Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- Sampling Methods | Types, Techniques & Examples

Sampling Methods | Types, Techniques & Examples
Published on September 19, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on June 22, 2023.
When you conduct research about a group of people, it’s rarely possible to collect data from every person in that group. Instead, you select a sample . The sample is the group of individuals who will actually participate in the research.
To draw valid conclusions from your results, you have to carefully decide how you will select a sample that is representative of the group as a whole. This is called a sampling method . There are two primary types of sampling methods that you can use in your research:
- Probability sampling involves random selection, allowing you to make strong statistical inferences about the whole group.
- Non-probability sampling involves non-random selection based on convenience or other criteria, allowing you to easily collect data.
You should clearly explain how you selected your sample in the methodology section of your paper or thesis, as well as how you approached minimizing research bias in your work.
Table of contents
Population vs. sample, probability sampling methods, non-probability sampling methods, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about sampling.
First, you need to understand the difference between a population and a sample , and identify the target population of your research.
- The population is the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about.
- The sample is the specific group of individuals that you will collect data from.
The population can be defined in terms of geographical location, age, income, or many other characteristics.
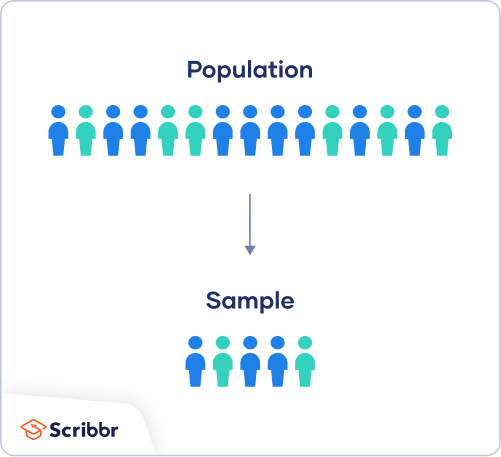
It is important to carefully define your target population according to the purpose and practicalities of your project.
If the population is very large, demographically mixed, and geographically dispersed, it might be difficult to gain access to a representative sample. A lack of a representative sample affects the validity of your results, and can lead to several research biases , particularly sampling bias .
Sampling frame
The sampling frame is the actual list of individuals that the sample will be drawn from. Ideally, it should include the entire target population (and nobody who is not part of that population).
Sample size
The number of individuals you should include in your sample depends on various factors, including the size and variability of the population and your research design. There are different sample size calculators and formulas depending on what you want to achieve with statistical analysis .
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Probability sampling means that every member of the population has a chance of being selected. It is mainly used in quantitative research . If you want to produce results that are representative of the whole population, probability sampling techniques are the most valid choice.
There are four main types of probability sample.
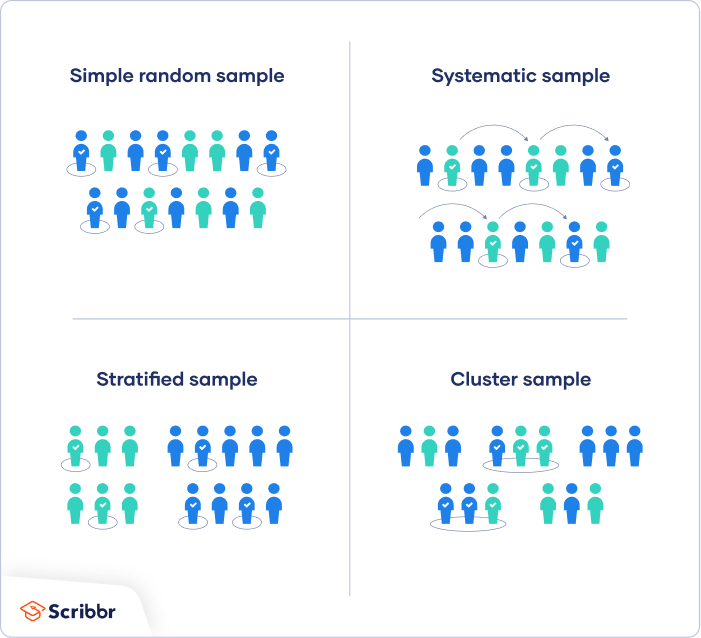
1. Simple random sampling
In a simple random sample, every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected. Your sampling frame should include the whole population.
To conduct this type of sampling, you can use tools like random number generators or other techniques that are based entirely on chance.
2. Systematic sampling
Systematic sampling is similar to simple random sampling, but it is usually slightly easier to conduct. Every member of the population is listed with a number, but instead of randomly generating numbers, individuals are chosen at regular intervals.
If you use this technique, it is important to make sure that there is no hidden pattern in the list that might skew the sample. For example, if the HR database groups employees by team, and team members are listed in order of seniority, there is a risk that your interval might skip over people in junior roles, resulting in a sample that is skewed towards senior employees.
3. Stratified sampling
Stratified sampling involves dividing the population into subpopulations that may differ in important ways. It allows you draw more precise conclusions by ensuring that every subgroup is properly represented in the sample.
To use this sampling method, you divide the population into subgroups (called strata) based on the relevant characteristic (e.g., gender identity, age range, income bracket, job role).
Based on the overall proportions of the population, you calculate how many people should be sampled from each subgroup. Then you use random or systematic sampling to select a sample from each subgroup.
4. Cluster sampling
Cluster sampling also involves dividing the population into subgroups, but each subgroup should have similar characteristics to the whole sample. Instead of sampling individuals from each subgroup, you randomly select entire subgroups.
If it is practically possible, you might include every individual from each sampled cluster. If the clusters themselves are large, you can also sample individuals from within each cluster using one of the techniques above. This is called multistage sampling .
This method is good for dealing with large and dispersed populations, but there is more risk of error in the sample, as there could be substantial differences between clusters. It’s difficult to guarantee that the sampled clusters are really representative of the whole population.
In a non-probability sample, individuals are selected based on non-random criteria, and not every individual has a chance of being included.
This type of sample is easier and cheaper to access, but it has a higher risk of sampling bias . That means the inferences you can make about the population are weaker than with probability samples, and your conclusions may be more limited. If you use a non-probability sample, you should still aim to make it as representative of the population as possible.
Non-probability sampling techniques are often used in exploratory and qualitative research . In these types of research, the aim is not to test a hypothesis about a broad population, but to develop an initial understanding of a small or under-researched population.
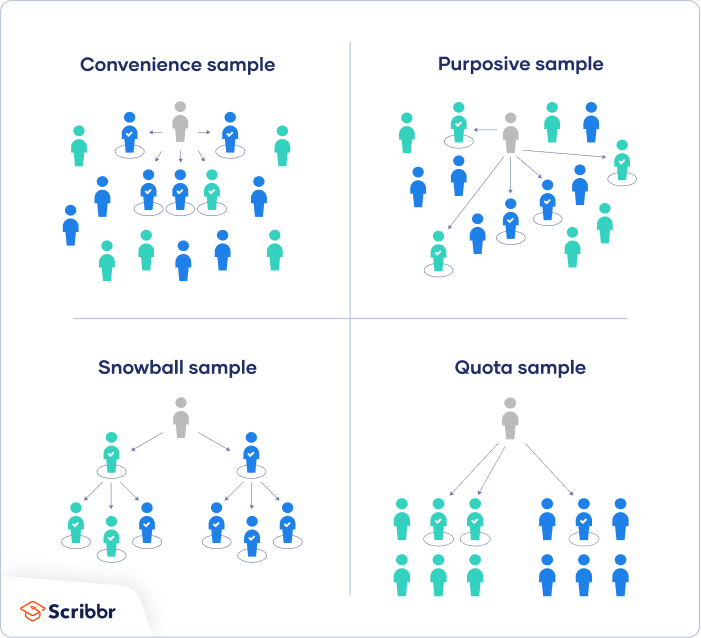
1. Convenience sampling
A convenience sample simply includes the individuals who happen to be most accessible to the researcher.
This is an easy and inexpensive way to gather initial data, but there is no way to tell if the sample is representative of the population, so it can’t produce generalizable results. Convenience samples are at risk for both sampling bias and selection bias .
2. Voluntary response sampling
Similar to a convenience sample, a voluntary response sample is mainly based on ease of access. Instead of the researcher choosing participants and directly contacting them, people volunteer themselves (e.g. by responding to a public online survey).
Voluntary response samples are always at least somewhat biased , as some people will inherently be more likely to volunteer than others, leading to self-selection bias .
3. Purposive sampling
This type of sampling, also known as judgement sampling, involves the researcher using their expertise to select a sample that is most useful to the purposes of the research.
It is often used in qualitative research , where the researcher wants to gain detailed knowledge about a specific phenomenon rather than make statistical inferences, or where the population is very small and specific. An effective purposive sample must have clear criteria and rationale for inclusion. Always make sure to describe your inclusion and exclusion criteria and beware of observer bias affecting your arguments.
4. Snowball sampling
If the population is hard to access, snowball sampling can be used to recruit participants via other participants. The number of people you have access to “snowballs” as you get in contact with more people. The downside here is also representativeness, as you have no way of knowing how representative your sample is due to the reliance on participants recruiting others. This can lead to sampling bias .
5. Quota sampling
Quota sampling relies on the non-random selection of a predetermined number or proportion of units. This is called a quota.
You first divide the population into mutually exclusive subgroups (called strata) and then recruit sample units until you reach your quota. These units share specific characteristics, determined by you prior to forming your strata. The aim of quota sampling is to control what or who makes up your sample.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Student’s t -distribution
- Normal distribution
- Null and Alternative Hypotheses
- Chi square tests
- Confidence interval
- Quartiles & Quantiles
- Cluster sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Data cleansing
- Reproducibility vs Replicability
- Peer review
- Prospective cohort study
Research bias
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Placebo effect
- Hawthorne effect
- Hindsight bias
- Affect heuristic
- Social desirability bias
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population . Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research. For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
In statistics, sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population.
Samples are used to make inferences about populations . Samples are easier to collect data from because they are practical, cost-effective, convenient, and manageable.
Probability sampling means that every member of the target population has a known chance of being included in the sample.
Probability sampling methods include simple random sampling , systematic sampling , stratified sampling , and cluster sampling .
In non-probability sampling , the sample is selected based on non-random criteria, and not every member of the population has a chance of being included.
Common non-probability sampling methods include convenience sampling , voluntary response sampling, purposive sampling , snowball sampling, and quota sampling .
In multistage sampling , or multistage cluster sampling, you draw a sample from a population using smaller and smaller groups at each stage.
This method is often used to collect data from a large, geographically spread group of people in national surveys, for example. You take advantage of hierarchical groupings (e.g., from state to city to neighborhood) to create a sample that’s less expensive and time-consuming to collect data from.
Sampling bias occurs when some members of a population are systematically more likely to be selected in a sample than others.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, June 22). Sampling Methods | Types, Techniques & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 7, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/sampling-methods/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, population vs. sample | definitions, differences & examples, simple random sampling | definition, steps & examples, sampling bias and how to avoid it | types & examples, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

What We Offer
With a comprehensive suite of qualitative and quantitative capabilities and 55 years of experience in the industry, Sago powers insights through adaptive solutions.
- Recruitment
- Communities
- Methodify® Automated research
- QualBoard® Digital Discussions
- QualMeeting® Digital Interviews
- Global Qualitative
- Global Quantitative
- In-Person Facilities
- Research Consulting
- Europe Solutions
- Neuromarketing Tools
- Trial & Jury Consulting
Who We Serve
Form deeper customer connections and make the process of answering your business questions easier. Sago delivers unparalleled access to the audiences you need through adaptive solutions and a consultative approach.
- Consumer Packaged Goods
- Financial Services
- Media Technology
- Medical Device Manufacturing
- Marketing Research
With a 55-year legacy of impact, Sago has proven we have what it takes to be a long-standing industry leader and partner. We continually advance our range of expertise to provide our clients with the highest level of confidence.
- Global Offices
- Partnerships & Certifications
- News & Media
- Researcher Events

Sago Launches AI Video Summaries on QualBoard to Streamline Data Synthesis

Sago Executive Chairman Steve Schlesinger to Receive Quirk’s Lifetime Achievement Award

16 Ways to Prepare for the Next Holiday Campaign
Drop into your new favorite insights rabbit hole and explore content created by the leading minds in market research.
- Case Studies
- Knowledge Kit

The Swing Voter Project Wisconsin: March 2024

The Deciders February 2024: African American voters in North Carolina
Get in touch

- Account Logins

Different Types of Sampling Techniques in Qualitative Research
- Resources , Blog

Key Takeaways:
- Sampling techniques in qualitative research include purposive, convenience, snowball, and theoretical sampling.
- Choosing the right sampling technique significantly impacts the accuracy and reliability of the research results.
- It’s crucial to consider the potential impact on the bias, sample diversity, and generalizability when choosing a sampling technique for your qualitative research.
Qualitative research seeks to understand social phenomena from the perspective of those experiencing them. It involves collecting non-numerical data such as interviews, observations, and written documents to gain insights into human experiences, attitudes, and behaviors. While qualitative research can provide rich and nuanced insights, the accuracy and generalizability of findings depend on the quality of the sampling process. Sampling is a critical component of qualitative research as it involves selecting a group of participants who can provide valuable insights into the research questions.
This article explores different types of sampling techniques used in qualitative research. First, we’ll provide a comprehensive overview of four standard sampling techniques used in qualitative research. and then compare and contrast these techniques to provide guidance on choosing the most appropriate method for a particular study. Additionally, you’ll find best practices for sampling and learn about ethical considerations researchers need to consider in selecting a sample. Overall, this article aims to help researchers conduct effective and high-quality sampling in qualitative research.
In this Article:
- Purposive Sampling
- Convenience Sampling
- Snowball Sampling
- Theoretical Sampling
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Sampling Technique
Practical approaches to sampling: recommended practices, final thoughts, get expert guidance on your sample needs.
Want expert input on the best sampling technique for your qualitative research project? Book a consultation for trusted advice.
Request a consultation
4 Types of Sampling Techniques and Their Applications
Sampling is a crucial aspect of qualitative research as it determines the representativeness and credibility of the data collected. Several sampling techniques are used in qualitative research, each with strengths and weaknesses. In this section, let’s explore four standard sampling techniques used in qualitative research: purposive sampling, convenience sampling, snowball sampling, and theoretical sampling. We’ll break down the definition of each technique, when to use it, and its advantages and disadvantages.
1. Purposive Sampling
Purposive sampling, or judgmental sampling, is a non-probability sampling technique commonly used in qualitative research. In purposive sampling, researchers intentionally select participants with specific characteristics or unique experiences related to the research question. The goal is to identify and recruit participants who can provide rich and diverse data to enhance the research findings.
Purposive sampling is used when researchers seek to identify individuals or groups with particular knowledge, skills, or experiences relevant to the research question. For instance, in a study examining the experiences of cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy, purposive sampling may be used to recruit participants who have undergone chemotherapy in the past year. Researchers can better understand the phenomenon under investigation by selecting individuals with relevant backgrounds.
Purposive Sampling: Strengths and Weaknesses
Purposive sampling is a powerful tool for researchers seeking to select participants who can provide valuable insight into their research question. This method is advantageous when studying groups with technical characteristics or experiences where a random selection of participants may yield different results.
One of the main advantages of purposive sampling is the ability to improve the quality and accuracy of data collected by selecting participants most relevant to the research question. This approach also enables researchers to collect data from diverse participants with unique perspectives and experiences related to the research question.
However, researchers should also be aware of potential bias when using purposive sampling. The researcher’s judgment may influence the selection of participants, resulting in a biased sample that does not accurately represent the broader population. Another disadvantage is that purposive sampling may not be representative of the more general population, which limits the generalizability of the findings. To guarantee the accuracy and dependability of data obtained through purposive sampling, researchers must provide a clear and transparent justification of their selection criteria and sampling approach. This entails outlining the specific characteristics or experiences required for participants to be included in the study and explaining the rationale behind these criteria. This level of transparency not only helps readers to evaluate the validity of the findings, but also enhances the replicability of the research.
2. Convenience Sampling
When time and resources are limited, researchers may opt for convenience sampling as a quick and cost-effective way to recruit participants. In this non-probability sampling technique, participants are selected based on their accessibility and willingness to participate rather than their suitability for the research question. Qualitative research often uses this approach to generate various perspectives and experiences.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, convenience sampling was a valuable method for researchers to collect data quickly and efficiently from participants who were easily accessible and willing to participate. For example, in a study examining the experiences of university students during the pandemic, convenience sampling allowed researchers to recruit students who were available and willing to share their experiences quickly. While the pandemic may be over, convenience sampling during this time highlights its value in urgent situations where time and resources are limited.
Convenience Sampling: Strengths and Weaknesses
Convenience sampling offers several advantages to researchers, including its ease of implementation and cost-effectiveness. This technique allows researchers to quickly and efficiently recruit participants without spending time and resources identifying and contacting potential participants. Furthermore, convenience sampling can result in a diverse pool of participants, as individuals from various backgrounds and experiences may be more likely to participate.
While convenience sampling has the advantage of being efficient, researchers need to acknowledge its limitations. One of the primary drawbacks of convenience sampling is that it is susceptible to selection bias. Participants who are more easily accessible may not be representative of the broader population, which can limit the generalizability of the findings. Furthermore, convenience sampling may lead to issues with the reliability of the results, as it may not be possible to replicate the study using the same sample or a similar one.
To mitigate these limitations, researchers should carefully define the population of interest and ensure the sample is drawn from that population. For instance, if a study is investigating the experiences of individuals with a particular medical condition, researchers can recruit participants from specialized clinics or support groups for that condition. Researchers can also use statistical techniques such as stratified sampling or weighting to adjust for potential biases in the sample.
3. Snowball Sampling
Snowball sampling, also called referral sampling, is a unique approach researchers use to recruit participants in qualitative research. The technique involves identifying a few initial participants who meet the eligibility criteria and asking them to refer others they know who also fit the requirements. The sample size grows as referrals are added, creating a chain-like structure.
Snowball sampling enables researchers to reach out to individuals who may be hard to locate through traditional sampling methods, such as members of marginalized or hidden communities. For instance, in a study examining the experiences of undocumented immigrants, snowball sampling may be used to identify and recruit participants through referrals from other undocumented immigrants.
Snowball Sampling: Strengths and Weaknesses
Snowball sampling can produce in-depth and detailed data from participants with common characteristics or experiences. Since referrals are made within a network of individuals who share similarities, researchers can gain deep insights into a specific group’s attitudes, behaviors, and perspectives.
4. Theoretical Sampling
Theoretical sampling is a sophisticated and strategic technique that can help researchers develop more in-depth and nuanced theories from their data. Instead of selecting participants based on convenience or accessibility, researchers using theoretical sampling choose participants based on their potential to contribute to the emerging themes and concepts in the data. This approach allows researchers to refine their research question and theory based on the data they collect rather than forcing their data to fit a preconceived idea.
Theoretical sampling is used when researchers conduct grounded theory research and have developed an initial theory or conceptual framework. In a study examining cancer survivors’ experiences, for example, theoretical sampling may be used to identify and recruit participants who can provide new insights into the coping strategies of survivors.
Theoretical Sampling: Strengths and Weaknesses
One of the significant advantages of theoretical sampling is that it allows researchers to refine their research question and theory based on emerging data. This means the research can be highly targeted and focused, leading to a deeper understanding of the phenomenon being studied. Additionally, theoretical sampling can generate rich and in-depth data, as participants are selected based on their potential to provide new insights into the research question.
Participants are selected based on their perceived ability to offer new perspectives on the research question. This means specific perspectives or experiences may be overrepresented in the sample, leading to an incomplete understanding of the phenomenon being studied. Additionally, theoretical sampling can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, as researchers must continuously analyze the data and recruit new participants.
To mitigate the potential for bias, researchers can take several steps. One way to reduce bias is to use a diverse team of researchers to analyze the data and make participant selection decisions. Having multiple perspectives and backgrounds can help prevent researchers from unconsciously selecting participants who fit their preconceived notions or biases.
Another solution would be to use reflexive sampling. Reflexive sampling involves selecting participants aware of the research process and provides insights into how their biases and experiences may influence their perspectives. By including participants who are reflexive about their subjectivity, researchers can generate more nuanced and self-aware findings.
Choosing the proper sampling technique is one of the most critical decisions a researcher makes when conducting a study. The preferred method can significantly impact the accuracy and reliability of the research results.
For instance, purposive sampling provides a more targeted and specific sample, which helps to answer research questions related to that particular population or phenomenon. However, this approach may also introduce bias by limiting the diversity of the sample.
Conversely, convenience sampling may offer a more diverse sample regarding demographics and backgrounds but may also introduce bias by selecting more willing or available participants.
Snowball sampling may help study hard-to-reach populations, but it can also limit the sample’s diversity as participants are selected based on their connections to existing participants.
Theoretical sampling may offer an opportunity to refine the research question and theory based on emerging data, but it can also be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
Additionally, the choice of sampling technique can impact the generalizability of the research findings. Therefore, it’s crucial to consider the potential impact on the bias, sample diversity, and generalizability when choosing a sampling technique. By doing so, researchers can select the most appropriate method for their research question and ensure the validity and reliability of their findings.
Tips for Selecting Participants
When selecting participants for a qualitative research study, it is crucial to consider the research question and the purpose of the study. In addition, researchers should identify the specific characteristics or criteria they seek in their sample and select participants accordingly.
One helpful tip for selecting participants is to use a pre-screening process to ensure potential participants meet the criteria for inclusion in the study. Another technique is using multiple recruitment methods to ensure the sample is diverse and representative of the studied population.
Ensuring Diversity in Samples
Diversity in the sample is important to ensure the study’s findings apply to a wide range of individuals and situations. One way to ensure diversity is to use stratified sampling, which involves dividing the population into subgroups and selecting participants from each subset. This helps establish that the sample is representative of the larger population.
Maintaining Ethical Considerations
When selecting participants for a qualitative research study, it is essential to ensure ethical considerations are taken into account. Researchers must ensure participants are fully informed about the study and provide their voluntary consent to participate. They must also ensure participants understand their rights and that their confidentiality and privacy will be protected.
A qualitative research study’s success hinges on its sampling technique’s effectiveness. The choice of sampling technique must be guided by the research question, the population being studied, and the purpose of the study. Whether purposive, convenience, snowball, or theoretical sampling, the primary goal is to ensure the validity and reliability of the study’s findings.
By thoughtfully weighing the pros and cons of each sampling technique, researchers can make informed decisions that lead to more reliable and accurate results. In conclusion, carefully selecting a sampling technique is integral to the success of a qualitative research study, and a thorough understanding of the available options can make all the difference in achieving high-quality research outcomes.
If you’re interested in improving your research and sampling methods, Sago offers a variety of solutions. Our qualitative research platforms, such as QualBoard and QualMeeting, can assist you in conducting research studies with precision and efficiency. Our robust global panel and recruitment options help you reach the right people. We also offer qualitative and quantitative research services to meet your research needs. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help improve your research outcomes.
Find the Right Sample for Your Qualitative Research
Trust our team to recruit the participants you need using the appropriate techniques. Book a consultation with our team to get started .

Building Trust Through Inclusive Healthcare Research Recruitment

OnDemand: Moderator Minutes: Maximizing Efficient with QualBoard – Streamline Your Projects with Support & AI

2024 Trends in Research: Fact or Fiction?

The Swing Voter Project in Michigan – February 2024

OnDemand: 5 Steps to High-Quality Data: Mitigating the Challenges of Data Quality in Quantitative Research

How Leading Brands Use Insights to Win Market Share

The Deciders January 2024: Trump-Voting Women Who Oppose Dobbs

The State of New Year’s Resolutions: A Closer Look at Mindsets and Habits

It’s Time to Change the Way We Write Screeners
Take a deep dive into your favorite market research topics

How can we help support you and your research needs?

BEFORE YOU GO
Have you considered how to harness AI in your research process? Check out our on-demand webinar for everything you need to know

- Subject List
- Take a Tour
- For Authors
- Subscriber Services
- Publications
- African American Studies
- African Studies
- American Literature
- Anthropology
- Architecture Planning and Preservation
- Art History
- Atlantic History
- Biblical Studies
- British and Irish Literature
- Childhood Studies
- Chinese Studies
- Cinema and Media Studies
- Communication
- Criminology
- Environmental Science
- Evolutionary Biology
- International Law
- International Relations
- Islamic Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Latino Studies
- Linguistics
- Literary and Critical Theory
- Medieval Studies
- Military History
- Political Science
- Public Health
- Renaissance and Reformation
- Social Work
- Urban Studies
- Victorian Literature
- Browse All Subjects
How to Subscribe
- Free Trials
In This Article Expand or collapse the "in this article" section Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Research Sampling Strategies
Introduction.
- Sampling Strategies
- Sample Size
- Qualitative Design Considerations
- Discipline Specific and Special Considerations
- Sampling Strategies Unique to Mixed Methods Designs
Related Articles Expand or collapse the "related articles" section about
About related articles close popup.
Lorem Ipsum Sit Dolor Amet
Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Aliquam ligula odio, euismod ut aliquam et, vestibulum nec risus. Nulla viverra, arcu et iaculis consequat, justo diam ornare tellus, semper ultrices tellus nunc eu tellus.
- Mixed Methods Research
- Qualitative Research Design
- Quantitative Research Designs in Educational Research

Other Subject Areas
Forthcoming articles expand or collapse the "forthcoming articles" section.
- Gender, Power, and Politics in the Academy
- Girls' Education in the Developing World
- Non-Formal & Informal Environmental Education
- Find more forthcoming articles...
- Export Citations
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Research Sampling Strategies by Timothy C. Guetterman LAST MODIFIED: 26 February 2020 DOI: 10.1093/obo/9780199756810-0241
Sampling is a critical, often overlooked aspect of the research process. The importance of sampling extends to the ability to draw accurate inferences, and it is an integral part of qualitative guidelines across research methods. Sampling considerations are important in quantitative and qualitative research when considering a target population and when drawing a sample that will either allow us to generalize (i.e., quantitatively) or go into sufficient depth (i.e., qualitatively). While quantitative research is generally concerned with probability-based approaches, qualitative research typically uses nonprobability purposeful sampling approaches. Scholars generally focus on two major sampling topics: sampling strategies and sample sizes. Or simply, researchers should think about who to include and how many; both of these concerns are key. Mixed methods studies have both qualitative and quantitative sampling considerations. However, mixed methods studies also have unique considerations based on the relationship of quantitative and qualitative research within the study.
Sampling in Qualitative Research
Sampling in qualitative research may be divided into two major areas: overall sampling strategies and issues around sample size. Sampling strategies refers to the process of sampling and how to design a sampling. Qualitative sampling typically follows a nonprobability-based approach, such as purposive or purposeful sampling where participants or other units of analysis are selected intentionally for their ability to provide information to address research questions. Sample size refers to how many participants or other units are needed to address research questions. The methodological literature about sampling tends to fall into these two broad categories, though some articles, chapters, and books cover both concepts. Others have connected sampling to the type of qualitative design that is employed. Additionally, researchers might consider discipline specific sampling issues as much research does tend to operate within disciplinary views and constraints. Scholars in many disciplines have examined sampling around specific topics, research problems, or disciplines and provide guidance to making sampling decisions, such as appropriate strategies and sample size.
back to top
Users without a subscription are not able to see the full content on this page. Please subscribe or login .
Oxford Bibliographies Online is available by subscription and perpetual access to institutions. For more information or to contact an Oxford Sales Representative click here .
- About Education »
- Meet the Editorial Board »
- Academic Achievement
- Academic Audit for Universities
- Academic Freedom and Tenure in the United States
- Action Research in Education
- Adjuncts in Higher Education in the United States
- Administrator Preparation
- Adolescence
- Advanced Placement and International Baccalaureate Courses
- Advocacy and Activism in Early Childhood
- African American Racial Identity and Learning
- Alaska Native Education
- Alternative Certification Programs for Educators
- Alternative Schools
- American Indian Education
- Animals in Environmental Education
- Art Education
- Artificial Intelligence and Learning
- Assessing School Leader Effectiveness
- Assessment, Behavioral
- Assessment, Educational
- Assessment in Early Childhood Education
- Assistive Technology
- Augmented Reality in Education
- Beginning-Teacher Induction
- Bilingual Education and Bilingualism
- Black Undergraduate Women: Critical Race and Gender Perspe...
- Blended Learning
- Case Study in Education Research
- Changing Professional and Academic Identities
- Character Education
- Children’s and Young Adult Literature
- Children's Beliefs about Intelligence
- Children's Rights in Early Childhood Education
- Citizenship Education
- Civic and Social Engagement of Higher Education
- Classroom Learning Environments: Assessing and Investigati...
- Classroom Management
- Coherent Instructional Systems at the School and School Sy...
- College Admissions in the United States
- College Athletics in the United States
- Community Relations
- Comparative Education
- Computer-Assisted Language Learning
- Computer-Based Testing
- Conceptualizing, Measuring, and Evaluating Improvement Net...
- Continuous Improvement and "High Leverage" Educational Pro...
- Counseling in Schools
- Critical Approaches to Gender in Higher Education
- Critical Perspectives on Educational Innovation and Improv...
- Critical Race Theory
- Crossborder and Transnational Higher Education
- Cross-National Research on Continuous Improvement
- Cross-Sector Research on Continuous Learning and Improveme...
- Cultural Diversity in Early Childhood Education
- Culturally Responsive Leadership
- Culturally Responsive Pedagogies
- Culturally Responsive Teacher Education in the United Stat...
- Curriculum Design
- Data Collection in Educational Research
- Data-driven Decision Making in the United States
- Deaf Education
- Desegregation and Integration
- Design Thinking and the Learning Sciences: Theoretical, Pr...
- Development, Moral
- Dialogic Pedagogy
- Digital Age Teacher, The
- Digital Citizenship
- Digital Divides
- Disabilities
- Distance Learning
- Distributed Leadership
- Doctoral Education and Training
- Early Childhood Education and Care (ECEC) in Denmark
- Early Childhood Education and Development in Mexico
- Early Childhood Education in Aotearoa New Zealand
- Early Childhood Education in Australia
- Early Childhood Education in China
- Early Childhood Education in Europe
- Early Childhood Education in Sub-Saharan Africa
- Early Childhood Education in Sweden
- Early Childhood Education Pedagogy
- Early Childhood Education Policy
- Early Childhood Education, The Arts in
- Early Childhood Mathematics
- Early Childhood Science
- Early Childhood Teacher Education
- Early Childhood Teachers in Aotearoa New Zealand
- Early Years Professionalism and Professionalization Polici...
- Economics of Education
- Education For Children with Autism
- Education for Sustainable Development
- Education Leadership, Empirical Perspectives in
- Education of Native Hawaiian Students
- Education Reform and School Change
- Educational Statistics for Longitudinal Research
- Educator Partnerships with Parents and Families with a Foc...
- Emotional and Affective Issues in Environmental and Sustai...
- Emotional and Behavioral Disorders
- Environmental and Science Education: Overlaps and Issues
- Environmental Education
- Environmental Education in Brazil
- Epistemic Beliefs
- Equity and Improvement: Engaging Communities in Educationa...
- Equity, Ethnicity, Diversity, and Excellence in Education
- Ethical Research with Young Children
- Ethics and Education
- Ethics of Teaching
- Ethnic Studies
- Evidence-Based Communication Assessment and Intervention
- Family and Community Partnerships in Education
- Family Day Care
- Federal Government Programs and Issues
- Feminization of Labor in Academia
- Finance, Education
- Financial Aid
- Formative Assessment
- Future-Focused Education
- Gender and Achievement
- Gender and Alternative Education
- Gender-Based Violence on University Campuses
- Gifted Education
- Global Mindedness and Global Citizenship Education
- Global University Rankings
- Governance, Education
- Grounded Theory
- Growth of Effective Mental Health Services in Schools in t...
- Higher Education and Globalization
- Higher Education and the Developing World
- Higher Education Faculty Characteristics and Trends in the...
- Higher Education Finance
- Higher Education Governance
- Higher Education Graduate Outcomes and Destinations
- Higher Education in Africa
- Higher Education in China
- Higher Education in Latin America
- Higher Education in the United States, Historical Evolutio...
- Higher Education, International Issues in
- Higher Education Management
- Higher Education Policy
- Higher Education Research
- Higher Education Student Assessment
- High-stakes Testing
- History of Early Childhood Education in the United States
- History of Education in the United States
- History of Technology Integration in Education
- Homeschooling
- Inclusion in Early Childhood: Difference, Disability, and ...
- Inclusive Education
- Indigenous Education in a Global Context
- Indigenous Learning Environments
- Indigenous Students in Higher Education in the United Stat...
- Infant and Toddler Pedagogy
- Inservice Teacher Education
- Integrating Art across the Curriculum
- Intelligence
- Intensive Interventions for Children and Adolescents with ...
- International Perspectives on Academic Freedom
- Intersectionality and Education
- Knowledge Development in Early Childhood
- Leadership Development, Coaching and Feedback for
- Leadership in Early Childhood Education
- Leadership Training with an Emphasis on the United States
- Learning Analytics in Higher Education
- Learning Difficulties
- Learning, Lifelong
- Learning, Multimedia
- Learning Strategies
- Legal Matters and Education Law
- LGBT Youth in Schools
- Linguistic Diversity
- Linguistically Inclusive Pedagogy
- Literacy Development and Language Acquisition
- Literature Reviews
- Mathematics Identity
- Mathematics Instruction and Interventions for Students wit...
- Mathematics Teacher Education
- Measurement for Improvement in Education
- Measurement in Education in the United States
- Meta-Analysis and Research Synthesis in Education
- Methodological Approaches for Impact Evaluation in Educati...
- Methodologies for Conducting Education Research
- Mindfulness, Learning, and Education
- Motherscholars
- Multiliteracies in Early Childhood Education
- Multiple Documents Literacy: Theory, Research, and Applica...
- Multivariate Research Methodology
- Museums, Education, and Curriculum
- Music Education
- Narrative Research in Education
- Native American Studies
- Note-Taking
- Numeracy Education
- One-to-One Technology in the K-12 Classroom
- Online Education
- Open Education
- Organizing for Continuous Improvement in Education
- Organizing Schools for the Inclusion of Students with Disa...
- Outdoor Play and Learning
- Outdoor Play and Learning in Early Childhood Education
- Pedagogical Leadership
- Pedagogy of Teacher Education, A
- Performance Objectives and Measurement
- Performance-based Research Assessment in Higher Education
- Performance-based Research Funding
- Phenomenology in Educational Research
- Philosophy of Education
- Physical Education
- Podcasts in Education
- Policy Context of United States Educational Innovation and...
- Politics of Education
- Portable Technology Use in Special Education Programs and ...
- Post-humanism and Environmental Education
- Pre-Service Teacher Education
- Problem Solving
- Productivity and Higher Education
- Professional Development
- Professional Learning Communities
- Program Evaluation
- Programs and Services for Students with Emotional or Behav...
- Psychology Learning and Teaching
- Psychometric Issues in the Assessment of English Language ...
- Qualitative Data Analysis Techniques
- Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Research Samp...
- Queering the English Language Arts (ELA) Writing Classroom
- Race and Affirmative Action in Higher Education
- Reading Education
- Refugee and New Immigrant Learners
- Relational and Developmental Trauma and Schools
- Relational Pedagogies in Early Childhood Education
- Reliability in Educational Assessments
- Religion in Elementary and Secondary Education in the Unit...
- Researcher Development and Skills Training within the Cont...
- Research-Practice Partnerships in Education within the Uni...
- Response to Intervention
- Restorative Practices
- Risky Play in Early Childhood Education
- Scale and Sustainability of Education Innovation and Impro...
- Scaling Up Research-based Educational Practices
- School Accreditation
- School Choice
- School Culture
- School District Budgeting and Financial Management in the ...
- School Improvement through Inclusive Education
- School Reform
- Schools, Private and Independent
- School-Wide Positive Behavior Support
- Science Education
- Secondary to Postsecondary Transition Issues
- Self-Regulated Learning
- Self-Study of Teacher Education Practices
- Service-Learning
- Severe Disabilities
- Single Salary Schedule
- Single-sex Education
- Single-Subject Research Design
- Social Context of Education
- Social Justice
- Social Network Analysis
- Social Pedagogy
- Social Science and Education Research
- Social Studies Education
- Sociology of Education
- Standards-Based Education
- Statistical Assumptions
- Student Access, Equity, and Diversity in Higher Education
- Student Assignment Policy
- Student Engagement in Tertiary Education
- Student Learning, Development, Engagement, and Motivation ...
- Student Participation
- Student Voice in Teacher Development
- Sustainability Education in Early Childhood Education
- Sustainability in Early Childhood Education
- Sustainability in Higher Education
- Teacher Beliefs and Epistemologies
- Teacher Collaboration in School Improvement
- Teacher Evaluation and Teacher Effectiveness
- Teacher Preparation
- Teacher Training and Development
- Teacher Unions and Associations
- Teacher-Student Relationships
- Teaching Critical Thinking
- Technologies, Teaching, and Learning in Higher Education
- Technology Education in Early Childhood
- Technology, Educational
- Technology-based Assessment
- The Bologna Process
- The Regulation of Standards in Higher Education
- Theories of Educational Leadership
- Three Conceptions of Literacy: Media, Narrative, and Gamin...
- Tracking and Detracking
- Traditions of Quality Improvement in Education
- Transformative Learning
- Transitions in Early Childhood Education
- Tribally Controlled Colleges and Universities in the Unite...
- Understanding the Psycho-Social Dimensions of Schools and ...
- University Faculty Roles and Responsibilities in the Unite...
- Using Ethnography in Educational Research
- Value of Higher Education for Students and Other Stakehold...
- Virtual Learning Environments
- Vocational and Technical Education
- Wellness and Well-Being in Education
- Women's and Gender Studies
- Young Children and Spirituality
- Young Children's Learning Dispositions
- Young Children's Working Theories
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
Powered by:
- [66.249.64.20|185.80.149.115]
- 185.80.149.115

Chapter 5. Sampling
Introduction.
Most Americans will experience unemployment at some point in their lives. Sarah Damaske ( 2021 ) was interested in learning about how men and women experience unemployment differently. To answer this question, she interviewed unemployed people. After conducting a “pilot study” with twenty interviewees, she realized she was also interested in finding out how working-class and middle-class persons experienced unemployment differently. She found one hundred persons through local unemployment offices. She purposefully selected a roughly equal number of men and women and working-class and middle-class persons for the study. This would allow her to make the kinds of comparisons she was interested in. She further refined her selection of persons to interview:
I decided that I needed to be able to focus my attention on gender and class; therefore, I interviewed only people born between 1962 and 1987 (ages 28–52, the prime working and child-rearing years), those who worked full-time before their job loss, those who experienced an involuntary job loss during the past year, and those who did not lose a job for cause (e.g., were not fired because of their behavior at work). ( 244 )
The people she ultimately interviewed compose her sample. They represent (“sample”) the larger population of the involuntarily unemployed. This “theoretically informed stratified sampling design” allowed Damaske “to achieve relatively equal distribution of participation across gender and class,” but it came with some limitations. For one, the unemployment centers were located in primarily White areas of the country, so there were very few persons of color interviewed. Qualitative researchers must make these kinds of decisions all the time—who to include and who not to include. There is never an absolutely correct decision, as the choice is linked to the particular research question posed by the particular researcher, although some sampling choices are more compelling than others. In this case, Damaske made the choice to foreground both gender and class rather than compare all middle-class men and women or women of color from different class positions or just talk to White men. She leaves the door open for other researchers to sample differently. Because science is a collective enterprise, it is most likely someone will be inspired to conduct a similar study as Damaske’s but with an entirely different sample.
This chapter is all about sampling. After you have developed a research question and have a general idea of how you will collect data (observations or interviews), how do you go about actually finding people and sites to study? Although there is no “correct number” of people to interview, the sample should follow the research question and research design. You might remember studying sampling in a quantitative research course. Sampling is important here too, but it works a bit differently. Unlike quantitative research, qualitative research involves nonprobability sampling. This chapter explains why this is so and what qualities instead make a good sample for qualitative research.
Quick Terms Refresher
- The population is the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about.
- The sample is the specific group of individuals that you will collect data from.
- Sampling frame is the actual list of individuals that the sample will be drawn from. Ideally, it should include the entire target population (and nobody who is not part of that population).
- Sample size is how many individuals (or units) are included in your sample.
The “Who” of Your Research Study
After you have turned your general research interest into an actual research question and identified an approach you want to take to answer that question, you will need to specify the people you will be interviewing or observing. In most qualitative research, the objects of your study will indeed be people. In some cases, however, your objects might be content left by people (e.g., diaries, yearbooks, photographs) or documents (official or unofficial) or even institutions (e.g., schools, medical centers) and locations (e.g., nation-states, cities). Chances are, whatever “people, places, or things” are the objects of your study, you will not really be able to talk to, observe, or follow every single individual/object of the entire population of interest. You will need to create a sample of the population . Sampling in qualitative research has different purposes and goals than sampling in quantitative research. Sampling in both allows you to say something of interest about a population without having to include the entire population in your sample.
We begin this chapter with the case of a population of interest composed of actual people. After we have a better understanding of populations and samples that involve real people, we’ll discuss sampling in other types of qualitative research, such as archival research, content analysis, and case studies. We’ll then move to a larger discussion about the difference between sampling in qualitative research generally versus quantitative research, then we’ll move on to the idea of “theoretical” generalizability, and finally, we’ll conclude with some practical tips on the correct “number” to include in one’s sample.
Sampling People
To help think through samples, let’s imagine we want to know more about “vaccine hesitancy.” We’ve all lived through 2020 and 2021, and we know that a sizable number of people in the United States (and elsewhere) were slow to accept vaccines, even when these were freely available. By some accounts, about one-third of Americans initially refused vaccination. Why is this so? Well, as I write this in the summer of 2021, we know that some people actively refused the vaccination, thinking it was harmful or part of a government plot. Others were simply lazy or dismissed the necessity. And still others were worried about harmful side effects. The general population of interest here (all adult Americans who were not vaccinated by August 2021) may be as many as eighty million people. We clearly cannot talk to all of them. So we will have to narrow the number to something manageable. How can we do this?
First, we have to think about our actual research question and the form of research we are conducting. I am going to begin with a quantitative research question. Quantitative research questions tend to be simpler to visualize, at least when we are first starting out doing social science research. So let us say we want to know what percentage of each kind of resistance is out there and how race or class or gender affects vaccine hesitancy. Again, we don’t have the ability to talk to everyone. But harnessing what we know about normal probability distributions (see quantitative methods for more on this), we can find this out through a sample that represents the general population. We can’t really address these particular questions if we only talk to White women who go to college with us. And if you are really trying to generalize the specific findings of your sample to the larger population, you will have to employ probability sampling , a sampling technique where a researcher sets a selection of a few criteria and chooses members of a population randomly. Why randomly? If truly random, all the members have an equal opportunity to be a part of the sample, and thus we avoid the problem of having only our friends and neighbors (who may be very different from other people in the population) in the study. Mathematically, there is going to be a certain number that will be large enough to allow us to generalize our particular findings from our sample population to the population at large. It might surprise you how small that number can be. Election polls of no more than one thousand people are routinely used to predict actual election outcomes of millions of people. Below that number, however, you will not be able to make generalizations. Talking to five people at random is simply not enough people to predict a presidential election.
In order to answer quantitative research questions of causality, one must employ probability sampling. Quantitative researchers try to generalize their findings to a larger population. Samples are designed with that in mind. Qualitative researchers ask very different questions, though. Qualitative research questions are not about “how many” of a certain group do X (in this case, what percentage of the unvaccinated hesitate for concern about safety rather than reject vaccination on political grounds). Qualitative research employs nonprobability sampling . By definition, not everyone has an equal opportunity to be included in the sample. The researcher might select White women they go to college with to provide insight into racial and gender dynamics at play. Whatever is found by doing so will not be generalizable to everyone who has not been vaccinated, or even all White women who have not been vaccinated, or even all White women who have not been vaccinated who are in this particular college. That is not the point of qualitative research at all. This is a really important distinction, so I will repeat in bold: Qualitative researchers are not trying to statistically generalize specific findings to a larger population . They have not failed when their sample cannot be generalized, as that is not the point at all.
In the previous paragraph, I said it would be perfectly acceptable for a qualitative researcher to interview five White women with whom she goes to college about their vaccine hesitancy “to provide insight into racial and gender dynamics at play.” The key word here is “insight.” Rather than use a sample as a stand-in for the general population, as quantitative researchers do, the qualitative researcher uses the sample to gain insight into a process or phenomenon. The qualitative researcher is not going to be content with simply asking each of the women to state her reason for not being vaccinated and then draw conclusions that, because one in five of these women were concerned about their health, one in five of all people were also concerned about their health. That would be, frankly, a very poor study indeed. Rather, the qualitative researcher might sit down with each of the women and conduct a lengthy interview about what the vaccine means to her, why she is hesitant, how she manages her hesitancy (how she explains it to her friends), what she thinks about others who are unvaccinated, what she thinks of those who have been vaccinated, and what she knows or thinks she knows about COVID-19. The researcher might include specific interview questions about the college context, about their status as White women, about the political beliefs they hold about racism in the US, and about how their own political affiliations may or may not provide narrative scripts about “protective whiteness.” There are many interesting things to ask and learn about and many things to discover. Where a quantitative researcher begins with clear parameters to set their population and guide their sample selection process, the qualitative researcher is discovering new parameters, making it impossible to engage in probability sampling.
Looking at it this way, sampling for qualitative researchers needs to be more strategic. More theoretically informed. What persons can be interviewed or observed that would provide maximum insight into what is still unknown? In other words, qualitative researchers think through what cases they could learn the most from, and those are the cases selected to study: “What would be ‘bias’ in statistical sampling, and therefore a weakness, becomes intended focus in qualitative sampling, and therefore a strength. The logic and power of purposeful sampling like in selecting information-rich cases for study in depth. Information-rich cases are those from which one can learn a great deal about issues of central importance to the purpose of the inquiry, thus the term purposeful sampling” ( Patton 2002:230 ; emphases in the original).
Before selecting your sample, though, it is important to clearly identify the general population of interest. You need to know this before you can determine the sample. In our example case, it is “adult Americans who have not yet been vaccinated.” Depending on the specific qualitative research question, however, it might be “adult Americans who have been vaccinated for political reasons” or even “college students who have not been vaccinated.” What insights are you seeking? Do you want to know how politics is affecting vaccination? Or do you want to understand how people manage being an outlier in a particular setting (unvaccinated where vaccinations are heavily encouraged if not required)? More clearly stated, your population should align with your research question . Think back to the opening story about Damaske’s work studying the unemployed. She drew her sample narrowly to address the particular questions she was interested in pursuing. Knowing your questions or, at a minimum, why you are interested in the topic will allow you to draw the best sample possible to achieve insight.
Once you have your population in mind, how do you go about getting people to agree to be in your sample? In qualitative research, it is permissible to find people by convenience. Just ask for people who fit your sample criteria and see who shows up. Or reach out to friends and colleagues and see if they know anyone that fits. Don’t let the name convenience sampling mislead you; this is not exactly “easy,” and it is certainly a valid form of sampling in qualitative research. The more unknowns you have about what you will find, the more convenience sampling makes sense. If you don’t know how race or class or political affiliation might matter, and your population is unvaccinated college students, you can construct a sample of college students by placing an advertisement in the student paper or posting a flyer on a notice board. Whoever answers is your sample. That is what is meant by a convenience sample. A common variation of convenience sampling is snowball sampling . This is particularly useful if your target population is hard to find. Let’s say you posted a flyer about your study and only two college students responded. You could then ask those two students for referrals. They tell their friends, and those friends tell other friends, and, like a snowball, your sample gets bigger and bigger.
Researcher Note
Gaining Access: When Your Friend Is Your Research Subject
My early experience with qualitative research was rather unique. At that time, I needed to do a project that required me to interview first-generation college students, and my friends, with whom I had been sharing a dorm for two years, just perfectly fell into the sample category. Thus, I just asked them and easily “gained my access” to the research subject; I know them, we are friends, and I am part of them. I am an insider. I also thought, “Well, since I am part of the group, I can easily understand their language and norms, I can capture their honesty, read their nonverbal cues well, will get more information, as they will be more opened to me because they trust me.” All in all, easy access with rich information. But, gosh, I did not realize that my status as an insider came with a price! When structuring the interview questions, I began to realize that rather than focusing on the unique experiences of my friends, I mostly based the questions on my own experiences, assuming we have similar if not the same experiences. I began to struggle with my objectivity and even questioned my role; am I doing this as part of the group or as a researcher? I came to know later that my status as an insider or my “positionality” may impact my research. It not only shapes the process of data collection but might heavily influence my interpretation of the data. I came to realize that although my inside status came with a lot of benefits (especially for access), it could also bring some drawbacks.
—Dede Setiono, PhD student focusing on international development and environmental policy, Oregon State University
The more you know about what you might find, the more strategic you can be. If you wanted to compare how politically conservative and politically liberal college students explained their vaccine hesitancy, for example, you might construct a sample purposively, finding an equal number of both types of students so that you can make those comparisons in your analysis. This is what Damaske ( 2021 ) did. You could still use convenience or snowball sampling as a way of recruitment. Post a flyer at the conservative student club and then ask for referrals from the one student that agrees to be interviewed. As with convenience sampling, there are variations of purposive sampling as well as other names used (e.g., judgment, quota, stratified, criterion, theoretical). Try not to get bogged down in the nomenclature; instead, focus on identifying the general population that matches your research question and then using a sampling method that is most likely to provide insight, given the types of questions you have.
There are all kinds of ways of being strategic with sampling in qualitative research. Here are a few of my favorite techniques for maximizing insight:
- Consider using “extreme” or “deviant” cases. Maybe your college houses a prominent anti-vaxxer who has written about and demonstrated against the college’s policy on vaccines. You could learn a lot from that single case (depending on your research question, of course).
- Consider “intensity”: people and cases and circumstances where your questions are more likely to feature prominently (but not extremely or deviantly). For example, you could compare those who volunteer at local Republican and Democratic election headquarters during an election season in a study on why party matters. Those who volunteer are more likely to have something to say than those who are more apathetic.
- Maximize variation, as with the case of “politically liberal” versus “politically conservative,” or include an array of social locations (young vs. old; Northwest vs. Southeast region). This kind of heterogeneity sampling can capture and describe the central themes that cut across the variations: any common patterns that emerge, even in this wildly mismatched sample, are probably important to note!
- Rather than maximize the variation, you could select a small homogenous sample to describe some particular subgroup in depth. Focus groups are often the best form of data collection for homogeneity sampling.
- Think about which cases are “critical” or politically important—ones that “if it happens here, it would happen anywhere” or a case that is politically sensitive, as with the single “blue” (Democratic) county in a “red” (Republican) state. In both, you are choosing a site that would yield the most information and have the greatest impact on the development of knowledge.
- On the other hand, sometimes you want to select the “typical”—the typical college student, for example. You are trying to not generalize from the typical but illustrate aspects that may be typical of this case or group. When selecting for typicality, be clear with yourself about why the typical matches your research questions (and who might be excluded or marginalized in doing so).
- Finally, it is often a good idea to look for disconfirming cases : if you are at the stage where you have a hypothesis (of sorts), you might select those who do not fit your hypothesis—you will surely learn something important there. They may be “exceptions that prove the rule” or exceptions that force you to alter your findings in order to make sense of these additional cases.
In addition to all these sampling variations, there is the theoretical approach taken by grounded theorists in which the researcher samples comparative people (or events) on the basis of their potential to represent important theoretical constructs. The sample, one can say, is by definition representative of the phenomenon of interest. It accompanies the constant comparative method of analysis. In the words of the funders of Grounded Theory , “Theoretical sampling is sampling on the basis of the emerging concepts, with the aim being to explore the dimensional range or varied conditions along which the properties of the concepts vary” ( Strauss and Corbin 1998:73 ).
When Your Population is Not Composed of People
I think it is easiest for most people to think of populations and samples in terms of people, but sometimes our units of analysis are not actually people. They could be places or institutions. Even so, you might still want to talk to people or observe the actions of people to understand those places or institutions. Or not! In the case of content analyses (see chapter 17), you won’t even have people involved at all but rather documents or films or photographs or news clippings. Everything we have covered about sampling applies to other units of analysis too. Let’s work through some examples.
Case Studies
When constructing a case study, it is helpful to think of your cases as sample populations in the same way that we considered people above. If, for example, you are comparing campus climates for diversity, your overall population may be “four-year college campuses in the US,” and from there you might decide to study three college campuses as your sample. Which three? Will you use purposeful sampling (perhaps [1] selecting three colleges in Oregon that are different sizes or [2] selecting three colleges across the US located in different political cultures or [3] varying the three colleges by racial makeup of the student body)? Or will you select three colleges at random, out of convenience? There are justifiable reasons for all approaches.
As with people, there are different ways of maximizing insight in your sample selection. Think about the following rationales: typical, diverse, extreme, deviant, influential, crucial, or even embodying a particular “pathway” ( Gerring 2008 ). When choosing a case or particular research site, Rubin ( 2021 ) suggests you bear in mind, first, what you are leaving out by selecting this particular case/site; second, what you might be overemphasizing by studying this case/site and not another; and, finally, whether you truly need to worry about either of those things—“that is, what are the sources of bias and how bad are they for what you are trying to do?” ( 89 ).
Once you have selected your cases, you may still want to include interviews with specific people or observations at particular sites within those cases. Then you go through possible sampling approaches all over again to determine which people will be contacted.
Content: Documents, Narrative Accounts, And So On
Although not often discussed as sampling, your selection of documents and other units to use in various content/historical analyses is subject to similar considerations. When you are asking quantitative-type questions (percentages and proportionalities of a general population), you will want to follow probabilistic sampling. For example, I created a random sample of accounts posted on the website studentloanjustice.org to delineate the types of problems people were having with student debt ( Hurst 2007 ). Even though my data was qualitative (narratives of student debt), I was actually asking a quantitative-type research question, so it was important that my sample was representative of the larger population (debtors who posted on the website). On the other hand, when you are asking qualitative-type questions, the selection process should be very different. In that case, use nonprobabilistic techniques, either convenience (where you are really new to this data and do not have the ability to set comparative criteria or even know what a deviant case would be) or some variant of purposive sampling. Let’s say you were interested in the visual representation of women in media published in the 1950s. You could select a national magazine like Time for a “typical” representation (and for its convenience, as all issues are freely available on the web and easy to search). Or you could compare one magazine known for its feminist content versus one antifeminist. The point is, sample selection is important even when you are not interviewing or observing people.
Goals of Qualitative Sampling versus Goals of Quantitative Sampling
We have already discussed some of the differences in the goals of quantitative and qualitative sampling above, but it is worth further discussion. The quantitative researcher seeks a sample that is representative of the population of interest so that they may properly generalize the results (e.g., if 80 percent of first-gen students in the sample were concerned with costs of college, then we can say there is a strong likelihood that 80 percent of first-gen students nationally are concerned with costs of college). The qualitative researcher does not seek to generalize in this way . They may want a representative sample because they are interested in typical responses or behaviors of the population of interest, but they may very well not want a representative sample at all. They might want an “extreme” or deviant case to highlight what could go wrong with a particular situation, or maybe they want to examine just one case as a way of understanding what elements might be of interest in further research. When thinking of your sample, you will have to know why you are selecting the units, and this relates back to your research question or sets of questions. It has nothing to do with having a representative sample to generalize results. You may be tempted—or it may be suggested to you by a quantitatively minded member of your committee—to create as large and representative a sample as you possibly can to earn credibility from quantitative researchers. Ignore this temptation or suggestion. The only thing you should be considering is what sample will best bring insight into the questions guiding your research. This has implications for the number of people (or units) in your study as well, which is the topic of the next section.
What is the Correct “Number” to Sample?
Because we are not trying to create a generalizable representative sample, the guidelines for the “number” of people to interview or news stories to code are also a bit more nebulous. There are some brilliant insightful studies out there with an n of 1 (meaning one person or one account used as the entire set of data). This is particularly so in the case of autoethnography, a variation of ethnographic research that uses the researcher’s own subject position and experiences as the basis of data collection and analysis. But it is true for all forms of qualitative research. There are no hard-and-fast rules here. The number to include is what is relevant and insightful to your particular study.
That said, humans do not thrive well under such ambiguity, and there are a few helpful suggestions that can be made. First, many qualitative researchers talk about “saturation” as the end point for data collection. You stop adding participants when you are no longer getting any new information (or so very little that the cost of adding another interview subject or spending another day in the field exceeds any likely benefits to the research). The term saturation was first used here by Glaser and Strauss ( 1967 ), the founders of Grounded Theory. Here is their explanation: “The criterion for judging when to stop sampling the different groups pertinent to a category is the category’s theoretical saturation . Saturation means that no additional data are being found whereby the sociologist can develop properties of the category. As he [or she] sees similar instances over and over again, the researcher becomes empirically confident that a category is saturated. [They go] out of [their] way to look for groups that stretch diversity of data as far as possible, just to make certain that saturation is based on the widest possible range of data on the category” ( 61 ).
It makes sense that the term was developed by grounded theorists, since this approach is rather more open-ended than other approaches used by qualitative researchers. With so much left open, having a guideline of “stop collecting data when you don’t find anything new” is reasonable. However, saturation can’t help much when first setting out your sample. How do you know how many people to contact to interview? What number will you put down in your institutional review board (IRB) protocol (see chapter 8)? You may guess how many people or units it will take to reach saturation, but there really is no way to know in advance. The best you can do is think about your population and your questions and look at what others have done with similar populations and questions.
Here are some suggestions to use as a starting point: For phenomenological studies, try to interview at least ten people for each major category or group of people . If you are comparing male-identified, female-identified, and gender-neutral college students in a study on gender regimes in social clubs, that means you might want to design a sample of thirty students, ten from each group. This is the minimum suggested number. Damaske’s ( 2021 ) sample of one hundred allows room for up to twenty-five participants in each of four “buckets” (e.g., working-class*female, working-class*male, middle-class*female, middle-class*male). If there is more than one comparative group (e.g., you are comparing students attending three different colleges, and you are comparing White and Black students in each), you can sometimes reduce the number for each group in your sample to five for, in this case, thirty total students. But that is really a bare minimum you will want to go. A lot of people will not trust you with only “five” cases in a bucket. Lareau ( 2021:24 ) advises a minimum of seven or nine for each bucket (or “cell,” in her words). The point is to think about what your analyses might look like and how comfortable you will be with a certain number of persons fitting each category.
Because qualitative research takes so much time and effort, it is rare for a beginning researcher to include more than thirty to fifty people or units in the study. You may not be able to conduct all the comparisons you might want simply because you cannot manage a larger sample. In that case, the limits of who you can reach or what you can include may influence you to rethink an original overcomplicated research design. Rather than include students from every racial group on a campus, for example, you might want to sample strategically, thinking about the most contrast (insightful), possibly excluding majority-race (White) students entirely, and simply using previous literature to fill in gaps in our understanding. For example, one of my former students was interested in discovering how race and class worked at a predominantly White institution (PWI). Due to time constraints, she simplified her study from an original sample frame of middle-class and working-class domestic Black and international African students (four buckets) to a sample frame of domestic Black and international African students (two buckets), allowing the complexities of class to come through individual accounts rather than from part of the sample frame. She wisely decided not to include White students in the sample, as her focus was on how minoritized students navigated the PWI. She was able to successfully complete her project and develop insights from the data with fewer than twenty interviewees. [1]
But what if you had unlimited time and resources? Would it always be better to interview more people or include more accounts, documents, and units of analysis? No! Your sample size should reflect your research question and the goals you have set yourself. Larger numbers can sometimes work against your goals. If, for example, you want to help bring out individual stories of success against the odds, adding more people to the analysis can end up drowning out those individual stories. Sometimes, the perfect size really is one (or three, or five). It really depends on what you are trying to discover and achieve in your study. Furthermore, studies of one hundred or more (people, documents, accounts, etc.) can sometimes be mistaken for quantitative research. Inevitably, the large sample size will push the researcher into simplifying the data numerically. And readers will begin to expect generalizability from such a large sample.
To summarize, “There are no rules for sample size in qualitative inquiry. Sample size depends on what you want to know, the purpose of the inquiry, what’s at stake, what will be useful, what will have credibility, and what can be done with available time and resources” ( Patton 2002:244 ).
How did you find/construct a sample?
Since qualitative researchers work with comparatively small sample sizes, getting your sample right is rather important. Yet it is also difficult to accomplish. For instance, a key question you need to ask yourself is whether you want a homogeneous or heterogeneous sample. In other words, do you want to include people in your study who are by and large the same, or do you want to have diversity in your sample?
For many years, I have studied the experiences of students who were the first in their families to attend university. There is a rather large number of sampling decisions I need to consider before starting the study. (1) Should I only talk to first-in-family students, or should I have a comparison group of students who are not first-in-family? (2) Do I need to strive for a gender distribution that matches undergraduate enrollment patterns? (3) Should I include participants that reflect diversity in gender identity and sexuality? (4) How about racial diversity? First-in-family status is strongly related to some ethnic or racial identity. (5) And how about areas of study?
As you can see, if I wanted to accommodate all these differences and get enough study participants in each category, I would quickly end up with a sample size of hundreds, which is not feasible in most qualitative research. In the end, for me, the most important decision was to maximize the voices of first-in-family students, which meant that I only included them in my sample. As for the other categories, I figured it was going to be hard enough to find first-in-family students, so I started recruiting with an open mind and an understanding that I may have to accept a lack of gender, sexuality, or racial diversity and then not be able to say anything about these issues. But I would definitely be able to speak about the experiences of being first-in-family.
—Wolfgang Lehmann, author of “Habitus Transformation and Hidden Injuries”
Examples of “Sample” Sections in Journal Articles
Think about some of the studies you have read in college, especially those with rich stories and accounts about people’s lives. Do you know how the people were selected to be the focus of those stories? If the account was published by an academic press (e.g., University of California Press or Princeton University Press) or in an academic journal, chances are that the author included a description of their sample selection. You can usually find these in a methodological appendix (book) or a section on “research methods” (article).
Here are two examples from recent books and one example from a recent article:
Example 1 . In It’s Not like I’m Poor: How Working Families Make Ends Meet in a Post-welfare World , the research team employed a mixed methods approach to understand how parents use the earned income tax credit, a refundable tax credit designed to provide relief for low- to moderate-income working people ( Halpern-Meekin et al. 2015 ). At the end of their book, their first appendix is “Introduction to Boston and the Research Project.” After describing the context of the study, they include the following description of their sample selection:
In June 2007, we drew 120 names at random from the roughly 332 surveys we gathered between February and April. Within each racial and ethnic group, we aimed for one-third married couples with children and two-thirds unmarried parents. We sent each of these families a letter informing them of the opportunity to participate in the in-depth portion of our study and then began calling the home and cell phone numbers they provided us on the surveys and knocking on the doors of the addresses they provided.…In the end, we interviewed 115 of the 120 families originally selected for the in-depth interview sample (the remaining five families declined to participate). ( 22 )
Was their sample selection based on convenience or purpose? Why do you think it was important for them to tell you that five families declined to be interviewed? There is actually a trick here, as the names were pulled randomly from a survey whose sample design was probabilistic. Why is this important to know? What can we say about the representativeness or the uniqueness of whatever findings are reported here?
Example 2 . In When Diversity Drops , Park ( 2013 ) examines the impact of decreasing campus diversity on the lives of college students. She does this through a case study of one student club, the InterVarsity Christian Fellowship (IVCF), at one university (“California University,” a pseudonym). Here is her description:
I supplemented participant observation with individual in-depth interviews with sixty IVCF associates, including thirty-four current students, eight former and current staff members, eleven alumni, and seven regional or national staff members. The racial/ethnic breakdown was twenty-five Asian Americans (41.6 percent), one Armenian (1.6 percent), twelve people who were black (20.0 percent), eight Latino/as (13.3 percent), three South Asian Americans (5.0 percent), and eleven people who were white (18.3 percent). Twenty-nine were men, and thirty-one were women. Looking back, I note that the higher number of Asian Americans reflected both the group’s racial/ethnic composition and my relative ease about approaching them for interviews. ( 156 )
How can you tell this is a convenience sample? What else do you note about the sample selection from this description?
Example 3. The last example is taken from an article published in the journal Research in Higher Education . Published articles tend to be more formal than books, at least when it comes to the presentation of qualitative research. In this article, Lawson ( 2021 ) is seeking to understand why female-identified college students drop out of majors that are dominated by male-identified students (e.g., engineering, computer science, music theory). Here is the entire relevant section of the article:
Method Participants Data were collected as part of a larger study designed to better understand the daily experiences of women in MDMs [male-dominated majors].…Participants included 120 students from a midsize, Midwestern University. This sample included 40 women and 40 men from MDMs—defined as any major where at least 2/3 of students are men at both the university and nationally—and 40 women from GNMs—defined as any may where 40–60% of students are women at both the university and nationally.… Procedure A multi-faceted approach was used to recruit participants; participants were sent targeted emails (obtained based on participants’ reported gender and major listings), campus-wide emails sent through the University’s Communication Center, flyers, and in-class presentations. Recruitment materials stated that the research focused on the daily experiences of college students, including classroom experiences, stressors, positive experiences, departmental contexts, and career aspirations. Interested participants were directed to email the study coordinator to verify eligibility (at least 18 years old, man/woman in MDM or woman in GNM, access to a smartphone). Sixteen interested individuals were not eligible for the study due to the gender/major combination. ( 482ff .)
What method of sample selection was used by Lawson? Why is it important to define “MDM” at the outset? How does this definition relate to sampling? Why were interested participants directed to the study coordinator to verify eligibility?
Final Words
I have found that students often find it difficult to be specific enough when defining and choosing their sample. It might help to think about your sample design and sample recruitment like a cookbook. You want all the details there so that someone else can pick up your study and conduct it as you intended. That person could be yourself, but this analogy might work better if you have someone else in mind. When I am writing down recipes, I often think of my sister and try to convey the details she would need to duplicate the dish. We share a grandmother whose recipes are full of handwritten notes in the margins, in spidery ink, that tell us what bowl to use when or where things could go wrong. Describe your sample clearly, convey the steps required accurately, and then add any other details that will help keep you on track and remind you why you have chosen to limit possible interviewees to those of a certain age or class or location. Imagine actually going out and getting your sample (making your dish). Do you have all the necessary details to get started?
Table 5.1. Sampling Type and Strategies
Further Readings
Fusch, Patricia I., and Lawrence R. Ness. 2015. “Are We There Yet? Data Saturation in Qualitative Research.” Qualitative Report 20(9):1408–1416.
Saunders, Benjamin, Julius Sim, Tom Kinstone, Shula Baker, Jackie Waterfield, Bernadette Bartlam, Heather Burroughs, and Clare Jinks. 2018. “Saturation in Qualitative Research: Exploring Its Conceptualization and Operationalization.” Quality & Quantity 52(4):1893–1907.
- Rubin ( 2021 ) suggests a minimum of twenty interviews (but safer with thirty) for an interview-based study and a minimum of three to six months in the field for ethnographic studies. For a content-based study, she suggests between five hundred and one thousand documents, although some will be “very small” ( 243–244 ). ↵
The process of selecting people or other units of analysis to represent a larger population. In quantitative research, this representation is taken quite literally, as statistically representative. In qualitative research, in contrast, sample selection is often made based on potential to generate insight about a particular topic or phenomenon.
The actual list of individuals that the sample will be drawn from. Ideally, it should include the entire target population (and nobody who is not part of that population). Sampling frames can differ from the larger population when specific exclusions are inherent, as in the case of pulling names randomly from voter registration rolls where not everyone is a registered voter. This difference in frame and population can undercut the generalizability of quantitative results.
The specific group of individuals that you will collect data from. Contrast population.
The large group of interest to the researcher. Although it will likely be impossible to design a study that incorporates or reaches all members of the population of interest, this should be clearly defined at the outset of a study so that a reasonable sample of the population can be taken. For example, if one is studying working-class college students, the sample may include twenty such students attending a particular college, while the population is “working-class college students.” In quantitative research, clearly defining the general population of interest is a necessary step in generalizing results from a sample. In qualitative research, defining the population is conceptually important for clarity.
A sampling strategy in which the sample is chosen to represent (numerically) the larger population from which it is drawn by random selection. Each person in the population has an equal chance of making it into the sample. This is often done through a lottery or other chance mechanisms (e.g., a random selection of every twelfth name on an alphabetical list of voters). Also known as random sampling .
The selection of research participants or other data sources based on availability or accessibility, in contrast to purposive sampling .
A sample generated non-randomly by asking participants to help recruit more participants the idea being that a person who fits your sampling criteria probably knows other people with similar criteria.
Broad codes that are assigned to the main issues emerging in the data; identifying themes is often part of initial coding .
A form of case selection focusing on examples that do not fit the emerging patterns. This allows the researcher to evaluate rival explanations or to define the limitations of their research findings. While disconfirming cases are found (not sought out), researchers should expand their analysis or rethink their theories to include/explain them.
A methodological tradition of inquiry and approach to analyzing qualitative data in which theories emerge from a rigorous and systematic process of induction. This approach was pioneered by the sociologists Glaser and Strauss (1967). The elements of theory generated from comparative analysis of data are, first, conceptual categories and their properties and, second, hypotheses or generalized relations among the categories and their properties – “The constant comparing of many groups draws the [researcher’s] attention to their many similarities and differences. Considering these leads [the researcher] to generate abstract categories and their properties, which, since they emerge from the data, will clearly be important to a theory explaining the kind of behavior under observation.” (36).
The result of probability sampling, in which a sample is chosen to represent (numerically) the larger population from which it is drawn by random selection. Each person in the population has an equal chance of making it into the random sample. This is often done through a lottery or other chance mechanisms (e.g., the random selection of every twelfth name on an alphabetical list of voters). This is typically not required in qualitative research but rather essential for the generalizability of quantitative research.
A form of case selection or purposeful sampling in which cases that are unusual or special in some way are chosen to highlight processes or to illuminate gaps in our knowledge of a phenomenon. See also extreme case .
The point at which you can conclude data collection because every person you are interviewing, the interaction you are observing, or content you are analyzing merely confirms what you have already noted. Achieving saturation is often used as the justification for the final sample size.
The accuracy with which results or findings can be transferred to situations or people other than those originally studied. Qualitative studies generally are unable to use (and are uninterested in) statistical generalizability where the sample population is said to be able to predict or stand in for a larger population of interest. Instead, qualitative researchers often discuss “theoretical generalizability,” in which the findings of a particular study can shed light on processes and mechanisms that may be at play in other settings. See also statistical generalization and theoretical generalization .
A term used by IRBs to denote all materials aimed at recruiting participants into a research study (including printed advertisements, scripts, audio or video tapes, or websites). Copies of this material are required in research protocols submitted to IRB.
Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods Copyright © 2023 by Allison Hurst is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Research Sampling Strategies
Sampling is a critical, often overlooked aspect of the research process. The importance of sampling extends to the ability to draw accurate inferences, and it is an integral part of qualitative guidelines across research methods. Sampling considerations are important in quantitative and qualitative research when considering a target population and when drawing a sample that will either allow us to generalize (i.e., quantitatively) or go into sufficient depth (i.e., qualitatively). While quantitative research is generally concerned with probability-based approaches, qualitative research typically uses nonprobability purposeful sampling approaches. Scholars generally focus on two major sampling topics: sampling strategies and sample sizes. Or simply, researchers should think about who to include and how many; both of these concerns are key. Mixed methods studies have both qualitative and quantitative sampling considerations. However, mixed methods studies also have unique considerations based on the relationship of quantitative and qualitative research within the study.
- Related Documents
Linking Research Questions to Mixed Methods Data Analysis Procedures 1
The purpose of this paper is to discuss the development of research questions in mixed methods studies. First, we discuss the ways that the goal of the study, the research objective(s), and the research purpose shape the formation of research questions. Second, we compare and contrast quantitative research questions and qualitative research questions. Third, we describe how to write mixed methods research questions, which we define as questions that embed quantitative and qualitative research questions. Finally, we provide a framework for linking research questions to mixed methods data analysis techniques. A major goal of our framework is to illustrate that the development of research questions and data analysis procedures in mixed method studies should occur logically and sequentially.
Mixed methods research in pedagogy: Characteristics, advantages and difficulties in application
The mixed methods research, as a new type of research, is discussed in the context of re-examining the relation between the two approaches, i.e. the possibility of not opposing, but connecting, combining and integrating them within research. The possibility to use such grounding in research as well could be quite important for pedagogy since the nature of the examined phenomena in this field is such that the majority has both quantitative and qualitative aspects. In order to explain the essence of a mixed methods research, the paper analyses its characteristics, first of all, what elements are combined, what is the nature of the relation between the combined elements and why they are combined, as well as its advantages and difficulties in application. The essential thing in a mixed methods research is the fact that combining refers to the research process as a whole, including the ontological and epistemological assumptions it is based on, which implies that the elements that are combined are understood rather broadly. The advantages and difficulties in application are considered in the context of the discussion of the possibility to combine all research elements, neutralise the limitations of quantitative and qualitative research methodology, implement the complex combining procedures etc.
How Marketers Conduct Mixed Methods Research
The complimentary nature of qualitative and quantitative research methods are examined with respect to a study assessing the market's view of a training and development institute in the Middle East. The qualitative portion consisted of focus groups conducted with seven distinct market segments served by the institute. The results proved insightful with respect to uncovering and understanding differences of opinion among the seven groups; however, taken alone, the qualitative research would have been very misleading with respect to the institute's standing in the Middle East.
Using Mixed-methods Research in Health & Education in Nepal
In the areas of health promotion and health education, mixed-methods research approach has become widely used. In mixed-methods research, also called multi-methods research, the researchers combine quantitative and qualitative research designs in a single study. This paper introduces the mixed-methods approach for use in research in health education. To illustrate this pragmatic research approach we are including an example of mixed-methods research as applied in Nepalese research.Journal of Health Promotion Vol.6 2008, p.45-48
Research Methods
<p class="MsoNormal" style="text-justify: inter-ideograph; text-align: justify; margin: 0in 34.2pt 0pt 0.5in;"><span style="font-size: 10pt;"><span style="font-family: Times New Roman;">This paper discusses three common research approaches, qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods, along with the various research designs commonly used when conducting research within the framework of each approach. Creswell (2002) noted that quantitative research is the process of collecting, analyzing, interpreting, and writing the results of a study, while qualitative research is the approach to data collection, analysis, and report writing differing from the traditional, quantitative approaches. This paper provides a further distinction between quantitative and qualitative research methods. This paper also presents a summary of the different research methods to conduct research in quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods studies.</span></span></p>
Distinguishing Between Quantitative and Qualitative Research: A Response to Morgan
This is a response to Morgan’s article ( Journal of Mixed Methods Research, 12(3), 268-279) on the qualitative/quantitative distinction. I argue that Morgan has mischaracterized my views on this distinction, and on the value of design typologies in mixed methods research, and that the qualitative/quantitative distinction is more productively framed on a different basis than the one he proposed.
Analysis of Community Preparedness Facing Erosion Disaster in Sambas Regency
This research was conducted to analyze the community's preparedness in the face of erosion in Sambas Regency, which is erosion caused by filing by river water. This research is a mixed methods research<em>.</em> This mixed research combines qualitative research and quantitative research, with a sample of people living in riverbank areas. The head of the local household was also asked for information on preparedness to face erosion disasters. The results of the research on community preparedness for erosion in Sambas District were based on the researchers' view that the community was not ready, people who had filled out the new research questionnaire were about 15% out of 100% who were ready. The results of interviews with residents indicated that there was no counselling, training on this preparedness was also one of the causes of the low level of community preparedness.
Kesejahteraan Anak Adopsi Usia Prasekolah (3-5 Tahun)
Child welfare is the responsibility of the family because the child is part of the family. However, in reality there are still many who neglect their children so that the children's welfare is threatened. Abandoned children need protection to ensure their survival. One of the efforts made in dealing with the problem of neglected children is through an institution-based child service program through child social service institutions. However, institution-based child services have not been optimal in realizing children's welfare. Thus, children who are in institution-based care need to be transferred to family-based care so that the child's welfare can be better. One of the permanent efforts to care for children is through adoption. The method used in this research is mixed methods research method. The design chosen in this study is Explanatory Sequential Mixed Methods, the researcher will measure the level of children's welfare with quantitative research first followed by qualitative research. The results of quantitative research regarding the welfare of preschool adopted children show that basically the welfare of adopted children is in the good category. The results of the qualitative research found that the background and reasons or motivation of adoptive parents to adopt an effect on the care of the adopted child so that the child's welfare can be better. Most adoptive parents do not yet have biological children, so the presence of adopted children is a complement to their long-awaited family. The opportunity they get for adoption makes them try to care for, nurture, and treat their adopted child very well. They always pay attention to children's physical development, children's psychological development, children's social development and children's cognitive development so that children's welfare can be achieved.
Change, Challenges, and Mixed Methods
This chapter discusses three ongoing issues related to the evaluation of qualitative research. First, the chapter considers whether a set of evaluation criteria is either determinative or changeable. Due to the evolving nature of qualitative research, it is likely that the way in which qualitative research is evaluated can change—not all at once, but gradually. Second, qualitative research has been criticized by newly resurrected positivists whose definitions of scientific research and evaluation criteria are narrow. “Politics of evidence” and a recent big-tent evaluation strategy are examined. Last, this chapter analyzes how validity criteria of qualitative research are incorporated into the evaluation of mixed methods research. The elements of qualitative research seem to be fairly represented but are largely treated as trivial. A criterion, the fit of research questions to design, is identified as distinctive in the review guide of the Journal of Mixed Methods Research.
Mixed Methods Research in Developing Country Contexts: Lessons From Field Research in Six Countries Across Africa and the Caribbean
Mixed methods research in developing countries has been increasing since the turn of the century. Given this, there is need to consolidate insights for future researchers. This article contributes to the methodological literature by exploring how cultural factors and logistical challenges in developing contexts interplay with mixed methods research design and implementation. Insights are based on the author’s research experience of using mixed methods in six projects across three African and three Caribbean countries. Three lessons are provided to aid researchers using mixed methods working in developing countries. First, cultural factors call for more reflexivity. Second, adopting a pragmatic research paradigm is necessary. And third, the research process should be iterative and adaptive.
Export Citation Format
Share document.
- Tools and Resources
- Customer Services
- Business Education
- Business Law
- Business Policy and Strategy
- Entrepreneurship
- Human Resource Management
- Information Systems
- International Business
- Negotiations and Bargaining
- Operations Management
- Organization Theory
- Organizational Behavior
- Problem Solving and Creativity
- Research Methods
- Social Issues
- Technology and Innovation Management
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Article contents
Sampling strategies for quantitative and qualitative business research.
- Vivien Lee Vivien Lee Psychology, University of Minnesota
- and Richard N. Landers Richard N. Landers Psychology, University of Minnesota
- https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190224851.013.216
- Published online: 23 March 2022
Sampling refers to the process used to identify and select cases for analysis (i.e., a sample) with the goal of drawing meaningful research conclusions. Sampling is integral to the overall research process as it has substantial implications on the quality of research findings. Inappropriate sampling techniques can lead to problems of interpretation, such as drawing invalid conclusions about a population. Whereas sampling in quantitative research focuses on maximizing the statistical representativeness of a population by a chosen sample, sampling in qualitative research generally focuses on the complete representation of a phenomenon of interest. Because of this core difference in purpose, many sampling considerations differ between qualitative and quantitative approaches despite a shared general purpose: careful selection of cases to maximize the validity of conclusions.
Achieving generalizability, the extent to which observed effects from one study can be used to predict the same and similar effects in different contexts, drives most quantitative research. Obtaining a representative sample with characteristics that reflect a targeted population is critical to making accurate statistical inferences, which is core to such research. Such samples can be best acquired through probability sampling, a procedure in which all members of the target population have a known and random chance of being selected. However, probability sampling techniques are uncommon in modern quantitative research because of practical constraints; non-probability sampling, such as by convenience, is now normative. When sampling this way, special attention should be given to statistical implications of issues such as range restriction and omitted variable bias. In either case, careful planning is required to estimate an appropriate sample size before the start of data collection.
In contrast to generalizability, transferability, the degree to which study findings can be applied to other contexts, is the goal of most qualitative research. This approach is more concerned with providing information to readers and less concerned with making generalizable broad claims for readers. Similar to quantitative research, choosing a population and sample are critical for qualitative research, to help readers determine likelihood of transfer, yet representativeness is not as crucial. Sample size determination in qualitative research is drastically different from that of quantitative research, because sample size determination should occur during data collection, in an ongoing process in search of saturation, which focuses on achieving theoretical completeness instead of maximizing the quality of statistical inference.
Theoretically speaking, although quantitative and qualitative research have distinct statistical underpinnings that should drive different sampling requirements, in practice they both heavily rely on non-probability samples, and the implications of non-probability sampling is often not well understood. Although non-probability samples do not automatically generate poor-quality data, incomplete consideration of case selection strategy can harm the validity of research conclusions. The nature and number of cases collected must be determined cautiously to respect research goals and the underlying scientific paradigm employed. Understanding the commonalities and differences in sampling between quantitative and qualitative research can help researchers better identify high-quality research designs across paradigms.
- non-probability sampling
- convenience sampling
- sample size
- quantitative research
- qualitative research
You do not currently have access to this article
Please login to access the full content.
Access to the full content requires a subscription
Printed from Oxford Research Encyclopedias, Business and Management. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 08 April 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [66.249.64.20|185.80.149.115]
- 185.80.149.115
Character limit 500 /500

Principles of Social Research Methodology pp 221–234 Cite as
Sampling Techniques for Quantitative Research
- Moniruzzaman Sarker ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3595-5838 4 &
- Mohammed Abdulmalek AL-Muaalemi 5
- First Online: 27 October 2022
3021 Accesses
8 Citations
In quantitative research, collecting data from an entire population of a study is impractical in many instances. It squanders resources like time and money which can be minimized by choosing suitable sampling techniques between probability and non-probability methods. The chapter outlines a brief idea about the different categories of sampling techniques with examples. Sensibly selecting among the sampling techniques allows the researcher to generalize the findings to a specific study context. Although probability sampling is more appealing to draw a representative sample, non-probability sampling techniques also enable the researcher to generalize the findings upon implementing the sampling strategy wisely. Moreover, adopting probability sampling techniques is not feasible in many situations. The chapter suggests selecting sampling techniques should be guided by research objectives, study scope, and availability of sampling frame rather than looking at the nature of sampling techniques.
- Sampling techniques
- Quantitative study
- Probability sampling
- Non-probability sampling
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Bryman, A., & Bell, E. (2015). Business research methods (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
Google Scholar
Clottey, T. A., & Grawe, S. J. (2014). Non-response bias assessment in logistics survey research: Use fewer tests? International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 44 (5), 412–426. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJPDLM-10-2012-0314
Article Google Scholar
Collier, J. E., & Bienstock, C. C. (2007). An analysis of how nonresponse error is assessed in academic marketing research. Marketing Theory, 7 (2), 163–183. https://doi.org/10.1177/1470593107076865
Cooper, D. R., Schindler, P. S., & Sun, J. (2006). Business research methods (9th ed.). McGraw-Hill Irwin.
Creswell, J. W. (2014). Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches (4th ed.). SAGE Publications, Incorporated.
Feild, L., Pruchno, R. A., Bewley, J., Lemay, E. P., & Levinsky, N. G. (2006). Using probability versus nonprobability sampling to identify hard-to-access participants for health-related research: Costs and contrasts. Journal of Aging and Health, 18 (4), 565–583. https://doi.org/10.1177/0898264306291420.
Hulland, J., Baumgartner, H., & Smith, K. M. (2017). Marketing survey research best practices: Evidence and recommendations from a review of JAMS articles. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 46 (1), 92–108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-017-0532-y
Lindner, J. R., Murphy, T. H., & Briers, G. E. (2001). Handling nonresponse in social science research. Journal of Agricultural Education, 42 (4), 43–53.
Malhotra, N. K., & Das, S. (2010). Marketing research: An applied orientation (6th ed.). Pearson Education.
Book Google Scholar
Marshall, M. N. (1996). Sampling for qualitative research. Family Practice, 13 (6), 522–526. https://doi.org/10.1093/fampra/13.6.522
Memon, M. A., Ting, H., Ramayah, T., Chuah, F., & Cheah, J.-H. (2017). A review of the methodological misconceptions and guidelines related to the application of structural equation modeling: A Malaysian scenario. Journal of Applied Structural Equation Modeling, 1 (1), i–xiii.
Rowley, J. (2014). Designing and using research questionnaires. Management Research Review, 37 (3), 308–330. https://doi.org/10.1108/MRR-02-2013-0027
Sarstedt, M., Bengart, P., Shaltoni, A. M., & Lehmann, S. (2018). The use of sampling methods in advertising research: A gap between theory and practice. International Journal of Advertising, 37 (4), 650–663. https://doi.org/10.1080/02650487.2017.1348329
Sax, L. J., Gilmartin, S. K., & Bryant, A. N. (2003). Assessing response rates and nonresponse bias in web and paper surveys. Research in Higher Education, 44 (4), 409–432. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1024232915870
Seddon, P. B., & Scheepers, R. (2012). Towards the improved treatment of generalization of knowledge claims in IS research: Drawing general conclusions from samples. European Journal of Information Systems, 21 (1), 6–21.
Sekaran, U., & Bougie, R. (2016). Research methods for business: A skill building approach (7th ed.). John Wiley & Sons.
Zikmund, W. G., Babin, B. J., Carr, J. C., & Griffin, M. (2013). Business research methods (9th ed.). Cengage Learning.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Assistant Professor of Marketing, Southamton Malysia Business School, University of Southamton Malysia, Johor Bahru, Malaysia
Moniruzzaman Sarker
Faculty of Business and Accountancy, University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
Mohammed Abdulmalek AL-Muaalemi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Moniruzzaman Sarker .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Centre for Family and Child Studies, Research Institute of Humanities and Social Sciences, University of Sharjah, Sharjah, United Arab Emirates
M. Rezaul Islam
Department of Development Studies, University of Dhaka, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Niaz Ahmed Khan
Department of Social Work, School of Humanities, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa
Rajendra Baikady
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Moniruzzaman Sarker, AL-Muaalemi, M.A. (2022). Sampling Techniques for Quantitative Research. In: Islam, M.R., Khan, N.A., Baikady, R. (eds) Principles of Social Research Methodology. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5441-2_15
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-5441-2_15
Published : 27 October 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-19-5219-7
Online ISBN : 978-981-19-5441-2
eBook Packages : Social Sciences
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Qualitative Sampling Methods
Affiliation.
- 1 14742 School of Nursing, University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio, TX, USA.
- PMID: 32813616
- DOI: 10.1177/0890334420949218
Qualitative sampling methods differ from quantitative sampling methods. It is important that one understands those differences, as well as, appropriate qualitative sampling techniques. Appropriate sampling choices enhance the rigor of qualitative research studies. These types of sampling strategies are presented, along with the pros and cons of each. Sample size and data saturation are discussed.
Keywords: breastfeeding; qualitative methods; sampling; sampling methods.
- Evaluation Studies as Topic*
- Research Design / standards
- Sample Size*
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- HHS Author Manuscripts

Purposeful sampling for qualitative data collection and analysis in mixed method implementation research
Lawrence a. palinkas.
1 School of Social Work, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA 90089-0411
Sarah M. Horwitz
2 Department of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, New York University, New York, NY
Carla A. Green
3 Center for Health Research, Kaiser Permanente Northwest, Portland, OR
Jennifer P. Wisdom
4 George Washington University, Washington DC
Naihua Duan
5 New York State Neuropsychiatric Institute and Department of Psychiatry, Columbia University, New York, NY
Kimberly Hoagwood
Purposeful sampling is widely used in qualitative research for the identification and selection of information-rich cases related to the phenomenon of interest. Although there are several different purposeful sampling strategies, criterion sampling appears to be used most commonly in implementation research. However, combining sampling strategies may be more appropriate to the aims of implementation research and more consistent with recent developments in quantitative methods. This paper reviews the principles and practice of purposeful sampling in implementation research, summarizes types and categories of purposeful sampling strategies and provides a set of recommendations for use of single strategy or multistage strategy designs, particularly for state implementation research.
Recently there have been several calls for the use of mixed method designs in implementation research ( Proctor et al., 2009 ; Landsverk et al., 2012 ; Palinkas et al. 2011 ; Aarons et al., 2012). This has been precipitated by the realization that the challenges of implementing evidence-based and other innovative practices, treatments, interventions and programs are sufficiently complex that a single methodological approach is often inadequate. This is particularly true of efforts to implement evidence-based practices (EBPs) in statewide systems where relationships among key stakeholders extend both vertically (from state to local organizations) and horizontally (between organizations located in different parts of a state). As in other areas of research, mixed method designs are viewed as preferable in implementation research because they provide a better understanding of research issues than either qualitative or quantitative approaches alone ( Palinkas et al., 2011 ). In such designs, qualitative methods are used to explore and obtain depth of understanding as to the reasons for success or failure to implement evidence-based practice or to identify strategies for facilitating implementation while quantitative methods are used to test and confirm hypotheses based on an existing conceptual model and obtain breadth of understanding of predictors of successful implementation ( Teddlie & Tashakkori, 2003 ).
Sampling strategies for quantitative methods used in mixed methods designs in implementation research are generally well-established and based on probability theory. In contrast, sampling strategies for qualitative methods in implementation studies are less explicit and often less evident. Although the samples for qualitative inquiry are generally assumed to be selected purposefully to yield cases that are “information rich” (Patton, 2001), there are no clear guidelines for conducting purposeful sampling in mixed methods implementation studies, particularly when studies have more than one specific objective. Moreover, it is not entirely clear what forms of purposeful sampling are most appropriate for the challenges of using both quantitative and qualitative methods in the mixed methods designs used in implementation research. Such a consideration requires a determination of the objectives of each methodology and the potential impact of selecting one strategy to achieve one objective on the selection of other strategies to achieve additional objectives.
In this paper, we present different approaches to the use of purposeful sampling strategies in implementation research. We begin with a review of the principles and practice of purposeful sampling in implementation research, a summary of the types and categories of purposeful sampling strategies, and a set of recommendations for matching the appropriate single strategy or multistage strategy to study aims and quantitative method designs.
Principles of Purposeful Sampling
Purposeful sampling is a technique widely used in qualitative research for the identification and selection of information-rich cases for the most effective use of limited resources ( Patton, 2002 ). This involves identifying and selecting individuals or groups of individuals that are especially knowledgeable about or experienced with a phenomenon of interest ( Cresswell & Plano Clark, 2011 ). In addition to knowledge and experience, Bernard (2002) and Spradley (1979) note the importance of availability and willingness to participate, and the ability to communicate experiences and opinions in an articulate, expressive, and reflective manner. In contrast, probabilistic or random sampling is used to ensure the generalizability of findings by minimizing the potential for bias in selection and to control for the potential influence of known and unknown confounders.
As Morse and Niehaus (2009) observe, whether the methodology employed is quantitative or qualitative, sampling methods are intended to maximize efficiency and validity. Nevertheless, sampling must be consistent with the aims and assumptions inherent in the use of either method. Qualitative methods are, for the most part, intended to achieve depth of understanding while quantitative methods are intended to achieve breadth of understanding ( Patton, 2002 ). Qualitative methods place primary emphasis on saturation (i.e., obtaining a comprehensive understanding by continuing to sample until no new substantive information is acquired) ( Miles & Huberman, 1994 ). Quantitative methods place primary emphasis on generalizability (i.e., ensuring that the knowledge gained is representative of the population from which the sample was drawn). Each methodology, in turn, has different expectations and standards for determining the number of participants required to achieve its aims. Quantitative methods rely on established formulae for avoiding Type I and Type II errors, while qualitative methods often rely on precedents for determining number of participants based on type of analysis proposed (e.g., 3-6 participants interviewed multiple times in a phenomenological study versus 20-30 participants interviewed once or twice in a grounded theory study), level of detail required, and emphasis of homogeneity (requiring smaller samples) versus heterogeneity (requiring larger samples) ( Guest, Bunce & Johnson., 2006 ; Morse & Niehaus, 2009 ; Padgett, 2008 ).
Types of purposeful sampling designs
There exist numerous purposeful sampling designs. Examples include the selection of extreme or deviant (outlier) cases for the purpose of learning from an unusual manifestations of phenomena of interest; the selection of cases with maximum variation for the purpose of documenting unique or diverse variations that have emerged in adapting to different conditions, and to identify important common patterns that cut across variations; and the selection of homogeneous cases for the purpose of reducing variation, simplifying analysis, and facilitating group interviewing. A list of some of these strategies and examples of their use in implementation research is provided in Table 1 .
Purposeful sampling strategies in implementation research
Embedded in each strategy is the ability to compare and contrast, to identify similarities and differences in the phenomenon of interest. Nevertheless, some of these strategies (e.g., maximum variation sampling, extreme case sampling, intensity sampling, and purposeful random sampling) are used to identify and expand the range of variation or differences, similar to the use of quantitative measures to describe the variability or dispersion of values for a particular variable or variables, while other strategies (e.g., homogeneous sampling, typical case sampling, criterion sampling, and snowball sampling) are used to narrow the range of variation and focus on similarities. The latter are similar to the use of quantitative central tendency measures (e.g., mean, median, and mode). Moreover, certain strategies, like stratified purposeful sampling or opportunistic or emergent sampling, are designed to achieve both goals. As Patton (2002 , p. 240) explains, “the purpose of a stratified purposeful sample is to capture major variations rather than to identify a common core, although the latter may also emerge in the analysis. Each of the strata would constitute a fairly homogeneous sample.”
Challenges to use of purposeful sampling
Despite its wide use, there are numerous challenges in identifying and applying the appropriate purposeful sampling strategy in any study. For instance, the range of variation in a sample from which purposive sample is to be taken is often not really known at the outset of a study. To set as the goal the sampling of information-rich informants that cover the range of variation assumes one knows that range of variation. Consequently, an iterative approach of sampling and re-sampling to draw an appropriate sample is usually recommended to make certain the theoretical saturation occurs ( Miles & Huberman, 1994 ). However, that saturation may be determined a-priori on the basis of an existing theory or conceptual framework, or it may emerge from the data themselves, as in a grounded theory approach ( Glaser & Strauss, 1967 ). Second, there are a not insignificant number in the qualitative methods field who resist or refuse systematic sampling of any kind and reject the limiting nature of such realist, systematic, or positivist approaches. This includes critics of interventions and “bottom up” case studies and critiques. However, even those who equate purposeful sampling with systematic sampling must offer a rationale for selecting study participants that is linked with the aims of the investigation (i.e., why recruit these individuals for this particular study? What qualifies them to address the aims of the study?). While systematic sampling may be associated with a post-positivist tradition of qualitative data collection and analysis, such sampling is not inherently limited to such analyses and the need for such sampling is not inherently limited to post-positivist qualitative approaches ( Patton, 2002 ).
Purposeful Sampling in Implementation Research
Characteristics of implementation research.
In implementation research, quantitative and qualitative methods often play important roles, either simultaneously or sequentially, for the purpose of answering the same question through convergence of results from different sources, answering related questions in a complementary fashion, using one set of methods to expand or explain the results obtained from use of the other set of methods, using one set of methods to develop questionnaires or conceptual models that inform the use of the other set, and using one set of methods to identify the sample for analysis using the other set of methods ( Palinkas et al., 2011 ). A review of mixed method designs in implementation research conducted by Palinkas and colleagues (2011) revealed seven different sequential and simultaneous structural arrangements, five different functions of mixed methods, and three different ways of linking quantitative and qualitative data together. However, this review did not consider the sampling strategies involved in the types of quantitative and qualitative methods common to implementation research, nor did it consider the consequences of the sampling strategy selected for one method or set of methods on the choice of sampling strategy for the other method or set of methods. For instance, one of the most significant challenges to sampling in sequential mixed method designs lies in the limitations the initial method may place on sampling for the subsequent method. As Morse and Neihaus (2009) observe, when the initial method is qualitative, the sample selected may be too small and lack randomization necessary to fulfill the assumptions for a subsequent quantitative analysis. On the other hand, when the initial method is quantitative, the sample selected may be too large for each individual to be included in qualitative inquiry and lack purposeful selection to reduce the sample size to one more appropriate for qualitative research. The fact that potential participants were recruited and selected at random does not necessarily make them information rich.
A re-examination of the 22 studies and an additional 6 studies published since 2009 revealed that only 5 studies ( Aarons & Palinkas, 2007 ; Bachman et al., 2009 ; Palinkas et al., 2011 ; Palinkas et al., 2012 ; Slade et al., 2003) made a specific reference to purposeful sampling. An additional three studies ( Henke et al., 2008 ; Proctor et al., 2007 ; Swain et al., 2010 ) did not make explicit reference to purposeful sampling but did provide a rationale for sample selection. The remaining 20 studies provided no description of the sampling strategy used to identify participants for qualitative data collection and analysis; however, a rationale could be inferred based on a description of who were recruited and selected for participation. Of the 28 studies, 3 used more than one sampling strategy. Twenty-one of the 28 studies (75%) used some form of criterion sampling. In most instances, the criterion used is related to the individual’s role, either in the research project (i.e., trainer, team leader), or the agency (program director, clinical supervisor, clinician); in other words, criterion of inclusion in a certain category (criterion-i), in contrast to cases that are external to a specific criterion (criterion-e). For instance, in a series of studies based on the National Implementing Evidence-Based Practices Project, participants included semi-structured interviews with consultant trainers and program leaders at each study site ( Brunette et al., 2008 ; Marshall et al., 2008 ; Marty et al., 2007; Rapp et al., 2010 ; Woltmann et al., 2008 ). Six studies used some form of maximum variation sampling to ensure representativeness and diversity of organizations and individual practitioners. Two studies used intensity sampling to make contrasts. Aarons and Palinkas (2007) , for example, purposefully selected 15 child welfare case managers representing those having the most positive and those having the most negative views of SafeCare, an evidence-based prevention intervention, based on results of a web-based quantitative survey asking about the perceived value and usefulness of SafeCare. Kramer and Burns (2008) recruited and interviewed clinicians providing usual care and clinicians who dropped out of a study prior to consent to contrast with clinicians who provided the intervention under investigation. One study ( Hoagwood et al., 2007 ), used a typical case approach to identify participants for a qualitative assessment of the challenges faced in implementing a trauma-focused intervention for youth. One study ( Green & Aarons, 2011 ) used a combined snowball sampling/criterion-i strategy by asking recruited program managers to identify clinicians, administrative support staff, and consumers for project recruitment. County mental directors, agency directors, and program managers were recruited to represent the policy interests of implementation while clinicians, administrative support staff and consumers were recruited to represent the direct practice perspectives of EBP implementation.
Table 2 below provides a description of the use of different purposeful sampling strategies in mixed methods implementation studies. Criterion-i sampling was most frequently used in mixed methods implementation studies that employed a simultaneous design where the qualitative method was secondary to the quantitative method or studies that employed a simultaneous structure where the qualitative and quantitative methods were assigned equal priority. These mixed method designs were used to complement the depth of understanding afforded by the qualitative methods with the breadth of understanding afforded by the quantitative methods (n = 13), to explain or elaborate upon the findings of one set of methods (usually quantitative) with the findings from the other set of methods (n = 10), or to seek convergence through triangulation of results or quantifying qualitative data (n = 8). The process of mixing methods in the large majority (n = 18) of these studies involved embedding the qualitative study within the larger quantitative study. In one study (Goia & Dziadosz, 2008), criterion sampling was used in a simultaneous design where quantitative and qualitative data were merged together in a complementary fashion, and in two studies (Aarons et al., 2012; Zazelli et al., 2008 ), quantitative and qualitative data were connected together, one in sequential design for the purpose of developing a conceptual model ( Zazelli et al., 2008 ), and one in a simultaneous design for the purpose of complementing one another (Aarons et al., 2012). Three of the six studies that used maximum variation sampling used a simultaneous structure with quantitative methods taking priority over qualitative methods and a process of embedding the qualitative methods in a larger quantitative study ( Henke et al., 2008 ; Palinkas et al., 2010; Slade et al., 2008 ). Two of the six studies used maximum variation sampling in a sequential design ( Aarons et al., 2009 ; Zazelli et al., 2008 ) and one in a simultaneous design (Henke et al., 2010) for the purpose of development, and three used it in a simultaneous design for complementarity ( Bachman et al., 2009 ; Henke et al., 2008; Palinkas, Ell, Hansen, Cabassa, & Wells, 2011 ). The two studies relying upon intensity sampling used a simultaneous structure for the purpose of either convergence or expansion, and both studies involved a qualitative study embedded in a larger quantitative study ( Aarons & Palinkas, 2007 ; Kramer & Burns, 2008 ). The single typical case study involved a simultaneous design where the qualitative study was embedded in a larger quantitative study for the purpose of complementarity ( Hoagwood et al., 2007 ). The snowball/maximum variation study involved a sequential design where the qualitative study was merged into the quantitative data for the purpose of convergence and conceptual model development ( Green & Aarons, 2011 ). Although not used in any of the 28 implementation studies examined here, another common sequential sampling strategy is using criteria sampling of the larger quantitative sample to produce a second-stage qualitative sample in a manner similar to maximum variation sampling, except that the former narrows the range of variation while the latter expands the range.
Purposeful sampling strategies and mixed method designs in implementation research
Criterion-i sampling as a purposeful sampling strategy shares many characteristics with random probability sampling, despite having different aims and different procedures for identifying and selecting potential participants. In both instances, study participants are drawn from agencies, organizations or systems involved in the implementation process. Individuals are selected based on the assumption that they possess knowledge and experience with the phenomenon of interest (i.e., the implementation of an EBP) and thus will be able to provide information that is both detailed (depth) and generalizable (breadth). Participants for a qualitative study, usually service providers, consumers, agency directors, or state policy-makers, are drawn from the larger sample of participants in the quantitative study. They are selected from the larger sample because they meet the same criteria, in this case, playing a specific role in the organization and/or implementation process. To some extent, they are assumed to be “representative” of that role, although implementation studies rarely explain the rationale for selecting only some and not all of the available role representatives (i.e., recruiting 15 providers from an agency for semi-structured interviews out of an available sample of 25 providers). From the perspective of qualitative methodology, participants who meet or exceed a specific criterion or criteria possess intimate (or, at the very least, greater) knowledge of the phenomenon of interest by virtue of their experience, making them information-rich cases.
However, criterion sampling may not be the most appropriate strategy for implementation research because by attempting to capture both breadth and depth of understanding, it may actually be inadequate to the task of accomplishing either. Although qualitative methods are often contrasted with quantitative methods on the basis of depth versus breadth, they actually require elements of both in order to provide a comprehensive understanding of the phenomenon of interest. Ideally, the goal of achieving theoretical saturation by providing as much detail as possible involves selection of individuals or cases that can ensure all aspects of that phenomenon are included in the examination and that any one aspect is thoroughly examined. This goal, therefore, requires an approach that sequentially or simultaneously expands and narrows the field of view, respectively. By selecting only individuals who meet a specific criterion defined on the basis of their role in the implementation process or who have a specific experience (e.g., engaged only in an implementation defined as successful or only in one defined as unsuccessful), one may fail to capture the experiences or activities of other groups playing other roles in the process. For instance, a focus only on practitioners may fail to capture the insights, experiences, and activities of consumers, family members, agency directors, administrative staff, or state policy leaders in the implementation process, thus limiting the breadth of understanding of that process. On the other hand, selecting participants on the basis of whether they were a practitioner, consumer, director, staff, or any of the above, may fail to identify those with the greatest experience or most knowledgeable or most able to communicate what they know and/or have experienced, thus limiting the depth of understanding of the implementation process.
To address the potential limitations of criterion sampling, other purposeful sampling strategies should be considered and possibly adopted in implementation research ( Figure 1 ). For instance, strategies placing greater emphasis on breadth and variation such as maximum variation, extreme case, confirming and disconfirming case sampling are better suited for an examination of differences, while strategies placing greater emphasis on depth and similarity such as homogeneous, snowball, and typical case sampling are better suited for an examination of commonalities or similarities, even though both types of sampling strategies include a focus on both differences and similarities. Alternatives to criterion sampling may be more appropriate to the specific functions of mixed methods, however. For instance, using qualitative methods for the purpose of complementarity may require that a sampling strategy emphasize similarity if it is to achieve depth of understanding or explore and develop hypotheses that complement a quantitative probability sampling strategy achieving breadth of understanding and testing hypotheses ( Kemper et al., 2003 ). Similarly, mixed methods that address related questions for the purpose of expanding or explaining results or developing new measures or conceptual models may require a purposeful sampling strategy aiming for similarity that complements probability sampling aiming for variation or dispersion. A narrowly focused purposeful sampling strategy for qualitative analysis that “complements” a broader focused probability sample for quantitative analysis may help to achieve a balance between increasing inference quality/trustworthiness (internal validity) and generalizability/transferability (external validity). A single method that focuses only on a broad view may decrease internal validity at the expense of external validity ( Kemper et al., 2003 ). On the other hand, the aim of convergence (answering the same question with either method) may suggest use of a purposeful sampling strategy that aims for breadth that parallels the quantitative probability sampling strategy.

Purposeful and Random Sampling Strategies for Mixed Method Implementation Studies
- (1) Priority and sequencing of Qualitative (QUAL) and Quantitative (QUAN) can be reversed.
- (2) Refers to emphasis of sampling strategy.

Furthermore, the specific nature of implementation research suggests that a multistage purposeful sampling strategy be used. Three different multistage sampling strategies are illustrated in Figure 1 below. Several qualitative methodologists recommend sampling for variation (breadth) before sampling for commonalities (depth) ( Glaser, 1978 ; Bernard, 2002 ) (Multistage I). Also known as a “funnel approach”, this strategy is often recommended when conducting semi-structured interviews ( Spradley, 1979 ) or focus groups ( Morgan, 1997 ). This approach begins with a broad view of the topic and then proceeds to narrow down the conversation to very specific components of the topic. However, as noted earlier, the lack of a clear understanding of the nature of the range may require an iterative approach where each stage of data analysis helps to determine subsequent means of data collection and analysis ( Denzen, 1978 ; Patton, 2001) (Multistage II). Similarly, multistage purposeful sampling designs like opportunistic or emergent sampling, allow the option of adding to a sample to take advantage of unforeseen opportunities after data collection has been initiated (Patton, 2001, p. 240) (Multistage III). Multistage I models generally involve two stages, while a Multistage II model requires a minimum of 3 stages, alternating from sampling for variation to sampling for similarity. A Multistage III model begins with sampling for variation and ends with sampling for similarity, but may involve one or more intervening stages of sampling for variation or similarity as the need or opportunity arises.
Multistage purposeful sampling is also consistent with the use of hybrid designs to simultaneously examine intervention effectiveness and implementation. An extension of the concept of “practical clinical trials” ( Tunis, Stryer & Clancey, 2003 ), effectiveness-implementation hybrid designs provide benefits such as more rapid translational gains in clinical intervention uptake, more effective implementation strategies, and more useful information for researchers and decision makers ( Curran et al., 2012 ). Such designs may give equal priority to the testing of clinical treatments and implementation strategies (Hybrid Type 2) or give priority to the testing of treatment effectiveness (Hybrid Type 1) or implementation strategy (Hybrid Type 3). Curran and colleagues (2012) suggest that evaluation of the intervention’s effectiveness will require or involve use of quantitative measures while evaluation of the implementation process will require or involve use of mixed methods. When conducting a Hybrid Type 1 design (conducting a process evaluation of implementation in the context of a clinical effectiveness trial), the qualitative data could be used to inform the findings of the effectiveness trial. Thus, an effectiveness trial that finds substantial variation might purposefully select participants using a broader strategy like sampling for disconfirming cases to account for the variation. For instance, group randomized trials require knowledge of the contexts and circumstances similar and different across sites to account for inevitable site differences in interventions and assist local implementations of an intervention ( Bloom & Michalopoulos, 2013 ; Raudenbush & Liu, 2000 ). Alternatively, a narrow strategy may be used to account for the lack of variation. In either instance, the choice of a purposeful sampling strategy is determined by the outcomes of the quantitative analysis that is based on a probability sampling strategy. In Hybrid Type 2 and Type 3 designs where the implementation process is given equal or greater priority than the effectiveness trial, the purposeful sampling strategy must be first and foremost consistent with the aims of the implementation study, which may be to understand variation, central tendencies, or both. In all three instances, the sampling strategy employed for the implementation study may vary based on the priority assigned to that study relative to the effectiveness trial. For instance, purposeful sampling for a Hybrid Type 1 design may give higher priority to variation and comparison to understand the parameters of implementation processes or context as a contribution to an understanding of effectiveness outcomes (i.e., using qualitative data to expand upon or explain the results of the effectiveness trial), In effect, these process measures could be seen as modifiers of innovation/EBP outcome. In contrast, purposeful sampling for a Hybrid Type 3 design may give higher priority to similarity and depth to understand the core features of successful outcomes only.
Finally, multistage sampling strategies may be more consistent with innovations in experimental designs representing alternatives to the classic randomized controlled trial in community-based settings that have greater feasibility, acceptability, and external validity. While RCT designs provide the highest level of evidence, “in many clinical and community settings, and especially in studies with underserved populations and low resource settings, randomization may not be feasible or acceptable” ( Glasgow, et al., 2005 , p. 554). Randomized trials are also “relatively poor in assessing the benefit from complex public health or medical interventions that account for individual preferences for or against certain interventions, differential adherence or attrition, or varying dosage or tailoring of an intervention to individual needs” ( Brown et al., 2009 , p. 2). Several alternatives to the randomized design have been proposed, such as “interrupted time series,” “multiple baseline across settings” or “regression-discontinuity” designs. Optimal designs represent one such alternative to the classic RCT and are addressed in detail by Duan and colleagues (this issue) . Like purposeful sampling, optimal designs are intended to capture information-rich cases, usually identified as individuals most likely to benefit from the experimental intervention. The goal here is not to identify the typical or average patient, but patients who represent one end of the variation in an extreme case, intensity sampling, or criterion sampling strategy. Hence, a sampling strategy that begins by sampling for variation at the first stage and then sampling for homogeneity within a specific parameter of that variation (i.e., one end or the other of the distribution) at the second stage would seem the best approach for identifying an “optimal” sample for the clinical trial.
Another alternative to the classic RCT are the adaptive designs proposed by Brown and colleagues ( Brown et al, 2006 ; Brown et al., 2008 ; Brown et al., 2009 ). Adaptive designs are a sequence of trials that draw on the results of existing studies to determine the next stage of evaluation research. They use cumulative knowledge of current treatment successes or failures to change qualities of the ongoing trial. An adaptive intervention modifies what an individual subject (or community for a group-based trial) receives in response to his or her preferences or initial responses to an intervention. Consistent with multistage sampling in qualitative research, the design is somewhat iterative in nature in the sense that information gained from analysis of data collected at the first stage influences the nature of the data collected, and the way they are collected, at subsequent stages ( Denzen, 1978 ). Furthermore, many of these adaptive designs may benefit from a multistage purposeful sampling strategy at early phases of the clinical trial to identify the range of variation and core characteristics of study participants. This information can then be used for the purposes of identifying optimal dose of treatment, limiting sample size, randomizing participants into different enrollment procedures, determining who should be eligible for random assignment (as in the optimal design) to maximize treatment adherence and minimize dropout, or identifying incentives and motives that may be used to encourage participation in the trial itself.
Alternatives to the classic RCT design may also be desirable in studies that adopt a community-based participatory research framework ( Minkler & Wallerstein, 2003 ), considered to be an important tool on conducting implementation research ( Palinkas & Soydan, 2012 ). Such frameworks suggest that identification and recruitment of potential study participants will place greater emphasis on the priorities and “local knowledge” of community partners than on the need to sample for variation or uniformity. In this instance, the first stage of sampling may approximate the strategy of sampling politically important cases ( Patton, 2002 ) at the first stage, followed by other sampling strategies intended to maximize variations in stakeholder opinions or experience.
On the basis of this review, the following recommendations are offered for the use of purposeful sampling in mixed method implementation research. First, many mixed methods studies in health services research and implementation science do not clearly identify or provide a rationale for the sampling procedure for either quantitative or qualitative components of the study ( Wisdom et al., 2011 ), so a primary recommendation is for researchers to clearly describe their sampling strategies and provide the rationale for the strategy.
Second, use of a single stage strategy for purposeful sampling for qualitative portions of a mixed methods implementation study should adhere to the same general principles that govern all forms of sampling, qualitative or quantitative. Kemper and colleagues (2003) identify seven such principles: 1) the sampling strategy should stem logically from the conceptual framework as well as the research questions being addressed by the study; 2) the sample should be able to generate a thorough database on the type of phenomenon under study; 3) the sample should at least allow the possibility of drawing clear inferences and credible explanations from the data; 4) the sampling strategy must be ethical; 5) the sampling plan should be feasible; 6) the sampling plan should allow the researcher to transfer/generalize the conclusions of the study to other settings or populations; and 7) the sampling scheme should be as efficient as practical.
Third, the field of implementation research is at a stage itself where qualitative methods are intended primarily to explore the barriers and facilitators of EBP implementation and to develop new conceptual models of implementation process and outcomes. This is especially important in state implementation research, where fiscal necessities are driving policy reforms for which knowledge about EBP implementation barriers and facilitators are urgently needed. Thus a multistage strategy for purposeful sampling should begin first with a broader view with an emphasis on variation or dispersion and move to a narrow view with an emphasis on similarity or central tendencies. Such a strategy is necessary for the task of finding the optimal balance between internal and external validity.
Fourth, if we assume that probability sampling will be the preferred strategy for the quantitative components of most implementation research, the selection of a single or multistage purposeful sampling strategy should be based, in part, on how it relates to the probability sample, either for the purpose of answering the same question (in which case a strategy emphasizing variation and dispersion is preferred) or the for answering related questions (in which case, a strategy emphasizing similarity and central tendencies is preferred).
Fifth, it should be kept in mind that all sampling procedures, whether purposeful or probability, are designed to capture elements of both similarity and differences, of both centrality and dispersion, because both elements are essential to the task of generating new knowledge through the processes of comparison and contrast. Selecting a strategy that gives emphasis to one does not mean that it cannot be used for the other. Having said that, our analysis has assumed at least some degree of concordance between breadth of understanding associated with quantitative probability sampling and purposeful sampling strategies that emphasize variation on the one hand, and between the depth of understanding and purposeful sampling strategies that emphasize similarity on the other hand. While there may be some merit to that assumption, depth of understanding requires both an understanding of variation and common elements.
Finally, it should also be kept in mind that quantitative data can be generated from a purposeful sampling strategy and qualitative data can be generated from a probability sampling strategy. Each set of data is suited to a specific objective and each must adhere to a specific set of assumptions and requirements. Nevertheless, the promise of mixed methods, like the promise of implementation science, lies in its ability to move beyond the confines of existing methodological approaches and develop innovative solutions to important and complex problems. For states engaged in EBP implementation, the need for these solutions is urgent.

Multistage Purposeful Sampling Strategies
Acknowledgments
This study was funded through a grant from the National Institute of Mental Health (P30-MH090322: K. Hoagwood, PI).

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

7.3: Sampling in Quantitative Research
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 12582

Learning Objectives
- Describe how probability sampling differs from nonprobability sampling.
- Define generalizability, and describe how it is achieved in probability samples.
- Identify the various types of probability samples, and provide a brief description of each.
Quantitative researchers are often interested in being able to make generalizations about groups larger than their study samples. While there are certainly instances when quantitative researchers rely on nonprobability samples (e.g., when doing exploratory or evaluation research), quantitative researchers tend to rely on probability sampling techniques. The goals and techniques associated with probability samples differ from those of nonprobability samples. We’ll explore those unique goals and techniques in this section.
Probability Sampling
Unlike nonprobability sampling, probability sampling refers to sampling techniques for which a person’s (or event’s) likelihood of being selected for membership in the sample is known. You might ask yourself why we should care about a study element’s likelihood of being selected for membership in a researcher’s sample. The reason is that, in most cases, researchers who use probability sampling techniques are aiming to identify a representative sample from which to collect data. A representative sample is one that resembles the population from which it was drawn in all the ways that are important for the research being conducted. If, for example, you wish to be able to say something about differences between men and women at the end of your study, you better make sure that your sample doesn’t contain only women. That’s a bit of an oversimplification, but the point with representativeness is that if your population varies in some way that is important to your study, your sample should contain the same sorts of variation.
Obtaining a representative sample is important in probability sampling because a key goal of studies that rely on probability samples is generalizability . In fact, generalizability is perhaps the key feature that distinguishes probability samples from nonprobability samples. Generalizability refers to the idea that a study’s results will tell us something about a group larger than the sample from which the findings were generated. In order to achieve generalizability, a core principle of probability sampling is that all elements in the researcher’s target population have an equal chance of being selected for inclusion in the study. In research, this is the principle of random selection . Random selection is a mathematical process that we won’t go into too much depth about here, but if you have taken or plan to take a statistics course, you’ll learn more about it there. The important thing to remember about random selection here is that, as previously noted, it is a core principal of probability sampling. If a researcher uses random selection techniques to draw a sample, he or she will be able to estimate how closely the sample represents the larger population from which it was drawn by estimating the sampling error. Sampling error is a statistical calculation of the difference between results from a sample and the actual parameters of a population.
Types of Probability Samples
There are a variety of probability samples that researchers may use. These include simple random samples, systematic samples, stratified samples, and cluster samples.
Simple random samples are the most basic type of probability sample, but their use is not particularly common. Part of the reason for this may be the work involved in generating a simple random sample. To draw a simple random sample, a researcher starts with a list of every single member, or element, of his or her population of interest. This list is sometimes referred to as a sampling frame . Once that list has been created, the researcher numbers each element sequentially and then randomly selects the elements from which he or she will collect data. To randomly select elements, researchers use a table of numbers that have been generated randomly. There are several possible sources for obtaining a random number table. Some statistics and research methods textbooks offer such tables as appendices to the text. Perhaps a more accessible source is one of the many free random number generators available on the Internet. A good online source is the website Stat Trek, which contains a random number generator that you can use to create a random number table of whatever size you might need ( stattrek.com/Tables/Random.aspx ). Randomizer.org also offers a useful random number generator ( http://randomizer.org ).
As you might have guessed, drawing a simple random sample can be quite tedious. Systematic sampling techniques are somewhat less tedious but offer the benefits of a random sample. As with simple random samples, you must be able to produce a list of every one of your population elements. Once you’ve done that, to draw a systematic sample you’d simply select every k th element on your list. But what is k , and where on the list of population elements does one begin the selection process? k is your selection interval or the distance between the elements you select for inclusion in your study. To begin the selection process, you’ll need to figure out how many elements you wish to include in your sample. Let’s say you want to interview 25 fraternity members on your campus, and there are 100 men on campus who are members of fraternities. In this case, your selection interval, or k , is 4. To arrive at 4, simply divide the total number of population elements by your desired sample size. This process is represented in Figure 7.5.
Figure 7.5 Formula for Determining Selection Interval for Systematic Sample

To determine where on your list of population elements to begin selecting the names of the 25 men you will interview, select a random number between 1 and k , and begin there. If we randomly select 3 as our starting point, we’d begin by selecting the third fraternity member on the list and then select every fourth member from there. This might be easier to understand if you can see it visually. Table 7.2 lists the names of our hypothetical 100 fraternity members on campus. You’ll see that the third name on the list has been selected for inclusion in our hypothetical study, as has every fourth name after that. A total of 25 names have been selected.
There is one clear instance in which systematic sampling should not be employed. If your sampling frame has any pattern to it, you could inadvertently introduce bias into your sample by using a systemic sampling strategy. This is sometimes referred to as the problem of periodicity . Periodicity refers to the tendency for a pattern to occur at regular intervals. Let’s say, for example, that you wanted to observe how people use the outdoor public spaces on your campus. Perhaps you need to have your observations completed within 28 days and you wish to conduct four observations on randomly chosen days. Table 7.3 shows a list of the population elements for this example. To determine which days we’ll conduct our observations, we’ll need to determine our selection interval. As you’ll recall from the preceding paragraphs, to do so we must divide our population size, in this case 28 days, by our desired sample size, in this case 4 days. This formula leads us to a selection interval of 7. If we randomly select 2 as our starting point and select every seventh day after that, we’ll wind up with a total of 4 days on which to conduct our observations. You’ll see how that works out in the following table.
Do you notice any problems with our selection of observation days? Apparently we’ll only be observing on Tuesdays. As you have probably figured out, that isn’t such a good plan if we really wish to understand how public spaces on campus are used. My guess is that weekend use probably differs from weekday use, and that use may even vary during the week, just as class schedules do. In cases such as this, where the sampling frame is cyclical, it would be better to use a stratified sampling technique . In stratified sampling, a researcher will divide the study population into relevant subgroups and then draw a sample from each subgroup. In this example, we might wish to first divide our sampling frame into two lists: weekend days and weekdays. Once we have our two lists, we can then apply either simple random or systematic sampling techniques to each subgroup.
Stratified sampling is a good technique to use when, as in our example, a subgroup of interest makes up a relatively small proportion of the overall sample. In our example of a study of use of public space on campus, we want to be sure to include weekdays and weekends in our sample, but because weekends make up less than a third of an entire week, there’s a chance that a simple random or systematic strategy would not yield sufficient weekend observation days. As you might imagine, stratified sampling is even more useful in cases where a subgroup makes up an even smaller proportion of the study population, say, for example, if we want to be sure to include both men’s and women’s perspectives in a study, but men make up only a small percentage of the population. There’s a chance simple random or systematic sampling strategy might not yield any male participants, but by using stratified sampling, we could ensure that our sample contained the proportion of men that is reflective of the larger population.
Up to this point in our discussion of probability samples, we’ve assumed that researchers will be able to access a list of population elements in order to create a sampling frame. This, as you might imagine, is not always the case. Let’s say, for example, that you wish to conduct a study of hairstyle preferences across the United States. Just imagine trying to create a list of every single person with (and without) hair in the country. Basically, we’re talking about a list of every person in the country. Even if you could find a way to generate such a list, attempting to do so might not be the most practical use of your time or resources. When this is the case, researchers turn to cluster sampling. Cluster sampling occurs when a researcher begins by sampling groups (or clusters) of population elements and then selects elements from within those groups.
Let’s take a look at a couple more examples. Perhaps you are interested in the workplace experiences of public librarians. Chances are good that obtaining a list of all librarians that work for public libraries would be rather difficult. But I’ll bet you could come up with a list of all public libraries without too much hassle. Thus you could draw a random sample of libraries (your cluster) and then draw another random sample of elements (in this case, librarians) from within the libraries you initially selected. Cluster sampling works in stages. In this example, we sampled in two stages. As you might have guessed, sampling in multiple stages does introduce the possibility of greater error (each stage is subject to its own sampling error), but it is nevertheless a highly efficient method.
Jessica Holt and Wayne Gillespie (2008)Holt, J. L., & Gillespie, W. (2008). Intergenerational transmission of violence, threatened egoism, and reciprocity: A test of multiple pychosocial factors affecting intimate partner violence. American Journal of Criminal Justice, 33 , 252–266. used cluster sampling in their study of students’ experiences with violence in intimate relationships. Specifically, the researchers randomly selected 14 classes on their campus and then drew a random subsample of students from those classes. But you probably know from your experience with college classes that not all classes are the same size. So if Holt and Gillespie had simply randomly selected 14 classes and then selected the same number of students from each class to complete their survey, then students in the smaller of those classes would have had a greater chance of being selected for the study than students in the larger classes. Keep in mind with random sampling the goal is to make sure that each element has the same chance of being selected. When clusters are of different sizes, as in the example of sampling college classes, researchers often use a method called probability proportionate to size (PPS). This means that they take into account that their clusters are of different sizes. They do this by giving clusters different chances of being selected based on their size so that each element within those clusters winds up having an equal chance of being selected.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- In probability sampling, the aim is to identify a sample that resembles the population from which it was drawn.
- There are several types of probability samples including simple random samples, systematic samples, stratified samples, and cluster samples.
- Imagine that you are about to conduct a study of people’s use of public parks. Explain how you could employ each of the probability sampling techniques described earlier to recruit a sample for your study.
- Of the four probability sample types described, which seems strongest to you? Which seems weakest? Explain.
- [email protected]
- Connecting and sharing with us

- Entrepreneurship
- Growth of firm
- Sales Management
- Retail Management
- Import – Export
- International Business
- Project Management
- Production Management
- Quality Management
- Logistics Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Human Resource Management
- Organizational Culture
- Information System Management
- Corporate Finance
- Stock Market
- Office Management
- Theory of the Firm
- Management Science
- Microeconomics
- Research Process
- Experimental Research
- Research Philosophy
- Management Research
- Writing a thesis
- Writing a paper
- Literature Review
- Action Research
- Qualitative Content Analysis
- Observation
- Phenomenology
- Statistics and Econometrics
- Questionnaire Survey
- Quantitative Content Analysis
- Meta Analysis
The differences between sampling in quantitative and qualitative research
The selection of a sample in quantitative and qualitative research is guided by two opposing philosophies. In quantitative research you attempt to select a sample in such a way that it is unbiased and represents the population from where it is selected. In qualitative research, number considerations may influence the selection of a sample such as: the ease in accessing the potential respondents; your judgement that the person has extensive knowledge about an episode, an event or a situation of interest to you; how typical the case is of a category of individuals or simply that it is totally different from the others. You make every effort to select either a case that is similar to the rest of the group or the one which is totally different. Such considerations are not acceptable in quantitative research.
The purpose of sampling in quantitative research is to draw inferences about the group from which you have selected the sample, whereas in qualitative research it is designed either to gain in-depth knowledge about a situation/event/episode or to know as much as possible about different aspects of an individual on the assumption that the individual is typical of the group and hence will provide insight into the group.
Similarly, the determination of sample size in quantitative and qualitative research is based upon the two different philosophies. In quantitative research you are guided by a predetermined sample size that is based upon a number of other considerations in addition to the resources available. However, in qualitative research you do not have a predetermined sample size but during the data collection phase you wait to reach a point of data saturation. When you are not getting new information or it is negligible, it is assumed you have reached a data saturation point and you stop collecting additional information.
Considerable importance is placed on the sample size in quantitative research, depending upon the type of study and the possible use of the findings. Studies which are designed to formulate policies, to test associations or relationships, or to establish impact assessments place a considerable emphasis on large sample size. This is based upon the principle that a larger sample size will ensure the inclusion of people with diverse backgrounds, thus making the sample representative of the study population. The sample size in qualitative research does not play any significant role as the purpose is to study only one or a few cases in order to identify the spread of diversity and not its magnitude. In such situations the data saturation stage during data collection determines the sample size.
In quantitative research, randomisation is used to avoid bias in the selection of a sample and is selected in such a way that it represents the study population. In qualitative research no such attempt is made in selecting a sample.You purposely select ‘information-rich’ respondents who will provide you with the information you need. In quantitative research, this is considered a biased sample.
Most of the sampling strategies, including some non-probability ones, described in this chapter can be used when undertaking a quantitative study provided it meets the requirements. However, when conducting a qualitative study only the non-probability sampling designs can be used.
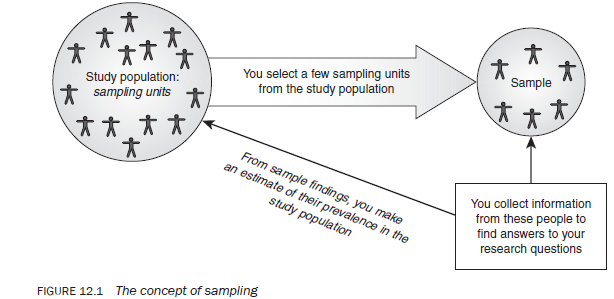
Source: Kumar Ranjit (2012), Research methodology: a step-by-step guide for beginners , SAGE Publications Ltd; Third edition.
29 Jul 2021
30 Jul 2021
6 thoughts on “ The differences between sampling in quantitative and qualitative research ”
These are really enormous ideas in concerning blogging.
You have touched some good things here. Any way keep up wrinting.
Dude these articles are amazing. They helped me a lot.
I want to thank you for your assistance and this post. It’s been great.
Thank you for writing this article!
Your articles are extremely helpful to me. Please provide more information!
You helped me a lot by posting this article and I love what I’m learning.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Username or email address *
Password *
Log in Remember me
Lost your password?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Probability sampling methods. Probability sampling means that every member of the population has a chance of being selected. It is mainly used in quantitative research. If you want to produce results that are representative of the whole population, probability sampling techniques are the most valid choice. There are four main types of ...
Key Takeaways: Sampling techniques in qualitative research include purposive, convenience, snowball, and theoretical sampling. Choosing the right sampling technique significantly impacts the accuracy and reliability of the research results. It's crucial to consider the potential impact on the bias, sample diversity, and generalizability when ...
However, mixed methods studies also have unique considerations based on the relationship of quantitative and qualitative research within the study. Sampling in Qualitative Research Sampling in qualitative research may be divided into two major areas: overall sampling strategies and issues around sample size.
In quantitative studies, the sampling plan, including sample size, is determined in detail in beforehand but qualitative research projects start with a broadly defined sampling plan. This plan enables you to include a variety of settings and situations and a variety of participants, including negative cases or extreme cases to obtain rich data.
Answer 1: In qualitative research, samples are selected subjectively according to. the pur pose of the study, whereas in quantitative researc h probability sampling. technique are used to select ...
You might remember studying sampling in a quantitative research course. Sampling is important here too, but it works a bit differently. Unlike quantitative research, qualitative research involves nonprobability sampling. This chapter explains why this is so and what qualities instead make a good sample for qualitative research.
Sampling Strategies in Qualitative Research In: The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Data Analysis By: Tim Rapley ... SAGE Research Methods. Page 2 of 21. Sampling Strategies in Qualitative Research. 1. 1. ... Within more quantitative work, when working with a random sample you need to be able ...
Any senior researcher, or seasoned mentor, has a practiced response to the 'how many' question. Mine tends to start with a reminder about the different philosophical assumptions undergirding qualitative and quantitative research projects (Staller, 2013).As Abrams (2010) points out, this difference leads to "major differences in sampling goals and strategies."(p.537).
This chapter explains how to design suitable sampling strategies for qualitative research. The focus of this chapter is purposive (or theoretical) sampling to produce credible and trustworthy explanations of a phenomenon (a specific aspect of society). A specific research question (RQ) guides the methodology (the study design or approach).It defines the participants, location, and actions to ...
Abstract. Qualitative sampling methods differ from quantitative sampling methods. It is important that one understands those differences, as well as, appropriate qualitative sampling techniques. Appropriate sampling choices enhance the rigor of qualitative research studies. These types of sampling strategies are presented, along with the pros ...
The importance of sampling extends to the ability to draw accurate inferences, and it is an integral part of qualitative guidelines across research methods. Sampling considerations are important in quantitative and qualitative research when considering a target population and when drawing a sample that will either allow us to generalize (i.e ...
Abstract. In gerontology the most recognized and elaborate discourse about sampling is generally thought to be in quantitative research associated with survey research and medical research. But sampling has long been a central concern in the social and humanistic inquiry, albeit in a different guise suited to the different goals.
However, probability sampling techniques are uncommon in modern quantitative research because of practical constraints; non-probability sampling, such as by convenience, is now normative. When sampling this way, special attention should be given to statistical implications of issues such as range restriction and omitted variable bias.
what is commonly referred to as qualitative from quantitative inquiry is the kind of sampling used. While qualitative research typically involves pur-poseful sampling to enhance understanding of the information-rich case (Patton, 1990), quantitative research ideally involves probability sampling to permit statistical inferences to be made. Although
Abstract. In quantitative research, collecting data from an entire population of a study is impractical in many instances. It squanders resources like time and money which can be minimized by choosing suitable sampling techniques between probability and non-probability methods. The chapter outlines a brief idea about the different categories of ...
Qualitative sampling methods differ from quantitative sampling methods. It is important that one understands those differences, as well as, appropriate qualitative sampling techniques. Appropriate sampling choices enhance the rigor of qualitative research studies. These types of sampling strategies are presented, along with the pros and cons of ...
Principles of Purposeful Sampling. Purposeful sampling is a technique widely used in qualitative research for the identification and selection of information-rich cases for the most effective use of limited resources (Patton, 2002).This involves identifying and selecting individuals or groups of individuals that are especially knowledgeable about or experienced with a phenomenon of interest ...
Basics of social research: Qualitative and quantitative approaches (2nd ed.). Boston, MA: Pearson.underscores the point that one should avoid attempting to make statistical generalizations from data collected using quota sampling methods.If you are interested in the history of polling, I recommend a recent book: Fried, A. (2011).
Probability Sampling. Unlike nonprobability sampling, probability sampling refers to sampling techniques for which a person's (or event's) likelihood of being selected for membership in the sample is known. You might ask yourself why we should care about a study element's likelihood of being selected for membership in a researcher's sample.
Qualitative sampling methods differ from quantitative sampling methods. It is important that one understands those differences, as well as, appropriate qualitative sampling techniques. Appropriate sampling choices enhance the rigor of qualitative research studies. These types of sampling strategies are presented, along with the pros and cons of ...
In quantitative research, this is considered a biased sample. Most of the sampling strategies, including some non-probability ones, described in this chapter can be used when undertaking a quantitative study provided it meets the requirements. However, when conducting a qualitative study only the non-probability sampling designs can be used.
In gerontology the most recognized and elaborate discourse about sampling is generally thought to be in quantitative research associated with survey research and medical research. But sampling has long been a central concern in the social and humanistic inquiry, albeit in a different guise suited to the different goals. There is a need for more ...
We conducted a mixed-methods exploratory sequential study that consisted of two phases: an initial qualitative phase, followed by a quantitative phase. This approach drew on the depth and breadth of data from qualitative and quantitative methods, resulting in richer data and a better understanding of the answers to our research questions [9-11 ...