You'll need JavaScript enabled to experience the full functionality of this site. Please enable JavaScript by following the instructions at enable-javascript.com .
Sorry, the browser you're currently using is not supported by this site. Please upgrade your browser by following the instructions at browser-update.org .
- Go to cgpbooks.co.uk
- Your Lessons


Decimal Partitioning Problems (Year 4)
Write a review

Choose your format:
Save to Your Lessons
Save to Homework
Share resource
Your download limit has been reached!
Check out our FAQs for more info.
This resource is suitable for the White Rose Maths Scheme of Learning, covering Summer Term Block 4 (Decimals B), Step 3 (Partition Decimals).
Children can practise spotting the ones, tenths and hundredths in a decimal using part-whole models, number cards and place value charts.
An answer sheet is included.
This worksheet is available in different levels. Please see the drop-down menu to select another level.
This resource is also available in a handy Lesson Pack, containing a selection of brilliant worksheets for this small step.
View Lesson Pack See all Year 4 White Rose
- Key Stage: Key Stage 2
- Subject: Maths
- Topic: White Rose Maths | Summer Term: Decimals B | Small Step 3
- Topic Group: Fractions, Decimals and Percentages
- Year(s): Year 4
- Media Type: PDF
- Resource Type: Worksheet
- Last Updated: 12/03/2024
- Resource Code: M2WAT16787
- Curriculum Point(s): Recognise and write decimal equivalents of any number of tenths or hundredths. Solve simple measure and money problems involving fractions and decimals to two decimal places.
Related Topics:
Other Teachers Downloaded...

Decimal Partitioning Problems: Foundation (Year 4)
- White Rose Maths | Summer Term: Decimals B | Small Step 3
- Key Stage 2 Maths

Partitioning Decimals (Year 4)

Decimal Partitioning Problems: Stretch (Year 4)

Tenths — Parts of a Whole Problems (Year 4)
- White Rose Maths | Summer Term: Decimals B | Small Step 1

Tenths — Parts of a Whole Problems: Stretch (Year 4)

Making a Whole with Tenths (Year 4)
No reviews (yet!)
Related Resources

Decimals — Perplexing Partitioning Problems (Year 4)
- White Rose Maths | Summer Term: Decimals B | Small Step 4

Decimals — Perplexing Partitioning Problems: Stretch (Year 4)

Decimals — Flexible Partitioning (Year 4)

Decimals — Perplexing Partitioning Problems: Foundation (Year 4)

Multiply and Divide Decimals — Missing Values: Foundation (Year 5)
- White Rose Maths | Summer Term: Decimals | Small Step 12

Dividing Decimals by 10, 100 and 1000: Foundation (Year 5)
- White Rose Maths | Summer Term: Decimals | Small Step 11

Dividing Decimals by 10, 100 and 1000 (Year 5)

Dividing Decimals by 10, 100 and 1000: Stretch (Year 5)

Multiply and Divide Decimals — Missing Values: Stretch (Year 5)
Cookies are disabled on your browser. This means some features of the site won't be fully available to you.
CGP uses cookies to give you a smooth shopping experience and to help us understand how well our site is working. To agree to us using all cookies, click 'Accept', or to reject optional cookies click 'Customise'.
Accept cookies Customise cookies
National Curriculum Resource Tool
Materials to support teachers and schools in embedding the National Curriculum
- National Curriculum Tool
Year 5 - Fractions (including decimals and percentages)
New curriculum.
compare and order fractions whose denominators are all multiples of the same number
- identify, name and write equivalent fractions of a given fraction, represented visually,including tenths and hundredths
- recognise mixed numbers and improper fractions and convert from one form to the other and write mathematical statements >1 as a mixed number[for example, 2 ⁄ 5 + 4 ⁄ 5 = 6 ⁄ 5 = 1 1 ⁄ 5 ]
- add and subtract fractions with the same denominator and denominators that are multiples of the same number
- multiply proper fractions and mixed numbers by whole numbers, supported by materials and diagrams
- read and write decimal numbers as fractions [for example, 0.71 = 71 ⁄ 100 ]
recognise and use thousandths and relate them to tenths, hundredths and decimal equivalents
- round decimals with two decimal places to the nearest whole number and to one decimal place
read, write, order and compare numbers with up to three decimal places
- solve problems involving number up to three decimal places
- recognise the per cent symbol (%) and understand that per cent relates to ‘number of parts per hundred’, and write percentages as a fraction with denominator 100, and as a decimal
- solve problems which require knowing percentage and decimal equivalents of 1 ⁄ 2 , 1 ⁄ 4 , 1 ⁄ 5 , 2 ⁄ 5 and those fractions with a denominator of a multiple of 10 or 25.
Non-Statutory Guidance
Pupils should be taught throughout that percentages, decimals and fractions are different ways of expressing proportions.
They extend their knowledge of fractions to thousandths and connect to decimals and measures.
Pupils connect equivalent fractions > 1 that simplify to integers with division and other fractions > 1 to division with remainders, using the number line and other models, and hence move from these to improper and mixed fractions.
Pupils connect multiplication by a fraction to using fractions as operators (fractions of), and to division, building on work from previous years. This relates to scaling by simple fractions, including fractions > 1.
Pupils practise adding and subtracting fractions to become fluent through a variety of increasingly complex problems. They extend their understanding of adding and subtracting fractions to calculations that exceed 1 as a mixed number.
Pupils continue to practise counting forwards and backwards in simple fractions.
Pupils continue to develop their understanding of fractions as numbers, measures and operators by finding fractions of numbers and quantities.
Pupils extend counting from year 4, using decimals and fractions including bridging zero, for example on a number line.
Pupils say, read and write decimal fractions and related tenths, hundredths and thousandths accurately and are confident in checking the reasonableness of their answers to problems.
They mentally add and subtract tenths, and one-digit whole numbers and tenths.
They practise adding and subtracting decimals, including a mix of whole numbers and decimals, decimals with different numbers of decimal places, and complements of 1 ( for example, 0.83 + 0.17 = 1).
Pupils should go beyond the measurement and money models of decimals, for example, by solving puzzles involving decimals.
Pupils should make connections between percentages, fractions and decimals(for example, 100% represents a whole quantity and 1% is 1 ⁄ 100 , 50% is 50 ⁄ 100 , 25% is 25 ⁄ 100 ) and relate this to finding ‘fractions of’.
Links and Resources
- Making connections
- Exemplification
Teachers should use every relevant subject to develop pupils’ mathematical fluency. Confidence in numeracy and other mathematical skills is a precondition of success across the national curriculum.
Teachers should develop pupils’ numeracy and mathematical reasoning in all subjects so that they understand and appreciate the importance of mathematics.
– National Curriculum in England Framework Document, September 2013, p10
Connections within Mathematics
Fractions, decimals and percentages are used in many other areas of mathematics.
When converting units of measure, children need a good understanding of decimals, e.g. converting cm to m, g to kg etc.
Children should also be required to use fractions and percentages when interpreting and evaluating data.
Fractions may be used when describing turns.
Making connections to this topic in adjacent year groups
Pupils should be taught to:
- recognise and show, using diagrams, families of common equivalent fractions
- count up and down in hundredths; recognise that hundredths arise when dividing an object by one hundred and dividing tenths by ten.
- solve problems involving increasingly harder fractions to calculate quantities, and fractions to divide quantities, including non-unit fractions where the answer is a whole number
- add and subtract fractions with the same denominator
- recognise and write decimal equivalents of any number of tenths or hundredths
- recognise and write decimal equivalents to ¼, ½, ¾
- find the effect of dividing a one- or two-digit number by 10 and 100, identifying the value of the digits in the answer as ones, tenths and hundredths
- round decimals with one decimal place to the nearest whole number
- compare numbers with the same number of decimal places up to two decimal places
- solve simple measure and money problems involving fractions and decimals to two decimal places
- use common factors to simplify fractions; use common multiples to express fractions in the same denomination
- compare and order fractions, including fractions > 1
- add and subtract fractions with different denominators and mixed numbers, using the concept of equivalent fractions
- multiply simple pairs of proper fractions, writing the answer in its simplest form [for example, ½, × ¼, = ⅛,]
- divide proper fractions by whole numbers [for example, ⅓ ÷ 2 = ⅙]
- associate a fraction with division and calculate decimal fraction equivalents [for example, 0.375] for a simple fraction [for example, ⅜ ]
- identify the value of each digit in numbers given to three decimal places and multiply and divide numbers by 10, 100 and 1000 giving answers up to three decimal places
- multiply one-digit numbers with up to two decimal places by whole numbers
- use written division methods in cases where the answer has up to two decimal places
- solve problems which require answers to be rounded to specified degrees of accuracy
- recall and use equivalences between simple fractions, decimals and percentages, including in different contexts
Cross-curricular and real life connections
Learners will encounter fractions, decimals and percentages in:
Measurement – when calculating measures for recipes, calculating journey times and fuel consumption
Money – working out the result of sales offers, tips/gratuities on bills, comparing prices
Statistics – interpreting and evaluating data e.g. 19% of the world’s population lives in China
- Teaching fractions with understanding: Part- whole concept
This article hosted by Nrich explores how children see fractions from an early age and the implications this can have for teaching practices. It includes ideas and images that can be used when presenting children with fractions work to build and extend their understanding of the part – whole relationship.
- History of Fractions
A fun article on the history of fractions that links well to the historical topic of Ancient Egypt.
- Math4life Fractions booklet (pdf)
A booklet that explains fractions, their uses and how they can be classified. There are some teaching and learning activities along with possible errors and misconceptions.
Maths4Life was written for those teaching adults but teachers of children will also find it very helpful.
- Fractions : difficult but crucial in mathematics learning (pdf) Nunes T. (2006) Teaching and Learning research briefing, no 13, London, The Institute of Education
An article exploring children’s intuitions about fractions and likely misconceptions that hinder progress through Key Stage 2 and beyond.
Activity A - Fractions ITP
An interactive program that allows you to model part-whole relationships using a strip divided in to equal parts. Relationships can be shown as fractions, decimals (to three places) or percentages.
Activity B - Fractions Jigsaw
A jigsaw-based activity that requires children to add and subtract fractions with the same and different denominators. Pieces must be matched to an answer that may be expressed in equivalent forms. It also includes multiplying fractions by a whole number.
Activity C - Peaches today, Peaches tomorrow…
A problem solving activity that requires children to find fractions of whole numbers. It provides plenty of practice and has many extension opportunities.
Activity D - Metre sticks and metre strips
Use classroom metre sticks/rulers and I metre long strips of paper to model relationships between a whole, tenths, hundreds and thousandths. Children can explore the size of 1, 2 and 3 decimal places and how they link to units of measurement. Labelling points with decimal, fraction and percentage equivalents can help to reinforce links between all three.
Activity E - Matching fractions, decimals and percentages
A pelmanism-style activity matching pairs of equivalent fractions, decimals and percentages. Points are awarded for correct answers and deducted for turning over cards without success.
Activity F - Using blank hundred squares
Use blank hundred squares to model and explore percentages, tenths and hundredths. Decimals, fractions and percentages can be represented by colouring in blank hundred squares which children can use to support addition and subtraction.
Useful Resources
- Moving digits ITP
- Clock faces to model different fractions
- Fractions ITP
Examples of what children should be able to do, in relation to each (boxed) Programme of Study statement
Children should be able to circle the two fractions that have the same value, or choose which one is the odd one out and justify their decision. 6 ⁄ 10 , 3 ⁄ 5 , 18 ⁄ 20 , 9 ⁄ 15
recognise mixed numbers and improper fractions and convert from one form to the other. Write mathematical statements >1 as a mixed number
Put the correct symbol, < or >, in each box.
3.03 ☐ 3.3 0.37 ☐ 0.327 Order these numbers: 0.27 0.207 0.027 2.07 2.7
(e.g. ⅖ + ⅘ = 6 ⁄ 5 = 1⅕)
How many halves in: 1 ½ 3 ½ 9 ½ …?
How many quarters in 1 ¼ 2 ¼ 5 ¼ ….?
multiply proper fractions and mixed numbers by whole numbers
What is 3 ⁄ 10 of: 50, 20, 100…?
What is ⅘ of 50, 35, 100….?
read and write decimal numbers as fractions (e.g. 0.71 = 71 ⁄ 100 )
What decimal is equal to 25 hundredths?
Write the total as a decimal:
4 + 6 ⁄ 10 + 2 ⁄ 100 =
Children partition decimals using both decimal and fraction notation, for example, recording 6.38 as 6 + 3 ⁄ 10 + 8 ⁄ 100 and as 6 + 0.3 + 0.08.
Recognise that: 0.007 is equivalent to 7 ⁄ 1000 6.305 is equivalent to 6305 ⁄ 1000
Write these numbers in order of size, starting with the smallest. 1.01, 1.001, 1.101, 0.11
solve problems involving numbers with up to three decimal places
8 tenths add 6 tenths makes 14 tenths, or 1 whole and 4 tenths. The 1 whole is 'carried' into the units column and the 4 tenths is written in the tenths column
recognise the per cent symbol (%) and understand that per cent relates to ‘number of parts per hundred’
Write in the missing numbers. 30% of ☐ is 60
write percentages as a fraction with denominator 100, and as a decimal
Shade 10% of this grid.
Which is bigger: 65% or ¾? How do you know?
What percentage is the same as 7 ⁄ 10 ? Explain how you know?
What is 31 ⁄ 100 as a percentage?
Which is a better mark in a test: 61% , or 30 out of 50? How do you know?
Year 4 and 5 extending their fractions work (NCETM video on Youtube)
A video demonstrating how children can use rods to explore which fractions, decimals and percentages are represented when compared to one whole.
Is there anything wrong with this page?
Subscribe to our newsletter
The NCETM is led and delivered by Tribal Education Services, with MEI as a key partner. Learn more about Tribal Education Services and what they do via the link to their website in 'About the NCETM'.
About this website
Stay connected.
- Skip to content
- Skip to search
- Staff portal (Inside the department)
- Student portal
- Key links for students
Other users
- Forgot password
Notifications
{{item.title}}, my essentials, ask for help, contact edconnect, directory a to z, how to guides, literacy and numeracy, flexible additive strategies - decimals.
This resource has been developed in partnership with the NSW Mathematics Strategy Professional Learning team, Curriculum Early Years and Primary Learners, and Literacy and Numeracy.
Using the resource
This resource is the last section of a four-part resource supporting additive thinking. Use this resource in conjunction with the other resources in this series in order to support a connected network of critical mathematical concepts, skills and understanding.
Supporting tasks
Full instructions on how to use each of these tasks - including materials, related tasks and learning intentions - are included in the resource available for download on this page .
Task 1: Decimals on a number line
Students visualise fractional quantities using an unmarked one-metre strip of paper
Variation 1: Students match fractional notation, word cards and images to the number line
Task 2: Making tenths and hundredths
Students partition paper into equal-sized parts to understand tenths and hundredths.
Variation 1: Students identify a part of their whole and record the fractions in a range of ways
Variation 2: Order the various fractions on a number line, comparing their models and counting forwards and backwards, naming and renaming
Variation 3: Make connections to metric units of measurement
Variation 4: Make connections to percentages
Task 3: Get your balance: tenths and hundredths
Students use a balance scale and weights to work out different ways of creating one kilogram.
Variation 1: Student use an unbalanced scale
Task 4: I’ll race you to zero: decimal place value
Students use mental strategies to subtract decimals using a 12 chart and dice.
Variation 1: Students make a number roll by cutting their 12 chart into strips and joining them into one number strip. Students can roll it up when out of use
Variation 2: Students use a 1 and 2-tenths chart
Task 5: More than or less than?
Students estimate and determine which of a set of problems are approximately equivalent to 250.
Variation 1: Student sort problems into less than and greater than categories
Variation 2: Change the target number and problems
Task 6: Roll 5 dice: decimal version
Students work out how many ways one number can be related to another using any operation.
Task 7: What can you say?
Students flexibly rename decimal fractions.
Task 8: How does knowing…?
Students adapt flexible strategies used with whole numbers to add and subtract decimal numbers.
Task 9: Red or black: decimals
Students adapt mental strategies used with whole numbers to add and subtract decimal numbers.
Task 10: Subtraction face-off: thousandths, hundredths and tenths
Students use an Explanation spinner and share the strategies used to work out differences.
Task 11: Number sentence battle
Students build number sentences using dice.
Task 12: Which would you work out in your head? Place value system
Students use mental, written and digital strategies to solve problems.
Variation 1: Change the questions examined by students
Download part 4 of the additive thinking series
- Flexible strategies with decimals (PDF 798 KB)
- Flexible strategies with decimals (DOCX 915 KB)
Related additive thinking resources
Part 1: Flexible strategies with combinations to 10
Part 2: Flexible strategies with 2-digit numbers
Part 3: Flexible strategies with 3-digit numbers
- Teaching and learning
Business Unit:
- Educational Standards
partition decimals
All Formats
Resource types, all resource types.
- Rating Count
- Price (Ascending)
- Price (Descending)
- Most Recent
Partition decimals

Partition Decimals Scoot Activity

Subtracting Using Partitioning ( Decimals ) Video & Follow Up Game

Adding Using Partitioning ( Decimals ) Video & Follow Up Game

Subtracting using Partitioning ( Decimals ) video - Flipped learning

Adding using Partitioning ( Decimals ) video - Flipped learning

BC Math Unit - Fractions and Decimals - Grade 4 Full Unit - Distance Learning


Place Value Tents: Ones, Tens, Hundreds, Thousands and Decimals

*NEW 2024* STAGE 3 REPRESENTING NUMBERS PART A (MILLIONS,BILLIONS, DECIMALS )

(BUNDLE) MONEY math Printables and Partitioning shapes 2nd grade

Number Expander - tens of thousands to decimal thousandths

Fraction and Decimal Equivalent Matching Card Games

Geometry Word Problems: Winter Theme (Quadrilaterals and Partitioning )

Three Decimal Places

Numbers to 1000 Partitioning Base 10 Block by Hundreds, Tens and Ones Task Cards

Fractions and Decimals are AMONG US

- Google Forms™
- Internet Activities
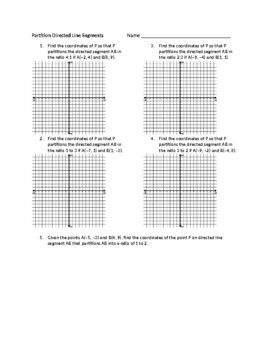
Partition Directed Line Segments Worksheet

- Word Document File

Tenths and Hundredths | Decimals

Number lines

Place Value Memory Game

Fraction Concepts Bundle! - Review Six Concepts

Fraction Puzzle Bundle, Plus Boom Card Link for Distance Learning

Mental Math Split Strategy Addition Game { Decimals }

Place Value Arrow Cards - Sample Set

Place Value Game - Differentiated & AC Linked F-Y6
- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think
KS2 Tutoring Programmes
Mastery-aligned lessons designed to plug individual gaps and delivered by specialist maths tutors
FREE daily maths challenges
A new KS2 maths challenge every day. Perfect as lesson starters - no prep required!

Partitioning Explained For Primary School
Sophie Bartlett
Partitioning is a phrase that even the youngest primary school child will probably know. Here we show you how Year 2 children are taught this skill to help them break down any number into its component parts. We also show how this skill is related to other areas of maths.
This article is part of our series designed for teachers to inform mathematical subject knowledge, and for parents to help support children with home learning . More free home learning resources are also available on this website.
What is partitioning?
Partitioning is a way of splitting numbers into smaller parts to make them easier to work with. Partitioning links closely to place value: a child will be taught to recognise that the number 54 represents 5 tens and 4 ones, which shows how the number can be partitioned into 50 and 4. By moving tens and ones between the two parts, the number can be partitioned in many other ways:

When shown a number (up to 7+ digits by Year 6), children should be able to partition them independently to show good understanding of place value. For example, 5,202,086 = 5,000,000 + 200,000 + 2,000 + 80 + 6.
See also: Division Worksheets
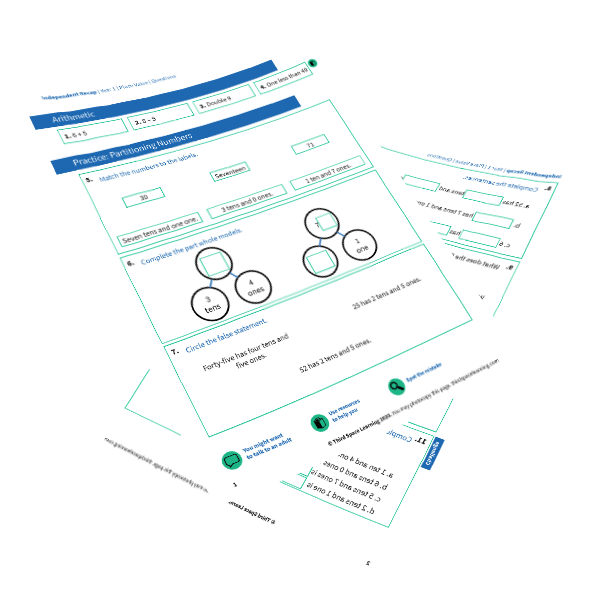
FREE Partioning Numbers Worksheet
This time-saving worksheet is for Year 1 partioning numbers and includes 4 arithmetic questions, 9 consolidation questions, and 1 challenge question.
When will my child learn about partitioning in primary school?
Partitioning is taught very early on in pupils’ maths lessons, but it is first mentioned in the national curriculum as non-statutory guidance for Year 2:
Pupils should partition numbers in different ways (for example, 23 = 20 + 3 and 23 = 10 + 13) to support subtraction. They become fluent and apply their knowledge of numbers to reason with, discuss and solve problems that emphasise the value of each digit in two-digit numbers. They begin to understand zero as a place holder .
In Year 3, the non-statutory guidance advises that children use larger numbers to at least 1000, applying partitioning related to place value using varied and increasingly complex problems, building on work in year 2 (for example, 146 = 100 + 40 and 6, 146 = 130 + 16).
How does partitioning relate to other areas of maths?
Children will use partitioning in many other areas of maths:
- Introducing column addition: 56 + 78 may be first calculated as (50 + 70) + (6 + 8)
- Introducing column subtraction : 56 – 22 may be first calculated as (50 – 20) + (6 – 2)
- Understanding exchanging in column subtraction: 32 – 18 may be first calculated as (30 – 10) + (2 – 8) until children realise that they can’t subtract 8 from 2 without reaching a minus number. Partitioning is important here in understanding why exchanging works. 32 can be partitioned into 20 + 12, so this subtraction can be recalculated as (20 – 10) + (12 – 8)
- Introducing multiplication: 34 x 6 may be first calculated as (30 x 6) + (4 x 6)
- Introducing division methods with multi-digit divisors, including long division , short division and bus stop method , which require pupils to use multiples of the divisor and to calculate division with remainders
See also: Division Questions
Wondering about how to explain other key maths vocabulary to children? Check out our Primary Maths Dictionary , or try these other terms:
- What Is Division ?
- What Is BODMAS (and BIDMAS)?
- Division For Kids: How To Teach Short Division (Bus Stop Method) And Long Division To Children
- How To Teach Division KS2: Maths Bootcamp [7]
- What We’ve Learnt From Teaching Our Long Division Lesson 2,968 Times
Practice questions
1) Write the missing numbers. 361 = ___ + 60 + 1 300 945 = 900 + __ + 5 40
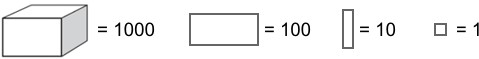
Write the value of each diagram. ( 1 st = 1,231) (2 nd = 2,013)
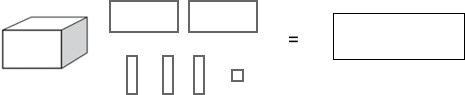
3) Match the sums that have the same answer.
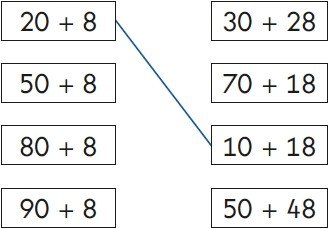
(2nd box to 1st box; 3rd box to 2nd box; 4th box to 4th box)
4) 700 + 20 + 3 = ( 723) 3,000 + 40 + 2 = ( 3,042) 2,000 + 300 = ( 2,300)
DO YOU HAVE STUDENTS WHO NEED MORE SUPPORT IN MATHS?
Every week Third Space Learning’s specialist primary maths tutors support thousands of students across hundreds of schools with weekly online 1 to 1 maths lessons designed to plug gaps and boost progress.
Since 2013 these personalised one to one lessons have helped over 150,000 primary and secondary students become more confident, able mathematicians.
Learn how the programmes are aligned to maths mastery teaching or request a personalised quote for your school to speak to us about your school’s needs and how we can help.
Related articles

What Is Estimation in Maths: Estimating Numbers Explained for Primary School Teachers and Parents

What Is A Carroll Diagram? Explained for Primary School Parents & Teachers

What Is Part Whole Model? Explained For Primary School Parents & Teachers

What Are Coordinates: Explained For Primary School Parents And Kids
FREE Ultimate Maths Vocabulary List [KS1 & KS2]
An A-Z of key maths concepts to help you and your pupils get started creating your own dictionary of terms.
Use as a prompt to get pupils started with new concepts, or hand it out in full and encourage use throughout the year.
Privacy Overview
- + ACCUPLACER Mathematics
- + ACT Mathematics
- + AFOQT Mathematics
- + ALEKS Tests
- + ASVAB Mathematics
- + ATI TEAS Math Tests
- + Common Core Math
- + DAT Math Tests
- + FSA Tests
- + FTCE Math
- + GED Mathematics
- + Georgia Milestones Assessment
- + GRE Quantitative Reasoning
- + HiSET Math Exam
- + HSPT Math
- + ISEE Mathematics
- + PARCC Tests
- + Praxis Math
- + PSAT Math Tests
- + PSSA Tests
- + SAT Math Tests
- + SBAC Tests
- + SIFT Math
- + SSAT Math Tests
- + STAAR Tests
- + TABE Tests
- + TASC Math
- + TSI Mathematics
- + ACT Math Worksheets
- + Accuplacer Math Worksheets
- + AFOQT Math Worksheets
- + ALEKS Math Worksheets
- + ASVAB Math Worksheets
- + ATI TEAS 6 Math Worksheets
- + FTCE General Math Worksheets
- + GED Math Worksheets
- + 3rd Grade Mathematics Worksheets
- + 4th Grade Mathematics Worksheets
- + 5th Grade Mathematics Worksheets
- + 6th Grade Math Worksheets
- + 7th Grade Mathematics Worksheets
- + 8th Grade Mathematics Worksheets
- + 9th Grade Math Worksheets
- + HiSET Math Worksheets
- + HSPT Math Worksheets
- + ISEE Middle-Level Math Worksheets
- + PERT Math Worksheets
- + Praxis Math Worksheets
- + PSAT Math Worksheets
- + SAT Math Worksheets
- + SIFT Math Worksheets
- + SSAT Middle Level Math Worksheets
- + 7th Grade STAAR Math Worksheets
- + 8th Grade STAAR Math Worksheets
- + THEA Math Worksheets
- + TABE Math Worksheets
- + TASC Math Worksheets
- + TSI Math Worksheets
- + AFOQT Math Course
- + ALEKS Math Course
- + ASVAB Math Course
- + ATI TEAS 6 Math Course
- + CHSPE Math Course
- + FTCE General Knowledge Course
- + GED Math Course
- + HiSET Math Course
- + HSPT Math Course
- + ISEE Upper Level Math Course
- + SHSAT Math Course
- + SSAT Upper-Level Math Course
- + PERT Math Course
- + Praxis Core Math Course
- + SIFT Math Course
- + 8th Grade STAAR Math Course
- + TABE Math Course
- + TASC Math Course
- + TSI Math Course
- + Number Properties Puzzles
- + Algebra Puzzles
- + Geometry Puzzles
- + Intelligent Math Puzzles
- + Ratio, Proportion & Percentages Puzzles
- + Other Math Puzzles
How to Perform Operations of Decimals: Word Problems
Greetings, budding mathematicians! Today, we're going to jump into an adventure with decimals. Working with decimals is a fundamental math skill that you'll use in many aspects of life, from managing money to measuring distances.

Introduction to Decimal Operations
First things first, let’s talk about decimals. A decimal is a way of representing a number that’s less than one, or a number that’s a whole and a fraction together. When you work with decimals, the same rules apply as when you’re working with whole numbers, but the decimal point plays a crucial role.
There are four major operations that you can perform on decimals:
- Subtraction
- Multiplication
Now, let’s tackle some word problems involving decimal operations.
Step-By-Step Guide to Solving Word Problems with Decimal Operations
Step 1: understand the problem.
First and foremost, carefully read through the problem. Identify what you know and what you need to find out.
Step 2: Plan the Solution
Next, decide which operation (addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division) will help you solve the problem. This will depend on what the problem is asking.
Step 3: Carry Out the Operation
Perform the operation on the decimals. Remember to align the decimal points when you’re adding or subtracting, and apply the rules for multiplication and division of decimals correctly.
Step 4: Check the Answer
Finally, check if your answer makes sense in the context of the problem.
Consider this problem: Laura bought \(2.3\) kilograms of apples and \(1.5\) kilograms of grapes. How many kilograms of fruit did she buy in total?
Step 1: Understand that you know the weight of apples and grapes separately, and you need to find the total weight.
Step 2: Realize that to find the total, you need to add the weights together.
Step 3: Add the weights: \(2.3\ kg + 1.5\ kg = 3.8\ kg\).
Step 4: Check that the answer makes sense. Laura bought \(2.3\ kg\) of apples and \(1.5\ kg\) of grapes, so it makes sense that she bought \(3.8\ kg\) in total.
Keep practicing with different word problems, and you’ll get the hang of decimal operations in no time. Remember, the more you practice, the better you’ll get. Happy calculating!
by: Effortless Math Team about 9 months ago (category: Articles )
Effortless Math Team
Related to this article, more math articles.
- 8th Grade STAAR Math FREE Sample Practice Questions
- How to Find Standard Deviation
- Decimals Demystified: From Standard Form to Expanded Form with Fractions
- 10 Most Common 6th Grade PARCC Math Questions
- 7 Best Headphones for Online Lessons
- What Are The Optimization Problems: Beginners Complete Guide
- How to Unlock the Secrets of Success: “ISEE Upper Level Math for Beginners” Solution Guide
- PSAT 10 Math Practice Test Questions
- Best Touchscreen Monitors for Teaching at Home
- How to Determine the Missing Number when Multiplying Decimals by Powers of 10
What people say about "How to Perform Operations of Decimals: Word Problems - Effortless Math: We Help Students Learn to LOVE Mathematics"?
No one replied yet.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Mastering Grade 6 Math Word Problems The Ultimate Guide to Tackling 6th Grade Math Word Problems
Mastering grade 5 math word problems the ultimate guide to tackling 5th grade math word problems, mastering grade 7 math word problems the ultimate guide to tackling 7th grade math word problems, mastering grade 2 math word problems the ultimate guide to tackling 2nd grade math word problems, mastering grade 8 math word problems the ultimate guide to tackling 8th grade math word problems, mastering grade 4 math word problems the ultimate guide to tackling 4th grade math word problems, mastering grade 3 math word problems the ultimate guide to tackling 3rd grade math word problems.
- ATI TEAS 6 Math
- ISEE Upper Level Math
- SSAT Upper-Level Math
- Praxis Core Math
- 8th Grade STAAR Math
Limited time only!
Save Over 45 %
It was $89.99 now it is $49.99
Login and use all of our services.
Effortless Math services are waiting for you. login faster!
Register Fast!
Password will be generated automatically and sent to your email.
After registration you can change your password if you want.
- Math Worksheets
- Math Courses
- Math Topics
- Math Puzzles
- Math eBooks
- GED Math Books
- HiSET Math Books
- ACT Math Books
- ISEE Math Books
- ACCUPLACER Books
- Premium Membership
- Youtube Videos
- Google Play
- Apple Store
Effortless Math provides unofficial test prep products for a variety of tests and exams. All trademarks are property of their respective trademark owners.
- Bulk Orders
- Refund Policy

- Home Learning
- Free Resources
- New Resources
- Free resources
- New resources
- Filter resources
- Childrens mental health
- Easter resources
Internet Explorer is out of date!
For greater security and performance, please consider updating to one of the following free browsers
Partitioning Lesson
This Year 4 Partitioning lesson covers the prior learning of place value in 3-digit numbers, before moving onto the main skill of partitioning numbers into thousands, hundreds, tens and ones, including unconventional partitioning.
The lesson starts with a prior learning worksheet to check pupils’ understanding. The interactive lesson slides recap the prior learning before moving on to the main skill. Children can then practise further by completing the activities and can extend their learning by completing an engaging extension task.
National Curriculum Objective
Mathematics Year 4: (4N4a) Identify, represent and estimate numbers using different representations
Mathematics Year 4: (4N6) Solve number and practical problems that involve 4N1 – 4N5 and with increasingly large positive numbers
Get the most from lessons!

Resources for teachers

Interactive activities for children
2 Teaching Support
Subscription

Lesson Slides
These lesson slides guide pupils through the prior learning of place value in 3-digit numbers, before moving onto the main skill of partitioning. There are a number of questions to check pupils' understanding throughout.

Modelling Powerpoint
This powerpoint can be used to model the questions that the children will complete on the Varied Fluency and Reasoning & Problem Solving worksheets as part of this lesson.

These are the same as the lesson slides on Classroom Secrets. You can assign this as an activity for pupils to access individually in school or remotely from home.

Video Tutorial
Aaron shows pupils how to use a part-whole model to partition numbers in this Partitioning 2-Digit Numbers Video Tutorial.
1 Prior Learning
This worksheet recaps place value in 3-digit numbers, before moving onto the main skill of partitioning numbers into thousands, hundreds, tens and ones, including unconventional partitioning.

In this Tens and Ones Partitioning Video Tutorial, Katie shows pupils how to partition a 2-digit number into tens and ones.
Interactive Challenge Activity
This Year 1 Partitioning Numbers Maths Challenge checks pupils' understanding of partitioning numbers within 100.
2 Varied Fluency
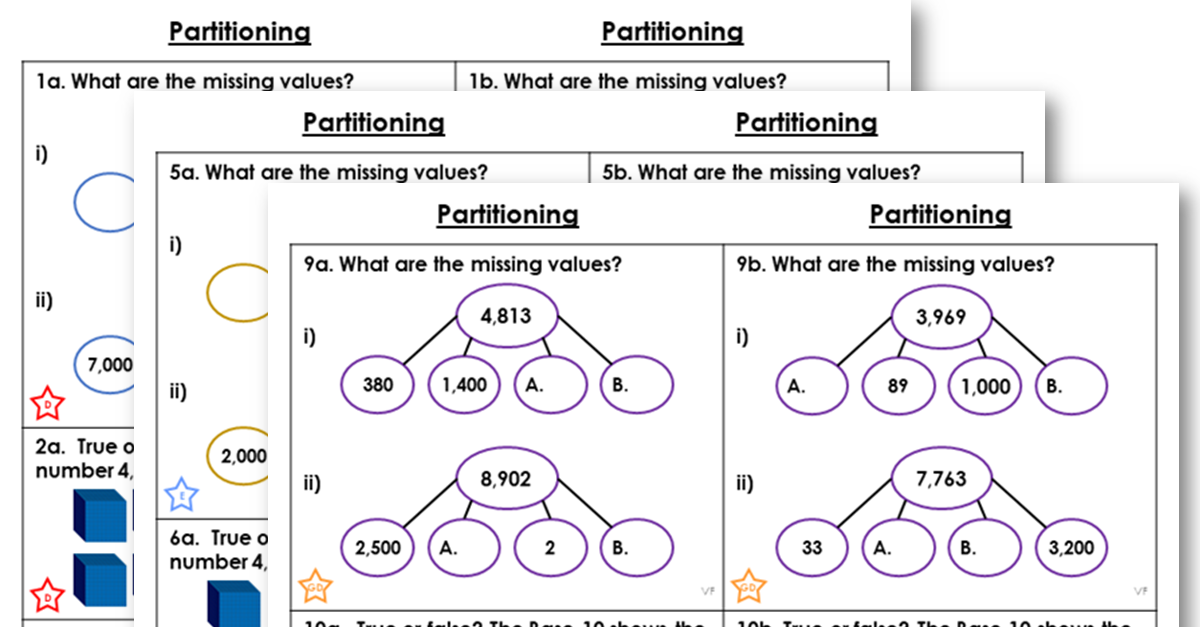
This worksheet includes varied fluency questions for pupils to practise the main skill for this lesson.
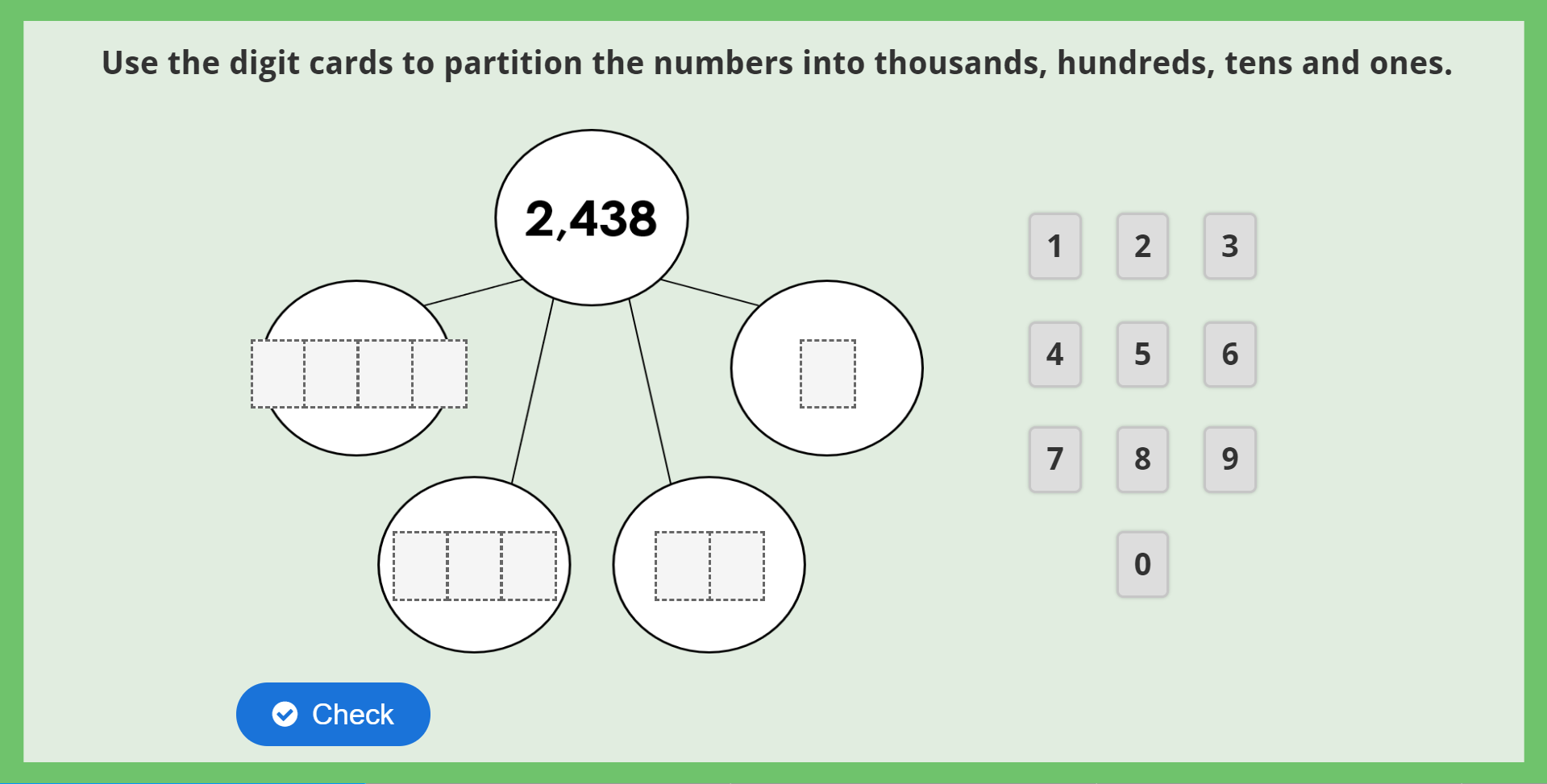
Interactive Activity
This Year 4 Partitioning Numbers Game checks pupils’ understanding of partitioning 4-digit numbers into thousands, hundreds, tens and ones.
2 Reasoning & Problem Solving
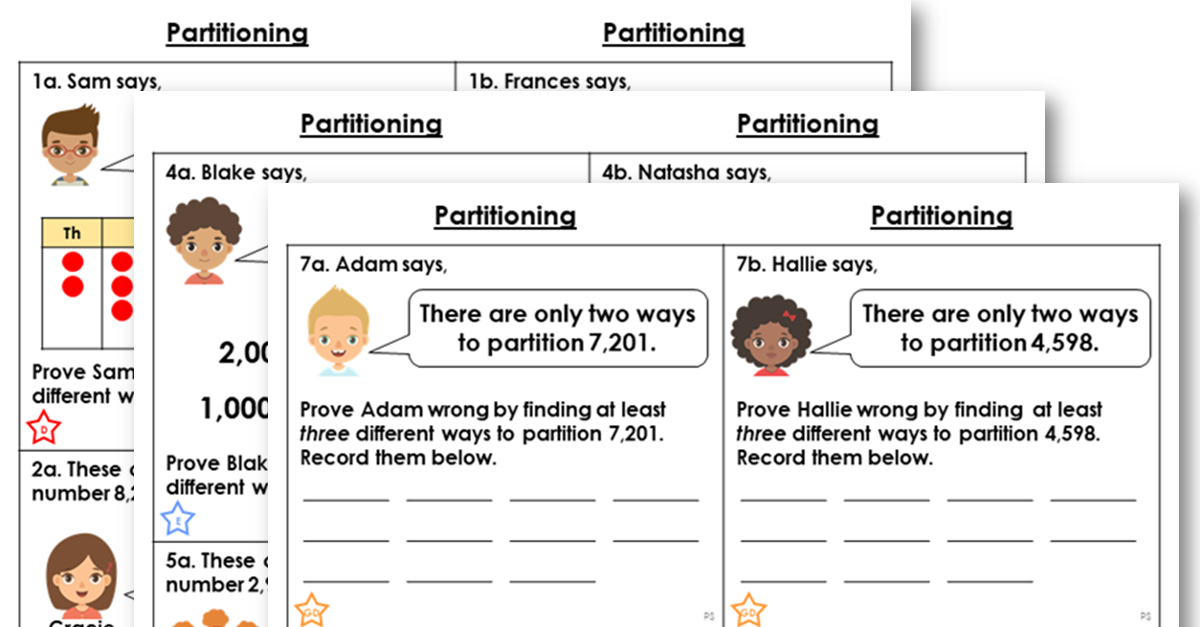
This differentiated worksheet includes reasoning and problem solving questions to support the teaching of this step.

This partitioning extension task includes a challenge activity which can be used to further pupils' understanding of the concepts taught in the partitioning.
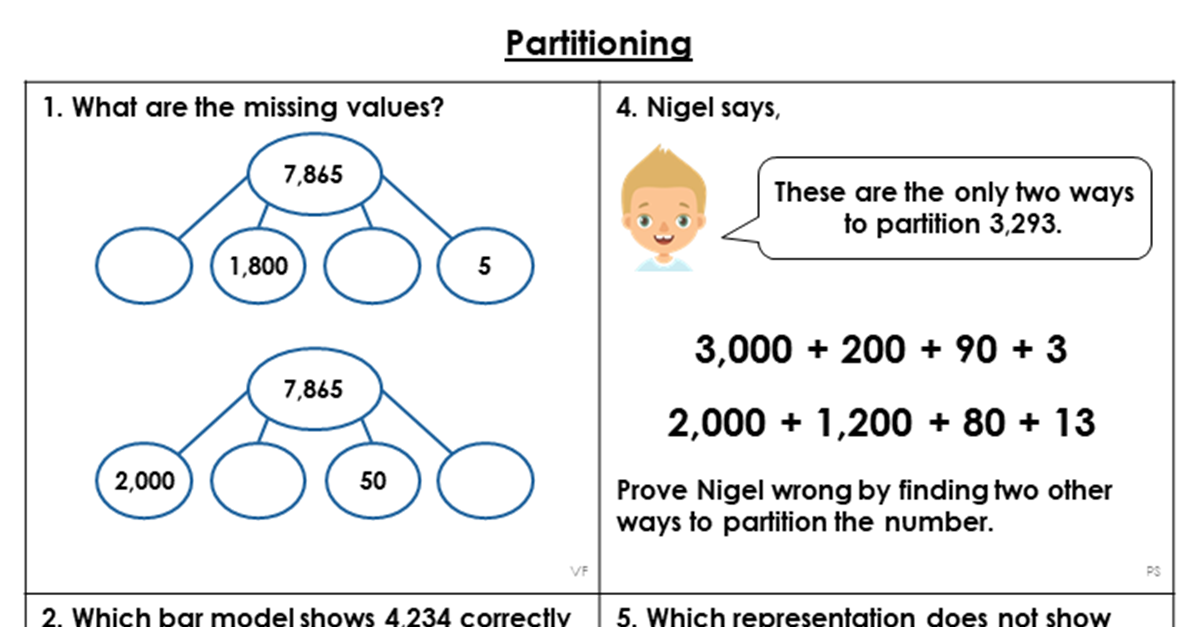
Mixed Practice
This worksheet includes varied fluency, reasoning and problem solving questions for pupils to practise the main skill of partitioning.
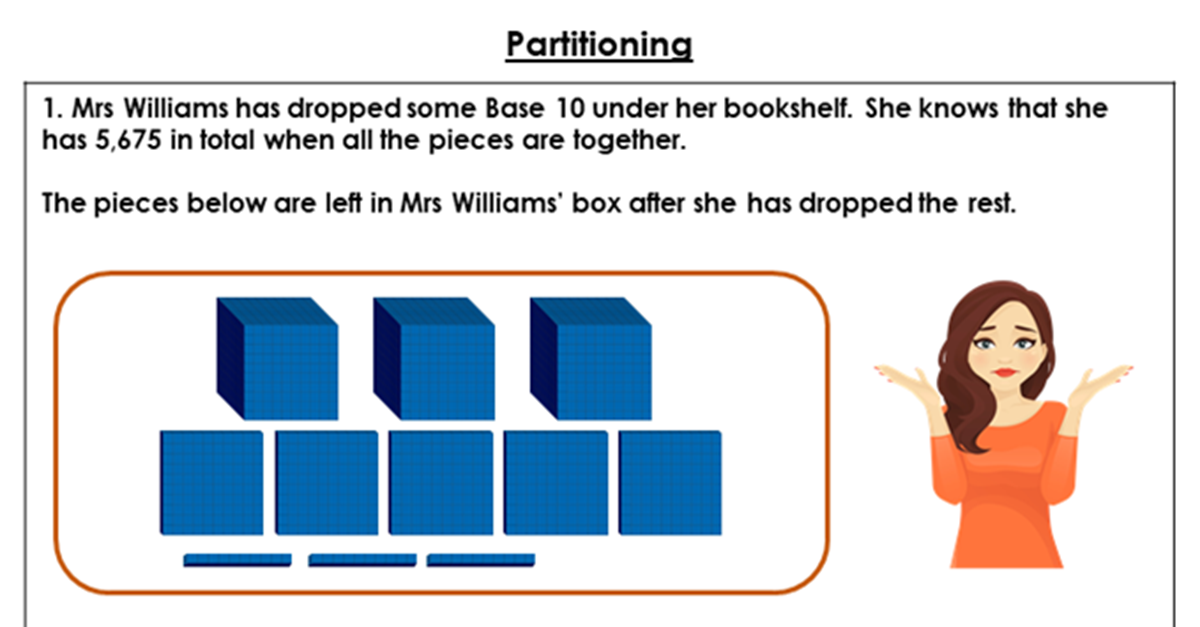
Discussion Problem
This worksheet includes two discussion problems which can be used in pairs or small groups to further pupils' understanding of the concepts taught in this lesson.
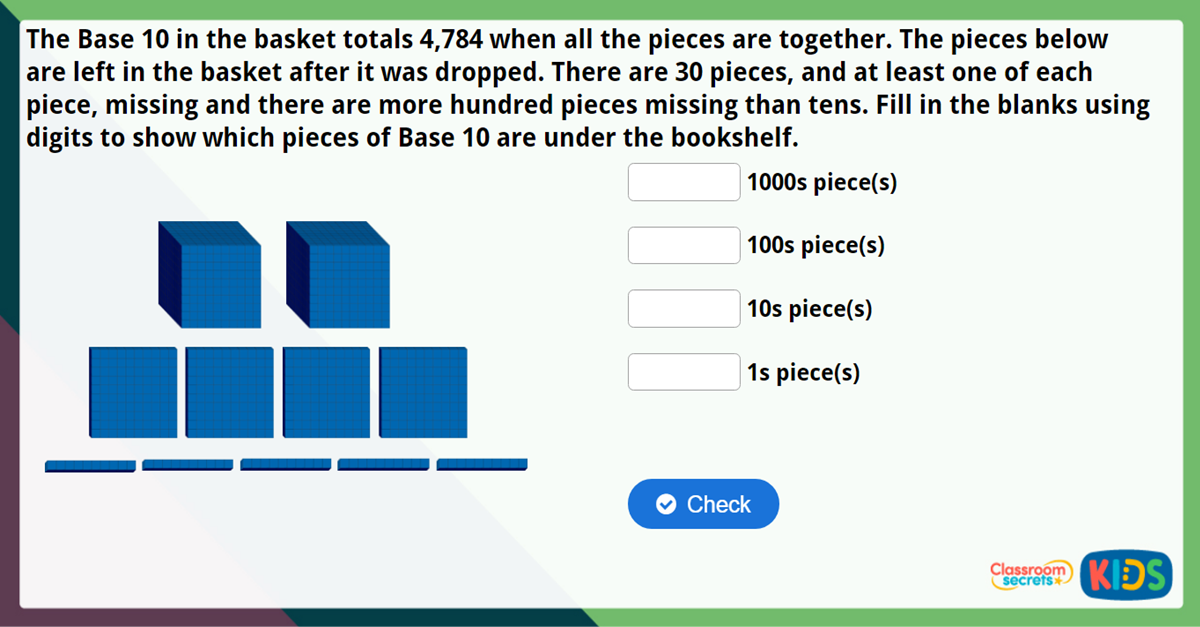
This Year 4 Partitioning Maths Challenge is designed to check pupils' ability to partition a number in to 1s, 10s, 100s and 1000s.
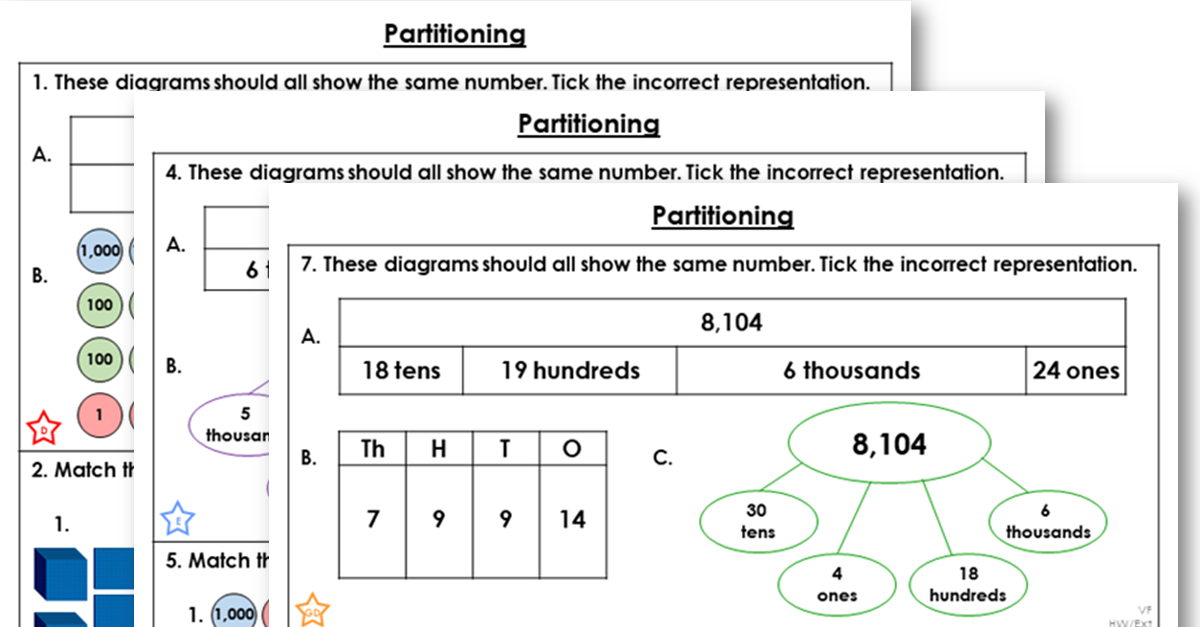
This differentiated worksheet includes varied fluency and reasoning and problem solving questions to support the teaching of this step.
2 Additional Activities
Home Learning Pack
This Autumn week 2 Maths pack contains varied fluency, reasoning and problem solving worksheets.
Consolidation Pack
This Place Value Consolidation Year 4 Autumn Block 1 resource is aimed at Year 4 Secure and has been designed to give children the opportunity to consolidate the skills they have learned in Block 1 – Place Value.

Learning Video Clip
Allegra is a tour guide who works in Rome. Today she is organising tours and exhibits in Vatican City, and she needs your knowledge of partitioning to help her.
D Download Packs
Stay in touch.
01422 419608
[email protected]
Interested in getting weekly updates from us? Then sign up to our newsletter here!

Information

- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
Copyright: Classroom Secrets 2024
Company number: 8401067
VAT number: 248 8245 74
- Terms & Conditions
Designed by Classroom Secrets
Operating with Decimals
Mathematics
Level 5 Level 6 Level 7

What is this sequence about?
This learning sequence aims to develop student proficiency when adding, subtracting, multiplying and dividing with decimals. A well-developed understanding of place value and number sense is critical for students to flexibly and intuitively operate with decimals. This sequence provides opportunities for students to consolidate their understanding of the continuous nature of the base 10 system and deepen their conceptual understanding about the role of estimation and efficient strategies when adding, subtracting, multiplying and dividing with decimals.
The sequence has been written by teachers for teachers. It has been designed to provide students with rich, engaging learning experiences that address the Victorian Curriculum. The sequence consists of four flexible stages, including suggested learning intentions.
Overview of stages
1. Decimal Number Sense
Suggested Learning Intentions
- To understand decimal place value to the thousandths
- To understand the relative size of decimals
3. Multiplying and Dividing by Powers of 10
- To understand that scientific notation can be used to describe infinitely large and infinitely small numbers
- To learn how to multiply and divide decimals using knowledge of place value in a base-10 system
2. Adding and Subtracting Decimals
- To solve decimal problems using rounding and estimation
- To use my understanding of place value to solve decimal problems
4. Multiplying and Dividing Decimals
- To recognise the appropriate operation when solving decimal problems in context
- To use my number sense when multiplying and dividing decimal problems
Prior knowledge
Before you commence this sequence, it is suggested that you ensure your students are familiar with terms and concepts of place value, tenths and hundredths ( VCMNA159 ) and the connection between fractions and decimals. Students should also have had experience using intuitive and flexible computation strategies for whole number ( VCMNA156 ), which includes rounding and estimation.
It will be helpful for students to have first explored the concepts contained in the ‘Fractions to decimals’ and ‘Colour in decimats’ stages of the Keeping it in Proportion: Fractions and Decimals sequence, that focus on comparing and ordering decimals ( VCMNA187 ; VCMNA190 ) as well as decimal place value ( VCMNA189 ).
You can find support for building students’ understanding of these concepts in the Mathematics Curriculum Companion . The Teaching Context and Teaching Ideas related to content descriptions VCMNA159 ; VCMNA189 and VCMNA190 may be particularly useful.
Teaching strategies
The Mathematics Curriculum Companion provides teachers with content knowledge, suggested teaching and learning ideas as well as links to other resources. Resources are organised by Mathematics strands and sub-strands and incorporate the proficiencies: Understanding, Fluency, Problem Solving and Reasoning. The Companion is an additional resource that you could refer to when you are planning how you might use the sequence in your school.
The sequence highlights opportunities to apply the High Impact Teaching Strategies (HITS) , which are a component of the Victorian Teaching and Learning Model .
The sequence highlights the use of a variety of scaffolding practices to help support students in the learning process, in particular:
- Collaborating
- Convince Me
Students should be able to understand and use the following concepts and terms by the end of the learning sequence:
You can find definitions of some of these terms in the F-10 Victorian Curriculum Mathematics Glossary . It is recommended that the explicit teaching of vocabulary occur throughout the learning sequence.
The Literacy in Mathematics section of the Literacy Teaching Toolkit provides several teaching strategies with worked examples demonstrating how teachers can use literacy to support student understanding of mathematical language. A further set of strategies demonstrate how teachers can develop students' literacy skills to support their mathematical problem solving.
Opportunities for formative and summative assessment are identified at different stages of the learning sequence. Look for the 'Assessment Opportunity' icon.
You may want to develop a rubric to assess students’ progress. A range of Formative Assessment resources are available from the Victorian Curriculum and Assessment Authority. This includes a Guide to Formative Assessment Rubrics , a series of modules to support you to develop your own formative assessment rubrics, and sample rubrics across six curriculum areas that demonstrate how you can put formative assessment rubrics into practice in the classroom.
In developing a rubric, you may wish to co-construct assessment criteria with your students. Each stage of the sequence provides sample success criteria for students working at Level 6.
The Victorian Curriculum and Assessment Authority has published annotated work samples that provide teachers with examples of student learning achievement at multiple levels for each strand of the Mathematics curriculum.
Victorian Curriculum connections
This sequence addresses content from the Victorian Curriculum in Mathematics and Critical and Creative Thinking. It is primarily designed for Level 6, but also addresses the following content descriptions from Level 5:
The sequence can be used to assess student achievement in relation to the following Achievement Standards from the Victorian Curriculum: Mathematics Level 5:
- Students solve simple problems involving the four operations using a range of strategies including digital technology
- Students estimate to check the reasonableness of answers and approximate answers by rounding
- Students order decimals and unit fractions and locate them on a number line
- Students continue patterns by adding or subtracting fractions and decimals.
This sequence addresses content from the Victorian Curriculum in Mathematics and Critical and Creative Thinking. It is primarily designed for Level 6, addressing the following content descriptions:
The sequence can be used to assess student achievement in relation to the following Achievement Standards from the Victorian Curriculum: Mathematics Level 6:
- Students make connections between the powers of 10 and the multiplication and division of decimals
- Students add, subtract and multiply decimals and divide decimals where the result is rational.
This sequence addresses content from the Victorian Curriculum in Mathematics and Critical and Creative Thinking. It is primarily designed for Level 6, but also addresses the following content descriptions from Level 7:
The sequence can be used to assess student achievement in relation to the following Achievement Standards from the Victorian Curriculum: Mathematics Level 7:
- Students solve problems involving all four operations with fractions, decimals, percentages and their equivalences
- Students make simple estimates to judge the reasonableness of results.
Learning Progressions
The Numeracy Learning Progressions support teachers to develop a comprehensive view of how numeracy develops over time. You can use the numeracy learning progressions to:
- identify the numeracy capability of your students
- plan targeted teaching strategies, especially for students achieving above or below the age-equivalent expected level in the Victorian Curriculum: Mathematics
- provide targeted feedback to students about their learning within and across the progressions.
The sequence is related to the following progressions:
Click on the Learning Progression to access more detailed descriptions of student learning at each level.
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

Decimals Reasoning and Problem Solving
Subject: Mathematics
Age range: 7-11
Resource type: Worksheet/Activity
Last updated
4 April 2022
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

These problems will give your Year 6 pupils the opportunity to reason and solve problems with decimals.
This is a sample resource.
For a full year’s worth of reasoning and problem solving for Year 6 please see:
https://www.tes.com/teaching-resource/reasoning-and-problem-solving-for-year-6-12201133
Creative Commons "NoDerivatives"
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have downloaded this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Reasoning and Problem Solving Write Decimals Reasoning and Problem Solving Write Decimals Developing 1a. A and D are true. B and C are false because the number as 6 ones and 1 tenth. 2a. 3.1 and 1.3 3a. Lena is correct. Kyle has partitioned the number into 1 tenth and 2 tenths. Expected 4a. B and C are true. A is false because the number has ...
Written to compliment the new White Rose Maths scheme of learning, this Diving into Mastery teaching pack supports the small step 4: Partition Decimals Flexibly from Summer Block B. Included in the pack is a PowerPoint and activity sheets to develop fluency, reasoning and problem solving skills. This will prove to be an excellent time saver for all Year 4 teachers.
Reasoning and Problem Solving Decimals up to 2d.p. Reasoning and Problem Solving Decimals up to 2d.p. Developing 1a. D is the odd one out as it represents 7.42. The others represent 7.24. 2a. 8.36 3a. Matt is incorrect as he has made 3.47 instead of 4.73. Expected 4a. A is the odd one out as it represents 5.3. The others represent 4.13.
Learned something new? Check out our free textbook and sign up for a free Mathspace account to learn more: https://bit.ly/mathspace-free-textbook In this vid...
Decimal Partitioning Problems: Foundation (Year 4) This resource is suitable for the White Rose Maths Scheme of Learning, covering Summer Term Block 4 (Decimals B), Step 3 (Partition Decimals). Children can practise spotting the ones, tenths and hundredths in a decimal using part-whole models and number cards.
This Partition Decimals Scoot Activity focuses identifying place value of tenths and hundredths and partitioning decimals as fractions.Included: - 24 decimal cards- Recording sheet- AnswersThis is designed to be completed as a Scoot or Write the Room activity with the cards placed around the classroom and students roaming to locate the cards and record their answers on the recording sheet.
What's included in the pack? Flexibly Partition Decimals reasoning and problem solving worksheet. Answer sheet. National Curriculum Objectives: Mathematics Year 4 (4F6b) Recognise and write decimal equivalents of any number of tenths or hundredths. Mathematics Year 4 (4F10b) Solve simple measure and money problems involving fractions and ...
Decimal Partitioning Problems (Year 4) This resource is suitable for the White Rose Maths Scheme of Learning, covering Summer Term Block 4 (Decimals B), Step 3 (Partition Decimals). Children can practise spotting the ones, tenths and hundredths in a decimal using part-whole models, number cards and place value charts. An answer sheet is included.
How to partition a number. Part of Maths Problem solving Year 3. Save to My Bitesize Remove from My Bitesize. ... How to solve maths problems. count. 1 of 4. What is the order of operations? count ...
Pupils should go beyond the measurement and money models of decimals, for example, by solving puzzles involving decimals. Pupils should make connections between percentages, fractions and decimals(for example, 100% represents a whole quantity and 1% is 1 ⁄ 100, 50% is 50 ⁄ 100, 25% is 25 ⁄ 100) and relate this to finding 'fractions of'.
Task 1: Decimals on a number line. Students visualise fractional quantities using an unmarked one-metre strip of paper. Variation 1: Students match fractional notation, word cards and images to the number line. Task 2: Making tenths and hundredths. Students partition paper into equal-sized parts to understand tenths and hundredths.
Browse partition decimals resources on Teachers Pay Teachers, a marketplace trusted by millions of teachers for original educational resources.
Pupils should partition numbers in different ways (for example, 23 = 20 + 3 and 23 = 10 + 13) to support subtraction. They become fluent and apply their knowledge of numbers to reason with, discuss and solve problems that emphasise the value of each digit in two-digit numbers. They begin to understand zero as a place holder.
Year 6 Number: Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Division Mental Calculations Lesson 3. Explore more than 40 "Partitioning Decimals" resources for teachers, parents and pupils as well as related resources on "Decimal Partitioning". Instant access to inspirational lesson plans, schemes of work, assessment, interactive activities ...
Step-By-Step Guide to Solving Word Problems with Decimal Operations Step 1: Understand the Problem. First and foremost, carefully read through the problem. Identify what you know and what you need to find out. Step 2: Plan the Solution. Next, decide which operation (addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division) will help you solve the ...
Created to complement the new White Rose Maths scheme of learning, this Diving into Mastery teaching pack is ideal for any Year 4 teacher. It supports the small step 3: Partition Decimals from Summer Block B. Included in the pack is a PowerPoint and activity sheets to develop fluency, reasoning and problem-solving skills. This will prove to be an invaluable resource for all Year 4 teachers.
Partitioning Lesson. This Year 4 Partitioning lesson covers the prior learning of place value in 3-digit numbers, before moving onto the main skill of partitioning numbers into thousands, hundreds, tens and ones, including unconventional partitioning. The lesson starts with a prior learning worksheet to check pupils' understanding.
Multiply and divide decimals by powers of 10 . Multiplying and Dividing Decimals. Select and apply efficient mental and written strategies and appropriate digital technologies to solve problems involving all four operations with whole numbers and make estimates for these computations . Adding and Subtracting Decimals
The pack includes worksheets with fluency, reasoning, and problem-solving activities, as well as a PowerPoint which helps model some of the questions included in the worksheets. Includes ascending and descending order. ... Step 3 Partition Decimals Teaching Pack. Year 4 Diving into Mastery: Step 2 Make a Whole with Hundredths Teaching Pack.
Decimals Reasoning and Problem Solving. Subject: Mathematics. Age range: 7-11. Resource type: Worksheet/Activity. File previews. pdf, 394.64 KB. These problems will give your Year 6 pupils the opportunity to reason and solve problems with decimals. This is a sample resource. For a full year's worth of reasoning and problem solving for Year 6 ...
In this comprehensive PlanIt Maths Y4 lesson pack, the children are shown that decimal numbers can be partitioned to help find the place value of each digit within that number and that this is known as standard partitioning. It supports the year 4 national curriculum aim of: "Recognise and write decimal equivalents of any number of tenths or hundredths." Children practise identifying the ...
Step 1: Step 2: The least decimal is 9.75. Now we must determine how 9.75 compares with the winning score. Answer: The last swimmer must get a score less than 9.75 s in order to win. Example 4: To make a miniature ice cream truck, you need tires with a diameter between 1.465 cm and 1.472 cm.
This is the perfect resource for your year 4 class. It has been written to align with White Rose's new scheme of work for year 4, Place Value in Autumn term, small step 7: Flexible Partitioning of Numbers to 10 000. Included in the pack is a PowerPoint that takes children through fluency, reasoning and problem-solving activities that help the children tackle this small step. Also, there are ...