

Research | Facilities
- Research Units
- Research Institute
Research Institute of Agriculture and Life Sciences
- Center for Food and Bioconvergence
- Plant Genomics and Breeding Institute

- TEL +82-2-880-4910~4
- FAX +82-2-873-7729
- Research support in the fields of agriculture and life sciences for securing supplies and various applications of biological resources, environment-friendly agricultural production, rural development, and conservation of the environment
- Attraction and efficient management of research funds
- Planning and supporting collaborative and interdisciplinary research
- Academic information service in agriculture and life sciences and technology
- Planning and supporting research activities through seminars, symposia, conferences, etc.
- Providing public information and education on agriculture, life science, and technology
- Publication of academic and general series, academic journals (Research in Agriculture and Life Sciences), and annual reports
Affilliated institutes
- Research Center
- Research Project
- Academic Facilities

75 Years of Organic Leadership
Rodale institute has been conducting groundbreaking research on regenerative organic agriculture since 1947., start exploring.
Latest blog posts » Latest research articles »
Pennsylvania Governor Josh Shapiro: Rodale Institute and Organic Agriculture “Key” to the Commonwealth’s Economic Growth
Nurturing Nature's Filter: Soil Health and its Influence on Water
RODALE INSTITUTE & HARVARD BUSINESS SCHOOL
Apply Now: USDA Climate-Smart Funding Program for Southern Piedmont Farmers
Get the latest organic news in your inbox
- Email Address *
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
What Matters Most
How we’re growing the organic movement
Organic Research
Scientific studies and trials, straight from the farm
Farmer Training
How to make the switch to regenerative organic
Consumer Education
Simple steps everyone can take to heal the planet
Organic vs. Conventional? Learn from our 40-year comparison
New online classes from regenerative organic experts, work with our organic consultants, on the farm.
View all events »
Workshop: Compost Like a Pro
California organic center monthly tours, earth day celebration at pocono organics, regeneration in action field day, join the movement. make a difference..
Rodale Institute is rated four stars by Charity Navigator.
An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Research and Science
From fostering continued economic growth to adapting to the effects of climate change and addressing food security, the United States can continue to be a leader in global agriculture. Each day, the work of USDA scientists and researchers touches the lives of all Americans - from the farm field to the kitchen table and from the air we breathe to the energy that powers our country.
The challenges facing agriculture, natural resources, and conservation are immense and can be addressed through robust research enterprise and educational programs. USDA intramural and extramural science helps to protect, secure, and improve our food, agricultural and natural resources systems.
USDA Science and Research Strategy, 2023-2026: Cultivating Scientific Innovation
The “ USDA Science and Research Strategy, 2023-2026: Cultivating Scientific Innovation (PDF, 21.4 MB)” presents a near-term vision for transforming U.S. agriculture through science and innovation, and outlines USDA’s highest scientific priorities. The S&RS is a call to action for USDA partners, stakeholders, and customers to join the conversation and help identify innovative research strategies that lead to real-world, practical solutions that help farmers, producers, and communities thrive.
Learn more and engage below:
USDA Science and Research Strategy
AGARDA: A Vision for Disruptive Science to Confront Audacious Challenges
Agriculture Advanced Research and Development Authority (AGARDA) Implementation Strategy (PDF, 1.8 MB) is a framework outlining a new approach for delivering disruptive breakthrough discoveries for agriculture.
Strengthening Our Research System
USDA has refocused its science agencies to ensure the most effective and efficient use of its resources, while leveraging the strengths of our partners across the scientific community.
The Office of the Chief Scientist (OCS) coordinates USDA research, education and Extension with scientists and researchers across the federal government and university and private partners, to make the best use of taxpayer investments. In 2012, OCS continued focus on the Research, Education and Economics Action Plan (PDF, 486 KB) and identified seven priority research topics:
- Global Food Supply and Security
- Climate and Energy Needs
- Sustainable Use of Natural Resources
- Nutrition and Childhood Obesity
- Food Safety
- Education and Science Literacy
- Rural-urban Interdependence/Rural Prosperity
The Agricultural Research Service (ARS) conducts research to develop and transfer solutions to agricultural problems of high national priority.
The Economic Research Service (ERS) , through science-based economic research and analysis, informs public policy and other decisions about agriculture, food, rural development, and environmental challenges.
The National Agricultural Statistics Service (NASS) conducts hundreds of surveys every year and prepares reports covering virtually every aspect of U.S. agriculture.
The National Institute of Food and Agriculture (NIFA) supports research, education and Extension programs in the Land-Grant University System and other partner organizations.
Enhancing the Productivity of American Agriculture and Ensuring the Safety of our Food Supply
USDA invests in research, development, and outreach of new varieties and technologies to mitigate animal/plant diseases and increase productivity, sustainability, and product quality. USDA research has supported America's farmers and ranchers in their work to produce a safe and abundant food supply for over 100 years. This work has helped feed the nation and sustain an agricultural trade surplus since the 1960s.
An additional focus is to establish more sustainable systems that enhance crop and animal health. Our scientists and university partners have revealed the genetic blueprints of a host of plants and animals including the genomes of apples, pigs, and turkeys, and in 2012, they furthered understanding of the tomato, bean, wheat and barley genomes -- key drivers in developing the resilience of those crops to feed growing populations.
NASS has developed animated U.S. crop progress and topsoil moisture maps , along with other resources, to help experts assess farmland data. USDA researchers also created the Maize Genome Database, an important tool to help farmers improve traits in a crop vital to the world. Meeting growing global demand for food, fiber, and biofuel requires robust investment in agricultural research and development (R&D) from both public and private sectors. USDA is a leader in remote sensing and mapping to visualize data in support of agricultural policy and business decision making as well as program operation. We ranked first worldwide among research institutions publishing on priority diseases in animal health including salmonellosis, avian influenza , mycobacterial disease, coccidiosis, campylobacterosis, mastitis and others.
USDA conducts and supports science that informs decisions and policies contributing to a safe food supply and the reduction of foodborne hazards. Our scientists found the primary site where the virus that causes foot-and-mouth disease begins infection in cattle and developed an improved vaccine against the disease. They are also working on new strategies to control mites and other major honey bee problems such as colony collapse disorder .
Improving Nutrition and Confronting Obesity
USDA builds the evidence base for food-based and physical activity strategies and develops effective education activities to promote health and reduce malnutrition and obesity in children and high-risk populations. For example, ARS evaluated school characteristics associated with healthier or less healthy food preparation practices and offerings and found that the school nutrition environment could be improved by requiring food service managers to hold nutrition-related college degrees, pass a food service training program, and by participating in a school-based nutrition program such as USDA Team Nutrition .
USDA-supported science is investigating the causes of childhood obesity so that our country can address the epidemic. In these efforts, USDA supports nutrition education programs and encourages Americans to consume more nutritious foods like fruits and vegetables. Our scientists are part of an international team that has found a way to boost the nutritional value of broccoli, tomatoes and corn, and have worked to find ways to bolster the nutritional content of other staple crops like oats and rice. USDA research has supported these efforts, showing how healthy foods can often cost less than foods that are high in saturated fat, added sugar and/or sodium.
In 2013, USDA updated the national assessment of urban and rural food deserts - low-income areas with limited access to affordable and nutritious food - and provided information on the socioeconomic and demographic characteristics that distinguish food deserts from other areas, for decision-makers and stakeholders concerned about access to healthy foods.
Conserving Natural Resources and Combating Climate Change
USDA develops and delivers science-based knowledge that empowers farmers, foresters, ranchers, landowners, resource managers, policymakers, and Federal agencies to manage the risks, challenges, and opportunities of climate variability, and that informs decision-making and improves practices in environmental conservation.
Our scientists are developing rice and corn crops that are drought- and flood-resistant and helping to improve the productivity of soil, as well as production systems that require increasing smaller amounts of pesticides or none at all.
Vegetation indices contained in VegScape have proven useful for assessing crop condition and identifying the aerial extent of floods, drought, major weather anomalies, and vulnerabilities of early/late season crops. This tool allows users to monitor and track weather anomalies' effects on crops in near real time and compare this information to historical data on localized levels or across States.
Additionally, our researchers have examined the potential impacts of a suite of climate scenarios on U.S. crop production. Studies like these will help policymakers, farmers, industry leaders and others better understand and adapt to a changing climate on America's crop production.
Our researchers created i-Tree , urban forest management software to help cities understand the value of urban trees through carbon sequestration, erosion protection, energy conservation and water filtration, and since 2009 have continued building on the success of the tool and expanding its use. Our scientists are conducting research on uses of wood, helping companies meet green building design standards and creating jobs using forest products. We have also worked with Major League Baseball to reduce the occurrence of broken baseball bats.
USDA supports families managing through tough economic times by helping residents save energy at home and conserve water, with a program run by Cooperative Extension and our land-grant university partners. Cooperative Extension-affiliated volunteer monitoring programs have engaged citizens in water monitoring to better understand the effects of climate change and/or aquatic invasive species on local waters. Collectively, these programs interacted with hundreds of local, State, and Federal partners. The programs help citizens detect the presence of invasive species and harmful algal blooms.
Science Education and Extension
USDA recognizes the importance of recruiting, cultivating, and developing the next generation of scientists, leaders, and a highly skilled workforce for food, agriculture, natural resources, forestry, environmental systems, and life sciences.
The NIFA interagency agreement with the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service leverages technology and innovation and involves youth in STEM outreach and exposure. Youth participants developed science process skills related to using GIS and research design, analyzing and interpreting data, and reporting findings to the community which has enabled them to become better consumers of science and citizens capable of making wise STEM policy choices.
USDA strives to provide effective research, education, and extension activities that inform public and private decision-making in support of rural and community development . NASS holds outreach events throughout the Census cycle with underserved and minority and disadvantaged farming groups to promote participation in the Census of Agriculture . With funding and support from NIFA, many Tribal Colleges are offering Reservation citizens training ranging from basic financial literacy to business start-up and marketing information so that families not only survive, but thrive.
In addition, the ERS Atlas of Rural and Small Town America brings together over 80 demographic, economic, and agricultural statistics for every county in all 50 states and assembles statistics in four broad categories -- people, jobs, agriculture, and geography.
Research and Science Centers and Databases
- Agricultural Network Information Center (AGNIC)
- Agricultural Online Access (AGRICOLA)
- Alternative Farming Systems Information Center (AFSIC)
- Animal Welfare Information Center (AWIC)
- Current Research Information Center (CRIS)
- Digital Desktop (DigiTop) for Employees
- Food and Nutrition Assistance Research Database
- Food and Nutrition Information Center
- Production, Supply and Distribution Online (PSD Online) Database
- Rural Information Center
- Water and Agricultural Information Center
Search Reset search Search
suggestions
INRAE is France's National Research Institute for Agriculture, Food and Environment, created on January 1, 2020, It was formed by the merger of INRA, the National Institute for Agricultural Research, and IRSTEA, the National Research Institute of Science and Technology for the Environment and Agriculture.
Science dedicated to life, humans, and the Earth
Humankind and the planet are facing global changes that will create new challenges for research to address: limiting the effects of and adapting to climate change; increasing food security and nutrition security; transitioning to new agricultural systems; preserving natural resources; restoring biodiversity; and anticipating and managing risks. It will also be important to consider more regional issues like living conditions, farmers' salaries, the economic competitiveness of companies, land use, and universal access to healthy and varied diets.
INRAE, the French National Research Institute for Agriculture, Food, and Environment was formed by the merger of INRA and IRSTEA on 1st January 2020
As the world's top institute for research on agriculture, food, and the environment *, INRAE will help address these concerns. It will use research, innovation, and support for public policies as tools to guide the emergence of sustainable agricultural and food production systems. The institute aims to carry out science dedicated to life, humans, and the Earth that uncovers solutions to our most pressing concerns.
INRAE was formed by the merger of INRA, the French National Institute for Agricultural Research, and IRSTEA, the French National Research Institute of Science and Technology for the Environment and Agriculture. Both institutes were known for the quality of their research and their great expertise. Their union has generated a critical research mass and has pooled their major infrastructures (e.g., observatories, technical platforms, data repositories), including some that are one of a kind in Europe. As a result, INRAE is uniquely suited to perform valuable research on numerous topics, including water resources, regional agricultural strategies, the preservation and restoration of biodiversity, risk anticipation and management, and digital agriculture.
Download INRAE leaflet (sept 2021)

(nouvelle fenêtre)
INRAE is committed to exploring the frontiers of science and performing high-calibre research that is globally relevant. The institute makes major contributions to European research and participates in European research programmes (e.g., via research networks, H2020 research projects, Marie Skłodowska-Curie Actions) and, as a result, is currently developing bilateral and trilateral partnerships. Our international collaborations focus on sharing laboratories or infrastructure, becoming integrated into research networks, and playing a role within international organisations.
"Our need for research has never been more urgent": find out more
* Based on the Web of Science (WOS) specialisation index score: INRAE's representation within the 10 following research domains/ INRAE's representation within all the WOS research domains at the international scale: Agriculture, Plant sciences, Veter inary sciences, Genetics & heredity, Food science & technology, Nutrition dietetics, Biotechnology & applied microbiology, Environmental sciences & ecology, Water resources, Microbiology.
Research that serves society
Our job is to
- produce and disseminate knowledge to help solve major societal challenges
- put this knowledge to work to foster innovation, provide expertise, and lend support to public policies
which we accomplish thanks to an approach based on
- interdisciplinary foresight analysis of current challenges
- research at the frontiers of knowledge that encourages breakthroughs
- academic partnerships at regional, national, European, and international scales that are firmly tied to regional structures within the system of higher education and research
- expertise and support that inform public policies from the local to the international level
- partnerships with the many stakeholders in the field: farmers, private companies, NGOs, regional governments...each with a variety of perspectives and approaches
- open-source tools for promoting innovation that allow the free exchange of ideas, knowledge, and experience
- infrastructure that enhances the sharing of research and data
- discussions with the general public to explain, debate, and contribute
In all of our work, we are committed to applying a code of ethical practices .

Using its research and its ability to produce, analyse, and exploit knowledge from a broad range of discipline-specific and interdisciplinary work, INRAE seeks to achieve conceptual, technological, and social breakthroughs; inform public policies; and boost crucial agricultural, dietary, and environmental transitions. We cannot do this alone. As a result, we have affiliated ourselves with governmental structures for higher education, research, and innovation in France and in Europe; we are developing national and international partnerships with a wide range of public and private stakeholders in our fields of specialisation; and we are engaging in conversations with the general public and any other interested parties.
An engaged institute
Our scientific axes and practices focus on subjects of societal importance, and our research results can nourish the important resulting debates. In all of our work, we are committed to applying a code of ethical practices rooted in responsibility, impartiality, integrity, dignity, and probity. We rely on the feedback provided by our ethics committee and our specialists in scientific conduct. In some areas, INRAE has adopted formal principles, positions, institutional strategies, or opinions, all informed by scientific ethics and integrity.
INRAE is playing a major role in research related to the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and is committed to adopting corporate social responsibility (CSR) principles so that the SDGs can be attained by 2030. The process requires a transformation in operations and professional practices. The institute’s CSR strategy is being implemented via an ambitious action plan.
Our objectives: use our rigorous scientific approach to serve the greater good, reflect on the ethical implications of our research, and adopt the principles of corporate social responsibility (CSR), thus promoting the UN’s 2030 Sustainable Development Goals.

Corporate social responsibility

Ethics, Scientific Integrity, and Code of Conduct for Research Projects

Ethics Committee
First evaluation by hcéres for inrae.
The evaluation of INRAE covered the period 2016-2020, the previous evaluations of INRA and Irstea by the High Council for the Evaluation of Research and Higher Education (Hcéres) having taken place in 2016 and 2018 respectively. In addition to INRAE's activities, the experts also examined the quality of the preparatory work and implementation of the merger of INRA and Irstea, INRAE's positioning, its strategy, governance and management.

Excerpts: "The committee has appreciated the considerable efforts that have led to a successful merger of INRA and Irstea and to the development of the INRAE 2030 plan. [It] considers that the new organisation offers important levers contributing to a leading position at the European and international levels, to a rich cross-fertilisation between the research teams from the two institutes and to a well thought-out pooling of support activities. [...] It has observed significant progress on certain weaknesses pointed out in previous evaluations of INRA and Irstea. [...]
The committee believes that INRAE will be faced with increasing demands in the forthcoming period in terms of research, expertise and support to public policies. The institute will have to make choices, and in particular prioritise its partnerships. It will have to continue to develop an impact culture and overcome a lack of capacity to continuously measure and monitor the impacts of its activities.
Hcéres evaluation report (in French) - October 2022 pdf - 1.06 MB
Agriculture, food, and the environment: overlapping themes
INRAE and its partners wish to tackle challenges that extend beyond national and industrial boundaries. We must therefore adopt transversal perspectives in our three key areas of study—agriculture, food, and the environment—if we wish to clearly account for their interactions. We need a systematic and interdisciplinary approach if we wish to develop sustainable solutions.
With the overarching goal of promoting sustainable development, our work is centred on six major themes:
- Climate change and risks
- Agroecology
- Biodiversity
- Food, global health
- Society and regional strategies

INRAE is deliberately organised in the form of a matrix, which helps the institute carry out its integrated multidisciplinary research for addressing society's greatest global challenges. To guide and accelerate the major transitions needed to enhance the sustainability of agricultural systems and food systems, INRAE carries out work at 18 research centres with strong regional ties that are clustered within 14 research divisions that have firmly established international partnerships. Metaprogrammes serve as links among the institute's research divisions, strengthening INRAE's interdisciplinary approach. The institute's work is also bolstered by its directorates dedicated to international affairs, open science, value creation, scientific expertise, and public policy support. Our various support departments (e.g., human resources, finance, purchasing) strive for maximum efficiency and espouse principles of social and environmental responsibility in alignment with our research objectives and our goal of serving society. The communications department works with all INRAE's staff to disseminate the institute's discoveries and engage in exchanges with stakeholders.
INRAE: a Public Scientific and Technical Research Establishment
Created on January 1, 2020, INRAE is a Public Scientific and Technical Research Establishment (EPST). It was formed by the merger of INRA, the French National Institute for Agricultural Research, and IRSTEA, the French National Research Institute of Science and Technology for the Environment and Agriculture. It is under the joint aegis of the Ministry of Higher Education, Research, and Innovation (MESRI) and the Ministry of Agriculture and Food (MAA). INRAE is also beginning to closely collaborate with the Ministry for the Ecological and Inclusive Transition (MTES) via various partnership agreements.
According to the official decree announcing its creation ( n° 2019-1046 du 10 octobre 2019 [in French]), INRAE has the following missions:
"to carry out, organise, and coordinate, on its own initiative or in response to a governmental request, all types of scientific and technological research in the domains of agriculture, food, forestry, the environment, water resources, biodiversity, the bioeconomy, the circular economy, the sustainable management of regions, and risk management in the specialised fields of research mentioned above."
"To this end, the institute will do the following: 1. Produce, publish, and disseminate the scientific knowledge that results from its research and scientific expertise work; 2. Allow, in the absence of any provisions or stipulations to the contrary, open access to scientific data and publications; 3. Participate in the creation of public policies and national and European research strategies; 4. Contribute to higher education and research-based education in its fields of specialisation; 5. Establish and make use of partnerships with establishments of higher education and research; 6. Contribute to the creation of innovative and socially responsible technologies by building upon the institute's skill set, expertise, and research discoveries; 7. Help develop scientific and technological expertise, prepare scientific expert reports, and participate in standardisation activities with a view to providing support for policies, foundations, and associations of recognised public interest and to generating solutions to sustainable development challenges; 8. Participate in discussions centred on the role of science and technology in society."
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Linkedin
- Share by email
- Share by link
link_copied
Welcome to FiBL
The Research Institute of Organic Agriculture FiBL is one of the world’s leading institutes in the field of organic agriculture.

30 perspectives
In the past year, more than 30 "anniversary voices" have taken a look at FiBL
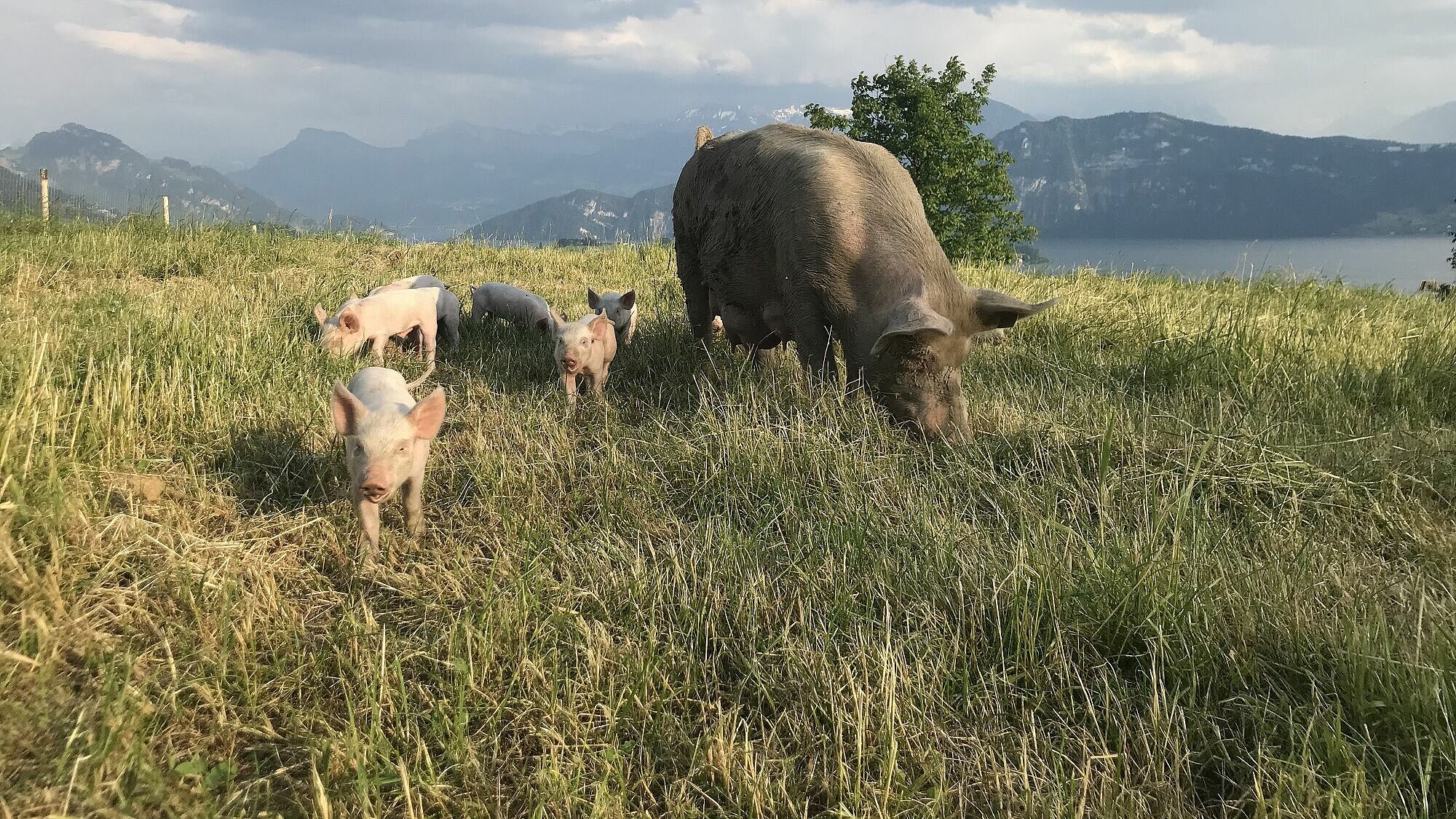

Citizen Science
In the research and educational project "SchweinErleben", the general public is asked to participate.

World of Organic Agriculture 2024
Latest figures on organic farming worldwide in the 25th edition of the statistical yearbook

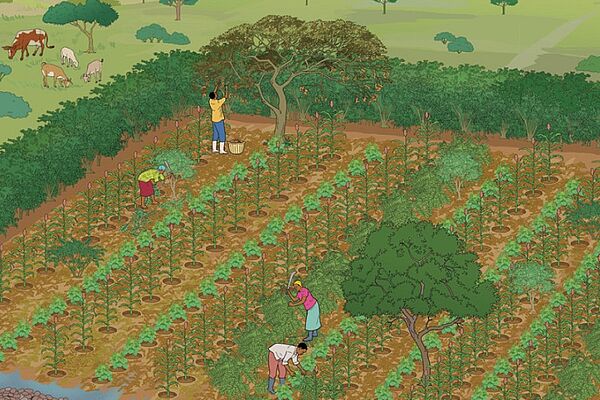
Policy dossier on agroecology in the tropics
Organic agriculture and agroecology show promise in achieving sufficient yields and income

A wealth of expertise in over 650 publications and more than 20 languages available for free download

No April Fool's joke: It all started 50 years ago

New training handbook on the EU Organic Regulation for organic producer groups

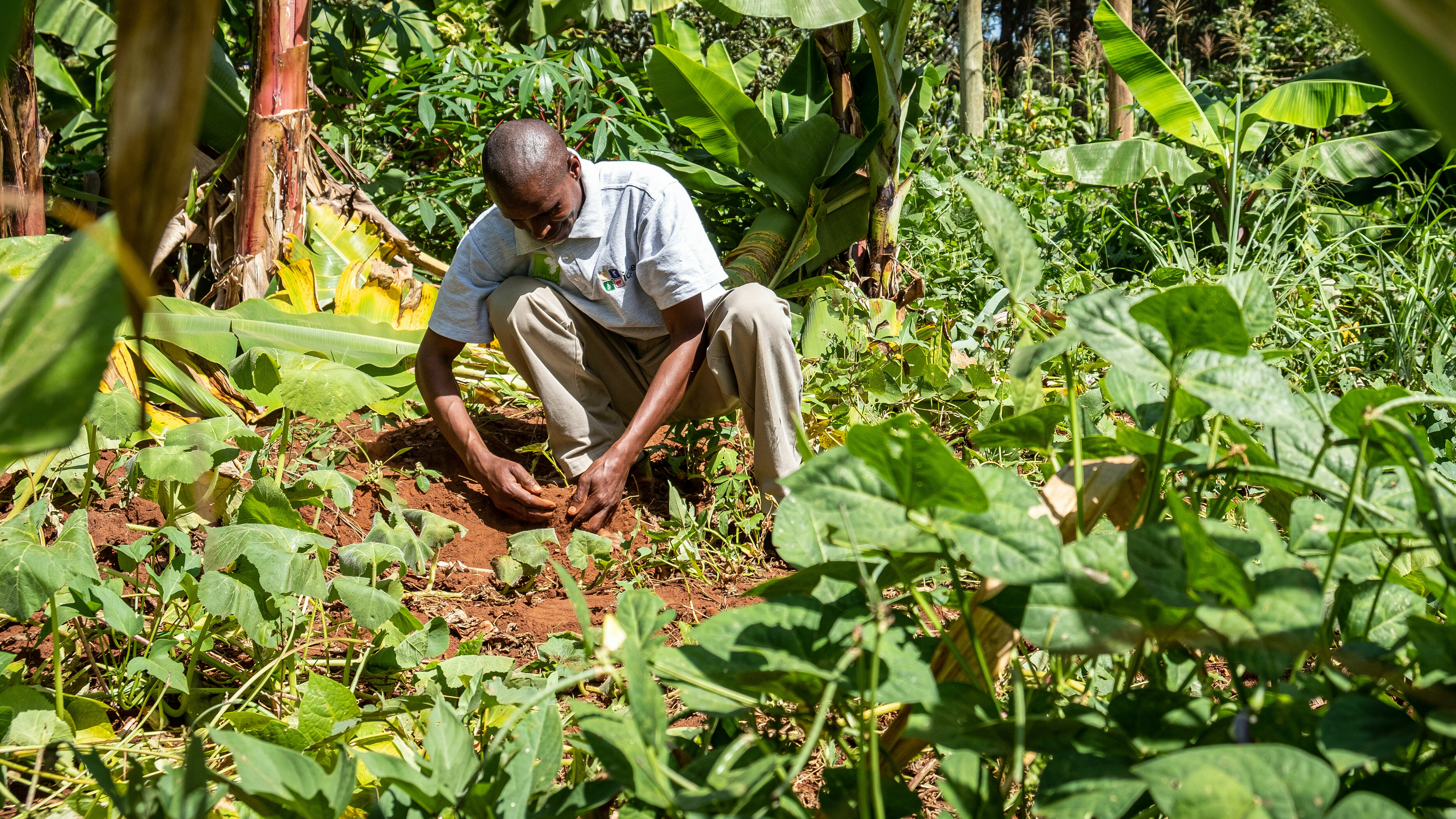
Benefits of agroforestry in the Sahel
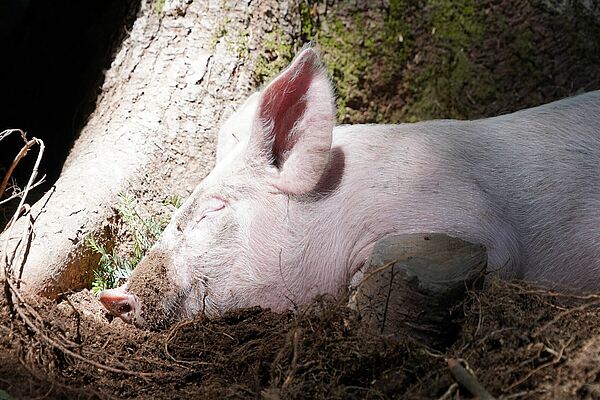

SchweinErleben: How wild are domestic pigs?

Anniversary voices: "A change of perspective is always needed"

OrganicYieldsUP – a new project to enhance organic crop yields across Europe
Bio kann jeder: vom acker auf die teller – bio in der schulverpflegung, online-fachberaterworkshop "arbeiten mit gruppen online", bio kann jeder: bio-catering biond (best practice) – bio in der kita- und schulverpflegung.

FiBL publications: Latest additions to the Organic Eprints archive
- Market opportunities and technical challenges for organic seed producers: focus on TECHNICAL CHALLENGES
- Screening suitable legumes for living mulches to support nitrogen dynamics and weed control in a durum wheat-forage sorghum crop sequence
- Land-free bioenergy from circular agroecology—a diverse option space and trade-offs
- Evaluation of seed treatments for the control of bean diseases (Bresov project)
- The feeding of heather (Calluna vulgaris) to Teladorsagia circumcincta infected lambs reduces parasitism but can detrimentally impact performance
- Farm gate profitability of organic and conventional farming systems in the tropics
- Spatio-temporal complementarity of floral resources sustains wild bee pollinators in agricultural landscapes
- Behavioural responses related to increasing core body temperature of grazing dairy cows experiencing moderate heat stress
- Carbon dioxide removal: A source of ambition or of delays? Examining expectations for CDR in Swiss climate policy
- Living Lab Methodologies and expamples of Living Labs in animal agriculture. First experiences from H2020 Project Roadmap
- Vision of 100% organic agriculture in Luxembourg in 2050: Resilience, environmental impacts and dietary change (VISION 2050)
- Affordable and eThical TracEability SysTEms to support proDucer-consumer relationships in small and medium supply chains (ATTESTED)
- Status quo of parasite control on organic pig breeding and fattening farms in the canton of Aargau
- Reaching 25% organic farmland in the EU by stronger and better-connected organic advisors and organic advisory services (OrganicAdviceNetwork)
- Hessisches Beratungsangebot für Kantinen und Großküchen "Zu Tisch: Kantine wird nachhaltig"

UPLB, KOICA, IRRI and Key Institutions to establish agri-genomics facilities to support national competitiveness

IRRI-Government of Odisha partnership to strengthen state’s specialty rice segment

IRRI-NARI agreement will revitalize Papua New Guinea’s rice industry

REMET-Rice Project supports joint training on soil spectroscopy for BSWM, UPLB, and IRRI scientists

We are addressing five impact challenges faced by farmers, consumers, and stakeholders, in the world’s rice-producing countries.
Where we work
We work with key actors from these regions through our in-country offices to develop actionable research analyses and recommendations on country-specific agricultural initiatives.
Beyond these areas, we also work with other country partners through our global research programs and networks.
Learn more about IRRI's regional initiatives here and explore how we can collaborate.

Southeast Asia
- Philippines
- South Korea
Abolish poverty and hunger with IRRI
Support our mission by being an irri donor or partner.
SpeedFlower: a comprehensive speed breeding protocol for indica and japonica rice
To increase rice yields and feed billions of people, it is essential to enhance genetic gains. however, the development of new varieties is hindered by longer generation times and seasonal constraints. to address these limitations, a speed breeding facility has been established and a robust speed breeding protocol, speedflower is developed that allows growing 4–5 generations of indica and/or japonica rice in a year. our findings reveal that a high red-to-blue (2r > 1b) spectrum ratio, followed by green, yellow and far-red (fr) light, along with a 24-h long day (ld) photoperiod for the initial 15 days of the vegetative phase, facilitated early flowering. this is further enhanced by 10-h short day (sd) photoperiod in the later stage and day and night temperatures of 32/30 °c, along with 65% humidity facilitated early flowering ranging from 52 to 60 days at high light intensity (800 μmol m−2 s−1). additionally, the use of prematurely harvested seeds and gibberellic acid treatment reduced the maturity duration by 50%. further, speedflower was validated on a diverse subset of 198 rice accessions from 3k rgp panel encompassing all 12 distinct groups of oryza sativa l. classes. our results confirmed that using speedflower one generation can be achieved within 58–71 days resulting in 5.1–6.3 generations per year across the 12 sub-groups. this breakthrough enables us to enhance genetic gain, which could feed half of the world's population dependent on rice..

Visit to the International Rice Research Institute 11/29/2022
Aiming to strengthen the government’s partnership and collaboration with the world’s premier research organization dedicated to reducing poverty and hunger through rice science to achieve his goals for the agricultural sector, president ferdinand r. marcos jr. visits the international rice research institute (irri) headquarters in los baños, laguna on november 29, 2022..

ASEAN-CGIAR Innovate for Food and Nutrition Security Regional Program
The asean-cgiar innovate for food and nutrition security regional program is a research collaboration among the asean member states, asean secretariat, and cgiar centers, with funding support from the government of australia and the united kingdom. the program’s vision for the next 10 years is to scale up and out bold integrated innovations that will enhance the resilience of asean's agri-food systems to climate change. this ambitious endeavor aims to deliver better livelihoods for food producers and other stakeholders along the value chain. it also seeks to ensure more affordable, nutritious, and healthy food for consumers while fostering a healthier natural environment for all. , for more information on the asean-cgiar innovate for food and nutrition security regional program, please contact: dr. jongsoo shin (asean-cgiar program director) and dr. stephan weise (asean-cgiar program co-director) [email protected].

Webinar: Climate-smart rice hybrids by Dr. Jauhar Ali

Flood resilience loci SUBMERGENCE 1 and ANAEROBIC GERMINATION 1 interact in seedlings established underwater
Tweets by irri

Agriculture Research Institute


The Agriculture Research Institute (ARI) engages the collective expertise of CSU colleges of agriculture and other related programs across the CSU, in partnership with agricultural and natural resource industries, to conduct applied research that benefits California agriculture, natural resources and food systems while cultivating the next generation of agricultural leaders.

Sydnee Winbush Helps Discover Bacteria That Degrade Pesticides
Sydnee Winbush grew up in the Moreno Valley in Southern California. Always interested in life sciences, she took an advanced placement human anatomy and physiology class in high school.

Undergraduate Research
From A Stable to the Laboratory Bench, Gabi Hernandez’s Unexpected Path to a Research Career
Gabriella “Gabi” Hernandez grew up riding horses in Chino Hills, California. When not in school, Hernandez spent her time at the Silver Rose Ranch, where she boarded her horse, gave riding lessons and helped teach at the ranch’s summer camps. - See more a

Biomass-To-Energy—Carisse Geronimo’s Research Helps Fight Climate Change
Clean power sources, such as wind, solar, hydropower and biomass-to-energy, will provide all of California’s energy by 2045.
More Highlights
- Washington State University
WSU to lead national AI research institute for agriculture
PULLMAN, Wash. – With a new $20 million federal grant, Washington State University will lead a multi-institutional research institute to develop artificial intelligence (AI) solutions to tackle some of agriculture’s biggest challenges related to labor, water, weather and climate change.

The new institute is one of 11 launched by the National Science Foundation and among two funded by the U.S. Department of Agriculture-National Institute of Food and Agriculture in 2021. It’s called the AgAID Institute , which is short for USDA-NIFA Institute for Agricultural AI for Transforming Workforce and Decision Support.
While traditional AI development involves scientists making tools and delivering them to end-users, the AgAID Institute will involve the people who will use the AI solutions—from farmers and workers to policy makers—in their development, said Ananth Kalyanaraman, a WSU computer science professor and the lead principal investigator for the Institute.
“People are very much part of the agricultural ecosystem. It’s not just plants growing. Humans manipulate crops on a daily basis and make complex decisions, such as how to allocate water or mitigate the effects of an incoming storm,” said Kalyanaraman, who also holds the Boeing Chair in WSU’s School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science. “We aim to partner human knowledge with AI tools in a way that amplifies the end outcomes where the whole is greater than the sum of its parts.”
The AgAID Institute will be a multi-disciplinary, collaborative effort involving faculty and scientists with expertise on a diverse range of areas in computer science, agriculture and agricultural outreach.
“Artificial intelligence has a key role to play in our ability to address the 21st century grand challenges in agriculture,” said Rich Koenig, interim dean of WSU’s College of Agricultural, Human, and Natural Resource Sciences . “Our agricultural stakeholders are looking forward to the new AI technologies that come out of this interdisciplinary Institute, in order to help them improve agricultural productivity and address uncertainties due to labor, weather, and climate.”
In addition to WSU, the Institute members include Oregon State University; University of California, Merced; University of Virginia; Carnegie Mellon University; Heritage University; Wenatchee Valley College; and Kansas State University. Private sector partners include IBM Research and the start-up innov8.ag.
The AgAID Institute will take an “adopt-adapt-amplify” approach, Kalyanaraman said. This means first the Institute will design AI solutions in partnership with the people who use the tools, so they are practical and more likely to be adopted. The researchers will also work to make solutions that can adapt to changing environments and that amplify productivity by combining human skills and machine capabilities to be more effective than either would be alone. For instance, pruning trees is a highly skilled task, but a beginner-level worker could benefit from an AI tool that provides expert guidance to help decide which is the best branch to prune. The task is done better, and the worker starts to learn from the feedback, and with a shortage of skilled labor, AI can benefit both the orchard and the worker, said Kalyanaraman.
“It’s a partnership. AI can help us basically bridge the divide between high-skilled and low-skilled workers,” he said.
Educating the workforce at all levels is central to the AgAID Institute not just to encourage AI adoption but as a matter of equity, according to the Institute leaders. The Institute plans multiple education programs from K-12 through higher education and worker training. The goal is to raise AI skill levels and open new career paths, which can improve pay and quality of life for agricultural workers. It can also attract more people to agriculture and computing professions.
The AgAID Institute will undertake several challenging test cases involving specialty crops, many of which grow in the Western United States, such as apples, cherries, mint and almonds. These crops encompass several major challenges: they require intensive labor and irrigation. They are also vulnerable to weather events and climate change. Specialty crops account for 87% of the U.S. agricultural workforce, and about 40% of these crops are perennial, requiring long-term management and resource planning.
The difficult challenges posed by these cases would mean AgAID Institute’s solutions would be rigorously tested before being transferred to other regions in the country, said Kalyanaraman.
“We know that AI has a serious potential to make groundbreaking discoveries and transform our decision-making capabilities in a data-informed way, but the technology needs to be developed in a very careful manner,” he said.
This award is part of a significant investment by the federal agencies in state of Washington AI leadership, noted U.S. Sen. Maria Cantwell. Two of the 11 funded institutes will be headed by universities in the state: in addition to the WSU-led AgAID Institute, the University of Washington will be leading the NSF AI Institute for Dynamic Systems.
“The state of Washington is already a leader in artificial intelligence,” said Cantwell. “From the University of Washington’s Tech Policy Lab that studies the grand challenges around artificial intelligence to Washington State University’s work in precision agriculture, we are more than ready for these two grants to help us understand more artificial intelligence applications. The UW will work in the area of complex systems to improve fields like manufacturing and WSU will work on improvements in farming.”
Rep. Cathy McMorris Rodgers expressed her support for the new AgAID Institute.
“Washington State University has long been a leader in agriculture, innovation and technology,” said McMorris Rodgers. “I was proud to be a part of the conversation at the university’s Agriculture AI Summit in October 2020 and am pleased to see that WSU received designation as the USDA-NIFA Institute for Agricultural AI for Transforming Workforce and Decision Support today. This institute, also known as AgAID, will integrate AI methods into agriculture operations for prediction, decision support and robotics-enabled agriculture to address the complex agricultural challenges facing Eastern Washington and the nation. I look forward to seeing the innovative work that will come out of this Institute to support our state’s agricultural industries.”
CAHNRS faculty and researchers include Qin Zhang, Bernadita Sallato-Carmona, Chad Kruger, Claudio Stockle, Georgine Yorgey, Jennifer Bolivar-Medina, Jonathan Yoder, Kirti Rajagopalan, Lav Khot, Lee Kalcsits, Manoj Karkee, Markus Keller, Matthew Whiting, Mike Brady, Nancy Deringer, Sindhu Sankaran, and Troy Peters.
- Old website
- Employee Corner
- Skip to Main Content
- Screen Reader Access
- A - A+ A A- --> A+ A A- A A
- English Eng Hin

भारतीय कृषि अनुसंधान परिषद indian council of agricultural research Ministry of agriculture and Farmers Welfare

भारतीय कृषि अनुसंधान परिषद indian council of agricultural research Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare

ICAR Institutions, Deemed Universities, National Research Centres, National Bureaux, Directorate/Project Directorates & Agricultural Technology Application Research Institutes

- Privacy Policy
- Web Information Manager
- Copyright Policy
- Hyperlinking Policy
- Accessibility Statement
@ Content Owned by Indian Council of Agricultural Research
@ Content Owned by Directorate of Knowledge Management in Agriculture
Copyrights © 2022 All Rights Reserved By Indian Council of Agricultural Research Krishi Bhavan
- Total Visitors: 20490005
Like on Facebook
Subscribe on Youtube
Follow on Twitter
Like on instagram

Agricultural Research Institute
Supporting agricultural research.
The California State University Agricultural Research Institute (ARI) is a diverse and comprehensive multi-campus applied agricultural and environmental research program that leverages state funding with university and industry capital and intellectual collateral through university-industry partnerships.
ARI's collective expertise is a collaboration of the CSU's four colleges of agriculture at California State University, Fresno; California State Polytechnic University, Pomona; California State Polytechnic University, San Luis Obispo; and California State University, Chico; and the state's agriculture and natural resource industries and allied business communities.
ARI projects and programs seek to resolve California farm, ranch and consumer challenges such as improving food quality and safety, increasing productivity and enhancing economic viability. Research also addresses emerging sustainability issues such as environmental compatibility and domestic and international competitiveness. In addition, ARI explores solutions for strategic gaps in our knowledge base that otherwise might not be studied by for-profit companies and institutions because there is little or no financial incentive to do so, despite their importance.
The ARI primarily focuses on finding immediate and practical solutions for high-priority challenges in the following general research categories:
- Agricultural Business
- Biodiversity
- Biotechnology
- Food Science/Safety/Security
- Natural Resources
- Production and Cultural Practices
- Public Policy
- Water and Irrigation Technology
The California State Polytechnic University, Pomona supports broader research areas within each of the areas listed above. To see a list of all 37 areas which we support click here .
The ARI receives a $4.37 million annual State General Fund budget allocation to support applied research and outreach activities. The ARI distributes this public funding to support scientifically peer-reviewed research that is annually matched at least one to one with industry and/or agency resources to fund high-priority research, development, and technology transfer activities, as well as public and industry education and outreach. ARI funding allocations are expressly designed to encourage CSU system and individual campus excellence through a combination of competitive research and capacity building enhancements. Individual campus funding is allocated through the respective colleges of agriculture on a competitive basis and must be utilized for agricultural, allied business or natural resources applied research. Research funding opportunities, however, are not exclusive to the colleges of agriculture.
Please don't hesitate to contact us with questions about the suitability of your project. We look forward to working with you!
- Old website
- Employee Corner
- Skip to Main Content
- Screen Reader Access
- A - A+ A A- --> A+ A A- A A
- English Eng Hin

भारतीय कृषि अनुसंधान परिषद indian council of agricultural research Ministry of agriculture and Farmers Welfare

भारतीय कृषि अनुसंधान परिषद indian council of agricultural research Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare

Institutions

- Privacy Policy
- Web Information Manager
- Copyright Policy
- Hyperlinking Policy
- Accessibility Statement
@ Content Owned by Indian Council of Agricultural Research
@ Content Owned by Directorate of Knowledge Management in Agriculture
Copyrights © 2022 All Rights Reserved By Indian Council of Agricultural Research Krishi Bhavan
- Total Visitors: 20492365
Like on Facebook
Subscribe on Youtube
Follow on Twitter
Like on instagram

Articles » Newsroom
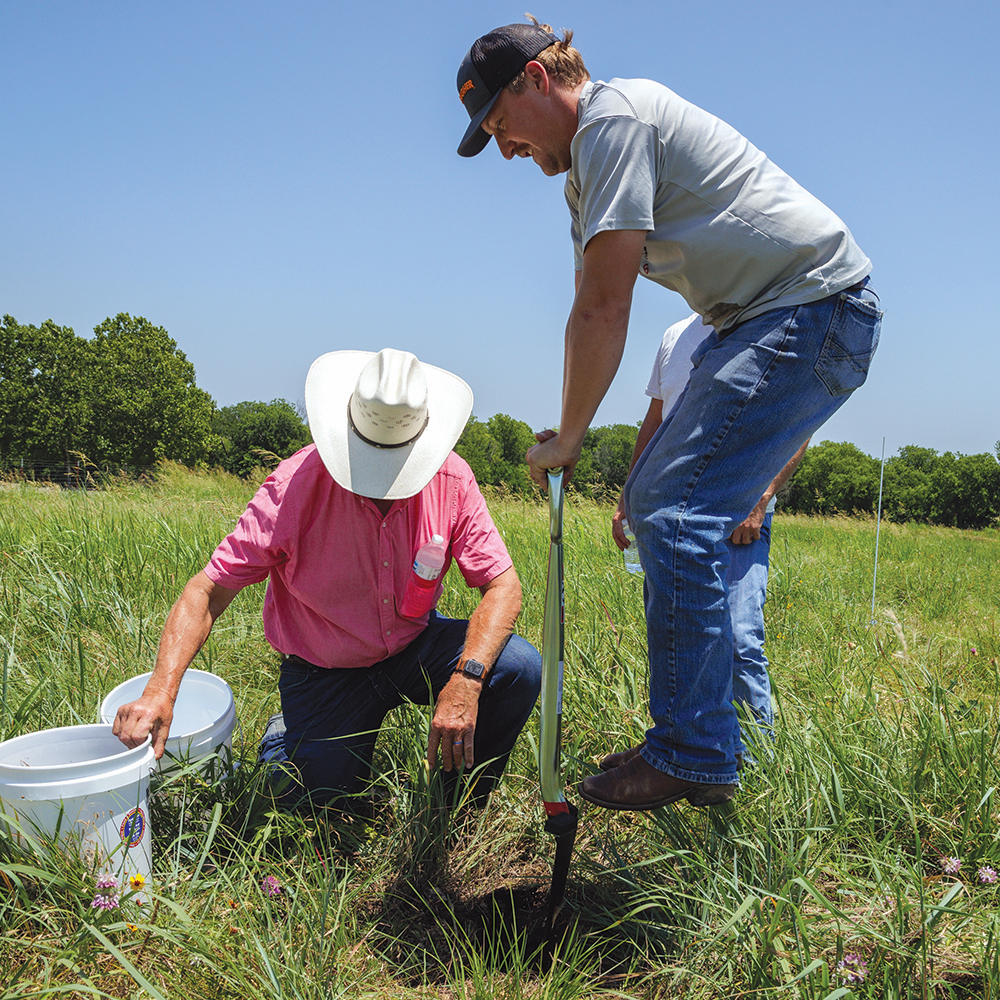
Noble Research Institute Achieves Agricultural Research Organization Status
Noble is now the nation’s largest 501(c)(3) independent agricultural research organization
Estimated read time: minutes
ARDMORE, Okla. (Dec. 5, 2023) – Noble Research Institute has been recognized formally as a 501(c)(3) public charity by virtue of being an agricultural research organization (ARO) by the Internal Revenue Service, retroactive to Jan. 1, 2018. With this designation, Noble is now the largest independent ARO in the U.S.
Noble’s journey to its ARO status was unique. In 2008, Noble began efforts to modify the Internal Revenue Code to recognize tax-exempt AROs as public charities. AROs must directly engage in the continuous active conduct of agricultural research in conjunction with a land-grant college or university or a non-land-grant college of agriculture.
Over the next seven years, more than 65 universities, associations and organizations as well as multiple legislators joined together to support the vital role AROs could play in infusing greater private philanthropy into public research to advance agriculture. The Internal Revenue Code section creating the ARO designation was signed into law in 2015. In 2018, Noble began the legal process of converting to an ARO. Upon completing this process, the IRS formally recognized Noble as an ARO.
“We are grateful for this final step in our journey to be recognized as an ARO,” said Steve Rhines, president and CEO of Noble Research Institute. “It has long been our goal to help build the public agricultural research capacity in the U.S. in ways that go beyond government funding. We look forward to continued work with our partners in both the public and private sectors to further our mission of regenerating 164 million acres of U.S. grazing lands.”
AROs, in conjunction with our nation’s agricultural research universities and as a complement to government laboratories, will take their place in identifying and solving significant agricultural challenges that must be addressed to create a sustainable future.
“AROs provide public agricultural research a full complement of philanthropic tools to reach individuals and families and provide them a charitable vehicle to advance public agricultural research,” Rhines said. “And in turn, Noble is committed to adding to the 78 years we have been serving America’s farmers and ranchers with research dedicated to regenerating grasslands and restoring our nation’s invaluable soil health.”
About Noble Research Institute
Noble Research Institute is the nation’s largest independent agriculture research organization, supporting ranchers and farmers with research, education and mentorship for regenerating soil health to improve their land, livestock and livelihood. Since 1945, Noble Research Institute has been a leading, trusted resource in agricultural research and education dedicated to land stewardship. Demonstrating our ongoing commitment to regenerating our nation’s grazing lands, Noble actively manages 13,500 acres of working ranch lands to provide real-world insights and applications for farmers and ranchers.
To learn more about Noble’s agricultural research and vision for 2040, visit www.noble.org .

Noble Research Institute is an independent nonprofit agricultural research organization dedicated to guiding farmers and ranchers in applying regenerative principles that yield healthier soil, more productive grazing land and business success.
At Noble, researchers, facilitators and ranch staff work together to share with farmers and ranchers the skills and tools to regenerate the land in a profitable manner. Noble is focused on the regenerative management of the nation’s grazing acres, which directly impacts pasture and range environments, wildlife, pecan production and livestock production. Regenerative management recognizes that each decision made on the ranch impacts the interactions of the soil, plants, water, animals, economics and people. Noble’s 14,000 acres of working ranch lands provide a living laboratory on which to demonstrate and practice regenerative principles and ideas to deliver value to farmers and ranchers across the U.S.
For media inquiries concerning the Noble Research Institute, please contact: Kim Leaston , Public Relations Specialist | 580-223-5810
For article reprint information, please visit our Media page.
Improve your land, your livestock and your livelihood… Today!
Build resiliency in your land and profitability for your ranching operation.

Article Reprint
For article reprint information, please visit our Media Page .
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
About Grants
The lifecycle of grants and cooperative agreements consists of four phases: Pre-Award, Award, Post-Award, and Close Out.
Access to Data
The National Institute of Food and Agriculture is committed to serving its stakeholders, Congress, and the public by using new technologies to advance greater openness.

Access Data Gateway
The Data Gateway enables users to find funding data, metrics, and information about research, education, and extension projects that have received grant awards from NIFA.
View Resources Page
This website houses a large volume of supporting materials. In this section, you can search the wide range of documents, videos, and other resources.

Featured Webinar
Second annual virtual grants support technical assistance workshop.
Check out this five-day workshop in March 2024 workshop, designed to help you learn about NIFA grants and resources for grants development and management.
The National Institute of Food and Agriculture provides leadership and funding for programs that advance agriculture-related sciences.

Cultivating the Future: Agricultural Innovations for Climate Resilience
As the world grapples with the impacts of climate change, extreme temperatures and tragic weather events tend to dominate the news. But a slower moving, less conspicuous threat looms in our future: the challenge of maintaining a sustainable, resilient agricultural system.
Supported in part by funding from USDA’s National Institute of Food and Agriculture as well as funding from other federal agencies, the University of Maryland College of Agriculture and Natural Resources’ (AGNR) research and Extension programs take a comprehensive, multi-disciplinary approach to that challenge.
“Climate smart agricultural practices that reduce environmental impact while also building system resilience will ensure that we maintain productive agricultural and forestry systems,” said Dr. Rachel Melnick, division director for Global Climate Change in NIFA’s Institute of Bioenergy, Climate and Environment. “The work highlighted by the University of Maryland are some excellent examples of how Land-grant Institutions are addressing the climate crisis.”
This following article was published by the University of Maryland College of Agriculture and is reprinted here with permission.
Slowing the Burn
According to the Environmental Protection Agency, agriculture of all forms accounts for approximately 10-11% of the total U.S. contribution to the greenhouse gasses that are heating Earth’s atmosphere. Finding ways to reduce emissions from agriculture while maintaining, and even increasing, yields is crucial to helping slow the warming process.
With over $1 million in funding from NASA, Associate Professor Stephanie Yarwood is leading an effort to use satellite data in unraveling the complex relationship between farming practices and nitrogen emissions. The primary contributors to greenhouse gasses from farmland0 are nitrogen compounds from animal waste and fertilizers. But the effects of different farming practices on nitrogen loss from farms, at various times and under diverse conditions, remains unclear. Yarwood’s project uses satellite data to identify “hot spots” and “hot moments” in time, when nitrogen compound levels rise in the atmosphere above farmlands. Her team will then examine the soil microbes to determine how they control the amount and kind of nitrogen released into the air and water, and the effect of various conservation practices on those processes.
“As a microbial ecologist who often thinks in scales no bigger than a shovel full of soil, it is exciting to be working with collaborators using satellites to think at much larger scales and understand these large, atmospheric effects,” Yarwood said.
The team’s ultimate goal is to create models to guide policymakers and stakeholders in reducing nitrogen emissions through climate-smart farming.
Meanwhile, Professor Richard Kohn is tackling farm emissions from another angle. Kohn is studying exactly how metabolism works in the guts of cattle, which burp up methane and account for nearly half of U.S. agriculture’s contribution to greenhouse gas.
Kohn’s lab has looked at alternative feeds, like algae that is purported to reduce methane from cows. But algae may just shift the composition of cow’s waste products away from methane to toxic compounds that are harmful to the cows and the environment. Kohn and his colleagues are evaluating different algae supplements to see if they can help cows produce less waste overall and convert more food to muscle, or meat.
“The goal is ultimately to feed cattle better, so we decrease methane emissions and at the same time make digestion more efficient,” Kohn said.
Adapting To Change
Already feeling the impacts of climate change, many farmers need help adapting to unpredictable conditions now, as well as in the future, because climate change not only brings new temperature and moisture levels, but it allows pests and diseases to spread into new territories. Researcher Chris Walsh began thinking about that decades ago. Now, through years of careful crossbreeding, he has developed two new breeds of apples that address a growing suite of problems for apple growers. His apples are heat-tolerant, blight-resistant, low-maintenance, and delicious-tasting.
While orchard fruits play a significant role in the world’s economy and diet, wheat and corn fill the nation’s granaries and provide a significant portion of the world’s calories. Both are facing environmental threats around the world.
After thousands of years of breeding for large grains and high yields, modern wheat lacks the genetic diversity essential to adapt to those emerging threats. Fortunately, an international team led by Professor Vijay Tiwari has sequenced the complete genome of an ancient variety of wheat known as einkorn. This breakthrough allows researchers to identify genetic traits like disease- and drought-tolerance, and potentially reintroduce those resilience genes into modern bread wheat.
When It’s Time to Pivot
Even with adapted crops and more efficient growing methods, there are places where change has already happened too fast to continue supporting crops. Across the globe, sea level is rising, and in the mid-Atlantic region, land is also sinking due to large geological shifts caused by climate change. The result is that saltwater intrudes into surface and groundwaters in low-lying areas, making the soils too salty for farming.
Alongside collaborators at University of Delaware and George Washington University, AGNR researchers Kate Tully and Rebecca Epanchin-Neil recently found that the area covered by visible salt patches on Delaware, Maryland and Virginia farmland nearly doubled from 2011 to 2019.
They estimated economic losses from the salt patches to be over $427,000, and what’s more, high salinity soils within 200 meters of salt patches accounted for an estimated crop loss of between $39-70 million annually. This is an especially acute problem for corn farmers, because corn is not very salt tolerant, yet it makes up a substantial portion of the crops grown in the region.
“Saltwater intrusion often happens in advance of sea level rise,” said Associate Professor Tully. “This research is the first visualization of this often-invisible symptom of climate change.”
Epanchin-Niell, also an associate professor, said their study can “help identify high risk areas and better target resources and support to regions where transitions are occurring.”
A Grassroots Solution
In the meantime, finding crops that can withstand salty soils could help keep agricultural lands profitable. And AGNR Extension agents are helping with that. Sarah Hirsh and Haley Sater just completed a two-year experiment planting Giant Miscanthus in fields belonging to a soy farmer who had three consecutive years of failed crops. Miscanthus is a tall, perennial grass that is often used for bedding in poultry operations, but it could be marketed for other animals, and for making paper and biofuels.
“Our experimental plots yielded successful harvests,” said Sater, “suggesting this could be an alternative crop that is easy-growing and low-maintenance.”
As a perennial, miscanthus doesn’t need replanting, and once it gets established, it outcompetes weeds and isn’t eaten by deer.
It sounds like a perfect solution, but of course, there is no silver bullet to solving the diverse and complex problems brought on by climate change. Miscanthus is just one tool among many that can help farmers stay profitable and sustainable. Whether it’s through a new view of satellite data, innovative cattle feed, genetically informed breeding, or a host of other initiatives, AGNR is helping pave the way for a resilient and adaptable agricultural future.
Latest Updates
- Latest Funding Opportunities
- Latest Blogs
- Latest Impacts
funding opportunity
Research facilities act program, agriculture and food research initiative - education and workforce development, agriculture and food research initiative - sustainable agricultural systems, nifa publishes report on veterinary medicine loan repayment program, helpful hints to understanding nifa’s funding opportunities, nevada researcher aims to improve sorghum hybrids for dairy cattle feed, grupo de mujeres provides education, community for spanish-speaking women, your feedback is important to us..
[{"value":"utm_source","text":"00N0I00000KT1fD"},{"value":"utm_medium","text":"00N0I00000KT1fI"},{"value":"campaignname","text":"00N0I00000KT1fN"},{"value":"uterm","text":"00N0I00000KT1fS"},{"value":"adgroupname","text":"00N0I00000KT1md"},{"value":"keyword","text":"00N0I00000KT1mx"},{"value":"creative","text":"00N0I00000KT1nR"},{"value":"devicemodel","text":"00N0I00000KT1ng"},{"value":"placement","text":"00N0I00000KT1nq"},{"value":"target","text":"00N0I00000KT1ot"},{"value":"device","text":"00N0I00000KT1o0"},{"value":"network","text":"00N0I00000KT1o5"},{"value":"matchtype","text":"00N0I00000KT1oA"},{"value":"gclid","text":"00N0I00000KT1oF"},{"value":"campaignname","text":"00N0I00000KT1nM"},{"value":"term","text":"00N0I00000KT1n7"}]

- Give to ISB
- FACULTY & RESEARCH
- STUDY AT ISB
- EXECUTIVE EDUCATION
- External Relations
- I-Venture @ ISB
- Hire from ISB
- ISB Advantage
- Partnerships & Associations
- History & Milestones
- Sustainability at ISB
- Faculty Directory
- Area Leaders
- Research Directory
- Research Centres & Institutes
- Research Initiatives
- Faculty Recruitment
- Institutional l Review Board (IRB)
- Post Graduate Programmes
- Advanced Management Programmes
- Doctoral Studies
- Programmes for Individuals
- Enterprise Solutions
- Public Sector Programmes
ISB Experience Tailored to you
Help us tailor the website experience to your taste. Make some selections to let the website work better for you.
I am Interested in
- ENTREPRENEUERSHIP
- GENERAL MANAGEMENT
- POLICY MAKING
- IT & ANALYTICS
- FAMILY BUSINESS
Suggestions for You

Research Centre

Published Papers
View Complete Profile
No record found

- Indian School of Business (ISB)
- News & Events
Students from Agriculture College and Research Institute, Kudumiyanmalai, visit ISB’s Mohali campus
By Team External Relations | Mar 22, 2024
The Indian School of Business hosted students from Agriculture College and Research Institute, Kudumiyanmalai, affiliated to Tamil Nadu Agriculture University, Coimbatore, at its Mohali Campus.
The students were visiting ISB as part of their All-India Study Tour programme.
The students were apprised about ISB’s programmes, its research and thought leadership, its initiatives and more. They were also taken for a detailed campus tour of the state-of-the-art campus, including the academic and recreational facilities, Learning Resource Centre and Atal Incubation Centre.
Visit of students from Agriculture College and Research Institute, Kudumiyanmalai, Tamil Nadu Agriculture University, Coimbatore

- Campus Life

We are one of the most decorated Agricultural Institutes in the country.
Our International Students
Admission in iari, minimum qualifications for admission to m.sc./m.tech./ ph.d..
The candidates must satisfy one of the qualifications as indicated against the relevant discipline to which admission is sought, and should have obtained a minimum of 60% marks or an overall grade point average of 6.60 out of 10.00 OR 3.25 out of 5.00 OR 2.60 out of 4.00 at the Bachelor's degree examination and a minimum of 60% marks or an overall grade point average of 6.50 out of 10.00 OR 3.25 out of 5.00 OR 2.60 out of 4.00 at the Master's degree examination. (Where OGPA is awarded, equivalence between OGPA and % marks will not be acceptable).
PROCEDURE OF APPLICATION
Important note for all candidates, financial assistance during studies at this institute.
No financial assistance or fellowship is granted by this Institute to the foreign students except such assistance that may be available to the sponsored candidates under the Cultural Exchange or Technical Assistance Programme of the Govt. of India or from the International Organisations etc. sponsoring them for the entire period of their studies at this Institute.
In addition to the above, students would be needing financial assistance for purchase of books, living allowance to meet the mess charges and other miscellaneous expenditure.
STUDENT'S SUPPORT SERVICES
ICAR-Indian Agricultural Research Institute
Pusa Campus, New Delhi - 110012 Find us : Google Maps
Popular Links
- About MDARD About MDARD collapsed link
- Animals Animals collapsed link
- Business Development Business Development collapsed link
- Environment Environment collapsed link
- Food & Dairy Food & Dairy collapsed link
- Lab Services Lab Services collapsed link
- Licensing Licensing collapsed link
- Plant & Pest Plant & Pest collapsed link
- Reports and Notices
- Boards, Councils, and Commissions
- Contact Us / File a Complaint
- Emergency Preparedness
- Michigan Food and Agriculture Jobs
- Laws and Regulations
- Online Services
Learn about MDARD's four bureaus, including contact information, by clicking the above link, or view specific information below.
- MDARD Leadership Team
- About Our Programs
- Annual Reports
- Boilerplate Reports
- Public Meeting Notices
- Food Inspection Reports
- Michigan Commission of Agriculture and Rural Development
- Commodity Organizations
- Agriculture Preservation Fund Board
- Michigan Craft Beverage Council
- Farm Produce Insurance Authority
- Fertilizer Research Advisory Committee
- Horse Racing Advisory Commission
- Large Carnivore Breeding Advisory Committee
- MAEAP Advisory Council
- Migrant Labor Housing Advisory Board
- Rural Development Fund Board
- Seed Potato Advisory Committee
Want to know how to contact the Michigan Department of Agriculture & Rural Development? On this page you will find phone numbers, email addresses, snail mail addresses, and online contact forms for everything we do here at MDARD. We even have a complaint form for those of you with complaints.
- Job Seekers
Laws and Regulations pertaining to and governing the actions and policies of the Michigan Department of Agriculture & Rural Development.
This area contains information for press and media agencies. Press Releases, Pics, Podcasts & Videos
List of services offered on Michigan.gov by MDARD
- Animal ID & Movement
- Veterinarian Resources
- Animal Diseases
- Exhibitions
- Animal Related Licensing
- Privately-Owned Cervids
- Animal Feed & Antibiotics
- Disposal of Dead Animals
- Animal Feed Safety
- Animal Welfare Fund
Animal ID and movement requirements in the State of Michigan
Animal health resources for veterinary professionals.
Diseases affecting, or potentially affecting, animals in Michigan
Requirements to exhibit livestock in Michigan and more.
- Resources for Exhibitions
Feed & Antibiotics
Rules governing the disposal of Bodies of Dead Animals (BODA).
- Economic & Community Development
- Success Stories
- International Marketing
- Qualified Small Distiller Certificate
- Grants & Funding Opportunities
- Producer Security
- Meet the Team
Information about how MDARD's Agriculture Development Division can help you grow your business in Michigan.
- Agricultural Preservation Fund Grants
- Animal Welfare Fund Grants
- County Fairs Capital Improvement Grants
- Farm Innovation Grants
- Farm Stress Grants
- Horticulture Fund Grants
- Food and Agriculture Investment Fund Grants
- Food Safety Education Fund Grants
- Livestock and Commodity Exposition Competitive Grants
- Michigan Craft Beverage Council Research Grants
- Minority Owned Food and Agriculture Business Capacity Building Grant
- Resilient Food Systems Infrastructure
- Rural Development Fund Grants
- Seafood Processors Pandemic Response and Safety Block Grant
- Specialty Crop Block Grants
- Value Added & Regional Food Systems Grants
- Wastewater Infrastructure Fund Grants
- Conservation Programs
- Conservation Reserve Enhancement Program (CREP)
- Farmland Preservation
- Intercounty Drains
- Migrant Labor Housing
- Michigan Agriculture Environmental Assurance Program (MAEAP)
- Right to Farm
Michigan's Conservation Reserve Enhancement Program (CREP) was created to help protect our environment and wildlife. Michigan is partnering with the federal government to implement conservation practices of great significance to the state, and valuable to the nation, in matters of soil erosion, water quality, and wildlife habitat.
Programs under the Private Forestlands Initiative, including the Forestry Assistance Program, Qualified Forester Registration, and Qualified Forest Program.
Good migrant labor housing is an essential element in securing an adequate supply of seasonal agricultural workers.
- Get Verified
- Educational Sessions
- MAEAP Events
- Request a Visit
- Resource Library
- Testimonials
- Conservation Technical Assistance Initiative (CTAI)
- Residential Water Stewardship
- Golf Course Water Stewardship
- Water Monitoring Program
- Clean Sweep
- Pesticide Container Recycling
- Water Use Reporting
- Aquifer Protection and Dispute Resolution Program
- Right to Farm Program
- Right to Farm Resources
- Site Selection
- Generally Accepted Agricultural Management Practices (GAAMPs)
- Spill Response
- Cottage Food
- Food Recalls
- Food Regulators
- Food Safety
- Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA)
- Dietary Supplements
The Cottage Food law, enacted in 2010, allows individuals to manufacture and store certain types of foods in an unlicensed home kitchen.
Resources for Regulators
- Animal Disease Analytical Testing Services
- Gasoline Information
- Retail Motor Fuel Outlet Licensing
- Find a Registered Serviceperson
- Serviceperson Examination Schedule
- Weights and Measures
- Search for MDARD Licenses, Certifications, and Registrations
- Find Businesses Licensed by MDARD
- Agricultural Products
- Food Industries
- Horse Breeder/Owner Awards Program
- Pesticide Licensing & Certification
- Retail Motor Fuel Outlet
- Weights & Measures Service Agency & Person
Find a licensed firm in Michigan, from pesticide businesses to retail establishments, and more.
- Agricultural Marketing and Bargaining Act
- Fertilizer and Bulk Storage Registration
- Grain Dealers
- Wholesale Potato Dealer
- Animal Control Officer
- Animal Feed License
- Animal Shelters
- Aquaculture
- Dead Animal Dealer/Renderer License
- Large Carnivore Breeding
- Large-Scale Dog Breeding Kennel Registration
- Livestock Dealer
- Riding Stables
- Food Establishment Licensing General Information
- County Fairs
- How to Apply for a Food Service License
- Bottled Water
For the registration of horses, breeders and owners so as to render them eligible for racing and breeder/owner awards.
- Agricultural Pesticide Dealer License
- Driftwatch Organic Farm Registry
- Golf Courses
- Pesticide Application Businesses
- Pesticide Applicator Certification
- Pesticide Laws and Regulations
- Pesticide Notification Registry
- Pesticide Registration
- Aerial Pesticide Applicators
- Restricted Use Pesticides Dealers
Retail Motor Fuel Outlet licensing information, applications and forms.
Information on Weights & Measures service person and agency registration, as well as weights and measures advisories.
- Agricultural Bulk Storage
- Fertilizer and Liming Materials
- Fruit and Vegetable Inspection
- Pesticide Enforcement
- Plant Health
Each new, existing, and proposed commercial pesticide or fertilizer bulk storage facility is required to register annually with the Michigan Department of Agriculture and Rural Development.
Information on how to acquire a feed license to manufacture or distribute commercial feed in Michigan.
- Animal Feed Complaints
- Commercial Animal Feed Licensing
- Commercial Animal Feed Tonnage
- Pet Food and Treats
Fertilizer License and Registration Requirements, as well as Liming License Requirements
- Pesticide Labels
- Restricted-Use Pesticides
- Managed Pollinator Protection
- Compliance Assurance Library
- Integrated Pest Management
- Organic Farm Registry and DriftWatch
- Pesticide Business Licensing
- Road Check Inspections
- Leadership Team
- Invasive Species
- Nursery Licensing and Inspection
- Plant Pathology
- Plant Pest Quarantines
- Seeds and Noxious Weeds
- Plant Health Certification and Export
- Industrial Hemp
- About MDARD
- Business Development
- Environment
- Food & Dairy
- Lab Services
- Plant & Pest
Search is currently unavailable. Please try again later.
Popular on michigan.gov
- Agriculture and Rural Development
- Civil Rights
- Health and Human Services
- Natural Resources
- Secretary of State
How Do I...
- Register to Vote
- Renew My License Plate
- View assistance programs
The web Browser you are currently using is unsupported, and some features of this site may not work as intended. Please update to a modern browser such as Chrome, Firefox or Edge to experience all features Michigan.gov has to offer.
- Google Chrome
- Microsoft Edge
MDARD Partners with Alliance for the Great Lakes, MSU Institute of Water Research, and LimnoTech to Deploy Nearly $5 million in Water Quality Monitoring in the Western Lake Erie Basin
April 03, 2024
Water quality research and data are fundamental to achieving environmental outcomes in the WLEB
LANSING Michigan Department of Agriculture and Rural Development (MDARD) Director Dr. Tim Boring today announced plans to partner with the Alliance for the Great Lakes for $4.86 million in funding over the next five years to the Alliance for the Great Lakes to expand water quality monitoring in the Western Lake Erie Basin (WLEB). The research effort utilizes expertise at Michigan State University's Institute of Water Research and LimnoTech , while leveraging $600,000 in funding from the Erb Family Foundation. This significant increase in research and monitoring will aid the state's strategy in developing a plan to combat harmful algal blooms in the WLEB.
"Improving our understanding of nutrient losses and transport in the WLEB is essential to accelerating progress on nutrient loading reductions," said Boring . "Our department has recognized the need for improved water quality monitoring in WLEB. We know that more holistic farm management focusing on soil health and regenerative agriculture principles can be expected to improve nutrient losses. Through the State of Michigan's Domestic Action Plan adaptive management approach of continuous assessment and improvement, the scientific outcomes of this work improve our ability to make meaningful progress toward water quality improvements."
"We are excited to partner with MDARD on this effort and applaud the leadership of Director Boring who has continually emphasized the importance of expanding monitoring and data collection to help guide conservation decision making," said Tom Zimnicki, Alliance for the Great Lakes Agriculture and Restoration Policy Director.
Harmful algal blooms occur when colonies of algae grow out of control. Some produce dangerous toxins which can have harmful effects on people and wildlife, but even non-toxic blooms can hurt the environment. The algal blooms need sunlight, slow-moving water, and nutrients to grow. Phosphorus pollution from human activity can make the problem worse, leading to blooms occurring more often.
Monitoring will begin later this spring in five priority HUC-12 sub-watersheds: Lime Creek, Stony Creek (South Branch River Raisin), Headwaters of the Saline River, Nile Ditch, and the S.S. LaPointe Drain. These subwatersheds were selected for more focused and accelerated activities including finer-scale water quality monitoring, completing agricultural inventories, prioritized BMP implementation, and assessing the costs associated with full implementation to achieve a 40 percent total phosphorus reduction goal. In-stream data collection will include stream flow, total phosphorus and soluble reactive phosphorus, turbidity, and total suspended solids. These gauge stations will be combined with soil moisture, precipitation, and tile outlet sensors deployed through the watershed to better understand the fate and transport of nutrients in the WLEB watershed.
Understanding, tracking, and predicting nutrient loads from the WLEB watershed is difficult due to the complex drivers of nutrient loss within sub-watersheds in the WLEB including variable weather, cropping systems, farm management, nutrient cycling. By increasing monitoring capacity in the WLEB at smaller sub-watershed scales, with an emphasis on deploying higher spatial density monitoring instrumentation, this research will improve the understanding of the impact of various drivers on nutrient transport and enable improved prioritization of conservation and land management practices to meet phosphorus reduction commitments set for Michigan s portion of the WLEB.
Visit the Taking Action on Lake Erie website to learn more about steps you can take to help reduce pollution and protect Michigan s natural resources.
Media Contact:
Mike Philip
Program Contact
517-512-0187
Tom Zimnicki
Alliance for Great Lakes contact
313-969-3499
Jennifer Holton
MDARD Media Contact
517-284-5724
Related News
Michigan tree fruit growers approve continuation referendum, highly pathogenic avian influenza detected in ionia county flock, mdard director appoints members to michigan seed potato advisory committee, highly pathogenic avian influenza detected in michigan dairy herd, mdard encourages owners to help keep pets safe this spring holiday season, mdard, mi agricultural preservation fund board awards $2 million to local farmland preservation programs, mdard's food and ag wastewater funding available for infrastructure fund grant program, video release: mdard celebrates march is reading month and michigan agriculture with lansing school district, michigan carrot producers to vote on program continuation.
Texas Biomedical Researchers study potential Bird Flu treatments and vaccines
by SBG San Antonio Staff Reports

SAN ANTONIO - Texas Biomedical Research Institute (Texas Biomed) has announced it’s researching potential vaccines and antivirals that could combat Avian Influenza, also known as H5N1 or Bird Flu.
These will be intended to combat strains that mirror those found in cows and chickens, and now one person in Texas.
This is only the second case of Bird Flu found in Humans in the United States, which officials say was contracted through contact with Dairy Cows.
“Thankfully, the risk of the current H5N1 case becoming widespread among people remains low,” says Larry Schlesinger, M.D., Texas Biomed President and CEO. “But viruses adapt and evolve – especially influenza viruses – which is why it is so critical to be studying them and developing vaccines and treatments well before they are needed.”
Researchers at Texas Biomed are using techniques learned from years of vaccine development for both Seasonal Influenza as well as the recent developments made as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The new initiative, hosted by Professor Luis Martinez-Sobrido, Ph.D.’s laboratory, will see the scope of research increased to include Avian Influenza, testing if current vaccines and antivirals would have any effect on stopping the spread or mitigating the virus’ impact.
“The genetic sequencing analysis from the CDC indicates that the H5N1 strain found in the patient does not have any mutations associated with resistance to current antiviral drugs,” says Prof. Martinez-Sobrido. “However, it is important to continue developing an array of countermeasures in case existing ones lose effectiveness.”
Fewer than 900 cases of bird flu infecting humans have been reported globally since 1996, however, infection has a fatality rate of about 50%.
Best Global Universities for Engineering in Russia
These are the top universities in Russia for engineering, based on their reputation and research in the field. Read the methodology »
To unlock more data and access tools to help you get into your dream school, sign up for the U.S. News College Compass !
Here are the best global universities for engineering in Russia
Itmo university, tomsk state university, tomsk polytechnic university, lomonosov moscow state university, novosibirsk state university, saint petersburg state university, peter the great st. petersburg polytechnic university, moscow institute of physics & technology, national research nuclear university mephi (moscow engineering physics institute).
See the full rankings
- Clear Filters
- # 307 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 696 in Best Global Universities (tie)
- # 364 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 587 in Best Global Universities (tie)
- # 396 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 879 in Best Global Universities (tie)
- # 632 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 355 in Best Global Universities
- # 809 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 579 in Best Global Universities (tie)
- # 847 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 652 in Best Global Universities
- # 896 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 679 in Best Global Universities (tie)
- # 902 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 475 in Best Global Universities (tie)
- # 915 in Best Universities for Engineering (tie)
- # 483 in Best Global Universities (tie)
Russian Defense Business Directory

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Research Institute of Agriculture and Life Sciences of Seoul National University was established on September 9, 2001, as an institute stemming from the Institute of Agricultural Science and Development (established in 1967) to integrate several institutes within the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences and to support research projects ...
Webinar: Overcoming Common Barriers to Organic Certification. Join the movement. Make a difference. Rodale Institute is rated four stars by Charity Navigator. Rodale Institute is a 501 (c) (3) nonprofit dedicated to growing the regenerative organic movement through agricultural research and education.
The National Institute of Food and Agriculture (NIFA) provides leadership and funding for programs that advance agriculture-related sciences. We invest in and support initiatives that ensure the long-term viability of agriculture. NIFA applies an integrated approach to ensure that groundbreaking discoveries in agriculture-related sciences and ...
The " USDA Science and Research Strategy, 2023-2026: Cultivating Scientific Innovation (PDF, 21.4 MB)" presents a near-term vision for transforming U.S. agriculture through science and innovation, and outlines USDA's highest scientific priorities. The S&RS is a call to action for USDA partners, stakeholders, and customers to join the ...
FAQ Knowledge Base. IARI Helpline Numbers for Farmers. Farmer WhatsApp Helpline : 9560297502 Pusa Helpline: 011-25841670 / 25841039 Pusa Agricom (1800-11-8989 Toll free) Students Corner. Lady Students' Adviser In-Charge, Placement Cell Ph: 011-25847649, 25733888 E-mail: placementcell [at]iari [dot]res [dot]in. Foreign Students' Adviser Dr ...
Created on January 1, 2020, INRAE is a Public Scientific and Technical Research Establishment (EPST). It was formed by the merger of INRA, the French National Institute for Agricultural Research, and IRSTEA, the French National Research Institute of Science and Technology for the Environment and Agriculture.
The Research Institute of Organic Agriculture FiBL is one of the world's leading institutes in the field of organic agriculture. 30 perspectives. In the past year, more than 30 "anniversary voices" have taken a look at FiBL. Citizen Science.
Visit to the International Rice Research Institute 11/29/2022. Aiming to strengthen the government's partnership and collaboration with the world's premier research organization dedicated to reducing poverty and hunger through rice science to achieve his goals for the agricultural sector, President Ferdinand R. Marcos Jr. visits the ...
The Indian Agricultural Research Institute ( IARI ), commonly known as the Pusa Institute, [3] is India's national institute for agricultural research, education and extension. The name Pusa Institute is derived from the fact that the institute was originally located in Pusa, Bihar as the Imperial Institute of Agricultural Research in 1911.
Our mission is to advance knowledge and understanding in the field of agriculture. IARI became a 'Deemed-to-be University' in 1958, Up to 1957, students numbering 903 were awarded Associateship of IARI, which was recognized as equivalent to the M.Sc. degree of Indian universities. Till February 2021, Post Graduate School, IARI has awarded 4444 ...
The Agricultural Research Institute (ARI) exemplifies the mission of the California State University system by working for California and its citizens through partnerships across the agricultural industry and beyond. Through the colleges of agriculture on four CSU campuses and allied disciplines across the CSU, the ARI conducts applied research ...
The Agriculture Research Institute (ARI) engages the collective expertise of CSU colleges of agriculture and other related programs across the CSU, in partnership with agricultural and natural resource industries, to conduct applied research that benefits California agriculture, natural resources and food systems while cultivating the next generation of agricultural leaders .
The institute was then known as Agricultural Research Institute (ARI) which functioned with five departments, namely Agriculture, Cattle Breeding, Chemistry, Economic Botany and Mycology. Bacteriology unit was added in 1907. The name of ARI was changed to Imperial Institute of Agricultural Research in 1911 and, in 1919 it was renamed as ...
The new institute is one of 11 launched by the National Science Foundation and among two funded by the U.S. Department of Agriculture-National Institute of Food and Agriculture in 2021. It's called the AgAID Institute, which is short for USDA-NIFA Institute for Agricultural AI for Transforming Workforce and Decision Support.
ICAR-Central Coastal Agricultural Research Institute, Ela, Old Goa, Goa: 31. ICAR-Indian Agricultural Statistics Research Institute, New Delhi: 32. ICAR-Indian Grassland and Fodder Research Institute, Jhansi: 33. ICAR-Indian Institute of Agricultural Biotechnology, Ranchi: 34. ICAR-Indian Institute of Horticultural Research, Bengaluru: 35.
Agricultural Research Institute Supporting Agricultural Research. The California State University Agricultural Research Institute (ARI) is a diverse and comprehensive multi-campus applied agricultural and environmental research program that leverages state funding with university and industry capital and intellectual collateral through university-industry partnerships.
ICAR-Central Tuber Crops Research Institute, Trivandrum: 28. ICAR-ICAR Research Complex for Eastern Region, Patna: 29. ICAR-ICAR Research Complex for NEH Region, Barapani: 30. ICAR-Central Coastal Agricultural Research Institute, Ela, Old Goa, Goa: 31. ICAR-Indian Agricultural Statistics Research Institute, New Delhi: 32.
Noble Research Institute is an independent nonprofit agricultural research organization dedicated to guiding farmers and ranchers in applying regenerative principles that yield healthier soil, more productive grazing land and business success.. At Noble, researchers, facilitators and ranch staff work together to share with farmers and ranchers the skills and tools to regenerate the land in a ...
Supported in part by funding from USDA's National Institute of Food and Agriculture as well as funding from other federal agencies, the University of Maryland College of Agriculture and Natural Resources' (AGNR) research and Extension programs take a comprehensive, multi-disciplinary approach to that challenge. "Climate smart agricultural practices that reduce environmental impact while ...
IITA and CGIAR launch agricultural research hub in Zambia. Lusaka, April 4 - The International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (IITA) announced today that it has gained full diplomatic status as an international organization working in Zambia, according to the Zambian government. This is coming on the eve of the launch of the Institute's ...
The Indian School of Business hosted students from Agriculture College and Research Institute, Kudumiyanmalai, affiliated to Tamil Nadu Agriculture University, Coimbatore, at its Mohali Campus. The students were visiting ISB as part of their All-India Study Tour programme. The students were apprised about ISB's programmes, its research and ...
Victor MUKHIN, Principal Scientific Researcher | Cited by 475 | of Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow (RAS) | Read 117 publications | Contact Victor MUKHIN
They both worked at the Agricultural Research Institute (INIA Chile) near Santiago, Chile, for three weeks in 2023. Lucas was researching virus pressure on beans and Carlos researched soybean development. ... Soybean Research Center 411 Borlaug Hall 1991 Upper Buford Circle Saint Paul, MN 55108 612-625-7773. Funding provided by. For Students ...
Indian Agricultural Research Institute has played a pivotal role in transforming Indian Agriculture by providing the country with highly trained manpower for agricultural research, teaching and extension. The IARI alumni who have helped in improving the agricultural production from merely 55 million tonnes in 1949-50 to 259 million tonnes today ...
The Indian Institute of Spices Research (IISR), Kozhikode has developed and validated three more new microbial formulations based on granular lime and gypsum to help farmers improve agricultural ...
Water quality research and data are fundamental to achieving environmental outcomes in the WLEB. LANSING Michigan Department of Agriculture and Rural Development (MDARD) Director Dr. Tim Boring today announced plans to partner with the Alliance for the Great Lakes for $4.86 million in funding over the next five years to the Alliance for the Great Lakes to expand water quality monitoring in the ...
The oblast is dominated by relatively infertile podsol soils which require fertilizers for commercial agriculture. On the hills there is more loam and the low-lying areas have more of bog ... MKB Raduga, National Research Institute of Aviation Systems, Krasnozavodsk Chemical Plant, Tikhomirov Scientific Research Institute of Instrument Design ...
SAN ANTONIO - Texas Biomedical Research Institute (Texas Biomed) has announced it's researching potential vaccines and antivirals that could combat Avian Influenza, also known as H5N1 or Bird Flu.
Germany. India. Italy. Japan. Netherlands. See the US News rankings for Engineering among the top universities in Russia. Compare the academic programs at the world's best universities.
Grafite-based materials have been developed for laser mirrors and for static elements of gas turbine engines. The institute has 40 research laboratories and a pilot production plant at the Moscow location. PRIMARY BUSINESS: Branch: Metallurgy; SIC Code: 3297, 3299, 3624, 3728, 3791, 3823.