Tips & Tricks: Advanced Work Assignment
[madrid] use the servicenow® advanced work assignment (awa) feature to automatically assign work items to your agents, based on their availability, capacity, and optionally, skills., awa pushes work to qualified agents using work item queues, routing conditions, and assignment criteria that you define. agents see their assignments in their agent workspace inbox., customers use different channels to request service, for example, chats, cases, or incidents. requests from customers create task or interaction records that store information about these objects, called work items., awa automatically routes work items to queues that focus on certain types of support, using criteria (such as priority or customer status) that you provide. queues can be defined based on need or type, for example product or critical cases. you also identify the agent groups responsible for work in the queue. awa then applies assignment rules that you set and uses agent availability, capacity, and skills (if defined) to assign work to the most qualified agent., advanced work assignment components, service channels, a means of providing customer service. awa offers base system channels for chats, cases, incidents, and walk-up centers. for each channel, you can set attributes such as agent capacity and utilization conditions to control the work handled in the channel., a single piece of work to be handled by an agent from start to completion. for example, one chat or one case are objects that are routed and assigned to agents., work item queues, a queue stores a work item for a specified service channel. awa admins can create queues that focus on certain types of support within the channel, such as vip customers or critical cases. awa routes work items to queues based on specific conditions or requirements that you define, such as customer status, or region. groups assigned to each queue handle the incoming work items. once work items are placed in a queue, awa can then assign items to available agents based on assignment rules and agent availability and capacity., assignment groups, agents belong to specific groups that are organized by the type of work assigned to them. you provide details about an assignment group including the name and description, manager, and group email. you can also set up roles, groups and group members, queues, and agent capacity overrides for agents in an assignment group., assignment rule, criteria that determines how work items are pushed to the appropriate agent within a qualified assignment group., agent capacity, the maximum number of work items on a particular service channel that an agent may actively work on at one time., agent availability, states that indicate agent presence and whether the agent is available for work or is busy or offline. awa uses the agent availability state to determine if an agent is able to receive work., inbox layout, a configuration tied to a service channel that defines which fields of a record representing a work item are shown in agent inboxes. a layout defines what the agent sees in agent workspace., advanced work assignment roles, awa adds the following roles for users who configure, manage, and receive work assignments., basic process for configuring awa, users with the awa_admin role determine:, what to route – configure the base service channels to be used., where to route – define the work item queues and the routing rules, execution order, work item sort order, and strategy, how to assign work items – define the assignment rules that determine the work items pushed to agents, what the agent sees – set the inbox card layouts and presence (availability) states that agents use in their agent workspace, for more information: https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/madrid-servicenow-platform/page/administer/advanced-work-assignment/concept/awa-overview.html.


Understanding Advanced Work Assignment – Not Every ServiceNow Module Uses Groups
With the ServiceNow Advanced Work Assignment (AWA) application, work is directly delivered to agents’ inboxes, so they don’t have to choose work items from queues manually. AWA routes and assigns work items automatically based on agent skills , capacity, and availability. By using assignment criteria, routing conditions, and work item queues that you define, AWA pushes work to the most qualified agents. Agents, on the other hand, use their AWA inbox to see their work items, accept or reject work items, and set their availability.
To request service, customers can use different channels, such as incidents, cases, or chats. Requests from customers create interaction or task records to store information about work items. Using criteria that you provide, Advanced Work Assignment routes work items to queues that focus on specific types of support. Users can define queues based on type or need, as well as identify the agent groups responsible for work in a certain queue. Then, AWA applies pre-set assignment rules to assign work to the most qualified person.
Components of Advanced Work Assignment
- Work Items are defined as any type of single piece of work that needs to be handled by an agent. For example, one case or one chat is a work item or object that gets routed and assigned to an agent.
- Service channels . AWA offers multiple base system channels for incidents, cases, chats, and walk-up centers. Service channels are a means of providing customer service. Assignment rule . Pre-set criteria that determine how objects will be pushed to the right agent within a certain assignment group.
- Assignment groups . Groups are organized by the type of work that’s assigned to them, and every agent belongs to a group. You provide a name, description, manager, group email, and other details about a group. You also set up roles, queues, group members, and agent capacity overrides.
- Work item queues. A specific type of work item for a service channel is stored in a queue. AWA routes work items to appropriate queues, based on specific requirements and conditions that you define.
- Inbox layout . A configuration that defines which field of a work item is shown in agent inboxes.
- Agent capacity and availability . Agent capacity refers to the maximum number of work items that an agent may work on at one time. Agent availability indicates agent presence and whether he or she is available for work, offline, or busy.
The Main Benefit of Using AWA
The main benefit of using AWA is increasing customer satisfaction rates. Advanced Work Assignment will help your clients assign work to the right agent more easily and in a shorter time period. Also, it means that an agent will have more time to resolve their requests. Because work assignments are set up based on agent’s skills, availability, and capacity, you will be sure that agents are available and have the right skills to fulfill a request with a high-quality solution in mind.
Reach out to Finite Partners if you need assistance with using ServiceNow and any of its integrations. Feel free to call us or ask a question on Twitter .
This website uses cookies to improve your experience. We'll assume you're ok with this, but you can opt-out if you wish. Read More

ServiceNow® Advanced Work Assignment (AWA) - a clever automation of your workload distribution

The proper distribution of tickets and workload is a key factor in providing rapid resolution and enhanced user experience in all enterprises. It used to be that assignments would go through several iterations and many conversations, sometimes even with end-user involvement, until the task finally landed on the proper agent to work on it. All of this is time-consuming, error-prone, and both a bottleneck and a single point of failure in the process. As an illustration of the nature of the challenge, consider the steps involved in finding an agent with the appropriate language skills in a multi-language environment.
The ServiceNow® Advanced Work Assignment (AWA) feature is a way to cleverly automate your workload distribution. Assigning work items to your agents is based on their availability, capacity, and optionally, skills. AWA uses queues, routing conditions, and assignment criteria to select the best-qualified agent for the task.

Figure 1. AWA Overview (Source: https://docs.servicenow.com/bundle/paris-servicenow-platform/page/administer/advanced-work-assignment/image/awa-overview-flow.png)
AWA was introduced with the Madrid release in early 2019 as a way to manage agents’ ITSM tasks. In recent releases, it has become available across the whole platform to take advantage of the huge benefits it offers.
AWA functionality is available and embedded into the Workspace environment, which is an advanced UI created and enhanced for fulfillers and agents. There is a dedicated inbox section where fulfillers and agents can monitor incoming tasks and requests. Agent availability is set according to their schedules and includes omnichannel presence, but the system also allows the agent to set their presence across one or more channels.

Figure 2. Agent availability in Workspace Inbox
Customers can interact with ServiceNow through different service channels such as incidents, cases, walk-ups, and chats. When the customer makes a request, a work item is created. This is a single piece of work that can be handled by an agent from start to finish.
Advanced Work Assignment allows the system to push work to agents. It uses configurable criteria to automatically route work items to queues that focus on various support channels. This lets the platform enforce assignments to the proper group or agents.
Queues collect and store a specific type of work item for a dedicated service channel. Queues can be configured to focus on a certain type of support, such as VIP customers or critical cases. AWA routes work items to queues based on specific conditions or requirements that you define, such as customer status or region. Groups assigned to each queue then handle the incoming work items. Once work items are placed in a queue, AWA can assign items to available agents based on assignment rules, agent availability, and capacity. In each queue, there is a possibility to set a timer that allows agents to respond to the work item.
Agent capacity is also configurable. Agent capacity is the maximum number of work items on a particular service channel that an agent may actively work on at one time. Another characteristic that is measured and managed by the platform is the agent affinity. There are three major types of affinities:
- Historical affinity, in which AWA tries to identify the best agent based on the agent's history of serving the same customer;
- Related task affinity, in which AWA tries to identify the best agent based on the agent's past assignments on related tasks.
- Account team affinity, in which AWA tries to identify the best agent based on the agent's responsibility or role in the account team.
If multiple rules are relevant, they can be ordered to be able to achieve the maximum result for this capacity.
Another adjustment is the possibility to set up the layout of the inbox. This is set in a configuration tied to a service channel that defines which fields of a record representing a work item are shown in agent inboxes. A layout defines what the agent sees in their corresponding Workspace area.

If a work item is rejected, the agent must provide a reason, such as being in a phone call with another customer. When a rejection occurs or the job is timed out, the work item is returned back to the queue to find the next available agent. Whenever an entry is missed by an agent or is timed out, AWA automatically marks the status of the user to ‘away’ to avoid sending additional assignments to them until they are available again.
After an agent accepts a work item, all relevant information is available to them, including historical data. During fulfillment, there may be a need for additional skills to complete the request; in this case, rerouting is an option.
Skill-based routing and assignment is an advanced part of AWA. One example of its usage is when a chat is initiated from a specific location, a required language skill can automatically be added to the conversation. This means that there is no need for separate dedicated queues only to the required skill - availability and capacity should be measured to properly route this work item.
AWA Overflow Strategy is another key feature. It automatically kicks in when one of the channels becomes overloaded - a backup group of agents can be utilized to work on the items. In this instance, cases are automatically routed to secondary or tertiary support groups to help take on work. There are two major benefits that this brings: First there is no proliferation of separate queues, which offers simpler queue management. Secondly, the work item stays in the queue, which means the integrity of the queue reports and work item reports is maintained. This is a very powerful concept which few competing products can match.
Advanced Work Assignment provides dedicated reports and dashboards, which enable managers to monitor work item handling so that agents can better support customer needs.

Figure 4. Advanced Work Assignment dashboard for Operations
The helpdesk or call center manager and team leads are the most experienced people within the team and their time is critical. By utilizing this feature they can be freed up from manual assignment to focus on monitoring, coaching, and training agents, which would be a better use of their time.
From a customer standpoint, there is less wait time and improved customer satisfaction, also known as CSAT.
This article was written by Bulcsu Boros , Principal ServiceNow Consultant at GuideVision.
Subscribe to our newsletter
You have successfully subscribed to our newsletter.
Please enter your details

Please download the latest version of Microsoft Edge to experience this website.
- Customer Value
- Case Studies
- Privacy policy
- Customer value
- Case studies
Bringing { life } into your enterprise services
The Now Platform® Washington DC release is live. Watch now!
ServiceNow Community servicenow community
- English (US)
- English (UK)
- Portuguese (Brazilian)
- ServiceNow Community
- Customer Service Management
- Customer Service Management articles
- CSM: Advanced Work Assignment (AWA) || Knowledge &...
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
CSM: Advanced Work Assignment (AWA) || Knowledge & Troubleshooting Resources

- Post History
04-29-2022 09:23 PM - edited 10-16-2022 08:22 AM
- Advanced Work Assignment
- 1,681 Views
Hi friends, thanks for all your support.You are always my encouragement to write new content. Seeing the response I decided to take leap forward and start composing video tutorials. I am yet to create a hand full of them.But I am confident your subscriptions and like will be my fuel to create more feature rich content. If you feel it is worthy please subscribe my video channel below.
At any time you can click on the to got my youtube channel
ServiceNow Customer Service Management.
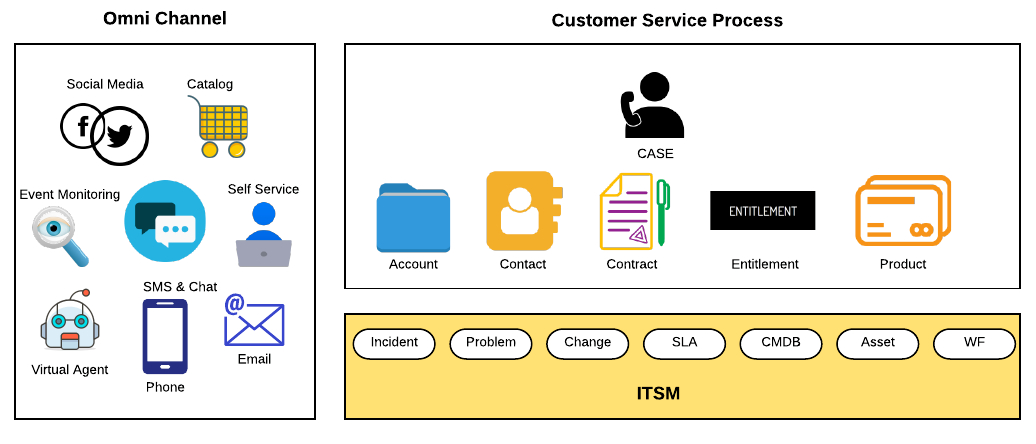
Introduction
CSM helps us to provide service and support to customer.
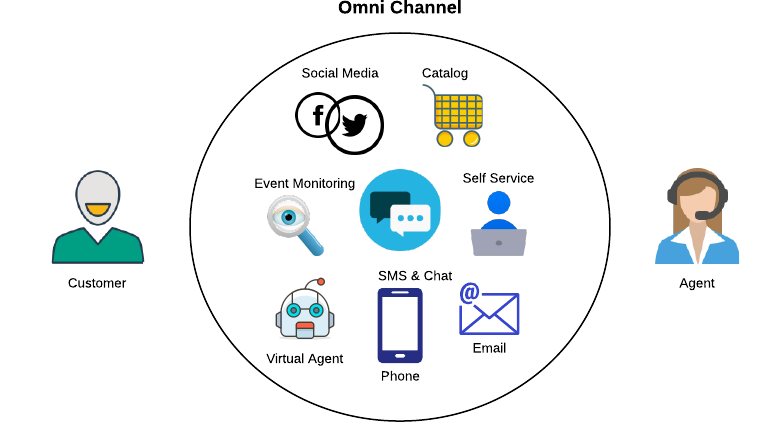
CSM application enables us to provide service and support for our external customers through communication channels such as web, email, chat, phone and social media. Customers contact our organization through this channels to seek assistance with the product or the service that they have purchased. Case Management helps organizations to effectively track and organize customer interactions. A customer/agent creates a new case to identify a customer question or an issue and to track the activities related to resolving the issue. Created cases are automatically routed to available customer service agent depending upon skill, availability and location.
.png)
High Level Architecture
Different Channel
Navigate to CSM module
.png)
Know your customer
Customer services cases store a variety of customer information such as accounts , contacts , consumers , assets , products , and service contracts .
The Customer Service Management application also stores information about account and contact relationships .
The foundation data enables agents to quickly and easily access case-related information.
Customer information includes the account and contact information for a customer or partner. Consumer information includes the name, phone number, and one or more addresses for a consumer.
A partner is a external customer that supports one or more customers. A partner account record stores information about a partner’s company.On a partner account record, the Partner field is enabled. A partner can report and manage cases on behalf of customers. A partner can also be a customer.
A consumer is a customer of a business-to-consumer (B2B) use case. A consumer record stores similar information as a contact record, such as the name, phone number, address, and email address. Consumers can have multiple addresses, one of which is the primary address.
An account is a supported external customer and the Account form stores the customer’s information, including the company name, contact names, addresses, phone numbers, and web and email addresses. An account can be a customer account, a partner account, or both.
An account can have one or more associated assets, service contracts, entitlements, and SLAs. An account can also be associated with the following entities:
- service contract
- entitlement
A contact is a user who is an employee of an account. A contact record stores information about a contact, such as the name, phone number, email and web address. An account can have multiple contacts but a contact can be associated with only one account. A contact can have one or more associated assets and service contracts. A contact can also have a user ID and can log in to the customer portal.
A service contract record stores information about the type of support that is provided to a designated company. A contract can include a company , contact and the specific assets that are covered. A contract can also include multiple service entitlements and SLAs.
7.Entitlements
An entitlement defines the type of support that a customer receives as well as the supported communication channels. An entitlement can be associated with a product, an asset, an account, or a contract.
An entitlement check is performed when a case is opened. This check takes into consideration the existing cases for the specific account, product, asset, and service contract. Entitlements can have associated workflows that drive recommended activities for a case.
Entitlements are counted on a per unit basis. The Unit field on the Service Entitlement form defines the unit type, either cases or hours.
Entitlements can also be tracked on a per unit basis. The Total Units field defines the total number of cases or hours available for this entitlement and the Remaining Units field tracks the number of units remaining. These counters are active if the Per Unit field is enabled.
Assign an asset to a customer contact who is responsible for managing that asset.
The system administrator can add a primary contact to an asset by selecting a user in the Primary Contact field on the Asset form. This field references the Contacts table and is filtered by the asset’s account.
The system administrator can also create relationships with additional contacts from the Asset Contacts related list on the Asset form.
When we create an asset contact relationship, we can select contacts from:
•The account that the asset belongs to.
•The partner of the account that the asset belongs to.
•Any contacts added to these accounts using contact relationships.
9.For Business-to-business (B2B) customers, configure these below entities
10.For Business-to-consumer (B2C) customers, configure these blow entities
Relationships
1.Bi-directional accounts
Create a relationship between two customer accounts or between a partner account and a customer account Once an account relationship record is created, it can be viewed on the Account form for either account in the Account Relationships related list.
2.Account relationship types
An account relationship is based on a defined account relationship type. Users with the system administrator role can define two types of relationships: partner-to-account and account-to-account.
3.Account relationship records
Once an account relationship type has been defined, users with the customer service manager role can use it to create relationship records between specific accounts or partners.
4.Account hierarchy
Use the account hierarchy feature to create a parent-child relationship between accounts. An account hierarchy represents the legal entity structure of the accounts and their relationships. It also represents an account’s customers, assets, and service entitlements.
Customer administrators can do the following for all of the accounts in the hierarchy:
.png)
Account hierarchy
.png)
5.Contact relationship
A contact relationship allows a contact with the customer role or customer administrator role to manage the account for which the contact relationship has been established. These contacts can view information and perform actions on behalf of the accounts, such as creating or updating cases from the customer portal.
To configure foundation data:
1.Create or import data for associated entities.
2.Assign roles to groups or to individual users.
3.Create service contracts and entitlements.
4.Create customer relationships, asset relationships, and account teams.
To create a customer account
Navigate to Customer Service > Customer > Accounts.
.png)
To create a partner account
Navigate to Customer Service > Customer > Partners.
.png)
- Fill in the fields on the Account form, as appropriate.
.png)
Create Contact
.png)
4.Enter the name of the contact’s company in the Account field.
- Select the Timezone.
- Select a Notification setting.
- Click Submit .
Create a consumer record
Consumer service agents and managers can create a consumer record from the Customer Service Management application.
.png)
4.Fill in the fields on the Primary Address tab.
A consumer can have multiple addresses but only one primary address. The primary address is stored in the Primary Address tab on the Consumer form and in the Addresses related list.
5.If desired, set any of the fields on the Preferences tab.
6.Click Submit .
The record is added to the Consumers table (csm_consumer) . The primary address is added to the Addresses related list and the Primary field is set to true.
Consumers can have multiple addresses, including one primary address.
Create contracts
.png)
Create Entitlements
1.Navigate to Customer Service > Contracts > Entitlements. You can also create an entitlement from the Entitlements related list on the Account and Contract forms.
.png)
Create Account relationship types
1.Navigate to Customer Service > Administration > Account Relationship Types.
.png)
2.Click New.
.png)
3.Fill in the fields on the Account Relationship Type form.
.png)
Account relationship records
- Navigate to Customer Service > Customer > Accounts or Partners.
- Select an account.
- From the Account Relationships related list, click New.
.png)
Create a relationship between accounts and Contact.
- In the Contact Relationships related list, click New.
- Fill in the fields on the Contact Relationship form.
.png)
Create asset contact relationships
Assign a primary contact to an asset
- Navigate to Customer Service > Products > Assets.
- Click the desired asset.
- Select a Primary Contact
.png)
Assign a contact to an asset
- Click New in the Asset Contacts related list. This displays a new Asset Contact form. The Asset field displays the selected asset and is read-only.
.png)
Enable the asset contact relationship property
.png)
Enable the Restrict Assets based on Contacts assigned to the assets property.
.png)
Case Management
The customer service case is the primary entity of the customer service application.
An agent creates a new case to identify a customer’s question or issue and to track the activities related to resolving the issue.
An agent also uses a case to track all of the communication to and from the customer, including the communication channels being used.
Case activities include any action that is taken to resolve an issue.This can include phone calls or emails, knowledge base research, conversations with subject matter experts, and dispatch requests to field service agents, as well as other activities.
From the Case form, an agent can associate and store the related information, such as the customer’s name, phone number, and company,account information,product and asset information,service contract and entitlement details, and any associated service level agreements (SLAs).
Case Management Process:
•Configure the Case form
•Create rules to route and assign customer service cases
•Assignment workbench
•Special handling notes
•Case and account escalation
•Case action status
•Automatically close customer service cases
.png)
Case Routing
Matching rules and assignment rules helps to route the cases to customer service agents.
Matching rules specify conditions that a case must meet before it can be routed to an agent.Then an assignment rule is used to route those cases to agents based on product knowledge and availability.
Matching Rules
Matching rules are based on two defined sets of conditions:
Matching rules are created using the Matching Rule form.
.png)
In the resource tab we have Matching field.
Four options are there
1.Selection Criteria
If you selected “Selection Criteria” Then you can get option Select Criteria as below
.png)
Matching criteria
.png)
The assignment workbench uses configurable matching criteria to evaluate the agents in a selected group and provide an overall ranking.
Several matching criteria are provided with the assignment workbench:
.png)
There are three types of matching criteria:
• Simple Match: creates one-to-one matching, such as matching the time zone of an agent with the time zone of a task location.
• Aggregate: uses a simple query and returns an aggregate result. For an aggregate type, select a table and create a filter, and then select an aggregate field such as the Assigned to field. This type of query returns a set of users.
• Scripted: uses a scripted query which returns a list of users.
.png)
At first create matching criteria.
Create Matching Rule and go to Resource tab and select Matching drop down as Selection criteria and selecting the desired matching criteria.
.png)
Click on New button
.png)
In the Use for field, specify how you want that matching criterion to be used:
• Ranking and display: uses the criterion to determine agent ranking and displays it in a column on the workbench.
• Display only: displays the criterion in a column on the workbench but does not use it to determine agent ranking.
• Ranking only: uses the criterion to determine agent ranking but does not display it on the workbench.
Ranking method
There are two ranking methods:
• More is better: for example, more availability is better when determining the agent ranking.
• Less is better: for example, fewer assigned cases are better when determining agent ranking.
Each matching criterion has an assigned weight. By default, the matching criteria in the Recommendation for Case Assignment matching rule have an assigned weight of 10. You can assign a higher weight to the criteria that are more important.
A threshold sets a minimum requirement for a criterion.
For example , set the threshold of the Matching Skills criterion to 3 if you want to see only those agents who have at least three of the required skills for a task .
For availability , set the threshold to the desired number of hours to display only those agents who have that minimum number of work hours available .
You can set the threshold in the Select Criteria related list on the Matching Rule form. If necessary, personalize the list and add the Threshold column.
Assignment Rules
Assignment Rules helps to automatically assign task to users and groups based on 3 different criteria
Applies to and assign to can work together to determine how cases are distributed
.png)
Scripted: When the criteria needs to be more customized
.png)
Create service level agreements
A service level agreement (SLA) is a record that specifies the time within which service must be provided.
The Customer Service Management application uses the standard ServiceNow SLA with customer service cases. An SLA can be attached to a service contract, to a company, and to a product and can be configured to start, pause, and stop based on any customer service case attributes.
Define an SLA for a customer service case
- Navigate to Customer Service > Cases > All.
- Select the desired case from the Cases list.
.png)
- Fill in the fields on the Task SLA form.
.png)
5.Click Submit.
CSM integration with Service Management
We can integrate CSM module with ITSM modules like Incident , Problem , Change , and Request Management .
This integration helps us to create Incident, Change, Problem and Request from Case and vice versa .
The integration with ITSM provides the following functionality:
•We can also create case from incident, problem, change, and request records.
•Agents can associate existing incident, problem, change, and request records with cases or remove associated records from cases.
•Customers can submit requests from the Customer Service Portal. A case is created for each request.
•Updates to records associated with a case automatically update the case work notes. (We have OOTB business rules to update the worknotes)
•Updates to cases with associated records can be used for customer communication.
•Agents and managers can view cases with Service Management-related indicators on the Customer Service dashboards.
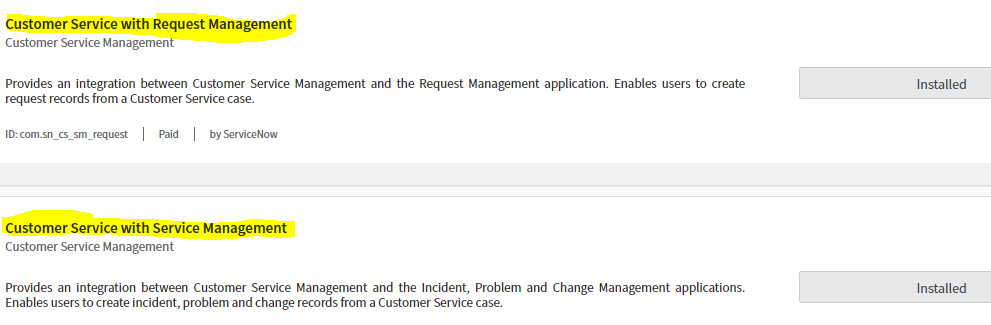
Required plugins for integration are as follows
•com.sn_cs_sm : For Incident, Problem and Change integration
Related Records
In the case form we have Related Records form section.This section includes the following fields:
•Change Request
•Caused by Change
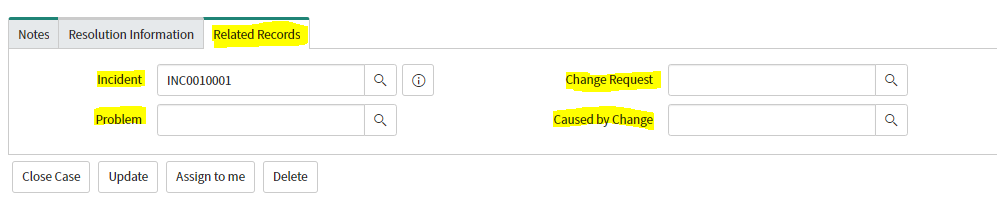
When an incident, problem, or change record is created from a case, or an existing record is associated with a case, the record number is added to the corresponding field.
Related list
In related list section of Case form we can see Incident,Change,Problem and Request related lists.
Agent can create new incident,change,Problem,request records from cases or associate existing Incident,Change,Problem and Request to cases.
When we create an Incident,Change,Problem,Request recods from cases we may want to copy the details like description,priority to the newly created incident/problem.
To do this, we can create an Display business rule that copies the parent.<fields> into the incident/problem
Below is the code:
CSM integration with Event Management
We can integrate CSM module with ITOM module like Event Management .
This integration helps us to create cases proactively from alerts either manually or through automation and track the accounts and the corresponding install base items affected by the alert.
- Navigate to System Definition > Plugins.
- Search for the plugin com.snc.proactive_cs_ops.
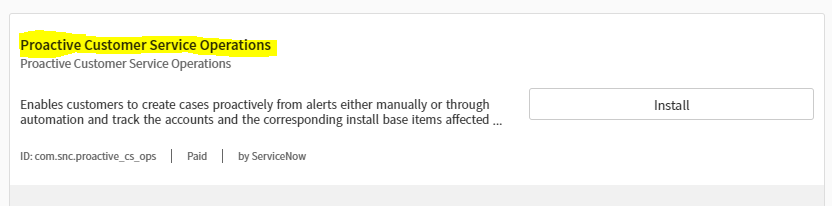
- Click Activate.
Note: Proactive Customer Service Operations is only available for customers who are licensed for the Customer Service Management application.
To activate Proactive Customer Service Operations, activate the Proactive Customer Service Operations Management plugin (com.snc.proactive_cs_ops). This plugin is not active by default.
Activating this plugin also installs the Major Issue Management, Customer Service Install Base Management, Customer Service with Service Management, Customer Service Case Action Status, and Task-Outage Relationship plugins.
Activate an alert rule to automatically create a proactive case from an alert
- Navigate to Event Management > Rules > Alert Management.
- Click Create Proactive Case.
- Select the Active check box.
- Click Update
Phone channel
External customers can reach out to customer service agents by phone. The Customer Service Management application uses both Computer Telephony Integration (CTI) and OpenFrame to provide phone support for customers.
CTI provides a way to integrate the Now Platform with telephony providers to support inbound and outbound calls.
With this integration, customer service agents can place and accept calls from customers, quickly identify customers and account information, and capture case-related information.
OpenFrame is a tool that enables CTI capability with telephony service providers. OpenFrame provides a communication frame that agents use to place and receive customer calls.
- Navigate to OpenFrame > Configurations to display the OpenFrame Configurations list.
.png)
- Fill in the fields, as appropriate
.png)
Notify provides support for SMS and voice channels on the ServiceNow platform for communicating internally with team members and externally with customers and contractors. The plug-in also provides APIs and workflow activities to achieve the above. Some customers directly make use of the APIs in their products others via products like Major Incident Management, On-Call and CTI Softphone.
Customer service chat channel
Customers can use the chat channel to communicate with a customer service agent. The chat communication channel uses the ServiceNow Connect Support feature to provide chat capability. You can also enable Virtual Agent to create or use predefined chatbot topics (conversations) for your users. The user always has the option of switching to a live agent.
The Customer Service Portal and Consumer Service Portal include a chat icon that customers can click to open a chat window and start a discussion with a customer service agent.
The chat request from the customer is either routed to a virtual agent or to an available agent with the required skill set. The agent can respond to the customer and, if necessary, create a new case or link the discussion to an existing case.
Agents must be added to the Customer Service chat support assignment group before they can receive chat requests. This assignment group is used by the Customer Service chat queue to route the chat requests.
Configure the customer service chat queue
https://www.learnnowlab.com/connect-support/
Activate Virtual Agent for CSM
Activate Virtual Agent for CSM to use the predefined Customer Service Virtual Agent topics (chatbot conversations) designed to help your customers complete common self-service tasks.
Activate the Customer Service Virtual Agent Conversations plugin (com.sn_csm.virtualagent) to access the predefined Customer Service topics.
Customer/Consumer Service Portal
The Customer / consumer Service Portal is a self-service web portal based on the ServiceNow Service Portal application.
The Customer Service Portal provides information and support for your customers.
Below is the Customer service portal home page
Agent Workspace for CSM
Agent Workspace for CSM supports the needs of agents handling customer inquiries, issues, and cases from multiple sources, including:
• Case agents, who handle cases created from the Customer or Consumer Service Portals or from inbound emails.
• Phone agents, who handle customer phone inquiries.
• Chat agents, who handle customer chat requests. Agent Workspace for CSM makes it easy for agents to efficiently manage multiple cases, accounts, customers, and consumers.
• The multi-tab interface improves agent productivity by enabling agents to easily navigate between records.
• The ribbon provides overview information in a way that quickly orients an agent to case details.
• The intuitive Case form layout minimizes scrolling by displaying case details side-by-side with the activity stream.
• Agent Assist enables agents to quickly search for information across multiple sources such as knowledge bases and community sites.
• Predictive Intelligence can provide agents with a list of similar cases and can also provide recommendations about major issues and major cases.
Agent Workspace for CSM landing pages
Landing pages provide customer service agents with an overview of their new, assigned, and high priority cases plus the cases assigned to their groups. Landing pages can also include analytics. Customer service agents can use these pages to quickly scan and access cases.
The CSM Landing Page is available for Agent Workspace for CSM. This landing page is included with the CSM Workspace plugin (com.snc.agent_workspace.csm). It includes components that display case information, plus visualizations that further break down the component data. Each visualization is connected to a data source. For example, the My High Priority Cases component includes visualizations for P1 and escalated cases. This landing page does not require a Performance Analytics license.
To add Performance Analytics information to the CSM Landing Page landing page, activate the Performance Analytics - Content Pack - Customer Service Management - Advanced plugin (com.snc.pa.customer_service_advanced). This plugin adds a section for My Organization’s Performance, which includes analytics for CSAT and New vs Closed Cases. Create landing pages for different agents and teams by cloning the CSM Landing Page and adding or modifying components and visualizations.
- Navigate to Agent Workspace > Landing Pages.
.png)
- Click the CSM Landing Page.
.png)
- Click Clone Page.
.png)
- Fill out the form.
.png)
- Configure permissions for users to access the landing page.
a. Click the UX Page Element Permissions related list.
.png)
b. Click New.
.png)
c. Select the role or group for the landing page to be visible.
.png)
d. Click Submit to save your permissions.
Configure a container: a. Click the UX Page Elements related list.
.png)
b. Click New Container or select an existing container. c. Fill out the form.
.png)
Configure a widget: a. Click New Visualization or select an existing widget.
.png)
b. Fill out the form.
.png)
Click Update to save changes to the landing page.
AWA for CSM overview
Use the ServiceNow®Advanced Work Assignment (AWA) for Customer Service Management feature to automatically assign work items to agents based on their availability, capacity, and skills. AWA for CSM pushes work to qualified agents using work item queues, routing conditions, and assignment criteria that you define. Agents see their assignments in their Agent Workspace inbox.
Work Assignment
Use the ServiceNow®Advanced Work Assignment (AWA) feature to automatically assign work items to your agents, based on their availability, capacity, and optionally, skills. AWA pushes work to qualified agents using work item queues, routing conditions, and assignment criteria that you define. Agents see their assignments in their Agent Workspace inbox.
Customers use different channels to request service, for example, chats, cases, or incidents. Requests from customers create task or interaction records that store information about these objects, called work items.
AWA automatically routes work items to queues that focus on certain types of support, using criteria (such as priority or customer status) that you provide. Queues can be defined based on need or type, for example product or critical cases. You also identify the agent groups responsible for work in the queue. AWA then applies assignment rules that you set and uses agent availability, capacity, and skills (if defined) to assign work to the most qualified agent.
Advanced Work Assignment components
Service channels A means of providing customer service. AWA offers base system channels for chats, cases, incidents, and walk-up centers. For each channel, you can set attributes such as agent capacity and utilization conditions to control the work handled in the channel.
A single piece of work to be handled by an agent from start to completion. For example, one chat or one case are objects that are routed and assigned to agents. Work item queues A queue stores a specific type of work item for a service channel. AWA admins can create queues that focus on certain types of support within the channel, such as VIP customers or critical cases. AWA routes work items to queues based on specific conditions or requirements that you define, such as customer status, or region. Groups assigned to each queue handle the incoming work items. Once work items are placed in a queue, AWA can then assign items to available agents based on assignment rules and agent availability and capacity.
Assignment groups
Agents belong to specific groups that are organized by the type of work assigned to them. You provide details about an assignment group including the name and description, manager, and group email. You can also set up roles, groups and group members, queues, and agent capacity overrides for agents in an assignment group.
Assignment rule Criteria that determines how work items are pushed to the appropriate agent within a qualified assignment group.
Agent capacity The maximum number of work items on a particular service channel that an agent may actively work on at one time.
Agent availability
States that indicate agent presence and whether the agent is available for work or is busy or offline. AWA uses the agent availability state to determine if an agent is able to receive work.
Inbox layout
A configuration tied to a service channel that defines which fields of a record representing a work item are shown in agent inboxes. A layout defines what the agent sees in Agent Workspace.
Basic process for configuring AWA
Users with the awa_admin role determine:
• What to route – Configure the base service channels to be used.
• Where to route – Define the work item queues and the routing rules, execution order, work item sort order, and strategy
• How to assign work items – Define the assignment rules that determine the work items pushed to agents
• What the agent sees – Set the inbox card layouts and presence (availability) states that agents use in their Agent Workspace inbox.
Get started with Advanced Work Assignment
- Activate the Advanced Work Assignment plugin for your instance.
.png)
Activate related AWA plugins to enable base system service channels and the Performance Analytics Solution for AWA. For example, activate the Agent Chat plugin to enable the Chat service channel and Agent Chat in Agent Workspace.
Configure the service channels that you activated.
o Create or modify an inbox layout.
o Override agent capacity as needed.
Create agent groups to which work items are assigned.
Create work item queues for your service channels.
o Define the pools of agents eligible for assignment (eligibility assignment).
o Set the sort order for work items in the queue.
Configure the work assignment rules used to push work to the appropriate agents.
Set the controls that agents use to manage their availability states and assignments in Agent Workspace.
o Create or update the presence states that agents use to indicate their availability.
o Create or update the reasons that agents use to decline work assignments.
Assignment Workbench:
Assignment Workbench enables customer service managers to assign tasks to the best agent available.
The workbench uses configurable criteria, such as skills and availability, to evaluate agents in a selected group and provide an overall ranking.Managers can view these results and use the simple UI to assign a task.
Configure the Assignment workbench
The assignment workbench configuration is stored in a matching rule that is based on the Selection criteria matching type. The default configuration uses the Recommendation for Case Assignment matching rule, which includes three of the four default matching criteria:
• Availability Today • Matching Skills • Assigned Cases
Based on these matching criteria, the workbench calculates and displays an overall rank for each agent in the group. You can modify or create matching criteria and the Recommendation for Case Assignment matching rule as needed or you can create your own configuration following these steps:
- Create one or more matching criteria.
- Create a matching rule with the Selection criteria matching type.
- Open the matching rule and add the desired matching criteria.
If you are using mandatory skills, you must replace the Matching Skills criterion in this matching rule with the Matching Skills - Mandatory Skills Support criterion to match agents with mandatory skills required for a case.
Open any case and click on find agent ion the Assigned to Field
.png)
Select the agent
.png)
- Understanding Request, RITM, Task in ServiceNow
- Steps to create a case in ServiceNow (CSM)
- Performance Analytics in 10 mins
- Event Management in 10 minutes - part1
- Event Management in 10 minutes - part2
- Custom Lookup List
- Script includes in 5 minutes
- Interactive Filter in 5 minutes
- UI Policy in 6 Minutes
- Client Side Script Versus Server Side Script in 3 minutes
- Performance Analytics
- Interactive Filter
- Configuration
- ServiceNow Scripts
- Script include
- Useful scripts
- Basic Glide Scripts
- Client Script
- Advance Glide Script
- Glide System Script
- Notification
- Core Application
- CAB Workbech
- Data Policy
- Connect Support
- Request,RITM,Task
- Service Catalogs
- Create Case From Email
/csm/-/csm/
- Event Management
- Integrations
- SSO Integration
- LDAP Integration
- SCCM Integration
- AWS Intergration
- Slack Integration
- CTI Integration
- Jira Integration
- Ebonding ServiceNow
- SOAP Integration
- IBM Netcool Integration
- VIP Mobile App Integration
- Rest Integration
- Service Portal
- Service Portal Widgets
- Interview Questions
- Send email with attachment
- Custom webapp
- Custom file attachment with field mapping
- Github Servicenow Integration
- Customer satisfaction survey
- Agent Workspace
- Advanced Script Include
- Ui page example
- Color on field label & field
- Slack integration usecase 1
- Slack integration usecase 2
- Service portal Widgets
- Spring Security Oauth2 configurations
- Springboot Testing
- Spring Basic Auth Security
- Jhipster Blueprint By Example
- Apache httpd cache
- Sso Integration
- Servicenow Discovery
- Ldap Integration
- Sccm Integration
- Aws Intergration
- Git Squash Example
- Generate Ppt From Template Java
- Servicenow slack integration
- Cti Integration
- Spring Cloud Gateway With Spring Security
- Microservice Design Pattern
- Ebonding Servicenow
- Script include in ServiceNow
- Soap Integration
- HR Service Delivery
- Useful Script ServiceNow
- Business Rules
- Basic glide scripts
- Performance analytics(PA) Interactive Filter
- Various Configurations in Performance analytics(PA)
- Performance Analytics(PA) Widgets
- Performance Analytics(PA) Indicator
- Performance Analytics(PA) Buckets
- Performance Analytics(PA) Automated Breakdown
- Vip Mobile App Integration
- Performance Analytics(PA) Scorecard
- Performance analytics(PA) Manual Breakdown
- Performance Analytics(PA) Dashboards
- User,Group & Roles
- ServiceNow interview questions
- Understanding the Request, RITM, Task
- Events in ServiceNow
- Advance glide script in ServiceNow
- CAB Workbench
- Performance analytics(PA)
- Performance Analytics(PA) Indicator source
- Glide System – Advance scripting in ServiceNow
With 9+ years of ITSM development experience,Chandrima likes to deep dive ServiceNow modules.She have extensively worked on PA,Service Portal,Event management.
University Policies
Alternative work assignments policy, 1.0 policy purpose.
The purpose of this policy is to standardize staff Alternative Work Assignments (AWAs) to promote workplace flexibility and greater work-life balance, enhance job performance, and provide best-in-class services to meet Brown’s needs.

2.0 To Whom the Policy Applies
This policy applies to all non-faculty employees in graded and ungraded staff positions, as well as all staff and faculty who approve AWAs, except where the AWAs are governed by collective bargaining agreements or in employee contracts. Bargaining unit staff should consult their collective bargaining agreement to review any flexibility provisions. If there is a conflict between the language in one of Brown’s union contracts and this AWA Policy, the union contract language shall prevail.
3.0 Policy Statement
An AWA is an agreement between the University and an employee in a staff position which includes modifications to work locations (e.g., employee’s residence), work schedules or other assignments that could differ from traditional University operating standards and practices. AWAs:
- must be in the University’s best interest and adhere to all laws;
- can vary by school/department/unit; and
- may not be suitable or available for every job type.
An AWA does not alter an employee’s employment relationship with the University or the obligation to observe all University rules, policies, and procedures. All existing terms and conditions of employment, such as job description, salary, benefits, vacation, leave and overtime, remain the same.
The employee’s manager and/or senior officer retains the discretion to decide the AWA type(s) available to staff based upon the manager-assigned Position Work Location (PWL) designated in Workday and unit operational needs. As determined and approved by the employee’s manager, AWAs may allow staff to work:
- full-time at an approved Alternative Worksite Location;
- a portion of time at an Alternative Worksite Location; or
- a Flexible Work Schedule (e.g., adjusted arrival and departure times, Compressed Workweeks).
AWAs must be documented in an AWA Agreement. Staff must:
- complete an AWA Agreement request in Workday;
- request any subsequent AWA Agreement changes in Workday; and
- receive an approved AWA Agreement prior to starting an AWA.
AWA Agreements are approved or denied by the employee’s manager and the unit’s HR Business Partner in Workday. When necessary, manager AWA approval delegation changes can be made at the discretion of the senior officer of the unit/division by contacting Workday Programs . AWA decisions may be appealed to the employee’s next level supervisor.
Employees will be required to complete a new AWA Agreement in Workday for the following reasons:
- PWL changes;
- to request a significant change in work schedule that will last beyond a duration of 60 days;
- promotions or position transfers to another unit;
- to request a different hybrid AWA type;
- to request or change a Flexible Work Schedule; and
- when an employee is approved to work remotely, and/or work at an Alternative Worksite Location outside the State of Rhode Island, and/or relocates back to the State of Rhode Island.
AWAs may be subject to periodic review by the employee’s manager and/or HR Business Partner. When operational needs require modification or cancellation of an AWA Agreement, written notice of at least 10 business days will be provided to the employee with an onsite or hybrid PWL, and written notice of at least 90 business days will be provided to an employee with a remote PWL.
Additional guidance and details on how to complete an AWA in Workday are in the AWA Job Aid.
4.0 Definitions
For the purpose of this policy, the terms below have the following definitions:
An agreement in Workday that details the specifics of an employee’s AWA, such as Alternative Worksite Location, in which the employee has attested that they will maintain University standards.
A formally designated non-University location where an employee performs some or all of their job responsibilities. An Alternative Worksite Location must be from a state where Brown is registered to do business, as determined by the University. Alternative Worksite Locations cannot be outside the United States due to significant variation in labor laws, benefits availability, tax consequences, and other considerations.
An arrangement where a traditional 37.5-hour, five-day workweek is lessened to fewer than five days of work.
An alternative schedule that allows an employee to work outside traditional hours based on employee needs within set parameters approved by their manager. Under a flex schedule, an employee might be required to work a standard number of core hours within a specified period, allowing the employee greater flexibility in starting and ending times. Examples include: adjusted arrival and departure times and Compressed Workweeks.
The employee’s assigned manager in Workday.
Indicates the location where the position’s work will be performed. PWLs are determined by the manager, in consultation with UHR, taking into consideration numerous factors, including specific job duties, the nature of the work performed, operation and business requirements, and impact on the department, and are not subject to review or appeal by the employee. The three types of PWLs are as follows:
- On-site: Job duties cannot be performed remotely and are required to be performed on-site at all times during the year.
- Hybrid: Job duties can be performed for part of the regular workweek or month, on a regular basis, from an Alternative Worksite Location. As a minimum threshold, an employee must work on average 20% of their work time onsite (on average 1 on-site workday a week or 4 on-site workdays a month), throughout the course of the year.
- Remote: All job duties can be performed remotely at an Alternative Worksite Location (e.g., employee’s residence) without disruption to business operations. The position may be required to work on-site in exceptional circumstances for a limited duration, such as for new hire orientation, on-site employee meetings/retreats, and/or critical/emergency situations based upon unit operational needs.
A position may be assigned more than one PWL (i.e., hybrid and remote) based upon position responsibilities and operational needs of the unit, but an employee can only have one AWA based upon their PWL designation(s).
5.0 Responsibilities
All individuals to whom this policy applies are responsible for becoming familiar with and following this policy. University supervisors are responsible for promoting the understanding of this policy and for taking appropriate steps to help ensure and enforce compliance with it.
In addition to responsibilities already assigned in this policy, the following offices/employees will accomplish additional actions.
HR Business Partner: Review and serve as the final approver of AWA Agreements in Workday.
Manager: Make PWL decisions for their staff positions, and review and approve AWA Agreements.
Senior Officer: Retain leadership authority and discretion to determine the PWL(s) and AWA type(s) available to staff within a unit/division, based upon position responsibilities and/or unit operational needs.
UHR: Review and approve remote PWLs. Determine AWA criteria, standards, and required procedures.
6.0 Consequences for Violating this Policy
Failure to comply with this and related policies is subject to disciplinary action, up to and including suspension without pay, or termination of employment or association with the University, in accordance with applicable disciplinary procedures.
7.0 Related Information
This policy is not a legal document. This policy does not confer a term of employment, nor is the language intended to establish a contract of employment, express or implied, between any employee and Brown University. The University reserves the right to change, amend or terminate any of its policies and supporting documents at any time for any reason.
Brown University is a community in which employees are encouraged to share workplace concerns with university leadership. Additionally, Brown’s Anonymous Reporting Hotline allows anonymous and confidential reporting on matters of concern online or by phone (877-318-9184).
The following information complements and supplements this document. The information is intended to help explain this policy and is not an all-inclusive list of policies, procedures, laws, and requirements.
7.1 Related Policies:
- Conflict of Interest and Commitment Policy
- Drug-Free Workplace Policy
- Employment Accommodations for Persons with Disabilities Policy
- Essential Positions Policy
- University Code of Conduct
- Work Schedules Policy
- Alternative Work Assignment Expense Reimbursement Policy
7.2 Related Procedures:
- AWA Job Aid
7.3 Related Forms: N/A
7.4 frequently asked questions: n/a, 7.5 other related information: n/a, policy owner and contact(s), policy owner: vice president for human resources, policy approved by: executive vice president for finance and administration, contact information:, policy history, policy issue date: january 30, 2019, policy effective date: june 30, 2023, policy update/review summary:.
Previous policy versions superseded by this policy:
- Alternative Work Assignments Policy, Effective Date: April 5, 2022
- Alternative Work Assignments Policy, Effective Date: June 14, 2021
- Alternative Work Assignments Policy, Effective Date: June 4, 2021
- Alternative Work Assignments Policy, Effective Date: April 23, 2020, Last Reviewed: May 8, 2020
- Alternative Work Arrangements (20.053), Revision Date: January 30, 2019
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Role assignment policies in Exchange Online
- 15 contributors
A role assignment policy is a collection of one or more end-user roles that enable users to manage their mailbox settings and distribution groups in Exchange Online. End-users roles are part of the role based access control (RBAC) permissions model in Exchange Online. You can assign different role assignment policies to different users to allow or prevent specific self-management features in Exchange Online. For more information, see Role assignment policies .
In Exchange Online, a default role assignment policy named Default Role Assignment Policy is specified by the mailbox plan that's assigned to users when their account is licensed. For more information about mailbox plans, see Mailbox plans in Exchange Online .
User roles and Outlook Web App policies are now available in Exchange admin center.
Role assignment policies are how end-user roles (as opposed to management roles) are assigned to users in Exchange Online. There are several ways you can use role assignment policies to assign permissions to users:
New users :
Change the end-user roles that are assigned to the default role assignment policy.
Create a custom role assignment policy and set it as the default. Note that this method only affects mailboxes that you create without specifying a role assignment policy or assigning a license (the license specifies the mailbox plan, which specifies the role assignment policy).
Specify a custom role assignment policy in the mailbox plan. For more information, see Use Exchange Online PowerShell to modify mailbox plans .
Existing users :
Assign a different license to the user. This will apply the settings of the different mailbox plan, which specifies the role assignment policy to apply.
Manually assign a custom role assignment policy to mailboxes.
The available end-user roles that you can assign to mailbox plans are described in the following table:
* This feature isn't available in all regions or organizations.
What do you need to know before you begin?
Estimated time to complete each procedure: less than 5 minutes.
The procedures in this topic require the Role Management RBAC role in Exchange Online. Typically, you get this permission via membership in the Organization Management role group (the Microsoft 365 or Office 365 Global administrator role). For more information, see Manage role groups in Exchange Online .
To open the Exchange admin center (EAC), see Exchange admin center in Exchange Online . To connect to Exchange Online PowerShell, see Connect to Exchange Online PowerShell .
Changes to permissions take effect after the user logs out and logs in again.
View roles assigned to a role assignment policy
Use the eac to view roles assigned to a role assignment policy.
In the EAC, click Roles > Admin roles . All of the role groups in your organization are listed here.
Select a role group. The details pane shows the Name , Description , and add the Permissions of the role group.
Use Exchange Online PowerShell to view roles assigned to a role assignment policy
To view the roles assigned to a role assignment policy, use the following syntax:
This example returns the roles that are assigned to the policy named Default Role Assignment Policy.
For detailed syntax and parameter information, see Get-ManagementRoleAssignment .
Note : To return a list of all available end-user roles, run the following command:
Add or remove roles from a role assignment policy
Use the eac to add or remove roles from a role assignment policy.
In the policy properties window that opens, do one of the following steps:
To add a role, select the check box next to the role.
To remove a role that's already assigned, clear the check box.
If you select a check box for a role that has child roles, the check boxes for the child roles are also selected. If you clear the check box of the parent role, the check boxes for the child roles are also cleared. You can select a child role by clearing the check box of the parent role and then selecting the individual child role.
When you're finished, click Save .
Use Exchange Online PowerShell to add roles to a role assignment policy
Adding a role to a role assignment policy creates a new role assignment with a unique name that's a combination of the names of the role and the role assignment policy.
To add roles to a role assignment policy, use the following syntax:
This example adds the role MyMailboxDelegation to the role assignment policy named Default Role Assignment Policy.
For detailed syntax and parameter information, see New-ManagementRoleAssignment .
Use Exchange Online PowerShell to remove roles from a role assignment policy
Use the procedure from the Use Exchange Online PowerShell to view roles assigned to a role assignment policy section earlier in this topic to find the name of the role assignment for the role that you want to remove (it's a combination of the names of the role and the role assignment policy).
To remove the role from the role assignment policy, use this syntax:
This example removes the MyDistributionGroups role from the role assignment policy named Default Role Assignment Policy.
For detailed syntax and parameter information, see Remove-ManagementRoleAssignment .
Create role assignment policies
Use the eac to create role assignment policies.
In the EAC, go to Roles > Admin roles and then click Add role group .
In the Add role group window, click Set up the basics section, configure the following settings and click Next :
Name : Enter a unique name for the role group.
Description : Enter an optional description for the role group.
Select the roles that you want to assign to the policy.
In the Add permissions section, select the roles and click Next . Roles define the scope of the tasks that the members assigned to this role group have permission to manage.
In the Assign admins section, select the users to assign to this role group and click Next . They'll have permissions to manage the roles that you assigned.
In the Review role group and finish section, verify all the details, and then click Add role group .
Click Done .
Use Exchange Online PowerShell to create role assignment policies
To create a role assignment policy, use the following syntax:
This example creates a new role assignment policy named Contoso Contractors that include the specified end-user roles.
For detailed syntax and parameter information, see New-RoleAssignmentPolicy .
Modify role assignment policies
You can use the EAC or Exchange PowerShell to Add or remove roles from a role assignment policy .
You can only use Exchange Online PowerShell to specify the default role assignment policy that's applied to new mailboxes that aren't assigned a license or a role assignment policy when they're created.
Otherwise, all you can do in the EAC or Exchange Online PowerShell is modify the name and description of the role assignment policy.
Use Exchange Online PowerShell to specify the default role assignment policy
To specify the default role assignment policy, use the following syntax:
This example configures Contoso Users as the default role assignment policy.
Note : The IsDefault switch is also available on the New-RoleAssignmentPolicy cmdlets.
For detailed syntax and parameter information, see Set-RoleAssignmentPolicy .
Remove role assignment policies
You can't remove the role assignment policy that's currently specified as the default. You first need to specify another role assignment policy as the default before you can delete the policy.
You can't remove a role assignment policy that's assigned to mailboxes. Use the procedures described in the Use Exchange Online PowerShell to modify role assignment policy assignments on mailboxes section to replace the role assignment policy that's assigned to mailboxes.
Use the EAC to remove role assignment policies
In the EAC, go to Roles > Admin roles .
Select the role group and click Delete .
Click Confirm in the confirmation window.
Use Exchange Online PowerShell to remove role assignment policies
To remove a role assignment policy, use the following syntax:
This example removes the role assignment policy named Contoso Managers.
For detailed syntax and parameter information, see Remove-RoleAssignmentPolicy .
View role assignment policy assignments on mailboxes
Use the eac to view role assignment policy assignments on mailboxes.
In the mailbox properties window that opens, click Mailbox features . The role assignment policy is shown in the Role assignment policy field.
Use Exchange Online PowerShell to view role assignment policy assignments on mailboxes
To see the role assignment policy assignment on a specific mailbox, use the following syntax:
This example returns the role assignment policy for the mailbox named Pedro Pizarro.
To return all mailboxes that have a specific role assignment policy assigned, use the following syntax:
This example returns all mailboxes that have the role assignment policy named Contoso Managers assigned.
Modify role assignment policy assignments on mailboxes
A mailbox can have only one role assignment policy assigned. The role assignment policy that you assign to the mailbox will replace the existing role assignment policy that's assigned.
Use the EAC to modify role assignment policy assignments on mailboxes
In the EAC, click Recipients > Mailboxes , and do one of the following steps:
Multiple mailboxes : Select multiple mailboxes of the same type (for example, User ) by selecting a mailbox, holding down the Shift key, and select another mailbox farther down in the list or by holding down the Ctrl key as you select each mailbox. In the details pane (that's now titled Bulk Edit ): click More options > click Update . In the Role Assignment Policy section, select the role assignment policy in the window that appears > click Save .
Use Exchange Online PowerShell to modify role assignment policy assignments on mailboxes
To change the role assignment policy assignment on a specific mailbox, use this syntax:
This example applies the role assignment policy named Contoso Managers to the mailbox named Pedro Pizarro.
To change the assignment for all mailboxes that have a specific role assignment policy assigned, use the following syntax:
This example changes the role assignment policy from Default Role Assignment Policy to Contoso Staff for all mailboxes that currently have Default Role Assignment Policy assigned.
Additional resources

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Advanced Work Assignment (AWA) was introduced Loading... Skip to page content Skip to chat. Skip to page content Skip to chat. Unsure where to start when troubleshooting Advanced Work Assignment? This article provides information about AWA architecture that may help resolve your issue.
This article covers how to associate skills to task records so that they will be considered in Advanced Work Assignment. Procedure 1) Setup an AWA queue with an assignment rule per our docs and check the
This article will brief on how to troubleshoot Advanced Work Assignment(AWA) assignment issue? especially for round-robin assignment scenario. Skip to page content Skip to chat. How to troubleshoot AWA round robin assignment issue - Support and Troubleshooting > Knowledge Base > Login here.
AWA then applies assignment rules that you set and uses agent availability, capacity, and skills (if defined) to assign work to the most qualified agent. Advanced Work Assignment components Service channels; A means of providing customer service. AWA offers base system channels for chats, cases, incidents, and walk-up centers.
For the most benefit, we recommend watching the Agent Chat & Advanced Work Assignment (AWA) Workshop playlist in order: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list...
Advanced Work Assignment lets you automatically assign work items to your agents, based on their availability, capacity, and optionally, skills. AWA pushes w...
Then, AWA applies pre-set assignment rules to assign work to the most qualified person. Components of Advanced Work Assignment. Work Items are defined as any type of single piece of work that needs to be handled by an agent. For example, one case or one chat is a work item or object that gets routed and assigned to an agent. ...
Victor Chen and Eliza Orchard show how to use Advanced Work Assignment to route your users to agents with the right set of skills to resolve their issues. T...
AWA then applies the assignment rules that you have set and uses agent availability, capacity, skills and affinity to assign work to the most qualified agent. In this way, agents have an assigned ...
AWA routes work items to queues based on specific conditions or requirements that you define, such as customer status or region. Groups assigned to each queue then handle the incoming work items. Once work items are placed in a queue, AWA can assign items to available agents based on assignment rules, agent availability, and capacity.
AWA then applies assignment rules that you set and use agent availability, capacity, and skills (if defined) to assign work to the most qualified agent. Advanced Work Assignment components. Service channels Work items Work item queues Assignment groups Assignment rule Agent capacity
This article details the steps to make use of Advanced Work Assignment to route work items to agents in Agent Workspace based on the needed skills. For example, if a work item requires the language skill
Therefore I created a new article Platform: Advanced Work Assignment (AWA) || Knowledge & Troubleshooting Resources. Please refer to that article for future updates. Advanced Work Assignment. Community-Pasted-Attachment-1651283805553.png. 127 KB.
In this session, we will introduce you to the latest in our ServiceNow platform innovations for routing and assigning work. Advanced Work Assignment enables ...
Assignment Group = Help Desk (this was put in place to attempt to prevent the items from re-routing via AWA once the incident is reassigned, but is not working) Queue: Active and has no conditions Assignment Rule: Active, no conditions. Assigns immediately with no wait. Assignment Eligibility: Linked to the Help Desk assignment group
AWA then applies assignment rules that you set and uses agent availability, capacity, and skills (if defined) to assign work to the most qualified agent. Advanced Work Assignment components. Service channels A means of providing customer service. AWA offers base system channels for chats, cases, incidents, and walk-up centers.
An AWA is an agreement between the University and an employee in a staff position which includes modifications to work locations (e.g., employee's residence), work schedules or other assignments that could differ from traditional University operating standards and practices. AWAs: must be in the University's best interest and adhere to all laws; ...
In AWA, in an assignment rule if you check "Reassign on timeout" and uncheck "allow agents to reject", chat is not reoffered to those agents it already offered the work item.
An Alternative Work Assignment (AWA) does not alter an employee's employment relationship with the University or the obligation to observe all University rules, policies and procedures. All existing terms and conditions of employment, such as job description, salary, benefits, vacation, leave and overtime, remain the same.
This is an episode within the Agent Chat & Advanced Work Assignment (AWA) Workshop Playlist. We recommend viewing the entire playlist to gain a comprehensive...
A role assignment policy is a collection of one or more end-user roles that enable users to manage their mailbox settings and distribution groups in Exchange Online. End-users roles are part of the role based access control (RBAC) permissions model in Exchange Online. You can assign different role assignment policies to different users to allow ...
The first step to configure the AWA is to create a service channel and Queue and based on the routing conditions the incidents will be routed to the available agents.
Technical Consultant Manan Bhatt walks us through ServiceNow® Advanced Work Assignment (AWA) Admin Experience in the ServiceNow Utah Release.Explore, impleme...