Quantitative Research
- Reference work entry
- First Online: 13 January 2019
- Cite this reference work entry

- Leigh A. Wilson 2 , 3
4195 Accesses
4 Citations
Quantitative research methods are concerned with the planning, design, and implementation of strategies to collect and analyze data. Descartes, the seventeenth-century philosopher, suggested that how the results are achieved is often more important than the results themselves, as the journey taken along the research path is a journey of discovery. High-quality quantitative research is characterized by the attention given to the methods and the reliability of the tools used to collect the data. The ability to critique research in a systematic way is an essential component of a health professional’s role in order to deliver high quality, evidence-based healthcare. This chapter is intended to provide a simple overview of the way new researchers and health practitioners can understand and employ quantitative methods. The chapter offers practical, realistic guidance in a learner-friendly way and uses a logical sequence to understand the process of hypothesis development, study design, data collection and handling, and finally data analysis and interpretation.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.

Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Babbie ER. The practice of social research. 14th ed. Belmont: Wadsworth Cengage; 2016.
Google Scholar
Descartes. Cited in Halverston, W. (1976). In: A concise introduction to philosophy, 3rd ed. New York: Random House; 1637.
Doll R, Hill AB. The mortality of doctors in relation to their smoking habits. BMJ. 1954;328(7455):1529–33. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.328.7455.1529 .
Article Google Scholar
Liamputtong P. Research methods in health: foundations for evidence-based practice. 3rd ed. Melbourne: Oxford University Press; 2017.
McNabb DE. Research methods in public administration and nonprofit management: quantitative and qualitative approaches. 2nd ed. New York: Armonk; 2007.
Merriam-Webster. Dictionary. http://www.merriam-webster.com . Accessed 20th December 2017.
Olesen Larsen P, von Ins M. The rate of growth in scientific publication and the decline in coverage provided by Science Citation Index. Scientometrics. 2010;84(3):575–603.
Pannucci CJ, Wilkins EG. Identifying and avoiding bias in research. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010;126(2):619–25. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181de24bc .
Petrie A, Sabin C. Medical statistics at a glance. 2nd ed. London: Blackwell Publishing; 2005.
Portney LG, Watkins MP. Foundations of clinical research: applications to practice. 3rd ed. New Jersey: Pearson Publishing; 2009.
Sheehan J. Aspects of research methodology. Nurse Educ Today. 1986;6:193–203.
Wilson LA, Black DA. Health, science research and research methods. Sydney: McGraw Hill; 2013.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Science and Health, Western Sydney University, Penrith, NSW, Australia
Leigh A. Wilson
Faculty of Health Science, Discipline of Behavioural and Social Sciences in Health, University of Sydney, Lidcombe, NSW, Australia
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Leigh A. Wilson .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Pranee Liamputtong
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Wilson, L.A. (2019). Quantitative Research. In: Liamputtong, P. (eds) Handbook of Research Methods in Health Social Sciences. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5251-4_54
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5251-4_54
Published : 13 January 2019
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-10-5250-7
Online ISBN : 978-981-10-5251-4
eBook Packages : Social Sciences Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
Share this entry
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

13 Pros and Cons of Quantitative Research Methods
Quantitative research utilizes mathematical, statistical, and computational tools to derive results. This structure creates a conclusiveness to the purposes being studied as it quantifies problems to understand how prevalent they are.
It is through this process that the research creates a projectable result which applies to the larger general population.
Instead of providing a subjective overview like qualitative research offers, quantitative research identifies structured cause-and-effect relationships. Once the problem is identified by those involved in the study, the factors associated with the issue become possible to identify as well. Experiments and surveys are the primary tools of this research method to create specific results, even when independent or interdependent factors are present.
These are the quantitative research pros and cons to consider.
List of the Pros of Quantitative Research
1. Data collection occurs rapidly with quantitative research. Because the data points of quantitative research involve surveys, experiments, and real-time gathering, there are few delays in the collection of materials to examine. That means the information under study can be analyzed very quickly when compared to other research methods. The need to separate systems or identify variables is not as prevalent with this option either.
2. The samples of quantitative research are randomized. Quantitative research uses a randomized process to collect information, preventing bias from entering into the data. This randomness creates an additional advantage in the fact that the information supplied through this research can then be statistically applied to the rest of the population group which is under study. Although there is the possibility that some demographics could be left out despite randomization to create errors when the research is applied to all, the results of this research type make it possible to glean relevant data in a fraction of the time that other methods require.
3. It offers reliable and repeatable information. Quantitative research validates itself by offering consistent results when the same data points are examined under randomized conditions. Although you may receive different percentages or slight variances in other results, repetitive information creates the foundation for certainty in future planning processes. Businesses can tailor their messages or programs based on these results to meet specific needs in their community. The statistics become a reliable resource which offer confidence to the decision-making process.
4. You can generalize your findings with quantitative research. The issue with other research types is that there is no generalization effect possible with the data points they gather. Quantitative information may offer an overview instead of specificity when looking at target groups, but that also makes it possible to identify core subjects, needs, or wants. Every finding developed through this method can go beyond the participant group to the overall demographic being looked at with this work. That makes it possible to identify trouble areas before difficulties have a chance to start.
5. The research is anonymous. Researchers often use quantitative data when looking at sensitive topics because of the anonymity involved. People are not required to identify themselves with specificity in the data collected. Even if surveys or interviews are distributed to each individual, their personal information does not make it to the form. This setup reduces the risk of false results because some research participants are ashamed or disturbed about the subject discussions which involve them.
6. You can perform the research remotely. Quantitative research does not require the participants to report to a specific location to collect the data. You can speak with individuals on the phone, conduct surveys online, or use other remote methods that allow for information to move from one party to the other. Although the number of questions you ask or their difficulty can influence how many people choose to participate, the only real cost factor to the participants involves their time. That can make this option a lot cheaper than other methods.
7. Information from a larger sample is used with quantitative research. Qualitative research must use small sample sizes because it requires in-depth data points to be collected by the researchers. This creates a time-consuming resource, reducing the number of people involved. The structure of quantitative research allows for broader studies to take place, which enables better accuracy when attempting to create generalizations about the subject matter involved. There are fewer variables which can skew the results too because you’re dealing with close-ended information instead of open-ended questions.
List of the Cons of Quantitative Research
1. You cannot follow-up on any answers in quantitative research. Quantitative research offers an important limit: you cannot go back to participants after they’ve filled out a survey if there are more questions to ask. There is a limited chance to probe the answers offered in the research, which creates fewer data points to examine when compared to other methods. There is still the advantage of anonymity, but if a survey offers inconclusive or questionable results, there is no way to verify the validity of the data. If enough participants turn in similar answers, it could skew the data in a way that does not apply to the general population.
2. The characteristics of the participants may not apply to the general population. There is always a risk that the research collected using the quantitative method may not apply to the general population. It is easy to draw false correlations because the information seems to come from random sources. Despite the efforts to prevent bias, the characteristics of any randomized sample are not guaranteed to apply to everyone. That means the only certainty offered using this method is that the data applies to those who choose to participate.
3. You cannot determine if answers are true or not. Researchers using the quantitative method must operate on the assumption that all the answers provided to them through surveys, testing, and experimentation are based on a foundation of truth. There are no face-to-face contacts with this method, which means interviewers or researchers are unable to gauge the truthfulness or authenticity of each result.
A 2011 study published by Psychology Today looked at how often people lie in their daily lives. Participants were asked to talk about the number of lies they told in the past 24 hours. 40% of the sample group reported telling a lie, with the median being 1.65 lies told per day. Over 22% of the lies were told by just 1% of the sample. What would happen if the random sampling came from this 1% group?
4. There is a cost factor to consider with quantitative research. All research involves cost. There’s no getting around this fact. When looking at the price of experiments and research within the quantitative method, a single result mist cost more than $100,000. Even conducting a focus group is costly, with just four groups of government or business participants requiring up to $60,000 for the work to be done. Most of the cost involves the target audiences you want to survey, what the objects happen to be, and if you can do the work online or over the phone.
5. You do not gain access to specific feedback details. Let’s say that you wanted to conduct quantitative research on a new toothpaste that you want to take to the market. This method allows you to explore a specific hypothesis (i.e., this toothpaste does a better job of cleaning teeth than this other product). You can use the statistics to create generalizations (i.e., 70% of people say this toothpaste cleans better, which means that is your potential customer base). What you don’t receive are specific feedback details that can help you refine the product. If no one likes the toothpaste because it tastes like how a skunk smells, that 70% who say it cleans better still won’t purchase the product.
6. It creates the potential for an unnatural environment. When carrying out quantitative research, the efforts are sometimes carried out in environments which are unnatural to the group. When this disadvantage occurs, the results will often differ when compared to what would be discovered with real-world examples. That means researchers can still manipulate the results, even with randomized participants, because of the work within an environment which is conducive to the answers which they want to receive through this method.
These quantitative research pros and cons take a look at the value of the information collected vs. its authenticity and cost to collect. It is cheaper than other research methods, but with its limitations, this option is not always the best choice to make when looking for specific data points before making a critical decision.
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research Methods & Data Analysis
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
What is the difference between quantitative and qualitative?
The main difference between quantitative and qualitative research is the type of data they collect and analyze.
Quantitative research collects numerical data and analyzes it using statistical methods. The aim is to produce objective, empirical data that can be measured and expressed in numerical terms. Quantitative research is often used to test hypotheses, identify patterns, and make predictions.
Qualitative research , on the other hand, collects non-numerical data such as words, images, and sounds. The focus is on exploring subjective experiences, opinions, and attitudes, often through observation and interviews.
Qualitative research aims to produce rich and detailed descriptions of the phenomenon being studied, and to uncover new insights and meanings.
Quantitative data is information about quantities, and therefore numbers, and qualitative data is descriptive, and regards phenomenon which can be observed but not measured, such as language.
What Is Qualitative Research?
Qualitative research is the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting non-numerical data, such as language. Qualitative research can be used to understand how an individual subjectively perceives and gives meaning to their social reality.
Qualitative data is non-numerical data, such as text, video, photographs, or audio recordings. This type of data can be collected using diary accounts or in-depth interviews and analyzed using grounded theory or thematic analysis.
Qualitative research is multimethod in focus, involving an interpretive, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them. Denzin and Lincoln (1994, p. 2)
Interest in qualitative data came about as the result of the dissatisfaction of some psychologists (e.g., Carl Rogers) with the scientific study of psychologists such as behaviorists (e.g., Skinner ).
Since psychologists study people, the traditional approach to science is not seen as an appropriate way of carrying out research since it fails to capture the totality of human experience and the essence of being human. Exploring participants’ experiences is known as a phenomenological approach (re: Humanism ).
Qualitative research is primarily concerned with meaning, subjectivity, and lived experience. The goal is to understand the quality and texture of people’s experiences, how they make sense of them, and the implications for their lives.
Qualitative research aims to understand the social reality of individuals, groups, and cultures as nearly as possible as participants feel or live it. Thus, people and groups are studied in their natural setting.
Some examples of qualitative research questions are provided, such as what an experience feels like, how people talk about something, how they make sense of an experience, and how events unfold for people.
Research following a qualitative approach is exploratory and seeks to explain ‘how’ and ‘why’ a particular phenomenon, or behavior, operates as it does in a particular context. It can be used to generate hypotheses and theories from the data.
Qualitative Methods
There are different types of qualitative research methods, including diary accounts, in-depth interviews , documents, focus groups , case study research , and ethnography.
The results of qualitative methods provide a deep understanding of how people perceive their social realities and in consequence, how they act within the social world.
The researcher has several methods for collecting empirical materials, ranging from the interview to direct observation, to the analysis of artifacts, documents, and cultural records, to the use of visual materials or personal experience. Denzin and Lincoln (1994, p. 14)
Here are some examples of qualitative data:
Interview transcripts : Verbatim records of what participants said during an interview or focus group. They allow researchers to identify common themes and patterns, and draw conclusions based on the data. Interview transcripts can also be useful in providing direct quotes and examples to support research findings.
Observations : The researcher typically takes detailed notes on what they observe, including any contextual information, nonverbal cues, or other relevant details. The resulting observational data can be analyzed to gain insights into social phenomena, such as human behavior, social interactions, and cultural practices.
Unstructured interviews : generate qualitative data through the use of open questions. This allows the respondent to talk in some depth, choosing their own words. This helps the researcher develop a real sense of a person’s understanding of a situation.
Diaries or journals : Written accounts of personal experiences or reflections.
Notice that qualitative data could be much more than just words or text. Photographs, videos, sound recordings, and so on, can be considered qualitative data. Visual data can be used to understand behaviors, environments, and social interactions.
Qualitative Data Analysis
Qualitative research is endlessly creative and interpretive. The researcher does not just leave the field with mountains of empirical data and then easily write up his or her findings.
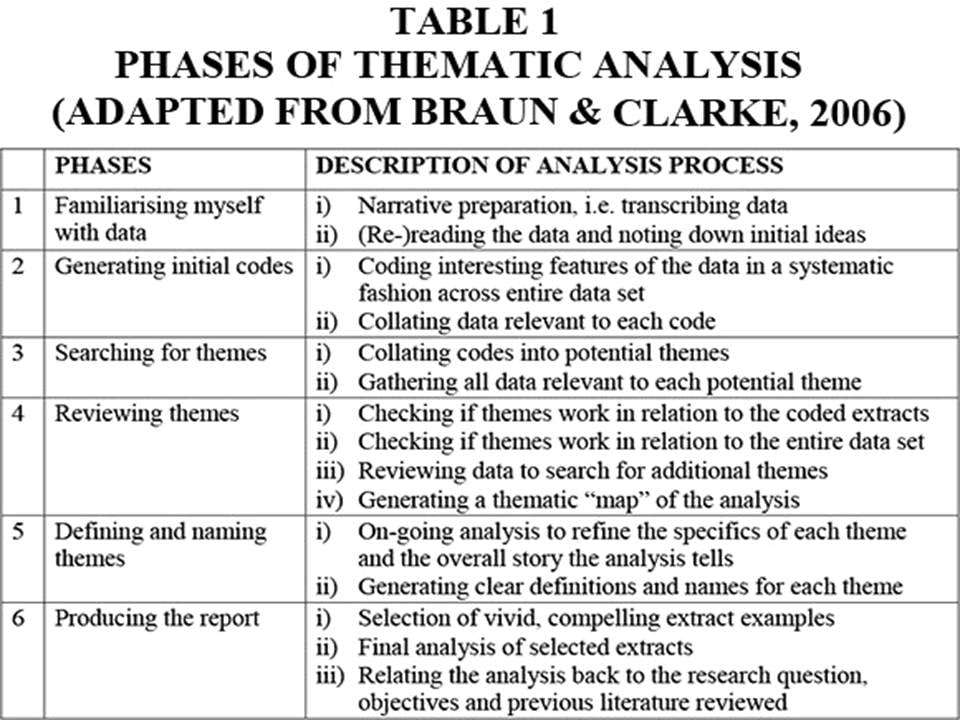
Qualitative interpretations are constructed, and various techniques can be used to make sense of the data, such as content analysis, grounded theory (Glaser & Strauss, 1967), thematic analysis (Braun & Clarke, 2006), or discourse analysis.
For example, thematic analysis is a qualitative approach that involves identifying implicit or explicit ideas within the data. Themes will often emerge once the data has been coded.
Key Features
- Events can be understood adequately only if they are seen in context. Therefore, a qualitative researcher immerses her/himself in the field, in natural surroundings. The contexts of inquiry are not contrived; they are natural. Nothing is predefined or taken for granted.
- Qualitative researchers want those who are studied to speak for themselves, to provide their perspectives in words and other actions. Therefore, qualitative research is an interactive process in which the persons studied teach the researcher about their lives.
- The qualitative researcher is an integral part of the data; without the active participation of the researcher, no data exists.
- The study’s design evolves during the research and can be adjusted or changed as it progresses. For the qualitative researcher, there is no single reality. It is subjective and exists only in reference to the observer.
- The theory is data-driven and emerges as part of the research process, evolving from the data as they are collected.
Limitations of Qualitative Research
- Because of the time and costs involved, qualitative designs do not generally draw samples from large-scale data sets.
- The problem of adequate validity or reliability is a major criticism. Because of the subjective nature of qualitative data and its origin in single contexts, it is difficult to apply conventional standards of reliability and validity. For example, because of the central role played by the researcher in the generation of data, it is not possible to replicate qualitative studies.
- Also, contexts, situations, events, conditions, and interactions cannot be replicated to any extent, nor can generalizations be made to a wider context than the one studied with confidence.
- The time required for data collection, analysis, and interpretation is lengthy. Analysis of qualitative data is difficult, and expert knowledge of an area is necessary to interpret qualitative data. Great care must be taken when doing so, for example, looking for mental illness symptoms.
Advantages of Qualitative Research
- Because of close researcher involvement, the researcher gains an insider’s view of the field. This allows the researcher to find issues that are often missed (such as subtleties and complexities) by the scientific, more positivistic inquiries.
- Qualitative descriptions can be important in suggesting possible relationships, causes, effects, and dynamic processes.
- Qualitative analysis allows for ambiguities/contradictions in the data, which reflect social reality (Denscombe, 2010).
- Qualitative research uses a descriptive, narrative style; this research might be of particular benefit to the practitioner as she or he could turn to qualitative reports to examine forms of knowledge that might otherwise be unavailable, thereby gaining new insight.
What Is Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research involves the process of objectively collecting and analyzing numerical data to describe, predict, or control variables of interest.
The goals of quantitative research are to test causal relationships between variables , make predictions, and generalize results to wider populations.
Quantitative researchers aim to establish general laws of behavior and phenomenon across different settings/contexts. Research is used to test a theory and ultimately support or reject it.
Quantitative Methods
Experiments typically yield quantitative data, as they are concerned with measuring things. However, other research methods, such as controlled observations and questionnaires , can produce both quantitative information.
For example, a rating scale or closed questions on a questionnaire would generate quantitative data as these produce either numerical data or data that can be put into categories (e.g., “yes,” “no” answers).
Experimental methods limit how research participants react to and express appropriate social behavior.
Findings are, therefore, likely to be context-bound and simply a reflection of the assumptions that the researcher brings to the investigation.
There are numerous examples of quantitative data in psychological research, including mental health. Here are a few examples:
Another example is the Experience in Close Relationships Scale (ECR), a self-report questionnaire widely used to assess adult attachment styles .
The ECR provides quantitative data that can be used to assess attachment styles and predict relationship outcomes.
Neuroimaging data : Neuroimaging techniques, such as MRI and fMRI, provide quantitative data on brain structure and function.
This data can be analyzed to identify brain regions involved in specific mental processes or disorders.
For example, the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) is a clinician-administered questionnaire widely used to assess the severity of depressive symptoms in individuals.
The BDI consists of 21 questions, each scored on a scale of 0 to 3, with higher scores indicating more severe depressive symptoms.
Quantitative Data Analysis
Statistics help us turn quantitative data into useful information to help with decision-making. We can use statistics to summarize our data, describing patterns, relationships, and connections. Statistics can be descriptive or inferential.
Descriptive statistics help us to summarize our data. In contrast, inferential statistics are used to identify statistically significant differences between groups of data (such as intervention and control groups in a randomized control study).
- Quantitative researchers try to control extraneous variables by conducting their studies in the lab.
- The research aims for objectivity (i.e., without bias) and is separated from the data.
- The design of the study is determined before it begins.
- For the quantitative researcher, the reality is objective, exists separately from the researcher, and can be seen by anyone.
- Research is used to test a theory and ultimately support or reject it.
Limitations of Quantitative Research
- Context: Quantitative experiments do not take place in natural settings. In addition, they do not allow participants to explain their choices or the meaning of the questions they may have for those participants (Carr, 1994).
- Researcher expertise: Poor knowledge of the application of statistical analysis may negatively affect analysis and subsequent interpretation (Black, 1999).
- Variability of data quantity: Large sample sizes are needed for more accurate analysis. Small-scale quantitative studies may be less reliable because of the low quantity of data (Denscombe, 2010). This also affects the ability to generalize study findings to wider populations.
- Confirmation bias: The researcher might miss observing phenomena because of focus on theory or hypothesis testing rather than on the theory of hypothesis generation.
Advantages of Quantitative Research
- Scientific objectivity: Quantitative data can be interpreted with statistical analysis, and since statistics are based on the principles of mathematics, the quantitative approach is viewed as scientifically objective and rational (Carr, 1994; Denscombe, 2010).
- Useful for testing and validating already constructed theories.
- Rapid analysis: Sophisticated software removes much of the need for prolonged data analysis, especially with large volumes of data involved (Antonius, 2003).
- Replication: Quantitative data is based on measured values and can be checked by others because numerical data is less open to ambiguities of interpretation.
- Hypotheses can also be tested because of statistical analysis (Antonius, 2003).
Antonius, R. (2003). Interpreting quantitative data with SPSS . Sage.
Black, T. R. (1999). Doing quantitative research in the social sciences: An integrated approach to research design, measurement and statistics . Sage.
Braun, V. & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology . Qualitative Research in Psychology , 3, 77–101.
Carr, L. T. (1994). The strengths and weaknesses of quantitative and qualitative research : what method for nursing? Journal of advanced nursing, 20(4) , 716-721.
Denscombe, M. (2010). The Good Research Guide: for small-scale social research. McGraw Hill.
Denzin, N., & Lincoln. Y. (1994). Handbook of Qualitative Research. Thousand Oaks, CA, US: Sage Publications Inc.
Glaser, B. G., Strauss, A. L., & Strutzel, E. (1968). The discovery of grounded theory; strategies for qualitative research. Nursing research, 17(4) , 364.
Minichiello, V. (1990). In-Depth Interviewing: Researching People. Longman Cheshire.
Punch, K. (1998). Introduction to Social Research: Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches. London: Sage
Further Information
- Designing qualitative research
- Methods of data collection and analysis
- Introduction to quantitative and qualitative research
- Checklists for improving rigour in qualitative research: a case of the tail wagging the dog?
- Qualitative research in health care: Analysing qualitative data
- Qualitative data analysis: the framework approach
- Using the framework method for the analysis of
- Qualitative data in multi-disciplinary health research
- Content Analysis
- Grounded Theory
- Thematic Analysis

10 Advantages & Disadvantages of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is a powerful tool for those looking to gather empirical data about their topic of study. Using statistical models and math, researchers evaluate their hypothesis.

Quantitative Research
When researchers look at gathering data, there are two types of testing methods they can use: quantitative research, or qualitative research. Quantitative research looks to capture real, measurable data in the form of numbers and figures; whereas qualitative research is concerned with recording opinion data, customer characteristics, and other non-numerical information.
Quantitative research is a powerful tool for those looking to gather empirical data about their topic of study. Using statistical models and math, researchers evaluate their hypothesis. An integral component of quantitative research - and truly, all research - is the careful and considered analysis of the resulting data points.
There are several key advantages and disadvantages to conducting quantitative research that should be considered when deciding which type of testing best fits the occasion.
5 Advantages of Quantitative Research
- Quantitative research is concerned with facts & verifiable information.
Quantitative research is primarily designed to capture numerical data - often for the purpose of studying a fact or phenomenon in their population. This kind of research activity is very helpful for producing data points when looking at a particular group - like a customer demographic. All of this helps us to better identify the key roots of certain customer behaviors.
Businesses who research their customers intimately often outperform their competitors. Knowing the reasons why a customer makes a particular purchasing decision makes it easier for companies to address issues in their audiences. Data analysis of this kind can be used for a wide range of applications, even outside the world of commerce.
- Quantitative research can be done anonymously.
Unlike qualitative research questions - which often ask participants to divulge personal and sometimes sensitive information - quantitative research does not require participants to be named or identified. As long as those conducting the testing are able to independently verify that the participants fit the necessary profile for the test, then more identifying information is unnecessary.
- Quantitative research processes don't need to be directly observed.
Whereas qualitative research demands close attention be paid to the process of data collection, quantitative research data can be collected passively. Surveys, polls, and other forms of asynchronous data collection generate data points over a defined period of time, freeing up researchers to focus on more important activities.
- Quantitative research is faster than other methods.
Quantitative research can capture vast amounts of data far quicker than other research activities. The ability to work in real-time allows analysts to immediately begin incorporating new insights and changes into their work - dramatically reducing the turn-around time of their projects. Less delays and a larger sample size ensures you will have a far easier go of managing your data collection process.
- Quantitative research is verifiable and can be used to duplicate results.
The careful and exact way in which quantitative tests must be designed enables other researchers to duplicate the methodology. In order to verify the integrity of any experimental conclusion, others must be able to replicate the study on their own. Independently verifying data is how the scientific community creates precedent and establishes trust in their findings.
5 Disadvantages of Quantitative Research
- Limited to numbers and figures.
Quantitative research is an incredibly precise tool in the way that it only gathers cold hard figures. This double edged sword leaves the quantitative method unable to deal with questions that require specific feedback, and often lacks a human element. For questions like, “What sorts of emotions does our advertisement evoke in our test audiences?” or “Why do customers prefer our product over the competing brand?”, using the quantitative research method will not derive a meaningful answer.
- Testing models are more difficult to create.
Creating a quantitative research model requires careful attention to be paid to your design. From the hypothesis to the testing methods and the analysis that comes after, there are several moving parts that must be brought into alignment in order for your test to succeed. Even one unintentional error can invalidate your results, and send your team back to the drawing board to start all over again.
- Tests can be intentionally manipulative.
Bad actors looking to push an agenda can sometimes create qualitative tests that are faulty, and designed to support a particular end result. Apolitical facts and figures can be turned political when given a limited context. You can imagine an example in which a politician devises a poll with answers that are designed to give him a favorable outcome - no matter what respondents pick.
- Results are open to subjective interpretation.
Whether due to researchers' bias or simple accident, research data can be manipulated in order to give a subjective result. When numbers are not given their full context, or were gathered in an incorrect or misleading way, the results that follow can not be correctly interpreted. Bias, opinion, and simple mistakes all work to inhibit the experimental process - and must be taken into account when designing your tests.
- More expensive than other forms of testing.
Quantitative research often seeks to gather large quantities of data points. While this is beneficial for the purposes of testing, the research does not come free. The grander the scope of your test and the more thorough you are in it’s methodology, the more likely it is that you will be spending a sizable portion of your marketing expenses on research alone. Polling and surveying, while affordable means of gathering quantitative data, can not always generate the kind of quality results a research project necessitates.
Key Takeaways

Numerical data is a vital component of almost any research project. Quantitative data can provide meaningful insight into qualitative concerns. Focusing on the facts and figures enables researchers to duplicate tests later on, and create their own data sets.
To streamline your quantitative research process:
Have a plan. Tackling your research project with a clear and focused strategy will allow you to better address any errors or hiccups that might otherwise inhibit your testing.
Define your audience. Create a clear picture of your target audience before you design your test. Understanding who you want to test beforehand gives you the ability to choose which methodology is going to be the right fit for them.
Test, test, and test again. Verifying your results through repeated and thorough testing builds confidence in your decision making. It’s not only smart research practice - it’s good business.
About Author

Send Your First Survey Today!
Set up and begin receiving results within minutes. Sign up for free, no contract required.
Helpfull is the easiest way to get feedback from thousands of people in minutes. Whether you're comparing images, text or surveys; our pool of qualified testers give you their real detailed opinion to help you make better decisions and be more informed.
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and Analysis
Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and Analysis
Table of Contents

Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is a type of research that collects and analyzes numerical data to test hypotheses and answer research questions . This research typically involves a large sample size and uses statistical analysis to make inferences about a population based on the data collected. It often involves the use of surveys, experiments, or other structured data collection methods to gather quantitative data.
Quantitative Research Methods

Quantitative Research Methods are as follows:
Descriptive Research Design
Descriptive research design is used to describe the characteristics of a population or phenomenon being studied. This research method is used to answer the questions of what, where, when, and how. Descriptive research designs use a variety of methods such as observation, case studies, and surveys to collect data. The data is then analyzed using statistical tools to identify patterns and relationships.
Correlational Research Design
Correlational research design is used to investigate the relationship between two or more variables. Researchers use correlational research to determine whether a relationship exists between variables and to what extent they are related. This research method involves collecting data from a sample and analyzing it using statistical tools such as correlation coefficients.
Quasi-experimental Research Design
Quasi-experimental research design is used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships between variables. This research method is similar to experimental research design, but it lacks full control over the independent variable. Researchers use quasi-experimental research designs when it is not feasible or ethical to manipulate the independent variable.
Experimental Research Design
Experimental research design is used to investigate cause-and-effect relationships between variables. This research method involves manipulating the independent variable and observing the effects on the dependent variable. Researchers use experimental research designs to test hypotheses and establish cause-and-effect relationships.
Survey Research
Survey research involves collecting data from a sample of individuals using a standardized questionnaire. This research method is used to gather information on attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors of individuals. Researchers use survey research to collect data quickly and efficiently from a large sample size. Survey research can be conducted through various methods such as online, phone, mail, or in-person interviews.

Quantitative Research Analysis Methods
Here are some commonly used quantitative research analysis methods:
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis is the most common quantitative research analysis method. It involves using statistical tools and techniques to analyze the numerical data collected during the research process. Statistical analysis can be used to identify patterns, trends, and relationships between variables, and to test hypotheses and theories.
Regression Analysis
Regression analysis is a statistical technique used to analyze the relationship between one dependent variable and one or more independent variables. Researchers use regression analysis to identify and quantify the impact of independent variables on the dependent variable.
Factor Analysis
Factor analysis is a statistical technique used to identify underlying factors that explain the correlations among a set of variables. Researchers use factor analysis to reduce a large number of variables to a smaller set of factors that capture the most important information.
Structural Equation Modeling
Structural equation modeling is a statistical technique used to test complex relationships between variables. It involves specifying a model that includes both observed and unobserved variables, and then using statistical methods to test the fit of the model to the data.
Time Series Analysis
Time series analysis is a statistical technique used to analyze data that is collected over time. It involves identifying patterns and trends in the data, as well as any seasonal or cyclical variations.
Multilevel Modeling
Multilevel modeling is a statistical technique used to analyze data that is nested within multiple levels. For example, researchers might use multilevel modeling to analyze data that is collected from individuals who are nested within groups, such as students nested within schools.
Applications of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research has many applications across a wide range of fields. Here are some common examples:
- Market Research : Quantitative research is used extensively in market research to understand consumer behavior, preferences, and trends. Researchers use surveys, experiments, and other quantitative methods to collect data that can inform marketing strategies, product development, and pricing decisions.
- Health Research: Quantitative research is used in health research to study the effectiveness of medical treatments, identify risk factors for diseases, and track health outcomes over time. Researchers use statistical methods to analyze data from clinical trials, surveys, and other sources to inform medical practice and policy.
- Social Science Research: Quantitative research is used in social science research to study human behavior, attitudes, and social structures. Researchers use surveys, experiments, and other quantitative methods to collect data that can inform social policies, educational programs, and community interventions.
- Education Research: Quantitative research is used in education research to study the effectiveness of teaching methods, assess student learning outcomes, and identify factors that influence student success. Researchers use experimental and quasi-experimental designs, as well as surveys and other quantitative methods, to collect and analyze data.
- Environmental Research: Quantitative research is used in environmental research to study the impact of human activities on the environment, assess the effectiveness of conservation strategies, and identify ways to reduce environmental risks. Researchers use statistical methods to analyze data from field studies, experiments, and other sources.
Characteristics of Quantitative Research
Here are some key characteristics of quantitative research:
- Numerical data : Quantitative research involves collecting numerical data through standardized methods such as surveys, experiments, and observational studies. This data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify patterns and relationships.
- Large sample size: Quantitative research often involves collecting data from a large sample of individuals or groups in order to increase the reliability and generalizability of the findings.
- Objective approach: Quantitative research aims to be objective and impartial in its approach, focusing on the collection and analysis of data rather than personal beliefs, opinions, or experiences.
- Control over variables: Quantitative research often involves manipulating variables to test hypotheses and establish cause-and-effect relationships. Researchers aim to control for extraneous variables that may impact the results.
- Replicable : Quantitative research aims to be replicable, meaning that other researchers should be able to conduct similar studies and obtain similar results using the same methods.
- Statistical analysis: Quantitative research involves using statistical tools and techniques to analyze the numerical data collected during the research process. Statistical analysis allows researchers to identify patterns, trends, and relationships between variables, and to test hypotheses and theories.
- Generalizability: Quantitative research aims to produce findings that can be generalized to larger populations beyond the specific sample studied. This is achieved through the use of random sampling methods and statistical inference.
Examples of Quantitative Research
Here are some examples of quantitative research in different fields:
- Market Research: A company conducts a survey of 1000 consumers to determine their brand awareness and preferences. The data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify trends and patterns that can inform marketing strategies.
- Health Research : A researcher conducts a randomized controlled trial to test the effectiveness of a new drug for treating a particular medical condition. The study involves collecting data from a large sample of patients and analyzing the results using statistical methods.
- Social Science Research : A sociologist conducts a survey of 500 people to study attitudes toward immigration in a particular country. The data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify factors that influence these attitudes.
- Education Research: A researcher conducts an experiment to compare the effectiveness of two different teaching methods for improving student learning outcomes. The study involves randomly assigning students to different groups and collecting data on their performance on standardized tests.
- Environmental Research : A team of researchers conduct a study to investigate the impact of climate change on the distribution and abundance of a particular species of plant or animal. The study involves collecting data on environmental factors and population sizes over time and analyzing the results using statistical methods.
- Psychology : A researcher conducts a survey of 500 college students to investigate the relationship between social media use and mental health. The data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify correlations and potential causal relationships.
- Political Science: A team of researchers conducts a study to investigate voter behavior during an election. They use survey methods to collect data on voting patterns, demographics, and political attitudes, and analyze the results using statistical methods.
How to Conduct Quantitative Research
Here is a general overview of how to conduct quantitative research:
- Develop a research question: The first step in conducting quantitative research is to develop a clear and specific research question. This question should be based on a gap in existing knowledge, and should be answerable using quantitative methods.
- Develop a research design: Once you have a research question, you will need to develop a research design. This involves deciding on the appropriate methods to collect data, such as surveys, experiments, or observational studies. You will also need to determine the appropriate sample size, data collection instruments, and data analysis techniques.
- Collect data: The next step is to collect data. This may involve administering surveys or questionnaires, conducting experiments, or gathering data from existing sources. It is important to use standardized methods to ensure that the data is reliable and valid.
- Analyze data : Once the data has been collected, it is time to analyze it. This involves using statistical methods to identify patterns, trends, and relationships between variables. Common statistical techniques include correlation analysis, regression analysis, and hypothesis testing.
- Interpret results: After analyzing the data, you will need to interpret the results. This involves identifying the key findings, determining their significance, and drawing conclusions based on the data.
- Communicate findings: Finally, you will need to communicate your findings. This may involve writing a research report, presenting at a conference, or publishing in a peer-reviewed journal. It is important to clearly communicate the research question, methods, results, and conclusions to ensure that others can understand and replicate your research.
When to use Quantitative Research
Here are some situations when quantitative research can be appropriate:
- To test a hypothesis: Quantitative research is often used to test a hypothesis or a theory. It involves collecting numerical data and using statistical analysis to determine if the data supports or refutes the hypothesis.
- To generalize findings: If you want to generalize the findings of your study to a larger population, quantitative research can be useful. This is because it allows you to collect numerical data from a representative sample of the population and use statistical analysis to make inferences about the population as a whole.
- To measure relationships between variables: If you want to measure the relationship between two or more variables, such as the relationship between age and income, or between education level and job satisfaction, quantitative research can be useful. It allows you to collect numerical data on both variables and use statistical analysis to determine the strength and direction of the relationship.
- To identify patterns or trends: Quantitative research can be useful for identifying patterns or trends in data. For example, you can use quantitative research to identify trends in consumer behavior or to identify patterns in stock market data.
- To quantify attitudes or opinions : If you want to measure attitudes or opinions on a particular topic, quantitative research can be useful. It allows you to collect numerical data using surveys or questionnaires and analyze the data using statistical methods to determine the prevalence of certain attitudes or opinions.
Purpose of Quantitative Research
The purpose of quantitative research is to systematically investigate and measure the relationships between variables or phenomena using numerical data and statistical analysis. The main objectives of quantitative research include:
- Description : To provide a detailed and accurate description of a particular phenomenon or population.
- Explanation : To explain the reasons for the occurrence of a particular phenomenon, such as identifying the factors that influence a behavior or attitude.
- Prediction : To predict future trends or behaviors based on past patterns and relationships between variables.
- Control : To identify the best strategies for controlling or influencing a particular outcome or behavior.
Quantitative research is used in many different fields, including social sciences, business, engineering, and health sciences. It can be used to investigate a wide range of phenomena, from human behavior and attitudes to physical and biological processes. The purpose of quantitative research is to provide reliable and valid data that can be used to inform decision-making and improve understanding of the world around us.
Advantages of Quantitative Research
There are several advantages of quantitative research, including:
- Objectivity : Quantitative research is based on objective data and statistical analysis, which reduces the potential for bias or subjectivity in the research process.
- Reproducibility : Because quantitative research involves standardized methods and measurements, it is more likely to be reproducible and reliable.
- Generalizability : Quantitative research allows for generalizations to be made about a population based on a representative sample, which can inform decision-making and policy development.
- Precision : Quantitative research allows for precise measurement and analysis of data, which can provide a more accurate understanding of phenomena and relationships between variables.
- Efficiency : Quantitative research can be conducted relatively quickly and efficiently, especially when compared to qualitative research, which may involve lengthy data collection and analysis.
- Large sample sizes : Quantitative research can accommodate large sample sizes, which can increase the representativeness and generalizability of the results.
Limitations of Quantitative Research
There are several limitations of quantitative research, including:
- Limited understanding of context: Quantitative research typically focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis, which may not provide a comprehensive understanding of the context or underlying factors that influence a phenomenon.
- Simplification of complex phenomena: Quantitative research often involves simplifying complex phenomena into measurable variables, which may not capture the full complexity of the phenomenon being studied.
- Potential for researcher bias: Although quantitative research aims to be objective, there is still the potential for researcher bias in areas such as sampling, data collection, and data analysis.
- Limited ability to explore new ideas: Quantitative research is often based on pre-determined research questions and hypotheses, which may limit the ability to explore new ideas or unexpected findings.
- Limited ability to capture subjective experiences : Quantitative research is typically focused on objective data and may not capture the subjective experiences of individuals or groups being studied.
- Ethical concerns : Quantitative research may raise ethical concerns, such as invasion of privacy or the potential for harm to participants.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide

Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- Write for Us
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Volume 21, Issue 4
- How to appraise quantitative research
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
This article has a correction. Please see:
- Correction: How to appraise quantitative research - April 01, 2019
- Xabi Cathala 1 ,
- Calvin Moorley 2
- 1 Institute of Vocational Learning , School of Health and Social Care, London South Bank University , London , UK
- 2 Nursing Research and Diversity in Care , School of Health and Social Care, London South Bank University , London , UK
- Correspondence to Mr Xabi Cathala, Institute of Vocational Learning, School of Health and Social Care, London South Bank University London UK ; cathalax{at}lsbu.ac.uk and Dr Calvin Moorley, Nursing Research and Diversity in Care, School of Health and Social Care, London South Bank University, London SE1 0AA, UK; Moorleyc{at}lsbu.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1136/eb-2018-102996
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
Introduction
Some nurses feel that they lack the necessary skills to read a research paper and to then decide if they should implement the findings into their practice. This is particularly the case when considering the results of quantitative research, which often contains the results of statistical testing. However, nurses have a professional responsibility to critique research to improve their practice, care and patient safety. 1 This article provides a step by step guide on how to critically appraise a quantitative paper.
Title, keywords and the authors
The authors’ names may not mean much, but knowing the following will be helpful:
Their position, for example, academic, researcher or healthcare practitioner.
Their qualification, both professional, for example, a nurse or physiotherapist and academic (eg, degree, masters, doctorate).
This can indicate how the research has been conducted and the authors’ competence on the subject. Basically, do you want to read a paper on quantum physics written by a plumber?
The abstract is a resume of the article and should contain:
Introduction.
Research question/hypothesis.
Methods including sample design, tests used and the statistical analysis (of course! Remember we love numbers).
Main findings.
Conclusion.
The subheadings in the abstract will vary depending on the journal. An abstract should not usually be more than 300 words but this varies depending on specific journal requirements. If the above information is contained in the abstract, it can give you an idea about whether the study is relevant to your area of practice. However, before deciding if the results of a research paper are relevant to your practice, it is important to review the overall quality of the article. This can only be done by reading and critically appraising the entire article.
The introduction
Example: the effect of paracetamol on levels of pain.
My hypothesis is that A has an effect on B, for example, paracetamol has an effect on levels of pain.
My null hypothesis is that A has no effect on B, for example, paracetamol has no effect on pain.
My study will test the null hypothesis and if the null hypothesis is validated then the hypothesis is false (A has no effect on B). This means paracetamol has no effect on the level of pain. If the null hypothesis is rejected then the hypothesis is true (A has an effect on B). This means that paracetamol has an effect on the level of pain.
Background/literature review
The literature review should include reference to recent and relevant research in the area. It should summarise what is already known about the topic and why the research study is needed and state what the study will contribute to new knowledge. 5 The literature review should be up to date, usually 5–8 years, but it will depend on the topic and sometimes it is acceptable to include older (seminal) studies.
Methodology
In quantitative studies, the data analysis varies between studies depending on the type of design used. For example, descriptive, correlative or experimental studies all vary. A descriptive study will describe the pattern of a topic related to one or more variable. 6 A correlational study examines the link (correlation) between two variables 7 and focuses on how a variable will react to a change of another variable. In experimental studies, the researchers manipulate variables looking at outcomes 8 and the sample is commonly assigned into different groups (known as randomisation) to determine the effect (causal) of a condition (independent variable) on a certain outcome. This is a common method used in clinical trials.
There should be sufficient detail provided in the methods section for you to replicate the study (should you want to). To enable you to do this, the following sections are normally included:
Overview and rationale for the methodology.
Participants or sample.
Data collection tools.
Methods of data analysis.
Ethical issues.
Data collection should be clearly explained and the article should discuss how this process was undertaken. Data collection should be systematic, objective, precise, repeatable, valid and reliable. Any tool (eg, a questionnaire) used for data collection should have been piloted (or pretested and/or adjusted) to ensure the quality, validity and reliability of the tool. 9 The participants (the sample) and any randomisation technique used should be identified. The sample size is central in quantitative research, as the findings should be able to be generalised for the wider population. 10 The data analysis can be done manually or more complex analyses performed using computer software sometimes with advice of a statistician. From this analysis, results like mode, mean, median, p value, CI and so on are always presented in a numerical format.
The author(s) should present the results clearly. These may be presented in graphs, charts or tables alongside some text. You should perform your own critique of the data analysis process; just because a paper has been published, it does not mean it is perfect. Your findings may be different from the author’s. Through critical analysis the reader may find an error in the study process that authors have not seen or highlighted. These errors can change the study result or change a study you thought was strong to weak. To help you critique a quantitative research paper, some guidance on understanding statistical terminology is provided in table 1 .
- View inline
Some basic guidance for understanding statistics
Quantitative studies examine the relationship between variables, and the p value illustrates this objectively. 11 If the p value is less than 0.05, the null hypothesis is rejected and the hypothesis is accepted and the study will say there is a significant difference. If the p value is more than 0.05, the null hypothesis is accepted then the hypothesis is rejected. The study will say there is no significant difference. As a general rule, a p value of less than 0.05 means, the hypothesis is accepted and if it is more than 0.05 the hypothesis is rejected.
The CI is a number between 0 and 1 or is written as a per cent, demonstrating the level of confidence the reader can have in the result. 12 The CI is calculated by subtracting the p value to 1 (1–p). If there is a p value of 0.05, the CI will be 1–0.05=0.95=95%. A CI over 95% means, we can be confident the result is statistically significant. A CI below 95% means, the result is not statistically significant. The p values and CI highlight the confidence and robustness of a result.
Discussion, recommendations and conclusion
The final section of the paper is where the authors discuss their results and link them to other literature in the area (some of which may have been included in the literature review at the start of the paper). This reminds the reader of what is already known, what the study has found and what new information it adds. The discussion should demonstrate how the authors interpreted their results and how they contribute to new knowledge in the area. Implications for practice and future research should also be highlighted in this section of the paper.
A few other areas you may find helpful are:
Limitations of the study.
Conflicts of interest.
Table 2 provides a useful tool to help you apply the learning in this paper to the critiquing of quantitative research papers.
Quantitative paper appraisal checklist
- 1. ↵ Nursing and Midwifery Council , 2015 . The code: standard of conduct, performance and ethics for nurses and midwives https://www.nmc.org.uk/globalassets/sitedocuments/nmc-publications/nmc-code.pdf ( accessed 21.8.18 ).
- Gerrish K ,
- Moorley C ,
- Tunariu A , et al
- Shorten A ,
Competing interests None declared.
Patient consent Not required.
Provenance and peer review Commissioned; internally peer reviewed.
Correction notice This article has been updated since its original publication to update p values from 0.5 to 0.05 throughout.
Linked Articles
- Miscellaneous Correction: How to appraise quantitative research BMJ Publishing Group Ltd and RCN Publishing Company Ltd Evidence-Based Nursing 2019; 22 62-62 Published Online First: 31 Jan 2019. doi: 10.1136/eb-2018-102996corr1
Read the full text or download the PDF:
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Psychol Med
- v.42(1); Jan-Feb 2020
Sample Size and its Importance in Research
Chittaranjan andrade.
Clinical Psychopharmacology Unit, Department of Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neurotoxicology, National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
The sample size for a study needs to be estimated at the time the study is proposed; too large a sample is unnecessary and unethical, and too small a sample is unscientific and also unethical. The necessary sample size can be calculated, using statistical software, based on certain assumptions. If no assumptions can be made, then an arbitrary sample size is set for a pilot study. This article discusses sample size and how it relates to matters such as ethics, statistical power, the primary and secondary hypotheses in a study, and findings from larger vs. smaller samples.
Studies are conducted on samples because it is usually impossible to study the entire population. Conclusions drawn from samples are intended to be generalized to the population, and sometimes to the future as well. The sample must therefore be representative of the population. This is best ensured by the use of proper methods of sampling. The sample must also be adequate in size – in fact, no more and no less.
SAMPLE SIZE AND ETHICS
A sample that is larger than necessary will be better representative of the population and will hence provide more accurate results. However, beyond a certain point, the increase in accuracy will be small and hence not worth the effort and expense involved in recruiting the extra patients. Furthermore, an overly large sample would inconvenience more patients than might be necessary for the study objectives; this is unethical. In contrast, a sample that is smaller than necessary would have insufficient statistical power to answer the primary research question, and a statistically nonsignificant result could merely be because of inadequate sample size (Type 2 or false negative error). Thus, a small sample could result in the patients in the study being inconvenienced with no benefit to future patients or to science. This is also unethical.
In this regard, inconvenience to patients refers to the time that they spend in clinical assessments and to the psychological and physical discomfort that they experience in assessments such as interviews, blood sampling, and other procedures.
ESTIMATING SAMPLE SIZE
So how large should a sample be? In hypothesis testing studies, this is mathematically calculated, conventionally, as the sample size necessary to be 80% certain of identifying a statistically significant outcome should the hypothesis be true for the population, with P for statistical significance set at 0.05. Some investigators power their studies for 90% instead of 80%, and some set the threshold for significance at 0.01 rather than 0.05. Both choices are uncommon because the necessary sample size becomes large, and the study becomes more expensive and more difficult to conduct. Many investigators increase the sample size by 10%, or by whatever proportion they can justify, to compensate for expected dropout, incomplete records, biological specimens that do not meet laboratory requirements for testing, and other study-related problems.
Sample size calculations require assumptions about expected means and standard deviations, or event risks, in different groups; or, upon expected effect sizes. For example, a study may be powered to detect an effect size of 0.5; or a response rate of 60% with drug vs. 40% with placebo.[ 1 ] When no guesstimates or expectations are possible, pilot studies are conducted on a sample that is arbitrary in size but what might be considered reasonable for the field.
The sample size may need to be larger in multicenter studies because of statistical noise (due to variations in patient characteristics, nonspecific treatment characteristics, rating practices, environments, etc. between study centers).[ 2 ] Sample size calculations can be performed manually or using statistical software; online calculators that provide free service can easily be identified by search engines. G*Power is an example of a free, downloadable program for sample size estimation. The manual and tutorial for G*Power can also be downloaded.
PRIMARY AND SECONDARY ANALYSES
The sample size is calculated for the primary hypothesis of the study. What is the difference between the primary hypothesis, primary outcome and primary outcome measure? As an example, the primary outcome may be a reduction in the severity of depression, the primary outcome measure may be the Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS) and the primary hypothesis may be that reduction in MADRS scores is greater with the drug than with placebo. The primary hypothesis is tested in the primary analysis.
Studies almost always have many hypotheses; for example, that the study drug will outperform placebo on measures of depression, suicidality, anxiety, disability and quality of life. The sample size necessary for adequate statistical power to test each of these hypotheses will be different. Because a study can have only one sample size, it can be powered for only one outcome, the primary outcome. Therefore, the study would be either overpowered or underpowered for the other outcomes. These outcomes are therefore called secondary outcomes, and are associated with secondary hypotheses, and are tested in secondary analyses. Secondary analyses are generally considered exploratory because when many hypotheses in a study are each tested at a P < 0.05 level for significance, some may emerge statistically significant by chance (Type 1 or false positive errors).[ 3 ]
INTERPRETING RESULTS
Here is an interesting question. A test of the primary hypothesis yielded a P value of 0.07. Might we conclude that our sample was underpowered for the study and that, had our sample been larger, we would have identified a significant result? No! The reason is that larger samples will more accurately represent the population value, whereas smaller samples could be off the mark in either direction – towards or away from the population value. In this context, readers should also note that no matter how small the P value for an estimate is, the population value of that estimate remains the same.[ 4 ]
On a parting note, it is unlikely that population values will be null. That is, for example, that the response rate to the drug will be exactly the same as that to placebo, or that the correlation between height and age at onset of schizophrenia will be zero. If the sample size is large enough, even such small differences between groups, or trivial correlations, would be detected as being statistically significant. This does not mean that the findings are clinically significant.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
This article focuses on the application of quantitative methods in schoolscape research, including a discussion of its advantages and disadvantages. This article seeks to rehabilitate the quantitative by re-theorizing the landscape in linguistic landscape (LL), moving from an area based study of visible forms to a poststructuralist and ...
Revised on June 22, 2023. Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analyzing numerical data. It can be used to find patterns and averages, make predictions, test causal relationships, and generalize results to wider populations. Quantitative research is the opposite of qualitative research, which involves collecting and analyzing ...
Jamshed (2014) advocates the use of interviewing and observation as two main methods. to have an in depth and extensive understanding of a complex reality. Qualitative studies ha ve been used in a ...
Quantitative Research for the Qualitative Researcher. 2014. SAGE Knowledge. Book chapter . Issues in Validity and Reliability. Show details Hide details. Daniel J. Boudah. Conducting Educational Research: Guide to Completing a Major Project. 2011. SAGE Knowledge. Entry . Quantitative Research.
The current Editorial presents an overview of the special issue, and describes the underlying, translational issues embedded within the issue. We highlight three main themes that emerged, and describe how this work will help to fuel the future directions of quantitative-based research within the Psychological Sciences.
Quantitative research is a type of research that focuses on collecting and analyzing numerical data to answer research questions. There are two main methods used to conduct quantitative research: 1. Primary Method. There are several methods of primary quantitative research, each with its own strengths and limitations.
Quantitative research methods are concerned with the planning, design, and implementation of strategies to collect and analyze data. Descartes, the seventeenth-century philosopher, suggested that how the results are achieved is often more important than the results themselves, as the journey taken along the research path is a journey of discovery. . High-quality quantitative research is ...
When collecting and analyzing data, quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings. Both are important for gaining different kinds of knowledge. Quantitative research. Quantitative research is expressed in numbers and graphs. It is used to test or confirm theories and assumptions.
Advantages of quantitative research 1,2. When choosing the right research methodology, also consider the advantages of quantitative research and how it can impact your study. Quantitative research methods are more scientific and rational. They use quantifiable data leading to objectivity in the results and avoid any chances of ambiguity.
Quantitative research is a way to conduct studies and examine data for trends and patterns. Researchers using quantitative methods often attempt to interpret the meaning of the data to find potential causal relationships between different variables. If you want to work in research, understanding this style can help you study issues through data ...
List of the Pros of Quantitative Research. 1. Data collection occurs rapidly with quantitative research. Because the data points of quantitative research involve surveys, experiments, and real-time gathering, there are few delays in the collection of materials to examine. That means the information under study can be analyzed very quickly when ...
3.1 Advantages There are some benefits of using qualitative research approaches and methods. Firstly, qualitative research approach produces the thick (detailed) description of participants' feelings, opinions, and experiences; and interprets the meanings of their actions (Denzin, 1989).
Qualitative research aims to produce rich and detailed descriptions of the phenomenon being studied, and to uncover new insights and meanings. Quantitative data is information about quantities, and therefore numbers, and qualitative data is descriptive, and regards phenomenon which can be observed but not measured, such as language.
5 Disadvantages of Quantitative Research. Limited to numbers and figures. Quantitative research is an incredibly precise tool in the way that it only gathers cold hard figures. This double edged sword leaves the quantitative method unable to deal with questions that require specific feedback, and often lacks a human element.
Here are some key characteristics of quantitative research: Numerical data: Quantitative research involves collecting numerical data through standardized methods such as surveys, experiments, and observational studies. This data is analyzed using statistical methods to identify patterns and relationships.
Title, keywords and the authors. The title of a paper should be clear and give a good idea of the subject area. The title should not normally exceed 15 words 2 and should attract the attention of the reader. 3 The next step is to review the key words. These should provide information on both the ideas or concepts discussed in the paper and the ...
The sample size for a study needs to be estimated at the time the study is proposed; too large a sample is unnecessary and unethical, and too small a sample is unscientific and also unethical. The necessary sample size can be calculated, using statistical software, based on certain assumptions. If no assumptions can be made, then an arbitrary ...