Join my VIP teacher email club!

Finally, a guide for upper elementary teachers that will show you how to teach research reports in a step-by-step format.
If you are struggling with teaching the research report process, you are not alone. Seriously, we’ve all been there!
I spent several years avoiding research reports to my 5th grade writers or simply depending on the Library-Media Specialist to teach the research process.
One year, I decided to take the plunge and teach my students how to research a topic and write a research report.
The process was clunky at first, but I learned a lot about how students approach research and how to guide them from choosing a topic to completing their final copies.
Before we discuss the HOW , let’s talk about the WHY .


Why You Should Be Assigning Research Reports to Your 5th and 6th Grade Students
I have three main reasons for assigning research reports to my students.
First, the skill involved in finding reliable sources and citing sources is valuable.
Beginning in 5th grade, and possibly even before, students need to be able to discern the reliability of a source . They should be able to spot propaganda and distinguish between reputable sources and phony ones.
Teaching the procedure for citing sources is important because my 5th grade students need to grasp the reality of plagiarism and how to avoid it.
By providing information about the sources they used, students are consciously avoiding copying the work of authors and learning to give credit where credit is due.
Second, by taking notes and organizing their notes into an outline, students are exercising their ability to find main ideas and corresponding details.
Being able to organize ideas is crucial for young writers.
Third, when writing research reports, students are internalizing the writing process, including organizing, writing a rough draft, proofreading/editing, and writing a final draft.
When students write research reports about topics of interest, they are fine-tuning their reading and writing skills.

How to Teach Step-By-Step Research Reports in Grades 5 & 6
As a veteran upper elementary teacher, I know exactly what is going to happen when I tell my students that we are going to start research reports.
There will be a resounding groan followed by students voicing their displeasure. (It goes something like this…. “Mrs. Bazzit! That’s too haaaaaaard!” or “Ugh. That’s boring!” *Sigh* I’ve heard it all, lol.)
This is when I put on my (somewhat fictional) excited teacher hat and help them to realize that the research report process will be fun and interesting.

Step 1: Help Students to Choose a Topic and Cite Sources for Research Reports
Students definitely get excited when they find out they may choose their own research topic. Providing choice leads to higher engagement and interest.
It’s best practice to provide a list of possible research topics to students, but also allow them to choose a different topic.
Be sure to make your research topics narrow to help students focus on sources. If students choose broad topics, the sources they find will overwhelm them with information.
Too Broad: American Revolution
Just Right: The Battle of Yorktown
Too Broad: Ocean Life
Just Right: Great White Shark
Too Broad: Important Women in History
Just Right: The Life of Martha Washington
Be sure to discuss appropriate, reliable sources with students.
I suggest projecting several examples of internet sources on your technology board. Ask students to decide if the sources look reliable or unreliable.
While teaching students about citing sources, it’s a great time to discuss plagiarism and ways to avoid it.
Students should never copy the words of an author unless they are properly quoting the text.
In fact, I usually discourage students from quoting their sources in their research reports. In my experience, students will try to quote a great deal of text and will border on plagiarism.
I prefer to see students paraphrase from their sources because this skill helps them to refine their summarization skills.
Citing sources is not as hard as it sounds! I find that my students generally use books and internet sources, so those are the two types of citations that I focus on.
How to cite a book:
Author’s last name, First name. Title of Book. City of Publication: Publisher, Date.
How to cite an internet article:
Author’s last name, First name (if available). “Title of Article or Page.” Full http address, Date of access.
If you continue reading to the bottom of this post, I have created one free screencast for each of the five steps of the research process!

Step 2: Research Reports: Take Notes
During this step, students will use their sources to take notes.
I do provide instruction and examples during this step because from experience, I know that students will think every piece of information from each source is important and they will copy long passages from each source.
I teach students that taking notes is an exercise in main idea and details. They should read the source, write down the main idea, and list several details to support the main idea.
I encourage my students NOT to copy information from the source but instead to put the information in their own words. They will be less likely to plagiarize if their notes already contain their own words.
Additionally, during this step, I ask students to write a one-sentence thesis statement. I teach students that a thesis statement tells the main point of their research reports.
Their entire research report will support the thesis statement, so the thesis statement is actually a great way to help students maintain a laser focus on their research topic.

Step 3: Make a Research Report Outline
Making an outline can be intimidating for students, especially if they’ve never used this organization format.
However, this valuable step will teach students to organize their notes into the order that will be used to write the rough draft of their reports.
Because making an outline is usually a new concept for my 5th graders, we do 2-3 examples together before I allow students to make their outlines for their research reports.
I recommend copying an outline template for students to have at their fingertips while creating their first outline.
Be sure to look over students’ outlines for organization, order, and accuracy before allowing them to move on to the next step (writing rough drafts).

Step 4: Write a Research Report Draft
During this step, each student will write a rough draft of his/her research report.
If they completed their outlines correctly, this step will be fairly simple.
Students will write their research reports in paragraph form.
One problem that is common among my students is that instead of writing in paragraphs, they write their sentences in list format.
I find that it’s helpful to write a paragraph in front of and with students to remind them that when writing a paragraph, the next sentence begins immediately after the prior sentence.
Once students’ rough drafts are completed, it’s time to proofread/edit!
To begin, I ask my students to read their drafts aloud to listen for their own mistakes.
Next, I ask my students to have two individuals look over their draft and suggest changes.

Step 5: Research Reports – Students Will Write Their Final Drafts!
It’s finally time to write final drafts!
After students have completed their rough drafts and made edits, I ask them to write final drafts.
Students’ final drafts should be as close to perfect as possible.
I prefer a typed final draft because students will have access to a spellchecker and other features that will make it easier to create their final draft.
Think of a creative way to display the finished product, because they will be SO proud of their research reports after all the hard work that went into creating them!
When grading the reports, use a rubric similar to the one shown in the image at the beginning of this section.
A detailed rubric will help students to clearly see their successes and areas of needed improvement.
Once students have completed their first research projects, I find that they have a much easier time with the other research topics assigned throughout the remainder of the school year.
If you are interested in a no-prep, step-by-step research report instructional unit, please click here to visit my Research Report Instructional Unit for 5th Grade and 6th Grade.

This instructional unit will guide students step-by-step through the research process, including locating reliable sources, taking notes, creating an outline, writing a report, and making a “works cited” page.
I’d like to share a very special free resource with you. I created five screencast videos, one for each step of the research report process. These screencasts pair perfectly with my Research Report Instructional Unit for 5th Grade and 6th Grade!
Research Report Step 1 Screencast
Research Report Step 2 Screencast
Research Report Step 3 Screencast
Research Report Step 4 Screencast
Research Report Step 5 Screencast

To keep this post for later, simply save this image to your teacher Pinterest board!
Hi, If i purchase your complete package on grade 5/6 writing does it come with your wonderful recordings on how to teach them? Thanks
Hi Gail! The recordings on this blog post can be used by anyone and I will leave them up 🙂 The writing bundle doesn’t come with any recordings but I did include step-by-step instructions for teachers. I hope this helps!
Thank you for sharing your information with everyone. I know how to write (I think, haha), but I wanted to really set my students up for success with their research and writing. Your directions and guides are just what I needed to jar my memory and help my students become original writers. Be blessed.
You are very welcome, Andrea! Thank you for this comment 🙂
Hi Andrea, I am a veteran teacher who has taught nothing but primary for 25 years. However, this is my first year in 5th. I’m so excited to have found your post. Can you direct me to how I can purchase your entire bundle for writing a 5-paragraph essay. Thanks, Sue
Sure, Susan, I can help with that! Here is the link for the 5th Grade Writing Bundle: https://www.teacherspayteachers.com/Product/5th-Grade-Writing-Bundle-3611643
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
You may also enjoy...

How to Celebrate Martin Luther King, Jr. Day in 5th Grade

Take Your Fifth & Sixth Grade Writers From “Blah” to BRILLIANT!

Teaching About Native American Cultural Groups with Respect and Sensitivity

“Teaching Virtually” – Ideas & Resources for Upper Elementary Teachers

Helpful Tips for Discussing Slavery in the Classroom

How to Make the U.S. Constitution Accessible for Students
What can i help you teach, find it here, let's connect, i'd love to connect with you.
Enter your first name and email address to join my exclusive VIP email club.
Copyright © 2020 | Thrive in Grade Five | All Rights Reserved
Quick Links

Writing Research Papers

This research writing unit of study is designed to guide your students through the research writing process.
This is a free writing unit of study from the curriculum corner..
This research writing collection includes mini lessons, anchor charts and more.
Mention the words “research writing” in an intermediate classroom and you might be met with moans & groans or perhaps even see fear in the eyes of some students.
In all seriousness though, writing can be intimidating for many children in our classrooms.
Guided and focused your mini-lessons can be helpful for students. Also, the more examples you can get students to interact with, the more they will understand the expectations. Finally, the more modeling that you do for them, the more they can view writing as less overwhelming.
Download the free resources to accompany this unit of study at the bottom of this post.

Lesson Ideas for Writing Research Papers:
Lesson 1: Noticings
- Begin by getting your students familiar with what research writing looks like.
- Have them work in pairs or small groups to read pieces of research writing. They will record their “noticings” about the writing.
- Then, come together in a community circle to discuss and create a class anchor chart.
- You will find a blank anchor chart and one with noticings already recorded.
- Here is a link we found that contains some student-created examples of research writing: Student Writing Models . Simply scroll through the grade levels for different samples.
Lesson 2: Opinion vs. Facts
- Begin with a brief review of opinions vs. facts.
- Use the six paragraphs we share in our resources to give your students some practice differentiating between the two.
- Each of the paragraphs contains both opinions and facts.
- Students will read the paragraphs and record the facts and opinions from their paragraph onto the recording page.

Lesson 3: Choosing a Topic
- We know that providing choice will allow for greater engagement and success. We want to help students to narrow their choices by giving them some guidance.
- Gather students and begin a discussion about choosing a research topic.
- Ask them to think of topics they already know a little about, have interest in or is important/relevant to their lives.
- You might pose the question “Why is that important in research writing?” and discuss their thoughts.
- For this lesson we have provided a page where students can individually brainstorm topics. You can circulate the room during this process to help students to narrow their topic.
- If you feel your class may need help to narrow their choices, think about giving them a broad topic, such as animals, and then have them choose a sub-topics from the bigger umbrella topic.
- If you feel like your students need an added level of support you might think about creating an anchor chart from a class brainstorming session about possible appropriate topics and then display this in your room.
Lesson 4: Where to Find Accurate Information about a Topic
- Help students to begin to understand where they might find accurate information about their topics.
- Where are the places you can begin to look for information about your topic?
- Why would the copyright date on a book be important in doing research?
- Is everything on the internet true?
- Why is it important for your research to contain accurate information?
- Where do you begin to look for information that will accurate
- One way to help students think through appropriate sites on the internet is to pass out the ten cards provided in our resources.
- Have students read the cards and discuss what kind of a website it is.
- Talk about whether they know or have heard of the sites. Would they consider the sites “trusted” enough to gain knowledge about their topics. Then have them talk about why or why not these sites would be trusted.
Lesson 5: Double Check Your Facts
- We want our students to get into the habit of double checking their facts. This will help ensure what they are learning is correct.
- To do this, you might want them to practice this skill. In this lesson use the page provided to have each student find and record a fact about a topic of their choice on the internet.
- The page then has students write where they found the fact, and also has them list a corresponding fact from a different source.
- Finally they determine if the facts are the same or different. You may have to further the lesson by discussing approximations. For example one site might say that an animal can weigh up to 1,500 pounds, while another might state that the animal weighs between 1,200 and 1,500 pounds.
- You will need to talk about how those facts might both be accurate even though they are stated differently. If they seem to check out, then help students generalize the information for a research paper.

Lesson 6: Taking Notes
- Sometimes giving students resources and a blank sheet of notebook paper can be too overwhelming. You have students who simply copy everything from the text or you have others who have no idea where to start.
- We need to guide them to read to pull out facts & relevant information.
- For this lesson we have provided various templates for note-taking. Whatever method or template you choose for helping your students learn to take notes, model it several times in front of the class Demonstrating for them how to write the notes as they read about a topic will be helpful.
- After initial teaching, you may find that you need to pull small groups for extra practice. Some might need a one-on-one conference.
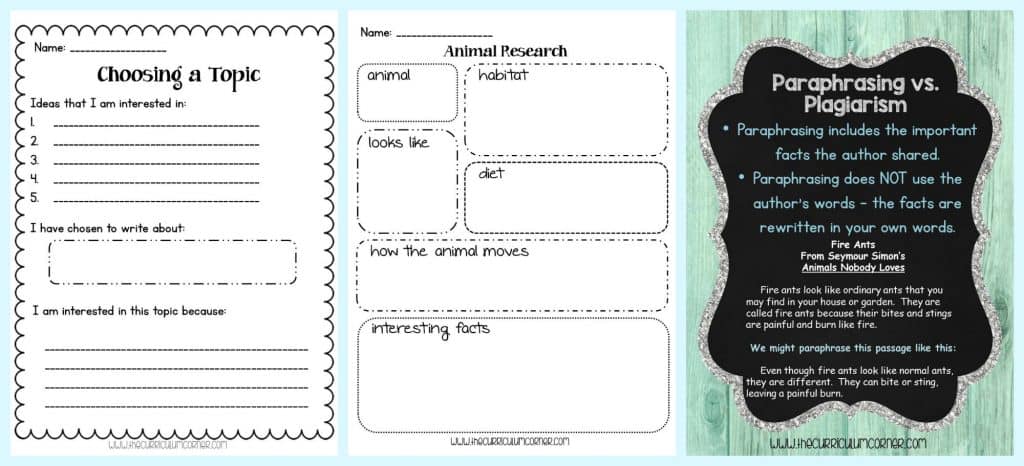
Lesson 7: Paraphrasing vs. Plagiarism
- Students will need to learn how to paraphrase their research. This will help them avoid plagiarizing words from their resources.
- Discuss why plagiarizing is something that they shouldn’t do in their writing because it is “stealing” another’s words.
- Tell the students that there is a way to use another author’s ideas in an appropriate way without copying their words. First, they need to paraphrase and then they need to cite the source where they found the information.
- Display the anchor chart “What is Paraphrasing” and discuss the definition.
- Next, pass out copies of “My Own Words” to pairs of students. Explain that their task will be to find a paragraph or passage in a nonfiction book. They will paraphrase the author’s words, keeping the same ideas.
- Finally, gather students together to share their paraphrasing efforts. Each pair of students can read the paragraph/passage from the book and then the paraphrasing that they wrote. Discuss the words and decisions the students made in their paraphrasing.
Lesson 8: Word Choice in Research Writing
- To help students think about making their writing more interesting, have them brainstorm words that could add voice to their writing.
- After working independently on the word choice page provided, have them meet with partners. They can talk about nouns, verbs and adjectives that relate to their topic.
Lesson 9: Writing Sketch
- This graphic organizer can be used for students to plan their writing.
- If your writers are more advanced you might choose to skip this step, It could be a big help for students who have taken notes and have too many facts.
- Be sure to model how to write the facts & ideas from your notes onto your planner. Students will see first hand how to make sure to only add what is relevant and important to their writing.
- Some questions you can pose: What will be the focus of each paragraph in your research writing? What do you want to include from your notes? Why is it important to the research? What facts don’t quite fit into the paragraphs you’ve decided upon? Should you change some of the paragraphs so that they better support the research and what you want your readers to learn?
- Once the planner is finished, they can use it as a guide to help their writing stay focused.
Lesson 10: Writing Introductions to Research
- Teach students how to think about their introduction as a way to grab their readers’ attention.
- Our anchor chart has some ideas to get writers started. You might also extend the anchor chart to include ideas from your students. (We have included some blank anchor charts at the very bottom of the download.)
- Discuss the parts that need to be included in the introductory paragraph first. Then, move on to some of the ways that might engage readers. As always be sure to model how you would go about writing an introductory paragraph using your Writing Sketch.
Lesson 11: Developing Your Paragraphs
- Next, help students stay focused and develop complete paragraphs.The next graphic organizer will get them to think through the specifics of each paragraph.
- Again, this may not be needed for all of the students in your classroom, but it might be something to think about using with all of them for at least their very first attempts at writing research papers.
- Model how to use the Writing Sketch planner to develop their paragraphs more fully on this organizer.
Lesson 12: Writing a Conclusion to Research
Providing a solid concluding paragraph is also something that needs modeled for your students.
Use the anchor chart with ideas to get you started with the modeling of this as well.
***If you would like for your students to write their first drafts on something that continues to support organization for them, you will find guided lined paper.
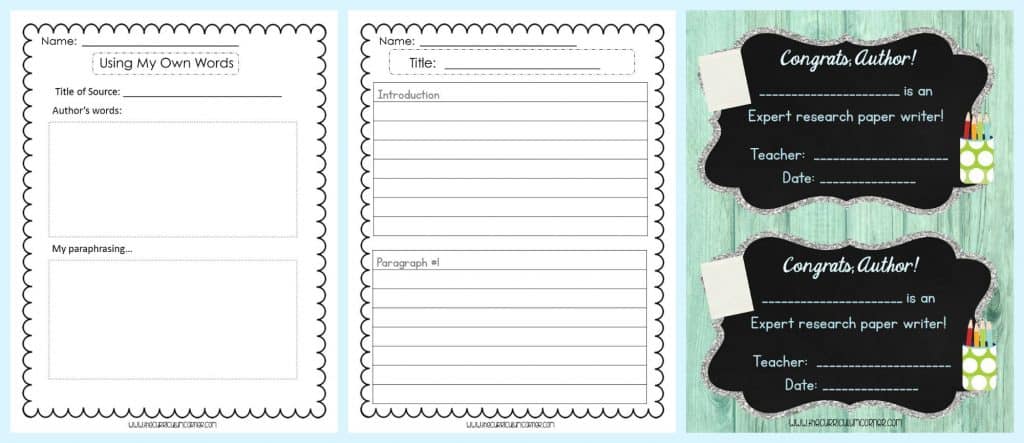
Lesson 13: Research Rendezvous Celebration
We love ending a unit of study with a celebration.
For this particular celebration, you might invite students to bring in a visual to help illustrate their topic.
Invite parents and other special adults from your building to the celebration and think about providing a snack.
You can also print out our “Congrats Author!” certificates to give to each student during the celebration.

All the research writing resources described above can be found in one download here:
Writing a Research Paper Resources
As with all of our resources, The Curriculum Corner creates these for free classroom use. Our products may not be sold. You may print and copy for your personal classroom use. These are also great for home school families!
You may not modify and resell in any form. Please let us know if you have any questions.
Dulce Hernandez
Thursday 8th of April 2021
Thank you so much. I tutor non-English speakers from K-9th grade. These resources are a God send!!
Monday 25th of May 2020
I cant download it, where do you download it?
Jill & Cathy
Wednesday 2nd of September 2020
Here is the link: https://www.thecurriculumcorner.com/thecurriculumcorner456/wp-content/pdf/writing/research/researchwriting.pdf
Graphic Organizer for Research Papers - The Curriculum Corner 4-5-6
Tuesday 19th of November 2019
[…] You might also like our unit of study for writing research papers:How to Write a Research Paper […]
Planning a Dynamic Writing Workshop - The Curriculum Corner 123
Thursday 14th of November 2019
[…] Writing Research Papers […]
Language Arts in the Middle School and High School Years
Thursday 11th of May 2017
[…] The middle school years can also be a good time to introduce writing a short research paper if your student is ready. Introduce how to do research, how to make an outline, and how to write a short research paper, including how to cite sources. Here’s a website that has a free introduction to writing research papers: https://www.thecurriculumcorner.com/thecurriculumcorner456/writing-research-papers/. […]
- Introduction writing: pieces of advice
- Selecting a project writing agency
- Purchasing papers from scratch
- Finding a writer at affordable price
- Choosing writing service
- Buying papers for cheap
- Philosophy project writing
- MLA paper writing hints
- 6th edition APA paper tips
- Writing a paper on smart material
- Analytical term paper samples
- Research project's building blocks
- Term paper: how to write quickly
- High school project writing
- 10-page project templates
- Key parts of your paper
- Grade 6 Science projects
- Creating a year 5 paper
- Essential parts of research projects
- Ordering term papers from scratch
- Buying papers via the Internet
- Searching for a good company
- Outsourcing paper writing effectively
- The purchase of term projects
- Crafting an MLA research paper
- WWII papers: basic elements
- Sample MLA projects
- Global warming paper tips
- Hiring term paper writers
- School bullying project writing
- Searching for qualified writers
- Editing company selection
- Purchasing papers without effort
- In quest of projects from scratch
- Managerial Accounting topic ideas
- Topics on History
- Six-page paper topic selection
- History of the USA: project ideas
- Nursing research paper topics
- Firm term project writing ideas
- Fail-safe research paper questions
- Child abuse: inventing paper ideas
- Unique topic suggestions
- Finding sample topic ideas
- Topics for a Psychology project
- Drugs: finding paper topics
- Ideas for a project on Culture
- College term project ideas
- Great term paper topic traits
- Paper ideas: bullying laws
- Chemistry research project questions
- Ideas for a Sports research paper
- Fresh topics in psychology
- Counseling psychology ideas
- Topic questions on German history
- Literature writing ideas
- Ideas for a paper on Down Syndrome
- Topic selection in astronomy
- Early American history topics
- Writing ideas for college
- Good topics about video games
- First steps
mkf research
Writing guides.
- First-class sample paper proposals
- Template documented papers
- Analyzing the paper structure
- An introduction to paper writing
- Outlining a research project
- High school research paper tips
- Formatting a term project outline
- Tips on college project crafting
- Getting example research projects
- Paper structure: chapter one
Need help with research paper? Order custom research papers from MyPaperDone writing service.
Excellent paper is not a dream with this website . They are writing essays, term papers and more.
It is easy to write my papers when I'm reading guides from educational resources.
Tips For Writing A Strong 5th Grade Research Paper
One of the most challenging assignments that you will have to do when it comes to your 5th grade assignments is to write a research paper. It is a larger paper than what you are used to writing. The idea is to create a research question about a topic that you are interested in and then work to answer it. The conclusion that you make on the subject will become your thesis statement and should be backed up with evidence. You will be able to write a strong paper for your class and edit it properly if you follow these important steps provided by Mypaperwriter.com experts.
Developing a strong topic
The first step to writing is to develop a topic to write about. When it comes to choosing a topic for a research paper, it is very important to make sure that you choose a topic that has enough information on it to write enough to reach your required page count and not so much that it will be hard to think of one thing to prove. If your topic is too broad or too narrow, you can either choose a sub topic or choose a topic that is more general. It should also be interesting for you because you will have to read a lot about it to conduct your research. If it is on a topic that you enjoy, the reading will be easier and more enjoyable.
Collecting evidence
Conduct some research on your topic by reading everything that you can find about your subject and taking notes. You will want to make sure that you identify where you got the information from so keep good track of it.
The next step is to plan out your paper. This will help you to decide on a focus and that focus will be the heart of your paper. An outline is a great way of finding out the best way to present your evidence.
Once you have written your paper, it is so important to make sure that you edit it as well. Even if you were very careful not to make any mistakes, it is possible that you made some small errors and there is no reason to lose points just because of these tiny issues. Read your paper out loud to get the best results when editing your paper. It will be a lot easier when you can hear how it sounds to find grammatical errors.
04-08-2024 © MKFresearch.com. All rights reserved. | Research & Writing For College Students
Scaffolding Methods for Research Paper Writing

- Resources & Preparation
- Instructional Plan
- Related Resources
Students will use scaffolding to research and organize information for writing a research paper. A research paper scaffold provides students with clear support for writing expository papers that include a question (problem), literature review, analysis, methodology for original research, results, conclusion, and references. Students examine informational text, use an inquiry-based approach, and practice genre-specific strategies for expository writing. Depending on the goals of the assignment, students may work collaboratively or as individuals. A student-written paper about color psychology provides an authentic model of a scaffold and the corresponding finished paper. The research paper scaffold is designed to be completed during seven or eight sessions over the course of four to six weeks.
Featured Resources
- Research Paper Scaffold : This handout guides students in researching and organizing the information they need for writing their research paper.
- Inquiry on the Internet: Evaluating Web Pages for a Class Collection : Students use Internet search engines and Web analysis checklists to evaluate online resources then write annotations that explain how and why the resources will be valuable to the class.
From Theory to Practice
- Research paper scaffolding provides a temporary linguistic tool to assist students as they organize their expository writing. Scaffolding assists students in moving to levels of language performance they might be unable to obtain without this support.
- An instructional scaffold essentially changes the role of the teacher from that of giver of knowledge to leader in inquiry. This relationship encourages creative intelligence on the part of both teacher and student, which in turn may broaden the notion of literacy so as to include more learning styles.
- An instructional scaffold is useful for expository writing because of its basis in problem solving, ownership, appropriateness, support, collaboration, and internalization. It allows students to start where they are comfortable, and provides a genre-based structure for organizing creative ideas.
- In order for students to take ownership of knowledge, they must learn to rework raw information, use details and facts, and write.
- Teaching writing should involve direct, explicit comprehension instruction, effective instructional principles embedded in content, motivation and self-directed learning, and text-based collaborative learning to improve middle school and high school literacy.
Common Core Standards
This resource has been aligned to the Common Core State Standards for states in which they have been adopted. If a state does not appear in the drop-down, CCSS alignments are forthcoming.
State Standards
This lesson has been aligned to standards in the following states. If a state does not appear in the drop-down, standard alignments are not currently available for that state.
NCTE/IRA National Standards for the English Language Arts
- 1. Students read a wide range of print and nonprint texts to build an understanding of texts, of themselves, and of the cultures of the United States and the world; to acquire new information; to respond to the needs and demands of society and the workplace; and for personal fulfillment. Among these texts are fiction and nonfiction, classic and contemporary works.
- 2. Students read a wide range of literature from many periods in many genres to build an understanding of the many dimensions (e.g., philosophical, ethical, aesthetic) of human experience.
- 3. Students apply a wide range of strategies to comprehend, interpret, evaluate, and appreciate texts. They draw on their prior experience, their interactions with other readers and writers, their knowledge of word meaning and of other texts, their word identification strategies, and their understanding of textual features (e.g., sound-letter correspondence, sentence structure, context, graphics).
- 4. Students adjust their use of spoken, written, and visual language (e.g., conventions, style, vocabulary) to communicate effectively with a variety of audiences and for different purposes.
- 5. Students employ a wide range of strategies as they write and use different writing process elements appropriately to communicate with different audiences for a variety of purposes.
- 6. Students apply knowledge of language structure, language conventions (e.g., spelling and punctuation), media techniques, figurative language, and genre to create, critique, and discuss print and nonprint texts.
- 7. Students conduct research on issues and interests by generating ideas and questions, and by posing problems. They gather, evaluate, and synthesize data from a variety of sources (e.g., print and nonprint texts, artifacts, people) to communicate their discoveries in ways that suit their purpose and audience.
- 8. Students use a variety of technological and information resources (e.g., libraries, databases, computer networks, video) to gather and synthesize information and to create and communicate knowledge.
- 12. Students use spoken, written, and visual language to accomplish their own purposes (e.g., for learning, enjoyment, persuasion, and the exchange of information).
Materials and Technology
Computers with Internet access and printing capability
- Research Paper Scaffold
- Example Research Paper Scaffold
- Example Student Research Paper
- Internet Citation Checklist
- Research Paper Scoring Rubric
- Permission Form (optional)
Preparation
Student objectives.
Students will
- Formulate a clear thesis that conveys a perspective on the subject of their research
- Practice research skills, including evaluation of sources, paraphrasing and summarizing relevant information, and citation of sources used
- Logically group and sequence ideas in expository writing
- Organize and display information on charts, maps, and graphs
Session 1: Research Question
You should approve students’ final research questions before Session 2. You may also wish to send home the Permission Form with students, to make parents aware of their child’s research topic and the project due dates.
Session 2: Literature Review—Search
Prior to this session, you may want to introduce or review Internet search techniques using the lesson Inquiry on the Internet: Evaluating Web Pages for a Class Collection . You may also wish to consult with the school librarian regarding subscription databases designed specifically for student research, which may be available through the school or public library. Using these types of resources will help to ensure that students find relevant and appropriate information. Using Internet search engines such as Google can be overwhelming to beginning researchers.
Session 3: Literature Review—Notes
Students need to bring their articles to this session. For large classes, have students highlight relevant information (as described below) and submit the articles for assessment before beginning the session.
Checking Literature Review entries on the same day is best practice, as it gives both you and the student time to plan and address any problems before proceeding. Note that in the finished product this literature review section will be about six paragraphs, so students need to gather enough facts to fit this format.
Session 4: Analysis
Session 5: original research.
Students should design some form of original research appropriate to their topics, but they do not necessarily have to conduct the experiments or surveys they propose. Depending on the appropriateness of the original research proposals, the time involved, and the resources available, you may prefer to omit the actual research or use it as an extension activity.
Session 6: Results (optional)
Session 7: conclusion, session 8: references and writing final draft, student assessment / reflections.
- Observe students’ participation in the initial stages of the Research Paper Scaffold and promptly address any errors or misconceptions about the research process.
- Observe students and provide feedback as they complete each section of the Research Paper Scaffold.
- Provide a safe environment where students will want to take risks in exploring ideas. During collaborative work, offer feedback and guidance to those who need encouragement or require assistance in learning cooperation and tolerance.
- Involve students in using the Research Paper Scoring Rubric for final evaluation of the research paper. Go over this rubric during Session 8, before they write their final drafts.
- Strategy Guides
Add new comment
- Print this resource
Explore Resources by Grade
- Kindergarten K

- Science Projects
- Project Guides
- STEM Activities
- Lesson Plans
- Video Lessons

Writing a Research Paper for Your Science Fair Project
- As you do your research, follow your background research plan and take notes from your sources of information. These notes will help you write a better summary.
- The history of similar experiments or inventions
- Definitions of all important words and concepts that describe your experiment
- Answers to all your background research plan questions
- Mathematical formulas, if any, that you will need to describe the results of your experiment
- For every fact or picture in your research paper you should follow it with a citation telling the reader where you found the information. A citation is just the name of the author and the date of the publication placed in parentheses like this: (Author, date). This is called a reference citation when using APA format and parenthetical reference when using the MLA format. Its purpose is to document a source briefly, clearly, and accurately.
- If you copy text from one of your sources, then place it in quotation marks in addition to following it with a citation. Be sure you understand and avoid plagiarism! Do not copy another person's work and call it your own. Always give credit where credit is due!
- Title page (with the title of your project, your name, and the date)
- Your report
- Bibliography
- Check with your teacher for additional requirements such as page numbers and a table of contents
Year after year, students find that the report called the research paper is the part of the science fair project where they learn the most. So, take it from those who preceded you, the research paper you are preparing to write is super valuable.
What Is a Research Paper?
The short answer is that the research paper is a report summarizing the answers to the research questions you generated in your background research plan . It's a review of the relevant publications (books, magazines, websites) discussing the topic you want to investigate.
The long answer is that the research paper summarizes the theory behind your experiment. Science fair judges like to see that you understand why your experiment turns out the way it does. You do library and Internet research so that you can make a prediction of what will occur in your experiment, and then whether that prediction is right or wrong, you will have the knowledge to understand what caused the behavior you observed.
From a practical perspective, the research paper also discusses the techniques and equipment that are appropriate for investigating your topic. Some methods and techniques are more reliable because they have been used many times. Can you use a procedure for your science fair project that is similar to an experiment that has been done before? If you can obtain this information, your project will be more successful. As they say, you don't want to reinvent the wheel!
If these reasons sound to you like the reasons we gave for doing background research, you're right! The research paper is simply the "write-up" of that research.
Special Information to Include in Your Research Paper
Many science experiments can be explained using mathematics. As you write your research paper, you'll want to make sure that you include as much relevant math as you understand. If a simple equation describes aspects of your science fair project, include it.
Writing the Research Paper
Note taking.
As you read the information in your bibliography, you'll want to take notes. Some teachers recommend taking notes on note cards. Each card contains the source at the top, with key points listed or quoted underneath. Others prefer typing notes directly into a word processor. No matter how you take notes, be sure to keep track of the sources for all your key facts.
How to Organize Your Research Paper
The best way to speed your writing is to do a little planning. Before starting to write, think about the best order to discuss the major sections of your report. Generally, you will want to begin with your science fair project question so that the reader will know the purpose of your paper. What should come next? Ask yourself what information the reader needs to learn first in order to understand the rest of the paper. A typical organization might look like this:
- Your science fair project question or topic
- Definitions of all important words, concepts, and equations that describe your experiment
- The history of similar experiments
- Answers to your background research questions
When and How to Footnote or Reference Sources
When you write your research paper you might want to copy words, pictures, diagrams, or ideas from one of your sources. It is OK to copy such information as long as you reference it with a citation. If the information is a phrase, sentence, or paragraph, then you should also put it in quotation marks. A citation and quotation marks tell the reader who actually wrote the information.
For a science fair project, a reference citation (also known as author-date citation) is an accepted way to reference information you copy. Citation referencing is easy. Simply put the author's last name, the year of publication, and page number (if needed) in parentheses after the information you copy. Place the reference citation at the end of the sentence but before the final period.
Make sure that the source for every citation item copied appears in your bibliography.
Reference Citation Format
Examples of reference citations using apa format.
Below are examples of how reference citations would look in your paper using the APA format.
"If you copy a sentence from a book or magazine article by a single author, the reference will look like this. A comma separates the page number (or numbers) from the year" (Bloggs, 2002, p. 37).
"If you copy a sentence from a book or magazine article by more than one author, the reference will look like this" (Bloggs & Smith, 2002, p. 37).
"Sometimes the author will have two publications in your bibliography for just one year. In that case, the first publication would have an 'a' after the publication year, the second a 'b', and so on. The reference will look like this" (Nguyen, 2000b).
"When the author is unknown, the text reference for such an entry may substitute the title, or a shortened version of the title for the author" (The Chicago Manual, 1993).
"For reference citations, only direct quotes need page numbers" (Han, 1995).
"Some sources will not have dates" (Blecker, n.d.).
Credit Where Credit Is Due!
When you work hard to write something, you don't want your friends to loaf and just copy it. Every author feels the same way.
Plagiarism is when someone copies the words, pictures, diagrams, or ideas of someone else and presents them as his or her own. When you find information in a book, on the Internet, or from some other source, you MUST give the author of that information credit in a citation. If you copy a sentence or paragraph exactly, you should also use quotation marks around the text.
The surprising thing to many students is how easy it is for parents, teachers, and science fair judges to detect and prove plagiarism. So, don't go there, and don't make us try to hunt you down!
How to Format Your Research Paper
Here is information on how to format your research paper .
Here is a sample research paper in MLA format.
Research Paper Checklist
Explore our science videos.

Research Topics for 5th Graders
Martha mendenhall.

Fifth Graders can do simple research projects and papers on a variety of topics. Offer them the opportunity to find out more about a famous person, a location such as an American state or an ancient city, an invention or landmark or a current event. Students can learn to gather research from books, magazines, newspapers and the internet, as well as document their findings with citations and footnotes.
Explore this article
- The History of…
- Current Events
1 Biography
Students choose a famous person of past or present. Have them consider the realms of politics, sports, film/TV, business, medicine, humanitarian interests, the military or other fields where individuals have made a significant contribution. Students can choose a modern day personality they greatly admire or someone from the past they would like to know more about. Have them research the details of this person’s life and require that they utilize more than one source for their research. You might decide to have them focus only on a particular time in the person’s life, narrowing the time period that students need to research.
Students can research statistics and points of interest about cities, states or countries. For example, students could each choose a separate state and research a list of questions relating to topics such as the history of the state, its population, its industries, natural resources and geographic description. Students could also research ancient cities and civilizations using a similar format. Consider assigning the creation of a map of the selected research location in addition to the written researched material .
3 The History of…
How did the celebration of Mardi Gras get started in New Orleans? Where did the Grand Canyon come from? What was the very first computer? Who invented baseball? The Yo-Yo? Chewing Gum? Students can research the origins of an event, a landmark, an invention, sport , toy or food. Have them choose a topic that really intrigues them, potentially answering a question that they have wondered about. In this way, students are making the real life connection between having an interest in or question about something and researching that topic in order to find out the answer.
4 Current Events
Students can learn to use the information available in magazines, newspapers and online when they choose a current event as a topic for research. Have a "Current Events Day" in your class and introduce some topics of local, national and international significance to your students. Share with them a variety of sources for each topic. As of this writing, students might consider researching events such the uprising in Egypt, the earthquake and tsunami in Japan or the wedding of Prince William and Kate Middleton. Students could also research the upcoming presidential election of 2012 and the effects of the ongoing economic recession on American citizens.
- 1 Pro Teacher Community: Help—Research Paper for 5th Grade!!
Related Articles

Cultural Heritage Projects for Kids

Activities for Black History Month for Upper-Grades...

Children's Research Projects for the Third Grade

Ancient Egypt Sixth-Grade Project Ideas

Informative Writing Topics for the 5th Grade

Greek Mythology Writing Activities for Middle School

Topics for Fourth-Grade Research Papers

School Projects on National Monuments

Ideas for a French Project

French Oral Presentation Ideas

2nd Grade School Activities on the First Thanksgiving

5th Grade Solar System Project Ideas

High School History Projects on the Industrial Revolution

1st Grade Lesson Plans on George Washington

How to Make a Fake Mummy's Tomb

African History Essay Topics

Pioneer Life School Projects

What Are Some Things Hawaii Is Famous for?

How to Write an Analytical Research Essay

How to Teach Ancient Greek History to Fifth Grade
Regardless of how old we are, we never stop learning. Classroom is the educational resource for people of all ages. Whether you’re studying times tables or applying to college, Classroom has the answers.
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Policy
- Manage Preferences
© 2020 Leaf Group Ltd. / Leaf Group Media, All Rights Reserved. Based on the Word Net lexical database for the English Language. See disclaimer .
how to write a research paper 5th grade
All Formats
Resource types, all resource types.
- Rating Count
- Price (Ascending)
- Price (Descending)
- Most Recent
How to write a research paper 5th grade

Common Core 5th Grade : Writing an Informative/Explanatory Text Research Paper

St Pattys day crafts & activities, March family project, 3th, 4th, 5th research


Forces Acting on Structures Workbook ( Grade 5 Ontario Science)

- Easel Activity

4th- 5th grade : How to Write a Research Paper - BrainPOP Edition

Worksheets for Teaching How to Write a Research Paper

ABC State Research Project

California History Enrichment Activities for 4th and 5th grade

ABC Revolutionary War Research Project

Expository Writing Unit | 4th Grade Lesson Plans | Unit 5

Writing a Research Report Paper Escape Room - 4th & 5th Print & Digital Activity

- Google Apps™
- Internet Activities

Research Project Quiz Game Four Library Lessons with Student Choice Topics

FIFTH GRADE RESEARCH SKILLS: BUNDLE

Our Changing Earth Webquest Research Project with STEM

Animal Research Project | How To Research | Frog | Report Writing Templates

HMH 5th grade SUPER bundle - comprehension and writing

Biography Report with Graphic Organizers and Writing Template

Research project in Spanish | Hispanic Heritage Month activities in Spanish

American Presidents Day Research Writing Project - 4th, 5th , 6th Grade

DBQ: How was music influential in the Revolutionary War? | Music & Social Studies

Research Paper - Research a Scientist

Ancient Civilizations Writing Project

Black History Research Project -3rd, 4th, 5th Grade {Digital}

- Google Docs™
United States Geography - US Regions & State Research Project Unit

Planet Research Project [Print & Go]

- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think
Writing Guides
- Project conclusion samples in APA
- College paper formatting
- Finding a reliable term paper writer
- Where to order term papers
- Crafting a conclusion in APA style
- How to buy custom term papers
- Where to find custom paper writers
- A guide on proposal writing
- Sources for project writing
- Writing on the water quality index
- Composing 9th grade papers
- Hiring a term paper writing service
- Formatting a project title page
- Scientific project writing
- Creating a thesis statement
- Composing a paper on Hamlet
- Project writing without citations
- Crafting a great paper proposal
- Finding a paper writing company
- Who can write my papers for me
- Research paper samples
Composing A Research Paper For 5th Grade Successfully
If you are in 5th grade there are a number of things that you need to learn about composing a research paper. There are students who normally think that it is impossible to do this at this age, but rest assured that this could not be any further from the truth. Over time you will come to realize that the easiest way for you to handle and deal with the challenges that you will face in the learning environment is to man up to them and face them upfront. There is no other way to go about this.
In as far as your research paper is concerned there are some things that you will need to learn ahead of this task. Of course your teachers will take their time to teach you some of them, but there are some highlights that you must always have in mind throughout. Some of the highlights that will help you at this stage will live on to assist you as you proceed to advanced years in your studies, to the point where you will be writing your dissertations and thesis papers all through college and at the university level. The following are some of the most important things that you need to pay attention to:
Always follow instructions
Discuss points clearly, do some research into your work, proofread your work before sending to your teacher.
There are instructions that are always provided for each task that you are given. The same applies for this paper. As a good student who needs to pass, there is every reason for you to ensure that you can follow these keenly.
Make sure that you address all the points in your paper clearly. Do not leave a shred of doubt in the mind of the reader. It is through an articulate discussion that you will be able to earn more points for your hard work.
Never make the mistake of working on any paper without advancing proper research into it. This is the only way for you to gather as much information as you need to present a strong paper.
Finally, before you send your paper to the teacher for marking, make sure that you read through it at least twice to correct any errors present.
© 2017 CSC Book Saver. All Rights Reserved. Proudly created by Jane Connor's team of writers.
Teaching 5th Graders How to Write a Thesis Statement

Our 5th-grade students write a 5 paragraph research paper about their choice of topics related to Ancient Egypt. Some of my students are writing about Egyptian pyramids, Egyptian Gods, and one has undertaken the task of writing about the role of Egyptian women in religion. All students are required to write “thin questions,” or questions that can be answered easily and with a fact, to get their minds going and then use their new knowledge to write a “thick question,” or overarching research question from which their thesis will be derived.
I can’t stress enough the importance of modeling how to write a thesis statement. Model, model, model. Bring in past students’ work, write your own thesis in front of them, do the thesis statement sheet (available below) with them a few times. Go slowly for each step. The idea isn’t getting your students to finish the thesis statement quickly, the idea is for them to learn how to craft their own argument and write it clearly.
In order to help them through the process of getting from thin question to thick question to thesis I used several sources to develop my own version of “Write a Thesis Statement in 5 Steps.” I was able to conference with students in small groups to help them look at their thick questions and their notes to develop a “because statement” for each of their papers. Once they had a “because statement,” students had to prove it using three facts from their notes. The next step and hardest step was synthesizing the question, the because statement, and the facts to write the thesis that will ultimately drive their body paragraphs and conclusion.
If you would like to use the “Write a Thesis Statement in 5 Steps” sheet, thesis statement in 5 steps . It is free, but if you do use it please tell me how it went!

Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
CherylAnne Amendola

Translate this page
Hundreds of scientific articles. written for kids. approved by scientists. free., search or filter, search articles, reading level.
- Elementary school (29)
- Lower high school (245)
- Middle school (183)
- Upper high school (94)
Scientific Topic
- Biodiversity and Conservation (85)
- Biology (69)
- Chemistry (13)
- Energy and Climate (57)
- Food and Agriculture (26)
- Health and Medicine (79)
- Paleoscience (18)
- Physical Science (18)
- Pollution (30)
- Social Science (55)
- Technology (22)
- Water Resources (48)
- All NGSS standards 2-LS4 (2) 3-5-ETS1 (3) 3-LS2 (1) 3-LS3 (2) 3-LS4 (3) 4-ESS3 (3) 4-LS1 (3) 4-PS3 (1) 4-PS4 (1) 5-ESS1 (1) 5-ESS3 (2) 5-PS1 (1) HS-ESS1 (3) HS-ESS2 (19) HS-ESS3 (81) HS-ESS4 (1) HS-ETS1 (12) HS-LS1 (71) HS-LS2 (84) HS-LS3 (27) HS-LS4 (48) HS-PS1 (5) HS-PS2 (2) HS-PS3 (5) HS-PS4 (3) MS-ESS1 (5) MS-ESS2 (14) MS-ESS3 (77) MS-ETS1 (6) MS-LS1 (66) MS-LS2 (74) MS-LS3 (14) MS-LS4 (23) MS-PS1 (3) MS-PS2 (1) MS-PS3 (4) MS-PS4 (3)
- All AP Environmental Science topics 1. The Living World: Ecosystems (68) 2. The Living World: Biodiversity (70) 3. Populations (142) 4. Earth Systems and Resources (30) 5. Land and Water Use (67) 6. Energy Resources and Consumption (18) 7. Atmospheric Pollution (11) 8. Aquatic and Terrestrial Pollution (45) 9. Global Change (97)
- All IB Biology topics 01. Cell biology (2) 02. Molecular biology (38) 03. Genetics (41) 04. Ecology (28) 05. Evolution and biodiversity (32) 06. Human physiology (66) 07. Nucleic acids (5) 08. Metabolism, cell respiration and photosynthesis (9) 09. Plant biology (7) 10. Genetics and evolution (12) 11. Animal physiology (56) A. Neurobiology and behaviour (42) B. Biotechnology and bioinformatics (59) C. Ecology and conservation (6) D. Human physiology (12)
- All Scientific Methods Agricultural yield data (6) Bacterial culture (1) Case study (47) Cell culture (5) Chromatography (2) Climate scenarios (25) Community jury (1) Controlled blinded study (2) Correlational study (1) CRISPR (1) CT (1) Data extrapolation (44) Data reconstruction (19) Data validation (35) DNA sequencing (36) ELISA (6) Experiment (134) Expert committee (1) Field study (40) Fluorescence imaging (11) Gene editing (10) GIS (3) GPS tracking (12) High resolution filming (1) Life cycle assessment (2) Mark-release-recapture (2) Mass spectrometry (11) Meta-analysis (4) Microscopy (22) Observation (47) Onsite study (1) PCR (Polymerase chain reaction) (16) Policy analysis (23) Proxy data (22) Radiocarbon dating (2) Remote sensing (1) Representative sampling (84) Risk analysis (9) Scientific modeling (115) Spectroscopy (1) Survey research (28) Systematic review (20) Tomography scans (2) Tree core sampling (4) X-ray scanner (2)
- All Scientific Figures Bar graph (101) Box and whisker plot (7) Data table (27) Dendrogram (1) Flow chart (4) Histogram (8) Line graph (26) Map (103) Microscopy image (31) Pictograph (85) Pie chart (10) Scatter plot (26) Time series graph (36) Venn diagram (4)
- Research Location Africa (40) Antarctica (2) Asia (34) Australia (15) Europe (74) North America (149) Ocean (38) South America (18) Space (5)
- All Scientist Affiliations Aarhus University (1) Adam Mickiewicz University (1) Aix-Marseille University (1) Amherst College (1) Arizona State University (4) Baylor University (1) Boston University (1) Brown University (1) California Institute of Technology (3) California State University (1) Cardiff University (2) CDC (3) Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles (1) Centre for Communicable Diseases Bangladesh (1) China Agricultural University (1) Chinese Academy of Sciences (1) City University of New York (1) Clemson University (2) Colorado State University (4) Columbia University (1) Complutense University (1) Cornell University (7) CSIRO (1) Duke University (6) Emory University (1) ETH Zurich (2) Five Gyres Institute (1) Forest Research Institute of Baden-Wuerttemberg (1) George Washington University (2) Georgetown University (2) Georgia Institute of Technology (1) Harvard University (10) Hebrew University of Jerusalem (1) Hokkaido University (1) IFPRI (1) Imperial College London (8) Indian Institute of Technology (1) INRS (3) Iowa State University (3) IRSTEA (1) ISAC (1) Johannes Kepler University (2) Johns Hopkins University (4) Katholieke Universiteit Leuven (1) King's College London (1) Kyoto University (1) Lancaster University (2) Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (2) Lehigh University (1) Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research (2) Leipzig University (1) London School of Economics (1) LSHTM (5) LSTM (1) Marine Biological Association UK (1) Max Planck Institute (4) McGill University (3) Merrimack College (1) Met Office UK (1) Missouri University of Science and Technology (1) MIT (4) Monash University (1) Murdoch Children's Research Institute (2) Museo Paleontológico Egidio Feruglio (1) Myongji University (1) Nanjing University (1) NASA (6) National Autonomous University of Mexico (1) National Clinical Research Center for Respiratory Diseases (1) National University of Ireland (1) Natural Resources Canada (2) New York University Abu Dhabi (1) NOAA (8) North Carolina State University (1) Northeastern University (2) Norwegian Institute for Nature Research (1) Norwegian University of Science and Technology (1) Oregon State University (1) Oswaldo Cruz Foundation (1) PATH (1) Peking University School of Public Health (1) Pennsylvania State University (4) Pepperdine University (1) Princeton University (2) Purdue University (1) Queen Mary University of London (2) Queensland University of Technology (1) RMIT University (1) Royal Netherlands Institute for Sea Research (1) RPI (1) RTI International (1) Rutgers University (1) San Diego State University (1) Seattle Pacific University (1) Stanford University (8) Stockholm University (2) Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences (1) Tampere University (1) Technical University of Denmark (1) Texas A&M University (3) The Francis Crick Institute (1) Trent University (1) Tulane University (2) UC Berkeley (10) UC Davis (4) UC Irvine (1) UC Los Angeles (6) UC Riverside (2) UC San Diego (2) UC Santa Barbara (1) UC Santa Cruz (2) UKCEH (1) United Nations Children’s Fund (1) Universidad Nacional de Colombia (1) Universit of Minnessotta (1) Universität of Osnabrück (1) University of Alaska (1) University of Alberta (1) University of Arizona (1) University of Arkansas (2) University of Auckland (1) University of Bern (1) University of Birmingham (2) University of Bologna (1) University of Bristol (1) University of British Columbia (4) University of Cambridge (3) University of Cape Town (1) University of Central Florida (1) University of Chicago (2) University of Cincinnati (1) University of Connecticut (1) University of Copenhagen (1) University of Dar es Salaam (1) University of East Anglia (1) University of Edinburgh (1) University of Exeter (1) University of Florida (5) University of Georgia (1) University of Groningen (1) University of Hawaii (1) University of Helsinki (2) University of Houston (2) University of Illinois (1) University of Konstanz (1) University of Lausanne (1) University of Leeds (1) University of Liverpool (1) University of London (2) University of Maine (1) University of Manitoba (1) University of Maryland (1) University of Miami (1) University of Michigan (2) University of Minnesota (2) University of Missouri (1) University of Montreal (2) University of Nebraska (1) University of New England Australia (2) University of North Carolina (2) University of Northern Colorado (1) University of Oklahoma (1) University of Otago (1) University of Oviedo (1) University of Oxford (3) University of Patras (1) University of Pennsylvania (2) University of Pittsburgh (1) University of Plymouth (4) University of Potsdam (1) University of Queensland (1) University of Reading (1) University of Rochester (1) University of Sassari (1) University of South Carolina (1) University of South Florida (1) University of Southern California (2) University of Southern Denmark (1) University of Southern Mississippi (1) University of Strathclyde (1) University of Texas (9) University of the Witwatersrand (2) University of Tokyo (1) University of Toulouse (3) University of Tübingen (1) University of Vienna (1) University of Virginia (2) University of Washington (8) University of Western Australia (3) University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee (1) University of York (1) University of Zurich (3) Uppsala University (1) USDA (1) USDA-ARS (2) UT Austin (1) Utah State University (1) Utrecht University (1) Virginia Commonwealth University (1) Virginia Tech (1) Wageningen University (2) Washington University (1) Weill Cornell Medicine (1) West Virginia University (1) Wildlife Conservation Society (1) Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (1) World Bank (1) World Health Organization (1) Yale University (5)
- All Additional Languages Afrikaans (1) Arabic (5) Bengali (1) Bulgarian (37) Burmese (1) Chinese (4) Danish (1) Dutch (3) French (17) German (4) Greek (1) Italian (1) Korean (1) Lao (1) Mongolian (1) Portuguese (2) Russian (2) Spanish (51) Swedish (1)
Articles by Publication Date
Where was the research.

How do bumble bees play?
+ Audio version of article + Links to lessons on bees and animal behavior + Blackboard version of article with bee footage

How can we tell whether we are talking to a computer or a person?
+ Audio version of article + Links to activities about AI and machine learning + Blackboard video version of article

How have the life choices of women in India changed over time?
+ Audio version of article + Links to lessons on demographics and empowering girls + Lesson Idea video

How do animals behave during a solar eclipse?
+ Audio version of article + Get involved: Link to citizen science projects about eclipses + Links to activities about solar eclipses

How do dolphin mothers speak with their babies?
+ Audio version of article + Links to lessons on dolphins and echolocation

What do parenting and brain size have to do with each other?
+ Audio version of article + Two reading levels available + Links to lessons on birds and brains

How does fear speech spread on social media?
+ Audio version of article + Links to lessons on identifying hate speech and misinformation + Link to lessons on how kids can navigate social media

How does the way we think affect our choices about vaccines?
+ Audio version of article + Links to lessons about vaccines and cognitive bias
Popular Articles

Why do measles survivors get sicker?

What can we learn from carbon on Mars?

What can we learn about dinosaur skin using a laser?

How well can a computer think?
Article collections.

Socially Important Scientific Research in 2024 Election Year

Gross and Disgusting Science Articles Collection

8 Research Articles on Women and Girls

High School Intro Biology Collection
Popular lesson ideas.

Data Graphing Activity for 4th-7th Graders

Articles Translated in Multiple Languages

SJK Recommends: The World’s Best STEM Resources. Free.

Ask-A-Scientist Podcast E2: Dr. Allison Master, social psychologist
Learn more about us, funding support by:.

Disclaimer: Funders play no role in article selection and writing.
Featured by:

- help_outline help
iRubric: 5th Grade Research Paper rubric

Addition (Basic)
Addition (Multi-Digit)
Algebra & Pre-Algebra
Comparing Numbers
Daily Math Review
Division (Basic)
Division (Long Division)
Hundreds Charts
Measurement
Multiplication (Basic)
Multiplication (Multi-Digit)
Order of Operations
Place Value
Probability
Skip Counting
Subtraction
Telling Time
Word Problems (Daily)
More Math Worksheets
Reading Comprehension
Reading Comprehension Gr. 1
Reading Comprehension Gr. 2
Reading Comprehension Gr. 3
Reading Comprehension Gr. 4
Reading Comprehension Gr. 5
Reading Comprehension Gr. 6
Reading & Writing
Reading Worksheets
Cause & Effect
Fact & Opinion
Fix the Sentences
Graphic Organizers
Synonyms & Antonyms
Writing Prompts
Writing Story Pictures
Writing Worksheets
More ELA Worksheets
Consonant Sounds
Vowel Sounds
Consonant Blends
Consonant Digraphs
Word Families
More Phonics Worksheets
Early Literacy
Build Sentences
Sight Word Units
Sight Words (Individual)
More Early Literacy
Punctuation
Subjects and Predicates
More Grammar Worksheets
Spelling Lists
Spelling Grade 1
Spelling Grade 2
Spelling Grade 3
Spelling Grade 4
Spelling Grade 5
Spelling Grade 6
More Spelling Worksheets
Chapter Books
Charlotte's Web
Magic Tree House #1
Boxcar Children
More Literacy Units
Animal (Vertebrate) Groups
Butterfly Life Cycle
Electricity
Matter (Solid, Liquid, Gas)
Simple Machines
Space - Solar System
More Science Worksheets
Social Studies
Maps (Geography)
Maps (Map Skills)
More Social Studies
Mother's Day
Father's Day
More Holiday Worksheets
Puzzles & Brain Teasers
Brain Teasers
Logic: Addition Squares
Mystery Graph Pictures
Number Detective
Lost in the USA
More Thinking Puzzles
Teacher Helpers
Teaching Tools
Award Certificates
More Teacher Helpers
Pre-K and Kindergarten
Alphabet (ABCs)
Numbers and Counting
Shapes (Basic)
More Kindergarten
Worksheet Generator
Word Search Generator
Multiple Choice Generator
Fill-in-the-Blanks Generator
More Generator Tools
Full Website Index
Research Project Templates
Research projects are easy and fun with these templates. Students can learn about dinosaurs, states, provinces, and more. Each template guides students through the research process by asking simple questions and requiring basic drawings. Each file also has a bibliography form that students can fill out at the end of each project, as well as a rubric to help teachers with grading.
Logged in members can use the Super Teacher Worksheets filing cabinet to save their favorite worksheets.
Quickly access your most used files AND your custom generated worksheets!
Please login to your account or become a member and join our community today to utilize this helpful feature.

Browse our complete collection of math worksheets. Topics include fractions, geometry, addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, graphing, measurement, and more!
Browse through our extensive collection of science worksheets. Topics include animals, plants, simple machines, human body, magnetism, outer space, electricity, and more.
Sample Worksheet Images
PDF with answer key:
PDF no answer key:
- Try for free
Research Paper Graphic Organizer
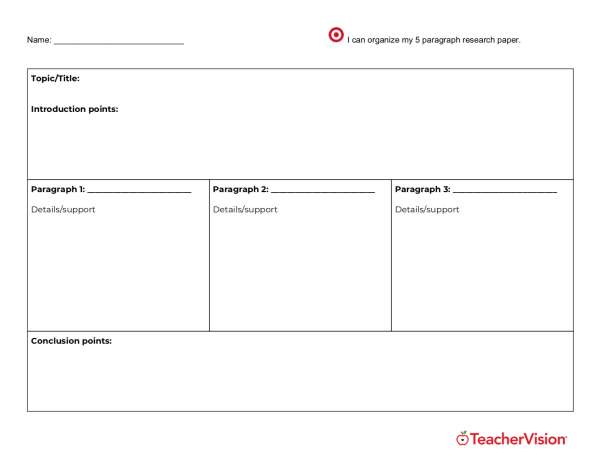
Help students to plan and prepare their research paper with this graphic organizer template.
This printable research graphic organizer is designed to help students synthesize their sources and ideas in order to ensure that they are ready to write. The template includes sections for students to outline the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusions, allowing them to organize and plan their research papers effectively.
Suitable for high school and middle school students and can be used for a variety of subjects and topics.
Discover our full collection of graphic organizers and browse by grade level or subject area to find ready-to-use printables and templates that save you time and support your learners.

Featured High School Resources

Related Resources

About the author

Contributor
About mikaela.

Advertisement
5 solar eclipse activities to do with children
From building an eclipse viewer to using the sun to pop balloons, here's a child-friendly activity guide for April's eclipse
By Abigail Beall
6 April 2024

There are plenty of fun eclipse activities to do with kids
Edwin Remsberg/Alamy
If you are planning to enjoy the total solar eclipse on 8 April with your children, here are a few activities you can do with them before and during the eclipse, to help them understand what causes a solar eclipse and get the most out of the experience.
1. Build an eclipse viewer
On the days leading up to the eclipse, you and your children can get excited about the big event by building an eclipse viewer . There are a few ways to do this – the first of which is a simple pinhole camera using two pieces of paper. Cut a hole in one piece of paper and cover it with aluminium foil, then poke a small hole in the foil. On the day of the eclipse, hold the paper up to let the sun beam through the hole and it will project a version of the eclipse onto a second piece of paper you place on the ground.
A slightly more complicated version involves a cereal or shoe box, placing paper at one end and cutting two holes in the other end. Over one of the two holes, you place some tin foil and, again, pierce it so that the sunlight can get through. More details on how to make both versions here .
Solar Eclipse 2024
On 8 April a total solar eclipse will pass over Mexico, the US and Canada. Our special series is covering everything you need to know, from how and when to see it to some of the weirdest eclipse experiences in history.
2. Build a solar eclipse model
Another activity that can be done ahead of the eclipse is building, or acting out, a model of the sun, moon and Earth to understand what a solar eclipse is . To build it, all you need is three sticks and three balls to place on top of the sticks. You can paint them or colour them in so that they resemble the sun, moon and Earth. Make sure the sun is bigger than the moon. Then, you can show your kids what an eclipse is by placing the sun in the centre, and moving Earth around the sun and the moon around Earth. When the three line up, with the moon in between the sun and Earth, we get a solar eclipse. When the moon is on the other side of Earth from the sun, we get lunar eclipses.
Your kids can also act out a solar eclipse. Give one of them a torch or flashlight, making them act as the sun, and ask them to shine the torch on a wall. The other, who is the moon, can move around until they block the torch light. They can both play around with moving forwards and backwards, to show why the distances between the moon, Earth and sun matter when it comes to eclipses.
Sign up to our Launchpad newsletter
Voyage across the galaxy and beyond with our space newsletter every month.
Total solar eclipse tours and cruises 2026 and 2027
We are working on some amazing ways to experience the forthcoming total solar eclipses in 2026 and 2027
3. Pop a balloon using sunlight
This is something that can be done on any sunny day. But on the day you are waiting for the total eclipse, you can show your kids how to use the power of sunlight to pop a balloon. You need a balloon and a magnifying glass for this activity. Blow up the balloon and then hold the magnifying glass up so that it magnifies the sunlight onto the balloon. Wait for a few minutes and, eventually, the balloon will pop. You can also make this more exciting by blowing up a white balloon inside a black one, and doing the same trick. The black balloon should pop, leaving the white balloon intact inside. You can use this to explain how black surfaces absorb sunlight, while light surfaces reflect them.
4. Play with shadows
On the day of the eclipse, while you are waiting for totality, the partial eclipse phase will last a few hours. You and your kids can get excited about the eclipse by noticing how shadows change, and playing around with this. If you have a tree nearby, look at the shadows it casts on the ground throughout the eclipse and you will see that they start to look like a sun with a bite taken out of it. This also works by crossing your fingers over each other and casting shadows on the ground. Another way to show the eclipse through shadows is using a colander, or anything with small holes in it. As the eclipse progresses, the shadows cast will start to take on the shape of the eclipse. You can punch a series of holes in a piece of paper to spell out a word or your kids’ names in these crescent shapes.
5. Draw shadows
This is another activity that can be done in the hours leading up to and after totality, again making the most of the interesting shadows created by a partially eclipsed sun. You can lay a big white piece of paper or sheet on the ground, and ask your kids to draw the shadows cast by different objects. If you do this at the start of the partial phase, and again closer to totality, they will be able to see how these shadows change as the eclipse progresses. You should notice that, in the lead-up to totality, shadows become much clearer as the amount of ambient light is reduced.
- solar eclipse 2024
Sign up to our weekly newsletter
Receive a weekly dose of discovery in your inbox! We'll also keep you up to date with New Scientist events and special offers.
More from New Scientist
Explore the latest news, articles and features
Eclipse 2024: 5 of the best pictures of the total solar eclipse
Eclipse 2024 live: watch the full nasa broadcast – latest, when is the next total solar eclipse visible from the uk, how a total solar eclipse in 1919 left physicists 'more or less agog', popular articles.
Trending New Scientist articles

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
I created five screencast videos, one for each step of the research report process. These screencasts pair perfectly with my Research Report Instructional Unit for 5th Grade and 6th Grade! Research Report Step 1 Screencast. Research Report Step 2 Screencast. Research Report Step 3 Screencast.
This video series will teach you how to write a research paper or report. Each episode leads you through each step of the writing process. In this video, you...
Fifth grade is a turning point for many students because it is the school year when academic demands increase. By fifth grade, it becomes clear which students exhibit gifts or challenges in certain areas, such as writing. Although most students will have written research papers in fourth grade or earlier, a fifth ...
Lesson Ideas for Writing Research Papers: Lesson 1: Noticings. Begin by getting your students familiar with what research writing looks like. Have them work in pairs or small groups to read pieces of research writing. They will record their "noticings" about the writing.
One of the most challenging assignments that you will have to do when it comes to your 5th grade assignments is to write a research paper. It is a larger paper than what you are used to writing. The idea is to create a research question about a topic that you are interested in and then work to answer it. The conclusion that you make on the ...
Research paper scaffolding provides a temporary linguistic tool to assist students as they organize their expository writing. Scaffolding assists students in moving to levels of language performance they might be unable to obtain without this support. An instructional scaffold essentially changes the role of the teacher from that of giver of ...
Most of the articles focus on animals, including issues such as biodiversity, conservation, and human impacts on the world. For convenience, you can download these 8 articles at once: Download 8 articles. We've published more than 30 articles suitable for 5th graders. Check out the full list here:
Worksheet. Two Truths and One Lie: Biography Edition. Use the game Two Truths and One Lie to help your students research facts about a famous person. Learners will research an important figure and then write down two true statements and one false statement. 5th grade.
Browse our printable 5th Grade Writing Research Papers resources for your classroom. Download free today!
Writing a Research Report (Gr. 5) Try this Language Arts printable in which students are introduced to writing and editing a research report through this writing process teacher model. It includes a model timeline, a blank timeline, and four different revisions of a sample paper. This activity works well as a part of your lesson or in a ...
These notes will help you write a better summary. The purpose of your research paper is to give you the information to understand why your experiment turns out the way it does. The research paper should include: The history of similar experiments or inventions. Definitions of all important words and concepts that describe your experiment.
This is one of the 5th grade research topics kids absolutely love! 6. Landforms - Deltas, Canyons, and Sand Dunes. A deep dive into the different landforms of the Earth is a must in any 5th-grade lesson plan. There is enough variety in these landforms that any single one of them would make a great research paper.
Fifth Graders can do simple research projects and papers on a variety of topics. Offer them the opportunity to find out more about a famous person, a location such as an American state or an ancient city, an invention or landmark or a current event. Students can learn to gather research from books, magazines, ...
Fifth Grade Fundamentals. This unit includes a 53 page powerpoint with how to write a research paper using research skills, paraphrasing, conventions, and index cards. It goes over the beginning steps and the note taking steps. It also includes writing guided questions and citing sources. It is in Power Point 2010 and links may not open on ...
Olivia Franklin. Engage students with interesting research topics, teach them skills to become adept independent researchers, and help them craft their end-of-unit research papers. CommonLit 360 is a comprehensive ELA curriculum for grades 6-12. Our standards-aligned units are highly engaging and develop core reading and writing skills.
Composing A Research Paper For 5th Grade Successfully. If you are in 5th grade there are a number of things that you need to learn about composing a research paper. There are students who normally think that it is impossible to do this at this age, but rest assured that this could not be any further from the truth. Over time you will come to ...
Video: How fifth graders research and organize essays. The essays kids write in fifth grade begin to become more complicated. So the work they do to organize their ideas is usually more complex, too. Watch this video from GreatSchools to see some ways kids this age develop their thoughts before writing an essay.
Writing a Compare-and-Contrast Essay (Gr. 5) Students are introduced to comparing and contrasting through this writing process teaching model. It includes a sample…. Browse our printable 5th Grade Writing Research Papers Graphic Organizers resources for your classroom. Download free today!
Today I had my very first experience teaching 5th-grade students how to write a thesis statement. I am a veteran middle school teacher to 7th and 8th-grade students, so the addition of teaching 5th-grade world history this year has been a blessing and a challenge. Our 5th-grade students write a 5 paragraph research paper […]
Science Journal for Kids and Teens. Hundreds of scientific articles. Written for kids. Approved by scientists. Free. Search Articles. Key Words. Reading Level. Elementary school.
5th Grade Research Paper 5th Grade Research Paper Points Earned 1-6=1 7-13=2 14-20=3 21-24=4 Rubric Code: PX9BCBW. By KimBap2 Ready to use Public Rubric Subject: Type: Writing Grade Levels: (none) Desktop Mode Mobile Mode ...
Research Project Templates. Research projects are easy and fun with these templates. Students can learn about dinosaurs, states, provinces, and more. Each template guides students through the research process by asking simple questions and requiring basic drawings. Each file also has a bibliography form that students can fill out at the end of ...
Teachers are turning to AI tools and platforms — such as ChatGPT, Writable, Grammarly and EssayGrader — to assist with grading papers, writing feedback, developing lesson plans and creating ...
Research Paper Graphic Organizer. Help students to plan and prepare their research paper with this graphic organizer template. This printable research graphic organizer is designed to help students synthesize their sources and ideas in order to ensure that they are ready to write. The template includes sections for students to outline the ...
2. Build a solar eclipse model. Another activity that can be done ahead of the eclipse is building, or acting out, a model of the sun, moon and Earth to understand what a solar eclipse is.To build ...