First, let's have an example:
Here is the number "forty-five and six-tenths" written as a decimal number:
The decimal point goes between Ones and Tenths.
45.6 has 4 Tens, 5 Ones and 6 Tenths, like this:
Now, let's discover how it all works ...

Place Value
It is all about Place Value !
When we write numbers, the position (or " place ") of each digit is important.
In the number 327 :
- the "7" is in the Ones position, meaning 7 ones (which is 7),
- the "2" is in the Tens position meaning 2 tens (which is twenty),
- and the "3" is in the Hundreds position, meaning 3 hundreds.
... and ...
And that is a Decimal Number!
We can continue with smaller and smaller values, from tenths , to hundredths , and so on, like in this example:
Have a play with decimal numbers yourself:
Large and Small
So, our Decimal System lets us write numbers as large or as small as we want, using the decimal point. Digits can be placed to the left or right of a decimal point, to show values greater than one or less than one.
The decimal point is the most important part of a Decimal Number. Without it we are lost, and don't know what each position means.
Zoom into decimals ...
Definition of decimal.
The word "Decimal" really means "based on 10" (From Latin decima : a tenth part ).
We sometimes say "decimal" when we mean anything to do with our numbering system, but a "Decimal Number" usually means there is a Decimal Point.
Ways to think about Decimal Numbers ...
... as a whole number plus tenths, hundredths, etc.
We can think of a decimal number as a whole number plus tenths, hundredths, etc:
Example 1: What is 2.3 ?
- On the left side is "2", that is the whole number part.
- The 3 is in the "tenths" position, meaning "3 tenths", or 3/10
- So, 2.3 is "2 and 3 tenths"
Example 2: What is 13.76 ?
- On the left side is "13", that is the whole number part.
- There are two digits on the right side, the 7 is in the "tenths" position, and the 6 is the "hundredths" position
- So, 13.76 is "13 and 7 tenths and 6 hundredths"
... as a Decimal Fraction
Or we can think of a decimal number as a Decimal Fraction.
A Decimal Fraction is a fraction where the denominator (the bottom number) is a number such as 10, 100, 1000, etc (in other words a power of ten )
... as a Whole Number and Decimal Fraction
Or we can think of a decimal number as a Whole Number plus a Decimal Fraction.
Those are all good ways to think of decimal numbers.
Helping with Math
Tenths as Decimals
Introduction.
The word decimal comes from the Latin word “Decem” meaning 10. . In algebra, a decimal number can be defined as a number whose complete part and the fractional part are separated by a decimal point. Before we learn what we mean by a tenth of decimal it is important to recall the place value system of decimals that defines the position of a tenth in a decimal number.
Place Value System of Decimals
We know that each place in the place value table has a value ten times the value of the next place on its right. In other words, the value of a place is one-tenth of the value of the next place on its left. We observe that if one digit moves one place left to right its value becomes one-tenth ($\frac{1}{10}$ ) of its previous value and when it moves two places left to right its value comes one-hundredth ( $\frac{1}{100}$ ) of its previous term and so on. Therefore, if we wish to move beyond ones place which is the case of decimals, we will have to extend the place value table by introducing the places of tenths ($\frac{1}{10}$ ), hundredths ($\frac{1}{100}$ ), thousandths ( $\frac{1}{1000}$ ) and so on.
Therefore, the place value table in case of a decimal number will be of the form –
For example, the decimal number 257.32 in the place value system will be written as –
A decimal or a decimal number may contain a whole number part and a decimal part. The following table shows the whole number part and the decimal part of some decimals –
Now, how do we read the decimals using the place value system? Let us find out.
Reading the Decimal Numbers using the Place Value System
In order to read decimals, the following steps are used –
- Read the whole number part
- Read the decimal point as point
- Read the number to the right of the decimal point. For example, 14.35 will be read as Fourteen point three five. Alternatively, the number to the right of the decimal point can also be read by reading the number to the right of the decimal point and naming the place value of the last digit. For instance, the number 8.527 can also be read as eight and five hundred twenty seven thousandths.
What are Tenths in a Decimal?
Consider the following figure. It is divided into ten equal parts and one part is shaded. The shaded part represents one-tenth of the whole figure. It is written as $\frac{1}{10}$. $\frac{1}{10}$ is also written as 0.1 which is read as “ point one “ or “ decimal one “.
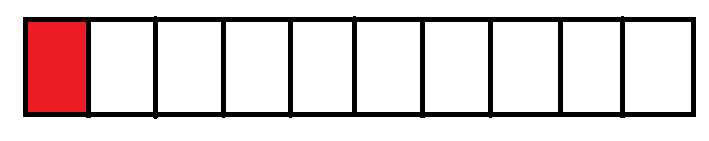
Thus the fraction $\frac{1}{10}$ is called one-tenth and is written as 0.1.
Also, 1 ones = 10 tenths.
Consider another figure. The below figure is divided into ten equal parts and three parts are shaded. The shaded parts represent three-tenths of the whole figure. It is written as $\frac{3}{10}$. $\frac{3}{10}$ is also written as 0.3 which is read as “ point three “ or “ decimal three “.
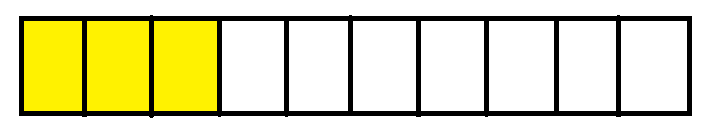
Thus the fraction $\frac{3}{10}$ is called three tenth and is written as 0.3.
Also, consider the below figure. The below figure is divided into ten equal parts and six parts are shaded. The shaded parts represent six-tenths of the whole figure. It is written as $\frac{6}{10}$. $\frac{6}{10}$ is also written as 0.6 which is read as “ point six “ or “ decimal six “.
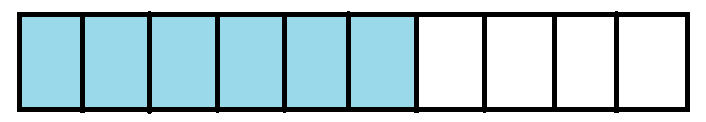
Thus the fraction $\frac{6}{10}$ is called six-tenth and is written as 0.6.
Similarly, $\frac{2}{10}$ , $\frac{4}{10}$ , $\frac{5}{10}$ , $\frac{7}{10}$ , $\frac{8}{10}$ and $\frac{9}{10}$ are called 2-tenths, 4-tenths, 7-tenths, 8-tenths and 9-tenths respectively and are denoted by 0.2 , 0.3 , 0.4 , 0.5 , 0.7 , 0.8 and 0.9 respectively.
Thus we have,
$\frac{1}{10}$ = 0.1 and is called one-tenths or 1 tenths
$\frac{2}{10}$ = 0.2 and is called two-tenths or 2 tenths
$\frac{3}{10}$ = 0.3 and is called three-tenths or 3 tenths
$\frac{4}{10}$ = 0.4 and is called four-tenths or 4 tenths
$\frac{5}{10}$ = 0.5 and is called five-tenths or 5 tenths
$\frac{6}{10}$ = 0.6 and is called six-tenths or 6 tenths
$\frac{7}{10}$ = 0.7 and is called seven-tenths or 7 tenths
$\frac{8}{10}$ = 0.8 and is called eight-tenths or 8 tenths
$\frac{9}{10}$ = 0.9 and is called nine-tenths or 9 tenths
$\frac{10}{10}$ = 1 and is called ten-tenths or 10 tenths
Also, $\frac{11}{10}$ = 11 tenths = 10 tenths + 1 tenths = 1 + $\frac{1}{10}$ = 1 + 0.1 = 1.1
$\frac{12}{10}$ = 12 tenths = 10 tenths + 2 tenths = 1 + $\frac{2}{10}$ = 1 + 0.2 = 1.2
$\frac{13}{10}$ = 13 tenths = 10 tenths + 3 tenths = 1 + $\frac{3}{10}$ = 1 + 0.3 = 1.3
Similarly, we have
$\frac{20}{10}$ = 20 tenths = 10 tenths + 10 tenths = 1 + 1 = 2
$\frac{21}{10}$ = 21 tenths = 20 tenths + 1 tenths = 2 + $\frac{1}{10}$ = 2 + 0.1 = 2.1
$\frac{22}{10}$ = 22 tenths = 20 tenths + 2 tenths = 2 + $\frac{2}{10}$ = 2 + 0.2 = 2.2
Thus a fraction of the form $\frac{Number}{10}$ is written as decimal obtained by putting decimal point by leaving one right-most digit.
For example, $\frac{325}{10}$ = 32.5 while $\frac{5894}{10}$ = 589.4
Let us understand it through an example.
Example Write each of the following as decimals
- Five ones and four tenths
- Twenty and one tenths
Solution We have been given the following and we need to write them as decimals. Let us do them one by one
Note that the whole value of the given decimal is 5 and the decimal part is four tenths. Therefore, we will proceed in the same manner as we defined different tenths above.
We will get,
Five ones and four tenths = 5 ones + 4 tenths = 5 + $\frac{4}{10}$ = 5 + 0.4 = 5.4
Hence, Five ones and four tenths In decimal form will be 5.4.
Note that the whole value of the given decimal is 20 and the decimal part is one-tenths. Therefore, we will proceed in the same manner as we defined different tenths above.
Twenty ones and one tenths = 20 ones + 1 tenths = 20 + $\frac{1}{10}$ = 20 + 0.1 = 20.1
Hence, Twenty ones and one tenths in decimal form will be 20.1.
Let us take another example.
- 20 + 7 + + $\frac{3}{10}$
- 500 + 3 + $\frac{7}{10}$
Solution We have been given an expanded form of two numbers and we are required to find the corresponding decimal number. Let us do them one by one.
We can see that there are two whole numbers and one fractional number.
Note that the whole values of the given decimal are 20 and 7 and the decimal part is three tenths. Therefore, we will proceed in the same manner as we defined different tenths above.
20 + 7 + $\frac{3}{10}$ = 20 + 7 + 0.3 = 27.3
Note that the whole values of the given decimal are 500 and 3 and the decimal part is seven tenths. Therefore, we will proceed in the same manner as we defined different tenths above.
500 + 3 + $\frac{7}{10}$ = 500 + 3 + 0.7 = 503.7
Let us now see how to plot the tenths of a decimal on a number line .
Representation of tenths of a decimal on a Number Line
Before we learn how to represent a tenth on a number let us recall what we understand by the term number line.
What is a number line?
A number line is a straight horizontal line with numbers placed at even intervals that provides a visual representation of numbers. Primary operations such as addition, subtraction , multiplication , and division can all be performed on a number line. The numbers increase as we move towards the right side of a number line while they decrease as we move left.
Representation on a Number Line

Above is a visual representation of a standard number line. As is clearly visible, as we move from left to right, there is an increase in the value of numbers while it decreases when we move from right to left.
We already know how to represent fractions on a number line . Let us now represent tenths of a decimal on a number line. We can understand this by an example.
Let us represent 0.4 on a number line. We can clearly see that there are 4 tenths in 0.4. Therefore in order to represent 0.4 on a number line we will divide the unit length between 0 and 1 into 10 equal parts and take 4 parts as shown below –
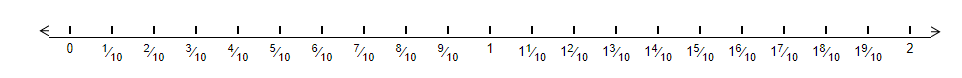
Now, we can know that 0.4 in fraction form is equal to 4/10. Hence we will mark 4/10 as 0.4 which is our desired mark on the number line.
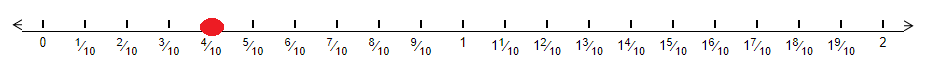
The steps that we used above to represent a tenth on a number line can be summarised as –
- We draw a number line between 0 and 1.
- We then raw 10 lines dividing the total distance between 0 and 1 into 10 equal parts.
- Now, one whole divided into 10 parts is equal to $\frac{1}{10}$.
- $\frac{1}{10}$ in decimal form is equal to 0.1.
- At each new line we are adding $\frac{1}{10}$ or 0.1.
- So, between 0 and 1 we have, 0 . 1 , 0 . 2 , . 0 . 3 , 0 . 4 , 0 . 5 , 0 . 6 , 0 . 7 , 0 . 8 and 0 . 9. Similarly, between 1 and 2 we have, 1 . 1 , 1 . 2 , 1 . 3 , 1 . 4 , 1 . 5 , 1 . 6 , 1 . 7 , 1 . 8 and 1 . 9.
- We can also say that the line representing $\frac{1}{2}$ or 0.5 is the half way mark between 0 and 1. Similarly, the line representing $1\frac{5}{10}$ or 1.5 is the half way mark between 1 and 2.
- Ten tenths is equal to one whole.
Now let us go through some solved examples on tenth of a decimal.
Solved Examples
Example 1 Label the missing decimal numbers on the number line.
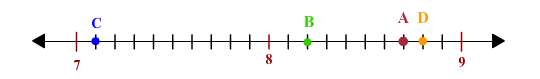
Solution We have been given four numbers marked as A , B , C and D on a number line and we need to find out which decimal numbers they represent. Let us mark them one by one.
We will start with completing the marking of the lines that have not been marked on the given number line. It can be clearly seen that there are 10 lines between two whole numbers on the number line. This means that the lines represent one tenth of the number in the decimal form. Therefore, the lines between 7 and 8 will be marked as 7 . 1 , 7 . 2 , 7 . 3 , 7 . 4 , 7 5 , 7 . 6 , 7 . 7 , 7 . 8 and d 7. 9. Similarly, We between the whole numbers 8 and 9 we have, 8 . 1 , 8 . 2 , 8 . 3 , 8 . 4 , 8 . 5 , 8 . 6 , 8 . 7 , 8 . 8 and 8 . 9. The number line so obtained will be –
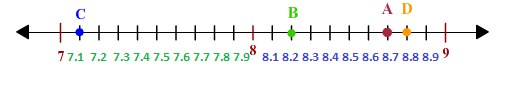
Now, we shall check the position of the four points on this number line.
We can see that from the number line above, the point A lies on the decimal number 8.7. Hence A = 8 . 7
Now, let us check the position of point B.
We can see that from the number line above, the point B lies on the decimal number 8.2. Hence B = 8 . 2
Now, let us check the position of point C.
We can see that from the number line above, the point C lies on the decimal number 7 . 1. Hence C = 7 . 1
Now, let us check the position of point D.
We can see that from the number line above, the point D lies on the decimal number 7 . 8 . Hence D = 7 . 8
Therefore, we have,
D = 7 . 8
Example 2 Between what two numbers is does the decimal number 5.4 lie on the number line?
Solution We have been given the decimal number 5.4 and we need to check between which two whole numbers will it lie.
On observing the number 5.4 we can see that the number represents a tenth of a decimal as it has one digit after the decimal point.
Also, we know that 5.4 = 5 + $\frac{4}{10}$
This means that 5.4 is equal to 5 whole parts plus 4 tenths. Et us plot it on the number line. we will have,
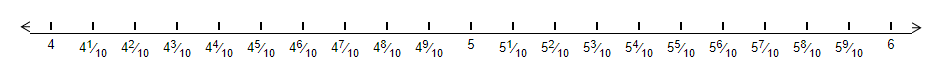
We can clealry see that 5.4 will lie between 5 and 6. The point on the number line will be –
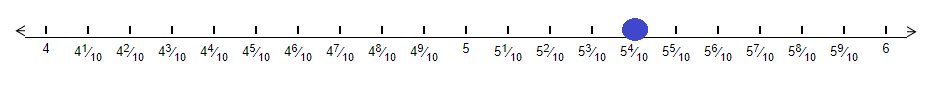
Hence, we can say that the number 5.4 will be between the whole numbers 5 and 6.
Example 3 Write the following fraction in decimal form
18 $\frac{5}{10}$
Solution We have been given the fraction 18 510 and we need to write it in decimal form. we can see that the given fraction has one whole number 18 and five tenth. We also know that 510 = 0.5 and is called five-tenths or 5 tenths. Therefore, we have,
18 $\frac{5}{10}$ = 18 + $\frac{5}{10}$ = 18 + 0.5 = 18.5
Hence, 18 $\frac{5}{10}$ = 18.5
Key Facts and Summary
- A decimal number can be defined as a number whose complete part and the fractional part are separated by a decimal point.
- The Place Value System is the system in which the position of a digit in a number determines its value. The place value of a digit in a number is the value it holds to be at the place in the number.
- In order to read decimals, we first
- Read the number to the right of the decimal point. For example, 14.35 will be read as Fourteen point three five.
- The fraction $\frac{1}{10}$ is called one-tenth and is written as 0.1.
- 1 ones = 10 tenths
- A number line is a straight horizontal line with numbers placed at even intervals that provides a visual representation of numbers. Primary operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division can all be performed on a number line.
Recommended Worksheets
Basic Operations of Decimals (Hanukkah Themed) Math Worksheets Word Problems Involving Decimals (Market Themed) Math Worksheets Rounding Decimals (Adventure Themed) Worksheets
Link/Reference Us
We spend a lot of time researching and compiling the information on this site. If you find this useful in your research, please use the tool below to properly link to or reference Helping with Math as the source. We appreciate your support!
<a href="https://helpingwithmath.com/tenths-as-decimals/">Tenths as Decimals</a>
"Tenths as Decimals". Helping with Math . Accessed on April 21, 2024. https://helpingwithmath.com/tenths-as-decimals/.
"Tenths as Decimals". Helping with Math , https://helpingwithmath.com/tenths-as-decimals/. Accessed 21 April, 2024.
Additional Decimals Theory:
Latest worksheets.
The worksheets below are the mostly recently added to the site.
Understanding the properties of rotations, reflections, and translations of 2D figures 8th Grade Math Worksheets

Solving Linear Equations in One Variable Integral Coefficients and Rational Coefficients 8th Grade Math Worksheets

Interpreting linear functions in a form of y=mx+b and its graph 8th Grade Math Worksheets

Performing Operations using Scientific Notation 8th Grade Math Worksheets

Understanding Irrational Numbers 8th Grade Math Worksheets

Understanding Fundamental Counting Principle and Probability of Events 7th Grade Math Worksheets

Solving Area, Volume, and Surface Area of 2D and 3D Objects 7th Grade Math Worksheets

Solving Proportional Relationships Between Two Quantities 7th Grade Math Worksheets

Solving Word Problems Involving Linear Equations and Linear Inequalities 7th Grade Math Worksheets

Understanding Supplementary, Complementary, Vertical and Adjacent Angles 7th Grade Math Worksheets


Decimals with tenths (one decimal digit) plus how to add them with mental math - 4th grade math
The first digit after the decimal point tells us the number of tenths (the tenths place). We convert between fractions and decimals, practicing this simple concept -- an introduction to decimals.
If you cannot see the video above, click here for an alternative video player.
In this second part of the lesson, I show how to add decimals with one decimal digit (tenths), such as 0.2 + 0.9 or 3.7 + 0.7, using mental math. Note that 0.2 + 0.9 is NOT 0.11! Lastly we also convert between centimeters and millimeters. This is a nice application of the concept just learned, since one millimeter is a tenth of a decimeter.
Mixed numbers to fractions and vice versa — video lesson
Math Mammoth Grade 4 curriculum
Back to the list of 4th grade videos
Back to the index of all videos

© 2006-2024 MathMammoth.com

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.8: Decimals
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 15123

Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Name and write decimals
- Round decimals
- Add and subtract decimals
- Multiply and divide decimals
- Convert decimals, fractions, and percents
A more thorough introduction to the topics covered in this section can be found in the Prealgebra chapter, Decimals .
Name and Write Decimals
Decimals are another way of writing fraction s whose denominators are powers of 10.
\[\begin{array} {ll} {0.1 = \frac { 1 } { 10 }} &{0.1 \text { is "one tenth" }} \\ {0.01 = \frac { 1 } { 100 }} &{0.01 \text { is "one hundredth }} \\ {0.001 = \frac { 1 } { 1,000 }} &{0.001 \text { is "one thousandth }} \\ {0.0001 = \frac { 1 } { 10,000 }} &{0.0001 \text { is "one ten-thousandth" }} \end{array}\]
Notice that “ten thousand” is a number larger than one, but “one ten-thousand th ” is a number smaller than one. The “th” at the end of the name tells you that the number is smaller than one.
When we name a whole number, the name corresponds to the place value based on the powers of ten. We read 10,000 as “ten thousand” and 10,000,000 as “ten million.” Likewise, the names of the decimal places correspond to their fraction values. Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\) shows the names of the place values to the left and right of the decimal point.

Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\)
Name the decimal \(4.3\).

Exercise \(\PageIndex{2}\)
Name the decimal \(6.7\).
six and seven tenths
Exercise \(\PageIndex{3}\)
Name the decimal \(5.8\).
five and eight tenths
We summarize the steps needed to name a decimal below.
NAME A DECIMAL.
- Name the number to the left of the decimal point.
- Write “and” for the decimal point.
- Name the “number” part to the right of the decimal point as if it were a whole number.
- Name the decimal place of the last digit.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{4}\)
Name the decimal: \(−15.571\).
Exercise \(\PageIndex{5}\)
Name the decimal: \(−13.461\).
negative thirteen and four hundred sixty-one thousandths
Exercise \(\PageIndex{6}\)
Name the decimal: \(−2.053\).
negative two and fifty-three thousandths
When we write a check we write both the numerals and the name of the number. Let’s see how to write the decimal from the name.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{7}\): How to Write decimals
Write “fourteen and twenty-four thousandths” as a decimal.

Exercise \(\PageIndex{8}\)
Write as a decimal: thirteen and sixty-eight thousandths.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{9}\)
Write as a decimal: five and ninety-four thousandths.
We summarize the steps to writing a decimal .
WRITE A DECIMAL.
- Place a decimal point under the word “and.” Translate the words before “and” into the whole number and place it to the left of the decimal point.
- If there is no “and,” write a “0” with a decimal point to its right.
- Mark the number of decimal places needed to the right of the decimal point by noting the place value indicated by the last word.
- Translate the words after “and” into the number to the right of the decimal point. Write the number in the spaces—putting the final digit in the last place.
- Fill in zeros for place holders as needed.
Round Decimals
Rounding decimals is very much like rounding whole numbers. We will round decimals with a method based on the one we used to round whole numbers.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{10}\)
Round 18.379 to the nearest hundredth.

Exercise \(\PageIndex{11}\)
Round to the nearest hundredth: 1.047.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{12}\)
Round to the nearest hundredth: 9.173.
We summarize the steps for rounding a decimal here.
ROUND DECIMALS.
- Locate the given place value and mark it with an arrow.
- Underline the digit to the right of the place value.
- Yes—add 1 to the digit in the given place value.
- No—do not change the digit in the given place value.
- Rewrite the number, deleting all digits to the right of the rounding digit.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{13}\)
Round 18.379 to the nearest
- whole number.
Round 18.379
1. to the nearest tenth
Exercise \(\PageIndex{14}\)
Round 6.582 to the nearest
Exercise \(\PageIndex{15}\)
Round 15.2175 to the nearest
Add and Subtract Decimals
To add or subtract decimals, we line up the decimal points. By lining up the decimal points this way, we can add or subtract the corresponding place values . We then add or subtract the numbers as if they were whole numbers and then place the decimal point in the sum.
ADD OR SUBTRACT DECIMALS.
- Write the numbers so the decimal points line up vertically.
- Use zeros as place holders, as needed.
- Add or subtract the numbers as if they were whole numbers. Then place the decimal point in the answer under the decimal points in the given numbers.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{16}\)
Add: \(23.5+41.38\).
\[\text{Write the numbers so that the decimal points line up vertically.} \quad \begin{array} {r} { 23.50 } \\ { + 41.38 } \\ \hline \end{array}\] \[\text{Put 0 as a placeholder after the 5 in 23.5. Remember, } \frac{5}{10} = \frac{50}{100}, \text{ so } 0.5 = 0.50 \quad \begin{array} {r} { 23.50 } \\ { + 41.38 } \\ \hline \end{array}\] \[\text{Add the numbers as if they were whole numbers . Then place the decimal point in the sum.} \quad \begin{array} {r} { 23.50 } \\ { + 41.38 } \\ \hline 64.88 \end{array}\]
Exercise \(\PageIndex{17}\)
Add: \(4.8+11.69\).
Exercise \(\PageIndex{18}\)
Add: \(5.123+18.47\).
Exercise \(\PageIndex{19}\)
Subtract: \(20−14.65\).
\[\begin{array} {ll} {\text{Write the numbers so that the decimal points line up vertically.}} &{ \begin{align} {20 - 14.65} \\ {20.} \\ {-14.65} \\ \hline \end{align}} \\ {\text{Remember, 20 is a whole number, so place the decimal point after the 0.}} &{} \end{array}\] \[\begin{array} {ll} {\text{Put zeros to the right as placeholders.}} &{ \begin{align} {20.00} \\ {-14.65} \\ \hline \end{align}} \end{array}\] \[\begin{array} {ll} {\text{Write the numbers so that the decimal points line up vertically.}} &{ \begin{align} {\tiny{9} \quad \tiny{9}\qquad} \\ {\small{1} \not{\small{10}} \not{\small10}\not{\small10}}\\ {\not{2}\not{0.}\not{0}\not{0}} \\ {-14.65} \\ \hline \\{5.35} \end{align}} \end{array}\]
Exercise \(\PageIndex{20}\)
Subtract: \(10−9.58\).
Exercise \(\PageIndex{21}\)
Subtract: \(50−37.42\).
Multiply and Divide Decimals
Multiplying decimals is very much like multiplying whole numbers—we just have to determine where to place the decimal point. The procedure for multiplying decimals will make sense if we first convert them to fractions and then multiply.
So let’s see what we would get as the product of decimals by converting them to fractions first. We will do two examples side-by-side. Look for a pattern!
Notice, in the first example, we multiplied two numbers that each had one digit after the decimal point and the product had two decimal places. In the second example, we multiplied a number with one decimal place by a number with two decimal places and the product had three decimal places.
We multiply the numbers just as we do whole numbers, temporarily ignoring the decimal point. We then count the number of decimal points in the factors and that sum tells us the number of decimal places in the product.
The rules for multiplying positive and negative numbers apply to decimals, too, of course!
When multiplying two numbers,
- if their signs are the same the product is positive .
- if their signs are different the product is negative .
When we multiply signed decimals, first we determine the sign of the product and then multiply as if the numbers were both positive. Finally, we write the product with the appropriate sign.
MULTIPLY DECIMALS.
- Determine the sign of the product.
- Write in vertical format, lining up the numbers on the right. Multiply the numbers as if they were whole numbers, temporarily ignoring the decimal points.
- Place the decimal point. The number of decimal places in the product is the sum of the number of decimal places in the factors.
- Write the product with the appropriate sign.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{22}\)
Multiply: \((−3.9)(4.075)\).
Exercise \(\PageIndex{23}\)
Multiply: \(−4.5(6.107)\).
\(−27.4815\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{24}\)
Multiply: −10.79(8.12).
\(−87.6148\)
In many of your other classes, especially in the sciences, you will multiply decimals by powers of 10 (10, 100, 1000, etc.). If you multiply a few products on paper, you may notice a pattern relating the number of zeros in the power of 10 to number of decimal places we move the decimal point to the right to get the product.
MULTIPLY A DECIMAL BY A POWER OF TEN.
- Move the decimal point to the right the same number of places as the number of zeros in the power of 10.
- Add zeros at the end of the number as needed.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{25}\)
Multiply 5.63
By looking at the number of zeros in the multiple of ten, we see the number of places we need to move the decimal to the right.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{26}\)
Multiply 2.58
Exercise \(\PageIndex{27}\)
Multiply 14.2
Just as with multiplication, division of decimals is very much like dividing whole numbers. We just have to figure out where the decimal point must be placed.
To divide decimals, determine what power of 10 to multiply the denominator by to make it a whole number. Then multiply the numerator by that same power of 10. Because of the equivalent fractions property, we haven’t changed the value of the fraction! The effect is to move the decimal points in the numerator and denominator the same number of places to the right. For example:
\[\begin{array} { c } { \frac { 0.8 } { 0.4 } } \\ { \frac { 0.8 ( 10 ) } { 0.4 ( 10 ) } } \\ { \frac { 8 } { 4 } } \end{array}\]
We use the rules for dividing positive and negative numbers with decimals, too. When dividing signed decimals, first determine the sign of the quotient and then divide as if the numbers were both positive. Finally, write the quotient with the appropriate sign.
We review the notation and vocabulary for division:
\[\begin{array} {ll} {} &{\underset{\text{quotient}}{c}} \\ {\underset{\text{dividend}}{a} \div \underset{\text{divisor}}{b} = \underset{\text{quotient}}{c}} & {\underset{\text{divisor}}{b})\overline{\underset{\text{dividend}}{a}}} \end{array}\]
We’ll write the steps to take when dividing decimals, for easy reference.
DIVIDE DECIMALS.
- Determine the sign of the quotient.
- Make the divisor a whole number by “moving” the decimal point all the way to the right. “Move” the decimal point in the dividend the same number of places—adding zeros as needed.
- Divide. Place the decimal point in the quotient above the decimal point in the dividend.
- Write the quotient with the appropriate sign.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{28}\)
Divide: \(−25.65\div (−0.06)\).
Remember, you can “move” the decimals in the divisor and dividend because of the Equivalent Fractions Property.

Exercise \(\PageIndex{29}\)
Divide: \(−23.492\div (−0.04)\).
Exercise \(\PageIndex{30}\)
Divide: \(−4.11\div(−0.12)\).
A common application of dividing whole numbers into decimals is when we want to find the price of one item that is sold as part of a multi-pack. For example, suppose a case of 24 water bottles costs \($3.99\). To find the price of one water bottle, we would divide \($3.99\) by 24. We show this division in Exercise \(\PageIndex{31}\). In calculations with money, we will round the answer to the nearest cent (hundredth).
Exercise \(\PageIndex{31}\)
Divide: \($3.99\div 24\).
Exercise \(\PageIndex{32}\)
Divide: \($6.99\div 36\).
Exercise \(\PageIndex{33}\)
Divide: \($4.99\div 12\).
Convert Decimals, Fractions, and Percents
We convert decimals into fractions by identifying the place value of the last (farthest right) digit. In the decimal 0.03 the 3 is in the hundredths place, so 100 is the denominator of the fraction equivalent to 0.03.
\[00.03 = \frac { 3 } { 100 }\]
Notice, when the number to the left of the decimal is zero, we get a fraction whose numerator is less than its denominator. Fractions like this are called proper fractions .
The steps to take to convert a decimal to a fraction are summarized in the procedure box.
CONVERT A DECIMAL TO A PROPER FRACTION.
- Determine the place value of the final digit.
- numerator—the “numbers” to the right of the decimal point
- denominator—the place value corresponding to the final digit
Exercise \(\PageIndex{34}\)
Write 0.374 as a fraction.
Did you notice that the number of zeros in the denominator of \(\dfrac{374}{1000}\) is the same as the number of decimal places in 0.374?
Exercise \(\PageIndex{35}\)
Write 0.234 as a fraction.
\(\dfrac{117}{500}\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{36}\)
Write 0.024 as a fraction.
\(\dfrac{3}{125}\)
We’ve learned to convert decimals to fractions. Now we will do the reverse—convert fractions to decimals. Remember that the fraction bar means division. So \(\dfrac{4}{5}\) can be written \(4\div 5\) or \(5)\overline{4}\). This leads to the following method for converting a fraction to a decimal.
CONVERT A FRACTION TO A DECIMAL.
To convert a fraction to a decimal, divide the numerator of the fraction by the denominator of the fraction.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{37}\)
Write \(-\dfrac{5}{8}\) as a decimal.
Since a fraction bar means division, we begin by writing \(\dfrac{5}{8}\) as \(8)\overline{5}\). Now divide.

Exercise \(\PageIndex{38}\)
Write \(-\dfrac{7}{8}\) as a decimal.
−0.875
Exercise \(\PageIndex{39}\)
Write \(-\dfrac{3}{8}\) as a decimal.
−0.375
When we divide, we will not always get a zero remainder. Sometimes the quotient ends up with a decimal that repeats. A repeating decimal is a decimal in which the last digit or group of digits repeats endlessly. A bar is placed over the repeating block of digits to indicate it repeats.
REPEATING DECIMAL
A repeating decimal is a decimal in which the last digit or group of digits repeats endlessly.
A bar is placed over the repeating block of digits to indicate it repeats.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{40}\)
Write \(\dfrac{43}{22}\) as a decimal.

Exercise \(\PageIndex{41}\)
Write \(\dfrac{27}{11}\) as a decimal.
\(2.\overline{45}\)
Exercise \(\PageIndex{42}\)
Write \(\dfrac{51}{22}\) as a decimal.
\(2.3\overline{18}\)
Sometimes we may have to simplify expressions with fractions and decimals together.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{43}\)
Simplify: \(\dfrac{7}{8}+6.4\).
First we must change one number so both numbers are in the same form. We can change the fraction to a decimal, or change the decimal to a fraction. Usually it is easier to change the fraction to a decimal.
Exercise \(\PageIndex{44}\)
Simplify: \(\dfrac{3}{8}+4.9\).
Exercise \(\PageIndex{45}\)
Simplify: \(5.7 + \dfrac{13}{20}\).
A percent is a ratio whose denominator is 100. Percent means per hundred. We use the percent symbol, %, to show percent.
A percent is a ratio whose denominator is 100.
Since a percent is a ratio, it can easily be expressed as a fraction. Percent means per 100, so the denominator of the fraction is 100. We then change the fraction to a decimal by dividing the numerator by the denominator.
\[\begin{array} {llll} {} &{\text{6%}} &{\text{78%}} &{\text{135%}} \\ {\text { Write as a ratio with denominator } 100. } &{\dfrac{6}{100}} &{\dfrac{78}{100}} &{\dfrac{135}{100}} \\ { \text { Change the fraction to a decimal by dividing}} &{0.06} &{0.78} &{1.35}\\ {\text{the numerator by the denominator.}} &{} &{} &{} \end{array}\]
Do you see the pattern? To convert a percent number to a decimal number, we move the decimal point two places to the left.

Exercise \(\PageIndex{46}\)
Convert each percent to a decimal:
Exercise \(\PageIndex{47}\)
Exercise \(\pageindex{48}\).
Converting a decimal to a percent makes sense if we remember the definition of percent and keep place value in mind.
To convert a decimal to a percent, remember that percent means per hundred. If we change the decimal to a fraction whose denominator is 100, it is easy to change that fraction to a percent.
\[\begin{array} {llll} {} &{0.83} &{1.05} &{0.075} \\ {\text {Write as a fraction }} &{\frac{83}{100}} &{\small{1}\frac{5}{100}} &{\frac{75}{1000}} \\ { \text {The denominator is 100.}} &{} &{\frac{105}{100}} &{\frac{7.5}{100}}\\ {\text{Write the ratio as a percent.}} &{\text{83%}} &{\text{105%}} &{\text{7.5%}} \end{array}\]
Recognize the pattern? To convert a decimal to a percent, we move the decimal point two places to the right and then add the percent sign .

Exercise \(\PageIndex{49}\)
Convert each decimal to a percent:
Exercise \(\PageIndex{50}\)
Exercise \(\pageindex{51}\), key concepts.
- Write ”and” for the decimal point.
- Look for the word ‘and’—it locates the decimal point. Place a decimal point under the word ‘and.’ Translate the words before ‘and’ into the whole number and place it to the left of the decimal point. If there is no “and,” write a “0” with a decimal point to its right.
- Translate the words after ‘and’ into the number to the right of the decimal point. Write the number in the spaces—putting the final digit in the last place.
- Is this digit greater than or equal to 5? Yes—add 1 to the digit in the given place value. No—do not change the digit in the given place value.
- Add or subtract the numbers as if they were whole numbers. Then place the decimal in the answer under the decimal points in the given numbers.
- Place the decimal point. The number of decimal places in the product is the sum of the decimal places in the factors.
- Make the divisor a whole number by “moving” the decimal point all the way to the right. “Move” the decimal point in the dividend the same number of places - adding zeros as needed.
- Write the fraction: numerator—the ‘numbers’ to the right of the decimal point; denominator—the place value corresponding to the final digit.
- Convert a Fraction to a Decimal Divide the numerator of the fraction by the denominator.

Reading & Math for K-5
- Kindergarten
- Learning numbers
- Comparing numbers
- Place Value
- Roman numerals
- Subtraction
- Multiplication
- Order of operations
- Drills & practice
- Measurement
- Factoring & prime factors
- Proportions
- Shape & geometry
- Data & graphing
- Word problems
- Children's stories
- Leveled Stories
- Context clues
- Cause & effect
- Compare & contrast
- Fact vs. fiction
- Fact vs. opinion
- Main idea & details
- Story elements
- Conclusions & inferences
- Sounds & phonics
- Words & vocabulary
- Reading comprehension
- Early writing
- Numbers & counting
- Simple math
- Social skills
- Other activities
- Dolch sight words
- Fry sight words
- Multiple meaning words
- Prefixes & suffixes
- Vocabulary cards
- Other parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Capitalization
- Narrative writing
- Opinion writing
- Informative writing
- Cursive alphabet
- Cursive letters
- Cursive letter joins
- Cursive words
- Cursive sentences
- Cursive passages
- Grammar & Writing
Breadcrumbs
- Math by topic

Download & Print Only $2.00
Decimals Worksheets
Decimals worksheets for grade 3 through grade 6.
Our decimal worksheets start with the conversion of simple fractions (denominators of 10 or 100) to decimals and progress to operations with multi-digit decimals, rounding and repeating decimals.
Choose your grade / topic:
Grade 3 decimals worksheets.
Fractions to decimals worksheets
Comparing, ordering, adding and subtracting decimals
Fraction to / from decimals worksheets
Decimal addition and subtraction worksheets
Decimal multiplication worksheets
Decimal division worksheets
Topics include:
- Converting decimals to fractions and mixed numbers
- Converting fractions and mixed numbers to decimals (denominators of 10)
- Comparing and ordering decimals
- Decimal addition (1 digit)
- Subtract 1-digit decimals from whole numbers
- Subtract 1-digit decimals from whole numbers (missing minuend / subtrahend)
- Decimal subtraction (1 digit)
Grade 4 fractions to decimals worksheets
- Convert decimals to fractions (tenths, hundredths)
- Convert decimals to mixed numbers (tenths, hundredths)
- Convert fractions to decimals (denominator of 10 or 100)
- Convert mixed numbers to decimals (denominator of 10 or 100)
Grade 4 decimals worksheets
- Decimal addition (1-digit)
- Decimal addition (1-digit), missing addends
- Decimal addition (1 or 2 digits)
- Decimal addition in columns (2 digit)
- Decimal subtraction (1-digit)
- Decimal subtraction (1-digit), missing minuend/subtrehnds
- Decimal subtraction (1 or 2 digits)
- Decimal subtraction in columns (2 digit)
- Add / subtract decimals using money notation
- Word problems: adding and subtracting decimals
Grade 5 fractions to / from decimals worksheets
- Convert decimals to fractions (tenths, hundredths), no simplification
- Convert decimals to fractions (tenths, hundredths), with simplification
- Convert decimals to mixed numbers
- Convert fractions to decimals (denominators of 10 or 100)
- Convert mixed numbers to decimals (denominators of 10 or 100)
- Convert mixed numbers to decimals (denominators of 10, 100 or 1000)
- Convert fractions to decimals (common denominators of 2, 4, 5, ...)
- Convert mixed numbers to decimals (common denominators of 2, 4, 5, ...)
- Convert fractions to decimals, with repeating decimals
Grade 5 decimals addition and subtraction worksheets
- Addition with 0-1 decimal digits
- Addition with 2 decimal digits
- Addition with 3 decimal digits
- Missing addend exercises
- Adding decimals in columns
- Subtract decimals (1-2 decimal digits)
- Subtract 1-2 digit decimals from whole numbers
- Missing minuend / subtrahend exercises
- Subtract decimals in columns
- Add / subtract with money notation
Grade 5 decimal multiplication
- Multiply whole numbers by 1 or 2 digit decimals
- Multiply decimals by decimals
- Missing factor exercises
- Multiplying by 10, 100, or 1,000 with up to 3 decimal digits
- Multiplying by 10, 100, or 1,000 with missing factors
- Multiply decimals by whole numbers in column form
- Multiply decimals by decimals in column form
- Multiply decimals with money notation.
- Decimal word problems (add / subtract / multiply)
Grade 5 decimal division worksheets
- Dividing decimals (1-digit, 2-digit) by whole numbers
- Dividing decimals by whole numbers, missing dividends or divisors
- Dividing decimals by decimals, quotient a whole number
- Dividing whole numbers by 10, 100 or 1,000
- Dividing whole numbers by 10, 100 or 1,000, with missing dividends or divisors
- Dividing 1-digit decimals by 10, 100 or 1,000
- Long division of decimals by whole numbers, no rounding
- Division of decimals with money notation.
Grade 6 fractions to / from decimals worksheets
- Convert decimals to decimals, with simplification
- Convert decimals to mixed numbers, with simplification
- Convert decimals to decimals (denominators are 10 or 100)
- Convert decimals to decimals (various denominators)
- Convert mixed numbers to decimals (various denominators)
Grade 6 decimals addition and subtraction worksheets
- Adding decimals with 0-3 digits
- Missing addend questions
- Adding decimals of varying length
- Subtracting decimals
- Subtracting decimals from whole numbers
- Missing minuend or subtrahend exercises
- Subtracting decimals in columns
- Subtracting decimals of varying length
Grade 6 decimal multiplication worksheets
- Multiply whole numbers by decimals
- Multiply decimals by decimals mentally (1-3 decimal digits)
- Multiply decimals by 10, 100 or 1,000
- Multiply decimals by powers of ten (10000, 100000 etc)
- Multiply decimals in columns (up to 4 digits)
- Missing factor questions
Grade 6 decimal division worksheets
- 1-2 digit decimals divided by whole numbers
- 1-2 digit decimals divided by decimals (quotient a whole number)
- Divide whole numbers by powers of ten
- Long division of decimals by whole numbers, division terminates
- Long division of decimals by whole numbers, with rounding
- Whole number long division, some answers repeat
- Long division of decimals by decimals
Related topics
Fractions worksheets
Money worksheets

Sample Decimals Worksheet
What is K5?
K5 Learning offers free worksheets , flashcards and inexpensive workbooks for kids in kindergarten to grade 5. Become a member to access additional content and skip ads.

Our members helped us give away millions of worksheets last year.
We provide free educational materials to parents and teachers in over 100 countries. If you can, please consider purchasing a membership ($24/year) to support our efforts.
Members skip ads and access exclusive features.
Learn about member benefits
This content is available to members only.
Join K5 to save time, skip ads and access more content. Learn More
- Forgot Password?
Powerful online learning at your pace

Extending Decimal Place Value Understanding Through Problem Solving
I was planning with my 5th-grade team today, and they’re getting ready to move into decimal place value. The 5th-grade standard is to extend decimal place value from the hundredths place to the thousandths place. We decided to start with a very quick Ticket In the week before the unit actually starts to get a feel for what the kiddos retained from 4th grade.
On Day 1, we’re going to focus on reading decimal numbers, starting out with decimals to the hundredths (4th-grade skill) and extending to the thousandths (5th-grade skill).
Write the following on the board/document camera: (2 x 100) + (3 x 10) + (6 x 1) + (1 x 0.1) + (5 x 0.01). Talk with your partner about how you would write this number in standard form. Accept responses and have a class discussion about which the class feels is the correct way to write the number. Be sure that they come to the conclusion that it should be written 236.15. Who thinks they can read the number? Accept responses. You may have students that try to read it two hundred thirty-six point fifteen because they often hear adults use that shortcut . Tell kiddos that mathematicians are more precise and would read it two hundred thirty-six and fifteen hundredths. We say the word and when we reach the decimal point, and we always include the decimal place value name.

Change the number to 1,236.158 by adding a 1 in the thousands place and an 8 in the thousandths place. Turn and talk to your partner. How should we label the place value position names of the new digits? You’re hoping that they will conclude that since the 1 is in the thousands place, then the 8 must be the thousandths place. Remember, you’re wanting them to see the relationship between the place value positions.
Continue practicing reading decimal numbers to the thousandths. Be sure to write the numbers with the place value names labeled to support the learning. Try letting the student who reads the number correctly be the one to write the next number.
Give a quick Ticket Out to determine how well students understood the concept.
Day 2 moves us into comparing decimals. Again, we’ll frame it in a problem-solving context.
Give each pair of students the two place value mats shown below, manipulative money (3 dollar bills, 10 dimes, and 10 pennies), and base-10 blocks (3 flats, 10 rods, and 10units).

Huh. I wonder which is bigger, 0.9 or 0.09? Let’s read these decimals to make sure we’re clear on them. Nine-tenths and nine-hundredths. Great! I’ve given you some materials. You may use these materials to prove your answer. You also need to be able to explain in words and pictures how you decided which is the bigger decimal.
Give students some time to work in pairs on the problem, and then come back together to discuss. See if students can make any generalizations.
Give students additional numbers to build and compare. Here are some good ones to try: 0.17 and 0.4; 1.08 and 1.18; 2.2 and 2.24; 1.5 and 1.67
Be sure to bring the class back together to discuss their results and strategies for comparing. If you feel they have really grasped this lesson, you might try…
Huh. I wonder which is bigger, 0.102 or 0.14? 🙂
Click here to grab your mats! Looking for additional decimal resources? Check out my Decimals & Fractions Using Models and Manipulatives unit. It’s a best-seller!

Similar Posts

Number of the Day with Ten Frames
One of the perks of being a math instructional coach is that you get to visit classrooms on a daily basis. On one of those visits, I observed this 1st-grade…

Problem-Solving vs Word Problems
I remember preparing for an interview for my first teaching position in the 90’s. I was told that I would likely be asked to explain my approach to teaching problem-solving….

Easy 3- and 4-Digit Place Value Game
Looking for an easy, yet powerful, 3- and 4-digit place value game? Well, I’ve got something for you today! Build the Biggest is my version of a well-known place value…

Telling Time to the Hour and Half Hour
The math standards are carefully aligned to gradually develop concepts over a period of time. A great example is telling time. In First Grade, students are required to tell time…

On a Roll: Adding Fractions
Today I have a little freebie for the older kiddos. On a Roll is a simple dice game for practicing adding fractions with like denominators and writing fractions greater than…

Effective Mathematics Teaching Practices
The past two years have been unimaginably difficult for teachers. Teaching, already a high-demand and oftentimes stressful profession, has been upended by the COVID pandemic. First, it was learning to…
13 Comments
Awesome! Thank you!
My pleasure!
Great ideas! I love connecting this to money.
It’s something that really clicks with the kiddos! They ALL know money! Ha ha.
Donna, these are really great ideas that I’ll save for next year. I love your tickets in and out too! Is there any way you could share “blank” ones that we could use for other concepts? We’re working on %, decimals, fractions now and I’d love to use your tickets! As always, you have great ideas for teaching math concepts.
Hey, Debbie! That’s actually why I uploaded them as Word documents, not PDF files. You can download them and change them however you want!
I just learned about a neat way to show place value with decimals (and do a little diagnosis of understanding of fractions), tho’ it’s a candy lesson and edible lessons have their issues… I s’pose it could be done with strips of paper, though. Start with 100 Twizzlers and show that place… then ten… then 1… Then … into Decimal land! what would 1/10 of the twizzler be? Break it off (but you can’t eat it yet…) That’s going ot be the tenths place. Then… take that little piece~ can you find 1/10 of it? Nifty room for discussion…
100 Twizzlers?! Yum! 🙂
Do you have any mats that are not decimal related., I managed to find some in my closet at school but your decimal ones are way cuter.
Oddly enough, Tami, I actually didn’t have a cute one for whole numbers. It was easy enough for me to modify the decimal one, though. Grab it here .
You’re amazing Donna, thank you
Thank you so much for the detailed information you share on your blog. Plus the resources! I was wondering if you have a post on how you would suggest introducing decimals to students in fourth? I’ve searched your posts but didn’t quite find one on this topic. Your insights are greatly appreciated!
- Pingback: 50 Decimal Activities to Strengthen Decimal Sense
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Administrator
- Teacher How To's
- How It works
- All Worksheets
- Math Worksheets
- ELA Worksheets
Tenths in Decimals Games
Introducing your kids to a complex concept through games is the best way to teach. With SplashLearn’s interactive games on the tenths place, kids will learn the concept of fractions & decimals by understanding place value. By playing these online games, they will have fun practicing every day.

CONTENT TYPE
- Lesson Plans
- Math (2,046)
- Number Sense (387)
- Number Recognition (65)
- Number Recognition Within 3 (9)
- Number Recognition Within 5 (23)
- Number Recognition Within 10 (31)
- Number Recognition Within 20 (6)
- Number Sequence (52)
- Number Sequence Within 3 (6)
- Number Sequence Within 5 (15)
- Number Sequence Within 10 (18)
- Number Sequence Within 20 (5)
- Number Sequence Within 50 (5)
- Number Sequence Within 100 (5)
- Number Sequence Within 120 (4)
- Counting (115)
- Counting Objects Within 3 (3)
- Counting Objects Within 5 (31)
- Counting Objects Within 10 (49)
- Counting Objects Within 20 (3)
- Writing Numbers (20)
- Writing Numbers Within 5 (5)
- Writing Numbers Within 10 (5)
- Writing Numbers Within 20 (10)
- Compare and Order Numbers (64)
- Compare Numbers (42)
- Compare Numbers within 10 (16)
- Compare Objects within 10 (6)
- Compare Numbers within 100 (6)
- Order Numbers (23)
- Order Numbers within 10 (3)
- Order Numbers within 20 (3)
- Skip Counting (24)
- Skip Count by 2 (6)
- Skip Count by 5 (7)
- Skip Count by 10 (8)
- Skip Count by 100 (3)
- Even and Odd Numbers (4)
- Place Value (122)
- Read and Write Numbers (93)
- Numbers up to 10 (5)
- Numbers up to 20 (6)
- Numbers up to 50 (7)
- Numbers up to 100 (7)
- Identify Teen Numbers (12)
- Expanded Form (8)
- 3-Digit Numbers in Expanded Form (6)
- 4-Digit Numbers in Expanded Form (1)
- 5-Digit Numbers in Expanded Form (1)
- Standard Form (11)
- 3-Digit Numbers in Standard Form (6)
- 4-Digit Numbers in Standard Form (4)
- 5-Digit Numbers in Standard Form (1)
- Word Form (3)
- 3-Digit Numbers in Word Form (1)
- 4-Digit Numbers in Word Form (1)
- 5-Digit Numbers in Word Form (1)
- Unit Form (17)
- 3-Digit Numbers in Unit Form (5)
- 4-Digit Numbers in Unit Form (4)
- 5-Digit Numbers in Unit Form (3)
- Place Value Chart (4)
- 3-Digit Numbers on Place Value Chart (2)
- 4-Digit Numbers on Place Value Chart (1)
- 5-Digit Numbers on Place Value Chart (1)
- Round Numbers (16)
- Round Numbers to the Nearest 10 (8)
- Round Numbers to the Nearest 100 (4)
- Addition (341)
- Embedded Numbers (3)
- Addition Sentences (10)
- Addition Sentence within 5 (5)
- Addition Sentence within 10 (5)
- Addition Properties (6)
- Add Using Models (8)
- Addition Strategies (142)
- Addition Strategies within 10 (55)
- Count All to Add (10)
- Count All to add within 5 (5)
- Count All to add within 10 (5)
- Count On to Add Strategy (15)
- Compose and Decompose Numbers (31)
- Number Bonds (17)
- Addition Strategies within 20 (59)
- Anchor 5 and 10 (9)
- Count On Strategy (10)
- Add with 10 (3)
- Make 10 Strategy (8)
- Doubles and Near Doubles Strategy to Add (22)
- Doubles Facts (3)
- Add Three Whole Numbers (7)
- Addition Strategies within 100 (23)
- Addition Strategies within 1000 (11)
- Add using multiples of 100 (7)
- Addition Facts (54)
- Fluently Add within 10 (38)
- Fluently Add within 20 (16)
- Equal Expressions (3)
- Addition Without Regrouping (67)
- Add within 100 without Regrouping (11)
- Add 2-digit number to 1-digit (5)
- Add 2-digit number to 2-digit (6)
- Add within 1000 without Regrouping (42)
- Add 10 to 3-digit numbers (5)
- Add 100 to 3-digit numbers (5)
- Add 3-digit number to 1-digit (6)
- Add 3-digit number to 2-digit (6)
- Add two 3-digit numbers (6)
- Add within 10000 without Regrouping (14)
- Addition With Regrouping (45)
- Add within 100 with Regrouping (10)
- Regroup and add 2-digit number to 1-digit (5)
- Regroup and add 2-digit numbers (5)
- Add within 1000 with Regrouping (19)
- Regroup ones and add (3)
- Regroup ones and tens and add (3)
- Regroup tens and add (3)
- Add within 10000 with Regrouping (16)
- Multi-digit Addition (10)
- Addition within 100000 (5)
- Addition within 1000000 (5)
- Subtraction (238)
- Subtraction Sentences (10)
- Subtraction Sentences within 5 (5)
- Subtraction Sentences within 10 (5)
- Subtract with Pictures (16)
- Subtract with Pictures within 5 (8)
- Subtract with Pictures within 10 (8)
- Subtract using Models (4)
- Subtraction Strategies (38)
- Subtraction Strategies within 10 (11)
- Count Back Strategy within 10 (5)
- Relate Addition and Subtraction within 10 (6)
- Subtraction Strategies within 20 (22)
- Count Back Strategy within 20 (10)
- Relate Addition and Subtraction within 20 (3)
- Doubles and Near Doubles Strategy to Subtract (4)
- Subtract from 10 Strategy (2)
- Subtraction Strategies within 100 (3)
- Subtraction Strategies within 1000 (4)
- Subtraction Facts (52)
- Fluently Subtract within 10 (38)
- Fluently Subtract within 20 (14)
- Subtraction Without Regrouping (71)
- Subtract within 100 without Regrouping (20)
- Subtract Multiples of 10 (5)
- Subtract within 1000 without Regrouping (39)
- Subtract within 10000 without Regrouping (12)
- Subtraction With Regrouping (39)
- Subtract within 100 with Regrouping (8)
- Subtract within 1000 with Regrouping (23)
- Subtract across Zeros (5)
- Subtract within 10000 with Regrouping (8)
- Multi-digit Subtraction (12)
- Subtraction within 100000 (8)
- Subtraction within 1000000 (4)
- Multiplication (199)
- Arrays (11)
- Equal Groups (12)
- Multiplication Sentences (7)
- Repeated Addition to Multiply (8)
- Multiplication on Number Line (6)
- Multi-digit Multiplication (39)
- Multiply 2-digit by 1-digit Numbers (9)
- Multiply 2-digit by 2-digit numbers (12)
- Multiply 3-digit by 1-digit Numbers (7)
- Multiply 3-digit by 2-digit numbers (4)
- Multiply 4-digit by 1-digit Numbers (7)
- Multiplication Properties (12)
- Associative Property (2)
- Commutative Property (4)
- Distributive Property (3)
- Multiply by 0 and 1 (3)
- Estimate Products (2)
- Multiply by multiples of 10 (4)
- Times Tables (85)
- Multiplication Facts (85)
- Multiplication Facts of 2 (9)
- Multiplication Facts of 3 (9)
- Multiplication Facts of 4 (9)
- Multiplication Facts of 5 (9)
- Multiplication Facts of 6 (9)
- Multiplication Facts of 7 (8)
- Multiplication Facts of 8 (8)
- Multiplication Facts of 9 (9)
- Multiplication Facts of 10 (5)
- Multiply by 11 (5)
- Multiply by 12 (5)
- Division (109)
- Division Facts (43)
- Division Facts of 2 (5)
- Division Facts of 3 (5)
- Division Facts of 4 (5)
- Division Facts of 5 (5)
- Division Facts of 6 (5)
- Division Facts of 7 (5)
- Division Facts of 8 (5)
- Division Facts of 9 (5)
- Division Facts of 10 (3)
- Divide on a Number Line (3)
- Long Division (37)
- Divide 2-digit by 1-digit Numbers (11)
- Divide 3-digit by 1-digit Numbers (9)
- Divide 4-digit by 1-digit Numbers (5)
- Divide Multiples of 10 or 100 (8)
- Estimate Quotients (3)
- Fractions (173)
- Identify Fractions (28)
- Identify fractions using models (8)
- Identify fractions on the number line (6)
- Compare Fractions (25)
- Compare fractions using visual models (3)
- Compare fractions using number lines (4)
- Compare fractions without visual models (1)
- Benchmark Fractions (6)
- Equivalent Fractions (19)
- Convert Fractions (15)
- Mixed Numbers as Fractions (15)
- Fractions Operations (86)
- Add and Subtract Fractions (38)
- Add Fractions (16)
- Estimate fraction sums (3)
- Subtract Fractions (10)
- Add and Subtract mixed numbers (14)
- Add mixed numbers (7)
- Subtract mixed numbers (7)
- Multiply Fractions (26)
- Divide fractions (8)
- Decimals (150)
- Identify tenths (7)
- Identify hundredths (8)
- Represent Decimals (12)
- Represent Decimals Using Models (8)
- Represent Decimals on Number Lines (4)
- Read and Write Decimals (11)
- Decimal Place Value (20)
- Compare and Order Decimals (33)
- Compare decimals (14)
- Order decimals (19)
- Round Decimals (12)
- Convert Between Decimals and Fractions (7)
- Convert Decimals to Fractions (7)
- Equivalent Decimals (17)
- Tenths to hundredths (9)
- Hundredths to tenths (8)
- Decimal Operations (39)
- Add Decimals (6)
- Subtract Decimals (6)
- Multiply Decimals (13)
- Divide Decimals (14)
- Types of Decimals (12)
- Geometry (128)
- Parallel lines (5)
- Angles (15)
- Positional Words (5)
- Shapes (92)
- 2d Shapes (76)
- Identify Quadrilaterals (11)
- Identify triangles (2)
- Attributes of 2D shapes (7)
- Sort 2D shapes (4)
- Partition 2D Shapes (12)
- Partition into equal parts (8)
- Halves, Thirds, and Fourths (8)
- 3d Shapes (10)
- Flat and Solid Shapes (11)
- Match 2D Shapes (9)
- Coordinate Planes (7)
- Measurement (175)
- Capacity (12)
- Comparing Measurements (23)
- Compare Weights (3)
- Group of Objects (4)
- Compare Lengths (14)
- Compare Heights (4)
- Conversion of Measurement Units (16)
- Data Handling (46)
- Organize and Interpret Data (41)
- Organize data in bar graphs (7)
- Organize data in line plots (6)
- Organize data in picture graphs (4)
- Interpret data in bar graphs (5)
- Interpret data in line plots (7)
- Interpret data in picture graphs (6)
- Sort Objects (5)
- Length (24)
- Measure Lengths (6)
- Measure Lengths using the ruler (6)
- Estimate Lengths (4)
- Area of Shapes (18)
- Area of 2D Shapes (5)
- Area as Additive (5)
- Perimeter (19)
- Perimeter of Shapes (19)
- AM and PM (2)
- Analog Clock (2)
- Elapsed Time (3)
- Time in Half Hours (4)
- Time in Hours (4)
- Time in Quarter Hours (7)
- Time to the Nearest 5 Minutes (11)
- Time to the Nearest Minute (2)
- Identify Coins (10)
- Counting Money (50)
- Compare Money (4)
- Count Money with Coins (22)
- Penny, Nickel, and Dime (10)
- Quarters and Half Dollar (9)
- Operations With Money (24)
- Add and Subtract Money (12)
- Multiply and Divide Money (7)
- Algebra (35)
- Patterns (14)
- Number Patterns (14)
- Numerical Expressions (9)
- Factors and Multiples (7)
- Prime and Composite Numbers (5)
- Word Problems (66)
- Addition and Subtraction Word Problems (46)
- Addition Word Problems (33)
- Addition Word Problems within 10 (6)
- Addition Word Problems within 20 (5)
- Addition Word Problems within 100 (15)
- Add to Compare Word Problems (11)
- Subtraction Word Problems (14)
- Subtraction Word Problems within 10 (3)
- Subtraction Word Problems within 100 (9)
- Subtract to Compare Word Problems (6)
- Multiplication and Division Word Problems (7)
- Multiplication Word Problems (4)
- Division Word Problems (3)
- Fraction Word Problems (3)
- Money Word Problems (10)
- ELA (2,367)
- Reading (2,209)
- Phonics (2,165)
- Bossy R (15)
- Words with AR (3)
- Words with ER (3)
- Words with IR (3)
- Words with OR (3)
- Words with UR (3)
- Diphthongs (4)
- Ending Consonant Blends (23)
- CK Blend (5)
- LF Blend (3)
- LK Blend (3)
- LT Blend (3)
- MP Blend (3)
- ND Blend (3)
- NK Blend (3)
- SK Blend (3)
- ST Blend (3)
- NG Blend (4)
- Beginning Consonant Blends (21)
- L Blend Words (12)
- BL Blend (5)
- CL Blend (3)
- FL Blend (5)
- GL Blend (3)
- PL Blend (3)
- SL Blend (3)
- R Blend Words (9)
- CR Blend (3)
- FR Blend (3)
- GR Blend (3)
- PR Blend (3)
- TR Blend (3)
- Alphabet (215)
- Letter A (9)
- Letter B (9)
- Letter C (9)
- Letter D (9)
- Letter E (9)
- Letter F (9)
- Letter G (9)
- Letter H (9)
- Letter I (9)
- Letter J (9)
- Letter K (9)
- Letter L (9)
- Letter M (9)
- Letter N (9)
- Letter O (9)
- Letter P (9)
- Letter Q (9)
- Letter R (9)
- Letter S (9)
- Letter T (9)
- Letter U (9)
- Letter V (9)
- Letter W (9)
- Letter X (9)
- Letter Y (9)
- Letter Z (9)
- Letter Sequence (54)
- ABC Song (20)
- Alphabetical Order (34)
- Letter Sounds (130)
- Letter Sound A (5)
- Letter Sound B (5)
- Letter Sound C (5)
- Letter Sound D (5)
- Letter Sound E (5)
- Letter Sound F (5)
- Letter Sound G (5)
- Letter Sound H (5)
- Letter Sound I (5)
- Letter Sound J (5)
- Letter Sound K (5)
- Letter Sound L (5)
- Letter Sound M (5)
- Letter Sound N (5)
- Letter Sound O (5)
- Letter Sound P (5)
- Letter Sound Q (5)
- Letter Sound R (5)
- Letter Sound S (5)
- Letter Sound T (5)
- Letter Sound U (5)
- Letter Sound V (5)
- Letter Sound W (5)
- Letter Sound X (5)
- Letter Sound Y (5)
- Letter Sound Z (5)
- Letter Recognition (215)
- Lowercase Letters (78)
- Uppercase Letters (78)
- Matching Lowercase and Uppercase Letters (59)
- Match Aa - Dd (9)
- Match Ee - Gg (7)
- Match Hh - Kk (9)
- Match Ll - Pp (11)
- Match Qq - Ss (7)
- Match Tt - Vv (7)
- Match Ww - Zz (9)
- Vowels (158)
- Long Vowel Sounds (75)
- Long A Vowel Sound (15)
- Long E Vowel Sound (17)
- Long I Vowel Sound (15)
- Long O Vowel Sound (15)
- Long U Vowel Sound (13)
- Magic - E (12)
- Magic E Words with Long Vowel A (3)
- Magic E Words with Long Vowel I (3)
- Magic E Words with Long Vowel O (3)
- Magic E Words with Long Vowel U (3)
- Short Vowel Sounds (81)
- Short A Vowel Sound (59)
- Short E Vowel Sound (26)
- Short I Vowel Sound (59)
- Short O Vowel Sound (44)
- Short U Vowel Sound (24)
- Vowel Teams (15)
- Words with AI and AY (3)
- Words with EA and EE (3)
- Words with IE and Y (3)
- Words with OA and OW (3)
- Words with OO (2)
- Words with UE and UI (1)
- Blending (587)
- CCVC Words (19)
- CVC Words (271)
- CVCC Words (34)
- Beginning Blending (34)
- CCVC and CCVCC Words (28)
- CVCC and CCVCC Words (46)
- Words With Bossy R (45)
- Words With Diphthongs (18)
- Words With Three Letter Blends (14)
- Words With Trigraphs (28)
- Words With Vowel Teams (50)
- Consonant Digraphs (8)
- Digraph CH (3)
- Digraph PH (2)
- Digraph SH (3)
- Digraph TH (2)
- Digraph WH (2)
- Double Consonants (8)
- FF Words (3)
- LL Words (3)
- SS Words (3)
- ZZ Words (3)
- Rhyming Words (61)
- Trigraphs (10)
- Soft Sounds (2)
- Words with Soft C (1)
- Words with Soft G (1)
- Three Letter Blends (5)
- Sight Words (975)
- Dolch Sight Words (567)
- Fry Sight Words (444)
- Reading Skills (44)
- Cause and Effect (6)
- Inference (6)
- Identify the Main Idea (13)
- Categorize Pictures into Groups (4)
- Choose a Suitable Heading (5)
- Prediction (6)
- Sequencing (13)
- Arrange Pictures in Order (3)
- Arrange Sentences in Order (4)
- Writing (184)
- Handwriting (124)
- Letter Tracing (124)
- Letter Tracing A (6)
- Letter Tracing B (6)
- Letter Tracing C (6)
- Letter Tracing D (6)
- Letter Tracing E (6)
- Letter Tracing F (6)
- Letter Tracing G (6)
- Letter Tracing H (6)
- Letter Tracing I (6)
- Letter Tracing J (6)
- Letter Tracing K (6)
- Letter Tracing L (6)
- Letter Tracing M (6)
- Letter Tracing N (6)
- Letter Tracing O (6)
- Letter Tracing P (6)
- Letter Tracing Q (6)
- Letter Tracing R (6)
- Letter Tracing S (6)
- Letter Tracing T (6)
- Letter Tracing U (6)
- Letter Tracing V (6)
- Letter Tracing W (6)
- Letter Tracing X (6)
- Letter Tracing Y (6)
- Letter Tracing Z (6)
- Writing Sight Words (60)
- General Knowledge (295)
- Vegetables (19)
- Fruits (24)
- Dessert (9)
- Animals (58)
- Underwater (9)
- Dinosaurs (8)
- Reptiles (9)
- Seasonal (28)
- Christmas (12)
- Halloween (8)
- Kitchen (11)
- Utensils (6)
- Musical Instruments (30)
- Transport (9)
- Vehicles (9)
- Insects (9)
- Professions (8)
- Monuments (8)
- Household Items (8)
- Flowers (8)
- Buildings (8)
- Art & Creativity (236)
- Coloring (181)
- Animals (32)
- Underwater (8)
- Reptiles (8)
- Vegetables (8)
- Transport (8)
- Vehicles (8)
- Musical Instruments (8)
- Kitchen (8)
- Utensils (5)
- Insects (8)
- Rhymes (25)
- Cooking (7)
- Stories (10)
- Logic & Thinking (16)
- Puzzles (11)
- Matching (3)
- Multiplayer (12)
- Time Based (12)
- Player vs Player (12)
- Motor Skills (16)
- Fine Finger Movement (9)
- Aiming and Precision (6)

Identify Tenths Using Fraction Models Game
Apply your knowledge of decimals to identify tenths using fraction models.

Shade the Parts To Show the Given Tenths Game
Have your own math-themed party by learning how to shade the parts to show the given tenths.

Change the Words into Decimal Numbers Game
Practice the superpower of decimals by learning how to change words into decimal numbers.

Identify Decimal Numbers Using Fraction Models Game
Add more arrows to your child’s math quiver by identifying decimal numbers using fraction models.

Fill in Color to Represent the Decimal Numbers Game
Fill in colors to represent the decimal numbers in this game.

Convert Fractions to Decimals Numbers Game
Use your math skills to convert fractions into decimals numbers.

Change Decimal Numbers into Fractions Game
Add more arrows to your child’s math quiver by learning to change decimal numbers into fractions.
Learning Decimals and Fractions
In Grade 3, the kids will learn decimals after having a clear concept of fractions. So, they will learn to write fractions and many mixed numbers having powers of 10 in the denominators. Let your children learn decimals through SplashLearn’s games on the tenth place.
While they play, they will learn to relate decimals to fraction values proficiently. Have a look at what you can offer your kids by choosing the platform of online interactive games:
- Change the Words into Decimal Numbers : By playing this game, students will learn to write decimals. They require choosing the appropriate answer from the given options.
- Identify Decimal Numbers using Fraction Models : By performing the smartly designed tasks in this game, your children will learn to use visual models to identify decimal notation for tenths.
- Fill in Color to Represent the Decimal Numbers: The game is designed to make the children practice the concept of decimals. Coloring the visual models with the given direction, they will receive a clear concept of decimals in their minds.
- Convert Fractions to Decimals Numbers : This game improves the proficiency level of your kids in decimals. They will achieve better problem-solving skills to convert fractions to decimals.
- Change Decimal Numbers into Fractions : After clearly understanding fraction to decimal conversion, this game will improve their concept of converting decimals to fractions.
SplashLearn’s games on the tenths place are stepwise designed to build a complete understanding of the decimals and fractions for the little mathematicians. Now, converting decimals to fractions or vice versa will not be a tough job for your kids.
Your one stop solution for all grade learning needs.

- Home Learning
- Free Resources
- New Resources
- Free resources
- New resources
- Filter resources
- Childrens mental health
- Easter resources
Internet Explorer is out of date!
For greater security and performance, please consider updating to one of the following free browsers
Equivalent Fractions and Decimals (tenths) – Reasoning and Problem Solving
Equivalent Fractions and Decimals (tenths) - Reasoning and Problem Solving
This worksheet includes a range of reasoning and problem solving questions for pupils to practise the main skills associated with finding equivalences between fractions and decimals as tenths.

Not a member? Sign up here.
What's included in the pack?
The Equivalent Fractions and Decimals (tenths) Reasoning and Problem Solving worksheet Answer sheet
National Curriculum Objectives:
(5F6a) Read and write decimal numbers as fractions [for example, 0.71 = 71/100]
This resource is available to download with a Premium subscription.
Our Mission
To help our customers achieve a life/work balance and understand their differing needs by providing resources of outstanding quality and choice alongside excellent customer support..
Yes, I want that!
Keep up to date by liking our Facebook page:
Membership login, stay in touch.
01422 419608
[email protected]
Interested in getting weekly updates from us? Then sign up to our newsletter here!

Information

- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
Copyright: Classroom Secrets 2024
Company number: 8401067
VAT number: 248 8245 74
- Terms & Conditions
Designed by Classroom Secrets
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search
Fractions and Decimals - tenths and hundredths - Fluency/Reasoning/Problem Solving
Subject: Mathematics
Age range: 7-11
Resource type: Worksheet/Activity
Last updated
4 March 2018
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest
Creative Commons "Sharealike"
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
Great problem solving/ application activities related to fraction and decimal equivalence!
Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user
Fantastic selection of resources! Thanks!
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
Advertisement
Getting a Handle on Fraction-to-Decimal Conversions
- Share Content on Facebook
- Share Content on LinkedIn
- Share Content on Flipboard
- Share Content on Reddit
- Share Content via Email
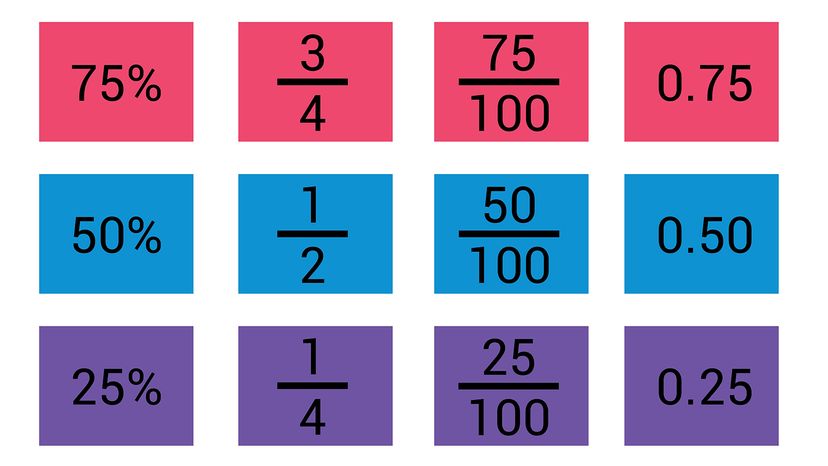
As you might recall from math class, fractions and decimals are two different ways of representing the same thing. A third option, percentages, is a close cousin of decimals. However, making use of this knowledge requires knowing how to convert one into the other.
Fraction to decimal conversion can be an opportunity to deepen your understanding of numbers and math. Sometimes the process will take more work, and sometimes less, but the operation is relatively straightforward.
What Are Fractions?
The case of improper fractions, what are decimals, going from fraction to decimal with a calculator, what is a repeating decimal, converting fractions to decimals using long division, how to convert a fraction to a percent, fraction-decimal conversion chart.
Fractions represent a division problem. If you look at the fraction 1/4, you can think of the line between the numbers (sometimes simply referred to as the "line," and sometimes as the "fraction bar") as a division sign.
That means that 1/4 is, in essence, saying "1 divided by 4."
That's all that fractions are. The top number, called the "numerator," is being divided by the bottom number, which is known as the "denominator." To calculate the decimal equivalent, you simply divide the numerator by the denominator, and you'll have your answer (which is 0.25, in this case).
If you're not a math maven, the sudden appearance of "improper" in the conversation might give you the heebie-jeebies. It may even trigger flashbacks of rational versus irrational numbers , as well as unpleasant memories of math exams.
Fear not! In this case, the phrase has a straightforward meaning: Whenever a fraction has a higher value numerator than denominator, you're looking at a so-called "improper fraction." This means that you're dealing with a number that is greater than 1.
This should make some intuitive sense, since the word "fraction" literally means "part of a whole." (In standard English, a "fraction" of something tends to connote a very small portion of that thing, but the essence is the same; it's a part, not the whole thing.)
Therefore, improper fractions are fractions that are more than a whole, such as 27/14 or 5/3.
A decimal is another way to represent a fraction — or, put differently, another way to write the part of a whole number. If we look back at the previous example of 1/4, we'll see that, if you divide 4 by 1, you'll get 0.25, which is the decimal equivalent of the fraction.
We haven't yet done the math problem that gives us the correct answer, but you're probably aware that 1/4, also known as a "quarter" or a "fourth," is 0.25. This is fairly easy to remember, since the coin we call the "quarter" has a value of 25 cents, and 4 of them together equal 1 dollar, or 100 cents.
You can also add them up:
Probably the easiest way to converting a fraction to decimal is to use a calculator. Chances are, you have a calculator app on your phone, and if you don't, you might still have a cheap calculator rattling around in a desk drawer.
Since you're now aware that a fraction is a straightforward division problem, once you've got your calculator at the ready, you can complete the necessary steps.
Let's start with 3/8. If you type "3 ÷ 8" into the calculator app, you'll get the decimal form: 0.375.
One nifty thing about calculators is their ability to handle some very big (or very small) numbers with ease. If you wanted to do the fraction to decimal conversion of 45/72, you would find your answer an instant.
Simply type 45 ÷ 72, and you'll get 0.625.
Not every fraction to decimal conversion yields a short string of numbers. Sometimes, you wind up with repeating decimals. Take the case of 2/3. If you type 2 ÷ 3 into your calculator, you'll get 0.66666666 and so on, for as many digits as your screen will allow.
This is a repeating decimal. Other fraction to decimal conversions that give you repeating digits are:
Here's the part that might require a refresher with grade-school mathematics. But don't stress: You'll find that once you get the basics of long division , you'll be every bit the decimal calculator that your phone now is. It will also require paper and a pencil, or anything to write with.
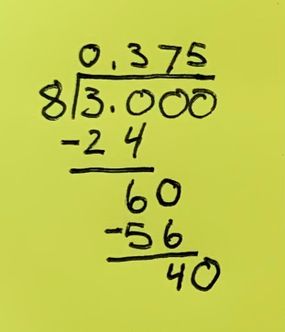
Let's dive into long division with a clear example. We'll use 3/8 to walk through this step-by-step process. Recall that 3/8 is equivalent to 3 ÷ 8.
- Set up the problem. Write the numerator (now called the dividend) 3 under the division bar and the divisor (formerly, the denominator) 8 outside the bar.
- Divide. But wait: 8 doesn't go into 3 evenly; 8 is a larger number than 3 (which is why we're getting fractions, not whole numbers, right?) .
- Add a 0. We get around this problem by adding a 0 after the 3. Now we're dealing with the more straightforward task of dividing 30 by 8.
- Divide again. How many times does 8 go into 30? Well, it goes in 3 times — not evenly (3 x 8 = 24), but that's okay. 24 is less than 30.
- Add a decimal. Put a decimal point before the 3 on top of the division bar. This is important, and it's what makes this fraction to decimal conversion work.
- Multiply. Multiplying the quotient (3) by the divisor (8) gives us an answer of 24: (3 x 8 = 24). Write 24 under the 30.
- Subtract. Subtract 24 from 30 to get 6. Draw a line under the 24, subtract, and write 6 below the line.
- Add another zero to the dividend. Now, bring down the 0, to sit next to the 6, making 60.
- Repeat the steps. 8 goes into 60 seven times (8 x 7 = 56), so write 7 above the bar next to the 3. Subtract 56 from 60 to get 4. Now, follow the same process you used in steps 1 through 8 and bring down the next zero. This gives you 40.
- Keep going until you have no remainder. Luckily for us, in this example, you're already there once you've reached that 40. 8 goes into 40 a clean 5 times. Put that 5 next to the 7, and you'll have your answer: 0.375.
Now you can say you know how to convert fractions to decimals using long division!
Luckily, adding percentages to the mix doesn't make things significantly more complex. In fact, once you become sufficiently comfortable with the fraction to decimal process, you really have only one more step to take.
In a sense, the decimal equivalent of a fraction is already a percent. All you have to do to make it official is to move the decimal point two positions to the right.
If you take the above example of 3/8, we know that the answer is .375. By shifting the decimal point two places to the right, you get 37.5. Now all that's left to do is throw a percentage sign (%) after the number.
Here are some common conversions in a handy-dandy reference chart.
Please copy/paste the following text to properly cite this HowStuffWorks.com article:
The home of mathematics education in New Zealand.
- Forgot password ?
- Resource Finder
Decimal Fractions – Tenths
The Ministry is migrating nzmaths content to Tāhurangi. Relevant and up-to-date teaching resources are being moved to Tāhūrangi (tahurangi.education.govt.nz). When all identified resources have been successfully moved, this website will close. We expect this to be in June 2024. e-ako maths, e-ako Pāngarau, and e-ako PLD 360 will continue to be available.
For more information visit https://tahurangi.education.govt.nz/updates-to-nzmaths
These exercises and activities are for students to use independently of the teacher to practise number properties.
Solve addition and subtraction problems involving decimal tenths.
Addition and Subtraction, AM (Stage 7)
- Jumping the number line (decimal fractions – tenths)
- Don’t subtract Add (decimal fractions – tenths)
- Near doubles (decimal fractions – tenths)
- x + 2.9 = 8.1 (decimal fractions – tenths)
- 2.3 + x = 7.1 (decimal fractions – tenths)
- 3.7 + x = 8.9 (decimal fractions – tenths)
- Make one (decimal fractions – tenths)
- 7.3 – 1.9 = x (decimal fractions – tenths)
Prior Knowledge
- Range of strategies to solve addition and subtraction problems with whole numbers.
- Understanding of place value structure including decimals
In this activity students use additive strategies to solve addition and subtraction with decimal numbers.
Comments on the Exercises
Make One Tenth Asks students to add a list of tenths by first adding up the pairs that add to 1.
Don't Subtract - Add! Asks students to solve subtraction problems involving tenths by reversing it to an addition problem.
Near Doubles Asks students to solve addition problems involving tenths by using the doubling strategy. For example, 7.8 + 7.7 as 16 - 0.5 = 15.5.
2.3 + ? = 7.1 Asks students to solve problems involving tenths by jumping a whole number on a number line then jumping back in tenths.
? + 2.9 = 8.1 Asks students to solve problems involving tenths by rearranging the equation and choosing an appropriate mental strategy.
3.7 + ? = 8.9 Asks students to solve problems involving tenths by mentally jumping up a number line.
7.3 - 1.9 = ? Asks students to solve problems involving tenths by first subtracting a whole then adding tneths to get the answer
These exercises and activities are based on the strategies used in Book 5 but use decimal fractions rather than whole numbers.
Related games/activities
Magic Squares (decimal fractions – tenths) Word (116KB) or PDF (26KB)
Spiders Web (decimal fractions – tenths) Word (40KB) or PDF (1KB)
Triangle puzzle (decimal fractions – tenths) Word (106KB) or PDF (1KB)
Dominoes (decimal fractions – tenths) Word (85KB) or PDF (3KB)
Dominoes2 (decimal fractions – tenths) Word (51KB) or PDF (19KB)
Flipping Decimal Fractions (decimal fractions – tenths) Word (79KB) or PDF (20KB)
First to the Draw (decimal fractions – tenths) Word (51KB) or PDF (19KB)
Log in or register to create plans from your planning space that include this resource.
- Printer-friendly version

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Reasoning and Problem Solving Tenths as Decimals Reasoning and Problem Solving Tenths as Decimals Developing 1a.Tanya is incorrect because the hundred square shows nine tenths shaded or 0.9 but she has written 0.7. 2a. Patrick is correct because there are six tenths shaded so 0.6 is the correct decimal. 3a. Any two from the following: 0.5, 0.6 ...
We can think of a decimal number as a whole number plus tenths, hundredths, etc: Example 1: What is 2.3 ? On the left side is "2", that is the whole number part. The 3 is in the "tenths" position, meaning "3 tenths", or 3/10; So, 2.3 is "2 and 3 tenths" Example 2: What is 13.76 ?
Reasoning and Problem Solving Tenths as Decimals Reasoning and Problem Solving Tenths as Decimals Developing 1a. Yes because he has used five counters to represent five tenths. 2a. C because it shows and the others are . 3a. 0.2, 0.4, 0.8, 0.9 Expected 4a. No because she has used eight straws instead of nine. 5a.
Introduction. The word decimal comes from the Latin word "Decem" meaning 10. . In algebra, a decimal number can be defined as a number whose complete part and the fractional part are separated by a decimal point. Before we learn what we mean by a tenth of decimal it is important to recall the place value system of decimals that defines the position of a tenth in a decimal number.
Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. ... Comparing decimals (tenths and hundredths) Compare decimals (tenths and hundredths) Math > 4th grade > ... Report a problem
In this second part of the lesson, I show how to add decimals with one decimal digit (tenths), such as 0.2 + 0.9 or 3.7 + 0.7, using mental math. Note that 0.2 + 0.9 is NOT 0.11! Lastly we also convert between centimeters and millimeters. This is a nice application of the concept just learned, since one millimeter is a tenth of a decimeter.
Decimal place value. The first digit after the decimal represents the tenths place. The next digit after the decimal represents the hundredths place. The remaining digits continue to fill in the place values until there are no digits left. Example: 0.81. The number 0. 8 1 is made up of 8 tenths and 1 hundredth. We can also write this as: or.
A common application of dividing whole numbers into decimals is when we want to find the price of one item that is sold as part of a multi-pack. For example, suppose a case of 24 water bottles costs $3.99. To find the price of one water bottle, we would divide $3.99 by 24. We show this division in Exercise 1.8.31.
WHAT IS INTRODUCTION TO DECIMALS (TENTHS & HUNDREDTHS)?. Decimal notation is an easy way to represent fractions with denominators of 10 or 100. Solving problems using decimal numbers can be much easier than solving those same problems using fractions. To better understand decimals…
Adding any decimals is almost like adding whole numbers. Make sure to line up the decimal points first! If there are any missing digits, then write 0's for them. Then add like you would with whole numbers. In the answer, put the decimal point directly underneath the lined-up decimal points. Have a blessed, wonderful day!
Find out by multiplying 4 by 0.3. Since multiplication is just repeated addition, 4 times 0.3 is the same as 0.3 + 0.3 + 0.3 + 0.3. Use decimal squares to model the addition. 0.3 means 3 parts out of 10. Show that 4 times. Next, count up all the tenths: there are 3, 6, 9, 12 tenths. To write this as a decimal, regroup 10 tenths to make 1 whole.
This detailed and comprehensive diving into mastery teaching pack aligns perfectly with Version 3.0 of the White Rose Maths scheme of learning for year 4 Spring Block 4 Step 2: Tenths as Decimals. This pack contains a variety of fluency, reasoning and problem-solving questions, giving all children the opportunity to develop their skills in writing tenths as decimals. Included in the pack is an ...
Decimal subtraction (1-digit), missing minuend/subtrehnds; Decimal subtraction (1 or 2 digits) Decimal subtraction in columns (2 digit) Add / subtract decimals using money notation; Word problems: adding and subtracting decimals; Grade 5 fractions to / from decimals worksheets. Convert decimals to fractions (tenths, hundredths), no simplification
10 Progressive Steps to Learn Decimals Step 1: Identify Tenths. When discussing tenths, we mean the first number right after the decimal point. In the decimal 0.7, the 7 is in the tenth place, representing 7 parts out of 10. ... Enhances Problem-Solving Skills: Learning about decimals improves problem-solving skills. It teaches kids how to ...
On Day 1, we're going to focus on reading decimal numbers, starting out with decimals to the hundredths (4th-grade skill) and extending to the thousandths (5th-grade skill). Write the following on the board/document camera: (2 x 100) + (3 x 10) + (6 x 1) + (1 x 0.1) + (5 x 0.01). Talk with your partner about how you would write this number in ...
Differentiation: Questions 1, 4 and 7 (Reasoning) Developing Explain whether a statement using decimals on a number line is correct. Counting forwards only in tenths. All increments marked and starting at zero. Expected Explain whether a statement using decimals on a number line is correct. Counting forwards or backwards in tenths.
Tenths in Decimals Games. Introducing your kids to a complex concept through games is the best way to teach. With SplashLearn's interactive games on the tenths place, kids will learn the concept of fractions & decimals by understanding place value. By playing these online games, they will have fun practicing every day. Personalized Learning.
Example 1: If 58 out of 100 students in a school are boys, then write a decimal for the part of the school that consists of boys. Analysis: We can write a fraction and a decimal for the part of the school that consists of boys. fraction decimal 0.58 Answer: 0.58 Example 2: A computer processes information in nanoseconds. A nanosecond is one billionth of a second.
This matching decimals math game will help kids learn to learn tenths and/or hundredths the fun way. Keep playing until the problems seem easy and you can solve them quickly. Keep track of your score and try to do better each time you play. ...
To use estimation to check the answer, round 2.53 to 3. 3 × 3 = 9, which is close to the answer. To multiply a decimal by a decimal, such as 0.7 times 0.3, use a model to show 0.3 as 3 parts out of. 10. To show 7 tenths of 3 tenths, split each tenth into 10 equal parts, and then color only 7 of the parts in each tenth.
The Equivalent Fractions and Decimals (tenths) Reasoning and Problem Solving worksheet Answer sheet. National Curriculum Objectives: (5F6a) Read and write decimal numbers as fractions [for example, 0.71 = 71/100] This resource is available to download with a Premium subscription.
Designed for those in Year 4, (4/5) to learn the fluency of converting tenths and hundredths to decimal numbers and vice versa. Includes missing number problems, number card problems and sequencing. Hope you find it useful.
Add a decimal. Put a decimal point before the 3 on top of the division bar. This is important, and it's what makes this fraction to decimal conversion work. Multiply. Multiplying the quotient (3) by the divisor (8) gives us an answer of 24: (3 x 8 = 24). Write 24 under the 30.
Asks students to solve problems involving tenths by rearranging the equation and choosing an appropriate mental strategy. 3.7 + ? = 8.9 Asks students to solve problems involving tenths by mentally jumping up a number line. 7.3 - 1.9 = ? Asks students to solve problems involving tenths by first subtracting a whole then adding tneths to get the ...
Supporting Standard. (5.7) Geometry and measurement. The student applies mathematical process standards to select appropriate units, strategies, and tools to solve problems involving measurement. The student is expected to. (A) solve problems by calculating conversions within a measurement system, customary or metric.