stress in several ways, including by establishing a routine, creating a homework space, encouraging breaks, and making homework fun with online games or math apps.

Lesson credits

Katie Wickliff
Katie holds a master’s degree in Education from the University of Colorado and a bachelor’s degree in both Journalism and English from The University of Iowa. She has over 15 years of education experience as a K-12 classroom teacher and Orton-Gillingham certified tutor. Most importantly, Katie is the mother of two elementary students, ages 8 and 11. She is passionate about math education and firmly believes that the right tools and support will help every student reach their full potential.

Parents, sign up for a DoodleMath subscription and see your child become a math wizard!
What we offer
Quick links
All rights reserved.

Are you a parent, teacher or student?
Get started for free!
Maths information pack
We ask for your contact info so we can send our info pack directly to your inbox for your convenience, exam prep information pack, case studies information pack.
Book a chat with our team

I’m new to Doodle

My school is already using Doodle

Information pack
We ask for your contact info so that our education consultants can get in touch with you and let you know a bit more about doodle., student login, which programme would you like to use.
DoodleMaths
DoodleTables
DoodleEnglish
DoodleSpell
If you’d like to use Doodle’s browser version, please visit this page on a desktop.
To log in to Doodle on this device, you can do so through our apps. You can find out how to download them here:
- EXPLORE Random Article
How to Avoid Homework Stress
Last Updated: March 28, 2019 References
This article was co-authored by Emily Listmann, MA . Emily Listmann is a private tutor in San Carlos, California. She has worked as a Social Studies Teacher, Curriculum Coordinator, and an SAT Prep Teacher. She received her MA in Education from the Stanford Graduate School of Education in 2014. There are 10 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been viewed 133,057 times.
Students of all kinds are often faced with what can seem like an overwhelming amount of homework. Although homework can be a source of stress, completing it can be a very rewarding and even relaxing experience if done in an organized and timely manner. Remember, homework is not intended as punishment, but is used to reinforce everything you’ve learned in class. Try to view it as a chance to sharpen your skills and understanding.
Managing Your Time

- Try to work earlier, rather than later, if possible. This way, you won’t be rushing to finish your work before bedtime.
- Find a time of day during which you can concentrate well. Some people work best in the afternoon, while others can concentrate better on a full stomach after dinner.
- Choose a time when you will have relatively few distractions. Mealtimes, times during which you have standing engagements, or periods usually used for socializing are not the best choices.
- Allow enough time to complete your work. Making sure the total time you allow yourself for homework is sufficient for you to complete all your assignments is crucial. [1] X Research source [2] X Research source

- Save an appropriate amount of time for projects considering your normal homework load.
- Estimate how much time you will need each day, week, and month depending on your usual workload. Allow yourself at least this much time in your schedule, and consider allotting a fair amount more to compensate for unexpected complications or additional assignments.
- Reserve plenty of time for bigger projects, as they are more involved, and it is harder to estimate how much time you might need to complete them.

- Get a day planner or a notebook to write down your homework assignments, and assign an estimated amount of time to each assignment. Make sure to always give yourself more time than you think you’ll need.
- Plan to finish daily homework every day, then divide up weekly homework over the course of the entire week.
- Rank assignments in due-date order. Begin on those assignments due first, and work your way though. Finishing assignments according to due-date will help you avoid having to hurry through homework the night before it must be handed in.
- Allow more time for more difficult subjects and difficult assignments. Each individual person will have their strong subjects—and those that come a little harder. Make sure you take into account which subjects are harder for you, and allow more time for them during your scheduling.
Working Hard at School and in Class

- If you’re too shy to ask questions, or don’t feel it’s appropriate to do so during class, write them down in your notebook and then ask the teacher or professor after class.
- If you don't understand a concept, ask your teacher to explain it again, with specifics.
- If you're having trouble with a math problem, ask the teacher to demonstrate it again using a different example.
- Remember, when it comes to learning and education, there are no bad questions.

- Pay attention to important terms and ideas. Make sure to note things your teacher stresses, key terms, and other important concepts.
- Write clearly and legibly. If you can’t read your handwriting, it’ll take you longer to reference your notes at home.
- Keep your notebook organized with dividers and labels. This way, you’ll be able to locate helpful information in a pinch and finish your homework quicker. [4] X Research source

- Get permission.
- Sit up front and close to the instructor.
- Make sure to label your recordings so you don't lose track of them.
- Try to listen to them that same day while everything is fresh in your mind.

- Work in class. If you finish a class assignment early, review your notes or start your homework.
- Study at lunch. If you have time at lunch, consider working on homework. You can do this leisurely by just reviewing what you’ll need to do at home, or you can just jump right into your work.
- Don't waste time. If you get to class early, use that time for homework. In addition, many schools let students go to the library during this unplanned time, and it's a great place to finish uncompleted assignments.
Doing Your Homework

- Get some fresh air
- Go for a short run
- Do push-ups
- Walk your dog
- Listen to music
- Have a snack

- Study groups break up the monotony of daily homework and make for a less stressful experience than trying to cram on your own.
- Note that each person should turn in individualized assignments rather than collaborating to find the answers.
Balancing Homework with Life

- AP or IB classes often have 2 or 3 times the amount of reading and homework as regular courses.
- Honors classes may have up to double the amount of work required as regular courses.
- College students need to consider whether they want to take the recommended course load (often 4 classes) or more. More classes might help you finish your degree sooner, but if you are juggling work and extracurricular activities, you might be overwhelmed. [8] X Research source [9] X Research source

- Rank your classes and activities in order of importance.
- Estimate (realistically) how long your academic and extracurricular activities will take.
- Figure out how much time you have overall.
- If you’ve over committed, you need to drop your lowest ranked class or activity.

- Make sure to reserve mealtimes for family, rather than working.
- Try to set aside the weekend for family, and work only if you need to catch up or get ahead.
- Don’t plan on working on holidays, even if you try, your productivity likely won’t be high.

- Pick a reasonable hour to go to sleep every night.
- Try to do your morning prep work like ironing clothes and making your lunch at night.
- Take a nap after school or after classes if you need. You’ll probably be able to do better work in less time if you are rested. [10] X Research source [11] X Research source
- If you’re in middle or high school, talk to your parents and your teachers about the issue and ask them to help you figure out a solution.
- If you’re a college student, reach out to your professors and advisor for help.
- If it takes you much longer to finish your homework than it takes other students, it may be due to a learning difference. Ask your parents to schedule a meeting with a learning specialist.
Community Q&A
- Ask for help when you need it. This is the biggest thing you should do. Don't worry if people think you're dumb, because chances are, you're making a higher grade than them. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 4
- Actually pay attention to the teacher and ask if you don't know how to do the work. The stress can go away if you know exactly what to do. Thanks Helpful 2 Not Helpful 2
- Recognize that some teachers get mad if you do separate homework assignments for different classes, so learn to be discreet about it. Thanks Helpful 3 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.webmd.com/parenting/features/coping-school-stress
- ↑ http://www.kidzworld.com/article/24574-how-to-avoid-homework-stress
- ↑ http://www.dartmouth.edu/~acskills/success/notes.html
- ↑ https://stressfreekids.com/10038/homework-stress
- ↑ http://www.huffingtonpost.com/rebecca-jackson/5-ways-to-relieve-homework-stress-in-5-minutes_b_6572786.html
- ↑ https://stressfreekids.com/11607/reduce-homework-stress
- ↑ https://www.washingtonpost.com/local/education/how-students-can-survive-the-ap-course-workload/2012/03/01/gIQA8u28qR_story.html
- ↑ http://www.usnews.com/education/high-schools/articles/2012/05/10/weigh-the-benefits-stress-of-ap-courses-for-your-student
- ↑ http://www.nationwidechildrens.org/sleep-in-adolescents
- ↑ https://www.google.com/?gws_rd=ssl#q=how+much+sleep+do+20+year+old+need
About this article

Reader Success Stories
Angelina Wiseman
Oct 12, 2016
Did this article help you?
Apr 17, 2017

- About wikiHow
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer

August 23, 2022 , Filed Under: Uncategorized
How to Manage Homework-Related Stress
Ask students what causes them the most stress, and the conversation will likely turn to homework. Students have complained about homework for practically as long as it has existed. While some dismiss these complaints as students’ laziness or lack of organization, there’s more to it than that. Many students face a lot of pressure to succeed in school, sports, work, and other areas. Also, more teens and young adults are dealing with mental health problems, with up to 40% of college students reporting symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Researchers and professionals debate over whether homework does more harm than good, but at least for now, homework is an integral part of education. How do students deal with heavy homework loads? It’s become common for overwhelmed students to use an essay service to help them complete their assigned tasks. Pulling all-nighters to finish assignments and study for tests is another strategy busy college students use, for better or worse.
If you’re a student that’s struggling to get all your homework done, make sure to take care of your mental health. School is important, but your health is more important. Try the following tips to help you stay on top of your busy schedule.
Make a Schedule
Time management is an important skill, but you can’t learn it without effort. The first step to managing your time more effectively is to make a schedule and stick to it. Use a calendar, planner, or an app to write down everything you need to get done. Set reminders for due dates and set aside time each day for studying. Don’t leave assignments for the last minute. Plan to finish your work well ahead of the due date in case something unexpected happens and you need more time. Make sure your schedule is realistic. Give yourself a reasonable amount of time to complete each task. And schedule time for hobbies and social activities too.
Find a Study Spot
Doing homework in a dedicated workspace can boost your productivity. Studying in bed could make you fall asleep, and doing homework in a crowded, noisy place can be distracting. You want to complete as much work as possible during your study sessions, so choose a place that’s free of distractions. Make sure you have everything you need within arm’s reach. Resist the temptation to check your notifications or social media feeds while you study. Put your phone in airplane mode if necessary so it doesn’t distract you. You don’t need a private office to study efficiently, but having a quiet, distraction-free place to do your homework can help you to get more done.
Get Enough Rest
An all-nighter every once in a while probably won’t do you any lasting harm. But a consistent lack of sleep is bad for your productivity and your health. Most young people need at least 7 hours of sleep every night, so make it your goal to go to bed on time. You’ll feel better throughout the day, have more energy, and improve your focus. Instead of dozing off while you’re doing homework, you’ll be more alert and productive if you get enough sleep.
It’s also important to spend time relaxing and enjoying your favorite activities. Hang out with friends, take a walk, or watch a movie. You’ll feel less stressed if you take some time for yourself.
Don’t Shoot for Perfection
It’s tempting to try to get a perfect grade on every test or assignment. But perfectionism only causes unnecessary stress and anxiety. If you consider yourself a perfectionist, you might spend too much time on less important tasks. Prioritize your assignments and put more time and effort into the most important ones.
Most people struggle with perfectionism because they’ve been taught they should do their best at everything. But you don’t have to go above and beyond for every assignment. That’s not to say you should turn in bad work. But putting in just enough effort to get by isn’t a bad thing. Don’t put pressure on yourself to be the best at everything. Focus on your most important assignments, and don’t spend too much time and effort perfecting the others.
Almost all students deal with the burden of homework-related stress. No one enjoys the anxiety of having a lot of assignments due and not enough time to complete them. But take advantage of this opportunity to learn organization and self-discipline, which will help you throughout your life. Try making a schedule and don’t forget to set aside time to rest. When it’s time to study, choose a quiet place where you can concentrate. Don’t neglect your health; if you’re feeling anxious or depressed, talk to a counselor or your doctor. School stress is hard to avoid, but if you take these steps you can reduce homework anxiety and have better control of your time.
The real voyage of discovery consists not in seeking new landscapes, but in having new eyes — Marcel Proust

South Kern Sol
- 2020 Census
- Immigration
- Kern Sol en Español
- Environment
- Arts & Culture
- In The 661: Youth Voices for Kern
Less homework, less stress: a different way of assigning homework
November 28, 2018 / Bryana Lozoya

Third-grade teacher Laura Afifi likes her students to be stress free. She knows she can’t control tensions at home, but one stress factor she can control is the amount of homework assigned to her students.
Afifi, a third-grade teacher at Colonel Howard Nichols Elementary School in east Bakersfield, assigns a little less homework to help students de-stress and spend more time acting their age.
“I feel like they need time to be kids too,” Afifi said.
Having folders full of homework packets with short deadlines can be straining for many students, she said.
Throughout her 19 years of teaching, Afifi has tried different homework methods. She started out assigning weekly homework packets, but stopped after noticing many of her students didn’t turn them in.
She needed to better prioritize her planning time, she said. Afifi spent too much time planning, checking and grading the packets, but many of her students weren’t turning them in.
Instead of packets, she now gives her students minimal homework that focuses on reading and book reports or special projects that have gotten more participation than the packets.
She sets reading goals and assigns a book report once a month. She also assigns projects quarterly and allows students to take home unfinished classwork.
Young students should spend their time being active, reading more and learning skills they need outside of a classroom, she said, instead of spending more time sitting and doing work.
“They’re sitting all day long in the classroom except for recess, and we’re asking a lot of them,” she said.
Students with less homework are less stressed, she said.
Afifi has heard stories of students in other classrooms crying because they felt so much pressure from homework overload.
“There’s a lot of stress during the day already because we have all of these expectations of them, and they’re sitting for such a long time that I really just want them to have some freedom,” Afifi said.
Although she is an advocate for less homework, she believes students should still have some work to do at home.
“I shouldn’t say ‘no homework never,’ it’s just I try to keep it as minimal as possible,” Afifi said.
Afifi is understanding when it comes to deadlines. She’s flexible with her students because she understands many families have busy schedules.
When it comes to in-class projects, Afifi does her best to prepare the assignment in advance, that way her students and their parents have ample time to prepare for the project. If some don’t, she provides the necessary materials.
However, having some home assignments is good because not everything can be done in the classroom, she said, especially if there are a lot of students.
So far, Afifi has not received any complaints from parents, the school or the district regarding her homework methods.
But for parents who want their kids to stay extra busy at home, Afifi is happy to point them to online resources they can use for their child.
She said, “If you need ideas, I can send you ideas.”
Editor’s note: Do you know someone who is worth profiling? Let us know by emailing [email protected].

Bryana Lozoya
- How It Works
- Sleep Meditation
- VA Workers and Veterans

- How It Works 01
- Sleep Meditation 02
- Mental Fitness 03
- Neurofeedback 04
- Healium for Business 05
- VA Workers and Veterans 06
- Sports Meditation 07
- VR Experiences 08
- Social Purpose 11
Does Homework Cause Stress? Exploring the Impact on Students’ Mental Health
How much homework is too much?

Jump to: The Link Between Homework and Stress | Homework’s Impact on Mental Health | Benefits of Homework | How Much Homework Should Teacher’s Assign? | Advice for Students | How Healium Helps
Homework has become a matter of concern for educators, parents, and researchers due to its potential effects on students’ stress levels. It’s no secret students often find themselves grappling with high levels of stress and anxiety throughout their academic careers, so understanding the extent to which homework affects those stress levels is important.
By delving into the latest research and understanding the underlying factors at play, we hope to curate insights for educators, parents, and students who are wondering is homework causing stress in their lives?
The Link Between Homework and Stress: What the Research Says
Over the years, numerous studies investigated the relationship between homework and stress levels in students.
One study published in the Journal of Experimental Education found that students who reported spending more than two hours per night on homework experienced higher stress levels and physical health issues . Those same students reported over three hours of homework a night on average.
This study, conducted by Stanford lecturer Denise Pope, has been heavily cited throughout the years, with WebMD eproducing the below video on the topic– part of their special report series on teens and stress :
Additional studies published by Sleep Health Journal found that long hours on homework on may be a risk factor for depression while also suggesting that reducing workload outside of class may benefit sleep and mental fitness .
Lastly, a study presented by Frontiers in Psychology highlighted significant health implications for high school students facing chronic stress, including emotional exhaustion and alcohol and drug use.
Homework’s Potential Impact on Mental Health and Well-being
Homework-induced stress on students can involve both psychological and physiological side effects.
1. Potential Psychological Effects of Homework-Induced Stress:
• Anxiety: The pressure to perform academically and meet homework expectations can lead to heightened levels of anxiety in students. Constant worry about completing assignments on time and achieving high grades can be overwhelming.
• Sleep Disturbances : Homework-related stress can disrupt students’ sleep patterns, leading to sleep anxiety or sleep deprivation, both of which can negatively impact cognitive function and emotional regulation.
• Reduced Motivation: Excessive homework demands could drain students’ motivation, causing them to feel fatigued and disengaged from their studies. Reduced motivation may lead to a lack of interest in learning, hindering overall academic performance.
2. Potential Physical Effects of Homework-Induced Stress:
• Impaired Immune Function: Prolonged stress could weaken the immune system, making students more susceptible to illnesses and infections.
• Disrupted Hormonal Balance : The body’s stress response triggers the release of hormones like cortisol, which, when chronically elevated due to stress, can disrupt the delicate hormonal balance and lead to various health issues.
• Gastrointestinal Disturbances: Stress has been known to affect the gastrointestinal system, leading to symptoms such as stomachaches, nausea, and other digestive problems.
• Cardiovascular Impact: The increased heart rate and elevated blood pressure associated with stress can strain the cardiovascular system, potentially increasing the risk of heart-related issues in the long run.
• Brain impact: Prolonged exposure to stress hormones may impact the brain’s functioning , affecting memory, concentration, and cognitive abilities.
The Benefits of Homework
It’s important to note that homework also offers many benefits that contribute to students’ academic growth and development, such as:
• Development of Time Management Skills: Completing homework within specified deadlines encourages students to manage their time efficiently. This valuable skill extends beyond academics and becomes essential in various aspects of life.
• Preparation for Future Challenges : Homework helps prepare students for future academic challenges and responsibilities. It fosters a sense of discipline and responsibility, qualities that are crucial for success in higher education and professional life.
• Enhanced Problem-Solving Abilities: Homework often presents students with challenging problems to solve. Tackling these problems independently nurtures critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
While homework can foster discipline, time management, and self-directed learning, the middle ground may be to strike a balance that promotes both academic growth and mental well-being .
How Much Homework Should Teachers Assign?
As a general guideline, educators suggest assigning a workload that allows students to grasp concepts effectively without overwhelming them . Quality over quantity is key, ensuring that homework assignments are purposeful, relevant, and targeted towards specific objectives.
Advice for Students: How to balance Homework and Well-being
Finding a balance between academic responsibilities and well-being is crucial for students. Here are some practical tips and techniques to help manage homework-related stress and foster a healthier approach to learning:
• Effective Time Management : Encourage students to create a structured study schedule that allocates sufficient time for homework, breaks, and other activities. Prioritizing tasks and setting realistic goals can prevent last-minute rushes and reduce the feeling of being overwhelmed.
• Break Tasks into Smaller Chunks : Large assignments can be daunting and may contribute to stress. Students should break such tasks into smaller, manageable parts. This approach not only makes the workload seem less intimidating but also provides a sense of accomplishment as each section is completed.
• Find a Distraction-Free Zone : Establish a designated study area that is free from distractions like smartphones, television, or social media. This setting will improve focus and productivity, reducing time needed to complete homework.
• Be Active : Regular exercise is known to reduce stress and enhance mood. Encourage students to incorporate physical activity into their daily routine, whether it’s going for a walk, playing a sport, or doing yoga.
• Practice Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques : Encourage students to engage in mindfulness practices, such as deep breathing exercises or meditation, to alleviate stress and improve concentration. Taking short breaks to relax and clear the mind can enhance overall well-being and cognitive performance.
• Seek Support : Teachers, parents, and school counselors play an essential role in supporting students. Create an open and supportive environment where students feel comfortable expressing their concerns and seeking help when needed.
How Healium is Helping in Schools
Stress is caused by so many factors and not just the amount of work students are taking home. Our company created a virtual reality stress management solution… a mental fitness tool called “Healium” that’s teaching students how to learn to self-regulate their stress and downshift in a drugless way. Schools implementing Healium have seen improvements from supporting dysregulated students and ADHD challenges to empowering students with body awareness and learning to self-regulate stress . Here’s one of their stories.
By providing students with the tools they need to self-manage stress and anxiety, we represent a forward-looking approach to education that prioritizes the holistic development of every student.
To learn more about how Healium works, watch the video below.
About the Author

Sarah Hill , a former interactive TV news journalist at NBC, ABC, and CBS affiliates in Missouri, gained recognition for pioneering interactive news broadcasting using Google Hangouts. She is now the CEO of Healium, the world’s first biometrically powered immersive media channel, helping those with stress, anxiety, insomnia, and other struggles through biofeedback storytelling. With patents, clinical validation, and over seven million views, she has reshaped the landscape of immersive media.
- Shop Sleeves
- How It Works
- Success Stories
- Customer Reviews
- Need Some Help?
- Returns & Refunds
- Ordering & Shipping
- Login / Register
Mortal Kombat
- No products in the cart.

- Newsletter Registration

How to Reduce Homework Stress at School
For many students, homework is one of the worst parts of school. Taking some of the stress from the school building home with you is not a good feeling.
According to a study from Stanford University , 56% of students see homework as a “primary” source of stress. And when stress can lead to poor sleep, less healthy eating habits, and reduced time for your social life, it quickly becomes apparent that school stress can be a serious problem.
So we want to talk about how to reduce homework stress—and how to begin while you’re still physically at school.
Ideas for Reducing Your Homework Stress:
Talk to teachers, TAs, and mentors while you’re at school:
If you need academic help to reduce your homework stress, take advantage of the fact that you’re around knowledgeable people at school! Don’t wait until you’re home when all you can do is panic and become anxious; ask for help when you can!
School is a place your brain associates with learning—so learn there:
Take advantage of free periods or gaps between classes and use that time to study, work on homework, and plan out your day while your brain is in that “academic” state.
Talk to your friends about homework:
Is there any phrase more comforting than “I haven’t started yet either,” said by a fellow student? Talking to friends and peers about schoolwork can be a great way to reduce homework stress because it helps you to maintain social activity while talking to someone experiencing the same issues as you.
If your stress comes from difficulty with time management, check out our tips and tricks to learn how time management reduces stress .
Bring your smart compression sleeve to school with you.

The sharper your focus, the clearer your head. And the less stressed you are going into class, the more likely you are to retain information. eSmartr’s smart compression sleeves can make all that easier by naturally increasing your focus as you wear it on your arm. Natural solutions are ideal solutions , after all, which is why smart compression is so powerful in a classroom!
One way or another, you probably have to go to school—and if you don’t, there’s a good chance you’re still spending the time in online classes —so making the best of your time there is a great way to reduce homework stress. You don’t have to get all of your work done at school, of course, but as long as you’re able to arm yourself with knowledge and confidence, you’ll be off to a great start—and with eSmartr on your arm you should have no trouble at all.
Related Blog Posts

How to Reduce Stress and Increase Concentration at Work

Places to Go to Relive Stress and Find Your Focus

Optimized Basketball Brain: Jrue Holiday, All Star

Smart Compression: Tools to Help with Anxiety

How to Improve Memory Without Drugs or Supplements

Natural Stress Relief: A Meditation Guide

Ten Things You Didn’t Know About Jrue Holiday

Stress vs. Anxiety – What Is the Difference?
Shop our sleeves with ease.
30-DAY HASSLE-FREE RETURNS OR EXCHANGES
Sign Up Newsletter
Sign up to the esmartr newsletter.

What people should know about stress, according to a doctor
Sign up for CNN’s Stress, But Less newsletter. Our six-part mindfulness guide will inform and inspire you to reduce stress while learning how to harness it .
There is no doubt that stress is a part of everyday life, but too much can have detrimental impacts on people’s physical and mental health.
I wanted to delve more into depth about the health impacts of stress during National Stress Awareness Month. What does stress do to the body? When does it become a problem, and what are some ways to cope with it? And what can people do with stressors such as a hard job or caregiving responsibilities that can’t just go away?
To help us answer these questions, I had a conversation with CNN wellness expert Dr. Leana Wen. Wen is an emergency physician and adjunct associate professor at George Washington University. She previously served as Baltimore’s health commissioner.
CNN: What does stress do to a person’s body?
Dr. Leana Wen: When people experience a perceived threat, a variety of hormones are released that make the heart beat faster and increase blood pressure and blood sugar. These hormones also divert energy away from other parts of the body, such as the immune system and digestive system. These are evolutionary adaptations that once helped people to respond to situations such as predators chasing after them. Such “fight or flight” responses are normal and may be helpful in modern-day life. For instance, they could help an athlete with a faster performance or a student with staying up to study for an exam.
The problem arises when the body’s stress response is continuous. A perpetual state of “fight or flight” could lead to many chronic problems. Individuals could experience anxiety and depression , and other mental health ailments. They could also have headaches, muscle tension, abdominal pain, sleep disturbances, decreased immunity to infections, and problems with memory and concentration . Chronic stress has also been linked to increased likelihoods of high blood pressure, diabetes, heart attack and stroke.
CNN: Everyone experiences stress, so when does it become a problem?
Wen: It’s natural for people to experience stress to discrete stressful events (those that have a clear onset such as the birth of a child, starting of a new job, a divorce or the death of a loved one) that happen in their lives. The problem is when stress becomes a chronic state of being.
Warning signs to look out for include signs or symptoms of mental health concerns or physical manifestations of stress—for instance, if someone starts having new heart palpitations, abdominal pain or headaches. In addition, some people may attempt to cope with stress by using alcohol or drugs. A change in substance use could be a red flag to look for underlying stressors.
People should also ask themselves if stress is negatively affecting their function at home, at work and with their friends. Someone who finds themselves unusually irritable and is lashing out at loved ones and colleagues may also be doing so because of excessive stress.
CNN: Why should we be aware of excessive stress and try to reduce it as a health priority?
Wen: We can think of stress as something in our lives that is modifiable, just like high blood pressure or high blood sugar. The stressor itself may not be able to be changed, just as we cannot change our genetic predisposition to hypertension or diabetes. However, our reaction to it is within our control. And it’s our reaction to the stressor that determines our health outcomes. If stress has detrimental effects on our health, just as high blood pressure and diabetes do, then we can and should look for ways to reduce these effects.
CNN: What are some ways we can cope with stress?
Wen: First, it’s important to clarify that there are good and bad ways to cope with stress. Some people may turn to these not-so-good ways because it may help them feel better in the short-term, but there are real risks. I mentioned drinking alcohol and using drugs—obviously, these are not healthy coping strategies. Neither are binge-eating or smoking.
I think it’s really important to be self-aware. Be honest with yourself: When you have faced stressful situations in the past, have you turned to these unhealthy ways to cope? If so, be on the lookout and work to prevent these behaviors during stressful times.
Also, try to anticipate when there will be stressful situations. Is there a big deadline at work coming up? A family gathering that is likely to elicit negative emotions? A difficult conversation with a loved one? Knowing that a stressful event may occur can help you anticipate your reaction and plan accordingly.
I advise, too, that people make a list of stress relief techniques that have worked for them in the past. And try new techniques. Deep breathing exercises are something everyone can try and help both in the moment of the stressful encounter and after, for example, as is mindfulness meditation .
I’m also a big fan of exercise. There is excellent scientific evidence that exercise is very effective at managing stress. Exercise reduces stress hormones and increases endorphins, which are “feel-good” neurotransmitters that can relax the body and improve mood.
CNN: What is your advice for people who have stressors in their lives—such as a hard job or caregiving responsibilities—that can’t easily go away?
Wen: This is really hard, because of course it would be ideal to address the stressors themselves. But many people have stressful situations that they can’t change.
It helps to be up front about that and acknowledge that changing the situation is not in your control. What is in your control, though, is your reaction to the situation.
Here is where self-awareness and self-care are so important. Learn to recognize when you are feeling especially stressed. Perhaps you feel tension in your neck and back muscles, or you have abdominal cramps or jitters. These are the times to practice deep breathing, meditation and other exercises that help you in the short-term.
For both short- and long-term benefit, it’s essential to make time for self-care. By that, I mean activities that you enjoy and that can take your mind off the stressful life situations. These could include taking a walk with a good friend, working in the garden, playing with your pets, reading a good book or otherwise participating in activities you enjoy. Think of the time you are putting aside for yourself as a kind of therapy; stress can make you unhealthy, so this is your way of giving yourself “treatment” to offset that stress.
Along those lines, knowing that stress is one factor that can impact your well-being, work to maximize the other aspects that contribute to overall health. Try to get adequate, restful sleep . Aim to eat healthy, whole foods and reduce your consumption of ultra-processed products. Make sure other chronic medical conditions, such as high blood pressure , are being treated. And do not wait to seek help from your mental health or primary care provider if the stress you are experiencing is leading to continuing mental health or physical distress.
For more CNN news and newsletters create an account at CNN.com

University of South Florida
Lifelong Learning
Office of University Community Partnerships
Main Navigation

8 Ways to Reduce Stress at Work
- Emily Young
- July 18, 2023
- Professional Development
- Text-based Story
Feeling stressed, down, or anxious? You’re in good company.
- Mental health “dramatically declined” in 2020, according to a Lancet study cited in CNBC , “with an estimated 53 million additional cases of major depressive disorders and 76 million additional cases of anxiety disorders seen globally.”
- Nearly 2 out of 5 surveyed adults said their mental health was only “fair or poor” in December 2022.
- 90% of surveyed US adults believe the country is “experiencing a mental health crisis” as of October 2022.
There is plenty to be stressed about. In the workplace, many employees are returning to the office, where expectations aren’t always clear. Layoffs have left some workers scrambling for jobs, and others are overburdened by new responsibilities. Outside of work, Americans are navigating ongoing public health crises, systemic inequalities, restrictions to civil liberties and political unrest . Plus, 70 percent of Americans are financially stressed, with the majority living paycheck to paycheck. And that’s not to mention personal stress.
“I think the stress has definitely always been there, there is just much more gravity to it now,” says Joshua Kwasnicki, the director of organizational development for the Crisis Center of Tampa Bay . “People are on edge. What’s happening at work, they’re carrying with them to their house, and what’s happening at home, they’re carrying with them to work.”
All this to say: Your feelings are valid, and it’s understandable if emotional distress has been interfering with your ability to concentrate at your job. That’s why we reached out to the Crisis Center, as well as the USF College of Behavioral and Community Sciences, for these eight ways to reduce stress at work.
8. Acknowledge That It’s Okay to Not Be Okay
If you’re feeling overwhelmed with stress at work, give yourself permission to be a human being – not simply a worker or employee . “You have to take care of yourself first,” says Julie Serovich, the dean of the College of Behavioral and Community Sciences at the University of South Florida. “It’s really hard to be productive in the workplace when you’ve got a lot of things going on, and so making sure that you put yourself as a priority is very important.”
Kwasnicki has a similar message: “It’s okay to not be okay,” he says. “At work, we pressure ourselves to succeed because that’s been the backbone of everything we’ve been taught: ‘you’ve just got to do it.’ But… people are going to struggle. Instead of thinking to [yourself], what’s wrong with me? They did it, why can’t I just do it? It’s okay to say, you know what, I need help with this. There’s no shame in that.”
A healthy workplace is inclusive, compassionate, and supportive — encouraging employees to take care of their mental and emotional health. (And if your workplace doesn’t allow you to ask for help or have an honest conversation about your needs, you might consider looking for a job elsewhere.)
7. Find Ways to Recharge
You’ve probably heard the term “work/life balance” a lot. But if you feel like this balancing act requires a Cirque du Soleil-level of acrobatics, you’re not alone. “We live in very different times from when that term was coined,” Kwasnicki says. Just think about how easy it is to check your email from home!
What should we do instead? Aim for a “work/life blend,” Kwasnicki suggests. “I never truly get away from work, and also, I’m not a robot — things happen in my life that I’m going to take into work with me. It’s okay to not be okay. So how do I blend the work and life in a way that makes sense to me?”
He encourages workers to reflect: “what is draining my energy at work? What can I do to re-energize?”
You might try something from this pleasant events list, adapted from the DBT Skills Training Handouts and Worksheets book by Marsha M. Linehan:
- Spend time outside — whether that’s five minutes on your lunch break or a nature walk after work.
- Listen to music.
- Play with a pet.
- Meditate or do yoga.
- Write down affirmations about your good qualities.
- Take a bath.
- Advocate for a cause.
- Watch a funny YouTube video.
- Tinker with your car.
- Plan a beach day.
- Hang out or call a loved one.
- Make a smoothie and drink it slowly.
- Join a sports team.
- Light a candle.
- Lift weights.
- Watch a favorite TV show or read a book.
- Remind yourself, “I have done a full day’s work.”
Looking for an excuse to pamper yourself this month? You can also try our 30-day Wellness Challenge, chock-full of activities designed to help you re-charge.
6. Practice Meditation and Mindfulness
Meditation — which has been practiced for thousands of years — has been shown to reduce anxiety and worry, increase alertness and productivity, decrease self-criticism and improve your sense of identity, according to The Anxiety and Phobia Workbook by Edmund J. Bourne. The great thing about meditation is that it’s short enough to integrate into your workday — as Serovich points out, many exercises are only a couple of minutes long. Carve some time out of your lunch break or swivel your chair and close your eyes after a particularly draining meeting.
To get started, Serovich recommends the free meditation app Insight Timer. Other popular, paid apps include Calm and Headspace.
Pro tip: Practice meditation a few times before you try it at work.
5. Always Check the Facts
These days, it’s easy to be overwhelmed by the state of the world. “You have news coming at you 24/7,” says Serovich. And let’s be honest — much of it isn’t good. How do you cope?
- Unplug when you can, and avoid doom scrolling — especially before bed.
- Take constructive action to address issues you care about. “Trust that other people will contribute as well and work towards a solution for that particular problem,” Serovich says.
- Fact check information: A lot of the information we ingest, particularly through social media, is inaccurate, which “sparks anxiety,” explains Serovich. So before you react to anything, check it against other reliable sources.
4. Talk to a Friend
“Oftentimes, people find great benefit just talking to a friend,” Serovich says. But how do you know whether you can trust that friend with your experience? By “slowly testing it out,” she explains. Try saying something simple, like “Sometimes I feel anxious at work. Do you ever feel that way?” See how they respond — if they share some vulnerability with you themselves or react in an affirming, supportive way, then you can “slowly open the door [with a] back and forth type of dialogue to see how far the person may be willing to talk.”
Reach out to help people that you see struggling, too. If you notice a coworker is having a hard time, you can ask something like, “You don’t seem yourself. Are you okay?” Not only does this compassion help the other person — “it helps us, too,” Serovich says.
Don’t be afraid of an uncomfortable conversation. For example, you may end up needing to ask your friend, “Do you have thoughts of suicide?” If the answer is yes, you can encourage them to call the Crisis Center’s 211 hotline. Or you can call the hotline in advance and ask advice for how to communicate to your friend or co-worker who is struggling.
“Even though we may feel uncomfortable, and even though we may get it just a little wrong, it’s okay,” Kwasnicki says. “The fact that somebody is there with us, sitting with us, talking with us about our issues, coming from a place of genuine care and compassion — that’s all that’s needed. Everything else will fall into place.”
Remember that it’s not your job to fix someone else’s problems, however. Your goal is to simply show compassion and perhaps connect your friend with some of the resources from this blog post.
3. Take Advantage of Your Company’s EAP Program
An Employee Assistance Program (EAP) is often part of a full benefits package. It gives you free, confidential access to licensed, professional counselors who can help you with whatever you’re struggling with — including financial stress, mental health issues, relationship struggles, health management, and work conflicts.
You might feel worried that your company will have access to your conversation with the EAP counselor — but don’t be. Whether the program is internal to the company or external, an EAP must abide by HIPAA regulations. They can’t even tell your employer that you’ve reached out to them. The EAP might ask for some general, anonymous data, but this is to help identify if there’s a unit in the company that’s struggling or to report how many people the program helped that month. If you have any concerns, “you can ask for what your rights are in terms of answering questions,” says Serovich.
2. Talk to a Therapist
If your company doesn’t offer an EAP program, or if you want a service that goes beyond what the EAP provides, consider making an appointment with a mental health counselor.
“Therapy is a good thing,” says Serovich. She recommends it for everyone — even if you are not struggling with a serious problem, you can “find benefit from a few sessions in therapy.”
How do you find a therapist ?
- You can ask your primary care doctor for a referral or a friend for a recommendation.
- You can search for a provider through reliable websites such as the American Psychiatric Association , the American Psychological Association , the Association for Behavioral and Cognitive Therapies , and the Anxiety and Depression Association of America .
- Your insurance website, if applicable, might list therapists who are covered by your plan.
- You can look up more information about potential therapists on Psychology Today and read reviews on sites such as Vitals, Healthgrades, and ZocDoc .
1. Call a Hotline
You might think that a crisis hotline isn’t meant for you — maybe you really aren’t in crisis enough to use it. What counts as a crisis, after all? Will you be taking up space meant for someone else if you call?
Kwasnicki encourages you to call: “There is no space that you’re filling up. There’s dozens and dozens of intervention specialists. That’s what they’re there for. That’s why we exist, so no one has to face crises alone. If you feel that you’re alone, that’s enough to call. If you feel that you do not have the resources, inner or outer resources, for you to navigate whatever crisis you’re facing, that’s what we’re here for.”
Here are some benefits of calling a crisis hotline:
- The crisis hotline acts not only as suicide prevention, but also “as a resource connection,” says Kwasnicki. The person answering your call is a trained, intervention specialist who can connect you to what you need — with or without insurance — from therapy to social services to help with food or clothing.
- You can call 211 anytime — someone is waiting to talk to you 24/7.
- It’s completely free, and “you can call as many times as you want,” says Kwasnicki.
- It’s confidential.
- You can also call the national 988 hotline , which will connect you to your local 211 crisis center.
If you found these tips useful, you’ll love USF’s free course addressing mental health in the workplace. USF has partnered with the Crisis Center of Tampa Bay to offer a seven session class that you can complete at your own pace. If you’d like a digital badge and certificate from the USF Office of Corporate Training and Professional Education , you can choose to pay a $179 fee.
REGISTER NOW
Return to article listing
Explore More Categories
- Director's Corner
- Hospitality
- Human Resources
- K-12 Education
- Leadership and Management
- Process Improvement
- Project Management
- Sales and Marketing
About Corporate Training and Professional Education
USF Corporate Training and Professional Education empowers people to craft their future without limits through engaging professional growth learning and certification programs. Its programs focus on an array of topics – human resources, project management, paralegal, process improvement, leadership skills, technology, and much more.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether. Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students ...
Does it stress you out, numb your brain from busywork or actually make you fall behind in your classes? Should we get rid of homework? In " The Movement to End Homework Is Wrong, " published ...
"Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development," wrote Pope. High-performing paradox In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded.
"Homework has perennially acted as a source of stress for students, so that piece of it is not new," Galloway says. "But especially in upper-middle-class communities, where the focus is on getting ahead, I think the pressure on students has been ratcheted up." Yet homework can be a problem at the other end of the socioeconomic spectrum as well.
Their study found that too much homework is associated with: • Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty ...
Next door, the kids have homework. This involves 30 minutes of child-wrangling and patience-testing five days a week, pressure-cooking the little downtime they have together as a family. Meanwhile ...
Here are 10 tips to help your child learn how to make homework less stressful. 1. Stick to a Schedule. Help your child plan out his or her time, scheduling time for homework, chores, activities, and sleep. Keep this schedule handy so your child knows what he or she should be working on, and when. 2.
Effects of homework stress at home. Both parents and students tend to get stressed out at the beginning of a new school year due to the impending arrival of homework.. Nightly battles centered on finishing assignments are a household routine in houses with students. Research has found that too much homework can negatively affect children. In creating a lack of balance between play time and ...
These days, nightly homework is a given in American schools, writes Kohn. "Homework isn't limited to those occasions when it seems appropriate and important. Most teachers and administrators aren't saying, 'It may be useful to do this particular project at home,'" he writes. "Rather, the point of departure seems to be, 'We've decided ahead of ...
5. Practice Makes Perfect. The Stanford study shows that repeated exposure to math problems through one-on-one tutoring helped students relieve their math anxiety (the authors' analogy was how a fear of spiders can be treated with repeated exposure to spiders in a safe environment). Find a tutor you love, and come back to keep practicing ...
Use a calm voice. When kids feel anxious about homework, they might get angry, yell, or cry. Avoid matching their tone of voice. Take a deep breath and keep your voice steady and calm. Let them know you're there for them. Sometimes kids just don't want to do homework. They complain, procrastinate, or rush through the work so they can do ...
7. Practice Mindfulness. Mindfulness techniques, such as meditation and deep-breathing exercises, can help you become more aware of your thoughts and feelings. This heightened awareness makes it easier to control your stress levels. Even a few minutes of mindfulness practice can make a world of difference. 8.
To reduce homework stress, students can try to implement effective time management techniques, such as breaking down assignments into manageable tasks and creating a study schedule that prioritizes important assignments. They can also explore homework alternatives, such as online resources and study groups, that can help them better understand ...
Encourage your child to start their homework as early as possible. Help them review their assignments, make a plan for what needs to be completed, and then dive in. Naturally, children are more tired later in the evening which can lead to more stress. 4. Encourage Breaks. If you can see your child becoming frustrated or overwhelmed by their ...
5. Stay positive. Try to think about your homework as a good thing. Keeping this positive attitude will avoid creating more stress, and might even energize you to get it done. In fact, the more engaged and interested you are in your work, the quicker it will seem to pass.
Use these seven tips to take the hassle out of homework, so you and your family can alleviate some of stress from busy school nights: Create a quiet space. Let your child choose a quiet place to do their homework. Homework time should be technology-free, meaning no cellphones or screens unless they are required for the assignment.
The first step to managing your time more effectively is to make a schedule and stick to it. Use a calendar, planner, or an app to write down everything you need to get done. Set reminders for due dates and set aside time each day for studying. Don't leave assignments for the last minute.
Keywords: homework, stress, mental health The outcomes of adolescent mental health is a threat to students' health and wellbeing, more so than it ever has been in the modern era. As of 2019, the CDC reported a nearly 40. percent increase in feelings of sadness or hopelessness over the last ten years, and similar.
Afifi, a third-grade teacher at Colonel Howard Nichols Elementary School in east Bakersfield, assigns a little less homework to help students de-stress and spend more time acting their age. "I feel like they need time to be kids too," Afifi said. Having folders full of homework packets with short deadlines can be straining for many students ...
1. Potential Psychological Effects of Homework-Induced Stress: • Anxiety: The pressure to perform academically and meet homework expectations can lead to heightened levels of anxiety in students. Constant worry about completing assignments on time and achieving high grades can be overwhelming. • Sleep Disturbances: Homework-related stress ...
And when stress can lead to poor sleep, less healthy eating habits, and reduced time for your social life, it quickly becomes apparent that school stress can be a serious problem. So we want to talk about how to reduce homework stress—and how to begin while you're still physically at school. Ideas for Reducing Your Homework Stress:
Here are ten tips to help kids and parents reduce the stress of homework time. 1. Have a Set Homework Space. This first tip is probably one of the most important recommendations you'll get. Children need a set space to work that is away from the usual distractions of the house.
They could also have headaches, muscle tension, abdominal pain, sleep disturbances, decreased immunity to infections, and problems with. memory and concentration. Chronic stress has also been ...
Spend time outside — whether that's five minutes on your lunch break or a nature walk after work. Listen to music. Play with a pet. Meditate or do yoga. Write down affirmations about your good qualities. Take a bath. Advocate for a cause. Watch a funny YouTube video. Tinker with your car.