- Library Home
- General (Summon)
- Books & Media (Catalogue)
- Indexes, Databases & Articles
- Research Guides
- UBC Research
- UBC Open Collections
- UBC Vancouver
- Asian Library
- Biomedical Branch Library
- Chapman Learning Commons Help Desk
- David Lam Management Research Library
- Education Library
- Irving K. Barber Learning Centre
- Koerner Library
- Law Library
- Music, Art and Architecture Library
- Rare Books and Special Collections
- Research Commons
- University Archives
- Woodward Library
- X wi7 x wa Library
- UBC Okanagan
- Okanagan Library
- Special Collections & Archives
- The Commons (Okanagan)
- UBC Virtual
- AskAway Chat Services
- Borrowing Services
- My Library Account
- How to Get Library Access
- See More...
- Electronic Access
- Connect to Library Resources
- OpenAthens Login Overview
- Computers & Technology
- Print, Copy, Scan
- Public Computers & Software
- Group & Silent Study Spaces
- Technology Spaces
- Guides for Library Users
- Undergraduate Students
- Faculty & Instructors
- Planning Your Research
- Getting Started on Your Research
- Finding Resources
- Journal Articles
- Evaluating & Citing Sources
- Evaluating Information Sources
- How to Cite
- Publishing Research
- Getting Started with cIRcle
- Building Your Academic Profile
- Collections
- Policies, Procedures and Guidelines
- Work with Us
- Accessing Library Resources?
- OpenAthens Login
- Add Browser Extension for Access
- Managing Your Account?
- My Library Account Login
- Need Citation Management?
- Citation Management Tools

The Research Paper Calculator
The Research Paper Calculator is a time management tool that breaks down research assignments into a series of manageable steps, while providing expert tips for success. Enter the assignment start date and due date to get planning!
About the Assignment Calculator
Brought to you by the Centre for Writing and Scholarly Communication , Chapman Learning Commons and UBC Library
Based on the original Assignment Calculator from the University of Minnesota Libraries .
Research Assignment Due? Stay on TRAC
How to Use The Research Assignment Calculator (TRAC) in Your Classroom
The Research Assignment Calculator (TRAC) helps you break down the research process into manageable steps, create a schedule, and meet your assignment deadline.
This time management tool gives you links to the UMGC library, Effective Writing Center, and other resources to help you with each stage of your research project.

Research Paper Planner
This timeline may include due dates on weekends and university holidays; depending on your plans you may need to make some adjustments., creating a presentation with slides.
View more 'research help' videos on our Youtube channel youtube.com/LibraryGeorgian
Creating a Video Assignment
Dissertation Calculator
Assignment start and due dates.
Enter the date you plan to start work and the due date of your assignment.
Required. Example: 12 31 2020
Assignment steps
Identify and refine your research question.
Your interest in your research questions will help you maintain focus on the dissertation process. The work you do may become the starting place for future research work and the next step in your career. Choose a topic that interests you and will help you advance your career. However, your choice of topic will depend on the requirements of your professors, advisors, program, department, college, university, and academic discipline. Review any documents or handbooks that outline the requirements and expectations.
- Examine the requirements, expectations, and methods used by your department, program, and advisor.
- University Digital Conservancy
- Digital Dissertations
- How to find dissertations and theses including older U of M print dissertations
- Set up a system for organizing your search results, citations, PDFs, primary sources, notes etc. using citation management tools (e.g. Zotero or EndNote) or other strategies. You can use these tools to create "in-text" citations and bibliographies or works cited lists as you write.
- In some cases, you will be given a research question or a list of topics to choose from by your advisor.In other cases, you will develop a topic based on your own research interests.
- Review departmental information to learn about faculty research areas and identify faculty who might be interested in working with you. Try Experts@Minnesota .
- Do a preliminary study of the literature related to your topics to understand previous research, key themes, issues, variables, methodologies, limitations, terminology, controversies, and gaps in the current research. Identify significant researchers and scholars working in the area. Consult a variety of sources such as websites, research blogs, books, journal articles, conferences, organizations, and other sources.
- Narrow your ideas to 2 or 3 possible research questions. Evaluate your question using criteria like feasibility, scope (too narrow or too broad), your level of interest, and future benefit to your career.
- Discuss your ideas with classmates, colleagues, mentors, and other professors for comment and feedback.
- Organize your research ideas into a pre-proposal for use in discussion and negotiation with your advisor.
- Revise and modify as needed based on comments gathered.
- Be sure that you and your advisor are in agreement about the research questions before drafting the final proposal.
- The ULibraries have many print and ebooks on the process of writing dissertations. Search for: dissertations, academic; academic writing dissertations; and report writing dissertations.
- Dissertations, from the University of North Carolina Writing Center
Percent time spent on this step: 5
Develop the research design and methodology
The research design is the strategy or blueprint for the collection, measurement, and analysis of your data (data can be numbers, images, texts, interview transcripts, etc.). Generally the design is the overall logical structure for your project and the methodology refers to the detailed steps for data collection and analysis. The type of design and method used is determined by the nature of your research question. Certain research designs and methods are core to specific fields of study or programs. Your design needs to be consistent with the requirements and expectations of your advisor, committee, and program.
- Understand that your choice of design and methods will influence the niche you develop for yourself within your department, your discipline, and the wider academic community.
- Read and review information about design and methodology (e.g. such as books on methodology) and study examples of how these strategies have been applied in research similar to yours (e.g. other dissertations, articles, etc.).
- Consider any philosophical and practical factors. Identify the theoretical approaches inherent in your design and methods.
- Use Sage Research Methods Online to learn more about design and methods.
- Search Libraries Search for books and articles on theory, design, methods, and analysis.
- Read about specific statistical techniques and software packages, for example, R, Tableau, NVivo, ATALAS.ti, SPSS, etc.. Some libraries and OIT labs have this software. Learn about statistical consulting services , if needed.
- Learn about data management best practices. Data management plans assist you in planning the types of data you will collect, standards to document your data (metadata), security measures to protect the confidentiality of your subjects and intellectual property, and methods for archiving and sharing your data.
- Review dissertations with similar designs and methods to learn about what worked well and what obstacles occurred.
Review literature & write a proposal or prospectus
Proposals generally include the title of your project, an introduction, literature review, and a description of the research design and methodology for your proposed dissertation. This is often used as the foundation for the first three chapters of the completed dissertation. Be sure to read other successful proposals as examples to guide your work. Check with your advisor, mentors, or department for examples.
- Writing an effective title from UMN Center of Writing
- Although this is the first section the reader comes to, you might want to write it last , since until then, you will not be absolutely sure what you are introducing.
- The introduction establishes the context for your research by briefly summarizing the current and background information about the topic. Use it to state the purpose of your work in the form of the hypothesis, question, or research problem, and briefly explain your rationale, theoretical perspective, design and methodological approach. Identify the significance and potential outcomes your project.
- The introduction might include acknowledgement of the previous work on which you are building, an explanation of the scope of your research, what will and will not be included, and a "road map" or "table of contents" to guide the reader to what lies ahead.
- Write in the future tense since it is a proposal. It can be changed and edited later once it becomes part of your dissertation.
- Tips for writing an introduction from University of North Carolina
- Develop an in-depth understanding of your topic and clarify why your research is significant.
- Ensure that your research is a unique contribution.
- Understand the broader discipline and field(s) of which your topic is a part. Position or frame your topic in your field and establish the link between existing research and your question.
- Explore important methodologies, controversies, and research issues.
- Identify names of key researchers, core journals, other research centers, or possible sources of funding.
- Explain your rationale for the research design and methodology and your plan to use and describe why it is appropriate for your research.
- Your reading and study of the literature should be very comprehensive as you prepare your proposal and later write your final literature review. Now is the time to immerse yourself in your topic.
- The written literature review is selective and does not include every article or source your find on your topic. Think of yourself as a curator at a museum. Select the most meaningful, representative works for your "exhibit" but you will have had to have read and critically evaluate many more sources that you don't include in your literature review.
- Build a workflow or system so you can keep track of sources (e.g. citation, PDF, etc.) including notes/rationale for sources you are using and for those you choose not to include (with your rationale for excluding them in case your advisor or committee have questions later).
- Determine the expectations and requirements for the proposal meeting, for example, find out what type of presentation, if any, is expected. Talk with colleagues who have completed this process to understand more about the meeting.
- Be sure that you have completed all the necessary forms from your department or college.
- Meet with your subject librarians and or librarians from related subjects to learn about useful library databases, keywords, citation tools, and specialized services for researchers.
- Go to workshops or watch recorded workshops from the University Libraries.
- Use the Center for Writing, Student Writing Support resources , especially for graduate writers resources.
- Review other dissertations both for ideas on how the literature review can be organized and for useful articles and other sources.
- Review what you already have written and presented for your course work and other projects.
- Use subject-specific databases , in addition to, Libraries Search to explore the literature in your field.
- Search article databases outside your discipline. Explore interdisciplinary databases such as Web of Science , Google Scholar , Scopus , JSTOR , Worldcat , etc.
- Browse and search in the core journals in your field. Try the tool Browzine to create a personal library.
- Decide if you need sources that are international in scope and use additional search strategies as needed.
- Identify non-digitized sources. Depending on your research area contact library archives or special collections and consult with curators or other staff to learn more about relevant resources.
- Use Interlibrary Loan to request materials not available at UMN Libraries for free.
- Use subject headings or a thesaurus within a database to find similar sources by concept rather than just keyword match.
- Review the bibliographies of articles and books to identify additional sources.
- Do "cited reference" searches to identify researchers that have cited other specific books or articles of interest. Use specialized tools like Web of Science , Google Scholar and other databases to trace the citations both backward and forward in time.
- Track where you have searched and your search terms by keeping a research log or journal ( view example ). This will help you identify the most productive sources and not repeat what you have already done. If needed you will be able to report your search strategies.
Percent time spent on this step: 15
Gather and analyze your data
After your proposal is approved, the next step is to implement your research plan by gathering and analyzing your "data." Before you begin there are more steps to consider if you have not completed.
- Obtain any needed human subject or animal care approval from the Institutional Review Board .
- Create a strategy to organize your files, contacts, observations, field notes, and bibliographic information.
- Implement a small pilot study before proceeding with the full data collection. This will help you to test your approach to ensure you are collecting data that reflects your research question. Document details such as time involved and issues in the study for either you or the participants. Determine if any modifications to your study need to occur before proceeding.
- Identify and test a strategy for transforming and analyzing the data (e.g. coding data, transcribing interviews, running statistics, etc.).
- Test your analysis method with the small pilot study or sample of your data.
- Create graphs, tables, images, and other outputs that illustrate your results.
- Meet regularly with your advisor to discuss and resolve any questions.
- Use Sage Research Methods Online to learn more about design and methods.
- Search Libraries Search for books and articles on data visualization, data mining, data processing, methods, and analysis.
Percent time spent on this step: 30
Write the Results and Discussion sections
- Use non-text objects to illustrate your results including tables, figures, images and visualizations. Illustrative objects should either be placed within the dissertation text or at the end of your dissertation.
- Summarize all your results whether they are statistically significant or not.
- Put raw data, survey instruments, and release forms, etc. into appendices if appropriate and required. Consider the Data Repository for the U of M (DRUM) to archive data.
- Include your research questions identified in the introduction. Describe how you have moved the field forward. Explain how your research enhances or fills a gap in existing research. Identify any unexpected or contradictory findings.
- Explain how your results relate to existing literature and if they are consistent with previous research.
- Describe how your results can be applied. This could take a variety of forms such as real world application, best practices or recommendations.
- Share the conclusion have reached because of your research.
- Explain limitations in your research and possibilities for future research on your topic.
- Meet with a subject librarian to do precise searching if you need to find additional sources.
- Meet with the Center for Writing for support with your writing process.
Percent time spent on this step: 25
Edit Dissertation draft & prepare for your defense
Although editing and revising occurs throughout the writing process, budget sufficient time to return to your draft for full-scale revision. Seeking feedback, reviewing, and editing your document helps you to:
- See your text from a reader's perspective.
- Bring together parts written at different times to create a coherent, connected whole.
- Make your ideas clear to others, which in turn, will result in better reader comments.
- Plan and negotiate your progress in consultation with your advisor and committee members.
- Examine the overall organization and identify what is no longer relevant and what sections need further development.
- Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist , from UW Madison
- Higher Order Concerns and Lower Order Concerns from Purdue
- Ask colleagues and others for specific types of feedback to guide the comments. Connect with your dissertation support network and members of your committee to receive constructive feedback.
- Help your readers help you by giving them a direction, for example in an email, in which you explain what you want to accomplish in the draft and list your specific questions and concerns.
- Identify potential readers' expertise and skills when deciding which parts of your dissertation you want them to review. For example, perhaps only people working in your lab can constructively comment on your "methods," while friends in other disciplines would give useful feedback on the "introduction."
- Respond to all comments even though you may decide to not incorporate a suggestion.
- Negotiate with your advisor and committee members to establish a process for submitting drafts for their feedback.
- Check all calculations, visual details, and citations for accuracy and validity and remove sources you are no longer citing or add new ones.
- Prepare the bibliography, appendix, title page, and acknowledgements.
- Be sure you are formatting your document to meet the dissertation submission and formatting requirements .
- You may or may not be expected to give a brief presentation at the beginning.
- Focus on the needs of your primary audience (your advisor and committee), either by consulting them directly or considering their feedback to your initial draft.
- Review your notes and rationale for making the decisions you made in your draft for example, including or excluding certain seminal theories, authors, and research methodologies.
- Remind yourself that at this point you are now the "expert" on your research and the goal of the defense is to present and share your expertise and seek feedback from interested readers.
- Dissertation Defense from Texas A&M
Finish and submit your dissertation
Your dissertation defense committee will have informed you that you passed your defense, or passed with minor revisions needed. In some cases, substantial revisions are needed before the committee members agree to pass the dissertation. The procedures, requirements, and timelines for completing the dissertation process may vary depending on the department and college with which you are affiliated and the type of doctorate you will receive. Once any needed revisions have been completed and approved, you are ready to finish the dissertation and submit the final version.
- Many departments have their own handbooks to guide students through the process with timelines and specific academic style guidelines. Consult the details in the doctoral handbook for your department and college.
- Review the Dissertation submission requirements .
- Review information about Copyright and Dissertations & Theses . You own the copyright usually and it is wise to consider your next with the content.
- You will retain your rights to your dissertation when submitting it to the UDC.
- The UDC copy of your dissertation will be freely available for you and others to read and link to with a permanent URL. Learn more about the benefits of the UDC for your dissertation.
- A copy of your dissertation is submitted to ProQuest/UMI Dissertation Publishing making information about your dissertation available through ProQuest Digital Dissertations. The full text of your dissertation will be available through libraries that subscribe to this product or copies may be purchased. You may also opt to make your dissertation available on an open access basis via ProQuest Open Access Publishing.
- Library Catalogue
Assignment Calculator: A time management tool for use with writing assignments

Break your assignment into steps
Use the Assignment Calculator to break down your writing assignments into a series of manageable steps -- each with a separate due date.
All you need to know is the date you will start working on the assignment (be realistic!) and your due date.
Read through your assignment guidelines and note requirements such as citation style and page limits.
If your topic is broad (e.g. "write an essay about healthcare") then narrow or focus your topic before you start researching. .
For more about narrowing your topic, try:
- Developing a Topic for a Research Paper: Narrowing Your Topic , a quick video (3 minutes) plus tips, from University of Regina's Archer Library.
- University of Nevada Las Vegas's Topic Narrowing tool , for a mind mapping approach.
Gather research from credible sources to develop your topic. There are many places to search for credible information, including the SFU Library or Google Scholar.
Review the information you find to understand your topic. You will want to pay attention to relevant beliefs, trends, thoughts, and facts, giving more emphasis to the kinds of information your assignment asks you to focus on.
For more on finding and evaluating sources, see:
- What is a scholarly journal ?: For how to identify and evaluate scholarly journals, magazines, and trade publications -- both print and online.
- Finding and evaluating resources : Tips for finding and evaluating the reliability of publications, whether you find them on the open web, in the Library Catalogue, using Google Scholar, or elsewhere.
- Search the SFU Library for tips for books, and journal articles, and tips from subject expert librarians.
Create an overall statement that both summarizes your research and indicates the significance of your main claim or argument.
Not every research paper needs an argumentative thesis statement, but if you’re asked to take a position on a topic, then your thesis statement should also be debatable.
Remember that an effective thesis statement presents both your main claim and your central reasons for making that claim.
You can always adjust your thesis statement as you draft your paper.
Looking for more?
- Try these tips on constructing a thesis statement from Walden University.
- You can also review these templates for argumentation , from the SFU Student Learning Commons.
Outline the main sections and/or paragraphs you plan to write about in your paper.
Each section or paragraph should tie in with your thesis statement. In your outline, make notes about how each section of your paper relates to your thesis statement.
Also note which facts, articles, and/or evidence you will use to support your claims.
- Try these suggestions for the essential sections of an outline from Walden University
- The University of Toronto's guide to organizing an essay has some good outlining examples
Refer to your outline and expand your ideas into complete sentences and paragraphs.
The writing doesn't need to be perfect -- just focus on getting your ideas written and solidifying the key points of your paper.
Note the research sources you think you will write about and/or use as evidence in your paper in your outline. Be sure to include where you found the information, who the author is, and when the source was published.
- Review these tips for writing a first draft from Berkeley
- Stuck? See these tips for overcoming writer's block: Writers Block (from Walden University) and Symptoms and Cures for Writer's Block (from Purdue University)
Revision takes time.
In this step, look again at your thesis and make sure your paper advances your argument. At this point you might need to make structural changes.
Where revision asks you to look at the structure, organization, and overall argument in your paper, editing is about taking a close look at your sentence structures, transitions, and the concision of your writing.
For more detailed tips and examples:
- Check out Revising the Draft from the Harvard College Writing Center
- To ensure your paper meets the assignment guidelines, and to check for cohesion, try Reverse Outlines: A Writer's Technique for Examining Organization (University of Wisconsin - Madison).
Make sure that all your sources are properly integrated and cited. This step is important for ensuring academic integrity.
- Review the guidelines of the citation style you have been asked to use (e.g. APA, MLA, Chicago).
- When do you need to cite? Test your knowledge with the SFU plagiarism tutorial .
- Need more help? Ask a Librarian your citation question.
Review the style, clarity and flow of your writing. Focus on individual sentences and look for common errors in sentence structure, punctuation, grammar, or usage. Read your work out loud to help you catch mistakes. Printing out and checking a hard copy can also help you to notice typos that you might miss on the screen.
Finally, format your paper to fit all your assignment guidelines.
- Try these techniques for sentence clarity from Purdue University.
- Review these Top 10 Self-Help Editing Tips from the Student Learning Commons
Submit your assignment, and you're done!
Remember that your instructor will provide you with helpful feedback on your assignment that can help you to improve both your writing and your writing process for future work.
If you ever get feedback that is unclear to you, you can bring it into the Student Learning Commons for discussion with one of our Peers or Graduate Writing Facilitators.
Book a consultation with the Student Learning Commons at any of these stages to get more support.
About this tool
These general steps will guide you through the process of writing most research-based essay assignments.
However every assignment is a little different -- so always refer to the your specific assignment guidelines, check with your TA or instructor if you have questions, and use your best judgement about which steps are necessary for you!
Further resources and more information
Looking for more types of assignments?
The University of Toronto Scarborough's Assignment Calculator includes steps for literature reviews, annotated bibliographies, lab reports, poster presentations, and more.
Attribution:
- Our Assignment Calculator is based on the Assignment Calculator by the University of Minnesota Libraries.
- The image at the top of this page is a cropped version of one created by Morten Oddvik ( CC BY 2.0 ).
- Get Help Here >

- 214-333-5320

Click here to use the
RESEARCH ASSIGNMENT CALCULATOR
How to Use the Research Calculator
This tool will help you stay on track and lead you to resources from libraries and writing centers to help you master the skills of planning, researching, drafting, and writing a research paper, thesis, or dissertation. This method of reverse scheduling is based on best practices for writing papers and theses developed by college and university faculty and librarians.

Fill in the due date of your assignment, then click on the Calculate Assignment Schedule button to see what steps you should follow and when you should have them completed. You can modify the due date at any time.
On the Timeline page you will be able to:
- print the schedule and
- set up email reminders for the due dates.
Or go directly to the Research Paper Planner: Guide and view the resources listed there without setting up a timeline.
- Deadlines provided by your instructor will supersede any provided by the Research Planning Timeline.
- If you are using this tool to plan an Honor's or Master's thesis your due date should be one month before the thesis (or chapter - if you are breaking it down) is due to your advisor.
- This timeline is a suggestion for efficient planning.
- WARNING: This timeline includes due dates on weekends and University holidays; depending on your plans you may need to make some adjustments.
"For I know the plans I have for you," declares the LORD, "plans to prosper you and not to harm you, plans to give you hope and a future." - Jeremiah 29:11
Vision Statement Building a great Christian university that is pleasing to God by producing Christ-centered servant leaders who are transforming the world.
- University Directory
- Parking Information
- © 2014 Dallas Baptist University
- Legal Notice
- Last Updated: Oct 17, 2023 2:12 PM
- URL: https://libguides.dbu.edu/research_calculator
Research Paper Planner
Tired of writing your paper the night before it's due? This Research Paper Planner will help you break down your assignment into manageable deadlines, track your progress, and connect with campus resources.
Give it a try:
Click the button below to make a copy of the planner into your Drive:
Copy the paper planner
Input the due date of one of your upcoming assignments and get started!
Writing a paper for the undergraduate science journal ? We have a special planner for you!

Just make a copy of the Undergraduate Science Journal Paper Planner and get started!
Related Resources
- Breaking Down Your Prompt 5-star editor review on merlot.org (Tutorial)
- Developing your Long Term Research Plan (Workshop)
- Research Logistics 5-star editor review on merlot.org (Workshop)
- Research Paper Planner (Handout)
- Student Success Guide on Taking an Online Course (Handout)
About this tutorial
Shannon Roux
Contributors
Whitney Arnold, Joanna Chen Cham, Janet Goins, Taylor Harper , Leigh Harris, Kelly Kistner, Simon Lee, Caitlin Meyer , Renee Romero , Shushanik Stepanyan, Mary Tran, Doug Worsham , Royson Lin , University of Minnesota Libraries Research Paper Calculator
https://uclalibrary.github.io/research-tips/research-tips/research-planner/
Learning Outcomes
- Break down assignments into manageable deadlines
- Track progress on assignments
- Identify campus resources
The Core Competencies for Research and Information Literacy at UCLA
- Define the goals, scope, and plan
University of Missouri
- Directories
- Maps & Floorplans
- Libraries A-Z
University Libraries
Research paper assistance calculators, research paper assistance calculators*, assignment calculators implemented across the country.
- University of Minnesota — Assignment Calculator http://www.lib.umn.edu/help/calculator/ https://www.lib.umn.edu/services/ac/dissertation-calculator — Dissertation Calculator
- University of Arkansas — Research Paper Wizard
- Rochester Institute of Technology — Assignment Calculator, Project Management Tool for Students
- SJSU Library Assignment Calculator
Research Paper Planner: Guide
- 1: Understand Your Assignment
- 2: Select & Focus Your Topic
- 3: Explore a Research Question
- 4: Design Your Research Strategy
- 5: Finding Sources
- 6: Read, Note, and Compare Sources
- 7: Write Thesis Statement
- 8: Writing the First Draft
- 9: Evaluate Your First Draft
- 10: Revise & Rewrite
- 11: Put Your Paper in Final Form
Reference Librarians

Welcome to the Research Paper Planner Guide
Welcome to the Guide portion of the BU Libraries' Research Paper Planner (RPP). This Guide contains links to helpful resources for each step of the research and writing process. If you have used the Timeline portion of the RPP the links in the Timeline will take you to the links for that step of the process.
This Guide may be used independently of the Timeline to locate resources for each of the following stages of the research and writing process; just click on the Step button to the left to get there.
Surprised that there are so many steps? Research conducted by librarians and teachers of writing has shown that breaking a research paper or thesis down into these steps is the "normal" process of writing for humanities and social science disciplines. Using these steps will help you approach your research assignment in a progressive manner that should produce a better final product. Give it a try and then use the evaluation for to the right to let us know how the RPP worked for you and suggest ways it could be improved.
This work is based on the University of Minnesota's Assignment Calculator but has been modified to meet the needs of the Baylor University community.
- Research Paper Planner: Timeline This link will take you to the Timeline portion of the Research Paper Planner where you can set a start and end date for your writing project, see the deadlines for each step, print out the Timeline for your project, and/or set up email alerts for each step of the research and writing process.
- Next: 1: Understand Your Assignment >>
- Last Updated: Jan 16, 2024 10:55 AM
- URL: https://libguides.baylor.edu/planner
University Libraries
One Bear Place #97148 Waco, TX 76798-7148
(254) 710-6702
Ask a Question
Copyright © Baylor® University . All rights reserved.
Report It | Title IX | Mental Health Resources | Anonymous Reporting | Legal Disclosures
Weekly hours for all locations
Assignment Calculator - Research Paper
- Current Select Dates
- Calculate Steps

Managing Research Projects
See the big picture, research paper calculator, develop a research question, dream and make notes, what resources do you need, research is messy, emotions while researching.
- Staying Organized
- Staying Motivated
- What happens after I'm done?
Planning for Long-Term Research Projects (3:57)
This video from the UCLA Library provides strategies for planning a research project that takes multiple quarters to complete.

The same is true when planning a research project.
Make sure you see the big picture of what is involved.
What are the expectations of the project?
- What does the description of the project say are the requirements or expectations? (e,g, assignment in a syllabus, goals of a grant, application for an internship, journal article requirements, art installation for a site, etc.)
- Write the description of the project and the expectations in your own words.
What is the scope of the project?
- write about friendships between black and white conductors and what drew them together
- a literature review, introduction, abstract, references
- Is an annotated bibliography needed?
- Do I need info about economic factors related to the underground railroad? Probably not.
- Research Paper Calculator This tool from the University of Minnesota Libraries allows you to enter the date you receive an assignment and the date it is due. The time needed for each step in the research process is then calculated, and intermediate dates provided. Works great for any thesis-driven/literature review papers.
- Dissertation Calculator This tool from the University of Minnesota Libraries allows you to enter the date you begin a large research project and the date it is due. The time needed for each step in the research process is then calculated, and intermediate dates provided. Works great for any empirical research papers, where one is gathering data.
Use a calculator like the ones above to lay out a timeline that works for you, taking into account when you'll have more and less time for the project. Below is a sample timeline by month, laying out tasks relating to research, reading, and writing.

1, "Finding a Topic for a First Research Project in a Particular Field
Start by listing topics relevant to your particular class and that interest you, then narrow them to one or two promising ones. If the topic is general, such as religious masks, you’ll have to do some random reading to narrow it. But read with a plan:
- Skim encyclopedia entries in your library or online. Start with standard ones such as the Encyclopaedia Britannica . Then consult specialized ones such as the Encyclopedia of Religion or the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy.
- Skim headings in specialized indexes such as the Philosopher’s Index, Psychological Abstracts, or Women’s Studies Abstracts. Use subheadings for ideas of how others have narrowed your topic.
- Google your topic, but not indiscriminately. Use Google Scholar, a search engine that focuses on scholarly journals and books. Skim the articles it turns up, especially their lists of sources.
When you know the general outline of your topic and how others have narrowed theirs, try to narrow yours. If you can’t, browse through journals and websites until your topic becomes more clearly defined. That takes time, so start early. "
Read chapter 3 of The Craft of Research for more detailed concrete steps and suggestions.
2. Develop a question
3. State the significance of the topic. Why is important to study the topic you identified?
Booth, Wayne C., et al. The Craft of Research , University of Chicago Press, 2016. ProQuest Ebook Central , http://ebookcentral.proquest.com/lib/spu/detail.action?docID=4785166. Created from spu on 2021-01-26 10:33:28.
- Set aside a block of uninterrupted time to mull over stuff.
- Scribble ideas down, all of them, related to the project.
- Write down important phrases.
- Create a document (spreadsheet, Word, Google Doc, pad of paper - whatever works for you) where you keep track of the terminology (keywords) you use for searches and the kinds of results those terms provide).
- Try using a concept map to see the big picture of your topic.

- Blank Concept Map
- Create a Concept Map

Consider what tools and resources you will need for your project.
For example:
- peer reviewed
- empirical research articles
- Databases to search
- Primary, secondary, or tertiary resources
- Permission from the IRB - Institutional Research Board

So, make a plan. (Right click and click on "Open link in new tab" in order to not lose track of the Managing Research Projects subject guide)
Talk to a librarian to help guide you on resources you should consider consulting.
For concrete details and suggestions, read Chapter 5, "From Problems to Resources," in The Craft of Research
Research is not only messy, it can be emotionally taxing.
Be aware of your thoughts, feelings, and actions as you begin the search for information. Dr. Carol Kuhlthau , Professor Emerita at Rutgers University, developed this 6 stage model to explain the affective (feelings), cognitive (thoughts) and physical (actions) common to each stage of researching.
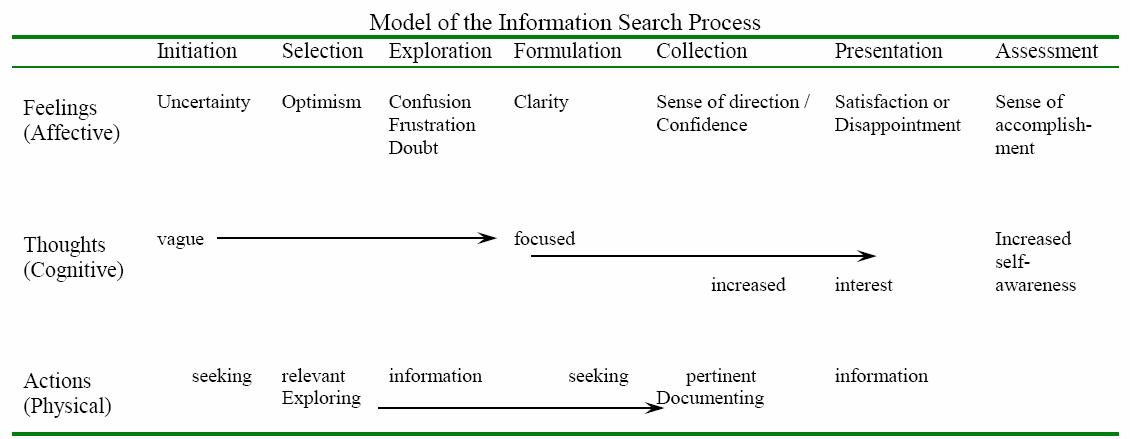
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Staying Organized >>
- Last Updated: Jan 30, 2024 3:40 PM
- URL: https://spu.libguides.com/ManagingProjects
How To Write a Research Paper
- 1. Understand the Assignment
- 2. Choose Topic & Write Thesis Statement
- 3. Create Concept Map & Keyword List
- 4. Research Your Topic
- 5. Create an Outline
- 6. Write the Paper
Assignment Calculator
Calculate Time Needed for Each Step
- The date you received the assignment
The date the final paper is due
The calculator will create a schedule for you. Please note that you will be redirected to San Jose State University's website.
- << Previous: 6. Write the Paper
- Next: Plagiarism >>
- Last Updated: Oct 31, 2023 9:15 AM
- URL: https://libguides.seminolestate.edu/researchpaper
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and Templates
Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and Templates
Table of Contents

Research paper format is an essential aspect of academic writing that plays a crucial role in the communication of research findings . The format of a research paper depends on various factors such as the discipline, style guide, and purpose of the research. It includes guidelines for the structure, citation style, referencing , and other elements of the paper that contribute to its overall presentation and coherence. Adhering to the appropriate research paper format is vital for ensuring that the research is accurately and effectively communicated to the intended audience. In this era of information, it is essential to understand the different research paper formats and their guidelines to communicate research effectively, accurately, and with the required level of detail. This post aims to provide an overview of some of the common research paper formats used in academic writing.

Research Paper Formats
Research Paper Formats are as follows:
- APA (American Psychological Association) format
- MLA (Modern Language Association) format
- Chicago/Turabian style
- IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) format
- AMA (American Medical Association) style
- Harvard style
- Vancouver style
- ACS (American Chemical Society) style
- ASA (American Sociological Association) style
- APSA (American Political Science Association) style
APA (American Psychological Association) Format
Here is a general APA format for a research paper:
- Title Page: The title page should include the title of your paper, your name, and your institutional affiliation. It should also include a running head, which is a shortened version of the title, and a page number in the upper right-hand corner.
- Abstract : The abstract is a brief summary of your paper, typically 150-250 words. It should include the purpose of your research, the main findings, and any implications or conclusions that can be drawn.
- Introduction: The introduction should provide background information on your topic, state the purpose of your research, and present your research question or hypothesis. It should also include a brief literature review that discusses previous research on your topic.
- Methods: The methods section should describe the procedures you used to collect and analyze your data. It should include information on the participants, the materials and instruments used, and the statistical analyses performed.
- Results: The results section should present the findings of your research in a clear and concise manner. Use tables and figures to help illustrate your results.
- Discussion : The discussion section should interpret your results and relate them back to your research question or hypothesis. It should also discuss the implications of your findings and any limitations of your study.
- References : The references section should include a list of all sources cited in your paper. Follow APA formatting guidelines for your citations and references.
Some additional tips for formatting your APA research paper:
- Use 12-point Times New Roman font throughout the paper.
- Double-space all text, including the references.
- Use 1-inch margins on all sides of the page.
- Indent the first line of each paragraph by 0.5 inches.
- Use a hanging indent for the references (the first line should be flush with the left margin, and all subsequent lines should be indented).
- Number all pages, including the title page and references page, in the upper right-hand corner.
APA Research Paper Format Template
APA Research Paper Format Template is as follows:
Title Page:
- Title of the paper
- Author’s name
- Institutional affiliation
- A brief summary of the main points of the paper, including the research question, methods, findings, and conclusions. The abstract should be no more than 250 words.
Introduction:
- Background information on the topic of the research paper
- Research question or hypothesis
- Significance of the study
- Overview of the research methods and design
- Brief summary of the main findings
- Participants: description of the sample population, including the number of participants and their characteristics (age, gender, ethnicity, etc.)
- Materials: description of any materials used in the study (e.g., survey questions, experimental apparatus)
- Procedure: detailed description of the steps taken to conduct the study
- Presentation of the findings of the study, including statistical analyses if applicable
- Tables and figures may be included to illustrate the results
Discussion:
- Interpretation of the results in light of the research question and hypothesis
- Implications of the study for the field
- Limitations of the study
- Suggestions for future research
References:
- A list of all sources cited in the paper, in APA format
Formatting guidelines:
- Double-spaced
- 12-point font (Times New Roman or Arial)
- 1-inch margins on all sides
- Page numbers in the top right corner
- Headings and subheadings should be used to organize the paper
- The first line of each paragraph should be indented
- Quotations of 40 or more words should be set off in a block quote with no quotation marks
- In-text citations should include the author’s last name and year of publication (e.g., Smith, 2019)
APA Research Paper Format Example
APA Research Paper Format Example is as follows:
The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health
University of XYZ
This study examines the relationship between social media use and mental health among college students. Data was collected through a survey of 500 students at the University of XYZ. Results suggest that social media use is significantly related to symptoms of depression and anxiety, and that the negative effects of social media are greater among frequent users.
Social media has become an increasingly important aspect of modern life, especially among young adults. While social media can have many positive effects, such as connecting people across distances and sharing information, there is growing concern about its impact on mental health. This study aims to examine the relationship between social media use and mental health among college students.
Participants: Participants were 500 college students at the University of XYZ, recruited through online advertisements and flyers posted on campus. Participants ranged in age from 18 to 25, with a mean age of 20.5 years. The sample was 60% female, 40% male, and 5% identified as non-binary or gender non-conforming.
Data was collected through an online survey administered through Qualtrics. The survey consisted of several measures, including the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) for depression symptoms, the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7) for anxiety symptoms, and questions about social media use.
Procedure :
Participants were asked to complete the online survey at their convenience. The survey took approximately 20-30 minutes to complete. Data was analyzed using descriptive statistics, correlations, and multiple regression analysis.
Results indicated that social media use was significantly related to symptoms of depression (r = .32, p < .001) and anxiety (r = .29, p < .001). Regression analysis indicated that frequency of social media use was a significant predictor of both depression symptoms (β = .24, p < .001) and anxiety symptoms (β = .20, p < .001), even when controlling for age, gender, and other relevant factors.
The results of this study suggest that social media use is associated with symptoms of depression and anxiety among college students. The negative effects of social media are greater among frequent users. These findings have important implications for mental health professionals and educators, who should consider addressing the potential negative effects of social media use in their work with young adults.
References :
References should be listed in alphabetical order according to the author’s last name. For example:
- Chou, H. T. G., & Edge, N. (2012). “They are happier and having better lives than I am”: The impact of using Facebook on perceptions of others’ lives. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 15(2), 117-121.
- Twenge, J. M., Joiner, T. E., Rogers, M. L., & Martin, G. N. (2018). Increases in depressive symptoms, suicide-related outcomes, and suicide rates among U.S. adolescents after 2010 and links to increased new media screen time. Clinical Psychological Science, 6(1), 3-17.
Note: This is just a sample Example do not use this in your assignment.
MLA (Modern Language Association) Format
MLA (Modern Language Association) Format is as follows:
- Page Layout : Use 8.5 x 11-inch white paper, with 1-inch margins on all sides. The font should be 12-point Times New Roman or a similar serif font.
- Heading and Title : The first page of your research paper should include a heading and a title. The heading should include your name, your instructor’s name, the course title, and the date. The title should be centered and in title case (capitalizing the first letter of each important word).
- In-Text Citations : Use parenthetical citations to indicate the source of your information. The citation should include the author’s last name and the page number(s) of the source. For example: (Smith 23).
- Works Cited Page : At the end of your paper, include a Works Cited page that lists all the sources you used in your research. Each entry should include the author’s name, the title of the work, the publication information, and the medium of publication.
- Formatting Quotations : Use double quotation marks for short quotations and block quotations for longer quotations. Indent the entire quotation five spaces from the left margin.
- Formatting the Body : Use a clear and readable font and double-space your text throughout. The first line of each paragraph should be indented one-half inch from the left margin.
MLA Research Paper Template
MLA Research Paper Format Template is as follows:
- Use 8.5 x 11 inch white paper.
- Use a 12-point font, such as Times New Roman.
- Use double-spacing throughout the entire paper, including the title page and works cited page.
- Set the margins to 1 inch on all sides.
- Use page numbers in the upper right corner, beginning with the first page of text.
- Include a centered title for the research paper, using title case (capitalizing the first letter of each important word).
- Include your name, instructor’s name, course name, and date in the upper left corner, double-spaced.
In-Text Citations
- When quoting or paraphrasing information from sources, include an in-text citation within the text of your paper.
- Use the author’s last name and the page number in parentheses at the end of the sentence, before the punctuation mark.
- If the author’s name is mentioned in the sentence, only include the page number in parentheses.
Works Cited Page
- List all sources cited in alphabetical order by the author’s last name.
- Each entry should include the author’s name, title of the work, publication information, and medium of publication.
- Use italics for book and journal titles, and quotation marks for article and chapter titles.
- For online sources, include the date of access and the URL.
Here is an example of how the first page of a research paper in MLA format should look:
Headings and Subheadings
- Use headings and subheadings to organize your paper and make it easier to read.
- Use numerals to number your headings and subheadings (e.g. 1, 2, 3), and capitalize the first letter of each word.
- The main heading should be centered and in boldface type, while subheadings should be left-aligned and in italics.
- Use only one space after each period or punctuation mark.
- Use quotation marks to indicate direct quotes from a source.
- If the quote is more than four lines, format it as a block quote, indented one inch from the left margin and without quotation marks.
- Use ellipses (…) to indicate omitted words from a quote, and brackets ([…]) to indicate added words.
Works Cited Examples
- Book: Last Name, First Name. Title of Book. Publisher, Publication Year.
- Journal Article: Last Name, First Name. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal, volume number, issue number, publication date, page numbers.
- Website: Last Name, First Name. “Title of Webpage.” Title of Website, publication date, URL. Accessed date.
Here is an example of how a works cited entry for a book should look:
Smith, John. The Art of Writing Research Papers. Penguin, 2021.
MLA Research Paper Example
MLA Research Paper Format Example is as follows:
Your Professor’s Name
Course Name and Number
Date (in Day Month Year format)
Word Count (not including title page or Works Cited)
Title: The Impact of Video Games on Aggression Levels
Video games have become a popular form of entertainment among people of all ages. However, the impact of video games on aggression levels has been a subject of debate among scholars and researchers. While some argue that video games promote aggression and violent behavior, others argue that there is no clear link between video games and aggression levels. This research paper aims to explore the impact of video games on aggression levels among young adults.
Background:
The debate on the impact of video games on aggression levels has been ongoing for several years. According to the American Psychological Association, exposure to violent media, including video games, can increase aggression levels in children and adolescents. However, some researchers argue that there is no clear evidence to support this claim. Several studies have been conducted to examine the impact of video games on aggression levels, but the results have been mixed.
Methodology:
This research paper used a quantitative research approach to examine the impact of video games on aggression levels among young adults. A sample of 100 young adults between the ages of 18 and 25 was selected for the study. The participants were asked to complete a questionnaire that measured their aggression levels and their video game habits.
The results of the study showed that there was a significant correlation between video game habits and aggression levels among young adults. The participants who reported playing violent video games for more than 5 hours per week had higher aggression levels than those who played less than 5 hours per week. The study also found that male participants were more likely to play violent video games and had higher aggression levels than female participants.
The findings of this study support the claim that video games can increase aggression levels among young adults. However, it is important to note that the study only examined the impact of video games on aggression levels and did not take into account other factors that may contribute to aggressive behavior. It is also important to note that not all video games promote violence and aggression, and some games may have a positive impact on cognitive and social skills.
Conclusion :
In conclusion, this research paper provides evidence to support the claim that video games can increase aggression levels among young adults. However, it is important to conduct further research to examine the impact of video games on other aspects of behavior and to explore the potential benefits of video games. Parents and educators should be aware of the potential impact of video games on aggression levels and should encourage young adults to engage in a variety of activities that promote cognitive and social skills.
Works Cited:
- American Psychological Association. (2017). Violent Video Games: Myths, Facts, and Unanswered Questions. Retrieved from https://www.apa.org/news/press/releases/2017/08/violent-video-games
- Ferguson, C. J. (2015). Do Angry Birds make for angry children? A meta-analysis of video game influences on children’s and adolescents’ aggression, mental health, prosocial behavior, and academic performance. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 10(5), 646-666.
- Gentile, D. A., Swing, E. L., Lim, C. G., & Khoo, A. (2012). Video game playing, attention problems, and impulsiveness: Evidence of bidirectional causality. Psychology of Popular Media Culture, 1(1), 62-70.
- Greitemeyer, T. (2014). Effects of prosocial video games on prosocial behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 106(4), 530-548.
Chicago/Turabian Style
Chicago/Turabian Formate is as follows:
- Margins : Use 1-inch margins on all sides of the paper.
- Font : Use a readable font such as Times New Roman or Arial, and use a 12-point font size.
- Page numbering : Number all pages in the upper right-hand corner, beginning with the first page of text. Use Arabic numerals.
- Title page: Include a title page with the title of the paper, your name, course title and number, instructor’s name, and the date. The title should be centered on the page and in title case (capitalize the first letter of each word).
- Headings: Use headings to organize your paper. The first level of headings should be centered and in boldface or italics. The second level of headings should be left-aligned and in boldface or italics. Use as many levels of headings as necessary to organize your paper.
- In-text citations : Use footnotes or endnotes to cite sources within the text of your paper. The first citation for each source should be a full citation, and subsequent citations can be shortened. Use superscript numbers to indicate footnotes or endnotes.
- Bibliography : Include a bibliography at the end of your paper, listing all sources cited in your paper. The bibliography should be in alphabetical order by the author’s last name, and each entry should include the author’s name, title of the work, publication information, and date of publication.
- Formatting of quotations: Use block quotations for quotations that are longer than four lines. Indent the entire quotation one inch from the left margin, and do not use quotation marks. Single-space the quotation, and double-space between paragraphs.
- Tables and figures: Use tables and figures to present data and illustrations. Number each table and figure sequentially, and provide a brief title for each. Place tables and figures as close as possible to the text that refers to them.
- Spelling and grammar : Use correct spelling and grammar throughout your paper. Proofread carefully for errors.
Chicago/Turabian Research Paper Template
Chicago/Turabian Research Paper Template is as folows:
Title of Paper
Name of Student
Professor’s Name
I. Introduction
A. Background Information
B. Research Question
C. Thesis Statement
II. Literature Review
A. Overview of Existing Literature
B. Analysis of Key Literature
C. Identification of Gaps in Literature
III. Methodology
A. Research Design
B. Data Collection
C. Data Analysis
IV. Results
A. Presentation of Findings
B. Analysis of Findings
C. Discussion of Implications
V. Conclusion
A. Summary of Findings
B. Implications for Future Research
C. Conclusion
VI. References
A. Bibliography
B. In-Text Citations
VII. Appendices (if necessary)
A. Data Tables
C. Additional Supporting Materials
Chicago/Turabian Research Paper Example
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Political Engagement
Name: John Smith
Class: POLS 101
Professor: Dr. Jane Doe
Date: April 8, 2023
I. Introduction:
Social media has become an integral part of our daily lives. People use social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram to connect with friends and family, share their opinions, and stay informed about current events. With the rise of social media, there has been a growing interest in understanding its impact on various aspects of society, including political engagement. In this paper, I will examine the relationship between social media use and political engagement, specifically focusing on how social media influences political participation and political attitudes.
II. Literature Review:
There is a growing body of literature on the impact of social media on political engagement. Some scholars argue that social media has a positive effect on political participation by providing new channels for political communication and mobilization (Delli Carpini & Keeter, 1996; Putnam, 2000). Others, however, suggest that social media can have a negative impact on political engagement by creating filter bubbles that reinforce existing beliefs and discourage political dialogue (Pariser, 2011; Sunstein, 2001).
III. Methodology:
To examine the relationship between social media use and political engagement, I conducted a survey of 500 college students. The survey included questions about social media use, political participation, and political attitudes. The data was analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Iv. Results:
The results of the survey indicate that social media use is positively associated with political participation. Specifically, respondents who reported using social media to discuss politics were more likely to have participated in a political campaign, attended a political rally, or contacted a political representative. Additionally, social media use was found to be associated with more positive attitudes towards political engagement, such as increased trust in government and belief in the effectiveness of political action.
V. Conclusion:
The findings of this study suggest that social media has a positive impact on political engagement, by providing new opportunities for political communication and mobilization. However, there is also a need for caution, as social media can also create filter bubbles that reinforce existing beliefs and discourage political dialogue. Future research should continue to explore the complex relationship between social media and political engagement, and develop strategies to harness the potential benefits of social media while mitigating its potential negative effects.
Vii. References:
- Delli Carpini, M. X., & Keeter, S. (1996). What Americans know about politics and why it matters. Yale University Press.
- Pariser, E. (2011). The filter bubble: What the Internet is hiding from you. Penguin.
- Putnam, R. D. (2000). Bowling alone: The collapse and revival of American community. Simon & Schuster.
- Sunstein, C. R. (2001). Republic.com. Princeton University Press.
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) Format
IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) Research Paper Format is as follows:
- Title : A concise and informative title that accurately reflects the content of the paper.
- Abstract : A brief summary of the paper, typically no more than 250 words, that includes the purpose of the study, the methods used, the key findings, and the main conclusions.
- Introduction : An overview of the background, context, and motivation for the research, including a clear statement of the problem being addressed and the objectives of the study.
- Literature review: A critical analysis of the relevant research and scholarship on the topic, including a discussion of any gaps or limitations in the existing literature.
- Methodology : A detailed description of the methods used to collect and analyze data, including any experiments or simulations, data collection instruments or procedures, and statistical analyses.
- Results : A clear and concise presentation of the findings, including any relevant tables, graphs, or figures.
- Discussion : A detailed interpretation of the results, including a comparison of the findings with previous research, a discussion of the implications of the results, and any recommendations for future research.
- Conclusion : A summary of the key findings and main conclusions of the study.
- References : A list of all sources cited in the paper, formatted according to IEEE guidelines.
In addition to these elements, an IEEE research paper should also follow certain formatting guidelines, including using 12-point font, double-spaced text, and numbered headings and subheadings. Additionally, any tables, figures, or equations should be clearly labeled and referenced in the text.
AMA (American Medical Association) Style
AMA (American Medical Association) Style Research Paper Format:
- Title Page: This page includes the title of the paper, the author’s name, institutional affiliation, and any acknowledgments or disclaimers.
- Abstract: The abstract is a brief summary of the paper that outlines the purpose, methods, results, and conclusions of the study. It is typically limited to 250 words or less.
- Introduction: The introduction provides a background of the research problem, defines the research question, and outlines the objectives and hypotheses of the study.
- Methods: The methods section describes the research design, participants, procedures, and instruments used to collect and analyze data.
- Results: The results section presents the findings of the study in a clear and concise manner, using graphs, tables, and charts where appropriate.
- Discussion: The discussion section interprets the results, explains their significance, and relates them to previous research in the field.
- Conclusion: The conclusion summarizes the main points of the paper, discusses the implications of the findings, and suggests future research directions.
- References: The reference list includes all sources cited in the paper, listed in alphabetical order by author’s last name.
In addition to these sections, the AMA format requires that authors follow specific guidelines for citing sources in the text and formatting their references. The AMA style uses a superscript number system for in-text citations and provides specific formats for different types of sources, such as books, journal articles, and websites.
Harvard Style
Harvard Style Research Paper format is as follows:
- Title page: This should include the title of your paper, your name, the name of your institution, and the date of submission.
- Abstract : This is a brief summary of your paper, usually no more than 250 words. It should outline the main points of your research and highlight your findings.
- Introduction : This section should introduce your research topic, provide background information, and outline your research question or thesis statement.
- Literature review: This section should review the relevant literature on your topic, including previous research studies, academic articles, and other sources.
- Methodology : This section should describe the methods you used to conduct your research, including any data collection methods, research instruments, and sampling techniques.
- Results : This section should present your findings in a clear and concise manner, using tables, graphs, and other visual aids if necessary.
- Discussion : This section should interpret your findings and relate them to the broader research question or thesis statement. You should also discuss the implications of your research and suggest areas for future study.
- Conclusion : This section should summarize your main findings and provide a final statement on the significance of your research.
- References : This is a list of all the sources you cited in your paper, presented in alphabetical order by author name. Each citation should include the author’s name, the title of the source, the publication date, and other relevant information.
In addition to these sections, a Harvard Style research paper may also include a table of contents, appendices, and other supplementary materials as needed. It is important to follow the specific formatting guidelines provided by your instructor or academic institution when preparing your research paper in Harvard Style.
Vancouver Style
Vancouver Style Research Paper format is as follows:
The Vancouver citation style is commonly used in the biomedical sciences and is known for its use of numbered references. Here is a basic format for a research paper using the Vancouver citation style:
- Title page: Include the title of your paper, your name, the name of your institution, and the date.
- Abstract : This is a brief summary of your research paper, usually no more than 250 words.
- Introduction : Provide some background information on your topic and state the purpose of your research.
- Methods : Describe the methods you used to conduct your research, including the study design, data collection, and statistical analysis.
- Results : Present your findings in a clear and concise manner, using tables and figures as needed.
- Discussion : Interpret your results and explain their significance. Also, discuss any limitations of your study and suggest directions for future research.
- References : List all of the sources you cited in your paper in numerical order. Each reference should include the author’s name, the title of the article or book, the name of the journal or publisher, the year of publication, and the page numbers.
ACS (American Chemical Society) Style
ACS (American Chemical Society) Style Research Paper format is as follows:
The American Chemical Society (ACS) Style is a citation style commonly used in chemistry and related fields. When formatting a research paper in ACS Style, here are some guidelines to follow:
- Paper Size and Margins : Use standard 8.5″ x 11″ paper with 1-inch margins on all sides.
- Font: Use a 12-point serif font (such as Times New Roman) for the main text. The title should be in bold and a larger font size.
- Title Page : The title page should include the title of the paper, the authors’ names and affiliations, and the date of submission. The title should be centered on the page and written in bold font. The authors’ names should be centered below the title, followed by their affiliations and the date.
- Abstract : The abstract should be a brief summary of the paper, no more than 250 words. It should be on a separate page and include the title of the paper, the authors’ names and affiliations, and the text of the abstract.
- Main Text : The main text should be organized into sections with headings that clearly indicate the content of each section. The introduction should provide background information and state the research question or hypothesis. The methods section should describe the procedures used in the study. The results section should present the findings of the study, and the discussion section should interpret the results and provide conclusions.
- References: Use the ACS Style guide to format the references cited in the paper. In-text citations should be numbered sequentially throughout the text and listed in numerical order at the end of the paper.
- Figures and Tables: Figures and tables should be numbered sequentially and referenced in the text. Each should have a descriptive caption that explains its content. Figures should be submitted in a high-quality electronic format.
- Supporting Information: Additional information such as data, graphs, and videos may be included as supporting information. This should be included in a separate file and referenced in the main text.
- Acknowledgments : Acknowledge any funding sources or individuals who contributed to the research.
ASA (American Sociological Association) Style
ASA (American Sociological Association) Style Research Paper format is as follows:
- Title Page: The title page of an ASA style research paper should include the title of the paper, the author’s name, and the institutional affiliation. The title should be centered and should be in title case (the first letter of each major word should be capitalized).
- Abstract: An abstract is a brief summary of the paper that should appear on a separate page immediately following the title page. The abstract should be no more than 200 words in length and should summarize the main points of the paper.
- Main Body: The main body of the paper should begin on a new page following the abstract page. The paper should be double-spaced, with 1-inch margins on all sides, and should be written in 12-point Times New Roman font. The main body of the paper should include an introduction, a literature review, a methodology section, results, and a discussion.
- References : The reference section should appear on a separate page at the end of the paper. All sources cited in the paper should be listed in alphabetical order by the author’s last name. Each reference should include the author’s name, the title of the work, the publication information, and the date of publication.
- Appendices : Appendices are optional and should only be included if they contain information that is relevant to the study but too lengthy to be included in the main body of the paper. If you include appendices, each one should be labeled with a letter (e.g., Appendix A, Appendix B, etc.) and should be referenced in the main body of the paper.
APSA (American Political Science Association) Style
APSA (American Political Science Association) Style Research Paper format is as follows:
- Title Page: The title page should include the title of the paper, the author’s name, the name of the course or instructor, and the date.
- Abstract : An abstract is typically not required in APSA style papers, but if one is included, it should be brief and summarize the main points of the paper.
- Introduction : The introduction should provide an overview of the research topic, the research question, and the main argument or thesis of the paper.
- Literature Review : The literature review should summarize the existing research on the topic and provide a context for the research question.
- Methods : The methods section should describe the research methods used in the paper, including data collection and analysis.
- Results : The results section should present the findings of the research.
- Discussion : The discussion section should interpret the results and connect them back to the research question and argument.
- Conclusion : The conclusion should summarize the main findings and implications of the research.
- References : The reference list should include all sources cited in the paper, formatted according to APSA style guidelines.
In-text citations in APSA style use parenthetical citation, which includes the author’s last name, publication year, and page number(s) if applicable. For example, (Smith 2010, 25).
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Research Paper Title – Writing Guide and Example

Research Paper Introduction – Writing Guide and...

Research Paper Conclusion – Writing Guide and...
- Assignment calculator
Assignment calculator for easy planning
- Get your writing tasks planned out
- Estimate assignment time
- Manage your schedule effectively
How our assignment calculator works
Take the first time towards effective time-management – use our assignment calculator to get a detailed plan of the writing process.
- Choose a start date
- Select your deadline
- Have your assignment outlined.
Other tools to ease your life
Check out these tools that may come in handy for writing an astounding essay.
Create a perfect title page formatted in line with the recent recommendations of APA, MLA or Chicago format.
Paste your text and get a great conclusion that wraps up all key points in the paper.
Convert words to pages or vice versa. Perfect if you don’t know how many words one page should have.
Tired of writing essays ?
Leave all the hard job to our professionals and they will handle the rest.
Get 10% off
By clicking on the “Write my essay” button, you accept our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. You further agree to receive promo and account-related emails.
Assignment calculator, planner & calendar – all-in-one solution
Use our smart planner and calculate your writing time with your eyes closed!
- Find out how many days you have before submitting your project.
- Get your writing assignment planned out to the last detail.
- Organize your schedule in several seconds.
The best thing about our assignment planner is that you can use it for multiple purposes. Do you want to see how much time it will take to complete your high-school or college assignment? Do you feel like your writing schedule needs more organized planning? Or maybe you want to outline the exact number of writing steps needed for task completion? Relying on our assignment schedule maker is a foolproof way to tackle any essay or research paper in time.
Why our writing calculator stands out
Enjoy the ultimate benefits that our writing calculator has to offer.
Don’t pay a cent to use our free essay calculator.
Plan as many writing tasks as you need.
Don’t waste time on registration – start planning now!
Input your due date and get your task planned instantly.
Plan any assignment ahead!
Keep the writing schedule organized with our assignment due date calendar! By using our smart tool, you will get any task done, be it an essay, a research paper, a term paper or a dissertation. Although handling the steps as they come may seem much easier, students often find themselves disorganized and unsystematic. It’s time that you finally sort all things out – and our timeline calculator will be of great help with that! Forget about being sidetracked once and for all. Our tool will provide you with an in-detail outline so you will always remain on the course till the finish line.
Research project calculator
This AI-powered research paper estimator is what you need when a research paper should be done soon. Did you know that 83% of students can’t submit their research work in time because of poor planning? For this reason, we have designed this handy assignment calculator. You will be able to find out how many steps you are away from finishing your study in a few seconds. Follow the given steps and you will definitely succeed!
Dissertation calculator & planner
It’s much more than just an assignment calculator! This ultimate tool will be your lifesaver when you need to estimate a dissertation timeline. This feature is completely free. Thus, every student can benefit from high-tech solutions. This tool will break the dissertation preparation process into smaller goals. An organized plan in front is surely what you need in order to write a structured study, even if it’s long as an arm.
Essay calculator
Get the most out of our essay time calculator. We made every effort to keep things simple and easy. All you need to do is choose the due date and our tool will do the rest. So if your essay deadline is just around the corner and every hour counts, there is no better way to write efficiently. This assignment calculator will estimate the time necessary for essay completion and break a task into manageable chunks.
Thesis calculator
This irreplaceable scheduler also works as a thesis calculator. Have to write a thesis but don’t know where to start? We’ve got you covered! With our calculator you will be able to perform your scientific work in an efficient way. Get an outline and find out the deadline for each stage of the research process. This way, you will always be in control of your schedule and won’t ever miss any due date.
Let an expert take care of your essay!
Entrust your assignment to proficient writers and receive TOP-quality paper before the deadline is over.
By clicking on the “Get expert help” button, you accept our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. You further agree to receive promo and account-related emails.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Research Paper Calculator is a time management tool that breaks down research assignments into a series of manageable steps, while providing expert tips for success. Enter the assignment start date and due date to get planning! Start Date. Due Date. About the Assignment Calculator.
The Research Assignment Calculator (TRAC) helps you break down the research process into manageable steps, create a schedule, and meet your assignment deadline. This time management tool gives you links to the UMGC library, Effective Writing Center, and other resources to help you with each stage of your research project. Based on the original ...
Assignment Calculator. Research Paper Planner. Research Paper/Essay. Begin Date: Due Date: Research Paper Planner. This tool will help you stay on track and lead you to resources from libraries and writing centers to help you more easily master the skills for planning, researching, drafting, and writing a research paper, essay, honors or master ...
The Assignment Calculator breaks down research and writing projects into manageable steps based on your due dates. Each step includes hints and "how-to" links. Select the type of assignment: Research paper. Speech. Lab report. Graduate students can get additional help using the Dissertation Calculator.
Critically read & evaluate sources. Evaluate sources based on your research question or working thesis. Use critical reading strategies (PDF) from the U of M's Center for Writing. How to read and comprehend scientific reserch articles (video, 5 mins) Take notes on readings while reading. Make notes on margins.
Identify and test a strategy for transforming and analyzing the data (e.g. coding data, transcribing interviews, running statistics, etc.). Test your analysis method with the small pilot study or sample of your data. Create graphs, tables, images, and other outputs that illustrate your results.
Use the Assignment Calculator to break down your writing assignments into a series of manageable steps -- each with a separate due date. ... Developing a Topic for a Research Paper: Narrowing Your Topic, a quick video (3 minutes) plus tips, from University of Regina's Archer Library.
How to Use the Research Calculator. This tool will help you stay on track and lead you to resources from libraries and writing centers to help you master the skills of planning, researching, drafting, and writing a research paper, thesis, or dissertation. This method of reverse scheduling is based on best practices for writing papers and theses ...
Research Paper Planner. Created by Shannon Roux. Tired of writing your paper the night before it's due? This Research Paper Planner will help you break down your assignment into manageable deadlines, track your progress, and connect with campus resources. Introduction to the Research Assignment Planner. Watch on.
University of Arkansas — Research Paper Wizard. Rochester Institute of Technology — Assignment Calculator, Project Management Tool for Students. SJSU Library Assignment Calculator. *Based on the original Assignment Calculator from the University of Minnesota Libraries.
This link will take you to the Timeline portion of the Research Paper Planner where you can set a start and end date for your writing project, see the deadlines for each step, print out the Timeline for your project, and/or set up email alerts for each step of the research and writing process. Next: 1: Understand Your Assignment >>. Last ...
Contact Us. University Libraries 401 W. Brooks St Norman, OK 73019 (405) 325-3341. Ask Us
The Research Calculator Classic based in Minnesota (link will take you to a new site). This Calculator is intended as a general time-management tool to help students with research papers in the Humanities. Research papers in other disciplines might require different steps and a different process, and each individual professor might require a ...
Research Paper Calculator. Research Paper Calculator. This tool from the University of Minnesota Libraries allows you to enter the date you receive an assignment and the date it is due. The time needed for each step in the research process is then calculated, and intermediate dates provided.
Use this Assignment Calculator created by San Jose State University to create a schedule for completing the various steps of your writing assignment. Enter: The date you received the assignment. The date the final paper is due. The calculator will create a schedule for you. Please note that you will be redirected to San Jose State University's ...
PaperRater's online essay checker is built for easy access and straightforward use. Get quick results and reports to turn in assignments and essays on time. 2. Advanced Checks. Experience in-depth analysis and detect even the most subtle errors with PaperRater's comprehensive essay checker and grader. 3.
Research indicates that teachers believethat technology, especially graphing calculators, would be helpful in the mathematics classroom. Zembat (2008) found that technology "gave ... allowed to use calculators only after they had exhausted their pencil and paper techniques. The calculator served as a bridge to higher mathematical ideas ...
Research paper format is an essential aspect of academic writing that plays a crucial role in the communication of research findings.The format of a research paper depends on various factors such as the discipline, style guide, and purpose of the research. It includes guidelines for the structure, citation style, referencing, and other elements of the paper that contribute to its overall ...
Kathryn Holmes. PDF | On Jun 25, 2014, Daniel Derome and others published Quantitative Measure and Analysis of a Scientific Calculator in Education | Find, read and cite all the research you need ...
Assignment calculator, planner & calendar - all-in-one solution. Use our smart planner and calculate your writing time with your eyes closed! Find out how many days you have before submitting your project. Get your writing assignment planned out to the last detail. Organize your schedule in several seconds. The best thing about our assignment ...
Include an opposing viewpoint to your main idea, if applicable. A good thesis statement acknowledges that there is always another side to the argument. So, include an opposing viewpoint (a counterargument) to your opinion. Basically, write down what a person who disagrees with your position might say about your topic.
API CALCULATOR - 2018 (TABLE - 2) (ACADEMIC / RESEARCH SCORE) BY CHINTAN MAHIDA. (For Faculty of Languages / Humanities /Arts / Social Sciences / Library /Education / Physical Education /Commerce / Management & other related disciplines) (1) Peer - Reviewed and Refereed Journals are same. Yet UGC has awakwardly augumented score of Research Paper.
The purpose of this paper is to address calculator and other technology use in the secondary and college classrooms, mostly in the US, and how it affects academic performance. ... Research and ...