- The Open University
- Guest user / Sign out
- Study with The Open University

My OpenLearn Profile
Personalise your OpenLearn profile, save your favourite content and get recognition for your learning
About this free course
Become an ou student, download this course, share this free course.

Start this free course now. Just create an account and sign in. Enrol and complete the course for a free statement of participation or digital badge if available.
7 Describing an ICT system: conclusion
We have arrived at a model of a communication system that illustrates the processes needed for communication. We have also looked at the different kinds of communication link that can be used to convey data, and how to express the rates at which they can convey data. In sections 8–14, we shall be looking at a computer system as an example of an ICT system where data manipulation and storage are the most important features.

Importance of ICT in Education Essay
Ict: introduction, teachers and their role in education, impact of ict in education, use of ict in education, importance of ict to students, works cited.
Information and Communication Technology is among the most indispensable tools that the business world relies on today. Virtually all businesses, in one way or another, rely on technology tools to carry out operations. Other organizations like learning institutions are not left behind technology-wise. ICT is increasingly being employed in contemporary learning institutions to ease the work of students and teachers.
Among the most commendable successes of employing ICT in learning institutions is e-learning, in which the ICT tools are used to access classrooms remotely. This paper explores the importance of the tools of the tools of ICT in education and the roles that these tools have played in making learning better and easier.
Teachers are scholars who have mastered specific subjects that form part of their specialty and help in imparting knowledge to students. Some of the roles that teachers play in academic institutions include designing syllabuses, preparing timetables, preparing for lessons and convening students for lessons, and carrying out continuous assessments on students.
Others include keeping records of academic reports, disciplinary records, and other records related to the activities of students in school, like the participation of students in games and other activities.
In cases where there are limitations such that it is impossible to convene people and resources together for learning. E-learning provides a very important and convenient way of teaching people. In such a case, a teacher provides learning materials and lessons online, which can be accessed by his/her students at their convenience.
The materials can be audio files of recorded classroom lessons, audio-visual files for lessons requiring visual information like practical or even text documents, and hypertext documents (Tinio 1). This method of teaching is also convenient for teachers because they are able to record lessons at their convenience, and the assessment of students involves less documentation.
This is because with the use of the internet, teachers are able to upload assignments and continuous assessments on the e-learning systems, and after students are done with the assignments, they use the system or emails to send their completed assignments to their teachers. This comes with a number of advantages which are brought about by having students complete assignments in soft copies.
One of these advantages is that feedback from teachers will be timely and it will be convenient for the teachers. Teachers can also use technology tools such as plagiarism software to check if students have copied the works of other scholars and thus establish the authenticity of the assignment. It can thus be argued that although e-learning systems have their disadvantages, they are very instrumental in teaching people whose schedules are tight and who may have limitations as far as accessing the classroom is concerned.
Therefore technology has been an influential and essential tool in the career of education, and several innovations have been made that have made teaching a much easier career. The paragraph below discusses other ways in which technology has been employed in the education career.
Teachers can also use the tools of ICT in other functions. One such function is keeping records of student performances and other kinds of records within the academic institution. This can be done by uploading the information to a Management Information System for the school or college, which should have a database for supporting the same. The information can also be stored in soft form in Compact Disks, Hard Drives, Flash Disks, or even Digital Video Disks (Obringer 1).
This ensures that information is properly stored and backed up and also ensures that records are not as bulky as they would have been in the absence of the tools of ICT. Such a system also ensures that information can easily be accessed and also ensures that proper privacy of the data is maintained.
Another way in which teachers can use the tools of ICT to ease their work is by employing tools like projectors for presentations of lessons, iPads for students, computers connected to the internet for communicating to students about continuous assessments, and the like (Higgins 1). This way, the teacher will be able to reduce the paperwork that he /she uses in his/her work, and this is bound to make his/her work easier.
For instance, if the teacher can access a projector, he/she can prepare a presentation of a lesson for his/her students, and this way, he will not have to carry textbooks, notebooks, and the like to the classroom for the lesson. The teacher can also post notes and relevant texts for a given course on the information system for the school or on an interactive website, and thus he/she will have more time for discussions during lessons.
Teachers can also, in consultation with IT specialists, develop real-time systems where students can answer questions related woo what they have learned in class and get automated results through the system (Masie 1).
This will help the students understand the concepts taught in class better, and this way, teachers will have less workload. Such websites will also help teachers to show the students how questions related to their specialty are framed early enough so that students can concentrate on knowledge acquisition during class hours.
This is as opposed to a case where the students remain clueless about the kind of questions they expect in exams and spend most of their time preparing for exams rather than reading extensively to acquire knowledge. ICT can also be sued by teachers to advertise the kind of services they offer in schools and also advertise the books and journals they have written. This can be achieved by using websites for the school or specific teachers or professors.
As evidenced in the discussion above, ICT is a very instrumental tool in education as a career. The specific tools of ICT used in education, as discussed above, include the use of ICT in distance learning, storage of student performance and other relevant information in databases and storage media, and the use of tools of ICT in classroom like projectors, iPads and the like. Since the invention of the internet and the subsequent popularity of computers, a lot of functions of education as a career have been made simpler.
These include the administration of continuous assessments, marking continuous assessments, giving feedback to students, and even checking the originality of the ideas expressed in the assignments and examinations. All in all, the impact that ICT has had in educational institutions is so much that school life without ICT is somehow impossible for people who are accustomed to using ICT.
Higgins, Steve. “Does ICT improve learning and teaching in schools”. 2007. Web.
Masie, Shank. “What is electronic learning?” 2007. Web.
Obringer, Ann. “ How E-Learning Works ”. 2008. Web.
Tinio, Victoria. “ICT in Education”. 2008. Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, November 22). Importance of ICT in Education. https://ivypanda.com/essays/ict-in-education/
"Importance of ICT in Education." IvyPanda , 22 Nov. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/ict-in-education/.
IvyPanda . (2023) 'Importance of ICT in Education'. 22 November.
IvyPanda . 2023. "Importance of ICT in Education." November 22, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/ict-in-education/.
1. IvyPanda . "Importance of ICT in Education." November 22, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/ict-in-education/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Importance of ICT in Education." November 22, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/ict-in-education/.
- E-Learning in the Academic Industry
- Effectiveness of Integrating ICT in Schools
- ICT for Disaster Management Systems
- Project Management: Building ICT Center
- The Future of E-Learning
- Ottawa Region ICT Centres Project
- ICT Disaster Management Systems
- Traditional Learning and E-Learning Differences
- E-Learning: Video, Television and Videoconferencing
- Nontakers Perceptiom Towards ICT
- Technological Advances in Education
- Computer Based Training Verses Instructor Lead Training
- Smart Classroom and Its Effect on Student Learning
- Use of Technology as a Learning Tool
- Computers & Preschool Children: Why They Are Required in Early Childhood Centers

Information Technology and the U.S. Workforce: Where Are We and Where Do We Go from Here? (2017)
Chapter: 7 conclusion, 7 conclusion.
Progress in many of the basic computing and information technologies has been rapid in recent years, and the committee does not expect the pace of change to slow down in the foreseeable future. While some technologies are reaching maturity now, many important technologies have enormous future potential. As more of the world’s information is digitized and more people and things are networked, the economics of the digital, networked economy will become ever more important. This includes the ability to make copies of goods and services at almost zero cost and deliver them anywhere on the planet almost instantaneously. Furthermore, digitization of products, services, processes, and interactions makes it possible to measure and manage work with far more precision. Data-driven decision making and machine learning provide vast opportunities for improving productivity, efficiency, accuracy, and innovation.
The committee expects important innovations to come in the area of artifical intelligence (AI) and robotics. Several decades ago, humans were unable to converse with machines using ordinary speech; now it is done routinely. Machines are learning to effectively translate from one language to another, a task once seen only in science fiction. We are moving from an era where machines were blind, unable to recognize even simple objects, to an era where they can distinguish faces, read street signs, and understand the content of photographs as well as—or better than—humans. They are being put to work reading X-ray and MRI images, advising doctors on potential drug interactions, helping lawyers
sift through documents, and composing simple stories about sports and finance for newspapers. Machines are becoming much better at reasoning and can now defeat the best humans at most games of skill, from checkers and chess to trivia and Go. Machines are learning to drive cars, which could potentially save thousands of lives in the United States and millions worldwide. Bipedal robots are learning to navigate stairs and uneven terrain, while their cheetah-like brethren can outrun even the fastest humans. Many of the technologies with the greatest impact will likely look unlike any human or animal, but will transport shelves of inventory throughout warehouses, assemble basic electronics in factories, fly to disaster zones with medicine, swim beneath the waves to gather data for oceanographers, and haunt computer networks in search of cyberattacks. In fact, many of these exist in some form already, although they are likely to become more widespread and more competent.
While there are undoubtedly important technological breakthroughs to come, it is critical to note that the technologies that exist today and those under active development have important implications for the workforce. They create opportunities for new products, services, organizational processes, and business models as well as opportunities for automating existing tasks, even whole occupations. Many cognitive and physical tasks will be replaced by machines. At the same time, we expect new job opportunities to emerge as increasingly capable combinations of humans and machines attack problems that previously have been intractable.
Advances in IT and automation will present opportunities to boost America’s overall income and wealth, improve health care, shorten the work week, develop new goods and services, and increase product safety and reliability.
These same advances could also lead to growing inequality, decreased job stability, increasing demands on workers to change jobs, and changes in business organization. There are also important implications for other aspects of society, both intended and unintended, not the least of which include potentially profound changes in education, privacy, security, social relationships, and even democracy.
The ultimate effects of these technologies are not predetermined. Rather, like all tools, computing and information technologies can be used in many different ways. The outcomes for the workforce and society at large depend on our choices. Technology can be a powerful tool. What do we want for our future society? How do we decide this?
Potential future technological capabilities and innovations are largely unpredictable, and their implications and interactions are complex. Investing in extensive and effective data gathering, a robust infrastructure for analyzing these data, and multidisciplinary research will enable a deeper
understanding of emerging changes in technology and the workforce. The results of this research will inform the adoption of policies that will help maximize the resilience and prosperity of the institutions, organizations, and individuals in our society.
Recent years have yielded significant advances in computing and communication technologies, with profound impacts on society. Technology is transforming the way we work, play, and interact with others. From these technological capabilities, new industries, organizational forms, and business models are emerging.
Technological advances can create enormous economic and other benefits, but can also lead to significant changes for workers. IT and automation can change the way work is conducted, by augmenting or replacing workers in specific tasks. This can shift the demand for some types of human labor, eliminating some jobs and creating new ones. Information Technology and the U.S. Workforce explores the interactions between technological, economic, and societal trends and identifies possible near-term developments for work. This report emphasizes the need to understand and track these trends and develop strategies to inform, prepare for, and respond to changes in the labor market. It offers evaluations of what is known, notes open questions to be addressed, and identifies promising research pathways moving forward.
READ FREE ONLINE
Welcome to OpenBook!
You're looking at OpenBook, NAP.edu's online reading room since 1999. Based on feedback from you, our users, we've made some improvements that make it easier than ever to read thousands of publications on our website.
Do you want to take a quick tour of the OpenBook's features?
Show this book's table of contents , where you can jump to any chapter by name.
...or use these buttons to go back to the previous chapter or skip to the next one.
Jump up to the previous page or down to the next one. Also, you can type in a page number and press Enter to go directly to that page in the book.
Switch between the Original Pages , where you can read the report as it appeared in print, and Text Pages for the web version, where you can highlight and search the text.
To search the entire text of this book, type in your search term here and press Enter .
Share a link to this book page on your preferred social network or via email.
View our suggested citation for this chapter.
Ready to take your reading offline? Click here to buy this book in print or download it as a free PDF, if available.
Get Email Updates
Do you enjoy reading reports from the Academies online for free ? Sign up for email notifications and we'll let you know about new publications in your areas of interest when they're released.
- My Teaching Philosophy
- ICT in Education
- Tool 1 - Mathsbuilder.com
- Tool 2 - IWB
- Tool 3 - iPad
- Unit Overview
- Curricular Connections and Unit Outcomes
- Teaching Strategies
- Learning Adjustments
- Teaching and Learning Sequence
- Assessment and Reflection
This site belongs to UNESCO's International Institute for Educational Planning

IIEP Learning Portal

Search form
- issue briefs
- Improve learning
Information and communication technology (ICT) in education
Information and communications technology (ict) can impact student learning when teachers are digitally literate and understand how to integrate it into curriculum..
Schools use a diverse set of ICT tools to communicate, create, disseminate, store, and manage information.(6) In some contexts, ICT has also become integral to the teaching-learning interaction, through such approaches as replacing chalkboards with interactive digital whiteboards, using students’ own smartphones or other devices for learning during class time, and the “flipped classroom” model where students watch lectures at home on the computer and use classroom time for more interactive exercises.
When teachers are digitally literate and trained to use ICT, these approaches can lead to higher order thinking skills, provide creative and individualized options for students to express their understandings, and leave students better prepared to deal with ongoing technological change in society and the workplace.(18)
ICT issues planners must consider include: considering the total cost-benefit equation, supplying and maintaining the requisite infrastructure, and ensuring investments are matched with teacher support and other policies aimed at effective ICT use.(16)
Issues and Discussion
Digital culture and digital literacy: Computer technologies and other aspects of digital culture have changed the ways people live, work, play, and learn, impacting the construction and distribution of knowledge and power around the world.(14) Graduates who are less familiar with digital culture are increasingly at a disadvantage in the national and global economy. Digital literacy—the skills of searching for, discerning, and producing information, as well as the critical use of new media for full participation in society—has thus become an important consideration for curriculum frameworks.(8)
In many countries, digital literacy is being built through the incorporation of information and communication technology (ICT) into schools. Some common educational applications of ICT include:
- One laptop per child: Less expensive laptops have been designed for use in school on a 1:1 basis with features like lower power consumption, a low cost operating system, and special re-programming and mesh network functions.(42) Despite efforts to reduce costs, however, providing one laptop per child may be too costly for some developing countries.(41)
- Tablets: Tablets are small personal computers with a touch screen, allowing input without a keyboard or mouse. Inexpensive learning software (“apps”) can be downloaded onto tablets, making them a versatile tool for learning.(7)(25) The most effective apps develop higher order thinking skills and provide creative and individualized options for students to express their understandings.(18)
- Interactive White Boards or Smart Boards : Interactive white boards allow projected computer images to be displayed, manipulated, dragged, clicked, or copied.(3) Simultaneously, handwritten notes can be taken on the board and saved for later use. Interactive white boards are associated with whole-class instruction rather than student-centred activities.(38) Student engagement is generally higher when ICT is available for student use throughout the classroom.(4)
- E-readers : E-readers are electronic devices that can hold hundreds of books in digital form, and they are increasingly utilized in the delivery of reading material.(19) Students—both skilled readers and reluctant readers—have had positive responses to the use of e-readers for independent reading.(22) Features of e-readers that can contribute to positive use include their portability and long battery life, response to text, and the ability to define unknown words.(22) Additionally, many classic book titles are available for free in e-book form.
- Flipped Classrooms: The flipped classroom model, involving lecture and practice at home via computer-guided instruction and interactive learning activities in class, can allow for an expanded curriculum. There is little investigation on the student learning outcomes of flipped classrooms.(5) Student perceptions about flipped classrooms are mixed, but generally positive, as they prefer the cooperative learning activities in class over lecture.(5)(35)
ICT and Teacher Professional Development: Teachers need specific professional development opportunities in order to increase their ability to use ICT for formative learning assessments, individualized instruction, accessing online resources, and for fostering student interaction and collaboration.(15) Such training in ICT should positively impact teachers’ general attitudes towards ICT in the classroom, but it should also provide specific guidance on ICT teaching and learning within each discipline. Without this support, teachers tend to use ICT for skill-based applications, limiting student academic thinking.(32) To support teachers as they change their teaching, it is also essential for education managers, supervisors, teacher educators, and decision makers to be trained in ICT use.(11)
Ensuring benefits of ICT investments: To ensure the investments made in ICT benefit students, additional conditions must be met. School policies need to provide schools with the minimum acceptable infrastructure for ICT, including stable and affordable internet connectivity and security measures such as filters and site blockers. Teacher policies need to target basic ICT literacy skills, ICT use in pedagogical settings, and discipline-specific uses. (21) Successful implementation of ICT requires integration of ICT in the curriculum. Finally, digital content needs to be developed in local languages and reflect local culture. (40) Ongoing technical, human, and organizational supports on all of these issues are needed to ensure access and effective use of ICT. (21)
Resource Constrained Contexts: The total cost of ICT ownership is considerable: training of teachers and administrators, connectivity, technical support, and software, amongst others. (42) When bringing ICT into classrooms, policies should use an incremental pathway, establishing infrastructure and bringing in sustainable and easily upgradable ICT. (16) Schools in some countries have begun allowing students to bring their own mobile technology (such as laptop, tablet, or smartphone) into class rather than providing such tools to all students—an approach called Bring Your Own Device. (1)(27)(34) However, not all families can afford devices or service plans for their children. (30) Schools must ensure all students have equitable access to ICT devices for learning.
Inclusiveness Considerations
Digital Divide: The digital divide refers to disparities of digital media and internet access both within and across countries, as well as the gap between people with and without the digital literacy and skills to utilize media and internet.(23)(26)(31) The digital divide both creates and reinforces socio-economic inequalities of the world’s poorest people. Policies need to intentionally bridge this divide to bring media, internet, and digital literacy to all students, not just those who are easiest to reach.
Minority language groups: Students whose mother tongue is different from the official language of instruction are less likely to have computers and internet connections at home than students from the majority. There is also less material available to them online in their own language, putting them at a disadvantage in comparison to their majority peers who gather information, prepare talks and papers, and communicate more using ICT. (39) Yet ICT tools can also help improve the skills of minority language students—especially in learning the official language of instruction—through features such as automatic speech recognition, the availability of authentic audio-visual materials, and chat functions. (2)(17)
Students with different styles of learning: ICT can provide diverse options for taking in and processing information, making sense of ideas, and expressing learning. Over 87% of students learn best through visual and tactile modalities, and ICT can help these students ‘experience’ the information instead of just reading and hearing it. (20)(37) Mobile devices can also offer programmes (“apps”) that provide extra support to students with special needs, with features such as simplified screens and instructions, consistent placement of menus and control features, graphics combined with text, audio feedback, ability to set pace and level of difficulty, appropriate and unambiguous feedback, and easy error correction. (24)(29)
Plans and policies
- India [ PDF ]
- Detroit, USA [ PDF ]
- Finland [ PDF ]
- Alberta Education. 2012. Bring your own device: A guide for schools . Retrieved from http://education.alberta.ca/admin/technology/research.aspx
- Alsied, S.M. and Pathan, M.M. 2015. ‘The use of computer technology in EFL classroom: Advantages and implications.’ International Journal of English Language and Translation Studies . 1 (1).
- BBC. N.D. ‘What is an interactive whiteboard?’ Retrieved from http://www.bbcactive.com/BBCActiveIdeasandResources/Whatisaninteractivewhiteboard.aspx
- Beilefeldt, T. 2012. ‘Guidance for technology decisions from classroom observation.’ Journal of Research on Technology in Education . 44 (3).
- Bishop, J.L. and Verleger, M.A. 2013. ‘The flipped classroom: A survey of the research.’ Presented at the 120th ASEE Annual Conference and Exposition. Atlanta, Georgia.
- Blurton, C. 2000. New Directions of ICT-Use in Education . United National Education Science and Culture Organization (UNESCO).
- Bryant, B.R., Ok, M., Kang, E.Y., Kim, M.K., Lang, R., Bryant, D.P. and Pfannestiel, K. 2015. ‘Performance of fourth-grade students with learning disabilities on multiplication facts comparing teacher-mediated and technology-mediated interventions: A preliminary investigation. Journal of Behavioral Education. 24.
- Buckingham, D. 2005. Educación en medios. Alfabetización, aprendizaje y cultura contemporánea, Barcelona, Paidós.
- Buckingham, D., Sefton-Green, J., and Scanlon, M. 2001. 'Selling the Digital Dream: Marketing Education Technologies to Teachers and Parents.' ICT, Pedagogy, and the Curriculum: Subject to Change . London: Routledge.
- "Burk, R. 2001. 'E-book devices and the marketplace: In search of customers.' Library Hi Tech 19 (4)."
- Chapman, D., and Mählck, L. (Eds). 2004. Adapting technology for school improvement: a global perspective. Paris: International Institute for Educational Planning.
- Cheung, A.C.K and Slavin, R.E. 2012. ‘How features of educational technology applications affect student reading outcomes: A meta-analysis.’ Educational Research Review . 7.
- Cheung, A.C.K and Slavin, R.E. 2013. ‘The effectiveness of educational technology applications for enhancing mathematics achievement in K-12 classrooms: A meta-analysis.’ Educational Research Review . 9.
- Deuze, M. 2006. 'Participation Remediation Bricolage - Considering Principal Components of a Digital Culture.' The Information Society . 22 .
- Dunleavy, M., Dextert, S. and Heinecke, W.F. 2007. ‘What added value does a 1:1 student to laptop ratio bring to technology-supported teaching and learning?’ Journal of Computer Assisted Learning . 23.
- Enyedy, N. 2014. Personalized Instruction: New Interest, Old Rhetoric, Limited Results, and the Need for a New Direction for Computer-Mediated Learning . Boulder, CO: National Education Policy Center.
- Golonka, E.M., Bowles, A.R., Frank, V.M., Richardson, D.L. and Freynik, S. 2014. ‘Technologies for foreign language learning: A review of technology types and their effectiveness.’ Computer Assisted Language Learning . 27 (1).
- Goodwin, K. 2012. Use of Tablet Technology in the Classroom . Strathfield, New South Wales: NSW Curriculum and Learning Innovation Centre.
- Jung, J., Chan-Olmsted, S., Park, B., and Kim, Y. 2011. 'Factors affecting e-book reader awareness, interest, and intention to use.' New Media & Society . 14 (2)
- Kenney, L. 2011. ‘Elementary education, there’s an app for that. Communication technology in the elementary school classroom.’ The Elon Journal of Undergraduate Research in Communications . 2 (1).
- Kopcha, T.J. 2012. ‘Teachers’ perceptions of the barriers to technology integration and practices with technology under situated professional development.’ Computers and Education . 59.
- Miranda, T., Williams-Rossi, D., Johnson, K., and McKenzie, N. 2011. "Reluctant readers in middle school: Successful engagement with text using the e-reader.' International journal of applied science and technology . 1 (6).
- Moyo, L. 2009. 'The digital divide: scarcity, inequality and conflict.' Digital Cultures . New York: Open University Press.
- Newton, D.A. and Dell, A.G. 2011. ‘Mobile devices and students with disabilities: What do best practices tell us?’ Journal of Special Education Technology . 26 (3).
- Nirvi, S. (2011). ‘Special education pupils find learning tool in iPad applications.’ Education Week . 30 .
- Norris, P. 2001. Digital Divide: Civic Engagement, Information Poverty, and the Internet Worldwide . Cambridge, USA: Cambridge University Press.
- Project Tomorrow. 2012. Learning in the 21st century: Mobile devices + social media = personalized learning . Washington, D.C.: Blackboard K-12.
- Riasati, M.J., Allahyar, N. and Tan, K.E. 2012. ‘Technology in language education: Benefits and barriers.’ Journal of Education and Practice . 3 (5).
- Rodriquez, C.D., Strnadova, I. and Cumming, T. 2013. ‘Using iPads with students with disabilities: Lessons learned from students, teachers, and parents.’ Intervention in School and Clinic . 49 (4).
- Sangani, K. 2013. 'BYOD to the classroom.' Engineering & Technology . 3 (8).
- Servon, L. 2002. Redefining the Digital Divide: Technology, Community and Public Policy . Malden, MA: Blackwell Publishers.
- Smeets, E. 2005. ‘Does ICT contribute to powerful learning environments in primary education?’ Computers and Education. 44 .
- Smith, G.E. and Thorne, S. 2007. Differentiating Instruction with Technology in K-5 Classrooms . Eugene, OR: International Society for Technology in Education.
- Song, Y. 2014. '"Bring your own device (BYOD)" for seamless science inquiry in a primary school.' Computers & Education. 74 .
- Strayer, J.F. 2012. ‘How learning in an inverted classroom influences cooperation, innovation and task orientation.’ Learning Environment Research. 15.
- Tamim, R.M., Bernard, R.M., Borokhovski, E., Abrami, P.C. and Schmid, R.F. 2011. ‘What forty years of research says about the impact of technology on learning: A second-order meta-analysis and validation study. Review of Educational Research. 81 (1).
- Tileston, D.W. 2003. What Every Teacher Should Know about Media and Technology. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press.
- Turel, Y.K. and Johnson, T.E. 2012. ‘Teachers’ belief and use of interactive whiteboards for teaching and learning.’ Educational Technology and Society . 15(1).
- Volman, M., van Eck, E., Heemskerk, I. and Kuiper, E. 2005. ‘New technologies, new differences. Gender and ethnic differences in pupils’ use of ICT in primary and secondary education.’ Computers and Education. 45 .
- Voogt, J., Knezek, G., Cox, M., Knezek, D. and ten Brummelhuis, A. 2013. ‘Under which conditions does ICT have a positive effect on teaching and learning? A call to action.’ Journal of Computer Assisted Learning. 29 (1).
- Warschauer, M. and Ames, M. 2010. ‘Can one laptop per child save the world’s poor?’ Journal of International Affairs. 64 (1).
- Zuker, A.A. and Light, D. 2009. ‘Laptop programs for students.’ Science. 323 (5910).
Related information
- Information and communication technologies (ICT)
Academic & Employability Skills
Subscribe to academic & employability skills.
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Join 397 other subscribers.
Email Address
How to write a conclusion
Posted in: academic writing , essay-writing

Your conclusion is very important as it presents the final words of your assignment. It should leave the reader satisfied that you have provided a thorough, well-researched and reasoned response to the assignment question.
Your conclusion should move from the specific to the general (Introductions move from general to specific). You can begin your conclusion by reformulating the thesis statement you wrote in your introduction. This will remind the reader of the purpose of your essay.
Your conclusion should also include some or all of the following elements:
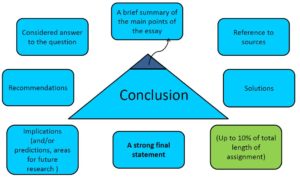
Here is a simple conclusion to illustrate how it works:
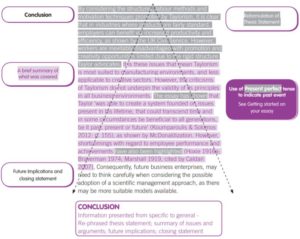
Example Conclusion from Hopkins, D. and Reid, T., 2018. The Academic Skills Handbook: Your Guid e to Success in Writing, Thinking and Communicating at University . Sage.
Share this:.
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
Click here to cancel reply.
- Email * (we won't publish this)
Write a response
How skills enrichment workshops have helped me improve my work
Third year BSc Biomedical Sciences student Sophie Benton tells us how skills enrichment workshops have increased her confidence with academic writing.

Meet the skills enrichment team
As the Skills Centre’s programme of academic and employability skills workshops gets underway, we introduce our friendly team of teachers, dedicated to sharing their expertise to help enrich your academic journey at Bath, and share some of their academic skills...

Five great reasons to attend a skills enrichment workshop this year
A common phrase we hear from students in the Skills Centre is: “Your support has been so useful – I wish I’d known about it sooner!” Malcolm Skene, Digital & Academic Skills Course Leader, introduces the skills enrichment programme and...

Implementation of ICT in Secondary Schools
- Reference work entry
- First Online: 01 January 2020
- Cite this reference work entry

- Pieter Hogenbirk 2
96 Accesses
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Australian Curriculum, AC (2013) http://www.australiancurriculum.edu.au/Curriculum/Overview
Beniger JR (1986) The control revolution: technological and economic origins of the information society. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA
Google Scholar
Galvin, Gilleran, Hogenbirk, Hunya, Selinger, Zeidler, Reflections on eTwinning, Collaborations, enrichment and added value (September 2006), Pedagogical issues (October 2006), Cultural understanding and integration, professional development (February 2007). www.etinning.net
Griffiths M (2002) The educational benefits of videogames. Educ Health 20(3). http://sheu.org.uk/sites/sheu.org.uk/files/imagepicker/1/eh203mg.pdf
Hattie J (2009) Visible Learning. http://visible-learning.org/2009/02/visible-learning-meta-study/
Hogenbirk P (1997) An educational tool for planning and monitoring the teaching-learning process in Dutch secondary education, ITEM, Hongkong. www.researchgate.net
Hogenbirk P, de Rijcke, et al. (2006), Pupils: it kicks, new ways of learning, Dutch Inspectorate of Education. http://www.rijksoverheid.nl/documenten-en-publicaties/brochures/2008/09/11/pupils-it-kicks.html
Hogenbirk P (2016) ICT in Education: literacy, enhancement and personalization, www.odino.nl/publicaties/ and https://www.researchgate.net/publication/303080210_ICT_in_Education_literacy_enhancement_and_personalization_1 . Note from UNESCO: “This paper was commissioned by the UNESCO International Bureau of Education (IBE). It has not been edited nor published by the team. The views and opinions expressed in this paper are those of the author and should not be attributed to the IBE-UNESCO. The paper can be cited with the following reference: “Paper commissioned by the UNESCO International Bureau of Education (IBE), ICT in Education: literacy, enhancement and personalization, please contact [email protected]”
Hogenbirk PG, van de Braak P (2008) ICT action school development on the basis of an inspectorates assessment. LYICT, Malaysia. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10639-012-9224-x
Hogenbirk PG, van de Braak P (2009) ICT action school development on the basis of an inspectorates assessment Part II, WCCE2009. Bento Conçalvez, Brasil. https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007%2F978-3-642-03115-1_13.pdf
Hogenbirk PG, van de Braak P (2011) ICT action school development on Helen Parkhurst Dalton school, IIGWE2011. Mombasa, Kenya. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/273160594_ICT_Action_School_Development_at_Helen_Parkhurst_Dalton_School_Part_III
ITEA’s Technology for All Americans Project (2006) http://www.iteea.org/TAA/Publications/TAA_Publications.html
Izmestiev D (2012) Personalized learning: a new ICT-enabled education approach. Unesco IITE, Moscow. http://unesdoc.unesco.org/images/0022/002202/220240E.pdf
Jensen JL, Kummer TA, Godoy PDDM (2015) Improvements from a flipped classroom may simply be the fruits of active learning. CBE Life Sci Educ 14(1):ar5
Article Google Scholar
Kennisnet (2015) Four in balance monitor 2015. https://www.kennisnet.nl/fileadmin/kennisnet/corporate/algemeen/Four_in_balance_monitor_2015.pdf , p 18
Moss S (2014, January) Making the most of ICT – what the research tells us. http://www.ictineducation.org/home-page/2014/1/29/making-the-most-of-ict-what-the-research-tells-us.html
National educational technology standards for students, 2nd edn. International Society for Technology in Education, ISTE, Eugene (2007)
Oblinger D (2006, May) Simulations, games, and learning. https://net.educause.edu/ir/library/pdf/eli3004.pdf
OECD (2006) Are students ready for a technology-rich world? What PISA studies tell us. OECD Publishing, Paris
Book Google Scholar
Oliver M, Trigwell K (2005) Can ‘blended learning’ be redeemed? In: E-Learning, vol 2, no 1. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.2304/elea.2005.2.1.17
Open University (2010) http://www.open.ac.uk/libraryservices/documents/Integrating_IL_Booklet_2010.pdf
Prensky M (2001) Digital natives, digital immigrants, from on the horizon, vol 9, no 5. MCB University Press. https://www.marcprensky.com/writing/Prensky%20-%20Digital%20Natives,%20Digital%20Immigrants%20-%20Part1.pdf
Recommendation of the European Parliament and of the Council of 18 December 2006 on key competences for lifelong learning, European Union (2006) http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex:32006H0962
van Oel B et al (2009a) P2V project, using the European framework for the evaluation of ICT in education. http://p2v.eun.org
van Oel B et al (2009b) P2V project, using the European framework for the evaluation of ICT in education. http://peerlearning.eun.org/shared/data/pdf/P2V_ICT_evaluation_framework_final.pdf
Voogt J, Pareja Roblin N (2010) 21st century skills, discussion paper. http://opite.pbworks.com/w/file/fetch/61995295/White%20Paper
Wing JM (2006) Computational thinking. Commun ACM 49. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/23142610_Computational_thinking_and_thinking_about_computing
Ziehe T (1999) Schule und Jugend – ein Differenzverhältnis. In: Neue Sammlung 39, 4, S. 619–629, ISSN 0028-3355
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Projectbureau Odino BV, Doorn, The Netherlands
Pieter Hogenbirk
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Pieter Hogenbirk .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Victoria University, Melbourne, VIC, Australia
Arthur Tatnall
Section Editor information
Faculty IV: Science and Technology, University of Siegen, Siegen, Germany
Sigrid Schubert
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Hogenbirk, P. (2020). Implementation of ICT in Secondary Schools. In: Tatnall, A. (eds) Encyclopedia of Education and Information Technologies. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-10576-1_26
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-10576-1_26
Published : 14 June 2020
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-10575-4
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-10576-1
eBook Packages : Computer Science Reference Module Computer Science and Engineering
Share this entry
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to conclude an essay | Interactive example

How to Conclude an Essay | Interactive Example
Published on January 24, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on July 23, 2023.
The conclusion is the final paragraph of your essay . A strong conclusion aims to:
- Tie together the essay’s main points
- Show why your argument matters
- Leave the reader with a strong impression
Your conclusion should give a sense of closure and completion to your argument, but also show what new questions or possibilities it has opened up.
This conclusion is taken from our annotated essay example , which discusses the history of the Braille system. Hover over each part to see why it’s effective.
Braille paved the way for dramatic cultural changes in the way blind people were treated and the opportunities available to them. Louis Braille’s innovation was to reimagine existing reading systems from a blind perspective, and the success of this invention required sighted teachers to adapt to their students’ reality instead of the other way around. In this sense, Braille helped drive broader social changes in the status of blindness. New accessibility tools provide practical advantages to those who need them, but they can also change the perspectives and attitudes of those who do not.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: return to your thesis, step 2: review your main points, step 3: show why it matters, what shouldn’t go in the conclusion, more examples of essay conclusions, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about writing an essay conclusion.
To begin your conclusion, signal that the essay is coming to an end by returning to your overall argument.
Don’t just repeat your thesis statement —instead, try to rephrase your argument in a way that shows how it has been developed since the introduction.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Next, remind the reader of the main points that you used to support your argument.
Avoid simply summarizing each paragraph or repeating each point in order; try to bring your points together in a way that makes the connections between them clear. The conclusion is your final chance to show how all the paragraphs of your essay add up to a coherent whole.
To wrap up your conclusion, zoom out to a broader view of the topic and consider the implications of your argument. For example:
- Does it contribute a new understanding of your topic?
- Does it raise new questions for future study?
- Does it lead to practical suggestions or predictions?
- Can it be applied to different contexts?
- Can it be connected to a broader debate or theme?
Whatever your essay is about, the conclusion should aim to emphasize the significance of your argument, whether that’s within your academic subject or in the wider world.
Try to end with a strong, decisive sentence, leaving the reader with a lingering sense of interest in your topic.
The easiest way to improve your conclusion is to eliminate these common mistakes.
Don’t include new evidence
Any evidence or analysis that is essential to supporting your thesis statement should appear in the main body of the essay.
The conclusion might include minor pieces of new information—for example, a sentence or two discussing broader implications, or a quotation that nicely summarizes your central point. But it shouldn’t introduce any major new sources or ideas that need further explanation to understand.
Don’t use “concluding phrases”
Avoid using obvious stock phrases to tell the reader what you’re doing:
- “In conclusion…”
- “To sum up…”
These phrases aren’t forbidden, but they can make your writing sound weak. By returning to your main argument, it will quickly become clear that you are concluding the essay—you shouldn’t have to spell it out.
Don’t undermine your argument
Avoid using apologetic phrases that sound uncertain or confused:
- “This is just one approach among many.”
- “There are good arguments on both sides of this issue.”
- “There is no clear answer to this problem.”
Even if your essay has explored different points of view, your own position should be clear. There may be many possible approaches to the topic, but you want to leave the reader convinced that yours is the best one!
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
- Argumentative
- Literary analysis
This conclusion is taken from an argumentative essay about the internet’s impact on education. It acknowledges the opposing arguments while taking a clear, decisive position.
The internet has had a major positive impact on the world of education; occasional pitfalls aside, its value is evident in numerous applications. The future of teaching lies in the possibilities the internet opens up for communication, research, and interactivity. As the popularity of distance learning shows, students value the flexibility and accessibility offered by digital education, and educators should fully embrace these advantages. The internet’s dangers, real and imaginary, have been documented exhaustively by skeptics, but the internet is here to stay; it is time to focus seriously on its potential for good.
This conclusion is taken from a short expository essay that explains the invention of the printing press and its effects on European society. It focuses on giving a clear, concise overview of what was covered in the essay.
The invention of the printing press was important not only in terms of its immediate cultural and economic effects, but also in terms of its major impact on politics and religion across Europe. In the century following the invention of the printing press, the relatively stationary intellectual atmosphere of the Middle Ages gave way to the social upheavals of the Reformation and the Renaissance. A single technological innovation had contributed to the total reshaping of the continent.
This conclusion is taken from a literary analysis essay about Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein . It summarizes what the essay’s analysis achieved and emphasizes its originality.
By tracing the depiction of Frankenstein through the novel’s three volumes, I have demonstrated how the narrative structure shifts our perception of the character. While the Frankenstein of the first volume is depicted as having innocent intentions, the second and third volumes—first in the creature’s accusatory voice, and then in his own voice—increasingly undermine him, causing him to appear alternately ridiculous and vindictive. Far from the one-dimensional villain he is often taken to be, the character of Frankenstein is compelling because of the dynamic narrative frame in which he is placed. In this frame, Frankenstein’s narrative self-presentation responds to the images of him we see from others’ perspectives. This conclusion sheds new light on the novel, foregrounding Shelley’s unique layering of narrative perspectives and its importance for the depiction of character.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Your essay’s conclusion should contain:
- A rephrased version of your overall thesis
- A brief review of the key points you made in the main body
- An indication of why your argument matters
The conclusion may also reflect on the broader implications of your argument, showing how your ideas could applied to other contexts or debates.
For a stronger conclusion paragraph, avoid including:
- Important evidence or analysis that wasn’t mentioned in the main body
- Generic concluding phrases (e.g. “In conclusion…”)
- Weak statements that undermine your argument (e.g. “There are good points on both sides of this issue.”)
Your conclusion should leave the reader with a strong, decisive impression of your work.
The conclusion paragraph of an essay is usually shorter than the introduction . As a rule, it shouldn’t take up more than 10–15% of the text.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, July 23). How to Conclude an Essay | Interactive Example. Scribbr. Retrieved April 11, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/conclusion/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, example of a great essay | explanations, tips & tricks, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing a Paper: Conclusions
Writing a conclusion.
A conclusion is an important part of the paper; it provides closure for the reader while reminding the reader of the contents and importance of the paper. It accomplishes this by stepping back from the specifics in order to view the bigger picture of the document. In other words, it is reminding the reader of the main argument. For most course papers, it is usually one paragraph that simply and succinctly restates the main ideas and arguments, pulling everything together to help clarify the thesis of the paper. A conclusion does not introduce new ideas; instead, it should clarify the intent and importance of the paper. It can also suggest possible future research on the topic.
An Easy Checklist for Writing a Conclusion
It is important to remind the reader of the thesis of the paper so he is reminded of the argument and solutions you proposed.
Think of the main points as puzzle pieces, and the conclusion is where they all fit together to create a bigger picture. The reader should walk away with the bigger picture in mind.
Make sure that the paper places its findings in the context of real social change.
Make sure the reader has a distinct sense that the paper has come to an end. It is important to not leave the reader hanging. (You don’t want her to have flip-the-page syndrome, where the reader turns the page, expecting the paper to continue. The paper should naturally come to an end.)
No new ideas should be introduced in the conclusion. It is simply a review of the material that is already present in the paper. The only new idea would be the suggesting of a direction for future research.
Conclusion Example
As addressed in my analysis of recent research, the advantages of a later starting time for high school students significantly outweigh the disadvantages. A later starting time would allow teens more time to sleep--something that is important for their physical and mental health--and ultimately improve their academic performance and behavior. The added transportation costs that result from this change can be absorbed through energy savings. The beneficial effects on the students’ academic performance and behavior validate this decision, but its effect on student motivation is still unknown. I would encourage an in-depth look at the reactions of students to such a change. This sort of study would help determine the actual effects of a later start time on the time management and sleep habits of students.
Related Webinar
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Thesis Statements
- Next Page: Writer's Block
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

ICT ASSIGNMENT 1

The aim of this assignment is to discuss the key innovations of the last ten years that have affected education technology. It will also explain the importance of these key innovations for all secondary school teachers, also a summary of education technology best practices, key challenges to these types of best practices faced by real world in secondary schools and challenges and contribution in facilitating and improving students' performance. After discussing the questions above, the conclusion and reference page will be established. Enger (2007:30) states that, educational technology is " the study and ethical practice sof facilitating learning and improving performance by creating, using and managing appropriate technological processes and resources ". Atkinson (2007), also states that, educational technology is " a field of study that investigates the process of analyzing, and designing developing, implementing, and evaluating the instructional environment and learning materials in order to improve teaching and learning ". Therefore, educational technology is the use of both physical hardware and educational theoretics. It encompasses several domains, including learning theory, computer-based training, online learning and where mobile technologies are used. It is important to keep or to know it that the purpose of educational technology also referred to as instructional technology is to improve education. However, education technology is important for all secondary school teachers because secondary school teachers are the drivers of secondary schools. Secondary school teachers have a responsibility to introduce, encourage and help pupils master technology, as well as subjects, as it applies to school and the future. Technology will be used in every aspect of the professional lives of current students, (Enger, 2007:35). Furthermore, by secondary teachers using educational technology, the classroom can be taken anywhere with all the knowledge and resources contained and deliverable on demand on a mobile device, pupils can learn at home or in the field. Mobile technology allows for greater collaboration between students promoting strong foundations in group work. Secondary teachers they have got responsibility of making sure that, pupils or learners are using this technology so that they can have access to any soft copy materials. Mobile technology helps learners a lot.
Related Papers
Use of ICT in teaching and learning at Primary School level
Liberty Mutude
This study sought to establish the use of ICT tools in a primary school classroom with reference to primary schools in High-Glen District. Relevant literature to the study was reviewed. The study utilised the descriptive survey design. The population for the study comprised of forty five teachers and five heads of primary schools. A purposive sample of primary schools located in High-Glen District were selected. From these primary schools, teachers and students were are also selected using the stratified random sampling technique. Questionnaires were used to collect data from primary school heads and teachers. Structured interviews were used to collect data from primary school students. Data collected through questionnaires and structured interviews were quantitatively analysed through calculating statistical measures such as percentages. The following major findings emerged from the data analysis. Firstly, ICT tools are being used for the purpose of enhancing teaching and learning in the classroom. Secondly, there is no ICT maturity in terms of experience and appreciation in the use of ICT tools. The other finding was that there high levels in shortage of ICT tools resulting in low tools to pupil ratio. Given the above findings and conclusions, therefore this study recommends that ICT tools be used for the purpose of enhancing learning and teaching in classroom through learner involvement. Secondly, the government should also aid in the provision of ICT tools in primary schools so that teachers and students get to practically use them. The other recommendation is that teachers need to be trained in using ICT for the benefit of learning and teaching processes.
eric hagenimana
IJIP Journal
ICT is changing processes of teaching and learning by adding elements of vitality to learning environments including virtual environments for the purpose. ICT can enhance the quality of education in several ways, by increasing learner motivation and engagement, by facilitating the acquisition of basic skills, and by enhancing teacher training. ICT provide-motivation to learn. ICT such as videos, television and multimedia computer software that combine text, sound, and colourful moving images can be used to provide challenging and authentic content that will engage the student in the learning process. The study was conducted in urban areas of Lucknow city of Uttar Pradesh, in the year 2016. A total of 150 samples which include students and their teachers of secondary level classes selected randomly by government and private schools. Data collected by self made questionnaire which is standardized by specific subject experts. For data analysis t-test was used in research. The result revealed that significance differences shown in use of ICT as an educational tool in secondary school education on the basis of teacher's age. The hypothesis was rejected. ICT in school management system will assist schools to plan for the effective use of digital technologies in their everyday practices to prepare students for the demands of an ever-changing world, to achieve powerful learning and teaching, and improve learning, teaching and administration. ICT as any object which allows students and teachers to get information through to electronic communication. (Singh & Mishra, 2016) ICT have demonstrated potential to increase the options, access, participation, and achievement for all students. The potentials of information and communication technology (ICT) to facilitate students' learning, improve teaching and enhance institutional administration had been established in literature. Teachers generate meaningful and engaging learning experiences for their students, strategically using ICT to enhance learning. ICT in secondary schools provide lots of opportunities to teachers to transform their practices by providing the learners with improved educational content and more effective teaching and learning methods. (
sevilay şahin
In this study, the effect of technology on learning and teaching in a classroom environment is invetigated. It is widely known that, the effect of technology in the classroom is highly productive. But to what extent and under what circumstances it should be applied depend on different factors such as; backround knowledge of teachers about the teaching equipments they use, the ability to use this technology, the methods, strategies and techniques about using it, students' perceptions of technology, technological supports offered by the school, etc. As a result, technology is not an end itself, it should be supported by some other mean.
SMART M O V E S J O U R N A L IJELLH
Abstract Technology is a tool to acquiring knowledge in particular field to solve the problems. Educational technology is prevailing to impart teaching, learning process effectively and efficiently. Teaching doesn’t stop with lectures but it needs the participation of students using different technical and technological gadgets to apply what is learnt in the classroom situation. At present apart from the teacher made gadgets, many electronically operated gadgets are in use to encourage self study and quality of education. In this paper we come to know how technology helps in both way for effective learning and teaching process. Key Words: Technology, education, skills, knowledge, technical
Journal of Education and Practice
Ardita Ceka
Today, Information and communication technology has become a way of life in which children are drawn. Today's children are beginning to use digital tools at a very young age, so that the school should respond to the needs of students. Also today it is impossible for any profession performs without the help of information technology. The computer and the Internet gives us endless possibilities and resources in improving the quality of work.Even in education, computer skills and additional equipment are needed, because they create great opportunities for teachers and inspire curiosity, imagination and interest of students.Teachers should not oppose change, but they should use new technology for better quality teaching and make it more interesting. The use of technology will positively improve results faculty and students.Teachers must carefully plan the use and integration of technology in teaching. How to integrate technology into teaching mainly depends on how many computers has...
Garima Malhotra
Learning is an on-going process and so is the innovation. Knowledge is an outcome of learning and technology is a result of innovation. Today, we belong to the networking age that surpass the communication age. In this age, the concept of education has become modern and elaborative. Now the focus has shifted from imparting knowledge to interaction, discussion and above all encouraging participation. It looks like teaching and technology or teaching with technology implies the dependency and integration of both on each other. This paper attempts to give an insight on how to integrate teaching with teachers learning for effective delivery of information and knowledge. The key focus of this paper is to find out the ways in which teachers can embrace their learning with the help of various tools of technology. And also how teachers can use technology to reach out to their students in most impressive style. To enable teachers to shift from their habitual approach to contemporary approach, Here the onus is on teachers’ to educate and impart knowledge in the most effective and efficient way. But this is only possible if their own education is able to strengthen their own knowledge. This paper describes the innovative approach adopted for the professional development of teachers. It focuses on integrating technology skills based on authentic learning situations. Through this paper an attempt is made to find out how Technology can play important role in both teachers education and teaching methods .how technology can be made interesting to use for learning over conventional methods. As a teacher the process of learning other than teaching become more imperative. It is cyclic in nature i.e. from learning to gaining to delivering to learning back. Where the exchange of knowledge will result in knowing something new not only for the students but for the teachers as well. This paper contains dynamics of teachers’ education integrating with technology both in their own learning and way of imparting it to students.
European Journal of Research and Reflection in Educational Sciences
Dr. Himendra Balalle
The extraordinary progress and technological growth in the world are witnessed. In recent years, technology has also emerged through laptops, smartphones, mobile phone software, websites, text messages and social networking platforms. This advancement indicates that technology in various environments, like the education sector, has benefited greatly. We can see the value of education technologies with different apps for distance education, the internet, teachers and students themselves. This article aim is to provide a summary of the significance and use of education technology in the classroom.
Shehu Abdullahi Ringim
RELATED PAPERS
LA ODE REZAMRIN
Rezaa Rezaa
Diagana Yacouba
Psicologia e Saúde em Debate
Taciano dos Reis Cardoso
Revista Livre de Sustentabilidade e Empreendedorismo
Rodrigo Pires Tribeck
Research in Agriculture Livestock and Fisheries
Shahrukh Rahman
Proceedings of the Conference on Categorical Algebra
Michael Barr
Journal of Neuro-Oncology
Michael Berens
GeoInformatica
Christopher Jones
Revista Española de Salud Pública
Mercedes Carrasco Portiño
Journal of Texture Studies
Domenico Castaldo
Gerard Kerkyacharian
Východoslovenský pravek X.
Peter Tajkov
Periodica Polytechnica Civil Engineering
Alban Kuriqi
Aquaculture Nutrition
Yuliang Wei
Jenny Mansour
Leonardo López Luján
Khadijeh Onsory
Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology
Paula Fresco
jose zamora
Ivana Resetnik
Anais Pr ncipais do Simpósio Brasileiro de Computação Aplicada à Saúde (SBCAS 2015)
Patrícia Davet
Saudi journal of medical and pharmaceutical sciences
Journal of Information Systems
David Tegarden
alessandro vitale-brovarone
arXiv (Cornell University)
Jaime Rocha
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Accessibility
- Artificial Intelligence
- Digital Equity Education Roundtables
- Educator Prep Programs
- Higher Education
- National Educational Technology Plan
- Artificial Intelligence and the Future of Teaching and Learning
- LGBTQI+ Students Online
- Higher Education National Education Technology Plan
- Advancing Digital Equity for All
- All Publications
- Building Technology Infrastructure for Learning
- Digital Literacy Accelerator
- Educational Technology in Teacher Preparation
- Education Blockchains
- Home Access Playbook
- Learning Continuity Scenarios
- Open Education
- Professional Learning
- Wireless Brief
As has ever been true, edtech holds vast potential to improve learning and teaching for every student and teacher in the United States. In recent years, driven by the emergency of a pandemic, schools have found themselves with more connectivity, devices, and digital resources than at any other moment in history. This current context presents a unique opportunity.
States, districts, and schools across the country can leverage this momentum of a narrowing access divide to focus key efforts in providing all teachers the time, support, and capacity they need to design authentic learning experiences for all learners supported by this proliferation of digital tools. They can set bold new visions of the skills, knowledge, and experiences all students must have as they progress through and graduate from PK-12. Furthermore, states, districts, and schools can eliminate barriers and uncover biases in practice that have historically limited innovative learning experiences supported by edtech to a predictable minority.
The nation can close the digital access, design, and use divides. The NETP includes examples from every state in the country where schools, districts, and their partners are proving it’s possible. For this possibility to reach all students will require an understanding that the kinds of instructional tasks students need to prepare them for the world they will inherit cannot rely on content alone. The instructional core requires attending to both content and people.
National Educational Technology Plan ( Back to Main )

Information and Communication Technology in Education
Globalization and technological change has created a new global economy which is powered by information and communication technology. Information and communication technology have become the basis for educational reform. This paper discusses ‘The use of information and communication technology in education’. Information and communications technology transforms the conventional educational system to a more modern and a better quality system. Information and communication technology helps transform the educational system in several ways. According to Cox (1997), information and communications technology helps in increasing the motivation levels of the students. Information and communication technology makes use of a combination of things and hence helps students learn faster.
Moreover, through networking information and communication technology can not only reuse the information again and again but this also increases learners motivation and helps students to participate in real world events. Information and communication technology also helps in a faster transfer of knowledge and skills (Intel, 2008). On the other hand ICT also helps in training teachers and instructors. It has been found out that the use of information and communication technology in educational institutions can empower students and hence motivate them to learn. The proper use of information and communication technology can change the teacher centred conventional method of teaching to a more learner centred or student centred learning. Hacking is an important issue in using information and communication technology in education. Equity in the use of information and communication technology is yet another issue in the education system. Information and communication technology supports active and collaborative learning. ICT enhanced learning promotes integrative approach to teaching and learning.
Use of Information and Communication Technology in Education
Introduction.
Technological change has been fostered in the past decade due to the increasing use of internet and communication technology. More and more people have started using internet as compares to before. In the first decade of its official beginning or its advent, internet was mainly used for research purposes. Even though almost all of the facilities of internet were present at that time, it was difficult for a common man to use it for quite many reasons. One important reason was the high initial cost of the equipment. On the other hand, only people who mastered UNIX operating system had the privilege of using the internet. However, today with user friendly windows systems and cheaper rates of computer equipments, computers and internet is available to all. In 1989, Tim Berners had tried very hard to make internet accessible to all by making the use of internet easy, however it was really in 1993 when the actual mass use of internet began. (Naughton, 2001)
Globalization and technological change has created a new global economy which is powered by information and communication technology. This technological change has brought serious concerns for educational institutions. Information and communication technology have become the basis for educational reform. This paper discusses ‘ The use of information and communication technology in education ’. How it represents educational transformations, how this transformation embeds the meaning of change in organizations and what are the pros and cons of such education, are a few questions which will be answered in this paper.
According to the World Bank
“ ICTs consist of hardware, software, networks and media for collection, storage, processing, transmission, and presentation of information (including voice, data, text and images” (World Bank, 2003).
Hence in other words it can be said that Information and communications technology is used to create, store and manage information. It includes computers, internet and even radio and television (Blurton, 2002).
Historical background
It was in 1980s when relatively low cost microcomputers were available. Due to this the issue of the use of information and communication technology in education was brought up. In the 1980s, the term microcomputer was used for information and communication technology which was later replaced by IT and then finally ICT. In 1992 e-mails started to become popular and the schools and colleges started to accept it as a quicker medium of information sharing. It was expected that microcomputers will make education more effective. However researches reflect that information and communication technology is merely a supplement to the existing curriculum and cannot fully replace it (RUCST, n.d). However, the governments of the developing nations are constantly trying to raise the educational standards be embedding information and communication technology in the curriculum. For this reason the ‘New Relationships’ plan which was announced in 2004 has suggested the government of UK to share management information nationwide with the help of internet technology (Bromley Information management strategy, 2006).
Information technology and education
Information and communications technology transforms the conventional educational system to a more modern and a better quality system. Information and communication technology helps transform the educational system in several ways. It not only motivates the learner but also facilitates this learning process (Haddad, 2002). The acquisition of basic skills in ICT is relatively easier and lead to a more creative human being.
According to Cox (1997), ICT helps in increasing the motivation levels of the students. It is true that students easily get bored with conventional teaching methods and if new methods of teaching are introduced which make use of ICT, it can definitely increase the motivation level of the students. This change can be noted by the positive effect on the behaviour and skills of the students (Comber, 2002).
Information and communication technology makes use of a combination of things and hence helps students learn faster. For example in a slide show put up with the help of a projector, information and communication technology makes use of text, images, motion and sometimes sound to motivate and pursue the learning process and hence transforms the traditional education system. Moreover, through networking information and communication technology can not only reuse the information again and again but this also increases learners motivation and helps students to participate in real world events. information and communication technology also helps in a faster transfer of knowledge and skills (Intel, 2008).
For example: television programs like sesame street not only helped children learn alphabets and words with the use of text, sound, colours and shapes but was relatively a faster way of learning too. This also motivated children to learn. On the other hand ICT also helps in training teachers and instructors. For example the Cyber teacher training centre (CTTC) developed in Korea provides a better way of vocational training for teachers. This training program helps the teachers to think creatively and bringing new ideas for teaching the students. Moreover, it also saves time as the teachers do not have to gather in a face to face meeting (Jung, 2002).It is essential for the teachers to have technology literacy so that they can impart this knowledge to their students. This includes use of computers, internet, web content and other networking and software programs (United Nations, 2008).
Even with so many benefits the use of ICT in education is not up to standard. According to a survey, the teachers use ICT mainly for word processing purposes rather then bringing in innovative methods of teaching. On the other hand the use of e-mail for contacting parents and information sharing has increased, but yet again needs improvement. The survey also reflected that the use of Information and communication technology in school’s classrooms was also very minimal. The graph below shows the how often IT is used in class. (Amas, 2008).When the respondents were asked how often they use ICT in the class it can be seen that 24% said that at least once a week and there were 45% who said never. This reflects the negligence in case of Information and communication technology use in classrooms.
It was then asked whether these schools had a website. The following pie chart reflects the number of schools having a website. In the primary schools almost 61% did not have website where as in secondary school almost 16%.
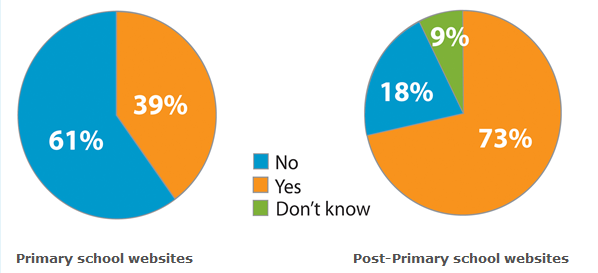
It has been found out that the use of information and communication technology in educational institutions can empower students and hence motivate them to learn. The proper use of information and communication technology can change the teacher centred conventional method of teaching to a more learner centred or student centred learning. However, even with so many advantages associated with the use of information and communication technology in education; there are some pedagogical issues too which can impact the education system in a negative way.
Hacking is an important issue in using information and communication technology in education. Students can hack into teacher’s computers and find the examination papers archived or can hack in to each other’s computers to cheat on tests or homework. Teachers who use information and communication technology in their classrooms have noticed that students can lose concentration if they fall prey to any kind of distraction which can come from the use of internet or the simple use of computer. Equity in the use of information and communication technology is yet another issue in the education system. The access to the computers, internet etc should not be favoured and each student should be able to access the ICT facilities equally.
An increase in the costs associated with the installation, damages and repairing can increase with the use of ICT in education. Hence, the biggest disadvantage of using ICT in educational institutions is the increased cost which might be a result of this implementation and might recur in future. Another issue which has been under discussion is the difference between the developed and underdeveloped nations which might result in inequity in the use of ICT in classrooms. Another disadvantage associated with the use of ICT in education is the need for having the same technology at home in order to access the information. This might not be possible for some students and hence traditional teachers believe that computers might never be able to replace teachers. Use of ICT results in decreased interaction of students as they tend to break down into smaller groups in an ICT embedded classroom.
The use in education
Information and communication technology supports active and collaborative learning. It helps the students to manipulate current information which is available at fingertips to remain updated and connect to the world. They can compare themselves with other students all over the world. ICT enhanced learning promotes integrative approach to teaching and learning. As ICT based learning is usually student based, therefore it helps the students to explore and learn rather than just sit and listen to the information being poured to them. The level of information absorbed in and ICT embedded classroom depends on the technology being used. According to Haddad (2002), there are five levels of technology which can be used in a classroom. This is presentation, demonstration, drill, practice, interaction and collaboration.
Here are a few advantages of ICT use in education.
- It not only increases students’ motivation towards studies but also increases the teacher’s enthusiasm to teach (Becta, 1998).
- Increases the c communication effectiveness between pupil and teachers (Becta, 2002)
- Enhanced and frequent feedback from the parents and student help the teachers to increase the motivation of students to study
- Parents can be as more involved in the student activities and can even have virtual meeting with the teachers which can enhance the level of communication (Flecknoe, 2001)
- Material and information can be easily shared by teachers and students
- Students have an increased sense of commitment, achievement and self worth (Cox, 1997)
The following reflects and summarizes the main advantages of using information technology in education.

From the above research it can be concluded that information and communication technology plays a very important role in education. With more use of this in the classrooms, the entire education system can be reformed. The use of information and communication technology helps boost the morale and increase the motivation level of students. Children are always ready to do something new. Introducing new methods of teaching and use of multimedia in classroom will help the students learn more. It is truly said that a picture is better than a thousand words; therefore it will take a teacher sometime to explain a certain phenomenon to children, whereas the use of visual aid will make it easier with a long lasting impact in the minds of the children.
Amas (2008). Education and ICT. Web.
Blurton, C., “New Directions of ICT-Use in Education”.
Bromley information management strategy (2006) ICT in education (administration) development plan (2004-2006). Education and libraries directorate.
COMBER, C., et al., 2002. ImpaCT2: learning at home and school: case studies. ICT in Schools Research and Evaluation Series,No. 8, DfES/Becta. Web.
Cox. J., 1997. Effects of information technology on students’ motivation: final report. NCET.
Flecknoe, M., (2001). The use of virtual classrooms for schoolim provement. BELMAS Annual conference, Newport Pagnell, Web.
Haddad,Wadi D. and Jurich, Sonia (2002),“ICT for Education: Potential and Potency”, in Haddad,W. & Drexler, A. (eds),Technologies for Education: Potentials, Parameters, and Prospects (Washington DC: Academy for Educational Development and Paris: UNESCO), pp. 34-37.
Intel (2008).ICT, Education Reform, and Economic Growth: A Conceptual Framework; Foxit Software Company, 2004 – 2007.
Jung, I.,“Issues and Challenges of Providing Onloine Inservice Teacher Training: Korea’s Experience”; Web.
Naughton, John: A Brief History of the Future: the origins of the Internet, Phoenix, 2001, pages.
RUCST (n.d). Pedagogical aspects of ICT. Web.
United Nations (2008) ICT Competency Standards For Teachers; Competency Standards Modules. By the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization.
World Bank. 2004a. World Bank Development Indicators 2004. Annual Report, Washington DC. Web.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2021, November 8). Information and Communication Technology in Education. https://studycorgi.com/information-and-communication-technology-in-education/
"Information and Communication Technology in Education." StudyCorgi , 8 Nov. 2021, studycorgi.com/information-and-communication-technology-in-education/.
StudyCorgi . (2021) 'Information and Communication Technology in Education'. 8 November.
1. StudyCorgi . "Information and Communication Technology in Education." November 8, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/information-and-communication-technology-in-education/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "Information and Communication Technology in Education." November 8, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/information-and-communication-technology-in-education/.
StudyCorgi . 2021. "Information and Communication Technology in Education." November 8, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/information-and-communication-technology-in-education/.
This paper, “Information and Communication Technology in Education”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: October 25, 2022 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.
Information Technology and Ethics/Conclusion
Conclusion [ edit | edit source ].
Privacy is a major concern in today's world with respect to our information and its chances of getting breached. Sharing information over the internet will not always ensure privacy as the internet is vast and deeply interconnected. However, we can put efforts into achieving privacy. Data protection comes through laws, policies, principles, and regulations. One such regulation is GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), whose primary purpose is to make companies or organizations accountable to users' data and reinforce the control of users on their personal data. GDPR can implement principles on how the user's data should be processed.
Apart from data protection in general terms, privacy plays a vital role in the healthcare industry. Because health care research and security assurance are essentially significant to society, it is a fundamental duty to save patient's data and privileges in order to enhance human health and medicinal services. Another reason for securing the individual's privacy is to build the interest of people to provide their data for clinical research for further study, which can increasingly help in improvising the research process. In return, this becomes more favorable to society in the way of encouraging access to new treatments, upgrading diagnostics, and thus drastically putting irresistible efforts towards forestall diseases. Privacy in health care includes different angles such as physical security this can be personal space, information of individuals, and decisional information.
The success or failure of a financial service firm can depend on how it balances the use of confidential customer information while maintaining privacy. To capitalize on emerging growth opportunities, financial firms need to be flexible in sharing confidential customer data—whether across different departments, affiliated partners, or non-affiliated third parties such as technology or outsourcing firms, while complying with regulations and protecting the company’s reputation. The key lies in this delicate balance between data sharing flexibility and maintaining data privacy.
Kids are often attracted by the lure of online games and social media. Children must be reminded never to share personally identifiable information or financial details with online applications or services and teach them the difference between safe and malicious applications. Popular social media services like Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok require users to be at least 13 years old to sign up, however, many underage users still join. The 13 year old age limit comes from the US Children's Online Privacy Protection Act. Educate children about the impacts of sharing sensitive details on social media and the risks of interacting with strangers online. If one wishes to monitor your children’s online activity, use parental controls on their device.
Without the cooperation or assistance of social media giants, privacy in social media is not completely achievable because it is entirely dependable on how they modify their settings and policies in the interest of the users' data protection provided with all the laws and regulations placed. Irrespective of how sophisticated or user friendly the platform is made, it is not as powerful as its users because ultimately its revenue is made through the users who are active on these social media platforms, which can be utilized to raise their voices which makes them codependent. Thus with changing times, many advanced technologies are getting invented through which privacy issues can still be persistent. This is a constant battle that can only be controlled through stringent laws and regulations, which includes creating awareness among consumers to champion their own privacy rights.
Privacy in finances is also very important. Whether they are protecting their own financial information, or they work at a financial institution and are protecting others, they have both a legal and ethical responsibility of the utmost importance to maintain. One of the most important things for people to do to keep finances safe is take good care of protecting private credentials. With those credentials, malicious actors can simply pose as someone they're not, and do whatever they want with the financial information they access. Also, if this privacy is violated, organizations with any sort of presence in the EU could face at minimum a €20 million fine.
- Book:Information Technology and Ethics
Navigation menu

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Conclusion of ict - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.
7 Describing an ICT system: conclusion. We have arrived at a model of a communication system that illustrates the processes needed for communication. We have also looked at the different kinds of communication link that can be used to convey data, and how to express the rates at which they can convey data. In sections 8-14, we shall be ...
Impact of ICT in Education. In cases where there are limitations such that it is impossible to convene people and resources together for learning. E-learning provides a very important and convenient way of teaching people. In such a case, a teacher provides learning materials and lessons online, which can be accessed by his/her students at ...
To write an assignment conclusion, follow the 7 simple steps below! Start a conclusion paragraph by indenting the first line or leaving a blank line in between the last main body paragraph and the conclusion. Use a suitable starting word or phrase to indicate the assignment is drawing to a close, such as, 'In summary' or 'With all this in ...
Conclusion. Progress in many of the basic computing and information technologies has been rapid in recent years, and the committee does not expect the pace of change to slow down in the foreseeable future. While some technologies are reaching maturity now, many important technologies have enormous future potential.
Collins (1991) suggested that in order for learning to be meaningful, it should be embedded in the same context that it will be used in later life. Therefore, ICT should become part of all curriculum areas, integrating technology into everyday educational practice, creating authentic learning environments where student can thrive at any skill ...
Information and Communications Technology (ICT) can impact student learning when teachers are digitally literate and understand how to integrate it into curriculum. Schools use a diverse set of ICT tools to communicate, create, disseminate, store, and manage information.(6) In some contexts, ICT has also become integral to the teaching-learning interaction, through such approaches as replacing ...
conclusion. Your conclusion is very important as it presents the final words of your assignment. It should leave the reader satisfied that you have provided a thorough, well-researched and reasoned response to the assignment question. Your conclusion should move from the specific to the general (Introductions move from general to specific).
This task required students to identify the recipients of an email displaying the "From," "To," and "Cc" fields. The task assessed students' familiarity with the conventions used to display the sender and recipients of emails. Figure 9.1. Example Level 1 task. Full size image.
This leads to the conclusion that it is the (difficult but challenging) assignment of practitioners and researchers in education to find the best ways of using ICT for enabling these types of pedagogical success factors. ICT Use for Changing the Organization of Learning: Transformation
Step 1: Return to your thesis. To begin your conclusion, signal that the essay is coming to an end by returning to your overall argument. Don't just repeat your thesis statement —instead, try to rephrase your argument in a way that shows how it has been developed since the introduction. Example: Returning to the thesis.
Writing a Conclusion. A conclusion is an important part of the paper; it provides closure for the reader while reminding the reader of the contents and importance of the paper. It accomplishes this by stepping back from the specifics in order to view the bigger picture of the document. In other words, it is reminding the reader of the main ...
ICT ASSIGNMENT 1. The aim of this assignment is to discuss the key innovations of the last ten years that have affected education technology. It will also explain the importance of these key innovations for all secondary school teachers, also a summary of education technology best practices, key challenges to these types of best practices faced ...
Concludes that under certain conditions, information and communication technologies (ICTs) can significantly enhance poor people's human and social capabilities and have a positive impact on their well-being. ICTs can enhance poor people's individual and collective agency; strengthen their existing individual or community assets; and enhance their informational capabilities. ICTs receive ...
Conclusion. As has ever been true, edtech holds vast potential to improve learning and teaching for every student and teacher in the United States. In recent years, driven by the emergency of a pandemic, schools have found themselves with more connectivity, devices, and digital resources than at any other moment in history. This current context ...
ICT in education. Source: Amas, 2008. Conclusion. From the above research it can be concluded that information and communication technology plays a very important role in education. With more use of this in the classrooms, the entire education system can be reformed.
Recommended for you. 8. ICT Assignment 1 semester 2023. Information Comprtance 100% (1) 2. Written test possible answers for the post of Administrative Officer Grade 12. Information Comprtance 95% (106) 4. ICT - Unit 1 - study notes.
6. Conclusion. In this introduction to the special issue on the role of ICT in socioeconomic development, we provide a conceptual multi-dimensional framework that considers four dimensions that impact socioeconomic development: policy, business, technology, and society.
Conclusion should not be longer than 10% from the word count. If a paper has 900 words, conclude it in 90. If there are 3000 words, then compose about 300. This will create great harmony, preventing your readers from feeling bored or overloaded. Present summary but don't copy previous sentences.
Here are four key tips for writing stronger conclusions that leave a lasting impression: 1. Include a topic sentence. Conclusions should always begin with a topic sentence. Restating the thesis from your introductory paragraph in the first sentence of your conclusion is an effective way to remind the reader of the main argument. 2. Use your ...
Data protection comes through laws, policies, principles, and regulations. One such regulation is GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), whose primary purpose is to make companies or organizations accountable to users' data and reinforce the control of users on their personal data. GDPR can implement principles on how the user's data should ...
Introduction to ICT Assignment 1 - Deadline March 09, 2021 Total marks: 30 Instructions: 1. The assignment has to be delivered as hard copy (your answer sheets) no later than the specified deadline. Make sure that you submit the assignment during the lecture hours on specified. 2. The assignment is to be submitted in groups of 2 students ...
Microsoft Word - ICT vol 1_08_09_2011.docx. 6. Conclusions and Recommendations. 6.1 Over the past decade, access to ICT in developing countries has grown rapidly, a development enabled by changes in technologies, policies, and markets. Increased access has unleashed the transformative potential of ICT, affecting the ways in which people ...