

Explore More
Stay in our orbit.
Stay connected with industry news, resources for English teachers and job seekers, ELT events, and more.

Explore Topics
- Global Elt News
- Job Resources
- Industry Insights
- Teaching English Online
- Classroom Games / Activities
- Teaching English Abroad
- Professional Development

Popular Articles
- 5 Popular ESL Teaching Methods Every Teacher Should Know
- 10 Fun Ways to Use Realia in Your ESL Classroom
- How to Teach ESL Vocabulary: Top Methods for Introducing New Words
- Advice From an Expert: TEFL Interview Questions & How to Answer Them
- What Is TESOL? What Is TEFL? Which Certificate Is Better – TEFL or TESOL?

What Is Reflective Teaching and Why Is It Important?
Gerald smith.
- June 11, 2022

If you feel that your teaching is becoming a bit stale or you’re unsure of a lesson’s effectiveness, reflective teaching is the best way to regain your confidence and interest in ESL education. Let’s take a closer look at what reflective teaching entails, why it’s important, and how you can implement reflective practices in your career.
Reflective teaching is covered in detail in the IDELTOnline™ course, Bridge’s most advanced professional TEFL certification, which can be used as a pathway to an MA TESOL at more than 1,600 universities.
What is Reflective Teaching?
Reflective teaching is a teacher’s practice of thinking, writing, and/or speaking about their lessons and their teaching methods and approaches.
It’s easy for teachers to get into a rut while teaching, where it feels like they’re delivering lessons on autopilot. Reflective teaching is a way to break out of that rut and become the best teacher you can be.
In his essay, “Reflective Practice for Language Teachers,” Thomas Farrell writes, “Reflective practice occurs, then, when teachers consciously take on the role of reflective practitioner and subject their own beliefs about teaching and learning to critical analysis, take full responsibility for their actions in the classroom, and continue to improve their teaching practice.”
Want to read the entire essay and get a more in-depth look at reflective teaching? Take the graduate-level IDELTOnline™ course.

Why is Reflective Teaching Important?
“Teachers who engage in reflective practice can develop a deeper understanding of their teaching, assess their professional growth, develop informed decision-making skills, and become proactive and confident in their teaching.” -Farrell
It improves your lesson plans
One of the main benefits of reflective teaching is that it helps you to become a better teacher who engages their students more and consistently improves their lesson plans .
By analyzing different aspects of lessons like teacher talking time or student collaboration, you can measure your success.
For example, if you remember that students weren’t engaged during an activity, you can analyze the reasons why. Maybe you didn’t set a clear context or you overexplained and slowed down student discovery. Or, maybe it didn’t have anything to do with your planning, and the students simply partied the previous night and didn’t want to discuss the differences between the present perfect and past simple.
Whatever the reason, reflective teaching can help you think of a solution.
It can help you break out of a teaching rut
The more you teach, the easier it is to get into a teaching rut. You reuse the same tried and tested activities, you tell the same old anecdotes, and you recycle the same tired grammar explanations.
While reusing activities is great, you need to make sure you’re not doing something that feels boring to you. When you’re not having fun, you can’t expect your students to have fun.
Farrell writes, “If teachers engage in reflective practice they can avoid such burnout because they take the time to stop and think about what is happening in their practice to make sense of it so that they can learn from their experiences rather than mindlessly repeat them year after year.”
Reflective teaching gets you to think about how to modify activities and lesson plans so they’re fresh and interesting for both you and your students.

It inspires you to try new things
When materials like ELT course book activities start to get boring, it’s time to try something new.
Online, there are tons of resources for up-to-date lesson plans. Personal favorites are Onestopenglish and TeachThis.com , but there are hundreds more, some free and some paid.
Another great way to try new things is to collaborate with a fellow teacher. This is easy when working at a language school, but you can also do this online through Facebook groups and Linkedin. Teachers even share lesson plans through Twitter.
It’s part of continuing professional development
Continuing professional development comes in many forms, such as Specialized TEFL/TESOL courses or Micro-credentials that offer targeted training. Reflective teaching is also an effective way to continue developing and expanding your teaching skills throughout your career.
While reflecting on your teaching, you can also think back to training from TEFL courses you’ve already taken and see if you’re fully utilizing what you studied in your online TEFL certification lessons.
Learn more about professional development for EFL teachers.
It provides opportunities to share your experience
Posting your teaching reflections in Facebook groups or on Linkedin helps start conversations around best teaching practices .
You’ll be surprised to see how many teachers have had the same experiences as you or will have suggestions on how to teach in new ways.
This not only allows you to offer and receive great feedback but also builds your network or community of teachers .
See the ways that the IDELTOnline™ sets you apart as a teacher.
What are the characteristics of reflective teaching?
Although reflective teaching can take many forms, there are a few characteristics that appear throughout all types of reflective practices:
- Reflective teaching notes what happens in the classroom, why it happens, and how it can be improved.
- If you are practicing reflective teaching, it’s rare that you will teach the same lesson again in the exact same way because reflective teaching challenges you. You’ll need to critique yourself and your go-to lesson plans.
- Although many teachers write their reflections down, not all reflective teaching needs to be written. Many teachers, instead, choose to speak about their lessons with a colleague or mentor, or what Farrell calls a “Critical Friend.”
- Reflective teaching is collaborative, often involving a head teacher or a colleague.
- Reflecting on and speaking about how your lessons go often leads to helpful insights.

What are some examples of reflective teaching?
Some ways of practicing reflective teaching include:
- Teaching journals: Write down classroom reflections in a journal.
- Classroom observations: Be observed either by a mentor or by recording the lesson and rewatching it yourself.
- Critical friends: Speak about your classes with a friend who can offer constructive criticism.
- Action research: Research something you struggle with, and maybe even take a course to improve specific teaching skills .
- Online groups: Teachers actively post online about reflective teaching in teacher development groups like the Bridge Teaching English Online Facebook Group . Posting online helps teachers get more recognition in the industry as well as organize their reflections.
- Blogs: Many teachers choose to share their reflections by creating their own EFL blogs . For example, Rachel Tsateri, an EL teacher and writer, published a reflective post on her teacher talking time (TTT) on her website, The TEFL Zone . Because Rachel read a lot of the literature around TTT, she was also engaging in action research, a rather academic but effective approach to reflective teaching.
- Teacher beliefs: Continue to develop and verbalize your own beliefs about what makes good teaching. Not sure where to start with your teaching beliefs? Learn about crafting an ESL philosophy of teaching statement.
Try different methods to find the right one for you. Journaling is an easy first step, but if you’re a more social teacher, you might prefer working with a critical friend or a teacher development group.
Teaching, a lot like learning, is a journey. No one becomes a great teacher overnight, so don’t be too hard on yourself when a lesson doesn’t go well. Instead, think critically about how you teach so you can continue to improve your students’ learning experiences and grow in your profession.
Want to learn more about reflective teaching and other best TEFL practices covered in the IDELTOnline™ course? Take a look at what this certification entails and whether it’s right for you.

Gerald Smith is an EL teacher, journalist and occasional poet. Originally from Texas, he now lives on a houseboat in Glasgow, Scotland with his partner and their two kittens.
- Center for Teaching Excellence
- Learning Tech
- Teaching Hub

Reflective Teaching Statements
The Reflective Teaching Statement (RTS) is a short reflective essay that describes an instructor's teaching philosophy, learning objectives, instructional methods, and learning and engagement strategies. This collection contains various resources, from helping you get started writing one to examples from different disciplines.
Updated: February 2024
What is a Reflective Teaching Statement?
This handout explains what a Reflective Teaching Statement is and what types of information it contains.
Reflective Teaching Statement: Getting Started
This handout provides questions that can help you get started writing.
Reflective Teaching Statement: General Guidelines and Possible Components
Reflective teaching statement: structure.
This handout includes suggestions to consider as you organize and write your statement.
Reflective Teaching Statement: Rubric
This handout helps you score the various components of your statement.
Reflective Teaching Statement: Examples
Review sample statements from various disciplines.
Teaching Philosophies and Teaching Dossiers Guide
This guide provides a robust resource for creating teaching dossiers and philosophy statements. It starts with an overview of a research-informed framework for developing teaching expertise and then describes how to create philosophy statements that ground your approaches to teaching across multiple contexts. The final sections of the guide focus on creating and evaluating teaching dossiers.
Want to recommend a resource to add to this collection? Send us an email.
Related results will be displayed below.
- Collections
- Faculty & Staff
Developing a reflective teaching practice
Our university is built on a commitment to using the power of discovery, creativity, and analytical thinking to solve challenges, including those we encounter in the process of teaching. While consulting the scholarship of teaching and learning is a good way to identify effective teaching strategies, the most important dimension of an effective teaching practice is reflection.
What is “reflective” teaching?
The American philosopher and educational reformer, John Dewey, considered reflection crucial to learning. As Dewey scholar, Carol Rodgers, notes, Dewey framed reflection as “a systematic, rigorous, disciplined way of thinking” that led to intellectual growth.
Because our students are so diverse and there’s so much variety in instructional contexts, good teaching requires instructors to observe, reflect upon, and adapt their teaching practice . In addition to identifying areas for improvement in your teaching, reflection is also core to an inclusive teaching practice.
Reflective practices
There are lots of ways to be thoughtful about your teaching, but here are a few for each point in the quarter.
Before the beginning of the quarter:
- Reflect on your course goals. What do you want students to be able to do by the time they leave your course?
- Reflect on your own mix of identities. How has privilege or oppression shaped your perspectives?
- Reflect on how your discipline creates knowledge and decides what knowledge is valuable. How has this constrained what and how you teach?
During the quarter:
- Keep a journal to briefly jot down your observations of student interactions and experiences in the classroom. Note things that are working and things you might want to change.
- Get an outside perspective. Ask a colleague to come observe a class and your interactions with students and/or course materials.
- Conduct a mid-quarter evaluation to gather information on how the course is going. Ask yourself what you can do to relieve the pain points that students identified in the evaluation.
At the end of the quarter:
- Reflect on your course data. What do your gradebook and course evaluations indicate about what worked well and what didn’t work so well? What can you do to improve students’ performance?
- Connect with a consultant to brainstorm ways to redesign assignments or improve your teaching practice.
- Dig into the scholarship of teaching and learning to find ideas for how others have improved their teaching practice in a certain area.
Reflecting on your identities and position
Your teaching emerges from your educational background and training, as well as from your personal history and experience. Reflecting on how who you are and what you have experienced shapes your teaching can help you identify ways to better connect with your students.
Positionality and intersectionality
Positionality refers to the social, cultural, and political contexts – including systems of power and oppression – that shape our identities. Our positionalities influence how we approach course design, choose content, teach, and assess student work. Recognizing how your own positionality impacts your teaching can help you create a more inclusive classroom.
On one level, intersectionality refers to the ways that the multiple dimensions of our identity intersect to shape our experience. Black feminist scholars have stressed how social systems based on things such as race, class, gender, sexual orientation, and disability combine to create an interlocking system that privileges some and oppresses others.
Reflecting on your own positionality and the intersectional nature of your identity can help you think more intentionally about your content choices, the materials you assign to your students, and even how the different aspects of your students’ identities may affect their experience in your class.
Empowering students
The relationships that define learning environments are, unavoidably, imbued with power. As an instructor, you hold a position of authority, and a level of implicit institutional power – you determine the content of your course, create assignments, and grade those assignments. But when students have agency in their courses, they are more likely to be engaged and invested in their own learning . Reflecting on the power structures that define your classrooms may help you find ways to recalibrate or redistribute power so that students become more active agents in the creation of disciplinary knowledge, as well as in their own learning.
As you reflect, you might consider adopting one or more of following strategies for empowering your students:
- Take on the role of a guide. Rather than aspiring to transmit information through lecture, consider ways to make students active participants and contributors in their learning. Develop student-driven activities and discussions that create constructive, cooperative learning environments that encourage students to learn together.
- Consider flipping your classroom . Devote the time you spend with students to interaction and collaboration. Create videos focused on your lecture material that students can watch (and rewatch) as a homework activity.
- Work with students to articulate community values and expectations. Consider building community agreements with students. Openly discuss how you will assess students’ work and allow students to ask questions and offer their own ideas for grading. A great way to get students involved in thinking about their own assessment is to co-create assessment rubrics.
- Encourage students to share their own knowledge and expertise. Ask students to think about what they already know about a course topic and how your course can help them build upon that knowledge. Challenge students to think critically about why and how course material is relevant to their own lives.
- Practice inclusive course design. Universal Design for Learning (UDL) principles can help make your teaching more inclusive and offer students more opportunities to engage and express their knowledge.
Reflective Teaching
Reflecting on our teaching experiences, from the effectiveness of assignments to the opportunities for student interaction, is key to refining our courses and overall teaching practice. Reflective teaching can also help us gain closure on what may have felt like an especially long and challenging semester.
Four Approaches to Reflective Teaching
The goal of critical self-reflection is to gain an increased awareness of our teaching from different vantage points (Brookfield 1995). Collecting multiple and varied perspectives on our teaching can help inform our intuitions about teaching through an evidence-based understanding of whether students are learning effectively. Stephen Brookfield, in Becoming a Critically Reflective Teacher , proposes four lenses to use when examining and assessing our teaching:
- The autobiographical. What do I see as the successes and challenges of the course? What went well, and what could be improved for next time? If I could do X again, how might I do it differently?
- The students’ eyes. What do students have to say about what enhanced their learning and what hindered their learning? What recommendations do students have to help improve the course for next time?
- Our colleagues’ experiences. What do my colleagues have to say about what went well for them this semester? What was challenging? If my colleagues are teaching similar courses and/or student populations, what are similarities or differences in our experiences? In our assignments?
- Theoretical literature What are evidence-based strategies for supporting student learning? What does the research have to say about how students learn best in similar courses? What does the research say about how students are experiencing higher education at this moment in time?
Collectively, these four lenses foster repeat engagement with members of our teaching and learning community, both on campus and the broader scholarly community. For Brookfield, however, the most important step to reflective teaching is to go beyond the collection of feedback (i.e., from self, student, peer, and scholarly work) by strategically adjusting our teaching methods and goals. By habitually reflecting on our practice, documenting changes and noting our progress, then making efforts to iterate again, we become student-centered, flexible, and innovative educators.
Selected Examples of Reflective Teaching Strategies
Reflecting on our teaching, or a colleague’s teaching, inherently starts from a place of subjectivity and self-reported experiences -- How do I, as the instructor, feel class went? What do students think about their learning environment? How do I think my assessments compare to a colleague’s in a similar course? Self-reflection, after all, is foundational to recognizing assumptions and biases in how we design and teach our courses. However, we can adjust our approach to reflection by grounding our thinking and feeling to a concrete classroom artifact or objective observation. The following examples for reflective teaching highlight different ways we can start with evidence.
Teaching Journal. Teaching journals are a way to document your teaching experience on a daily or weekly basis. After each class, spend about five minutes recording your thoughts on the day’s lesson and interactions with students. What went well? What was challenging? If I could redo something, what would it be and what would I do differently? At the end of the semester, use your reflections to assess your experience as a whole and make informed decisions regarding future instructional changes. Consider these questions from a 2018 CTL Article .
Were your stated learning outcomes well aligned with class activities and assignments? Did student learning and engagement meet your expectations? Any surprises?
Were there course concepts and materials that students struggled with? Are there opportunities to approach teaching these concepts in a new way?
Are there course policies or other campus resources you can add to your syllabus or bCourses site so students have the information from the start?
Did you encounter any new approaches or practices during the semester, perhaps from a colleague or CTL workshop, that can help you save time and energy?
Assignment Wrapper. The goal of exam wrappers (link is external) is to guide students through a review of their learning and testing experience to inform future adjustments to their learning process. Adapt this exercise to structure your review of an assignment or activity.
Reflect on the design of the assignment. How is this assignment designed to help prepare students to achieve one or more stated learning objectives?
Reflect on the implementation of the assignment. Did student learning and engagement meet your expectations? Were there any surprises?
Reflect on how you communicated your expectations to students. Did you explain how this assignment connects to the broader picture of learning in the course? Did you describe what an exemplary submission or deliverable looks like?
Reflection on the experience as a whole. What adjustments might you make to set students up for success or enhance their learning?
Peer Review of Materials. Find a trusted colleague who teaches a similar course -- similarities may include disciplinary content, course structure, enrollment size, course placement in a curriculum (e.g., introductory or advanced course), and student demographics. Select one assignment, activity, or lecture material (e.g., presentation slides, handouts) to review and gather feedback on. Use this opportunity to discuss the strengths and challenges of designing and using this teaching artifact in the context of what is similar between your courses.
Literature Scan of a Similar Assignment, Activity, or Digital Tool. Select one assignment, activity, or educational technology tool you use in your course. Then, search the literature on education research for articles describing how other instructors use the same teaching method in their courses. Education research explores the conditions under which teaching strategies, such as active learning techniques , values affirmations and social belonging interventions , and inclusive teaching techniques , impact student learning. Scholars consider both lab and authentic classroom contexts, and explore disciplinary-based teaching strategies. When comparing teaching methods, consider the following questions.
What is similar or different to the design or implementation described in the study and my teaching method?
What findings and takeaways can I generalize, adjust, and apply to my teaching context?
How might my teaching method build on the author’s findings?
New to education research? Consider starting with CBE-Life Sciences Education’s repository (link is external) of annotated peer-reviewed articles to unpack various aspects of an education study.
References and Resources For Further Reading
Bailey, K. M., Curtis, A., and Nunan, D. (2001). Pursuing Professional Development: The Self as Source. Boston: Heinle, Cengage Learning.
Brookfield, Stephen. (1995). Becoming a Critically Reflective Teacher. San-Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
“ End-of-the-Semester Reflection from the Teachers Point of View (link is external) ”. Faculty Evaluation and Coaching Department, Academy of Art University.
Fink, L. D. (2003). Creating Significant Learning Experiences: An Integrated Approach to Designing College Courses. San-Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
“ Reflective Teaching (link is external) ”. Poorvu Center for Teaching and Learning, Yale.
Toven-Lindsday, Brit. (2018). “ No Time Like the Present ”. Center for Teaching and Learning, UC Berkeley.
Weimer, Maryellen. (2002). Learner-Centered Teaching: Five Key Changes to Practice. San-Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
What is Reflective Teaching? Lessons Learned from ELT Teachers from the Philippines
- Regular Article
- Published: 11 January 2018
- Volume 27 , pages 91–98, ( 2018 )
Cite this article

- Paolo Nino Valdez ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4404-350X 1 ,
- Jocelyn Amor Navera 1 &
- Jerico Juan Esteron 1
1283 Accesses
11 Citations
2 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Reflection is an essential dimension of effective teaching. It prompts classroom teachers to subject themselves to a process of self-observation or self-evaluation. By reflecting on what they do in the classroom, teachers specifically explore their teaching practices and beliefs and whether these, indeed, work. This then may lead teachers to continue or modify their teaching strategies for the improvement of their class instruction. Grounded on the notions of reflective practice (in: Kumaradivelu 2003 ; Freeman 2002 ; Borg 2003 ), this brief report aims to share insights from a case study conducted in the Philippines. Initially, the study presents challenges teachers face in the Philippine education system in terms of actualizing reflective teaching. Using a case study approach among teachers taking a master’s class on English Language Teaching issues, the presentation proceeds with discussing the teachers’ views on reflective teaching and the existing challenges faced in actualizing this practice in their respective contexts. The presentation further identifies teachers’ contrasting views about existing theoretical viewpoints on reflective teaching that may serve as potential areas for further investigation.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Social Learning Theory—Albert Bandura

Ethical Considerations of Conducting Systematic Reviews in Educational Research


Teacher-Student Interactions: Theory, Measurement, and Evidence for Universal Properties That Support Students’ Learning Across Countries and Cultures
Benson, P. (2009). Learner autonomy. TESOL Quarterly, 47 (4), 839–842.
Article Google Scholar
Borg, S. (2003). Teacher cognition in language teaching: A review of research on what language teachers think, know, believe, and do. Language Teaching, 36 (2), 81–109. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0261444803001903 .
Borg, S. (2012). Current approaches to language teacher cognition research: A methodological analysis. In R. Barnard & A. Burns (Eds.), Research language teacher cognition and practice (pp. 11–29). Bristol, UK: Multilingual Matters.
Google Scholar
Brookfield, S. D. (1995). Becoming a critically reflective teacher . San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
de la Rosa, P. (2005). Toward a more reflective teaching practice: Revisiting excellence in teaching. Asia Pacific Education Review, 6 (2), 170–176.
Department of Education. (2016). DO no. 39, s. 2016—Adoption of the Basic Education Research Agenda [PDF document]. http://www.deped.gov.ph/sites/default/files/order/2016/DO_s2016_039.pdf.
Farrell, T.S.C. (2008). Reflective practice in the professional development of teachers of adult English language learners. Washington, DC: Center for Applied Linguistics. http://www.cal.org/caelanetwork/pd_resources/CAELABrief-ReflectivePractice.pdf
Freeman, D. (2002). The hidden side of the work: Teacher knowledge and learning to teach. Language Teaching, 35, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0261444801001720 .
Freire, P. (1970). Pedagogy of the oppressed . New York: Seabury Press.
Hacker, P., & Barkhuizen, G. (2008). Autonomous teachers, autonomous cognition: Developing personal theories through reflection in language teacher education. In T. Lamb & H. Reinders (Eds.), Learner autonomy: Concepts, realities and issues (pp. 161–186). Philadelphia/Amsterdam: John Benjamins.
Chapter Google Scholar
Jay, J. K., & Johnson, K. L. (2002). Capturing complexity: A typology of reflective practice for teacher education. Teaching and Teacher Education, 18 (1), 78–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0742-051X(01)00051-8 .
Kumaradivelu, B. (2003). Beyond methods: Macrostrategies for language teaching . New Haven/London: Yale University Press.
Kumaradivelu, B. (2006). Understanding language teaching: From method to postmethod . New York/London: Taylor and Francis.
Martin, I. P. (2005). Conflicts and implications in Philippine education: Implications for ELT. In D. T. Dayag & J. S. Quakenbush (Eds.), Linguistics and language education in the Philippines and beyond: A festschrift in honor of Ma. Lourdes S. Bautista (pp. 267–280). Manila: Linguistic Society of the Philippines.
Ocampo, D. S. (2014). The K to 12 Curriculum [PDF document]. http://industry.gov.ph/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/6th-TID-Usec.-Ocampos-Presentation-on-K-to-12.pdf.
Perfecto, M. R. G. (2012). Contextual factors in teacher decision making: Extending the woods model. Asia Pacific Education Researcher, 21 (3), 474–483.
Rañosa-Madrunio, M., Tarrayo, V. N., Tupas, R., & Valdez, P. N. (2016). Learner autonomy: English language teachers’ beliefs and practices in the Philippines. In R. Barnard & J. Li (Eds.), Language learner autonomy: Teachers’ beliefs and practices in Asian contexts (pp. 114–133). Phnom Penh: IDP Education (Cambodia) Ltd.
Schön, D. A. (1983). The reflective practitioner: How professionals think in action . New York, USA: Basic Books Inc.
Valdez, P., & Lapinid, M. R. (2015). The constraints of math teachers in the conduct of action research: A rights analysis. Malaysian Journal of Learning and Instruction, 12, 1–19.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of English and Applied Linguistics, Brother Andrew Gonzalez College of Education, De La Salle University, 1501 Andrew Gonzalez Hall, DLSU 2401 Taft Avenue, 1004, Manila, Philippines
Paolo Nino Valdez, Jocelyn Amor Navera & Jerico Juan Esteron
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Paolo Nino Valdez .
Appendix A: Informed Consent Form
Dear Student:
We are conducting a research on the reflective teaching and challenges in applying reflective teaching in the workplace. We seek your participation through our interview and responding to this simple survey. Rest assured that your participation in the study will not have any bearing on your grades for the class. Moreover, data that will be gathered shall be used exclusively for the aforementioned purposes. Likewise, data that you will provide shall be treated with utmost confidentiality. Therefore, your confirmation shall mean that you agree to participate in this project.
Researchers
Name (optional):
Levels/subjects taught:
Years of teaching experience:
Reflective exercise:
The set of questions do not have right or wrong answers as these do not have a bearing on your grades.
What is reflective teaching for you, and how do you practice it in the classroom?
Does your workplace allow you to become a reflective teacher? What could be the possible impediments to achieving this, and in what way can your institution help you become reflective teachers?
How does reflective teaching affect your view or practice of:
Work as teachers?
Students as language learners?
School as an institution of progress?
Interview questions:
Could you narrate some experiences related to the application of reflective teaching? What was your goal? And were these goals met?
In what ways do you think your institution has been helpful or not helpful in making you a reflective teacher? Could you cite specific instances concerning this?
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Valdez, P.N., Navera, J.A. & Esteron, J.J. What is Reflective Teaching? Lessons Learned from ELT Teachers from the Philippines. Asia-Pacific Edu Res 27 , 91–98 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-018-0368-3
Download citation
Published : 11 January 2018
Issue Date : April 2018
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-018-0368-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- English Language Teaching
- Philippine education
- Reflective teaching
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Professional development
- Taking responsibility for professional development
Reflective teaching: Exploring our own classroom practice
Reflective teaching means looking at what you do in the classroom, thinking about why you do it, and thinking about if it works - a process of self-observation and self-evaluation.

By collecting information about what goes on in our classroom, and by analysing and evaluating this information, we identify and explore our own practices and underlying beliefs. This may then lead to changes and improvements in our teaching.
Reflective teaching is therefore a means of professional development which begins in our classroom.
- Why it is important
- Teacher diary
- Peer observation
- Recording lessons
- Student feedback
Why it is important Many teachers already think about their teaching and talk to colleagues about it too. You might think or tell someone that "My lesson went well" or "My students didn't seem to understand" or "My students were so badly behaved today."
However, without more time spent focussing on or discussing what has happened, we may tend to jump to conclusions about why things are happening. We may only notice reactions of the louder students. Reflective teaching therefore implies a more systematic process of collecting, recording and analysing our thoughts and observations, as well as those of our students, and then going on to making changes.
- If a lesson went well we can describe it and think about why it was successful.
- If the students didn't understand a language point we introduced we need to think about what we did and why it may have been unclear.
- If students are misbehaving - what were they doing, when and why?
Beginning the process of reflection You may begin a process of reflection in response to a particular problem that has arisen with one or your classes, or simply as a way of finding out more about your teaching. You may decide to focus on a particular class of students, or to look at a feature of your teaching - for example how you deal with incidents of misbehaviour or how you can encourage your students to speak more English in class.
The first step is to gather information about what happens in the class. Here are some different ways of doing this.
Teacher diary This is the easiest way to begin a process of reflection since it is purely personal. After each lesson you write in a notebook about what happened. You may also describe your own reactions and feelings and those you observed on the part of the students. You are likely to begin to pose questions about what you have observed. Diary writing does require a certain discipline in taking the time to do it on a regular basis.
Here are some suggestions for areas to focus on to help you start your diary.
Download diary suggestions 51k
Peer observation Invite a colleague to come into your class to collect information about your lesson. This may be with a simple observation task or through note taking. This will relate back to the area you have identified to reflect upon. For example, you might ask your colleague to focus on which students contribute most in the lesson, what different patterns of interaction occur or how you deal with errors.
Recording lessons Video or audio recordings of lessons can provide very useful information for reflection. You may do things in class you are not aware of or there may be things happening in the class that as the teacher you do not normally see.
- How much do you talk?
- What about?
- Are instructions and explanations clear?
- How much time do you allocate to student talk?
- How do you respond to student talk?
- Where do you stand?
- Who do you speak to?
- How do you come across to the students?
Student feedback You can also ask your students what they think about what goes on in the classroom. Their opinions and perceptions can add a different and valuable perspective. This can be done with simple questionnaires or learning diaries for example.
What to do next Once you have some information recorded about what goes on in your classroom, what do you do?
- Think You may have noticed patterns occurring in your teaching through your observation. You may also have noticed things that you were previously unaware of. You may have been surprised by some of your students' feedback. You may already have ideas for changes to implement.
- If you have colleagues who also wish to develop their teaching using reflection as a tool, you can meet to discuss issues. Discussion can be based around scenarios from your own classes.
- Using a list of statements about teaching beliefs (for example, pairwork is a valuable activity in the language class or lexis is more important than grammar) you can discuss which ones you agree or disagree with, and which ones are reflected in your own teaching giving evidence from your self-observation.
- Read You may decide that you need to find out more about a certain area. There are plenty of websites for teachers of English now where you can find useful teaching ideas, or more academic articles. There are also magazines for teachers where you can find articles on a wide range of topics. Or if you have access to a library or bookshop, there are plenty of books for English language teachers.
- Ask Pose questions to websites or magazines to get ideas from other teachers. Or if you have a local teachers' association or other opportunities for in-service training, ask for a session on an area that interests you.
Conclusion Reflective teaching is a cyclical process, because once you start to implement changes, then the reflective and evaluative cycle begins again.
- What are you doing?
- Why are you doing it?
- How effective is it?
- How are the students responding?
- How can you do it better?
As a result of your reflection you may decide to do something in a different way, or you may just decide that what you are doing is the best way. And that is what professional development is all about.
Julie Tice, Teacher, Trainer, Writer, British Council Lisbon
This article was first published in 2004
Well organized
Greetings, The steps explained in reflective teaching are quite practical, no matter how many years educators put into their experience, properly guided ideas will definitely enhance how to engage our students, at the end of the day, what matters is how the learning took place in the classroom. and reflect on how i inspired my students to deliver the content, the reflective teaching practice not only helps to get back and analyze, but helps the educator to be more organized, thank you for the wonderful article.
- Log in or register to post comments
Wonderful advice
Thank you very much for these suggestions. They are wonderful.
online journal
Reflecting teaching.
Dear Editor, This is a very useful article for English teachers and trainers. Teaching diary is a must for all teachers and trainers.
JVL NARASIMHA RAO
Reflecting on your teaching
Dear Julie,
An excellent article. Nothing can be more important then self reflection, i.e. looking inwardly to find out what you did, how you did it and how and what you need to do to make it better. Unfortunately we seldome reflect on ourselves.
I would like to introduce few simple questions every teacher should ask after completing a lesson:
1. Can I state one thing thet the students took back with them after my lesson?
2. Can I state one thing that I wanted to do but was not able to it becasue of insufficient time?
3. Can I state one thing that I should not have done in this lesson?
4. Can I state one thing that I think I did well?
Answers to these questions will enable the teacher to do better in the future.
Research and insight
Browse fascinating case studies, research papers, publications and books by researchers and ELT experts from around the world.
See our publications, research and insight
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Reflective Essay on Learning and Teaching

2019, International Journal of Arts and Social Science (IJASS)
Learning and teaching are inextricably intertwined. The principal objective of education is learning, and the means used to fulfil this aim is teaching. Considering that these two phenomena are inseparable, it can therefore be deduced that teaching has to be carried out for learning to take place. In light of the afore-mentioned, this reflective essay deals with some of my personal experiences in learning and teaching from my secondary years to my tertiary years and beyond. It is a reflection about my academic formation and how certain experiences and individuals in my life have shaped the way that I teach and whom I have become as a teacher. More importantly, this reflective essay highlights the transformative reflection that I experienced, during my postgraduate studies, in my attempts to become a better and more effective teacher. It is underscored that teachers have the responsibility to engage in continuous reflective practice as the principal means of improving and sustaining effective didactic practices. Effective teaching results in effective learning. Keywords: higher education, language(s), learning, learning and teaching, teaching.
Related Papers
Research in Pedagogy
Jelena Maksimović
Mustafa Shalaby , Ashwaq Naif Almuqati
Since the beginning of the 20th-century specialists have strived for ways that could comprise language teaching methods, which can ensure the best results in language training and teaching classes. And there are various methods, especially in the first half of this century. Some language teaching experts progressed further than methods with the hope of earning more results. Only some of teachers' encouraged towards what is known as reflective teaching (RT).The process of bridging the gap between experience and learning is called Reflection. RT teacher requires a good self-observations of self-assessment, the need to go on patrol in a way to ensure that teachers understand their classes so that they make their own classroom process improvements where needed. RT is the process by which teachers reflect on their classroom procedures for collecting and analysing the descriptive facts that will be modified to show where the change can be made. RT gives teachers material and professional flexibility for teachers. This paper elaborates on the process of reflection practice and deliberates the effects for foreign/second language educators.
Gregory J Light
Book Chapter
Abeer Althaqafi
To have a voice means to be reflexive and reflexivity is a social scientific variety of self-consciousness (Delamont, 1992). Reflection is important, and some might acknowledge that they do not really know how to get the best from it. According to Ghaye (2011), reflective practices help us understand the links between what we do and how we might improve our effectiveness. Reflective practices help people to understand the significance of work, and provide new insights for developing this work. They also help us understand the links between feeling, thinking and doing -how we feel affects how we think- (ibid, 2011). This paper will try to help teachers to develop their understanding and skills of learning through reflection. It is hoped that this work can help teachers to explore the power and potency of reflecting on strengths and weaknesses, make sense of teaching and be the best that they can be.
Parviz Maftoon
Reflective teaching as the self-inquiry and evaluation of teacher performance has turned to be a buzzword in language teaching. In spite of the fact that theoretical foundations and perspectives of reflective teaching have been sufficiently investigated, some practical considerations, such as the role of the language teacher and learnersùnique personalities, as well as socio-cultural effects, have received scant attention in the literature. This paper is an attempt to study those issues and the conditions required to pave the way for better understanding and applying reflective teaching so that it can lead to more practical changes in the teaching process.
Telma Gimenez
IOLC Conference
Reflective teaching goes through an analytical process of self-observation and self-evaluation. Self-reflection can be one of the effective means of finding out one’s strengths and drawbacks in respect of teachers’ professional development. Teacher education has directly or indirectly been connected to the reflective teaching practice. Capturing the actual picture of language teaching directly or indirectly leads to look at what the teacher does in the classroom. A teacher can collect information and then bring necessary changes to teaching by reflecting upon his/her own teaching practices. But the fact is, the process of reflection should be systematic and carried out by some carefully designed steps. There are some important ways or methods of conducting the process of reflection like peer observation, recording lessons, student feedback. A teacher can invite a colleague to come into the class to collect information about the lesson and to have students’ opinions and perceptions as well. The respective teacher may also record the lessons regularly to have the actual picture of the class. After collecting authentic information the teacher can Think, Talk, Read and Ask while going through some structured steps. Thus this paper will focus on a cyclical process of reflective teaching that once starts and keeps going by implementing changes. Reflections might go on continuously by posing different rhetoric questions like, What I am doing? Why I am doing? Is the teaching method effective? What are the problems? and What could be the solutions?. This is how the teacher’s professional development is related to the evaluative cycle of reflective teaching. This paper, therefore, attempts to discuss the findings of a study that investigated the role that reflective teaching can play in effective English language teaching contexts and in the field of teachers’ professional development. Most importantly this paper offers recommendations by suggesting a well-designed procedure for reflective teaching in ESL/EFL classroom.
Martin Blaszk
Reflection in teacher development is important as it can help both experiencedand novice teachers to better understand the processes theyare involved in. It can also be used to aid evaluation processes. This paperpresents a small scale study that involved undergraduate Englishphilology students from Gdańsk University who were studying for theteacher specialisation. One of its purposes was to trial a strategy forfeedback that could be used to mediate an already existing model ofassessment for students’ taught lessons, which previous to the studyused only a prescribed set of assessment criteria. Another purpose wasto promote a reflective turn in both the student-teacher and academicmentor (myself), which would then inform the discussions that tookplace after each observed lesson. In addition to this, I was interested tofind out if this strategy would generate a suitable quality and quantityof information, so that it might be used for further research. Overall,the strategy proved a use...
Asian EFL Journal
Using qualitative case study methodology, this article explores a language teacher’s development as a reflective practitioner, while she was engaged on a three-year in-service BA (TESOL) programme in the Middle East. Data gained from observations and interviews reveal evidence of growth in her reflective qualities, skills and capacity to reflect critically, as she learned to solve teaching problems, drawing on public as well as personal theories. The constructivist nature of the BA (TESOL) programme concerned was integral to her development, as was a warm, supportive environment in the school she taught in. Interview data that uncovered early career experiences emphasises the need for pre-service courses to prepare teachers thoroughly for the challenges they face.
European Educational Research Journal
Marit H Hoveid
RELATED PAPERS
Van Medical Journal
Tolga Özkan
Revista Dissertar
Ari Francisco Barbosa
Cadernos de Literatura Comparada
Maria Lúcia Dal Farra
Journal of North Khorasan University of Medical Sciences
Fatemeh Nooshinfard
Boaz Langford
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
Robert Rountree
Informationen aus Orthodontie & Kieferorthopädie
Eric Stelnicki
CIÊNCIA, TECNOLOGIA E DESENVOLVIMENTO RURAL: COMPARTILHANDO CONHECIMENTOS INOVADORES E EXPERIÊNCIAS
Wellington Andrade
Simon Stuart
Procedia Computer Science
Irina Petrova
Applied General Topology
Leonardo Pinheiro
International Journal of Clinical & Medical Microbiology
Carissa Choong
SAHWA Scientific Paper
Bahgat Korany
African Health Sciences
Chiazor Onyia
Lecture Notes in Computer Science
Cosmin Bonchis
Istanbul University - DergiPark
Umut Burak Geyikçi
Clinical Microbiology Reviews
Thomas Jaenisch
BMC Microbiology
natalia gonzalez castillo
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
Séverin Pistre
Lily Wisker
e-cadernos CES
Leonice Lima
Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation
Jonathan Treisman
Weather and Forecasting
Ridwan Siddique
Fertility and Sterility
Minnie Malik
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

- Schools & departments

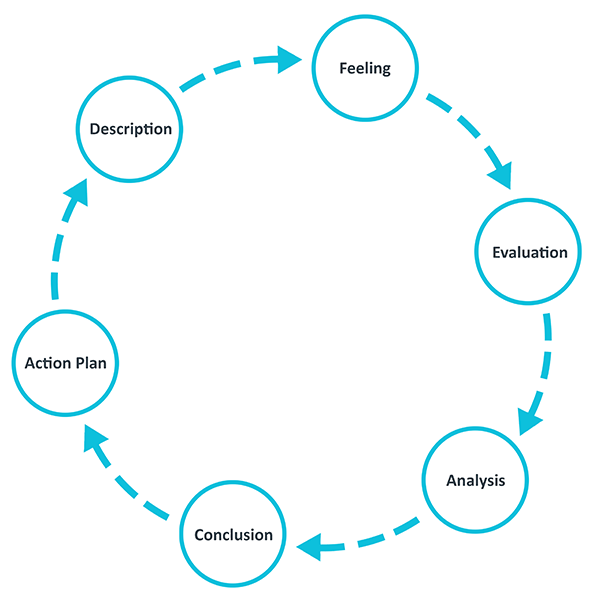
Gibbs' Reflective Cycle
One of the most famous cyclical models of reflection leading you through six stages exploring an experience: description, feelings, evaluation, analysis, conclusion and action plan.
Gibbs' Reflective Cycle was developed by Graham Gibbs in 1988 to give structure to learning from experiences. It offers a framework for examining experiences, and given its cyclic nature lends itself particularly well to repeated experiences, allowing you to learn and plan from things that either went well or didn’t go well. It covers 6 stages:
- Description of the experience
- Feelings and thoughts about the experience
- Evaluation of the experience, both good and bad
- Analysis to make sense of the situation
- Conclusion about what you learned and what you could have done differently
- Action plan for how you would deal with similar situations in the future, or general changes you might find appropriate.
Below is further information on:
- The model – each stage is given a fuller description, guiding questions to ask yourself and an example of how this might look in a reflection
- Different depths of reflection – an example of reflecting more briefly using this model
This is just one model of reflection. Test it out and see how it works for you. If you find that only a few of the questions are helpful for you, focus on those. However, by thinking about each stage you are more likely to engage critically with your learning experience.
This model is a good way to work through an experience. This can be either a stand-alone experience or a situation you go through frequently, for example meetings with a team you have to collaborate with. Gibbs originally advocated its use in repeated situations, but the stages and principles apply equally well for single experiences too. If done with a stand-alone experience, the action plan may become more general and look at how you can apply your conclusions in the future.
For each of the stages of the model a number of helpful questions are outlined below. You don’t have to answer all of them but they can guide you about what sort of things make sense to include in that stage. You might have other prompts that work better for you.
Description
Here you have a chance to describe the situation in detail. The main points to include here concern what happened. Your feelings and conclusions will come later.
Helpful questions:
- What happened?
- When and where did it happen?
- Who was present?
- What did you and the other people do?
- What was the outcome of the situation?
- Why were you there?
- What did you want to happen?
Example of 'Description'
Here you can explore any feelings or thoughts that you had during the experience and how they may have impacted the experience.
- What were you feeling during the situation?
- What were you feeling before and after the situation?
- What do you think other people were feeling about the situation?
- What do you think other people feel about the situation now?
- What were you thinking during the situation?
- What do you think about the situation now?
Example of 'Feelings'
Here you have a chance to evaluate what worked and what didn’t work in the situation. Try to be as objective and honest as possible. To get the most out of your reflection focus on both the positive and the negative aspects of the situation, even if it was primarily one or the other.
- What was good and bad about the experience?
- What went well?
- What didn’t go so well?
- What did you and other people contribute to the situation (positively or negatively)?
Example of 'Evaluation'
The analysis step is where you have a chance to make sense of what happened. Up until now you have focused on details around what happened in the situation. Now you have a chance to extract meaning from it. You want to target the different aspects that went well or poorly and ask yourself why. If you are looking to include academic literature, this is the natural place to include it.
- Why did things go well?
- Why didn’t it go well?
- What sense can I make of the situation?
- What knowledge – my own or others (for example academic literature) can help me understand the situation?
Example of 'Analysis'
Conclusions.
In this section you can make conclusions about what happened. This is where you summarise your learning and highlight what changes to your actions could improve the outcome in the future. It should be a natural response to the previous sections.
- What did I learn from this situation?
- How could this have been a more positive situation for everyone involved?
- What skills do I need to develop for me to handle a situation like this better?
- What else could I have done?
Example of a 'Conclusion'
Action plan.
At this step you plan for what you would do differently in a similar or related situation in the future. It can also be extremely helpful to think about how you will help yourself to act differently – such that you don’t only plan what you will do differently, but also how you will make sure it happens. Sometimes just the realisation is enough, but other times reminders might be helpful.
- If I had to do the same thing again, what would I do differently?
- How will I develop the required skills I need?
- How can I make sure that I can act differently next time?
Example of 'Action Plan'
Different depths of reflection.
Depending on the context you are doing the reflection in, you might want use different levels of details. Here is the same scenario, which was used in the example above, however it is presented much more briefly.
Adapted from
Gibbs G (1988). Learning by Doing: A guide to teaching and learning methods. Further Education Unit. Oxford Polytechnic: Oxford.
12 Reflective Teaching Examples

Reflective teaching is a process where teachers reflect on their own teaching practices and learn from their own experiences.
This type of reflection allows teachers to see what works well in their classrooms and what needs improvement. Reflective teaching also helps teachers to understand the impact that their teaching has on students.
Examples of reflective teaching include observing other teachers, taking notes on your own teaching practice, reading about how to improve yourself, and asking for feedback from your students to achieve self-improvement.
Reflective Teaching Examples
1. reflection-in-practice.
Reflection in practice is a concept by David Schon which involves small moments of reflection throughout your day.
Instead of pausing at the end of your activities and reflecting upon what you did, Schon argues that good practitioners reflect in the moment and make tiny changes from moment-to-moment. This is the difference between reflection on practice and reflection in practice. “Reflection on” occurs once the lesson is over. Reflection in occurs during the lesson.
For example, as you’re doing a question-and-answer session with your class, you might realize that the students are tuning out and getting bored. In order to resolve this problem, you might choose to get the students all to stand up and play heads or tails for questions you ask them. This might get the kinesthetic learners re-engaged in the lesson and salvage it from its impending implosion.
Related Article: 15 Action Research Examples
2. Conducting Classroom Observations
Another way to do reflective teaching is to start a classroom observation routine. Create a template for your observations (e.g. listing each student’s name down the side, with notes beside it) and take notes on students’ work.
You could, for example, choose to observe how well students responded to a new classroom intervention. These written observations can form the basis for changes that you can make to your work as you progress.
Similarly, you could make observations about students’ interactions after changing the classroom layout. This can help you edit and refine your chosen layout in order to maximize student learning and figure out the best location for each student.
3. Pivoting based on Formative Feedback
Reflective teachers also try to obtain formative feedback from students in order to gather data that can form the basis of their reflection.
An example of formative feedback is a pre-test a month before the exams.
This pre-test can help the teacher understand the general areas of weakness for their students, and acts as the basis for a pivot in their teaching practices. The teacher may, for example, identify a specific math challenge that the majority of the students had trouble with. They can then put extra focus on that challenge for the next few weeks so the students can ace that challenge in the end-of-term test.
In this way, formative feedback is a core tool for teachers in their formative feedback toolkit.
4. Keeping a Teaching Diary
A personal teaching diary can help teachers to identify trends in their behaviors (and the behaviors of their students) that can help teachers to improve.
For example, in my teaching diary, I will often take notes about how I reacted to certain events. I’ll note my reaction as well as things I did well, ways I effectively self-regulated , and things I did poorly. If I’m taking notes on an answer to a student’s question, I might note that something I did well was “give a clear answer” but an area for improvement might be “I failed to follow-up later in the day to check my student’s comprehension”.
Incidentally, teaching diaries can be extremely useful for self-performance reviews . Bring your teaching diary into the performance review and go over it with your line manager. They will be super impressed with your reflective practice!
5. Receiving Student Evaluations
Despite how much we may despise student evaluations, they can contain important tidbits of information for us.
I often like to compare my evaluations from one to the next to see if there are changes in the student trend. I’ll also work really hard on one aspect of my teaching and see if I can get students to take notice and leave a comment in the evaluation.
For example, one semester, I decided to implement a tech intervention (I let students use an educational app in class). The students used the app, and it turns out – they didn’t like it!
Without the student evaluation, I wouldn’t have been able to identify this problem and work on solving it. You can read all about that study here, which I published in an academic journal.
6. Debriefing with a Mentor
Having a mentor has been invaluable for me in my career. By sitting down with a mentor, I learn a lot about my strengths and weaknesses.
Mentors tend to bring out reflectiveness in all of us. After all, they’re teachers who want us to improve ourselves.
Your mentor may ask you open-ended questions to get you to reflect, or discuss some new points and concepts that you haven’t thought about before. In this process, you’re being prompted to reflect on your on teaching practice and compare what you do to the new ideas that have been presented. You may ask yourself questions like “do I do that?” or “do I need to improve in that area?”
7. Using Self-Reflection Worksheets
Self-reflection worksheets are a good ‘cheat’ for figuring out how to do self-reflection for people who struggle.
You can find these worksheets online through services like Teachers Pay Teachers. They often involve daily activities like:
- Write down one thing you struggled with today.
- Write down one big win.
- Write down one thing you will actively try to work on tomorrow.
These worksheets are simple prompts (that don’t need to take up too much time!) that help you to bring to the front of your consciousness all those thoughts that have been brewing in your mind, so you can think about ways to act upon them tomorrow.
See Also: Self-Reflection Examples
8. Changing Lesson Plans Based on Previous Experiences
At the end of each unit of work, teachers need to look at their lesson plans and self-assess what changes are required.
Everyone is aware of that teacher who’s had the same lesson plan since 2015. They seem lazy for failing to modernize and innovate in their practice.
By contrast, the reflective practitioner spends a moment at the end of the lesson or unit and thinks about what changes might need to be made for next time the lesson is taught.
They might make changes if the information or knowledge about the topic changes (especially important in classes that engage with current events!). Similarly, you might make changes if you feel that there was a particular point in the lesson where there was a lull and you lost the students’ attention.
9. Professional Development Days
Professional development days are a perfect opportunity for reflective teaching.
In fact, the leader of the professional development day is likely to bake reflectiveness into the event. They may prepare speeches or provide activities specifically designed for teachers to take a step back and reflect.
For example, I remember several moments in my career where we had a guest speaker attend our PD day and gave an inspiring speech about the importance of teachers for student development. These events made me think about what I was doing and the “bigger picture” and made me redouble my efforts to be an excellent teacher.
10. Implementing 2-Minute Feedback
The 2-minute feedback concept is excellent for reflective practice. For this method, you simply spend the last 2 minutes of the class trying to get feedback from your students.
One of the easiest ways to do this is to give students a post-it note at the end of the lesson. Have them write on one side something they liked about the lesson and on the other something they didn’t like. Then, you can read the feedback to reflect on how to improve.
With younger students, you can do ‘hands up’ for students and ask them how confident they are with the topic.
For online lessons, I’ve put a thermometer up on the screen and asked students to draw on the thermometer how confident that are (line at the top means very confident, line at the bottom means not confident at all).
11. Reading Books
Books are excellent for helping us to reflect and contemplate. There is a wide range of books for teachers, from philosophical ones like Pedagogy of the Oppressed to very practical workbooks.
Through reading, we encounter new ideas that challenge our current ideas. As we pick up new ideas and information, we interrogate our current thoughts and find ways to assimilate them into our new thinking. Sometimes, that requires us to change our own current opinions or thoughts, and challenge us to consistently improve.
In this way, reading books about teaching is an inherently reflective practice. It makes us better practitioners and more thoughtful people.
12. Listening to Podcasts
Like books, podcasts enable us to consume information that can help us pause and reflect.
I personally love podcasts because I find them easier to consume than books. The conversations and dialogue in podcasts help me to feel immersed in a conversation with close friends. Good podcasts hosts make you feel like they’re grappling with the exact same concerns and emotions as you are – and it’s a motivating experience.
Good podcasts for teachers include The Cult of Pedagogy and Teachers on Fire. These podcasts help me to reflect on my own teaching practice and continue to learn new things that I can compare to my own approaches and integrate when I feel they offer new insights that are valuable.
There are many ways to incorporate reflective practice into your teaching. By taking the time to reflect on your teaching, you can identify areas where you can improve and make changes to your practice. This will help you to become a more effective teacher and better meet the needs of your students. Through reflective practice, you can also develop a stronger sense of who you are as a teacher and what your personal teaching philosophy is.
Drew, C. & Mann, A. (2018). Unfitting, uncomfortable, unacademic: a sociological critique of interactive mobile phone apps in lectures. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-018-0125-y
Lousberg, L., Rooij, R., Jansen, S. et al. Reflection in design education. Int J Technol Des Educ. 30, 885–897 (2020). doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10798-019-09532-6

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
2 thoughts on “12 Reflective Teaching Examples”
Dr Chris Drew, this article is useful for teachers like me. I really appreciate your hard work. Thank you for being a helpful professor. Sandy
Dr, Chris Drew. First of all Congratulations. This article is handy for me as I am doing my teacher training course. You did a good job, explaining in a simple manner so, anyone can understand easily. Thank you so much. Alka
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Reflective Essay on Different Aspects of Teaching Practice
There are numerous areas of teaching which I need to improve upon, yet I have chosen to focus this essay on some of the fundamental factors to becoming a successful teacher: behaviour management and acting on feedback.
Behaviour Management
On placement I had to be careful to ensure that I had the correct level of formality in my relationships with pupils. This seems to be particularly apt in Mathematics where a significant amount of concentration and effort are needed. Haggerty (2002) suggests that a mathematics teacher needs to be relatively formal, in part due to the subject’s complex properties.
Being overfamiliar with pupils can diminish a teacher’s authority. Initially, in the first few weeks of the placement I was too informal with pupils and failed to progress from a teaching assistant-pupil to a teacher-pupil relationship adequately which requires a formal rather than informal, consultative register (Joos, 1972). However, my good relationship with pupils allowed me to contribute to their learning informally such as regularly helping pupils with maths homework outside of lessons and doing intervention and group work. Pupils seemed to thrive on the support I gave them. The informal, incidental learning (Marsick and Watkins, 1990) that took place clearly supplemented their formal lessons well.
Pupils gained a relational understanding (Skemp, 1977) of the topics they were learning due to my detailed explanations of how and why the maths worked. A great example of this was a colleague informing me of a Y11 student’s progress I had been working closely with: she was now achieving a C in Maths having only being at a grade D/E before, thus making her a candidate to sit the GCSE Higher Maths paper.
However, the rapport I had with pupils sometimes negatively impacted on my experiences in the classroom: particularly in my Year 9 class, where pupils misbehaved as they saw me as more of a student than a proper teacher. After consulting with the regular class teacher, I tried to remedy this by being stricter and tolerating disruption less. Capel and Gervis (2005) suggest that teachers who have high expectations of behaviour from their class tend to get their students to behave well. I found this to be true.
I tried to model the standard of behaviour I expected from the pupils, always being smart and punctual. I greeted pupils at the door at the beginning of the lesson and treated them fairly in the hope they would see me as a role model and copy my behaviour and thought processes (Bandura, 1977). This technique only partially solved the problem. My Year 7 and 8 classes behaved quite well but my Year 9 class was still disruptive, though they behaved better than at the start of my placement. I was teaching more lessons by my third week on placement and this naturally helped me gain some authority as pupils became more used to me as a teacher.
To try and improve the behaviour of my Year 9 group, I tried an alternative approach with them. I raised the volume of my voice, had zero-tolerance on misbehaviour and enforced heavy sanctions such as after-school detentions towards those who did misbehave. Interestingly, this worked on some students and not on others. This is perhaps explained by a University of New Hampshire report (2012) which stated that although some students who have a dearth of discipline at home will respond to this method, pupils who have controlling parents are less likely to respond to this strategy well. This is validated by my own experiences. I become more authoritarian instead of my intended authoritative manner (Ferlazzo, 2012) and damaged the rapport I had with students, creating conflict. Kearney et al. (1991) explain that students who dislike their teacher do not perform to their full potential in lessons, which was certainly true in my Year 9 class.
One approach that I did observe in an NQT’s lesson was to use formal register at the start of the lesson in teacher exposition before gradually using more informal language to assist students through activities and build a rapport with pupils. I found this to be successful in lessons when I trialled this approach. I also noticed that I was a lot more informal and relaxed when working with smaller groups of students as a teaching assistant. Pascarella and Terenzini (1991) explain that small group sizes are effective when a teacher has a large amount of interaction with students and motivates them which is something I always tried to do in my practice.
Gates (2001) highlights a lack of relevance to real life in Mathematics lessons as being a factor in misbehaviour in students. To try and engage students more, I provided more situations where pupils could see the content in a real-life context. Examples included having interesting facts at the start of the lesson such as why there are 360 degrees in a circle and having worded, practical questions on worksheets. As well as establishing strong cross-curricular links with Literacy, this allowed pupils to see the practical uses of mathematics which could motivate them more (Chambers, 2008) and add authenticity to their learning. Cockcroft (1982) suggests that it is hard to implement situations like this in every maths lesson. This is one of the limitations of this method. For example, algebraic topics are harder to link to real life than richer geometry modules. One target I got from my tutor was to have more purpose and meaning in my lessons, which I tried to achieve by chunking lessons into fast-paced activities with links to the real world. This worked for some pupils, but not all: less confident pupils preferred a slower-paced lesson where they had time to understand concepts.
Overall, I was quite a confident and recognisable figure to pupils, which had advantages and disadvantages. Ollerton (2004) argues that an informal teacher-pupil relationship can stimulate negative and disrespectful behaviour from students. This was partially true, particularly in my Year 9 class. This was because many pupils viewed me as a visitor or substitute, a common problem for student teachers on placement (Pope and Shivlock, 2008). However, after increased interaction with students in and out the classroom, they started to respect me more which is crucial to successful learning (Comer, 1995). It seems that the correct balance of being formal, yet approachable is required to be a successful teacher.
Acting on Feedback
Throughout placement I constantly reflected on my practice. I acted on and listened to feedback from experienced teachers. I did so as then they could give me the benefit of their expertise, thus increasing my Zone of Proximal Development (Vygotsky, 1978) by getting closer to their level of teaching capability.
Constant reflection is something that is needed to be an effective teacher. Ofsted (2012) established that the most successful mathematics teachers constantly strived to develop their practice. I kept a daily diary but this was not a sophisticated enough tool to use in my reflections. Schon (1991) states that, in order to become a reflective practitioner, you have to critically analyse your own strengths and weaknesses. My own interpretation of this was to relate theory to practice. From studying feedback given to me, I concluded that my biggest shortfall was in behaviour management. In order to try and overcome this barrier, I applied Honey and Mumford’s (2006) model of learning to a particular scenario involving my Year 9 class who often misbehaved in my lessons:
- Activist- The initial experience/stimuli of misbehaviour that happened in a Year 9 class I was teaching. Although not malicious in any way, students were loud and off task.
- Reflector- This is where I reviewed the experience and sought to understand why they were behaving like that by considering the internal/external conditions which affected their behaviour. I concluded that it was partially because of my teaching style, not having a clear and consistent routine and the school’s weak behaviour policy. It was also due to external factors like it being the last period on a Friday, meaning the students were desperate to get home and not in the mood to listen to me.
- Theorist- When contemplating the situation, I realised that it was not actually all my fault and that there were other factors causing their misbehaviour such as the time of day and the day of the week.
- Pragmatist- When I thought about how I was going to change this, I addressed each set of factors in turn. In terms of the internal factors, I set out clear expectations of behaviour of my class as well as a fixed classroom routine which calmed them down. For the external factors, I made it clear to the class that it was irrelevant that my lesson was last period on a Friday.
Going through this cycle of reflection enabled me to enhance my practice and learn experientially (Kolb, 1976) by reflecting on what I had made mistakes on and how to correct it. In this situation, I did note that the class started to behave better though I need to improve more in this area. However, there are limitations to this style of reflection. Davies (2012) states that it is quite elaborate and may distract from teaching practice. In addition, Price (2004) states that this model of reflection doesn’t really address any major issues. The amount of time spent reflecting on the problem did hinder me in my teaching practice.
To improve further, I needed to look at alternative models of reflection and learning through enactment and getting more voluntary experience in schools. Whilst on placement, I only taught lower school pupils and I need to gain experience teaching KS4 pupils. Observing and assisting experienced teachers will only increase my learning of the teaching profession. I will observe how to manage different classes to improve my performance and consistency in the classroom (Collinson, 1994; Bobek, 2004).
The placement I undertook really developed me as a teacher. I feel a lot more confident leading a class and have more of a teacher presence, particularly when dealing with younger students. I have started to control classes better and feel comfortable dealing with misbehaviour in the lower school. Conversely, I feel I need more practice at handling older students. Future actions I will take to improve my practice is to teach more challenging classes and older year groups in my summer placement to try and become more confident at leading a class.
I feel I have established a solid and reliable model of reflection which allowed me to change my practice and respond well to challenging incidents (see earlier example with my Year 9 class) and establish a plan of action. However, I do need to make sure that I continually reflect and amend my teaching style to suit different types of classes. I have always got on well with pupils and my varied abilities allow me to contribute a lot more to a school than just being a maths teacher.
Ofsted (2008) identify ‘subject expertise’, pedagogical knowledge and strong classroom management as the triumvirate of attributes needed to be a successful mathematics teacher. I feel I can demonstrate these skills well at an individual or group level. If I am comfortable displaying these skills at a whole class level I feel I will become a successful teacher.
Reference List
Bandura, A. (1977) Social Learning Theory. New York: General Learning Press.
Bobek, B. L. (2002) ‘Teacher Longevity- A key to career longevity’, The Clearing House, 75 (4), pp. 202-205.
Capel, S. and Gervis, M. (2005) ‘Motivating pupils’ in Capel, S., Leask, M. and Turner, T. (eds.) Learning to Teach in the Secondary School: A companion to school experience. 4 th edn.
Carroll, H. (1950) ‘A scale of measuring teacher-pupil attributes and teacher-pupil rapport’, Psychological Monographs- General and Applied, 64 (6), pp. 24-27.
Chambers, P. (2008) Teaching Mathematics: Developing as a Reflective Secondary Teacher. London: Sage.
Cockcroft, W. (1982) The Report of the Committee of Inquiry into the Teaching of Mathematics in Schools.
Collinson, V. (1994) Teachers as Learners: Exemplary teachers’ perceptions of personal and professional renewal. Bethesda, MD: Austin and Winfield.
Comer, J. (1995) Lecture given at Education Service Center, Houston.
Davies, S. (2012) ‘Embracing reflective practice’, Education for Primary Care, 23, pp. 9-12.
Ferlazzo, L. (2012) ‘Students who challenge us: Eight things skilled teachers think, say and do.’, Educational Leadership , 70 (2), pp. 100-105.
Gates, P. (2001) Issues in the Teaching of Mathematics. London: Routledge.
Great Britain. Ofsted (2008) Mathematics: Understanding the Score. London: Department for Education.
Great Britain. DfE (2012) Standards for Meeting Qualified Teacher Status. London: Department for Education.
Great Britain. Department for Business, Innovation and Skills (2009) The White Paper: Learning Revolution. London: Department for Business, Innovation and Skills.
Honey, P. and Mumford, A. (2006) The Learning Styles Questionnaire, 80-item version. Maidenhead: Peter Honey Publications.
Joos, M. (1972) Language and cultural diversity in American Education. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Kearney, P., Plax, T. G., Hayes, E. R. and Ivey, M. J. (1991) ‘College teacher misbehaviours: what students don’t like about what teachers say and do.’, Communication Quarterly, 39 (4), pp. 325-340.
Kolb, D. A. (1976) The Learning Style Inventory: Technical Manual. Boston: McBer.
Ollerton, M. (2004) Getting the Buggers to Add Up. London: Continuum.
Pascarella, E. and Terenzini, P. (1991) How College affects students. San Francisco: Jossey Bass.
Pope, M. and Shivlock, K. (2008) Successful Teaching Placements in Secondary Schools. Learning Matters: Exeter.
Price, A. (2004) ‘Encouraging reflection and critical thinking in practice’, Nursing Standard, 18 (47), pp. 123-129.
Schon, D. A. (1991) The Reflective Turn: Case Studies In and On Educational Practice. New York: Teachers Press, Columbia University.
Skemp, R. (1977), ‘Relational Understanding and Instrumental Understanding’, Mathematics Teaching, 77, pp. 20-26.
University of New Hampshire (2012) Controlling parents more likely to have delinquent children. Massachusetts: Science Daily.
Watkins, K. and Marsick, V. (1990) Informal and Incidental Learning in the Workplace. London.
Vygostky, L. S. (1978) Mind in Society: the development of higher psychological processes. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Cite this page
Similar essay samples.
- Essay on Budweiser: Wind Never Felt Better
- Essay on Amazon Stock News
- Monitoring pain response with deep brain stimulation
- Essay on the Basic Parts for a Successful Training Program
- Essay on Florence B Price Biography
- Essay on Macroeconomic Indicators of Globalization

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
ISSN: 2581-7922, Volume 2 Issue 5, September-October 2019. Kerwin A. Livingstone, PhD Page 57. Reflective Essay on Learning and Teaching. Kerwin Anthony Livingstone, PhD. Applied Linguist/Language ...
Reflective teaching is a teacher's practice of thinking, writing, and/or speaking about their lessons and their teaching methods and approaches. It's easy for teachers to get into a rut while teaching, where it feels like they're delivering lessons on autopilot. Reflective teaching is a way to break out of that rut and become the best ...
Teaching Philosophy Statement: A Reflection about Teaching and Learning Debra Burns Melican. My role as a teacher is to open the door to knowledge and critical thinking as wide as needed for all to enter. While I recognize that self-direction is an important tool for learning that works well for some students, I also recognize that other ...
Reflective teaching involves examining one's underlying beliefs about teaching and learning and one's alignment with actual classroom practice before, during and after a course is taught. When teaching reflectively, instructors think critically about their teaching and look for evidence of effective teaching. This critical analysis can draw ...
Reflective practice is usually considered a form of cyclical and systematic inquiry where teachers carefully collect evidence about their teaching practice in order to analyze, interpret, and evaluate their experiences with the intention to improve their future teaching (Farrell, 2016a; Mathew & Peechattu, 2017). It is also a meaning-making
The Reflective Teaching Statement (RTS) is a short reflective essay that describes an instructor's teaching philosophy, learning objectives, instructional methods, and learning and engagement strategies. This collection contains various resources, from helping you get started writing one to examples from different disciplines.
As Dewey scholar, Carol Rodgers, notes, Dewey framed reflection as "a systematic, rigorous, disciplined way of thinking" that led to intellectual growth. Because our students are so diverse and there's so much variety in instructional contexts, good teaching requires instructors to observe, reflect upon, and adapt their teaching practice.
Four Approaches to Reflective Teaching. The goal of critical self-reflection is to gain an increased awareness of our teaching from different vantage points (Brookfield 1995). Collecting multiple and varied perspectives on our teaching can help inform our intuitions about teaching through an evidence-based understanding of whether students are ...
Reflection is an essential dimension of effective teaching. It prompts classroom teachers to subject themselves to a process of self-observation or self-evaluation. By reflecting on what they do in the classroom, teachers specifically explore their teaching practices and beliefs and whether these, indeed, work. This then may lead teachers to continue or modify their teaching strategies for the ...
Reflective teaching means looking at what you do in the classroom, thinking about why you do it, and thinking about if it works - a process of self-observation and self-evaluation. By collecting information about what goes on in our classroom, and by analysing and evaluating this information, we identify and explore our own practices and ...
Reflective Essay on Learning and Teaching. 2019, International Journal of Arts and Social Science (IJASS) Learning and teaching are inextricably intertwined. The principal objective of education is learning, and the means used to fulfil this aim is teaching. Considering that these two phenomena are inseparable, it can therefore be deduced that ...
The process of reflective teaching provides a dynamic basis for teacher action. This is a teacher-based and action-research movement with self-reflection on teachers' teaching. As a reflective practitioner, a teacher should have good analytical and evaluative skills to process practical inquiry about teaching and make pragmatic judgment.
Gibbs' Reflective Cycle was developed by Graham Gibbs in 1988 to give structure to learning from experiences. It offers a framework for examining experiences, and given its cyclic nature lends itself particularly well to repeated experiences, allowing you to learn and plan from things that either went well or didn't go well. It covers 6 stages:
Methods. In order to assess the efficacy of reflective essays for social research methods education and training, undergraduate students enrolled on the social research methods module described above were invited to complete a short, qualitative survey (see online Appendix A).As well as offering the potential for rich data on student experiences of completing the assignment (Braun et al ...
1 Choose a tone. Before you begin to write your reflective essay, choose a tone. Because a reflective essay is more personal than an academic essay, you don't need to use a strict, formal tone. You can also use personal pronouns like I and me in your essay because this essay is about your personal experiences.
Reflective teaching also helps teachers to understand the impact that their teaching has on students. Examples of reflective teaching include observing other teachers, taking notes on your own teaching practice, reading about how to improve yourself, and asking for feedback from your students to achieve self-improvement. Contents show.
Chambers, P. (2008) Teaching Mathematics: Developing as a Reflective Secondary Teacher. London: Sage. Cockcroft, W. (1982) The Report of the Committee of Inquiry into the Teaching of Mathematics in Schools. Collinson, V. (1994) Teachers as Learners: Exemplary teachers' perceptions of personal and professional renewal.
Reflective Teaching Approach Essay. 898 Words4 Pages. Technological University of the Philippines. College of Industrial Education. Professional Industrial Education Department. Ayala Boulevard, Ermita, Manila. Analysis of the Reflective Teaching Approach: input to the Teaching Model Framework for Industrial/Technology Education in the College ...