1.1 What Is Economics, and Why Is It Important?
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Discuss the importance of studying economics
- Explain the relationship between production and division of labor
- Evaluate the significance of scarcity
Economics is the study of how humans make decisions in the face of scarcity. These can be individual decisions, family decisions, business decisions or societal decisions. If you look around carefully, you will see that scarcity is a fact of life. Scarcity means that human wants for goods, services and resources exceed what is available. Resources, such as labor, tools, land, and raw materials are necessary to produce the goods and services we want but they exist in limited supply. Of course, the ultimate scarce resource is time- everyone, rich or poor, has just 24 expendable hours in the day to earn income to acquire goods and services, for leisure time, or for sleep. At any point in time, there is only a finite amount of resources available.
Think about it this way: In 2015 the labor force in the United States contained over 158 million workers, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. The total land area was 3,794,101 square miles. While these are certainly large numbers, they are not infinite. Because these resources are limited, so are the numbers of goods and services we produce with them. Combine this with the fact that human wants seem to be virtually infinite, and you can see why scarcity is a problem.

Introduction to FRED
Data is very important in economics because it describes and measures the issues and problems that economics seek to understand. A variety of government agencies publish economic and social data. For this course, we will generally use data from the St. Louis Federal Reserve Bank's FRED database. FRED is very user friendly. It allows you to display data in tables or charts, and you can easily download it into spreadsheet form if you want to use the data for other purposes. The FRED website includes data on nearly 400,000 domestic and international variables over time, in the following broad categories:
- Money, Banking & Finance
- Population, Employment, & Labor Markets (including Income Distribution)
- National Accounts (Gross Domestic Product & its components), Flow of Funds, and International Accounts
- Production & Business Activity (including Business Cycles)
- Prices & Inflation (including the Consumer Price Index, the Producer Price Index, and the Employment Cost Index)
- International Data from other nations
- U.S. Regional Data
- Academic Data (including Penn World Tables & NBER Macrohistory database)
For more information about how to use FRED, see the variety of videos on YouTube starting with this introduction.
If you still do not believe that scarcity is a problem, consider the following: Does everyone require food to eat? Does everyone need a decent place to live? Does everyone have access to healthcare? In every country in the world, there are people who are hungry, homeless (for example, those who call park benches their beds, as Figure 1.2 shows), and in need of healthcare, just to focus on a few critical goods and services. Why is this the case? It is because of scarcity. Let’s delve into the concept of scarcity a little deeper, because it is crucial to understanding economics.
The Problem of Scarcity
Think about all the things you consume: food, shelter, clothing, transportation, healthcare, and entertainment. How do you acquire those items? You do not produce them yourself. You buy them. How do you afford the things you buy? You work for pay. If you do not, someone else does on your behalf. Yet most of us never have enough income to buy all the things we want. This is because of scarcity. So how do we solve it?
Visit this website to read about how the United States is dealing with scarcity in resources.
Every society, at every level, must make choices about how to use its resources. Families must decide whether to spend their money on a new car or a fancy vacation. Towns must choose whether to put more of the budget into police and fire protection or into the school system. Nations must decide whether to devote more funds to national defense or to protecting the environment. In most cases, there just isn’t enough money in the budget to do everything. How do we use our limited resources the best way possible, that is, to obtain the most goods and services we can? There are a couple of options. First, we could each produce everything we each consume. Alternatively, we could each produce some of what we want to consume, and “trade” for the rest of what we want. Let’s explore these options. Why do we not each just produce all of the things we consume? Think back to pioneer days, when individuals knew how to do so much more than we do today, from building their homes, to growing their crops, to hunting for food, to repairing their equipment. Most of us do not know how to do all—or any—of those things, but it is not because we could not learn. Rather, we do not have to. The reason why is something called the division and specialization of labor , a production innovation first put forth by Adam Smith ( Figure 1.3 ) in his book, The Wealth of Nations .
The Division of and Specialization of Labor
The formal study of economics began when Adam Smith (1723–1790) published his famous book The Wealth of Nations in 1776. Many authors had written on economics in the centuries before Smith, but he was the first to address the subject in a comprehensive way. In the first chapter, Smith introduces the concept of division of labor , which means that the way one produces a good or service is divided into a number of tasks that different workers perform, instead of all the tasks being done by the same person.
To illustrate division of labor, Smith counted how many tasks went into making a pin: drawing out a piece of wire, cutting it to the right length, straightening it, putting a head on one end and a point on the other, and packaging pins for sale, to name just a few. Smith counted 18 distinct tasks that different people performed—all for a pin, believe it or not!
Modern businesses divide tasks as well. Even a relatively simple business like a restaurant divides the task of serving meals into a range of jobs like top chef, sous chefs, less-skilled kitchen help, servers to wait on the tables, a greeter at the door, janitors to clean up, and a business manager to handle paychecks and bills—not to mention the economic connections a restaurant has with suppliers of food, furniture, kitchen equipment, and the building where it is located. A complex business like a large manufacturing factory, such as the shoe factory ( Figure 1.4 ), or a hospital can have hundreds of job classifications.
Why the Division of Labor Increases Production
When we divide and subdivide the tasks involved with producing a good or service, workers and businesses can produce a greater quantity of output. In his observations of pin factories, Smith noticed that one worker alone might make 20 pins in a day, but that a small business of 10 workers (some of whom would need to complete two or three of the 18 tasks involved with pin-making), could make 48,000 pins in a day. How can a group of workers, each specializing in certain tasks, produce so much more than the same number of workers who try to produce the entire good or service by themselves? Smith offered three reasons.
First, specialization in a particular small job allows workers to focus on the parts of the production process where they have an advantage. (In later chapters, we will develop this idea by discussing comparative advantage .) People have different skills, talents, and interests, so they will be better at some jobs than at others. The particular advantages may be based on educational choices, which are in turn shaped by interests and talents. Only those with medical degrees qualify to become doctors, for instance. For some goods, geography affects specialization. For example, it is easier to be a wheat farmer in North Dakota than in Florida, but easier to run a tourist hotel in Florida than in North Dakota. If you live in or near a big city, it is easier to attract enough customers to operate a successful dry cleaning business or movie theater than if you live in a sparsely populated rural area. Whatever the reason, if people specialize in the production of what they do best, they will be more effective than if they produce a combination of things, some of which they are good at and some of which they are not.
Second, workers who specialize in certain tasks often learn to produce more quickly and with higher quality. This pattern holds true for many workers, including assembly line laborers who build cars, stylists who cut hair, and doctors who perform heart surgery. In fact, specialized workers often know their jobs well enough to suggest innovative ways to do their work faster and better.
A similar pattern often operates within businesses. In many cases, a business that focuses on one or a few products (sometimes called its “ core competency ”) is more successful than firms that try to make a wide range of products.
Third, specialization allows businesses to take advantage of economies of scale , which means that for many goods, as the level of production increases, the average cost of producing each individual unit declines. For example, if a factory produces only 100 cars per year, each car will be quite expensive to make on average. However, if a factory produces 50,000 cars each year, then it can set up an assembly line with huge machines and workers performing specialized tasks, and the average cost of production per car will be lower. The ultimate result of workers who can focus on their preferences and talents, learn to do their specialized jobs better, and work in larger organizations is that society as a whole can produce and consume far more than if each person tried to produce all of their own goods and services. The division and specialization of labor has been a force against the problem of scarcity.
Trade and Markets
Specialization only makes sense, though, if workers can use the pay they receive for doing their jobs to purchase the other goods and services that they need. In short, specialization requires trade.
You do not have to know anything about electronics or sound systems to play music—you just buy an iPod or MP3 player, download the music, and listen. You do not have to know anything about artificial fibers or the construction of sewing machines if you need a jacket—you just buy the jacket and wear it. You do not need to know anything about internal combustion engines to operate a car—you just get in and drive. Instead of trying to acquire all the knowledge and skills involved in producing all of the goods and services that you wish to consume, the market allows you to learn a specialized set of skills and then use the pay you receive to buy the goods and services you need or want. This is how our modern society has evolved into a strong economy.
Why Study Economics?
Now that you have an overview on what economics studies, let’s quickly discuss why you are right to study it. Economics is not primarily a collection of facts to memorize, although there are plenty of important concepts to learn. Instead, think of economics as a collection of questions to answer or puzzles to work. Most importantly, economics provides the tools to solve those puzzles.
Consider the complex and critical issue of education barriers on national and regional levels, which affect millions of people and result in widespread poverty and inequality. Governments, aid organizations, and wealthy individuals spend billions of dollars each year trying to address these issues. Nations announce the revitalization of their education programs; tech companies donate devices and infrastructure, and celebrities and charities build schools and sponsor students. Yet the problems remain, sometimes almost as pronounced as they were before the intervention. Why is that the case? In 2019, three economists—Esther Duflo, Abhijit Banerjee, and Michael Kremer—were awarded the Nobel Prize for their work to answer those questions. They worked diligently to break the widespread problems into smaller pieces, and experimented with small interventions to test success. The award citation credited their work with giving the world better tools and information to address poverty and improve education. Esther Duflo, who is the youngest person and second woman to win the Nobel Prize in Economics, said, "We believed that like the war on cancer, the war on poverty was not going to be won in one major battle, but in a series of small triumphs. . . . This work and the culture of learning that it fostered in governments has led to real improvement in the lives of hundreds of millions of poor people.”
As you can see, economics affects far more than business. For example:
- Virtually every major problem facing the world today, from global warming, to world poverty, to the conflicts in Syria, Afghanistan, and Somalia, has an economic dimension. If you are going to be part of solving those problems, you need to be able to understand them. Economics is crucial.
- It is hard to overstate the importance of economics to good citizenship. You need to be able to vote intelligently on budgets, regulations, and laws in general. When the U.S. government came close to a standstill at the end of 2012 due to the “fiscal cliff,” what were the issues? Did you know?
- A basic understanding of economics makes you a well-rounded thinker. When you read articles about economic issues, you will understand and be able to evaluate the writer’s argument. When you hear classmates, co-workers, or political candidates talking about economics, you will be able to distinguish between common sense and nonsense. You will find new ways of thinking about current events and about personal and business decisions, as well as current events and politics.
The study of economics does not dictate the answers, but it can illuminate the different choices.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/principles-economics-3e/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Steven A. Greenlaw, David Shapiro, Daniel MacDonald
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Principles of Economics 3e
- Publication date: Dec 14, 2022
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-economics-3e/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/principles-economics-3e/pages/1-1-what-is-economics-and-why-is-it-important
© Jan 23, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
1.1 What Is Economics, and Why Is It Important?
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Discuss the importance of studying economics
- Explain the relationship between production and division of labor
- Evaluate the significance of scarcity
Economics is the study of how humans make decisions in the face of scarcity. These can be individual decisions, family decisions, business decisions or societal decisions. If you look around carefully, you will see that scarcity is a fact of life. Scarcity means that human wants for goods, services and resources exceed what is available. Resources, such as labor, tools, land, and raw materials are necessary to produce the goods and services we want but they exist in limited supply. Of course, the ultimate scarce resource is time- everyone, rich or poor, has just 24 hours in the day to try to acquire the goods they want. At any point in time, there is only a finite amount of resources available.
Think about it this way: the total land area of the main Hawaiian islands is only 10,931 square miles. Because land and other natural resources are limited, so are the numbers of goods and services we can produce with them. Combine this with the fact that human wants seem to be virtually infinite, and you can see why scarcity is a problem.
If you still do not believe that scarcity is a problem, consider the following: Does everyone need food to eat? Does everyone need a decent place to live? Does everyone have access to healthcare? In Hawaiʻi there are people who are hungry, homeless, and in need of healthcare, just to focus on a few critical goods and services. Why is this the case? It is because of scarcity. Let’s delve into the concept of scarcity a little deeper, because it is crucial to understanding economics.
What is a good and what is a service?
Goods have a physical tangible presence, for example, a pizza or a scissors. Services have no physical tangible presence but have economic value (people are willing to pay to get this service). Examples of services include the delivery of a pizza or getting your hair cut.
Only around 20% of workers in the US work at jobs where they produce goods. The percentage is even smaller in Hawaiʻi: only 4% of workers in Hawaiʻi produce goods! What are the main services produced in Hawaiʻi and what are the main goods?
The Problem of Scarcity
Think about all the things you consume: food, shelter, clothing, transportation, healthcare, and entertainment. How do you acquire those items? You do not produce them yourself. You buy them. How do you afford the things you buy? You work for pay. Or if you do not, someone else does on your behalf. Yet most of us never have enough to buy all the things we want. This is because of scarcity. So how do we solve it?
Visit this website to read about how the United States is dealing with scarcity in resources.
Every society, at every level, must make choices about how to use its resources. Families must decide whether to spend their money on a new car or a fancy vacation. Towns must choose whether to put more of the budget into police and fire protection or into the school system. Nations must decide whether to devote more funds to national defense or to protecting the environment. In most cases, there just isn’t enough money in the budget to do everything. So why do we not each just produce all of the things we consume? The simple answer is most of us do not know how, but that is not the main reason. (When you study economics, you will discover that the obvious choice is not always the right answer—or at least the complete answer. Studying economics teaches you to think in a different of way.) Think back to pioneer days, when individuals knew how to do so much more than we do today, from building their homes, to growing their crops, to hunting for food, to repairing their equipment. Most of us do not know how to do all—or any—of those things. It is not because we could not learn. Rather, we do not have to. The reason why is something called the division and specialization of labor , a production innovation first put forth by Adam Smith in his book, The Wealth of Nations .
The Division of and Specialization of Labor
The formal study of economics began when Adam Smith (1723–1790) published his famous book The Wealth of Nations in 1776. Many authors had written on economics in the centuries before Smith, but he was the first to address the subject in a comprehensive way. In the first chapter, Smith introduces the division of labor , which means that the way a good or service is produced is divided into a number of tasks that are performed by different workers, instead of all the tasks being done by the same person.
To illustrate the division of labor, Smith counted how many tasks went into making a pin: drawing out a piece of wire, cutting it to the right length, straightening it, putting a head on one end and a point on the other, and packaging pins for sale, to name just a few. Smith counted 18 distinct tasks that were often done by different people—all for a pin, believe it or not!
Modern businesses divide tasks as well. Even a relatively simple business like a restaurant divides up the task of serving meals into a range of jobs like top chef, sous chefs, less-skilled kitchen help, servers to wait on the tables, a greeter at the door, janitors to clean up, and a business manager to handle paychecks and bills—not to mention the economic connections a restaurant has with suppliers of food, furniture, kitchen equipment, and the building where it is located (check out the video below). A complex business like a large manufacturing factory or a hospital can have hundreds of job classifications.
The Division of Labor at work at Marukame Udon in Waikiki:
Why the Division of Labor Increases Production
When the tasks involved with producing a good or service are divided and subdivided, workers and businesses can produce a greater quantity of output. In his observations of pin factories, Smith observed that one worker alone might make 20 pins in a day, but that a small business of 10 workers (some of whom would need to do two or three of the 18 tasks involved with pin-making), could make 48,000 pins in a day. How can a group of workers, each specializing in certain tasks, produce so much more than the same number of workers who try to produce the entire good or service by themselves? Smith offered three reasons.
First, specialization in a particular small job allows workers to focus on the parts of the production process where they have an advantage. (In later chapters, we will develop this idea by discussing comparative advantage .) People have different skills, talents, and interests, so they will be better at some jobs than at others. The particular advantages may be based on educational choices, which are in turn shaped by interests and talents. Only those with medical degrees qualify to become doctors, for instance. For some goods, specialization will be affected by geography—it is easier to be a wheat farmer in North Dakota than in Florida, but easier to run a tourist hotel in Florida than in North Dakota. If you live in or near a big city, it is easier to attract enough customers to operate a successful dry cleaning business or movie theater than if you live in a sparsely populated rural area. Whatever the reason, if people specialize in the production of what they do best, they will be more productive than if they produce a combination of things, some of which they are good at and some of which they are not.
Second, workers who specialize in certain tasks often learn to produce more quickly and with higher quality. This pattern holds true for many workers, including assembly line laborers who build cars, stylists who cut hair, and doctors who perform heart surgery. In fact, specialized workers often know their jobs well enough to suggest innovative ways to do their work faster and better.
A similar pattern often operates within businesses. In many cases, a business that focuses on one or a few products (sometimes called its “ core competency ”) is more successful than firms that try to make a wide range of products.
Third, specialization allows businesses to take advantage of economies of scale , which means that for many goods, as the level of production increases, the average cost of producing each individual unit declines. For example, if a factory produces only 100 cars per year, each car will be quite expensive to make on average. However, if a factory produces 50,000 cars each year, then it can set up an assembly line with huge machines and workers performing specialized tasks, and the average cost of production per car will be lower. The ultimate result of workers who can focus on their preferences and talents, learn to do their specialized jobs better, and work in larger organizations is that society as a whole can produce and consume far more than if each person tried to produce all of their own goods and services. The division and specialization of labor has been a force against the problem of scarcity.
Trade and Markets
Specialization only makes sense, though, if workers can use the pay they receive for doing their jobs to purchase the other goods and services that they need. In short, specialization requires trade.
You do not have to know anything about electronics or sound systems to play music—you just buy an iPod or MP3 player, download the music and listen. You do not have to know anything about artificial fibers or the construction of sewing machines if you need a jacket—you just buy the jacket and wear it. You do not need to know anything about internal combustion engines to operate a car—you just get in and drive. Instead of trying to acquire all the knowledge and skills involved in producing all of the goods and services that you wish to consume, the market allows you to learn a specialized set of skills and then use the pay you receive to buy the goods and services you need or want. This is how our modern society has evolved into a strong economy.
Why Study Economics?
Now that we have gotten an overview on what economics studies, let’s quickly discuss why you are right to study it. Economics is not primarily a collection of facts to be memorized, though there are plenty of important concepts to be learned. Instead, economics is better thought of as a collection of questions to be answered or puzzles to be worked out. Most important, economics provides the tools to work out those puzzles. If you have yet to be been bitten by the economics “bug,” there are other reasons why you should study economics.
- Virtually every major problem facing the world today, from global warming, to world poverty, to the conflicts in Syria, Afghanistan, and Somalia, has an economic dimension. If you are going to be part of solving those problems, you need to be able to understand them. Economics is crucial.
- It is hard to overstate the importance of economics to good citizenship. You need to be able to vote intelligently on budgets, regulations, and laws in general. When the U.S. government came close to a standstill at the end of 2012 due to the “fiscal cliff,” what were the issues involved? Did you know?
- A basic understanding of economics makes you a well-rounded thinker. When you read articles about economic issues, you will understand and be able to evaluate the writer’s argument. When you hear classmates, co-workers, or political candidates talking about economics, you will be able to distinguish between common sense and nonsense. You will find new ways of thinking about current events and about personal and business decisions, as well as current events and politics.
The study of economics does not dictate the answers, but it can illuminate the different choices.
Key Concepts and Summary
Economics seeks to solve the problem of scarcity, which is when human wants for goods and services exceed the available supply. A modern economy displays a division of labor, in which people earn income by specializing in what they produce and then use that income to purchase the products they need or want. The division of labor allows individuals and firms to specialize and to produce more for several reasons: a) It allows the agents to focus on areas of advantage due to natural factors and skill levels; b) It encourages the agents to learn and invent; c) It allows agents to take advantage of economies of scale. Division and specialization of labor only work when individuals can purchase what they do not produce in markets. Learning about economics helps you understand the major problems facing the world today, prepares you to be a good citizen, and helps you become a well-rounded thinker.
Self-Check Questions
- What is scarcity? Can you think of two causes of scarcity?
- Residents of the town of Smithfield like to consume hams, but each ham requires 10 people to produce it and takes a month. If the town has a total of 100 people, what is the maximum amount of ham the residents can consume in a month?
- A consultant works for $200 per hour. She likes to eat vegetables, but is not very good at growing them. Why does it make more economic sense for her to spend her time at the consulting job and shop for her vegetables?
- A computer systems engineer could paint his house, but it makes more sense for him to hire a painter to do it. Explain why.
Review Questions
- Give the three reasons that explain why the division of labor increases an economy’s level of production.
- What are three reasons to study economics?
Critical Thinking Questions
- Suppose you have a team of two workers: one is a baker and one is a chef. Explain why the kitchen can produce more meals in a given period of time if each worker specializes in what they do best than if each worker tries to do everything from appetizer to dessert.
- Why would division of labor without trade not work?
- Can you think of any examples of free goods, that is, goods or services that are not scarce?
Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor. 2015. “The Employment Situation—February 2015.” Accessed March 27, 2015. http://www.bls.gov/news.release/pdf/empsit.pdf.
Williamson, Lisa. “US Labor Market in 2012.” Bureau of Labor Statistics . Accessed December 1, 2013. http://www.bls.gov/opub/mlr/2013/03/art1full.pdf.
Answers for Self-Check Questions
- Scarcity means human wants for goods and services exceed the available supply. Supply is limited because resources are limited. Demand, however, is virtually unlimited. Whatever the supply, it seems human nature to want more.
- 100 people / 10 people per ham = a maximum of 10 hams per month if all residents produce ham. Since consumption is limited by production, the maximum number of hams residents could consume per month is 10.
- She is very productive at her consulting job, but not very productive growing vegetables. Time spent consulting would produce far more income than it what she could save growing her vegetables using the same amount of time. So on purely economic grounds, it makes more sense for her to maximize her income by applying her labor to what she does best (i.e. specialization of labor).
- The engineer is better at computer science than at painting. Thus, his time is better spent working for pay at his job and paying a painter to paint his house. Of course, this assumes he does not paint his house for fun!
Principles of Microeconomics - Hawaii Edition Copyright © 2018 by John Lynham is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Importance of economics in our daily lives
Economics affects our daily lives in both obvious and subtle ways. From an individual perspective, economics frames many choices we have to make about work, leisure, consumption and how much to save. Our lives are also influenced by macro-economic trends, such as inflation, interest rates and economic growth.
Summary – why economics is important
- The opportunity costs we face in deciding what to buy – how to use time
- How to maximise our economic utility and avoid behavioural bias
- How the macro-economic – inflation, economic growth and employment prospects affect our living standards.
- Individual markets like housing market can influence our standard of living.
- Understanding issues like externalities. We may not like paying petrol tax, but if we see it helps to reduce pollution and congestion and the tax revenue is used to subsides public transport, it gives a different perspective.
Economic choices – opportunity cost
We are constantly faced with choices. It may be a matter of limited time. For example, at the weekend:
- We could spend 8 hours working in a cafe at the Minimum Wage of £7.83
- Or we could spend 8 hours studying for our A-Levels.
- Alternatively, we could choose to spend 8 hours of leisure (sleeping in, Facebook e.t.c.)
Each choice has an opportunity cost. The opportunity cost of earning 8*£7.83 = £62.64 is that we don’t have time to study. This could lead to poorer exam results, which could lead to lower future earning potential. Choosing to maximise our income in the short term (earning £62 a day) may reduce our lifetime earnings and could be a poor decision – unless working in a cafe doesn’t affect our future earnings. We may feel job experience more useful than an essay on allocative efficiency.
The problem is that when making decisions about whether to study, work or pursue leisure, we may forget or ignore long-term effects. Deciding to spend all our free time earning £62 is something we may regret later in life. Economists suggest education is a merit good – meaning people may underestimate the benefits of studying. Under-consumption of education is an example of market failure.
Considering opportunity cost can help us make better decisions. If we act on instinct, we may choose the most pleasurable or easiest course of action, but the best decision in the short term may not be best in long term.
Choice of study vs leisure
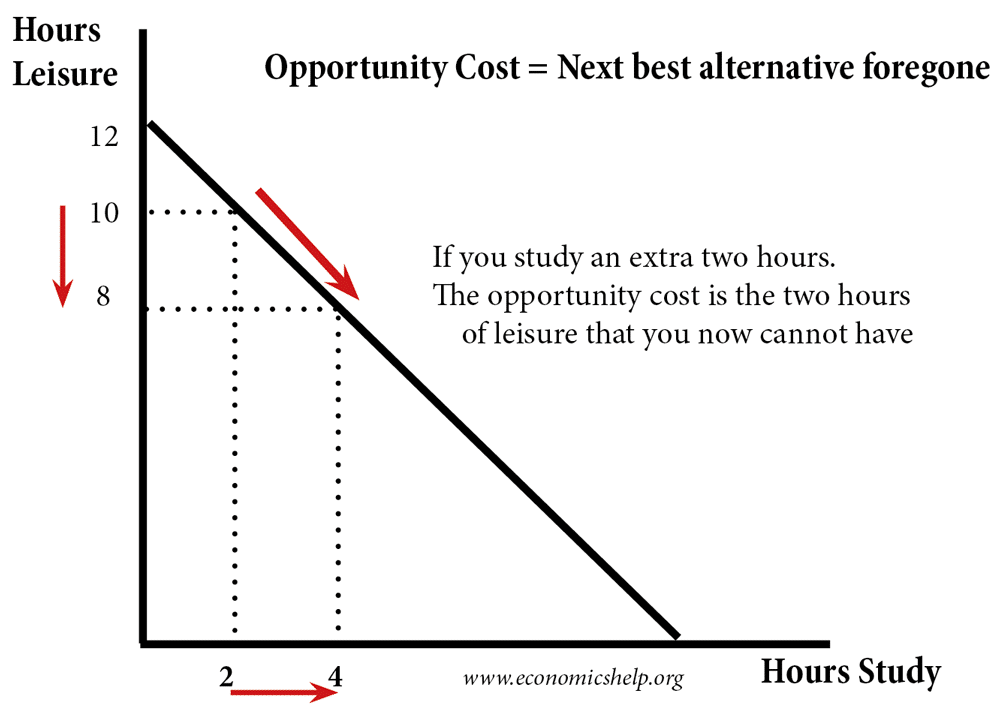
A production possibility frontier showing a simple trade off – time spent working or time spent on leisure.
Another important element of life is work. Which job will give the most satisfaction? It is not just about finding a well-paid job, we tend to gain most job satisfaction when we feel part of the process and a degree of responsibility and influence. Behavioural economists such as Dan Ariely have examined motivations for work and find that income/bonuses is less important than suggested by neo-liberal economic theory.
Nudges and rational behaviour
In traditional economics, it is assumed individuals are rational and utility maximising. In other words, it is assumed we calculate decision to maximise our economic welfare – spending money only on those goods which give us satisfaction.
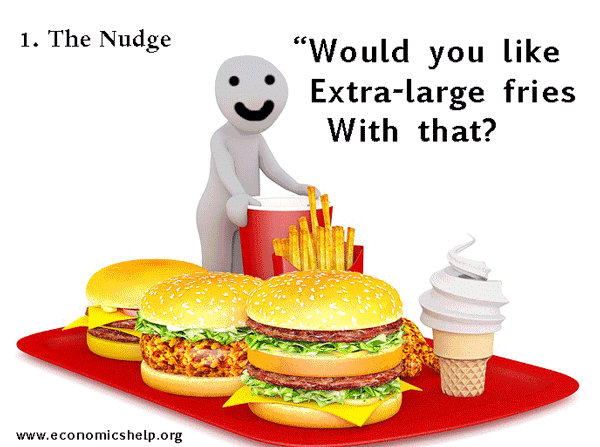
However, behavioural economists note that we are often influenced by irrational and non-utility maximising influences. For example, companies which ‘ nudge ‘ us to make decisions which harm our welfare – e.g. super-sized portions, we don’t really need but cause us to become less healthy.
The importance of the insights of behavioural economics is that we can become aware of factors which may cause us to make sub-optimal decisions. We can try to resist commercial nudges – which encourage us to consume goods which don’t really benefit us.
Behavioural economics and bias
A recent development in economics is the work of behavioural economics – which places more emphasis on elements of psychology. For example, are humans really rational utility maximisers – as suggested by traditional economic theory? Behavioural economics suggests not – but humans are influenced by emotional factors, such as loss aversion (we prefer the status quo, to losing what we have), present time period bias .
Importance of the macroeconomy on our daily lives
When making decisions we don’t tend to first look at leading economic indicators. But, perceptions about the economic outlook can influence certain decisions. For example, those aware of the current economic situation may be aware the depth of the recession which makes a period of low-interest rates more likely. This suggests that if you could get a mortgage, mortgage payments would be cheaper, but, saving would give a poor return.
However, the bad state of the economy and high unemployment rate is a factor that may encourage students to stay on and study. Since youth unemployment is currently very high, it makes more sense to spend three years getting a degree rather than going straight on to the job market.
The only problem is that many other students are thinking the same. Hence the competition for university places is becoming much stronger.
How to survive a period of inflation?

Suppose, we are living in a period of high inflation, how would that affect our economic welfare?
The real value of our savings will decline – unless we can secure an interest rate higher than the rate of inflation. In periods of high inflation, it may be advisable to take out index-linked savings – saving accounts and bonds which give an interest rate related to the inflation rate.
If we cannot secure a good interest rate, an option is to invest in commodities or assets which can protect their value better than ordinary savings accounts
How will we be affected by rising interest rates?
If interest rates increase, then it will increase the cost of mortgage payments and interest on loans and credit cards. It can be problematic for individuals who are over-extended on credit. Higher interest rates can also lead to a slowing economy and increase the risk of unemployment.
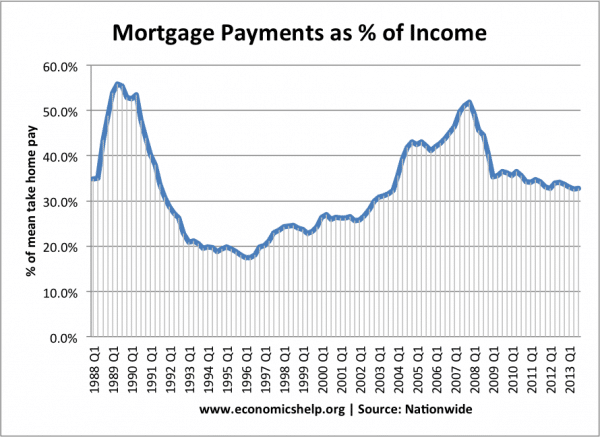
Mortgage affordability. High-interest rates in the late 1980s caused mortgage payments to take over 50% of take-home pay from households.
See The effect of higher interest rates .
If we are considering investing in the stock market or housing market, what can economics teach us?
One cautionary tale is that of irrational exuberance – avoid getting caught up in asset booms – where investor confidence gets carried away and people end up buying shares/assets – even though the price has become overvalued.
Externalities
When choosing what to consume and produce, we often ignore externalities. For example, driving into city centre may contribute to pollution and congestion. The social cost of driving is higher than the private cost. Would our living standards be increased by supporting a congestion charge? At first glance, no – we pay higher taxes. But, if there are external costs a higher tax can lead to a more socially efficient level.
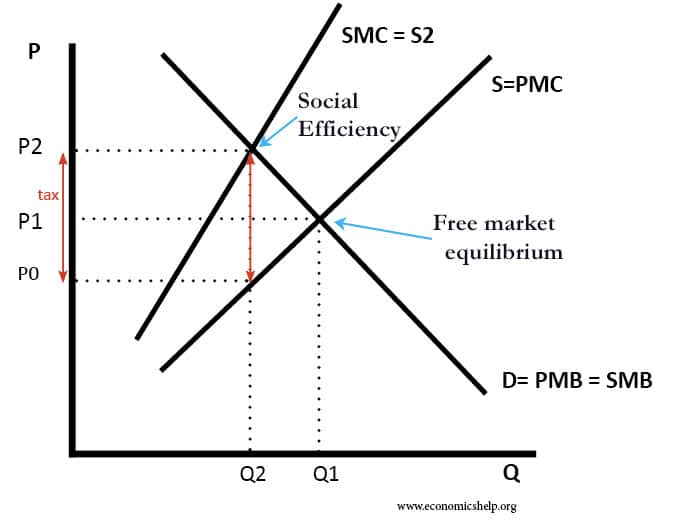
A tax can shift output from Q1 to Q2 (which is more socially efficient)
Limitations of economics
As a final thought – is economics overvalued? As a society do we give too much weighting to maximising income, profit and GDP? In a sense, traditional economics encourages us to view life from an economic/monetary perspective. But, perhaps this causes us to miss out on more important issues, such as spiritual understanding, concern for the environment, concern for others and getting the correct work/life balance.
- Economics in everyday life
- The importance of economics
10 thoughts on “Importance of economics in our daily lives”
Economics is important but sometimes I feel that people like us, accounts in the end fail in many other aspects of life because economics is always our main consideration.
economics is the one important in our daily life.but some people can appreciate how important this.we need to cooperate all people in fair situation like reach even if poor.
,,kathrina,,
ECONOMICS IS IMPORTANT IN OUR DAILY LIVING BECAUSE IT MAKES USE OF SCIENTIFIC PROCEDURE OF FINDINGS.
it isimportant coz it widens our undersatnding which in turn improves the standards of living
economic is important because its science as we as art…….. now how much science and art are important ?……. woooooooooo
Thank you for this informative article on how economics affects our daily lives. I found the opportunity cost to be very interesting, like when you mentioned how we all make choices about what to do with our time and could spend either 8 hours working, 8 hours studying, or 8 hours doing something fun or relaxing. It’s tough to make economic choices on a daily basis but this article was a great beginning insight into how beginning economics work.
This article was very helpful and informative.👍
I have been looking for this Economics of Everyday Life article since long time. Thanks author.
very helpful article, but please help us with references next time. thank you
Comments are closed.
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Social justice
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
The power of economics to explain and shape the world
Press contact :.

Previous image Next image
Nobel Prize-winning economist Esther Duflo sympathizes with students who have no interest in her field. She was such a student herself — until an undergraduate research post gave her the chance to learn first-hand that economists address many of the major issues facing human and planetary well-being. “Most people have a wrong view of what economics is. They just see economists on television discussing what’s going to happen to the stock market,” says Duflo, the Abdul Latif Jameel Professor of Poverty Alleviation and Development Economics. “But what people do in the field is very broad. Economists grapple with the real world and with the complexity that goes with it.”
That’s why this year Duflo has teamed up with Professor Abhijit Banerjee to offer 14.009 (Economics and Society’s Greatest Problems), a first-year discovery subject — a class type designed to give undergraduates a low-pressure, high-impact way to explore a field. In this case, they are exploring the range of issues that economists engage with every day: the economic dimensions of climate change, international trade, racism, justice, education, poverty, health care, social preferences, and economic growth are just a few of the topics the class covers. “We think it’s pretty important that the first exposure to economics is via issues,” Duflo says. “If you first get exposed to economics via models, these models necessarily have to be very simplified, and then students get the idea that economics is a simplistic view of the world that can’t explain much.” Arguably, Duflo and Banerjee have been disproving that view throughout their careers. In 2003, the pair founded MIT’s Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab, a leading antipoverty research network that provides scientific evidence on what methods actually work to alleviate poverty — which enables governments and nongovernmental organizations to implement truly effective programs and social policies. And, in 2019 they won the Nobel Prize in economics (together with Michael Kremer of the University of Chicago) for their innovative work applying laboratory-style randomized, controlled trials to research a wide range of topics implicated in global poverty. “Super cool”
First-year Jean Billa, one of the students in 14.009, says, “Economics isn’t just about how money flows, but about how people react to certain events. That was an interesting discovery for me.”
It’s also precisely the lesson Banerjee and Duflo hoped students would take away from 14.009, a class that centers on weekly in-person discussions of the professors’ recorded lectures — many of which align with chapters in Banerjee and Duflo’s book “Good Economics for Hard Times” (Public Affairs, 2019). Classes typically start with a poll in which the roughly 100 enrolled students can register their views on that week’s topic. Then, students get to discuss the issue, says senior Dina Atia, teaching assistant for the class. Noting that she finds it “super cool” that Nobelists are teaching MIT’s first-year students, Atia points out that both Duflo and Banerjee have also made themselves available to chat with students after class. “They’re definitely extending themselves,” she says. “We want the students to get excited about economics so they want to know more,” says Banerjee, the Ford Foundation International Professor of Economics, “because this is a field that can help us address some of the biggest problems society faces.” Using natural experiments to test theories
Early in the term, for example, the topic was migration. In the lecture, Duflo points out that migration policies are often impacted by the fear that unskilled migrants will overwhelm a region, taking jobs from residents and demanding social services. Yet, migrant flows in normal years represent just 3 percent of the world population. “There is no flood. There is no vast movement of migrants,” she says. Duflo then explains that economists were able to learn a lot about migration thanks to a “natural experiment,” the Mariel boat lift. This 1980 event brought roughly 125,000 unskilled Cubans to Florida over a matter a months, enabling economists to study the impacts of a sudden wave of migration. Duflo says a look at real wages before and after the migration showed no significant impacts. “It was interesting to see that most theories about immigrants were not justified,” Billa says. “That was a real-life situation, and the results showed that even a massive wave of immigration didn’t change work in the city [Miami].”
Question assumptions, find the facts in data Since this is a broad survey course, there is always more to unpack. The goal, faculty say, is simply to help students understand the power of economics to explain and shape the world. “We are going so fast from topic to topic, I don’t expect them to retain all the information,” Duflo says. Instead, students are expected to gain an appreciation for a way of thinking. “Economics is about questioning everything — questioning assumptions you don’t even know are assumptions and being sophisticated about looking at data to uncover the facts.” To add impact, Duflo says she and Banerjee tie lessons to current events and dive more deeply into a few economic studies. One class, for example, focused on the unequal burden the Covid-19 pandemic has placed on different demographic groups and referenced research by Harvard University professor Marcella Alsan, who won a MacArthur Fellowship this fall for her work studying the impact of racism on health disparities.
Duflo also revealed that at the beginning of the pandemic, she suspected that mistrust of the health-care system could prevent Black Americans from taking certain measures to protect themselves from the virus. What she discovered when she researched the topic, however, was that political considerations outweighed racial influences as a predictor of behavior. “The lesson for you is, it’s good to question your assumptions,” she told the class. “Students should ideally understand, by the end of class, why it’s important to ask questions and what they can teach us about the effectiveness of policy and economic theory,” Banerjee says. “We want people to discover the range of economics and to understand how economists look at problems.”
Story by MIT SHASS Communications Editorial and design director: Emily Hiestand Senior writer: Kathryn O'Neill
Share this news article on:
Related links.
- Class 14.009 (Economics and Society’s Greatest Problems)
- Esther Duflo
- Abhijit Banerjee
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab
- Department of Economics
- Video: "Lighting the Path"
Related Topics
- Education, teaching, academics
- Climate change
- Immigration
- Health care
- School of Humanities Arts and Social Sciences
Related Articles

Popular new major blends technical skills and human-centered applications

Report: Economics drives migration from Central America to the U.S.

MIT economists Esther Duflo and Abhijit Banerjee win Nobel Prize
Previous item Next item
More MIT News

This 3D printer can figure out how to print with an unknown material
Read full story →

For Julie Greenberg, a career of research, mentoring, and advocacy
Reevaluating an approach to functional brain imaging
Propelling atomically layered magnets toward green computers

MIT Haystack scientists prepare a constellation of instruments to observe the solar eclipse’s effects

Q&A: Tips for viewing the 2024 solar eclipse
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- *New* Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
7 Reasons Why You Should Study Economics
- 30 Nov 2017
An economics course can teach you the fundamentals needed to decipher graphs and other important financial data, as well as the tools to develop a successful business strategy.
But how can you know if studying economics is right for you? Consider the possible outcomes of various economics programs and how they compare to your personal and professional goals.
What Is Economics?
At its core, economics is the study of how individuals, groups, and nations manage and use resources.
Economics can be broken down into microeconomics , which examines individual decisions, and macroeconomics , which is concerned with the economy as a whole. Both types of economics utilize historical trends and current conditions to inform business decision-making and make predictions of how markets will behave in the future.
Why Is Studying Economics Important?
Students who choose to study economics not only gain the skills needed to understand complex markets but come away with strong analytical and problem-solving skills, as well as the business acumen necessary to succeed in the professional world.
In fact, economics can be useful for professionals in all industries and aspects of daily life, not just in business.
Access your free e-book today.
7 Reasons to Study Economics
Here’s a look at seven advantages of studying economics and how it can benefit both your organization and career.
1. You'll Expand Your Vocabulary
Whether it’s scarcity (limited resources), opportunity cost (what must be given up to obtain something else), or equilibrium (the price at which demand equals supply), an economics course will give you fluency in fundamental terms needed to understand how markets work. Even if you don’t use these words often in your current role, studying these economic terms will give you a better understanding of market dynamics as a whole and how they apply to your organization.
2. You’ll Put New Terms into Practice
Economics isn’t just learning a set of technical words, it’s actually using them to develop a viable business strategy . Once you understand the terms, it’s easier to use theories and frameworks, like Porter’s Five Forces and SWOT analyses, to assess situations and make a variety of economic decisions for your organization. For example, many companies need to decide whether to pursue a bundled or unbundled pricing model or strategize for the best ways to maximize revenue .
3. You’ll Understand Your Own Spending Habits
Economics will teach you about how your organization and its market behaves, but also offer insights into your own spending habits and values. For example, Willingness to Pay (WTP) is the maximum amount someone is willing to pay for a good or service. There’s frequently a gap between hypothetical and actual WTP, and learning about it can help you decode your own behavior and enable you to make wiser financial decisions.

For Shamari Benton, the concepts he learned in Economics for Managers opened his eyes to how everyday decisions are infused with economic calculations and principles.
“A simple grocery store visit becomes filled with economic references and analytical ponders,” Benton says.
4. You’ll Master the Nuances of the Field
Many people think of economics as just curves, models, and relationships , but in reality, economics is much more nuanced. Much of economic theory is based on assumptions of how people behave rationally, but it’s important to know what to do when those assumptions fail. Learning about cognitive biases that affect our economic decision-making processes arms you with the tools to predict human behavior in the real world, whether people act rationally or irrationally.
5. You’ll Learn How to Leverage Economic Tools
Learning economic theory is one thing, but developing the tools to make business decisions is another. Economics will teach you the basics and also give you concrete tools for analysis. For example, conjoint analysis is a statistical approach to measuring consumer demand for specific product features. This tool will allow you to get at the surprisingly complicated feature versus price tradeoffs that consumers make every day.
For example, imagine you work for Apple Inc. and you want to know what part of the iPhone should improve: Battery life, screen size, or camera. A conjoint analysis will let you know which improvements customers care about and which are worth the company’s time and money.
6. You’ll Be Better-Prepared for Graduate School
In addition to helping you make better decisions in both your personal and professional life, learning economics is also beneficial if you’re considering a graduate business degree. Studying economics can equip you with the problem-solving skills and technical knowledge needed to prepare for an MBA .
An MBA typically includes courses in finance, accounting, management, marketing, and economics, so if you decide an MBA is right for you, you’ll already be one step ahead. Furthermore, a foundational knowledge of economics enables you to use economic theories and frameworks to decide if graduate school is worth the financial investment.
7. You’ll Improve Your Career Prospects
An education in economics can improve your employability in a variety of industries. According to the World Economic Forum's Future of Jobs Report , analytical thinking and complex problem-solving skills top the list of transferable skills that employers will find increasingly important by 2025, both of which can be gained by studying economics.
In addition, many careers require knowledge of economic concepts, models, and relationships. Some possible career paths for economics students include finance, banking, insurance, politics, and healthcare administration . You’ll also be able to further your career in your current industry, as an understanding of the economics that power your industry can help you to be more effective in your role.

Options for Studying Economics
There are many options available for those looking to pursue an education in economics. Depending on your personal and professional goals, your current stage in life, and other important factors, you may choose to pursue an undergraduate or graduate degree in economics or take an online economics course to expand your future career opportunities.
Whether you're new to the business world or an experienced manager, having a thorough understanding of how markets work, pricing strategy, and consumer behavior is essential to success.
Do you want to take your career to the next level? Explore our eight-week online course Economics for Managers or other business essentials courses to learn how to apply economic principles to business decisions.
This post was updated on June 8, 2022. It was originally published on November 30, 2017.

About the Author

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.2: What Economics Is and Why It's Important
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 103661
Economics is the study of how humans make decisions in the face of scarcity. These can be individual decisions, family decisions, business decisions or societal decisions. If you look around carefully, you will see that scarcity is a fact of life. Scarcity means that human wants for goods, services and resources exceed what is available. Resources, such as labor, tools, land, and raw materials are necessary to produce the goods and services we want but they exist in limited supply. Of course, the ultimate scarce resource is time- everyone, rich or poor, has just 24 hours in the day to try to acquire the goods they want. At any point in time, there is only a finite amount of resources available.
Think about it this way: In 2015 the labor force in the United States contained over 158.6 million workers, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Similarly, the total area of the United States is 3,794,101 square miles. These are large numbers for such crucial resources, however, they are limited. Because these resources are limited, so are the numbers of goods and services we produce with them. Combine this with the fact that human wants seem to be virtually infinite, and you can see why scarcity is a problem.
Scarcity of Resources

If you still do not believe that scarcity is a problem, consider the following: Does everyone need food to eat? Does everyone need a decent place to live? Does everyone have access to healthcare? In every country in the world, there are people who are hungry, homeless (for example, those who call park benches their beds, as shown in Figure), and in need of healthcare, just to focus on a few critical goods and services. Why is this the case? It is because of scarcity. Let’s delve into the concept of scarcity a little deeper, because it is crucial to understanding economics.
The Problem of Scarcity
Think about all the things you consume: food, shelter, clothing, transportation, healthcare, and entertainment. How do you acquire those items? You do not produce them yourself. You buy them. How do you afford the things you buy? You work for pay. Or if you do not, someone else does on your behalf. Yet most of us never have enough to buy all the things we want. This is because of scarcity. So how do we solve it?
Visit this website to read about how the United States is dealing with scarcity in resources.
Every society, at every level, must make choices about how to use its resources. Families must decide whether to spend their money on a new car or a fancy vacation. Towns must choose whether to put more of the budget into police and fire protection or into the school system. Nations must decide whether to devote more funds to national defense or to protecting the environment. In most cases, there just isn’t enough money in the budget to do everything. So why do we not each just produce all of the things we consume? The simple answer is most of us do not know how, but that is not the main reason. (When you study economics, you will discover that the obvious choice is not always the right answer—or at least the complete answer. Studying economics teaches you to think in a different of way.) Think back to pioneer days, when individuals knew how to do so much more than we do today, from building their homes, to growing their crops, to hunting for food, to repairing their equipment. Most of us do not know how to do all—or any—of those things. It is not because we could not learn. Rather, we do not have to. The reason why is something called the division and specialization of labor , a production innovation first put forth by Adam Smith , Figure 2, in his book, The Wealth of Nations .

Firgure 2: Adam Smith introduced the idea of dividing labor into discrete tasks. (Credit: Wikimedia Commons)
The Division of and Specialization of Labor
The formal study of economics began when Adam Smith (1723–1790) published his famous book The Wealth of Nations in 1776. Many authors had written on economics in the centuries before Smith, but he was the first to address the subject in a comprehensive way. In the first chapter, Smith introduces the division of labor , which means that the way a good or service is produced is divided into a number of tasks that are performed by different workers, instead of all the tasks being done by the same person.
To illustrate the division of labor, Smith counted how many tasks went into making a pin: drawing out a piece of wire, cutting it to the right length, straightening it, putting a head on one end and a point on the other, and packaging pins for sale, to name just a few. Smith counted 18 distinct tasks that were often done by different people—all for a pin, believe it or not!
Modern businesses divide tasks as well. Even a relatively simple business like a restaurant divides up the task of serving meals into a range of jobs like top chef, sous chefs, less-skilled kitchen help, servers to wait on the tables, a greeter at the door, janitors to clean up, and a business manager to handle paychecks and bills—not to mention the economic connections a restaurant has with suppliers of food, furniture, kitchen equipment, and the building where it is located. A complex business like a large manufacturing factory, such as the shoe factory shown in Figure 3, or a hospital can have hundreds of job classifications.
Division of Labor

Why the Division of Labor Increases Production
When the tasks involved with producing a good or service are divided and subdivided, workers and businesses can produce a greater quantity of output. In his observations of pin factories, Smith observed that one worker alone might make 20 pins in a day, but that a small business of 10 workers (some of whom would need to do two or three of the 18 tasks involved with pin-making), could make 48,000 pins in a day. How can a group of workers, each specializing in certain tasks, produce so much more than the same number of workers who try to produce the entire good or service by themselves? Smith offered three reasons.
First, specialization in a particular small job allows workers to focus on the parts of the production process where they have an advantage. (In later chapters, we will develop this idea by discussing comparative advantage .) People have different skills, talents, and interests, so they will be better at some jobs than at others. The particular advantages may be based on educational choices, which are in turn shaped by interests and talents. Only those with medical degrees qualify to become doctors, for instance. For some goods, specialization will be affected by geography—it is easier to be a wheat farmer in North Dakota than in Florida, but easier to run a tourist hotel in Florida than in North Dakota. If you live in or near a big city, it is easier to attract enough customers to operate a successful dry cleaning business or movie theater than if you live in a sparsely populated rural area. Whatever the reason, if people specialize in the production of what they do best, they will be more productive than if they produce a combination of things, some of which they are good at and some of which they are not.
Second, workers who specialize in certain tasks often learn to produce more quickly and with higher quality. This pattern holds true for many workers, including assembly line laborers who build cars, stylists who cut hair, and doctors who perform heart surgery. In fact, specialized workers often know their jobs well enough to suggest innovative ways to do their work faster and better.
A similar pattern often operates within businesses. In many cases, a business that focuses on one or a few products (sometimes called its “ core competency ”) is more successful than firms that try to make a wide range of products.
Third, specialization allows businesses to take advantage of economies of scale , which means that for many goods, as the level of production increases, the average cost of producing each individual unit declines. For example, if a factory produces only 100 cars per year, each car will be quite expensive to make on average. However, if a factory produces 50,000 cars each year, then it can set up an assembly line with huge machines and workers performing specialized tasks, and the average cost of production per car will be lower. The ultimate result of workers who can focus on their preferences and talents, learn to do their specialized jobs better, and work in larger organizations is that society as a whole can produce and consume far more than if each person tried to produce all of their own goods and services. The division and specialization of labor has been a force against the problem of scarcity.
Trade and Markets
Specialization only makes sense, though, if workers can use the pay they receive for doing their jobs to purchase the other goods and services that they need. In short, specialization requires trade.
You do not have to know anything about electronics or sound systems to play music—you just buy an iPod or MP3 player, download the music and listen. You do not have to know anything about artificial fibers or the construction of sewing machines if you need a jacket—you just buy the jacket and wear it. You do not need to know anything about internal combustion engines to operate a car—you just get in and drive. Instead of trying to acquire all the knowledge and skills involved in producing all of the goods and services that you wish to consume, the market allows you to learn a specialized set of skills and then use the pay you receive to buy the goods and services you need or want. This is how our modern society has evolved into a strong economy.
Why Study Economics?
Now that we have gotten an overview on what economics studies, let’s quickly discuss why you are right to study it. Economics is not primarily a collection of facts to be memorized, though there are plenty of important concepts to be learned. Instead, economics is better thought of as a collection of questions to be answered or puzzles to be worked out. Most important, economics provides the tools to work out those puzzles. If you have yet to be been bitten by the economics “bug,” there are other reasons why you should study economics.
- Virtually every major problem facing the world today, from global warming, to world poverty, to the conflicts in Syria, Afghanistan, and Somalia, has an economic dimension. If you are going to be part of solving those problems, you need to be able to understand them. Economics is crucial.
- It is hard to overstate the importance of economics to good citizenship. You need to be able to vote intelligently on budgets, regulations, and laws in general. When the U.S. government came close to a standstill at the end of 2012 due to the “fiscal cliff,” what were the issues involved? Did you know?
- A basic understanding of economics makes you a well-rounded thinker. When you read articles about economic issues, you will understand and be able to evaluate the writer’s argument. When you hear classmates, co-workers, or political candidates talking about economics, you will be able to distinguish between common sense and nonsense. You will find new ways of thinking about current events and about personal and business decisions, as well as current events and politics.
The study of economics does not dictate the answers, but it can illuminate the different choices.
Key Concepts and Summary
Economics seeks to solve the problem of scarcity, which is when human wants for goods and services exceed the available supply. A modern economy displays a division of labor, in which people earn income by specializing in what they produce and then use that income to purchase the products they need or want. The division of labor allows individuals and firms to specialize and to produce more for several reasons: a) It allows the agents to focus on areas of advantage due to natural factors and skill levels; b) It encourages the agents to learn and invent; c) It allows agents to take advantage of economies of scale. Division and specialization of labor only work when individuals can purchase what they do not produce in markets. Learning about economics helps you understand the major problems facing the world today, prepares you to be a good citizen, and helps you become a well-rounded thinker.
Bureau of Labor Statistics, U.S. Department of Labor. 2015. "The Employment Situation—February 2015." Accessed March 27, 2015. www.bls.gov/news.release/pdf/empsit.pdf.
Williamson, Lisa. “US Labor Market in 2012.” Bureau of Labor Statistics . Accessed December 1, 2013. www.bls.gov/opub/mlr/2013/03/art1full.pdf.
We serve the public by pursuing a growing economy and stable financial system that work for all of us.
- Center for Indian Country Development
- Opportunity & Inclusive Growth Institute
Monetary Policy
- Banking Supervision
- Financial Services
- Community Development & Outreach
- Board of Directors
- Advisory Councils
Work With Us
- Internships
- Job Profiles
- Speakers Bureau
- Doing Business with the Minneapolis Fed
Overview & Mission
The ninth district, our history, diversity & inclusion.
- Region & Community
We examine economic issues that deeply affect our communities.
- Request a Speaker
- Publications Archive
- Agriculture & Farming
- Community & Economic Development
- Early Childhood Development
- Employment & Labor Markets
- Indian Country
- K-12 Education
- Manufacturing
- Small Business
- Regional Economic Indicators
Community Development & Engagement
The bakken oil patch.
We conduct world-class research to inform and inspire policymakers and the public.
Research Groups
Economic research.
- Immigration
- Macroeconomics
- Minimum Wage
- Technology & Innovation
- Too Big To Fail
- Trade & Globalization
- Wages, Income, Wealth
Data & Reporting
- Income Distributions and Dynamics in America
- Minnesota Public Education Dashboard
- Inflation Calculator
- Recessions in Perspective
- Market-based Probabilities
We provide the banking community with timely information and useful guidance.
- Become a Member Bank
- Discount Window & Payments System Risk
- Appeals Procedures
- Mergers & Acquisitions (Regulatory Applications)
- Business Continuity
- Paycheck Protection Program Liquidity Facility
- Financial Studies & Community Banking
- Market-Based Probabilities
- Statistical & Structure Reports
Banking Topics
- Credit & Financial Markets
- Borrowing & Lending
- Too Big to Fail
For Consumers
Large bank stress test tool, banking in the ninth archive.
We explore policy topics that are important for advancing prosperity across our region.
Policy Topics
- Labor Market Policies
- Public Policy
Racism & the Economy
Why it's important to understand economics.
December 1, 1998

Article Highlights
Economic literacy invaluable in communication and decision making
Econ knowledge essential to informed opinions
More focus needed in pre-college curriculum
The case for economic literacy is a strong one. George Stigler, a Nobel Laureate in economics, probably stated it best almost three decades ago when he wrote: "The public has chosen to speak and vote on economic problems, so the only open question is how intelligently it speaks and votes." In Stigler's view, economic literacy is special because it contributes to two classes of knowledge. First, it serves as a "means of communication among people, incorporating a basic vocabulary or logic that is so frequently encountered that the knowledge should be possessed by everyone." Second, it is a "type of knowledge frequently needed and yet not susceptible to economical purchase from experts."
Economic literacy certainly contributes to the first class of knowledge. People like to think and talk about the economic issues that affect them as consumers, workers, producers, investors, citizens and in other roles they assume over a lifetime. Economic literacy also gives people the tools for understanding their economic world and how to interpret events that will either directly or indirectly affect them. Nations benefit from having an economically literate population because it improves the public's ability to comprehend and evaluate critical issues. This understanding is especially important in democracies that rely on the active support and involvement of its citizens.
Economic literacy contributes to a second class of knowledge. For some economic decisions, such as buying a home or investing in the stock market, it is possible to hire professional or technical help when making a choice, but in most cases it is neither economical nor practical for an individual to hire a skilled professional every time an economic decision needs to be made. Even when such advice is given, the final choice must be made by the individual, not the adviser. What this means is that each person must ultimately serve as his or her own economist in making many economic choices, whether those choices involve buying a product, getting a loan, voting on candidates and economic issues, or something else. Economic literacy improves the competence of each individual for making personal and social decisions about the multitude of economic issues that will be encountered over a lifetime.
Economic Education
Whether there is a case for economic literacy, however, is not the most important question that needs to be answered. George Stigler and many other distinguished economists and individuals have already made that case. The more essential question to be asked is: How can we improve economic literacy in our society? Answering that question naturally turns the focus to economic education.
The development of economic literacy must begin in the schools. Even young children are capable of learning basic economic concepts that help them understand their economic world. In the secondary years, that initial foundation can be expanded to include instruction in a broader set of economic ideas and concepts. This additional education gives students greater capacity to understand more complex personal or national economic issues.
Some may think that economics is too difficult a subject to be taught to children and youth, and that such instruction should wait until college. Nothing could be more incorrect. No one would even think of making such an argument for math or science education. Waiting until students are in college to teach economics is simply a matter of "too little and too late." The majority of students end their formal education with secondary school, and even those students who continue their learning at a college or university may not take an economics course. The fact is that the best opportunity for economic education occurs before graduation from high school.
There are three essential ingredients for effective economic education in the schools. First, teachers must be knowledgeable about the subject and be able to help students learn how to use basic economic concepts to analyze personal and social issues. Second, good curriculum guides and instructional materials are needed that present economic content at an appropriate level for the student to understand. Third, economics must have a central place in the school curriculum—similar to math, science, history and language arts—so that substantial classroom time is devoted to economics instruction.
Over the past 40 years there has been a significant improvement in each area.
Teachers now have more economic knowledge because they are taking more economics courses. Instruction in economics in the classroom is more analytical and less descriptive because of the development of curriculum guides and national standards. There are now many high quality textbooks and supplementary materials for instruction. More high school graduates are completing an economics course and more instructional time is devoted to economics throughout the school curriculum.
The Evidence
Although there has been progress, much more needs to be accomplished in the coming decades if we are to produce an economically literate population. A major problem in this nation is that too few students are receiving an economic education before they graduate from high school. A study of high school transcripts shows that only about 44 percent of high school students take a separate course in economics. This course is usually offered in the 12th grade as an elective and lasts for only a semester. Although more states have made economics a required course for students, only 16 states require high school graduates to take some sort of economics course before graduation.
Given this situation—that fewer than half of high school graduates take a course in economics—it should not be surprising that study after study show that there is widespread economic illiteracy among youth and the American public. In one such study, I administered the Test of Economic Literacy , an achievement measure covering basic economic concepts, to 11th and 12th grade students nationwide and found that students supplied correct answers to less than half the questions. In another study I conducted with The Gallup Organization, I found that less than four in 10 high school seniors or adults could answer basic questions about economic terms and concepts that are essential for understanding economic events and issues reported in the news media. No matter what the economic content of questions or the test format, the study results remain the same—youth and adults show a great deal of ignorance when it comes to basic economics.
Youth are aware of their deficiencies because they give themselves low self-assessments of economic understanding in survey studies. Some 87 percent of high school seniors rated their knowledge and understanding of economic and economic issues as only fair or poor . (Among the general public, 83 percent gave the same responses.) One reason for these low self-ratings is that high school students are well aware that they are not receiving an adequate education in economics. When asked whether they were taught a lot , a little or nothing at all about how the economy works, 76 percent said that they were taught little or nothing . (Compare that percentage with the 7 percent who said they were taught little or nothing about mathematics.) In addition, both high school students and the general public had a recommendation for what should be done: Over 96 percent said the nation's schools should teach more about how our economy works.

The Consequences
The question that can be asked at this point in the discussion is "So what?" Why does it matter whether a student has taken an economics course or knows something about basic economic concepts? The answer is that economic knowledge has a direct and substantive effect on people's opinions about economic issues. This relationship can be illustrated with two examples from national survey studies.
The microeconomic example goes to the heart of support for a market economy. One knowledge question asked youth to respond to the following statement: To the best of your knowledge, the prices of most products in a competitive market, like the United States, are determined by: (a) supply and demand for products; (b) the consumer price index; (c) local, state, or the Federal government; (d) the monetary policy of the Federal Reserve. Just five in 10 youth knew that the prices of most products in a competitive market were determined by supply and demand. Two in 10 thought that prices were determined by the consumer price index. Another two in 10 believed that prices were determined by government. The remainder either thought prices were set by the monetary policy of the Federal Reserve or did not know.
Knowing what determines prices in a market economy and accepting the outcomes are two different things. If demand or supply conditions change, prices in a competitive market will rise and fall. Having a basic understanding of how markets work does not always mean that people will like price changes, especially if prices rise, but it should increase the probability of accepting the market outcome.
An opinion question was also asked to probe the degree of support among youth for the operation of competitive markets: A bicycle manufacturer raises the price of bikes because the demand increased even though the cost of producing bikes has not increased. Do you think the manufacturer should be allowed to raise prices? Two-thirds of youth said they were opposed to allowing the bike manufacturer to raise prices, which is certainly not a ringing endorsement of competitive markets. In fact, there are many examples of businesses raising prices based on increased demand. The prices for seasonal clothing are higher at the beginning of the season than at the end. Airfare rises in peak travel periods. Auto dealers raise prices (or give fewer discounts) when particular models become popular.
When you cross-tabulate the responses to the economic knowledge and opinion questions, a distinct pattern emerges. Among youth who knew that supply and demand determined the prices in a competitive market, 60 percent would allow the bike manufacturer to raise prices. Among youth who gave an incorrect response to the knowledge question, only 41 percent thought the bike manufacturer should be allowed to increase prices. The differences in the percentages show that what many youth know about how markets work directly affects their acceptance of the market result.
For a macroeconomic example, the basic economic question was: What is an example of monetary policy? Would it be a change in: (a) the discount rate; (b) a change in Federal government spending; or (c) a change in corporate profits. Only 17 percent of high school students knew that a change in the discount rate was an example of a change in monetary policy. About four in 10 thought it was a change in government spending (fiscal policy), about two in 10 thought it was a change in corporate profits, and another two in 10 did not know.
Although most high school students were ignorant of what monetary policy was, they were quite willing to give their opinion on this monetary policy question: Who should set monetary policy? Should it be: (a) the President; (b) the Congress; (c) the Federal Reserve; or (d) the United States Treasury? This issue is important because it determines whether there will be an independent central bank, isolated from direct political pressure, that can effectively control the money supply and maintain price stability. Only 16 percent of youth thought the Federal Reserve should be responsible for setting monetary policy.
When responses from the monetary policy knowledge and opinion questions were cross-tabulated, they show that there were significant differences in the support for the Federal Reserve having control over monetary policy in the United States based on the respondent's correct or incorrect responses to the knowledge question. Among high school students who could give a correct example of a change in monetary policy, 32 percent thought it should be set by the Federal Reserve, but among high school students who gave incorrect examples only 15 percent thought that monetary policy should be set by the Federal Reserve.
Similar cross-tabulations of opinion and knowledge questions on such topics as unemployment, the federal budget, economic growth, profits or trade protectionism could be performed with survey data to demonstrate the same point. Survey data have also been collected from the general public on these topics and the cross-tabulations show the same patterns as those for youth. The survey findings clearly indicate that what youth and adults know about basic economics affects what they think about an economic issue. What is especially disturbing is that people who have no basic knowledge about an economic issue are quite willing to state an opinion on that issue. This knowledge deficiency affects people's ability to evaluate economic matters and produces uninformed opinions. Among the informed, of course, there will still be differences about what should be done on an issue, but it provides a solid basis for a reasonable discussion of economic alternatives.
The development of basic economic literacy is an important goal for a democratic society that relies heavily on informed citizenry and personal economic decision-making. To achieve that goal will require that significant gaps in the economic education of youth be closed by giving economics a more central place in the school curriculum. More economics coursework at the precollege level sets a foundation for economic literacy, but it is only the beginning. As George Stigler reminded us long ago: "We shall have to combine vast efforts and creative experimentations if we are to produce the first economically literate society in history."
Stigler, George J. (1970). "The Case, if Any, for Economic Literacy," Journal of Economic Education , 1:2, 77-84.
Walstad, William B. (ed.). (1994). An International Perspective on Economic Education . Boston: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Walstad, William B. (1996). "Economic Knowledge and the Formation of Economic Opinions and Attitudes." In P. Lunt and A. Furnham (eds.), Economic Socialization: The Economic Beliefs and Behaviours of Young People (pp. 162-182). Cheltenham, UK: Edward Elgar.
Walstad, William B. (1996). Youth and Entrepreneurship . Kansas City, MO: Kauffman Center for Entrepreneurial Leadership, Inc.
Walstad, William B. (1997). "The Effects of Economic Knowledge on Public Opinion of Economic Issues," Journal of Economic Education , 28:3, 195-205.
Walstad, William B. and Larsen, M. (1992). A National Survey of American Economic Literacy . Lincoln, NE: The Gallup Organization.
Walstad is director of the National Center for Research in Economic Education and Edwin Faulkner Professor of Economics at the University of Nebraska-Lincoln. Since 1992 he has been associate editor of the Journal of Economic Education and is a past president of the National Association of Economic Educators. Walstad, who is the author of several hundred scholarly works in economic education, is also well known for his national assessments of economic understanding and prepared a report on American economic literacy with The Gallup Organization in 1992.
Walstad received his doctorate in economics from the University of Minnesota and served on the economics faculty at the University of Missouri-St. Louis prior to coming to Nebraska.
Related Content

Choices and consequences in the real “game of life”

Choosing a school is hard. Tailored information can help.

When Do Informational Interventions Work? Experimental Evidence from New York City High School Choice
Sign up for news and events.

What is economic growth? And why is it so important?
The goods and services that we all need are not just there – they need to be produced – and growth means that their quality and quantity increase..
Good health, a place to live, access to education, nutrition, social connections, respect, peace, human rights, a healthy environment, and happiness. These are just some of the many aspects we care about in our lives.
At the heart of many of these aspects that we care about are needs for which we require particular goods and services . Think of those that are needed for the goals on the list above – the health services from nurses and doctors, the home you live in, or the teachers who provide education.
Poverty, prosperity, and growth are often measured in monetary terms, most commonly as people’s income. But while monetary measures have some important advantages, they have the big disadvantage that they are abstract. In the worst case, monetary measures – like GDP per capita – are so abstract that we forget what they are actually about: people’s access to goods and services.
The point of this text is to show why economic growth is important and how the abstract monetary measures tell us about the reality of people’s material living conditions around the world and throughout history:
- In the first part, I want to explain what economic growth is and why it is so difficult to measure.
- In the second part, I will discuss the advantages and disadvantages of several measures of growth, and you will find the latest data on several of these measures so that we can see what they tell us about how people’s material living conditions have changed.
What are these goods and services that I’m talking about?
Have a look around yourself right now. Many of the things you see are products that were produced by someone so that you can use them: the trousers you are wearing, the device you are reading this on, the electricity that powers it, the furniture around you, the toilet that is nearby, the sewage system it is connected to, the bus or car or bicycle you took to get where you are, the food you had this morning, the medications you will receive when you get sick, every window in your home, every shirt in your wardrobe, and every book on your shelf.
At some point in the past, many of these products were not available. The majority did not have access to the most basic goods and services they needed. A recent study on the history of global poverty estimates that just two centuries ago, roughly three-quarters of the world "could not afford a tiny space to live, food that would not induce malnutrition, and some minimum heating capacity.” 1
Let’s look at the history of the last item on that list above, books.
A few centuries ago, the only way to produce a book was for a scribe to copy it word-for-word by hand. Book production was a slow process; it took a scribe about eight months of daily work to produce a single copy of the Bible. 2
It was so laborious that only very few books were produced. The chart shows the estimates of historians. 3
But then, in the 15th century, the goldsmith Johannes Gutenberg combined the idea of movable letters with the mechanism that he knew from the wine presses in his hometown. He developed the printing press. Gutenberg developed a new production technology, and it changed things dramatically. Instead of spending months to produce one book, a worker was now able to produce several books a day.
As the printing press spread across Europe, book production soared. Books, which were previously only available to a tiny elite, became available to more and more people.
This is one example of how growth is possible and what economic growth is : an increase in the production of goods and services that people produce for each other.
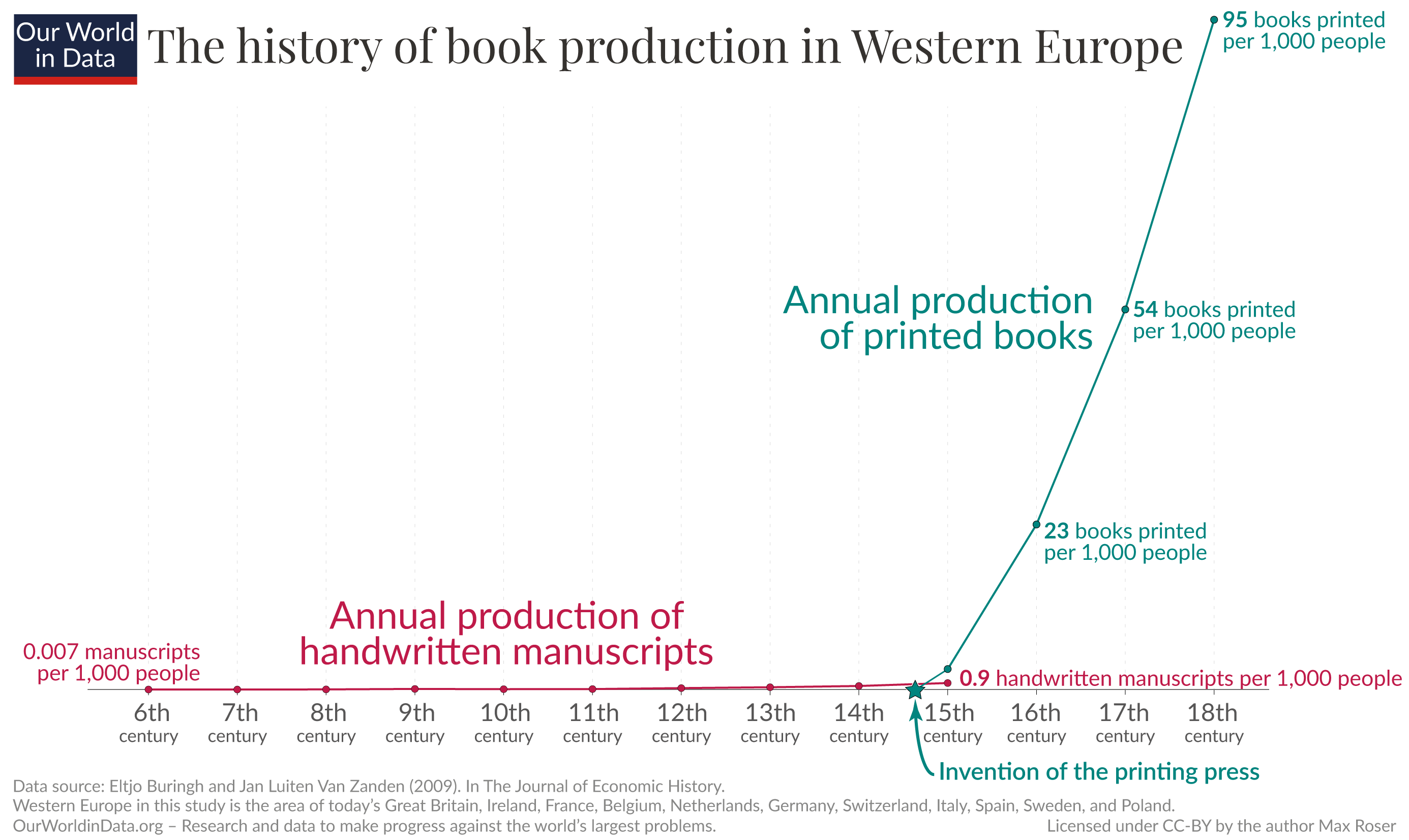
A list of goods and services that people produce for each other
Before we get to a more detailed definition of economic growth, it’s helpful to remind ourselves of the astonishingly wide range of goods and services that people produce. I think this is helpful because measures of economic output can easily become abstract. This abstraction means we easily lose the mental connection to the goods and services such measures actually talk about.
This list of goods and services isn’t meant as a definitive list, but it helped me to think about the relevance of poverty and growth: 4
At home: Light in your home at night; the sewage system; a shower; vacuum cleaner; fridge; heating; air conditioning; electricity; windows; a toilet – even a flush toilet; soap; a balcony or a garden; running water; warm water; cutlery and dishes; a hut – or even a warm apartment or house; an oven; sewing machine; a stove (that doesn’t poison you ); carpet; toilet paper; trash bags; music recordings or even online streaming of the world’s music and film; garbage collection; radio; television; a washing machine; 5 furniture; telephone; a comfortable bed, and a room for one’s own.
Food: The most fundamental need is to have enough food. For much of human history, a large share of people suffered from hunger , and millions still do .
But we also need to have a richer and more varied diet to get all of the nutrients we need. Unfortunately, billions still suffer from micronutrient deficiency .
Also, think of clean drinking water; reliable markets and stores with a wide range of available goods; food that rarely poisons you (pasteurized milk, for example); spices; tea and coffee; kitchen utensils and practical ingredients (from a bag of flour to canned soups or a yogurt); chocolate and sweets; fresh fruit and vegetables; bread; take-away food or the possibility to go to a restaurant; ways to protect your food from spoiling (from the cold chain that delivers the goods to the cellophane to wrap it with); wine or beer; fertilizer ( very important); and tractors to work the fields.
Knowledge: Education from primary up to university level; books; data that allows us to understand the world around us; newspapers; vocational training; kindergartens; and scientific knowledge to understand ourselves and the world around us.
Infrastructure: Public transportation with buses, subways, and trains; roads; paved roads; airplanes; bridges; financial services (including bank accounts, ATMs, and credit cards); cities; a network of competent workers that can help you to fix problems; postal services (that delivers fast); national parks; street cleaning; public swimming pools (even private pools); firefighters; parks; online shopping; weather forecasts; and a waste management system.
Tools and technologies: Pencils, ballpoint pens, and paper; lawnmowers; cars; car mechanics; bicycles; power tools like drills (even battery-powered ones); a watch; computers and laptops; smartphones (with GPS and a good camera); being able to stay in touch with distant friends or family members (or even visiting them); GPS; batteries; telephones and mobiles; video calls; WiFi; and the internet right here.
Social services: Caretakers for those who are disabled, sick, or elderly; protection from crime; non-profit organizations financed by the public, by donations or by philanthropies; insurance (against many different risks); and a legal system with judges and lawyers that implement the rule of law.
There is also a wide range of transfer payments, which in themselves are not services (they are transfers) but which become more affordable as a society becomes more prosperous: sick leave and disability benefits; unemployment benefits; and being able to help others with a regular donation of some of your income to an effective charity . 6
Life and free time : tents; travel and holidays; surfboards; skis; board games; hotels; playgrounds; children’s toys; courses to learn hobbies (from painting to musical instruments or courses on the environment around us); a football; pets; the cinema, theater or a music concert; clothes (even comfortable and good-looking ones that keep you warm and protect you from the rain); shoes (even shoes for different purposes); shoe repair; the contraceptive pill and the ability to choose if and when to have children; sports classes from rock climbing to pilates and yoga; cigarettes (not all goods that people produce for each other are good for them); 7 a musical instrument; a camera; and parties to celebrate life.
Health and staying well: Dentists; antibiotics; surgeries; anesthesia; mental health care from psychologists and psychiatrists; vaccines; public sewage; a haircut; a massage; midwives; ambulances; modern medicine; band-aids; pharmaceutical drugs; sanitary pads; toothbrushes; dental floss (some do floss); disinfectants; glasses; sunglasses; contact lenses; hearing aids; and hospitals – including very well-equipped, modern hospitals that offer CT scans, which include intensive care units and allow heart or brain surgery or organ transplants.
Specific needs and wishes: Most of the products listed above are generally helpful to people. But often, the goods and services that are most important to one individual are very specific.
As I’m writing this, I have a big cast on my left leg after I broke it. These days, I depend on products that I had no use for just three weeks ago. To move around, I need two long crutches, and to prevent thrombosis, I need to inject a blood thinner every day. After I broke my leg, I needed the service of nurses and doctors. They had to rely on a range of medical equipment, such as X-ray machines. To get back on my feet, I might need the service of physiotherapists.
We all have very specific needs or wishes for particular goods and services. Some needs arise from bad luck, like an injury. Others are due to a new phase in life – think of the specific goods and services you need when you have a baby or when you take care of an elderly person. And yet others are due to specific interests – think of the needs of a fisherman, or a pianist, or a painter.
All of these goods and services do not just magically appear. They need to be produced. At some point in the past, the production of most of them was zero, and even the most essential ones were extremely scarce. So, if you want to know what economic growth means for your life, look at the list above.
What is economic growth?
So, how can we define what economic growth is?
A definition that can be found in so many publications that I don’t know which one to quote is that economic growth is “an increase in the amount of goods and services produced per head of the population over a period of time.”
The definition in the Oxford Dictionary is almost identical: “Economic growth is the increase in the production of goods and services per head of population over a stated period of time”. And the definition in the Cambridge Dictionary is similar. It defines growth as “an increase in the economy of a country or an area, especially of the value of goods and services the country or area produces.”
In the following footnote, you find more definitions. Bringing these definitions together and taking into account the economic literature more broadly, I suggest the following definition: Economic growth is an increase in the quantity and quality of the economic goods and services that a society produces.
I prefer a definition that is slightly longer than most others. If you want a shorter definition, you can speak of ‘products’ rather than ‘goods and services’, and you can speak of ‘value’ rather than mentioning both the quantity and quality aspects separately.
The most important change in quantity is from zero to one when a new product becomes available. Many of the most important changes in history became possible when new goods and services were developed; think of antibiotics, vaccines, computers, or the telephone.
You find more thoughts on the definition of growth in the footnote. 8
What are economic goods and services?
Many definitions of economic growth simply speak of the production of ‘goods and services’ collectively. This sidesteps a key difficulty in its definition and measurement. Economic growth is not concerned with all goods and services but with a subset of them: economic goods and services.
In everything we do – even in our most mundane activities – we continuously ‘produce’ goods and services in some form. Early in the morning, once we’ve brushed our teeth and made ourselves toast, we have already produced one service and one good. Should we count the tooth-brushing and the toast-making towards the economic production of the country we live in? The question of where to draw the line isn’t easy to answer. But we have to draw the line somewhere. If we don’t, we end up with a concept of production that is so broad that it becomes meaningless; we’d produce a service with every breath we take and every time we scratch our nose.
The line that we have to draw to define the economic goods and services is called the ‘production boundary’. The sketch illustrates the idea. The production boundary defines those goods and services that we consider when we speak about economic growth.
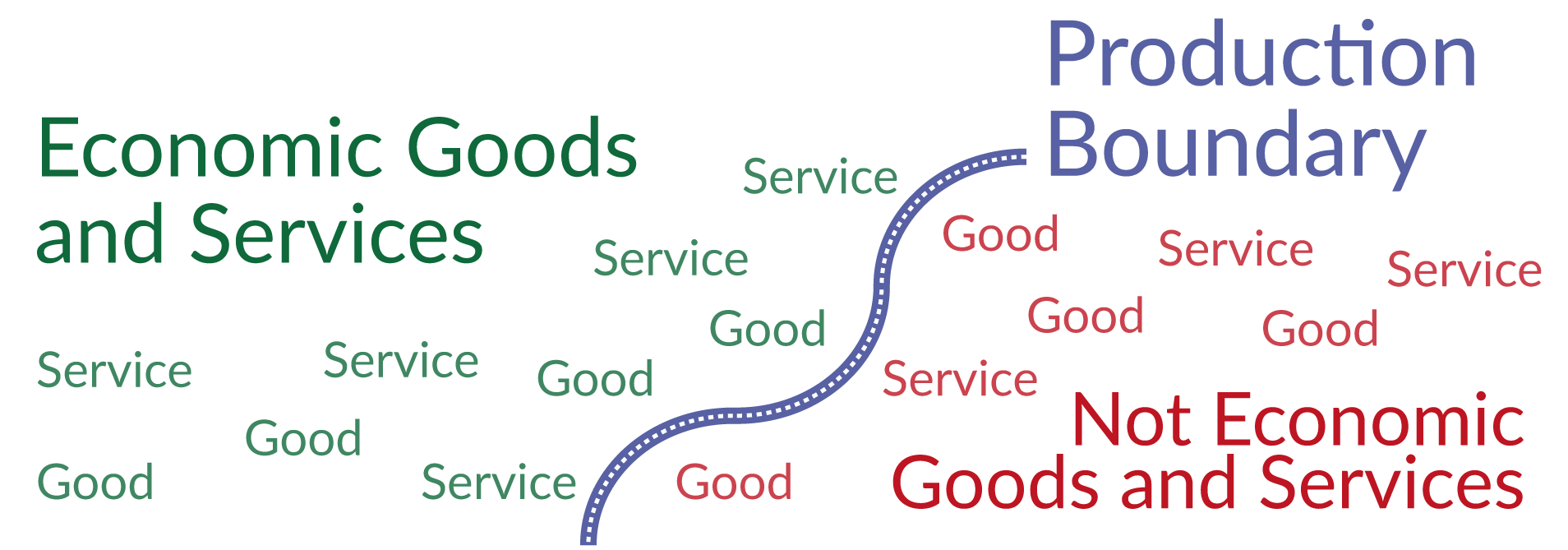
For a huge number of goods or services, there is no question that they are of the ‘economic’ type. But for some of them, it can be complicated to decide on which side of the production boundary they fall. One example is the question of whether the production of illegal goods should be included. Another is whether production within a household should be included – should we consider it as economic production if we grow tomatoes in our backyard and make soup from them? Different authors and different measurement frameworks have given different answers to these questions. 9
There are some characteristics that are helpful in deciding on which side of the boundary a particular product falls. 10 Economic goods and services are those that can be produced and that are scarce in relation to the demand for them. They stand in contrast to free goods, like sunlight, which are abundant, or those many important aspects in our lives that cannot be produced, like friendships. 11 Our everyday language has this right: we don’t refer to the sun or our friendships as a good or service that we ‘produce’.
An economic good or service is provided by people to each other as a solution to a problem they are faced with, and this means that they are considered useful by the person who demands it.
A last characteristic that helps decide whether you are looking at an economic product is “delegability”. An activity is considered to be production in an economic sense if it can be delegated to someone else. This would include many of the goods and services on that long list we considered earlier but would exclude your breathing, for example.
Because economic goods are scarce in relation to the demand for them, human effort is required to produce them. 12 A shorter way of defining growth is, therefore, to say that it is an increase in the production of those products that people produce for each other.
The majority of goods and services on that long list above are uncontroversially of the economic type – everything from the light bulbs and furniture in your home to the roads and bridges that connect your home with the rest of the world. They are scarce in relation to the demand for them and have to be produced by someone; their production is delegable, and they are considered useful by those who want them.
It’s worth recognizing that many of the difficulties in defining the production boundary arise from the effort to make measures of economic production as comparable as possible.
To give just one concrete example of the type of considerations that make the discussion about specific definitions so difficult, let’s look at how the production boundary is drawn in the housing sector.
Imagine two countries that are identical except for one aspect: home ownership. In Country A, everyone rents their homes, and the total sum of annual rent amounts to €2 billion per year. In Country B, everyone owns their own home, and no one pays rent. To provide housing is certainly an economic service, but if we only counted monetary transactions, then we would get the false impression that the value of goods and services in Country A is €2 billion higher than in Country B. To avoid such misjudgment, the production boundary includes the housing services that are provided without any monetary transactions. In National Accounts, statisticians take into account the “imputed rental value of owner-occupied housing” – those households who own their home get assigned an imputed rental value. In the imagined scenario, these imputed rents would amount to €2 billion in Country B so that the prosperity of people in these two countries would be judged to be identical.
It is the case more broadly that National Account figures (like GDP) do include important non-market goods and services that are not included in household survey measures of people’s income. GDP does not only include the housing services by owner-occupied housing but also the provision of most goods and services that are provided by the government or nonprofit institutions.
How can we measure economic growth?
Many discussions about economic growth are extraordinarily confusing. People often talk past one another.
I believe the key reason for this is that the discussion of what economic growth is gets muddled up with how it is measured .
While it is straightforward enough to define what growth is, measuring growth is very, very difficult.
In the worst cases, measures of growth are mixed up with a definition of growth. Growth is often measured as an increase in income or inflation-adjusted GDP per capita. But these measures are not the definition of it – just like life expectancy is a measure of population health but is certainly not the definition of population health.
To see how difficult it is to measure growth, take a moment to think about how you would measure it. How would you determine whether the quantity and quality of all economic goods and services produced by a society increased or decreased over time?
Finding a measure means that you have to find a way to express a huge amount of relevant information in a single metric. As the sketch shows, you have to first measure the quantity and quality of all the many, many goods and services that get produced and then find a way to aggregate all of these measurements into one summarizing metric. No matter what measure you propose for such a difficult task, there will always be problems and shortcomings in any proposal you might make.
In the following section, I will show four possible ways of measuring growth and present some data for each of them to see how they can inform us about the history of material living conditions.
Measuring economic growth by tracking access to particular goods and services
One possible way to measure growth is to make a list of some specific products that people want and to see what share of the population has access to them.
We do this very often at Our World in Data . The chart here shows the share of the world population that has access to four basic resources. All of these statistics measure some particular aspect of economic growth.
You can switch this chart to any country in the world via the “Change country” option. You will find that, judged by this metric, some countries achieved rapid growth – like Indonesia – while others only saw very little growth, like Chad.
The advantage of measuring growth in this way is that it is concrete. It makes clear what exactly is growing, and it’s clear which particular goods and services people gain access to.
The downside is that it only captures a small part of economic growth. There are many other goods and services that people want in addition to water, electricity, sanitation, and cooking technology. 13
You could, of course, expand this approach of measuring growth to many more goods and services, but this is usually not done for both practical and ethical considerations:
One practical reason is that a list of all the products that people value would be extremely long. Keeping lists that track people’s access to all products would be a daunting task: hundreds of different toothbrushes, thousands of different dentists, hundreds of thousands of different dishes in different restaurants, and many millions of different books. 14 If you wanted to measure growth across all goods and services in this way, you’d soon employ half the country in the statistical office.
In practice, any attempt to measure growth as access to particular products, therefore, means that you look only at a relatively small number of very particular goods and services that statisticians or economists are interested in. This is problematic for ethical reasons. It should not be up to the statisticians or economists to determine which few products should be considered valuable.
You might have realized this problem already when you read my list at the beginning of this text. You might have disagreed with the things that I put on that list and thought that some other goods and services were missing. This is why it is important to track incomes and not just access to particular goods: measuring people’s income is a way of measuring the options that they have rather than the choices that they make. It respects people’s judgment to decide for themselves what they find most important for their lives.
On our site, you find many more such metrics of growth that capture whether people have access to particular goods and services:
- This chart shows the share of US households having access to specific technologies.
- This chart shows the share that has health insurance.
- This chart shows access to schools.
Measuring economic growth by tracking the ratio between people’s income and the prices of particular goods and services
To measure the options that a person’s income represents, we have to compare their income with the prices of the goods and services that they want. We have to look at the ratio between income and prices.
The chart here does this for one particular product – books – and brings us back to the history of growth in the publishing sector that we started with. 15 Shown is the ratio between the average income that a worker receives and the price of a book. It shows how long the average worker had to work to buy one book. Note that this data is plotted on a logarithmic axis.
Before the invention of the printing press in the 15th century, the price was often as high as several months of work. The fact that books were unaffordable for almost everyone should not be surprising. It corresponds to what we’ve seen earlier that it took a scribe several months to produce a single book.
The chart also shows how this changed when the printing press increased the productivity of publishing. As the labor required to produce a book declined from many months of work to less than a day, the price fell from months of wages to mere hours.
This shows us how an innovation in technology raises productivity and how an increase in production makes it more affordable. How it increases the options that people have.
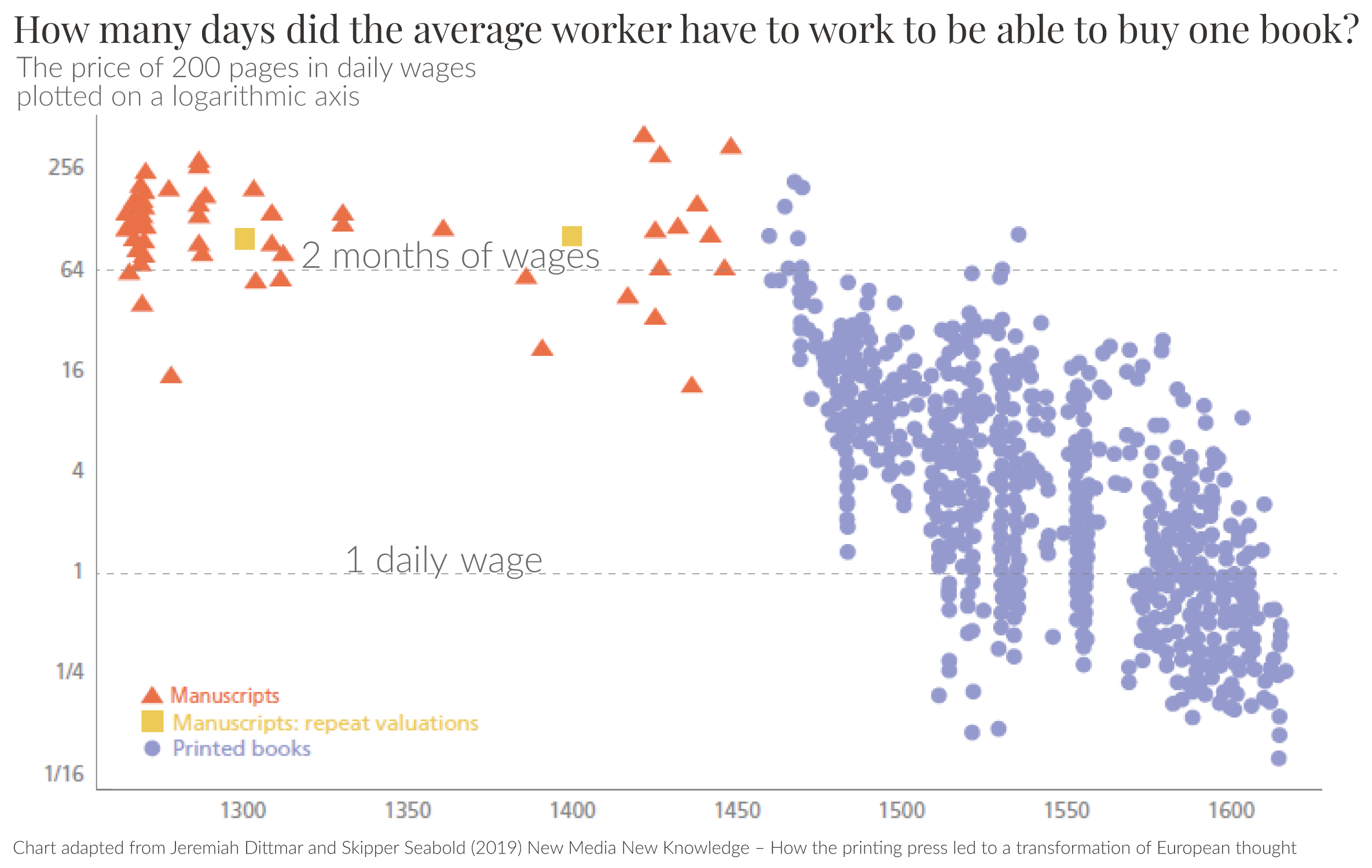
Global inequality: How do incomes compare in countries around the world?
In the previous section, we measured growth as the ratio between income and the price of one particular good. But of course, we could do the same for all the many goods and services that people want. This ratio – the ratio between the nominal income that people receive and the prices that people have to pay for goods and services – is called ‘real income’ . 16
Real income = Nominal income / price of goods and services
Real income grows when people’s nominal income increases or when the prices of goods and services decrease.
In contrast to many of the other metrics on Our World in Data, a person’s real income does not matter for its own sake but because it is a means to an end. A means to many ends, in fact.
Economic growth – measured as an increase in people’s real income – means that the ratio between people’s income and the prices of what they can buy is increasing: goods and services become more affordable, and people become less poor. It is because a person has more choices as their income grows that economists care so much about these monetary measures of prosperity.
The two most prominent measures of real income are GDP per capita and people’s incomes, as determined through household surveys.
They are shown in this chart.
Before we get back to the question of economic growth, let’s see what these measures of real income tell us about the economic inequality in the world today.
Both measures show that global inequality is very large. In a rich country like Denmark, an average person can purchase goods and services for $54 a day, while the average Ethiopian can only afford goods and services that cost $3 per day.
Both measures of real incomes in this chart are measured in international dollars, which means that they take into account the level of prices in each country (using purchasing power parity conversion factors). This price adjustment is done in such a way that one international-$ is equivalent to the purchasing power of one US-$ in the US . An income of int.-$3 in Ethiopia, for example, means that it allows you to purchase goods and services in Ethiopia that would cost US-$3 in the US . All dollar values in this text are given in international dollars, even though I often shorten it to just the $-sign.
If you are living in a rich country and you want to have a sense of what it means to live in a poor country – where incomes are 20 times lower – you can imagine that the prices for everything around you suddenly increase 20-fold. 17 If all the things you buy suddenly get 20-times more expensive your real income is 20-times lower. A loaf of bread doesn’t cost $2 but $40, a pair of jeans costs $400, and an old car costs $40,000. If you ask yourself how these price increases would change your daily consumption and your day-to-day life, you can get a sense of what it means to live in a poor country.
The two shown measures of real income differ:
- The data on the vertical axis is based on surveys in which researchers go from house to house and ask people about their economic situation. In some countries, people are asked about their income, while in other countries, people are asked about their expenditure – expenditure is income minus savings. In poor countries, these two measures are close to each other since poor people do not have the chance to save much.
- On the other hand, GDP per capita starts at the aggregate level and divides the income of the entire economy by the number of people in that country. GDP per capita is higher than per capita survey income because GDP is a more comprehensive measure of income. As we’ve discussed before, it includes an imputed rental value of owner-occupied housing and other differences, such as government expenditure.
Income as a measure of economic prosperity is much more abstract than the metrics we looked at previously. The comparison of incomes of people around the world in this scatterplot measures options, not choices. It shows us that the economic options for billions of people are very low. The majority of the world lives on very low incomes of less than $20, $10, or even $5 per day. In the next section, we’ll see how poverty has changed over time.
- GDP per capita vs. Daily income of the poorest 10%
- GDP per capita vs. Daily average income
Global poverty and growth: How have incomes changed around the world?
Economic growth, as we said before, is an increase in the production of the quantity and quality of the economic goods and services that a society produces. The total income in a society corresponds to the total sum of goods and services the society produces – everyone’s spending is someone else’s income. This means that the average income corresponds to the level of average production, so that the average income in a society increases when the production of goods and services increases.
Average production = average income
In this final section, let’s see how incomes have changed over time, first as documented in survey incomes and then via GDP per capita.
Measuring economic growth by tracking incomes as reported in household surveys
The chart shows the income of people around the world over time, as reported in household surveys. It shows the share of the world population that lives below different poverty lines: from extremely low poverty lines up to $30 per day, which corresponds to notions of poverty in high-income countries .
Many of the poorest people in the world rely on subsistence farming and do not have a monetary income. To take this into account and make a fair comparison of their living standards, the statisticians who produce these figures estimate the monetary value of their home production and add it to their income.
Again, the prices of goods and services are taken into account: these are measures of real incomes. As explained before, incomes are adjusted for price differences between countries, and they are also adjusted for inflation. As a consequence of these two adjustments, incomes are expressed in international dollars in 2017 prices, which means that these income measures express what you would have been able to buy with US dollars in the US in 201 7.
Global economic growth can be seen in this chart as an increasing share of the population living on higher incomes. In 2000 two thirds of the world lived on less than $6.85 per day. In the following 19 years, this share fell by 22 percentage points.
In 2020 and 2021 — during the economic recession that followed the pandemic — the size of the world economy declined, and the share of people in poverty increased . As soon as global data for this period is available, we will update this chart.
The data shows that global poverty has declined, no matter what poverty line you choose. It also shows that the majority of the world still lives on very low incomes. As we’ve seen, we can describe the same reality from the production side: the global production of the goods and services that people want has increased, but there is still not enough production of even very basic products. Most people in the world do not have access to them.
An advantage of household survey data over GDP per capita is that it captures the inequality of incomes within a country. You can explore this inequality with this chart by switching to see the data for an individual country via the ‘Change country’ button.
Measuring economic growth by tracking GDP per capita
GDP per capita is a broader measure of real income, and in contrast to survey income, it also takes government expenditures into account. A lot of thinking has gone into the construction of this very prominent metric so that it is comparable not only over time but also across countries. This makes it especially useful as a measure to understand the economic inequality in the world, as we’ve seen above. 18
Another advantage of this measure is that historians have reconstructed estimates of GDP per capita that go back many centuries. This historical research is an extremely laborious task , and researchers have dedicated many years of work to these reconstructions. The ‘Maddison Project’ brings together these long-run reconstructions from various researchers, and thanks to these efforts, we have a good understanding of how incomes have changed over time.
The chart shows how average incomes in different world regions have changed over the last two centuries. Looking at the latest data, you see again the very large inequality between different parts of the world today. You now also see the history of how we got here: small increases in production in some world regions and very large increases in those regions where people have the highest incomes today.
One of the very first countries to achieve sustained economic growth was the United Kingdom. In this chart, we see the reconstructions of GDP per capita in the UK over the last centuries.
It is no accident that the shape of this chart is very similar to the chart on book production at the beginning of this text – very low and almost flat for many generations and then quickly rising. Both of these developments are driven by changes in production.
Average income corresponds to average production, and societies around the world were able to produce very few goods and services in the past. There were no major exceptions to this reality. As we see in this chart, global inequality was much lower than today: the majority of people around the world were very poor.
To get a sense of what this means, you can again take the approach we’ve used to understand the inequality in the world today. When incomes in today’s rich countries were 20 times lower, it was as if all the prices around you today would suddenly increase 20-fold. But in addition to this, you have to consider that all the goods and services that were developed since then disappeared – no bicycle, no internet, no antibiotics. All that’s left for you are the goods and services of the 17th century, but all of them are 20 times more expensive than today. The majority of people around the world, including in today’s richest countries, live in deep poverty.
Just as we’ve seen in the history of book production, this changed once new production technologies were introduced. The printing press was an exceptionally early innovation in production technology; most innovations happened in the last 250 years. The starting point of this rise out of poverty is called the Industrial Revolution.
The printing press made it possible to produce more books. The many innovations that made up the Industrial Revolution made it possible to increase the production of many goods and services. Compare the effort that it takes for a farmer to reap corn with a scythe to the possibilities of a farmer with a tractor or a combined harvester, or think of the technologies that made overland travel faster – from walking on foot to traveling in a horse buggy to taking the train or car; or think of the effort it took to build those roads that the buggies once traveled on with the modern machinery that allows us to produce the corresponding public infrastructure today .
The production of a myriad of different goods and services followed trajectories very similar to the production of books – flat and low in the past and then steeply increasing. The rise in average income that we see in this chart is the result of the aggregation of all these production increases.
In the past, before societies achieved economic growth, the only way for anyone to become richer was for someone else to become poorer; the economy was a zero-sum game. In a society that achieves economic growth, this is no longer the case. When average incomes increase, it becomes possible for people to become richer without someone else becoming poorer.
This transition from a zero-sum to a positive-sum economy is the most important change in economic history (I wrote about it here ) and made it possible for entire societies to leave the extreme poverty of the past behind.
Conclusion: The history of global poverty reduction has just begun
The chart shows the global history of extreme poverty and economic growth.
In the top left panel, you can see how global poverty has declined as incomes increased; in the other eight panels, you see the same for all world regions separately. The starting point of each trajectory shows the data for 1820 and tells us that two centuries ago, the majority of people lived in extreme poverty, no matter where in the world they were at home.
Back then, it was widely believed that widespread poverty was inevitable. But this turned out to be wrong. The trajectories show how incomes and poverty have changed in each world region. All regions achieved growth – the goods and services that people need saw their production and quality increase – and the share living in extreme poverty declined. 19
This historical research was done by Michail Moatsos and is based on the ‘cost of basic needs’-approach as suggested by Robert Allen (2017) and recommended by the late Tony Atkinson. 20 The name ‘extreme poverty’ is appropriate as this measure is based on an extremely low poverty threshold. It takes us back to what I mentioned at the very beginning; this historical research tells us – as the author puts it – that three-quarters of the world "could not afford a tiny space to live, food that would not induce malnutrition, and some minimum heating capacity.”
Since then, all world regions have made progress against extreme poverty – some much earlier than others – but in particular, in Sub-Saharan Africa, the share of people living in deep poverty is still very high.
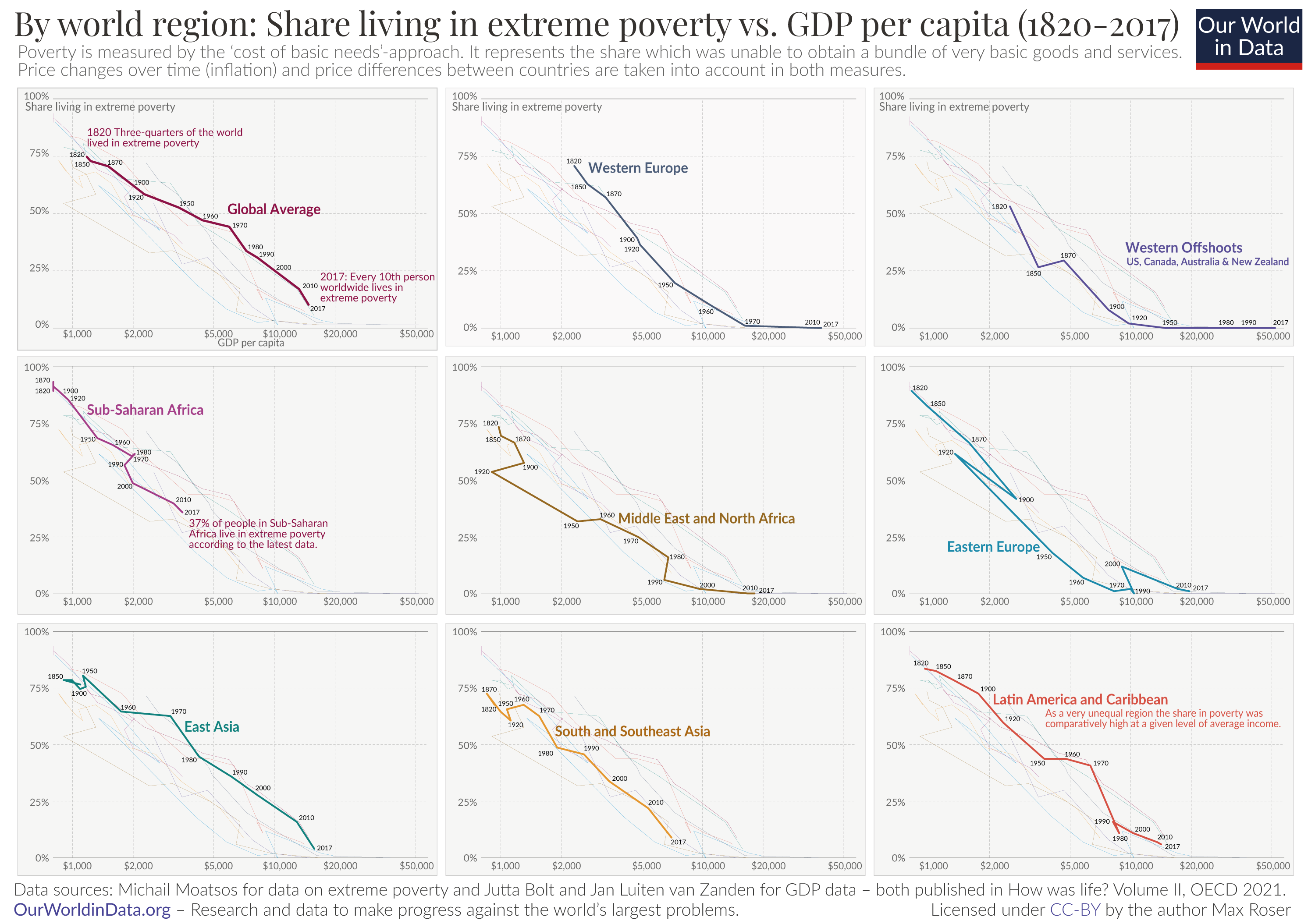
The last two centuries were the first time in human history that societies have achieved sustained economic growth, and the decline of global poverty is one of the most important achievements in history. But it is still a very long way to go.
This is what we see in this final chart. The red line shows the share of people living in extreme poverty that we just discussed. Additionally, you now also see the share living on less than $3.65, $6.85, and $30 per day. 21
The world today is very unequal, and the majority of the world still lives in poverty: 47% live on less than $6.85 per day, and 84% live on less than $30. Even after two centuries of progress, we are still in the early stages. The history of global poverty reduction has only just begun.
That the world has made substantial progress but nevertheless still has a long way to go is the case for many of the world’s very large problems. I’ve written before that all three statements are true at the same time: The world is much better, the world is awful, and the world can be much better. This is very much the case for global poverty. The world is much less poor than in the past, but it is still very poor, and it remains one of the largest problems we face.
Some writers suggest we can end poverty by simply reducing global inequality. This is not the case. I’m very much in favor of reducing global inequality, and I hope I do what I can to contribute to this. But it is important to be clear that a reduction of inequality alone would still mean that billions around the world would live in very poor conditions. Those who don’t see the importance of growth are not aware of the extent of global poverty. The production of many crucial goods and services has to increase if we want to end it. How much economic growth is needed to achieve this? This is the question I answered in this recent text .
To solve the problems we face, it is not enough to increase overall production. We also need to make good decisions about which goods and services we want to produce more of and which ones we want less of. Growth doesn’t just have a rate, it also has a direction, and the direction we choose matters – for our own happiness and for achieving a sustainable future .
I hope this text was helpful in making clear what economic growth is. It is necessary to remind ourselves of that because we mostly talk about poverty and growth in monetary terms. The monetary measures have the disadvantage that they are abstract, perhaps so abstract that we even forget what growth is actually about and why it is so important. The goods and services that we all need are not just there – they need to be produced – and economic growth means that the quality and quantity of these goods and services increase, from the food that we eat to the public infrastructure we rely on.
The history of economic growth is the history of how societies leave widespread poverty behind by finding ways to produce more of the goods and services that people need – all the very many goods and services that people produce for each other: look around you now.
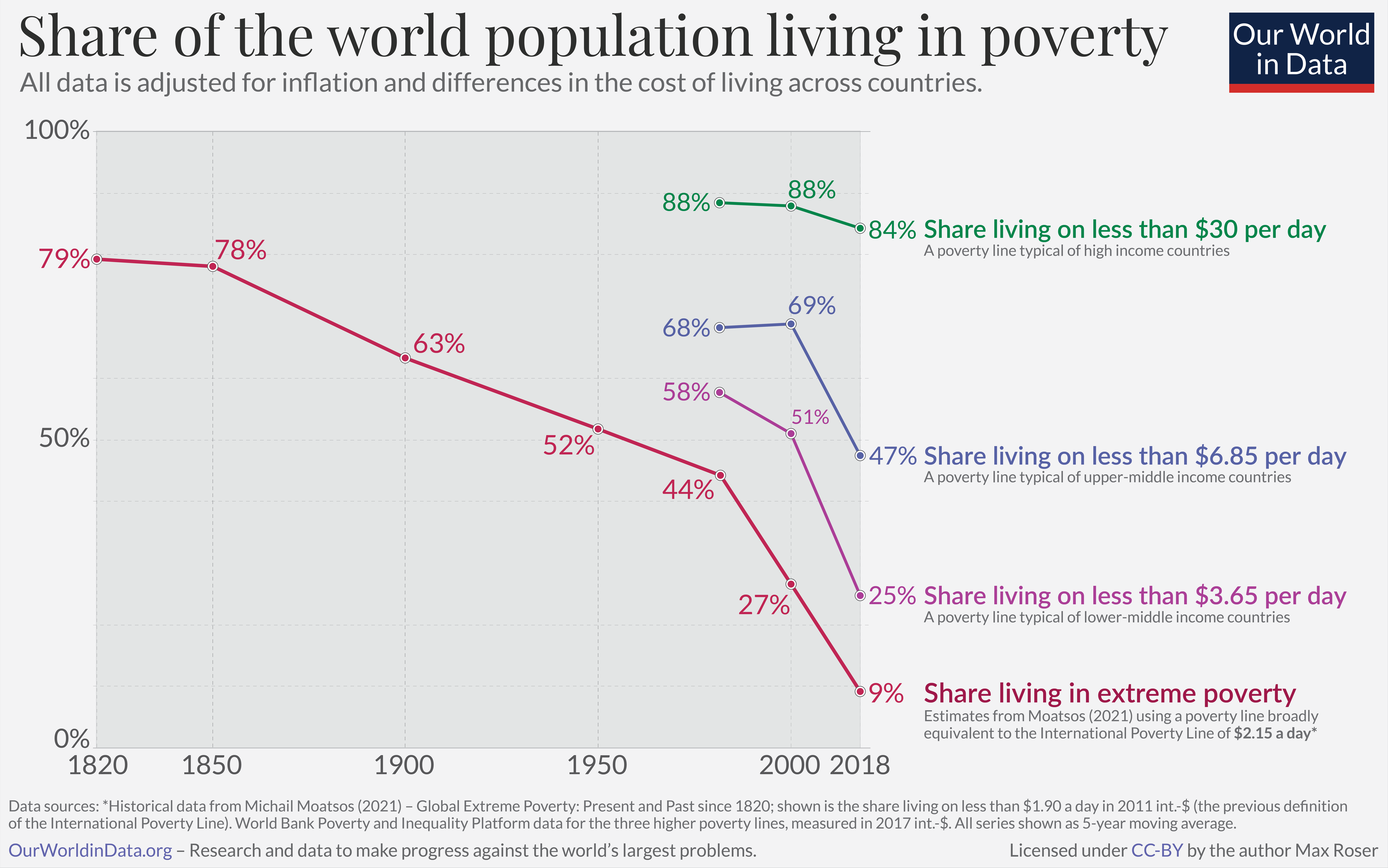
Acknowledgments: I would like to thank Joe Hasell and Hannah Ritchie for very helpful comments on draft versions of this article.
Our World in Data presents the data and research to make progress against the world’s largest problems. This article draws on data and research discussed in our topic pages on Economic Inequality , Global Poverty , and Economic Growth .
Version history: In October 2023, I copy-edited this article; it was a minor update, and nothing substantial was changed.
Michail Moatsos (2021) – Global extreme poverty: Present and past since 1820. Published in OECD (2021), How Was Life? Volume II: New Perspectives on Well-being and Global Inequality since 1820 , OECD Publishing, Paris, https://doi.org/10.1787/3d96efc5-en .
At the time when material prosperity was so poor, living conditions were extremely poor in general; close to half of all children died .
Historian Gregory Clark reports the estimate that scribes were able to copy about 3,000 words of plain text per day.
See Clark (2007) – A Farewell to Alms: A Brief Economic History of the World. Clark (2007). In it, Clark quotes his earlier working paper with Patricia Levin as the source of these estimates. Gregory Clark and Patricia Levin (2001) – “How Different Was the Industrial Revolution? The Revolution in Printing, 1350–1869.”
There are about 760,000 words in the bible (it differs between various translations and languages; here is an overview of some translations).
This implies that the production of one copy of the Bible meant 253.3 days (8.3 months) of daily work.
Copying the text was not the only step in the production process for which productivity was low. The ink had to be made, parchment had to be produced and cut, and many other steps involved laborious work.
Wikipedia’s article about scribes reports sources that estimate that the production time per bible was even longer than 8 months.
Clark himself states in the same publication that “Prior to that innovation, books had to be copied by hand, with copyists on works with just plain text still only able to copy 3,000 words per day. Producing one copy of the Bible at this rate would take 136 man-days.” Since the product of 136 and 3000 is only 408,000, it is unclear to me how Clark has arrived at this estimate – 408,000 words are fewer words than in the Tanakh and other versions of the bible.
The data is taken from Eltjo Buringh and Jan Luiten Van Zanden (2009) – Charting the “Rise of the West”: Manuscripts and Printed Books in Europe, a Long-Term Perspective from the Sixth through Eighteenth Centuries. In The Journal of Economic History Vol. 69, No. 2 (June 2009), pp. 409-445. Online here .
Western Europe in this study is the area of today’s Great Britain, Ireland, France, Belgium, Netherlands, Germany, Switzerland, Italy, Spain, Sweden, and Poland.
On the history and economics of book production, see also the historical work of Jeremiah Dittmar.
I’ve relied on several sources to produce this list. One source was the simple descriptions of the consumption bundles that are relied upon for CPI measurement – like this one from Germany’s statistical office . And I have also relied on the national accounts themselves.
This list is also inspired partly by this list of Gwern and I’m also grateful for the feedback that I got via Twitter to earlier versions of this list. [ Here I shared the list on Twitter ]
This is Hans Rosling’s talk on the magic of the washing machine – worth watching if you haven’t seen it.
Of course all of these transfer payments have a service component to them, someone is managing the payment of the disability benefits etc.
Because smoking causes a large amount of suffering and death I do not find cigarettes valuable, but my opinion is not what matters for a list of goods and services that people produce for each other. Whether some good is considered to be part of the domestic product depends on whether it is a good that some people want, not whether you or I want it. More on this below.
Very similar to the definitions given above is the definition that Kimberly Amadeo gives: “Economic growth is an increase in the production of goods and services over a specific period.”
“Economic growth is an increase in the production of economic goods and services, compared from one period of time to another” is the definition at Investopedia .
Alternatively, to my definition, I think it can be useful to think of economic growth as not directly concerned with the output as such but with the capacity to produce this output. The NASDAQ’s glossary defines growth in that way: “An increase in the nation's capacity to produce goods and services.”
Wikipedia defines economic growth as follows: “Economic growth can be defined as the increase in the inflation-adjusted market value of the goods and services produced by an economy over time.” Definitions that are based on how growth is measured strike me as wrong – just like life expectancy is a measure of population health and hardly the definition of population health. I will get back to this mistake further below in this text.
An aspect that I emphasize more explicitly than others is the quality of the goods and services. People obviously do just care about the number of goods, and in the literature on growth, the measurement of changes in quality is a central question. Many definitions speak more broadly about the ‘value’ of the goods and services that are produced, but I think it is worth emphasizing that growth is also concerned with a rise in the quality of goods and services.
OECD – Measuring the Non-Observed Economy: A Handbook .
The relevant numbers are not small. For the US alone, “illegal drugs add $108 billion to measured nominal GDP in 2017, illegal prostitution adds $10 billion, illegal gambling adds $4 billion, and theft from businesses adds $109 billion” if they were to be included in the US National Accounts. This is according to the report by Rachel Soloveichik (2019) – Including Illegal Activity in the U.S. National Economic Accounts . Published by the BEA.
Ironmonger (2001) – Household Production. In International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences. Pages 6934-6939. https://doi.org/10.1016/B0-08-043076-7/03964-4
Or for some longer run data on the US: Danit Kanal and Joseph Ted Kornegay (2019) – Accounting for Household Production in the National Accounts: An Update, 1965–2017 . In the Survey of Current Business.
Helpful references that discuss how the production boundary is drawn (and how it changed over time) are: Lequiller and Blades – Understanding National Accounts (available in various editions) Diane Coyle (2016) – GDP: A Brief but Affectionate History https://press.princeton.edu/books/paperback/9780691169859/gdp
The definition of the production boundary by Statistics Finland
Itsuo Sakuma (2013) – The Production Boundary Reconsidered. In The Review of Income and Wealth. Volume 59, Issue 3; Pages 556-567.
Diane Coyle (2017) – Do-it-Yourself Digital: The Production Boundary and the Productivity Puzzle. ESCoE Discussion Paper 2017-01, Available at SSRN: http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2986725
A more general way of thinking about free goods and services is to consider them as those for which the supply is hugely greater than the demand.
Their production, therefore, has an opportunity cost, which means that if someone obtains an economic good, someone is giving up on something for it – this can either be the person themselves or society more broadly. Free goods, in contrast, are provided with zero opportunity cost to society.
It is also the case that the international statistics on these measures often have very low cutoffs for what it means ‘to have access’; this is, for example, the case for what it means to have access to energy.
10 years ago, Google counted there were 129,864,880 different books, and since then, the number has increased further by many thousands of new books every day.
This chart is from Jeremiah Dittmar and Skipper Seabold (2019) – New Media New Knowledge – How the printing press led to a transformation of European thought . I was unfortunately not able to find the raw data anywhere and could not redraw this chart; if someone knows where this (or comparable) data can be found, please let me know.
In the language of economists, the nominal value is measured in terms of money, whereas the real value is measured against goods or services. This means that the real income is the income adjusted for inflation (it is adjusted for the changes in prices of goods and services). Thereby, it allows comparisons that tell us the quantity and quality of the goods and services that people were able to purchase at different points in time.
I learned this way of thinking about it from Twitter user @Kirsten3531, who responded with this idea to a tweet of mine here https://twitter.com/Kirsten3531/status/1389553625308045317
We’ve discussed one such consideration that is crucial for comparability when we consider how to take into account the value of owner-occupied housing.
Whether economic growth translates into the reduction of poverty depends not only on the growth itself but also on how the distribution of income changes. The poverty metrics shown in this chart and in previous charts take both of these aspects – the average level of production/income and its distribution – into account.
Jutta Bolt and Jan Luiten van Zanden (2021) – The GDP data in the chart is taken from The Long View on Economic Growth: New Estimates of GDP, How Was Life? Volume II: New Perspectives on Well-being and Global Inequality since 1820 , OECD Publishing, Paris, https://doi.org/10.1787/3d96efc5-en .
The latest data point for the poverty data refers to 2018, while the latest data point for GDP per capita refers to 2016. In the chart, I have chosen the middle year (2017) as the reference year.
The ‘cost of basic needs’-approach was recommended by the ‘World Bank Commission on Global Poverty’, headed by Tony Atkinson, as a complementary method in measuring poverty.
The report for the ‘World Bank Commission on Global Poverty’ can be found here .
Tony Atkinson – and, after his death, his colleagues – turned this report into a book that was published as Anthony B. Atkinson (2019) – Measuring Poverty Around the World. You find more information on Atkinson’s website .
The CBN-approach Moatsos’ work is based on what was suggested by Allen in Robert Allen (2017) – Absolute poverty: When necessity displaces desire. In American Economic Review, Vol. 107/12, pp. 3690-3721, https://doi.org/10.1257/aer.20161080 .
Moatsos describes the methodology as follows: “In this approach, poverty lines are calculated for every year and country separately, rather than using a single global line. The second step is to gather the necessary data to operationalize this approach alongside imputation methods in cases where not all the necessary data are available. The third step is to devise a method for aggregating countries’ poverty estimates on a global scale to account for countries that lack some of the relevant data.” In his publication – linked above – you find much more detail on all of the shown poverty data. The speed at which extreme poverty declined increased over time, as the chart shows. Moatsos writes, “It took 136 years from 1820 for our global poverty rate to fall under 50%, then another 45 years to cut this rate in half again by 2001. In the early 21st century, global poverty reduction accelerated, and in 13 years, our global measure of extreme poverty was halved again by 2014.”
These are the same global poverty estimates – based on household surveys – we discussed above.
Cite this work
Our articles and data visualizations rely on work from many different people and organizations. When citing this article, please also cite the underlying data sources. This article can be cited as:
BibTeX citation
Reuse this work freely
All visualizations, data, and code produced by Our World in Data are completely open access under the Creative Commons BY license . You have the permission to use, distribute, and reproduce these in any medium, provided the source and authors are credited.
The data produced by third parties and made available by Our World in Data is subject to the license terms from the original third-party authors. We will always indicate the original source of the data in our documentation, so you should always check the license of any such third-party data before use and redistribution.
All of our charts can be embedded in any site.
Our World in Data is free and accessible for everyone.
Help us do this work by making a donation.
Economics Defined with Types, Indicators, and Systems
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is Economics?
Understanding economics, microeconomics, macroeconomics, what is the role of an economist, what are economic indicators, economic systems, schools of economic theory.
- Economics FAQs
The Bottom Line
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
Economics is a social science that focuses on the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The study of economics is primarily concerned with analyzing the choices that individuals, businesses, governments, and nations make to allocate limited resources. Economics has ramifications on a wide range of other fields, including politics, psychology, business, and law.
Key Takeaways
- Economics is the study of how people allocate scarce resources for production, distribution, and consumption, both individually and collectively.
- The field of economics is connected with and has ramifications on many others, such as politics, government, law, and business.
- The two branches of economics are microeconomics and macroeconomics.
- Economics focuses on efficiency in production and exchange.
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and the Consumer Price Index (CPI) are two of the most widely used economic indicators.
Zoe Hansen / Investopedia
Assuming humans have unlimited wants within a world of limited means, economists analyze how resources are allocated for production, distribution, and consumption.
The study of microeconomics focuses on the choices of individuals and businesses, and macroeconomics concentrates on the behavior of the economy on an aggregate level.
One of the earliest recorded economists was the 8th-century B.C. Greek farmer and poet Hesiod who wrote that labor, materials, and time needed to be allocated efficiently to overcome scarcity. The publication of Adam Smith's 1776 book An Inquiry Into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations sparked the beginning of the current Western contemporary economic theories.
Microeconomics studies how individual consumers and firms make decisions to allocate resources. Whether a single person, a household, or a business, economists may analyze how these entities respond to changes in price and why they demand what they do at particular price levels.
Microeconomics analyzes how and why goods are valued differently, how individuals make financial decisions, and how they trade, coordinate, and cooperate.
Within the dynamics of supply and demand, the costs of producing goods and services, and how labor is divided and allocated, microeconomics studies how businesses are organized and how individuals approach uncertainty and risk in their decision-making.
Macroeconomics is the branch of economics that studies the behavior and performance of an economy as a whole. Its primary focus is recurrent economic cycles and broad economic growth and development.
It focuses on foreign trade, government fiscal and monetary policy, unemployment rates, the level of inflation, interest rates, the growth of total production output, and business cycles that result in expansions, booms, recessions, and depressions.
Using aggregate indicators, economists use macroeconomic models to help formulate economic policies and strategies.
An economist studies the relationship between a society's resources and its production or output, and their opinions help shape economic policies related to interest rates, tax laws, employment programs, international trade agreements, and corporate strategies.
Economists analyze economic indicators such as gross domestic product and the consumer price index to identify potential trends or make economic forecasts.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), 38% of all economists in the United States work for a federal or state agency. Economists are also employed as consultants, professors, by corporations, or as part of economic think tanks.
Economic indicators detail a country's economic performance. Published periodically by governmental agencies or private organizations, economic indicators often have a considerable effect on stocks, employment, and international markets. They may predict future economic conditions that will move markets and guide investment decisions.
Gross domestic product (GDP)
The gross domestic product (GDP) is considered the broadest measure of a country's economic performance. It calculates the total market value of all finished goods and services produced in a country in a given year. In the U.S., the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) also issues a regular report during the latter part of each month. Many investors, analysts, and traders focus on the advance GDP report and the preliminary report, both issued before the final GDP figures because the GDP is considered a lagging indicator , meaning it can confirm a trend but can't predict a trend.
The GDPNow forecasting model, used by the Federal Reserve, provides a "nowcast" of the official estimate before its release by estimating GDP growth using a methodology similar to the one used by the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis.
Retail sales
Reported by the U.S. Department of Commerce (DOC) during the middle of each month, the retail sales report measures the total receipts, or dollar value, of all merchandise sold in stores. Sampling retailers across the country acts as a proxy of consumer spending levels. Consumer spending represents more than two-thirds of GDP, proving useful to gauge the economy's general direction.
Industrial production
The industrial production report, released monthly by the Federal Reserve, reports changes in the production of factories, mines, and utilities in the U.S. One measure included in this report is the capacity utilization rate , which estimates the portion of productive capacity that is being used rather than standing idle in the economy. Capacity utilization in the range of 82% to 85% is considered "tight" and can increase the likelihood of price increases or supply shortages in the near term. Levels below 80% are interpreted as showing "slack" in the economy, which may increase the likelihood of a recession .
Employment Data
The Bureau of Labor Statistics releases employment data in a report called the nonfarm payrolls on the first Friday of each month. Sharp increases in employment indicate prosperous economic growth and potential contractions may be imminent if significant decreases occur. These are generalizations, however, and it is important to consider the current position of the economy.
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
The Consumer Price Index (CPI), also issued by the BLS, measures the level of retail price changes, and the costs that consumers pay, and is the benchmark for measuring inflation . Using a basket that is representative of the goods and services in the economy, the CPI compares the price changes month after month and year after year. This report is an important economic indicator and its release can increase volatility in equity, fixed income, and forex markets. Greater-than-expected price increases are considered a sign of inflation, which will likely cause the underlying currency to depreciate.
Five economic systems illustrate historical practices used to allocate resources to meet the needs of the individual and society.
Primitivism
In primitive agrarian societies, individuals produced necessities from building dwellings, growing crops, and hunting game at the household or tribal level.
A political and economic system of Europe from the 9th to 15th century, feudalism was defined by the lords who held land and leased it to peasants for production, who received a promise of safety and security from the lord.
With the advent of the industrial revolution, capitalism emerged and is defined as a system of production where business owners organize resources including tools, workers, and raw materials to produce goods for market consumption and earn profits. Supply and demand set prices in markets in a way that can serve the best interests of society.
Socialism is a form of a cooperative production economy. Economic socialism is a system of production in which there is limited or hybrid private ownership of the means of production. Prices, profits, and losses are not the determining factors used to establish who engages in the production, what to produce and how to produce it.
Communism holds that all economic activity is centralized through the coordination of state-sponsored central planners with common ownership of production and distribution.
Many economic theories have evolved as societies and markets have grown and changed. However, three disciplines of economics, neoclassical, Keynesian, and Marxian, have influenced modern society.
The principles of neoclassical economics are often used as a framework to illustrate the virtues of capitalism, including the tendency of market prices to reach equilibrium as the volume of supply and demand changes. The optimal valuation of resources emerges from the forces of individual desire and scarcity.
John Maynard Keynes developed the theory of Keynesian economics during the Great Depression. Arguing against neoclassical theory, Keynes showed that restrained markets and government intervention in markets create a stable and equitable economic system. He advocated for a monetary policy designed to boost demand and investor confidence during economic downturns.
Marxian economics is defined in Karl Marx's work Das Kapital . Marxian economics is a rejection of the classical view of economics, arguing against the idea that the free market, an economic system determined by supply and demand with little or no government control, benefits society. He espoused that capitalism only benefits a select few and that the ruling class becomes richer by extracting value out of cheap labor provided by the working class.
What Is a Command Economy?
A command economy is an economy in which production, investment, prices, and incomes are determined centrally by a government. A communist society has a command economy.
What Is Behavioral Economics?
Behavioral economics combines psychology, judgment, decision-making, and economics to understand human behavior. Branches of economic thought continue to grow and change. One such example is the progressive branch of bioeconomics that models economic decisions in terms of managing resources.
Who Has Influenced the Study of Economics in the 21st Century?
Since 2000, several economists have won the Nobel Prize in economics, including David Card for his contributions to labor economics, Angus Deaton for his study of consumption, poverty, and welfare, and Paul Krugman for his analysis of trade patterns.
Economics is a branch of the social sciences focused on the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Microeconomics is a type of economics that is concerned with the behavior of individual people and businesses, while macroeconomics considers broader trends affecting nations and larger economies. In the U.S., a number of key economic indicators, including GDP and CPI, are important tools for economists to measure trends and make forecasts .
Brandon Dupont. "The History of Economic Ideas: Economic Thought in Contemporary Context," Pages 12-13. Routledge, Taylor & Francis Group. 2017.
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. " Economists ."
Bureau of Economic Analysis. " Gross Domestic Product ."
Atlanta Federal Reserve. " GDPNow ."
United States Census Bureau. " Monthly Retail Trade ."
John Locke Foundation. " Consumer Spending Slows Even as GDP Reverses Six-Month Trend ."
Federal Reserve. " Industrial Production and Capacity Utilization - G.17 ."
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. " Economic News Releases ."
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. " Consumer Price Index ."
Bureau of Labor Statistics. " Dueling Economies ."
- Economics Defined with Types, Indicators, and Systems 1 of 33
- Economy: What It Is, Types of Economies, Economic Indicators 2 of 33
- A Brief History of Economics 3 of 33
- Is Economics a Science? 4 of 33
- Finance vs. Economics: What's the Difference? 5 of 33
- Macroeconomics Definition, History, and Schools of Thought 6 of 33
- Microeconomics Definition, Uses, and Concepts 7 of 33
- 4 Economic Concepts Consumers Need To Know 8 of 33
- Law of Supply and Demand in Economics: How It Works 9 of 33
- Demand-Side Economics Definition, Examples of Policies 10 of 33
- Supply-Side Theory: Definition and Comparison to Demand-Side 11 of 33
- What Is a Market Economy and How Does It Work? 12 of 33
- Command Economy: Definition, How It Works, and Characteristics 13 of 33
- Economic Value: Definition, Examples, Ways To Estimate 14 of 33
- Keynesian Economics Theory: Definition and How It's Used 15 of 33
- What Is Social Economics, and How Does It Impact Society? 16 of 33
- Economic Indicator: Definition and How to Interpret 17 of 33
- Top 10 U.S. Economic Indicators 18 of 33
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Formula and How to Use It 19 of 33
- What Is GDP and Why Is It So Important to Economists and Investors? 20 of 33
- Consumer Spending: Definition, Measurement, and Importance 21 of 33
- Retail Sales: Definition, Measurement, and Use As an Economic Indicator 22 of 33
- Job Market: Definition, Measurement, Example 23 of 33
- The Top 25 Economies in the World 24 of 33
- What Are Some Examples of Free Market Economies? 25 of 33
- Is the United States a Market Economy or a Mixed Economy? 26 of 33
- Primary Drivers of the Chinese Economy 27 of 33
- Japan Inc.: What It is, How It Works, History 28 of 33
- The Fundamentals of How India Makes Its Money 29 of 33
- European Union (EU): What It Is, Countries, History, Purpose 30 of 33
- The German Economic Miracle Post WWII 31 of 33
- The Economy of the United Kingdom 32 of 33
- How the North Korean Economy Works 33 of 33
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-521333258-7d026570f0be4d3f99d6b542d49d2a0d.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Topic 1: Introductory Concepts and Models
1.1 What Is Economics, and Why Is It Important?
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Discuss the importance of studying economics
- Explain the relationship between production and division of labor
- Evaluate the significance of scarcity
At its core, Economics is the study of how humans make decisions in the face of scarcity. These can be individual decisions, family decisions, business decisions or societal decisions. If you look around carefully, you will see that scarcity is a fact of life. Scarcity means that human wants for goods, services and resources exceed what is available. Resources, such as labor, tools, land, and raw materials are necessary to produce the goods and services we want but they exist in limited supply. Of course, the ultimate scarce resource is time – everyone, rich or poor, has just 24 hours in the day to try to acquire the goods they want. At any point in time, there is only a finite amount of resources available.
Think about it this way: In 2016, the labor force in Canada contained 19.4 million workers, according to Statistics Canada. The total area of the Canada is 9.99 million square kilometres. These are large numbers for such crucial resources, however, they are limited. Because these resources are limited, so are the numbers of goods and services we produce with them. Combine this with the fact that human wants seem to be virtually infinite, and you can see why scarcity is a problem.

If you still do not believe that scarcity is a problem, consider the following: Does everyone need food to eat? Does everyone need a decent place to live? Does everyone have access to healthcare? In every country in the world, there are people who are hungry, homeless, and in need of healthcare, just to focus on a few critical goods and services. Why is this the case? It is because of scarcity. Let’s delve into the concept of scarcity a little deeper, because it is crucial to understanding economics.
The Problem of Scarcity
Think about all the things you consume: food, shelter, clothing, transportation, healthcare, and entertainment. How do you acquire those items? You do not produce them yourself. You buy them. How do you afford the things you buy? You work for a wage. Or if you do not, someone else does on your behalf. Yet most of us never have enough to buy all the things we want. This is because of scarcity. So how do we solve the problem of scarcity?
Every society, at every level, must make choices about how to use its resources. Families must decide whether to spend their money on a new car or a vacation. Towns must choose whether to put more of the budget into police and fire protection or into the school system. Nations must decide whether to devote more funds to national defence or to protecting the environment. In most cases, there just isn’t enough money in the budget to do everything. So why do we not each just produce all of the things we consume? The simple answer is most of us do not know how, but that is not the main reason. Think back to pioneer days, when individuals knew how to do many more practical tasks than we do today, from building their homes, to growing crops, to hunting for food, or repairing their equipment. Most of us do not know how to do all—or any—of those things. It is not because we could not learn. Rather, we do not have to. The reason why is something called the division and specialization of labor , a production innovation first put forth by Adam Smith in his book, The Wealth of Nations (See Figure 2).

The Division of and Specialization of Labor
The formal study of economics began when Adam Smith (1723–1790) published his famous book The Wealth of Nations in 1776. Many authors had written on economics in the centuries before Smith, but he was the first to address the subject in a comprehensive way. In the first chapter, Smith introduces the division of labor , which means that the way a good or service is produced is divided into a number of tasks that are performed by different workers, instead of all the tasks being done by the same person.
To illustrate the division of labor, Smith counted how many tasks went into making a pin: drawing out a piece of wire, cutting it to the right length, straightening it, putting a head on one end and a point on the other, and packaging pins for sale, to name just a few. Smith counted 18 distinct tasks that were often done by different people—all for a pin!
Modern businesses divide tasks as well. Even a relatively simple business like a restaurant divides up the task of serving meals into a range of jobs like top chef, sous chefs, kitchen help, servers to wait on the tables, a greeter at the door, janitors to clean up, and a business manager to handle paychecks and bills—not to mention the economic connections a restaurant has with suppliers of food, furniture, kitchen equipment, and the building where it is located. A complex business like a large manufacturing factory, such as the shoe factory shown in Figure 3 can have hundreds of job classifications.

Why the Division of Labor Increases Production
When the tasks involved with producing a good or service are divided and subdivided, workers and businesses can produce a greater quantity of output. In his observations of pin factories, Smith observed that one worker alone might make 20 pins in a day, but that a small business of 10 workers (some of whom would need to do two or three of the 18 tasks involved with pin-making), could make 48,000 pins in a day. How can a group of workers, each specializing in certain tasks, produce so much more than the same number of workers who try to produce the entire good or service by themselves? Smith offered three reasons.
First, specialization in a particular small job allows workers to focus on the parts of the production process where they have an advantage. (In later topics, we will develop this idea by discussing comparative advantage .) People have different skills, talents, and interests, so they will be better at some jobs than at others. The particular advantages may be based on educational choices, which are in turn shaped by interests and talents. Only those with medical degrees qualify to become doctors, for instance. For some goods, specialization will be affected by geography—it is easier to be a wheat farmer in Saskatchewan than in British Columbia, but easier to run a tourist hotel in BC than in Saskatchewan. If you live in or near a big city, it is easier to attract enough customers to operate a successful dry cleaning business or movie theater than if you live in a sparsely populated rural area. Whatever the reason, if people specialize in the production of what they do best, they will be more productive than if they produce a combination of things, some of which they are good at and some of which they are not.
Second, workers who specialize in certain tasks often learn to produce more quickly and with higher quality. This pattern holds true for many workers, including assembly line laborers who build cars, stylists who cut hair, and doctors who perform heart surgery. In fact, specialized workers often know their jobs well enough to suggest innovative ways to do their work faster and better.
Third, specialization allows businesses to take advantage of economies of scale , which means that for many goods, as the level of production increases, the average cost of producing each individual unit declines. For example, if a factory produces only 100 cars per year, each car will be quite expensive to make on average. However, if a factory produces 50,000 cars each year, then it can set up an assembly line with huge machines and workers performing specialized tasks, and the average cost of production per car will be lower. The ultimate result of workers who can focus on their preferences and talents, learn to do their specialized jobs better, and work in larger organizations is that society as a whole can produce and consume far more than if each person tried to produce all of their own goods and services. The division and specialization of labor has been a force against the problem of scarcity.
Trade and Markets
However, specialization only makes sense if workers can use the pay they receive for doing their jobs to purchase the other goods and services that they need. In short, specialization requires trade.
You do not have to know anything about electronics or sound systems to play music—you just buy a phone, download the music and listen. You do not have to know anything about artificial fibers or the construction of sewing machines to wear a jacket—you just buy the jacket and wear it. You do not need to know anything about internal combustion engines to operate a car—you just get in and drive. Instead of trying to acquire all the knowledge and skills involved in producing all of the goods and services that you wish to consume, the market allows you to learn a specialized set of skills and then use the pay you receive to buy the goods and services you need or want. This is how our modern society has evolved into a strong economy.
Why Study Economics?
Now that we have an overview of what economics studies, let’s quickly discuss why you are right to study it. Economics is not primarily a collection of facts to be memorized, though there are plenty of important concepts to be learned. Instead, economics is better thought of as a collection of questions to be answered or puzzles to be worked out. Most important, economics provides the tools to work out those puzzles. If you have yet to be been bitten by the economics “bug,” here are some other reasons why you should study economics:
- Virtually every major problem facing the world today, from global warming, to world poverty, to the conflicts in Syria, Afghanistan, and Somalia, has an economic dimension. If you are going to be part of solving those problems, you need to be able to understand them. Economics is crucial.
- It is hard to overstate the importance of economics to good citizenship. You need to be able to vote intelligently on budgets, regulations, and laws in general.
- A basic understanding of economics makes you a well-rounded thinker. When you read articles about economic issues, you will understand and be able to evaluate the writer’s argument. When you hear classmates, co-workers, or political candidates talking about economics, you will be able to distinguish between common sense and nonsense. You will find new ways of thinking about current events and about personal and business decisions, as well as current events and politics.
The study of economics does not dictate the answers, but it can illuminate the different choices.
Economics seeks to understand and address the problem of scarcity, which is when human wants for goods and services exceed the available supply. A modern economy displays a division of labor, in which people earn income by specializing in what they produce and then use that income to purchase the products they need or want. The division of labor allows individuals and firms to specialize and to produce more for several reasons: a) It allows the agents to focus on areas of advantage due to natural factors and skill levels; b) It encourages the agents to learn and invent; c) It allows agents to take advantage of economies of scale. Division and specialization of labor only work when individuals can purchase what they do not produce in markets. Learning about economics helps you understand the major problems facing the world today, prepares you to be a good citizen, and helps you become a well-rounded thinker.
Principles of Microeconomics Copyright © 2017 by University of Victoria is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Feedback/errata.
Comments are closed.

Wednesday, November 1, 2017
Importance of economic growth, why economic growth is important.
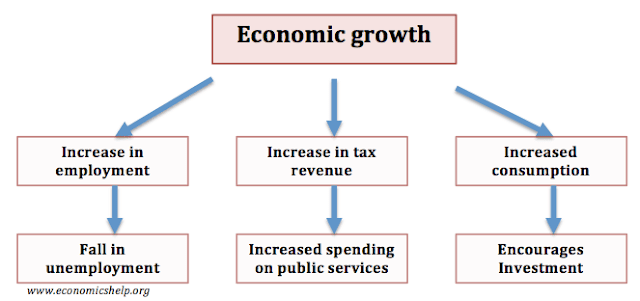
- Reduction in poverty . Increased national output means households can enjoy more goods and services. For countries with significant levels of poverty, economic growth can enable vastly improved living standards. For example, in the nineteenth century, absolute poverty was widespread in Europe, a century of economic growth has lifted nearly everyone out of this state of poverty. Economic growth is particularly important in developing economies.
- Reduced Unemployment . A stagnant economy leads to higher rates of unemployment and the consequent social misery. Economic growth leads to higher demand and firms are likely to increase employment.
- Improved public services . Higher economic growth leads to higher tax revenues (even with tax rates staying the same). With higher growth, incomes and profit, the government will receive more income tax, corporation tax and expenditure taxes. The government can then spend more on public services.

- Political aspect . Elected politicians have a vested interest in higher economic growth. Higher growth enables vote pleasing policies such as tax cuts and/or more public spending.
Virtuous cycle of economic growth
- Countries with positive rates of economic growth will create a virtuous cycle
- Economic growth will encourage inward investment as firms seek to benefit from rising demand
- Higher growth leads to improved tax revenues which can be spent on long-term public sector works, such as improved transport and communication. This helps long-term growth.
- Confidence to invest. Higher growth encourages firms to take risks - innovate and invest in future products and productive capacity.
Limitations of economic growth
- Inequality and distribution . Economic growth doesn't necessarily reduce relative poverty, it depends on the distribution of incomes. Economic growth could bypass the poorest in society. For example in the 1980s, the Gini coefficient rose sharply - the richest 1% gained dis proportionality more.
- Negative externalities . Economic growth can cause negative externalities such as pollution, higher crime rates and congestion which actually reduce living standards. For example, China has experienced very rapid economic growth but is now experience very serious levels of air pollution in major cities.
- Economic growth may conflict with the environment . e.g. increased carbon production is leading to global warming. Economic growth may bring benefits in the short-term, but costs in the long-term.
- It depends on what is produced . The Soviet Union has fantastic rates of economic growth, but, often through producing a lot of steel and pig iron that was not actually very useful.
- Economic growth can be unsustainable . If growth is too rapid, it will cause inflation, current account deficit and can lead to boom and bust.
- Does happiness actually increase? Theories of hedonistic relativism suggest (beyond a certain level) increasing output has no effect on changing life quality or happiness.
- Causes of Economic Growth
- Benefits of economic growth
- The Importance of Economics
3 comments:
No one is explaining clearly WHY the UK deficit has got so much worse so suddenly in 2009. What items are (roughly) responsible for each part of the increase?
2008 Financial Crisis, read the following: https://www.ifs.org.uk/publications/13302
Are the answers the same with why economists take much attention to economic growth matters
Post a Comment
Economics Essay Topics: Valuable Tips

Economics is a subject that has gained immense popularity in recent times. It deals with interesting economics topics like the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Moreover, it is a social science that provides insights into how individuals, businesses, and governments make decisions that affect the overall economy. Given its importance, economics essays have become a crucial part of the curriculum for students pursuing various degrees.
Short Description
In this article, our essay writer will take you on a journey through various exciting topics in economics. We'll cover everything from big-picture concepts like macroeconomics to more focused ideas like microeconomics, international trade, and economic policy. Our goal is to help you find the perfect topic for your economics essay—one that matches your interests and demonstrates your understanding of how economics affects the real world.
🎓 What is Economics: Understanding the Importance
Before we dive into the different economics essay topics, it is crucial to understand what economics is and its importance. Economics is a social science that deals with the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. It is concerned with how individuals, businesses, and governments make decisions about allocating resources to satisfy their unlimited wants and needs.
Economics as a science provides a framework for analyzing society's production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. It helps us understand how markets work and how they can be improved to increase efficiency and welfare. Moreover, economic principles have significant implications for various social issues, including poverty, inequality, environmental sustainability, and public policy. By studying economics essay topics, we can gain insights into these issues and develop policies that promote rapid economic growth and social welfare.

When it comes to economics, the range of essay topics is vast and covers various aspects of human interactions on different levels. With so many possibilities to explore, we understand the difficulty of narrowing down your options. That's why our ' write me an essay ' experts are here to offer their guidance and support. We're ready to help you select the ideal topic if you wish to learn how to write informative essay on economics.

🧩 Tips for Choosing Your Ideal Topic
Choosing a topic is the first and most crucial step in writing an economics essay. Your topic will determine the direction and scope of your essay. Here are some tips for choosing the ideal topic from our finance essay writing service :
Tip 1: Understand the relevance of economics to daily life and choose a topic with practical applications.
Recognize that economics plays a significant role in our everyday lives, as it encompasses the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Therefore, when selecting a topic, ensure its societal relevance. For instance, you might consider exploring 'The Impact of Automation on Employment Rates' or 'The Role of Government Regulations in Controlling Inflation.'
Tip 2: Opt for narrow economics research topics to make them more manageable and allow for in-depth exploration.
Instead of tackling broad subjects like 'International Trade,' narrow down your focus to something like 'The Effects of Tariffs on Small Businesses in the Agriculture Sector' or 'The Relationship Between Exchange Rates and Export Performance in Developing Countries.' By delving deeper into a specific aspect, you can provide more detailed financial analysis and insights.
Tip 3: Conduct preliminary research to identify current topics, debates, and research gaps.
Before finalizing your topic, engage in preliminary research to gain an understanding of recent trends and issues in economics. Explore academic journals, news articles, and books to discover areas that warrant further exploration. For example, you might come across intriguing research gaps such as 'The Impact of Cryptocurrencies on Financial Markets' or 'The Role of Behavioral Economics in Shaping Consumer Decision-Making.'
Tip 4: Seek input from peers or professors to enhance your topic selection process.
Collaborate with your peers during brainstorming sessions to generate fresh ideas and gain different perspectives on potential topics. Additionally, seek guidance from your professor, who can offer valuable insights and feedback to refine your chosen topic. For instance, you can discuss your ideas with classmates and receive suggestions like 'The Influence of Economic Policies on Income Inequality' or receive expert advice from your professor on 'The Implications of Globalization on Developing Economies.'
And if you want expert assistance in applying theoretical concepts to practice and creating an exceptional paper, then address your request to our custom essay writing services .

🗒 Economics Essay Topics: A Comprehensive List
If you are looking for a comprehensive list of interesting economics essay topics, you have come to the right place. Here are some ideas that you can consider:

- The role of central banks in fiscal policy: You can explore the role of central banks in implementing fiscal policies, such as setting interest rates, regulating money supply, and managing inflation.
- The effects of automation on the labor market: You can explore the impact of automation on the labor market, including the displacement of workers and the emergence of new job opportunities.
- The impact of immigration on the labor market: You can explore the impact of immigration on the labor market, including the effects on wages, employment opportunities, and economic growth.
- The economics of climate change: You can explore the economic impact of climate change, including the costs of mitigation and adaptation measures, the effects on industries, and the role of governments in addressing the issue.
- The economics of healthcare: You can explore the economics of healthcare, including the costs of healthcare, the role of insurance companies, and the impact of healthcare policies on the economy.
- The role of government in the economy: You can explore the role of governments in implementing economic policies, including fiscal and monetary policies, and the impact of these policies on the economy.
- The impact of globalization on the economy: You can explore the economic implications of globalization, including the effects on industries, trade, and employment opportunities.
- The economics of poverty and inequality: You can explore the economics of poverty and inequality, including the causes and effects of poverty and inequality and the role of governments in addressing these issues.
- The economics of education: You can explore the economics of education, including the costs of education, the impact of education on economic growth, and the role of governments in promoting education.
- The role of competition in the marketplace: You can explore the role of competition in promoting economic growth, innovation, and consumer welfare.
- The economics of entrepreneurship: You can explore the economics of entrepreneurship, including the factors that promote entrepreneurship, the impact of entrepreneurship on the economy, and the role of governments in promoting entrepreneurship.
- The impact of quantitative easing on economic recovery: You can explore the consequences of large-scale asset purchases and their influence on inflation, employment rates, and overall economic stability.
- The economics of renewable energy transition: You can analyze the costs, benefits, and challenges associated with adopting renewable energy technologies and their potential effects on energy prices, employment, and environmental sustainability.
- The role of technological innovation in economic development: You can examine the impact of research and development, technological diffusion, and digitalization on productivity, job creation, and competitiveness in various sectors of the economy.
- Behavioral economics and consumer decision-making: You can examine concepts such as cognitive biases, heuristics, and framing effects and explore how these factors shape consumer behavior, market outcomes, and the effectiveness of public policies.
Ready to Advance Yourself in the Economics Field?
Get the essay that will have even experts in awe!
🧮 Macroeconomics Essay Topics
Macroeconomics is a fascinating and complex field of study that aims to understand the overall performance of an economy. It takes into account various factors such as economic growth, inflation, unemployment, and trade policies. If you are looking for some thought-provoking macroeconomics essay topics, here are a few that you might find interesting:
- The role of digital currencies (cryptocurrencies) in the global economy and their impact on monetary policy.
- The economics of aging populations: Analyzing the challenges and opportunities associated with demographic shifts.
- The impact of trade wars and protectionist policies on global economic growth and international trade.
- The economics of happiness and well-being: Investigating the relationship between economic factors and subjective measures of life satisfaction.
- The role of government spending in stimulating economic growth and addressing income inequality.
- The economics of urbanization: Examining the effects of urban growth on productivity, income distribution, and resource allocation.
- The impact of automation and artificial intelligence on employment and the future of work.
- The economics of climate change: Analyzing the economic costs and benefits of climate policies and the transition to a low-carbon economy.
- The role of financial markets in transmitting economic shocks and their implications for systemic risk and financial stability.
- The economics of inequality: Investigating the causes and consequences of income and wealth disparities within and between countries.
📉 Microeconomics Essay Topics
Microeconomics focuses on the behavior of individual consumers and businesses in the market. The principles of microeconomics are used to analyze how these entities make decisions, interact with each other, and influence the overall economy. If you're interested in exploring this field further, here are some microeconomics essay topics that you might find interesting:
- Behavioral economics and its implications for consumer decision-making.
- The impact of artificial intelligence and automation on labor economics and income inequality.
- Pricing strategies in the sharing economy: A critical analysis of platforms like Uber and Airbnb.
- The economics of addiction: Analyzing the factors influencing consumer behavior and the effects on individual welfare.
- The role of information and asymmetry in financial markets: Examining the impact on investor decision-making and market efficiency.
- Game theory and its application in strategic decision-making in business and economics.
- The economics of innovation and entrepreneurship: Studying the factors that drive technological advancements and their impact on economic growth.
- Health economics: Analyzing the relationship between healthcare expenditure, access, and health outcomes.
- The economics of education: Investigating the determinants of educational attainment and its effects on individual and societal welfare.
- The economics of discrimination: Examining the economic implications of bias based on race, gender, or other factors in labor markets and beyond.
🎏 International Economics Essay Topics
International economics deals with the economic interactions between countries, including trade, investment, and migration. Here are some international economic relations topics:
- The impact of trade liberalization on developing economies: A comparative analysis of different trade policies and their effects on economic growth and income distribution.
- The role of foreign direct investment (FDI) in promoting technological transfer and industrial development in emerging markets.
- The economics of global supply chains: Analyzing the benefits and challenges of interconnected production networks in the context of international trade.
- The implications of Brexit on the European Union and the United Kingdom: Assessing the economic consequences and potential trade arrangements.
- The role of international institutions (such as the World Trade Organization, International Monetary Fund, etc.) in governing global economic relations: Evaluating their effectiveness and relevance in modern world economics.
- The economics of currency exchange rates: Examining the factors influencing exchange rate movements and their impact on trade and investment flows.
- The rise of protectionist policies and their implications for global trade: Assessing the economic consequences and potential risks associated with trade barriers.
- The impact of international migration on labor markets and economic development: Analyzing the effects of immigration policies and the role of migrant workers in host countries.
- The economics of foreign aid: Evaluating the effectiveness of foreign aid in promoting economic development and reducing poverty in recipient countries.
- The economics of regional economic integration: Examining the benefits and challenges of regional trade agreements, such as the European Union or the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN).
📉 Behavioral Economics Essay Topics
Behavioral economics combines psychology and economics to analyze how people make decisions. Here are some behavioral economics essay topics:
- The influence of socio-economic norms on consumer behavior and decision-making.
- The impact of framing effects on individual choices and decision-making processes.
- The role of default options in shaping consumer behavior and encouraging desirable outcomes.
- Prospect theory and its implications for understanding risk-taking behavior.
- Nudging strategies and their effectiveness in promoting positive behaviors and outcomes.
- The role of behavioral economics in understanding and addressing irrational financial decision-making.
- Behavioral economics interventions to promote sustainable and environmentally friendly behaviors.
- The psychology of pricing: How behavioral economics principles influence consumer perception of value.
- The influence of emotional factors on consumer decision-making processes.
- Behavioral biases in investment decision-making and their impact on financial markets.
🚑 Healthcare Economics Essay Topics
Healthcare economics analyzes how the healthcare system operates, including the costs and benefits of healthcare interventions. Here are some healthcare economics essay topics:
- The impact of healthcare insurance coverage on access to care and health outcomes.
- The role of economic incentives in shaping healthcare provider behavior and the quality of care.
- The economics of pharmaceutical pricing and its effects on affordability and access to medications.
- The cost-effectiveness of preventive healthcare interventions and their implications for healthcare spending.
- The economics of healthcare disparities and the role of social determinants of health in driving inequities.
- The impact of healthcare market competition on prices, quality, and innovation.
- The role of health technology assessment in informing healthcare resource allocation decisions.
- The economic evaluation of alternative healthcare delivery models, such as telemedicine and community health clinics.
- The impact of healthcare reforms and policy changes on healthcare costs and access to care.
- The economics of aging populations and the challenges of financing healthcare for the elderly.
🌎 Consumerism Essay Topics
Consumerism refers to the cultural and economic mindset that encourages the acquisition of goods and services. Here are some consumerism essay topics:
- The effects of consumerism on individual well-being and happiness.
- Consumerism and its impact on environmental sustainability and resource depletion.
- The role of advertising and marketing in shaping consumer behavior and promoting consumerism.
- Consumerism and its relationship with materialism and the pursuit of social status.
- The influence of consumerism on personal debt and financial well-being.
- Consumerism and its effects on societal values, culture, and social relationships.
- The ethical implications of consumerism and the responsibilities of consumers in a globalized world.
- The role of consumer activism in challenging and reshaping consumerism.
- Consumerism and its impact on mental health and psychological well-being.
- The future of consumerism in the digital age and the rise of e-commerce and online shopping.
📚 Economic History Topics
Economic history is a field of study that examines the historical development of economic systems, policies, and institutions, as well as the social, political, and cultural factors that have influenced economic outcomes over time. Here are the 10 interesting topics:
- The Industrial Revolution and its impact on economic development and societal transformation.
- Economic consequences of colonialism: examining the long-term effects on former colonies' economies.
- The Great Depression: causes, consequences, and policy responses.
- The role of institutions in economic development: a comparative study of different countries and regions.
- The rise and fall of economic empires: analyzing the economic power of ancient civilizations.
- The economic effects of wars and conflicts throughout history.
- The evolution of money and financial systems: from barter to digital currencies.
- The economic impact of technological advancements: case studies from different time periods.
- Economic inequality over time: trends, drivers, and consequences.
- The role of trade and globalization in shaping economic history: exploring patterns and impacts.
📊 Public Finance Research Topics
Public finance research focuses on the study of the government's role in the allocation, distribution, and management of resources within an economy. It encompasses the analysis of public revenues, expenditures, taxation policies, and the impact of government interventions on economic outcomes and social welfare. Here are 10 relevant economics papers topics:
- The impact of government spending on economic growth and development.
- The effectiveness of fiscal policy in managing economic downturns and promoting stability.
- The role of taxation in income redistribution and reducing income inequality.
- The economics of public debt and its implications for economic stability and future generations.
- The efficiency and equity implications of different tax systems (e.g., progressive, regressive, flat).
- The economic consequences of public infrastructure investment and its role in promoting economic productivity.
- The evaluation of government subsidies and incentives in promoting desired behaviors and industries.
- The economics of public-private partnerships and their effectiveness in delivering public goods and services.
- The impact of social welfare programs on labor supply, poverty reduction, and income mobility.
- The economics of environmental policy and the use of market-based instruments to address externalities.
Closing Remarks
To wrap up, economics is a subject that offers insights into how the world works. It provides a framework for analyzing complex social issues, including poverty, inequality, and public policy. Therefore, exploring economics essays topics is an excellent way of understanding the subject's relevance in the real world.
By following the tips for choosing your ideal topic and exploring the comprehensive list of economics topics for an essay, you can write an insightful and inspiring paper that contributes to the ongoing dialogue on economics.
Looking for Someone to Reduce Your College Stress?
Our expert writers can craft A+ essays when you want and how you want
Related Articles
.webp)
How to Write a Good Economics Essay
Governor November 28, 2019 Real World Applications 3 Comments
Many students ask “How to write an economics essay?” This Guide to Writing a Good Economics Essay is applicable to both IB economics as well as the Singapore JC A-Level H2 economics examinations. Many of the pointers here are also applicable to large-mark case study questions.
6 Steps to Writing a Good Economics Essay
Step 1: dissect the question.
Make sure you analyse and fully understand the KEYWORDS and REQUIREMENTS of the question. This is a very important skill that is taught in our economics tuition classes .
For example, “Best”, “Most Effective” are closely related but mean different things.
Paraphrase the question to make it simpler if necessary.
Take note of the command word (eg: Explain, Discuss) as it determines the approach needed for the essay, for example, whether two sides are needed or one side is sufficient. Below are some common examples found in economics essay questions:
Command Words Action Required
Account for Explain why
Analyse Break it down into step-by-step explanations
Assess For & Against. Consider other factors.
Compare Identify Similarities & Differences
Distinguish Point out differences
Discuss Explore both sides
Evaluate The Good and The Bad.
Explain Show why and how
Explain whether Cover both possibilities
Examine Look closely. How so and how not so?
To What Extent Yes…..But….Judgment
Remember to look out for the context in the question. This is usually given in the form of a country (eg: Singapore). The examples in your essay must be tailored to this particular context (for example, do not suggest interest rate policy for Singapore as that is considered infeasible in the Singapore context). If no context is given, any real-world example can be used.
Keep in mind the question throughout the essay and remember to always answer the question. Don’t go off-point!
Common Examiner’s Comment : Not Answering Question (NAQ))
Step 2: Plan Your Answer
Take some time to consider what economic framework you will use to approach the question. Scribble down your main thesis and anti-thesis points. Ensure they ANSWER THE QUESTION.
Step 3: Essay Introduction
In the introduction, include definitions of keywords in the question and spell out the economic framework you will employ for your answer as well as key definitions.
Step 4: Body of Essay
In the body , there will be several paragraphs.
The number of points/paragraphs depends on the question. It is common to require 2 main points for each 10 mark essay and similarly for 15 mark essay questions. Under each main point, there may be 1-2 sub-points.
Use one paragraph for each sub-point you are making.
However, do not be too focussed on the number of points or paragraphs. The key is to answer the question.
For each body paragraph , use TET’s PEEL(ED) structure. Include only one main idea per paragraph.
- Point – Write your point in the first sentence so that markers will know what the paragraph will be about. The topic sentence must directly answer the question!
- Explanation – Explain what you mean
- Elaboration – Provide further analysis with clear step-by-step economic reasoning. This part may be done with examples as well as diagrams.
- Link – Link your explanations back to the Point and to answer the question.
- Exemplification – Give an example to support your reasoning. It can be statistics or real-world examples (for Case Studies, evidences from the Case must be uncovered!)
- Diagram – Where possible, araw an appropriate diagram with correct labelling and refer to it in your answer. This is crucial to show economic reasoning. Diagrams are very important for economics essays!
These are of course much easier said than done! Thus, students in our economics tuition classes are regularly honed to achieve such output including with tips and tricks to spark off the correct thinking process.
Our resources including the Study Guides for A Level and IB economics also provide a very powerful and handy reference on the depth of analysis required to score the highest marks.
Common Examiner’s Comment : Mere statements and claims. No economic rigour.
Step 5: In-Body Evaluation
This applies especially to the 15 mark essays for A-Level Economics. A total of 5 marks is catered for Evaluation. Students should attempt to achieve about 2-3 in-body evaluation marks by pointing out how the thesis and anti-thesis points may not be true due to certain assumptions made that may not hold. Students may write “However,….may not necessarily happen……It would depend on whether….”. This statement can be written after the associated sub-point has been made.
Step 6: CONCLUDING SECTION
This only applies to the 15 mark essay questions.
Earn more evaluation marks by making a reasoned judgement. Deliver your verdict like a Judge!
Check back on the question before you embark on this. Ensure your judgement answers the question.
So the question now is, how does a judge arrive at and deliver a verdict? Certainly, you should not be summarising or merely paraphrasing your main points in the conclusion. Obviously, you cannot expect more marks by saying the same thing over and over again!
After a verdict and reasons have been provided, consider providing further relevant insights and/or recommendations.
Common Examiner’s Comment : Repetitive. Mere Summary.
Here are some quite common types of Concluding Sections
- Consider the relative importance of thesis and anti-thesis factors. Which factors are most important or pertinent in the given context? For example, certain policies better fit specifc types of economies.
- Consider short-term vs long-term pros and cons. Do the short-term benefits outweigh the long-term costs? Is the policy more effective in the long-term, and if so, how pressing is the problem that needs to be addressed?
- Suggest a multi-policy approach, in which each policy has strengths and weaknesses that allow them to complement each other.
There is no way to really memorise evaluation points as every question and context is different. After all, you are being tested on higher-order thinking!
There are other evaluation tips that our students will receive but the key point here is that the training of the mind to think and apply economics is essential. That is where our weekly economics lessons come into play and that is why our students are often asked questions in class and trained to think on their feet. As ex-student Xue Min from YIJC testified, Chief Tutor Mr. Kelvin Hong does not just spoon-feeds our students but mentors them in their thinking to arrive at the answers. This was different from other tutors that her classmates experienced and eventually this was the key to Xue Min’s A grade.
In your essay, write in simple and clear sentences. Everything you write should be value-adding. You do not have to spend time showing off vocabulary as no extra points are awarded for language. Focus on economic reasoning. Use succinct and effective examples which support the point you are trying to make as well as accurate diagrammatic analyses.
For samples of great economics essays, please check out our free Economics Model Essays and sample Past JC A-Level Economics Questions and Answers .
For our econs publications that are sold worldwide, please check out our A Level & IB Economics Study Guides and Model Essays Publications
About The Economics Tutor
Founded by Kelvin Hong in 1998, The Economics Tutor is one of the leading economics tuition in Singapore. We provide a comprehensive program to guide students in understanding complex economic concepts and applying them through case study analyses, essay writing and discussion of real world events.
For 24 years, the way we teach JC Economics Tuition (A Level Economics Tuition) and IB Economics Tuition classes helped learners appreciate economics and everything it entails on a much larger scale. We take things step-by-step, implement effective techniques in memorising frameworks and give every student the chance to nurture their ideas.
We don’t just solely focus on helping you get stellar grades and perfect scores. We make sure that we also hone the critical thinking skills and investment / business decisions you can use outside the four walls of your classroom.
Looking for a fun, engaging and probably the best economics tutor in Singapore? Look no further—check out our extensive and high quality economics resources on the website such as our IB and A Level Economics Publication. Click here to order .
Book your lesson today and master the nuances of economics in our next class!
its good knowledgeable post regarding ib economics commentaries. i just wanted to admin can i use your blog as reference to my students .
Go ahead. We are all for helping students learn economics well.
Thank you, A lot of info!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
See You In Our Next Econs Lesson!
5.0 stars out of 130 G o o g l e reviews
#1 Economics Tuition Singapore – Kelvin Hong - The Economics Tutor
- +65 9336 7511
- [email protected]
- About JC A Level Economics
- About IB Economics
- Testimonials
- A Level & IB Economics Study Guides and Model Essays
- Blog Resources
- Economics Videos
- Economics Notes, Infographics & Mindmaps
- Real-World Examples
- Economics Definitions
- Past A Level Economics Questions & Answers
- Fees & Schedule
- Register / Schedule a Class
- Bishan Economics Tuition
Copyright © 2024 The Economics Tutor
Economics and Its Meaning in Everyday Life Research Paper
Introduction, modern economics, profit maximisation, social benefit.
Economics is the social science of making sufficient choices or decisions and studies how people interact in their society economically. This paper introduces the subject of economics and unfolds what it is all about. We live in a society where economics is a valuable need in order for us to understand and handle any problems that may occur in the future. The basic economic problem is scarcity, where people’s wants and needs are unlimited. Every time a need is satisfied, a new need is then created thus, creates the unlimited wants and needs of the human characteristic. The problem of scarcity results in allocation, which is the process of choosing needs that will be gratified and how many resources we will use in order to satisfy them. Because there are so many wants waiting to be satisfied, there are only so many resources to fulfill those wants. Limited resources are the condition of there not being enough resources to fulfill all wants and needs.
Since economics is all about making choices, people must understand the cost and benefits of any choice in order to make competent choices. Opportunity cost and Opportunity benefits guide the decisions process of individuals and countries and determine the goods to which they are going to be produced. However, Opportunity cost is the option that you must give up when you make a choice, and opportunity benefit is what you gain by making a certain decision. An example of opportunity cost and opportunity benefit is assumed one night you have a stack of homework waiting for you to do, but when your parents get home, they demand that you go out with them to eat dinner and catch a flick afterward. Yet you really want to do your homework and study, but you give up your education time to spend the night with your parents. Your opportunity cost of this is what you give up, and that is your study time; however, you do gain a benefit from giving up your homework, and that is a movie and a casual dinner with your parents.
Every society has basic economic questions, and when responding to these questions, societies must balance the needs of individuals with the needs of society together. The subject Economics is divided into two separate branches: microeconomics which examines the choices of individuals regarding one product, one firm, or one industry, and macroeconomics examines the conduct of the whole economy at once. Everything in life has a theory; in economics, the importance of theory is a simplified description of reality. The economic theory helps to understand the economic systems, which are the combination of social and individual decision-making it uses to answer the three economic questions. Economist uses an ideological tool called a budget constraint that is the mixture of goods that can be acquired although it is given a limited amount of income. A person goes through life they will make economic decisions as a consumer, as a worker, and as a citizen that will make an understanding of economic theory an important part of everyday life. (Cubitt, 2005).
Countries such as the United States use a variance of approaches in order to answer the basic economic questions. A market economy is buyers and sellers and is the state of trade as determined by prices, supply, and demand. The question of what to produce is decided by individual consumers and producers in the marketplace by using the price system. A command economy is all about government planners deciding what is produced and available for sale. A traditional economy is where prices are set because of holidays. A mixed economy is a combination of a market, command, and traditional economy. Although the U.S. has a great economy, the main economic problem still lies in our hands. Scarcity and choice exist in all economies. However, like our society, other societies use different combinations of individual and social choices to allocate resources.
Modern economics vs. political economy, as it used to be called-dates back to1776. It begins with the American Revolution. A man named Adam Smith, a Scottish philosopher, published a book called Smith’s work is considered the first example of modern economics. In some places, Smith is most famous for suggesting that businesses always try to monopolize markets and raise prices. Economists credit Adam Smith’s theory of the invisible hand – the idea that a market economy will operate so that no one can be made better off without making someone else worse off. It is as if an invisible hand is guiding the markets when in reality, the markets merely reflect the activities of those trading in them.
When prices for some widely consumed good or service surge or when some company s profits appear to reach stratospheric levels, the popular press seems to return to St. Augustine and ask what is the just price. Others maintain that economics began much, much earlier. Economics figures in most national elections. John Kennedy was elected during the recession that plagued the prior administration; the recession ended in the second month of Kennedy s term as he demonstrated a combination of timing and luck matched by few Presidents. Franklin D. Roosevelt s landslide victory in 1936-based on his efforts to turn back the Great Depression- set the course for the next several decades of U.S. politics. The economy is telling us what s happening and what could happen next. To understand the economy, you have to look at how the economy is measured, scaled, and gauged. How big, rich fast-growing it is. The economy in the United States and increasingly throughout the world is organized into markets. Markets are where we trade things- someone s labor, time, and effort for his wage; or hard-earned dollars for a car.
Markets are rather old-maybe as old as civilization itself. Markets are crucial to understanding the economy. They include much more than the stock market, although that one is quite interesting. Markets exist for almost anything-time and labor, art, cars, things we make, and services we buy. Most markets have common elements, patterns that make buying a car and getting a second opinion before surgery almost the same thing. As the axiom goes, the only constant changes. In the economy, changes occur all the time. They are what shift prices ad gives rise to opportunities.
Economics is the rules of the game, how we organize society. Most of what we see as important in everyday life is organized by the economy. On a day-to-day basis, economics has to do with what kind of job we have or don’t have; with how much money we can earn; with what things cost; with whether we can save and invest enough for a comfortable future; with how much we need tomorrow and with how well off our children will be in coming years. Economics is why we have jobs. Why we work, why we earn incomes, why money matters, and why markets are important. Economic ideas contribute to the way our society is organized. That the kind of organization we have today has evolved gradually doesn’t t make the principles behind it any less important. It evolved through history to the current arrangement and is still changing and evolving. The social fabric is always likely to be changing. Many of the principles behind the current organization depend on economics and include many ideas.
Principles of economics include Private property- we can own land, houses, tools, books, and all kinds of other goods and use them, or dispose of them, as we wish. Another is a job. We have jobs and earn income with our labor. Human rights-we do to own other people and don’t have pre-emptive rights to someone else s labor and property. Markets- the way we exchange private property or exchange labor for income is through a voluntary bargaining process called a market. We use money as a way to store wealth and to buy and sell things we own, including our own labor.
The thing that distinguishes markets and money from other elements of the economy is that they are a little more fundamental. In almost any society based on private property, both money and markets are present. Not much private property is needed to give rise to markets and money just enough so that people have some things to exchanges and need a way to keep track of how much money they have. Trading has been practiced since before recorded history. Ancient tribes traded with one another to get essential tools that were hard to make locally. (Samuelson, 2005) Today economist speaks of gains form trade.
The most misunderstood part of economics is in public debates. Recently the political arena has echoed with arguments over the budget deficit and the national debt. We hear every possible opinion, from claims that we are about to drown in our own red ink, to suggestions that we ignore the debt, to claims that cutting our taxes will lead to larger tax revenues for the government and a drop in the deficit. Some of these arguments are involved; the difference between the national debt and the budget deficit is rather straightforward. Each year the government collects taxes and spends money. When expenditures exceed revenues, the government is left with a gap. This gap is the deficit.
Expenditures cover a wide range of items, including social security benefits, Medicare and Medicaid payments, salaries of government workers, foreign aid, and government purchases from paper clips to jet planes. The numbers and reports on the national debt have another important complication. The government saves some revenues by investing them in Treasury bonds. Measurement of economics has a venerable history. For a long time, people thought the only thing to economics was measuring or counting. Forecasts almost always require numbers- at times to provide a forecast that really gets specific, at other times to make a vague forecast look specific enough to be worth paying for. (Fontaine, 2005) Sometimes economics drives the way we measure. As we look at the unemployment rate, deciding what we measure often involves understanding the economy and its various sectors and markets larger.
Some longer-term issues related to the deficit are also legitimate concerns. Over the last few decades, the proportion of total income that America saves and invests in forth future has declined. If we invest less today, there will be less wealth tomorrow. One reflection of the decline in savings is the rise of the deficit. Simply worrying about the deficit, some politicians argue, is the wrong response. Increasing savings is the right response. Japan, in its peak years of economic growth, had far more savings and a far larger than in the United States.
One of the more recent developments in mathematics, physics, and related sciences is a collection of studies alternately referred to as complexity theory, self-organization, and chaos theory. While some commentators may argue that economics has a special claim on chaos, there are interesting parallels between many of these studies and economics. (Keen, 2004) One of the ideas behind these theories is that at times a collection of objects- animals, computer programs, people, or almost anything else-will seem to become very well organized without any systematic communication or planning.
The economy surrounds us, and it plays a large part in our lives. It has more impact than the weather on how we live and how well we live. Economics runs through other parts of our lives as well. If the economy is in a recession or a depression, it hits a lot of people. The economy helps us keep track of the nation’s standing. The economic system has grown since Adam Smith s book. Right now, since the economy is good, it is easy to get jobs. During a recession or a depression, the economy is the indication of what is going wrong and what to fix. Everyday life is circled around the economy. The different kinds of markets provide a different understanding. The stock market also is an indicator of the economy. The stock market shows the sales and wealth of the different markets around our country. If the economy is good, we know it. It shows everywhere, and politicians don’t hesitate to base an election on how well they did or how awful the economy was under another politician. It will make or break the politician.
All of the businesses have common factors. They all provide products in the form of goods or services. For example, books, food, fitness training, utilities, etc., some of the products provided by businesses are needed by customers. They are, in essence, providing necessities, for example, basic food and clothing. Some businesses, on the other hand, provided products that customers can be persuaded to want through advertising. For example, luxury food, fashion clothing, or a holiday, etc. A business may therefore be defined as; an organization that provides goods or services which satisfy customer needs and wants.
The objective of profit maximization brings with it an imperative question to be considered in great detail; should businesses maximize profits? Businesses have a social responsibility. They need to aim to reduce pollution, improve safety levels, and preserve jobs, etc. firms, in the effort to maximize profits, go against many social and ethical issues, for example, if materials needed by a firm can be found cheaper abroad, profit-maximizing firms will by from countries whose political regimes, the U.K. public may not approve of. It is argued, however, that in order to pay attention to aspects, such as pollution levels, and preservation of jobs, etc., the firm needs to be financially stable. In other words, they need to be making a profit. The importance of profit is just one aspect of the profit-maximizing position of a firm, which adopts the profit-maximizing objective. (Ernst, 2007).
In a short conclusion to the profit-maximizing objective of a firm, one might suggest that there is only one valid definition of a business’s purpose: to create a customer. Profits, then, are the results of being in business. They test how efficiently a business has created a customer in terms of the cost to the business in relation to the revenue gained through the customer.
The size of a firm displays a close correlation to sales revenue. As such, sales revenue is often considered a surrogate. It is said that although high levels of profit bring with it benefits to the owners or shareholders of a firm, high levels of sales revenue, on the other hand, brings with it benefits for managers, for example, higher levels of income.
One major difference to note between profit maximization and revenue maximization is the term to which the objectives are set. A firm whose overall objective is profit maximization is said to have such an objective set long term. In other words, the objective is hoped to be met over a five-year period. A firm whose overall objective, on the other hand, is revenue maximization, is said to have such an objective set short term, the objective is hoped to be met over a two-year period. (Fullbrook, 2004) Perhaps another significant difference to note is that of by whom such objectives have been set. Managers had both the ability and motivation to pursue objectives other than Profit Maximisation, and as we will see soon, this ability and motivation of firm’s managers extend to them being able to pursue Non-Maximising objectives, for example, Social Benefit. Similarly to Revenue Maximisation, controllers of a firm are more interested in objectives that satisfy them, such as Salary, prestige, and status, and job security. (MacKenzie, 2003).
As with those who commit to Revenue Maximising objectives, those who set Growth Maximisation as their objective do so with consideration of what growth the owners in the firm want to see, such as profit, sales, and market share. These different sets of objectives are reconciled by concentrating on the growth of the size of the firm, which in turn will bring with it high salaries and status for managers and larger profits and market shares to keep the shareholders happy. As with the Profit Maximising objective, growth maximization has to limit factors or constraints, both managerial and financial. Finding a product or a market to expand can prove problematic to the management team of a firm. Having found an area of expansion, the management team also faces the limitation of remaining in control of such expansions.
In order to become a growth-driven company, investments need to be made. The funds required for such investments are ever-increasing and can be obtained by either internal investments by the use of retained profit, or external investments funded by borrowing, the latter creating further liabilities for the firm. (Amos, 1994) If either of the aforementioned means of investments is not closely controlled, the risk of either takeovers or shareholder revolt is increased, which intern would have a knock-on effect on the job security of management. Ensuring that the growth of demand is matched equally by the growth in capital supplied can satisfy the above constraints. Control of the leverage revenue will help to keep the level of borrowing in check. Control of the liquidity ratio can prevent a firm from becoming insolvent. Finally, via the retention ratio, profits can be distributed sufficiently in order to keep shareholders happy.
Businesses have a significant contribution to social welfare; we visited this idea earlier when discussing the profit maximization objective of a firm, where one stated the importance of pollution reduction and job security etc. By paying attention to the social welfare of consumers and employees, those within firms will benefit. Namely, suppliers of capital, labor, and other resources that have in the past received substantial returns for their contribution to the improvement of social welfare. Consumers can also benefit where social benefit is the key objective of a firm, through increasing the quality and quantity of the goods and services available to them for consumption.
The public can, in many ways, be the backbone of a firm. They state that the very existence of certain firms is a result of public consent and that as such, those firms that are amongst the most successful tend to be those that exercise socially responsible behavior. It is said that Social Benefit is not a maximizing objective because, in order to be an objective, it would be required to be measurable. Rather, the social benefit is considered in terms of what combinations of goods and services should be produced? How many goods and services should be provided? And finally, how they should be distributed.
There are five main maximization objectives of a firm. You will have noticed throughout the descriptions a mention of the differentiation between managers and owners of a firm. Most large firms tend to be run by professional management teams rather than the owner of the firm. As such, conflicts in the interests or direction of the firm can and do happen. Such conflicts occur as a result of differences between the objectives of the owners and of the managers, also referred to as controllers. The main aim of the owner of a firm is that of maximization of the overall value of the firm, whether that is maintained through profit maximization, revenue maximization, management utility theory, company growth, or indeed social benefit.
The above conflicting interests of a firm’s progression can be better defined as the principal-agent problem, whereby objectives, different to those of the principle, also referred to as the owner, are pursued by the agent, also referred to as the controller or manager. The problem or conflict occurs when the principle has difficulty enforcing their contracts upon the agent or when the monitoring of the agent to verify that they are furthering the principle’s objectives becomes unjustifiably costly.
In economics, profits are not merely an objective; they are, in fact, the very reason for the existence of the business enterprise. The statement alone opens discussions regarding the existence of a firm. For Example, A charity shop, by its very nature, does not thrive on profit as a means of existence, rather, it relies on the generosity of the general public, and therefore it would be fair to suggest that the objective of most charity shops is a social benefit. The nature of a business, its size, location, and management model will all together determine the route to which the company wishes to follow. Thus the objectives it will set. When looking into any business, large or small, one will see that no single decision is clear, there are many clouds surrounding the smallest of decisions, and so the analysis of firms, and in particular, the objectivity of a firm, cannot be made in black and white, there is simply too much about the organization, macro and microeconomics, politics and social factors to consider, all of which are ever-changing.
Amos, Orley. Economic Literacy . Hawthornel, New Jersey: Career Press, (1994).
Cubitt, Robin (2005) “Experiments and the Domain of Economic Theory,” Journal of Economic Methodology 12: 297-210.
Ernst, Z. (2007) “Philosophical Issues Arising from Experimental Economics”, Philosophy Compass, Blackwell.
Fontaine, P. and R. Leonard (2005) The Experiment in the History of Economics London: Routledge.
Fullbrook, Edward, What’s Wrong With Economics, Anthem, (2004).
Keen, Steve, Debunking Economics, Zed Books, (2004).
MacKenzie, D. F. Muniesa and L. Siu (eds.) (2003): Do Economists Make Markets? On the Performativity of Economics. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Samuelson, L. (2005) “Economic Theory and Experimental Economics”, Journal of Economic Literature 43: 65-107.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2021, October 25). Economics and Its Meaning in Everyday Life. https://ivypanda.com/essays/economics-and-its-meaning-in-everyday-life/
"Economics and Its Meaning in Everyday Life." IvyPanda , 25 Oct. 2021, ivypanda.com/essays/economics-and-its-meaning-in-everyday-life/.
IvyPanda . (2021) 'Economics and Its Meaning in Everyday Life'. 25 October.
IvyPanda . 2021. "Economics and Its Meaning in Everyday Life." October 25, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/economics-and-its-meaning-in-everyday-life/.
1. IvyPanda . "Economics and Its Meaning in Everyday Life." October 25, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/economics-and-its-meaning-in-everyday-life/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Economics and Its Meaning in Everyday Life." October 25, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/economics-and-its-meaning-in-everyday-life/.
- Utility Maximization and Consumer Behavior
- Consumer’s Utility and its Maximization
- Profit Maximization of Medicare
- Economic Principles of Substitution and Maximization
- Share Holder Wealth Maximization Vis a Vis Social Responsibility
- Profit Maximization in Various Market Structures
- Profit Maximization and Legal Business Forms
- Disney Resort in California: Profits Maximization
- Profit Maximization in the Price-Sensitive Airline Industry
- Determinants of Wages: Earning Potential Maximization
- The Synergy Between Capitalism and Democracy
- "The End of Oil" by Paul Roberts
- Pitt County: Urban Economics and Export-Based Theories
- Marx and Weber in Relation to History: Materialism and Existential Idealism
- Reductionist Effect in Macroeconomics

Essay on Economics
Economics, often described as the study of scarcity, is a dynamic and vital field that examines how individuals, businesses, governments, and nations make choices on allocating resources to satisfy their wants and needs. It delves into how these groups interact within a market economy to influence the distribution of wealth and resources. This essay aims to provide a thorough understanding of the fundamental principles of economics, its branches, and its significance in our daily lives and the global market.
The Essence of Economics
At its core, economics is about choice and the impact of our choices on each other. It involves the analysis of how people use their limited resources to fulfill unlimited wants. This scarcity of resources means making decisions on how best to use them – whether it’s a family budgeting their income or a country deciding how to use its natural resources.
Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
The Two Branches of Economics Economics is broadly divided into two categories: microeconomics and macroeconomics.
- Microeconomics: This branch focuses on the behavior of individuals and firms in making decisions regarding the allocation of limited resources. It studies market mechanisms that establish relative prices among goods and services and allocates limited resources among various uses. Microeconomics looks at issues like consumer behavior, individual labor markets, and the theory of firms.
- Macroeconomics: Contrasting microeconomics, macroeconomics deals with the performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole. This includes regional, national, and global economies. Macroeconomics involves studying economy-wide phenomena such as inflation, price levels, the rate of economic growth, national income, gross domestic product (GDP), and changes in unemployment.
The Role of Supply and Demand
One of the most fundamental concepts in economics is the theory of supply and demand. It is the backbone of a market economy.
- Demand: This refers to how much of a product or service is desired by buyers. The quantity demanded is the amount of a product people are willing to buy at a certain price.
- Supply: Supply represents how much the market can offer. The quantity supplied refers to the amount of a certain good producers are willing to supply when receiving a certain price.
The relationship between demand and supply underlies the forces behind the allocation of resources. In market economy theories, demand and supply theory will allocate resources in the most efficient way possible.
The Significance of Economic Theories and Models
Economic theories and models are crucial as they help economists make predictions and understand the complex world of finance. For instance, the Keynesian economic model suggests that government spending should increase during times of economic crisis to boost demand. On the other hand, supply-side economics advocates for lower taxes and less regulation to stimulate business growth.
- Understanding Economic Dynamics
- Predicting Economic Trends
- Policy Formulation and Decision Making
- Business Strategy Development
- Crisis Management and Resolution Understanding Consumer Behavior
- Resource Allocation and Efficiency
- Technological Impact Analysis
Economic Policies and Their Impact
Economic policies play a crucial role in shaping a nation’s financial stability, growth, and the overall well-being of its citizens. Understanding these policies and their impacts is vital for students, educators, and anyone interested in the workings of economic systems. Here are some key points on this topic:
- Definition : Monetary policy involves the management of a country’s money supply and interest rates by the central bank.
- Impact : It influences inflation, employment rates, and economic growth. For example, lower interest rates can stimulate borrowing and spending, boosting economic growth.
- Definition : Trade policy includes tariffs, trade agreements, and quotas.
- Impact : It determines a country’s trade relationships with others. For instance, free trade agreements can boost exports and imports, leading to economic growth, but may also impact domestic industries.
- Definition : This involves rules or laws designed to control business practices.
- Impact : It can protect consumers, ensure fair competition, and prevent monopolies. However, overregulation may hinder business innovation and efficiency.
- Definition : This policy governs how a country manages its currency in relation to others.
- Impact : A strong currency can reduce the cost of imports but may harm exporters by making their products more expensive in foreign markets.
- Definition : This involves how the government collects taxes and what it taxes.
- Impact : Tax incentives can encourage investment and savings, while high income taxes might discourage individual earnings and innovation.
- Definition : It’s the strategy for managing a country’s debt.
- Impact : Responsible debt management ensures a country can finance its needs and maintain financial stability. Excessive public debt can lead to financial crises and reduced spending on public services.
- Definition : These policies relate to government programs for healthcare, education, and social security.
- Impact : They can redistribute wealth and reduce inequality but may also require high taxes and government spending.
Global Economics: Trade, Markets, and Economies
Global economics is another vital aspect. It includes studying international trade, global markets, and the economies of different countries. It deals with issues like trade deficits, currency exchange rates, and international economic policies. It helps in understanding how economies are interconnected in the global scenario.
Economics is an essential field of study that offers invaluable insights into how societies use their resources and distribute wealth and goods. It’s a discipline that not only helps us understand the world better but also equips us with the knowledge to make informed decisions in our personal and professional lives. Whether it’s a student, a business professional, a government official, or a homemaker, an understanding of economics can contribute significantly to making sound decisions and understanding the complexities of the global economy.
Essay Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Generate an essay on the importance of extracurricular activities for student development
Write an essay discussing the role of technology in modern education.
Essay on Economics: Nature and Scope of Economics
Subject-matter of Economics:
Economics has a subject-matter of its own. We can know something about the subject-matter of Economics from its definitions given above.
The student already knows about Mathematics, History and Geography. But Economics is new to him and he cannot say what it is about.
We can say that Economics studies man’s life and work, not the whole of it, but only one aspect of it. It does not study how a person is born, how he grows up and dies. This is the work of another science named Biology.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Economics does not study how human body is made up and how it functions. That is the subject of Physiology. Economics does not tell us how a man thinks. It is Psychology which studies man’s mind. Economics does not study the human organization like the State. This is the subject of Political Science. Economics only tells us how a man utilizes his limited resources for the satisfaction of his unlimited wants. A man has a limited amount of money and time; but his wants are unlimited. He must so spend the money and time he has that he derives maximum satisfaction. This is the subject-matter of Economics.
Economic Activities:
If we look around, we see the farmer tilling his field, the workman working in the factory, the clerk at his desk, the doctor attending to his pleats, the teacher teaching his students, and so on. They are all engaged in what is called economic activity. They earn money to satisfy their wants. It is with this part of man’s life that Economics deals.
We may say that when a man is engaged in an economic activity he is busy earning money. But he does not want money for its own sake. He needs it to buy things which satisfy his wants. The purpose of all economic activity is the desire to purchase goods to satisfy human wants. Neither good nor money is an end in itself. They are needed for the satisfaction of human wants and to promote human welfare.
A man wants food, clothes and shelter. To get these things he must have money. For getting money, lie must work or make an effort. Effort leads to satisfaction. Thus, Wants—Efforts—Satisfaction, sums up the subject-matter of Economics. This circle of economic activity is shown in the adjoining diagram.
In a primitive society, the connection between wants, efforts and satisfaction is close and direct. A primitive man feels hungry; he picks up some fruit, eats it, and is satisfied. But in a modern society things are not so simple and straight. Here a man produces what he does not consume and consumes that he does not produce. The shoe-maker produces shoes, but he cannot use them all by himself. He sells them for money with which he buys the things he needs. This work of selling what you do not want and buying what you want is called exchange. Today the process of exchange comes in between wants, efforts and satisfaction.
Nowadays most of the things we need are made in factories. To make them the worker gives his labour, the landlord his land, the capitalist his capital, while the businessman organizes the work of all these. They all get a reward in money. The laborer earns wages, the landlord gets rent, the capitalist gets interest, while the entrepreneur’s reward is profit. Economics studies how these incomes—wages, rent, interest, and profits—are determined. The process is called Distribution. Like Exchange, Distribution also comes in between effort and satisfaction in a modern society.
Thus, we can say that the subject-matter of Economics is Consumption (i.e., the satisfaction of wants), Production (i.e., producing things or creating utilities or making an effort to satisfy our wants), Exchange and its mechanism (i.e., money, credit and banking, etc.) and finally Distribution (i.e., sharing of all that is produced in the country among workers, landlords, capitalists and organizers). In addition, Economics also studies Public Finance. Thus it is indeed a very wide subject.
Modern View:
The above view of the subject-matter of Economics is the traditional view. The view that is widely accepted today is far more comprehensive. The traditional subject-matter explained above is now regarded as constituting only one part of Economics, viz., Price Theory or also called Micro-Economics. According to modern approach, the scope or the subject-matter of Economics is not only the price theory but also the study of the economy as a whole. We study, for instance, how the income of an Economy is generated and how the level of a country’s income and employment is determined.
In other words, we also study the factors that determine a country’s national income, savings, investment, output, employment, general price level, etc. Such a study of the economy as a whole is called Macro-Economics. Hence we study both micro-economics and macro-economics.
More recently, economists have begun to pay special attention to how an economy grows, i.e., how the under-developed countries grow into developed economies and the developed economies grow still further. Economics thus also includes study of economic growth.
Conclusion:
In sum, the subject-matter of Economics, according to the view held today, includes price theory (or micro-economics), income and employment theory (or macro-economic) and growth theory. Thus, broadly speaking Economics may be described as a study of the economic system under which men live and work. It deals with decisions regarding the commodities and services to be produced in the Economy, how to produce them most economically and how to provide for the growth of the economy.
Divisions of Economics:
Traditional Approach:
According to the old view, the study of Economics is divided into four main departments or divisions, viz., Consumption, Production, Exchange, and Distribution. In Consumption, we study the nature of human wants as well as the principles governing their satisfaction. The law of diminishing marginal utility, law of Substitution, the law of family expenditure and consumer’s surplus are of special importance. We also study the nature of demand, whether it is elastic or inelastic, as well as the law of demand.
In Production, we study how man makes efforts to satisfy his wants by producing wealth. In particular, we see how the four agents of production, viz., land, labour, capital and organisation, co-operate and combine in the work of production. We study each of these agents, their importance and the conditions of their efficiency.
In the third department of Economics, viz., Exchange, we discuss how in the various market forms buying and selling are done and how prices are determined. This happens through the interaction of the forces of demand and supply.
The fourth department, Distribution, is devoted to the study of the respective shares that go to the four agents—land, labour, capital and organization. These shares take the form respectively of rent, wages, interest and profit. In Distribution, we study how the share of each agent of production is determined.
It is usual to divide Economics into these four departments only. But in addition to these, we have to study also the problems of Public Finance. Here we discuss how governments get money and how they spend it. Thus, it involves a consideration of taxation and allied questions.
Modern Approach:
It is only an old approach to divide Economics into these four divisions. The modern approach is different. The study of Economics is now usually divided into two parts: (a) Income Theory or Macro-economic; and (b) Price Theory or Micro-economics.
In Income Theory or Macro-economics, we study the working of the economic system as a whole. That is, we study what determines the level of income in a country, its total expenditure, total employment and the general price level (not the prices of individual commodities or services). We also study what causes fluctuations in these total quantities. In Macro-economics, we also study how the economy as a whole grows or develops. This is the aggregative approach.
In Micro-Economics, we study the determination of prices. We no longer divide the study of Economics into Consumption, Production, Exchange and Distribution. They are all covered by price theory. We shall see that prices are determined by the interaction of demand and supply. The theory of demand covers consumption and supply covers production.
According to the old arrangement, in exchange we studied commodity prices and in distribution we studied factor prices, i.e., rent, wages, interest and profit. But in price theory we study both product prices (i.e., exchange) and factor prices (i.e., distribution). Thus, all the old four divisions of Economics are covered in what we now call Micro-economics or Price Theory.
In Micro-economics, we study small individual parts of the economy. For instance, we study the individual consumer’s behaviour or that of an individual, firm or what happens in any particular industry. In the price analysis, we study the determination of the price of an individual commodity or of a particular factor of production, i.e., its reward. In the case of demand and supply, we study the demand and supply of an individual commodity or a factor. We study the income of an individual or of a firm in an industry, and not the national income.
We ‘assume in micro-approach full employment in the economy and on that assumption, the economic problem is mainly of resource allocation or the theory of price. That is why till recently Economics concerned itself mainly with the theory of value and distribution and it ignored the study of the economic system as a whole.
In recent years, thanks to the late Lord Keynes, increasing attention has been given to the analysis of the economic system as a whole. This is Macro-economics. It studies aggregates or average of the entire economy, such as national income, output and employment, total consumption, total savings and investment, aggregate demand and aggregate supply, and so on. In this approach full employment is not assumed. We study the determinants of full employment and see how the fullest possible employment can be attained.
The macro-approach is essential, for what is true of the parts may not be true of the whole. After all, the problem of the aggregate is not merely a matter of adding or multiplying what happens in respect of the various individual parts of the economy. As has been pointed out already, of late great attention has also begun to be paid to the analysis of how an economy grows. Growth Economics has thus become a very important part of macro-economics today.
It may, however, be understood clearly that neither of these two approaches, viz., micro and macro, alone is adequate for the analysis of .the economy. It is essential to integrate the two approaches to arrive at a correct solution of the economic problems.
Inter-relation of the Departments of Economics:
The four departments of Economics—Consumption, Production, Exchange and Distribution—do not stand apart in watertight compartments. This division of the, subject into four parts is for the convenience of study only. Actually, the subject is one complete whole and these departments are closely related to one another. Let us see how.
Consumption and Production:
The close relation between the two is quite obvious. It is the consumer’s desire to consume which leads to production. Consumption too, in its turn, depends on the volume and nature of production. Unless there is production, there cannot be any consumption. The two are thus mutually dependent.
Consumption and Exchange:
These are the days of specialization. People produce what they do not consume—at any rate not the whole of it—and they consume what they do not produce. Exchange is thus essential if consumers are to satisfy their wants. Consumption thus depends on Exchange. But unless there are consumers, no exchange is called for. Hence exchange and consumption depend on each other.
Consumption and Distribution:
Consumption is also closely related to Distribution. In Distribution, we discuss the share that goes to each of the agents of production out of the national income. Now, it is clear that if consumers are well supplied with the necessaries of life, they will be able to work better, produce more and be entitled to a greater share of the created wealth. Consumption thus influences Distribution.
In its turn, the nature of Consumption depends on the Distribution of wealth in a community. What a person consumes depends on the income he gets. If his wages are low, his consumption of goods and services too will be low and his standard of living will be low.
Now days the problems of Distribution are regarded as important as those of Production, perhaps even more so. The real welfare of the people depends not so much on the aggregate production of wealth in the country, but on how wealth is distributed in the community. Hence economic welfare depends on the respective shares accruing to the different sections of the community.
Production and Exchange:
Production is incomplete without Exchange. Articles produced must reach the hands of the consumers and this is impossible without Exchange. The system of buying and selling and the existence of markets stimulate production. But Exchange also depends on Production. Unless goods are produced, the question of exchanging them does not arise. There is thus inter-dependence between Production and Exchange.
Production and Distribution:
The greater the volume of production in a country, the greater would be the share of each agent of production. The nature of Distribution, therefore, depends on the total volume of Production. Goods must be produced before they can be distributed. In its turn, Production, too, depends on Distribution.
The methods and character of Distribution determine the income of a group. An individual’s income affects his efficiency, which, in its turn, determines the volume of production. If workers are paid better wages, the productive efficiency of the community will certainly improve. Production will consequently be larger. Hence one department depends on the other.
Exchange and Distribution:
Exchange assists Distribution. A man gets his share of the national income in the form of money. But he does not want money for its own sake. He has to buy things he needs. He is able to secure these things only through exchange.
It is clear, then, that the various departments of Economics are closely inter-related. Each one of them depends on the other, and they act and react upon one another. We may repeat that we have split Economics into these divisions only for the sake of convenience of study. They are not water-tight compartments. They are closely inter-related. We may also repeal, however, that dividing Economics into Consumption, Production, Exchange and Distribution is only the traditional approach.
The divisions and their inter-relation- ship according to the modern approach have already been indicated above. That is, the study of Economics is split into two parts, viz., micro-economics (i.e., Price Theory) and Macros economics (i.e., Theory of Income and Employment).
Scope of Economics:
While discussing the subject-matter and definition of Economics, we have said something about the scope of Economics too. But there are a few more things which we have to discuss in considering the scope of Economics. ‘Scope’ means the sphere of study. We have to consider what Economics studies and what lies beyond it.
The scope of Economics will be brought out by discussing the following:
(a) The subject-matter of Economics.
(b) Economics is a Social Science.
(c) Whether Economics is a Science or an Art?
(d) If Economics is a science, whether it is a positive science or a normative science?
Economics—a Social Science:
We have seen that Economics studies human beings. But it does not study them as isolated individuals living aloof in jungles or in mountain caves. Rather, it studies man living in organized society, exchanging his goods for those of others, influencing them by his actions and being influenced by them in turn. He depends on them, and they on him. Economics is thus a social science and not one dealing with individual isolated human beings. Interest has now almost completely shifted to the economy as a whole, how it grows and develops, the factors that hinder its growth and the measures that would help or accelerate it.
Positive Science or Normative Science?
A positive science explains the ‘why’ and ‘wherefore’ of things, i.e., their causes and effects. A normative science, on the other hand, discusses the Tightness or wrongness of things. Economists hold different views on this point. Some economists think that Economics is only a positive science and as such explains why things are as they are. It is neutral as regards ends. Others think that it is a normative science and tells us as the things ought to be.
Our view is that Economics is both a positive and a normative science. It not only tells us why certain things happen, it also says whether it is the right thing to happen. For example, we know that a few people in the world are very rich while the masses are very poor.. Economics should explain not only the causes of this unequal distribution of wealth, but it should also say whether this is good or bad. It might well say that wealth ought to be fairly distributed. Further, it should suggest the methods of doing it.
A Science or an Art?
When a student joins a college, he has to choose between two groups of subjects—Science subjects and Arts subjects. In the former group are included Physics, Chemistry, and Biology, and in the latter History, Civics, Economics, Philosophy, Sanskrit, etc. According to this classification, Economics falls in the Arts group. But this is not a sound classification, and does not help us in deciding whether Economics is a science or an art.
Let us first understand what the terms “science” and “art” really mean. A science is a systematized body of knowledge. A branch of knowledge becomes systematized when relevant facts have been collected and analyzed in a manner that we can “trace the effects back to their causes and project causes forward to their effects.” Then it is called a science.
In other words, when laws have been discovered explaining facts, it becomes a science. Facts are like beads. But mere beads do not make a necklace. When a thread runs through the beads, it becomes a necklace. The laws or general principles are like this thread and govern the facts of that science. A science lays down general principles which help to explain things and guide us.
The knowledge of Economics has advanced a great deal. It has reached a stage when its facts have been collected and carefully analysed, and ‘laws’ or general principles explaining facts have been laid down. Thus, the study of Economics has become so thoroughly systematized that it is entitled to be called a science. But Economics is also an art. An ‘art’ lays down precepts or formulae to guide people who want to achieve a certain aim. The aim might be the removal of poverty from a country, or the production of more wheat from an acre of land.
Many English economists consider that Economics is a pure science and not an art. They claim that its function is merely to explore and explain and not to help in the solution of practical problems. Yet many others are of the opinion that Economics is also an art. Economics does undoubtedly help us in solving many practical problems of the day. It is not a mere theory; it has great practical use. It is both light-giving and fruit-bearing. Hence, Economics is both a science and an art.
We may, then, sum up the scope of Economics by saying that it studies ran’s actions in relation to wealth from the social point of view. It does not merely explore and explain but it also advocates and condemns. It not only investigates facts and discovers truths, but it also prescribes rules of life and passes judgment as to what is right and what is wrong. It is also both an art and a science. The scope of Economics is very wide indeed.
Relation of Economics with Other Sciences:
Economics has relation with almost all other sciences. All sciences have been developed by man for the benefit of mankind. As a science, which is primarily concerned with man’s welfare, Economics freely makes use of the other sciences in its study. It uses, in its own reasoning, the conclusions at which the other sciences may have reached. But its relation with social sciences like Politics, History and Ethics is the closest. Let us consider this relationship.
Economics and Politics:
Economics and Politics are very closely mixed up these days. All political events have their roots in economic causes. All political problems are economic in nature. If you follow discussions in the legislature, you will find that most of the time of the legislature is taken up by economic matters.
Political institutions also affect economic conditions, and vice versa. Dictatorship moulds economic conditions in a different manner from a democracy. Foreign rule in India was largely responsible for Indian poverty. Thus, there is a very close connection between Economics and Politics.
Economics and History:
Economics makes use of History in understanding the background of the present-day economic problems. History is also useful in establishing or verifying economic theories and laws. But History is incomplete unless it discusses the economic condition of man. History must devote its attention to the discussion of the economic condition of the people. It does not merely tell a tale of kings. Thus,
Economics without History has no root;
History without Economics has no fruit.
Economics and Ethics
Ethics is a science of what ought to be. It tells us whether a thing is right or wrong. Now ethical or moral considerations govern all economic activity. The economist cannot justify immoral activities. Some modern, economists (e.g., Robbins), however, think that Economics is a pure science arid as such it is not concerned with right or wrong. It is said to concern itself merely with means, and ends lie outside its scope. It is regarded as neutral as regards ends. The ends may be good or the ends may be bad, Economics is not concerned.
But our view is that Economics cannot be dissociated from Ethics. Ethics is indeed a handmaid of Economics. The economists are being called upon more and more to give their advice in economic affairs, and they should not shirk this task. That is why it is said that Economics is both a positive science and a normative science.
Economic Laws:
Definition of an Economic Law :
Like every other science, Economics, too, has drawn its own set of generalizations, which are called the laws of Economics. These laws are supposed to govern and explain all economic activity.
In the words of Marshall, economic laws may be defined thus:
“Economic laws, or statements of economic tendencies, are those social laws, which relate to branches of conduct in which the strength of the motives chiefly concerned can be measured by money price.” In terms of Robbins’s definition of economic activity, we might say that economic laws are statements of uniformities which govern human behaviour concerning the utilization of limited resources for the achievement of unlimited ends. These, in short, are the principles according to which we act when engaged in our ordinary business of life or in an economic activity.
Comparison of Economic Laws with Other Laws:
Let us compare economic laws with the laws of the government, with the laws of morality and with the natural laws.
Economic Laws and Government Laws:
The laws of the government are coercive; there is a penalty attached to their breach, but there is no penalty for breaking an economic law. For instance, there is no punishment it a consumer or a producer does not try to derive maximum benefit from his resources, economic laws are not binding or compulsory. They just tell us what will happen under certain conditions.
Economic Laws and Moral Laws:
The laws of morality merely indicate how we should act in order to satisfy public opinion or our own conscience. Economic laws and laws of ethics or morality belong to two different planes. Economic laws explain the business behaviour of a person, whereas moral laws govern his moral behaviour. Telling a lie is bad morally but many businessmen tell lies and make money. But by and large economic behaviour must conform to the dictates of morality.
Economic Laws and Laws of Natural Sciences:
The laws of natural sciences can be stated with precision and they have a universal validity. Economic laws are not exact or definite. In short, the nature of economic laws is not indicated by the word “must” as in the case of government laws, or by “ought”, as in the case of moral laws, but their nature is indicated by the phrase, “other things being equal” (ceteris paribus).
Economic Laws and Laws of the Social Sciences:
Economic laws may not be as definite and exact as the laws of physical sciences but as compared with other social sciences, Economics is in a very happy position. Other social sciences like History and Political Science have really no Laws worth the name; they may have some generalizations. Although it is generally said that history repeats itself, yet he will be a bold historian indeed who can even remotely guess the course of future events. Political Science is in no better position.
But economic laws are more exact and definite than laws of other social sciences. We shall look in vain in other social sciences for laws like the law of diminishing marginal utility or the law of diminishing marginal return or the law of equi-marginal returns and the theory of comparative costs or for the tools of measurement of elasticity of demand or consumers’ surplus.
The superiority of Economics lies in the fact that economic phenomena are capable of being measured in money price. This measuring rod of money is altogether missing in other social sciences. Hence, economic laws compare very favorably with laws of other social sciences,
Nature of Economic Laws:
From the above discussion, we can understand something about the nature of economic laws. Some economic laws are axiomatic in character, e.g., greater gain is preferred to smaller gain. Also, there are other economic laws which are of the nature of physical laws, e.g., the law of diminishing return. But most of the economic laws are hypothetical. They hold good under certain conditions.
Given certain conditions certain results will follow. They will hold good only if certain conditions are fulfilled. If the conditions are not fulfilled, they will not hold good. For instance, we say that when demand increases, price will rise. But price will rise only if supply has remained unchanged. If supply has increased in the meantime, price may even fall or at any rate, it will not rise. That is why the phrase ”other things being equal” is attached to all economic laws. This means that an Economic law holds good if the relevant conditions remain the same.
It follows from the above that economic laws are not certain or definite. The material of Economics is complex and ever-shifting. There is a great deal of economic friction arising out of custom and law. Social disabilities and legal restrictions obstruct the operation of an economic law. There is also a preponderance of the human element. All these factors impart an element of uncertainty to economic laws. They lack the definiteness and exactitude found in laws of sciences like Physics.
Marshall has compared economic laws to the laws of tides rather than to the simple laws of gravitation. The law of gravitation tells us something that is definite and certain. For example, a ball thrown upwards must fall back on earth. The earth’s gravity pulls everything towards it. There is no exception. On the other hand, one can never be sure about the time of the tide or the level to which it will rise.
It depends on so many factors, e.g., the relative position of the earth and the moon. Uncertainty surrounds laws of economics too like the laws of tides since they too relate to a complex phenomenon. That is why economic laws have been compared with laws of tides rather than with the simple laws of gravitation.
It may, however, be repeated that the laws of economics are more exact than those of any other social science, because the economic phenomena are capable of being measured in money price. This measuring rod of money is not available to any other social science like History and Political Science. Hence, economic phenomena are more predictable than those of History or Political Science.
We can also say that economic laws are statements of tendencies. That is, they only indicate what is likely to happen and not what must happen. Economic laws are inevitable and inescapable if the necessary assumptions are fulfilled. But these assumptions are not always fulfilled. Hence economic laws lack predictability.
“There is no convenient yard-stick by which to measure the currents in business affairs, for these are subject to gusts of fear or perhaps of fantastic optimism as unpredictable as earthquakes.” We cannot, therefore, say what will happen next, because it depends on the fulfillment of so many conditions. We can only say what is likely to happen. Economic laws are, therefore, merely statements of tendencies or of statistical probabilities.
Their Applicability:
One controversial point about economic laws is about their applicability. The Classical Economists were of the opinion that economic laws were immutable, eternal, inexorable and so universally applicable, without any qualification whatsoever. The Historical School, on the other hand, emphasized their relativity and insisted that they had only a limited application to a given environment. Bagehot, for example, declared that the laws of Economics propounded in England were applicable to “a grown-up society of competitive commerce.
Modern economic opinion inclines to the view that inasmuch as economic laws are based on essentials of human nature, they hold good of almost all communities. But, in the formulation of actual economic policies, allowance must be made for varying local condition… Who can doubt that Gresham’s law, the quantity theory of money, the law of diminishing utility, the law of choice and host of other economic laws are independent of sociological and political conditions? Given the conditions under which they are true, the conclusions to which they point are inescapable. “If the data they postulate are given, then the consequences they predict necessarily follow.”
To say that economic laws are historic-relative and that they have no relevance outside certain historical conditions is wrong. The fact is that they are based t>n very wide human experience and have almost a universal applicability.
Methods of Economics:
Two methods are generally used in formulating economic generalisations or laws, viz., the Deductive Method and the Inductive Method.
Deductive Method:
In the deductive method, we start with a few indisputable facts about human nature or general principles and draw inferences about individual or particular cases. For instance, we assume that self-interest alone governs human behaviour and we explain or predict about the behaviour of a particular individual on this assumption.
Merits of Deductive Method:
Several advantages are claimed for the deductive method:
(a) It is a simple method and helps in explaining complex economic phenomena.
(b) It is certain. If the assumptions are correct, the result must follow.
(c) It is easy to apply this method. Elaborate Statistical information is not required for its application.
(d) Since observation and experimentation are not possible where human behaviour is concerned, we have to rely on the deductive method.
Limitations:
(a) The underlying assumptions may turn out to be untrue thus vitiating the inference drawn.
(b) The deductive method makes Economies dogmatic, because there is a tendency to regard assumptions as always valid.
(c) This method is dangerous when practical policies are formulated on imperfect assumptions.
Inductive Method:
In the inductive method, we first collect relevant facts and on their basis draw conclusions. That is, we go up from ‘particulars’ to ‘general?’, whereas in the deductive method, we come down from generals to particulars. In the inductive method, we rely on observation and experimentation for collecting facts.
Hence this method has a sound basis. But the danger is that hurried conclusions may be drawn from insufficient, incorrect or partially correct facts. History provides experiments in the form of measures adopted. Large number of statistical publications is brought out in every country. These and other materials facilitate the application of the inductive method in modern terms.
Conclusion: Integration of the Two Methods:
We find that both deductive and inductive methods suffer from certain shortcomings. Hence the solution lies in the application of both so that one supplements the other. It is remarked; that both methods are needed in economic theorising as right and left foot is both-needed for walking.
Thus, “true solution of the contest about method is not to be found in the selection of deduction or induction but in the acceptance of deduction and induction.” (Wagner). Which of the two methods is to be used in particular situation depends on the nature of the inquiry, the material in hand and the stage which the inquiry has reached.
In short, the true scientific method thus consists of three different stages, viz.,
(i) Construction of theories.
(ii) The deduction of conclusions or predictions from the theories.
(iii) The testing of theories.
Importance of Economics:
Economics is considered these days as one of the most important branches of knowledge. Every educated person is keen to know something about Economics, if he has not studied it already. The number of persons eager to study the subject is increasing from year to year. It at once shows the popularity and the importance of Economics. Study of Economics is useful in several ways. Economics has got theoretical as well as practical importance.
Theoretical Importance:
Informative:
Economics teaches us many interesting and instructive facts about man’s behaviour when he is engaged in economic activity. The inner working of his mind in economic matters is revealed to us. We come to understand the various motives which guide men in economic affairs. It is both a fascinating and a fruitful study.
Mental Training:
Economic reasoning trains our mind as reasoning does in other sciences: It enables us to think clearly and judge correctly and thus affords useful mental exercise. A careful student of Economics can easily see through the game of politicians who want to deceive the general public. He will not be misled by cheap newspaper propaganda. No doubt, “Economics is no philosopher’s stone to turn everything it touches into gold, but it will help at least to distinguish gold from baser metals.”
Understanding Functioning of the Economic System:
The study of Economics helps us to understand how the complicated economic system of today functions almost automatically without any central control. Every economic disturbance somehow tends to smoothen itself out. For example, if there is a shortage of a commodity, its price will rise. This will cut down unnecessary demand so that the demand will be brought down to the level of supply. This is how economic system adjusts itself in all spheres.
Teaches Mutual Dependence:
Economics teaches us the important lesson of the mutual dependence of man on man. We come to realize how we depend on others for the satisfaction of our wants, and how others depend on us. It clearly brings home to us the bond that binds worker to worker, industry to industry and country to country. This knowledge adds to our sense of responsibility and understanding, and thus leads to better work and a happier society.
Useful Citizenship:
The study of Economics makes us useful and intelligent citizens. Most of the problems today are fundamentally economic in character. It is only Economics that can give us a correct understanding of the problems of agriculture, industry, trade, transport, etc.
Economics enables us to shape and mould the State policies for solving these problems. A student of Economics can easily understand questions relating to taxation, currency, exchange, etc. Thus, it is clear that the study of Economics goes to build up a body of keen, intelligent and useful citizens. The knowledge of Economics enables everyone to perform one’s duties more intelligently and, therefore, more efficiently.
Practical Importance:
Besides the knowledge that Economics gives us, it has a great practical value in life. Economics is a science which is closely related to life. In most government departments, knowledge of Economics is found useful and is sometimes considered indispensable.
Professional Value:
The study of Economics is very useful in several professions. It is useful to the banker, to the businessman, to the agriculturist, and to the industrialist. As a matter of fact, it is useful to all.
Useful for Householders:
A householder will arrange his expenditure much better if he has studied Economics. He can prepare a family budget and put his household expenditure on a rational basis.
Useful for Labour Leaders:
A labour leader who knows Economics is able to fight for the rights of labour more effectively. He can understand clearly the conditions of industry. He will, thus, know when to yield a point gracefully and when to stand firm in the matter of workers’ demands.
Solving Problem of Poverty:
Finally, it is Economics that we look up to for solving the problem of poverty. ‘Economics alone will not build a millennium; but in that building—(and in whatever preliminary pulling down may be necessary), it is an essential tool.’ In view of what has been said above, it is clear that the study of Economics is not only useful in ordinary life, but also serves as an excellent mental discipline.
Importance of Economics for Under-developed Economies:
The study of Economics has a special significance for an under-developed economy. In the backward and under-developed countries, the major problem is how to remove poverty and unemployment and to raise living standards. These problems can be solved by accelerating economic development.
The economists have evolved a theory of economic development. From the study of this theory, we can know the causes which have retarded economic growth and how the process of development can be initiated and growth accelerated. The theory of economic growth and planning, which is now an important branch of Economics, furnishes an invaluable guide to the economically backward countries.
Economists all the world over are now taking keen interest in the problems facing the poverty-stricken and under-developed countries. The result is that the literature on economic growth has enormously increased. This literature is of immense benefit for the people and the governments of the backward countries.
Most of them have adopted planning techniques to bring about rapid economic development and raise living standards of their people so as to catch up with the advanced and affluent nations of the world. A great deal has already been achieved in this direction.
Related Articles:
- Agricultural Economics: Meaning, Scope and Nature
- Nature of Economics: Economics as a Science and an Art
- Economics as a Social Science (With Diagram)
- The Scope of Economics

Finished Papers
Customer Reviews
As we have previously mentioned, we value our writers' time and hard work and therefore require our clients to put some funds on their account balance. The money will be there until you confirm that you are fully satisfied with our work and are ready to pay your paper writer. If you aren't satisfied, we'll make revisions or give you a full refund.
Dr.Jeffrey (PhD)
Estelle Gallagher
Types of Paper Writing Services
When you write an essay for me, how can I use it?
Perfect Essay
Finished Papers
Johan Wideroos
We hire a huge amount of professional essay writers to make sure that our essay service can deal with any subject, regardless of complexity. Place your order by filling in the form on our site, or contact our customer support agent requesting someone write my essay, and you'll get a quote.
I work with the same writer every time. He knows my preferences and always delivers as promised. It’s like having a 24/7 tutor who is willing to help you no matter what. My grades improved thanks to him. That’s the story.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Our mission is to improve educational access and learning for everyone. OpenStax is part of Rice University, which is a 501 (c) (3) nonprofit. Give today and help us reach more students. This free textbook is an OpenStax resource written to increase student access to high-quality, peer-reviewed learning materials.
Economics is the study of how humans make decisions in the face of scarcity. These can be individual decisions, family decisions, business decisions or societal decisions. If you look around carefully, you will see that scarcity is a fact of life. Scarcity means that human wants for goods, services and resources exceed what is available.
Economics is concerned with the optimal distribution of resources in society. The subject involves. Understanding what happens in markets and the macroeconomy. Examining statistics about the state of the economy and explaining their significance. Understanding different policy options and evaluating their likely outcomes.
Economics affects our daily lives in both obvious and subtle ways. From an individual perspective, economics frames many choices we have to make about work, leisure, consumption and how much to save. Our lives are also influenced by macro-economic trends, such as inflation, interest rates and economic growth.
Evaluate the significance of scarcity. Economics is the study of how humans make decisions in the face of scarcity. These can be individual decisions, family decisions, business decisions or societal decisions. If you look around carefully, you will see that scarcity is a fact of life. Scarcity means that human wants for goods, services and ...
Conclusion. Economics is important for many areas of society. It can help improve living standards and make society a better place. Economics is like science in that it can be used to improve living standards and also to make things worse. It partly depends on the priorities of society and what we consider most important.
In 14.009 (Economics and Society's Greatest Problems), a ... "Students should ideally understand, by the end of class, why it's important to ask questions and what they can teach us about the effectiveness of policy and economic theory," Banerjee says. "We want people to discover the range of economics and to understand how economists ...
Here's a look at seven advantages of studying economics and how it can benefit both your organization and career. 1. You'll Expand Your Vocabulary. Whether it's scarcity (limited resources), opportunity cost (what must be given up to obtain something else), or equilibrium (the price at which demand equals supply), an economics course will ...
Economics is the study of how humans make decisions in the face of scarcity. These can be individual decisions, family decisions, business decisions or societal decisions. If you look around carefully, you will see that scarcity is a fact of life. Scarcity means that human wants for goods, services and resources exceed what is available.
The development of basic economic literacy is an important goal for a democratic society that relies heavily on informed citizenry and personal economic decision-making. To achieve that goal will require that significant gaps in the economic education of youth be closed by giving economics a more central place in the school curriculum. More ...
to succeed as a writer of economics and offers an overview of the writing process from beginning to end. Chapter 2 describes the basic methods economists use to analyze data and communicate their ideas. Chapter 3 offers suggestions for finding and focusing your topic, including standard economic sources and techniques for doing economic research.
Volume II: New Perspectives on Well-being and Global Inequality since 1820. "Economic growth is an increase in the production of goods and services over a specific period.". "Economic growth is an increase in the production of economic goods and services, compared from one period of time to another".
Economics is a social science concerned with the production, distribution and consumption of goods and services. It studies how individuals, businesses, governments and nations make choices on ...
Make sure that the topic you choose is interesting and engaging enough for you to grasp the reader's attention. Among the main topics you can discuss in economics research are: Fundamental economics, cost to benefit analysis, and importance of decision-making; Macroeconomics, supply, and demand; Microeconomics, market structure, and ...
At its core, Economics is the study of how humans make decisions in the face of scarcity. These can be individual decisions, family decisions, business decisions or societal decisions. If you look around carefully, you will see that scarcity is a fact of life. Scarcity means that human wants for goods, services and resources exceed what is ...
Importance of Economic Growth. Economic growth means a rise in real GDP; effectively this means a rise in national income, national output and total expenditure. Economic growth should enable a rise in living standards and greater consumption of goods and services. As a result, economic growth is often seen as the 'holy grail' of macroeconomics.
Given its importance, economics essays have become a crucial part of the curriculum for students pursuing various degrees. Short Description. In this article, our essay writer will take you on a journey through various exciting topics in economics. We'll cover everything from big-picture concepts like macroeconomics to more focused ideas like ...
6 Steps to Writing a Good Economics Essay. Make sure you analyse and of the question. This is a very important skill that is taught in our . For example, "Best", "Most Effective" are closely related but mean different things. Paraphrase the question to make it simpler if necessary. Take note of the (eg: Explain, Discuss) as it ...
Abstract. Economics is the social science of making sufficient choices or decisions and studies how people interact in their society economically. This paper introduces the subject of economics and unfolds what it is all about. We live in a society where economics is a valuable need in order for us to understand and handle any problems that may ...
Essay on Economics. Economics, often described as the study of scarcity, is a dynamic and vital field that examines how individuals, businesses, governments, and nations make choices on allocating resources to satisfy their wants and needs. It delves into how these groups interact within a market economy to influence the distribution of wealth ...
Subject-matter of Economics: Economics has a subject-matter of its own. We can know something about the subject-matter of Economics from its definitions given above. The student already knows about Mathematics, History and Geography. But Economics is new to him and he cannot say what it is about. We can say that Economics studies man's life and work, not the whole of it, but only one aspect of ...
Susan Devlin. #7 in Global Rating. 4.9 (2939 reviews) Essay On Economics And Its Importance, Entry Level Resume For Csr, Essay That Talk About Tecumseh, Essay On Punctuality 120 Words, What Is The Cost Of Custom Essay, Essay On The Rti Problem Solving Process, Grade 9 French Homework.
The collapsed Francis Scott Key Bridge lies on top of the container ship Dali in Baltimore, Maryland, on March 29, 2024. The collapse of Baltimore's Francis Scott Key Bridge is likely to send ...
First of all, all of them are highly skilled professionals and have higher academic degrees like Masters and PhDs. Secondly, all the writers have work experience of more than 5 years in this domain of academic writing. They are responsible for. Omitting any sign of plagiarism. Formatting the draft. Delivering order before the allocated deadline.