Best 10 BCG Matrix Examples for Students
Discover more helpful information.
BCG Matrix is an apparatus utilized to incorporate methodology to break down specialty units or product offerings dependent on two factors: relative piece of the overall industry and the market development rate. By joining these two factors into a matrix, an organization can plot their specialty units as needs are and figure out where to dispense extra (financial) assets, where to money out, and where to strip.
The primary reason for the BCG Matrix is accordingly to settle on speculation choices on a corporate level. Contingent upon how well the unit and the business are doing, four different classification names can be credited to every group:
- Question Marks
This article covers every classification and how to utilize the BCG Matrix appropriately.

10 Examples of BCG Matrix (of famous companies)
The BCG Model depends on items as opposed to administrations, be that as it may, it applies to both. You could utilize this if checking on a scope of items, particularly before growing new ones. Here are the example list:
1. BCG Matrix of Coca-Cola
A world-driving ready-to-drink refreshment company, Coca-Cola Company has more than 500 soda pop brands, from Fuse Tea to Oasis to Lilt to Powerade. Yet, none of them is anyplace near the coke brand in terms of mindfulness, income, and benefit.
Stage 1. Choose the Product/Firm/Brand
We pick the firm Coca-Cola for investigation. Also, you need to identify the market, as the picked market is beverages, diet cokes, and mineral water.
Stage 2. Calculate Relative Market Share & Find out the Market Growth Rate
By and tremendous Growth rate in Coke is that it is no: in more than 200 countries.
Stage 3. Draw the Circles on a Matrix

2. BCG Matrix of Samsung
Stage 1. choose the product/firm/brand.
We pick the firm Samsung for investigation.
The picked market is the consumer electronics industry which incorporates smartphones, computers, tablets, etc.
Stage 3. Calculate Relative Market Share
By and tremendous Growth rate in Samsung home appliances by making 60% of the sales.
Stage 4. Draw the circles on a matrix

3. BCG Matrix of L'Oréal
We pick the firm L'Oréal for investigation.
Stage 2. Identify Market
The picked market is the Cosmetics Industry, which essentially incorporates Skincare, Makeup, Haircare, Hair shading, and Fragrances.
Stage 4. Find out the Market Growth rate
By and tremendous Growth rate in Cosmetics Industry (starting at 2018) = 4.8%
Stage 5. Draw the circles on a matrix
Note: Just follow the above pattern with every example and BCG matrix you will be making for your class.

4. BCG Matrix of PepsiCo

5. BCG Matrix of Apple

6. BCG Matrix of Nestle

7. BCG Matrix of Unilever

8. BCG Matrix of McDonalds

9. BCG Matrix of KFC

10. BCG Matrix of Amazon

What is BCG Matrix?
The Boston Consulting Group's item portfolio matrix ( BCG matrix ), otherwise called the Growth/Share Matrix, is a vital arranging device that enables a business to consider development openings by inspecting its arrangement of items to choose where to contribute to suspend or create things. It's otherwise called the Growth/Share Matrix. The Matrix is separated into four quadrants dependent on an investigation of market development and the relative peace of the overall industry.
It depends on the mix of market development and the overall industry comparative with the following best contender.
High Growth, High Market Share
Star units are pioneers in the classification. Items situated in this quadrant are appealing as they are located in a hearty class, and these items are exceptionally serious in the classification.
2. Question Marks
High Growth, Low Market Share
Like the name proposes, the future capability of these items is dubious. Since the development rate is high here, with the correct systems and ventures, they can become Cash cows and, at last, Stars if they have a flat piece of the overall industry so that off-base ventures can downsize them to Dogs significantly after loads of speculation.
3. Cash Cows
Low Growth, High Market Share
In the long run, if you are working for quite a while working in the business, advertising development may decay, and incomes deteriorate. At this stage, your Stars are probably going to change into Cash Cows. Since they despise everything that has a substantial relative piece of the overall industry in a deteriorating (developed) market, benefits and cash streams are relied upon to be high. As a result of the lower development rate, ventures required ought to likewise below. Along these lines, cash cows ordinarily produce cash in an overabundance of the measure of money expected to keep up the business. This 'overabundance cash' should be 'drained' from the Cash Cow for interests in different specialty units (Stars and Question Marks). Cash Cows eventually carry parity and security to a portfolio.
Low Growth, Low Market Share
Dogs hold a flat piece of the overall industry contrasted with contenders. Neither do they create cash, nor do they require huge cash. As a rule, the resources are not worth putting into because they create low or negative cash returns and may need enormous entireties of money to help. Because of the flat piece of the pie, these items face cost inconveniences.
How to Make a BCG Matrix Diagram?
So far, we realize products are ordered in four sorts. Presently we will see on what premise and how that order is done. We will comprehend the five procedures of improving a BCG matrix by making one for L'Oréal in the areas to follow.
Stage 1. Choose the Product
BCG matrix can be utilized to operate Business Units, separate brands, products, or firms as a unit itself. The decision of the group impacts the entire investigation. Along these lines, characterizing the unit is essential.
Stage 2. Define the Market
A mistakenly characterized market can prompt a weak characterization of products. For instance, if we investigate Daimler's Mercedes-Benz vehicle brand in the traveler vehicle market, it would wind up as a dog (it holds under 20% relative market share). However, it would be a cash cow in the extravagant vehicle market. Characterizing the market is a significant pre-imperative for a better understanding of the portfolio position.
Stage 3. Calculate the Relative Market Share
Market share is the level of the entire market taken into account by your company, estimated either in income terms or unit volume terms.
We utilize Relative Market Share in a BCG matrix, contrasting our product deals and the main adversary's sales for a similar product.
Relative Market Share = Product's business this year/Leading opponent's business this year
For instance, if your rival's market share in the vehicle business was 25% and your association's image market share was 10% around the same time, your relative market share would be just 0.4. The relative market share is given on the x-axis.
Stage 4. Find out the Market Development Rate
The business development rate can be effortlessly found through free online sources. It can likewise be determined by deciding the healthy income development of the leading firms. The market development rate is estimated in rate terms.
Market development rate was typically given side-effects (business this year – Product's business a year ago)/Product's business a year ago.
Markets with high development are ones where the total market share accessible is growing, so there are a lot of chances for all organizations to bring in cash.
Stage 5. Draw the Circles on a Matrix
Having determined the above measures, you have to plot the brands on the Matrix simply on EdrawMind desktop version. It has the premade templates for BCG. All you have to do is put up the data just like we did with every example.
The x-axis shows the relative market share, and the they-pivot shows the business development rate. You can plan a hover for every unit/brand/product, the size of which ought to relate to the extent of income created by it in a perfect world.
Taken these variables together, you can attract the perfect way to follow the BCG Matrix, from start-up to market pioneer. Question Marks and Stars should be financed with ventures produced with Cash Cows. What's more, Dogs should be stripped or exchanged to let loose cash with minimal potential and use it somewhere else. At long last, you will require a reasonable arrangement of Question Marks, Stars, and Cash Cows to guarantee positive cash streams later on.

[2023] Story Summary Examples

7 Types of Organizational Charts (With Examples)

Sunburst Chart: Explained with Examples & Templates

Story Outline Examples

To-Do List Mind Map Template


Case Studies: Using the BCG Matrix for Product Portfolio Analysis
Introduction.
The BCG Growth-Share Matrix is an analytical tool used to help develop an understanding of a company's product portfolio. It is designed to analyze how each of a company’s products contribute to overall growth and identify patterns in investments, potential opportunities, and weaknesses. This article will explain the four categories of the BCG Matrix and how to use the matrix for product portfolio analysis.
What is the BCG Growth-Share Matrix?
The acronym BCG stands for Boston Consulting Group . The Matrix was created by the BCG in the 1970s to help businesses analyze their product lines and manage their investment portfolios. The matrix categories are based on two variables: market growth rate and market share relative to the largest competitor. The four categories of the matrix are Stars, Cash Cows, Question Marks, and Dogs.
How to use the BCG Matrix to understand the product portfolio?
- Stars – Products that generate the most income that have high growth rate and market share.
- Cash Cows – Products with low growth rate but high market share.
- Question Marks – Products with high growth rate but low market share.
- Dogs – Products with low growth rate and low market share.
Using the BCG Matrix , companies can identify which products would be most beneficial for their portfolio and where to focus future investments. Through careful analysis, companies can identify profitable product lines that should be maintained and which products may need to be cut.
Advantages of the BCG Matrix
The BCG Matrix is a portfolio management tool used by companies to help determine the optimal allocation of resources to maximize growth potential and profitability. Understanding how to leverage resources is a key component of efficient portfolio management, and the BCG Matrix helps organizations do just that.
A. Identify Cash Cows, Stars, Dogs, and Question Marks
The BCG Matrix is a visual representation of a company’s product portfolio. It plots four categories that can be used to classify the various products in the portfolio: Cash Cows, Stars, Dogs, and Question Marks. Cash Cows are products that generate revenue but do not have high potential for growth. They are the most reliable source of revenue for the company. Stars, on the other hand, are products that have high potential for growth but require high amounts of resources from the company to reach this potential. Dogs are products that have low revenue and low growth potential, while Question Marks are products that have uncertain prospects but could potentially generate high growth.
B. Understand how to maximize resources
The BCG Matrix provides a method for examining how to efficiently allocate resources in a portfolio. First, Cash Cows should be leveraged for revenue generation, as they will bring in the most revenue with the least amount of effort. For Stars, resources should be allocated to ensure that their growth potential can be realized, as they will eventually become Cash Cows. The resources allocated to Dogs should be minimized, as they are not likely to ever achieve growth potential, while Question Marks should be evaluated carefully to determine if they are worth investing in. By understanding how to best utilize resources in the portfolio, companies can maximize growth potential and profitability.
The BCG Matrix is an effective tool for product portfolio analysis due to its ability to quickly identify and classify products in the portfolio. By understanding how to allocate resources according to the categories of the BCG Matrix , organizations can maximize their growth potential and profitability.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using the BCG Matrix
The BCG Matrix, also known as the Boston Consulting Group Matrix , is a tool used for analyzing products in a business portfolio. This approach can help an organization identify which products are underperforming and which may require additional resources. It can also help organizations determine which products are the most profitable and which should be discarded. Here is a step-by-step guide to using the BCG Matrix for product portfolio analysis.
Determine the Relative Market Share of Organization’s Products
The first step in product portfolio analysis is to determine the relative market share of each product. This can be done by looking at the total market share of the product and comparing it to the total market share of competing products. The relative market share of each product is the share of the total market that the product holds. Calculate the relative market share of the organization’s products to establish a baseline.
Compare the Product's Market Share with Market Growth Rates
The next step is to compare the product’s market share with the market growth rate. To do this, calculate the market share index for each product. This index is the ratio of the products market share to the market growth rate. Products with a market share index of 1.0 or above are considered to be stars, while products with a share index between 0.5 and 0.99 are considered to be question marks. Products with a share index of 0.5 or below are considered dogs.
The analysis should also take into account any changes in the growth rate of the market. If the market growth rate drops, the relative market share of the product may also drop, and this should be taken into account when analyzing the product.
Case Study: Microsoft
Assess the contribution of different products to company success.
Microsoft is a worldwide leader in numerous technology and software fields. The company is constantly striving to provide cutting-edge products and services to customers, and is one of the most prominent names in computing technology. In order to ensure success, Microsoft continually assesses the contribution of each of its products to the company’s overall success, especially in the context of its portfolio of products. One method of assessing the contribution of products to company success is through the use of the BCG Matrix.
Define the life cycle of products
The BCG Matrix is a tool used to classify products according to their stage in the product life cycle. Developed by the Boston Consulting Group, this tool defines four stages of product development: growing products, cash cows, dogs and problem children. Each stage in the product life cycle will help Microsoft identify the products which are contributing the most, or least, to company success, providing a useful way to assess its portfolio.
Growth products are characterized by high market share and high growth of the market. Cash cows are characterized by high market share and low or zero growth of the market. Dogs are characterized by low or zero market share and low or zero growth of the market. Finally, problem children are characterized by low market share but high growth of the market.
Using the BCG Matrix, Microsoft can accurately and strategically assess the contribution each of its products makes to company success. The company can then use this information to adjust the product portfolio to maximize their return on investment. By doing so, Microsoft can ensure that it remains a leader in the technology sector, while also ensuring its continued profitability and success.
Business Goal: Amazon
Amazon is the world’s most successful online retailer, and its business goal is to deliver the right mix of products and services to its customers in order to generate the maximum return on investment. In order to do this, Amazon needs to effectively manage its product portfolio and use methods such as the BCG Matrix to analyze which products and services will yield the highest returns.
Portfolio Analysis
The BCG Matrix (or the Boston Consulting Group matrix) is a tool used to analyze a company's product portfolio and determine which products should be given priority based on their growth rate and market share. With the BCG Matrix, products are categorized into four types: Stars, Cash Cows, Dogs, and Question Marks. Stars are products that have a high market share and a high growth rate, Cash Cows are products that have a high market share but have a low growth rate, Dogs are products that have a low market share, and Question Marks are products that have a low market share but have a high growth rate.
The goal of portfolio analysis is to analyze the products in order to identify the products that will help the company most in achieving its business goals. In Amazon's case, this means identifying the products that will bring in the most revenue and make the most profit in the shortest amount of time. This can be done by selecting the products that fall into the Star and Cash Cow categories of the BCG Matrix.
Prioritization and Valuation
Once the products that are most likely to yield the highest returns have been identified, Amazon must prioritize them by assigning a value to each one. This value should take into account the amount of resources that will be required to achieve each product's potential and the expected return on investment. This will help Amazon prioritize its resources and focus on the products that will provide the biggest returns. This process can also help Amazon assess which products should be discontinued or sold to another company if they are not expected to yield significant returns.
Once the products have been prioritized and valued, Amazon must then allocate resources to the top priorities and make sure that they are adequately supported. This will help ensure that the products have the best chance to succeed and that Amazon achieves its business goals.
Challenges with the BCG Matrix
The BCG Matrix provides a powerful tool for analyzing a company’s product portfolio , but it is not without its challenges. As with all strategies, there are potential risks and challenges, related to the accurate interpretation of data and estimated performance of individual products.
Assuring Accurate Data and Estimations
When utilizing the BCG Matrix , one of the primary challenges is ensuring that the data and estimations used to gauge the performance of products are accurate. If the assumptions used to classify a product into a certain category are inaccurate, the analysis may yield a misleading result. To avoid this, companies should take the time to evaluate individual products carefully and ensure that the data used for analysis is up-to-date.
Costs of Resources to Maintain a Portfolio
The BCG Matrix is an effective tool for managing portfolios, but it may also be costly. Companies that use the BCG Matrix may find themselves allocating significant resources towards maintaining the portfolio, including funds, personnel, and technology. This can be especially challenging for smaller companies that may not have the necessary resources to invest. It’s important for companies to carefully weigh the costs and benefits of implementing the BCG Matrix before making any decisions .
When used correctly, the BCG Matrix can be an invaluable tool for managing product portfolios. However, to get the most out of the strategy, companies must be aware of the potential challenges and risks that accompany its implementation. With sufficient planning and consideration, the BCG Matrix can help companies optimize their portfolios and gain competitive advantage in their respective markets.
Case studies are an effective way to better understand a topic. The analysis of a product portfolio by applying the BCG Matrix is essential to assessing the trends and patterns of the marketplace. With this tool, you can determine which products are succeeding and failing, as well as establish strategies on how these products should be managed.
Benefits of the BCG Matrix
- Provides a simple framework for analyzing a product portfolio
- Offers insight into trends and patterns of the marketplace
- Gives you a holistic view of the product portfolio
- Evaluates the potential future impact of the product portfolio
Overview of the Steps to Apply the BCG Matrix to Product Portfolio Analysis
- Gather information on the products in the portfolio
- Plot the products on the BCG Matrix , taking into account their relative market share and market growth
- Assign a course of action to each product in the portfolio
- Monitor the products and their performance within the portfolio
The BCG Matrix is an effective tool for analyzing product portfolios. With this approach, you can gain a better understanding of your products’ performance in the marketplace, enabling you to make informed decisions on their strategy, positioning, and resources allocation.

Immediate Download
MAC & PC Compatible
Free Email Support
Related aticles

The Benefits of Excel Dashboards for Data Analysts

Unlock the Power of Real-Time Data Visualization with Excel Dashboards

Unlocking the Potential of Excel's Data Dashboard

Unleashing the Benefits of a Dashboard with Maximum Impact in Excel

Exploring Data Easily and Securely: Essential Features for Excel Dashboards

Unlock the Benefits of Real-Time Dashboard Updates in Excel

Unleashing the Power of Excel Dashboards

Understanding the Benefits and Challenges of Excel Dashboard Design and Development

Leverage Your Data with Excel Dashboards

Crafting the Perfect Dashboard for Excel

An Introduction to Excel Dashboards

How to Create an Effective Excel Dashboard
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.

Subscribe for Free Business and Finance Resources
What is the bcg matrix explaining its components and quadrants.
If you're interested in breaking into finance, check out our Private Equity Course and Investment Banking Course , which help thousands of candidates land top jobs every year.
Understanding BCG Matrix
Strategic analysis is crucial in the world of finance, helping professionals make informed decisions to drive growth and maximize returns.
One such tool that has stood the test of time is the BCG Matrix . Developed by the Boston Consulting Group , this matrix offers a systematic approach to analyzing a company's portfolio of products or business units.

In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the BCG Matrix, explore its components and quadrants, and discuss how it can be applied to make strategic decisions in the finance industry.
What is the BCG Matrix?
The BCG Matrix, also known as the Growth-Share Matrix, is a visual representation of a company's portfolio of products or business units . It was developed by the Boston Consulting Group in the 1970s and is widely used across industries to assess the strategic position of different offerings.
By plotting products or units on a matrix based on their market growth rate and relative market share, the BCG Matrix provides valuable insights into the potential and profitability of each element in the portfolio .
Components of the BCG Matrix

Market Growth Rate
The market growth rate refers to the rate at which a particular market is growing . It is an important factor to consider when analyzing a company's portfolio because high-growth markets tend to offer greater opportunities for expansion and profitability. By assessing the market growth rate, finance professionals can identify industries or sectors with significant growth potential and allocate resources accordingly.
Relative Market Share
Relative market share is a measure of a company's market share compared to its competitors in a specific market . It provides insights into a company's competitive position and its ability to capture a significant portion of the market. A high relative market share indicates a strong market presence, which can lead to economies of scale, pricing power, and competitive advantages.
Quadrants of the BCG Matrix
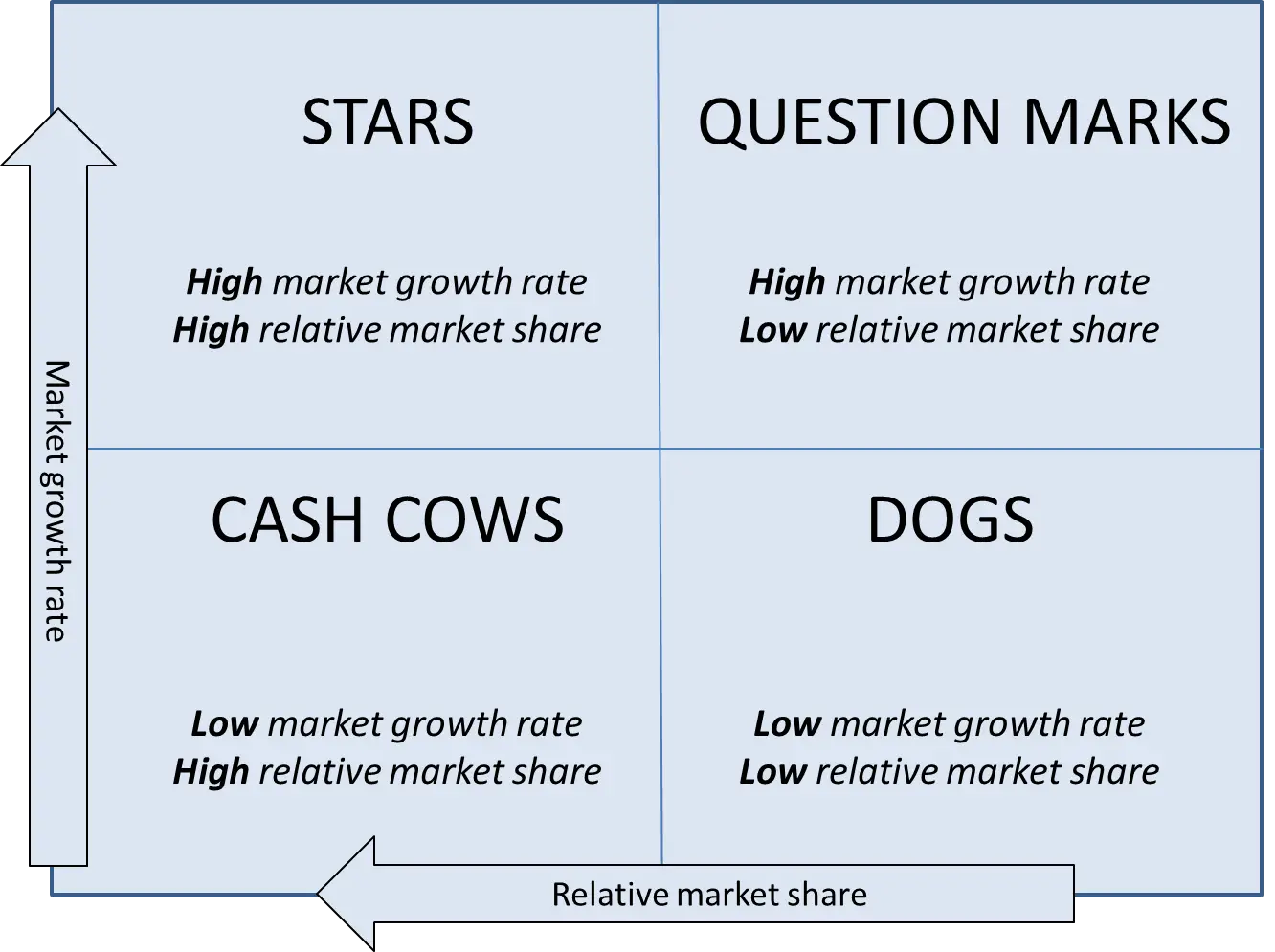
The BCG Matrix divides the portfolio into four quadrants, each representing a different strategic outlook. Let's explore each quadrant:
Stars represent products or business units with a high market growth rate and a high relative market share . These are the growth drivers of a company's portfolio. Stars require substantial investment to sustain their growth trajectory and capture the market's potential. While they generate revenue, they also consume resources to fuel their expansion. Companies should develop strategies to support and maximize the potential of stars, as they can become future cash cows.
For example Tesla's electric vehicles (EVs) in the early 2010s. With a high market growth rate and a dominant market share in the electric vehicle industry, Tesla was considered a star. The company invested heavily in expanding its manufacturing capacity and charging infrastructure to capitalize on the growing demand for EVs.
Cash cows are products or business units with a low market growth rate but a high relative market share . These offerings have reached maturity and generate significant cash flow for the company. Cash cows typically have established customer bases and enjoy economies of scale, resulting in healthy profit margins. Finance professionals should focus on sustaining and extracting value from cash cows to fund other areas of the business .
Example Microsoft's Office Suite. Although the market growth rate for office productivity software is relatively low, Microsoft's Office Suite dominates the market with a high relative market share. This product line generates substantial revenue and profit, which supports the company's investments in other emerging areas, such as cloud computing.
Question Marks (Problem Children)
Question marks, also known as problem children or wildcards, are products or business units with a high market growth rate but a low relative market share . They require careful analysis and strategic decision-making due to the uncertainty surrounding their potential. Question marks may either become stars or fail to gain market traction. Companies need to assess the viability and potential of question marks and allocate resources accordingly.
Example: Uber's food delivery service, Uber Eats, during its early years. With the rapid growth of the food delivery market, Uber Eats had a high market growth rate. However, it faced intense competition from established players like DoorDash. Uber had to strategically invest in marketing and partnerships to gain market share and compete effectively.
Dogs represent products or business units with both a low market growth rate and a low relative market share . These offerings have limited potential and may not generate substantial returns. Companies should evaluate dogs to determine if they can be revitalized or if divestment is a more appropriate course of action.
Example: BlackBerry's smartphones in the mid-2010s. With declining market share and a lack of innovation compared to competitors like Apple and Samsung, BlackBerry's smartphones became dogs in the market. The company eventually shifted its focus to software and services.
Analyzing and Applying the BCG Matrix
To conduct a BCG Matrix analysis, finance professionals should follow these steps:
Gather relevant data and information, such as market growth rates and market shares .
Plot the products or business units on the matrix based on their market growth rate and relative market share.
Interpreting the results and making strategic decisions involves:
Identifying resource allocation priorities based on the quadrant placement.
Developing growth strategies for stars and question marks.
Considering divestment or restructuring options for dogs.
Maximizing the potential and profitability of cash cows.
By applying the BCG Matrix, finance professionals can make informed decisions that optimize resource allocation, drive growth, and enhance overall portfolio performance.
Limitations and Considerations
While the BCG Matrix is a valuable tool, it has some limitations:
The matrix focuses solely on two dimensions (market growth rate and relative market share), neglecting other factors such as competitive dynamics, industry trends, and external factors.
The matrix assumes that a high market share leads to profitability, which may not always hold true.
Industries with different characteristics may require modifications to the matrix for accurate analysis.
Finance professionals should complement the BCG Matrix with other analytical tools and consider the specific context of their industry and market to gain a comprehensive understanding of their portfolio.
Case Study: Application of the BCG Matrix
Let's consider a hypothetical case study to illustrate the application of the BCG Matrix.
Company X operates in the technology industry and has a diverse portfolio of products. After conducting a BCG Matrix analysis, the company identifies the following:
Product A: High market growth rate, high relative market share (star)
Product B : Low market growth rate, high relative market share (cash cow)
Product C: High market growth rate, low relative market share (question mark)
Product D: Low market growth rate, low relative market share (dog)
Based on this analysis, Company X develops strategies to further invest in Product A to maintain its growth trajectory, sustain Product B to continue generating cash flow, evaluate potential opportunities for Product C, and consider divestment or restructuring options for Product D.
The BCG Matrix is a powerful tool for strategic analysis in finance. By analyzing a company's portfolio based on market growth rate and relative market share, finance professionals can make data-driven decisions to allocate resources effectively, identify growth opportunities, and maximize profitability.
The BCG Matrix provides a structured framework for evaluating products or business units and helps finance professionals navigate the complexities of portfolio management.
- Business 101
Recent Posts
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs: A Tool for Effective Business Management
Figurative Language: A Useful Tool for Business Professionals
What is Strategic Planning and Why is it Important in Business?

The Only Course You'll Need To Understand Marketing Like Never Before
How to Get Started with Marketing and Design Your Career in 5 Steps

BCG Matrix of Nestle [Detailed] Nestlé is a common house-hold brand for us since years. Think fast and tell me what all Nestlé products you love! I bet NesCafe, Maggi or chocolates like Kit-Kat made it to your favourite list. Now, have you ever wondered, that do firms also treat its products differently? How do they decide which brands to keep? Where to add new products? When to produce more goods? If yes, then this article is definitely curated for you. Give it a read and see how firms solve these critical questions.
Nestle is one of the world’s leading FMCG company. Most likely, dream company for most of the B-school students too. It has its presence in about 187 countries. Think how many market-segments and strategies it would be catering to! In order to understand their strategies, we have to get to know how BCG matrix of Nestle works.
To serve its immensely heterogenous customers, they maintain a broad brand portfolio, with numerous products under it. And, yet is successfully leading in most of the markets worldwide.
Boston Consulting group’s product portfolio matrix is designed to help with long term strategic planning, to help a business consider growth opportunities. This is done by reviewing its portfolio of products to decide where to invest, to discontinue or develop products.
So, let’s not wait anymore, and start digging!
What is BCG matrix?
BCG matrix isn’t a new phenomenon. And, in the changing digital landscape, we can slurp a lot of information from it. In fact, we can also apply it for developing better marketing strategies.
We will begin with understanding what are the quadrants of this matrix, how to interpret it, and many more things!
So, the Matrix is divided into 4 quadrants based on an analysis of market growth and relative market share, as shown in the diagram below.
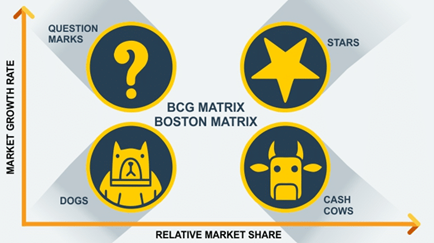
Source: superheuristics.com
This matrix is, put simply, a portfolio management framework that helps companies decide how to prioritize their different businesses. It is a table, split into four quadrants, each with its own unique symbol that represents a certain degree of profitability. Quadrants being- question marks, stars, pets (often represented by a dog), and cash cows.
Now, let’s understand these quadrants better.
Each of the four quadrants represents a specific combination of relative market share, and growth:
Low Growth, High Share: Firms should milk these “cash cows” for cash to reinvest.
High Growth, High Share: Firms must invest in these “stars” as they have high future potential.
High Growth, Low Share: Firms should invest in or discard these “question marks,” depending on their chances of becoming stars.
Low Share, Low Growth: Firms should liquidate, divest, or reposition these “pets.”
Okay, so imagine that you have your matrix. Is your problem solved? No more critical decisions? The answer is “no”. Your task as an MBA is to interpret what the BCG matrix of Nestle shows you.
For instance, “pets” might look like the least attractive product. Will you discard it? Or push it to become cash cow or star later?
Also Read: The BCG Matrix – What is it and how to use it
Next, we should now start our analysis of BCG matrix of Nestle, India

Marketing Concepts Mastery Course
Learn the essential marketing concepts. Create the best outcomes from MBA without depending on placements!
Understand BCG Matrix, SWOT Analysis, Ansoff Matrix and many other important marketing frameworks just like an expert MBA professional would. Solidify your concepts by building a personal brand in marketing.
BCG Matrix of Nestle India
Here I am taking the case of Nestle, India specifically. Because, I aim at making it easily relatable for you. Now its time to check out the BCG Matrix of Nestlé and what products of the company fall under what Quadrant.
For Nestle, there are some products those have been undoubtedly the Cash Cows. They are- Nestle’s Maggi Noodles, NesCafe and its popular chocolates like KitKat, Munch.
With a market share of 80-85 %, Maggi Noodles holds a pseudo-monopoly in the market and have a high customer loyalty.
These products need very less investment. In fact, they are already available at every nook and cranny. And loved my most of us!
Stars
In the case of Nestle, Nestle’s Mineral Water and Nestle’s Nescafe Coffee (like Nescafe Latte) fall in the Star quadrant of the BCG Matrix of Nestle.
With the growing number of health-conscious customers, these products have the potential to produce greater ROI later. Even though, it might take heavy investment to make Nestle-brand visible in that market, they may turn to cash-cows pretty soon!

Source: nestlepurelife.com
Question Mark
Now this is an interesting bunch of products!
Nestle Everyday, Nestlé slim and Nestlé Milk maid are some of the milk and milk-based products from the house of Nestlé. And they come under Question Mark category.
This domain needs a higher investment, because its in the phase of development. And it is a high-risk decision to invest in them too. Like for example, “É by Nescafé” ! Nestle aims to revolutionize coffee-making with this new smart coffee maker.

Source: enescafe.in
Products under this category are not expected to bring in any significant capital. So future investment is seen as a wastage by firms, it could be invested in a Question mark or Star category instead.
I believe Nestle Milo and Koko Crunch can be put in this category. They did not have any significant grasp in the market.

Source: Nestle.com
Its time to dig deeper. Let’s see how Nestle “milked” their Cash-Cow Maggi!!
Maggi- Milking the Cash cow!

Source: nestle.in
Do you know how has Nestle uses this as an opportunity?
Let me tell you some sad facts first. Nielsen points out that 85% of all consumer packaged goods (CPG) product launches flop.
Yet, Nestle never steps back from launching new products. And what’s a better way to do that than launching under the safety-net of “Maggi” brand?
Firstly, new variants of existing product lines have more chances of surviving out. Secondly, if gaining popularity then same distribution channels can be used, without extra efforts. And thirdly, analysts have noticed that Nestle doesn’t even feel the need to advertise them.
And lastly, as consumer already love Maggi’s brand, they hardly spend time for purchase decisions.
Now, the next segment is to know what strategy to follow, based on the growth-share matrix??
What Next to do with the Growth-Share Matrix?
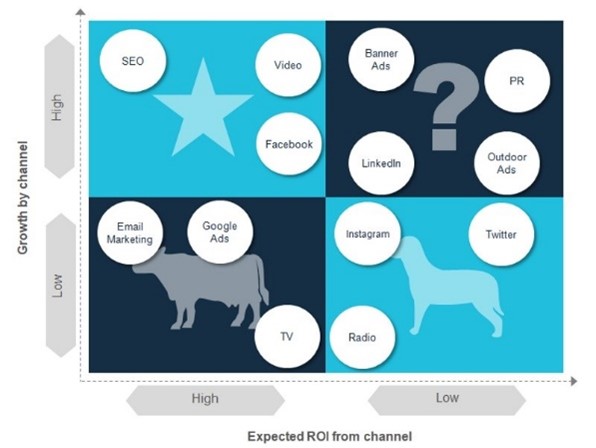
We can use this matrix to decide on multiple fronts. Starting from resource allocation to utilization of marketing channels or platforms.
It can help grow a company’s expected ROI per channel. Now, it may vary for different B2B and B2C businesses and even across industry sectors.
For instance, high growth and high returns, investing in organic search (SEO) may be a good choice. At the other end of the scale, we have not witnessed companies growing exponentially and achieving high ROI as a result of Twitter alone.
Source: yewbiz.com
You can apply different strategy according to the quadrant you are in. The above image summaries a generic trend followed in the industry.
For understanding how the resource allocation is decided by firms do read our article on BCG matrix of ITC .
It tells you about how the matrix can help you to understand which resource allocation-strategy to use for which category. The strategies that are used by marketers are- Build, Hold, Harvest and Divest.

Case Analysis Blueprint Course
Use marketing frameworks like these to solve business case studies with ease
Frameworks like the BCG framework are extremely crucial to analyze the most complex case studies. Get to know how to analyze a marketing case study comprehensively in just 5 slides. Which means that the next time you need to analyze a case, you know exactly how to ace the case
We learnt why companies need a BCG matrix and what it is. Why it's such an essential tool for marketers.
We created The BCG Matrix of Nestle, keeping its broad product portfolio in mind. We identified the Matrix's various components, namely- Star, Cash Cow, Question Mark and Dog.

Next, we analysed how Nestle “milked” a cash cow- Maggi. Since Maggi is a well-know brand, hopefully this article provided a lucid clarity on how Nestle benefits from it.
And then we can see how can the matrix be used in order to decide where to invest and what platform to use, according to the quadrant.
Hope this article helped you!
You May Also Like

What is Transnational Strategy in International Business? Why are most of the offerings at a McDonald's in India are different from a McDonald's at Singapore and even more different from a McDonald's in China. And yet, why everything about their food, their ambiance and their promise to you feels exactly the same? These are some characteristics of a Transnational Strategy on display. Read on to know more about what is Transnational Strategy and how can a brand adopt it.

The Ansoff Matrix – identify your next growth strategy When you are seeking business growth, should you create new products or venture into a new market. Or, do both? The Ansoff Matrix helps you take that decision for your business growth

Understanding Rural Marketing and Rural Marketing Strategy How to develop a Rural Marketing Strategy? What is Rural marketing? You might face these questions if you are pursuing a Marketing Specialisation or are a Marketing Aspirant. Read on to explore the nuances of Rural Market along with its Opportunities and Challenges.
Core Competency Framework – Why Starbucks wants to be your ‘third place’ Starbucks wants to be your 'third place' after your home and workplace. They do everything to make this promise come true. But why don't they promise you, so vehemently, about serving you the best coffee in the world. The Core Competency Framework will help us find out.

5 Secondary Market Research Tools and Techniques
Understanding the Communication Mix Most of the marketing articles and theories talk about finding that right marketing mix for your product. Still, that amazing strategy will go in vain if you don't understand how to communicate that to your consumers. But why? Why is it essential for you, as a B-school student, to understand the mechanics of communications mix and its various elements? Read this article to know why!

About the Author: Surabhi Bhuyan
Use Our Resources and Tools to Get Started With Your Preparation!
2x2 matrices and the bcg matrix, a 2x2 matrix is an elegant instrument to effectively communicate insights.
A two-by-two matrix is a simple and effective way of presenting information. It is very popular in consulting because it provides a big picture of options that are MECE . The matrix is generally divided into four segments , which indicate different strategic actions for each option within the respective segment. Single options are plotted into the matrix, taking two key decision criteria into account . The chosen two dimensions are independent of each other. Hence, criteria need to be carefully selected.
Use a 2x2 matrix in your interviews as a visual summary of the findings
It is recommended to use matrices (if possible) in case interviews, as it will show the interviewer that you can break down complex ideas and communicate these in a structured manner. A matrix is an ideal tool to synthesize complex ideas into simple options.
As an example, imagine you need to make an investment decision
Question: In which business segments should we invest further?
Important data:
- Importance for our business (fraction of the overall revenue)
- Expected performance (Growth)
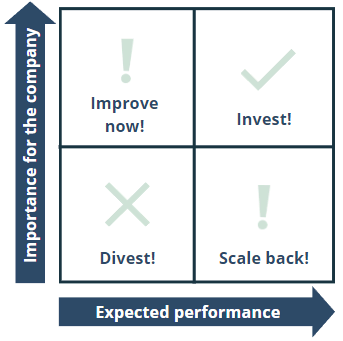
Key takeaways for a 2x2 matrix
- Scatter graph of two variables.
- Provides an effective overview of where to focus first before further analysis.
- Limited to only two variables.
The most known two-by-two matrix is the BCG matrix
The BCG matrix, also called the growth-share matrix, helps assess a company’s current product portfolio based on the product life cycle and the experience curve . Since both criteria are hard to quantify, proxies are used to illustrate them. The product life cycle is reflected by market growth, and the relative market share mirrors a company’s experience curve. Based on these two criteria, investment or divestment decisions can be taken for single products once they are plotted into the matrix.
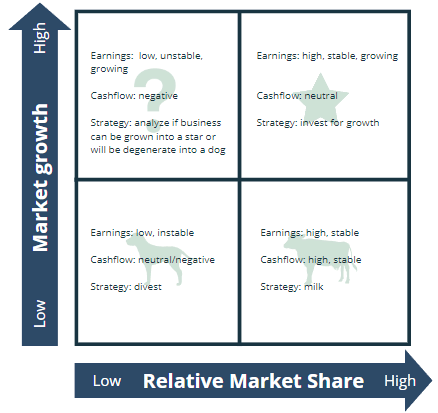
- Low relative market share in a slow-growing mature market.
- Products mostly do not generate profit and may usually just break even.
- Divest , as these products have a negative effect on the overall profitability of the company.
Question Marks:
- Low relative market share in a relatively young but promising market (growing).
- Potential of becoming stars if market share can be increased.
- If necessary market share is not reached, likely to turn into a poor dog , as soon as the market gets more mature.
- Careful analyses are needed to determine if to invest or not.
- High market share in a slowly growing / mature market.
- Creates the highest cash flow.
- There is no further investment due to limited/ no growth potential, but trying to “ milk ” as long as possible.
- High market share in a promising market.
- To turn a star into a future cash cow, heavy investment is needed to fight competition and expand market share.
Key takeaways for the BCG matrix
- Helps to analyze where to invest or divest .
- Ideally, a product should develop from a question mark to a star to a cash cow.
- IMPORTANT : This should only be referred to as BCG matrix when interviewing with BCG , otherwise it is the growth-share matrix .
Use the Ansoff matrix to analyze revenue growth options for a company
Besides the BCG matrix, the Ansoff matrix is one of the most known two-by-two matrices. The underlying question of this graph is how a company could achieve future growth in terms of revenue . Here, four different strategic options are available: market penetration , market development , product development, or diversification .
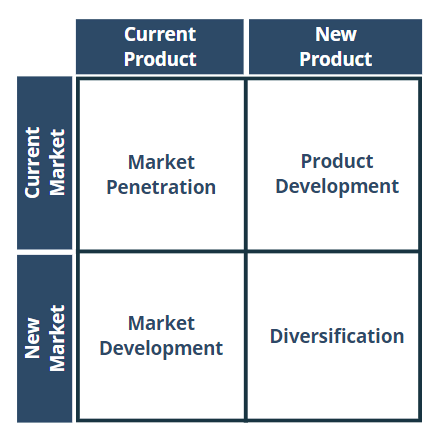
Market Penetration
- A Company is trying to grow within an existing market with existing products.
- It can be achieved by attracting new customers (first buyers), which bought previously from competitors (stealing market share).
- Low risk and growth potential.
Market Development
- A Company is trying to grow in a new market with existing products.
- New markets could be on a regional, national or international level.
- Risk and growth potential are considered to be higher than the ones of a market penetration strategy.
Product Development
- A Company is trying to grow within an existing market but with new products.
- New products do not need to be necessarily new , but can also be adaptions or updates to existing products developed using companies core competencies.
- Risk and growth potential are comparable to these of a market development strategy.
Diversification
- A Company is trying to grow in a new market with a new product.
- 3 diversification strategies can be distinguished: horizontal, concentric, and lateral.
- Horizontal diversification: products are often unrelated to current products, but have the potential to attract current customers.
- Concentric diversification: products often display synergies with current products and have the potential to attract new customers.
- Lateral diversification: new products have no relation or synergies with current products.
- Risk and growth potential are the highest of all strategies.
Key takeaways for the Ansoff matrix
- Helps in answering how future growth should be achieved.
- 4 different strategies can be distinguished: market penetration, market development, product development, and diversification.
- Each strategy has a different growth and risk potential.
Questions on This Article
What is the difference between 2by2 matrix decision making and bcg matrix, what parameters should be taken into consideration when deciding where we stand on each of the axes, can you take a typical example about horizontal ,concentric and lateral products, related cases.

Save 40% on Online Finance Courses
- The Investment Banker Micro-degree
- The Project Financier Micro-degree
- The Private Equity Associate Micro-degree
- The Research Analyst Micro-degree
- The Portfolio Manager Micro-degree
- The Restructurer Micro-degree
- Fundamental Series
- Asset Management
- Markets and Products
- Corporate Finance
- Mergers & Acquisitions
- Financial Statement Analysis
- Private Equity
- Financial Modeling
- Try for free
- Pricing Full access for individuals and teams
- View all plans
- Public Courses
- Investment Banking
- Investment Research
- Equity Research
- Professional Development for Finance
- Commercial Banking
- Data Analysis
- Team Training
- Felix Continued education, eLearning, and financial data analysis all in one subscription
- Learn more about felix
- Publications
- Online Courses
- Classroom Courses
- My Store Account
- Learning with Financial Edge
- Certification
- Masters in Investment Banking MSc
- Student Discount
- Find out more
- Diversity and Inclusion
- The Investment banker
- The Private Equity
- The Portfolio manager
- The real estate analyst
- The credit analyst
- Felix: Learn online
- Masters Degree
- Public courses
By Oliver Sealey |
Reviewed By Rebecca Baldridge |
May 17, 2022
What is the BCG Matrix?
The Boston Consulting Group (BCG) designed its four-celled matrix, the BCG Matrix, to aid in long-term strategic planning. The matrix is used to assess the growth opportunities of different products/brands that an organization has in its portfolio based on relative market share and market growth rates across industries/sectors.
The matrix makes it possible to examine the business potential and market environment of different products and brands, which enables the company to decide where to invest, divest, or develop new products.
For credit analysts, the matrix can be a helpful framework for analyzing business risk, an essential part of deciding the credit-worthiness of a company.
In this article we’ll examine how the matrix categorizes products, giving examples. We’ll then see what actions companies can take having decided on the categories. Finally we’ll look at some of the limitations of the matrix.

Key Learning Points
- The BCG matrix is divided into four quadrants and is based on two parameters, relative market share and market growth rate
- The BCG Matrix includes four categories: stars, cash cows, question marks, and dogs
- To calculate the relative market share of a product, divide its market share by the market share of the product’s largest competitor
- This matrix can help businesses make good choices around their portfolio. For example, it can help companies decide which products should be their focus and which should be discontinued
- Care should be exercised around the use of the matrix. It can over-simplify concepts due to its two axis nature
- “High” and “low” market share and market growth determine which category a product ends up in, but deciding what “high” is can be difficult
- Defining the market can also be difficult. Deciding define the market broadly or more narrowly will make a big difference to the matrix and the categories it suggests for a company’s products.
BCG Matrix – Key Terminologies
The BCG matrix is divided into four quadrants and is based on two parameters – relative market share and the market growth rate. The horizontal axis of this matrix represents relative market share, while the vertical axis represents the market growth rate. The four cells of this matrix are designated stars, cash cows, question marks, and dogs. There are general actions associated with the 4 different types, but in the real world companies may of course decide to do something completely different if it suits their plans!
“High” and “Low”
The axes are categorized by “high” and “low”, which means there may be some difficult choices. When analyzing market growth, 10% is often used to decide a market is “high” growth. This can seem arbitrary. Imagine two markets, one with 10.1% growth, and another with 9.9% growth. Some judgement may be needed to decide what “high” and “low” mean in BCG market growth.
Market share is somewhat easier to analyze. The market share of all players in the market are compared. If the market share of the company being analyzed is greater than its next biggest rival, it’s deemed “high” (we’ll look at how that works in more detail later in this article).
Four Quadrants of the BCG Matrix
The four quadrants of the BCG Matrix are:

Exhibit high growth and command a high market share. A company should invest more in stars, as they are well-established products or brands in high-growth markets. Stars are leading brands in exciting markets. The Apple Watch in 2022 is a star. It’s selling around a third of smartwatches worldwide and has more than three times the market share of its nearest rival, Huawei. The market is predicted to grow by around 28% every year at this point, making it a very high-growth market. Despite being the market leader Apple will have to hold its position. This means it will have to spend a great deal on marketing, and making sure its product stays competitive. Because of this, as of 2022 the Apple watch probably isn’t the most cash-positive product in Apple’s portfolio. If Apple keep spending and making good choices, the watch market may mature and the Apple watch may become a cash cow. This would be the best outcome according to the BCG matrix.
Exhibit low market growth but command high market share. These are the ideal products to have, according to the BCG matrix. They are leading brands, in slower markets. It may seem counterintuitive that slower market growth would be seen as positive, but cash cows require little investment. The brand is dominant, and the fewer new buyers to the market will naturally gravitate to the brand. The market is less frenetic than before, and the company doesn’t have to spend as much cash winning the hearts and minds of all that growth!
The cash these products generate can be invested elsewhere. This is an important part of BCG, not immediately obvious from the diagram. The portfolio of a company should be a pipeline, with cash-positive products (primarily the cash cow) paying for the development of question marks and stars.
Coca-Cola has been a cash cow product for the Coca-Cola company for a long time. As of 2023, it holds around 46% of the soft drink market sales, far beyond its nearest rival. The market growth is modest, around 3.2% per year at this point. Coca-Cola has created excellent positive cashflows for the company, which they can use for other ventures such as their less mature food business. The part of Coca-Cola that doesn’t fit as well is the marketing spend. You’re probably aware of Coca-Cola adverts. A better BCG fit would have Coca-Cola not feeling the need to spend so much on marketing. Again, the real world means not everything fits nicely into a matrix.
Question Marks
Show high growth but command low market share. Question marks require significant investment to maintain or increase market share, but are excellent prospects for the company.
Question marks are usually recently introduced products with sound commercial prospects. With sufficient investment, they have the potential to become stars. If neglected, they may become dogs. Wise companies will know if they can’t build a question mark into a star. They’ll divest despite the exciting market.
It’s easy to think of examples of successful question marks, just think of any star or cash cow and rewind some years. It’s more interesting to think of a failed question mark. You could argue that Google Glass was a question mark that went wrong. Their wearable smart glasses were introduced around 2013. At that point, their market share of wearable tech was small, as not many wearable glasses were being sold compared to e.g. watches (this does rely on us putting glasses in with the broader “wearables” market, highlighting one issue of BCG: defining the market). But, the market was growing. It was arguably a case of “too early”, which is fairly common in tech. Google found the technology wasn’t quite good enough, and presumably was having to spend colossal amounts of money behind the scenes to develop, market and distribute the glasses. They ended up halting the production of the glasses in 2015.
Have both low growth and low market share. The bad performance may be due to high costs, inferior quality, or a lack of effective marketing.
Unless there is some hope of gaining market share, a company is wise to dispose of these products if they are a drain on cash. Dogs are often, but don’t have to be, cash negative.
Imagine you are the undisputed market leader in producing vinyl records in the 1990s. You probably have a great cash cow, but the years to come will reduce that to a dog. CDs and streaming will make your position obsolete and turn your product into a dog. It may be tempting to divest all dogs, but they may still be cash-generative. Vinyl now commands a premium price, so although they represent a slim minority of music sales it is still probably worth being in the market.
BCG Matrix – Advantages and Lim itations
The BCG matrix is very useful for manufacturing companies since an understanding of a product’s market position is imperative to understanding its growth potential. The BCG matrix can also be used to assess the market share of a product relative to competing products. The matrix offers a useful framework for allocating resources to particular products.
However, the matrix does have certain limitations. First, markets may be less clearly defined than the matrix suggests. Moreover, it doesn’t offer information about what the competition is doing. Second, the market growth rate and relative market share are not the only indicators of profitability. Third, this four-quadrant approach may be overly simplistic considering the dynamic nature of markets and industries/sectors. Finally, a high market share does not always result in strong profits given that high costs may also be involved in maintaining that market share.
BCG Matrix – How to use the BCG Matrix
Using five parameters – the definition of the market, relative market share, market growth rate, cash generation, and usage of cash – a company should allocate its products to the relevant quadrant. Based on this allocation, the company can determine which products to invest in and which to discontinue.
It might be noted that defining the market is the most important step. If a market is incorrectly defined, the product could be incorrectly classified. The relative market share is calculated by dividing the selected product’s market share (or revenue) by the market share or revenue of the largest competitor in the sector. Moreover, it’s also necessary to calculate the market growth rate. This can be estimated by assessing the average revenue growth of the leading companies within the product sector.
BCG Matrix – Advantages and Limitations
The BCG matrix is very useful for companies since an understanding of a product’s market position is useful for understanding its growth potential. The BCG matrix can also be used to assess the market share of a product relative to competing products. The matrix offers a useful framework for allocating resources to particular products and building a healthy pipeline in a product portfolio.
However, the matrix does have certain limitations. First, markets may be less clearly defined than the matrix suggests. We’ve seen in the examples that you could narrowly define the vinyl market, or put it as part of the wider music market.
Market growth rate and relative market share are not the only indicators of profitability. We saw that vinyl still has good cashflows for some companies, and question marks may not always be the best to build if it is a pointless drain on company resources with no future.
Finally, we need to be mindful that categorizing by “high” and “low” may lead to some products that are very similar being given different categories. Our earlier example of a 9.9 and 10.1% market growth is relevant here. Some judgment and discussion would be needed to get the most out of the matrix in this case.
Calculating Relative Market Share
The relative market share is used to compare a company’s brand market share with the market share of its largest competitor in the industry. When we calculate relative market share, the market leader’s market share is used as the benchmark.
Relative Market Share Formula:
Relative Market Share = % market share of the company’s product divided by the market share of the largest competing product.
Below we’ve calculated the hypothetical relative market shares of two products from one company using the market share of the largest competitor in that industry. If you’d like to practice this yourself, please see the download attached to this article. This attachment has more products to practice on beyond what’s in the graphic below.

Brand B appears to be dominant in its market, far beyond the share of its nearest rival, rival 1. It is a star or cash cow, depending on the market growth.
Brand A is lagging. It operates in a different market to brand B, and can’t compete on share with its rival 1. It will be a question mark or dog.
The BCG matrix can be a helpful tool for thinking about a company’s portfolio. It creates clear categories and can create great discussions about the balance of products, their cashflows, and their future. It can also suggest sensible actions to create that balance. However, it should be treated with care. It is arguably too simple, reducing the world to two axes. It’s also important to think carefully about what the market is before starting the analysis.
For credit analysts, BCG can create a clear set of categories and language when putting together presentations on a company’s business risk.
If you’re interested in learning more about the world of business, you may be interested in our Investment Banking course . This course gives you the same training as new hires in the top investment banks and covers a wide range of subjects.
Additional resources
Porters Five Forces
Credit Risk
Financial Modeling Course
Share this article
Bcg matrix workout example.
Sign up to access your free download and get new article notifications, exclusive offers and more.
Recommended Course

B2U – Business-to-you.com
THE place that brings real life business, management and strategy to you
BCG Matrix: Portfolio Analysis in Corporate Strategy
BCG Matrix (also known as the Boston Consulting Group analysis, the Growth-Share matrix, the Boston Box or Product Portfolio matrix) is a tool used in corporate strategy to analyse business units or product lines based on two variables: relative market share and the market growth rate. By combining these two variables into a matrix, a corporation can plot their business units accordingly and determine where to allocate extra (financial) resources, where to cash out and where to divest. The main purpose of the BCG Matrix is therefore to make investment decisions on a corporate level. Depending on how well the unit and the industry is doing, four different category labels can be attributed to each unit: Dogs, Question Marks, Cash Cows and Stars. This article will cover each of these categories and how to properly use the BCG Matrix yourself.
Figure 1: BCG Matrix
BCG Matrix Example: Samsung’s Product Portfolio
Samsung is a conglomerate consisting of multiple strategic business units (SBUs) with a diverse set of products. Samsung sells phones, cameras, TVs, microwaves, refrigerators, laundry machines, and even chemicals and insurances. This is a smart corporate strategy to have because it spreads risk among a large variety of business units. In case something might happen to the camera industry for instance, Samsung is still likely to have positive cash flows from other business units in other product categories. This helps Samsung to cope with the financial setback elsewhere. However even in a well balanced product portfolio, corporate strategists will have to make decisions on allocating money to and distributing money across all of those business units. Where do you put most of the money and where should you perhaps divest? The BCG Matrix uses Relative Market Share and the Market Growth Rate to determine that.

BCG Matrix Video Tutorial
Relative Market Share
The creator of the BCG Matrix used this variable to actually measure a company’s competitiveness . The exact measure for Relative Market Share is the focal company’s share relative to its largest competitor. So if Samsung has a 20 percent market share in the mobile phone industry and Apple (its largest competitor) has 60 percent so to speak, the ratio would be 1:3 (0.33) implying that Samsung has a relatively weak position. If Apple only had a share of 10 percent, the ratio would be 2:1 (2.0), implying that Samsung is in a relatively strong position, which might be reflected in above average profits and cash flows. The cut-off point here is 1.0, meaning that the focal company should at least have a similar market share as its largest competitor in order to have a high relative market share. The assumption in this framework is that an increase in relative market share will result in an increase in the generation of cash , since the focal company benefits from economies of scales and thus gains a cost advantage relative to its competitors.
Market Growth Rate
The second variable is the Market Growth Rate , which is used to measure the market attractiveness . Rapidly growing markets are what organizations usually strive for, since they are promising for interesting returns on investments in the long term. The drawback however is that companies in growing markets are likely to be in need for investments in order to make growth possible. The investments are for example needed to fund marketing campaigns or to increase capacity. High or low growth rates can vary from industry to industry, but the cut-off point in general is usually chosen around 10 percent per annum. This means that if Samsung would be operating in an industry where the market is growing 12 percent a year on average, the market growth rate would be considered high.
Question Marks
Ventures or start-ups usually start off as Question Marks . Question Marks (or Problem Children) are businesses operating with a low market share in a high growth market. They have the potential to gain market share and become Stars (market leaders) eventually. If managed well, Question Marks will grow rapidly and thus consume a large amount of cash investments. If Question Marks do not succeed in becoming a market leader, they might degenerate into Dogs when market growth declines after years of cash consumption. Question marks must therefore be analyzed carefully in order to determine whether they are worth the investment required to grow market share.
Stars are business units with a high market share (potentially market leaders) in a fast-growing industry. Stars generate large amounts of cash due to their high relative market share but also require large investments to fight competitors and maintain their growth rate. Successfully diversified companies should always have some Stars in their portfolio in order to ensure future cash flows in the long term. Apart from the assurance that Stars give for the future, they are also very good to have for your corporate’s image.
Eventually after years of operating in the industry, market growth might decline and revenues stagnate. At this stage, your Stars are likely to transform into Cash Cows . Because they still have a large relative market share in a stagnating (mature) market, profits and cash flows are expected to be high. Because of the lower growth rate, investments needed should also be low. Cash cows therefore typically generate cash in excess of the amount of cash needed to maintain the business. This ‘excess cash’ is supposed to be ‘milked’ from the Cash Cow for investments in other business units (Stars and Question Marks). Cash Cows ultimately bring balance and stability to a portfolio.
Business units in a slow-growth or declining market with a small relative market share are considered Dogs. These units typically break even (they neither create nor consume a large amount of cash) and generate barely enough cash to maintain the business’s market share. These businesses are therefore not so interesting for investors. Since there is still money involved in these business units that could be used in units with more potential, Dogs are likely to be divested or liquidated.
Figure 2: Cash Flows and Desired Movement in BCG Matrix
BCG Matrix and the Product Life Cycle
The BCG matrix has a strong connection with the Product Life Cycle . The Question Marks represent products or SBU’s that are in the introduction phase. This is when new products are being launched in the market. Stars are SBU’s or products in their growth phase. This is when sales are increasing at their fastest rate. Cash Cows are in the maturity phase: when sales are near their highest, but the rate of growth is slowing down due to saturation in the market. And Dogs are in the decline phase: the final stage of the cycle, when sales begin to fall.
Figure 3: BCG Matrix and Product Life Cycle
BCG Matrix In Sum
Taken all of these factors together, you can draw the ideal path to follow in the BCG Matrix, from start-up to market leader. Question Marks and Stars are supposed to be funded with investments generated by Cash Cows. And Dogs need to be divested or liquidated to free up cash with little potential and use it elsewhere. In the end, you will need a balanced portfolio of Question Marks, Stars and Cash Cows to assure positive cash flows in the future. If you want to know more about HOW to spend these investments in order to grow a business unit, you might want to read more about the Ansoff Matrix . Besides the BCG Matrix, there are other portfolio management frameworks you might want to have a look at such as the GE McKinsey Nine Box Matrix .
Further Reading:
- Henderson, B. (1970). Growth-Share Matrix. BCG Perspectives.
- https://www.bcgperspectives.com/content/articles/corporate_strategy_portfolio_management_strategic_planning_growth_share_matrix_bcg_classics_revisited/
- https://www.bcg.com/publications/1970/strategy-the-product-portfolio.aspx
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on X (Opens in new window)
- ← Marketing Funnel: Visualizing the Customer Journey
- Value Chain Analysis: An Internal Assessment of Competitive Advantage →
10 thoughts on “ BCG Matrix: Portfolio Analysis in Corporate Strategy ”
Simple, easy to follow and moreover Clear and Perfect presentation Sir.
impressing thank you so much……well articulated easily understandable tutorial/lecture.
Thank you, all the videos have helped me with my studies and progress in my MBA
Great videos, really helps
Great video it was really easy to follow!!
From ILOVEADIAN
This is a great video. Explained BCG matrix succinctly
Fantastic breakdown of the BCG matrix. greatly simplified!
What a powerful presantation of the BCG Matrix. You are simply the best.
Great website. It helps to add further clarity and more context to my textbook.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Boston Consulting Group (BCG) Matrix Explained
When it comes to marketing theories, the Boston Consulting Group (BCG) Matrix stands out as a pivotal analytical tool, guiding businesses in portfolio management and strategic planning.
Developed in the 1970s by the Boston Consulting Group, this growth share matrix has become a fundamental part of strategic business analysis.
At its prime, the BCG Growth-Share Matrix was used by over half of the Fortune 500 companies. While it is not as widely used today, it is still an integral part of marketing theory teachings in business school.
Its main purpose is to help companies evaluate their product lines or business units in terms of growth prospects and market share.
The BCG Matrix provides a straightforward approach to understanding where a company’s strengths lie and where it may need to make adjustments for long-term success.
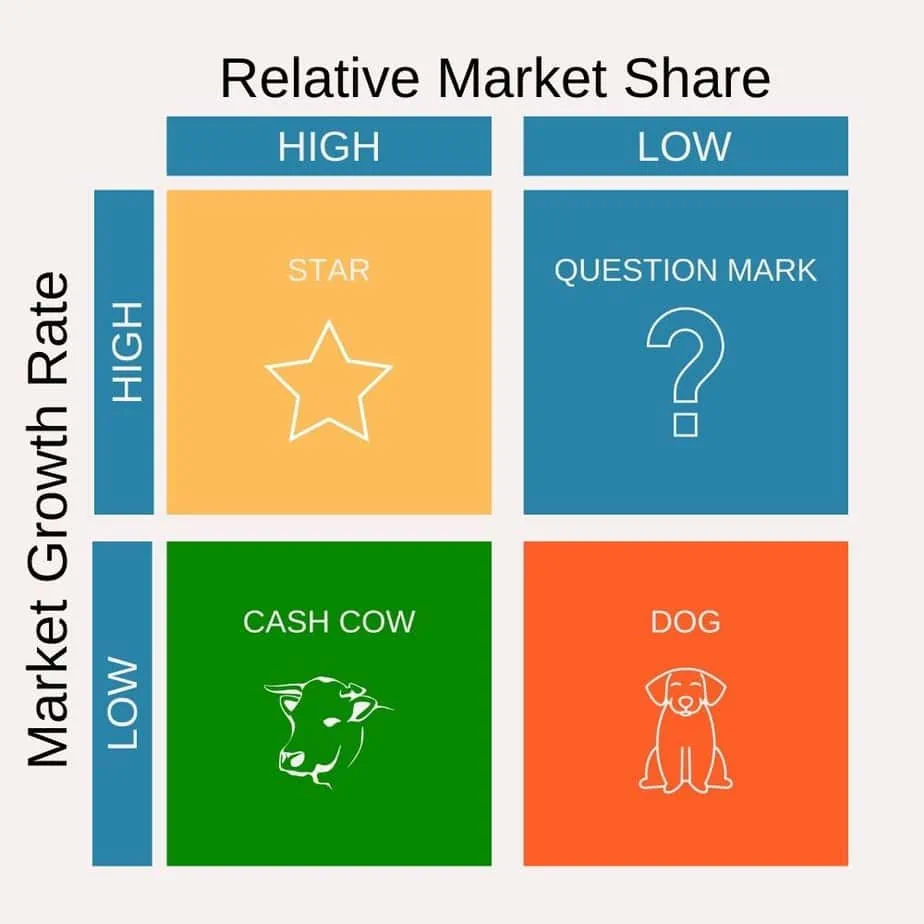
Table of Contents
Core Concepts of the BCG Matrix Model
At its core, the BCG Matrix is based on the concept of product life cycles and market dynamics.
It allows a market leader to come up with a cost advantage that is not easily replicated by competitors.
The idea is that if a business wants to gain market share, then they will need to provide a significant investment in a competitive package.
The growth share matrix classifies business units or products into four distinct categories – Stars, Question Marks, Cash Cows, and Dogs.
These categories are determined based on two key factors: market growth rate and relative market share.
Market Growth Rate
This factor assesses the market attractiveness by evaluating the growth rate of the overall market in which the business unit operates. A high growth rate implies a growing market with potential opportunities for expansion.
Relative Market Share
This measures the strength or dominance of a business unit in its market, compared to its competitors. A high market share indicates a strong, well-established position in the market.
Strategic Implications of Each Quadrant
Each quadrant of the BCG Matrix suggests a different strategic role for the business unit:
Stars: High-Growth, High-Share
These units have high market growth and high market share. They are leaders in a growing market and typically require substantial investment to maintain or grow their position. Stars are seen as potential market leaders and can generate significant revenues.
Question Marks: High-Growth, Low-Share
Characterized by high market growth but low market share, these units are risky. They require a lot of cash to increase market share but have the potential to become Stars. The key strategy here in these high growth markets is to invest heavily or divest.
Cash Cows: Low-Growth, High-Share
With low market growth but high market share, these units are the profit generators for a company. They require little investment and produce steady cash flow. The strategy is usually to maintain and harvest profits.
Dogs: Low-Share, Low-Growth
These have both low market growth and low market share. They are often seen as non-viable in the long term and are candidates for divestiture. The strategy here is usually to minimize investment and consider phasing out.
Applying the BCG Matrix in Business
Implementing the BCG Matrix in a business context involves a structured approach:
- Identifying and Categorizing Business Units: Start by listing all business units or products and categorizing them into one of the four quadrants of the BCG Matrix. This categorization is based on their market growth rate and relative market share.
- Evaluating Market Growth and Market Share: Analyze market data to determine the growth rate of the market each unit operates in and its position relative to competitors. This will involve market research and analysis of internal data.
- Strategic Recommendations for Each Category: Depending on which quadrant a business unit falls into, develop specific strategies. For instance, invest in Question Marks with potential to become Stars, while managing Cash Cows to support these investments.
The BCG Matrix is a straightforward yet powerful tool that can guide businesses in making informed strategic decisions about where to allocate resources for maximum impact and profitability. The next sections of the article will delve into real-world applications and examples of the BCG Matrix, its advantages and limitations, and its modern-day adaptations and relevance.
BCG Matrix in Practice: Case Studies
To illustrate the practical application of the BCG Matrix, let’s consider a few real-world examples from various industries:
- Technology Industry Example: A tech company used the BCG Matrix to categorize its diverse range of products. Its emerging AI technology was classified as a Question Mark due to its high growth potential but low market share. In contrast, its established software suite was a Cash Cow, commanding a high market share in a mature market.
- Consumer Goods Industry Example: A consumer goods company applied the BCG Matrix to its product line. A newly launched health drink, rapidly gaining popularity, was identified as a Star. Meanwhile, an older line of household cleaning products, stable but with little growth, was categorized as a Cash Cow.
- Automotive Industry Example: An automotive manufacturer used the BCG Matrix to strategize its portfolio. Its electric vehicle range, in a high-growth market but with fierce competition, was seen as a Question Mark. In contrast, its line of diesel trucks, in a declining market but with a strong customer base, was a Dog.
Advantages and Limitations of the BCG Matrix
The BCG Matrix is a valuable tool, but like all models, it has its strengths and weaknesses:
Advantages:
The BCG Matrix is straightforward and easy to use, providing clear visualization of a company’s product or business unit portfolio.
It assists in resource allocation decisions, helping companies prioritize investments in products with the most growth potential.
Limitations:
The model relies heavily on the market growth rate and market share as the only factors, which can oversimplify complex market dynamics.
It may not accurately reflect the potential of newer markets or products that have not yet achieved high market share but have high potential.
Modern Applications and Adaptations of the BCG Matrix
In the dynamic business environment of today, the BCG Matrix continues to be relevant, with certain adaptations:
- Integration with Digital Metrics: Modern businesses often integrate digital analytics into the BCG Matrix analysis, using online consumer engagement and digital market trends as additional factors.
- Application Across Diverse Markets: The BCG Matrix is adaptable to various markets, including digital services and emerging technologies, where traditional market share and growth rates may be interpreted differently.
The Origins of the BCG Matrix: Bruce Henderson’s Contribution
The concept of the Boston Consulting Group (BCG) Matrix is closely tied to the insights of Bruce Henderson, the founder of BCG. Henderson was instrumental in popularizing this strategic tool through his pivotal essay, “The Product Portfolio.”
Published in the 1970s, this essay laid the groundwork for what would become a seminal model in business strategy.
In “The Product Portfolio,” Henderson introduced the idea of categorizing a company’s offerings into a matrix based on market growth and market share.
His innovative approach provided businesses with a clear, visual method for evaluating their product lines and making informed strategic decisions.
This essay not only cemented Henderson’s legacy in the field of management consulting but also marked the beginning of the widespread adoption of the BCG Matrix in corporate strategy.
The Boston Consulting Group Matrix remains a powerful tool for strategic business analysis. It offers a simplified yet effective way to visualize and strategize business units or product lines based on market growth and relative market share.
While it has limitations, its adaptability and straightforward approach make it a valuable model for businesses looking to optimize their product portfolios in today’s rapidly evolving market landscape. By understanding and applying the principles of the BCG Matrix, companies can make more informed decisions about where to focus their efforts and investments for long-term growth and success.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Is Your Business Being Found Online?

Free Digital Marketing Report ($150 Value)
Your Business Website Could Be Losing You Money: Here’s Why and What to Do
Achieving product-market fit: unlocking the success of your mvp, 9 different types of propaganda techniques used in advertising, why ai transcription is revolutionizing content marketing, the beginner’s guide to amazon ppc advertising, competitive intelligence: the ultimate guide to gaining a strategic advantage in business, skills that transform competent developers into outstanding ones, the inbound advantage: how b2b inbound marketing fuels sustainable growth, read more articles about business..

Every business should have an online presence in this digital age. An online presence helps visitors and potential customers find you and also allows you to advertise your products and services to more people. A website is crucial because many people will look you up...

Gaining strategic advantage and outsmarting competition has become vital for business success in an increasingly complex global landscape. With rapidly evolving technology shifts, market expectations, and regulations, organizations need practical approaches leveraging...

Why Deleting Old Tweets Matters for Your Business Image
In today's advanced digital world, a business's social media presence is a cornerstone of its brand image. As time gets trendier and people's tastes get more advanced, your social media, like Twitter, needs to get an upgrade, too. Deleting old tweets may...

Customer Engagement and Relationship Building: Fostering Loyalty through Interactive Events
In today’s competitive landscape, businesses are constantly searching for innovative ways to foster loyalty among their customers. One of the most effective strategies involves creating experiences that not only engage consumers but also build long-lasting...

Optimizing Your Restaurant’s Operations: From Newsletter Software to Equipment Acquisition
Running a restaurant involves more than just creating a menu and serving food. It's about crafting a unique experience, engaging with customers, and managing operations seamlessly to ensure the best possible service. Technology and effective strategies are cornerstone...

7 Game-Changing Steps to Register Your Small Business for Marketing Dominance
You have a brilliant business idea. A product or service that will change lives, disrupt industries, and leave a lasting impact. But before you can unleash your vision upon the world, there's a crucial step you can't afford to overlook: properly registering your small...
BCG Matrix (2024): Meaning and Example [+ Template]
Home » BCG Matrix | 🕑
Gust de Backer
November 3, 2023, 10 reacties.
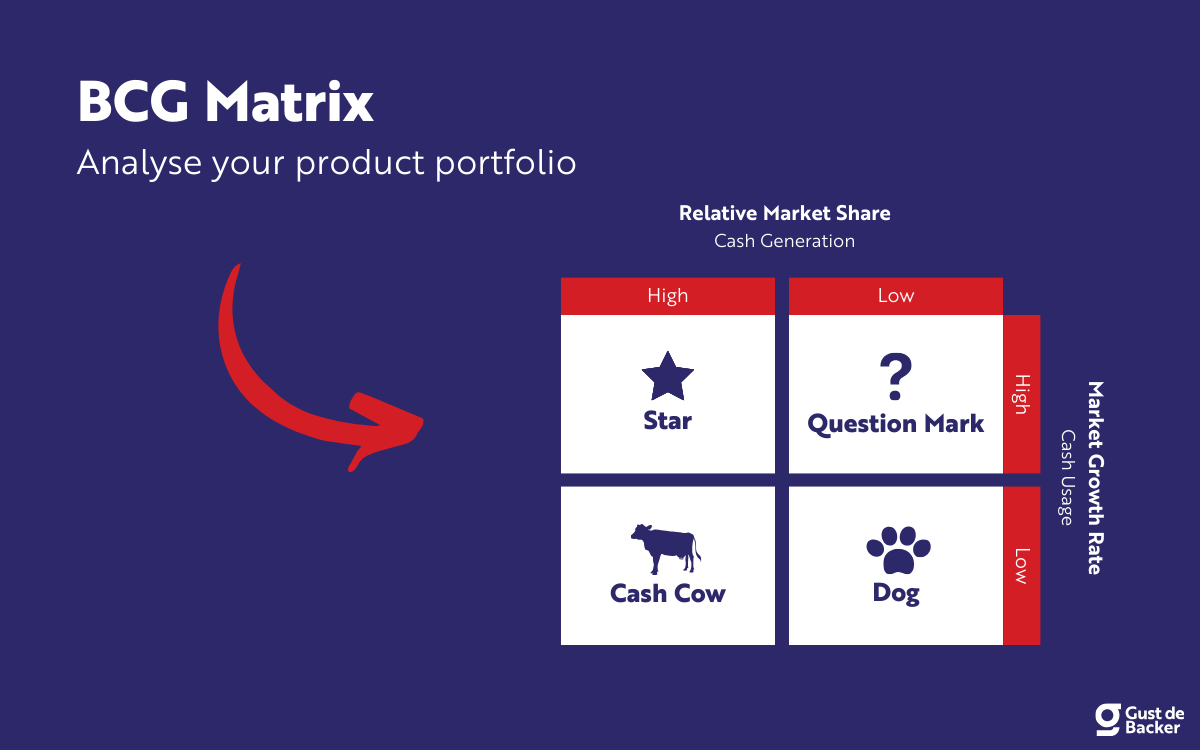
The BCG Matrix also known as the Boston Consulting Group Growth-Share Matrix is a strategic marketing model for assessing product lines for relative market growth and sales volume.
Do you have several products or services that you want to know what their performance is relative to each other and what’s left in terms of market?
Instead of guessing which products to focus on, you can map them out in an orderly fashion and decide which product lines are better stopped and which are worth investing in.
I’m going to show you:
- What the BCG Matrix is
- How to fill in the BCG Matrix
- What you ultimately do with the results of the BCG Matrix
Let’s get started
Table of Contents
What is the BCG Matrix?
The BCG Matrix is a strategic marketing model invented by the Boston Consulting Group .
Companies use the BCG Matrix (portfolio analysis) to compare different products or services against each other to determine whether companies should:
- Continue producing
- Stop producing
- Or invest in it
The BCG Matrix helps companies allocate resources in a way that maximizes the following:
- Market share and market growth
- Company growth
- Long-term profitability for each product line
By understanding where products fall in the BCG Matrix, companies can more effectively determine how to allocate resources.
Four quadrants of the BCG Matrix
The BCG Matrix has four quadrants into which products can fall:

In this, it is notable that you often see that products have a certain Product Lifecycle :

1. Question Marks – Construction
Low market share and high market growth.
The “Question Marks” are a product group in which there is a low market share, but where the market is actually showing high growth.
These products are not necessarily very profitable at this time, but have potential to gain market share with the right investments .
It is therefore possible to build a ‘Question Mark’ into a ‘Star’.
If you introduce a new smartwatch to the market, it will be difficult to gain ground, despite the fact that the market is growing rapidly.
This is because large companies already have strong differentiation combined with large market budgets.
2. Stars – Holding
High market share and high market growth.
The ‘Stars’ are a product group with a high market share and a fast growing market.
These products are profitable and it is worthwhile to continue investing in this product group so that they at least maintain their market share and perhaps even continue to grow.
The Apple Smartwatch is an example of a product where Apple has a high market share and the smartwatch market is experiencing strong growth.
3. Cash Cows – Harvesting
High market share and low market growth.
The ‘Cash Cows’ are a product group with a high market share and a market with hardly any growth.
These products are already profitable with little growth potential in the market. The desired strategy here is to invest as little as possible and still maintain the market position.
The revenue generated from a Cash Cow can be invested in Stars or Question Marks.
Rocket ice creams are an example of OLA, a market with relatively low growth where OLA has a large market share.
The money OLA earns from its rocket ice creams they can invest in, for example, alcoholic ice creams in which there is still a lot of market potential.
4. Dogs – Divestment
Low market share and low market growth.
The Dogs are a product group with a low market share and a market that will hardly grow.
These products are loss-making and have no potential to become profitable.
You want to stop investing in a ‘Dog’, because there is nothing more to be gained from it.
Suppose that a new pharmaceutical company starts developing a corona vaccine in 2023, they will find themselves in a market in which they have virtually no market share and there is no market growth to gain that share.
Points of criticism of the BCG Matrix
Besides being a good model for mapping the (potential) performance of your various product lines, the BCG Matrix also has some criticisms:
- Market share does not guarantee profitability.
- Market growth can be influenced by the company (by boosting).
- The matrix leaves out competition.
- Some products are very interdependent in practice.
- Declining / collapsing markets are not taken into account.
- Both axes are assigned the same prioritization, in practice this need not be so and depends on the business strategy.
The model is easy to use, but needs context to ultimately base decisions on it.
BCG Matrix example
Download the BCG Matrix here:

Good choice! Check your e-mail for the resources...
How do you complete the BCG Matrix?
Start by identifying your own products or services. Which products do you want to include in the portfolio analysis?
To determine your own market share and the market share of your biggest competitor you will need to know how big the total market is.
Based on the size of the total market, calculate your own market share.
Based on the total size of the market, calculate the market share of your competitor so that the relative market share can be calculated.
Determine how much the market is going to grow in the coming period.
To fill in the size of the circles you need to indicate how much sales you do per product category.
Taking Apple as an example…
If we enter that into the BCG Matrix we get the following visualization:

Getting started…
If all goes well, you are now armed with enough knowledge to formulate your portfolio strategy….
Now I want to know from you, what do you think is the most effective method of measuring product performance?
Let me know in a comment.
P.S. should you want additional help please let me know at [email protected]
Frequently Asked Questions
The BCG Matrix, also known as the Boston Consulting Group Growth-Share Matrix, is a model that helps organizations analyze their product portfolios and make resource allocation decisions. The matrix plots strategic business units (SBUs) on a graph to help organizations assess their competitive position in the marketplace and identify potential opportunities.
A BCG portfolio analysis is a way to measure how well a company is performing by looking at its various activities and products. It can help a company decide where to invest its money and which products to stop with.
Market growth is calculated by determining the percentage increase in sales from one year to the next. This figure is then multiplied by the total value of sales from the previous year to determine the market value.
A cash cow is a product or service that generates a large amount of stable, ongoing revenue. A cash cow is usually not the most innovative product or service, but it is reliable and profitable.
The BCG matrix is a strategic marketing model used to help a company decide where to allocate its resources. The matrix is divided into four quadrants: -Stars: high market share and high growth -Questrels: high market share but low growth -Cash Cows: low market share but high growth -Dogs: low market share and low growth. An example of how the BCG matrix can be used would be two companies competing in the same industry. Company A has a large market share but is not growing as fast as Company B. Company B has a small market share but is growing fast. In this case, Company A is considered a cash cow and Company B is considered a star.
I try to help business surpass their growth ceiling with my content.
Sounds interesting?
Let’s connect on LinkedIn!
BCG Matrix | Business Strategy | Customer Development Process | Market Research | Marketing and Sales | Marketing Strategy | Product-market Fit | Value Proposition Canvas
Gust’s Must-Reads 👇🏼
- TAM SAM SOM
- Value Proposition
- Brainstorming
- Decision Making Unit
- Product-Market Fit
- North Star Metric
- Market Research
- Customer Development
- Growth Hacking
- Brand Identity
- Customer Journey
- Account-Based Marketing
![case study bcg matrix OGSM Model (2024): How-to & Examples [+ Template]](https://gustdebacker.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/OGSM-Model.png)
OGSM Model (2024): How-to & Examples [+ Template]
OGSM Model: a solution that helps with strategic planning and goal setting. You know where you want to go, but you don't have a clear picture of how you're going to get there. Ideas and goals are often not realized because there is no clear planning associated with...
Rapid Experimentation: The Road To Innovation (Complete Guide)
You read it left and right, companies that owe much of their success to experimentation.... Of course, experimentation can be understood in a hugely broad way, so in this article I'm going to get you started with: Understanding why experimentation is important...
![case study bcg matrix Cognitive Biases (2024): Complete List of 151 Biases [Psychology]](https://gustdebacker.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/151-Cognitive-Biases.png)
Cognitive Biases (2024): Complete List of 151 Biases [Psychology]
Cognitive biases, there are so many of them... Decisions we make based on emotion, cognitive biases are irrational 'errors' that are programmed into people's brains and affect the decision-making process. Plenty of different articles have been written and an entire...
10 Comments
This is very good explanation. May Allah increase your knowledge.
Thank you, Kiran!
the example given by your explanation is wrong as you have mentioned as the company A would become the question or questol and the Company B shall become the cash cow
Thank you for the comment! I have adjusted it.
Cash Cows are units with high market share and low market growth, not the other way round.
Thanks for the comment Babatola! Where do you see this mistake?
I really find this helpful
Thank you, Alinafe!
Thank for helping me ,I have really understood the matrix
Thank you, Deborah!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
You have Successfully Subscribed!

Text for Mobile
What is the BCG Matrix? Definition, Example, Template and Guide
How to use the bcg matrix model for your organization or business.
The ‘Boston Consulting group’s ‘abbreviation is the BCG matrix. This BCG matrix is designed to help long-term strategic planning for the benefit of the business and its growth opportunities by means of a review of its product portfolio to decide on the most suitable investment to obtain maximum Return on Investment. This also determines about discontinuing as well as developing products. It is also named the Growth Share Matrix.

How Do You Prepare a BCG Matrix?
BCG matrix is prepared by executing the following steps:
Step 1: Selection of the Product:
BCG matrix is utilised for this purpose by:
- Analysis of Business Units,
- Separation of brands, products or considering an organisation as a unit
Step 2: By defining and market study
Step 3: By comparison and by calculation of the relative market share
Step 4: a study of the market growth rate.
Step 5: Draw the circles on a matrix.
What Are the Four Categories of BCG MATRIX?
It is primarily based on planning in a portfolio-dependent study and observation. So, a company’s business units can be classified into four categories:
- Question Marks
It is necessary to conceptualise better the above four processes related to the BCG matrix by making one for L’Oréal in the following sections.
How Do You Find a BCG MATRIX?
By following the steps indicated below, you can find a BCG matrix.
Step 1: Induction of BCG Matrix.
Step 2: Reach the Ribbon > Insert > Other Charts and click Bubble Chart.
Step 3: Change X-axis values.
Step 4: Click Edit to change the source of data.
Step 5: Change series X values.
Step 6: Selection of Relative Market Share values.
Step 7: Your BCG Matrix chart is a bit changed.

How to Find Market Growth Rate?
The growth rate of industries can be easily estimated using free online resources. Alternatively, it can be calculated by counting the reputed companies’ average growth rate of revenue. Usually, the Market growth rate is represented in percentage terms.
The market growth rate is usually estimated by the formula stated below:
(Product’s sales in the current year – Product’s sales of the previous year)/Product sales last year
High growth-rated markets are the ones where the total market share gained is expanding; this results in many advantages for all companies in gaining monetary profit.

Step 5: Drawing the Circles over a Matrix
After the above calculation, it needs only to plot the brands on the matrix. The x-axis represents or shows the relative market share, and the y-axis indicates the company’s growth rate. A similar circle can be plotted for each unit, brand, and Product, and the size of which must correspond ideally to the company’s revenue.
What do the Question Marks Signify In the BCG Matrix?
The feature of question marks represents a business to have high growth prospects but a low share in the market. They consume a significant amount of cash but with little return. Ultimately, ‘question marks ‘lose money. However, as these business units increase, they have the potentiality to upgrade into stars by entering a higher growth-oriented market.
How to Use a BCG Matrix?
After defining four categories of the BCG market, we can review the strategies of the company by using each category as discussed below:

Stars: The location of the products in this quadrant is highly attractive as they are located in a robust category, and these products are highly competitive. A huge potential has been found in this category for high revenue growth. This is due to its high market share and high growth rate. It is expensive to develop but is worth investment for promotion to the long extent of its Product Life Cycle. In the event of its success, a star may be a cash cow in the event of maturity, assuming they keep the same market share unchanged.
Strategic Choices, As Indicated Below:
- Vertical Integration,
- Horizontal Integration,
- Market Penetration,
- Market Development, And
- Product Development

Question Marks: Most businesses start as question marks. Huge investments are necessary to achieve or protect market share. The question mark sector has the potential to become stars category and ultimately c ash cows but can also become dogs or exits. It requires high Investments for question marks; otherwise, this categor y may result in negative cash flow.
Like stars, the category of Question also does not always succeed; if, after a large investment, they cannot fetch profit and gain market share, they become the dog category. Therefore, careful observation and review are necessary before investing in this category.
Strategic Choices Are The Follows:
- Market Development,
- Product Development,
- Process of Investment.

Cash Cows: In this category, cash generates profits by investing as little cash as possible. It needs low-cost support and needs to be managed for continued profits & cash flow. Large corporate or SBUs are considered efficient and innovative and should have the potential to become stars. It requires maintaining a healthy market status and should defend the market share of the business house or investors. The company should take advantage of sales volume and leverage the size of its operations. It can support other businesses too.
Strategic Choices: Product Development, Diversification

Dogs: Low market share makes it a face of cost disadvantages, so they need enough cash to reach break-even, but they are rarely, if ever, worth investing. This Dog sector should be liquidated if there are fewer prospects for gaining market share. This is at a declining stage of the Product Life Cycle, requiring a minimum number of dogs in the company.
Advantages of BCG Matrix
- It is simple and easily understood.
- It can quickly and merely show the opportunities open to you,
- This can identify how corporate cash resources can be invested suitably to maximize a company’s growth and profitability.
- BCG Matrix can prepare a framework for allocating resources among different products
Limitations of BCG Matrix
This type of matrix has two-dimensional applications as given below:
- Relative market share and
- Market growth rate
Limitations are indicated below:
- BCG matrix is not the only indicator of the profitability of a business, attractiveness or success.
- It does not care for the effects of synergy from brand to brand.
- A company which has a minimum market share can become profitable as well.
- It has been observed that a High market share does not always produce high profits since there is also a high cost in obtaining a high market share.
- It has been observed that dogs may benefit the business or other products in achieving and gaining a competitive advantage.
- It does not care for small competitors with a fast-growing market share component.

Get Instant Help with your BCG Matrix Assignment
If you are a marketing student and given assignment writing tasks , say on (BCG) Boston matrix, then you can seek Boston matrix assignment help from the Assignment provider of Casestudyhelp.com.
Casestudyhelp.com provides 24×7 live support and online chat, as well as solves direct inquiries of the students of Business Law, Contractual Law and BCG Matrix Business case studies which help them in their BCG Matrix Assignment Help .
Why Choose Us?
We hope this writing by our Casestudyhelp.com will help students write on the BCG market and related studies. We can improve your writing skill. Our quality of work benefits us in maintaining a crowd of loyal customers. They provide us with excellent client perception.
- Our Product is 100 % Original–and is free of plagiarism. We use Free ‘Turnitin’ software for checking.
- We provide free Rework –we give all Rework and modifications free.
- 24/7 Customer Assistance–we provide round-the-clock customer assistance by our experts free of cost.
If you require any writing assignment help, please get in touch with us early.
- Revolutionizing Digital Communication: The Power of Olly and AI
- AI-Powered Video Editing with Snapy.ai: The Future of Content Creation is Here
- Dawn of AI-Powered Video Editing: Transform Your Videos with Silence Remover Online
- The Dawn of Generative AI: Why and How to Adopt it for your Business
- Harnessing the Power of Generative AI for Business Innovation: An Exclusive Consultancy Approach
Original content with a single minded focus on value addition.

BCG Matrix of Amul: Analyzing the taste of India
Amongst the first few classes in any business school, you come across the BCG matrix. Over the course of the 5 decades that it has been around, the BCG matrix has been used by a lot of Fortune 500 companies in learning to prioritize their various businesses. It allows companies to assess and prioritize their various businesses according to the market share and growth potential. Hence, it is called the growth-share matrix.
The BCG matrix has been a stalwart of the strategy and marketing departments of companies for a very long time. It has grown to give rise to another important tool called the GE matrix. Despite the changes, and the additions to it, the BCG matrix hasn’t lost its charm. It is the reliable, worthy grandfather of matrices used by companies. Since, it is such a classic, let us understand it in terms of a classic company – Amul. Presenting for you, the BCG Matrix of Amul:
The taste of India
As you think of Amul, you immediately begin to visualize the creamy butter that you spread on any eatable possible since childhood. As an Indian, we will find it near impossible to think of India without Amul. Though it seems that Amul has been around forever, that’s not the case. However, like the BCG matrix, Amul also has a history as rich as its cheese. It was formed in 1946, way before the BCG matrix was even a nugget of an idea, and has been the stalwart of the milk industry in India. Amul has become one of the most widely known brands in the industry and is famous for the amount of jobs it has created over the years in addition to its quality products.

Over the years, Amul has diversified their offerings, entering into different milk and milk product markets. This has not only increased their competition, but has also allowed them to secure revenues from otherwise niche sectors like camel milk, etc.
A brand is defined by the need it serves, and by the attention it garners. Amul has managed to do both. In addition to being our go-to in the culinary sector, the brand has also snatched our attention with the witty, satirical billboards they put up in accordance with the current affairs. Truly, Amul is the Taste of India.
You must be wondering why this piece has introduced the BCG matrix, and Amul in the same breath since both are in absolutely different domains. Allow me to draw a connection between the two by saying that we are about to perform an analysis of Amul using the BCG matrix.
The Growth matrix of Amul
We know that there are 4 quadrants in the BCG matrix – Cash Cow, Star, Question Mark, and Dog. These 4 quadrants represent the permutations of the type of growth and market share possible. Let’s see these quadrants in more detail, especially related to Amul..
The Cash Cows
Amul’s ‘Cash Cow’ is coincidentally its cow milk. Looking at it more closely, we can also surmise that Amul Butter, and Amul Cheese, are also its ‘Cash Cows’. These three products generate a steady, high revenue to fuel the other products of the brand. They hold high shares in markets that have relatively low growth. That is saying something, considering the amount of brands and popups in the dairy industry due to the changing trends.
This category of products is the focus of the show. On one hand you have the ever-reliable ‘Cash Cow’ with a constant influx of cash- as its name suggests, on the other hand you have the ‘Star’- which not only brings home the bucks, but also rings in 1 st in the popularity contest. Amul yet again has more than one product in this category- Amul Ghee, and Amul Ice Cream. ‘Star’ products have the characteristic of holding a high market share, in markets with high growth potential- the most desired quadrant. Companies often invest a lot of cash that comes in from the ‘Cash Cow’ category into the ‘Star’ products’ promotions, and development. Amul Ice Creams have very targeted advertisements, and are constantly being worked on to become more appealing to the public by the use of words like ‘creamy’, ‘medium-fat’, etc.
The Question Marks
As the name suggests, ‘Question Mark’ products aren’t those that have a questionable future. They are just products that have potential to grow, but require a little more attention and careful planning to go the right way. Often companies employ funds for researching into the scope of the ‘Question Mark’ products. These products are in high growth markets with a low market share. They essentially can also become the rising ‘Star’ products with the correct attention, and investments. Amul Lassi falls under this category as it already is in a highly populated market. However, it is steadily making a name for itself against its close competitors like Aarey and Govardhan. The advertisements for Amul Lassi are also targeted to make it a faster growing product.
This category kind of suggests that the company/brand does not see much potential in these products. The ‘Dog’ products for Amul will be Amul Cookies, and Amul Pizza. These products have a low growth and market share- often seen as not profitable for the company. Thus, the companies don’t invest much in product changes or promotions. They are often either discontinued, or kept in low production.
Oh to be Amul in a pandemic stricken world! At a time when companies are losing business left, right, and center, Amul is going steady. Having a couple of products in the ‘Cash Cow’, and the ‘Star’ category defines how credible and heavily-preferred this brand is. Hopefully, you now know a little more about both the BCG matrix, and Amul than you did previously!
The author of this piece is Mahek Mirchandani , drop her a thank you note. To read more of business concepts, head here .
If you liked the piece, why not share it with your best friend?
Get more of these pieces directly in your inbox, subscribe for free , here .
- BCG Matrix with examples of 4 popular brands
- Top 5 Management Lessons from Mahabharata (Part – I)
You May Also Like

Logo Analysis: What logos say about their brands?

The 101 of Consumer Promotions with Examples

101 of Consumer Insights for Brand Managers
2 thoughts on “ bcg matrix of amul: analyzing the taste of india ”.
Pingback: Unlocking in the Lockdown: The story of Amul | CaseReads
Pingback: BCG Matrix With Examples Of 4 Popular Brands
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Strategic Analysis Hub
Bcg matrix of l’oreal .
L’Oreal BCG Matrix (Boston Consulting Group) is a strategic analysis tool that allows you to analyze the business units and product portfolio of the company. The key insight gained from the BCG matrix analysis offers you further investment opportunities. Today, we’ll discuss the BCG matrix of L’Oreal as a BCG matrix analysis example; it analyzes the market share and growth potential of every business unit and market share in the form of four main quadrants; stars, cash cows, question marks, and dogs.
Eugene Schueller established the personal care and cosmetic company L’Oreal in 1909. L’Oreal is the world’s leading and largest cosmetic brand. Some of the main products and services of cosmetic and personal care product manufacturing company L’Oreal in different categories are as follows;
Some of the main subsidiary brands of L’Oreal are as follows;
- NYX Cosmetics
- Matrix Essentials
Some of the leading products of L’Oreal in the British market are as follows;
- Hair Conditioner
- Face Cream & Lotion
- Face powder and tinted moisturizer
- Cleansing cream
- Hairstyle product
Bruce Henderson founded the BCG Matrix or the growth-share matrix in 1968, and it allows you to analyze the different market share and growth rates of the portfolio product. The matrix comprises two dimensions; market share and growth rate. It has four quadrants like the following
- Stars are when a high market share and high growth rate
- Cash cows have when high market share and a low growth rate
- The question mark is low market share and high growth rate
- The dog is when low market share and low growth rate
Let’s discuss the BCG matrix of L’Oreal as a BCG matrix analysis example;
BCG Matrix of L’Oreal
The four main quadrants of the BCG matrix of L’Oreal are as follows;
Stars of L’Oreal
I-consumer products.
The consumer products of L’Oreal have earned a position in the star quadrants of the matrix because they have a high market share and high growth rate. Some of the star consumer products and brands are as follows;
- L’Oreal Shampoo
- L’Oreal Paris
These brands have established a strong position in the global market and a large database of customer markets. The analysis of high market share and high growth rate outlines that the consumer products of L’Oreal have a high growth potential and high revenue. As a result, the high growth rate and revenue would attract the attention of the market and a lot of competitors.
II-Defensive Approach
In order to retain market share, revenue, and profitability, L’Oreal has to invest a significant amount of capital resources to defend the cosmetic company’s market position. The investment as a defensive strategy helped the company in the following ways;
- Retaining current customers
- Attracting new customers
- New geographical market penetration
- Product line expansion
It would impact the product lifecycle and the market growth rate; it would slow down the product movement from a high growth rate of star to the slow growth rate of a cash cow position.
III-Product Innovation
L’Oreal invests a significant amount of resources in research and development. It has allowed the company to launch innovative products and offer unique customer experience. That’s how the cosmetic brand has fought off the competition and retained its position in the market.
Cash Cows of L’Oreal
I-professional products & brands.
Professional products and brands have earned a position in the cash cows quadrants of the matrix. It outlines that they have a high market share and slow growth rate in the mature and saturated market. Some of the main professional products and brands in the cash cows quadrants are as follows;
Usually, cash cows are the most stable area of any business or company, and the objective of the company is to retain its market share. These brands offer high-quality products and they have established a large market share. When the market is growing, the acquisition rate is slow and the customer retention rate is higher.
II-Cash Surplus
Slow growth and high market share mean that the cash cow professional products are generating a significant amount of cash surplus for the company. L’Oreal reinvests the cash earned from the professional unit to the other consumer product units of the company because they usually require a large investment. However, it shows that the earned revenue from the professional department is much more than its investment.
Question Marks of L’Oreal
I-luxury products & brands.
The luxury products and brands of L’Oreal earned the position in the question marks quadrants of the BCG matrix. It shows that those products and sub-brands have a low market share and high growth rate. Some of the luxury products and brands of L’Oreal in the question mark segment are as follows;
- IT Cosmetics
- KES SAINT Laurent
The analysis of luxury products and brands in the question market shows that they have a high growth potential to become the star. Newly acquired brands and small brand projects usually fall under this category, but they face fierce competition in the
II-Capital Investment
In order to attract the attention of customers, L’Oreal should invest a significant amount of capital resources in the growing products and sub-brands. The invested resources carry a lot of resources, they may either pay off or would result in the form of wastage of investment.
However, new customer acquisition is a great strategy of the company that helps a company to transform question marks products into cash cows and stars.
Dogs of L’Oreal
I-active products.
The active products and sub-brands of L’Oreal earned a position in the dog quadrants of the matrix. The dog quadrants mean that they have a low market share and slow growth rate. Some of the active products and sub-brands of L’Oreal fall in the dog quadrants as follows;
- SKIN CEUTICALS
- LA ROCHE-POSAY
The dog quadrant analysis shows that they are smaller brands and they haven’t attracted the attention of the customer market and face the challenge of tough competition.
II-Divestment
The cosmetic brand should carefully analyze these segments, if they don’t show any sign of improvement, then the company should consider divestment and sell them off. Divestment is a great strategic approach for the dog quadrant products. Instead of wasting resources on non-growing products and brands, L’Oreal should focus on growing products.
Conclusion: L’Oreal BCG Matrix
After an in-depth study of the BCG matrix of L’Oreal; we have the realized that BCG (Boston Consulting Group) matrix is a highly useful tool for analyzing market share and growth rate. If you are learning about L’Oreal BCG matrix analysis as a BCG matrix analysis example of a cosmetic brand, then you should keep in mind the abovementioned elements involved in the quadrants of cash cows, stars, question marks, and dogs.

Ahsan is an accomplished researcher and has a deep insight in worldly life affairs. He goes Live 3 days a week on various social media platforms. Other than research writing, he’s a very interesting person.
Related Posts

Porter’s Five Forces Analysis of Coffee Industry

Ansoff Matrix of Facebook Meta

BCG Matrix of Colgate
We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Database >
- Essays Samples >
- Essay Types >
- Case Study Example
Bcg Matrix Case Studies Samples For Students
3 samples of this type
Do you feel the need to examine some previously written Case Studies on Bcg Matrix before you begin writing an own piece? In this free directory of Bcg Matrix Case Study examples, you are given an exciting opportunity to examine meaningful topics, content structuring techniques, text flow, formatting styles, and other academically acclaimed writing practices. Implementing them while crafting your own Bcg Matrix Case Study will definitely allow you to complete the piece faster.
Presenting the finest samples isn't the only way our free essays service can aid students in their writing endeavors – our experts can also create from point zero a fully customized Case Study on Bcg Matrix that would make a genuine basis for your own academic work.
BCG And Portfolio Analysis: Free Sample Case Study To Follow
Coca cola marketing strategy case study examples, nokia strategic audit case study example, leung man hong.
Don't waste your time searching for a sample.
Get your case study done by professional writers!
Just from $10/page
Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here are the example list: 01 BCG Matrix of Coca-Cola. 02 BCG Matrix of Samsung. 03 BCG Matrix of L'Oréal. 04 BCG Matrix of PepsiCo. 05 BCG Matrix of Apple. 06 BCG Matrix of Nestle. 07 BCG Matrix of Unilever. 08 BCG Matrix of McDonalds.
The BCG Matrix is a tool used internally by management to assess the current state of value of a firm's units or product lines, aiding the company in deciding which units to either keep, sell ...
The BCG Growth-Share Matrix is an analytical tool used to help develop an understanding of a company's product portfolio. It is designed to analyze how each of a company's products contribute to overall growth and identify patterns in investments, potential opportunities, and weaknesses. This article will explain the four categories of the ...
The BCG Matrix, also known as the Growth-Share Matrix, is a visual representation of a company's portfolio of products or business units. It was developed by the Boston Consulting Group in the 1970s and is widely used across industries to assess the strategic position of different offerings. By plotting products or units on a matrix based on ...
A detailed analysis of BCG matrix of Nestle, which has numerous brands under it like Maggi. ... Boston Consulting group's product portfolio matrix is designed to help with long term strategic planning, to help a business consider growth opportunities. ... Get to know how to analyze a marketing case study comprehensively in just 5 slides ...
For a company with a big portfolio, it's important to assess its product lines regularly to see which product is profitable, which is making losses, and wh...
The most known two-by-two matrix is the BCG matrix. The BCG matrix, also called the growth-share matrix, helps assess a company's current product portfolio based on the product life cycle and the experience curve.Since both criteria are hard to quantify, proxies are used to illustrate them.The product life cycle is reflected by market growth, and the relative market share mirrors a company ...
4 Components of the BCG Matrix. On a BCG matrix graph, the vertical axis considers the growth rate from low to high, whereas the horizontal axis considers the relative market share from high to low. The axes help divide the matrix into four different quadrants: Dogs, Question Marks, Cash Cows, and Stars. Let's discuss each quadrant one by one.
The BCG matrix is divided into four quadrants and is based on two parameters, relative market share and market growth rate. The BCG Matrix includes four categories: stars, cash cows, question marks, and dogs. To calculate the relative market share of a product, divide its market share by the market share of the product's largest competitor.
BCG Matrix Video Tutorial. Relative Market Share. The creator of the BCG Matrix used this variable to actually measure a company's competitiveness.The exact measure for Relative Market Share is the focal company's share relative to its largest competitor. So if Samsung has a 20 percent market share in the mobile phone industry and Apple (its largest competitor) has 60 percent so to speak ...
According to the BCG matrix, this candy is your 'Dog'- low growth, and low market share. 'Dogs' are the products that many managers view as cash disadvantages, and are usually scrapped or removed from active circulation. Diet Coke is an example of a 'Dog' of the Coca-Cola company.
The Boston Consulting Group Matrix (BCG Matrix), also referred to as the product portfolio matrix, is a business planning tool used to evaluate the strategic position of a firm's brand portfolio. The BCG Matrix is one of the most popular portfolio analysis methods. It classifies a firm's product and/or services into a two-by-two matrix.
BCG Matrix in Practice: Case Studies. To illustrate the practical application of the BCG Matrix, let's consider a few real-world examples from various industries: Technology Industry Example: A tech company used the BCG Matrix to categorize its diverse range of products. Its emerging AI technology was classified as a Question Mark due to its ...
The BCG matrix is a strategic marketing model used to help a company decide where to allocate its resources. The matrix is divided into four quadrants: -Stars: high market share and high growth. -Questrels: high market share but low growth. -Cash Cows: low market share but high growth. -Dogs: low market share and low growth.
The 'Boston Consulting group's 'abbreviation is the BCG matrix. This BCG matrix is designed to help long-term strategic planning for the benefit of the business and its growth opportunities by means of a review of its product portfolio to decide on the most suitable investment to obtain maximum Return on Investment.
The BCG matrix has been a stalwart of the strategy and marketing departments of companies for a very long time. It has grown to give rise to another important tool called the GE matrix. Despite the changes, and the additions to it, the BCG matrix hasn't lost its charm. It is the reliable, worthy grandfather of matrices used by companies.
Step 5: Draw the Circles on a Matrix. Once you have determined each product or business unit's market share and growth rate, the next step is to draw the circles on a matrix. The BCG matrix is a simple two-by-two grid with a market share on the x-axis and a growth rate on the y-axis.
The Boston Consulting Group (BCG) Matrix (or growth-share matrix) is a way to examine your product portfolio and identify areas for investment, growth, or di...
After an in-depth study of the BCG matrix of L'Oreal; we have the realized that BCG (Boston Consulting Group) matrix is a highly useful tool for analyzing market share and growth rate. If you are learning about L'Oreal BCG matrix analysis as a BCG matrix analysis example of a cosmetic brand, then you should keep in mind the abovementioned ...
The BCG matrix, also known as a growth/share matrix, is a business tool that you can use to help you create strategic, long-term plans regarding investment in competitiveness and market attractiveness. It is a framework for portfolio management that allows you to prioritize different products. You can write a BCG matrix as a table that is ...
In the following mini-case study, you are required to categorize the corporation's business portfolio into the four boxes of the BCG (Boston Consulting Group) model. You then need to decide how the management should allocate $250 million funds available across their strategic business units (SBUs), using the BCG matrix as your guide.
BCG And Portfolio Analysis: Free Sample Case Study To Follow. 1. Prerequisites. In order to conduct a complete BCG-analysis we need the market growth rate and market share of each SBU as well as market shares of their main competitors to calculate relative market share. Since in the assignment we have only market shares of the business units ...
The BCG Matrix is a business method that was created by the Boston Consulting Group in the 1970's. This business method bases its theory on the life cycle of products. Also known as the Boston Box or Grid. BCG Charts are divided into four types of scenarios. Stars.