- Memberships

Kepner Tregoe Method of Problem Solving
Kepner Tregoe Method of Problem Solving: this article explains the Kepner Tregoe Method , also known as the KT-method , developed by Charles Kepner and Benjamin Tregoe in a practical way. Next to what this is, this article also highlights rational processes, the importance of cause and that this method is effective. After reading, you’ll have a basic understanding of this problem solving process. Enjoy reading!
What is the Kepner Tregoe Method?
Problems occur in any given organization. Often there is pressure of time to solve the problems and it is debatable what the right way of solving these problems is.
The Kepner Tregoe method or KT-method is a problem analysis model in which the “problem” is disconnected from the “decision” . An English synonym for this problem solving method is Problem Solving and Decision Making (PSDM).

Traditional thinking pattern
The founders Charles Kepner and Benjamin Tregoe developed a rational working method in the 1960s in which they researched and identified the troubleshooting skills of people.
Throughout the centuries mankind has learned to deal with complexity and to (directly) anticipate on this. As a consequence, the traditional thinking pattern became a part of human nature.
When solving problems people search for the answer to the following four questions:
- What happened?
- Why did it happen?
- How should we act?
- What will be the (future) result?
Kepner Tregoe method: rational processes
To break through this traditional pattern Charles Kepner and Benjamin Tregoe came up with four rational processes in which four fundamental questions are reflected:
1. Situation analysis
This clarifies the problem situation (what happened).
1.1 Problem analysis
Here the actual cause of the problem and the relationship between cause and result are searched for (why did it happen).
1.2 Decision analysis
Based on the decision making criteria, choices are made to arrive at potential problem resolutions (how should we act).
1.3 Potential Problem analysis
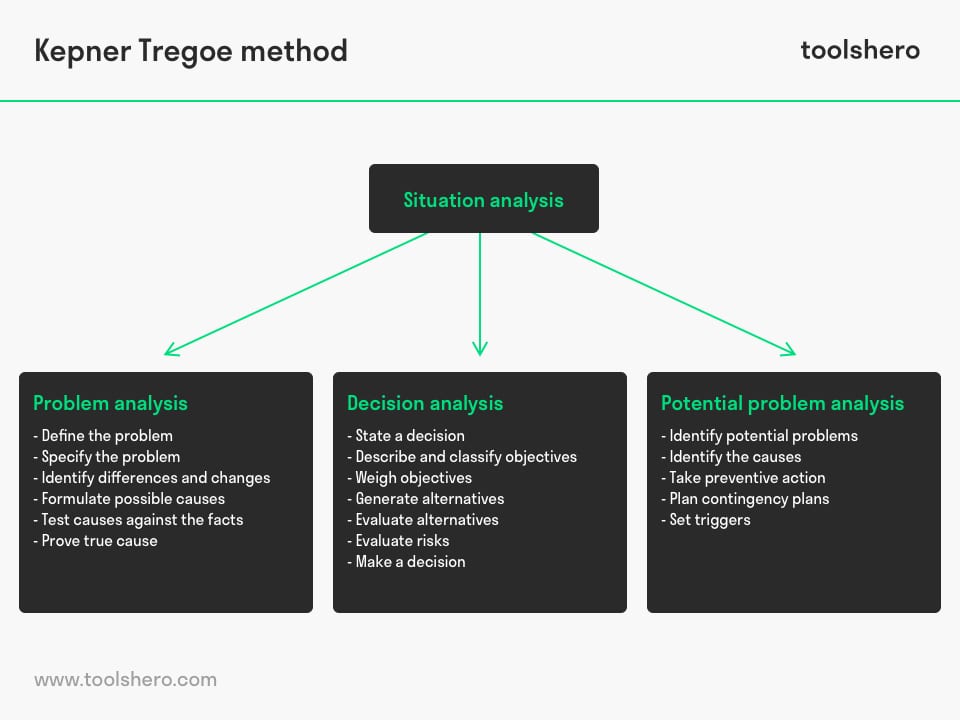
Figure 1 – Kepner Tregoe Method Analysis
Distinction
According to the KT-method, different tasks involve different problems, which in turn need different approaches. A situation analysis will clarify the distinctions in all these processes and as a result it will be possible to search for suitable solutions. This situation analysis provides an insight into necessity, priority and urgency of the various tasks.
When it has become clear which tasks are to be prioritized (action list) preparations can be made for potential problems. By using a good problem analysis in advance, a process will be created to prevent future problems or in emergencies, to limit the damage.
The strengths of this method does not stop there. Apart from the fact that problems are specified in terms such as “what, where, when and how big”, the Kepner Tregoe Method focuses on anything that cannot be the cause of the problem.
Certain causes are therefore excluded. Based on a “this is” and “this is not” analysis a clear overview of possible causes can be created and this makes the troubleshooting process consistent.
The Kepner Tregoe Method is efficient
The KT-method deploys an efficient troubleshooting process. Through research Charles Kepner and Benjamin Tregoe discovered that the registration of a problem is not a uniform process. In spite of the available information, people usually process information badly, misinterpret this or overlook important matters.
In addition, Charles Kepner and Benjamin Tregoe examined the discrepancies between successful and less successful troubleshooting.
They discovered that a predetermined logical method facilitates the search for the causes of a problem. In their “Best practice in troubleshooting” , they describe this methodology, which forms the basis for this method.
The Kepner Tregoe Method is Effective
This method is universal and is still used today in many organizations to track down problems and identify potential causes. Apart from the fact that the Kepner Tregoe Method leads to an explanation of problems, it also helps improve mutual understanding within an organization.

It’s Your Turn
What do you think? Is the Kepner Tregoe Method applicable in today’s modern organizations? Do you recognize the practical explanation or do you have more suggestions? What are your success factors for the good Kepner Tregoe Method set up?
Share your experience and knowledge in the comments box below.
More information
- Lussier, R. N. (2005). Management fundamentals: concepts. applications, skill development . Cengage Learning .
- Payne, S. L. & Marty, C.S. (1966). The Rational Manager: A Systematic Approach to Problem Solving and Decision Making . Journal of Marketing. Vol. 30 Issue 1, p97.
- Kepner, C. H. & Tregoe, B. B. (1965). The Rational Manager . McGraw-Hill.
How to cite this article: Mulder, P. (2012). Kepner Tregoe Method . Retrieved [insert date] from Toolshero: https://www.toolshero.com/problem-solving/kepner-tregoe-method/
Original publication date: 06/30/2012 | Last update: 12/09/2023
Add a link to this page on your website: <a href=”https://www.toolshero.com/problem-solving/kepner-tregoe-method/”>Toolshero: Kepner Tregoe Method</a>
Did you find this article interesting?
Your rating is more than welcome or share this article via Social media!
Average rating 3.7 / 5. Vote count: 30
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?

Patty Mulder
Patty Mulder is an Dutch expert on Management Skills, Personal Effectiveness and Business Communication. She is also a Content writer, Business Coach and Company Trainer and lives in the Netherlands (Europe). Note: all her articles are written in Dutch and we translated her articles to English!
Related ARTICLES

Soft Systems Methodology (SSM) by Peter Checkland

Convergent Thinking: the Definition and Theory

CATWOE Analysis: theory and example

Means End Analysis: the basics and example

Systems Thinking: Theory and Definition

5 Whys Root Cause Analysis (Toyoda)
Also interesting.

Crowdsourcing: the meaning, definition and some examples

Systematic Inventive Thinking (SIT)

Linear Thinking by Edward De Bono explained
4 responses to “kepner tregoe method of problem solving”.
I am stunned to read that the Kepner Tregoe Method “…… IS STILL used today in many organizations to track down problems and identify potential causes…..”. I have used it all the time along my career as a manager of organizations, with extreme success. As a tool for identifying problems, as a tool for taking better decisions. So, please, I would appreciate to know what kind of system is being used now instead of an approach like K-T, to have provoked your comment about the existence of an alternative way of thinking.
Other than KT, I also use the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) Like KT, it forces discipline and analysis and it helps to explain why decisions are made with understandable background and data. Many of the old Total Quality Management tools are also useful for solving problems and making good management decisions. Nominal Group Technique, Pareto Charts, and weighted multivoting are all quite useful. ITIL is the new way of thinking, but it can be rather dry and robotic unless it is underpinned with good decision tools.
Thank you for your comment and sharing your experience Pete.
Seems that I naturally deal with problems this way without knowing a name for it. In fact, it seems obvious to me that this approach should be taken anyway.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
BOOST YOUR SKILLS
Toolshero supports people worldwide ( 10+ million visitors from 100+ countries ) to empower themselves through an easily accessible and high-quality learning platform for personal and professional development.
By making access to scientific knowledge simple and affordable, self-development becomes attainable for everyone, including you! Join our learning platform and boost your skills with Toolshero.

POPULAR TOPICS
- Change Management
- Marketing Theories
- Problem Solving Theories
- Psychology Theories
ABOUT TOOLSHERO
- Free Toolshero e-book
- Memberships & Pricing

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 8 min read
The Kepner-Tregoe Matrix
Making unbiased, risk-assessed decisions.
By the Mind Tools Content Team

No matter what position you hold, from the board room to the mailroom, you make decisions every day.
And the end result in business is directly linked to the quality of the decisions made at each point along the way.
So, not surprisingly, decision-making is a universally important competence in business. Some decisions clearly have a greater impact on the business than others, but the underlying skill is the same: the difference is in the scope and depth of the process you go through to reach your decision.
One reason why decision-making can be so problematic is that the most critical decisions tend to have to be made in the least amount of time. You feel pressured and anxious. The time pressure means taking shortcuts, jumping to conclusions, or relying heavily on instinct to guide your way.
Kepner-Tregoe: Taking the Guesswork out of Decision-Making
In your organization, you've probably heard of someone who made it all the way to VP by relying on his gut to make decisions. At the other extreme is the guy who simply can't make a decision because he analyzes the situation to death. The bottom line is, you have to make decisions, and you have to make good decisions. Poor decisions are bad for business. Worse still, one poor decision can lead to others, and so the impact can be compounded and lead to more and more problems down the line.
Thankfully, decision-making is a skill set that can be learned and improved on. Somewhere between instinct and over-analysis is a logical and practical approach to decision-making that doesn't require endless investigation, but helps you weigh up the options and impacts.
One such approach is called the Kepner-Tregoe Matrix. It provides an efficient, systematic framework for gathering, organizing and evaluating decision-making information. The approach was developed by Charles H. Kepner and Benjamin B. Tregoe in the 1960s and they first wrote about it in the business classic, The Rational Manager (1965). The approach is well-respected and used by many of the world's top organizations including NASA and General Motors. [1]
The Kepner-Tregoe Approach
The Kepner-Tregoe approach is based on the premise that the end goal of any decision is to make the "best possible" choice. This is a critical distinction: the goal is not to make the perfect choice, or the choice that has no defects. So the decision maker must accept some risk. And an important feature of the Kepner-Tregoe Matrix is to help evaluate and mitigate the risks of your decision.
The Kepner-Tregoe Matrix approach guides you through the process of setting objectives, exploring and prioritizing alternatives, exploring the strengths and weaknesses of the top alternatives, and of choosing the final "best" alternative. It then prompts you to generate ways to control the potential problems that will crop up as a consequence of your decision.
This type of detailed problem and risk analysis helps you to make an unbiased decision. By skipping this analysis and relying on gut instinct, your evaluation will be influenced by your preconceived beliefs and prior experience – it's simply human nature. The structure of the Kepner-Tregoe approach limits these conscious and unconscious biases as much as possible.
The Kepner-Tregoe Matrix comprises four basic steps:
- Situation Appraisal – identify concerns and outline the priorities.
- Problem Analysis – describe the exact problem or issue by identifying and evaluating the causes.
- Decision Analysis – identify and evaluate alternatives by performing a risk analysis for each and then make a final decision.
- Potential Problem Analysis – evaluate the final decision for risk and identify the contingencies and preventive actions necessary to minimize that risk.
Going through each stage of this process will help you come to the "best possible choice", given your knowledge and understanding of the issues that bear on the decision.
How to Use the Tool
The Kepner-Tregoe Matrix is an in-depth approach that can be supported by detailed instruction and worksheets. As an overview of the approach, the following steps show the general principles of how the Kepner-Tregoe approach can apply to a decision-making situation:
1. Prepare a decision statement.
- This is a general overview of what the decision is expected to achieve (the key objective).
- The statement should discuss the action that is required and the result that is desired.
2. Establish strategic requirements ("Must Haves").
- What "musts" will the final decision provide, allow for, include, etc.? For example: we must have 10 percent cost saving, we must include four color choices, the rope must hold 200 lbs.
- These requirements are absolute – there is no compromise.
3. Establish operational objectives ("Want to Haves").
- What do you "want" the final decision to support?
- By identifying the wants you can rank the alternatives according to which ones satisfy the most, or most important, wants.
4. Identify the restraints (Limits).
- What are the things that will limit your ability to do exactly what you want/need?
- These are typically resource constraints like money, materials, and time.
5. Rank the operational objectives and assign relative weights.
- For each "want", assign a rating of 1 – 10 based on the degree of importance.
6. Generate a list of alternatives.
- Think of as many alternative courses of action as you can. Don't be too concerned that they all meet the "musts" and "wants" you just defined. You will rank these alternatives in the next step.
- Brainstorming is a good approach for generating your list of alternatives.
7. Assign a relative score for each alternative.
- First, eliminate any alternatives that do not meet the "musts" – these are not worth considering any further.
- For the first alternative, go through each objective (want) and rate how well the alternative satisfies it using a 1 – 10 scale.
- Multiply the weight of the objective by the satisfaction rating to come up with a weighted score for each objective.
- Add the weighted scores to determine the total weighted score.
- Repeat the process for each alternative.
8. From the total weighted score for each alternative, rank the top two or three alternatives.
- Remember to make sure that the alternatives you choose meet all the "must" criteria.
9. For the top alternatives, generate a list of potential problems (adverse effects) for each.
- Rank the potential problems for each alternative according to probability and significance.
- Obtain a total weighted score for the adverse effect (adversity rating).
10. Analyze the alternative ranking and the adversity rating and make a final decision.
11. decide on mitigating actions for the chosen alternative..
- Look at each of the adverse effects already identified and generate a list of proactive responses to reduce the probability of each.
- Continuously monitor these probabilities and take action as needed.
The Kepner-Tregoe Matrix is a well-respected and systematic approach for making decisions. The matrix process forces users to be well-organized and thorough.
By weighting and ranking both the benefits and risks, it helps you choose the very best alternatives.
Using the Kepner-Tregoe approach requires patience and a commitment: the payoff for the time invested is good, unbiased decision-making that makes good business sense.
[1] Kepner, C. and Tregoe, B. (1965). ' The Rational Manager .' McGraw-Hill Book Company.
Kepner-Tregoe is a trademark of Kepner-Tregoe, Inc. See www.kepner-tregoe.com .
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
An introduction to business continuity management.
An Introduction to Business Continuity Management and Why it is So Important
Book Insights
Disruptive Analytics: Charting Your Strategy for Next-Generation Business Analytics
Thomas W. Dinsmore
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Get 30% off your first year of Mind Tools
Great teams begin with empowered leaders. Our tools and resources offer the support to let you flourish into leadership. Join today!
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Latest Updates

Decision-Making Mistakes and How to Avoid Them

Using Decision Trees
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Better processes.
Tools and techniques to design business processes that deliver results

Essential Strategy
Discover a range of strategic planning tools to set your organization up for success
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
How to have a good day: think bigger, feel better and transform your working life.
Caroline Webb
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast

Victor Leung

Understanding the Kepner-Tregoe Technique - A Guide to Enhanced Problem-Solving and Decision-Making

In the dynamic world of business, the ability to efficiently solve problems and make decisions is crucial for success. The Kepner-Tregoe technique, developed by Charles H. Kepner and Benjamin B. Tregoe, is a structured methodology that aids in the systematic analysis and resolution of problems. This blog post delves into the essence of the Kepner-Tregoe technique, exploring its key components and benefits.
What is the Kepner-Tregoe Technique?
The Kepner-Tregoe technique is a problem-solving and decision-making framework that provides a systematic approach for identifying, analyzing, and resolving issues. It consists of four main processes:
Problem Analysis : This process involves defining the problem, understanding its nature, and diagnosing the root cause. By distinguishing between what is known and unknown, the problem is clarified, making it easier to identify potential solutions.
Decision Analysis : This step is crucial for making informed decisions. It involves evaluating alternatives against a set of objectives and identifying the risks associated with each option. This helps in selecting the most feasible and beneficial solution.
Potential Problem (or Opportunity) Analysis : Here, the focus shifts to forecasting future issues or opportunities. This proactive approach helps in preparing for potential challenges and capitalizing on opportunities that may arise from the decision made.
Situation Appraisal : This involves assessing the situation to prioritize issues, plan the next steps, and allocate resources effectively. It helps in managing multiple problems or decisions simultaneously.
Benefits of the Kepner-Tregoe Technique
Enhanced Problem-Solving Skills : The technique fosters a deep understanding of the problem, leading to more effective solutions.
Improved Decision-Making : By systematically evaluating alternatives, the technique ensures that decisions are well-informed and aligned with objectives.
Risk Management : It helps in identifying potential risks and prepares organizations to mitigate them effectively.
Efficient Resource Allocation : By prioritizing issues, the technique ensures that resources are used optimally.
Fosters Team Collaboration : The structured approach encourages teamwork and clear communication, making it easier to reach a consensus.
Implementing the Kepner-Tregoe Technique
To effectively implement the Kepner-Tregoe technique, organizations should:
Train Employees : Provide training to develop the necessary skills for applying the technique.
Encourage a Systematic Approach : Foster a culture where problems are approached methodically, using the Kepner-Tregoe processes.
Utilize in Various Scenarios : Apply the technique across different types of problems and decisions to maximize its benefits.
Regularly Review and Refine : Continuously assess the effectiveness of the technique and make adjustments as needed.
The Kepner-Tregoe technique is a powerful tool for organizations seeking to enhance their problem-solving and decision-making capabilities. By providing a structured approach, it not only leads to better outcomes but also promotes a culture of strategic thinking and collaboration. Implementing this technique can be a game-changer for businesses aiming to navigate complexities with greater confidence and efficiency.
Ready for more?

An official website of the Department of Health & Human Services

- Search All AHRQ Sites
- Email Updates
Informing Improvement in Care Quality, Safety, and Efficiency
- Contact DHR
Kepner-Tregoe Matrix
A Kepner-Tregoe matrix is used to find causes of a problem. It isolates the who, what, when, where, and how aspects of an event, keeping the focus on the elements that have an impact on the event and eliminating the elements that do not. This allows you to compare what the problem is, with what it is not, illuminating distinctive features of the problem and pointing out its potential causes.
To clarify what the problem is not about.
When identifying the causes of quality problems.
When brainstorming.
1. DESCRIBE THE EVENT in a clear manner so it can be understood by everyone.
2. PRODUCE AN EMPTY MATRIX of six rows by four columns. Fill the headings of the 4 colums with the following: "performance shortcoming," "is," "is not," and "distinction." Below the top row, fill the row headings of the rows with the following: "what occurs, what objects are affected?," "where does the problem occur?", "when does the problem occur?", "extent of shortcomings?", and "who is involved?"
3. RECORD THE PROBLEM OR EVENT under analysis in the upper left-hand corner of the matrix.
4. DESCRIBE WHAT DID OR DOES OCCUR using the "is" column. Determine the objects affected and what specifically occurs. Determine the location of the event. Determine when the event occurs, whether it has recurred, whether it happens in conjunction with any other events, and any patterns observed.
5. DETERMINE THE EXTENT OF THE PROBLEM. Think about how many objects had problems and how many problems each object had. Determine the severity of the problems.
6. DETERMINE WHO is involved in the event. However, ensure that this step does not assign blame.
7. IDENTIFY CIRCUMSTANCES that could occur but do not recur using the "is not" column.
8. Examine the "is" and "is not" columns to IDENTIFY WHAT IS DIFFERENT OR UNUSUAL about events where the problem exists versus where it is absent ("is" versus "is not"). Record your observations in the "distinctions" column.
9. FOR EACH DISTINCTION DETERMINE whether it relates to a known change. Examine how the change could have caused the problem. Record all possible causes.
10. TEST ALL POSSIBLE CAUSES BY DETERMINING whether the each item in the "is" and "is not" columns can be explained by the cause. The most likely cause explains every aspect of the problem.
11. PLAN AN EXPERIMENT TO VERIFY THE CAUSE(S) identified, if possible.
Can be used at any stage of a process improvement effort.
Is a useful tool for problem discovery and resolution.
Offers exhaustive process for accurate problem definition.
Is time consuming.
Andersen B. Tools for analyzing the performance shortcoming. In: O'Mara P, editor. Business process improvement toolkit. 2nd ed. Milwaukee, WI: ASQ Quality Press; 2007. p. 123-55.
Tague N. The tools. In: O'Mara P, editor. The quality toolbox. 2nd ed. Milwaukee, WI: ASQ Quality Press; 2005. p. 93-521.
Lighter D. Process orientation in health care quality. In: Moore C, editor. Quality management in health care: principles and methods. 2nd ed. Sudbury, MA: Jones and Bartlett Publishers; 2004. p. 43-101.
- Director's Corner
- Current Priorities
- Executive Summary
- Research Spotlight
- Research Themes and Findings
- Research Dissemination
- Research Overview
- 2020 Year in Review
- 2019 Year in Review
- Engaging and Empowering Patients
- Optimizing Care Delivery for Clinicians
- Supporting Health Systems in Advancing Care Delivery
- Our Experts
- Search AHRQ-Funded Projects
- AHRQ-Funded Projects Map
- AHRQ Digital Healthcare Research Publications Database
- A Practical Guide for Implementing the Digital Healthcare Equity Framework
- ePROs in Clinical Care
- Guide to Integrate Patient-Generated Digital Health Data into Electronic Health Records in Ambulatory Care Settings
- Health IT Survey Compendium
- Time and Motion Studies Database
- Health Information Security and Privacy Collaboration Toolkit
- Implementation in Independent Pharmacies
- Implementation in Physician Offices
- Children's Electronic Health Record (EHR) Format
- Project Resources Archives
- Archived Tools & Resources
- National Webinars
- Funding Opportunities
- Digital Healthcare Research Home
- 2018 Year in Review Home
- Research Summary
- Research Spotlights
- 2019 Year in Review Home
- Annual Report Home

Kepner Tregoe Problem Solving
- Post last modified: 4 September 2023
- Reading time: 13 mins read
- Post category: Production Management

Drs. Charles Kepner and Benjamin Tregoe created this model in the 1950s, and it has since been utilised to solve some of the most difficult challenges, including troubleshooting the Apollo 13 crisis and safely guiding the stricken spacecraft back to Earth. It is likely to work for an organisation if it worked for NASA.
Table of Content
- 1.1.1 Recognise Priorities at All Levels
- 1.1.2 Recognise What Others Are Doing
- 1.1.3 Examine the Processes and SOPs That Are in Place:
- 1.2.1 Problem Identification
- 1.2.2 Identify the Root Cause
- 1.2.3 5 Whys
- 1.3.1 Generate Potential Solutions
- 1.3.2 Structured Brainstorming
- 1.3.3 Mind Map
- 1.3.4 Choose the Best Solution
- 1.4.1 Risk Identification and Assessment
- 1.4.2 De-Risk
The Kepner-Tregoe framework consists of four reasonable assessments that assist in identifying problems, developing solutions, and minimising risks. They are explained as follows:
Situation Analysis
Problem analysis, decision analysis, potential problem analysis.
Step one of the Kepner-Trego method, situation analysis, is dedicated to just that. The following are some topics to think about when assessing your circumstance:
Recognise Priorities at All Levels
Examine your organisation’s mission, vision, values, priorities and goals at every level. Consider how each level is linked to the others.
Recognise What Others Are Doing
Examine the priorities of your organisation from the outside now that you know what they are. What are the other businesses doing in your area? What are the actions of industry and academia? What is making the news these days? Such inquiries will assist you in identifying the external factors that form your surroundings.
Examine the Processes and SOPs That Are in Place:
What tools, methods, and workflows does your team, organisation, or firm use to get things done? How do people exchange and consume data? The answers to these questions will assist you in gaining a better understanding of how things work. And understanding how things function is the first step in figuring out what is not working. Take into account upcoming events.
Now that you have a better understanding of your surroundings, it is time to find out what is wrong and why. This section will assist you in doing so.
Problem Identification
The first step is to make a list of potential issues. Does not it appear to be simple? Not so fast, my friend. Remember that you may be a new employee, a new manager, or a new team member. Therefore, even though you collected reams of data for your Situation Analysis, you may be having trouble putting the puzzle together. That is OK. Here are two methods for bringing your issues into sharper focus.
Identify the Root Cause
How do you know your problem is the proper one now that you have recognised it? You most likely have no idea. That is why, to make sure you are dealing with the appropriate issue, you should undertake a root cause analysis. The ‘5 Whys’ method is my preferred strategy for this.
To investigate the sources and effects that underlay a problem, the ‘5 Whys’ approach to root cause analysis is applied. You begin by describing your issue and inquiring as to why it is occurring. Continue in this manner 3–5 times more till you have figured out what is causing your difficulty.
Now that you have figured out what is causing the problem, you can make a list of alternative remedies, compare them, and pick the best one.
Generate Potential Solutions
In general, the quality of your selection will be proportional to the number of solutions you develop. If you are gifted in this area, this is where your imagination will shine. Here are two strategies to get your creative juices flowing if you are weak in that department.
Structured Brainstorming
One of the most efficient strategies to come up with new ideas is to use structured brainstorming. Begin by forming a group of at least two and no more than ten individuals. Write the underlying problem on a whiteboard, hand out post-it notes, and urge the group to brainstorm as many remedies as they can in ten minutes, placing each sticky note on the whiteboard. To avoid groupthink, this must be done quietly.
Next, assign two members of the group to organise the sticky notes into groups or themes. Depending on the number of ideas created, this should take 2–5 minutes. In the next step, these themes and their solutions will be compared against one another.
A thought map is another important tool for generating solutions. A mind map is a creative, hierarchical way of visualising the interdependence of thoughts. Begin by jotting down your fundamental reason in the middle of a page. Expand your thinking and make a list of prospective workstreams, solutions, and initiatives for each. When you let go of your inhibitions and write the first thing that comes to mind, mind mapping works best.
Choose the Best Solution
Your capacity to make good decisions will determine a large part of your success as a people manager. As a result, you should not take chances when selecting a remedy. Instead, use a methodical approach to guarantee you are picking the finest option. Pros and cons lists and decision matrices are two excellent methods for doing so.
You have made it to the last but most important step: assessing potential issues. Your desire to move forward with implementation is probably stronger than it has ever been. But take your time. Step 4 will save you a lot of time and aggravation in the long run. This is where you will identify, appraise, and decide on risk management strategies.
Risk Identification and Assessment
Make a list of the potential dangers associated with your suggested remedy. In the automobile example above, you may see the possibility of the car breaking down or not being able to afford the car payment as a risk. Conduct a brainstorming session if you are having trouble identifying dangers. Examine the likelihoods and effects of the za you have identified next.
In our case, the chances of our new vehicle breaking down are low, but the repercussions may be severe if the problem is not covered under warranty or if we break down in a dangerous section of town with our infant in the car. If we are employed, the chances of not being able to afford the automobile payment are slim, but what if we lose our job? Were we going to be able to afford the car? If we default on the loan, we would have a negative mark on our credit, which will limit our purchasing power.
There are five risk management strategies to choose from, and you must select one for each risk you have identified:
- Assume: Assuming a risk means you have detected it but haven’t taken any steps to mitigate it. You simply accept the possibility and deal with the ramifications if it does. This is an effective method for low-probability, low-impact threats.
- Reduce: Taking pre-emptive actions to lessen the impact of risk so that the repercussions are smaller and easier to fix is known as risk reduction or risk mitigation. A notable example of a risk mitigation approach is the use of seat belts. A seat belt will not prevent an accident from occurring, but it will lessen the chance of injuries.
- Transfer: Offloading risk to another entity is known as risk transfer. A bank that bundles a portfolio of high-risk loans and sells them to another institution is an example of risk transfer to a third party.
- Exploit: When a risk has the potential to have a positive impact, you exploit it. In such instances, you should take precautions to guarantee that the risk does not arise. Assume we are creating an electric vehicle, and there is a chance demand will outstrip supply. You may take advantage of this danger by creating a new facility, stockpiling more resources, and recruiting more personnel.
- Avoid: Taking deliberate measures to avoid danger is known as risk avoidance. The recent postponing of international gatherings in reaction to the COVID-19 outbreak is a good example of risk avoidance. Amid a global epidemic, event organisers have judged that the risk of big gatherings is too severe.
Let us understand the application of Kepner-Tregoe model for a decision of buying a pre-owned car by an individual.
You Might Also Like
What is inventory management objective, importance, control techniques,, what is quality improvement basics, models and tools, quality certifications and award, what is quality measurement, cost of quality, learning from quality gurus, what is dmaic process, types of production system, what is materials management objectives, classification, systems approach, dynamics, what is total quality management objectives, principles, application, techniques, what is plant location factors, analysis, significance, selection criteria, what is purchasing management meaning, importance, aspects, objectives,, what is product design process, factors affecting, process design, process of purchasing management, leave a reply cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
World's Best Online Courses at One Place
We’ve spent the time in finding, so you can spend your time in learning
Digital Marketing
Personal growth.

Development
Using the Kepner-Tregoe Methodology for Effective Problem-Solving
The Kepner-Tregoe methodology is a problem-solving and decision-making framework that helps individuals and organizations systematically analyze problems, make decisions, and manage risks. Developed by Charles Kepner and Benjamin Tregoe in the 1950s, the methodology has been widely adopted by businesses, governments, and other organizations worldwide. One of the core components of the Kepner-Tregoe methodology is the use of a matrix to identify the root cause of a problem. In this article, we will explore how the matrix works and how it can be used to solve complex problems.
The Kepner-Tregoe methodology consists of four distinct steps: Situation Appraisal, Problem Analysis, Decision Analysis, and Potential Problem Analysis. Each step is designed to help individuals and teams approach complex problems in a structured and systematic way. In this article, we will focus on the Problem Analysis step, which involves identifying the root cause of a problem using a matrix.
The Problem Analysis step begins with defining the problem. This step involves clearly stating the problem and its impact on the organization. Next, the team identifies the symptoms of the problem. Symptoms are the visible or measurable indicators of the problem. Once the symptoms are identified, the team uses a matrix to identify the root cause of the problem.
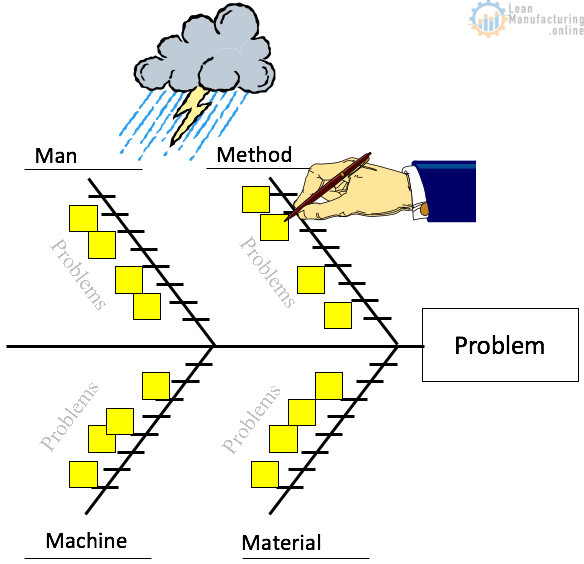
The matrix used in the Kepner-Tregoe methodology is called the Cause and Effect Analysis matrix, also known as the Ishikawa or fishbone diagram. The matrix is a visual tool that helps individuals and teams identify the underlying causes of a problem. The matrix is structured like a fishbone, with the problem or effect at the head of the fishbone and the potential causes of the problem branching off like a fish’s bones.
To use the matrix, the team first identifies the problem or effect that needs to be analyzed. This is written at the head of the fishbone. Next, the team identifies the major categories of potential causes that may be contributing to the problem. These categories are written on the main branches of the fishbone. Examples of potential categories include people, processes, technology, and the environment.
Once the major categories are identified, the team begins to brainstorm the potential causes within each category. Each potential cause is written on a small branch of the fishbone. The team continues to brainstorm potential causes until all potential causes have been identified.
Once the potential causes have been identified, the team begins to analyze each cause to determine its likelihood of contributing to the problem. This analysis involves evaluating each potential cause based on its ability to explain the symptoms of the problem. The team also considers the likelihood that each potential cause is contributing to the problem and the potential impact of each cause on the organization.
Based on this analysis, the team can identify the root cause of the problem. The root cause is the underlying issue causing the problem’s symptoms. Once the root cause has been identified, the team can develop and implement a solution to address the problem.
In conclusion, the Kepner-Tregoe methodology is a powerful tool for problem-solving and decision-making. The Problem Analysis step, which uses the Cause and Effect Analysis matrix, is a critical methodology component. By using the matrix, teams can systematically identify the root cause of a problem and develop effective solutions. Whether you are an individual or a team member, the Kepner-Tregoe methodology can help you approach complex problems confidently and clearly.
References: Kepner, C. H., & Tregoe, B. B. (2013). The new rational manager. Princeton, NJ: Princeton Research Press. Wu, T. (2019). An overview of the Kepner-Tregoe problem-solving methodology. Journal of Applied Management and Entrepreneurship
- More By sensei
- More In Blog

Maximize Efficiency with the Right Plant Layout: A Comprehensive Guide
Harnessing Business Excellence in Manufacturing Through the PDCA Approach
The Fishbone Diagram
Unlock the Power of Continuous Learning with Udemy’s Frequent Sales

How to Ace Your Next Job Interview: Expert Insights and Strategies

Mastering the Trio: Project, Program & Portfolio Management

Behaviors that kill employee motivation

Common Interview Questions for Project Management Roles
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Most Popular

4M Analysis Process
The purpose of this procedure is to define the steps to do a 4M …

PDCA – A Process Approach

OPL – One Point Lesson Template – Free Download

5S Audit Checklist and Report

Why-Why Analysis
Blog Search

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- About Our Ads
Brought to you by:

Can You Analyze This Problem?
By: Perrin Stryker
The Kepner-Tregoe approach replaces hit-or-miss methods with a systematic method of problem solving and decision making. Managers who train in this concept of problem analysis often discover that…
- Length: 6 page(s)
- Publication Date: May 1, 1965
- Discipline: Negotiation
- Product #: 65312-PDF-ENG
What's included:
- Educator Copy
$4.50 per student
degree granting course
$7.95 per student
non-degree granting course
Get access to this material, plus much more with a free Educator Account:
- Access to world-famous HBS cases
- Up to 60% off materials for your students
- Resources for teaching online
- Tips and reviews from other Educators
Already registered? Sign in
- Student Registration
- Non-Academic Registration
- Included Materials
The Kepner-Tregoe approach replaces hit-or-miss methods with a systematic method of problem solving and decision making. Managers who train in this concept of problem analysis often discover that their reasoning methods in handling problems and decisions are faulty. Readers test their own reasoning powers against the problems presented in a case history, based on an actual situation, and can then compare the results of their analysis with the solutions presented in a subsequent article, How to Analyze That Problem (July-August 1965). The main issues of the case involve questions concerning production, labor relations, and personnel.
May 1, 1965
Discipline:
Negotiation
Harvard Business Review
65312-PDF-ENG
We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
- Our Courses
Intro to Problem Analysis - eLearning
Don’t have the time or budget for full training? Become more aware of Kepner-Tregoe Problem Analysis with this introduction course.
The Kepner-Tregoe Problem Analysis (PA) tool has been used for over 60 years by problem solvers globally to find root cause. World-class troubleshooters use PA in operations, manufacturing, IT, customer support, and in many other applications.
In this 45-minute, self-paced course, you will be introduced to KT PA and complete a short knowledge assessment. This course can't replace full training in a workshop, but you will learn about the skills that expert troubleshooters are using to solve their toughest problems. With your purchase, you will be able to download relevant chapters from Kepner-Tregoe's New Rational Manager book and be provided a discount for a future KT training workshop.
You should take this course if:
- A full training course isn't possible right now, but you'd still like to learn about the main steps of KT Problem Analysis
- You'll be asked to participate in KT problem-solving activities at work and want to understand the approach that will be used at a high-level
- You'd like to read the relevant chapters from KT's New Rational Manager book
What you will learn:
- An overview of the 4 steps of KT PA
- Some examples of when KT PA can be used effectively
- Have your understanding tested in a short knowledge assessment
So what are you waiting for? Let us introduce you to KT Problem Analysis today.
The course is self-paced, 45-minutes long, and you'll have 90 days to complete it once you purchase it. To view the course, your device will need to meet these requirements .
If you need the skills to be a key problem solver at your company and want more robust training, please see our instructor-led workshops .
Questions? Email [email protected] for additional information.
Added to your cart:
© 2019 Kepner-Tregoe | All rights reserved
ABOUT KEPNER-TREGOE
For sixty years, KT has empowered companies to solve thousands of problems. We’ve had a front-row seat to help our clients navigate major business milestones. Sixty years of inquisitive teams asking the right questions that propel businesses forward. Sixty years of empowering organizations to become better. We’ve helped organizations tackle questions both large and small from tactical to the most strategic. This ongoing dialog has helped plant managers optimize people and processes and helped IT managers avert data and security breaches.
"I used to be afraid to be assigned a root cause evaluation, but not anymore. I know that I just need to follow a systematic process and get the right people involved."
– Maintenance Supervisor
KT'S PROBLEM SOLVING BASICS
$99 eLearning Course
WORKSHOP NAME Problem Solving Basics
COURSE TYPE Self-Paced, Online
OVERVIEW Research shows that the #1 skill organizations will require by 2020 is the ability to solve complex problems. The key to being an effective problem solver is knowing which type of problem you’re trying to solve, the tools to use, and how they complement each other. In this 90-minute, self-paced course, you will learn about the problem solving ecosystem, the basics of the different tools available, and when to employ each tool.
YOU SHOULD TAKE THIS IF YOU... 1. Feel overwhelmed by the different types of problems you're asked to solve 2. Have heard about (and maybe used) many different problem-solving tools, like 5 Whys, Fishbones, Six Sigma, and IS/IS NOTs, but don't know which to choose 3. Want a brief overview of Kepner-Tregoe's Problem Analysis, the root cause analysis tool that helped bring home Apollo 13
WHAT YOU WILL LEARN 1. How to identify the type of problem you are trying to solve 2. How to choose the right tool to fix each problem 3. How each tool can work effectively with KT’s Problem Analysis to solve the toughest problems
PROVEN SUCCESS ACROSS MULTIPLE INDUSTRIES
MANUFACTURING
FINANCIAL SERVICES
FOOD & BEVERAGE
116 Village Blvd., Suite 300 Princeton, NJ 08540 US
+1 609-921-2806 Toll Free: 800-537-6378
CONSUMER PRODUCTS
TRY A PREVIEW OF PROBLEM SOLVING BASICS FOR FREE
Learn the basics of problem solving tools and methods.
Problem Solving Basics $99 eLearning Course
Simulation-based training solutions
Learning best-practice problem solving techniques using state-of-the-art simulation technology, engineers have gaming systems at home – let´s give them one at work to make learning fun.
Our simulation-based programs that feature robots and gamification, bring the fun into learning with interactive and responsive troubleshooting exercises.
Learning through simulation helps individuals develop a deeper understanding of complex concepts and provides the opportunity to experience consequences of their actions in a safe to fail environment.
We know there is no substitute for hands-on experience with troubleshooting. That is why our simulation has realistic elements such as time pressure and “information overload” embedded into the experience, creating a sense of urgency and risk – just like problem solving in day-to-day work environments.
It also creates a highly engaging and collaborative team-building experience. Working through exercises together, celebrating successes, and overcoming setbacks, strengthens bonds and helps develop a team spirit between group members. Virtually all our participants state that their team-collaboration skills, and confidence in their peers, has been improved!
At KT, we are committed to continuously improving the learner experience and the return-on-investment for our clients. We have invested in innovative simulation learning experiences to help learners become active participants in the learning journey, leading to more immediate and deeper skill development, which leads to faster and more impactful business results.
Benefits of Simulation-based learning
Simulation offerings.
Frontline for Operations →
Frontline for ITSM & Tech Support →
Troubleshooting Simulation →
Risk Mitigation for Operations →
Risk Mitigation for IT →
Troubleshooting Simulation Team Championship →
Subscribe to the KT Newsletter

COMMENTS
The founders Charles Kepner and Benjamin Tregoe developed a rational working method in the 1960s in which they researched and identified the troubleshooting skills of people. Throughout the centuries mankind has learned to deal with complexity and to (directly) anticipate on this. As a consequence, the traditional thinking pattern became a part ...
The Kepner-Tregoe Matrix comprises four basic steps: Situation Appraisal - identify concerns and outline the priorities. Problem Analysis - describe the exact problem or issue by identifying and evaluating the causes. Decision Analysis - identify and evaluate alternatives by performing a risk analysis for each and then make a final decision.
Skills developed during a Kepner-Tregoe Problem Solving & Decision Making (PSDM) workshop enable you to: Conduct root cause analysis (RCA) on complex problems. Make tough decisions aligned with operational priorities. Identify and plan for the resolution of high-priority issues. Understand and proactively manage risks and opportunities.
First developed in the 1960s by Charles Kepner and Benjamin Tregoe, the Kepner-Tregoe process is a systematic approach to problem-solving used in a variety of industries, including business and government. The process involves four key steps: situation appraisal, problem analysis, decision analysis, and. potential problem analysis.
Benjamin Tregoe and Charles Kepner were originally researching the way our minds work - how we solve problems and make decisions. They were interested in the factors that make someone a good problem solver, for example. They formulated an approach that attempts to emulate the thought patterns of someone with excellent problem solving skills.
The Kepner-Tregoe technique is a problem-solving and decision-making framework that provides a systematic approach for identifying, analyzing, and resolving issues. It consists of four main processes: Problem Analysis: This process involves defining the problem, understanding its nature, and diagnosing the root cause. By distinguishing between ...
In this era of digital transformation, an agile mindset is required to quickly assess complex situations, solve problems, and make good decisions. The KT Problem Solving Learning Path provides a foundational understanding of Kepner-Tregoe's Situation Appraisal and Problem Analysis methodologies combining the power of dynamic application-based ...
Email [email protected] for additional information. The key to being an effective problem solver is knowing which type of problem you're trying to solve, the tools to use, and how they complement each other. In this 90-minute, self-paced course, you will learn about the problem solving ecosystem, the basics of the different ...
A Kepner-Tregoe matrix is used to find causes of a problem. It isolates the who, what, when, where, and how aspects of an event, keeping the focus on the elements that have an impact on the event and eliminating the elements that do not. This allows you to compare what the problem is, with what it is not, illuminating distinctive features of the problem and pointing out its potential causes.
In this video, there is an overview of the Kepner-Tregoe systematic problem-solving method which explores finding the cause of a problem by identifying when the problem does and when the problem ...
Kepner Tregoe Problem Solving. 4 September 2023. 13 mins read. Production Management. Drs. Charles Kepner and Benjamin Tregoe created this model in the 1950s, and it has since been utilised to solve some of the most difficult challenges, including troubleshooting the Apollo 13 crisis and safely guiding the stricken spacecraft back to Earth.
The Kepner-Tregoe methodology is a problem-solving and decision-making framework that helps individuals and organizations systematically analyze problems, make decisions, and manage risks. Developed by Charles Kepner and Benjamin Tregoe in the 1950s, the methodology has been widely adopted by businesses, governments, and other organizations ...
The Kepner-Tregoe approach replaces hit-or-miss methods with a systematic method of problem solving and decision making. Managers who train in this concept of problem analysis often discover that their reasoning methods in handling problems and decisions are faulty. Readers test their own reasoning powers against the problems presented in a case history, based on an actual situation, and can ...
These self-paced virtual courses will introduce you to the world of problem solving. You'll find content about lots of different tools, such as 5 Whys and Fishbones in Problem Solving Basics and intros to Kepner-Tregoe's suite of tools for root cause analysis, decision making, and risk mitigation.
Highlights from Kepner-Tregoe and Cisco presentation at TSW Conference 2011. Part I of a presentation from Dave Broenen of Cisco Systems on how Cisco turned the tables to get profitable results from their support organization. In this video Dave challenges the natural affinity of service organizations to favor software and technical training as ...
The Kepner-Tregoe Problem Analysis (PA) tool has been used for over 60 years by problem solvers globally to find root cause. World-class troubleshooters use PA in operations, manufacturing, IT, customer support, and in many other applications. In this 45-minute, self-paced course, you will be introduced to KT PA and complete a short knowledge ...
The Kepner-Tregoe Method was developed by Charles Kepner and Benjamin Tregoe in the 1950s as a way to help managers and engineers solve technical problems. It is based on the principle of rational ...
How each tool can work effectively with KT's Problem Analysis to solve the toughest problems. PROVEN SUCCESS ACROSS MULTIPLE INDUSTRIES. MANUFACTURING. FINANCIAL SERVICES. FOOD & BEVERAGE. 116 Village Blvd., Suite 300. Princeton, NJ 08540 US. +1 609-921-2806. Toll Free: 800-537-6378.
1. An explanation of the Kepner-Tregoe approach to problem solving and decision making. Most of the informa tion was taken from an analysis of the book, The Rational Manager. 2. A comparison of the Kepner-Tregoe approach to other systems and ideas of problem solving and decision making.
Kepner-Tregoe Thailand, LLC 230 CS Tower, 9th Floor Rajchadaphisaek Road Huaykwang, Bangkok 10320 Thailand Malaysia +603-7660-9128
Kepner-Tregoe Problem Solving methods and training have been helping companies and individuals improve their Problem Solving skills and processes since 1953 with a proven track record of success. We understand that every organization is different and through our experience we can help you identify and implement the right Problem Solving tools ...
Kepner-Tregoe workshops are held in many major cities throughout the world and are open for enrollment with the option to attend a public or a virtual class at a time that suits your schedule. ... Building Beyond A Problem Solving Culture. ... Within the first year following KT training and the introduction of problem-management tools, client ...
Kepner-Tregoe Thailand, LLC 230 CS Tower, 9th Floor Rajchadaphisaek Road Huaykwang, Bangkok 10320 Thailand Malaysia +603-7660-9128
Kepner-Tregoe workshops are held in many major cities throughout the world and are open for enrollment with the option to attend a public or a virtual class at a time that suits your schedule. You will learn KT concepts and practice realistic case studies with peers from many different industries.