Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Employee Exit Interviews
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
Market Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Secondary Research

Try Qualtrics for free
Secondary research: definition, methods, & examples.
19 min read This ultimate guide to secondary research helps you understand changes in market trends, customers buying patterns and your competition using existing data sources.
In situations where you’re not involved in the data gathering process ( primary research ), you have to rely on existing information and data to arrive at specific research conclusions or outcomes. This approach is known as secondary research.
In this article, we’re going to explain what secondary research is, how it works, and share some examples of it in practice.
Free eBook: The ultimate guide to conducting market research
What is secondary research?
Secondary research, also known as desk research, is a research method that involves compiling existing data sourced from a variety of channels . This includes internal sources (e.g.in-house research) or, more commonly, external sources (such as government statistics, organizational bodies, and the internet).
Secondary research comes in several formats, such as published datasets, reports, and survey responses , and can also be sourced from websites, libraries, and museums.
The information is usually free — or available at a limited access cost — and gathered using surveys , telephone interviews, observation, face-to-face interviews, and more.
When using secondary research, researchers collect, verify, analyze and incorporate it to help them confirm research goals for the research period.
As well as the above, it can be used to review previous research into an area of interest. Researchers can look for patterns across data spanning several years and identify trends — or use it to verify early hypothesis statements and establish whether it’s worth continuing research into a prospective area.
How to conduct secondary research
There are five key steps to conducting secondary research effectively and efficiently:
1. Identify and define the research topic
First, understand what you will be researching and define the topic by thinking about the research questions you want to be answered.
Ask yourself: What is the point of conducting this research? Then, ask: What do we want to achieve?
This may indicate an exploratory reason (why something happened) or confirm a hypothesis. The answers may indicate ideas that need primary or secondary research (or a combination) to investigate them.
2. Find research and existing data sources
If secondary research is needed, think about where you might find the information. This helps you narrow down your secondary sources to those that help you answer your questions. What keywords do you need to use?
Which organizations are closely working on this topic already? Are there any competitors that you need to be aware of?
Create a list of the data sources, information, and people that could help you with your work.
3. Begin searching and collecting the existing data
Now that you have the list of data sources, start accessing the data and collect the information into an organized system. This may mean you start setting up research journal accounts or making telephone calls to book meetings with third-party research teams to verify the details around data results.
As you search and access information, remember to check the data’s date, the credibility of the source, the relevance of the material to your research topic, and the methodology used by the third-party researchers. Start small and as you gain results, investigate further in the areas that help your research’s aims.
4. Combine the data and compare the results
When you have your data in one place, you need to understand, filter, order, and combine it intelligently. Data may come in different formats where some data could be unusable, while other information may need to be deleted.
After this, you can start to look at different data sets to see what they tell you. You may find that you need to compare the same datasets over different periods for changes over time or compare different datasets to notice overlaps or trends. Ask yourself: What does this data mean to my research? Does it help or hinder my research?
5. Analyze your data and explore further
In this last stage of the process, look at the information you have and ask yourself if this answers your original questions for your research. Are there any gaps? Do you understand the information you’ve found? If you feel there is more to cover, repeat the steps and delve deeper into the topic so that you can get all the information you need.
If secondary research can’t provide these answers, consider supplementing your results with data gained from primary research. As you explore further, add to your knowledge and update your findings. This will help you present clear, credible information.
Primary vs secondary research
Unlike secondary research, primary research involves creating data first-hand by directly working with interviewees, target users, or a target market. Primary research focuses on the method for carrying out research, asking questions, and collecting data using approaches such as:
- Interviews (panel, face-to-face or over the phone)
- Questionnaires or surveys
- Focus groups
Using these methods, researchers can get in-depth, targeted responses to questions, making results more accurate and specific to their research goals. However, it does take time to do and administer.
Unlike primary research, secondary research uses existing data, which also includes published results from primary research. Researchers summarize the existing research and use the results to support their research goals.
Both primary and secondary research have their places. Primary research can support the findings found through secondary research (and fill knowledge gaps), while secondary research can be a starting point for further primary research. Because of this, these research methods are often combined for optimal research results that are accurate at both the micro and macro level.
Sources of Secondary Research
There are two types of secondary research sources: internal and external. Internal data refers to in-house data that can be gathered from the researcher’s organization. External data refers to data published outside of and not owned by the researcher’s organization.
Internal data
Internal data is a good first port of call for insights and knowledge, as you may already have relevant information stored in your systems. Because you own this information — and it won’t be available to other researchers — it can give you a competitive edge . Examples of internal data include:
- Database information on sales history and business goal conversions
- Information from website applications and mobile site data
- Customer-generated data on product and service efficiency and use
- Previous research results or supplemental research areas
- Previous campaign results
External data
External data is useful when you: 1) need information on a new topic, 2) want to fill in gaps in your knowledge, or 3) want data that breaks down a population or market for trend and pattern analysis. Examples of external data include:
- Government, non-government agencies, and trade body statistics
- Company reports and research
- Competitor research
- Public library collections
- Textbooks and research journals
- Media stories in newspapers
- Online journals and research sites
Three examples of secondary research methods in action
How and why might you conduct secondary research? Let’s look at a few examples:
1. Collecting factual information from the internet on a specific topic or market
There are plenty of sites that hold data for people to view and use in their research. For example, Google Scholar, ResearchGate, or Wiley Online Library all provide previous research on a particular topic. Researchers can create free accounts and use the search facilities to look into a topic by keyword, before following the instructions to download or export results for further analysis.
This can be useful for exploring a new market that your organization wants to consider entering. For instance, by viewing the U.S Census Bureau demographic data for that area, you can see what the demographics of your target audience are , and create compelling marketing campaigns accordingly.
2. Finding out the views of your target audience on a particular topic
If you’re interested in seeing the historical views on a particular topic, for example, attitudes to women’s rights in the US, you can turn to secondary sources.
Textbooks, news articles, reviews, and journal entries can all provide qualitative reports and interviews covering how people discussed women’s rights. There may be multimedia elements like video or documented posters of propaganda showing biased language usage.
By gathering this information, synthesizing it, and evaluating the language, who created it and when it was shared, you can create a timeline of how a topic was discussed over time.
3. When you want to know the latest thinking on a topic
Educational institutions, such as schools and colleges, create a lot of research-based reports on younger audiences or their academic specialisms. Dissertations from students also can be submitted to research journals, making these places useful places to see the latest insights from a new generation of academics.
Information can be requested — and sometimes academic institutions may want to collaborate and conduct research on your behalf. This can provide key primary data in areas that you want to research, as well as secondary data sources for your research.
Advantages of secondary research
There are several benefits of using secondary research, which we’ve outlined below:
- Easily and readily available data – There is an abundance of readily accessible data sources that have been pre-collected for use, in person at local libraries and online using the internet. This data is usually sorted by filters or can be exported into spreadsheet format, meaning that little technical expertise is needed to access and use the data.
- Faster research speeds – Since the data is already published and in the public arena, you don’t need to collect this information through primary research. This can make the research easier to do and faster, as you can get started with the data quickly.
- Low financial and time costs – Most secondary data sources can be accessed for free or at a small cost to the researcher, so the overall research costs are kept low. In addition, by saving on preliminary research, the time costs for the researcher are kept down as well.
- Secondary data can drive additional research actions – The insights gained can support future research activities (like conducting a follow-up survey or specifying future detailed research topics) or help add value to these activities.
- Secondary data can be useful pre-research insights – Secondary source data can provide pre-research insights and information on effects that can help resolve whether research should be conducted. It can also help highlight knowledge gaps, so subsequent research can consider this.
- Ability to scale up results – Secondary sources can include large datasets (like Census data results across several states) so research results can be scaled up quickly using large secondary data sources.
Disadvantages of secondary research
The disadvantages of secondary research are worth considering in advance of conducting research :
- Secondary research data can be out of date – Secondary sources can be updated regularly, but if you’re exploring the data between two updates, the data can be out of date. Researchers will need to consider whether the data available provides the right research coverage dates, so that insights are accurate and timely, or if the data needs to be updated. Also, fast-moving markets may find secondary data expires very quickly.
- Secondary research needs to be verified and interpreted – Where there’s a lot of data from one source, a researcher needs to review and analyze it. The data may need to be verified against other data sets or your hypotheses for accuracy and to ensure you’re using the right data for your research.
- The researcher has had no control over the secondary research – As the researcher has not been involved in the secondary research, invalid data can affect the results. It’s therefore vital that the methodology and controls are closely reviewed so that the data is collected in a systematic and error-free way.
- Secondary research data is not exclusive – As data sets are commonly available, there is no exclusivity and many researchers can use the same data. This can be problematic where researchers want to have exclusive rights over the research results and risk duplication of research in the future.
When do we conduct secondary research?
Now that you know the basics of secondary research, when do researchers normally conduct secondary research?
It’s often used at the beginning of research, when the researcher is trying to understand the current landscape . In addition, if the research area is new to the researcher, it can form crucial background context to help them understand what information exists already. This can plug knowledge gaps, supplement the researcher’s own learning or add to the research.
Secondary research can also be used in conjunction with primary research. Secondary research can become the formative research that helps pinpoint where further primary research is needed to find out specific information. It can also support or verify the findings from primary research.
You can use secondary research where high levels of control aren’t needed by the researcher, but a lot of knowledge on a topic is required from different angles.
Secondary research should not be used in place of primary research as both are very different and are used for various circumstances.
Questions to ask before conducting secondary research
Before you start your secondary research, ask yourself these questions:
- Is there similar internal data that we have created for a similar area in the past?
If your organization has past research, it’s best to review this work before starting a new project. The older work may provide you with the answers, and give you a starting dataset and context of how your organization approached the research before. However, be mindful that the work is probably out of date and view it with that note in mind. Read through and look for where this helps your research goals or where more work is needed.
- What am I trying to achieve with this research?
When you have clear goals, and understand what you need to achieve, you can look for the perfect type of secondary or primary research to support the aims. Different secondary research data will provide you with different information – for example, looking at news stories to tell you a breakdown of your market’s buying patterns won’t be as useful as internal or external data e-commerce and sales data sources.
- How credible will my research be?
If you are looking for credibility, you want to consider how accurate the research results will need to be, and if you can sacrifice credibility for speed by using secondary sources to get you started. Bear in mind which sources you choose — low-credibility data sites, like political party websites that are highly biased to favor their own party, would skew your results.
- What is the date of the secondary research?
When you’re looking to conduct research, you want the results to be as useful as possible , so using data that is 10 years old won’t be as accurate as using data that was created a year ago. Since a lot can change in a few years, note the date of your research and look for earlier data sets that can tell you a more recent picture of results. One caveat to this is using data collected over a long-term period for comparisons with earlier periods, which can tell you about the rate and direction of change.
- Can the data sources be verified? Does the information you have check out?
If you can’t verify the data by looking at the research methodology, speaking to the original team or cross-checking the facts with other research, it could be hard to be sure that the data is accurate. Think about whether you can use another source, or if it’s worth doing some supplementary primary research to replicate and verify results to help with this issue.
We created a front-to-back guide on conducting market research, The ultimate guide to conducting market research , so you can understand the research journey with confidence.
In it, you’ll learn more about:
- What effective market research looks like
- The use cases for market research
- The most important steps to conducting market research
- And how to take action on your research findings
Download the free guide for a clearer view on secondary research and other key research types for your business.
Related resources
Market intelligence 10 min read, marketing insights 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, qualitative vs quantitative research 13 min read, qualitative research questions 11 min read, qualitative research design 12 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
Published on June 19, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on June 22, 2023.
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research.
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research , which involves collecting and analyzing numerical data for statistical analysis.
Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, history, etc.
- How does social media shape body image in teenagers?
- How do children and adults interpret healthy eating in the UK?
- What factors influence employee retention in a large organization?
- How is anxiety experienced around the world?
- How can teachers integrate social issues into science curriculums?
Table of contents
Approaches to qualitative research, qualitative research methods, qualitative data analysis, advantages of qualitative research, disadvantages of qualitative research, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about qualitative research.
Qualitative research is used to understand how people experience the world. While there are many approaches to qualitative research, they tend to be flexible and focus on retaining rich meaning when interpreting data.
Common approaches include grounded theory, ethnography , action research , phenomenological research, and narrative research. They share some similarities, but emphasize different aims and perspectives.
Note that qualitative research is at risk for certain research biases including the Hawthorne effect , observer bias , recall bias , and social desirability bias . While not always totally avoidable, awareness of potential biases as you collect and analyze your data can prevent them from impacting your work too much.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Each of the research approaches involve using one or more data collection methods . These are some of the most common qualitative methods:
- Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes.
- Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations.
- Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among a group of people.
- Surveys : distributing questionnaires with open-ended questions.
- Secondary research: collecting existing data in the form of texts, images, audio or video recordings, etc.
- You take field notes with observations and reflect on your own experiences of the company culture.
- You distribute open-ended surveys to employees across all the company’s offices by email to find out if the culture varies across locations.
- You conduct in-depth interviews with employees in your office to learn about their experiences and perspectives in greater detail.
Qualitative researchers often consider themselves “instruments” in research because all observations, interpretations and analyses are filtered through their own personal lens.
For this reason, when writing up your methodology for qualitative research, it’s important to reflect on your approach and to thoroughly explain the choices you made in collecting and analyzing the data.
Qualitative data can take the form of texts, photos, videos and audio. For example, you might be working with interview transcripts, survey responses, fieldnotes, or recordings from natural settings.
Most types of qualitative data analysis share the same five steps:
- Prepare and organize your data. This may mean transcribing interviews or typing up fieldnotes.
- Review and explore your data. Examine the data for patterns or repeated ideas that emerge.
- Develop a data coding system. Based on your initial ideas, establish a set of codes that you can apply to categorize your data.
- Assign codes to the data. For example, in qualitative survey analysis, this may mean going through each participant’s responses and tagging them with codes in a spreadsheet. As you go through your data, you can create new codes to add to your system if necessary.
- Identify recurring themes. Link codes together into cohesive, overarching themes.
There are several specific approaches to analyzing qualitative data. Although these methods share similar processes, they emphasize different concepts.
Qualitative research often tries to preserve the voice and perspective of participants and can be adjusted as new research questions arise. Qualitative research is good for:
- Flexibility
The data collection and analysis process can be adapted as new ideas or patterns emerge. They are not rigidly decided beforehand.
- Natural settings
Data collection occurs in real-world contexts or in naturalistic ways.
- Meaningful insights
Detailed descriptions of people’s experiences, feelings and perceptions can be used in designing, testing or improving systems or products.
- Generation of new ideas
Open-ended responses mean that researchers can uncover novel problems or opportunities that they wouldn’t have thought of otherwise.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Researchers must consider practical and theoretical limitations in analyzing and interpreting their data. Qualitative research suffers from:
- Unreliability
The real-world setting often makes qualitative research unreliable because of uncontrolled factors that affect the data.
- Subjectivity
Due to the researcher’s primary role in analyzing and interpreting data, qualitative research cannot be replicated . The researcher decides what is important and what is irrelevant in data analysis, so interpretations of the same data can vary greatly.
- Limited generalizability
Small samples are often used to gather detailed data about specific contexts. Despite rigorous analysis procedures, it is difficult to draw generalizable conclusions because the data may be biased and unrepresentative of the wider population .
- Labor-intensive
Although software can be used to manage and record large amounts of text, data analysis often has to be checked or performed manually.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Chi square goodness of fit test
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to systematically measure variables and test hypotheses . Qualitative methods allow you to explore concepts and experiences in more detail.
There are five common approaches to qualitative research :
- Grounded theory involves collecting data in order to develop new theories.
- Ethnography involves immersing yourself in a group or organization to understand its culture.
- Narrative research involves interpreting stories to understand how people make sense of their experiences and perceptions.
- Phenomenological research involves investigating phenomena through people’s lived experiences.
- Action research links theory and practice in several cycles to drive innovative changes.
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organizations.
There are various approaches to qualitative data analysis , but they all share five steps in common:
- Prepare and organize your data.
- Review and explore your data.
- Develop a data coding system.
- Assign codes to the data.
- Identify recurring themes.
The specifics of each step depend on the focus of the analysis. Some common approaches include textual analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, June 22). What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 16, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/qualitative-research/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, qualitative vs. quantitative research | differences, examples & methods, how to do thematic analysis | step-by-step guide & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- HHS Author Manuscripts

Qualitative Secondary Analysis: A Case Exemplar
Judith ann tate.
The Ohio State University, College of Nursing
Mary Beth Happ
Qualitative secondary analysis (QSA) is the use of qualitative data collected by someone else or to answer a different research question. Secondary analysis of qualitative data provides an opportunity to maximize data utility particularly with difficult to reach patient populations. However, QSA methods require careful consideration and explicit description to best understand, contextualize, and evaluate the research results. In this paper, we describe methodologic considerations using a case exemplar to illustrate challenges specific to QSA and strategies to overcome them.
Health care research requires significant time and resources. Secondary analysis of existing data provides an efficient alternative to collecting data from new groups or the same subjects. Secondary analysis, defined as the reuse of existing data to investigate a different research question ( Heaton, 2004 ), has a similar purpose whether the data are quantitative or qualitative. Common goals include to (1) perform additional analyses on the original dataset, (2) analyze a subset of the original data, (3) apply a new perspective or focus to the original data, or (4) validate or expand findings from the original analysis ( Hinds, Vogel, & Clarke-Steffen, 1997 ). Synthesis of knowledge from meta-analysis or aggregation may be viewed as an additional purpose of secondary analysis ( Heaton, 2004 ).
Qualitative studies utilize several different data sources, such as interviews, observations, field notes, archival meeting minutes or clinical record notes, to produce rich descriptions of human experiences within a social context. The work typically requires significant resources (e.g., personnel effort/time) for data collection and analysis. When feasible, qualitative secondary analysis (QSA) can be a useful and cost-effective alternative to designing and conducting redundant primary studies. With advances in computerized data storage and analysis programs, sharing qualitative datasets has become easier. However, little guidance is available for conducting, structuring procedures, or evaluating QSA ( Szabo & Strang, 1997 ).
QSA has been described as “an almost invisible enterprise in social research” ( Fielding, 2004 ). Primary data is often re-used; however, descriptions of this practice are embedded within the methods section of qualitative research reports rather than explicitly identified as QSA. Moreover, searching or classifying reports as QSA is difficult because many researchers refrain from identifying their work as secondary analyses ( Hinds et al., 1997 ; Thorne, 1998a ). In this paper, we provide an overview of QSA, the purposes, and modes of data sharing and approaches. A unique, expanded QSA approach is presented as a methodological exemplar to illustrate considerations.
QSA Typology
Heaton (2004) classified QSA studies based on the relationship between the secondary and primary questions and the scope of data analyzed. Types of QSA included studies that (1) investigated questions different from the primary study, (2) applied a unique theoretical perspective, or (3) extended the primary work. Heaton’s literature review (2004) showed that studies varied in the choice of data used, from selected portions to entire or combined datasets.
Modes of Data Sharing
Heaton (2004) identified three modes of data sharing: formal, informal and auto-data. Formal data sharing involves accessing and analyzing deposited or archived qualitative data by an independent group of researchers. Historical research often uses formal data sharing. Informal data sharing refers to requests for direct access to an investigator’s data for use alone or to pool with other data, usually as a result of informal networking. In some instances, the primary researchers may be invited to collaborate. The most common mode of data sharing is auto-data, defined as further exploration of a qualitative data set by the primary research team. Due to the iterative nature of qualitative research, when using auto-data, it may be difficult to determine where the original study questions end and discrete, distinct analysis begins ( Heaton, 1998 ).
An Exemplar QSA
Below we describe a QSA exemplar conducted by the primary author of this paper (JT), a member of the original research team, who used a supplementary approach to examine concepts revealed but not fully investigated in the primary study. First, we describe an overview of the original study on which the QSA was based. Then, the exemplar QSA is presented to illustrate: (1) the use of auto-data when the new research questions are closely related to or extend the original study aims ( Table 1 ), (2) the collection of additional clinical record data to supplement the original dataset and (3) the performance of separate member checking in the form of expert review and opinion. Considerations and recommendations for use of QSA are reviewed with illustrations taken from the exemplar study ( Table 2 ). Finally, discussion of conclusions and implications is included to assist with planning and implementation of QSA studies.
Research question comparison
Application of the Exemplar Qualitative Secondary Analysis (QSA)
Aitken, L. M., Marshall, A. P., Elliott, R., & McKinley, S. (2009). Critical care nurses' decision making: sedation assessment and management in intensive care. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 18 (1), 36–45.
Morse, J., & Field, P. (1995). Qualitative research methods for health professionals. (2nd ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publishing.
Patel, R. P., Gambrell, M., Speroff, T.,…Strength, C. (2009). Delirium and sedation in the intensive care unit: Survey of behaviors and attitudes of 1384 healthcare professionals. Critical Care Medicine, 37 (3), 825–832.
Shehabi, Y., Botha, J. A., Boyle, M. S., Ernest, D., Freebairn, R. C., Jenkins, I. R., … Seppelt, I. M. (2008). Sedation and delirium in the intensive care unit: an Australian and New Zealand perspective. Anaesthesia & Intensive Care, 36 (4), 570–578.
Tanios, M. A., de Wit, M., Epstein, S. K., & Devlin, J. W. (2009). Perceived barriers to the use of sedation protocols and daily sedation interruption: a multidisciplinary survey. Journal of Critical Care, 24 (1), 66–73.
Weinert, C. R., & Calvin, A. D. (2007). Epidemiology of sedation and sedation adequacy for mechanically ventilated patients in a medical and surgical intensive care unit. Critical Care Medicine , 35(2), 393–401.
The Primary Study
Briefly, the original study was a micro-level ethnography designed to describe the processes of care and communication with patients weaning from prolonged mechanical ventilation (PMV) in a 28-bed Medical Intensive Care Unit ( Broyles, Colbert, Tate, & Happ, 2008 ; Happ, Swigart, Tate, Arnold, Sereika, & Hoffman, 2007 ; Happ et al, 2007 , 2010 ). Both the primary study and the QSA were approved by the Institutional Review Board at the University of Pittsburgh. Data were collected by two experienced investigators and a PhD student-research project coordinator. Data sources consisted of sustained field observations, interviews with patients, family members and clinicians, and clinical record review, including all narrative clinical documentation recorded by direct caregivers.
During iterative data collection and analysis in the original study, it became apparent that anxiety and agitation had an effect on the duration of ventilator weaning episodes, an observation that helped to formulate the questions for the QSA ( Tate, Dabbs, Hoffman, Milbrandt & Happ, 2012 ). Thus, the secondary topic was closely aligned as an important facet of the primary phenomenon. The close, natural relationship between the primary and QSA research questions is demonstrated in the side-by-side comparison in Table 1 . This QSA focused on new questions which extended the original study to recognition and management of anxiety or agitation, behaviors that often accompany mechanical ventilation and weaning but occur throughout the trajectory of critical illness and recovery.
Considerations when Undertaking QSA ( Table 2 )
Practical advantages.
A key practical advantage of QSA is maximizing use of existing data. Data collection efforts represent a significant percentage of the research budget in terms of cost and labor ( Coyer & Gallo, 2005 ). This is particularly important in view of the competition for research funding. Planning and implementing a qualitative study involves considerable time and expertise not only for data collecting (e.g., interviews, participant observation or focus group), but in establishing access, credibility and relationships ( Thorne, 1994 ) and in conducting the analysis. The cost of QSA is often seen as negligible since the outlay of resources for data collection is assumed by the original study. However, QSA incurs costs related to storage, researcher’s effort for review of existing data, analysis, and any further data collection that may be necessary.
Another advantage of QSA is access to data from an assembled cohort. In conducting original primary research, practical concerns arise when participants are difficult to locate or reluctant to divulge sensitive details to a researcher. In the case of vulnerable critically ill patients, participation in research may seem an unnecessary burden to family members who may be unwilling to provide proxy consent ( Fielding, 2004 ). QSA permits new questions to be asked of data collected previously from these vulnerable groups ( Rew, Koniak-Griffin, Lewis, Miles, & O'Sullivan, 2000 ), or from groups or events that occur with scarcity ( Thorne, 1994 ). Participants’ time and effort in the primary study therefore becomes more worthwhile. In fact, it is recommended that data already collected from existing studies of vulnerable populations or about sensitive topics be analyzed prior to engaging new participants. In this way, QSA becomes a cumulative rather than a repetitive process ( Fielding, 2004 ).
Data Adequacy and Congruency
Secondary researchers must determine that the primary data set meets the needs of the QSA. Data may be insufficient to answer a new question or the focus of the QSA may be so different as to render the pursuit of a QSA impossible ( Heaton, 1998 ). The underlying assumptions, sampling plan, research questions, and conceptual framework selected to answer the original study question may not fit the question posed during QSA ( Coyer & Gallo, 2005 ). The researchers of the primary study may have selectively sampled participants and analyzed the resulting data in a manner that produced a narrow or uneven scope of data ( Hinds et al., 1997 ). Thus, the data needed to fully answer questions posed by the QSA may be inadequately addressed in the primary study. A critical review of the existing dataset is an important first step in determining whether the primary data fits the secondary questions ( Hinds et al., 1997 ).
Passage of Time
The timing of the QSA is another important consideration. If the primary study and secondary study are performed sequentially, findings of the original study may influence the secondary study. On the other hand, studies performed concurrently offer the benefit of access to both the primary research team and participants member checking ( Hinds et al., 1997 ).
The passage of time since the primary study was conducted can also have a distinct effect on the usefulness of the primary dataset. Data may be outdated or contain a historical bias ( Coyer & Gallo, 2005 ). Since context changes over time, characteristics of the phenomena of interest may have changed. Analysis of older datasets may not illuminate the phenomena as they exist today.( Hinds et al., 1997 ) Even if participants could be re-contacted, their perspectives, memories and experiences change. The passage of time also has an affect on the relationship of the primary researchers to the data – so auto-data may be interpreted differently by the same researcher with the passage of time. Data are bound by time and history, therefore, may be a threat to internal validity unless a new investigator is able to account for these effects when interpreting data ( Rew et al., 2000 ).
Researcher stance/Context involvement
Issues related to context are a major source of criticism of QSA ( Gladstone, Volpe, & Boydell, 2007 ). One of the hallmarks of qualitative research is the relationship of the researcher to the participants. It can be argued that removing active contact with participants violates this premise. Tacit understandings developed in the field may be difficult or impossible to reconstruct ( Thorne, 1994 ). Qualitative fieldworkers often react and redirect the data collection based on a growing knowledge of the setting. The setting may change as a result of external or internal factors. Interpretation of researchers as participants in a unique time and social context may be impossible to re-construct even if the secondary researchers were members of the primary team ( Mauthner, Parry, & Milburn, 1998 ). Because the context in which the data were originally produced cannot be recovered, the ability of the researcher to react to the lived experience may be curtailed in QSA ( Gladstone et al., 2007 ). Researchers utilize a number of tactics to filter and prioritize what to include as data that may not be apparent in either the written or spoken records of those events ( Thorne, 1994 ). Reflexivity between the researcher, participants and setting is impossible to recreate when examining pre-existing data.
Relationship of QSA Researcher to Primary Study
The relationship of the QSA researcher to the primary study is an important consideration. When the QSA researcher is not part of the original study team, contractual arrangements detailing access to data, its format, access to the original team, and authorship are required ( Hinds et al., 1997 ). The QSA researcher should assess the condition of the data, documents including transcripts, memos and notes, and clarity and flow of interactions ( Hinds et al., 1997 ). An outline of the original study and data collection procedures should be critically reviewed ( Heaton, 1998 ). If the secondary researcher was not a member of the original study team, access to the original investigative team for the purpose of ongoing clarification is essential ( Hinds et al., 1997 ).
Membership on the original study team may, however, offer the secondary researcher little advantage depending on their role in the primary study. Some research team members may have had responsibility for only one type of data collection or data source. There may be differences in involvement with analysis of the primary data.
Informed Consent of Participants
Thorne (1998) questioned whether data collected for one study purpose can ethically be re-examined to answer another question without participants’ consent. Many institutional review boards permit consent forms to include language about the possibility of future use of existing data. While this mechanism is becoming routine and welcomed by researchers, concerns have been raised that a generic consent cannot possibly address all future secondary questions and may violate the principle of full informed consent ( Gladstone et al., 2007 ). Local variations in study approval practices by institutional review boards may influence the ability of researchers to conduct a QSA.
Rigor of QSA
The primary standards for evaluating rigor of qualitative studies are trustworthiness (logical relationship between the data and the analytic claims), fit (the context within which the findings are applicable), transferability (the overall generalizability of the claims) and auditabilty (the transparency of the procedural steps and the analytic moves processes) ( Lincoln & Guba, 1991 ). Thorne suggests that standard procedures for assuring rigor can be modified for QSA ( Thorne, 1994 ). For instance, the original researchers may be viewed as sources of confirmation while new informants, other related datasets and validation by clinical experts are sources of triangulation that may overcome the lack of access to primary subjects ( Heaton, 2004 ; Thorne, 1994 ).
Our observations, derived from the experience of posing a new question of existing qualitative data serves as a template for researchers considering QSA. Considerations regarding quality, availability and appropriateness of existing data are of primary importance. A realistic plan for collecting additional data to answer questions posed in QSA should consider burden and resources for data collection, analysis, storage and maintenance. Researchers should consider context as a potential limitation to new analyses. Finally, the cost of QSA should be fully evaluated prior to making a decision to pursue QSA.
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the National Institute of Nursing Research (RO1-NR07973, M Happ PI) and a Clinical Practice Grant from the American Association of Critical Care Nurses (JA Tate, PI).
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Disclosure statement: Drs. Tate and Happ have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose that relate to the content of this manuscript and do not anticipate conflicts in the foreseeable future.
Contributor Information
Judith Ann Tate, The Ohio State University, College of Nursing.
Mary Beth Happ, The Ohio State University, College of Nursing.
- Broyles L, Colbert A, Tate J, Happ MB. Clinicians’ evaluation and management of mental health, substance abuse, and chronic pain conditions in the intensive care unit. Critical Care Medicine. 2008; 36 (1):87–93. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Coyer SM, Gallo AM. Secondary analysis of data. Journal of Pediatric Health Care. 2005; 19 (1):60–63. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fielding N. Getting the most from archived qualitative data: Epistemological, practical and professional obstacles. International Journal of Social Research Methodology. 2004; 7 (1):97–104. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gladstone BM, Volpe T, Boydell KM. Issues encountered in a qualitative secondary analysis of help-seeking in the prodrome to psychosis. Journal of Behavioral Health Services & Research. 2007; 34 (4):431–442. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Happ MB, Swigart VA, Tate JA, Arnold RM, Sereika SM, Hoffman LA. Family presence and surveillance during weaning from prolonged mechanical ventilation. Heart & Lung: The Journal of Acute and Critical Care. 2007; 36 (1):47–57. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Happ MB, Swigart VA, Tate JA, Hoffman LA, Arnold RM. Patient involvement in health-related decisions during prolonged critical illness. Research in Nursing & Health. 2007; 30 (4):361–72. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Happ MB, Tate JA, Swigart V, DiVirgilio-Thomas D, Hoffman LA. Wash and wean: Bathing patients undergoing weaning trials during prolonged mechanical ventilation. Heart & Lung: The Journal of Acute and Critical Care. 2010; 39 (6 Suppl):S47–56. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Heaton J. Secondary analysis of qualitative data. Social Research Update. 1998;(22) [ Google Scholar ]
- Heaton J. Reworking Qualitative Data. London: SAGE Publications; 2004. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hinds PS, Vogel RJ, Clarke-Steffen L. The possibilities and pitfalls of doing a secondary analysis of a qualitative data set. Qualitative Health Research. 1997; 7 (3):408–424. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lincoln YS, Guba EG. Naturalistic inquiry. Beverly Hills, CA: Sage Publishing; 1991. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mauthner N, Parry O, Milburn K. The data are out there, or are they? Implications for archiving and revisiting qualitative data. Sociology. 1998; 32 :733–745. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rew L, Koniak-Griffin D, Lewis MA, Miles M, O'Sullivan A. Secondary data analysis: new perspective for adolescent research. Nursing Outlook. 2000; 48 (5):223–229. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Szabo V, Strang VR. Secondary analysis of qualitative data. Advances in Nursing Science. 1997; 20 (2):66–74. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tate JA, Dabbs AD, Hoffman LA, Milbrandt E, Happ MB. Anxiety and agitation in mechanically ventilated patients. Qualitative health research. 2012; 22 (2):157–173. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Thorne S. Secondary analysis in qualitative research: Issues and implications. In: Morse JM, editor. Critical Issues in Qualitative Research. Second. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE; 1994. [ Google Scholar ]
- Thorne S. Ethical and representational issues in qualitative secondary analysis. Qualitative Health Research. 1998; 8 (4):547–555. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- What is Secondary Research? + [Methods & Examples]

In some situations, the researcher may not be directly involved in the data gathering process and instead, would rely on already existing data in order to arrive at research outcomes. This approach to systematic investigation is known as secondary research.
There are many reasons a researcher may want to make use of already existing data instead of collecting data samples, first-hand. In this article, we will share some of these reasons with you and show you how to conduct secondary research with Formplus.
What is Secondary Research?
Secondary research is a common approach to a systematic investigation in which the researcher depends solely on existing data in the course of the research process. This research design involves organizing, collating and analyzing these data samples for valid research conclusions.
Secondary research is also known as desk research since it involves synthesizing existing data that can be sourced from the internet, peer-reviewed journals , textbooks, government archives, and libraries. What the secondary researcher does is to study already established patterns in previous researches and apply this information to the specific research context.
Interestingly, secondary research often relies on data provided by primary research and this is why some researches combine both methods of investigation. In this sense, the researcher begins by evaluating and identifying gaps in existing knowledge before adopting primary research to gather new information that will serve his or her research.
What are Secondary Research Methods?
As already highlighted, secondary research involves data assimilation from different sources, that is, using available research materials instead of creating a new pool of data using primary research methods. Common secondary research methods include data collection through the internet, libraries, archives, schools and organizational reports.
- Online Data
Online data is data that is gathered via the internet. In recent times, this method has become popular because the internet provides a large pool of both free and paid research resources that can be easily accessed with the click of a button.
While this method simplifies the data gathering process , the researcher must take care to depend solely on authentic sites when collecting information. In some way, the internet is a virtual aggregation for all other sources of secondary research data.
- Data from Government and Non-government Archives
You can also gather useful research materials from government and non-government archives and these archives usually contain verifiable information that provides useful insights on varying research contexts. In many cases, you would need to pay a sum to gain access to these data.
The challenge, however, is that such data is not always readily available due to a number of factors. For instance, some of these materials are described as classified information as such, it would be difficult for researchers to have access to them.
- Data from Libraries
Research materials can also be accessed through public and private libraries. Think of a library as an information storehouse that contains an aggregation of important information that can serve as valid data in different research contexts.
Typically, researchers donate several copies of dissertations to public and private libraries; especially in cases of academic research. Also, business directories, newsletters, annual reports and other similar documents that can serve as research data, are gathered and stored in libraries, in both soft and hard copies.
- Data from Institutions of Learning
Educational facilities like schools, faculties, and colleges are also a great source of secondary data; especially in academic research. This is because a lot of research is carried out in educational institutions more than in other sectors.
It is relatively easier to obtain research data from educational institutions because these institutions are committed to solving problems and expanding the body of knowledge. You can easily request research materials from educational facilities for the purpose of a literature review.
Secondary research methods can also be categorized into qualitative and quantitative data collection methods . Quantitative data gathering methods include online questionnaires and surveys, reports about trends plus statistics about different areas of a business or industry.
Qualitative research methods include relying on previous interviews and data gathered through focus groups which helps an organization to understand the needs of its customers and plan to fulfill these needs. It also helps businesses to measure the level of employee satisfaction with organizational policies.
When Do We Conduct Secondary Research?
Typically, secondary research is the first step in any systematic investigation. This is because it helps the researcher to understand what research efforts have been made so far and to utilize this knowledge in mapping out a novel direction for his or her investigation.
For instance, you may want to carry out research into the nature of a respiratory condition with the aim of developing a vaccine. The best place to start is to gather existing research material about the condition which would help to point your research in the right direction.
When sifting through these pieces of information, you would gain insights into methods and findings from previous researches which would help you define your own research process. Secondary research also helps you to identify knowledge gaps that can serve as the name of your own research.
Questions to ask before conducting Secondary Research
Since secondary research relies on already existing data, the researcher must take extra care to ensure that he or she utilizes authentic data samples for the research. Falsified data can have a negative impact on the research outcomes; hence, it is important to always carry out resource evaluation by asking a number of questions as highlighted below:
- What is the purpose of the research? Again, it is important for every researcher to clearly define the purpose of the research before proceeding with it. Usually, the research purpose determines the approach that would be adopted.
- What is my research methodology? After identifying the purpose of the research, the next thing to do is outline the research methodology. This is the point where the researcher chooses to gather data using secondary research methods.
- What are my expected research outcomes?
- Who collected the data to be analyzed? Before going on to use secondary data for your research, it is necessary to ascertain the authenticity of the information. This usually affects the data reliability and determines if the researcher can trust the materials. For instance, data gathered from personal blogs and websites may not be as credible as information obtained from an organization’s website.
- When was the data collected? Data recency is another factor that must be considered since the recency of data can affect research outcomes. For instance, if you are carrying out research into the number of women who smoke in London, it would not be appropriate for you to make use of information that was gathered 5 years ago unless you plan to do some sort of data comparison.
- Is the data consistent with other data available from other sources? Always compare and contrast your data with other available research materials as this would help you to identify inconsistencies if any.
- What type of data was collected? Take care to determine if the secondary data aligns with your research goals and objectives.
- How was the data collected?
Advantages of Secondary Research
- Easily Accessible With secondary research, data can easily be accessed in no time; especially with the use of the internet. Apart from the internet, there are different data sources available in secondary research like public libraries and archives which are relatively easy to access too.
- Secondary research is cost-effective and it is not time-consuming. The researcher can cut down on costs because he or she is not directly involved in the data collection process which is also time-consuming.
- Secondary research helps researchers to identify knowledge gaps which can serve as the basis of further systematic investigation.
- It is useful for mapping out the scope of research thereby setting the stage for field investigations. When carrying out secondary research, the researchers may find that the exact information they were looking for is already available, thus eliminating the need and expense incurred in carrying out primary research in these areas.
Disadvantages of Secondary Research
- Questionable Data: With secondary research, it is hard to determine the authenticity of the data because the researcher is not directly involved in the research process. Invalid data can affect research outcomes negatively hence, it is important for the researcher to take extra care by evaluating the data before making use of it.
- Generalization: Secondary data is unspecific in nature and may not directly cater to the needs of the researcher. There may not be correlations between the existing data and the research process.
- Common Data: Research materials in secondary research are not exclusive to an individual or group. This means that everyone has access to the data and there is little or no “information advantage” gained by those who obtain the research.
- It has the risk of outdated research materials. Outdated information may offer little value especially for organizations competing in fast-changing markets.
How to Conduct Online Surveys with Formplus
Follow these 5 steps to create and administer online surveys for secondary research:
- Sign into Formplus
In the Formplus builder, you can easily create an online survey for secondary research by dragging and dropping preferred fields into your form. To access the Formplus builder, you will need to create an account on Formplus.
Once you do this, sign in to your account and click on “Create Form ” to begin.
- Edit Form Title
Click on the field provided to input your form title, for example, “Secondary Research Survey”.
- Click on the edit button to edit the form.
- Add Fields: Drag and drop preferred form fields into your form in the Formplus builder inputs column. There are several field input options for questionnaires in the Formplus builder.
- Edit fields
- Click on “Save”
- Preview form.
- Customize your Form
With the form customization options in the form builder, you can easily change the outlook of your form and make it more unique and personalized. Formplus allows you to change your form theme, add background images and even change the font according to your needs.
- Multiple Sharing Options
Formplus offers multiple form sharing options which enables you to easily share your questionnaire with respondents. You can use the direct social media sharing buttons to share your form link to your organization’s social media pages.
You can send out your survey form as email invitations to your research subjects too. If you wish, you can share your form’s QR code or embed it on your organization’s website for easy access.
Why Use Formplus as a Secondary Research Tool?
- Simple Form Builder Solution
The Formplus form builder is easy to use and does not require you to have any knowledge in computer programming, unlike other form builders. For instance, you can easily add form fields to your form by dragging and dropping them from the inputs section in the builder.
In the form builder, you can also modify your fields to be hidden or read-only and you can create smart forms with save and resume options, form lookup, and conditional logic. Formplus also allows you to customize your form by adding preferred background images and your organization’s logo.
- Over 25 Form Fields
With over 25 versatile form fields available in the form builder, you can easily collect data the way you like. You can receive payments directly in your form by adding payment fields and you can also add file upload fields to allow you receive files in your form too.
- Offline Form feature
With Formplus, you can collect data from respondents even without internet connectivity . Formplus automatically detects when there is no or poor internet access and allows forms to be filled out and submitted in offline mode.
Offline form responses are automatically synced with the servers when the internet connection is restored. This feature is extremely useful for field research that may involve sourcing for data in remote and rural areas plus it allows you to scale up on your audience reach.
- Team and Collaboration
You can add important collaborators and team members to your shared account so that you all can work on forms and responses together. With the multiple users options, you can assign different roles to team members and you can also grant and limit access to forms and folders.
This feature works with an audit trail that enables you to track changes and suggestions made to your form as the administrator of the shared account. You can set up permissions to limit access to the account while organizing and monitoring your form(s) effectively.
- Embeddable Form
Formplus allows you to easily add your form with respondents with the click of a button. For instance, you can directly embed your form in your organization’s web pages by adding Its unique shortcode to your site’s HTML.
You can also share your form to your social media pages using the social media direct sharing buttons available in the form builder. You can choose to embed the form as an iframe or web pop-up that is easy to fill.
With Formplus, you can share your form with numerous form respondents in no time. You can invite respondents to fill out your form via email invitation which allows you to also track responses and prevent multiple submissions in your form.
In addition, you can also share your form link as a QR code so that respondents only need to scan the code to access your form. Our forms have a unique QR code that you can add to your website or print in banners, business cards and the like.
While secondary research can be cost-effective and time-efficient, it requires the researcher to take extra care in ensuring that the data is authentic and valid. As highlighted earlier, data in secondary research can be sourced through the internet, archives, and libraries, amongst other methods.
Secondary research is usually the starting point of systematic investigation because it provides the researcher with a background of existing research efforts while identifying knowledge gaps to be filled. This type of research is typically used in science and education.
It is, however, important to note that secondary research relies on the outcomes of collective primary research data in carrying out its systematic investigation. Hence, the success of your research will depend, to a greater extent, on the quality of data provided by primary research in relation to the research context.

Connect to Formplus, Get Started Now - It's Free!
- primary secondary research differences
- primary secondary research method
- secondary data collection
- secondary research examples
- busayo.longe

You may also like:
Recall Bias: Definition, Types, Examples & Mitigation
This article will discuss the impact of recall bias in studies and the best ways to avoid them during research.

Primary vs Secondary Research Methods: 15 Key Differences
Difference between primary and secondary research in definition, examples, data analysis, types, collection methods, advantages etc.
Exploratory Research: What are its Method & Examples?
Overview on exploratory research, examples and methodology. Shows guides on how to conduct exploratory research with online surveys
What is Pure or Basic Research? + [Examples & Method]
Simple guide on pure or basic research, its methods, characteristics, advantages, and examples in science, medicine, education and psychology
Formplus - For Seamless Data Collection
Collect data the right way with a versatile data collection tool. try formplus and transform your work productivity today..

- Teesside University Student & Library Services
- Learning Hub Group
Research Methods
Secondary research.
- Primary Research
What is Secondary Research?
Advantages and disadvantages of secondary research, secondary research in literature reviews, secondary research - going beyond literature reviews, main stages of secondary research, useful resources, using material on this page.
- Quantitative Research This link opens in a new window
- Qualitative Research This link opens in a new window
- Being Critical This link opens in a new window
- Subject LibGuides This link opens in a new window

Secondary research
Secondary research uses research and data that has already been carried out. It is sometimes referred to as desk research. It is a good starting point for any type of research as it enables you to analyse what research has already been undertaken and identify any gaps.
You may only need to carry out secondary research for your assessment or you may need to use secondary research as a starting point, before undertaking your own primary research .
Searching for both primary and secondary sources can help to ensure that you are up to date with what research has already been carried out in your area of interest and to identify the key researchers in the field.
"Secondary sources are the books, articles, papers and similar materials written or produced by others that help you to form your background understanding of the subject. You would use these to find out about experts’ findings, analyses or perspectives on the issue and decide whether to draw upon these explicitly in your research." (Cottrell, 2014, p. 123).
Examples of secondary research sources include:.
- journal articles
- official statistics, such as government reports or organisations which have collected and published data
Primary research involves gathering data which has not been collected before. Methods to collect it can include interviews, focus groups, controlled trials and case studies. Secondary research often comments on and analyses this primary research.
Gopalakrishnan and Ganeshkumar (2013, p. 10) explain the difference between primary and secondary research:
"Primary research is collecting data directly from patients or population, while secondary research is the analysis of data already collected through primary research. A review is an article that summarizes a number of primary studies and may draw conclusions on the topic of interest which can be traditional (unsystematic) or systematic".
Secondary Data
As secondary data has already been collected by someone else for their research purposes, it may not cover all of the areas of interest for your research topic. This research will need to be analysed alongside other research sources and data in the same subject area in order to confirm, dispute or discuss the findings in a wider context.
"Secondary source data, as the name infers, provides second-hand information. The data come ‘pre-packaged’, their form and content reflecting the fact that they have been produced by someone other than the researcher and will not have been produced specifically for the purpose of the research project. The data, none the less, will have some relevance for the research in terms of the information they contain, and the task for the researcher is to extract that information and re-use it in the context of his/her own research project." (Denscombe, 2021, p. 268)
In the video below Dr. Benedict Wheeler (Senior Research Fellow at the European Center for Environment and Human Health at the University of Exeter Medical School) discusses secondary data analysis. Secondary data was used for his research on how the environment affects health and well-being and utilising this secondary data gave access to a larger data set.
As with all research, an important part of the process is to critically evaluate any sources you use. There are tools to help with this in the Being Critical section of the guide.
Louise Corti, from the UK Data Archive, discusses using secondary data in the video below. T he importance of evaluating secondary research is discussed - this is to ensure the data is appropriate for your research and to investigate how the data was collected.
There are advantages and disadvantages to secondary research:
Advantages:
- Usually low cost
- Easily accessible
- Provides background information to clarify / refine research areas
- Increases breadth of knowledge
- Shows different examples of research methods
- Can highlight gaps in the research and potentially outline areas of difficulty
- Can incorporate a wide range of data
- Allows you to identify opposing views and supporting arguments for your research topic
- Highlights the key researchers and work which is being undertaken within the subject area
- Helps to put your research topic into perspective
Disadvantages
- Can be out of date
- Might be unreliable if it is not clear where or how the research has been collected - remember to think critically
- May not be applicable to your specific research question as the aims will have had a different focus
Literature reviews
Secondary research for your major project may take the form of a literature review . this is where you will outline the main research which has already been written on your topic. this might include theories and concepts connected with your topic and it should also look to see if there are any gaps in the research., as the criteria and guidance will differ for each school, it is important that you check the guidance which you have been given for your assessment. this may be in blackboard and you can also check with your supervisor..
The videos below include some insights from academics regarding the importance of literature reviews.
Secondary research which goes beyond literature reviews
For some dissertations/major projects there might only be a literature review (discussed above ). For others there could be a literature review followed by primary research and for others the literature review might be followed by further secondary research.
You may be asked to write a literature review which will form a background chapter to give context to your project and provide the necessary history for the research topic. However, you may then also be expected to produce the rest of your project using additional secondary research methods, which will need to produce results and findings which are distinct from the background chapter t o avoid repetition .
Remember, as the criteria and guidance will differ for each School, it is important that you check the guidance which you have been given for your assessment. This may be in Blackboard and you can also check with your supervisor.
Although this type of secondary research will go beyond a literature review, it will still rely on research which has already been undertaken. And, "just as in primary research, secondary research designs can be either quantitative, qualitative, or a mixture of both strategies of inquiry" (Manu and Akotia, 2021, p. 4) .
Your secondary research may use the literature review to focus on a specific theme, which is then discussed further in the main project. Or it may use an alternative approach. Some examples are included below. Remember to speak with your supervisor if you are struggling to define these areas.
Some approaches of how to conduct secondary research include:
- A systematic review is a structured literature review that involves identifying all of the relevant primary research using a rigorous search strategy to answer a focused research question.
- This involves comprehensive searching which is used to identify themes or concepts across a number of relevant studies.
- The review will assess the q uality of the research and provide a summary and synthesis of all relevant available research on the topic.
- The systematic review LibGuide goes into more detail about this process (The guide is aimed a PhD/Researcher students. However, students on other levels of study may find parts of the guide helpful too).
- Scoping reviews aim to identify and assess available research on a specific topic (which can include ongoing research).
- They are "particularly useful when a body of literature has not yet been comprehensively reviewed, or exhibits a complex or heterogeneous nature not amenable to a more precise systematic review of the evidence. While scoping reviews may be conducted to determine the value and probable scope of a full systematic review, they may also be undertaken as exercises in and of themselves to summarize and disseminate research findings, to identify research gaps, and to make recommendations for the future research." (Peters et al., 2015) .
- This is designed to summarise the current knowledge and provide priorities for future research.
- "A state-of-the-art review will often highlight new ideas or gaps in research with no official quality assessment." (Baguss, 2020) .
- "Bibliometric analysis is a popular and rigorous method for exploring and analyzing large volumes of scientific data." (Donthu et al., 2021)
- Quantitative methods and statistics are used to analyse the bibliographic data of published literature. This can be used to measure the impact of authors, publications, or topics within a subject area.
The bibliometric analysis often uses the data from a citation source such as Scopus or Web of Science .
- This is a technique used to combine the statistic results of prior quantitative studies in order to increase precision and validity.
- "It goes beyond the parameters of a literature review, which assesses existing literature, to actually perform calculations based on the results collated, thereby coming up with new results" (Curtis and Curtis, 2011, p. 220)
(Adapted from: Grant and Booth, 2009, cited in Sarhan and Manu, 2021, p. 72 )
- Grounded Theory is used to create explanatory theory from data which has been collected.
- "Grounded theory data analysis strategies can be used with different types of data, including secondary data." ( Whiteside, Mills and McCalman, 2012 )
- This allows you to use a specific theory or theories which can then be applied to your chosen topic/research area.
- You could focus on one case study which is analysed in depth, or you could examine more than one in order to compare and contrast the important aspects of your research question.
- "Good case studies often begin with a predicament that is poorly comprehended and is inadequately explained or traditionally rationalised by numerous conflicting accounts. Therefore, the aim is to comprehend an existent problem and to use the acquired understandings to develop new theoretical outlooks or explanations." ( Papachroni and Lochrie, 2015, p. 81 )
Main stages of secondary research for a dissertation/major project
In general, the main stages for conducting secondary research for your dissertation or major project will include:
Click on the image below to access the reading list which includes resources used in this guide as well as some additional useful resources.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License .
- << Previous: Primary Research
- Next: Quantitative Research >>
- Last Updated: Aug 11, 2022 3:41 PM
- URL: https://libguides.tees.ac.uk/researchmethods
What is Secondary Research? Types, Methods, Examples
Appinio Research · 20.09.2023 · 13min read

Have you ever wondered how researchers gather valuable insights without conducting new experiments or surveys? That's where secondary research steps in—a powerful approach that allows us to explore existing data and information others collect.
Whether you're a student, a professional, or someone seeking to make informed decisions, understanding the art of secondary research opens doors to a wealth of knowledge.
What is Secondary Research?
Secondary Research refers to the process of gathering and analyzing existing data, information, and knowledge that has been previously collected and compiled by others. This approach allows researchers to leverage available sources, such as articles, reports, and databases, to gain insights, validate hypotheses, and make informed decisions without collecting new data.
Benefits of Secondary Research
Secondary research offers a range of advantages that can significantly enhance your research process and the quality of your findings.
- Time and Cost Efficiency: Secondary research saves time and resources by utilizing existing data sources, eliminating the need for data collection from scratch.
- Wide Range of Data: Secondary research provides access to vast information from various sources, allowing for comprehensive analysis.
- Historical Perspective: Examining past research helps identify trends, changes, and long-term patterns that might not be immediately apparent.
- Reduced Bias: As data is collected by others, there's often less inherent bias than in conducting primary research, where biases might affect data collection.
- Support for Primary Research: Secondary research can lay the foundation for primary research by providing context and insights into gaps in existing knowledge.
- Comparative Analysis : By integrating data from multiple sources, you can conduct robust comparative analyses for more accurate conclusions.
- Benchmarking and Validation: Secondary research aids in benchmarking performance against industry standards and validating hypotheses.
Primary Research vs. Secondary Research
When it comes to research methodologies, primary and secondary research each have their distinct characteristics and advantages. Here's a brief comparison to help you understand the differences.
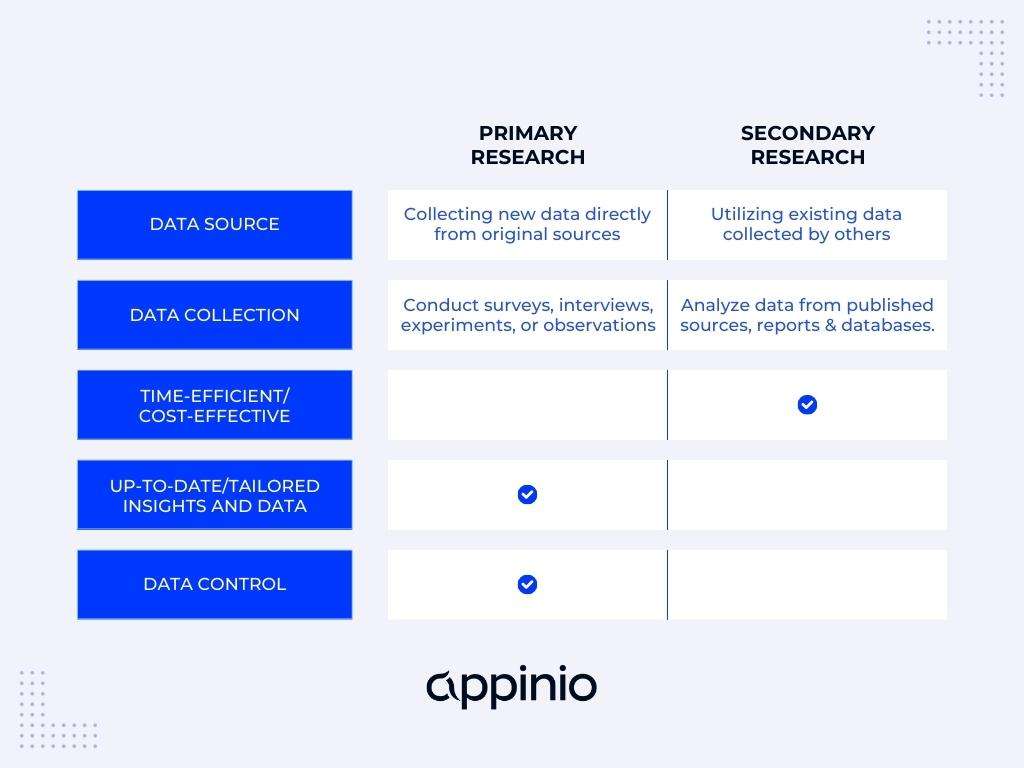
Primary Research
- Data Source: Involves collecting new data directly from original sources.
- Data Collection: Researchers design and conduct surveys, interviews, experiments, or observations.
- Time and Resources: Typically requires more time, effort, and resources due to data collection.
- Fresh Insights: Provides firsthand, up-to-date information tailored to specific research questions.
- Control: Researchers control the data collection process and can shape methodologies.
Secondary Research
- Data Source: Involves utilizing existing data and information collected by others.
- Data Collection: Researchers search, select, and analyze data from published sources, reports, and databases.
- Time and Resources: Generally more time-efficient and cost-effective as data is already available.
- Existing Knowledge: Utilizes data that has been previously compiled, often providing broader context.
- Less Control: Researchers have limited control over how data was collected originally, if any.
Choosing between primary and secondary research depends on your research objectives, available resources, and the depth of insights you require.
Types of Secondary Research
Secondary research encompasses various types of existing data sources that can provide valuable insights for your research endeavors. Understanding these types can help you choose the most relevant sources for your objectives.
Here are the primary types of secondary research:
Internal Sources
Internal sources consist of data generated within your organization or entity. These sources provide valuable insights into your own operations and performance.
- Company Records and Data: Internal reports, documents, and databases that house information about sales, operations, and customer interactions.
- Sales Reports and Customer Data: Analysis of past sales trends, customer demographics, and purchasing behavior.
- Financial Statements and Annual Reports: Financial data, such as balance sheets and income statements, offer insights into the organization's financial health.
External Sources
External sources encompass data collected and published by entities outside your organization.
These sources offer a broader perspective on various subjects.
- Published Literature and Journals: Scholarly articles, research papers, and academic studies available in journals or online databases.
- Market Research Reports: Reports from market research firms that provide insights into industry trends, consumer behavior, and market forecasts.
- Government and NGO Databases: Data collected and maintained by government agencies and non-governmental organizations, offering demographic, economic, and social information.
- Online Media and News Articles: News outlets and online publications that cover current events, trends, and societal developments.
Each type of secondary research source holds its value and relevance, depending on the nature of your research objectives. Combining these sources lets you understand the subject matter and make informed decisions.
How to Conduct Secondary Research?
Effective secondary research involves a thoughtful and systematic approach that enables you to extract valuable insights from existing data sources. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to navigate the process:
1. Define Your Research Objectives
Before delving into secondary research, clearly define what you aim to achieve. Identify the specific questions you want to answer, the insights you're seeking, and the scope of your research.
2. Identify Relevant Sources
Begin by identifying the most appropriate sources for your research. Consider the nature of your research objectives and the data type you require. Seek out sources such as academic journals, market research reports, official government databases, and reputable news outlets.
3. Evaluate Source Credibility
Ensuring the credibility of your sources is crucial. Evaluate the reliability of each source by assessing factors such as the author's expertise, the publication's reputation, and the objectivity of the information provided. Choose sources that align with your research goals and are free from bias.

4. Extract and Analyze Information
Once you've gathered your sources, carefully extract the relevant information. Take thorough notes, capturing key data points, insights, and any supporting evidence. As you accumulate information, start identifying patterns, trends, and connections across different sources.
5. Synthesize Findings
As you analyze the data, synthesize your findings to draw meaningful conclusions. Compare and contrast information from various sources to identify common themes and discrepancies. This synthesis process allows you to construct a coherent narrative that addresses your research objectives.
6. Address Limitations and Gaps
Acknowledge the limitations and potential gaps in your secondary research. Recognize that secondary data might have inherent biases or be outdated. Where necessary, address these limitations by cross-referencing information or finding additional sources to fill in gaps.
7. Contextualize Your Findings
Contextualization is crucial in deriving actionable insights from your secondary research. Consider the broader context within which the data was collected. How does the information relate to current trends, societal changes, or industry shifts? This contextual understanding enhances the relevance and applicability of your findings.
8. Cite Your Sources
Maintain academic integrity by properly citing the sources you've used for your secondary research. Accurate citations not only give credit to the original authors but also provide a clear trail for readers to access the information themselves.
9. Integrate Secondary and Primary Research (If Applicable)
In some cases, combining secondary and primary research can yield more robust insights. If you've also conducted primary research, consider integrating your secondary findings with your primary data to provide a well-rounded perspective on your research topic.
You can use a market research platform like Appinio to conduct primary research with real-time insights in minutes!
10. Communicate Your Findings
Finally, communicate your findings effectively. Whether it's in an academic paper, a business report, or any other format, present your insights clearly and concisely. Provide context for your conclusions and use visual aids like charts and graphs to enhance understanding.
Remember that conducting secondary research is not just about gathering information—it's about critically analyzing, interpreting, and deriving valuable insights from existing data. By following these steps, you'll navigate the process successfully and contribute to the body of knowledge in your field.
Secondary Research Examples
To better understand how secondary research is applied in various contexts, let's explore a few real-world examples that showcase its versatility and value.
Market Analysis and Trend Forecasting
Imagine you're a marketing strategist tasked with launching a new product in the smartphone industry. By conducting secondary research, you can:
- Access Market Reports: Utilize market research reports to understand consumer preferences, competitive landscape, and growth projections.
- Analyze Trends: Examine past sales data and industry reports to identify trends in smartphone features, design, and user preferences.
- Benchmark Competitors: Compare market share, customer satisfaction, and pricing strategies of key competitors to develop a strategic advantage.
- Forecast Demand: Use historical sales data and market growth predictions to estimate demand for your new product.
Academic Research and Literature Reviews
Suppose you're a student researching climate change's effects on marine ecosystems. Secondary research aids your academic endeavors by:
- Reviewing Existing Studies: Analyze peer-reviewed articles and scientific papers to understand the current state of knowledge on the topic.
- Identifying Knowledge Gaps: Identify areas where further research is needed based on what existing studies still need to cover.
- Comparing Methodologies: Compare research methodologies used by different studies to assess the strengths and limitations of their approaches.
- Synthesizing Insights: Synthesize findings from various studies to form a comprehensive overview of the topic's implications on marine life.
Competitive Landscape Assessment for Business Strategy
Consider you're a business owner looking to expand your restaurant chain to a new location. Secondary research aids your strategic decision-making by:
- Analyzing Demographics: Utilize demographic data from government databases to understand the local population's age, income, and preferences.
- Studying Local Trends: Examine restaurant industry reports to identify the types of cuisines and dining experiences currently popular in the area.
- Understanding Consumer Behavior: Analyze online reviews and social media discussions to gauge customer sentiment towards existing restaurants in the vicinity.
- Assessing Economic Conditions: Access economic reports to evaluate the local economy's stability and potential purchasing power.
These examples illustrate the practical applications of secondary research across various fields to provide a foundation for informed decision-making, deeper understanding, and innovation.
Secondary Research Limitations
While secondary research offers many benefits, it's essential to be aware of its limitations to ensure the validity and reliability of your findings.
- Data Quality and Validity: The accuracy and reliability of secondary data can vary, affecting the credibility of your research.
- Limited Contextual Information: Secondary sources might lack detailed contextual information, making it important to interpret findings within the appropriate context.
- Data Suitability: Existing data might not align perfectly with your research objectives, leading to compromises or incomplete insights.
- Outdated Information: Some sources might provide obsolete information that doesn't accurately reflect current trends or situations.
- Potential Bias: While secondary data is often less biased, biases might still exist in the original data sources, influencing your findings.
- Incompatibility of Data: Combining data from different sources might pose challenges due to variations in definitions, methodologies, or units of measurement.
- Lack of Control: Unlike primary research, you have no control over how data was collected or its quality, potentially affecting your analysis. Understanding these limitations will help you navigate secondary research effectively and make informed decisions based on a well-rounded understanding of its strengths and weaknesses.
Secondary research is a valuable tool that businesses can use to their advantage. By tapping into existing data and insights, companies can save time, resources, and effort that would otherwise be spent on primary research. This approach equips decision-makers with a broader understanding of market trends, consumer behaviors, and competitive landscapes. Additionally, benchmarking against industry standards and validating hypotheses empowers businesses to make informed choices that lead to growth and success.
As you navigate the world of secondary research, remember that it's not just about data retrieval—it's about strategic utilization. With a clear grasp of how to access, analyze, and interpret existing information, businesses can stay ahead of the curve, adapt to changing landscapes, and make decisions that are grounded in reliable knowledge.
How to Conduct Secondary Research in Minutes?
In the world of decision-making, having access to real-time consumer insights is no longer a luxury—it's a necessity. That's where Appinio comes in, revolutionizing how businesses gather valuable data for better decision-making. As a real-time market research platform, Appinio empowers companies to tap into the pulse of consumer opinions swiftly and seamlessly.
- Fast Insights: Say goodbye to lengthy research processes. With Appinio, you can transform questions into actionable insights in minutes.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Harness the power of real-time consumer insights to drive your business strategies, allowing you to make informed choices on the fly.
- Seamless Integration: Appinio handles the research and technical complexities, freeing you to focus on what truly matters: making rapid data-driven decisions that propel your business forward.
Join the loop 💌
Be the first to hear about new updates, product news, and data insights. We'll send it all straight to your inbox.
Get the latest market research news straight to your inbox! 💌
Wait, there's more

17.04.2024 | 25min read
Quota Sampling: Definition, Types, Methods, Examples

15.04.2024 | 34min read
What is Market Share? Definition, Formula, Examples

11.04.2024 | 34min read
What is Data Analysis? Definition, Tools, Examples
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Secondary Data – Types, Methods and Examples
Secondary Data – Types, Methods and Examples
Table of Contents

Secondary Data
Definition:
Secondary data refers to information that has been collected, processed, and published by someone else, rather than the researcher gathering the data firsthand. This can include data from sources such as government publications, academic journals, market research reports, and other existing datasets.
Secondary Data Types
Types of secondary data are as follows:
- Published data: Published data refers to data that has been published in books, magazines, newspapers, and other print media. Examples include statistical reports, market research reports, and scholarly articles.
- Government data: Government data refers to data collected by government agencies and departments. This can include data on demographics, economic trends, crime rates, and health statistics.
- Commercial data: Commercial data is data collected by businesses for their own purposes. This can include sales data, customer feedback, and market research data.
- Academic data: Academic data refers to data collected by researchers for academic purposes. This can include data from experiments, surveys, and observational studies.
- Online data: Online data refers to data that is available on the internet. This can include social media posts, website analytics, and online customer reviews.
- Organizational data: Organizational data is data collected by businesses or organizations for their own purposes. This can include data on employee performance, financial records, and customer satisfaction.
- Historical data : Historical data refers to data that was collected in the past and is still available for research purposes. This can include census data, historical documents, and archival records.
- International data: International data refers to data collected from other countries for research purposes. This can include data on international trade, health statistics, and demographic trends.
- Public data : Public data refers to data that is available to the general public. This can include data from government agencies, non-profit organizations, and other sources.
- Private data: Private data refers to data that is not available to the general public. This can include confidential business data, personal medical records, and financial data.
- Big data: Big data refers to large, complex datasets that are difficult to manage and analyze using traditional data processing methods. This can include social media data, sensor data, and other types of data generated by digital devices.
Secondary Data Collection Methods
Secondary Data Collection Methods are as follows:
- Published sources: Researchers can gather secondary data from published sources such as books, journals, reports, and newspapers. These sources often provide comprehensive information on a variety of topics.
- Online sources: With the growth of the internet, researchers can now access a vast amount of secondary data online. This includes websites, databases, and online archives.
- Government sources : Government agencies often collect and publish a wide range of secondary data on topics such as demographics, crime rates, and health statistics. Researchers can obtain this data through government websites, publications, or data portals.
- Commercial sources: Businesses often collect and analyze data for marketing research or customer profiling. Researchers can obtain this data through commercial data providers or by purchasing market research reports.
- Academic sources: Researchers can also obtain secondary data from academic sources such as published research studies, academic journals, and dissertations.
- Personal contacts: Researchers can also obtain secondary data from personal contacts, such as experts in a particular field or individuals with specialized knowledge.
Secondary Data Formats
Secondary data can come in various formats depending on the source from which it is obtained. Here are some common formats of secondary data:
- Numeric Data: Numeric data is often in the form of statistics and numerical figures that have been compiled and reported by organizations such as government agencies, research institutions, and commercial enterprises. This can include data such as population figures, GDP, sales figures, and market share.
- Textual Data: Textual data is often in the form of written documents, such as reports, articles, and books. This can include qualitative data such as descriptions, opinions, and narratives.
- Audiovisual Data : Audiovisual data is often in the form of recordings, videos, and photographs. This can include data such as interviews, focus group discussions, and other types of qualitative data.
- Geospatial Data: Geospatial data is often in the form of maps, satellite images, and geographic information systems (GIS) data. This can include data such as demographic information, land use patterns, and transportation networks.
- Transactional Data : Transactional data is often in the form of digital records of financial and business transactions. This can include data such as purchase histories, customer behavior, and financial transactions.
- Social Media Data: Social media data is often in the form of user-generated content from social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. This can include data such as user demographics, content trends, and sentiment analysis.
Secondary Data Analysis Methods
Secondary data analysis involves the use of pre-existing data for research purposes. Here are some common methods of secondary data analysis:
- Descriptive Analysis: This method involves describing the characteristics of a dataset, such as the mean, standard deviation, and range of the data. Descriptive analysis can be used to summarize data and provide an overview of trends.
- Inferential Analysis: This method involves making inferences and drawing conclusions about a population based on a sample of data. Inferential analysis can be used to test hypotheses and determine the statistical significance of relationships between variables.
- Content Analysis: This method involves analyzing textual or visual data to identify patterns and themes. Content analysis can be used to study the content of documents, media coverage, and social media posts.
- Time-Series Analysis : This method involves analyzing data over time to identify trends and patterns. Time-series analysis can be used to study economic trends, climate change, and other phenomena that change over time.
- Spatial Analysis : This method involves analyzing data in relation to geographic location. Spatial analysis can be used to study patterns of disease spread, land use patterns, and the effects of environmental factors on health outcomes.
- Meta-Analysis: This method involves combining data from multiple studies to draw conclusions about a particular phenomenon. Meta-analysis can be used to synthesize the results of previous research and provide a more comprehensive understanding of a particular topic.
Secondary Data Gathering Guide
Here are some steps to follow when gathering secondary data:
- Define your research question: Start by defining your research question and identifying the specific information you need to answer it. This will help you identify the type of secondary data you need and where to find it.
- Identify relevant sources: Identify potential sources of secondary data, including published sources, online databases, government sources, and commercial data providers. Consider the reliability and validity of each source.
- Evaluate the quality of the data: Evaluate the quality and reliability of the data you plan to use. Consider the data collection methods, sample size, and potential biases. Make sure the data is relevant to your research question and is suitable for the type of analysis you plan to conduct.
- Collect the data: Collect the relevant data from the identified sources. Use a consistent method to record and organize the data to make analysis easier.
- Validate the data: Validate the data to ensure that it is accurate and reliable. Check for inconsistencies, missing data, and errors. Address any issues before analyzing the data.
- Analyze the data: Analyze the data using appropriate statistical and analytical methods. Use descriptive and inferential statistics to summarize and draw conclusions from the data.
- Interpret the results: Interpret the results of your analysis and draw conclusions based on the data. Make sure your conclusions are supported by the data and are relevant to your research question.
- Communicate the findings : Communicate your findings clearly and concisely. Use appropriate visual aids such as graphs and charts to help explain your results.
Examples of Secondary Data
Here are some examples of secondary data from different fields:
- Healthcare : Hospital records, medical journals, clinical trial data, and disease registries are examples of secondary data sources in healthcare. These sources can provide researchers with information on patient demographics, disease prevalence, and treatment outcomes.
- Marketing : Market research reports, customer surveys, and sales data are examples of secondary data sources in marketing. These sources can provide marketers with information on consumer preferences, market trends, and competitor activity.
- Education : Student test scores, graduation rates, and enrollment statistics are examples of secondary data sources in education. These sources can provide researchers with information on student achievement, teacher effectiveness, and educational disparities.
- Finance : Stock market data, financial statements, and credit reports are examples of secondary data sources in finance. These sources can provide investors with information on market trends, company performance, and creditworthiness.
- Social Science : Government statistics, census data, and survey data are examples of secondary data sources in social science. These sources can provide researchers with information on population demographics, social trends, and political attitudes.
- Environmental Science : Climate data, remote sensing data, and ecological monitoring data are examples of secondary data sources in environmental science. These sources can provide researchers with information on weather patterns, land use, and biodiversity.
Purpose of Secondary Data
The purpose of secondary data is to provide researchers with information that has already been collected by others for other purposes. Secondary data can be used to support research questions, test hypotheses, and answer research objectives. Some of the key purposes of secondary data are:
- To gain a better understanding of the research topic : Secondary data can be used to provide context and background information on a research topic. This can help researchers understand the historical and social context of their research and gain insights into relevant variables and relationships.
- To save time and resources: Collecting new primary data can be time-consuming and expensive. Using existing secondary data sources can save researchers time and resources by providing access to pre-existing data that has already been collected and organized.
- To provide comparative data : Secondary data can be used to compare and contrast findings across different studies or datasets. This can help researchers identify trends, patterns, and relationships that may not have been apparent from individual studies.
- To support triangulation: Triangulation is the process of using multiple sources of data to confirm or refute research findings. Secondary data can be used to support triangulation by providing additional sources of data to support or refute primary research findings.
- To supplement primary data : Secondary data can be used to supplement primary data by providing additional information or insights that were not captured by the primary research. This can help researchers gain a more complete understanding of the research topic and draw more robust conclusions.
When to use Secondary Data
Secondary data can be useful in a variety of research contexts, and there are several situations in which it may be appropriate to use secondary data. Some common situations in which secondary data may be used include:
- When primary data collection is not feasible : Collecting primary data can be time-consuming and expensive, and in some cases, it may not be feasible to collect primary data. In these situations, secondary data can provide valuable insights and information.
- When exploring a new research area : Secondary data can be a useful starting point for researchers who are exploring a new research area. Secondary data can provide context and background information on a research topic, and can help researchers identify key variables and relationships to explore further.
- When comparing and contrasting research findings: Secondary data can be used to compare and contrast findings across different studies or datasets. This can help researchers identify trends, patterns, and relationships that may not have been apparent from individual studies.
- When triangulating research findings: Triangulation is the process of using multiple sources of data to confirm or refute research findings. Secondary data can be used to support triangulation by providing additional sources of data to support or refute primary research findings.
- When validating research findings : Secondary data can be used to validate primary research findings by providing additional sources of data that support or refute the primary findings.
Characteristics of Secondary Data
Secondary data have several characteristics that distinguish them from primary data. Here are some of the key characteristics of secondary data:
- Non-reactive: Secondary data are non-reactive, meaning that they are not collected for the specific purpose of the research study. This means that the researcher has no control over the data collection process, and cannot influence how the data were collected.
- Time-saving: Secondary data are pre-existing, meaning that they have already been collected and organized by someone else. This can save the researcher time and resources, as they do not need to collect the data themselves.
- Wide-ranging : Secondary data sources can provide a wide range of information on a variety of topics. This can be useful for researchers who are exploring a new research area or seeking to compare and contrast research findings.
- Less expensive: Secondary data are generally less expensive than primary data, as they do not require the researcher to incur the costs associated with data collection.
- Potential for bias : Secondary data may be subject to biases that were present in the original data collection process. For example, data may have been collected using a biased sampling method or the data may be incomplete or inaccurate.
- Lack of control: The researcher has no control over the data collection process and cannot ensure that the data were collected using appropriate methods or measures.
- Requires careful evaluation : Secondary data sources must be evaluated carefully to ensure that they are appropriate for the research question and analysis. This includes assessing the quality, reliability, and validity of the data sources.
Advantages of Secondary Data
There are several advantages to using secondary data in research, including:
- Time-saving : Collecting primary data can be time-consuming and expensive. Secondary data can be accessed quickly and easily, which can save researchers time and resources.
- Cost-effective: Secondary data are generally less expensive than primary data, as they do not require the researcher to incur the costs associated with data collection.
- Large sample size : Secondary data sources often have larger sample sizes than primary data sources, which can increase the statistical power of the research.
- Access to historical data : Secondary data sources can provide access to historical data, which can be useful for researchers who are studying trends over time.
- No ethical concerns: Secondary data are already in existence, so there are no ethical concerns related to collecting data from human subjects.
- May be more objective : Secondary data may be more objective than primary data, as the data were not collected for the specific purpose of the research study.
Limitations of Secondary Data
While there are many advantages to using secondary data in research, there are also some limitations that should be considered. Some of the main limitations of secondary data include:
- Lack of control over data quality : Researchers do not have control over the data collection process, which means they cannot ensure the accuracy or completeness of the data.
- Limited availability: Secondary data may not be available for the specific research question or study design.
- Lack of information on sampling and data collection methods: Researchers may not have access to information on the sampling and data collection methods used to gather the secondary data. This can make it difficult to evaluate the quality of the data.
- Data may not be up-to-date: Secondary data may not be up-to-date or relevant to the current research question.
- Data may be incomplete or inaccurate : Secondary data may be incomplete or inaccurate due to missing or incorrect data points, data entry errors, or other factors.
- Biases in data collection: The data may have been collected using biased sampling or data collection methods, which can limit the validity of the data.
- Lack of control over variables: Researchers have limited control over the variables that were measured in the original data collection process, which can limit the ability to draw conclusions about causality.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Primary Data – Types, Methods and Examples

Qualitative Data – Types, Methods and Examples

Research Data – Types Methods and Examples

Quantitative Data – Types, Methods and Examples

Information in Research – Types and Examples
- Find My Rep
You are here
Qualitative Secondary Research A Step-By-Step Guide
- Claire Largan
- Theresa Morris - University College Birmingham, UK
- Description
Perfect for those doing dissertations and research projects, it provides an accessible introduction to the theory of secondary research and sets out the advantages and limitations of using this kind of research. Drawing on years of teaching and research experience, the authors
· Offer step-by-step advice on how to use qualitative secondary data · Walk you through each stage of the research process · Provide practical, ethical tools to help you with your project · Show you how to avoid the potential pitfalls of using secondary data.
Clear and easy to understand, this book is a ready-made toolkit for successfully using qualitative secondary data. From beginner level and beyond, this no-nonsense guide takes the confusion and worry out of doing a secondary research project.
I recommend this book to students and more experienced researchers who want to conduct qualitative secondary research. It is a timely and accessible guide.
Overall, the authors have written a well thought out, accessible and comprehensive book, which is a welcome addition to a relatively small literature on secondary data and documentary analysis.
I will definitely be using this in my own research, to ensure that I have not forgotten important elements in my research design and analysis, and will be recommending chapter 5 (ethics in qualitative secondary research) as additional reading in the ethics chapter of my forthcoming book aimed at undergraduate student
Concise and coherent text on QSR. Have been searching for a text that is accessible for students that will allow them to reflect on their progress as researchers while also equipping them with a voice to justify their choices. This meets those parameters.
This is an excellent introductory text for a methodology that has become accepted practice and increasingly expected by research funding bodies. Making full use of collected data is an ethical principle and will prepare students well for future practice.
Very good resource for students and graduates alike. Definitely a must-read and should-work-with book :-)
The contents of the book allows students to carry out research with ease, the book has an easy flow and many useful areas for undergraduates to follow and complete any research work
This book should be an essential companion for anyone undertaking a research project. This underrepresented topic area is broken down into comprehensive chapters that provide a practical approach whilst prompting critical reflection also. Highly recommended.
a well-crafted and accessibly-written textbook which willl be very useful to students at several levels
This is an essential and accessible book for all undergraduate and postgraduate students wishing to carry out secondary research. This book offers a step-by-step guide into the processes of qualitative research, whilst allowing readers to develop their own critical thinking skills.
Miss Novlett Mitchell University College Birmingham
This book provides insights about qualititavie research and it is very useful for every dissertation module. I am so glad I had the opportunity to include it in my module
Preview this book
For instructors.
Please select a format:
Select a Purchasing Option
- Electronic Order Options VitalSource Amazon Kindle Google Play eBooks.com Kobo
Related Products

SAGE Research Methods is a research methods tool created to help researchers, faculty and students with their research projects. SAGE Research Methods links over 175,000 pages of SAGE’s renowned book, journal and reference content with truly advanced search and discovery tools. Researchers can explore methods concepts to help them design research projects, understand particular methods or identify a new method, conduct their research, and write up their findings. Since SAGE Research Methods focuses on methodology rather than disciplines, it can be used across the social sciences, health sciences, and more.
With SAGE Research Methods, researchers can explore their chosen method across the depth and breadth of content, expanding or refining their search as needed; read online, print, or email full-text content; utilize suggested related methods and links to related authors from SAGE Research Methods' robust library and unique features; and even share their own collections of content through Methods Lists. SAGE Research Methods contains content from over 720 books, dictionaries, encyclopedias, and handbooks, the entire “Little Green Book,” and "Little Blue Book” series, two Major Works collating a selection of journal articles, and specially commissioned videos.
- IND +91 8754467066
- UK +44 - 753 714 4372
- [email protected]

Secondary Data
The data those have been collected already and readily available from other sources are called as secondary data. when compared to primary data, these secondary data are cheaper and more quickly obtainable..

The data those have been collected already and readily available from other sources are called as secondary data. When compared to primary data, these secondary data are cheaper and more quickly obtainable. Usually, desk-based research is used to collect secondary data. After arriving at the secondary data, the researcher should examine the validity and reliability. Thus, the researcher should consider the secondary data which is highly valid and well-referenced in academic articles (Creswell, 2003).
Types of secondary data
Secondary data is categorised into internal (from the organization which is under observation) data which is routinely supplied by management and external (from outside the organization) data which is obtained from various resources such as internet, journals, books, directories, Non-governmental statistical data and Census data.

Figure 1. Types of Secondary data (Source: http://www.ilo.org)
Based on the suggestions of Bryman (1989); Dale et al., (1988); Hakim, (1982 ) the secondary data is also classified into documentary data, survey based data and multiple source secondary data.
Documentary data
Written documents like notices, correspondence, minutes of meetings, reports to shareholders, diaries, transcripts of speeches and administrative and public records will come under this category. Non-written documents such as Tape and video recordings, pictures, drawings, films and television programmes, DVD/CD can also be considered as documentary data.
Survey-based secondary data
The data collected by questionnaires that have already been analyzed for their original purpose are called as survey-based secondary data. They can be from:
- Continuous/regular surveys
- Ad hoc surveys
Multiple-source secondary data
Multiple-source secondary data can be from either documentary or on survey data, or it could be the combination of these data. These data can be used in cohort studies those have been done for the same population over a period of time and also to develop area-based data sets.
Sources of secondary data
Reports from central, state or local government
Reports from international firms and foreign governments
Journals, magazines and books
Publications from research scholars, universities and research groups- are the major sources of secondary data (Dash, 2011).
Uses of secondary data
Although all data is intended to provide information for analysis and decision making, secondary data can be used in several ways in the context and conduct of a research/consultancy project. In accordance to Malhotra and Birks (2000) and McDaniel and Gates (2004) secondary data can be useful to
- To identify the research problem
- To develop a strategy to arrive at the solutions for the research problem
- To construct a sampling plan
- To formulate a suitable research design
- To find out the answers for certain research questions or to test some hypotheses
- To interpret primary data
- To validate the outcomes from qualitative research
- To identify the potential problems
- To obtain the required background information and to improve the credibility of the study.
Evaluation of secondary data
The researcher has to view the secondary data with the same caution as he does with any primary data. He has to check whether he could access the data and the available secondary data could support him to arrive at the research objectives. Based on the following criteria the researcher should evaluate the secondary data resources (Stewart, 1984).
Methodology
It is necessary to evaluate the secondary data based on the methodology through which it has been collected (Stewart, 1984). Hence, the researcher has to evaluate the factors like sampling procedure, size of sample, rate of response, field work procedures and data analysis methods.
Error/accuracy
Accuracy of the data from the secondary resource should be assessed by the researcher in order to make sure about the trustworthiness of his study. However, the specifications as well as the methodologies won’t be given in detail to the researcher. As a result, it is often very tough to assess the accuracy of secondary data. However, the researcher could check the accuracy through triangulation research.
Date of data collection
As the secondary data is associated with the events those have already happened, it is usually outdated. Hence the researcher has to view the date of data collection, duration between data collection and publication and the relevancy of the data with respect to existing situations. In the case of census data, date of data collection is the major issue as it is collected once in few years.
Purpose of data collection
Again, by definition, secondary data is data that was collected with some other purpose or objective than that which the researcher/consultant now addressing this data is concerned with. The researcher must assess the extent to which data collected with another purpose or specific objective in mind is appropriate and relevant to the researcher’s situation or problem.
Nature: content of data
The data with high validity and accuracy can’t be useful if the content of the data is not good. Sometimes, there may be no proper link between the relationships examined by the data and the measurement categories adopted by the researcher. For example, the data may consider the relationship between salary levels and motivation. However, motivation may have been defined and measured in a way that is inconsistent or inappropriate with how the researcher considering the secondary data wishes to measure motivation.
Dependability/source credibility
It is suggested that the factors such as expertise, credibility and overall trustworthiness of the source should be considered by the researcher while evaluating the secondary data resources. In general, Government reports are found to be more credible than other commercial sources of secondary data. If the researcher knows the provider of the data or the primary data collection methodologies adopted by the researcher or the source of the primary data (whether original or acquired source), dependability and source credibility will become high (Stewart ,1984).
These are the key factors associated with the evaluation of secondary data resources. In addition to these factors other features such as costs and benefits, issues in access as well as control over data quality will also be considered while evaluating the secondary data (Stewart & Kamins, 1993; Denscombe, 1998).
Advantages of secondary data
Researchers (Boslaugh, 2007) have observed the following advantages with secondary data:
- Less resource requirements
- Inconspicuous method
- Applicable for longitudinal studies
- Comparative and contextual data can be obtained
- Lead to unforeseen discoveries
- Durability of data
Disadvantages of secondary data
- The purpose for which the data is collected may not match the objectives of the researcher. Sometimes, it may be very difficult to get the access to the data
- Aggregations and definitions may not match the expectations of the researcher.
- The researcher has no control over data quality
Using more than one method
Sometimes, the researcher may be in a situation to adopt more than one method of data collection. For example, he may conduct secondary research followed by observation and focus group interviews. As this approach is the combination of two or more methods it is referred to as triangulation. Most of the management and consultancy research are not exclusive, and dichotomous. They may include both qualitative and quantitative research. On the other hand, focus groups and surveys can be done together for experimental research.
Factors affecting the selection of the research method
The research methodology adopted by the researcher has extreme influence over the success of the study. Hence, he should be very careful while selecting the research methodology. To arrive at the outcomes with expected quality, he should consider various factors while selecting the research methods. Among them, validity, reliability, and generalizability are the important factors that influence the selection of research method.
Validity and reliability of measures
The two important parts of research process are validity and reliability of measures. As stated by (Bryman & Cramer, 2005) “It is generally accepted that when a concept has been operationally defined, in that a measure of it has been proposed, the ensuring measurement device should be both valid and reliable”. Accuracy or exactness of data is related to the validity measure (Churchill & Lacobucci, 2002) which denotes the accuracy of the survey instrument (Litwin, 1995). As stated by Oppenheim(1984), Baines and Chansarkar (2002), Parasuraman, (1991), Peterson, (2000), validity measure could check whether the survey instrument measures the variables under study. Validity can be inferred through direct assessment employing validity and indirect assessment via reliability (Churchill & Lacobucci , 2002).
Generalizability
Generalizability, another dimension of validity is related to the degree with which the research outcomes could be generalised to other situations. Generalizability of data is crucial in two aspects. (i) Sampling is often used in the generation of data in the process of research and consultancy projects. The researcher should be able, to examine the extent to which results from the sample will also be present in the wider population from which the sample is obtained. Thus, Generalizability, is not associated only with the data collection methods but also with sample design and sampling method. (ii) The extent to which the data and results of a particular research project can be generalized to other situations. This, of course, is crucial in developing theories and particularly in the deductive approach to research.
Hence, it is understood that these three measures are found to support the researcher to generate scientific and reproducible research outcomes. It was believed that these three measures were developed for conducting research in the field of physical sciences where quantitative data is mostly used (Easterby-Smith et al., 2002).
Objectives/purpose of research
The objectives and purpose of the research extremely influences the selection of the research method. For example, the researcher may attempt to arrive at the solutions for a particular set of questions in his study. Hence, he could choose the methodology or techniques based on these objectives.
Skills and expertise of the researcher
It is true that an experienced researcher could opt for any kind of alternative research methodology and data-collection techniques. But each and every researcher can’t be an expert in all types of research methods. The researcher should opt for the methodology in which he has the high degree of expertise and familiarity. This factor is the major determinant for the success of the study/research.
Cost/budgets
The cost of the proposed research methodology is an important factor in determining the choice of research methods. Mostly, cost of the data collection method is high in many projects. Sometimes, the most effective research methodology in quality and potential value may be rejected in favour of a slightly less effective research methodology which is cheaper.
The researcher should consider the time given to complete the research while choosing the research methodology. If he has allotted with short duration, he should not opt for time consuming data collection methods such as large-scale surveys.
Availability
To make the study easier, the researcher should opt for readily available and accessible research methods. As the secondary data is already available, it is very easy to collect them. Sometimes, the data may not be available. In this case it is necessary to choose an alternative method to collect data.
Preferences/values of the consultant
The consultant should not allow his/her preferences and values to influence the choice of research methodology and he/she should give importance for the preferences of the client and the validity and cost of the methods.
Preferences/values of the client
Preferences and values of the client are found to extremely influence the choice of alternative research methodologies in the case of consultancy research projects. For example, the consultancy may feel that data for a particular project can be effectively collected through observation. But the client may tell that his department won’t allow observation method. In this case, it is necessary to discuss in terms of research methodology at the contracting stage of the consultancy process.
Ethical, legal and other issues
The consultant and client should consider and take care of several issues while selecting alternative research methodologies. Ethical issues concerned with the choice of research methodology and data collection techniques are one of these issues. Sometimes, there may be some issues in informing the participants that they are under observation (Wysocki 2004). On the other hand, there may be some issues in terms of collection, storage and uses of data. Most of the countries deal these issues with the help of legislation. For example, Data Protection Act has been passed in the UK to deal these issues.
Some of the factors should consider before utilizing secondary data
At Statswork, we are very conscious in collecting the secondary data include
- 1. Checking the reliability of data
- 2. Accuracy and quality of data for specific research goal (level of accuracy and quality)
- 3. Suitability of data
How do I contact Statswork expert for secondary data collection?
You can reach us at any time in a week (between Monday to Saturday, 09.00 am to 06.00 pm IST) at +91 87544 46690 or fill up this form or Just mail us via LinkedIn.
MAIN SERVICES
Hire a statistician, statswork popup.

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
- 3rd Party Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
This website uses Google Analytics to collect anonymous information such as the number of visitors to the site, and the most popular pages.
Keeping this cookie enabled helps us to improve our website.
Please enable Strictly Necessary Cookies first so that we can save your preferences!
Top Secondary Market Research Companies | Desk Research Companies
Apr 16, 2024
7 min. read
Secondary research companies give you an instant path to insights, offering a shortcut to understanding your customer journey . Rather than set up and conduct resource-intensive studies on your own, these companies pull data from multiple sources to help inform your next best actions.
Also known as desk research companies , secondary research companies help you preserve your time and resources when launching new marketing initiatives. They explore online databases, social media, libraries, industry experts, market research studies, and many other places on your behalf, all with your goals in mind.
Desk research is a fraction of the cost of primary research and can save you time and effort compared with traditional methods. Let’s explore the top secondary market research companies to help you capitalize on readily available data.
What are the Top Secondary Research Companies?
We chose these top secondary research companies based on their focus on desk research , approaches, and reputation. Here are the best secondary research companies to start your journey:
B2B International
Geo strategy partners, markelytics solutions, kantar marketplace, thrive analytics, ascendant consulting firm, sis international research.

Meltwater’s AI-enabled Consumer Intelligence solution is one of the most powerful of its kind, offering insights into brands, consumers, and the media landscape. It puts the power of desk research into your hands, allowing you to command new insights as needed.
What makes Meltwater’s technology stand out is its ability to answer questions you have yet to ask. Using AI , market research expertise, and data science, our platform helps you track topics and trending content, understand audiences, identify new segments and markets, and meet your customers where they are — and you don’t have to know where to start in order to gain these insights. Meltwater recognizes sentiments and how people are discussing various topics, opening the door to new insights and ideas you haven’t yet thought to explore.
With billions of data points updated in real time, users can monitor trends or conduct new desk research whenever they need it. Multiple users can research, collaborate, and share reports of their findings—all from one platform.
Want to learn more about how Meltwater can bolster your secondary market research efforts? Simply fill out the form at the bottom of this post and we'll be in touch.

Specializing in B2B market research , B2B International offers desk research as part of its market research services . They conduct research regarding brand and communications, customer segments , markets, product positioning, and thought leadership to help brands cut through the noise and get in front of their target audiences.
Their secondary research service hinges on quality internet research. They use a combination of libraries, databases, online directories, and similar sources. They’re constantly expanding their resource pool and often combine secondary research with primary research like interviews and surveys to build a comprehensive study.

myMRPlace is unique in that it serves as a marketplace for secondary market research companies. It matches you based on the type of desk research you need, allowing you to connect with only the companies that can help you.
These companies use a variety of desk research techniques and aren’t limited to basic Google and Bing searches. Industry reports, books, white papers, reviews, articles, and enterprise data sources may contribute to the process.
This marketplace approach removes some of the risks associated with buying secondary research . You don’t know what data is available until you look for it, so working with a secondary research company comes with some risk. If there’s little or no data available on the topic you need, you could waste precious resources and have your questions go unanswered.
myMRPlace focuses on helping you find the right data supplier for the job. You can share your project requirements, which go to more than 800 companies in 90 countries. Companies will provide you with a quote before you begin, allowing you more control over your project and budget.

Geo Strategy Partners is a full-service market research company specializing in industrial and technology companies. Desk research is an integral part of market research because it serves as a starting point for important questions, competitive analyses , and insights to guide a winning strategy.
The firm relies on a combination of qualitative and quantitative research techniques and tools. Projects typically include analyzing market trends, identifying competitors, characterizing the type and size of new opportunities, and predicting market trends , among other things. With these findings, customers can answer key questions about new products to develop, new territories to enter, and how to create go-to-market strategies.

Markelytics harnesses the power of technology to deliver insights in rapidly evolving industries. Specializing in research for companies in automotive, e-commerce, education, financial services, fashion, healthcare, and others, the firm collects digital research from all corners of the world to fuel business strategies.
Speed is the name of the game, with technology helping to remove redundant processes and deliver quick insights. The company leans heavily on resources that are available digitally, helping to bring context and action to their findings so businesses can make informed decisions.
Tip: Learn how to increase your organization's speed to insight in our Insight-Driven Marketing Guide .

Based in the UK, Kantar Marketplace puts the power of automation in your desk research processes. This automated platform combines human expertise with technology to help you learn more about markets and the people driving them. The platform not only offers secondary data but also transforms the data into easy-to-understand visuals for faster decision-making.
Kantar also gives you the option to pay as you go (so you only pay for what you need) or choose a paid subscription for ongoing insights.

From market and customer research to advisory services, Thrive Analytics offers 360 degrees of marketing insights. With a combination of traditional and innovative methodologies, the firm specializes in digital marketing aspects to create robust strategies.
Like many secondary research companies, Thrive Analytics uses a combination of primary and secondary data to create a complete picture. Data analysis is among their core specialties, helping you to make sense of the research and numbers so you’ll know what to do next.

Ascendant Consulting Firm helps you harness readily available insights into consumers, competitors, and markets. The team deploys a variety of market research strategies, including secondary research , to help companies make key decisions for long-term business health.
With nearly 100 combined years of experience in qualitative and quantitative research, the firm uses popular approaches like regression analyses and projective techniques to think like a customer (or competitor).
Read more about how Pernod Ricard and Haleon use Meltwater to transform their market research processes.

SIS International Research is a full-service market research and intelligence firm offering primary and secondary research services. They work with B2B and B2C companies across multiple markets, including healthcare, food and beverage, FinTech, and industrial clients.
Secondary or desktop research is one of the firm’s many offerings, often complemented by primary research, competitive intelligence , product development, and brand positioning. They offer global coverage to give companies both broad and granular insights into people, products, and places. With experience spanning nearly 40 years, the high volume of primary research they produce shows promise for companies seeking reliable secondary sources.
Choosing the Right Desk Research Company
Empowering your research with secondary data means choosing the right companies and sources from the start. It’s important to remember that secondary research is limited, so we suggest choosing companies that:
- Have access to data related to your topic or needs
- Can pull data from a variety of sources
- Have expertise in your field or industry
- Demonstrates a track record of quality data and reports
- Maintains clear, open communication to ensure you receive the best results
The more variety in sources you have, the better chance you have of finding relevant data to address your questions. That’s what makes Meltwater’s Consumer Intelligence suite so powerful—it captures billions of data points in real time across social media, news websites, podcasts, and offline channels to help you gain a comprehensive understanding so you can move forward with confidence.
Learn how Meltwater can help your secondary market research when you request a demo by filling out the form below.
Continue Reading

Secondary Research Guide: Definition, Methods, Examples

What Is Desk Research? Meaning, Methodology, Examples
How To Do Market Research: Definition, Types, Methods

The 13 Best Market Research Tools

Personalization at Scale: Removing Guesswork from Consumer Research

The Marketers Guide to Unified Reporting

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Secondary research is a research method that uses data that was collected by someone else. In other words, whenever you conduct research using data that already exists, you are conducting secondary research. On the other hand, any type of research that you undertake yourself is called primary research. Example: Secondary research.
This article provides a guideline for a new secondary qualitative data research methodology that draws on a range of existing methods and adds a procedural structure for a complete analysis from the beginning to end, to help remove ambiguity regarding the process. ... Critical Issues in Qualitative Research Methods, 1, 263-279. Google Scholar.
SDA involves investigations where data collected for a previous study is analyzed - either by the same researcher(s) or different researcher(s) - to explore new questions or use different analysis strategies that were not a part of the primary analysis (Szabo and Strang, 1997).For research involving quantitative data, SDA, and the process of sharing data for the purpose of SDA, has become ...
Secondary research, also known as desk research, is a research method that involves compiling existing data sourced from a variety of channels. This includes internal sources (e.g.in-house research) or, more commonly, external sources (such as government statistics, organizational bodies, and the internet).
Concerns about secondary data analysis when using qualitative data. The primary concerns about SDA with qualitative data surround rigor and ethics from a number of stakeholder perspectives, including research participants, funders, and the researchers themselves. Heaton (2004) suggests that a strength of secondary analysis of qualitative data ...
Qualitative Research, Secondary Analysis, Online Research Data . ... Typical Data Types . Online open access qualitative data can be viewed as belonging to one of three categories: scholarly research data; credible current and historical textual or visual data that
logical foundations of quantitative and qualitative research, and across different traditions of qualitative research (HEATON 2004). Later, in section 4.2 of this paper, I outline different types of secondary analysis that have been employed in practice, and describe the extent to which each has been used to date. 2.3 Modes of secondary analysis
Secondary analysis of data collected by another researcher for a different purpose, or SDA, is increasing in the medical and social sciences. This is not surprising, given the immense body of health care-related research performed worldwide and the potential beneficial clinical implications of the timely expansion of primary research (Johnston, 2014; Tripathy, 2013).
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research. Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and ...
Abstract. Qualitative secondary analysis (QSA) is the use of qualitative data that was collected by someone else or was collected to answer a different research question. Secondary analysis of qualitative data provides an opportunity to maximize data utility, particularly with difficult-to-reach patient populations.
Qualitative secondary analysis (QSA) is the use of qualitative data collected by someone else or to answer a different research question. Secondary analysis of qualitative data provides an opportunity to maximize data utility particularly with difficult to reach patient populations. However, QSA methods require careful consideration and ...
Common secondary research methods include data collection through the internet, libraries, archives, schools and organizational reports. Online Data. Online data is data that is gathered via the internet. In recent times, this method has become popular because the internet provides a large pool of both free and paid research resources that can ...
Abstract. Qualitative secondary analysis (QSA) is the use of qualitative data that was collected by someone else or was collected to answer a different research question. Secondary analysis of qualitative data provides an opportunity to maximize data utility, particularly with difficult-to-reach patient populations.
Although this type of secondary research will go beyond a literature review, it will still rely on research which has already been undertaken. And, "just as in primary research, secondary research designs can be either quantitative, qualitative, or a mixture of both strategies of inquiry" (Manu and Akotia, 2021, p. 4).
Secondary Research. Data Source: Involves utilizing existing data and information collected by others. Data Collection: Researchers search, select, and analyze data from published sources, reports, and databases. Time and Resources: Generally more time-efficient and cost-effective as data is already available.
Qualitative Research. Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding people's beliefs, attitudes, behaviors, and experiences through the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. It seeks to answer research questions through the examination of subjective data, such as interviews, focus groups, observations, and textual analysis.
Types of secondary data are as follows: Published data: Published data refers to data that has been published in books, magazines, newspapers, and other print media. Examples include statistical reports, market research reports, and scholarly articles. Government data: Government data refers to data collected by government agencies and departments.
the downfalls of secondary data analysis, particularly in the setting of forced migration research when using online, publicly accessible data. Step 1. Formulation of Research Questions. Setting a research aim is important regardless of whether the data is from a primary or secondary source (Taylor & Ussher, 2001).
Conducting qualitative research is time-consuming and includes conducting in-depth interviews, observing participants, transcribing interviews, and analyzing data. ... options for obtaining and assessing a qualitative data set, types of secondary qualitative analysis, and how to report this type of research in a scholarly journal. In conclusion ...
Click to continue
This practical book will guide you through finding, managing and analysing qualitative secondary data in an error-free way. Perfect for those doing dissertations and research projects, it provides an accessible introduction to the theory of secondary research and sets out the advantages and limitations of using this kind of research.
While many books and articles guide various qualitative research methods and analyses, there is currently no concise resource that explains and differentiates among the most common qualitative approaches. We believe novice qualitative researchers, students planning the design of a qualitative study or taking an introductory qualitative research course, and faculty teaching such courses can ...
Usually, desk-based research is used to collect secondary data. After arriving at the secondary data, the researcher should examine the validity and reliability. Thus, the researcher should consider the secondary data which is highly valid and well-referenced in academic articles (Creswell, 2003). Types of secondary data
Their secondary research service hinges on quality internet research. They use a combination of libraries, databases, online directories, and similar sources. They're constantly expanding their resource pool and often combine secondary research with primary research like interviews and surveys to build a comprehensive study.