

2019 Best Papers published in the Environmental Science journals of the Royal Society of Chemistry

In 2019, the Royal Society of Chemistry published 180, 196 and 293 papers in Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts , Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology , and Environmental Science: Nano , respectively. These papers covered a wide range of topics in environmental science, from biogeochemical cycling to water reuse to nanomaterial toxicity. And, yes, we also published papers on the topic of the environmental fate, behavior, and inactivation of viruses. 1–10 We are extremely grateful that so many authors have chosen our journals as outlets for publishing their research and are equally delighted at the high quality of the papers that we have had the privilege to publish.
Our Associate Editors, Editorial Boards, and Advisory Boards were enlisted to nominate and select the best papers from 2019. From this list, the three Editors-in-Chief selected an overall best paper from the entire Environmental Science portfolio. It is our pleasure to present the winners of the Best Papers in 2019 to you, our readers.
Overall Best Paper
In this paper, Johansson et al. examine sea spray aerosol as a potential transport vehicle for perfluoroalkyl carboxylic and sulfonic acids. The surfactant properties of these compounds are well known and, in fact, key to many of the technical applications for which they are used. The fact that these compounds are enriched at the air–water interface makes enrichment in sea spray aerosols seem reasonable. Johansson et al. systematically tested various perfluoroalkyl acids enrichment in aerosols under conditions relevant to sea spray formation, finding that longer chain lengths lead to higher aerosol enrichment factors. They augmented their experimental work with a global model, which further bolstered the conclusion that global transport of perfluoroalkyl acids by sea spray aerosol is and will continue to be an important process in determining the global distribution of these compounds.
Journal Best Papers
Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts
First Runner-up Best Paper: Yamakawa, Takami, Takeda, Kato, Kajii, Emerging investigator series: investigation of mercury emission sources using Hg isotopic compositions of atmospheric mercury at the Cape Hedo Atmosphere and Aerosol Monitoring Station (CHAAMS), Japan , Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts , 2019, 21 , 809–818, DOI: 10.1039/C8EM00590G .
Second Runner-up Best Paper: Avery, Waring, DeCarlo, Seasonal variation in aerosol composition and concentration upon transport from the outdoor to indoor environment , Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts , 2019, 21 , 528–547, DOI: 10.1039/C8EM00471D .
Best Review Article: Cousins, Ng, Wang, Scheringer, Why is high persistence alone a major cause of concern? Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts , 2019, 21 , 781–792, DOI: 10.1039/C8EM00515J .
Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology
First Runner-up Best Paper: Yang, Lin, Tse, Dong, Yu, Hoffmann, Membrane-separated electrochemical latrine wastewater treatment , Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. , 2019, 5 , 51–59, DOI: 10.1039/C8EW00698A .
Second Runner-up Best Paper: Genter, Marks, Clair-Caliot, Mugume, Johnston, Bain, Julian, Evaluation of the novel substrate RUG™ for the detection of Escherichia coli in water from temperate (Zurich, Switzerland) and tropical (Bushenyi, Uganda) field sites , Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. , 2019, 5 , 1082–1091, DOI: 10.1039/C9EW00138G .
Best Review Article: Okoffo, O’Brien, O’Brien, Tscharke, Thomas, Wastewater treatment plants as a source of plastics in the environment: a review of occurrence, methods for identification, quantification and fate , Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. , 2019, 5 , 1908–1931, DOI: 10.1039/C9EW00428A .
Environmental Science: Nano
First Runner-up Best Paper: Janković, Plata, Engineered nanomaterials in the context of global element cycles , Environ. Sci.: Nano , 2019, 6 , 2697–2711, DOI: 10.1039/C9EN00322C .
Second Runner-up Best Paper: González-Pleiter, Tamayo-Belda, Pulido-Reyes, Amariei, Leganés, Rosal, Fernández-Piñas, Secondary nanoplastics released from a biodegradable microplastic severely impact freshwater environments , Environ. Sci.: Nano , 2019, 6 , 1382–1392, DOI: 10.1039/C8EN01427B .
Best Review Article: Lv, Christie, Zhang, Uptake, translocation, and transformation of metal-based nanoparticles in plants: recent advances and methodological challenges , Environ. Sci.: Nano , 2019, 6 , 41–59, DOI: 10.1039/C8EN00645H .
Congratulations to the authors of these papers and a hearty thanks to all of our authors. As one can clearly see from the papers listed above, environmental science is a global effort and we are thrilled to have contributions from around the world. In these challenging times, we are proud to publish research that is not only great science, but also relevant to the health of the environment and the public. Finally, we also wish to extend our thanks to our community of editors, reviewers, and readers. We look forward to another outstanding year of Environmental Science , reading the work generated not just from our offices at home, but also from back in our laboratories and the field.
Kris McNeill, Editor-in-Chief
Paige Novak, Editor-in-Chief
Peter Vikesland, Editor-in-Chief
- A. B Boehm, Risk-based water quality thresholds for coliphages in surface waters: effect of temperature and contamination aging, Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts , 2019, 21 , 2031–2041, 10.1039/C9EM00376B .
- L. Cai, C. Liu, G. Fan, C Liu and X. Sun, Preventing viral disease by ZnONPs through directly deactivating TMV and activating plant immunity in Nicotiana benthamiana , Environ. Sci.: Nano , 2019, 6 , 3653–3669, 10.1039/C9EN00850K .
- L. W. Gassie, J. D. Englehardt, N. E. Brinkman, J. Garland and M. K. Perera, Ozone-UV net-zero water wash station for remote emergency response healthcare units: design, operation, and results, Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. , 2019, 5 , 1971–1984, 10.1039/C9EW00126C .
- L. M. Hornstra, T. Rodrigues da Silva, B. Blankert, L. Heijnen, E. Beerendonk, E. R. Cornelissen and G. Medema, Monitoring the integrity of reverse osmosis membranes using novel indigenous freshwater viruses and bacteriophages, Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. , 2019, 5 , 1535–1544, 10.1039/C9EW00318E .
- A. H. Hassaballah, J. Nyitrai, C. H. Hart, N. Dai and L. M. Sassoubre, A pilot-scale study of peracetic acid and ultraviolet light for wastewater disinfection, Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. , 2019, 5 , 1453–1463, 10.1039/C9EW00341J .
- W. Khan, J.-Y. Nam, H. Woo, H. Ryu, S. Kim, S. K. Maeng and H.-C. Kim, A proof of concept study for wastewater reuse using bioelectrochemical processes combined with complementary post-treatment technologies, Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. , 2019, 5 , 1489–1498, 10.1039/C9EW00358D .
- J. Heffron, B. McDermid and B. K. Mayer, Bacteriophage inactivation as a function of ferrous iron oxidation, Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. , 2019, 5 , 1309–1317, 10.1039/C9EW00190E .
- S. Torii, T. Hashimoto, A. T. Do, H. Furumai and H. Katayama, Impact of repeated pressurization on virus removal by reverse osmosis membranes for household water treatment, Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. , 2019, 5 , 910–919, 10.1039/C8EW00944A .
- J. Miao, H.-J. Jiang, Z.-W. Yang, D.-y. Shi, D. Yang, Z.-Q. Shen, J. Yin, Z.-G. Qiu, H.-R. Wang, J.-W. Li and M. Jin, Assessment of an electropositive granule media filter for concentrating viruses from large volumes of coastal water, Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol. , 2019, 5 , 325–333, 10.1039/C8EW00699G .
- K. L. Nelson, A. B. Boehm, R. J. Davies-Colley, M. C. Dodd, T. Kohn, K. G. Linden, Y. Liu, P. A. Maraccini, K. McNeill, W. A. Mitch, T. H. Nguyen, K. M. Parker, R. A. Rodriguez, L. M. Sassoubre, A. I. Silverman, K. R. Wigginton and R. G. Zepp, Sunlight mediated inactivation of health relevant microorganisms in water: a review of mechanisms and modeling approaches, Environ. Sci.: Processes Impacts , 2018, 20 , 1089–1122, 10.1039/C8EM00047F .
- Search by keyword
- Search by citation
Page 1 of 5
Northward expansion trends and future potential distribution of a dragonfly Ischnura senegalensis Rambur under climate change using citizen science data in South Korea
Citizen science is becoming a mainstream approach of baseline data collection to monitor biodiversity and climate change. Dragonflies (Odonata) have been ranked as the highest priority group in biodiversity mo...
- View Full Text
Morphological variables restrict flower choice of Lycaenid butterfly species: implication for pollination and conservation
Butterflies make an important part for plant-pollinator guild. These are nectar feeder or occasionally pollen feeder and thus proboscis of the butterfly species are considered as one of the most important vari...
Honey bees and their brood: a potentially valuable resource of food, worthy of greater appreciation and scientific attention
Despite the consumption of bee brood in several parts of the world, particularly in the tropical areas, the practice has received comparatively little attention. We have reviewed all the available information ...
Attributes and references to honey bees (Insecta; Hymenoptera; Apidae) and their products in some Asian and Australian societies’ folkloristic domains
References to insects in myths, stories, and idioms can be found in almost any culture, but with regard to references involving honey bee species in the Asia-Australian region, little information is available....
RETRACTED ARTICLE: Major environmental factors and traits of invasive alien plants determining their spatial distribution
As trade increases, the influx of various alien species and their spread to new regions are prevalent and no longer a special problem. Anthropogenic activities and climate changes have made the distribution of...
Spatial distribution of halophytes and environment factors in salt marshes along the eastern Yellow Sea
Salt marshes provide a variety of ecosystem services; however, they are vulnerable to human activity, water level fluctuations, and climate change. Analyses of the relationships between plant communities and e...
PollMap: a software for crop pollination mapping in agricultural landscapes
Ecosystem service mapping is an important tool for decision-making in landscape planning and natural resource management. Today, pollination service mapping is based on the Lonsdorf model (InVEST software) tha...
Current status of alert alien species management for the establishment of proactive management systems in Korea
Some of the introduced alien species introduced settle, multiply, and spread to become invasive alien species (IAS) that threaten biodiversity. To prevent this, Korea and other countries legally designate and ...
Dust and sandstorm: ecosystem perspectives on dryland hazards in Northeast Asia: a review
A review of the literature was carried out to study dust and sandstorm (DSS) in terms of its ecosystem processes and relationship to other dryland disasters in Northeast Asia. Drylands are ecosystems that incl...
Changes in nocturnal insect communities in forest-dominated landscape relevant to artificial light intensity
Artificial light at night has recently been identified as a major factor adversely affecting global insect diversity. Here, we compared the insect diversity in Gwangneung Forest Biosphere Reserve, specifically...
Occurrence and diet analysis of sea turtles in Korean shore
Sea turtles, which are globally endangered species, have been stranded and found as bycatch on the Korean shore recently. More studies on sea turtles in Korea are necessary to aid their conservation. To invest...
Quantifying how urban landscape heterogeneity affects land surface temperature at multiple scales
Landscape metrics have been widely applied to quantifying the relationship between land surface temperature and urban spatial patterns and have received acceptable verification from landscape ecologists but so...
The relationship of mean temperature and 9 collected butterfly species’ wingspan as the response of global warming
Organism body size is a basic characteristic in ecology; it is related to temperature according to temperature-size rule. Butterflies are affected in various aspects by climate change because they are sensitiv...
Non-deep physiological dormancy in seeds of Euphorbia jolkinii Boiss. native to Korea
Euphorbia jolkinii Boiss. is a perennial species native to Jeju Island and the southern coastal area of Korea. Particularly on Jeju Island, the yellow flowers of E. jolkinii Boiss. have a high ornamental value be...
Predation of the Japanese keelback ( Hebius vibakari Boie, 1826) by the Slender racer ( Orientocoluber spinalis Peters, 1866)
The Slender racer ( Orientocoluber spinalis Peters, 1866) has recently been reclassified to the new genus Orientocoluber from Hierophis . Ecological knowledge of this species is limited due to its highly mobile beh...
Major environmental factors and traits of invasive alien plants determine their spatial distribution: a case study in Korea
As trade increases, the influx of various alien species and their spread to new regions are prevalent, making them a general problem globally. Anthropogenic activities and climate change have led to alien spec...
Distribution and habitat use of the endangered Siberian flying squirrel Pteromys volans (Rodentia: Sciuridae)
Understanding the habitat characteristics of the endangered Siberian flying squirrel Pteromys volans is the first step in conserving and managing the forests it requires for nesting, gliding, and feeding. Therefo...
How effective are artificial nests in attracting bees? A review
Recent declines in bee populations, along with increasing demand for pollination services in urban, agricultural, and natural environments, have led to strategies to attract wild bees to these areas. One of th...
Tissue-specific systemic responses of the wild tobacco Nicotiana attenuata against stem-boring herbivore attack
Plants are able to optimize defense responses induced by various herbivores, which have different feeding strategies. Local and systemic responses within a plant after herbivory are essential to modulate herbi...
Estimating potential range shift of some wild bees in response to climate change scenarios in northwestern regions of Iran
Climate change is occurring rapidly around the world, and is predicted to have a large impact on biodiversity. Various studies have shown that climate change can alter the geographical distribution of wild bee...
Trends in the effects of climate change on terrestrial ecosystems in the Republic of Korea
In this review, we aimed to synthesize the current knowledge on the observed and projected effects of climate change on the ecosystems of Korea (i.e., the Republic of Korea (ROK) or South Korea), as well as th...
Principle of restoration ecology reflected in the process creating the National Institute of Ecology
The creation of the National Institute of Ecology began as a national alternative project to preserve mudflats instead of constructing the industrial complexes by reclamation, and achieve regional development....
Small-scale spatial genetic structure of Asarum sieboldii metapopulation in a valley
Asarum sieboldii Miq., a species of forest understory vegetation, is an herbaceous perennial belonging to the family Aristolochiaceae. The metapopulation of A. sieboldii is distributed sparsely and has a short se...
Diel and seasonal activity pattern of alien sika deer with sympatric mammalian species from Muljangori-oreum wetland of Hallasan National Park, South Korea
Sika deer, Cervus nippon , were originally introduced to South Korea from Japan and Taiwan for commercial farming purposes. Unfortunately, they were released into the wild during religious events and have since be...
Effects of different day length and wind conditions to the seedling growth performance of Phragmites australis
To understand shade and wind effects on seedling traits of common reed ( Phragmites australis ), we conducted a mesocosm experiment manipulating day length (10 h daytime a day as open canopy conditions or 6 h dayti...
Categorized wetland preference and life forms of the vascular plants in the Korean Peninsula
In 2020, a categorized list of wetland preferences, major habitats, and life forms of 4145 vascular plant taxa occurring in the Korean Peninsula was published by the National Institute of Biological Resources....
Elevational distribution ranges of vascular plant species in the Baekdudaegan mountain range, South Korea
The climate is changing rapidly, and this may pose a major threat to global biodiversity. One of the most distinctive consequences of climate change is the poleward and/or upward shift of species distribution ...
Study on the photosynthetic characteristics of Eutrema japonica (Siebold) Koidz. under the pulsed LEDs for simulated sunflecks
The sunfleck is an important light environmental factor for plants that live under the shade of trees. Currently, the smartfarm has a system that can artificially create these sunfleks. Therefore, it was inten...
Influence of trees and associated variables on soil organic carbon: a review
The level of soil organic carbon (SOC) fluctuates in different types of forest stands: this variation can be attributed to differences in tree species, and the variables associated with soil, climate, and topo...
Comparison of ecophysiological and leaf anatomical traits of native and invasive plant species
To address the lack of evidence supporting invasion by three invasive plant species ( Imperata cylindrica, Lantana camara, and Chromolaena odorata ) in tropical ecosystems, we compared the ecophysiological and leaf...
Effects of soil water content and light intensity on the growth of Molinia japonica in montane wetlands in South Korea
Montane wetlands are unique wetland ecosystems with distinct physicochemical characteristics, and Molinia japonica often makes dominant communities in montane wetlands in South Korea. In order to figure out the e...
First detection of ranavirus in a wild population of Dybowski’s brown frog ( Rana dybowskii ) in South Korea
Ranavirus is an emerging infectious disease which has been linked to mass mortality events in various amphibian species. In this study, we document the first mass mortality event of an adult population of Dybo...
Cushion plant Silene acaulis is a pioneer species at abandoned coal piles in the High Arctic, Svalbard
Abandoned coal piles after the closure of mines have a potential negative influence on the environment, such as soil acidification and heavy metal contamination. Therefore, revegetation by efficient species is...
Vegetation structure and distribution characteristics of Symplocos prunifolia , a rare evergreen broad-leaved tree in Korea
In Korea, Symplocos prunifolia Siebold. & Zucc. is only found on Jeju Island. Conservation of the species is difficult because little is known about its distribution and natural habitat. The lack of research and ...
Growth performance of planted population of Pinus roxburghii in central Nepal
Climate change has altered the various ecosystem processes including forest ecosystem in Himalayan region. Although the high mountain natural forests including treelines in the Himalayan region are mainly repo...
Correction to: Application of smart mosquito monitoring traps for the mosquito forecast systems by Seoul Metropolitan city
An amendment to this paper has been published and can be accessed via the original article.
The original article was published in Journal of Ecology and Environment 2020 44 :13
Correction to: Effect of precipitation on soil respiration in a temperate broad-leaved forest
The original article was published in Journal of Ecology and Environment 2018 42 :10
Effects of cutting and sowing seeds of native species on giant ragweed invasion and plant diversity in a field experiment
Ambrosia trifida is a highly invasive annual plant, but effective control methods have not been proposed. Among various eradication methods, cutting is a simple measure to control invasive plants, and sowing seed...
Mid-term (2009-2019) demographic dynamics of young beech forest in Albongbunji Basin, Ulleungdo, South Korea
The stem exclusion stage is a stage of forest development that is important for understanding the subsequent understory reinitiation stage and maturation stage during which horizontal heterogeneity is formed. ...
Annual and spatial variabilities in the acorn production of Quercus mongolica
Genus Quercus is a successful group that has occupied the largest area of forest around the world including South Korea. The acorns are an important food source for both wild animals and humans. Although the repr...
Prevalence of Puccinia abrupta var. partheniicola and its impact on Parthenium hysterophorus in Kathmandu Valley, Nepal
Parthenium hysterophorus is a noxious invasive weed in tropical and subtropical regions of the world, including Nepal. Among 11 species of biological control agents released to control P. hysterophorus in Ausrtal...
Ecological impact of fast industrialization inferred from a sediment core in Seocheon, West Coast of Korean Peninsula
Rapid industrialization has caused various impacts on nature, including heavy metal pollution. However, the impacts of industrialization vary depending on the types of industrializing activity and surrounding ...
Influence of roadkill during breeding migration on the sex ratio of land crab ( Sesarma haematoche )
Adult land crabs generally live on land while their larvae live in the sea. In the case of Sesarma haematoche , female crabs migrate from land to sea to release the larvae at the high tide of syzygy night. Artific...
Population structure and regeneration of Himalayan endemic Larix species in three high-altitude valleys in Nepal Himalaya
The Himalayan forests are of great importance to sustain the nature and community resource demands. These forests are facing pressures both from anthropogenic activities and ongoing global climatic changes. Po...
Otolith microchemistry reveals the migration patterns of the flathead grey mullet Mugil cephalus (Pisces: Mugilidae) in Korean waters
The flathead grey mullet Mugil cephalus has the widest distribution among mugilid species. Recent studies based on mitochondrial DNA sequences showed that the species comprises at least 14 different groups, three...
Population size, group and age structure of geladas ( Theropithecus gelada ) in escarpments of Eastern Tigray, Ethiopia: implication for conservation
Geladas ( Theropithecus gelada ), endemic to Ethiopia, are distributed closely related to the escarpments and gorge systems of the country, and large populations are found in the Simien Mountain National Park. This...
Coexistence of plant species under harsh environmental conditions: an evaluation of niche differentiation and stochasticity along salt marsh creeks
Ecologists have achieved much progress in the study of mechanisms that maintain species coexistence and diversity. In this paper, we reviewed a wide range of past research related to these topics, focusing on ...
Re-emergence of the Glossy Ibis ( Plegadis falcinellus ) in inland South Korea
Glossy Ibis ( Plegadis falcinellus ), which has never been recorded in South Korea, appeared on Jeju Island in 2018 and re-emerged in the inland area of Seocheon-gun (South Chungcheong Province) and in Goyang-si (G...
Diet composition of the Korean wild boar Sus scrofa coreanus (Suidae) at Mt. Jeombongsan, Korea
Korean wild boars ( Sus scrofa coreanus Heude), because of their adaptability, are a widespread large mammal; however, they sometimes cause problems by invading farms and eating the crops, creating insufficiencies...
Review on the succession process of Pinus densiflora forests in South Korea: progressive and disturbance-driven succession
Most of the Pinus densiflora forests, occupying the largest area, have been restored in South Korea since the 1970s. As young pioneer forests, the succession process is under way. Since the forests are distribute...
Journal of Ecology and Environment
ISSN: 2288-1220
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]

Sustainable Development with Renewable Energy
The 10th International Conference on Energy and Environment Research—ICEER 2023
- Conference proceedings
- © 2024
- Nídia S. Caetano 0
Departamento de Engenharia Química, Instituto Superior de Engenharia do Porto, Porto, Portugal
You can also search for this editor in PubMed Google Scholar
- Addresses energy decarbonization
- Discusses how and why renewable energy can be more sustainable
- Includes case studies relevant to renewable energy production systems
Part of the book series: Environmental Science and Engineering (ESE)
Included in the following conference series:
- ICEER: International Conference on Energy and Environment Research
Conference proceedings info: ICEER 2023.
152 Accesses
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this book
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Other ways to access
Licence this eBook for your library
Institutional subscriptions
Table of contents (38 papers)
Front matter.
- Renewable Energy
Agrivoltaic System Development Barriers from European Legislative Framework Perspective
Approach to short-term planning of the development of distribution electrical networks.
- Stefka Nedelcheva, Petya Tsvetkova
Influence of the Neutral Grounding Mode on the Reliability of Actively Adaptive Electric Grids
- Hristo Ilchev

Technical Feasibility and Optimization of Photovoltaic Solar Panels in the Central Area of Peru
- Kattia Eliana Melgar Dionicio, Cesar Augusto Ravines Salazar, Anieval Peña-Rojas, Frans Carhuamaca Castro, Geraldine Yupanqui Fernandez
Gasification of Animal Fat Using Dolomite as Particle Bed in a Downdraft Fixed Bed Reactor
- A. L. Araujo, F. T. Silva, A. Ribeiro, J. B. L. M. Campos, R. M. Pilão
Energy Production from Agro-Wastes: Comparative Studies for Wine Vinasse and Pig Slurry
- Andreia D. Santos, Rosa M. Quinta-Ferreira, Luís M. Castro
Energy Recovery and Greenhouse Gas Emission Reduction Potential of Bio-Waste in South American Countries
- H. Romero, M. Farias, G. Armijos, W. Torres, A. Castillo
Modelling, Simulation and Forecasting of Energy and Carbon Markets
The effect of blade curvature on the pico scale undershot water wheel performance.
- Warjito, Rafi Adhi Pranata, Budiarso, Muhammad Mizan, Kevin Geraldo, Farhan Rizqi Syahnakri
Variation of Blade Angle on the Performance of the Undershot Waterwheel on the Pico Scale
- Warjito, Kevin Geraldo, Budiarso, Muhammad Mizan, Rafi Adhi Pranata, Farhan Rizqi Syahnakri
Investigation of Coconut Methyl Ester (CME)-Palm Oil Methyl Ester (POME)-Diesel Blends Volatility
- Natalina Damanik, Iswan Prahastono, Tatang Hernas Soerawidjaja, Iman Kartolaksono Reksowardojo, Tubagus Ahmad Fauzi Soelaiman, Handrea Bernando Tambunan
Hardware-in-the-Loop Simulation Based on Internet of Things: An Energy Community Digital Twin Case Study
- Modar Zheiry, Luis Gomes, Pedro Faria, Zita Vale
Mathematical Modeling of a Sustainable Dewatering Process for Blueberries and Raspberries Preservation
- Sérgio Lopes, Rafael Santos, Dulcineia Wessel, Isabel Brás, Maria Elisabete Silva, Tânia Ferreira et al.
- Energy Efficiency
Thermal Comfort, Solar Exposure, Energy Production, and Carbon Reduction of Court-Yarded Clustered Sustainable Housing in Arid Regions
- Mohammad Fahmy, Hatem Mahmoud, Ibrahim Elwy, Marwa Abdelalim, Bassel Essam
Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Recovery System for Potential Application in the European Cement Industry
- G. Cevolani, G. Messina, C. Salvini, A. Giovannelli
Comparison Between Centrifugal and Inward Radial Turbines for Organic Rankine Cycle Plants
- E. M. Archilei, C. Salvini, A. Giovannelli
Preliminary Results from the Use of Pear Waste in Single-Chamber Microbial Fuel Cells
- Segundo Rojas-Flores, Renny Nazario-Naveda, Santiago M. Benites, Moisés Gallozzo-Cardenas
Other volumes
- Sustainable Buildings
- Advanced Energy Technologies
- Modelling, Simulation
About this book
This proceedings book contains the full papers of the 10th edition of the International Conference on Energy and Environment Research, ICEER 2023, that took place in Madrid, Spain during October 7–9, 2023. ICEER 2023 is a joint organization of the School of Engineering (ISEP) of the Polytechnic of Porto (P.Porto) and the SCIEI, with collaboration of the Dipartimento di Ingegneria of the Università degli studi "Roma Tre", CIETI and LEPABE research groups. This book includes all the well prepared full papers presented at ICEER 2023.
Editors and Affiliations
Nídia S. Caetano
About the editor
She was the Sub-Director of the Chemical Engineering Department of ISEP for the Infrastructures and Facilities (2014-2016), Course Director of the MSc in Sustainable Energies of the Mechanical Engineering Department of ISEP (March 2013 to June 2018) and Sub-Director of the same MSc (September 2010 to March 2013 and June2018 to June 2022).
Nídia Caetano was the Advisor of the President of ISEP for Environment/Sustainability (2007 to 2018); Vice-President of APESB (Portuguese Association of Sanitary and Environmental Engineering) from 2019-2020 and from 2022; President of the Fiscal Board of the OERN (Order of the Engineers the Northern Region) from 2022.
Nídia Caetano is External Researcher with LEPABE – Laboratory for Process Engineering, Environment, Biotechnology and Energy, Faculty of Engineering, University of Porto, Rua Dr. Roberto Frias, 4200-465 Porto, Portugal, and ALiCE – Associate Laboratory in Chemical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, University of Porto, Rua Dr. Roberto Frias, 4200-465 Porto, Portugal, and Collaborator at CIETI/ISEP/P.Porto. She funded and is the Coordinator of the Microalgae research laboratory of ISEP in 2008. She was the supervisor of several post-doctoral researchers, PhD and Master students. She has intense activity as project evaluator of national and international agencies.
Nídia Caetano is Associate Editor for Biomass of Renewable Energy (Elsevier), Member of the Editorial Advisory Board of Algal Research (Elsevier), Review Editor in Sustainable Energy Systems and Policies (Frontiers) and Member of the Editorial Board of Green Technology, Resilience, and Sustainability (Springer). She Guest Edited 20 Special Issues in several international journals (Elsevier, Frontiers, Springer, MDPI), and Guest Edited one book of the Environmental Science and Engineering book series (Springer) has authored or co-authored +250 conference and journal papers with peer review, 20 book chapters, and was the Keynote Speaker or Invited Lecturer of several international conferences.
She has organized and been the conference or program chair of international conferences (ICEER series, from 2016, TEEM, JTIR, ISWA/APESB Beacon conference in Luanda and in Lobito, among others).
Bibliographic Information
Book Title : Sustainable Development with Renewable Energy
Book Subtitle : The 10th International Conference on Energy and Environment Research—ICEER 2023
Editors : Nídia S. Caetano
Series Title : Environmental Science and Engineering
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-54394-4
Publisher : Springer Cham
eBook Packages : Engineering , Engineering (R0)
Copyright Information : The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2024
Hardcover ISBN : 978-3-031-54393-7 Published: 30 April 2024
Softcover ISBN : 978-3-031-54396-8 Due: 31 May 2024
eBook ISBN : 978-3-031-54394-4 Published: 29 April 2024
Series ISSN : 1863-5520
Series E-ISSN : 1863-5539
Edition Number : 1
Number of Pages : XXXIV, 498
Number of Illustrations : 33 b/w illustrations, 158 illustrations in colour
Topics : Mechanical Engineering , Industrial Chemistry/Chemical Engineering
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- MyU : For Students, Faculty, and Staff
Catherine French, NAE
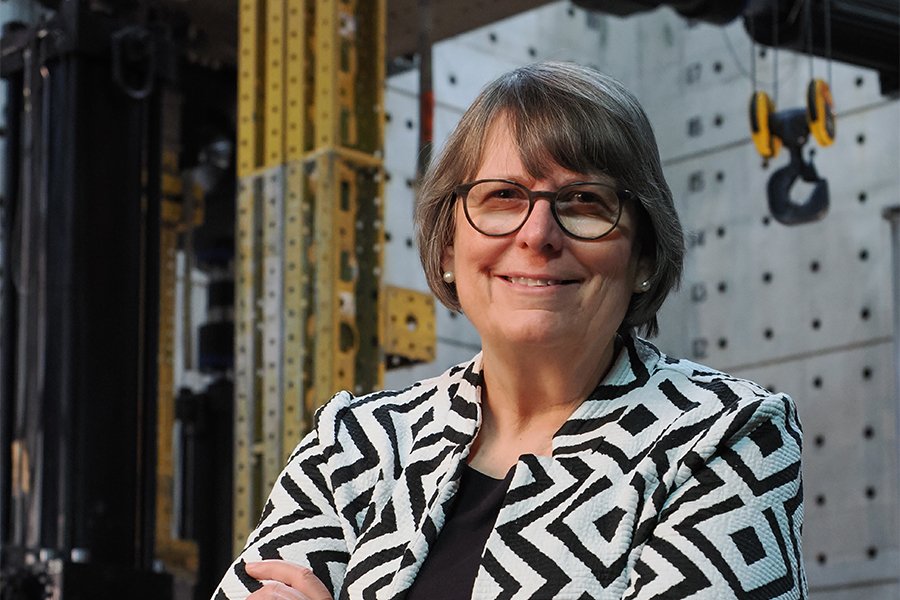

Professor Catherine E. Wolfgram French has been elected to the National Academy of Engineering (NAE). This is among the highest professional distinctions awarded to an engineer. The NAE elected only 114 new members and 21 foreign members this year.
French joins previously elected members from the Department of Civil, Environmental, and Geo- Engineering: Professor Emmanuel Detournay and Professors Emeriti Steve Crouch, Charles Fairhurst, and Theodore Galambos.
Catherine French, a College of Science and Engineering Distinguished Professor in the Department of Civil, Environmental, and Geo- Engineering, is a renowned structural engineer. She was recognized by NAE for “design, safety, and construction of structural concrete buildings and bridges.” Her research interests include the behavior of reinforced and prestressed concrete structural systems, field monitoring of structures, numerical and experimental investigations of structural systems including time-dependent and environmental effects, evaluation and repair of damaged structures, and development and application of new aterials. French led the creation of the Multi-Axial Subassemblage Testing (MAST) Laboratory in 2004. She has served on the national concrete building code committee for nearly 30 years. Her research on reinforced and prestressed concrete structural systems led to new guidelines to improve public safety.
French has received national recognition for her contributions in the area of structural engineering, and for her teaching, leadership, and research. She received the highest honors from the American Society of Civil Engineers (Distinguished Member 2018) and the American Concrete Institute (ACI Honorary Member 2019).
French started her academic career at UMN, following in the footsteps of her father, who earned his Electrical Engineering degree at UMN, and two sisters (Electrical Engineering and Math Education). After completing her bachelor’s degree in 1979, French went on to complete her master’s and Ph.D. at the University of Illinois at Urbana- Champaign. French then returned to UMN as a new faculty member in 1984. She was the first female professor in civil engineering.
Since 2019, she has been a member of the University of Minnesota Academy of Distinguished Teachers. She has mentored more than 85 graduate students, postdoctoral researchers, and visiting scholars. She also has published and edited more than 175 research papers and discussions.

In addition to her academic and professional accomplishments, French counts relationships among her great fortunes. “I have been very fortunate with a supportive family, with great students, colleagues, and collaborators. My graduate advisor Mete Sozen had a huge impact on my pursuing a Ph.D. and was very supportive throughout my career. And my family is so important to me!”
Two UMN professors and six alumni elected to NAE this year.
Related news releases
- Randal Barnes receives Horace T Morace Award
- Catherine French elected to the National Academy of Engineering
- How is our environment affected by wide use of antibiotics?
- The next generation of transportation engineers: Ben Rosenblad
- Judy Yang Receives NSF CAREER Award
- Future undergraduate students
- Future transfer students
- Future graduate students
- Future international students
- Diversity and Inclusion Opportunities
- Learn abroad
- Living Learning Communities
- Mentor programs
- Programs for women
- Student groups
- Visit, Apply & Next Steps
- Information for current students
- Departments and majors overview
- Departments
- Undergraduate majors
- Graduate programs
- Integrated Degree Programs
- Additional degree-granting programs
- Online learning
- Academic Advising overview
- Academic Advising FAQ
- Academic Advising Blog
- Appointments and drop-ins
- Academic support
- Commencement
- Four-year plans
- Honors advising
- Policies, procedures, and forms
- Career Services overview
- Resumes and cover letters
- Jobs and internships
- Interviews and job offers
- CSE Career Fair
- Major and career exploration
- Graduate school
- Collegiate Life overview
- Scholarships
- Diversity & Inclusivity Alliance
- Anderson Student Innovation Labs
- Information for alumni
- Get engaged with CSE
- Upcoming events
- CSE Alumni Society Board
- Alumni volunteer interest form
- Golden Medallion Society Reunion
- 50-Year Reunion
- Alumni honors and awards
- Outstanding Achievement
- Alumni Service
- Distinguished Leadership
- Honorary Doctorate Degrees
- Nobel Laureates
- Alumni resources
- Alumni career resources
- Alumni news outlets
- CSE branded clothing
- International alumni resources
- Inventing Tomorrow magazine
- Update your info
- CSE giving overview
- Why give to CSE?
- College priorities
- Give online now
- External relations
- Giving priorities
- Donor stories
- Impact of giving
- Ways to give to CSE
- Matching gifts
- CSE directories
- Invest in your company and the future
- Recruit our students
- Connect with researchers
- K-12 initiatives
- Diversity initiatives
- Research news
- Give to CSE
- CSE priorities
- Corporate relations
- Information for faculty and staff
- Administrative offices overview
- Office of the Dean
- Academic affairs
- Finance and Operations
- Communications
- Human resources
- Undergraduate programs and student services
- CSE Committees
- CSE policies overview
- Academic policies
- Faculty hiring and tenure policies
- Finance policies and information
- Graduate education policies
- Human resources policies
- Research policies
- Research overview
- Research centers and facilities
- Research proposal submission process
- Research safety
- Award-winning CSE faculty
- National academies
- University awards
- Honorary professorships
- Collegiate awards
- Other CSE honors and awards
- Staff awards
- Performance Management Process
- Work. With Flexibility in CSE
- K-12 outreach overview
- Summer camps
- Outreach events
- Enrichment programs
- Field trips and tours
- CSE K-12 Virtual Classroom Resources
- Educator development
- Sponsor an event
- Open access
- Published: 18 April 2024
Research ethics and artificial intelligence for global health: perspectives from the global forum on bioethics in research
- James Shaw 1 , 13 ,
- Joseph Ali 2 , 3 ,
- Caesar A. Atuire 4 , 5 ,
- Phaik Yeong Cheah 6 ,
- Armando Guio Español 7 ,
- Judy Wawira Gichoya 8 ,
- Adrienne Hunt 9 ,
- Daudi Jjingo 10 ,
- Katherine Littler 9 ,
- Daniela Paolotti 11 &
- Effy Vayena 12
BMC Medical Ethics volume 25 , Article number: 46 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
1214 Accesses
6 Altmetric
Metrics details
The ethical governance of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in health care and public health continues to be an urgent issue for attention in policy, research, and practice. In this paper we report on central themes related to challenges and strategies for promoting ethics in research involving AI in global health, arising from the Global Forum on Bioethics in Research (GFBR), held in Cape Town, South Africa in November 2022.
The GFBR is an annual meeting organized by the World Health Organization and supported by the Wellcome Trust, the US National Institutes of Health, the UK Medical Research Council (MRC) and the South African MRC. The forum aims to bring together ethicists, researchers, policymakers, research ethics committee members and other actors to engage with challenges and opportunities specifically related to research ethics. In 2022 the focus of the GFBR was “Ethics of AI in Global Health Research”. The forum consisted of 6 case study presentations, 16 governance presentations, and a series of small group and large group discussions. A total of 87 participants attended the forum from 31 countries around the world, representing disciplines of bioethics, AI, health policy, health professional practice, research funding, and bioinformatics. In this paper, we highlight central insights arising from GFBR 2022.
We describe the significance of four thematic insights arising from the forum: (1) Appropriateness of building AI, (2) Transferability of AI systems, (3) Accountability for AI decision-making and outcomes, and (4) Individual consent. We then describe eight recommendations for governance leaders to enhance the ethical governance of AI in global health research, addressing issues such as AI impact assessments, environmental values, and fair partnerships.
Conclusions
The 2022 Global Forum on Bioethics in Research illustrated several innovations in ethical governance of AI for global health research, as well as several areas in need of urgent attention internationally. This summary is intended to inform international and domestic efforts to strengthen research ethics and support the evolution of governance leadership to meet the demands of AI in global health research.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
The ethical governance of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in health care and public health continues to be an urgent issue for attention in policy, research, and practice [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]. Beyond the growing number of AI applications being implemented in health care, capabilities of AI models such as Large Language Models (LLMs) expand the potential reach and significance of AI technologies across health-related fields [ 4 , 5 ]. Discussion about effective, ethical governance of AI technologies has spanned a range of governance approaches, including government regulation, organizational decision-making, professional self-regulation, and research ethics review [ 6 , 7 , 8 ]. In this paper, we report on central themes related to challenges and strategies for promoting ethics in research involving AI in global health research, arising from the Global Forum on Bioethics in Research (GFBR), held in Cape Town, South Africa in November 2022. Although applications of AI for research, health care, and public health are diverse and advancing rapidly, the insights generated at the forum remain highly relevant from a global health perspective. After summarizing important context for work in this domain, we highlight categories of ethical issues emphasized at the forum for attention from a research ethics perspective internationally. We then outline strategies proposed for research, innovation, and governance to support more ethical AI for global health.
In this paper, we adopt the definition of AI systems provided by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) as our starting point. Their definition states that an AI system is “a machine-based system that can, for a given set of human-defined objectives, make predictions, recommendations, or decisions influencing real or virtual environments. AI systems are designed to operate with varying levels of autonomy” [ 9 ]. The conceptualization of an algorithm as helping to constitute an AI system, along with hardware, other elements of software, and a particular context of use, illustrates the wide variety of ways in which AI can be applied. We have found it useful to differentiate applications of AI in research as those classified as “AI systems for discovery” and “AI systems for intervention”. An AI system for discovery is one that is intended to generate new knowledge, for example in drug discovery or public health research in which researchers are seeking potential targets for intervention, innovation, or further research. An AI system for intervention is one that directly contributes to enacting an intervention in a particular context, for example informing decision-making at the point of care or assisting with accuracy in a surgical procedure.
The mandate of the GFBR is to take a broad view of what constitutes research and its regulation in global health, with special attention to bioethics in Low- and Middle- Income Countries. AI as a group of technologies demands such a broad view. AI development for health occurs in a variety of environments, including universities and academic health sciences centers where research ethics review remains an important element of the governance of science and innovation internationally [ 10 , 11 ]. In these settings, research ethics committees (RECs; also known by different names such as Institutional Review Boards or IRBs) make decisions about the ethical appropriateness of projects proposed by researchers and other institutional members, ultimately determining whether a given project is allowed to proceed on ethical grounds [ 12 ].
However, research involving AI for health also takes place in large corporations and smaller scale start-ups, which in some jurisdictions fall outside the scope of research ethics regulation. In the domain of AI, the question of what constitutes research also becomes blurred. For example, is the development of an algorithm itself considered a part of the research process? Or only when that algorithm is tested under the formal constraints of a systematic research methodology? In this paper we take an inclusive view, in which AI development is included in the definition of research activity and within scope for our inquiry, regardless of the setting in which it takes place. This broad perspective characterizes the approach to “research ethics” we take in this paper, extending beyond the work of RECs to include the ethical analysis of the wide range of activities that constitute research as the generation of new knowledge and intervention in the world.
Ethical governance of AI in global health
The ethical governance of AI for global health has been widely discussed in recent years. The World Health Organization (WHO) released its guidelines on ethics and governance of AI for health in 2021, endorsing a set of six ethical principles and exploring the relevance of those principles through a variety of use cases. The WHO guidelines also provided an overview of AI governance, defining governance as covering “a range of steering and rule-making functions of governments and other decision-makers, including international health agencies, for the achievement of national health policy objectives conducive to universal health coverage.” (p. 81) The report usefully provided a series of recommendations related to governance of seven domains pertaining to AI for health: data, benefit sharing, the private sector, the public sector, regulation, policy observatories/model legislation, and global governance. The report acknowledges that much work is yet to be done to advance international cooperation on AI governance, especially related to prioritizing voices from Low- and Middle-Income Countries (LMICs) in global dialogue.
One important point emphasized in the WHO report that reinforces the broader literature on global governance of AI is the distribution of responsibility across a wide range of actors in the AI ecosystem. This is especially important to highlight when focused on research for global health, which is specifically about work that transcends national borders. Alami et al. (2020) discussed the unique risks raised by AI research in global health, ranging from the unavailability of data in many LMICs required to train locally relevant AI models to the capacity of health systems to absorb new AI technologies that demand the use of resources from elsewhere in the system. These observations illustrate the need to identify the unique issues posed by AI research for global health specifically, and the strategies that can be employed by all those implicated in AI governance to promote ethically responsible use of AI in global health research.
RECs and the regulation of research involving AI
RECs represent an important element of the governance of AI for global health research, and thus warrant further commentary as background to our paper. Despite the importance of RECs, foundational questions have been raised about their capabilities to accurately understand and address ethical issues raised by studies involving AI. Rahimzadeh et al. (2023) outlined how RECs in the United States are under-prepared to align with recent federal policy requiring that RECs review data sharing and management plans with attention to the unique ethical issues raised in AI research for health [ 13 ]. Similar research in South Africa identified variability in understanding of existing regulations and ethical issues associated with health-related big data sharing and management among research ethics committee members [ 14 , 15 ]. The effort to address harms accruing to groups or communities as opposed to individuals whose data are included in AI research has also been identified as a unique challenge for RECs [ 16 , 17 ]. Doerr and Meeder (2022) suggested that current regulatory frameworks for research ethics might actually prevent RECs from adequately addressing such issues, as they are deemed out of scope of REC review [ 16 ]. Furthermore, research in the United Kingdom and Canada has suggested that researchers using AI methods for health tend to distinguish between ethical issues and social impact of their research, adopting an overly narrow view of what constitutes ethical issues in their work [ 18 ].
The challenges for RECs in adequately addressing ethical issues in AI research for health care and public health exceed a straightforward survey of ethical considerations. As Ferretti et al. (2021) contend, some capabilities of RECs adequately cover certain issues in AI-based health research, such as the common occurrence of conflicts of interest where researchers who accept funds from commercial technology providers are implicitly incentivized to produce results that align with commercial interests [ 12 ]. However, some features of REC review require reform to adequately meet ethical needs. Ferretti et al. outlined weaknesses of RECs that are longstanding and those that are novel to AI-related projects, proposing a series of directions for development that are regulatory, procedural, and complementary to REC functionality. The work required on a global scale to update the REC function in response to the demands of research involving AI is substantial.
These issues take greater urgency in the context of global health [ 19 ]. Teixeira da Silva (2022) described the global practice of “ethics dumping”, where researchers from high income countries bring ethically contentious practices to RECs in low-income countries as a strategy to gain approval and move projects forward [ 20 ]. Although not yet systematically documented in AI research for health, risk of ethics dumping in AI research is high. Evidence is already emerging of practices of “health data colonialism”, in which AI researchers and developers from large organizations in high-income countries acquire data to build algorithms in LMICs to avoid stricter regulations [ 21 ]. This specific practice is part of a larger collection of practices that characterize health data colonialism, involving the broader exploitation of data and the populations they represent primarily for commercial gain [ 21 , 22 ]. As an additional complication, AI algorithms trained on data from high-income contexts are unlikely to apply in straightforward ways to LMIC settings [ 21 , 23 ]. In the context of global health, there is widespread acknowledgement about the need to not only enhance the knowledge base of REC members about AI-based methods internationally, but to acknowledge the broader shifts required to encourage their capabilities to more fully address these and other ethical issues associated with AI research for health [ 8 ].
Although RECs are an important part of the story of the ethical governance of AI for global health research, they are not the only part. The responsibilities of supra-national entities such as the World Health Organization, national governments, organizational leaders, commercial AI technology providers, health care professionals, and other groups continue to be worked out internationally. In this context of ongoing work, examining issues that demand attention and strategies to address them remains an urgent and valuable task.
The GFBR is an annual meeting organized by the World Health Organization and supported by the Wellcome Trust, the US National Institutes of Health, the UK Medical Research Council (MRC) and the South African MRC. The forum aims to bring together ethicists, researchers, policymakers, REC members and other actors to engage with challenges and opportunities specifically related to research ethics. Each year the GFBR meeting includes a series of case studies and keynotes presented in plenary format to an audience of approximately 100 people who have applied and been competitively selected to attend, along with small-group breakout discussions to advance thinking on related issues. The specific topic of the forum changes each year, with past topics including ethical issues in research with people living with mental health conditions (2021), genome editing (2019), and biobanking/data sharing (2018). The forum is intended to remain grounded in the practical challenges of engaging in research ethics, with special interest in low resource settings from a global health perspective. A post-meeting fellowship scheme is open to all LMIC participants, providing a unique opportunity to apply for funding to further explore and address the ethical challenges that are identified during the meeting.
In 2022, the focus of the GFBR was “Ethics of AI in Global Health Research”. The forum consisted of 6 case study presentations (both short and long form) reporting on specific initiatives related to research ethics and AI for health, and 16 governance presentations (both short and long form) reporting on actual approaches to governing AI in different country settings. A keynote presentation from Professor Effy Vayena addressed the topic of the broader context for AI ethics in a rapidly evolving field. A total of 87 participants attended the forum from 31 countries around the world, representing disciplines of bioethics, AI, health policy, health professional practice, research funding, and bioinformatics. The 2-day forum addressed a wide range of themes. The conference report provides a detailed overview of each of the specific topics addressed while a policy paper outlines the cross-cutting themes (both documents are available at the GFBR website: https://www.gfbr.global/past-meetings/16th-forum-cape-town-south-africa-29-30-november-2022/ ). As opposed to providing a detailed summary in this paper, we aim to briefly highlight central issues raised, solutions proposed, and the challenges facing the research ethics community in the years to come.
In this way, our primary aim in this paper is to present a synthesis of the challenges and opportunities raised at the GFBR meeting and in the planning process, followed by our reflections as a group of authors on their significance for governance leaders in the coming years. We acknowledge that the views represented at the meeting and in our results are a partial representation of the universe of views on this topic; however, the GFBR leadership invested a great deal of resources in convening a deeply diverse and thoughtful group of researchers and practitioners working on themes of bioethics related to AI for global health including those based in LMICs. We contend that it remains rare to convene such a strong group for an extended time and believe that many of the challenges and opportunities raised demand attention for more ethical futures of AI for health. Nonetheless, our results are primarily descriptive and are thus not explicitly grounded in a normative argument. We make effort in the Discussion section to contextualize our results by describing their significance and connecting them to broader efforts to reform global health research and practice.
Uniquely important ethical issues for AI in global health research
Presentations and group dialogue over the course of the forum raised several issues for consideration, and here we describe four overarching themes for the ethical governance of AI in global health research. Brief descriptions of each issue can be found in Table 1 . Reports referred to throughout the paper are available at the GFBR website provided above.
The first overarching thematic issue relates to the appropriateness of building AI technologies in response to health-related challenges in the first place. Case study presentations referred to initiatives where AI technologies were highly appropriate, such as in ear shape biometric identification to more accurately link electronic health care records to individual patients in Zambia (Alinani Simukanga). Although important ethical issues were raised with respect to privacy, trust, and community engagement in this initiative, the AI-based solution was appropriately matched to the challenge of accurately linking electronic records to specific patient identities. In contrast, forum participants raised questions about the appropriateness of an initiative using AI to improve the quality of handwashing practices in an acute care hospital in India (Niyoshi Shah), which led to gaming the algorithm. Overall, participants acknowledged the dangers of techno-solutionism, in which AI researchers and developers treat AI technologies as the most obvious solutions to problems that in actuality demand much more complex strategies to address [ 24 ]. However, forum participants agreed that RECs in different contexts have differing degrees of power to raise issues of the appropriateness of an AI-based intervention.
The second overarching thematic issue related to whether and how AI-based systems transfer from one national health context to another. One central issue raised by a number of case study presentations related to the challenges of validating an algorithm with data collected in a local environment. For example, one case study presentation described a project that would involve the collection of personally identifiable data for sensitive group identities, such as tribe, clan, or religion, in the jurisdictions involved (South Africa, Nigeria, Tanzania, Uganda and the US; Gakii Masunga). Doing so would enable the team to ensure that those groups were adequately represented in the dataset to ensure the resulting algorithm was not biased against specific community groups when deployed in that context. However, some members of these communities might desire to be represented in the dataset, whereas others might not, illustrating the need to balance autonomy and inclusivity. It was also widely recognized that collecting these data is an immense challenge, particularly when historically oppressive practices have led to a low-trust environment for international organizations and the technologies they produce. It is important to note that in some countries such as South Africa and Rwanda, it is illegal to collect information such as race and tribal identities, re-emphasizing the importance for cultural awareness and avoiding “one size fits all” solutions.
The third overarching thematic issue is related to understanding accountabilities for both the impacts of AI technologies and governance decision-making regarding their use. Where global health research involving AI leads to longer-term harms that might fall outside the usual scope of issues considered by a REC, who is to be held accountable, and how? This question was raised as one that requires much further attention, with law being mixed internationally regarding the mechanisms available to hold researchers, innovators, and their institutions accountable over the longer term. However, it was recognized in breakout group discussion that many jurisdictions are developing strong data protection regimes related specifically to international collaboration for research involving health data. For example, Kenya’s Data Protection Act requires that any internationally funded projects have a local principal investigator who will hold accountability for how data are shared and used [ 25 ]. The issue of research partnerships with commercial entities was raised by many participants in the context of accountability, pointing toward the urgent need for clear principles related to strategies for engagement with commercial technology companies in global health research.
The fourth and final overarching thematic issue raised here is that of consent. The issue of consent was framed by the widely shared recognition that models of individual, explicit consent might not produce a supportive environment for AI innovation that relies on the secondary uses of health-related datasets to build AI algorithms. Given this recognition, approaches such as community oversight of health data uses were suggested as a potential solution. However, the details of implementing such community oversight mechanisms require much further attention, particularly given the unique perspectives on health data in different country settings in global health research. Furthermore, some uses of health data do continue to require consent. One case study of South Africa, Nigeria, Kenya, Ethiopia and Uganda suggested that when health data are shared across borders, individual consent remains necessary when data is transferred from certain countries (Nezerith Cengiz). Broader clarity is necessary to support the ethical governance of health data uses for AI in global health research.
Recommendations for ethical governance of AI in global health research
Dialogue at the forum led to a range of suggestions for promoting ethical conduct of AI research for global health, related to the various roles of actors involved in the governance of AI research broadly defined. The strategies are written for actors we refer to as “governance leaders”, those people distributed throughout the AI for global health research ecosystem who are responsible for ensuring the ethical and socially responsible conduct of global health research involving AI (including researchers themselves). These include RECs, government regulators, health care leaders, health professionals, corporate social accountability officers, and others. Enacting these strategies would bolster the ethical governance of AI for global health more generally, enabling multiple actors to fulfill their roles related to governing research and development activities carried out across multiple organizations, including universities, academic health sciences centers, start-ups, and technology corporations. Specific suggestions are summarized in Table 2 .
First, forum participants suggested that governance leaders including RECs, should remain up to date on recent advances in the regulation of AI for health. Regulation of AI for health advances rapidly and takes on different forms in jurisdictions around the world. RECs play an important role in governance, but only a partial role; it was deemed important for RECs to acknowledge how they fit within a broader governance ecosystem in order to more effectively address the issues within their scope. Not only RECs but organizational leaders responsible for procurement, researchers, and commercial actors should all commit to efforts to remain up to date about the relevant approaches to regulating AI for health care and public health in jurisdictions internationally. In this way, governance can more adequately remain up to date with advances in regulation.
Second, forum participants suggested that governance leaders should focus on ethical governance of health data as a basis for ethical global health AI research. Health data are considered the foundation of AI development, being used to train AI algorithms for various uses [ 26 ]. By focusing on ethical governance of health data generation, sharing, and use, multiple actors will help to build an ethical foundation for AI development among global health researchers.
Third, forum participants believed that governance processes should incorporate AI impact assessments where appropriate. An AI impact assessment is the process of evaluating the potential effects, both positive and negative, of implementing an AI algorithm on individuals, society, and various stakeholders, generally over time frames specified in advance of implementation [ 27 ]. Although not all types of AI research in global health would warrant an AI impact assessment, this is especially relevant for those studies aiming to implement an AI system for intervention into health care or public health. Organizations such as RECs can use AI impact assessments to boost understanding of potential harms at the outset of a research project, encouraging researchers to more deeply consider potential harms in the development of their study.
Fourth, forum participants suggested that governance decisions should incorporate the use of environmental impact assessments, or at least the incorporation of environment values when assessing the potential impact of an AI system. An environmental impact assessment involves evaluating and anticipating the potential environmental effects of a proposed project to inform ethical decision-making that supports sustainability [ 28 ]. Although a relatively new consideration in research ethics conversations [ 29 ], the environmental impact of building technologies is a crucial consideration for the public health commitment to environmental sustainability. Governance leaders can use environmental impact assessments to boost understanding of potential environmental harms linked to AI research projects in global health over both the shorter and longer terms.
Fifth, forum participants suggested that governance leaders should require stronger transparency in the development of AI algorithms in global health research. Transparency was considered essential in the design and development of AI algorithms for global health to ensure ethical and accountable decision-making throughout the process. Furthermore, whether and how researchers have considered the unique contexts into which such algorithms may be deployed can be surfaced through stronger transparency, for example in describing what primary considerations were made at the outset of the project and which stakeholders were consulted along the way. Sharing information about data provenance and methods used in AI development will also enhance the trustworthiness of the AI-based research process.
Sixth, forum participants suggested that governance leaders can encourage or require community engagement at various points throughout an AI project. It was considered that engaging patients and communities is crucial in AI algorithm development to ensure that the technology aligns with community needs and values. However, participants acknowledged that this is not a straightforward process. Effective community engagement requires lengthy commitments to meeting with and hearing from diverse communities in a given setting, and demands a particular set of skills in communication and dialogue that are not possessed by all researchers. Encouraging AI researchers to begin this process early and build long-term partnerships with community members is a promising strategy to deepen community engagement in AI research for global health. One notable recommendation was that research funders have an opportunity to incentivize and enable community engagement with funds dedicated to these activities in AI research in global health.
Seventh, forum participants suggested that governance leaders can encourage researchers to build strong, fair partnerships between institutions and individuals across country settings. In a context of longstanding imbalances in geopolitical and economic power, fair partnerships in global health demand a priori commitments to share benefits related to advances in medical technologies, knowledge, and financial gains. Although enforcement of this point might be beyond the remit of RECs, commentary will encourage researchers to consider stronger, fairer partnerships in global health in the longer term.
Eighth, it became evident that it is necessary to explore new forms of regulatory experimentation given the complexity of regulating a technology of this nature. In addition, the health sector has a series of particularities that make it especially complicated to generate rules that have not been previously tested. Several participants highlighted the desire to promote spaces for experimentation such as regulatory sandboxes or innovation hubs in health. These spaces can have several benefits for addressing issues surrounding the regulation of AI in the health sector, such as: (i) increasing the capacities and knowledge of health authorities about this technology; (ii) identifying the major problems surrounding AI regulation in the health sector; (iii) establishing possibilities for exchange and learning with other authorities; (iv) promoting innovation and entrepreneurship in AI in health; and (vi) identifying the need to regulate AI in this sector and update other existing regulations.
Ninth and finally, forum participants believed that the capabilities of governance leaders need to evolve to better incorporate expertise related to AI in ways that make sense within a given jurisdiction. With respect to RECs, for example, it might not make sense for every REC to recruit a member with expertise in AI methods. Rather, it will make more sense in some jurisdictions to consult with members of the scientific community with expertise in AI when research protocols are submitted that demand such expertise. Furthermore, RECs and other approaches to research governance in jurisdictions around the world will need to evolve in order to adopt the suggestions outlined above, developing processes that apply specifically to the ethical governance of research using AI methods in global health.
Research involving the development and implementation of AI technologies continues to grow in global health, posing important challenges for ethical governance of AI in global health research around the world. In this paper we have summarized insights from the 2022 GFBR, focused specifically on issues in research ethics related to AI for global health research. We summarized four thematic challenges for governance related to AI in global health research and nine suggestions arising from presentations and dialogue at the forum. In this brief discussion section, we present an overarching observation about power imbalances that frames efforts to evolve the role of governance in global health research, and then outline two important opportunity areas as the field develops to meet the challenges of AI in global health research.
Dialogue about power is not unfamiliar in global health, especially given recent contributions exploring what it would mean to de-colonize global health research, funding, and practice [ 30 , 31 ]. Discussions of research ethics applied to AI research in global health contexts are deeply infused with power imbalances. The existing context of global health is one in which high-income countries primarily located in the “Global North” charitably invest in projects taking place primarily in the “Global South” while recouping knowledge, financial, and reputational benefits [ 32 ]. With respect to AI development in particular, recent examples of digital colonialism frame dialogue about global partnerships, raising attention to the role of large commercial entities and global financial capitalism in global health research [ 21 , 22 ]. Furthermore, the power of governance organizations such as RECs to intervene in the process of AI research in global health varies widely around the world, depending on the authorities assigned to them by domestic research governance policies. These observations frame the challenges outlined in our paper, highlighting the difficulties associated with making meaningful change in this field.
Despite these overarching challenges of the global health research context, there are clear strategies for progress in this domain. Firstly, AI innovation is rapidly evolving, which means approaches to the governance of AI for health are rapidly evolving too. Such rapid evolution presents an important opportunity for governance leaders to clarify their vision and influence over AI innovation in global health research, boosting the expertise, structure, and functionality required to meet the demands of research involving AI. Secondly, the research ethics community has strong international ties, linked to a global scholarly community that is committed to sharing insights and best practices around the world. This global community can be leveraged to coordinate efforts to produce advances in the capabilities and authorities of governance leaders to meaningfully govern AI research for global health given the challenges summarized in our paper.
Limitations
Our paper includes two specific limitations that we address explicitly here. First, it is still early in the lifetime of the development of applications of AI for use in global health, and as such, the global community has had limited opportunity to learn from experience. For example, there were many fewer case studies, which detail experiences with the actual implementation of an AI technology, submitted to GFBR 2022 for consideration than was expected. In contrast, there were many more governance reports submitted, which detail the processes and outputs of governance processes that anticipate the development and dissemination of AI technologies. This observation represents both a success and a challenge. It is a success that so many groups are engaging in anticipatory governance of AI technologies, exploring evidence of their likely impacts and governing technologies in novel and well-designed ways. It is a challenge that there is little experience to build upon of the successful implementation of AI technologies in ways that have limited harms while promoting innovation. Further experience with AI technologies in global health will contribute to revising and enhancing the challenges and recommendations we have outlined in our paper.
Second, global trends in the politics and economics of AI technologies are evolving rapidly. Although some nations are advancing detailed policy approaches to regulating AI more generally, including for uses in health care and public health, the impacts of corporate investments in AI and political responses related to governance remain to be seen. The excitement around large language models (LLMs) and large multimodal models (LMMs) has drawn deeper attention to the challenges of regulating AI in any general sense, opening dialogue about health sector-specific regulations. The direction of this global dialogue, strongly linked to high-profile corporate actors and multi-national governance institutions, will strongly influence the development of boundaries around what is possible for the ethical governance of AI for global health. We have written this paper at a point when these developments are proceeding rapidly, and as such, we acknowledge that our recommendations will need updating as the broader field evolves.
Ultimately, coordination and collaboration between many stakeholders in the research ethics ecosystem will be necessary to strengthen the ethical governance of AI in global health research. The 2022 GFBR illustrated several innovations in ethical governance of AI for global health research, as well as several areas in need of urgent attention internationally. This summary is intended to inform international and domestic efforts to strengthen research ethics and support the evolution of governance leadership to meet the demands of AI in global health research.
Data availability
All data and materials analyzed to produce this paper are available on the GFBR website: https://www.gfbr.global/past-meetings/16th-forum-cape-town-south-africa-29-30-november-2022/ .
Clark P, Kim J, Aphinyanaphongs Y, Marketing, Food US. Drug Administration Clearance of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Enabled Software in and as Medical devices: a systematic review. JAMA Netw Open. 2023;6(7):e2321792–2321792.
Article Google Scholar
Potnis KC, Ross JS, Aneja S, Gross CP, Richman IB. Artificial intelligence in breast cancer screening: evaluation of FDA device regulation and future recommendations. JAMA Intern Med. 2022;182(12):1306–12.
Siala H, Wang Y. SHIFTing artificial intelligence to be responsible in healthcare: a systematic review. Soc Sci Med. 2022;296:114782.
Yang X, Chen A, PourNejatian N, Shin HC, Smith KE, Parisien C, et al. A large language model for electronic health records. NPJ Digit Med. 2022;5(1):194.
Meskó B, Topol EJ. The imperative for regulatory oversight of large language models (or generative AI) in healthcare. NPJ Digit Med. 2023;6(1):120.
Jobin A, Ienca M, Vayena E. The global landscape of AI ethics guidelines. Nat Mach Intell. 2019;1(9):389–99.
Minssen T, Vayena E, Cohen IG. The challenges for Regulating Medical Use of ChatGPT and other large Language models. JAMA. 2023.
Ho CWL, Malpani R. Scaling up the research ethics framework for healthcare machine learning as global health ethics and governance. Am J Bioeth. 2022;22(5):36–8.
Yeung K. Recommendation of the council on artificial intelligence (OECD). Int Leg Mater. 2020;59(1):27–34.
Maddox TM, Rumsfeld JS, Payne PR. Questions for artificial intelligence in health care. JAMA. 2019;321(1):31–2.
Dzau VJ, Balatbat CA, Ellaissi WF. Revisiting academic health sciences systems a decade later: discovery to health to population to society. Lancet. 2021;398(10318):2300–4.
Ferretti A, Ienca M, Sheehan M, Blasimme A, Dove ES, Farsides B, et al. Ethics review of big data research: what should stay and what should be reformed? BMC Med Ethics. 2021;22(1):1–13.
Rahimzadeh V, Serpico K, Gelinas L. Institutional review boards need new skills to review data sharing and management plans. Nat Med. 2023;1–3.
Kling S, Singh S, Burgess TL, Nair G. The role of an ethics advisory committee in data science research in sub-saharan Africa. South Afr J Sci. 2023;119(5–6):1–3.
Google Scholar
Cengiz N, Kabanda SM, Esterhuizen TM, Moodley K. Exploring perspectives of research ethics committee members on the governance of big data in sub-saharan Africa. South Afr J Sci. 2023;119(5–6):1–9.
Doerr M, Meeder S. Big health data research and group harm: the scope of IRB review. Ethics Hum Res. 2022;44(4):34–8.
Ballantyne A, Stewart C. Big data and public-private partnerships in healthcare and research: the application of an ethics framework for big data in health and research. Asian Bioeth Rev. 2019;11(3):315–26.
Samuel G, Chubb J, Derrick G. Boundaries between research ethics and ethical research use in artificial intelligence health research. J Empir Res Hum Res Ethics. 2021;16(3):325–37.
Murphy K, Di Ruggiero E, Upshur R, Willison DJ, Malhotra N, Cai JC, et al. Artificial intelligence for good health: a scoping review of the ethics literature. BMC Med Ethics. 2021;22(1):1–17.
Teixeira da Silva JA. Handling ethics dumping and neo-colonial research: from the laboratory to the academic literature. J Bioethical Inq. 2022;19(3):433–43.
Ferryman K. The dangers of data colonialism in precision public health. Glob Policy. 2021;12:90–2.
Couldry N, Mejias UA. Data colonialism: rethinking big data’s relation to the contemporary subject. Telev New Media. 2019;20(4):336–49.
Organization WH. Ethics and governance of artificial intelligence for health: WHO guidance. 2021.
Metcalf J, Moss E. Owning ethics: corporate logics, silicon valley, and the institutionalization of ethics. Soc Res Int Q. 2019;86(2):449–76.
Data Protection Act - OFFICE OF THE DATA PROTECTION COMMISSIONER KENYA [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2023 Sep 30]. https://www.odpc.go.ke/dpa-act/ .
Sharon T, Lucivero F. Introduction to the special theme: the expansion of the health data ecosystem–rethinking data ethics and governance. Big Data & Society. Volume 6. London, England: SAGE Publications Sage UK; 2019. p. 2053951719852969.
Reisman D, Schultz J, Crawford K, Whittaker M. Algorithmic impact assessments: a practical Framework for Public Agency. AI Now. 2018.
Morgan RK. Environmental impact assessment: the state of the art. Impact Assess Proj Apprais. 2012;30(1):5–14.
Samuel G, Richie C. Reimagining research ethics to include environmental sustainability: a principled approach, including a case study of data-driven health research. J Med Ethics. 2023;49(6):428–33.
Kwete X, Tang K, Chen L, Ren R, Chen Q, Wu Z, et al. Decolonizing global health: what should be the target of this movement and where does it lead us? Glob Health Res Policy. 2022;7(1):3.
Abimbola S, Asthana S, Montenegro C, Guinto RR, Jumbam DT, Louskieter L, et al. Addressing power asymmetries in global health: imperatives in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. PLoS Med. 2021;18(4):e1003604.
Benatar S. Politics, power, poverty and global health: systems and frames. Int J Health Policy Manag. 2016;5(10):599.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the outstanding contributions of the attendees of GFBR 2022 in Cape Town, South Africa. This paper is authored by members of the GFBR 2022 Planning Committee. We would like to acknowledge additional members Tamra Lysaght, National University of Singapore, and Niresh Bhagwandin, South African Medical Research Council, for their input during the planning stages and as reviewers of the applications to attend the Forum.
This work was supported by Wellcome [222525/Z/21/Z], the US National Institutes of Health, the UK Medical Research Council (part of UK Research and Innovation), and the South African Medical Research Council through funding to the Global Forum on Bioethics in Research.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Physical Therapy, Temerty Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada
Berman Institute of Bioethics, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA
Bloomberg School of Public Health, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA
Department of Philosophy and Classics, University of Ghana, Legon-Accra, Ghana
Caesar A. Atuire
Centre for Tropical Medicine and Global Health, Nuffield Department of Medicine, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK
Mahidol Oxford Tropical Medicine Research Unit, Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand
Phaik Yeong Cheah
Berkman Klein Center, Harvard University, Bogotá, Colombia
Armando Guio Español
Department of Radiology and Informatics, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, GA, USA
Judy Wawira Gichoya
Health Ethics & Governance Unit, Research for Health Department, Science Division, World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland
Adrienne Hunt & Katherine Littler
African Center of Excellence in Bioinformatics and Data Intensive Science, Infectious Diseases Institute, Makerere University, Kampala, Uganda
Daudi Jjingo
ISI Foundation, Turin, Italy
Daniela Paolotti
Department of Health Sciences and Technology, ETH Zurich, Zürich, Switzerland
Effy Vayena
Joint Centre for Bioethics, Dalla Lana School of Public Health, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
JS led the writing, contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. JA contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. CA contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. PYC contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. AE contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. JWG contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. AH contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. DJ contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. KL contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. DP contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper. EV contributed to conceptualization and analysis, critically reviewed and provided feedback on drafts of this paper, and provided final approval of the paper.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to James Shaw .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Shaw, J., Ali, J., Atuire, C.A. et al. Research ethics and artificial intelligence for global health: perspectives from the global forum on bioethics in research. BMC Med Ethics 25 , 46 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-024-01044-w
Download citation
Received : 31 October 2023
Accepted : 01 April 2024
Published : 18 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-024-01044-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Artificial intelligence
- Machine learning
- Research ethics
- Global health
BMC Medical Ethics
ISSN: 1472-6939
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Articles in 2023
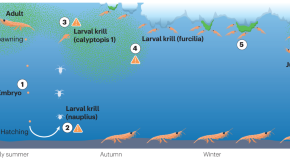
Climate change impacts on Antarctic krill behaviour and population dynamics
Krill are food sources for megafauna, are drivers of carbon export and are being impacted by sea-ice declines and changing climate conditions. This Review examines changes in krill populations, habitats and behaviour in the Southern Ocean, and discusses their potential drivers and implications for fishery management in the future.
- So Kawaguchi
- Angus Atkinson
- Devi Veytia
Publisher Correction: Non-perennial segments in river networks
- Thibault Datry
- Andrew J. Boulton
- Klement Tockner
Towards scientific forecasting of magmatic eruptions
Volcanic eruptions are major natural hazards, but forecasting their activity remains challenging. This Review discusses scientific and monitoring approaches used to forecast magmatic eruptions.
- Valerio Acocella
- Maurizio Ripepe
- Erouscilla Joseph
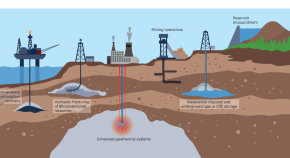
The physical mechanisms of induced earthquakes
Induced earthquakes can occur during several industrial activities, including geothermal developments and underground storage. This Review discusses the current physics-based understanding of induced earthquakes and the implications for forecasting, monitoring, seismic hazard and risk assessments and mitigation strategies.
- Mohammad J. A. Moein
- Cornelius Langenbruch
- Serge Shapiro
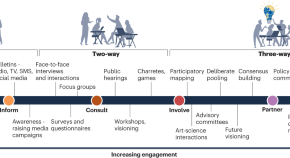
Disaster risk communication requires dissemination, dialogue and participation
Disaster risk communication traditionally focuses on authorities conveying hazard and risk information to at-risk populations, with little consideration of local community knowledge. To enable risk reduction and resilience, disaster management must forge partnerships with local communities and empower citizen-led initiatives.
- I. S. Stewart
- E. Yahya Menteşe

Non-perennial segments in river networks
Non-perennial segments of rivers undergo cycles of flowing, non-flowing and dry phases, influencing ecosystem dynamics and services across the river network. This Review describes the occurrence, ecology and future of these intermittent and ephemeral flows and highlights the importance of protecting these segments.
Controversies of carbon dioxide removal
Various methods of carbon dioxide removal (CDR) are being pursued in response to the climate crisis, but they are mostly not proven at scale. Climate experts are divided over whether CDR is a necessary requirement or a dangerous distraction from limiting emissions. In this Viewpoint, six experts offer their views on the CDR debate.
- Kevin Anderson
- Holly Jean Buck
Climate change impacts on crop yields
Warmer temperatures, increased CO 2 concentrations and changing water availability affect cereal crop production. This Review examines changes in crop yield in response to these variables and discusses adaptation strategies.
- Ehsan Eyshi Rezaei
- Heidi Webber
- Dilys Sefakor MacCarthy
Publisher Correction: Evidence and attribution of the enhanced land carbon sink
- Sophie Ruehr
- Trevor F. Keenan
- César Terrer

Ghost forests stand apart
An article in Soil & Environmental Health finds ghost forests are distinct from freshwater forested wetlands and salt marshes.
- Laura Zinke

Mitigating ghost fishing
An article in Marine Policy assessed the abundance and causes of discarded fishing gear in Kerala, India, to help inform fishing debris management practices.
The anthropogenic salt cycle
Widespread use of salts in food, construction, road deicing and industry is driving salinization of water, soil and air. This Review describes the anthropogenic salt cycle, compares it with natural processes and examines its environmental consequences.
- Sujay S. Kaushal
- Gene E. Likens
- Megan A. Rippy

Halloween-like solar storm impacts
An article in Space Weather estimates that an event like the Halloween solar storm of 2003 could cause large economic losses in the aviation sector if it occurred in the present day.
Environmental impacts and remediation of dye-containing wastewater
Wastewater dyes from textile, food and pharmaceutical industries are a major environmental concern. This Review discusses the environmental impacts of dye-containing wastewater and explores both conventional and emerging remediation strategies.
- Jiuyang Lin
- Bart Van der Bruggen
Author Correction: Irrigation in the Earth system
- Sonali McDermid
- Mallika Nocco
- Tokuta Yokohata
Mechanisms of tropical Pacific decadal variability
Several mechanisms have been put forward to explain tropical Pacific decadal variability, the contributions of which are debated. This Review outlines the different drivers of tropical Pacific decadal variability, summarizing that tropical pycnocline adjustment to wind forcing and Rossby wave activity is likely the dominant mechanism, albeit with uncertainty.
- Antonietta Capotondi
- Shayne McGregor
- Tongtong Xu
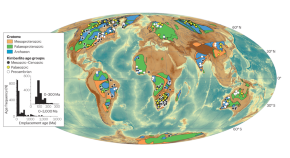
Genesis and evolution of kimberlites
Kimberlites are rare volcanic rocks with unusually deep origins. This Review explores the origin and evolution of kimberlite melts and their insights into mantle composition and dynamics.
- Andrea Giuliani
- Max W. Schmidt
- Yana Fedortchouk

Darkening clouds after restrictions in maritime sulfur emissions
An article in Atmos. Chem. Phys . found that reductions in maritime sulfur emissions led to less reflective clouds above a major shipping corridor, with potential implications for regional warming.
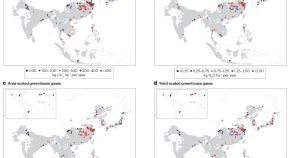
Greenhouse gas emissions and mitigation in rice agriculture
Rice paddies account for a large proportion of total agricultural methane and nitrous oxide emissions. This Review outlines the characteristics, changes and mitigation options for these emissions, highlighting the benefits of water and organic matter management.
- Xiangchen Zhu
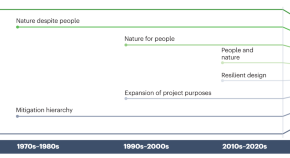
Jointly advancing infrastructure and biodiversity conservation
Infrastructure development and biodiversity conservation are often planned and executed in isolation. However, outcomes from these efforts are interlinked, with coordinated actions required to jointly address sustainability challenges. Natural infrastructure — encompassing a spectrum of natural to conventional solutions — is key to the infrastructure–biodiversity connection and should be brought into large-scale application.
- S. Kyle McKay
- Seth J. Wenger
- Todd S. Bridges
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

COMMENTS
A Multidisciplinary Journal of Environmental Sciences and Engineering. Environmental Research is a multi-disciplinary journal publishing high quality and novel information about anthropogenic issues of global relevance and applicability in a wide range of environmental disciplines, and …. View full aims & scope. $3590. Article publishing charge.
Environmental sciences articles from across Nature Portfolio. Environmental science is the multidisciplinary study of all aspects of the Earth's physical and biological environments. It ...
In 2019, the Royal Society of Chemistry published 180, 196 and 293 papers in Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts, Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology, and Environmental Science: Nano, respectively. These papers covered a wide range of topics in environmental science, from biogeochemical cycling to water reuse to ...
Earth, Environment and Ecology Top 100 of 2023. This collection highlights the most downloaded* Earth science, environmental science and ecology research papers published by Scientific Reports in ...
This collection highlights our most downloaded* Earth, environment and ecology papers published in 2022. Featuring authors from aroud the world, these papers showcase valuable research from an ...
In two-thirds of trials, conservation either improved the state of biodiversity (absolute positive impacts, 45.4%), or at least slowed declines (relative positive impacts, 20.6%). However, in one-fifth of trials, biodiversity under the intervention declined more than no action (absolute negative impacts, 20.6%), whereas in a smaller number of ...
We are proud to introduce Current Research in Environmental Sustainability (CRSUST), a new primary research journal from Elsevier.CRSUST publishes original papers and short communications that cover all aspects of environmental sustainability. Current Research in Environmental Sustainability is a gold open access (OA) journal, which means articles are permanently and freely available.
The Journal of Environmental Studies and Sciences is the official publication of the Association of Environmental Sciences and Studies (AESS). Editor-in-Chief. Teresa Lloro. Impact factor. 2.1 (2022) 5 year impact factor. 1.7 (2022) Submission to first decision (median) 15 days.
Salt marshes provide a variety of ecosystem services; however, they are vulnerable to human activity, water level fluctuations, and climate change. Analyses of the relationships between plant communities and e... Jaesang Chung, Jae Hyun Kim and Eun Ju Lee. Journal of Ecology and Environment 2021 45 :28.
Call For Papers Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Environmental Health. This Virtual Special Issue aims to capture the latest research advances in the applications of artificial intelligence and machine learning for environmental health studies. Submit your manuscript by June 30, 2024. Learn More
Environmental science ; a study of your surrounding. It includes climate change, remediation, toxicology, environmental impact assessment,... | Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles ...
The International Journal of Environmental Research (IJER) is an international and multidisciplinary platform for researchers across the globe to swiftly publish, share and discuss new findings and developments in environmental science, engineering, and management.IJER is an interdisciplinary journal concerned with all aspects of the environment. These include but are not limited to air, water ...
2. Research Methods. In recent years, researchers have increasingly used quantitative and qualitative research (mixed methods) techniques to expand the scope and improve the analytic power of their studies [29,30].Quantitative research method is a statistical and interpretive technique used to describe or explain the meaning and relationships of a phenomenon under investigation.
This review collected some important reports and scientific papers on the emerging environmental problems that will feature prominently in the future. Global renewable power production (2017 ...
Short-term and long-term adverse effects on human health are observed. VOCs are responsible for indoor air smells. Short-term exposure is found to cause irritation of eyes, nose, throat, and mucosal membranes, while those of long duration exposure include toxic reactions ( 92 ).
A new study finds that strategically integrating floating solar panels on reservoirs could substitute 20-100% of Africa's planned hydropower by 2050. For the Zambezi watercourse, this approach ...
Secondary data is used to identify sustainability issues such as environmental, social, and economic viability. To better understand the problem, gathered the information in this report from various media outlets, research agencies, policy papers, newspapers, and other sources. This review is a sectorial assessment of climate change mitigation ...
Paper topics include environmental management, resources and conservation, agriculture, global issues, institutional issues, and other topics. These papers are either authored by NCEE economists or produced with funding from NCEE. The working papers are distributed for purposes of information and discussion. The opinions and findings expressed ...
The mission of Environmental Education Researchis toadvance research-based and scholarly understandings of environmental and sustainability education.The journal achieves this by publishing peer reviewed research and scholarship on all aspects of environmental education, sourced from around the world and diverse schools of thought and practice in inquiry.
The „environmental crisis‟ is caused due to environment and ecological changes as a result of. developmental process of the 'economic and technological man" of the present century. In fact if ...
This proceedings book contains the full papers of the 10th edition of the International Conference on Energy and Environment Research, ICEER 2023, that took place in Madrid, Spain during October 7-9, 2023. ICEER 2023 is a joint organization of the School of Engineering (ISEP) of the Polytechnic of Porto (P.Porto) and the SCIEI, with ...
Call for Papers Special Issue on Environmental Management and Biomedical Research. Submission deadline: Tuesday, 10 September 2024. Objective of the issue Background: The Special Issue serves as a scholarly platform dedicated to the intersection of Environmental Management and Biomedical Research.
European Institute on Economics and the Environment, Working Paper 22-1 (2022). Neal, T. The importance of external weather effects in projecting the macroeconomic impacts of climate change.
Professor Catherine E. Wolfgram French has been elected to the National Academy of Engineering (NAE). This is among the highest professional distinctions awarded to an engineer. The NAE elected only 114 new members and 21 foreign members this year. French joins previously elected members from the Department of Civil, Environmental, and Geo- Engineering: Professor Emmanuel Detournay and ...
The ethical governance of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in health care and public health continues to be an urgent issue for attention in policy, research, and practice. In this paper we report on central themes related to challenges and strategies for promoting ethics in research involving AI in global health, arising from the Global Forum on Bioethics in Research (GFBR), held in Cape Town ...
Introduction. Research environments matter. Environmental considerations such as robust cultures of research quality and support for researchers are thought to be the most influential predictors of research productivity.1, 2 Over 25 years ago, Bland and Ruffin1 identified 12 characteristics of research‐favourable environments in the international academic medicine literature spanning the ...
Facing the increasingly complex and uncertain external environment, the reasonable control of investment risk is the key to realizing the sound operation and high-quality development of enterprises. Based on the innovation perspective, this paper takes A-share non-financial listed companies from 2007 to 2021 as the research sample to explore the impact of the corporate risk-taking level on the ...
Research Highlight 27 Oct 2023 Environmental impacts and remediation of dye-containing wastewater Wastewater dyes from textile, food and pharmaceutical industries are a major environmental concern.