- Utility Menu

GA4 Tracking Code
fa51e2b1dc8cca8f7467da564e77b5ea
- Make a Gift
- Join Our Email List
- Problem Solving in STEM
Solving problems is a key component of many science, math, and engineering classes. If a goal of a class is for students to emerge with the ability to solve new kinds of problems or to use new problem-solving techniques, then students need numerous opportunities to develop the skills necessary to approach and answer different types of problems. Problem solving during section or class allows students to develop their confidence in these skills under your guidance, better preparing them to succeed on their homework and exams. This page offers advice about strategies for facilitating problem solving during class.
How do I decide which problems to cover in section or class?
In-class problem solving should reinforce the major concepts from the class and provide the opportunity for theoretical concepts to become more concrete. If students have a problem set for homework, then in-class problem solving should prepare students for the types of problems that they will see on their homework. You may wish to include some simpler problems both in the interest of time and to help students gain confidence, but it is ideal if the complexity of at least some of the in-class problems mirrors the level of difficulty of the homework. You may also want to ask your students ahead of time which skills or concepts they find confusing, and include some problems that are directly targeted to their concerns.
You have given your students a problem to solve in class. What are some strategies to work through it?
- Try to give your students a chance to grapple with the problems as much as possible. Offering them the chance to do the problem themselves allows them to learn from their mistakes in the presence of your expertise as their teacher. (If time is limited, they may not be able to get all the way through multi-step problems, in which case it can help to prioritize giving them a chance to tackle the most challenging steps.)
- When you do want to teach by solving the problem yourself at the board, talk through the logic of how you choose to apply certain approaches to solve certain problems. This way you can externalize the type of thinking you hope your students internalize when they solve similar problems themselves.
- Start by setting up the problem on the board (e.g you might write down key variables and equations; draw a figure illustrating the question). Ask students to start solving the problem, either independently or in small groups. As they are working on the problem, walk around to hear what they are saying and see what they are writing down. If several students seem stuck, it might be a good to collect the whole class again to clarify any confusion. After students have made progress, bring the everyone back together and have students guide you as to what to write on the board.
- It can help to first ask students to work on the problem by themselves for a minute, and then get into small groups to work on the problem collaboratively.
- If you have ample board space, have students work in small groups at the board while solving the problem. That way you can monitor their progress by standing back and watching what they put up on the board.
- If you have several problems you would like to have the students practice, but not enough time for everyone to do all of them, you can assign different groups of students to work on different – but related - problems.
When do you want students to work in groups to solve problems?
- Don’t ask students to work in groups for straightforward problems that most students could solve independently in a short amount of time.
- Do have students work in groups for thought-provoking problems, where students will benefit from meaningful collaboration.
- Even in cases where you plan to have students work in groups, it can be useful to give students some time to work on their own before collaborating with others. This ensures that every student engages with the problem and is ready to contribute to a discussion.
What are some benefits of having students work in groups?
- Students bring different strengths, different knowledge, and different ideas for how to solve a problem; collaboration can help students work through problems that are more challenging than they might be able to tackle on their own.
- In working in a group, students might consider multiple ways to approach a problem, thus enriching their repertoire of strategies.
- Students who think they understand the material will gain a deeper understanding by explaining concepts to their peers.
What are some strategies for helping students to form groups?
- Instruct students to work with the person (or people) sitting next to them.
- Count off. (e.g. 1, 2, 3, 4; all the 1’s find each other and form a group, etc)
- Hand out playing cards; students need to find the person with the same number card. (There are many variants to this. For example, you can print pictures of images that go together [rain and umbrella]; each person gets a card and needs to find their partner[s].)
- Based on what you know about the students, assign groups in advance. List the groups on the board.
- Note: Always have students take the time to introduce themselves to each other in a new group.
What should you do while your students are working on problems?
- Walk around and talk to students. Observing their work gives you a sense of what people understand and what they are struggling with. Answer students’ questions, and ask them questions that lead in a productive direction if they are stuck.
- If you discover that many people have the same question—or that someone has a misunderstanding that others might have—you might stop everyone and discuss a key idea with the entire class.
After students work on a problem during class, what are strategies to have them share their answers and their thinking?
- Ask for volunteers to share answers. Depending on the nature of the problem, student might provide answers verbally or by writing on the board. As a variant, for questions where a variety of answers are relevant, ask for at least three volunteers before anyone shares their ideas.
- Use online polling software for students to respond to a multiple-choice question anonymously.
- If students are working in groups, assign reporters ahead of time. For example, the person with the next birthday could be responsible for sharing their group’s work with the class.
- Cold call. To reduce student anxiety about cold calling, it can help to identify students who seem to have the correct answer as you were walking around the class and checking in on their progress solving the assigned problem. You may even want to warn the student ahead of time: "This is a great answer! Do you mind if I call on you when we come back together as a class?"
- Have students write an answer on a notecard that they turn in to you. If your goal is to understand whether students in general solved a problem correctly, the notecards could be submitted anonymously; if you wish to assess individual students’ work, you would want to ask students to put their names on their notecard.
- Use a jigsaw strategy, where you rearrange groups such that each new group is comprised of people who came from different initial groups and had solved different problems. Students now are responsible for teaching the other students in their new group how to solve their problem.
- Have a representative from each group explain their problem to the class.
- Have a representative from each group draw or write the answer on the board.
What happens if a student gives a wrong answer?
- Ask for their reasoning so that you can understand where they went wrong.
- Ask if anyone else has other ideas. You can also ask this sometimes when an answer is right.
- Cultivate an environment where it’s okay to be wrong. Emphasize that you are all learning together, and that you learn through making mistakes.
- Do make sure that you clarify what the correct answer is before moving on.
- Once the correct answer is given, go through some answer-checking techniques that can distinguish between correct and incorrect answers. This can help prepare students to verify their future work.
How can you make your classroom inclusive?
- The goal is that everyone is thinking, talking, and sharing their ideas, and that everyone feels valued and respected. Use a variety of teaching strategies (independent work and group work; allow students to talk to each other before they talk to the class). Create an environment where it is normal to struggle and make mistakes.
- See Kimberly Tanner’s article on strategies to promoste student engagement and cultivate classroom equity.
A few final notes…
- Make sure that you have worked all of the problems and also thought about alternative approaches to solving them.
- Board work matters. You should have a plan beforehand of what you will write on the board, where, when, what needs to be added, and what can be erased when. If students are going to write their answers on the board, you need to also have a plan for making sure that everyone gets to the correct answer. Students will copy what is on the board and use it as their notes for later study, so correct and logical information must be written there.
For more information...
Tipsheet: Problem Solving in STEM Sections
Tanner, K. D. (2013). Structure matters: twenty-one teaching strategies to promote student engagement and cultivate classroom equity . CBE-Life Sciences Education, 12(3), 322-331.
- Designing Your Course
- A Teaching Timeline: From Pre-Term Planning to the Final Exam
- The First Day of Class
- Group Agreements
- Classroom Debate
- Flipped Classrooms
- Leading Discussions
- Polling & Clickers
- Teaching with Cases
- Engaged Scholarship
- Devices in the Classroom
- Beyond the Classroom
- On Professionalism
- Getting Feedback
- Equitable & Inclusive Teaching
- Advising and Mentoring
- Teaching and Your Career
- Teaching Remotely
- Tools and Platforms
- The Science of Learning
- Bok Publications
- Other Resources Around Campus
7.5 Problem-Solving
Questions to Consider:
- How can determining the best approach to solve a problem help you generate solutions?
- Why do thinkers create multiple solutions to problems?
When we’re solving a problem, whether at work, school, or home, we are being asked to perform multiple, often complex, tasks. The most effective problem-solving approach includes some variation of the following steps:
- Determine the issue(s)
- Recognize other perspectives
- Think of multiple possible results
- Research and evaluate the possibilities
- Select the best result(s)
- Communicate your findings
- Establish logical action items based on your analysis
Determining the best approach to any given problem and generating more than one possible solution to the problem constitutes the complicated process of problem-solving. People who are good at these skills are highly marketable because many jobs consist of a series of problems that need to be solved for production, services, goods, and sales to continue smoothly. Think about what happens when a worker at your favorite coffee shop slips on a wet spot behind the counter, dropping several drinks she just prepared. One problem is the employee may be hurt, in need of attention, and probably embarrassed; another problem is that several customers do not have the drinks they were waiting for; and another problem is that stopping production of drinks (to care for the hurt worker, to clean up her spilled drinks, to make new drinks) causes the line at the cash register to back up. A good manager has to juggle all of these elements to resolve the situation as quickly and efficiently as possible. That resolution and return to standard operations doesn’t happen without a great deal of thinking: prioritizing needs, shifting other workers off one station onto another temporarily, and dealing with all the people involved, from the injured worker to the impatient patrons.
Determining the Best Approach
Faced with a problem-solving opportunity, you must assess the skills you will need to create solutions. Problem-solving can involve many different types of thinking. You may have to call on your creative, analytical, or critical thinking skills—or more frequently, a combination of several different types of thinking—to solve a problem satisfactorily. When you approach a situation, how can you decide what is the best type of thinking to employ? Sometimes the answer is obvious; if you are working a scientific challenge, you likely will use analytical thinking; if you are a design student considering the atmosphere of a home, you may need to tap into creative thinking skills; and if you are an early childhood education major outlining the logistics involved in establishing a summer day camp for children, you may need a combination of critical, analytical, and creative thinking to solve this challenge.
What sort of thinking do you imagine initially helped in the following scenarios? How would the other types of thinking come into resolving these problems?
- Analytical thinking
- Creative thinking
- Critical thinking
Write a one- to two-sentence rationale for why you chose the answers you did on the above survey.
Generating Multiple Solutions
Why do you think it is important to provide multiple solutions when you’re going through the steps to solve problems? Typically, you’ll end up only using one solution at a time, so why expend the extra energy to create alternatives? If you planned a wonderful trip to Europe and had all the sites you want to see planned out and reservations made, you would think that your problem-solving and organizational skills had quite a workout. But what if when you arrived, the country you’re visiting is enmeshed in a public transportation strike experts predict will last several weeks if not longer? A back-up plan would have helped you contemplate alternatives you could substitute for the original plans. You certainly cannot predict every possible contingency—sick children, weather delays, economic downfalls—but you can be prepared for unexpected issues to come up and adapt more easily if you plan for multiple solutions.
Write out at least two possible solutions to these dilemmas:
- Your significant other wants a birthday present—you have no cash.
- You have three exams scheduled on a day when you also need to work.
- Your car needs new tires, an oil change, and gas—you have no cash. (Is there a trend here?)
- You have to pass a running test for your physical education class, but you’re out of shape.
Providing more than one solution to a problem gives people options. You may not need several options, but having more than one solution will allow you to feel more in control and part of the problem-solving process.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/college-success/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Amy Baldwin
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: College Success
- Publication date: Mar 27, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/college-success/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/college-success/pages/7-5-problem-solving
© Sep 20, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Module 5: Thinking and Analysis
Problem-solving, learning objectives.
- Describe how critical thinking skills can be used to problem-solve
For most people, a typical day is filled with critical thinking and problem-solving challenges. In fact, critical thinking and problem-solving go hand-in-hand. They both refer to using knowledge, facts, and data to solve problems effectively. But with problem-solving, you are specifically identifying, selecting, and defending your solution. Below are some examples of using critical thinking to problem-solve:
- Your roommate was upset and said some unkind words to you, which put a crimp in the relationship. You try to see through the angry behaviors to determine how you might best support the roommate and help bring the relationship back to a comfortable spot.
- Your campus club has been languishing on account of lack of participation and funds. The new club president, though, is a marketing major and has identified some strategies to interest students in joining and supporting the club. Implementation is forthcoming.
- Your final art class project challenges you to conceptualize form in new ways. On the last day of class when students present their projects, you describe the techniques you used to fulfill the assignment. You explain why and how you selected that approach.
- Your math teacher sees that the class is not quite grasping a concept. She uses clever questioning to dispel anxiety and guide you to new understanding of the concept.
- You have a job interview for a position that you feel you are only partially qualified for, although you really want the job and you are excited about the prospects. You analyze how you will explain your skills and experiences in a way to show that you are a good match for the prospective employer.
- You are doing well in college, and most of your college and living expenses are covered. But there are some gaps between what you want and what you feel you can afford. You analyze your income, savings, and budget to better calculate what you will need to stay in college and maintain your desired level of spending.

Problem-Solving Activity
Now let’s practice problem solving by working through the following activity.
Contribute!
Improve this page Learn More
- College Success. Authored by : Linda Bruce. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- wocintech stock - 178. Authored by : WOCinTech Chat. Located at : https://flic.kr/p/FiGVWt . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike

Don’t Just Tell Students to Solve Problems. Teach Them How.
The positive impact of an innovative uc san diego problem-solving educational curriculum continues to grow.
- Daniel Kane - [email protected]
Published Date
Share this:, article content.
Problem solving is a critical skill for technical education and technical careers of all types. But what are best practices for teaching problem solving to high school and college students?
The University of California San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering is on the forefront of efforts to improve how problem solving is taught. This UC San Diego approach puts hands-on problem-identification and problem-solving techniques front and center. Over 1,500 students across the San Diego region have already benefited over the last three years from this program. In the 2023-2024 academic year, approximately 1,000 upper-level high school students will be taking the problem solving course in four different school districts in the San Diego region. Based on the positive results with college students, as well as high school juniors and seniors in the San Diego region, the project is getting attention from educators across the state of California, and around the nation and the world.
{/exp:typographee}
In Summer 2023, th e 27 community college students who took the unique problem-solving course developed at the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering thrived, according to Alex Phan PhD, the Executive Director of Student Success at the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering. Phan oversees the project.
Over the course of three weeks, these students from Southwestern College and San Diego City College poured their enthusiasm into problem solving through hands-on team engineering challenges. The students brimmed with positive energy as they worked together.
What was noticeably absent from this laboratory classroom: frustration.
“In school, we often tell students to brainstorm, but they don’t often know where to start. This curriculum gives students direct strategies for brainstorming, for identifying problems, for solving problems,” sai d Jennifer Ogo, a teacher from Kearny High School who taught the problem-solving course in summer 2023 at UC San Diego. Ogo was part of group of educators who took the course themselves last summer.
The curriculum has been created, refined and administered over the last three years through a collaboration between the UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering and the UC San Diego Division of Extended Studies. The project kicked off in 2020 with a generous gift from a local philanthropist.
Not getting stuck
One of the overarching goals of this project is to teach both problem-identification and problem-solving skills that help students avoid getting stuck during the learning process. Stuck feelings lead to frustration – and when it’s a Science, Technology, Engineering and Math (STEM) project, that frustration can lead students to feel they don’t belong in a STEM major or a STEM career. Instead, the UC San Diego curriculum is designed to give students the tools that lead to reactions like “this class is hard, but I know I can do this!” – as Ogo, a celebrated high school biomedical sciences and technology teacher, put it.
Three years into the curriculum development effort, the light-hearted energy of the students combined with their intense focus points to success. On the last day of the class, Mourad Mjahed PhD, Director of the MESA Program at Southwestern College’s School of Mathematics, Science and Engineering came to UC San Diego to see the final project presentations made by his 22 MESA students.
“Industry is looking for students who have learned from their failures and who have worked outside of their comfort zones,” said Mjahed. The UC San Diego problem-solving curriculum, Mjahed noted, is an opportunity for students to build the skills and the confidence to learn from their failures and to work outside their comfort zone. “And from there, they see pathways to real careers,” he said.
What does it mean to explicitly teach problem solving?
This approach to teaching problem solving includes a significant focus on learning to identify the problem that actually needs to be solved, in order to avoid solving the wrong problem. The curriculum is organized so that each day is a complete experience. It begins with the teacher introducing the problem-identification or problem-solving strategy of the day. The teacher then presents case studies of that particular strategy in action. Next, the students get introduced to the day’s challenge project. Working in teams, the students compete to win the challenge while integrating the day’s technique. Finally, the class reconvenes to reflect. They discuss what worked and didn't work with their designs as well as how they could have used the day’s problem-identification or problem-solving technique more effectively.
The challenges are designed to be engaging – and over three years, they have been refined to be even more engaging. But the student engagement is about much more than being entertained. Many of the students recognize early on that the problem-identification and problem-solving skills they are learning can be applied not just in the classroom, but in other classes and in life in general.
Gabriel from Southwestern College is one of the students who saw benefits outside the classroom almost immediately. In addition to taking the UC San Diego problem-solving course, Gabriel was concurrently enrolled in an online computer science programming class. He said he immediately started applying the UC San Diego problem-identification and troubleshooting strategies to his coding assignments.
Gabriel noted that he was given a coding-specific troubleshooting strategy in the computer science course, but the more general problem-identification strategies from the UC San Diego class had been extremely helpful. It’s critical to “find the right problem so you can get the right solution. The strategies here,” he said, “they work everywhere.”
Phan echoed this sentiment. “We believe this curriculum can prepare students for the technical workforce. It can prepare students to be impactful for any career path.”
The goal is to be able to offer the course in community colleges for course credit that transfers to the UC, and to possibly offer a version of the course to incoming students at UC San Diego.
As the team continues to work towards integrating the curriculum in both standardized high school courses such as physics, and incorporating the content as a part of the general education curriculum at UC San Diego, the project is expected to impact thousands more students across San Diego annually.
Portrait of the Problem-Solving Curriculum
On a sunny Wednesday in July 2023, an experiential-learning classroom was full of San Diego community college students. They were about half-way through the three-week problem-solving course at UC San Diego, held in the campus’ EnVision Arts and Engineering Maker Studio. On this day, the students were challenged to build a contraption that would propel at least six ping pong balls along a kite string spanning the laboratory. The only propulsive force they could rely on was the air shooting out of a party balloon.
A team of three students from Southwestern College – Valeria, Melissa and Alondra – took an early lead in the classroom competition. They were the first to use a plastic bag instead of disposable cups to hold the ping pong balls. Using a bag, their design got more than half-way to the finish line – better than any other team at the time – but there was more work to do.
As the trio considered what design changes to make next, they returned to the problem-solving theme of the day: unintended consequences. Earlier in the day, all the students had been challenged to consider unintended consequences and ask questions like: When you design to reduce friction, what happens? Do new problems emerge? Did other things improve that you hadn’t anticipated?
Other groups soon followed Valeria, Melissa and Alondra’s lead and began iterating on their own plastic-bag solutions to the day’s challenge. New unintended consequences popped up everywhere. Switching from cups to a bag, for example, reduced friction but sometimes increased wind drag.
Over the course of several iterations, Valeria, Melissa and Alondra made their bag smaller, blew their balloon up bigger, and switched to a different kind of tape to get a better connection with the plastic straw that slid along the kite string, carrying the ping pong balls.
One of the groups on the other side of the room watched the emergence of the plastic-bag solution with great interest.
“We tried everything, then we saw a team using a bag,” said Alexander, a student from City College. His team adopted the plastic-bag strategy as well, and iterated on it like everyone else. They also chose to blow up their balloon with a hand pump after the balloon was already attached to the bag filled with ping pong balls – which was unique.
“I don’t want to be trying to put the balloon in place when it's about to explode,” Alexander explained.
Asked about whether the structured problem solving approaches were useful, Alexander’s teammate Brianna, who is a Southwestern College student, talked about how the problem-solving tools have helped her get over mental blocks. “Sometimes we make the most ridiculous things work,” she said. “It’s a pretty fun class for sure.”
Yoshadara, a City College student who is the third member of this team, described some of the problem solving techniques this way: “It’s about letting yourself be a little absurd.”
Alexander jumped back into the conversation. “The value is in the abstraction. As students, we learn to look at the problem solving that worked and then abstract out the problem solving strategy that can then be applied to other challenges. That’s what mathematicians do all the time,” he said, adding that he is already thinking about how he can apply the process of looking at unintended consequences to improve both how he plays chess and how he goes about solving math problems.
Looking ahead, the goal is to empower as many students as possible in the San Diego area and beyond to learn to problem solve more enjoyably. It’s a concrete way to give students tools that could encourage them to thrive in the growing number of technical careers that require sharp problem-solving skills, whether or not they require a four-year degree.
You May Also Like
Servicenow developer david loo returns to his roots to accept cse’s distinguished alumni award, take 10 with a triton: carrie metzgar is chasing stars, medical innovator: farah sheikh, uc san diego receives $6.7m to develop whole-body inflammation imaging, stay in the know.
Keep up with all the latest from UC San Diego. Subscribe to the newsletter today.
You have been successfully subscribed to the UC San Diego Today Newsletter.
Campus & Community
Arts & culture, visual storytelling.
- Media Resources & Contacts
Signup to get the latest UC San Diego newsletters delivered to your inbox.
Award-winning publication highlighting the distinction, prestige and global impact of UC San Diego.
Popular Searches: Covid-19 Ukraine Campus & Community Arts & Culture Voices
Center for Teaching
Teaching problem solving.
Print Version
Tips and Techniques
Expert vs. novice problem solvers, communicate.
- Have students identify specific problems, difficulties, or confusions . Don’t waste time working through problems that students already understand.
- If students are unable to articulate their concerns, determine where they are having trouble by asking them to identify the specific concepts or principles associated with the problem.
- In a one-on-one tutoring session, ask the student to work his/her problem out loud . This slows down the thinking process, making it more accurate and allowing you to access understanding.
- When working with larger groups you can ask students to provide a written “two-column solution.” Have students write up their solution to a problem by putting all their calculations in one column and all of their reasoning (in complete sentences) in the other column. This helps them to think critically about their own problem solving and helps you to more easily identify where they may be having problems. Two-Column Solution (Math) Two-Column Solution (Physics)
Encourage Independence
- Model the problem solving process rather than just giving students the answer. As you work through the problem, consider how a novice might struggle with the concepts and make your thinking clear
- Have students work through problems on their own. Ask directing questions or give helpful suggestions, but provide only minimal assistance and only when needed to overcome obstacles.
- Don’t fear group work ! Students can frequently help each other, and talking about a problem helps them think more critically about the steps needed to solve the problem. Additionally, group work helps students realize that problems often have multiple solution strategies, some that might be more effective than others
Be sensitive
- Frequently, when working problems, students are unsure of themselves. This lack of confidence may hamper their learning. It is important to recognize this when students come to us for help, and to give each student some feeling of mastery. Do this by providing positive reinforcement to let students know when they have mastered a new concept or skill.
Encourage Thoroughness and Patience
- Try to communicate that the process is more important than the answer so that the student learns that it is OK to not have an instant solution. This is learned through your acceptance of his/her pace of doing things, through your refusal to let anxiety pressure you into giving the right answer, and through your example of problem solving through a step-by step process.
Experts (teachers) in a particular field are often so fluent in solving problems from that field that they can find it difficult to articulate the problem solving principles and strategies they use to novices (students) in their field because these principles and strategies are second nature to the expert. To teach students problem solving skills, a teacher should be aware of principles and strategies of good problem solving in his or her discipline .
The mathematician George Polya captured the problem solving principles and strategies he used in his discipline in the book How to Solve It: A New Aspect of Mathematical Method (Princeton University Press, 1957). The book includes a summary of Polya’s problem solving heuristic as well as advice on the teaching of problem solving.

Teaching Guides
- Online Course Development Resources
- Principles & Frameworks
- Pedagogies & Strategies
- Reflecting & Assessing
- Challenges & Opportunities
- Populations & Contexts
Quick Links
- Services for Departments and Schools
- Examples of Online Instructional Modules

4.6 Problem-Solving
Questions to consider:.
- How can determining the best approach to solve a problem help you generate solutions?
- Why do thinkers create multiple solutions to problems?
When we’re solving a problem, whether at work, school, or home, we are being asked to perform multiple, often complex, tasks. The most effective problem-solving approach includes some variation of the following steps:
- Determine the issue(s)
- Recognize other perspectives
- Think of multiple possible results
- Research and evaluate the possibilities
- Select the best result(s)
- Communicate your findings
- Establish logical action items based on your analysis
Determining the best approach to any given problem and generating more than one possible solution to the problem constitutes the complicated process of problem-solving. People who are good at these skills are highly marketable because many jobs consist of a series of problems that need to be solved for production, services, goods, and sales to continue smoothly. Think about what happens when a worker at your favorite coffee shop slips on a wet spot behind the counter, dropping several drinks she just prepared. One problem is the employee may be hurt, in need of attention, and probably embarrassed; another problem is that several customers do not have the drinks they were waiting for; and another problem is that stopping production of drinks (to care for the hurt worker, to clean up her spilled drinks, to make new drinks) causes the line at the cash register to back up. A good manager has to juggle all of these elements to resolve the situation as quickly and efficiently as possible. That resolution and return to standard operations doesn’t happen without a great deal of thinking: prioritizing needs, shifting other workers off one station onto another temporarily, and dealing with all the people involved, from the injured worker to the impatient patrons.
Determining the Best Approach
Faced with a problem-solving opportunity, you must assess the skills you will need to create solutions. Problem-solving can involve many different types of thinking. You may have to call on your creative, analytical, or critical thinking skills—or more frequently, a combination of several different types of thinking—to solve a problem satisfactorily. When you approach a situation, how can you decide what is the best type of thinking to employ? Sometimes the answer is obvious; if you are working a scientific challenge, you likely will use analytical thinking; if you are a design student considering the atmosphere of a home, you may need to tap into creative thinking skills; and if you are an early childhood education major outlining the logistics involved in establishing a summer day camp for children, you may need a combination of critical, analytical, and creative thinking to solve this challenge.
What sort of thinking do you imagine initially helped in the following scenarios? How would the other types of thinking come into resolving these problems?
- Analytical thinking
- Creative thinking
- Critical thinking
Write a one- to two-sentence rationale for why you chose the answers you did on the above survey.
Generating Multiple Solutions
Why do you think it is important to provide multiple solutions when you’re going through the steps to solve problems? Typically, you’ll end up only using one solution at a time, so why expend the extra energy to create alternatives? If you planned a wonderful trip to Europe and had all the sites you want to see planned out and reservations made, you would think that your problem-solving and organizational skills had quite a workout. But what if when you arrived, the country you’re visiting is enmeshed in a public transportation strike experts predict will last several weeks if not longer? A back-up plan would have helped you contemplate alternatives you could substitute for the original plans. You certainly cannot predict every possible contingency—sick children, weather delays, economic downfalls—but you can be prepared for unexpected issues to come up and adapt more easily if you plan for multiple solutions.
Write out at least two possible solutions to these dilemmas:
- Your significant other wants a birthday present—you have no cash.
- You have three exams scheduled on a day when you also need to work.
- Your car needs new tires, an oil change, and gas—you have no cash. (Is there a trend here?)
- You have to pass a running test for your physical education class, but you’re out of shape.
Providing more than one solution to a problem gives people options. You may not need several options, but having more than one solution will allow you to feel more in control and part of the problem-solving process.
Source: OpenStax College Success is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution License v4.0
Strategies for First Year College Success Copyright © by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Become a great problem solver
Learn by doing with interactive problem solving that’s effective and fun. master concepts in 15 minutes a day., data analysis, computer science, programming & ai, science & engineering, join over 10 million people learning on brilliant, over 50,000 5-star reviews on ios app store and google play.

Master concepts in 15 minutes a day
Whether you’re a complete beginner or ready to dive into machine learning and beyond, Brilliant makes it easy to level up fast with fun, bite-sized lessons.
Effective, hands-on learning
Visual, interactive lessons make concepts feel intuitive — so even complex ideas just click. Our real-time feedback and simple explanations make learning efficient.
Learn at your level
Students and professionals alike can hone dormant skills or learn new ones. Progress through lessons and challenges tailored to your level. Designed for ages 13 to 113.
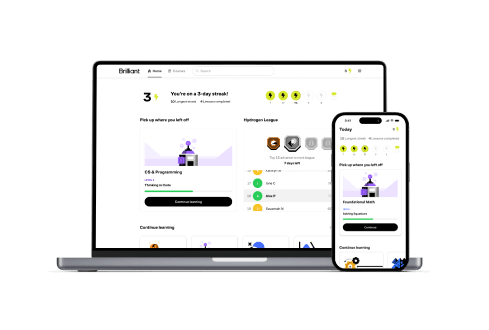
Guided bite-sized lessons
We make it easy to stay on track, see your progress, and build your problem solving skills one concept at a time.
Stay motivated
Form a real learning habit with fun content that’s always well-paced, game-like progress tracking, and friendly reminders.
Guided courses for every journey
All of our courses are crafted by award-winning teachers, researchers, and professionals from MIT, Caltech, Duke, Microsoft, Google, and more.
- Foundational Math
- Software Development
- Foundational Logic
- Data Science
- High School Math
- Engineering
- Statistics and Finance
Courses in Foundational Math
- Solving Equations
- Measurement
- Mathematical Fundamentals
- Reasoning with Algebra
- Functions and Quadratics

10k+ Ratings

60k+ Ratings
We use cookies to improve your experience on Brilliant. Learn more about our cookie policy and settings .
- Apply Apply
- Request Information Get Info
- Visit NLC Visit Us
- Our College
- Strategic Planning
- College Offices
- Request Information

Northeast Lakeview College is a public community college that is focused on student success through the offering of Associate degrees and continuing education, promoting engagement in civic activities and organizations, and encouraging participation in cultural and enrichment programs.
- Cyber Defense
- Find Your Program
- Online Learning
- Instructional Innovation Center
- Academic Calendar
- Academic Resources
- Tutoring Services
- High School Programs
- Mexican American Studies
- Honors Academy
- Workforce Training Network

Northeast Lakeview College provides a collaborative, supportive academic community to help you achieve your learning goals.
- Alamo Anytime: Enrollment Help Videos
- Bacterial Meningitis Vaccinations
- NLC Advantage Program
- How to Apply
- Paying for College
- Assessment Center
- Outreach and Recruitment
- Registration & Payment Deadlines

Admissions & Aid
The Northeast Lakeview College Admissions and Records Department is here to assist you with the enrollment process. We have an open door admissions policy to ensure that every person has the opportunity to get a college education.
- Current Students
- Campus Life
- Students with Children

Experience NLC
A center for educational excellence, Northeast Lakeview College combines innovative classroom instruction with hands-on experience to provide exemplary enrichment opportunities. As the newest community college in the nation, we provide a variety of degree plans, flexible course schedules, and a small, student-focused environment.
- Public Relations
- Publications
- Congratulations Graduates 2019
- Congratulations Graduates 2022
- Congratulations Graduates 2023
- Special Events
- COVID-19 Information & Resources

News and Events
The News and Events of NLC

Northeast Lakeview College
A center for educational excellence, Northeast Lakeview College combines innovative classroom instruction with hands-on experience to provide exemplary enrichment opportunities.
- Campus Maps
- NLC Calendar
- Tools For School
- Communication
- Reading Comprehension
Problem Solving
- Self-Efficacy
- Time Management
Problem solving is central to success in any college course. Throughout their academic careers and their lives, students will encounter problems that need to be solved. These problems may range from the personal (how to pay for college) to the interpersonal (how to work with a partner on a project) to the occupational (how to solve an issue relating to school or work). Although every course requires students to engage in problem-solving, mathematics is a course that students readily associate with the task—the questions written on a whiteboard or on a page are more often than not math problems that need to be solved.
Although problem solving is a task that students engage in throughout their academic careers, they frequently have little experience in the metacognitive process of problem solving. Traditionally, students are taught subject-specific tools to apply to a subject-specific problem (example: how to add or how to use a dictionary) rather than problem solving strategies. This results in students who do not understand the process behind problem solving and has a direct impact on student success. Research indicates students who are successful problem solvers are those who are taught how to use and develop metacognitive problem-solving techniques and who engage in the deliberate and reflective process of problem solving (Mason et al.) Problem solving is a multi-step process that students must be taught and must have practice engaging in. Although multiple problem-solving processes exist, some more complex than others, most of them include variations of Polya’s four-stepped approach:
- understanding--What is the problem? What is the purpose? What is known/ unknown?
- planning--How does this connect to prior knowledge? Where are there gaps in knowledge? How to proceed?
- solving--How to carry out the plan? Where to stop and check progress along the way?
- reflection--Is the solution correct? What have I learned?
Students who are not college-ready in math struggle with problem-solving as a process. Often, they try to answer problems by using subject-specific tools like formulas or equations without stopping to understand the problem and engage in problem-solving. This results in students who frequently fail to arrive at a solution and end feeling defeated and demoralized about their success in math (Yuan 99). Students who are not college-ready in math benefit from being taught stepped problem-solving techniques and strategies, practicing those steps, and reflecting on their learning. Engaging in this process results in students who are able to make connections and understand the material that they otherwise would not (Yuan 99-104). Students in Soar Towards Success will be taught problem-solving strategies and engage in this metacognitive process. This practice will benefit students in all their courses and will help them develop the necessary readiness skills for their college-level math courses.
SELECT COUNTRY
- Overview of OWIS Singapore
- Mission, Vision and Values
- Creating Global Citizens
- Parent Partnerships
- Global Schools Foundation (GSF)
- Academic & Examination Board (AEB)
- Awards & Accreditations
- Admissions Overview
- Apply Online
- Book a Tour
- Application Process
- School Fees
- Scholarship
- Admissions Events and Webinars
- Entry Requirements
- Regulations
- Learning & Curricula at OWIS
- IB Primary Years Programme (Ages 3 to 11)
- Modified Cambridge (Ages 12 to 14)
- Cambridge IGCSE (Ages 15 to 16)
- IB Diploma Programme (Ages 17 to 18)
- Chinese-English Bilingual Programme (Ages 7 to 11)
- Co-scholastic Learning Programmes
- English as an Additional Language (EAL) Programme
- After-School Programme (CCAs)
- Overview of OWIS Nanyang
- Welcome Message
- Early Childhood
- Primary School
- Secondary School
- Learning Environment
- Academic Results & University Offers
- Pastoral Care & Student Well-Being
- School Calendar
- Join Our Open House
- Overview of OWIS Suntec
- Overview of OWIS Digital Campus
- Blogs & Insights
- School Stories
- In the Media
- E-books & Downloads
- Public vs Private School
- Relocating to Singapore
OWIS SINGAPORE
Strategies to develop problem-solving skills in students.

- November 14, 2023

Students need the freedom to brainstorm, develop solutions and make mistakes — this is truly the only way to prepare them for life outside the classroom. When students are immersed in a learning environment that only offers them step-by-step guides and encourages them to focus solely on memorisation, they are not gaining the skills necessary to help them navigate in the complex, interconnected environment of the real world.
Choosing a school that emphasises the importance of future-focussed skills will ensure your child has the abilities they need to survive and thrive anywhere in the world. What are future-focussed skills? Students who are prepared for the future need to possess highly developed communication skills, self-management skills, research skills, thinking skills, social skills and problem-solving skills. In this blog, I would like to focus on problem-solving skills.
What Are Problem-Solving Skills?
The Forage defines problem-solving skills as those that allow an individual to identify a problem, come up with solutions, analyse the options and collaborate to find the best solution for the issue.
Importance of Problem-Solving in the Classroom Setting
Learning how to solve problems effectively and positively is a crucial part of child development. When children are allowed to solve problems in a classroom setting, they can test those skills in a safe and nurturing environment. Generally, when they face age-appropriate issues, they can begin building those skills in a healthy and positive manner.
Without exposure to challenging situations and scenarios, children will not be equipped with the foundational problem-solving skills needed to tackle complex issues in the real world. Experts predict that problem-solving skills will eventually be more sought after in job applicants than hard skills related to that specific profession. Students must be given opportunities in school to resolve conflicts, address complex problems and come up with their own solutions in order to develop these skills.
Benefits of Problem-Solving Skills for Students

Learning how to solve problems offers students many advantages, such as:
Improving Academic Results
When students have a well-developed set of problem-solving skills, they are often better critical and analytical thinkers as well. They are able to effectively use these 21st-century skills when completing their coursework, allowing them to become more successful in all academic areas. By prioritising problem-solving strategies in the classroom, teachers often find that academic performance improves.
Developing Confidence
Giving students the freedom to solve problems and create their own solutions is essentially permitting them to make their own choices. This sense of independence — and the natural resilience that comes with it — allows students to become confident learners who aren’t intimidated by new or challenging situations. Ultimately, this prepares them to take on more complex challenges in the future, both on a professional and social level.
Preparing Students for Real-World Challenges
The challenges we are facing today are only growing more complex, and by the time students have graduated, they are going to be facing issues that we may not even have imagined. By arming them with real-world problem-solving experience, they will not feel intimidated or stifled by those challenges; they will be excited and ready to address them. They will know how to discuss their ideas with others, respect various perspectives and collaborate to develop a solution that best benefits everyone involved.
The Best Problem-Solving Strategies for Students

No single approach or strategy will instil a set of problem-solving skills in students. Every child is different, so educators should rely on a variety of strategies to develop this core competency in their students. It is best if these skills are developed naturally.
These are some of the best strategies to support students problem-solving skills:
Project-Based Learning
By providing students with project-based learning experiences and allowing plenty of time for discussion, educators can watch students put their problem-solving skills into action inside their classrooms. This strategy is one of the most effective ways to fine-tune problem-solving skills in students. During project-based learning, teachers may take notes on how the students approach a problem and then offer feedback to students for future development. Teachers can address their observations of interactions during project-based learning at the group level or they can work with students on an individual basis to help them become more effective problem-solvers.
Encourage Discussion and Collaboration in the Classroom Setting
Another strategy to encourage the development of problem-solving skills in students is to allow for plenty of discussion and collaboration in the classroom setting. When students interact with one another, they are naturally developing problem solving skills. Rather than the teacher delivering information and requiring the students to passively receive information, students can share thoughts and ideas with one another. Getting students to generate their own discussion and communication requires thinking skills.
Utilising an Inquiry-Based approach to Learning
Students should be presented with situations in which their curiosity is sparked and they are motivated to inquire further. Teachers should ask open-ended questions and encourage students to develop responses which require problem-solving. By providing students with complex questions for which a variety of answers may be correct, teachers get students to consider different perspectives and deal with potential disagreement, which requires problem-solving skills to resolve.
Model Appropriate Problem-Solving Skills
One of the simplest ways to instil effective problem-solving skills in students is to model appropriate and respectful strategies and behaviour when resolving a conflict or addressing an issue. Teachers can showcase their problem-solving skills by:
- Identifying a problem when they come across one for the class to see
- Brainstorming possible solutions with students
- Collaborating with students to decide on the best solution
- Testing that solution and examining the results with the students
- Adapting as necessary to improve results or achieve the desired goal
Prioritise Student Agency in Learning
Recent research shows that self-directed learning is one of the most effective ways to nurture 21st-century competency development in young learners. Learning experiences that encourage student agency often require problem-solving skills. When creativity and innovation are needed, students often encounter unexpected problems along the way that must be solved. Through self-directed learning, students experience challenges in a natural situation and can fine-tune their problem-solving skills along the way. Self-directed learning provides them with a foundation in problem-solving that they can build upon in the future, allowing them to eventually develop more advanced and impactful problem-solving skills for real life.
21st-Century Skill Development at OWIS Singapore
Problem-solving has been identified as one of the core competencies that young learners must develop to be prepared to meet the dynamic needs of a global environment. At OWIS Singapore, we have implemented an inquiry-driven, skills-based curriculum that allows students to organically develop critical future-ready skills — including problem-solving. Our hands-on approach to education enables students to collaborate, explore, innovate, face-challenges, make mistakes and adapt as necessary. As such, they learn problem-solving skills in an authentic manner.
For more information about 21st-century skill development, schedule a campus tour today.
About Author
David swanson, latest blogs.

- April 8, 2024
Transforming Experiential Learning Through Skill Studios at OWIS Digital Campus

- March 26, 2024
Beyond the Classroom: Exploring IBDP’s Impact on College and Career Readiness

- March 12, 2024

Unpacking the IB PYP: A Comprehensive Guide for Parents

- March 11, 2024
Embarking on a Journey Through the Art Spaces at OWIS Digital Campus*

- March 4, 2024
Recommended Storybooks for Preschoolers

- February 27, 2024
Transitioning From the American Curriculum to an IB School in Singapore
Related blog posts.

- Holistic development

- Culture & Values
- Testimonial
Fostering Confidence in Education: The Dynamic Blend of Diversity and Academic Excellence at OWIS Digital Campus*
- December 18, 2023

OWIS Teachers Explain: How we make language learning interesting in the Chinese-English Bilingual Programme
- April 19, 2022
nanyang Campus
- +65 6914 6700
- [email protected]
- 21 Jurong West Street 81, Singapore 649075
- +65-83183027
Digital Campus
- #01-02, Global Campus Village, 27 Punggol Field Walk, Singapore 828649
Suntec Campus
- 1 Raffles Blvd, Singapore 039593
OWIS Nanyang is accredited for the IB PYP, Cambridge IGCSE and IB DP. OWIS Suntec is a Candidate School** for the IB PYP. This school is pursuing authorisation as an IB World School. These are schools that share a common philosophy—a commitment to high quality, challenging, international education that OWIS believes is important for our students.**Only schools authorised by the IB Organization can offer any of its four academic programmes: the Primary Years Programme (PYP), the Middle Years Programme (MYP), the Diploma Programme, or the Career-related Programme (CP). Candidate status gives no guarantee that authorisation will be granted. For further information about the IB and its programmes, visit www.ibo.org CPE Registration Number: 200800495N | Validity Period: 24 February 2023 to 23 February 2027.

Quick Links:
Virtual and in-person Campus Tours Available
Internet Explorer is no longer supported
Please upgrade to Microsoft Edge , Google Chrome , or Firefox .
Lo sentimos, la página que usted busca no se ha podido encontrar. Puede intentar su búsqueda de nuevo o visitar la lista de temas populares.
Get this as a PDF
Enter email to download and get news and resources in your inbox.
Share this on social
Preparing for college emotionally, not just academically.
Problem-solving skills can help students keep from being overwhelmed
Writer: Juliann Garey
Clinical Experts: Lindsey Giller, PsyD , Lindsay Macchia, PhD
What You'll Learn
- Why is the transition to college hard for some students?
- What skills can college students use to make a successful transition?
- What can parents do to help kids maintain good mental health in college?
The transition to college can be hard on kids’ mental health. Teenagers living away from home for the first time may experience academic stress while also trying to make new friends, build routines, and stay physically healthy. All these changes at once can be overwhelming for college kids.
Parents can help kids prepare for these emotional challenges before college starts. First, try to avoid solving problems for your teen. Instead, let them know that you empathize and you’re there for support. The goal is to let them know that it’s okay to feel upset, and that you believe in their ability to get through hard emotions and solve their own problems.
Practicing mindfulness together at home can also help. Mindfulness is about observing how you’re feeling in the moment without judging yourself. It can help teens learn to reduce the intensity of their emotions. You can also encourage your child to think ahead about what they’ll do when they run into challenges in college. What kinds of issues could come up? Who would they call if they were upset?
Finally, self-care is a big part managing difficult emotions. Help kids build a toolkit of activities they know make them feel better. It might be deep breathing, going on a run, or listening to music. College is often a hard place to maintain healthy habits, so encourage your teenager to build these habits ahead of time. Getting enough sleep, eating nutritious food, and getting regular exercise are all important ways for college students to stay mentally healthy.
Tuition isn’t the only thing that’s relentlessly on the rise on American college campuses. Multiple studies show a significant increase in college mental health problems in the last few years, and campus counseling services report being overwhelmed with students seeking help .
Why so much emotional distress, especially during the first year away from home? Everything from academic pressure to over-protective parenting to excessive engagement in social media has been blamed for the spike in anxiety and depression .
What’s clear is that adolescents making the transition from high school to college need not only academic skills to ace the classwork, and time-management skills to stay afloat, but emotional problem-solving skills to handle the challenges. As parents, we can’t shadow them in the freshman dorm, but we can help supply them, before they leave home, with a toolbox of skills and habits to use when they become stressed or overwhelmed.
“What we’re seeing is a lot of kids are getting through middle school and high school doing okay, but they go off to college and it’s too much,” says Lindsey Giller , PsyD, a clinical psychologist in the Mood Disorders Center at the Child Mind Institute. Some kids are just overwhelmed by organization and time management issues, increased academic pressure and managing their lives independently — the emotional roller-coaster of a new social universe.
And if they’re away from home, they don’t have the support network they’ve been used to. This is especially true of kids who find themselves on a large campus where it’s difficult to get to know their professors and harder to find their social niche.
“Often the result,” says Lindsay Macchia , PhD, a clinical psychologist at the Child Mind Institute, “is what’s called emotional dysregulation — their mood is all over the charts. What we want to figure out is what skills are going to help them re-regulate and take better control over their mood, so it doesn’t get in the way of their friendships, their academics, or typical day-to-day life.”
College mental health skills
So how do we prepare our kids for the rigors and life challenges that college brings?
One increasingly popular answer is teaching them skills derived from Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT). DBT was originally designed for adults with borderline personality disorder, who experience extreme emotional instability. But DBT skills are, more and more, being used successfully to treat almost any kind of emotional dysregulation.
While traditional DBT is an intensive, highly structured program, Drs. Giller and Macchia note that basic DBT skills can be adapted to help prepare incoming college students to better handle the challenges of college.
What would that look like? “Near the end of high school,” explains Dr. Macchia, “parents can shift the family dynamic to encourage kids to be more independent, and practice emotional regulation and problem-solving skills for themselves.” Here’s how you can help.
Don’t try to ‘fix’ every problem
Many of us have grown used to jumping in at the first sign that our child is distressed, to come to the rescue.
“The first thing parents should do is stop trying to fix things,” says David Romano, a psychotherapist and member of Active Minds , an advocacy organization that works to encourage open discussion of mental health on college campuses, to avoid suicides. Romano, who sees a lot of college-bound adolescents, says that what teens need to hear, especially when they’re feeling depressed, anxious or overwhelmed, is that “It’s okay not to feel okay.” The goal is to validate their feelings, but not solve their problems.
When parents notice that their teen is in distress, Dr. Giller suggests responses like:
- “I see you’re really struggling right now.”
- “I’m guessing that this is really hard for you.”
- “I see that thinking about this test tomorrow is making you really anxious.”
And then, let them deal with the problem knowing you’re there as a support net. “That can build a bridge so the teen can start thinking on their own, using their own problem-solving skills, while still feeling listened to and heard by their parent and supported in that way,” says Dr. Giller.
Practice mindfulness with your teen
Mindfulness , the ability to be present in the moment and to be nonjudgmental towards yourself and others, is at the core of DBT. It’s learning to live in the present moment — not project into the future — without judging your thoughts and emotions. An example of a nonjudgmental reframe to reduce emotional intensity could be to think, “Wow, I didn’t do as well as I wanted on that exam,” rather than “I suck, I can’t make it in this school” explains Dr. Giller.
Sometimes mindfulness means just stopping to notice how you’re feeling internally, noticing what’s around you and even taking some deep breaths before deciding how best to handle a difficult situation.
Help your child establish good self-care
Self-care is often the first thing sacrificed in the first year away from home. Self-care involves “making sure to take care of your body in order to promote the best mood you can,” Dr. Macchia says. “And so it includes making sure your sleep hygiene is as consistent as possible, that you’re not staying up all night, you’re limiting drugs and alcohol , getting regular exercise and healthy eating . All of it is an attempt to keep your mood as regulated as possible.”
Sleep is one of the first things stressed college students sacrifice, so helping kids establish and practice good sleep habits before they leave home is crucial. It’s important for college-bound students to understand that sleep deprivation can not only make academic functioning more difficult, it can also make it harder for them to exercise self-control, make good decisions and regulate their mood.
Eating habits also affect mood: the college years are when the majority of eating disorders develop , as overwhelmed students attempt to gain a sense of control by restricting their diet. Restricted eating, in turn, undermines judgment and contributes to depression.
“Taking care of themselves physically in order to take care of their mental health is one key to reducing the likelihood that unwanted emotions will flare in the first place, or become so intense they’re overwhelming,” says Dr. Giller.
Work on planning and ‘coping ahead’
A lot of distress can be avoided by helping kids learn to plan ahead. That means not only thinking through how they’re going to get a big assignment done, and thinking carefully about how they use their time, but planning how they’ll handle challenging situations. Hana, 17, is about to go off to college next year. She’s done two rounds of traditional DBT and she says it’s done a lot to prepare her for leaving home and college life. One of the key skills she is using to prepare is called “coping ahead.”
“It’s essentially just preparing yourself to be equipped to emotionally handle a certain experience,” she explains. That could involve practicing what you would say in different potentially triggering scenarios. Who would you call if you were feeling depressed? What would you do if you got a bad grade?
“More than anything I think people don’t like being blindsided,” she said, “and this is a way to sort of expect the worst but also hope for the best. I’m expecting the worst, which is why I’m coping ahead, but I’m hoping for the best, so there’s some optimism there.”
Develop strategies for self-soothing
Even with a good foundation in practicing time management skills and “coping ahead,” there are going to be times when your teen will feel overwhelmed. But, borrowing from DBT skills, you and your child can make a plan for what to do when difficult emotions are threatening to take over. “They can come up with a written plan that includes weighing the pros and cons and thinking through consequences,” says Dr. Giller. “And then they can take a picture of it on their phone and have easy access to it when they anticipate or experience something that may be challenging.”
The goal is a toolbox of things to try when they are feeling highly emotional or overwhelmed — things that will make them feel better instead of spinning out of control. “It’s having some things that people can really use when they feel they’re on overload,” Dr. Giller says. It could include specific pieces of music, going for a run, or things to touch or smell that have a calming effect.
No formal training or individual therapy is necessary for establishing good habits and coping skills, but when a parent and teen work in tandem, they can establish a strong foundation for starting college. And starting early — before there’s a difficult situation to deal with — is a good idea. As Romano says, “If you don’t use the skills you lose them, so it’s about practicing them all the time. It’s about making and maintaining mental health.”
Was this article helpful?
Explore popular topics, subscribe to our newsletters.
" * " indicates required fields

Don’t Miss Out
Sign up for more articles and parenting tips direct to your inbox.

10 Problem Solving Activities for College Students
Problems are not stop signs, they are guidelines – Robert H. Schuller.
Rightly quoted by Schuller, every problem comes with a solution that needs exploration through creative thinking and analysis. Problems appear in different sizes and nature and any one solution does not apply to all of them. Hence, it is essential to acquire and practice the necessary problem-solving skills that help students deal with various challenges at different stages and areas of life.
Problems cannot be avoided however, we can always equip young adults with the necessary skills to tackle them. As college students start their journey of making new friends, building networks, and understanding a fresh world of opportunities, they are likely to come across various difficulties. For example, some college-going students might find it hard to communicate with their fellow mates while others may find it awkward to offer answers to a question asked by teachers.
Know that it is not wrong to have minor difficulties in the college year. However, it is significant to indulge students in problem-solving skills through creative games and exercises. Problem-solving skills include time management, critical thinking, and decision-making. These skills can be fostered through interesting problem-solving activities. Activities that indulge students in communication and coordination also help them become better problem solvers. In this blog post, we will explore different activities that help a growth mindset in college students.
Engaging problem-solving activities for college students
Real-life problem solving does not follow any standard procedures or formulas just like solving a mathematical problem does. It requires one to critically analyze the problem from every possible angle and come up with creative, innovative, and practical possible solutions for the same. Given that, the below-mentioned activities are based on a combination of various essential skills that play an important role in overall development.
1. What’s the Situation?
College students are likely to come across many problems in everyday group discussions and projects. This activity focuses on expanding their thought process and building a growth mindset.

- To conduct this activity, divide students into teams of 3 each
- Now, write different situations on a chit of paper and put them all in a bowl
- Call each team and let them read the situation aloud
- For example, the situation can be about hierarchical problems in a group, lack of coordination with other students, or dealing with a bully
- Give 5 minutes to the team for brainstorming and invite an open discussion of the solution
- Inspire the students to contribute and share their views
Being an analytical thinking activity , it helps students carefully analyze situations and brainstorm potential solutions. Teachers can also offer thoughtful insights into situations.
2. Clarity of Words
Communication is an important aspect of a problem as it is needed for analyzing the problem and discussing solutions. This activity purely focuses on joint efforts to solve a problem within a stipulated time frame.

- To conduct this activity, get building blocks and divide the students into teams of 4
- Now, give the structure of the final product to an only team member
- The other team members should have all the building blocks
- One team member guides the other 3 members to start with the construction without having the final image
- The team member with the image is responsible for communication
- Calculate the time taken by each team and share results at the end
Problem-solving skills enhance when teams come together to only focus on the solution and get it done. Such an activity inspires teams to think creatively and also improve their active listening skills.
3. Where’s the Key?
Treasure hunts are always fun; however, this activity comes with a twist. The activity incorporates communication, coordination, and brainstorming between team members.

- To conduct this activity, divide the students into teams of 3 members each
- Now, hide a key somewhere in the college
- Give teams different hints at different levels to find the key
- For example, the first hint can be in the library and the second one can be in the auditorium
- As students find the hint, offer them the next one and that’s how the leading team shall find the key
Solving realistic problems and getting solutions from different clues enhances creative thinking in students. They are more likely to develop a problem-solving mindset due to the challenging environment.
4. Survival of the Fittest!
When students face a real situation, they are more likely to broaden their horizons and think practically. This activity focuses on understanding life situations and being active throughout the process.

- To conduct this activity, set a situation for students
- For example, the situation can be how students are stranded on an island
- Now, write the names of different elements that are needed for survival on an island
- Out of the list, students can only select 5 elements to survive
- Once they have selected, present different scenarios where they need to think about the usage of elements to solve the problem
- Invite an open discussion about solutions and cross-question them to make it interesting
This activity can either be conducted individually or in teams. It offers practical learning where students learn the application of solutions rather than just finding them.
5. How many Solutions?
At times, there might be no problem but many solutions that one can think of. This tricky activity tests the critical thinking of students with reference to everyday life.

- To conduct this activity, have many different products in a box
- Now, ask students to pick one and think of different uses
- For example, if it is toothpaste, it can be used to clean teeth, clean mirrors, and even clean glass surfaces
- Have many such products and let students think of as many solutions a product can offer
With creative thinking, students get an opportunity to understand and maximize the usage of existing products. It helps develop realistic solutions for everyday life with common products.
6. Puzzled Us!
Puzzles are commonly used in various activities to motivate communication, thinking, and problem-solving in students. The activity is focused to help students solve something really common in an uncommon manner.

- To conduct this activity, get two huge puzzles and divide the class into two teams
- Let the class turn into an activity area
- Now, jumble some pieces of the puzzle and let students find the missing pieces from the other team
- Here, both teams shall start building the final puzzle but simultaneously keep finding the missing pieces too
- Reward the team that finishes the puzzle first
As you mismatch some pieces of the puzzle, you are indirectly asking students to focus on the big picture. Along with problem-solving skills, leadership skills are also enhanced in this activity.
7. Quick Fix!
Finding solutions to a problem is a time-consuming process, however, some situations demand promptness. This activity focuses on empowering college students to think creatively in a quick manner.

- To conduct this activity, have many balloons in the class
- Each balloon should have a problem stated in a chit
- Now, divide the students into teams and make chits of all roll numbers of students
- Pick one chit and that roll number needs to burst the balloon
- As the student bursts, he/she needs to read the problem aloud and offer a quick solution to it within a minute
- Reward the student who successfully offers creative solutions at the end
When students are set in a challenging mood, they are more likely to arrive at solutions at a faster pace. It enables individualistic thought processes without worrying about right and wrong.
8. Hey, Challenge Me!
Everyday problems are also a unique way to foster this skill in students. This activity mainly focuses on analyzing everyday problems and finding solutions in a creative way.
- To conduct this activity, divide students into teams of 4 members each
- Now, let 2 teams sit opposite each other for the round
- Team A needs to vocalize their everyday problems and Team B needs to find creative solutions that are workable in nature
- For example, a member from Team A might say how he/she faces problems when communicating with senior teachers
- To this, Team B now has to come up with viable solutions and solve the problem. For example, Team B might suggest Team A’s member take his/her friend along when communicating with senior teachers
- The teacher needs to be the decider if the solutions offered are valid and workable
As students get an opportunity to vocalize their issues, other students are likely to get motivated and raise their voices too. In such a way, students can find common ground and deal with bigger problems in unity.
Problems come in different natures and situations. It is equally important to teach students how to deal with different problems in different ways. This activity purely focuses on taking the right course of action to solve the matter at hand.

- To conduct this activity, make 3 cards – Act, Confront, and Apologize
- Now, place the 3 cards on the table and be ready with as many situations as possible
- Call one student and speak the situation aloud
- After listening, students need to decide the course of action to solve the problem at hand
- My friend did not choose me for the group project. It is bothering me but I am not able to do anything.
- I was scolded by a teacher for an imperfect presentation. However, I’m not very good at it.
- My mind is occupied with the thought of flood conditions in other countries.
- For such situations, students have to choose if they want to act, confront or apologize
- Ask them to state reasons as to why they would choose a particular card and how will it solve the problem
Students are more likely to broaden their thinking capabilities when given situations that they don’t exactly relate to. With such an activity, instruct them about examples of self-management skills which allows them to better understand their choices in the problem-solving concept.
10. Brand Failure!
Giving realistic situations to students helps them become better at problem-solving. It also allows them to look at the big picture and solve problems from different perspectives.

- To conduct this activity, turn the classroom into an office
- Now, make teams of 10 students each and let them sit just the way employees sit for a conference
- For example, you may present the case study of how the product of Nestlé, Maggi, was banned due to contents of lead and MSG found in it
- After this, invite an open discussion as to how they would tackle the problem
- Ask them to think of marketing campaigns or advertisement initiatives to deal with the problem
As students learn about branding and facing problems from the consumer perspective, they get a border opportunity to think like marketing managers. It boosts their confidence as no solution is right or wrong.
Wrapping up…
Problem-solving activities are an effective way to showcase students’ various problems and how to deal with them. Practical application of skills helps to boost their morale. As college students are also exposed to problems of different levels and perspectives, they are more likely to learn, evolve and become thoughtful of their actions. It should be noted that every student learns at a different pace and encouraging them to arrive at creative solutions is a must-do!
Along with this, teachers can also use different examples of problem-solving skills , games, and interesting quotes to create a diversified learning environment. In conclusion, the skill is an essential step for students to perform better in their future endeavors with a growth-oriented focus.
An engineer, Maths expert, Online Tutor and animal rights activist. In more than 5+ years of my online teaching experience, I closely worked with many students struggling with dyscalculia and dyslexia. With the years passing, I learned that not much effort being put into the awareness of this learning disorder. Students with dyscalculia often misunderstood for having just a simple math fear. This is still an underresearched and understudied subject. I am also the founder of Smartynote -‘The notepad app for dyslexia’,
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- Our Mission
Using Games and Design Challenges to Teach Students About Managing Conflict
By introducing students to activities that scaffold conflict, teachers can provide low-stakes lessons to prepare kids to navigate it in healthy ways.

As second-grade teachers, we know that our students are exploring new relationships, changing social dynamics, and feeling the emotional weight that these interactions can have. Our students often encounter conflict as we ask them to take risks, stand up for what they believe in, and share their thoughts and opinions. With this in mind, we created and piloted a three-pronged hands-on approach to building both comfort and skills around managing conflict.
Our approach includes cooperative games and design challenges as well as good-to-know and problem jars. Each part is designed to allow our students to encounter consistent developmentally appropriate and varying types of conflict in order to build problem-solving skills. Throughout each activity, students are put in a variety of mixed groupings where they are confronted with increasingly complex challenges, last-minute changes, and peer leadership opportunities that shift the social dynamics. We are excited to share our approach and help other teachers implement these ideas.
The first few weeks of the year are all about community-building, developing routines, and getting to know our students better as people and learners. Cooperative games are a fantastic way to help students build relationships and begin to collaborate together as a group. As we thought through where we wanted to start, we knew that we wanted to focus on cooperative games that were easy to prepare, low cost, and easy to introduce and play quickly as either a whole or partial group. We wanted students to practice thinking flexibly, shifting roles, and finding success and failure collectively.
Some of our favorite games are the balloon challenge, the colored dots game, and the airplane game. While we introduced many of these games throughout the first semester, we revisited more complex versions, adjusted group sizes, and pushed our students to work through challenges with increasing independence as the year progressed.
Having had some experience with design challenges in the past, we knew that we could use them to push students in unique ways, and these activities tend to be excellent breeding grounds for conflict. We also love that they provide students an opportunity to work in small, fluid groupings and complete a challenge together using varying materials that are low cost and common.
Starting Point
To begin, students are introduced to the challenge and have a five-minute brainstorming period in which they create a plan as a group. After five minutes have lapsed, students then get their materials and begin creating for 10 to 20 minutes, depending on the challenge. There is never a winner who is celebrated or recognized; instead, we commend students for working together. Once the timer has ended, students reflect upon the process through both a group discussion and independently as part of an exit ticket.
Examples of design challenges that our students love are cup stacking, the Play-Doh–and–toothpick building challenge, and the egg-drop challenge . We found that both assigning leadership roles within their groups and increasing the difficulty level pushed students to overcome new challenges and discomfort. Feel free to be inspired by these activities, but change them as you see fit.
We know that effective assessment tools help drive instruction and build our understanding of our students’ feelings and needs. To this end, we created multiple types of both formal and informal assessments that can be completed quickly and easily to help maintain consistency and encourage our students to be reflective about themselves as problem solvers.
Our students fill out an exit ticket based on the Likert scale that allows us to track how their understanding of conflict has changed over time after engaging in both cooperative games and design challenges.
Checking In
Finally, we know that students love their teachers, seek their approval, and enjoy sharing what is going on in their own lives. The good-to-know jar and problem jar offer students a space where they can check in with their own emotional experiences, identities, and culture, and use their real-life problems to share what is on their mind and help them navigate tricky feelings that they may feel uncomfortable sharing verbally.
The two jars are accessible to students throughout the week. Students contribute to these jars anonymously, and each student is encouraged to submit either a good-to-know or a problem throughout the week. On Fridays, we read through the problem jar as a class and talk through possible solutions or just acknowledge that some problems can’t be solved right away but that by talking about them, we are communicating that we will work harder to figure out a plan together.
Giving students a space to see that we, as their teachers, take their thoughts and opinions seriously and then connect their problems with real, immediate action is important in encouraging our students to be problem solvers. We also ask our students to consider how they naturally approach and respond to conflict. Providing them with this opportunity for self-reflection allows them to identify their personal strengths and challenges. The better we know each other, the more comfortable we’ll be with sharing how we feel and engaging in productive conflict.

7 Skills for Engineering Students to be Gained in College Days
Table of contents.
- April 9, 2024
- Takshashila
- Student Resources

A college education provides the perfect environment to discover your hidden talents. You’ll be immersed in hands-on learning through labs, projects and internships during your studies. This gives you a taste of real-world engineering while gaining applicable skills to set you up for future success.
Beyond technical abilities, an engineering degree cultivates transferable “soft” skills in areas like communication , leadership, collaboration and adaptability. Employers highly value these in any industry, as they indicate a well-rounded individual who can effectively manage complex projects.
Let’s discover the 7 skills for engineering students to be gained in college days.
Build Valuable Skills to Excel in Your Career
Due to constant technological advancement, engineering offers exciting long-term career prospects with top-quality skill sets instilled into your mind. Demand for qualified and skilled professionals is strong across many specialisations like software, mechanical, biomedical, etc.
As an engineering student and aspiring professional, you will be presented with countless opportunities daily to grow your abilities, take on new challenges, and shape your future career path . How you approach these opportunities and what you gain from each experience will ultimately determine your long-term success.
7 Significant Skills for Engineering Students
While academic achievement and technical competency are undoubtedly important, the most impressive graduates are those who also focus on developing soft skills, gaining hands-on experience outside the classroom, and continuously expanding their knowledge base.
Here are 7 skills for engineering students to gain in college days
#1 Problem-Solving Skills

Problem-solving is one of the most important abilities an engineering student can gain in college. According to a National Association of Colleges and Employers survey, problem-solving is the #1 skill employers seek in new graduates.
Some helpful problem-solving strategies to focus on include brainstorming multiple potential solutions, researching background information, identifying constraints and requirements through experiments or simulations, analysing results, and iterating on your approach.
Throughout your coursework, you’ll be presented with challenging technical problems that require logical thinking and out-of-the-box creativity. Being able to tackle tough technical problems systematically will serve you extremely well in your future career.
#2 Creativity and innovation

Creativity and innovation are highly valued skills for any engineer. Whether designing new products, improving processes, or solving complex problems, thinking outside the box is essential.
During college, seek opportunities to explore these abilities through hands-on projects, competitions, and entrepreneurial initiatives. Statistics show that up to 90% of engineering employers value hands-on project experience, as it demonstrates real-world problem-solving skills beyond textbooks.
Actively seeking opportunities to flex your creative muscles during college lays the foundation for a career of continuous learning, improvement, and innovation. Engineering is all about pushing boundaries, so don’t be afraid to take risks and think outside the box as you gain these highly valued 21st-century job skills.
#3 Communication

Strong communication skills are absolutely essential for engineering careers. They allow you to effectively share complex technical information with clients and colleagues from diverse backgrounds.
Both written and verbal communication are vital. As an engineer, you’ll need to write detailed reports, proposals, manuals and emails on a regular basis. Statistics show that engineers spend over 30% of their time communicating through writing.
Presentation skills are also key. You must pitch ideas, update teams, or teach others how to operate machinery. Communication is the glue that holds teams together through planning, problem-solving and meeting deadlines.
Group work and collaboration are integral parts of engineering projects. The good news is that your college experience provides many opportunities to strengthen these abilities. From group assignments and presentations to networking at career fairs and internships, take advantage of every chance to practice explaining technical concepts simply and concisely.
#4 Leadership

Leadership is one of the most valuable skills an engineering student can gain in college. Leadership experience shows employers that you’re ready to take on greater responsibilities early in your career.
There are many ways to build your leadership skills as a student. Serving as the president of an engineering club is a great option for taking initiative and organising events. You could also lead a service project to apply your technical knowledge to helping the community.
Hands-on leadership experience has added benefits, too. Studies found that students who held campus leadership positions reported higher levels of self-confidence, communication skills and career readiness after college compared to non-leaders.
#5 Attention to detail

Attention to detail is crucial for any engineer to develop, as even the smallest errors can have significant consequences. Engineering work requires meticulous precision across all design, testing and production stages. As a student, you’ll gain valuable experience applying this skill through your coursework and projects.
Studies show that engineering students who develop excellent attention to detail are up to 25% more likely to land their ideal job after graduation. Employers recognise the importance of this trait, as it ensures safety, quality and efficiency.
Developing this skill starts in the classroom. Make sure to double-check your calculations, thoroughly document your methods and results, and have others review your work to catch any errors. When conducting lab experiments, pay close attention to procedures, measurements and clean-up.
Proper documentation and organisation are also crucial. Over time, this attention to fine details will become second nature through the repetition of careful work habits. The hands-on experience of real-world engineering applications will further reinforce your commitment to accuracy and precision.
#6 Design thinking

Design thinking is a creative, iterative process that engineers can use to address problems in a more human-centred way. It involves empathising with end users to understand their needs and generate innovative ideas without immediately focusing on solutions.
During your college career, take on open-ended projects that allow the exploration of multiple design concepts before converging on a solution. Learning to think like a designer will strengthen your ability to develop technology with true user benefits in mind.
Statistics show that incorporating design thinking leads to products and services that are 93% more likely to succeed in the market. Design thinking also cultivates important soft skills. The process requires strong communication, collaboration, and out-of-the-box creativity, all highly desirable workplace qualities.
#7 Time Management

As an engineering student, you’ll have to carefully balance your course load, assignments, projects, extracurriculars and any part-time work you do. Developing strong time management skills is essential for staying on top of your workload without getting overwhelmed.
One of the best ways to develop strong time management habits is through scheduling and prioritisation. Learn to prioritise tasks, estimate time commitments realistically, and structure your schedule efficiently.
It’s also important to learn when you study best. Are you a morning person who focuses well on early classes? Or a night owl who does deep work after dinner? Understanding your energy levels and productivity patterns allows you to structure your time effectively.
Taking short breaks after every 90 minutes of work or so helps refresh your focus, while longer breaks on weekends prevent burnout. Proper rest is essential for retaining information and performing at your best in classes and projects.
Upgrade Your Student-Self With Top Industry Skills From Takshashila University
As one of India’s top universities, Takshashila prides itself on providing students with the best education that goes beyond the classroom. Through our industry-integrated programs and emphasis on hands-on learning, students gain invaluable real-world skills that set them up for long-term career success.
At Takshashila University , we know that excelling as an engineer in today’s rapidly changing business landscape requires more than strong technical abilities. Through challenging coursework, collaborative projects, and leadership opportunities, our students learn how to tackle complex issues, advocate for ideas, and adapt seamlessly to new challenges – skills that will serve them well throughout their careers and beyond.
When you choose Takshashila, you join a community of innovators dedicated to creating the leaders of tomorrow. By making the most of our industry-integrated programs and emphasising skill-building, our students graduate well-equipped to start successful careers and transform the world through their ideas, work, and continued success.
Develop the Skills That Will Launch Your Engineering Career
Your college years present a unique opportunity to gain experience, grow as a professional, and lay the foundation for a rewarding career. However, making the most of this time is important by actively seeking opportunities to build the technical abilities and soft skills employers desire. As an engineering student, focusing on hands-on learning through challenging coursework and extracurricular projects will vastly improve your technical proficiency. Thus, these 7 skills for engineering students to be gained in college days can make you versatile in your career.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are the 7 skills of a professional engineer?
The top 7 skills of a professional engineer are – Problem-solving – Creativity – Communication skills – Leadership – Attention to detail – Design thinking – Time Management
- What skills do you gain from studying engineering ?
In the course of engineering, you acquire the following skills – Logical thinking – Critical analysis – Decision making – Time management – Creative Thinking
- What is the key skill of an engineer?
The key skills of an engineer are – Precision – Innovation – Decision making – Leadership – Communication
- How do I improve my engineering skills?
You can improve your engineering skills in the following ways – Define Your Objectives – Improving Your Problem-Solving Skill – Focus on the details. – Build soft skills. – Learn from mistakes
- What are soft skills?
Soft skills are qualities that improve your character and morals, such as teamwork, adaptability, leadership, and understanding.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Recent Posts
A college education provides the perfect environment to discover your hidden talents. You’ll be immersed in hands-on learning through labs, projects and internships during your

Is it a Good Idea to do an MBA After a Masters?
There can be valid arguments on both sides that students in your position should carefully consider. Pursuing higher education is a deeply personal journey that

Top 15 Engineering Colleges in India With Their Major Specialities
Engineering is one of the most sought-after streams for higher education in India. Every year, thousands of students attempt to secure admission into the top

Top 10 Skills Required For MBA Students That The Companies Look For!
Imagine the following scenario: you are an MBA student preparing to embark on your journey into the business world, armed with your newly earned degree.
- Computer Science
- Mathematics
- Business Studies
- Economics & Accountancy
State Board
- 12th Commerce
- Accountancy
Enquire to Download Question Papers
Top searches:.
Admission Enquiry 2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Flickr.com. Another great problem solving skill is using process of elimination to eliminate possible solutions to a problem that might not make sense. Like on an exam where choices might be unfitting for the question, there are answers, or solutions to problems that might not be applicable to the given situation.
Problem Solving in STEM. Solving problems is a key component of many science, math, and engineering classes. If a goal of a class is for students to emerge with the ability to solve new kinds of problems or to use new problem-solving techniques, then students need numerous opportunities to develop the skills necessary to approach and answer ...
Problem solving is a necessary skill in all disciplines and one that the Sheridan Center is focusing on as part of the Brown Learning Collaborative, which provides students the opportunity to achieve new levels of excellence in six key skills traditionally honed in a liberal arts education - critical reading, writing, research, data ...
3 Ways to Improve Student Problem-Solving. 1. Slow reveal graphs: The brilliant strategy crafted by K-8 math specialist Jenna Laib and her colleagues provides teachers with an opportunity to gradually display complex graphical information and build students' questioning, sense-making, and evaluating predictions.
The most effective problem-solving approach includes some variation of the following steps: Determine the issue (s) Recognize other perspectives. Think of multiple possible results. Research and evaluate the possibilities. Select the best result (s) Communicate your findings. Establish logical action items based on your analysis.
In fact, critical thinking and problem-solving go hand-in-hand. They both refer to using knowledge, facts, and data to solve problems effectively, but with problem-solving, you are specifically identifying, selecting, and defending your solution. Applying the strategies described in the action checklist below can help you utilize critical ...
By College Raptor Staff Published on November 6, 2023. Critical thinking, research, creativity, analytical skills, communication skills, decision-making skills, and adaptability are the 7 most important problem-solving skills you need to succeed personally and professionally. You'll likely hear the term 'problem-solving skills' tossed ...
Here are a few effective strategies: Project-Based Learning: Projects that require planning, execution, and evaluation naturally involve problem-solving. For example, a project where students need to build a model bridge within a budget encourages them to solve logistical and financial problems. Group Work: Group work allows students to face ...
They both refer to using knowledge, facts, and data to solve problems effectively. But with problem-solving, you are specifically identifying, selecting, and defending your solution. Below are some examples of using critical thinking to problem-solve: Your roommate was upset and said some unkind words to you, which put a crimp in the relationship.
The findings indicated that the students' problem-solving skills improved consistently in the upper, middle, and lower academic groups that were taught by implementing RICOSRE. Keywords: problem-solving skills development; RICORSE 1. Introduction Problem-solving skills are multifaceted mental activities involving cognitive skills [1]
Problem-solving skills are advantageous when resolving complicated and multidimensional challenges. Problem-solving skills can be developed through active learning models that engage students in the learning process. One active learning model is RICOSRE. The main focus of RICOSRE is problem-solving activities in (1) reading; (2) identifying the problem; (3) constructing the solution; (4 ...
The UC San Diego problem-solving curriculum, Mjahed noted, is an opportunity for students to build the skills and the confidence to learn from their failures and to work outside their comfort zone. "And from there, they see pathways to real careers," he said. Jennifer Ogo, a teacher from Kearny High School, taught the problem-solving course ...
Make students articulate their problem solving process . In a one-on-one tutoring session, ask the student to work his/her problem out loud. This slows down the thinking process, making it more accurate and allowing you to access understanding. When working with larger groups you can ask students to provide a written "two-column solution.".
The most effective problem-solving approach includes some variation of the following steps: Determine the issue (s) Recognize other perspectives. Think of multiple possible results. Research and evaluate the possibilities. Select the best result (s) Communicate your findings. Establish logical action items based on your analysis.
Critical thinking is one of the most frequently discussed higher order skills, believed to play a central role in logical thinking, decision making, and problem solving (Butler, 2012; Halpern, 2003).It is also a highly contentious skill in that researchers debate about its definition; its amenability to assessment; its degree of generality or specificity; and the evidence of its practical ...
to help students develop their problem-solving skills, as each individual needs these skills to deal with complex and multidimensional challenges. Educ. Sci. 2022 , 12 , 196 15 of 17
Learn by doing with interactive problem solving that's effective and fun. Master concepts in 15 minutes a day. ... Students and professionals alike can hone dormant skills or learn new ones. ... and build your problem solving skills one concept at a time. Stay motivated. Form a real learning habit with fun content that's always well-paced ...
Problem solving is central to success in any college course. Throughout their academic careers and their lives, students will encounter problems that need to be solved. These problems may range from the personal (how to pay for college) to the interpersonal (how to work with a partner on a project) to the occupational (how to solve an issue ...
Another strategy to encourage the development of problem-solving skills in students is to allow for plenty of discussion and collaboration in the classroom setting. When students interact with one another, they are naturally developing problem solving skills. Rather than the teacher delivering information and requiring the students to passively ...
With depression and anxiety on the rise, college students need emotional problem solving skills to handle the challenges of a new social and academic environment. Here are skills to teach and practice before they leave home. ... Problem-solving skills can help students keep from being overwhelmed . Writer: Juliann Garey. Clinical Experts: ...
Problem-solving skills are the ability to identify problems, brainstorm and analyze answers, and implement the best solutions. An employee with good problem-solving skills is both a self-starter and a collaborative teammate; they are proactive in understanding the root of a problem and work with others to consider a wide range of solutions ...
Along with problem-solving skills, leadership skills are also enhanced in this activity. 7. Quick Fix! Finding solutions to a problem is a time-consuming process, however, some situations demand promptness. This activity focuses on empowering college students to think creatively in a quick manner.
Our approach includes cooperative games and design challenges as well as good-to-know and problem jars. Each part is designed to allow our students to encounter consistent developmentally appropriate and varying types of conflict in order to build problem-solving skills. Throughout each activity, students are put in a variety of mixed groupings ...
Liddic was a finance major in college, but he agrees with Gwyn on the underlying skills needed for success. "I learned nearly my entire role while training with JPMorgan—not while I was in ...
Here are 7 skills for engineering students to gain in college days #1 Problem-Solving Skills. Problem-solving is one of the most important abilities an engineering student can gain in college. According to a National Association of Colleges and Employers survey, problem-solving is the #1 skill employers seek in new graduates.