- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » 500+ Qualitative Research Titles and Topics

500+ Qualitative Research Titles and Topics
Table of Contents

Qualitative research is a methodological approach that involves gathering and analyzing non-numerical data to understand and interpret social phenomena. Unlike quantitative research , which emphasizes the collection of numerical data through surveys and experiments, qualitative research is concerned with exploring the subjective experiences, perspectives, and meanings of individuals and groups. As such, qualitative research topics can be diverse and encompass a wide range of social issues and phenomena. From exploring the impact of culture on identity formation to examining the experiences of marginalized communities, qualitative research offers a rich and nuanced perspective on complex social issues. In this post, we will explore some of the most compelling qualitative research topics and provide some tips on how to conduct effective qualitative research.
Qualitative Research Titles
Qualitative research titles often reflect the study’s focus on understanding the depth and complexity of human behavior, experiences, or social phenomena. Here are some examples across various fields:
- “Understanding the Impact of Project-Based Learning on Student Engagement in High School Classrooms: A Qualitative Study”
- “Navigating the Transition: Experiences of International Students in American Universities”
- “The Role of Parental Involvement in Early Childhood Education: Perspectives from Teachers and Parents”
- “Exploring the Effects of Teacher Feedback on Student Motivation and Self-Efficacy in Middle Schools”
- “Digital Literacy in the Classroom: Teacher Strategies for Integrating Technology in Elementary Education”
- “Culturally Responsive Teaching Practices: A Case Study in Diverse Urban Schools”
- “The Influence of Extracurricular Activities on Academic Achievement: Student Perspectives”
- “Barriers to Implementing Inclusive Education in Public Schools: A Qualitative Inquiry”
- “Teacher Professional Development and Its Impact on Classroom Practice: A Qualitative Exploration”
- “Student-Centered Learning Environments: A Qualitative Study of Classroom Dynamics and Outcomes”
- “The Experience of First-Year Teachers: Challenges, Support Systems, and Professional Growth”
- “Exploring the Role of School Leadership in Fostering a Positive School Culture”
- “Peer Relationships and Learning Outcomes in Cooperative Learning Settings: A Qualitative Analysis”
- “The Impact of Social Media on Student Learning and Engagement: Teacher and Student Perspectives”
- “Understanding Special Education Needs: Parent and Teacher Perceptions of Support Services in Schools
Health Science
- “Living with Chronic Pain: Patient Narratives and Coping Strategies in Managing Daily Life”
- “Healthcare Professionals’ Perspectives on the Challenges of Rural Healthcare Delivery”
- “Exploring the Mental Health Impacts of COVID-19 on Frontline Healthcare Workers: A Qualitative Study”
- “Patient and Family Experiences of Palliative Care: Understanding Needs and Preferences”
- “The Role of Community Health Workers in Improving Access to Maternal Healthcare in Rural Areas”
- “Barriers to Mental Health Services Among Ethnic Minorities: A Qualitative Exploration”
- “Understanding Patient Satisfaction in Telemedicine Services: A Qualitative Study of User Experiences”
- “The Impact of Cultural Competence Training on Healthcare Provider-Patient Communication”
- “Navigating the Transition to Adult Healthcare Services: Experiences of Adolescents with Chronic Conditions”
- “Exploring the Use of Alternative Medicine Among Patients with Chronic Diseases: A Qualitative Inquiry”
- “The Role of Social Support in the Rehabilitation Process of Stroke Survivors”
- “Healthcare Decision-Making Among Elderly Patients: A Qualitative Study of Preferences and Influences”
- “Nurse Perceptions of Patient Safety Culture in Hospital Settings: A Qualitative Analysis”
- “Experiences of Women with Postpartum Depression: Barriers to Seeking Help”
- “The Impact of Nutrition Education on Eating Behaviors Among College Students: A Qualitative Approach”
- “Understanding Resilience in Survivors of Childhood Trauma: A Narrative Inquiry”
- “The Role of Mindfulness in Managing Work-Related Stress Among Corporate Employees: A Qualitative Study”
- “Coping Mechanisms Among Parents of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder”
- “Exploring the Psychological Impact of Social Isolation in the Elderly: A Phenomenological Study”
- “Identity Formation in Adolescence: The Influence of Social Media and Peer Groups”
- “The Experience of Forgiveness in Interpersonal Relationships: A Qualitative Exploration”
- “Perceptions of Happiness and Well-Being Among University Students: A Cultural Perspective”
- “The Impact of Art Therapy on Anxiety and Depression in Adult Cancer Patients”
- “Narratives of Recovery: A Qualitative Study on the Journey Through Addiction Rehabilitation”
- “Exploring the Psychological Effects of Long-Term Unemployment: A Grounded Theory Approach”
- “Attachment Styles and Their Influence on Adult Romantic Relationships: A Qualitative Analysis”
- “The Role of Personal Values in Career Decision-Making Among Young Adults”
- “Understanding the Stigma of Mental Illness in Rural Communities: A Qualitative Inquiry”
- “Exploring the Use of Digital Mental Health Interventions Among Adolescents: A Qualitative Study”
- “The Psychological Impact of Climate Change on Young Adults: An Exploration of Anxiety and Action”
- “Navigating Identity: The Role of Social Media in Shaping Youth Culture and Self-Perception”
- “Community Resilience in the Face of Urban Gentrification: A Case Study of Neighborhood Change”
- “The Dynamics of Intergenerational Relationships in Immigrant Families: A Qualitative Analysis”
- “Social Capital and Economic Mobility in Low-Income Neighborhoods: An Ethnographic Approach”
- “Gender Roles and Career Aspirations Among Young Adults in Conservative Societies”
- “The Stigma of Mental Health in the Workplace: Employee Narratives and Organizational Culture”
- “Exploring the Intersection of Race, Class, and Education in Urban School Systems”
- “The Impact of Digital Divide on Access to Healthcare Information in Rural Communities”
- “Social Movements and Political Engagement Among Millennials: A Qualitative Study”
- “Cultural Adaptation and Identity Among Second-Generation Immigrants: A Phenomenological Inquiry”
- “The Role of Religious Institutions in Providing Community Support and Social Services”
- “Negotiating Public Space: Experiences of LGBTQ+ Individuals in Urban Environments”
- “The Sociology of Food: Exploring Eating Habits and Food Practices Across Cultures”
- “Work-Life Balance Challenges Among Dual-Career Couples: A Qualitative Exploration”
- “The Influence of Peer Networks on Substance Use Among Adolescents: A Community Study”
Business and Management
- “Navigating Organizational Change: Employee Perceptions and Adaptation Strategies in Mergers and Acquisitions”
- “Corporate Social Responsibility: Consumer Perceptions and Brand Loyalty in the Retail Sector”
- “Leadership Styles and Organizational Culture: A Comparative Study of Tech Startups”
- “Workplace Diversity and Inclusion: Best Practices and Challenges in Multinational Corporations”
- “Consumer Trust in E-commerce: A Qualitative Study of Online Shopping Behaviors”
- “The Gig Economy and Worker Satisfaction: Exploring the Experiences of Freelance Professionals”
- “Entrepreneurial Resilience: Success Stories and Lessons Learned from Failed Startups”
- “Employee Engagement and Productivity in Remote Work Settings: A Post-Pandemic Analysis”
- “Brand Storytelling: How Narrative Strategies Influence Consumer Engagement”
- “Sustainable Business Practices: Stakeholder Perspectives in the Fashion Industry”
- “Cross-Cultural Communication Challenges in Global Teams: Strategies for Effective Collaboration”
- “Innovative Workspaces: The Impact of Office Design on Creativity and Collaboration”
- “Consumer Perceptions of Artificial Intelligence in Customer Service: A Qualitative Exploration”
- “The Role of Mentoring in Career Development: Insights from Women in Leadership Positions”
- “Agile Management Practices: Adoption and Impact in Traditional Industries”
Environmental Studies
- “Community-Based Conservation Efforts in Tropical Rainforests: A Qualitative Study of Local Perspectives and Practices”
- “Urban Sustainability Initiatives: Exploring Resident Participation and Impact in Green City Projects”
- “Perceptions of Climate Change Among Indigenous Populations: Insights from Traditional Ecological Knowledge”
- “Environmental Justice and Industrial Pollution: A Case Study of Community Advocacy and Response”
- “The Role of Eco-Tourism in Promoting Conservation Awareness: Perspectives from Tour Operators and Visitors”
- “Sustainable Agriculture Practices Among Smallholder Farmers: Challenges and Opportunities”
- “Youth Engagement in Climate Action Movements: Motivations, Perceptions, and Outcomes”
- “Corporate Environmental Responsibility: A Qualitative Analysis of Stakeholder Expectations and Company Practices”
- “The Impact of Plastic Pollution on Marine Ecosystems: Community Awareness and Behavioral Change”
- “Renewable Energy Adoption in Rural Communities: Barriers, Facilitators, and Social Implications”
- “Water Scarcity and Community Adaptation Strategies in Arid Regions: A Grounded Theory Approach”
- “Urban Green Spaces: Public Perceptions and Use Patterns in Megacities”
- “Environmental Education in Schools: Teachers’ Perspectives on Integrating Sustainability into Curricula”
- “The Influence of Environmental Activism on Policy Change: Case Studies of Grassroots Campaigns”
- “Cultural Practices and Natural Resource Management: A Qualitative Study of Indigenous Stewardship Models”
Anthropology
- “Kinship and Social Organization in Matrilineal Societies: An Ethnographic Study”
- “Rituals and Beliefs Surrounding Death and Mourning in Diverse Cultures: A Comparative Analysis”
- “The Impact of Globalization on Indigenous Languages and Cultural Identity”
- “Food Sovereignty and Traditional Agricultural Practices Among Indigenous Communities”
- “Navigating Modernity: The Integration of Traditional Healing Practices in Contemporary Healthcare Systems”
- “Gender Roles and Equality in Hunter-Gatherer Societies: An Anthropological Perspective”
- “Sacred Spaces and Religious Practices: An Ethnographic Study of Pilgrimage Sites”
- “Youth Subcultures and Resistance: An Exploration of Identity and Expression in Urban Environments”
- “Cultural Constructions of Disability and Inclusion: A Cross-Cultural Analysis”
- “Interethnic Marriages and Cultural Syncretism: Case Studies from Multicultural Societies”
- “The Role of Folklore and Storytelling in Preserving Cultural Heritage”
- “Economic Anthropology of Gift-Giving and Reciprocity in Tribal Communities”
- “Digital Anthropology: The Role of Social Media in Shaping Political Movements”
- “Migration and Diaspora: Maintaining Cultural Identity in Transnational Communities”
- “Cultural Adaptations to Climate Change Among Coastal Fishing Communities”
Communication Studies
- “The Dynamics of Family Communication in the Digital Age: A Qualitative Inquiry”
- “Narratives of Identity and Belonging in Diaspora Communities Through Social Media”
- “Organizational Communication and Employee Engagement: A Case Study in the Non-Profit Sector”
- “Cultural Influences on Communication Styles in Multinational Teams: An Ethnographic Approach”
- “Media Representation of Women in Politics: A Content Analysis and Audience Perception Study”
- “The Role of Communication in Building Sustainable Community Development Projects”
- “Interpersonal Communication in Online Dating: Strategies, Challenges, and Outcomes”
- “Public Health Messaging During Pandemics: A Qualitative Study of Community Responses”
- “The Impact of Mobile Technology on Parent-Child Communication in the Digital Era”
- “Crisis Communication Strategies in the Hospitality Industry: A Case Study of Reputation Management”
- “Narrative Analysis of Personal Stories Shared on Mental Health Blogs”
- “The Influence of Podcasts on Political Engagement Among Young Adults”
- “Visual Communication and Brand Identity: A Qualitative Study of Consumer Interpretations”
- “Communication Barriers in Cross-Cultural Healthcare Settings: Patient and Provider Perspectives”
- “The Role of Internal Communication in Managing Organizational Change: Employee Experiences”
Information Technology
- “User Experience Design in Augmented Reality Applications: A Qualitative Study of Best Practices”
- “The Human Factor in Cybersecurity: Understanding Employee Behaviors and Attitudes Towards Phishing”
- “Adoption of Cloud Computing in Small and Medium Enterprises: Challenges and Success Factors”
- “Blockchain Technology in Supply Chain Management: A Qualitative Exploration of Potential Impacts”
- “The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Personalizing User Experiences on E-commerce Platforms”
- “Digital Transformation in Traditional Industries: A Case Study of Technology Adoption Challenges”
- “Ethical Considerations in the Development of Smart Home Technologies: A Stakeholder Analysis”
- “The Impact of Social Media Algorithms on News Consumption and Public Opinion”
- “Collaborative Software Development: Practices and Challenges in Open Source Projects”
- “Understanding the Digital Divide: Access to Information Technology in Rural Communities”
- “Data Privacy Concerns and User Trust in Internet of Things (IoT) Devices”
- “The Effectiveness of Gamification in Educational Software: A Qualitative Study of Engagement and Motivation”
- “Virtual Teams and Remote Work: Communication Strategies and Tools for Effectiveness”
- “User-Centered Design in Mobile Health Applications: Evaluating Usability and Accessibility”
- “The Influence of Technology on Work-Life Balance: Perspectives from IT Professionals”
Tourism and Hospitality
- “Exploring the Authenticity of Cultural Heritage Tourism in Indigenous Communities”
- “Sustainable Tourism Practices: Perceptions and Implementations in Small Island Destinations”
- “The Impact of Social Media Influencers on Destination Choice Among Millennials”
- “Gastronomy Tourism: Exploring the Culinary Experiences of International Visitors in Rural Regions”
- “Eco-Tourism and Conservation: Stakeholder Perspectives on Balancing Tourism and Environmental Protection”
- “The Role of Hospitality in Enhancing the Cultural Exchange Experience of Exchange Students”
- “Dark Tourism: Visitor Motivations and Experiences at Historical Conflict Sites”
- “Customer Satisfaction in Luxury Hotels: A Qualitative Study of Service Excellence and Personalization”
- “Adventure Tourism: Understanding the Risk Perception and Safety Measures Among Thrill-Seekers”
- “The Influence of Local Communities on Tourist Experiences in Ecotourism Sites”
- “Event Tourism: Economic Impacts and Community Perspectives on Large-Scale Music Festivals”
- “Heritage Tourism and Identity: Exploring the Connections Between Historic Sites and National Identity”
- “Tourist Perceptions of Sustainable Accommodation Practices: A Study of Green Hotels”
- “The Role of Language in Shaping the Tourist Experience in Multilingual Destinations”
- “Health and Wellness Tourism: Motivations and Experiences of Visitors to Spa and Retreat Centers”
Qualitative Research Topics
Qualitative Research Topics are as follows:
- Understanding the lived experiences of first-generation college students
- Exploring the impact of social media on self-esteem among adolescents
- Investigating the effects of mindfulness meditation on stress reduction
- Analyzing the perceptions of employees regarding organizational culture
- Examining the impact of parental involvement on academic achievement of elementary school students
- Investigating the role of music therapy in managing symptoms of depression
- Understanding the experience of women in male-dominated industries
- Exploring the factors that contribute to successful leadership in non-profit organizations
- Analyzing the effects of peer pressure on substance abuse among adolescents
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with disabilities in the workplace
- Understanding the factors that contribute to burnout among healthcare professionals
- Examining the impact of social support on mental health outcomes
- Analyzing the perceptions of parents regarding sex education in schools
- Investigating the experiences of immigrant families in the education system
- Understanding the impact of trauma on mental health outcomes
- Exploring the effectiveness of animal-assisted therapy for individuals with anxiety
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful intergenerational relationships
- Investigating the experiences of LGBTQ+ individuals in the workplace
- Understanding the impact of online gaming on social skills development among adolescents
- Examining the perceptions of teachers regarding technology integration in the classroom
- Analyzing the experiences of women in leadership positions
- Investigating the factors that contribute to successful marriage and long-term relationships
- Understanding the impact of social media on political participation
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with mental health disorders in the criminal justice system
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful community-based programs for youth development
- Investigating the experiences of veterans in accessing mental health services
- Understanding the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on mental health outcomes
- Examining the perceptions of parents regarding childhood obesity prevention
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful multicultural education programs
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with chronic illnesses in the workplace
- Understanding the impact of poverty on academic achievement
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with autism spectrum disorder in the workplace
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful employee retention strategies
- Investigating the experiences of caregivers of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease
- Understanding the impact of parent-child communication on adolescent sexual behavior
- Examining the perceptions of college students regarding mental health services on campus
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful team building in the workplace
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with eating disorders in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of mentorship on career success
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with physical disabilities in the workplace
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful community-based programs for mental health
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with substance use disorders in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of social media on romantic relationships
- Examining the perceptions of parents regarding child discipline strategies
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful cross-cultural communication in the workplace
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with anxiety disorders in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of cultural differences on healthcare delivery
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with hearing loss in the workplace
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful parent-teacher communication
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with depression in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of childhood trauma on adult mental health outcomes
- Examining the perceptions of college students regarding alcohol and drug use on campus
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful mentor-mentee relationships
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with intellectual disabilities in the workplace
- Understanding the impact of work-family balance on employee satisfaction and well-being
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with autism spectrum disorder in vocational rehabilitation programs
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful project management in the construction industry
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with substance use disorders in peer support groups
- Understanding the impact of mindfulness meditation on stress reduction and mental health
- Examining the perceptions of parents regarding childhood nutrition
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful environmental sustainability initiatives in organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with bipolar disorder in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of job stress on employee burnout and turnover
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with physical disabilities in recreational activities
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful strategic planning in nonprofit organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with hoarding disorder in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of culture on leadership styles and effectiveness
- Examining the perceptions of college students regarding sexual health education on campus
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful supply chain management in the retail industry
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with personality disorders in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of multiculturalism on group dynamics in the workplace
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with chronic pain in mindfulness-based pain management programs
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful employee engagement strategies in organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with internet addiction disorder in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of social comparison on body dissatisfaction and self-esteem
- Examining the perceptions of parents regarding childhood sleep habits
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful diversity and inclusion initiatives in organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with schizophrenia in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of job crafting on employee motivation and job satisfaction
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with vision impairments in navigating public spaces
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful customer relationship management strategies in the service industry
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with dissociative amnesia in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of cultural intelligence on intercultural communication and collaboration
- Examining the perceptions of college students regarding campus diversity and inclusion efforts
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful supply chain sustainability initiatives in organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with obsessive-compulsive disorder in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of transformational leadership on organizational performance and employee well-being
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with mobility impairments in public transportation
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful talent management strategies in organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with substance use disorders in harm reduction programs
- Understanding the impact of gratitude practices on well-being and resilience
- Examining the perceptions of parents regarding childhood mental health and well-being
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful corporate social responsibility initiatives in organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with borderline personality disorder in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of emotional labor on job stress and burnout
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with hearing impairments in healthcare settings
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful customer experience strategies in the hospitality industry
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with gender dysphoria in gender-affirming healthcare
- Understanding the impact of cultural differences on cross-cultural negotiation in the global marketplace
- Examining the perceptions of college students regarding academic stress and mental health
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful supply chain agility in organizations
- Understanding the impact of music therapy on mental health and well-being
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with dyslexia in educational settings
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful leadership in nonprofit organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with chronic illnesses in online support groups
- Understanding the impact of exercise on mental health and well-being
- Examining the perceptions of parents regarding childhood screen time
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful change management strategies in organizations
- Understanding the impact of cultural differences on international business negotiations
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with hearing impairments in the workplace
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful team building in corporate settings
- Understanding the impact of technology on communication in romantic relationships
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful community engagement strategies for local governments
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of financial stress on mental health and well-being
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful mentorship programs in organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with gambling addictions in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of social media on body image and self-esteem
- Examining the perceptions of parents regarding childhood education
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful virtual team management strategies
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with dissociative identity disorder in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of cultural differences on cross-cultural communication in healthcare settings
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with chronic pain in cognitive-behavioral therapy programs
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful community-building strategies in urban neighborhoods
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with alcohol use disorders in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of personality traits on romantic relationships
- Examining the perceptions of college students regarding mental health stigma on campus
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful fundraising strategies for political campaigns
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with traumatic brain injuries in rehabilitation programs
- Understanding the impact of social support on mental health and well-being among the elderly
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with chronic illnesses in medical treatment decision-making processes
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful innovation strategies in organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with dissociative disorders in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of cultural differences on cross-cultural communication in education settings
- Examining the perceptions of parents regarding childhood physical activity
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful conflict resolution in family relationships
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with opioid use disorders in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of emotional intelligence on leadership effectiveness
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with learning disabilities in the workplace
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful change management in educational institutions
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with eating disorders in recovery support groups
- Understanding the impact of self-compassion on mental health and well-being
- Examining the perceptions of college students regarding campus safety and security measures
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful marketing strategies for nonprofit organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with postpartum depression in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of ageism in the workplace
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with dyslexia in the education system
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with anxiety disorders in cognitive-behavioral therapy programs
- Understanding the impact of socioeconomic status on access to healthcare
- Examining the perceptions of parents regarding childhood screen time usage
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful supply chain management strategies
- Understanding the impact of parenting styles on child development
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with addiction in harm reduction programs
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful crisis management strategies in organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with trauma in trauma-focused therapy programs
- Examining the perceptions of healthcare providers regarding patient-centered care
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful product development strategies
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with autism spectrum disorder in employment programs
- Understanding the impact of cultural competence on healthcare outcomes
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with chronic illnesses in healthcare navigation
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful community engagement strategies for non-profit organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with physical disabilities in the workplace
- Understanding the impact of childhood trauma on adult mental health
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful supply chain sustainability strategies
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with personality disorders in dialectical behavior therapy programs
- Understanding the impact of gender identity on mental health treatment seeking behaviors
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with schizophrenia in community-based treatment programs
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful project team management strategies
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with obsessive-compulsive disorder in exposure and response prevention therapy programs
- Understanding the impact of cultural competence on academic achievement and success
- Examining the perceptions of college students regarding academic integrity
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful social media marketing strategies
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with bipolar disorder in community-based treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of mindfulness on academic achievement and success
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with substance use disorders in medication-assisted treatment programs
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with anxiety disorders in exposure therapy programs
- Understanding the impact of healthcare disparities on health outcomes
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful supply chain optimization strategies
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with borderline personality disorder in schema therapy programs
- Understanding the impact of culture on perceptions of mental health stigma
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with trauma in art therapy programs
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful digital marketing strategies
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with eating disorders in online support groups
- Understanding the impact of workplace bullying on job satisfaction and performance
- Examining the perceptions of college students regarding mental health resources on campus
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful supply chain risk management strategies
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with chronic pain in mindfulness-based pain management programs
- Understanding the impact of cognitive-behavioral therapy on social anxiety disorder
- Understanding the impact of COVID-19 on mental health and well-being
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with eating disorders in treatment programs
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful leadership in business organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with chronic pain in cognitive-behavioral therapy programs
- Understanding the impact of cultural differences on intercultural communication
- Examining the perceptions of teachers regarding inclusive education for students with disabilities
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with depression in therapy programs
- Understanding the impact of workplace culture on employee retention and turnover
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with traumatic brain injuries in rehabilitation programs
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful crisis communication strategies in organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with anxiety disorders in mindfulness-based interventions
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with chronic illnesses in healthcare settings
- Understanding the impact of technology on work-life balance
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with learning disabilities in academic settings
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful entrepreneurship in small businesses
- Understanding the impact of gender identity on mental health and well-being
- Examining the perceptions of individuals with disabilities regarding accessibility in public spaces
- Understanding the impact of religion on coping strategies for stress and anxiety
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with chronic illnesses in complementary and alternative medicine treatments
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful customer retention strategies in business organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with postpartum depression in therapy programs
- Understanding the impact of ageism on older adults in healthcare settings
- Examining the perceptions of students regarding online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful team building in virtual work environments
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with gambling disorders in treatment programs
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with chronic illnesses in peer support groups
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful social media marketing strategies for businesses
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with ADHD in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of sleep on cognitive and emotional functioning
- Examining the perceptions of individuals with chronic illnesses regarding healthcare access and affordability
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with borderline personality disorder in dialectical behavior therapy programs
- Understanding the impact of social support on caregiver well-being
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with chronic illnesses in disability activism
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful cultural competency training programs in healthcare settings
- Understanding the impact of personality disorders on interpersonal relationships
- Examining the perceptions of healthcare providers regarding the use of telehealth services
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with dissociative disorders in therapy programs
- Understanding the impact of gender bias in hiring practices
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with visual impairments in the workplace
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful diversity and inclusion programs in the workplace
- Understanding the impact of online dating on romantic relationships
- Examining the perceptions of parents regarding childhood vaccination
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful communication in healthcare settings
- Understanding the impact of cultural stereotypes on academic achievement
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with substance use disorders in sober living programs
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful classroom management strategies
- Understanding the impact of social support on addiction recovery
- Examining the perceptions of college students regarding mental health stigma
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful conflict resolution in the workplace
- Understanding the impact of race and ethnicity on healthcare access and outcomes
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with post-traumatic stress disorder in treatment programs
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful project management strategies
- Understanding the impact of teacher-student relationships on academic achievement
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful customer service strategies
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with social anxiety disorder in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of workplace stress on job satisfaction and performance
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with disabilities in sports and recreation
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful marketing strategies for small businesses
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with phobias in treatment programs
- Understanding the impact of culture on attitudes towards mental health and illness
- Examining the perceptions of college students regarding sexual assault prevention
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful time management strategies
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with addiction in recovery support groups
- Understanding the impact of mindfulness on emotional regulation and well-being
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with chronic pain in treatment programs
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful conflict resolution in romantic relationships
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with autism spectrum disorder in social skills training programs
- Understanding the impact of parent-child communication on adolescent substance use
- Examining the perceptions of parents regarding childhood mental health services
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful fundraising strategies for non-profit organizations
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with chronic illnesses in support groups
- Understanding the impact of personality traits on career success and satisfaction
- Exploring the experiences of individuals with disabilities in accessing public transportation
- Analyzing the factors that contribute to successful team building in sports teams
- Investigating the experiences of individuals with chronic pain in alternative medicine treatments
- Understanding the impact of stigma on mental health treatment seeking behaviors
- Examining the perceptions of college students regarding diversity and inclusion on campus.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

200+ Funny Research Topics

500+ Sports Research Topics

300+ American History Research Paper Topics

500+ Cyber Security Research Topics

500+ Environmental Research Topics

500+ Economics Research Topics
About Journal
American Journal of Qualitative Research (AJQR) is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal that publishes qualitative research articles from a number of social science disciplines such as psychology, health science, sociology, criminology, education, political science, and administrative studies. The journal is an international and interdisciplinary focus and greatly welcomes papers from all countries. The journal offers an intellectual platform for researchers, practitioners, administrators, and policymakers to contribute and promote qualitative research and analysis.
ISSN: 2576-2141
Call for Papers- American Journal of Qualitative Research
American Journal of Qualitative Research (AJQR) welcomes original research articles and book reviews for its next issue. The AJQR is a quarterly and peer-reviewed journal published in February, May, August, and November.
We are seeking submissions for a forthcoming issue published in February 2024. The paper should be written in professional English. The length of 6000-10000 words is preferred. All manuscripts should be prepared in MS Word format and submitted online: https://www.editorialpark.com/ajqr
For any further information about the journal, please visit its website: https://www.ajqr.org
Submission Deadline: November 15, 2023
Announcement
Dear AJQR Readers,
Due to the high volume of submissions in the American Journal of Qualitative Research , the editorial board decided to publish quarterly since 2023.
Volume 8, Issue 1
Current issue.
Social distancing requirements resulted in many people working from home in the United Kingdom during the COVID-19 pandemic. The topic of working from home was often discussed in the media and online during the pandemic, but little was known about how quality of life (QOL) and remote working interfaced. The purpose of this study was to describe QOL while working from home during the COVID-19 pandemic. The novel topic, unique methodological approach of the General Online Qualitative Study ( D’Abundo & Franco, 2022a), and the strategic Social Distancing Sampling ( D’Abundo & Franco, 2022c) resulted in significant participation throughout the world (n = 709). The United Kingdom subset of participants (n = 234) is the focus of this article. This big qual, large qualitative study (n >100) included the principal investigator-developed, open-ended, online questionnaire entitled the “Quality of Life Home Workplace Questionnaire (QOLHWQ)” and demographic questions. Data were collected peak-pandemic from July to September 2020. Most participants cited increased QOL due to having more time with family/kids/partners/pets, a more comfortable work environment while being at home, and less commuting to work. The most cited issue associated with negative QOL was social isolation. As restrictions have been lifted and public health emergency declarations have been terminated during the post-peak era of the COVID-19 pandemic, the potential for future public health emergencies requiring social distancing still exists. To promote QOL and work-life balance for employees working remotely in the United Kingdom, stakeholders could develop social support networks and create effective planning initiatives to prevent social isolation and maximize the benefits of remote working experiences for both employees and organizations.
Keywords: qualitative research, quality of life, remote work, telework, United Kingdom, work from home.
(no abstract)
This essay reviews classic works on the philosophy of science and contemporary pedagogical guides to scientific inquiry in order to present a discussion of the three logics that underlie qualitative research in political science. The first logic, epistemology, relates to the essence of research as a scientific endeavor and is framed as a debate between positivist and interpretivist orientations within the discipline of political science. The second logic, ontology, relates to the approach that research takes to investigating the empirical world and is framed as a debate between positivist qualitative and quantitative orientations, which together constitute the vast majority of mainstream researchers within the discipline. The third logic, methodology, relates to the means by which research aspires to reach its scientific ends and is framed as a debate among positivist qualitative orientations. Additionally, the essay discusses the present state of qualitative research in the discipline of political science, reviews the various ways in which qualitative research is defined in the relevant literature, addresses the limitations and trade-offs that are inherently associated with the aforementioned logics of qualitative research, explores multimethod approaches to remedying these issues, and proposes avenues for acquiring further information on the topics discussed.
Keywords: qualitative research, epistemology, ontology, methodology
This paper examines the phenomenology of diagnostic crossover in eating disorders, the movement within or between feeding and eating disorder subtypes or diagnoses over time, in two young women who experienced multiple changes in eating disorder diagnosis over 5 years. Using interpretative phenomenological analysis, this study found that transitioning between different diagnostic labels, specifically between bulimia nervosa and anorexia nervosa binge/purge subtype, was experienced as disempowering, stigmatizing, and unhelpful. The findings in this study offer novel evidence that, from the perspective of individuals diagnosed with EDs, using BMI as an indicator of the presence, severity, or change of an ED may have adverse consequences for well-being and recovery and may lead to mischaracterization or misclassification of health status. The narratives discussed in this paper highlight the need for more person-centered practices in the context of diagnostic crossover. Including the perspectives of those with lived experience can help care providers working with individuals with eating disorders gain an in-depth understanding of the potential personal impact of diagnosis changing and inform discussions around developing person-focused diagnostic practices.
Keywords: feeding and eating disorders, bulimia nervosa, diagnostic labels, diagnostic crossover, illness narrative
Often among the first witnesses to child trauma, educators and therapists are on the frontline of an unfolding and multi-pronged occupational crisis. For educators, lack of support and secondary traumatic stress (STS) appear to be contributing to an epidemic in professional attrition. Similarly, therapists who do not prioritize self-care can feel depleted of energy and optimism. The purpose of this phenomenological study was to examine how bearing witness to the traumatic narratives of children impacts similar helping professionals. The study also sought to extrapolate the similarities and differences between compassion fatigue and secondary trauma across these two disciplines. Exploring the common factors and subjective individual experiences related to occupational stress across these two fields may foster a more complete picture of the delicate nature of working with traumatized children and the importance of successful self-care strategies. Utilizing Constructivist Self-Development Theory (CSDT) and focus group interviews, the study explores the significant risk of STS facing both educators and therapists.
Keywords: qualitative, secondary traumatic stress, self-care, child trauma, educators, therapists.
This study explored the lived experiences of residents of the Gulf Coast in the USA during Hurricane Katrina, which made landfall in August 2005 and caused insurmountable destruction throughout the area. A heuristic process and thematic analysis were employed to draw observations and conclusions about the lived experiences of each participant and make meaning through similar thoughts, feelings, and themes that emerged in the analysis of the data. Six themes emerged: (1) fear, (2) loss, (3) anger, (4) support, (5) spirituality, and (6) resilience. The results of this study allude to the possible psychological outcomes as a result of experiencing a traumatic event and provide an outline of what the psychological experience of trauma might entail. The current research suggests that preparedness and expectation are key to resilience and that people who feel that they have power over their situation fare better than those who do not.
Keywords: mass trauma, resilience, loss, natural disaster, mental health.
Women from rural, low-income backgrounds holding positions within the academy are the exception and not the rule. Most women faculty in the academy are from urban/suburban areas and middle- and upper-income family backgrounds. As women faculty who do not represent this norm, our primary goal with this article is to focus on the unique barriers we experienced as girls from rural, low-income areas in K-12 schools that influenced the possibilities for successfully transitioning to and engaging with higher education. We employed a qualitative duoethnographic and narrative research design to respond to the research questions, and we generated our data through semi-structured, critical, ethnographic dialogic conversations. Our duoethnographic-narrative analyses revealed six major themes: (1) independence and other benefits of having a working-class mom; (2) crashing into middle-class norms and expectations; (3) lucking and falling into college; (4) fish out of water; (5) overcompensating, playing middle class, walking on eggshells, and pushing back; and (6) transitioning from a working-class kid to a working class academic, which we discuss in relation to our own educational attainment.
Keywords: rurality, working-class, educational attainment, duoethnography, higher education, women.
This article draws on the findings of a qualitative study that focused on the perspectives of four Indian American mothers of youth with developmental disabilities on the process of transitioning from school to post-school environments. Data were collected through in-depth ethnographic interviews. The findings indicate that in their efforts to support their youth with developmental disabilities, the mothers themselves navigate multiple transitions across countries, constructs, dreams, systems of schooling, and services. The mothers’ perspectives have to be understood against the larger context of their experiences as citizens of this country as well as members of the South Asian diaspora. The mothers’ views on services, their journey, their dreams for their youth, and their interpretation of the ideas anchored in current conversations on transition are continually evolving. Their attempts to maintain their resilience and their indigenous understandings while simultaneously negotiating their experiences in the United States with supporting their youth are discussed.
Keywords: Indian-American mothers, transitioning, diaspora, disability, dreams.
This study explored the influence of yoga on practitioners’ lives ‘off the mat’ through a phenomenological lens. Central to the study was the lived experience of yoga in a purposive sample of self-identified New Zealand practitioners (n=38; 89.5% female; aged 18 to 65 years; 60.5% aged 36 to 55 years). The study’s aim was to explore whether habitual yoga practitioners experience any pro-health downstream effects of their practice ‘off the mat’ via their lived experience of yoga. A qualitative mixed methodology was applied via a phenomenological lens that explicitly acknowledged the researcher’s own experience of the research topic. Qualitative methods comprised an open-ended online survey for all participants (n=38), followed by in-depth semi-structured interviews (n=8) on a randomized subset. Quantitative methods included online outcome measures (health habits, self-efficacy, interoceptive awareness, and physical activity), practice component data (tenure, dose, yoga styles, yoga teacher status, meditation frequency), and socio-demographics. This paper highlights the qualitative findings emerging from participant narratives. Reported benefits of practice included the provision of a filter through which to engage with life and the experience of self-regulation and mindfulness ‘off the mat’. Practitioners experienced yoga as a self-sustaining positive resource via self-regulation guided by an embodied awareness. The key narrative to emerge was an attunement to embodiment through movement. Embodied movement can elicit self-regulatory pathways that support health behavior.
Keywords: embodiment, habit, interoception, mindfulness, movement practice, qualitative, self-regulation, yoga.
Historically and in the present day, Black women’s positionality in the U.S. has paradoxically situated them in a society where they are both intrinsically essential and treated as expendable. This positionality, known as gendered racism, manifests commonly in professional environments and results in myriad harms. In response, Black women have developed, honed, and practiced a range of coping styles to mitigate the insidious effects of gendered racism. While often effective in the short-term, these techniques frequently complicate Black women’s well-being. For Black female clinicians who experience gendered racism and work on the frontlines of community mental health, myriad bio-psycho-social-spiritual harms compound. This project provided an opportunity for Black female clinicians from across the U.S. to share their experiences during the dual pandemics of COVID-19 and anti-Black violence. I conducted in-depth interviews with clinicians (n=14) between the ages of 30 and 58. Using the Listening Guide voice-centered approach to data generation and analysis, I identified four voices to help answer this project’s central question: How do you experience being a Black female clinician in the U.S.? The voices of self, pride, vigilance, and mediating narrated the complex ways participants experienced their workplaces. This complexity seemed to be context-specific, depending on whether the clinicians worked in predominantly White workplaces (PWW), a mix of PWW and private practice, or private practice exclusively. Participants who worked only in PWW experienced the greatest stress, oppression, and burnout risk, while participants who worked exclusively in private practice reported more joy, more authenticity, and more job satisfaction. These findings have implications for mentoring, supporting, and retaining Black female clinicians.
Keywords: Black female clinicians, professional experiences, gendered racism, Listening Guide voice-centered approach.
The purpose of this article is to speak directly to the paucity of research regarding Dominican American women and identity narratives. To do so, this article uses the Listening Guide Method of Qualitative Inquiry (Gilligan, et al., 2006) to explore how 1.5 and second-generation Dominican American women narrated their experiences of individual identity within American cultural contexts and constructs. The results draw from the emergence of themes across six participant interviews and showed two distinct voices: The Voice of Cultural Explanation and the Tides of Dominican American Female Identity. Narrative examples from five participants are offered to illustrate where 1.5 and second-generation Dominican American women negotiate their identity narratives at the intersection of their Dominican and American selves. The article offers two conclusions. One, that participant women use the Voice of Cultural Explanation in order to discuss their identity as reflected within the broad cultural tensions of their daily lives. Two, that the Tides of Dominican American Female Identity are used to express strong emotions that manifest within their personal narratives as the unwanted distance from either the Dominican or American parts of their person.
Keywords: Dominican American, women, identity, the Listening Guide, narratives
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
Published on June 19, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on June 22, 2023.
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research.
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research , which involves collecting and analyzing numerical data for statistical analysis.
Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, history, etc.
- How does social media shape body image in teenagers?
- How do children and adults interpret healthy eating in the UK?
- What factors influence employee retention in a large organization?
- How is anxiety experienced around the world?
- How can teachers integrate social issues into science curriculums?
Table of contents
Approaches to qualitative research, qualitative research methods, qualitative data analysis, advantages of qualitative research, disadvantages of qualitative research, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about qualitative research.
Qualitative research is used to understand how people experience the world. While there are many approaches to qualitative research, they tend to be flexible and focus on retaining rich meaning when interpreting data.
Common approaches include grounded theory, ethnography , action research , phenomenological research, and narrative research. They share some similarities, but emphasize different aims and perspectives.
Note that qualitative research is at risk for certain research biases including the Hawthorne effect , observer bias , recall bias , and social desirability bias . While not always totally avoidable, awareness of potential biases as you collect and analyze your data can prevent them from impacting your work too much.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Each of the research approaches involve using one or more data collection methods . These are some of the most common qualitative methods:
- Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes.
- Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations.
- Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among a group of people.
- Surveys : distributing questionnaires with open-ended questions.
- Secondary research: collecting existing data in the form of texts, images, audio or video recordings, etc.
- You take field notes with observations and reflect on your own experiences of the company culture.
- You distribute open-ended surveys to employees across all the company’s offices by email to find out if the culture varies across locations.
- You conduct in-depth interviews with employees in your office to learn about their experiences and perspectives in greater detail.
Qualitative researchers often consider themselves “instruments” in research because all observations, interpretations and analyses are filtered through their own personal lens.
For this reason, when writing up your methodology for qualitative research, it’s important to reflect on your approach and to thoroughly explain the choices you made in collecting and analyzing the data.
Qualitative data can take the form of texts, photos, videos and audio. For example, you might be working with interview transcripts, survey responses, fieldnotes, or recordings from natural settings.
Most types of qualitative data analysis share the same five steps:
- Prepare and organize your data. This may mean transcribing interviews or typing up fieldnotes.
- Review and explore your data. Examine the data for patterns or repeated ideas that emerge.
- Develop a data coding system. Based on your initial ideas, establish a set of codes that you can apply to categorize your data.
- Assign codes to the data. For example, in qualitative survey analysis, this may mean going through each participant’s responses and tagging them with codes in a spreadsheet. As you go through your data, you can create new codes to add to your system if necessary.
- Identify recurring themes. Link codes together into cohesive, overarching themes.
There are several specific approaches to analyzing qualitative data. Although these methods share similar processes, they emphasize different concepts.
Qualitative research often tries to preserve the voice and perspective of participants and can be adjusted as new research questions arise. Qualitative research is good for:
- Flexibility
The data collection and analysis process can be adapted as new ideas or patterns emerge. They are not rigidly decided beforehand.
- Natural settings
Data collection occurs in real-world contexts or in naturalistic ways.
- Meaningful insights
Detailed descriptions of people’s experiences, feelings and perceptions can be used in designing, testing or improving systems or products.
- Generation of new ideas
Open-ended responses mean that researchers can uncover novel problems or opportunities that they wouldn’t have thought of otherwise.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Researchers must consider practical and theoretical limitations in analyzing and interpreting their data. Qualitative research suffers from:
- Unreliability
The real-world setting often makes qualitative research unreliable because of uncontrolled factors that affect the data.
- Subjectivity
Due to the researcher’s primary role in analyzing and interpreting data, qualitative research cannot be replicated . The researcher decides what is important and what is irrelevant in data analysis, so interpretations of the same data can vary greatly.
- Limited generalizability
Small samples are often used to gather detailed data about specific contexts. Despite rigorous analysis procedures, it is difficult to draw generalizable conclusions because the data may be biased and unrepresentative of the wider population .
- Labor-intensive
Although software can be used to manage and record large amounts of text, data analysis often has to be checked or performed manually.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Chi square goodness of fit test
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to systematically measure variables and test hypotheses . Qualitative methods allow you to explore concepts and experiences in more detail.
There are five common approaches to qualitative research :
- Grounded theory involves collecting data in order to develop new theories.
- Ethnography involves immersing yourself in a group or organization to understand its culture.
- Narrative research involves interpreting stories to understand how people make sense of their experiences and perceptions.
- Phenomenological research involves investigating phenomena through people’s lived experiences.
- Action research links theory and practice in several cycles to drive innovative changes.
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organizations.
There are various approaches to qualitative data analysis , but they all share five steps in common:
- Prepare and organize your data.
- Review and explore your data.
- Develop a data coding system.
- Assign codes to the data.
- Identify recurring themes.
The specifics of each step depend on the focus of the analysis. Some common approaches include textual analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, June 22). What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 5, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/qualitative-research/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, qualitative vs. quantitative research | differences, examples & methods, how to do thematic analysis | step-by-step guide & examples, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
131 Interesting Qualitative Research Topics For High Scoring Thesis

Qualitative research topics are undoubtedly not easy. While statistics enthralls some students, others don’t like the subject. That’s because qualitative assignments entail cognitive analysis, which complicates them. But apart from the hardships of completing the projects, selecting topics for qualitative research papers is also a challenge.
This article presents a list of 130-plus qualitative research topic ideas to help learners that struggle to get titles for their papers. It is helpful because many learners have difficulties picking titles that will make their essays impressive to educators. But before presenting the topics, this article defines qualitative research.
What Is Qualitative Research?
Qualitative research is an investigative and innovative abstract data analysis. When writing a qualitative research paper, a learner analyzes intangible data. Qualitative researchers code the data after or during collection. Therefore, having top-notch research topics is necessary for a first-class essay.
Knowing how to write a qualitative research paper is vital because it helps the student deliver a copy that provides a clear picture of an event or situation. A researcher can achieve this via practical experience, reliable reporting, and conversations. Gathering raw data is the initial step in qualitative research. A researcher can gather raw data by conducting reviews, observations, and surveys. Also, researchers can use creative methods to collect data.
Best Examples Of Qualitative Research Topics
Qualitative research covers many things. Here are examples of topics that learners can explore in their qualitative study.
- What causes stigma around some health challenges?
- Stigma facing the people living with disabilities- What is the cause?
- Can Pro Bono legal assistance improve the criminal justice system?
- How the less privileged can benefit from Pro Bono services
- The educational challenges facing rural children- Are there ways to help them?
- Child labor causes- How to mitigate the practice
- Substance and drugs- What are young people abusing more?
- How alcohol affects college students
- Can food insecurity interfere with children’s performance in school?
- Food banks intricacies- Understanding the challenge in low-income areas
- Free education- Does it have socioeconomic benefits?
- Culture and female harm- What’s the connection?
- The impact of social media on physical and social engagement among teens in urban areas
- Using medication to treat depression- What are the health benefits?
- Investigating peer educators’ efficiency in creating awareness of health and social issues
- Gender-based violence- What causes it in rural areas, and how does it affect victims?
- Sexual reproductive health challenges of child brides- Are there ways to control it?
- Investigating the causes of school dropout among teenagers
- How to address school dropout among young adults
- Investigating the deteriorating academic pursuit in Third-World countries
- Social activities- Do they have benefits for depressed people?
- Investigating cerebral palsy and the stigma that people associate with it.
- Living with disabilities- Are there social implications?
- The impact of ableism on disabled people
- Exploring the promotion and benefits of feminist values
- Why should society promote free education in all learning environments?
- What causes food insecurities among low-income earners?
- Food and housing insecurity- What are the root causes?
- What are the effects of displacement- Investigating the homeless people’s mental health
These are good examples of qualitative research topics. However, a student that picks a title in this category should research it extensively to impress the educator with their work.
Qualitative Nursing Research Topics
Professors ask students to write about qualitative topics when pursuing nursing studies. Here are issues to consider in this category.
- How does the nurse-patient relationship affect health outcomes?
- How can nurses deal with complex patients?
- How can nurses provide culturally competent care?
- How do personal beliefs affect nursing practice?
- What is the impact of spirituality on nursing care?
- How does the nurse’s role change when working with terminally ill patients?
- What challenges do nurses face when providing end-of-life care?
- How can nurses best support families whose members have serious illnesses?
- What are the unique challenges of caring for elderly patients?
- How does the nurse’s role change when working in a hospice setting?
- Health outreach programs- What are the most effective ways to execute them?
- Effective methods of curbing drug abuse
- Effective ways to help rape survivors
- How can nurses administer care to female genital mutilation victims?
- How to care for special needs individuals
- Anxiety and depression symptoms
- Methods of administering care to Dyslexia patients
- How to help individuals dealing with mental disorders
- Signs of Alzheimer’s disease in older people
- How to provide primary patient care
These are good qualitative research topics for students pursuing nursing studies. Nevertheless, learners must research any of these titles before writing their papers.
Qualitative Research Topics In Education
Most topics spring up from the education niche despite fitting other specifications. Here are examples of qualitative research topics that include the education niche.
- Are guidance and counseling essential in schools?
- How computer literacy affects education
- Why governments in developing schools should encourage adult education
- Autistic children’s education- Which learning style suits them?
- Is mental health education relevant in the modern school curriculum?
- Exploring the learning conditions for kids in third world countries
- Child education and food insecurity- What is the connection?
- The impact of virtual learning on high school students
- How does alcoholism affect a student and their education?
- Homeschooling- What are its advantages and disadvantages?
- How do teachers’ beliefs about intelligence affect their teaching?
- What is the teacher’s role in developing a student’s self-concept?
- Does race or ethnicity play a role in how teachers treat their students?
- What are the teachers’ experiences with teaching students with special needs?
- What methods do effective teachers use to motivate their students?
- What are the most effective ways to teach reading and writing?
- How does technology use affect how teachers teach, and students learn?
- What are the challenges faced by teachers in rural areas?
- What are the challenges faced by teachers in urban areas?
- How do charter schools differ from traditional public schools?
Many topics and issues in the education system allow learners to find subjects to investigate and cover in their papers quickly. And this is not an exhaustive qualitative research topic list in this field. Nevertheless, it covers the most exciting ideas to explore.
Qualitative Research Topics In Public Health
Educators ask students to write academic papers while studying the public health sector. And this provides insights into crucial and relevant aspects of this sector. Here are qualitative research topics examples in this category.
- How does the public health sector manage epidemics?
- The role of public health in disaster management
- Evaluating the effectiveness of public health campaigns
- An analysis of the factors that hinder effective public health delivery
- Access to healthcare: A study of rural and urban populations
- Health needs assessment of refugees
- Mental health support within the public health sector
- The role of technology in public health
- Understanding and addressing health disparities
- Sexual and reproductive health rights in the public health discourse
- How immunization benefits people in rural areas
- What causes water-borne diseases, and how can society mitigate them?
- Symptoms of high blood pressure among young people
- How antenatal care helps pregnant women
- How to boost breast cancer awareness
These are excellent qualitative research paper topics in the public health sector. Nevertheless, learners need sufficient time and resources to investigate their preferred titles in this category to write winning papers.
Qualitative Research Topics In Project Management
Project management writing focuses on ways to achieve results and goals while basing the achievement on the process. This subject covers planning, structuring, proffering, and controlling ways to execute plans to accomplish desired goals. Here are research topics for qualitative research in project management.
- How effective communication strategies can impact the outcome of a project
- How different leadership styles affect team productivity during a project
- The role of conflict management in ensuring successful project outcomes
- Gender differences in the perception and understanding of project risk
- The impact of organizational culture on a project’s likelihood of success
- How different project management methodologies affect its outcome
- The effect of stakeholder involvement on project success
- How to manage virtual teams effectively to ensure successful project outcomes
- What motivates project managers to achieve successful results?
- How can project managers create a positive work environment that leads to successful outcomes?
- What challenges do project managers face when trying to achieve successful outcomes?
- How can project management be used to achieve social change?
- What are the ethical implications of project management?
- What are the global impacts of project management?
- Ways to achieve sustainable development through project management
These are topics to explore in project management. Nevertheless, learners need adequate time to investigate their chosen titles and write winning essays.
Qualitative Research Topics In Political Science
Qualitative research can also cover political science. Investigating this field enables people to understand it better and can be broad. Here are sample titles to consider in for your scientific thesis .
- How do social media affect the way people engage with politics?
- What motivates people to vote?
- How does voting behavior change over time?
- What are the consequences of gerrymandering?
- How does campaign finance influence elections?
- Interest groups- What is their role in politics?
- How do the media cover politics?
- What are the effects of political scandals?
- How does public opinion influence policymakers?
- How feminism enhanced the American politics
- The adverse effects of misrepresentation
- The American democracy- A look into its dimensions
- Colorism, racism, and classism- How the American ideologies differ
- What causes an election crisis?
- Two-party system- What challenges does it face in America?
- Black women’s inclusion in the American politics
- Should America have a multi-party system?
- Why mass media matters in politics’ scrutiny and promotion
While political science is a broad field, these narrow topics help learners handle their research effectively. Pick any of these ideas to write a winning essay.
Topics For Ethnography Qualitative Research
Ethnographic research entails studying and paying attention to society and describing it. Here are topics to consider for a research paper in this field.
- Studying a subculture: Reasons people join and stay in gangs
- How does social media use vary by culture?
- An ethnographic study of a homeless shelter or soup kitchen
- Understanding the lives of sex workers through ethnography
- The impact of religion on family life
- How does parenting vary between cultures?
- How do children learn and socialize in different cultures?
- What is the effect of migration on family life?
- What are the experiences of refugees?- An explorative case study
- What is the impact of poverty on family life?
- How do people in different cultures understand and experience mental illness?
- What is the role of the family in other cultures?
- What are the end-of-life experiences and beliefs around death in different cultures?
This article has presented easy qualitative research topics. However, some need time and resources to investigate and write quality papers. Therefore, pick your paper title carefully to write an essay that will earn you an excellent grade.
Get Quality Writing Help Online
Maybe you have a title for your paper but not time for writing a unique, top-notch thesis. In that case, get the best dissertation services from our writers. We’re educated, native ENL writers with a proven track record of exceeding customers’ expectations. Our team helps university, college, and high school learners complete their writing and editing assignments. Whether writing a research paper is a requirement for a degree or a diploma course, we can help you. Contact us to get quality, custom, and cheap help from qualified experts in your study field.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates
Criteria for Good Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Review
- Regular Article
- Open access
- Published: 18 September 2021
- Volume 31 , pages 679–689, ( 2022 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article
- Drishti Yadav ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2974-0323 1
73k Accesses
25 Citations
71 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
This review aims to synthesize a published set of evaluative criteria for good qualitative research. The aim is to shed light on existing standards for assessing the rigor of qualitative research encompassing a range of epistemological and ontological standpoints. Using a systematic search strategy, published journal articles that deliberate criteria for rigorous research were identified. Then, references of relevant articles were surveyed to find noteworthy, distinct, and well-defined pointers to good qualitative research. This review presents an investigative assessment of the pivotal features in qualitative research that can permit the readers to pass judgment on its quality and to condemn it as good research when objectively and adequately utilized. Overall, this review underlines the crux of qualitative research and accentuates the necessity to evaluate such research by the very tenets of its being. It also offers some prospects and recommendations to improve the quality of qualitative research. Based on the findings of this review, it is concluded that quality criteria are the aftereffect of socio-institutional procedures and existing paradigmatic conducts. Owing to the paradigmatic diversity of qualitative research, a single and specific set of quality criteria is neither feasible nor anticipated. Since qualitative research is not a cohesive discipline, researchers need to educate and familiarize themselves with applicable norms and decisive factors to evaluate qualitative research from within its theoretical and methodological framework of origin.
Similar content being viewed by others

What is Qualitative in Qualitative Research
Patrik Aspers & Ugo Corte

Qualitative Research: Ethical Considerations
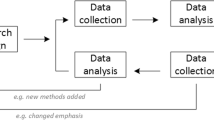
How to use and assess qualitative research methods
Loraine Busetto, Wolfgang Wick & Christoph Gumbinger
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
“… It is important to regularly dialogue about what makes for good qualitative research” (Tracy, 2010 , p. 837)
To decide what represents good qualitative research is highly debatable. There are numerous methods that are contained within qualitative research and that are established on diverse philosophical perspectives. Bryman et al., ( 2008 , p. 262) suggest that “It is widely assumed that whereas quality criteria for quantitative research are well‐known and widely agreed, this is not the case for qualitative research.” Hence, the question “how to evaluate the quality of qualitative research” has been continuously debated. There are many areas of science and technology wherein these debates on the assessment of qualitative research have taken place. Examples include various areas of psychology: general psychology (Madill et al., 2000 ); counseling psychology (Morrow, 2005 ); and clinical psychology (Barker & Pistrang, 2005 ), and other disciplines of social sciences: social policy (Bryman et al., 2008 ); health research (Sparkes, 2001 ); business and management research (Johnson et al., 2006 ); information systems (Klein & Myers, 1999 ); and environmental studies (Reid & Gough, 2000 ). In the literature, these debates are enthused by the impression that the blanket application of criteria for good qualitative research developed around the positivist paradigm is improper. Such debates are based on the wide range of philosophical backgrounds within which qualitative research is conducted (e.g., Sandberg, 2000 ; Schwandt, 1996 ). The existence of methodological diversity led to the formulation of different sets of criteria applicable to qualitative research.
Among qualitative researchers, the dilemma of governing the measures to assess the quality of research is not a new phenomenon, especially when the virtuous triad of objectivity, reliability, and validity (Spencer et al., 2004 ) are not adequate. Occasionally, the criteria of quantitative research are used to evaluate qualitative research (Cohen & Crabtree, 2008 ; Lather, 2004 ). Indeed, Howe ( 2004 ) claims that the prevailing paradigm in educational research is scientifically based experimental research. Hypotheses and conjectures about the preeminence of quantitative research can weaken the worth and usefulness of qualitative research by neglecting the prominence of harmonizing match for purpose on research paradigm, the epistemological stance of the researcher, and the choice of methodology. Researchers have been reprimanded concerning this in “paradigmatic controversies, contradictions, and emerging confluences” (Lincoln & Guba, 2000 ).
In general, qualitative research tends to come from a very different paradigmatic stance and intrinsically demands distinctive and out-of-the-ordinary criteria for evaluating good research and varieties of research contributions that can be made. This review attempts to present a series of evaluative criteria for qualitative researchers, arguing that their choice of criteria needs to be compatible with the unique nature of the research in question (its methodology, aims, and assumptions). This review aims to assist researchers in identifying some of the indispensable features or markers of high-quality qualitative research. In a nutshell, the purpose of this systematic literature review is to analyze the existing knowledge on high-quality qualitative research and to verify the existence of research studies dealing with the critical assessment of qualitative research based on the concept of diverse paradigmatic stances. Contrary to the existing reviews, this review also suggests some critical directions to follow to improve the quality of qualitative research in different epistemological and ontological perspectives. This review is also intended to provide guidelines for the acceleration of future developments and dialogues among qualitative researchers in the context of assessing the qualitative research.
The rest of this review article is structured in the following fashion: Sect. Methods describes the method followed for performing this review. Section Criteria for Evaluating Qualitative Studies provides a comprehensive description of the criteria for evaluating qualitative studies. This section is followed by a summary of the strategies to improve the quality of qualitative research in Sect. Improving Quality: Strategies . Section How to Assess the Quality of the Research Findings? provides details on how to assess the quality of the research findings. After that, some of the quality checklists (as tools to evaluate quality) are discussed in Sect. Quality Checklists: Tools for Assessing the Quality . At last, the review ends with the concluding remarks presented in Sect. Conclusions, Future Directions and Outlook . Some prospects in qualitative research for enhancing its quality and usefulness in the social and techno-scientific research community are also presented in Sect. Conclusions, Future Directions and Outlook .
For this review, a comprehensive literature search was performed from many databases using generic search terms such as Qualitative Research , Criteria , etc . The following databases were chosen for the literature search based on the high number of results: IEEE Explore, ScienceDirect, PubMed, Google Scholar, and Web of Science. The following keywords (and their combinations using Boolean connectives OR/AND) were adopted for the literature search: qualitative research, criteria, quality, assessment, and validity. The synonyms for these keywords were collected and arranged in a logical structure (see Table 1 ). All publications in journals and conference proceedings later than 1950 till 2021 were considered for the search. Other articles extracted from the references of the papers identified in the electronic search were also included. A large number of publications on qualitative research were retrieved during the initial screening. Hence, to include the searches with the main focus on criteria for good qualitative research, an inclusion criterion was utilized in the search string.
From the selected databases, the search retrieved a total of 765 publications. Then, the duplicate records were removed. After that, based on the title and abstract, the remaining 426 publications were screened for their relevance by using the following inclusion and exclusion criteria (see Table 2 ). Publications focusing on evaluation criteria for good qualitative research were included, whereas those works which delivered theoretical concepts on qualitative research were excluded. Based on the screening and eligibility, 45 research articles were identified that offered explicit criteria for evaluating the quality of qualitative research and were found to be relevant to this review.
Figure 1 illustrates the complete review process in the form of PRISMA flow diagram. PRISMA, i.e., “preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses” is employed in systematic reviews to refine the quality of reporting.
PRISMA flow diagram illustrating the search and inclusion process. N represents the number of records
Criteria for Evaluating Qualitative Studies
Fundamental criteria: general research quality.
Various researchers have put forward criteria for evaluating qualitative research, which have been summarized in Table 3 . Also, the criteria outlined in Table 4 effectively deliver the various approaches to evaluate and assess the quality of qualitative work. The entries in Table 4 are based on Tracy’s “Eight big‐tent criteria for excellent qualitative research” (Tracy, 2010 ). Tracy argues that high-quality qualitative work should formulate criteria focusing on the worthiness, relevance, timeliness, significance, morality, and practicality of the research topic, and the ethical stance of the research itself. Researchers have also suggested a series of questions as guiding principles to assess the quality of a qualitative study (Mays & Pope, 2020 ). Nassaji ( 2020 ) argues that good qualitative research should be robust, well informed, and thoroughly documented.
Qualitative Research: Interpretive Paradigms
All qualitative researchers follow highly abstract principles which bring together beliefs about ontology, epistemology, and methodology. These beliefs govern how the researcher perceives and acts. The net, which encompasses the researcher’s epistemological, ontological, and methodological premises, is referred to as a paradigm, or an interpretive structure, a “Basic set of beliefs that guides action” (Guba, 1990 ). Four major interpretive paradigms structure the qualitative research: positivist and postpositivist, constructivist interpretive, critical (Marxist, emancipatory), and feminist poststructural. The complexity of these four abstract paradigms increases at the level of concrete, specific interpretive communities. Table 5 presents these paradigms and their assumptions, including their criteria for evaluating research, and the typical form that an interpretive or theoretical statement assumes in each paradigm. Moreover, for evaluating qualitative research, quantitative conceptualizations of reliability and validity are proven to be incompatible (Horsburgh, 2003 ). In addition, a series of questions have been put forward in the literature to assist a reviewer (who is proficient in qualitative methods) for meticulous assessment and endorsement of qualitative research (Morse, 2003 ). Hammersley ( 2007 ) also suggests that guiding principles for qualitative research are advantageous, but methodological pluralism should not be simply acknowledged for all qualitative approaches. Seale ( 1999 ) also points out the significance of methodological cognizance in research studies.
Table 5 reflects that criteria for assessing the quality of qualitative research are the aftermath of socio-institutional practices and existing paradigmatic standpoints. Owing to the paradigmatic diversity of qualitative research, a single set of quality criteria is neither possible nor desirable. Hence, the researchers must be reflexive about the criteria they use in the various roles they play within their research community.
Improving Quality: Strategies
Another critical question is “How can the qualitative researchers ensure that the abovementioned quality criteria can be met?” Lincoln and Guba ( 1986 ) delineated several strategies to intensify each criteria of trustworthiness. Other researchers (Merriam & Tisdell, 2016 ; Shenton, 2004 ) also presented such strategies. A brief description of these strategies is shown in Table 6 .
It is worth mentioning that generalizability is also an integral part of qualitative research (Hays & McKibben, 2021 ). In general, the guiding principle pertaining to generalizability speaks about inducing and comprehending knowledge to synthesize interpretive components of an underlying context. Table 7 summarizes the main metasynthesis steps required to ascertain generalizability in qualitative research.
Figure 2 reflects the crucial components of a conceptual framework and their contribution to decisions regarding research design, implementation, and applications of results to future thinking, study, and practice (Johnson et al., 2020 ). The synergy and interrelationship of these components signifies their role to different stances of a qualitative research study.

Essential elements of a conceptual framework
In a nutshell, to assess the rationale of a study, its conceptual framework and research question(s), quality criteria must take account of the following: lucid context for the problem statement in the introduction; well-articulated research problems and questions; precise conceptual framework; distinct research purpose; and clear presentation and investigation of the paradigms. These criteria would expedite the quality of qualitative research.
How to Assess the Quality of the Research Findings?
The inclusion of quotes or similar research data enhances the confirmability in the write-up of the findings. The use of expressions (for instance, “80% of all respondents agreed that” or “only one of the interviewees mentioned that”) may also quantify qualitative findings (Stenfors et al., 2020 ). On the other hand, the persuasive reason for “why this may not help in intensifying the research” has also been provided (Monrouxe & Rees, 2020 ). Further, the Discussion and Conclusion sections of an article also prove robust markers of high-quality qualitative research, as elucidated in Table 8 .
Quality Checklists: Tools for Assessing the Quality
Numerous checklists are available to speed up the assessment of the quality of qualitative research. However, if used uncritically and recklessly concerning the research context, these checklists may be counterproductive. I recommend that such lists and guiding principles may assist in pinpointing the markers of high-quality qualitative research. However, considering enormous variations in the authors’ theoretical and philosophical contexts, I would emphasize that high dependability on such checklists may say little about whether the findings can be applied in your setting. A combination of such checklists might be appropriate for novice researchers. Some of these checklists are listed below:
The most commonly used framework is Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research (COREQ) (Tong et al., 2007 ). This framework is recommended by some journals to be followed by the authors during article submission.
Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR) is another checklist that has been created particularly for medical education (O’Brien et al., 2014 ).
Also, Tracy ( 2010 ) and Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP, 2021 ) offer criteria for qualitative research relevant across methods and approaches.
Further, researchers have also outlined different criteria as hallmarks of high-quality qualitative research. For instance, the “Road Trip Checklist” (Epp & Otnes, 2021 ) provides a quick reference to specific questions to address different elements of high-quality qualitative research.
Conclusions, Future Directions, and Outlook
This work presents a broad review of the criteria for good qualitative research. In addition, this article presents an exploratory analysis of the essential elements in qualitative research that can enable the readers of qualitative work to judge it as good research when objectively and adequately utilized. In this review, some of the essential markers that indicate high-quality qualitative research have been highlighted. I scope them narrowly to achieve rigor in qualitative research and note that they do not completely cover the broader considerations necessary for high-quality research. This review points out that a universal and versatile one-size-fits-all guideline for evaluating the quality of qualitative research does not exist. In other words, this review also emphasizes the non-existence of a set of common guidelines among qualitative researchers. In unison, this review reinforces that each qualitative approach should be treated uniquely on account of its own distinctive features for different epistemological and disciplinary positions. Owing to the sensitivity of the worth of qualitative research towards the specific context and the type of paradigmatic stance, researchers should themselves analyze what approaches can be and must be tailored to ensemble the distinct characteristics of the phenomenon under investigation. Although this article does not assert to put forward a magic bullet and to provide a one-stop solution for dealing with dilemmas about how, why, or whether to evaluate the “goodness” of qualitative research, it offers a platform to assist the researchers in improving their qualitative studies. This work provides an assembly of concerns to reflect on, a series of questions to ask, and multiple sets of criteria to look at, when attempting to determine the quality of qualitative research. Overall, this review underlines the crux of qualitative research and accentuates the need to evaluate such research by the very tenets of its being. Bringing together the vital arguments and delineating the requirements that good qualitative research should satisfy, this review strives to equip the researchers as well as reviewers to make well-versed judgment about the worth and significance of the qualitative research under scrutiny. In a nutshell, a comprehensive portrayal of the research process (from the context of research to the research objectives, research questions and design, speculative foundations, and from approaches of collecting data to analyzing the results, to deriving inferences) frequently proliferates the quality of a qualitative research.
Prospects : A Road Ahead for Qualitative Research
Irrefutably, qualitative research is a vivacious and evolving discipline wherein different epistemological and disciplinary positions have their own characteristics and importance. In addition, not surprisingly, owing to the sprouting and varied features of qualitative research, no consensus has been pulled off till date. Researchers have reflected various concerns and proposed several recommendations for editors and reviewers on conducting reviews of critical qualitative research (Levitt et al., 2021 ; McGinley et al., 2021 ). Following are some prospects and a few recommendations put forward towards the maturation of qualitative research and its quality evaluation:
In general, most of the manuscript and grant reviewers are not qualitative experts. Hence, it is more likely that they would prefer to adopt a broad set of criteria. However, researchers and reviewers need to keep in mind that it is inappropriate to utilize the same approaches and conducts among all qualitative research. Therefore, future work needs to focus on educating researchers and reviewers about the criteria to evaluate qualitative research from within the suitable theoretical and methodological context.
There is an urgent need to refurbish and augment critical assessment of some well-known and widely accepted tools (including checklists such as COREQ, SRQR) to interrogate their applicability on different aspects (along with their epistemological ramifications).
Efforts should be made towards creating more space for creativity, experimentation, and a dialogue between the diverse traditions of qualitative research. This would potentially help to avoid the enforcement of one's own set of quality criteria on the work carried out by others.
Moreover, journal reviewers need to be aware of various methodological practices and philosophical debates.
It is pivotal to highlight the expressions and considerations of qualitative researchers and bring them into a more open and transparent dialogue about assessing qualitative research in techno-scientific, academic, sociocultural, and political rooms.
Frequent debates on the use of evaluative criteria are required to solve some potentially resolved issues (including the applicability of a single set of criteria in multi-disciplinary aspects). Such debates would not only benefit the group of qualitative researchers themselves, but primarily assist in augmenting the well-being and vivacity of the entire discipline.
To conclude, I speculate that the criteria, and my perspective, may transfer to other methods, approaches, and contexts. I hope that they spark dialog and debate – about criteria for excellent qualitative research and the underpinnings of the discipline more broadly – and, therefore, help improve the quality of a qualitative study. Further, I anticipate that this review will assist the researchers to contemplate on the quality of their own research, to substantiate research design and help the reviewers to review qualitative research for journals. On a final note, I pinpoint the need to formulate a framework (encompassing the prerequisites of a qualitative study) by the cohesive efforts of qualitative researchers of different disciplines with different theoretic-paradigmatic origins. I believe that tailoring such a framework (of guiding principles) paves the way for qualitative researchers to consolidate the status of qualitative research in the wide-ranging open science debate. Dialogue on this issue across different approaches is crucial for the impending prospects of socio-techno-educational research.
Amin, M. E. K., Nørgaard, L. S., Cavaco, A. M., Witry, M. J., Hillman, L., Cernasev, A., & Desselle, S. P. (2020). Establishing trustworthiness and authenticity in qualitative pharmacy research. Research in Social and Administrative Pharmacy, 16 (10), 1472–1482.
Article Google Scholar
Barker, C., & Pistrang, N. (2005). Quality criteria under methodological pluralism: Implications for conducting and evaluating research. American Journal of Community Psychology, 35 (3–4), 201–212.
Bryman, A., Becker, S., & Sempik, J. (2008). Quality criteria for quantitative, qualitative and mixed methods research: A view from social policy. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 11 (4), 261–276.
Caelli, K., Ray, L., & Mill, J. (2003). ‘Clear as mud’: Toward greater clarity in generic qualitative research. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 2 (2), 1–13.
CASP (2021). CASP checklists. Retrieved May 2021 from https://casp-uk.net/casp-tools-checklists/
Cohen, D. J., & Crabtree, B. F. (2008). Evaluative criteria for qualitative research in health care: Controversies and recommendations. The Annals of Family Medicine, 6 (4), 331–339.
Denzin, N. K., & Lincoln, Y. S. (2005). Introduction: The discipline and practice of qualitative research. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), The sage handbook of qualitative research (pp. 1–32). Sage Publications Ltd.
Google Scholar
Elliott, R., Fischer, C. T., & Rennie, D. L. (1999). Evolving guidelines for publication of qualitative research studies in psychology and related fields. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 38 (3), 215–229.
Epp, A. M., & Otnes, C. C. (2021). High-quality qualitative research: Getting into gear. Journal of Service Research . https://doi.org/10.1177/1094670520961445
Guba, E. G. (1990). The paradigm dialog. In Alternative paradigms conference, mar, 1989, Indiana u, school of education, San Francisco, ca, us . Sage Publications, Inc.
Hammersley, M. (2007). The issue of quality in qualitative research. International Journal of Research and Method in Education, 30 (3), 287–305.
Haven, T. L., Errington, T. M., Gleditsch, K. S., van Grootel, L., Jacobs, A. M., Kern, F. G., & Mokkink, L. B. (2020). Preregistering qualitative research: A Delphi study. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 19 , 1609406920976417.
Hays, D. G., & McKibben, W. B. (2021). Promoting rigorous research: Generalizability and qualitative research. Journal of Counseling and Development, 99 (2), 178–188.
Horsburgh, D. (2003). Evaluation of qualitative research. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 12 (2), 307–312.
Howe, K. R. (2004). A critique of experimentalism. Qualitative Inquiry, 10 (1), 42–46.
Johnson, J. L., Adkins, D., & Chauvin, S. (2020). A review of the quality indicators of rigor in qualitative research. American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education, 84 (1), 7120.
Johnson, P., Buehring, A., Cassell, C., & Symon, G. (2006). Evaluating qualitative management research: Towards a contingent criteriology. International Journal of Management Reviews, 8 (3), 131–156.
Klein, H. K., & Myers, M. D. (1999). A set of principles for conducting and evaluating interpretive field studies in information systems. MIS Quarterly, 23 (1), 67–93.
Lather, P. (2004). This is your father’s paradigm: Government intrusion and the case of qualitative research in education. Qualitative Inquiry, 10 (1), 15–34.
Levitt, H. M., Morrill, Z., Collins, K. M., & Rizo, J. L. (2021). The methodological integrity of critical qualitative research: Principles to support design and research review. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 68 (3), 357.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (1986). But is it rigorous? Trustworthiness and authenticity in naturalistic evaluation. New Directions for Program Evaluation, 1986 (30), 73–84.
Lincoln, Y. S., & Guba, E. G. (2000). Paradigmatic controversies, contradictions and emerging confluences. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), Handbook of qualitative research (2nd ed., pp. 163–188). Sage Publications.
Madill, A., Jordan, A., & Shirley, C. (2000). Objectivity and reliability in qualitative analysis: Realist, contextualist and radical constructionist epistemologies. British Journal of Psychology, 91 (1), 1–20.
Mays, N., & Pope, C. (2020). Quality in qualitative research. Qualitative Research in Health Care . https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119410867.ch15
McGinley, S., Wei, W., Zhang, L., & Zheng, Y. (2021). The state of qualitative research in hospitality: A 5-year review 2014 to 2019. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly, 62 (1), 8–20.
Merriam, S., & Tisdell, E. (2016). Qualitative research: A guide to design and implementation. San Francisco, US.
Meyer, M., & Dykes, J. (2019). Criteria for rigor in visualization design study. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 26 (1), 87–97.
Monrouxe, L. V., & Rees, C. E. (2020). When I say… quantification in qualitative research. Medical Education, 54 (3), 186–187.
Morrow, S. L. (2005). Quality and trustworthiness in qualitative research in counseling psychology. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 52 (2), 250.
Morse, J. M. (2003). A review committee’s guide for evaluating qualitative proposals. Qualitative Health Research, 13 (6), 833–851.
Nassaji, H. (2020). Good qualitative research. Language Teaching Research, 24 (4), 427–431.
O’Brien, B. C., Harris, I. B., Beckman, T. J., Reed, D. A., & Cook, D. A. (2014). Standards for reporting qualitative research: A synthesis of recommendations. Academic Medicine, 89 (9), 1245–1251.
O’Connor, C., & Joffe, H. (2020). Intercoder reliability in qualitative research: Debates and practical guidelines. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 19 , 1609406919899220.
Reid, A., & Gough, S. (2000). Guidelines for reporting and evaluating qualitative research: What are the alternatives? Environmental Education Research, 6 (1), 59–91.
Rocco, T. S. (2010). Criteria for evaluating qualitative studies. Human Resource Development International . https://doi.org/10.1080/13678868.2010.501959
Sandberg, J. (2000). Understanding human competence at work: An interpretative approach. Academy of Management Journal, 43 (1), 9–25.
Schwandt, T. A. (1996). Farewell to criteriology. Qualitative Inquiry, 2 (1), 58–72.
Seale, C. (1999). Quality in qualitative research. Qualitative Inquiry, 5 (4), 465–478.
Shenton, A. K. (2004). Strategies for ensuring trustworthiness in qualitative research projects. Education for Information, 22 (2), 63–75.
Sparkes, A. C. (2001). Myth 94: Qualitative health researchers will agree about validity. Qualitative Health Research, 11 (4), 538–552.
Spencer, L., Ritchie, J., Lewis, J., & Dillon, L. (2004). Quality in qualitative evaluation: A framework for assessing research evidence.
Stenfors, T., Kajamaa, A., & Bennett, D. (2020). How to assess the quality of qualitative research. The Clinical Teacher, 17 (6), 596–599.
Taylor, E. W., Beck, J., & Ainsworth, E. (2001). Publishing qualitative adult education research: A peer review perspective. Studies in the Education of Adults, 33 (2), 163–179.
Tong, A., Sainsbury, P., & Craig, J. (2007). Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): A 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. International Journal for Quality in Health Care, 19 (6), 349–357.
Tracy, S. J. (2010). Qualitative quality: Eight “big-tent” criteria for excellent qualitative research. Qualitative Inquiry, 16 (10), 837–851.
Download references
Open access funding provided by TU Wien (TUW).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Informatics, Technische Universität Wien, 1040, Vienna, Austria
Drishti Yadav
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Drishti Yadav .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Yadav, D. Criteria for Good Qualitative Research: A Comprehensive Review. Asia-Pacific Edu Res 31 , 679–689 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-021-00619-0
Download citation
Accepted : 28 August 2021
Published : 18 September 2021
Issue Date : December 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-021-00619-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Qualitative research
- Evaluative criteria
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Write my thesis
- Thesis writers
- Buy thesis papers
- Bachelor thesis
- Master's thesis
- Thesis editing services
- Thesis proofreading services
- Buy a thesis online
- Write my dissertation
- Dissertation proposal help
- Pay for dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help online
- Buy dissertation online
- Cheap dissertation
- Dissertation editing services
- Write my research paper
- Buy research paper online
- Pay for research paper
- Research paper help
- Order research paper
- Custom research paper
- Cheap research paper
- Research papers for sale
- Thesis subjects
- How It Works
Qualitative Research Topics & Ideas For Students

Do you have difficulty finding a qualitative research title for your project? If you are, you need not worry because you are not alone. However, there are many unique qualitative titles you can explore for your research. You just need a few qualitative research title examples to get you started. Qualitative research is focused on data obtained through a researcher’s first-hand observations, natural setting recording, artifacts, case studies, documents, questionnaires, and interviews. The findings in qualitative research are usually non-numerical. Also, it is common in humanities and social sciences. This post provides over 100 qualitative research topics you can consider.
- The Best Qualitative Research Topics That Impress the Teacher
Exceptional Qualitative Research Topics In Social Science
Qualitative research title examples for students, fantastic examples of qualitative research titles, good topics to start for qualitative research, qualitative research topics in education, quick examples of qualitative research topics, qualitative research topics in the philippines, qualitative researches topics about humanity & social science, great choices of qualitative research title examples, qualitative research topics for students to think about, our examples of the best qualitative research topics that impress the teacher.
An excellent research topic will help you earn a good grade. Consider any example of a qualitative research title from the following options:
- The impacts of social media on physical social engagement in society
- The benefits of treating mental disorders with medication
- The effects of Gender-Based Violence on women’s social lives in rural areas
- The decline of academic pursuit in third-world countries
- Sexual workers: the stigma they experience
- How has the promotion of feminist values influenced workplaces?
- Free education: its impact in third-world countries
- What is the correlation between education and success?
- Ableism: its effects on disabled people in society
- Food insecurity in third-world nations
The topic of your research paper can influence how easily you can conduct your study and draw conclusions.
Here are fantastic examples of qualitative research titles:
- Female harm: how it is influenced by culture
- The socioeconomic impacts of free education
- The link between food insecurity and poor performance in schools
- Alcoholism among college students: a critical study
- How to mitigate child labor in our society
- The root causes of child labor in Latin America
- The stigma of living with transmissive medical conditions
- The root cause of the stigma of people living with disabilities
- How to identify depression in small children
- Signs of autism in kids below two years old
Choosing a qualitative research topic is not a task you should take lightly because it can influence your performance. Here are some noteworthy qualitative research titles examples:
- Basic patient care policies in developing nations
- The impacts of alcoholism on education
- Adult learning: what does it entail?
- Homeschooling: Is it the latest trend after the pandemic?
- Does computer literacy influence the quality of education kids enjoy?
- How to effectively teach students with learning disabilities
- The relationship between poor education systems and crime rates in third-world countries
- Student bullying: the psychological impacts
- Should high school students go through university preparedness programs?
- research writing in high schools: its significance
Are you looking for qualitative research topic examples to start your study? Below are some creative examples to consider:
- Remote tests: are they as effective as in-class tests?
- The value of social activities in academic institutions
- Why should healthcare be free in all countries?
- The implications of racist laws on society
- The reception of COVID-19 vaccines and treatments
- What is the difference between foreign policies in first-world and third-world nations?
- Racism and Colorism: what is the difference?
- Dissecting the causes of low voter turnouts in the 21 st century
- The challenges of social media on kid’s brain development
- The inclusion of black women in American politics and its impacts
When competing with several brilliant minds, a good research topic can do you greatly. The following qualitative research examples titles are a great place to start:
- Should school uniforms be discarded for high schoolers?
- The need for equal representation in global politics
- The implications of police brutality on politics
- The role of parental care in foster kids
- The distinction between Islamic values and Christian values
- The correlation between political instability and migration
- Sex trafficking and violence against women: what is the link?
- How can global governments eradicate homelessness?
- Fraternities and sororities: are they still relevant?
- The role of literature in promoting societal changes
Qualitative research is popular in the education field and other social sciences. Choose a qualitative research title example on the subject of education from the following list:
- Effectively introducing foreign languages in the high school curriculum
- How can teachers help students with disabilities improve their learning?
- The link between social activities and comprehension among students
- Research writing in high schools: is it necessary?
- How has virtual learning influenced teacher-student relationships?
- The implications of allowing smartphones in classes
- Should all schools introduce sign language lessons in their curriculum?
- Student loans: their impacts on black students
- The impacts of race on college acceptance rates
- Poverty and education: what is the link?
- Ethnic and socioeconomic causes of poor school attendance in developing worlds
- Various teaching methods and their efficiency
- Efficient teaching methods for children below two years
- Why do students perform better in humanities than in sciences?
- The difference between college acceptance and completion in most nations
- Remote learning in developing countries
- What are the best ways of approaching bullying in schools?
- How do teachers promote inequality among students?
- Does social class influence academic performance negatively or positively?
- How do teachers shape their students’ personalities?
Coming up with a qualitative research title can be hard because of the numerous subject areas and the issue of uniqueness. Therefore, we have prepared the following qualitative title examples for you:
- How to promote oral learning in classrooms
- Political instability in developing countries: its economic impacts
- The impacts of weather on social activities
- Boredom and poor-decision making: the connection
- Exploring the connection between attachment types and love languages
- Socioeconomic impacts of instability on a country
- How does social media impact the perception of reality
- Reality TV shows: are they a true reflection of reality?
- How culture applies to different age groups
- Is social media influencing the loss of cultural values?
You can base your research topic on a specific region or nation, like the Philippines. A sample qualitative research title can get you started. You can pick a sample qualitative research title from the ideas below:
- Why are so many Philippines residents migrating to America?
- The impact of politics on migration in the Philippines
- How has violence led to food insecurity in rural areas in the Philippines?
- The Philippine education system: an overview
- How cultural norms influence social activities in the Philippines
- Gender roles in the Philippines society
- How popular Filipino cultures have served as agents of social change in the nation
- The link between male dominance and GBV in the Philippines
- Barriers to clean hygiene in health centers in the Philippines
- The spread of COVID in rural areas in the Philippines
Most top performers in research subjects attribute their success to choosing the best title for qualitative research. Here are some qualitative research topics about humanities and social science to promote good performance:
- The impact of poor market rivalry on supply and demand
- The role of parents in shaping kids’ morals
- Is social media the root cause of poor societal morals?
- How does alcohol impact a person’s normal behavior?
- How often should adults engage in sporting activities?
- Children’s eating habits and their influences
- Low socioeconomic backgrounds and their impacts on self-esteem
- The effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on the world’s views on viral diseases
- How can school-going kids manage depression
- Causes of mental challenges among school-going kids
Finding a good topic for qualitative research is a critical task that requires a lot of thought and research. However, we have simplified the process with the following qualitative topic ideas:
- Pop music and erratic youth behavior: is there a link?
- How do public figures influence cultures?
- Ideas for improving healthcare in developing nations
- Possible solutions for alleviating the food crisis in developing nations
- New ways of mitigating viral diseases
- Social media trends among the elderly
- Quarantine as a mitigation approach for infectious diseases
- Promoting social justice in patriarchal societies
- Worrying trends among the young population
- Emerging marketing trends in 2023
Qualitative research for college and high school students helps improve reading, writing, and intellectual skills. Here are some qualitative research examples and topic ideas for students :
- How to detect and prevent natural disasters beforehand
- Can the whole world have the same education system?
- What is the most effective therapy for patients recuperating from brain surgery?
- Possible solutions for promoting ethical practices in telehealth
- Can addicts overcome addiction without therapy?
- The latest technology trends and their impacts?
- How can global governments promote mental health awareness?
- Have smartphones caused reduced attention spans among users?
- Sexual violence in rural areas
- The introduction of Islam in African nations
We Are Here for You
Qualitative research is an investigative analysis of intangible or inexact data, mostly non-numerical. The title of qualitative research you choose will guide your entire research process and influence its conclusions. Do you need a paper or an example of a research title qualitative topic? Our expert team is ready to write it for you.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Qualitative Study
Affiliations.
- 1 University of Nebraska Medical Center
- 2 GDB Research and Statistical Consulting
- 3 GDB Research and Statistical Consulting/McLaren Macomb Hospital
- PMID: 29262162
- Bookshelf ID: NBK470395
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems. Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervene or introduce treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypotheses as well as further investigate and understand quantitative data. Qualitative research gathers participants' experiences, perceptions, and behavior. It answers the hows and whys instead of how many or how much. It could be structured as a stand-alone study, purely relying on qualitative data or it could be part of mixed-methods research that combines qualitative and quantitative data. This review introduces the readers to some basic concepts, definitions, terminology, and application of qualitative research.
Qualitative research at its core, ask open-ended questions whose answers are not easily put into numbers such as ‘how’ and ‘why’. Due to the open-ended nature of the research questions at hand, qualitative research design is often not linear in the same way quantitative design is. One of the strengths of qualitative research is its ability to explain processes and patterns of human behavior that can be difficult to quantify. Phenomena such as experiences, attitudes, and behaviors can be difficult to accurately capture quantitatively, whereas a qualitative approach allows participants themselves to explain how, why, or what they were thinking, feeling, and experiencing at a certain time or during an event of interest. Quantifying qualitative data certainly is possible, but at its core, qualitative data is looking for themes and patterns that can be difficult to quantify and it is important to ensure that the context and narrative of qualitative work are not lost by trying to quantify something that is not meant to be quantified.
However, while qualitative research is sometimes placed in opposition to quantitative research, where they are necessarily opposites and therefore ‘compete’ against each other and the philosophical paradigms associated with each, qualitative and quantitative work are not necessarily opposites nor are they incompatible. While qualitative and quantitative approaches are different, they are not necessarily opposites, and they are certainly not mutually exclusive. For instance, qualitative research can help expand and deepen understanding of data or results obtained from quantitative analysis. For example, say a quantitative analysis has determined that there is a correlation between length of stay and level of patient satisfaction, but why does this correlation exist? This dual-focus scenario shows one way in which qualitative and quantitative research could be integrated together.
Examples of Qualitative Research Approaches
Ethnography
Ethnography as a research design has its origins in social and cultural anthropology, and involves the researcher being directly immersed in the participant’s environment. Through this immersion, the ethnographer can use a variety of data collection techniques with the aim of being able to produce a comprehensive account of the social phenomena that occurred during the research period. That is to say, the researcher’s aim with ethnography is to immerse themselves into the research population and come out of it with accounts of actions, behaviors, events, etc. through the eyes of someone involved in the population. Direct involvement of the researcher with the target population is one benefit of ethnographic research because it can then be possible to find data that is otherwise very difficult to extract and record.
Grounded Theory
Grounded Theory is the “generation of a theoretical model through the experience of observing a study population and developing a comparative analysis of their speech and behavior.” As opposed to quantitative research which is deductive and tests or verifies an existing theory, grounded theory research is inductive and therefore lends itself to research that is aiming to study social interactions or experiences. In essence, Grounded Theory’s goal is to explain for example how and why an event occurs or how and why people might behave a certain way. Through observing the population, a researcher using the Grounded Theory approach can then develop a theory to explain the phenomena of interest.
Phenomenology
Phenomenology is defined as the “study of the meaning of phenomena or the study of the particular”. At first glance, it might seem that Grounded Theory and Phenomenology are quite similar, but upon careful examination, the differences can be seen. At its core, phenomenology looks to investigate experiences from the perspective of the individual. Phenomenology is essentially looking into the ‘lived experiences’ of the participants and aims to examine how and why participants behaved a certain way, from their perspective . Herein lies one of the main differences between Grounded Theory and Phenomenology. Grounded Theory aims to develop a theory for social phenomena through an examination of various data sources whereas Phenomenology focuses on describing and explaining an event or phenomena from the perspective of those who have experienced it.
Narrative Research
One of qualitative research’s strengths lies in its ability to tell a story, often from the perspective of those directly involved in it. Reporting on qualitative research involves including details and descriptions of the setting involved and quotes from participants. This detail is called ‘thick’ or ‘rich’ description and is a strength of qualitative research. Narrative research is rife with the possibilities of ‘thick’ description as this approach weaves together a sequence of events, usually from just one or two individuals, in the hopes of creating a cohesive story, or narrative. While it might seem like a waste of time to focus on such a specific, individual level, understanding one or two people’s narratives for an event or phenomenon can help to inform researchers about the influences that helped shape that narrative. The tension or conflict of differing narratives can be “opportunities for innovation”.
Research Paradigm
Research paradigms are the assumptions, norms, and standards that underpin different approaches to research. Essentially, research paradigms are the ‘worldview’ that inform research. It is valuable for researchers, both qualitative and quantitative, to understand what paradigm they are working within because understanding the theoretical basis of research paradigms allows researchers to understand the strengths and weaknesses of the approach being used and adjust accordingly. Different paradigms have different ontology and epistemologies . Ontology is defined as the "assumptions about the nature of reality” whereas epistemology is defined as the “assumptions about the nature of knowledge” that inform the work researchers do. It is important to understand the ontological and epistemological foundations of the research paradigm researchers are working within to allow for a full understanding of the approach being used and the assumptions that underpin the approach as a whole. Further, it is crucial that researchers understand their own ontological and epistemological assumptions about the world in general because their assumptions about the world will necessarily impact how they interact with research. A discussion of the research paradigm is not complete without describing positivist, postpositivist, and constructivist philosophies.
Positivist vs Postpositivist
To further understand qualitative research, we need to discuss positivist and postpositivist frameworks. Positivism is a philosophy that the scientific method can and should be applied to social as well as natural sciences. Essentially, positivist thinking insists that the social sciences should use natural science methods in its research which stems from positivist ontology that there is an objective reality that exists that is fully independent of our perception of the world as individuals. Quantitative research is rooted in positivist philosophy, which can be seen in the value it places on concepts such as causality, generalizability, and replicability.
Conversely, postpositivists argue that social reality can never be one hundred percent explained but it could be approximated. Indeed, qualitative researchers have been insisting that there are “fundamental limits to the extent to which the methods and procedures of the natural sciences could be applied to the social world” and therefore postpositivist philosophy is often associated with qualitative research. An example of positivist versus postpositivist values in research might be that positivist philosophies value hypothesis-testing, whereas postpositivist philosophies value the ability to formulate a substantive theory.
Constructivist
Constructivism is a subcategory of postpositivism. Most researchers invested in postpositivist research are constructivist as well, meaning they think there is no objective external reality that exists but rather that reality is constructed. Constructivism is a theoretical lens that emphasizes the dynamic nature of our world. “Constructivism contends that individuals’ views are directly influenced by their experiences, and it is these individual experiences and views that shape their perspective of reality”. Essentially, Constructivist thought focuses on how ‘reality’ is not a fixed certainty and experiences, interactions, and backgrounds give people a unique view of the world. Constructivism contends, unlike in positivist views, that there is not necessarily an ‘objective’ reality we all experience. This is the ‘relativist’ ontological view that reality and the world we live in are dynamic and socially constructed. Therefore, qualitative scientific knowledge can be inductive as well as deductive.”
So why is it important to understand the differences in assumptions that different philosophies and approaches to research have? Fundamentally, the assumptions underpinning the research tools a researcher selects provide an overall base for the assumptions the rest of the research will have and can even change the role of the researcher themselves. For example, is the researcher an ‘objective’ observer such as in positivist quantitative work? Or is the researcher an active participant in the research itself, as in postpositivist qualitative work? Understanding the philosophical base of the research undertaken allows researchers to fully understand the implications of their work and their role within the research, as well as reflect on their own positionality and bias as it pertains to the research they are conducting.
Data Sampling
The better the sample represents the intended study population, the more likely the researcher is to encompass the varying factors at play. The following are examples of participant sampling and selection:
Purposive sampling- selection based on the researcher’s rationale in terms of being the most informative.
Criterion sampling-selection based on pre-identified factors.
Convenience sampling- selection based on availability.
Snowball sampling- the selection is by referral from other participants or people who know potential participants.
Extreme case sampling- targeted selection of rare cases.
Typical case sampling-selection based on regular or average participants.
Data Collection and Analysis
Qualitative research uses several techniques including interviews, focus groups, and observation. [1] [2] [3] Interviews may be unstructured, with open-ended questions on a topic and the interviewer adapts to the responses. Structured interviews have a predetermined number of questions that every participant is asked. It is usually one on one and is appropriate for sensitive topics or topics needing an in-depth exploration. Focus groups are often held with 8-12 target participants and are used when group dynamics and collective views on a topic are desired. Researchers can be a participant-observer to share the experiences of the subject or a non-participant or detached observer.
While quantitative research design prescribes a controlled environment for data collection, qualitative data collection may be in a central location or in the environment of the participants, depending on the study goals and design. Qualitative research could amount to a large amount of data. Data is transcribed which may then be coded manually or with the use of Computer Assisted Qualitative Data Analysis Software or CAQDAS such as ATLAS.ti or NVivo.
After the coding process, qualitative research results could be in various formats. It could be a synthesis and interpretation presented with excerpts from the data. Results also could be in the form of themes and theory or model development.
Dissemination
To standardize and facilitate the dissemination of qualitative research outcomes, the healthcare team can use two reporting standards. The Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research or COREQ is a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. The Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR) is a checklist covering a wider range of qualitative research.
Examples of Application
Many times a research question will start with qualitative research. The qualitative research will help generate the research hypothesis which can be tested with quantitative methods. After the data is collected and analyzed with quantitative methods, a set of qualitative methods can be used to dive deeper into the data for a better understanding of what the numbers truly mean and their implications. The qualitative methods can then help clarify the quantitative data and also help refine the hypothesis for future research. Furthermore, with qualitative research researchers can explore subjects that are poorly studied with quantitative methods. These include opinions, individual's actions, and social science research.
A good qualitative study design starts with a goal or objective. This should be clearly defined or stated. The target population needs to be specified. A method for obtaining information from the study population must be carefully detailed to ensure there are no omissions of part of the target population. A proper collection method should be selected which will help obtain the desired information without overly limiting the collected data because many times, the information sought is not well compartmentalized or obtained. Finally, the design should ensure adequate methods for analyzing the data. An example may help better clarify some of the various aspects of qualitative research.
A researcher wants to decrease the number of teenagers who smoke in their community. The researcher could begin by asking current teen smokers why they started smoking through structured or unstructured interviews (qualitative research). The researcher can also get together a group of current teenage smokers and conduct a focus group to help brainstorm factors that may have prevented them from starting to smoke (qualitative research).
In this example, the researcher has used qualitative research methods (interviews and focus groups) to generate a list of ideas of both why teens start to smoke as well as factors that may have prevented them from starting to smoke. Next, the researcher compiles this data. The research found that, hypothetically, peer pressure, health issues, cost, being considered “cool,” and rebellious behavior all might increase or decrease the likelihood of teens starting to smoke.
The researcher creates a survey asking teen participants to rank how important each of the above factors is in either starting smoking (for current smokers) or not smoking (for current non-smokers). This survey provides specific numbers (ranked importance of each factor) and is thus a quantitative research tool.
The researcher can use the results of the survey to focus efforts on the one or two highest-ranked factors. Let us say the researcher found that health was the major factor that keeps teens from starting to smoke, and peer pressure was the major factor that contributed to teens to start smoking. The researcher can go back to qualitative research methods to dive deeper into each of these for more information. The researcher wants to focus on how to keep teens from starting to smoke, so they focus on the peer pressure aspect.
The researcher can conduct interviews and/or focus groups (qualitative research) about what types and forms of peer pressure are commonly encountered, where the peer pressure comes from, and where smoking first starts. The researcher hypothetically finds that peer pressure often occurs after school at the local teen hangouts, mostly the local park. The researcher also hypothetically finds that peer pressure comes from older, current smokers who provide the cigarettes.
The researcher could further explore this observation made at the local teen hangouts (qualitative research) and take notes regarding who is smoking, who is not, and what observable factors are at play for peer pressure of smoking. The researcher finds a local park where many local teenagers hang out and see that a shady, overgrown area of the park is where the smokers tend to hang out. The researcher notes the smoking teenagers buy their cigarettes from a local convenience store adjacent to the park where the clerk does not check identification before selling cigarettes. These observations fall under qualitative research.
If the researcher returns to the park and counts how many individuals smoke in each region of the park, this numerical data would be quantitative research. Based on the researcher's efforts thus far, they conclude that local teen smoking and teenagers who start to smoke may decrease if there are fewer overgrown areas of the park and the local convenience store does not sell cigarettes to underage individuals.
The researcher could try to have the parks department reassess the shady areas to make them less conducive to the smokers or identify how to limit the sales of cigarettes to underage individuals by the convenience store. The researcher would then cycle back to qualitative methods of asking at-risk population their perceptions of the changes, what factors are still at play, as well as quantitative research that includes teen smoking rates in the community, the incidence of new teen smokers, among others.
Copyright © 2024, StatPearls Publishing LLC.
- Introduction
- Issues of Concern
- Clinical Significance
- Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
- Review Questions
Publication types
- Study Guide
- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions
Qualitative Research
What is qualitative research.
Qualitative research is the methodology researchers use to gain deep contextual understandings of users via non-numerical means and direct observations. Researchers focus on smaller user samples—e.g., in interviews—to reveal data such as user attitudes, behaviors and hidden factors: insights which guide better designs.
“ There are also unknown unknowns, things we don’t know we don’t know.” — Donald Rumsfeld, Former U.S. Secretary of Defense
- Transcript loading…
See how you can use qualitative research to expose hidden truths about users and iteratively shape better products.
Qualitative Research Focuses on the “Why”
Qualitative research is a subset of user experience (UX) research and user research . By doing qualitative research, you aim to gain narrowly focused but rich information about why users feel and think the ways they do. Unlike its more statistics-oriented “counterpart”, quantitative research , qualitative research can help expose hidden truths about your users’ motivations, hopes, needs, pain points and more to help you keep your project’s focus on track throughout development. UX design professionals do qualitative research typically from early on in projects because—since the insights they reveal can alter product development dramatically—they can prevent costly design errors from arising later. Compare and contrast qualitative with quantitative research here:
Regarding care with opinions, it’s easy to be subjective about qualitative data, which isn’t as comprehensively analyzable as quantitative data. That’s why design teams also apply quantitative research methods, to reinforce the “why” with the “what”.
Qualitative Research Methods You Can Use to Get Behind Your Users
You have a choice of many methods to help gain the clearest insights into your users’ world – which you might want to complement with quantitative research methods. In iterative processes such as user-centered design , you/your design team would use quantitative research to spot design problems, discover the reasons for these with qualitative research, make changes and then test your improved design on users again. The best method/s to pick will depend on the stage of your project and your objectives. Here are some:
Diary studies – You ask users to document their activities, interactions, etc. over a defined period. This empowers users to deliver context-rich information. Although such studies can be subjective—since users will inevitably be influenced by in-the-moment human issues and their emotions—they’re helpful tools to access generally authentic information.
Structured – You ask users specific questions and analyze their responses with other users’.
Semi-structured – You have a more free-flowing conversation with users, but still follow a prepared script loosely.
Ethnographic – You interview users in their own environment to appreciate how they perform tasks and view aspects of tasks.

Usability testing
Moderated – In-person testing in, e.g., a lab.
Unmoderated – Users complete tests remotely: e.g., through a video call.
Guerrilla – “Down-the-hall”/“down-and-dirty” testing on a small group of random users or colleagues.

User observation – You watch users get to grips with your design and note their actions, words and reactions as they attempt to perform tasks.

Qualitative research can be more or less structured depending on the method.
Qualitative Research – How to Get Reliable Results
Some helpful points to remember are:
Participants – Select a number of test users carefully (typically around 5). Observe the finer points such as body language. Remember the difference between what they do and what they say they do.
Moderated vs. unmoderated – You can obtain the richest data from moderated studies, but these can involve considerable time and practice. You can usually conduct unmoderated studies more quickly and cheaply, but you should plan these carefully to ensure instructions are clear, etc.
Types of questions – You’ll learn far more by asking open-ended questions. Avoid leading users’ answers – ask about their experience during, say, the “search for deals” process rather than how easy it was. Try to frame questions so users respond honestly: i.e., so they don’t withhold grievances about their experience because they don’t want to seem impolite. Distorted feedback may also arise in guerrilla testing, as test users may be reluctant to sound negative or to discuss fine details if they lack time.
Location – Think how where users are might affect their performance and responses. If, for example, users’ tasks involve running or traveling on a train, select the appropriate method (e.g., diary studies for them to record aspects of their experience in the environment of a train carriage and the many factors impacting it).
Overall, no single research method can help you answer all your questions. Nevertheless, The Nielsen Norman Group advise that if you only conduct one kind of user research, you should pick qualitative usability testing, since a small sample size can yield many cost- and project-saving insights. Always treat users and their data ethically. Finally, remember the importance of complementing qualitative methods with quantitative ones: You gain insights from the former; you test those using the latter.
Learn More about Qualitative Research
Take our course on User Research to see how to get the most from qualitative research.
Read about the numerous considerations for qualitative research in this in-depth piece.
This blog discusses the importance of qualitative research , with tips.
Explore additional insights into qualitative research here .
Literature on Qualitative Research
Here’s the entire UX literature on Qualitative Research by the Interaction Design Foundation, collated in one place:
Learn more about Qualitative Research
Take a deep dive into Qualitative Research with our course User Research – Methods and Best Practices .
How do you plan to design a product or service that your users will love , if you don't know what they want in the first place? As a user experience designer, you shouldn't leave it to chance to design something outstanding; you should make the effort to understand your users and build on that knowledge from the outset. User research is the way to do this, and it can therefore be thought of as the largest part of user experience design .
In fact, user research is often the first step of a UX design process—after all, you cannot begin to design a product or service without first understanding what your users want! As you gain the skills required, and learn about the best practices in user research, you’ll get first-hand knowledge of your users and be able to design the optimal product—one that’s truly relevant for your users and, subsequently, outperforms your competitors’ .
This course will give you insights into the most essential qualitative research methods around and will teach you how to put them into practice in your design work. You’ll also have the opportunity to embark on three practical projects where you can apply what you’ve learned to carry out user research in the real world . You’ll learn details about how to plan user research projects and fit them into your own work processes in a way that maximizes the impact your research can have on your designs. On top of that, you’ll gain practice with different methods that will help you analyze the results of your research and communicate your findings to your clients and stakeholders—workshops, user journeys and personas, just to name a few!
By the end of the course, you’ll have not only a Course Certificate but also three case studies to add to your portfolio. And remember, a portfolio with engaging case studies is invaluable if you are looking to break into a career in UX design or user research!
We believe you should learn from the best, so we’ve gathered a team of experts to help teach this course alongside our own course instructors. That means you’ll meet a new instructor in each of the lessons on research methods who is an expert in their field—we hope you enjoy what they have in store for you!
All open-source articles on Qualitative Research
How to do a thematic analysis of user interviews.

- 1.2k shares
- 3 years ago
How to Visualize Your Qualitative User Research Results for Maximum Impact

- 2 years ago
Creating Personas from User Research Results

Best Practices for Qualitative User Research

Card Sorting

Contextual Interviews and How to Handle Them

Understand the User’s Perspective through Research for Mobile UX

- 10 mths ago
Ethnography
7 simple ways to get better results from ethnographic research.

Semi-structured qualitative studies
Pros and cons of conducting user interviews.

Workshops to Establish Empathy and Understanding from User Research Results

How to Moderate User Interviews

- 4 years ago
Question Everything

Adding Quality to Your Design Research with an SSQS Checklist
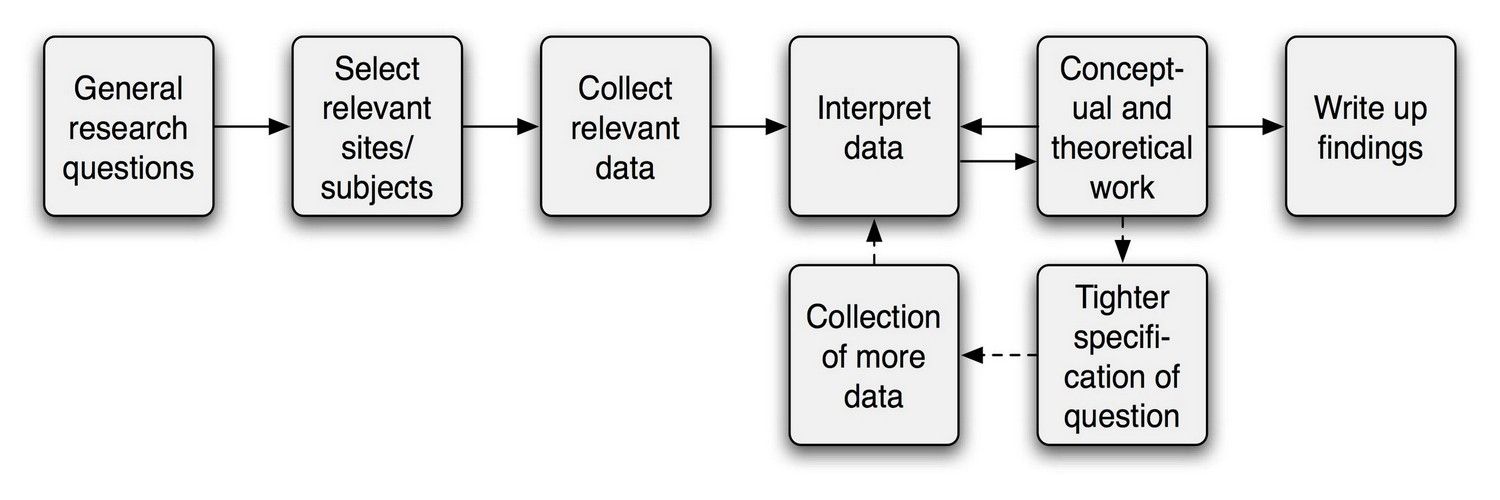
- 8 years ago
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this page , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.

Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share the knowledge!
Share this content on:
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this page.
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
300 Qualitative Research Topics For Easy Academic Victory

You are on the right page if you are looking for a perfect qualitative research topic and have difficulty finding it.
Writing a qualitative research paper is not a piece of cake. Let alone the research and writing; the first and most significant challenge is finding the qualitative research topic that is a perfect fit for you. You have to be sure about a handful of things to decide the best topic for you, and you can ace it. First and most important, you must choose a topic that you find appealing and motivating. If you are not interested in a topic, not only will it tire you, but it will make your research dull and exhausting as well. Two, choose a relevant topic that adds value to the academia. Last but not least, there must be enough data about the theme that you are about to choose. In case of any confusion, concerns, or questions, you can consult for paper writing help from Paper Perk .
Table of Contents
Qualitative Research Topics: Psych, Education, Health, Medicine & More
Wandering around the internet looking for qualitative research topics can be exhausting. We are writing this article to make it a one-stop solution for you. There is enough inspiration to come up with the most suitable topic for you, no matter your academic area.
Psychological Qualitative Research Topics
- Emotional Intelligence: Can it be an excellent alternative to IQ?
- Oxytocin in autistic children.
- Meditation: A means to control emotions
- Emotional dependency during pregnancy
- Schizophrenia: Causes and treatment
- Post-traumatic stress disorder: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
- Psychology of physical attraction in opposite sexes
- What is a borderline personality disorder? Facts and myths
- Psychological elements in electronic media: Marketing, persuasion, and propaganda
- Psychology in public relations
- Psychology in international relations
- Causes of depression and what to do to avoid it?
- Detailed analysis of speech disorders
- Criminal psychology and the origin of serial killers
- Psychological aspects of the aging process
- The character of NGOs regarding awareness about mental health
- How to prevent child abuse with the help of psychology?
- Aspects of criminal psychology
- Emotional imbalance: Causes, symptoms, and treatment
- Memory loss? Is it a neural problem or a psychological problem?
- The secrets to well-being
- Mental disorders in teens
Read More: Psychology Research Paper Topics
Political Qualitative Research Topics

- What role did masons’ living conditions have in forming workers’ political movements ?
- How do presidential elections matter?
- Political compass: A critical analysis
- Is a representative democracy genuinely democratic?
- How has Europe evolved in terms of democracy?
- Democratic evolution in the United States in the last three centuries
- Is democracy a myth or a reality?
- Why is voter abstention a danger to democracy?
- Role of minorities in the United States politics
- Freedom of expression in developing countries
- Freedom of expression under Islamist regimes
- Misconduct on television: Awareness and Legislation
Read More: Political Science Research Topics
Qualitative Research Topics for Art and Culture

- Is history a universally shared concept?
- Can a man be indifferent to art?
- How do we articulate the link between science and technology?
- What is the purpose of art?
- What does the artist show us? Expression and symbolism
- What is an artist? What does an artist do?
- What is an artist?
- Is art always transgressive?
- Work of art: The proof of the freedom of the spirit
- Can art compete with nature?
- Does art only have the function of freeing us from our passions?
- Passion and emotion in art
- Absurd surrealism
- Grotesque surrealism
- Different movements in art
- Progress and evolution of art
- The art of the middle ages
- The art of the renaissance
- Is the work of art necessarily beautiful?
- Does art change our relationship with reality?
- Does the critic able to regard something as art or not?
- Does the experience of beauty necessarily pass through the work of art?
- Things that art teaches us, artists, as a technician
- Importance of meaning in a work of art
- Meaningless art and absurdist existentialism
- The need for a model in the production of art
- Can we conceive of a society without art?
- Different aspects of society are defined and differentiated by art
- The fear of industrial production among the artists
- Dystopian art: The ability to predict the future among artists
- Elements that distinguish the work of art from any object
- Why the artists deserve a special place in the world
- Rules and regulations in art
- Reproduction of art: Plagiarism in art and harm of repetition
- Art and escapism
- Anachronistic art and the element of satire
- Should the artist seek to please the audience
- Can we blame a work of art for not being worth anything?
- Does every human being understand and appreciate art?
- Do you think that, according to Aristotle’s formula, art is an “imitation of nature”?
- Why does what we dislike in life please us in a work of art?
- Does art seem to be a “revolt against the tyranny of desire”?
- Why do we apply the term “creation” to artistic activity?
- Sacrosanctity of art and human duty to uphold it
Read More: Music Research Topics
Qualitative Research Topics Involving Environment Issues

- Advantages and disadvantages of technology for the environment
- Benefits of environmental education in children
- Methods to make modern society aware of the environment
- Alternative energies
- Nuclear energy production: An alternative to the planet’s growing energy demand
- X degree care for the environment
- Analyze the advantages and disadvantages of the different types of renewable energy
- Need to develop environmentally friendly products
- Documentation of experience: Protection of nature
- Elements involved in environmental deterioration
- Environment and strategies for sustainability
- Environmental activism in adolescents and young people
- Sustainability and security for environmental justice
- Raising awareness about the protection of the environment through sports, literature, and culture
- Environment influenced by collective and individual actions
- Awareness of the advantages and disadvantages of the use of technologies
- Effects and causes of acid rain and groundwater
- Ways to live sustainably or focus on a specific aspect of sustainability
- Recent disasters caused by global warming
- Greenhouse effect and melting ice
- Importance of renewable energy
- Wildlife and endangered species
- Air quality and pollution
- Water quality in underdeveloped countries
- Famines caused by environmental changes
- Various recycling programs: Which one is the most effective
- Awareness to participate in the initiatives about the protection of the environment
- How deforestation has affected animals or how it is related to climate change
- Importance of the coral reef, the dangers of its destruction, or preservation strategies
Read More: Best Legal Research Paper Topics
Qualitative Research Topics on Public Relations

- Public Relations and socio-productive activity
- Organizational Communication and Public Relations
- Ethics in the practice of Public Relations
- Epistemological foundations of Public Relations.
- Factors that limit the practice of Public Relations.
- Public Relations is a strategic factor of the company.
- Relationship workers and professional practice in the United States
- Corporate image and Public Relations
- Corporate identity and Public Relations.
- Public Relations and social enterprise
- Public Relations as an integration factor.
- Profile of the teacher of Public Relations.
- Legislation of Public Relations in Europe
- The free exercise of Public Relations
- Public Relations and the labor market
- Public Relations and digital communication
- History of Public Relations in Europe
- History of Public Relations in the United States
- History of Public Relations in Canada
- Semiology and Public Relations
- Linguistics and Public Relations
- Indicators to evaluate Public Relations programs
- Planning of Public Relations in organizations
- Public Relations through radio and television
- University teaching in Public Relations
Read More: Criminal Justice Research Paper Topics
Qualitative Research Topics for High School Students

- How has technological development helped hospitals?
- Benefits of technological advances in the classroom
- Advantages and disadvantages of technology in children
- How and why are fun activities different during every stage of the educational period, Montessori, school, college, and university?
- Most dangerous challenges that must be avoided as students
- Challenges made by celebrities: How do future career choices and jobs look for you in the next decade?
- The pros and cons of viral challenges from Tiktok and reels
- How/what do social networks help?
- Disadvantages of social networks
- Problems of social network in adolescents
- What is the most suitable age for children to have a social media presence?
- Toxic behaviors accompanied by social media: Prevention and Solution
Read More: Chemistry Research Topics
Educational Qualitative Research Topics

- History of education
- How education has changed over time in one place
- Importance of sports and games in early childhood education
- Possible results of adding playtime to education
- Pros and cons of a grading system
- Most effective grading methods
- How tests affect the success or mental health of students
- Assessment methods: Such as standardized tests or open tests
- Investigate how dress codes affect student performance
- Different schools of learning
- Qualities that effective teachers possess
- Effects of teaching and lesson planning
- Different approaches of public and private schools
- Pros or cons of a charter school systems
- How class size and number of students affect student performance
- Qualities of an Effective Teacher
- The length of the school day, or the length of breaks, and how the durations affect the progress of the students
- How the start time of school affects performance
Read More: Biology Research Paper Topics
Qualitative Research Topics for Business and Economy
- The chartered accountant and the client: what relationship today?
- How does the arrival of the low-cost accountant change differentiation practices in accounting?
- Law and accounting: how do the new laws impact the profession of a chartered accountant?
- Accountants, why are they so difficult to recruit?
- How does accounting make it possible to assess the state of health of a company?
- Accounting and new technologies: the future or the end of the accountant?
- Can inequalities be reduced with new technologies?
- What distribution of wealth in France (or other)?
- Why do companies relocate?
- Protectionism or free trade?
- Has the organization of work changed after the pandemic?
- Do flexibility and home-working reduce unemployment?
- Should we be afraid of financial bubbles?
- Financial crises, similar cogs? Are we headed to a new recession?
- What is money, and who creates it?
- The stock market against growth?
- How does economic growth lead to sustainable development?
- What is the impact of innovation on growth?
- What role does investment play?
- What are the keys to productivity?
- Is it possible to measure economic growth?
- Why do stock markets crash?
Read More Law / Legal Research Paper Topics
Medical Qualitative Research Topics

- Current situation of palliative care in health institutions in the United States
- Complications of acute diarrheal disease in children under five years of age
- Nutritional status of surgical oncology patients and its relationship with postoperative complications
- Cost-effectiveness of cervical cancer screening strategies in California
- Thyroid cancer and risk factors in patients treated at San Jose Hospital
- Communicative processes in American ancestral medicine
- Seronegative rheumatoid arthritis in a patient with a pulmonary septic complication
- Telemedicine and Tele-health of the inhabitants of Massachusetts
- Feasibility study and technical, infrastructure and human sustainability for the implementation of the care model
- Epidemiological profile of the general surgery outpatient service
- Physical activity and sport as determinants of health
- Cost of treatment and follow-up of people with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
- National Health System for the formal introduction of the family doctor
- How is the social security system in France unsustainable?
- Comparative study of health systems in the United States and Europe?
- Allergies and intolerances, what are the differences for lactose?
- Is gluten intolerance an actual disease?
- Social inequalities in health in rural countries
- Public health policy or health policy
- Public health at the European level, what public policies
- Public health in developing countries
- Public health and environmental issues through the prism of red meat consumption
- Communication of medicines when advertising is prohibited
Related: Medical research paper writing services
Qualitative Research Topics for Law and Crime
- Consequences of the death penalty.
- Capital offenses: Law, persecution, and penalties
- Classic methods used in the death penalty
- Arguments for or against this punishment
- The stipulation for others and the promise of a stronghold
- Consumer protection in the American Law
- The social attributions of the captain of the ship
- Recent developments in the constitutional justice
- Reframing the civil code
- Critical analysis of the scope of the principle of free justice
- Institutions of the criminal records
- Equality of the creditors in collective proceedings
- Risk management in expertise
- The repressive jurisdiction of the court of peace in the event of insufficiency of the judges
- Labor law and the rights of workers
- Secularism and labor law: Question of religion in business
- The Management of transit migration
- The legal framework of bank credit
- Legal regime of intellectual rights
- Compensation for moral damage
- Family criminal law in the relation between parents and children
- Unilateral termination of the contract
- Role of the military in public prosecution
- Critical analysis of the pre-jurisdictional procedure regarding human rights
- The fault of the administration in land matters
- The subsequent attitude of the victim and compensation for the damages
- Action for retrocession in the event of excessive liberalities
- The exploitation of child labor under Labor Law
- Reflection on the introduction of the system of the dematerialization of bearer shares
- Study on the feasibility of a structure for the amicable settlement of consumer disputes
- The life insurance contract
- Legal liability of the community pharmacist
- The legal age of marriage: legislative, jurisprudential, and doctrinal approach
- Protection of the unpaid seller in the event of insolvency of the buyer
- The renewal of the employment contract
- The regulatory framework for outdoor advertising, signs, and pre-sign
- Extra-judicial resolution of land disputes
Read More: Research Paper Topics
Qualitative Research Topics Concerning Drug Abuse

- Drug use in adolescents
- Consequences of excessive drug use
- Legal and illegal addictive substances
- Effects of drugs on the brain
- Effects of alcohol and tobacco
- Social science research on drugs
- Psychological research on drugs
- Biomedical research in the field of drugs
- Drug addiction treatment
- Cannabis in Europe: a study of social research
- Drug expectations
- Dynamics of drug cartels: Perception, politics, and markets
- Sources and uses of methamphetamine
- Sensation seeking
- Contribution of research in psychology on drugs
- Drug research: recent developments
- in the field of psychology
- Places of cannabis consumption
- Drug prevention for the most vulnerable young people
- Cannabis retail markets
- Cultivation of cannabis at home
- Cannabis Dependence and the Strength of Marijuana
- Cannabis and youth
- Cannabis and schizophrenia
Read More: Social Work Research Topics
Women Issues and Rights Qualitative Research Topics

- How to educate teens about pregnancy
- Women’s rights violations in the middle east
- Forced-Hijab conflict in Iran
- How to live a healthy pregnancy period
- Access to health is a fundamental right: what role can parliaments play in ensuring health for women and children?
- The wave of feminist movements in the Middle East
- The situation of women and children in times of conflict
- The role of women parliamentarians in the prevention of national and international terrorism and in the promotion of peace
- Promoting women’s participation and gender equality in multilateral negotiations
- The contribution of women to the establishment of a new global financial and economic model
- Feminism in Egypt
- Impact of the media on the status of women and image of women politicians in the media
- Poverty and extreme poverty: women as victims of this phenomenon and as key actors in the fight to eradicate it
- Complementarity of women’s rights and children’s rights
- Health and well-being of older people, especially women
- Women in Armed Conflict
- Feminism in the South Asian Subcontinent
- Violence against women
- Role of women in ensuring environmental protection within the framework of development
- Women in the informal economic sector and their access to microcredits
- Women in economic life and the world of work
- Impact of women on the democratic process
- Women in the political process
- Women’s rights violations in Africa
- Financing women’s electoral campaigns
- Women’s political and electoral training
- Women in political parties
- United Nations Initiatives for Women’s Education and the role of Malala Yousafzai
- Women in national parliaments
- The partnership between men and women in politics
Still feel the need to know more? It is noble to be insatiable about knowledge, so here are 402 More Research Paper Topics for you.
As we said in the beginning, writing a qualitative research paper is not a piece of cake. But after reading all these topics above, you now know that it is not rocket science either. All you need is a little commitment and a pint of inspiration potion that we have above 300 research paper topics.
If you still need professional qualitative research writing services, you can get to know our writers or contact us. We are online 24/7 with immediate responses to offer you research paper help .
Order Original Papers & Essays
Your First Custom Paper Sample is on Us!
Timely Deliveries
No Plagiarism & AI
100% Refund
Try Our Free Paper Writing Service
Related blogs.

Connections with Writers and support
Privacy and Confidentiality Guarantee
Average Quality Score
- Open access
- Published: 03 April 2024
The environmental awareness of nurses as environmentally sustainable health care leaders: a mixed method analysis
- Olga María Luque-Alcaraz ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1598-1422 1 , 2 , 3 , 5 ,
- Pilar Aparicio-Martínez ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2940-8697 3 , 4 ,
- Antonio Gomera ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0603-3017 2 &
- Manuel Vaquero-Abellán ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0602-317X 2 , 3 , 4
BMC Nursing volume 23 , Article number: 229 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
239 Accesses
6 Altmetric
Metrics details
People worldwide are concerned with the possibility of climate change, microplastics, air pollution, and extreme weather affecting human health. Countries are implementing measures to reduce environmental impacts. Nurses play a vital role, primarily through Green Teams, in the process of promoting sustainable practices and minimizing the environmental footprint of health care facilities. Despite existing knowledge on this topic, assessing nurses’ environmental awareness and behavior, including the barriers they face, is crucial with regard to improving sustainable health care practices.
To analyze the environmental awareness and behavior of nurses, especially nurse leaders, as members of the Green Team and to identify areas for improvement with regard to the creation of a sustainable environment.
A sequential mixed-method study was conducted to investigate Spanish nurses. The study utilized an online survey and interviews, including participant observation. An online survey was administered to collect quantitative data regarding environmental awareness and behavior. Qualitative interviews were conducted with environmental nurses in specific regions, with a focus on Andalusia, Spain.
Most of the surveyed nurses ( N = 314) exhibited moderate environmental awareness (70.4%), but their environmental behavior and activities in the workplace were limited (52.23% of participants rarely performed relevant actions, and 35.03% indicated that doing so was difficult). Nurses who exhibited higher levels of environmental awareness were more likely to engage in sustainable behaviors such as waste reduction, energy conservation, and environmentally conscious purchasing decisions ( p < 0.05). Additionally, the adjusted model indicated that nurses’ environmental behavior and activities in the workplace depend on the frequency of their environmental behaviors outside work as well as their sustainable knowledge ( p < 0.01). The results of the qualitative study ( N = 10) highlighted certain limitations in their daily practices related to environmental sustainability, including a lack of time, a lack of bins and the pandemic. Additionally, sustainable environmental behavior on the part of nursing leadership and the Green Team must be improved.
Conclusions
This study revealed that most nurses have adequate knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors related to environmental sustainability both inside and outside the workplace. Limitations were associated with their knowledge and behaviors outside of work. This study also highlighted the barriers and difficulties that nurses face in their attempts to engage in adequate environmental behaviors in the workplace. Based on these findings, interventions led by nurses and the Green Team should be developed to promote sustainable behaviors among nurses and address the barriers and limitations identified in this research.
Graphical Abstract
Peer Review reports
Introduction
The impact of climate change on human society is a global concern, especially with regard to microplastics, resource shortages, air pollution, droughts, and extreme weather. Such consequences affect human health both directly and indirectly, resulting in an increase in pathologies and a deterioration in medical attention [ 1 , 2 ]. In this context, diverse measures aimed at reducing the environmental impact of daily activities and minimizing the ecological footprint thereof [ 3 ] have been implemented by multiple countries [ 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 ]; these activities have been framed as environmental regulations in line with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) [ 8 ].
The SDGs are being integrated into governments and a variety of other contexts, including the health care system. Spain is dedicated to such a goal, i.e., that of promoting a greener and more democratic health care transition. To achieve this goal, strategic plans have been developed to mitigate the effects of climate change [ 9 , 10 ]. One specific such program is the Strategic Health and Environment Plan (PESMA) [ 11 ], whose aim is to enhance the synergy between health and the environment innovatively by assessing the impact of the population in terms of 14 environmental indicators [ 12 ].
One such indicator focuses on the resources and support needed for sustainable practices, especially for nurses, due to the impact of the environment on their work [ 13 , 14 ]. The PESMA highlights the fact that health care providers should be included in strategies to reduce carbon footprints, build resilience to address the challenges associated with climate change and embrace a leadership role in the task of promoting sustainable health care practices [ 13 , 14 , 15 , 16 ]. Another critical aspect of PESMA focuses on education, training, and incentives that can promote sustainable behavior among health care workers, especially nurses [ 17 , 18 ]. As frontline health care workers, nurses have a unique opportunity to advocate for sustainable practices and reduce the environmental impact of the health care system. Nurses’ knowledge and behavior are limited despite the fact that nurses have positive attitudes toward environmental sustainability [ 19 ].
This situation stands in contrast to the role of nurses in the creation of more sustainable hospitals via the “Green Team” [ 20 ]. The Green Team, which originated in the United States of America a decade ago, is a committee that is responsible for finding and implementing sustainability projects to decrease the environmental impacts of daily operations. Members of various departments collaborate with sustainability staff to detect opportunities, spread awareness, and promote staff involvement in line with the Committee’s mission [ 21 ]. The team, which typically consists of and is led by nurses, aims to increase awareness of the health care industry’s effect on the environment and to develop tactics to mitigate the adverse environmental effects of hospitals.
In Spain, Green Teams, which span multiple disciplines and usually led by nursing professionals, are committed to sustainable change in health care [ 22 ]. Environmental nursing leaders on Green Teams control environmental sustainability in health care settings and provide education, resources, and support to other professionals with regard to the implementation of sustainable practices [ 23 ]. Accordingly, all nurses can contribute to the tasks of mitigating the impact of climate change on public health outcomes and promoting sustainable health for all [ 24 ]. These actions improve nurses’ knowledge, attitudes, and behavior in terms of sustainability and promote sustainable practices in health care settings, thus leading to a better understanding of the barriers faced by nurses in this context [ 24 , 25 , 26 ].
However, measuring and identifying nurses’ environmental awareness is essential for the promotion of sustainable hospitals [ 27 , 28 ]. Multidimensional indicators have been proposed for this purpose [ 16 ], the responsibility for which lies with nurse leaders on Green Teams. Nurses are responsible for promoting sustainability in health care organizations, as discussed by Kallio et al. (2018) [ 29 ], as well as for promoting nursing competencies related to environmental sustainability [ 30 ]. Several studies, including Harris et al. (2009) and Phiri et al. (2022), have examined nurses’ roles in environmental health and the effects of their leadership on the promotion of sustainability, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, thereby emphasizing the importance of leadership [ 31 , 32 ].
As Ojemeni et al. (2019) discussed, leadership effectiveness in Green Teams, nursing teams and health care organizations must prioritize quality control and health care improvement to ensure sustainable development [ 33 ].
The topic of environmental management in health care organizations has been studied extensively, and an environmental or ecological model of care for promoting sustainability has been proposed [ 34 ]. As environmental creators and leaders on Green Teams, nurses are vital for minimizing hazardous waste in health care settings and improving awareness [ 35 ].
Although nurses have some degree of existing knowledge and awareness of sustainability, it is crucial to assess their proficiency in environmental matters and to gauge their environmental awareness. Such an evaluation can help identify areas for improvement within clinical management units [ 20 , 33 , 36 ]. Education and training programs can effectively promote sustainable behavior among nurses, but interventions should also address the barriers they face in their attempts to implement sustainable practices [ 37 ]. Therefore, it is imperative to examine the factors that foster sustainable behavior among nurses and to identify effective interventions that can promote sustainable health care practices and minimize the environmental footprint of health care facilities. Accordingly, this study aimed to analyze the environmental awareness and behavior of nurses, especially nurse leaders, as members of the Green Team and to identify areas for improvement with regard to creating a sustainable environment.
Study design
A sequential mixed-method study was conducted based on an online survey and interviews with a representative sample of Spanish nurses, including participant observation.
The study was divided into two phases. In the first phase, a cross-sectional, descriptive exploratory analysis was performed; this analysis relied on the results revealed using the Nurse’s Environmental Awareness Tool in Spanish (NEAT-es) [ 38 ], which was divided into three subscales: nursing awareness scale (NAS), environmental behaviors outside the workplace (PEB) and sustainable behaviors in the workplace (NPEB). In the second phase, qualitative interviews with environmental nurses (see Supplementary file 1 ) were conducted in regions featuring specific environmental units that were available in person (Andalusia).
Participants
The participants were recruited from public and private institutions associated with the National Health System, particularly from the nursing staff. The scope of the study focused on Spain, and the sample included all the nursing staff who completed the questionnaire and met the inclusion criteria.
The sampling process focused on the population of nurses in Spain in 2020, which was estimated to consist of 388,153 nurses. Therefore, a random sample of 314 participating individuals was sufficient to estimate the population with 95% confidence and an accuracy of +/- 2% units, which was expected to account for approximately 90% of the overall population. The inclusion and exclusion criteria used for the sample focused on nursing staff, nursing care auxiliary technicians, and students with relevant degrees, as this members of this group have the most significant presence in the health system and engage in direct and daily contact with environmental management in health centers (hospitals, primary care centers, sociosanitary centers and others). The remaining health and nonhealth personnel were excluded.
Additionally, the person from each unit who served as the environmental coordinator and other nurses from the ward who were members of the Green Team were asked to participate in the interviews and observations. The environmental coordinators, most of who were nursing supervisors, were determined based on the number of members of the Green Team and the sampling calculation used for the observational study. The interviews took place after various sessions, talks, or courses pertaining to environmental sustainability at the clinical management units.
Data collection
An intentional sampling process was implemented, and the data collection period spanned from November 2019 to March 2021. The observational data were collected in Spain via messages and posts on social media with the goal of quantifying nurses’ environmental awareness.
The initial sample of qualitative study included five environmental nursing leaders (NLs), 14 registered nurses (RNs), and ten nursing undergraduates. The final sample was reduced when the interviews reached data saturation ( N = 10, five NLs, and five RNs). Before the interviews, a focal group composed of one nurse, one physician, two engineers and a psychologist was tested using the questions included in this research as part of a pilot study ( Supplementary file 1 ). These interviews were conducted at the beginning of the participant’s shift, usually in the morning, and they featured a median time of 30 min, a minimum of 20 min and a maximum of one hour per participant.
One researcher (O.A.L.) also observed nurses during their daily work after the interview from a position within the ward as an added team member or staff member. Nevertheless, the observer did not highlight mistakes or sustainability issues during the observation process. No other researcher was involved in this step of the ethnographic analysis to avoid bias with regard to observing a variety of tasks ranging from preparing medication to implementing treatments.
The data collected through the interviews were recorded on a Samsung Galaxy 31 A, and observations were collected in a field notebook based on the Google Keep and Evernote mobile applications from November 2019 to mid-March 2021. This study was conducted at a regional level 1 hospital in southern Spain, particularly in various clinical management units (neurosurgery, internal medicine, cardiology, traumatology, and COVID-19 units, among others), and it focused on nursing supervisors, who are the leaders who bear responsibility for environmental awareness (NLs), and registered nurses (RNs) who were members of the Green Team.
Data analysis
The quantitative data were analyzed by reference to descriptive statistics, including the mean, standard deviation (SD), and 95% confidence interval (CI); the relative frequencies of the variables were also analyzed. Normalization tests, Kolmogorov‒Smirnov tests with Lilliefors correction, and Q‒Q tests were used to compare the goodness-of-fit to an average data distribution with regard to continuous or discrete quantitative variables. The comparison of two or three independent means was performed using Student’s t test and analyses of variance for each variable. The Χ 2 test with Yates’ correction was used to compare percentages and Pearson’s correlation (r) coefficients across the quantitative variables. Finally, associations among the NPEB and the other variables were studied through multiple linear regression. Participant observation was used to support the qualitative study of the reflective ethnographic type [ 39 , 40 ], and this process ended when the data reached saturation. Two researchers developed transcripts for the interviews based on the recorded interviews and added descriptions based on the notes from the field notebook. The identification of themes and patrons was based on a process of triangulation among the researchers and by cross-checking the results. The interviews with nurses were analyzed to summarize the content analysis and identify keywords and concurrency among the terms. The themes thus identified included Green Teams, sustainable environmental behaviors, environment awareness, leadership barriers and limitations and areas for improvement.
EPIDAT (version 4.2) and SPSS (version 25) software were used to support the quantitative analysis. The computer program ATLAS.ti (version 22) and the Office Package with Microsoft Word Excel (version 2019) were used for the interviews and the visualization of the keywords based on the themes identified based on the records, observations and field notebooks.
Nurses’ awareness, knowledge, attitudes and skills.
The ages of the Spanish staff, mainly nurses, included in this study ( N = 314) ranged from 19 to 68, with a mean age of 37.02 ± 12.7, CI = 95%, 35.6–38.4 years); in addition, 76.4% of these participants were women with more than 20 years of working experience (35.1%), and the majority were registered nurses (70.4%). Moreover, 113 (36%) participants worked at a local or regional hospital (30%) and were employees of a public institution (85.3%). Half of the nurses (157) worked only a morning shift (Table 1 ) in Andalusia, Madrid, or Catalonia (62.4%). The diverse autonomous regions on which this research focused were homogenously distributed and structured in line with the population. The analysis of these areas was also based on the specific inclusion of environmental units led by nurses (Andalusia, Madrid, and Catalonia), in contrast with regions featuring undetermined units or leaders related to this topic (such as Valencia) (37.5%).
Regarding nursing awareness, nurses scored higher on the PEB (31.83 ± 8.02 CI 95% 30.94–32.72 with regard to frequency vs. 32.36 ± 7.15 CI 95% 31.57–33.15 with respect to difficulty) than on the NAS (26.13 ± 9.91 CI 95% 25.03–27.23 with regard to knowledge vs. 47.39 ± 5.97 CI 95% 46.73–48.05 with respect to impact) and the NPEB (23.82 ± 6.45 CI 95% 23.10-24.53 with regard to frequency vs. 25.71 ± 6.31 CI 95% 25.01–26.41 with respect to difficulty). These results indicated that environmental knowledge among the Spanish population was limited (55.7%), although the nurses included in this research were aware of their potential impact on the environment (70.4%). The PEB subscale focused mostly on following environmental guidelines in their homes (57.3%) because these sustainable domestic tasks are easier for them (63.1%) than tasks in the professional field. The second subscale, NPEB, indicated that sustainable activities such as recycling were easy for the participants (57.6%), but sometimes they engaged in such activities less frequently than they would like (52.2%) (Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 ).
Representation of the frequency of nursing environmental behavior
Difficulty of engaging in adequate environmental behaviors
The sociodemographic variables indicated differences among the NEAT subscales (Table 2 ). Gender, working experience (with a median value of 10 years), and the position held in the institution and region were relevant with regard to environmental knowledge ( p < 0.01), environmental behavior outside the workplace ( p < 0.01), and environmental behavior in the workplace ( p < 0.01).
The NPEB was associated with the worst scores, thereby reflecting the nurses’ environmental behavior and activities in the workplace (52.23% rarely performed relevant activities, and 35.03% indicated that doing so was difficult) (Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 ). The NPEB values pertaining to environmental behavior were positively linked to age ( r = 0.412; p < 0.001), NAS knowledge ( r = 0.526; p < 0.001), PEB frequency ( r = 0. 57; p < 0.001), PEB difficulty ( r = 0.329; p < 0.001), and finally, difficulty performing adequate environmental behaviors ( r = 0.499; p < 0.001). Additionally, the value of the NPEB with regard to the difficulty of performing adequate environmental behaviors was positively associated with age ( r = 0.149; p = 0.008), NAS knowledge ( r = 0.249; p < 0.001), PEB frequency ( r = 0. 244; p < 0.001) and PEB difficulty ( r = 0.442; p < 0.001).
Based on the relevance of certain sociodemographic variables, the nurses’ environmental awareness (NAS) and their behavior outside the workplace (PEB), linear multiple regression was performed to investigate nursing behavior in the workplace (NPEB). The initial model (square sum = 488.655; p < 0.0001) indicated that age, the impact of nursing awareness (NAS), and the frequency of sustainable behaviors outside the workplace (PEB) were not relevant to nursing behavior in the workplace (NPEB) in terms of the frequency of performing adequate behavior or the difficulties experienced ( p > 0.05). Based on these results, the adjusted model was calculated (Table 3 ), indicating that NPEB depends on PEB frequency and NAS knowledge ( p < 0.01).
Nursing environmental behavior in the context of Green Teams: Barriers and areas for improvement.
The participants in the qualitative study ( N = 10) included nine women and one man; their median age was 49 years; they exhibited an interval quartile range of 35–60; they had levels of working experience ranging between 20 and 30 years, and they worked only in the mornings (7/10). Furthermore, the group including nurses and nursing supervisors (5/10) exhibited higher levels of education (see Supplementary file 2 ). The themes identified via repetition and associations during the interviews and observations indicated links among nurses’ responsibilities on the Green Team since they conformed to the nature of such teams (i). This team and nursing leaders identified sustainable environmental behavior (ii) that could improve environmental awareness (iii), knowledge, aptitude, and skills. The nurses who are responsible for sustainable changes should be the leaders (iv), and the relevant barriers and limitations (v) and areas for improvement (vi) in diverse areas should be identified simultaneously.
Green teams were linked to nursing responsibilities in the context of environmental sustainability.
In the interviews, the Green Teams, led by environmental leader nurses and comprising various staff members, were identified as crucial committees dedicated to enhancing environmental awareness and knowledge among hospital staff. Participants indicated that these teams facilitated regular meetings to discuss sustainable practices and played a pivotal role in testing behaviors and knowledge related to environmental sustainability. The Green Teams were highlighted as platforms for fostering collaboration and discussion surrounding sustainable practices. Participants noted that these teams facilitated the main purpose of the team and its members to improve the hospital staff’s knowledge and attitudes via meetings (RN 2,3 and NL 1,3). Subsequently, the NL also indicated a key role of the team in the testing of behaviors and knowledge. The behavior of registered nurses should be tested using questions according to the NLs. Also, the NLs are included in disponibility of of proper disposal methods for medical waste:
“So, where is the rubbish bin for medicines, that white one that you showed in the session that is used for the remains of medicines that we do not give to patients?” [(NL5)]
By such comments, it can be inferred that the Green Team not only disseminates information, manages the training and measures knowledge but also ensures that staff members understand and adhere to best practices in waste management. These tasks of the NLs and other RNs in the Green Team contribute to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of environmental sustainability efforts within the hospital.
Sustainable environmental behaviors were emerged by Green Teams.
The results of the analysis indicated some degree of resistance among the nurses working at the clinical management units with regard to their lack of competencies, especially those pertaining to knowledge, skills and attitudes. The comments from the interviews highlighted potential factors contributing to this resistance, including age-related differences, varying levels of awareness, and challenges in applying the principles of reduce, reuse, and recycle (the three Rs). For instance, one repetitive comment expressed a sentiment of uncertainty, stating “It is what is, but we don’t know it or what to do with it” (RN 3,4,5, and NL 2,3).
“We know what the light packing is, and they (maintenance people) installed it to reduce the lights and reduce the expense and cost, but we don’t know what to do with the rubbish bins” [(NL 4)]
This comment highlights a disconnect between awareness of specific sustainable initiatives and the practical knowledge to implement them effectively. All comments reflect the importance of addressing knowledge gaps and providing practical guidance to support nurses in adopting sustainable environmental behaviours. By acknowledging and addressing these challenges, healthcare facilities can enhance their environmental stewardship efforts and promote a culture of sustainability among staff members.
Environmental awareness were drawn from the nursing responsibilities that led to the creation of the Green Team.
The comments indicated that environmental awareness among nurses was influenced by training sessions and courses on environmental sustainability. After receiving training featuring lectures and courses on environmental sustainability, the leaders also reflected on the ways in which nurses put the recommendations made during the environmental sustainability courses into practice. Moreover, the leaders indicated that education should be beyond formal training sessions. The environmental leaders were interested in supplementing these courses with environmental education practices for the general population, as noted, for example, in reports of discharge from patient care or cycling on the ward. These activities indicated the ideal of including a holistic approach to sustainability within the healthcare setting.
Relevant statements included, “We have to separate residues according to the material… light plastic goes to… it is important for the unit and all of us” (NL 2,5). One key point that the referees and registered nurses highlighted pertained to the climate, particularly the lack of water (NL 1–5 and RN 1,2).
“The drought is getting worse; I don’t know how we are going to keep up… we hope it rains soon” [(RN1)]
Overall, the interviews shed light on the efforts to foster environmental awareness among nurses through formal training and practical integration into everyday practices. These observations emphasize the importance of ongoing education and action in addressing environmental concerns within healthcare settings.
Leadership, which was linked by comments to the Green Teams.
The interviews revealed that leadership, particularly within the context of Green Teams, is crucial in promoting environmental awareness and fostering a culture of sustainability among nursing staff. All the participants ( n = 10) indicated that the presence of adequate knowledge, meetings and awareness among nursing staff were the most important factors. These factors were identified as key drivers in promoting sustainable practices within the healthcare environment. NLs indicated the importance of creating a supportive working environment where nurses feel comfortable asking questions and seeking clarification without fear of negative feedback. Relevant statements included, “It is key to receive feedback from the nurses and provide a good working environment so that they can ask questions and reflect without negative comments” (NL 1,2,4, and RN 1,2). This working environment allowed the registered nurses to ask for help regarding the three Rs:
“Could you remind me (referring to the environmental coordinator) how the sustainable guidelines were included in the discharge report for the continuity of care; I remember some things from the course you gave us, but I want to convey it completely to my patient” [(RN2)]
Barriers and limitations, were drawn from nurses’ responsibilities.
Several nurses indicated that the difficulties they encountered with regard to performing environmental behaviors pertained to the lack of time, adequate bins, and space as well as the limited number of nurses per patient in the wards. Despite these challenges, participants noted a positive outcome in the form of increased awareness of sustainability issues among nurses, indicating a growing recognition of the importance of environmental stewardship within the healthcare setting. One factor that increased the barriers to environmental adequacy was the pandemic, which increased waste and rubbish. Despite these challenges, participants noted a positive outcome in the form of increased awareness of sustainability issues among nurses, indicating a growing recognition of the importance of environmental stewardship within the healthcare setting. Relevant statements included “There are not enough green rubbish bins for COVID waste” (EL 1,4,5 and RN1,2) and “How are we going to recycle if we don’t even have time to care for patients?” (RN 1,2 and NL 3).
All these comments indicated the barriers the nurses faced, but they also suggested possibilities for improvement. The pandemic, despite overloading nurses, also improved their awareness.
Areas subject to improvement emerged from nursing responsibilities, limitations and leadership.
Nurses indicated that despite their general levels of environmental awareness and the courses they had received, participants performed better regarding their recycling behaviors at home than at the hospital. Participants acknowledged performing better in recycling practices within their personal spaces, suggesting a potential gap in translating theoretical knowledge into practical action within the healthcare environment. Relevant statements included “It’s just that I recycle almost everything in my house, especially glass…, but here, there is no time…” (RN 1,4,5).
Moreover, time constraints emerged as a significant barrier impeding nurses’ ability to engage fully in environmental sustainability efforts. Participants cited the demanding nature of their work, particularly in the context of patient care responsibilities, as limiting their capacity to prioritize sustainability initiatives. This highlights the need for strategies to streamline environmental practices and integrate them seamlessly into nurses’ daily routines without adding undue burden.
Some statements also highlighted nurses’ willingness to improve paperwork and records. Nurses recognized the importance of incorporating environmental considerations into patient discharge reports and other documentation processes but sought further guidance on how to effectively implement these practices. Relevant statements included “Can you tell me how the patient’s continuity care report upon discharge was included in the recommendations for environmental sustainability… I want to do the report well with what you gave us in the clinical session the other day…” [(NL4)]
These comments indicated the opportunities for improvement in fostering a culture of environmental sustainability within the hospital setting. By addressing the identified challenges and providing targeted support and guidance, especially the lack of time, nurses can contribute to environmental stewardship efforts more effectively.
The current research highlights the relevance of nurses as promoters of environmentally sustainable behaviors in their roles as members of Green Teams and important leaders. The findings suggest that nurses exhibit acceptable knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors with regard to environmental sustainability both inside and outside the workplace. These results are complemented by a qualitative analysis indicating that such behaviors originate from nursing responsibility, Green Teams, leadership identification of barriers and areas of improvement. Both analyses highlight the fact that environmental nursing behavior in the workplace depends on sustainable behaviors outside the workplace. The qualitative analysis also identifies diverse barriers to the task of promoting sustainable behavior within the workplace, such as the COVID-19 pandemic and the need for more time to be allocated to this process. One key point identified by both analyses is that nurses have acceptable levels of knowledge; however, their attitudes, although as yet imperfect, are improving.
Several studies of nurses’ awareness of environmental sustainability have revealed that nurses exhibit moderate levels of awareness and a considerable degree of concern regarding the health impacts of climate change [ 37 , 42 , 43 ], as reflected in the NEAT-es results.
Interestingly, the participants exhibited a tendency to perform environmentally sustainable behaviors more consistently in their personal lives than in professional settings. These results are consistent with previous research on registered nurse and nursing students [ 36 , 41 , 42 ]. According to Swedish research, nurses generally recognize environmental issues but may lack awareness of the environmental impact of health care [ 43 ]. Polivka Barbara J. et al. (2012) highlighted the gap between nurses’ knowledge of sustainability and workplace behaviors, thereby emphasizing the need for education and training programs to promote sustainable practices [ 44 ]. These issues were also observed in a study conducted in Taiwan, which revealed that while nursing students exhibit positive attitudes toward sustainability, their knowledge and behaviors are inadequate [ 45 ].
By conducting qualitative analysis, this research also identified multiple barriers to the adoption of sustainable practices among nurses, including time constraints, disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, a lack of bins, and a lack of health care personnel. These findings are in line with those reported in other research, but certain barriers (in terms of resources, time, and support) to the implementation of sustainable practices in the workplace remain [ 29 ]. This study suggests that interventions should be designed to address these barriers and promote sustainable behavior among nurses, a suggestion which is consistent with the current research. These findings highlight the importance of comprehending nurses’ perspectives on environmental sustainability in health care contexts as well as the necessity for targeted interventions and support mechanisms [ 46 ]. The tasks assigned to nursing leaders and the Green Team involved addressing these barriers and promoting sustainable practices among nurses in the context of their professional roles. Environmental nursing leaders seem to be crucial with regard to establishing a more environmentally conscious health care environment, which is in line with recommendations to create a greener health care system [ 21 , 31 ]. Despite the results of the interviews, some global qualitative studies of nurses’ views on environmental issues have exhibited variations across countries [ 47 , 48 ]. In Sweden, nurses already exhibit pro-sustainability attitudes before the introduction of the 2030 SDGs [ 16 ]. However, the integration of environmental sustainability education into nursing programs can prepare future nurses more effectively to address the challenges associated with climate change and promote sustainable health outcomes [ 49 ].
Limitations
Although this investigation provides valuable insights, it is important to acknowledge its limitations. First, the study was conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic in Spain, which may have influenced the results due to the unique circumstances and stressors faced by health care workers during this period. Additionally, the assessment of nurses’ environmental awareness was performed on a larger scale, i.e., across multiple regions, and therefore may not accurately reflect individual attitudes and behaviors since the qualitative investigations focused on a specific region. However, this approach was adopted to minimize the risk of the ecological fallacy. Future studies could explore individual perspectives and experiences by reference to more diverse and representative samples.
Despite these limitations, this research is highly relevant because it sheds light on the role of nurses in the task of promoting environmental sustainability in health care settings. The research also emphasized the role of nursing leadership in the tasks of promoting environmental sustainability and providing nurses with the necessary resources and support to implement sustainable practices.
In conclusion, while nurses generally exhibit acceptable levels of knowledge, attitudes, and behaviors regarding environmental sustainability, a notable gap persists in terms of the frequency of sustainable actions within the professional settings in which they operate. This finding highlights the importance of closely aligning nurses’ personal and professional sustainability practices.
The qualitative analysis conducted as part of this study identified several barriers to the adoption of sustainable practices among nurses, including time constraints, disruptions resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic, issues with waste disposal, and challenges related to health care personnel. Despite the fact that these findings are in line with those reported in previous research, persistent barriers such as limited resources, time, and support hinder the implementation of sustainable practices in the workplace. Therefore, interventions aimed at addressing these barriers and promoting sustainable behavior among nurses are essential, as highlighted by both current research and the corresponding qualitative insights. Therefore, nursing leaders and Green Teams are pivotal with regard to overcoming these barriers and fostering sustainable practices within health care environments. Environmental nursing leaders in particular are instrumental to the cultivation of a more environmentally conscious health care system, thereby aligning with recommendations for greener health care practices.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed as part of the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Romanello M, Di Napoli C, Drummond P, Green C, Kennard H, Lampard P, et al. The 2022 report of the Lancet countdown on health and climate change: health at the mercy of fossil fuels. Lancet. 2022;400(10363):1619–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01540-9
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Watts N, Amann M, Ayeb-Karlsson S, Belesova K, Bouley T, Boykoff M, et al. The Lancet countdown on health and climate change: from 25 years of inaction to a global transformation for public health. Lancet. 2018;391(10120):581–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32464-9
Fadhullah W, Imran NIN, Ismail SNS, Jaafar MH, Abdullah H. Household solid waste management practices and perceptions among residents in the East Coast of Malaysia. BMC Public Health. 2022;22(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-12274-7
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Castañeda-Hidalgo H, Visovsky C, Hernández DE, González-Quirarte NH, Compeán-Ortiz L, Campiño SM. Nursing’s contributions to Sustainable Development Goals in Latin America through education, leadership, and partnerships. Int J Nurs Studi. 2021;121:104004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2021.104004
Article Google Scholar
Dossey BM, Rosa WE, Beck DM. Nursing and the Sustainable Development Goals: from Nightingale to now. Am J Nurs. 2019;119(5):44–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.NAJ.0000557912.35398.8f
Rosa WE, Dossey BM, Koithan M, Kreitzer MJ, Manjrekar P, Meleis AI, et al. Nursing theory in the Quest for the Sustainable Development Goals. Nurs Sci Q. 2020;33(2):178–82. https://doi.org/10.1177/0894318420903495
United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs. Sustainable Development Knowledge Platform. In: Open Working Group proposal for Sustainable Development Goals. 2023. https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/content/documents/1579SDGs Proposal.pdf.Accessed 17 Apr 2023.
Sanahuja JA. El Pacto Verde, NextGenerationEU y la nueva Europa geopolítica. In: Fundación Carolina.2022. https://www.fundacioncarolina.es/dt_fc_63/ . Accessed 17 Apr 2023.
Boto-Álvarez A, García-Fernández R. Implementation of the 2030 Agenda Sustainable Development Goals in Spain. Sustainability. 2020;12(6):2546. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12062546
Gomera Martínez A,Villamandos, de la Torre F, Vaquero Abellán. M,. Measurement and categorization of environmental awareness in university students: the contribution of the University to strengthen it. Ambientalización curricular y sostenibilidad. Nuevos retos de profesionalización docente. 2012;16(2):215– 28.
Ministerio de Sanidad. Plan Estratégico de Salud y Medioambiente 2022–2026. In: Ministerio para la Transición Ecológica y el Reto Demográfico.2021. https://www.sanidad.gob.es/ciudadanos/pesma/docs/241121_PESMA.pdf . Accessed 25 Apr 2023.
Ministerio de Sanidad. Plan Estratégico de Salud y Medioambiente. In: 1 a Programa de Actuación. Ministerio para la Transición Ecológica y el Reto Demográfico;2022. https://www.sanidad.gob.es/ciudadanos/pesma/docs/1er_PA_PESMA.pdf . Accessed 25 Apr 2023.
Hart J. Health Care without Harm: taking Environmental Action to improve lives and the planet. Integr Complement Ther. 2022;28(5):251–4. https://doi.org/10.1089/ict.2022.29036.pro
Health Care Without Harm. Hospitales que curan el planeta. In: Informe sobre el trabajo de los miembros de la Red Global de Hospitales Verdes y Saludables en América Latina. Red Global de Hospitales Verdes y Saludables en America Latina. 2022. https://saludsindanio.org/sites/default/files/documents-files/7287/Hospitales que curan el planeta 2022-FINAL_web_0 %281%29_0.pdf . Accessed 25 Apr 2023.
McDermott-Levy R. The nurse’s role on green teams: an environmental health opportunity. Pa Nurse. 2011;66(1):17–21.
PubMed Google Scholar
Schenk E, Johnson S. Nurse-sensitive environmental indicators: a qualitative study. J Nurs Manag. 2022;30(8):4378–86. https://doi.org/10.1111/jonm.13861 . Epub 2022 Oct 20.
Eckelman MJ, Sherman JD, MacNeill AJ. Life cycle environmental emissions and health damages from the Canadian healthcare system: an economic-environmental-epidemiological analysis. PLoS Med. 2018;15(7):e1002623. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002623
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Mateen A, Nisar QA, Nasir N. Fostering pro-environmental behaviors in the healthcare organizations: an empirical analysis of psychological and strategic factors. Asia Pac Manage Rev. 2023;28(1):13–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmrv.2022.01.004
Michie S, West R. Sustained behavior change is key to preventing and tackling future pandemics. Nat Med. 2021;27(5):749–52. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-021-01345-2
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Mejia EA, Sattler B. Starting a Health Care System Green Team. AORN J. 2009;90(1):33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aorn.2009.03.001
Practice Green Health. Comparison chart of hospital green teams and their structure. 2019. https://practicegreenhealth.org/sites/default/files/2019-02/Comparison chart of hospitals green team structure_2017.pdf . Accessed 1st Frebuary 2024.
Dickman E, Backler C, Berg CD, Komandt M, Schiller J. Climate change and oncology nursing: a call to action. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2022;26(1):109–13. https://doi.org/10.1188/22.CJON.109-113
de la Gámez J, Padilla Fortes A. Análisis De La producción científica visible en internet de Los técnicos de salud ambiental del Servicio Andaluz De Salud. Rev GeI Inf Doc. 2010;20:409–25.
Google Scholar
Filho W. Non-conventional learning on sustainable development: achieving the SDGs. Environ Sci Eur. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-021-00525-8 . 33;97.
Filho W, Tripathi S, Andrade Guerra JB, Gine R, Orlovic Lovren V, Willats J. Using the sustainable development goals towards a better understanding of sustainability challenges. Int J Sustainable Dev World Ecol. 2018;26:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504509.2018.1505674
Portela Dos Santos O, Melly P, Joost S, Verloo H. Climate Change, Environmental Health, and challenges for nursing Discipline. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(9):5682. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20095682
Sattler B, Randall KS, Choiniere D. Reducing Hazardous Chemical exposures in the neonatal intensive care unit: a New Role for nurses. Crit Care Nurs Q. 2012;35(1):102–11. https://doi.org/10.1097/CNQ.0b013e31823b2084
Trent L, Law J, Grimaldi D. Create intensive care green teams, there is no time to waste. Intensive Care Med. 2023;49(4):440–3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-023-07015-w
Kallio H, Pietilä AM, Johnson M, Kangasniemi M. Environmental responsibility in hospital care: findings from a qualitative study. J Hosp Adm. 2018;7(5):56. https://doi.org/10.5430/jha.v7n5p56
Rosa WE, Catton H, Davidson PM, Hannaway CJ, Iro E, Klopper HC, et al. Nurses and midwives as Global Partners to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals in the Anthropocene. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2021;53(5):552–60. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnu.12672
Harris N, Pisa L, Talioaga S, Vezeau T. Hospitals going green: a holistic view of the issue and the critical role of the nurse leader. Holist Nurs Pract. 2009;23(2):101–11. https://doi.org/10.1097/HNP.0b013e3181a110fe
Phiri MM, MacPherson EE, Panulo M, Chidziwisano K, Kalua K, Chawanangwa M, Chirambo, et al. Preparedness for and impact of COVID-19 on primary health care delivery in urban and rural Malawi: a mixed methods study. BMJ Open. 2022;12(6):e051125. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2021-051125
Ojemeni MT, Karanja V, Cadet G, Charles A, Dushimimana E, McMahon C, et al. Fostering nursing leadership: an important key to achieving sustainable development goals and universal health care. Int J Nurs Stud. 2019;100:103421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2019.103421
German E. The environmental or ecological model of care. Nriagu JO. Encyclopedia of Environmental Health. Netherlands:Elsevier Science; 2019. pp. 447–50.
Vasset F, Fagerstrøm L, Frilund M. Sustainable Nursing Leadership in Nordic Health Care Organizations. Scand J Caring Sci. 2021;14(2):2–1527.
Kallio H, Pietilä AM, Kangasniemi M. Environmental responsibility in nursing in hospitals: a modified Delphi study of nurses’ views. J Clin Nurs. 2020;29(21–22):4045–56. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.15429
Richardson J, Grose J, Bradbury M, Kelsey J. Developing awareness of sustainability in nursing and midwifery using a scenario-based approach: evidence from a pre and post educational intervention study. Nurse Educ Today. 2017;54:51–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2017.04.022
Luque-Alcaraz OM, Gomera A, Ruíz Á, Aparicio-Martinez P, Vaquero-Abellan M. Validation of the Spanish Version of the questionnaire on environmental awareness in nursing (NEAT). Healthcare. 2022;10(8):1420. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare10081420
Amezcua M. El Trabajo De Campo Etnográfico En Salud. Index Enferm (Gran). 2000;30:30–5.
Jamali HR. Does research using qualitative methods (grounded theory, ethnography, and phenomenology) have more impact? Libr Inform Sci Res. 2018;40(3):201–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lisr.2018.09.002
Cowie J, Nicoll A, Dimova ED, Campbell P, Duncan EA. The barriers and facilitators influencing the sustainability of hospital-based interventions: a systematic review. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020;20(1):588. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-020-05434-9
Kircher M, Doheny BM, Raab K, Onello E, Gingerich S, Potter T. Understanding the knowledge, attitudes, and practices of Healthcare professionals toward Climate Change and Health in Minnesota. Challenges. 2022;13(2):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/challe13020057
Boström M, Andersson E, Berg M, Gustafsson K, Gustavsson E, Hysing E, et al. Conditions for transformative learning for Sustainable Development: A Theoretical Review and Approach. Sustainability. 2018;10(12):4479. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10124479
Polivka BJ, Chaudry RV, Crawford JM. Public Health nurses’ knowledge and attitudes regarding Climate Change. Environ Health Perspecti. 2012;120(3):321–5. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.1104025
Hsieh PL, Chen SH, Chang LC. School nurses’ perceptions, knowledge, and related factors Associated with evidence-based practice in Taiwan. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15(9):1845. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15091845
Rojas-Perez HL, Díaz-Vásquez MA, Díaz-Manchay RJ, Zeña-Ñañez S, Failoc-Rojas VE, Smith D. Nurses’ environmental practices in Northern Peruvian hospitals. Workplace Health Saf. 2024;72(2):68–74. https://doi.org/10.1177/21650799231163130
Anåker A, Nilsson M, Holmner Å, Elf M. Nurses’ perceptions of climate and environmental issues: a qualitative study. J Adv Nurs. 2015;71(8):1883–91. https://doi.org/10.1111/jan.12655
Kallio H, Pietilä AM, Johnson M, Kangasniemi M. Systematic methodological review: developing a framework for a qualitative semi-structured interview guide. J Adv Nurs. 2016;72(12):2954–65. https://doi.org/10.1111/jan.13031
International Council of Nurses. International Nurses Day 2023 report. Value, protect, respect and invest in our nurses for a sustainable future for nursing and health care.2023. https://www.icn.ch/news/icn-marks-international-nurses-day-launch-its-our-nurses-our-future-campaign . Accessed 25 Apr 2023.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Excellent Official Nursing School and all the professionals who participated in this research for their support.
This research received no external funding; however, the project did receive an award from the Excellent Official Nursing School in Cordoba, Spain, in 2020.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Neurosurgery Department, Hospital Universitario Reina Sofía, Andalusian Health Care System, 14071, Cordoba, Spain
Olga María Luque-Alcaraz
Environmental Protection Office (SEPA), University of Córdoba, Campus Rabanales, 14014, Córdoba, Spain
Olga María Luque-Alcaraz, Antonio Gomera & Manuel Vaquero-Abellán
GE 10 Research Groups of Clinical-Epidemiological Research in Primary Care, University Biomedical Program for Occupational Medicine, Occupational Epidemiology and Sustainability, Maimonides Institute of Biomedicine of Cordoba (IMIBIC), 14071, Cordoba, Spain
Olga María Luque-Alcaraz, Pilar Aparicio-Martínez & Manuel Vaquero-Abellán
Nursing, Pharmacology and Physiotherapy Department, Faculty of Medicine and Nursing, University of Cordoba, 14071, Cordoba, Spain
Pilar Aparicio-Martínez & Manuel Vaquero-Abellán
GA16 Lifestyles, Innovation and Health, Maimonides Institute of Biomedicine of Cordoba (IMIBIC), 14071, Cordoba, Spain
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
A.G. and M. V-A. conceived and designed the study, and O.M. L. and P.A-M. acquired the data, analyzed and interpreted the data, and drafted the article. The publication and supervision of the article were the responsibility of A.G. and M. V-A. All authors contributed equally to the writing and preparation of the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Pilar Aparicio-Martínez .
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate.
Ethical approval was obtained from the Ethics Committee of Reina Sofia Hospital of Cordoba, which is part of the Andalusian Health Care System in Spain (Act No. 267, ref.3605). This research was in line with the Organic Law 3/2018 of December 5 on the Protection of Personal Data and Guarantee of Digital Rights as well as the Nursing Ethics Code and the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki. The participants were informed of the study’s purpose before participation; their informed consent was obtained, and they were informed that they were able to withdraw from the study at any stage. All the data were obtained after informed consent was collected; in addition, the data were anonymized and saved securely in a database, thereby maintaining all stipulations of the Personal Data Law.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Supplementary material 2, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Luque-Alcaraz, O.M., Aparicio-Martínez, P., Gomera, A. et al. The environmental awareness of nurses as environmentally sustainable health care leaders: a mixed method analysis. BMC Nurs 23 , 229 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-01895-z
Download citation
Received : 26 June 2023
Accepted : 26 March 2024
Published : 03 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-01895-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Environmental health
- Attitude of health personnel
- Sustainable development
- Health Knowledge, attitudes, and practices
- Organizational Culture
BMC Nursing
ISSN: 1472-6955
- General enquiries: [email protected]
This paper is in the following e-collection/theme issue:
Published on 4.4.2024 in Vol 11 (2024)
Studies of Social Anxiety Using Ambulatory Assessment: Systematic Review
Authors of this article:

- Javier Fernández-Álvarez 1, 2 , PhD ;
- Desirée Colombo 1 , PhD ;
- Juan Martín Gómez Penedo 3 , PhD ;
- Maitena Pierantonelli 4 , MSc ;
- Rosa María Baños 4, 5, 6 , Prof Dr ;
- Cristina Botella 1, 6 , Prof Dr
1 Department of Basic and Clinical Psychology and Psychobiology, Jaume I University, Castellon de la Plana, Spain
2 Fundación Aiglé, Buenos Aires, Argentina
3 Facultad de Psicología, Universidad de Buenos Aires (CONICET), Buenos Aires, Argentina
4 Polibienestar Research Institute, University of Valencia, Valencia, Spain
5 Department of Personality, Evaluation, and Psychological Treatments, University of Valencia, Valencia, Spain
6 Ciber Fisiopatologia Obesidad y Nutricion (CB06/03 Instituto Salud Carlos III), Madrid, Spain
Corresponding Author:
Javier Fernández-Álvarez, PhD
Department of Basic and Clinical Psychology and Psychobiology
Jaume I University
Avda. Vicent Sos Baynat s/n
Castellon de la Plana, 12071
Phone: 34 964 72 80 0
Email: [email protected]
Background: There has been an increased interest in understanding social anxiety (SA) and SA disorder (SAD) antecedents and consequences as they occur in real time, resulting in a proliferation of studies using ambulatory assessment (AA). Despite the exponential growth of research in this area, these studies have not been synthesized yet.
Objective: This review aimed to identify and describe the latest advances in the understanding of SA and SAD through the use of AA.
Methods: Following the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines, a systematic literature search was conducted in Scopus, PubMed, and Web of Science.
Results: A total of 70 articles met the inclusion criteria. The qualitative synthesis of these studies showed that AA permitted the exploration of the emotional, cognitive, and behavioral dynamics associated with the experience of SA and SAD. In line with the available models of SA and SAD, emotion regulation, perseverative cognition, cognitive factors, substance use, and interactional patterns were the principal topics of the included studies. In addition, the incorporation of AA to study psychological interventions, multimodal assessment using sensors and biosensors, and transcultural differences were some of the identified emerging topics.
Conclusions: AA constitutes a very powerful methodology to grasp SA from a complementary perspective to laboratory experiments and usual self-report measures, shedding light on the cognitive, emotional, and behavioral antecedents and consequences of SA and the development and maintenance of SAD as a mental disorder.
Introduction
Social anxiety (SA) is a normal and adaptive manifestation that all human beings experience in anticipation of a potential interactional threat. Similar to any adaptive response, it is enormously beneficial, particularly in protecting people from potential dangers that may arise from social interactions [ 1 ]. However, this adaptive response is sometimes exacerbated, and instead of preparing the individual for optimal performance, it becomes paralyzing, triggering intense fear, catastrophic thoughts, and avoidance behaviors, among other characteristic manifestations. When this pathological response becomes habitual in anticipation and confrontation of social interactions, it is referred to as SA disorder (SAD).
Accordingly, SAD is understood as a prevalent clinical condition characterized by intense fear and avoidance of social situations. SAD is a heterogeneous clinical condition that usually entails high levels of dysfunction in the lives of people who experience it. This heterogeneous nature of SAD is marked by the dynamic deployment of cognitions, emotions, and behaviors in the interaction with others and in different contexts [ 2 ].
Ambulatory Assessment
Ambulatory assessment (AA) serves as an umbrella term that includes specific techniques such as experience sampling methods, ecological momentary assessment, or daily retrospective methods. These techniques constitute a research methodology of paramount significance in the field of clinical psychology and psychotherapy, enabling researchers and clinicians to gather in-depth, ecologically valid data from individuals. Unlike traditional assessment methods that rely on retrospective self-reporting, AA involves the repeated real-time measurement and gauging of various aspects of an individual’s experiences, behaviors, and physiological responses. The fact that it entails multiple assessments over a certain period makes AA an optimal tool to explore within-person fluctuations and trajectories of these experiences and behaviors.
Moreover, AA circumvents the biases that usual retrospective reports may have because it is usually implemented in momentary assessments or recent retrospective reports (eg, daily diaries [ 3 ]). Owing to the variability of psychological processes such as affective and emotional dynamics [ 4 ], AA can more precisely determine the fluctuation of symptoms. In addition, owing to the possibility of incorporating sensors and biosensors, AA can provide multimodal assessment, overcoming the biases of self-reports [ 5 ].
Over the last few years, there has been an increasing interest in exploring the use of AA in clinical psychology and psychotherapy. Owing to the incorporation of digital technologies, namely, mobile phones, AA has become a very powerful add-on for clinical researchers [ 6 ], first and foremost due to the possibility that AA provides of capturing data in real time, thus grasping contextual aspects from naturalistic settings that laboratory-based assessment does not allow for [ 7 , 8 ]. SA symptoms are particularly contextually bound, and thus, it is of utmost relevance to consider the sensitivity of the context [ 2 ].
All these characteristics have a central and common pursuit to personalize models of psychopathology [ 9 ]. There is no doubt that every person has a certain and unique composition of traits that may lead to functional and dysfunctional states in continuous interaction with the context. Therefore, the revolution of AA is helping foster the creation of tailored models with intensive longitudinal data, which can shed light on the factors that may lead people to experience and behave in adaptive or maladaptive ways.
In this sense, AA proves to be a suitable tool for capturing the co-occurrence of symptoms and psychological processes, offering crucial insights into the antecedents and consequences of SA with enhanced accuracy. This, in turn, facilitates a comprehensive understanding of the factors contributing to the appearance and maintenance of SA and SAD. Given the dimensional nature of SA, AA can shed light on the differences among clinical, subclinical, and healthy participants.
The understanding of SAD in ecological settings may also lead to improving psychological treatments. The insights gained through AA can contribute to refining therapeutic approaches by investigating mechanisms of change [ 10 ]. However, to the best of our knowledge, no systematic review has synthesized the available evidence analyzing the strengths and limitations of the current state of the art.
For all the aforementioned reasons, AA provides a range of advantages that justify its exponential growth as a research methodology in clinical psychology. Although a plethora of research has implemented AA in individuals with SA, these data have not been synthesized yet. Hence, the main aim of this review was to identify studies that used AA to explore SA.
This review followed the recommendations of the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) statement [ 11 ]. The full protocol was registered before the data analysis [ 12 ].
Literature Search
Scopus, PubMed, and Web of Science literature searches were conducted. The search strategy for PubMed is available in Multimedia Appendix 1 and was adapted to the syntax requirements of each database. No filters were included in the searches. The reference lists of eligible articles were manually reviewed to identify additional relevant publications.
Inclusion Criteria
To be included, the studies had to fulfill the following criteria: (1) studies that focused on participants with SAD or SA symptoms; (2) studies that used AA to explore the dynamics of SA, correlates of SA, or the feasibility of AA for SA assessment; (3) articles that included any sort of discussion regarding SA in AA (this criterion was included given that some articles fulfilled all the previous criteria but featured no specific discussion on SA); (4) articles published in peer-reviewed journals in English; and (5) studies that presented at least one active AA or passive data collected via sensor signals (eg, geo-mapping, accelerometer, or GPS) from a phone or smartwatch multiple times per day. Articles were excluded if they (1) were not empirical studies; (2) used a child or adolescent sample; and (3) did not use a daily diary, experience sampling, or AA approach that included assessment and discussion of SA.
Study Selection and Data Extraction
A database search was conducted until August 31, 2023. The literature search produced a total of 14,504 articles, 8926 (61.54%) of which were retained after removing duplicates. A total of 1.23% (110/8926) of these articles were retrieved after title and abstract screening. The subsequent application of the selection criteria resulted in the inclusion of 50% (55/110) of the articles, adding another 15 studies that were identified through citation searching. In total, we included 70 studies ( Figure 1 ). Studies were independently selected by 2 researchers, and disagreements were resolved through consensus.

Using premade tables, the following information was extracted: author and year of publication, study design, follow-up period and sample size and characteristics, aims of the study, measures collected through AA, app name in the case of smartphone-based AA, participation rate (ie, response to recruitment), attrition rate, compliance with AA questions, incentives, outcomes explored, AA measures, frequency of AA, and main findings.
Finally, to summarize the main information, 2 of the authors proposed categories. To form a category, it was required that at least 2 of the included studies addressed the same or a similar topic. To reach an agreement, the resulting categories underwent thorough discussion between the first and fourth authors. This criterion was applied to the “Principal themes explored” section. For the “Emerging topics” section, the criterion for category inclusion was based on relevance regarding addressing a key aspect of the literature that had not been explored before.
Sample Characteristics
Of the 70 studies selected for this systematic review, 29 (41%) used the same sample ( Textbox 1 ). Given that a large proportion of the studies were conducted in university settings, most of the included participants were undergraduate students and, therefore, young adults. Moreover, all the studies (70/70, 100%) were conducted in high-income countries, principally in the United States. A total of 43% (30/70) of the studies included both healthy and clinical populations. In total, 21% (15/70) of the studies were conducted only with clinical participants, whereas 36% (25/70) were conducted with healthy individuals exploring the dynamics of SA. In addition, 33% (23/70) of the studies included comorbid samples, mainly those with other anxiety or depressive disorders. Regarding gender, most studies (57/70, 81%) included more women than men. This reflects the prevalence rates of SAD, which have been shown to be higher in women than in men [ 13 ]. Table S1 in Multimedia Appendix 2 [ 14 - 81 ] and Table S2 in Multimedia Appendix 3 [ 14 - 81 ] summarize the characteristics and main findings of the included studies.
Studies with the same samples
- Blalock et al [ 14 , 15 ], Farmer and Kashdan [ 16 ], Goodman et al [ 17 , 18 ], Kashdan and Farmer [ 19 ], and Kashdan et al [ 20 , 21 ]
- Daniel et al [ 22 , 82 , 83 ] and Beltzer et al [ 23 ]
- Daniel et al [ 24 ], Daros et al [ 25 ], and Ladis et al [ 26 ]
- Doorley et al [ 27 , 28 ]
- Goodman et al [ 29 - 32 ]
- Oren-Yagoda et al [ 33 - 36 ]
- O’Toole et al [ 37 , 38 ]
- Villanueva et al [ 39 ] and Rinner et al [ 40 ]
Methodological Characteristics of the Studies
Sampling frequency.
There were 2 types of sampling identified among the included studies. On the one hand, there were some studies that implemented a daily diary, which typically entails an end-of-day report. On the other hand, other AA studies comprised different numbers of daily assessments and diverse types of prompt contingencies. The duration of the AA ranged from 4 to 35 days. The most commonly implemented study duration was 14 days.
Although a large proportion of the studies (63/70, 90%) used a fixed or random scheduled prompt structure, a range of studies incorporated an event-contingent design [ 40 - 45 ]. Indeed, SA determinants, correlates, and consequences are particularly triggered in interpersonal situations, and event-contingent designs may be suitable for detecting relevant moments. Finally, studies such as those by Daniel et al [ 24 ], Helbig-Lang et [ 46 ], and Kashdan et al [ 20 ] included a mix of different types of data collection, combining random prompt, event-contingent, and end-of-day records.
Compliance rates typically indicate the percentage of prompts or days that the participants completed on average. Compliance rates ranged from 40% to 95%, with average compliance across studies of 73.72% of prompts (SD 15.93%; median 80%).
Statistical Analysis
The vast majority of the studies (61/70, 87%) used hierarchical linear models to account for the nested nature of the collected data. A total of 4% (3/70) of the studies used a combination of hierarchical linear models and structural equation modeling [ 43 , 45 , 79 ], 1% (1/70) of the studies used machine learning techniques [ 47 ], 3% (2/70) of the studies calculated ANOVA models [ 23 , 42 ], and 1% (1/70) of the studies ran ordinary least squares regression [ 48 ].
Methodological Design Characteristics
Table 1 summarizes the principal methodological characteristics of each study. Power analysis to calculate the needed sample size (which was rarely conducted; 15/70, 21% of the studies) and the psychometric properties of the AA questions (37/70, 53% of the studies) were the 2 criteria that were reported the least, whereas the percentage of AA compliance (56/70, 80% of the studies) and attrition rates of AA (46/70, 66% of the studies) were the criteria that were reported the most among the studies in this review.
a AA: ambulatory assessment.
b Presence.
d N/A: not applicable.
Principal Themes Explored
Affective and emotional dynamics.
Naragon-Gainey [ 43 ] explored structural models of affect and internalizing symptoms. While the between-person variance in negative affect (NA) and concurrent levels of NA predicted SA, positive affect (PA) did not. This lack of significance contradicted many other AA studies that yielded significant between-person associations between lower levels of PA and higher levels of NA with SA [ 16 , 20 , 30 , 54 , 57 , 58 , 61 , 69 , 70 ].
Individuals with SAD showed not only higher overall levels of NA but also more emotional instability, which was not the case for PA [ 16 ]. These authors even suggested that the interaction between NA and instability could explain the appearance of SAD.
Discrete Emotions
As suggested by Rozen and Aderka [ 84 ], there is a wide range of discrete emotions that have not been integrated into classic models of SAD. In that sense, AA allows for a nuanced study of single emotions and how they are interconnected not only with each other but also with other cognitive-affective processes and behaviors.
First, Kashdan and Collins [ 70 ] revealed that SA was related to less time spent feeling happy and relaxed and more time spent feeling angry. The results also showed that happy moments were aroused in companion to others. The fact that SA was associated with fewer and less intense positive emotions and more anger episodes was independent of being with others or alone.
Oren-Yagoda et al [ 35 ] investigated the role of envy, showing that visual modes of communication are related to elevated envy compared to voice or text communication. In addition, envy predicted subsequent anxiety above and beyond previous anxiety as well as other negative emotions.
Loneliness is a defining emotion of people with SAD, and Oren-Yagoda et al [ 36 ] found that this relationship was also confirmed in an ecological setting using AA. A significant association was predicted in certain social situations (ie, negativity, positivity, and meaningfulness). Moreover, the relationship between loneliness and anxiety was shown to be reciprocal in individuals with SAD (loneliness predicted anxiety and anxiety predicted loneliness). This deleterious reciprocity was not found in healthy controls.
Finally, Oren-Yagoda et al [ 34 ] investigated the fluctuations of pride in individuals diagnosed with SAD. The results indicated that levels of pride were lower in patients with SAD than in nondiagnosed controls, although when pride was experienced, it predicted a reduction in anxiety levels.
Emotion Regulation
Emotion regulation (ER) was by far the most explored construct among the studies that implemented AA in individuals with SA. This may be explained by the fact that ER is a dynamic process, and AA is very suitable for detecting affect changes and fluctuations in daily life. In addition, not only are ER and SA symptoms highly context sensitive, but mounting research has also shown their interdependence [ 85 ], which justifies the importance of exploring how individuals with SAD use ER in daily life.
Discrete Strategies
Several studies explored only 1 strategy. For example, Kashdan et al [ 20 ] found that individuals with SAD experienced greater experiential avoidance than healthy individuals. Using the same sample, Kashdan et al [ 21 ] found that momentary experiential avoidance presented a stronger association with anxiety during social interactions for individuals with SAD than for individuals without SAD.
Similarly, another study explored the role of emotional suppression, demonstrating that, on days in which SA symptoms increased, the use of suppression tended also to increase [ 61 , 69 ]. The same was found by Beltzer et al [ 23 ], who identified that days with high levels of SA and expressive suppression led to fewer positive emotions.
Farmer and Kashdan [ 61 ] implemented a 2-week diary, showing that high SA was related to positive emotion suppression, fewer positive social events, and fewer positive emotions on subsequent days. In contrast, low SA was associated with fewer negative social events on the days after cognitive reappraisal was used to reduce distress. However, the use of cognitive reappraisal did not lead to any changes in people with high SA.
Meanwhile, Farmer and Kashdan [ 16 ] found that individuals with SAD were 3 times more likely to present acute shifts in NA, which may be a particular experience of this anxiety disorder and not others. This acute shift in NA may lead to experiencing emotions as uncontrollable and threatening, which in turn could explain the higher use of suppression.
Goodman et al [ 63 ] showed that alcohol consumption moderated the negative association between SA and a range of healthy social interactions such as laughter or feelings of acceptance; that is, SA was not related to the perceived quality of interpersonal interactions when participants consumed alcohol, suggesting that alcohol consumption may be a reinforcer of SA. These findings suggest that ER plays a central role in the experience of individuals with SAD who try to explicitly control their emotions and are aware of the effort they make to do so. In a different but related study, Goodman and Kashdan [ 29 ] found that both anxiety and pain were interfering factors in goal attainment, as well as finding an inverse association between daily meaning in life and perceived emotion-related goal interference.
Substance Use
Alcohol consumption and SAD are highly comorbid given that, among individuals with SAD, it is frequent to resort to alcohol as a coping strategy or, in other words, as an ER strategy. By means of AA, it is possible to detect how these 2 phenomena are interrelated. Therefore, several studies explored this topic. Battista et al [ 52 ] examined the relationship between alcohol consumption and SA, revealing that, after each alcoholic drink consumed, SA tended to decrease 2 hours later. Contrary to what the authors expected, this association was not explained by the level of trait SA.
Goodman et al [ 63 ] showed that alcohol consumption moderated the negative association between SA and a range of healthy social interactions such as laughter or feelings of acceptance; that is, alcohol consumption SA was no longer related to the perceived quality of interpersonal interactions, suggesting that SA may be a reinforcer of SA. This reinforcement could be either negative (attenuation of anxiety) or positive (better perception of social situations), which was the main finding of Goodman et al [ 64 ]. The results of this study yielded evidence supporting the negative reinforcement hypothesis such that people with SAD presented higher coping motives (negative reinforcers) but equal levels of affiliation motives (positive reinforcers).
Walukevich-Dienst et al [ 80 ] revealed that consuming substances as a coping strategy in SA is related to heavier consumption, especially on drinking days, which may be a risk factor for the development of an alcohol use disorder. Moreover, when there were SA coping motives, the consequences were more negative compared to days without SA coping motives. Interestingly, levels of SA at baseline were not moderators of these associations, indicating that the coping motive is more important than the antecedent levels of SA.
Kim and Kwon [ 73 ] showed that individuals with SAD had a higher increase rate of alcohol craving when they were tense and lonely and experiencing SA in comparison to individuals without a diagnosis of SAD. These results were moderated by the rate of rumination in the SAD group and avoidance in the non-SAD group. O’Grady et al [ 75 ] explored the role of social-contextual events in the relationship between trait SA and drinking. The results revealed a positive association between trait SA and drinking on the evenings of days in which the individuals experienced an embarrassing situation. This was significantly higher than in healthy participants, suggesting a behavioral maladaptive ER strategy to cope with the intensified levels of SA.
In addition, Buckner et al [ 56 ] studied the association between SA, cannabis use, cannabis craving, and situational variables. This study showed that SA interacted with cannabis craving predicting cannabis use, which sets out a complex relationship between SA and cannabis use and not a simple association (ie, cannabis use as a response to increased state SA).
In the study by Buckner et al [ 57 ], they showed that baseline SA was associated with increases in NA throughout the days in which the participants were monitored but was also significantly associated with postquit withdrawal. Participants with higher levels of SA presented more severe postquit withdrawal symptoms as well as an increase in NA during a cessation attempt. For this reason, the authors suggested that those participants may particularly benefit from intervention and treatment strategies.
Finally, Papp et al [ 76 ] found that students with higher levels of SA presented a stronger association between NA and prescription misuse. This study included externalizing and internalizing symptoms (depression and SA symptoms), and moderation was shown to be significant only for internalizing symptoms. This may indicate differential patterns of substance use as an ER strategy according to different personality traits.
The Complexity of ER: Polyregulation and Flexibility
Some studies incorporated a range of ER strategies in the AA process, which is in line with the current idea of polyregulation , that is, that individuals usually implement a range of strategies simultaneously [ 86 ]. For example, Daros et al [ 25 ] measured various strategies, and after clustering through a factorial analysis, 2 categories of ER strategies were considered for the analyses: avoidant and engagement strategies. However, the authors did not find any significant results for these 2 macrocategories.
On the basis of the model by Gross, Blalock et al [ 14 ] examined both suppression and cognitive reappraisal in SA in comparison to healthy individuals. Both groups presented worse emotional experiences when they suppressed positive versus negative emotions as well as when reappraising negative versus positive emotions. This suggests that suppression may be an adaptive strategy not to feel negative emotions, whereas reappraisal may be effective in increasing positive states. Interestingly, individuals with SAD showed more positive emotions after reappraising negative emotional states to feel fewer negative emotions than the healthy controls.
However, none of these previous examples explicitly framed their studies under the concept of emotion polyregulation, as did Ladis et al [ 26 ]. By including 8 strategies (problem-solving, introspection, distraction, acceptance, thought suppression, seeking advice, cognitive reappraisal, and expressive suppression), the authors systematically explored how often polyregulation occurs in daily life. Overall, the results yielded nonsignificant SA correlates of polyregulation, suggesting that it may be more dependent on within-person differences.
In addition to polyregulation, flexibility has been shown to be central in ER literature to distinguish adaptive from maladaptive regulatory processes [ 87 ]. Given that flexibility is mostly dependent on context, AA emerges as a very useful tool. O’Toole et al [ 38 ] investigated this specific topic in individuals with high and low SA and considered type and intensity as 2 contextual factors. This study revealed that SA moderated the relationship between emotion intensity and experiential avoidance. In individuals with high SA, there was a stronger association between experiential avoidance and specific emotions, such as guilt, nervousness, and sadness.
The study conducted by Beltzer et al [ 23 ] presents an illustrative example of how ER can be better explained by contextual triggers than by the adaptative or maladaptive continuum. The authors created an algorithm based on the 10 most used strategies to generate an ecological momentary intervention (EMI) based on contextual triggers. This algorithm was tested with a group of strategies (disengagement, engagement, and aversive cognitive perseveration) and with 10 individual single strategies compared with a random policy and a behavior policy, with ER effectiveness being the observed outcome. The contextual algorithm improved other policies in cases in which the top 10 strategies were considered separately. However, when the strategies were grouped into categories, the algorithm did not outperform the random recommender or the observed ER strategies.
Goodman et al [ 32 ] also explored ER flexibility considering 2 components of flexibility: the evaluation of contextual demands and matching regulatory strategies to contextual demands. The results indicated that people with SAD considered momentary assessments to be more anxiety provoking while presenting similar patterns to those of control participants when gauging contextual demands, particularly those related to perceived controllability. That is, some disengagement strategies (rumination, thought suppression, and expressive suppression) were found to be unrelated to perceived controllability. This means that these strategies were used independently of perceived controllability in a certain context. However, contrary to previous results, participants with SAD yielded similar patterns to those of control participants in response to anxiety intensity.
Higher anxiety ratings predicted greater use of all strategies regardless of the type of strategy used. In addition, this study showed that people with SAD may be more prone to use thought suppression but not engagement strategies, which is inconsistent with previous studies.
In other studies, a specific component of the heterogeneous and complex process of ER was explored. Although most clinical research on ER tends to simplify the discussion on putatively maladaptive (eg, expressive suppression) or adaptive (eg, cognitive reappraisal) strategies, there is a range of potential explanatory variables that set a more complex scenario than implementing certain strategies or not. For example, one study [ 24 ] investigated the perception of ER effectiveness, which is based on a robust research line that revolves around how goals shape and determine ER deployment and outcomes [ 88 ]. Daniel et al [ 24 ] found that, depending on the way in which effectiveness is measured (either judgment of effectiveness or change in affect), the results differ. While the judgment of effectiveness indicates that avoidance‐oriented ER attempts are less effective than engagement‐oriented ER attempts, changes in self-reported effects following ER attempts present the opposite results.
Similarly, Goodman et al [ 18 ] explored the extent to which beliefs of ER determine the use of specific patterns. In laboratory settings, De Castella et al [ 89 ] demonstrated that individuals with SAD presented low emotional self-efficacy, or the belief that emotions cannot be changed, but the results obtained by Goodman et al [ 18 ] provide ecological validity to a result that confirms the interdependency between cognitions and emotions [ 90 ].
Another approach is to calculate ER diversity, defined as the variety, frequency, and evenness of the implemented ER. Finally, Daniel et al [ 22 ] studied whether ER diversity predicted SA severity. The results showed that diversity within avoidance-oriented strategies was associated with both trait and state SA levels. At a more specific level of analysis, participants who responded more evenly and deployed a vast array of avoidance-oriented strategies more frequently were more prone to belonging to the high-SA group.
Emotion Clarity and Differentiation
Another important aspect that has been of increasing interest in the ER literature is linked to convergent processes such as emotion clarity and differentiation. Emotion clarity is defined as the ability to identify, distinguish, and describe specific emotions [ 91 ]. Park and Naragon-Gainey [ 45 ] found that lower momentary clarity was related to increases in subsequent momentary internalizing symptoms (ie, anxiety and depressive symptoms). This association was explained by an unsuccessful use of ER.
A total of 4% (3/70) of the studies examined emotion differentiation in individuals with SAD [ 19 , 37 , 48 ]. Emotion differentiation is conceptualized as the ability to recognize, identify, and label broad emotional experiences into discrete emotion categories [ 92 ]. Kashdan and Farmer [ 19 ] demonstrated that an increase in SA symptoms is linked to an impairment in negative emotion differentiation (ie, the ability to label and describe differences among negative emotions). In particular, it was found that negative emotion differentiation plays a relevant role in implementing more effective ER strategies. For example, Seah et al [ 48 ] conducted 2 studies that showed that negative emotion differentiation moderated the positive relationship between rumination and social avoidance. Similarly, O’Toole et al [ 37 ] showed that individuals with both high SA and poor negative emotion differentiation presented the least use of cognitive reappraisal. In addition, individuals with high SA used more suppression strategies despite the ability to differentiate positive emotions.
Perseverative Cognition and Mind Wandering
Although the most common variable that has been studied in individuals with SAD is postevent processing (PEP), there is a great overlap between PEP and rumination. In essence, both revolve around the perseverative thinking of past events, but PEP is strictly related to social interactions, including an important component of the actual interventions that both the individual and the others may have done or said. In total, 6% (4/70) of the studies used AA to examine processes related to PEP and rumination.
Helbig-Lang et al [ 46 ] studied individuals diagnosed with SAD to explore predictors of higher PEP levels. The results showed that higher PEP was predicted by self-attention, NA, social performance situations, and the use of safety behaviors. In addition, Badra et al [ 50 ] investigated PEP in a nonclinical sample of undergraduate students with high and low SA scores. Although no differences were detected between the groups, PEP was reduced to a single item, and no additional information on the social context was collected, which could have affected the results.
Another study that explored PEP showed that it decreased after a speech task [ 68 ]. The between-level average differed from the person-specific trajectories. This was the case not only for the decrease in PEP after the speech task but also in the temporal cascading relationship between PEP and the next measurement of PEP. The level of anxiety in the speech task predicted engagement in PEP, and this activated a more intense experience of the negative balanced memory, indicating the interconnectedness of cognitive-affective processes.
Bailey et al [ 51 ] studied perseverative cognition (worry and rumination) using physiological measures and found that there was a higher use of this type of repetitive thinking related to lower heart rate variability after negative social interactions. Finally, potential changes in momentary PEP throughout treatment were explored by Katz et al [ 41 ] showing that cognitive behavioral group therapy reduced levels of PEP.
In total, 3% (2/70) of the studies explored mind wandering, which is both an interesting and controversial topic. Traditionally, it was considered that mind wandering was just a negative process given that it was linked to the opposite of having a mindful disposition. However, the latest research has shown that it could be related to less boredom, more creativity, and a better mental health state [ 93 ].
In the study by Arch et al [ 49 ], the authors investigated differences in the frequency, range of content, and correlates of internal off-task thinking (ie, mind wandering). Relative to on-task thinking, internal off-task thinking was associated with worse mood, more self-focus, and less thought controllability for those with SAD compared to healthy controls. In addition, participants with SAD engaged in internal unrelated task thinking more frequently than those in the control group and presented more unintentional mind wandering on a trait questionnaire.
Specific Interactional Triggers, Patterns, and Activities
Geyer et al [ 62 ] investigated the association between NA in social interactions and perceived enjoyment of those interactions to explore specific real-time contributors to negative perceptions often experienced by individuals with SA. The results revealed that this association was more negative when SA was more severe, although the sample consisted of undiagnosed individuals.
Meanwhile, Blalock et al [ 15 ] studied the experience of flow in social and nonsocial situations in individuals with SAD and healthy participants. The results were contrary to the hypotheses, revealing that individuals with SAD presented flow more frequently in social situations than healthy participants. The authors explained this unexpected result using the concept of flow, which includes the component of experiencing a challenging situation as a defining feature. It is reasonable to think that people with SAD experience normal social interactions as more challenging than healthy participants.
In one study, the association between sexual activity and SA was explored in nonclinical individuals [ 71 ]. As could be expected, sexual activity was influenced by SA such that individuals with SA reported their sexual episodes as less pleasurable and reported being less connected with their partners as well as presenting a lower frequency of sexual activity. Overall, these results suggest that sexual activity is not fulfilling when experiencing SA.
Goodman et al [ 30 ] conducted 2 AA studies in which they concluded that, although individuals with SAD present fewer and less satisfying social relationships, they enjoy social interactions when they occur, which might indicate that they are happier with others than alone. In other words, experiencing SA and the relative concern about socializing does not hinder the pleasure of socializing.
These results are aligned with those of other 2 studies conducted on undergraduate students [ 54 , 83 ], which showed that SA was not related to a lower desire to be with others. However, in the study by Brown et al [ 54 ], a preference for solitude was found in interactions with unfamiliar people.
Villanueva et al [ 39 ] revealed that individuals with SAD presented a higher number of social interactions through their mobile phones than the control group. They were also the group with the least number of social interactions (vs the control group and individuals with depression). In-person interactions (ie, face-to-face) were revealed to be less related to increases in NA and decreases in PA.
In the study by Doorley et al [ 27 ], no significant association was found between the medium of communication (ie, digital vs face-to-face communication) and SA. That is, in both media, there was an association between SA and less positive and more negative emotions. Oren-Yagoda and Aderka [ 33 ] also explored media of communication in individuals diagnosed with SAD. In this case, the focus was on the media of communication and the associated perceptions and emotions. Individuals with SAD usually preferred to use voice and text media to a greater extent than visual media. However, the authors found that, despite this preference, when visual media were implemented, immediate increases in positive perceptions and emotions were experienced by people with SAD. These results support the idea that the selected medium functions as a safety behavior.
Meanwhile, Russell et al [ 44 ] revealed that individuals with SAD presented higher levels of submissive behavior and lower levels of dominant behavior compared to control participants. However, this was true in the presence of anxiety-eliciting cues, which means that there are certain situations that can be perceived as safe environments. In contexts of emotional security, all individuals with SAD presented an enhanced agreeable and deceased quarrelsome behavior, also meaning that there might be situations of security in which individuals with SAD can respond to positive appraisals with enhanced affiliative behavior.
Hur et al [ 66 ] found that individuals with SAD benefit more from having close friends, family members, and romantic partners in terms of resulting in lower levels of NA, anxiety, and depression compared to control participants. However, they tend to spend less time with those companions. These results emphasize the intact capacity of individuals with SAD to enhance their mood through social interactions.
In this line, Hannah Lee [ 65 ] obtained consistent results, suggesting a tight connection between the levels of SA and the degree of unfamiliarity and judgmentalness in the interactions. Namely, individuals with higher levels of SA presented a stronger association with the 2 processes as a consequence of being more sensitive to experiencing anxiety when facing interactions of the same level of unfamiliarity and judgmentalness compared to people with lower levels of trait SA.
Čolić et al [ 59 ] were the first to explore depersonalization and derealization in embarrassing situations. They showed that people with SAD presented more embarrassing social interactions than control participants, and as a result, they also presented more depersonalization and derealization, which can be seen as responses to strong emotions (including embarrassment) as well as attempts to cope with situational challenges.
Cognitive Factors
Social comparison is another important aspect to explore in individuals with SAD given that they usually tend to see themselves with a negative self-image [ 94 , 95 ]. In another study, Brown et al [ 54 ] showed that SA was associated with greater self-consciousness, which can also be aligned with the negative self-view that characterizes SAD.
Goodman et al [ 31 ] found that SA is related to less favorable and more unstable social comparisons, which can be explained by a negative self-image. Moreover, they demonstrated that, when people with SAD make less favorable social comparisons, they are especially fearful of others’ evaluations.
In a recent study, Brown et al [ 55 ] investigated interpersonal distress in heightened SA symptoms as predictors of suicidal ideation. Specifically, this study showed that hurdles to seeking social support and social comparisons mediated suicidal ideation.
Models of SAD have emphasized the central role of fear of evaluation in the appearance and maintenance of this clinical condition. This construct has been included in cognitive models related to attentional biases and negative interpretations of the self [ 96 - 98 ]. Although negative evaluation was considered a core dimension in early models of SAD, fear of positive evaluation has emerged as an important topic in recent years [ 78 , 99 ].
Another study explored anxiety sensitivity cognitive concerns and fear of negative evaluation as 2 potential predictors of SA amplification. Anxiety sensitivity cognitive concerns were shown to uniquely amplify arousal as a consequence of social stress, whereas fear of negative evaluation predicted anxiety fluctuations, indicating that these 2 cognitive constructs may be associated with SA in different ways [ 79 ].
By implementing 2 AA studies, Reichenberger et al [ 78 ] explored the interaction of both positive and negative evaluation, affect, and stress reactivity. Although the results were not fully in line with the hypotheses, fear of negative evaluation was negatively associated with PA. In addition, the results revealed that the closeness of the relationships was paramount to determine when the interaction was significant, with closer relationships being less anxiety provoking. Consistent with these results, positive and negative feedback seeking has been shown to be higher in individuals with SAD than in healthy participants [ 81 ], all of which is aligned with the mounting evidence developed in cross-sectional or laboratory settings. Similarly, Doorley et al [ 28 ] demonstrated that self-perceived intense positive events, which are normally reduced in SA, paradoxically provided more psychological benefits (reduced anxiety and motivation toward social situations as well as an increased sense of belonging).
Moreover, Nanamori et al [ 74 ] studied triggers of self-focused attention, which is another key component of classic cognitive models of SAD. The results showed that perception of gaze, evaluation, and authority predicted self-focused attention from the observer’s perspective, whereas perception of gaze also predicted self-focus on body sensation. Moreover, the perception of positive response and that of a stranger predicted self-focus on body sensation hinged on sex, suggesting that the positive response perception of female participants acted as a predictor of the self-focus on body sensation.
Emerging Topics
Use of aa to assess psychological interventions.
Daniel et al [ 83 ], Katz et al [ 41 ], and Kivity and Huppert [ 72 ] implemented AA to explore the course of treatment. In the case of Katz et al [ 41 ], PEP, a putative maintenance factor of SA symptoms, was assessed over the course of a cognitive behavioral therapy intervention with a subset of the 60 included participants answering an AA. The intervention yielded significant reductions in both general and momentary PEP, and both types of PEP were significant predictors of SA severity after treatment.
Another study was conducted by Kivity and Huppert [ 72 ]. It explored how ER in individuals with high and low SA responded to a practice of cognitive reappraisal using self-report, laboratory tasks, and daily diaries. Although the group with high SA presented lower symptom severity and greater self-efficacy of reappraisal, daily anxiety was not significantly different.
Daniel et al [ 83 ] conducted a randomized controlled trial testing whether cognitive bias modification for interpretation could decrease negative interpretation bias. Both the active and control conditions received an AA throughout the treatment period (5 weeks). While the active group also received cognitive bias modification training, the control group only answered the AA. A total of 2 publications were identified from this study, reporting self-report and passive sensing outcome measures. Despite the interesting approach of incorporating multimodal assessment, both analyses yielded nonsignificant results.
Use of Sensors and Biosensors in AA
Over the last few years, new advancements in wearable sensors and biosensors have enabled us to incorporate them into AA studies. In the case of SA, this has led to a considerable body of evidence. Specifically, Bailey et al [ 51 ], Boukhechba et al [ 53 ], Chow et al [ 58 ], Daniel et al [ 82 ], Di Matteo et al [ 60 ], and Jacobson et al [ 47 ] conducted studies using sensors (GPS location and accelerometers) and biosensors (heart rate and heart rate variability).
Bailey et al [ 51 ] investigated perseverative cognition in relation to the parasympathetic nervous system, which is considered of utmost relevance in the regulation of stress and emotions [ 100 ]. In this study, individuals with both depression and SAD were monitored, and individuals with SAD presented the highest frequency of daily perseverative cognition, which was statistically associated with lower heart rate variability, moderated by negative social interactions. Jacobson and Bhattacharya [ 67 ] showed that spending time indoors was associated with anxiety and avoidance symptoms, and this association was significantly higher in individuals with SAD than in those with generalized anxiety disorder.
Boukhechba et al [ 53 ] and Chow et al [ 58 ] used GPS and Jacobson et al [ 47 ] used an accelerometer to demonstrate the capability of passive sensing to predict the severity of SA symptomology according to the level of activity. Moreover, Di Matteo et al [ 60 ] designed an app to capture ambient audio, GPS location, screen state, and light sensor data, and this app was shown to be able to identify SAD patterns of behavior in a relatively accurate way.
Exploring Idiographic Comorbidity Patterns
Although a vast array of studies included heterogeneous samples in terms of their diagnosis, only Piccirillo and Rodebaugh [ 77 ] had the objective of exploring SAD and major depressive disorder comorbidity, aiming to model person-specific trajectories of cognitive-affective and behavioral dimensions related to these disorders. By including only cisgender women with comorbid SAD and major depressive disorder, this study showed the utmost relevance in disentangling between-person, within-person, and person-specific patterns. For example, loneliness was revealed to be a common predictor of depressive mood and social avoidance at the group level; however, this was not the case when examining the idiographic networks.
Transcultural Differences
Only 1% (1/70) of the studies examined potential variations between different cultural groups. Lee et al [ 42 ] explored differences between European Americans and Asian Americans, showing that both groups experienced the same number of anxious events during social situations but Asian Americans presented more negative emotions in those moments.
Principal Findings
Our review of 70 original studies using AA to explore SA showed that this methodology provides valuable real-time information on the momentary association of SA with several variables, such as context, affective dynamics, emotional states and regulation, social interactions, and other consequences and antecedents. This comprehensive understanding can contribute to better insights into the appearance and maintenance of symptoms and of this clinical disorder.
Aligned with the burgeoning literature on AA, affect and emotional dynamics emerged as the most studied topics. These investigations revealed a trend of an increase in NA levels leading to a heightened experience of SA, as well as a growing attention to positive emotions and PA deficits in individuals with SAD. This review also supports the notion that negative emotions and affect are not enough to distinguish normal from pathological SA. As demonstrated by Park and Naragon-Gainey [ 45 ], AA may help shed light on the structural models of affect both between and within individuals’ variances, evidence that traditional cross-sectional research or long-term longitudinal research may not capture.
Most interestingly, most of the studies exploring affect trends explored them coupled with ER strategies, consistently extending the vast literature in this regard. Exacerbated NA and PA and dysfunctional strategies to cope with them form a dysfunctional pattern that may be responsible for the appearance and maintenance of SA and SAD [ 85 ]. The studies revealed that the interpersonal encounters of individuals with SAD may differ from those of controls in terms of ER use and type of ER strategy. Specifically, both intra- and interpersonal regulatory mechanisms have been shown to be associated with increasing levels of SA. In clinical populations, what was shown to influence the levels of SA was not the use of certain strategies but rather the lack of effectiveness of their use. However, this was not the case in healthy populations. Accordingly, a potential difference between SA symptoms in healthy and clinical populations may lie on the effectiveness or underuse of ER strategies.
In line with the mounting evidence exploring suppression and both experiential and behavioral avoidance in individuals with SAD, this systematic review showed coherent and robust results across the included studies concerning the maladaptive use of these 2 strategies. People with SAD may present an overreliance on the use of suppression and avoidance [ 85 ], resulting in a range of negative outcomes such as an increase in NA and a decrease in PA.
In contrast, cognitive reappraisal, a putatively effective strategy, does not yield straightforward results. The problem with individuals with SAD is more the ineffective use of cognitive reappraisal rather than the scarce use of this strategy, although the studies did not seem to coherently yield conclusive results.
Taken together, the results on affective dynamics and ER indicate how appropriate AA can be to study these processes, especially in the case of SA and SAD. AA may be particularly helpful in disentangling between- and within-person effects, which the literature demonstrates can have different or even contrary results, especially in the context of psychological interventions [ 101 ].
As a key takeaway message, AA shows that individuals with high SA symptoms or a diagnosis of SAD may not use a narrower repertoire of ER strategies but rather implement that repertoire with less skillfulness or less ability to identify when it is appropriate to implement a certain strategy. In this sense, it is essential to continue exploring the role of polyregulation and flexibility to identify which specific facet of ER contributes as a mechanism of action of SAD.
In that vein, substance use can be seen as a maladaptive behavior that functions as a behavioral strategy to regulate emotions and cope with situations that elicit symptoms of SA. This is particularly recurrent in SA-provoking situations, constituting a reinforcement cycle that operates similarly to other safety behaviors. In particular, alcohol consumption may function as a negative reinforcer, attenuating the negative self-perceived quality of interpersonal encounters and anxiety levels. When this occurs, alcohol use becomes a rapidly established maladaptive behavior with negative consequences.
In addition, maladaptive cognitions, emotional mechanisms, and behaviors were found to be activated when levels of anxiety increased. More specifically, cognitive aspects such as beliefs in capacity, effectiveness in regulating emotions, and the ability to differentiate emotions appear to be relevant in explaining how SA is activated.
As a general takeaway message, there is ample evidence showing the mutual directionality between cognitive and affective or emotional facets and behaviors in the appearance and maintenance of SAD. The several sections in which the studies were categorized constitute just one way of organizing the information. However, many of these studies can be understood as forms of cognition or ER or specific interactional patterns. A clear example is alcohol consumption, which is a behavior that, in the context of SAD, can be understood as an ER strategy.
In that sense, ER is currently a trending topic in AA, but it is important to integrate this increasing amount of knowledge into classic cognitive models. This is pertinent for psychopathological developments in general, and SAD is not an exception. Over the years, the most influential developments in SAD have been cognitive and behavioral models [ 96 , 98 ]. Paradoxically, in this review, cognitive processes remained an underexplored area. An example of this is mental imagery, which has been shown to be a transdiagnostic process that explains the appearance and maintenance of a range of clinical conditions, including SAD [ 94 ]; however, there is a dearth of studies on this crucial construct.
An additional line of research that needs to be further explored is comorbidity to explore the mutual dependency of certain groups of signs and symptoms. However, given the lack of network analyses, this mutual dependency was not explored in depth. For example, there was only one study exploring suicidal ideation and attempts despite the ample existing literature on AA in suicide research [ 102 ] and the strong association between suicide and SA [ 103 ]. In the same vein, the relationship among personality, personality pathology, and SA is a relevant topic in contemporary psychopathology that could be further explored using AA strategies. Indeed, there is a growing body of evidence exploring personality and personality pathology dynamics and states, which should be considered in future studies of SA [ 9 ].
Another issue worth discussing revolves around the incorporation of AA into psychological interventions. This is an increasingly used practice and may be well integrated with routine outcome monitoring procedures that have been shown to yield significant effects when implemented in both controlled and naturalistic interventions [ 104 ]. Routine outcome monitoring is an increasingly implemented strategy that can connect research and practice in unprecedented ways. With that aim, it is necessary to create simple visualization interfaces to feed back the trajectories of certain patient variables. Some efforts have already been made in this direction [ 105 ]. If these endeavors are further developed, they can be used by clinicians as a clinical tool, and at the same time, researchers can collect naturalistic data.
Another topic with a lot of potential is the incorporation of behavioral and physiological processes by means of sensors and biosensors. Multimethod measurements that incorporate both passive and active assessments can be of tremendous relevance to harness the affordances of each approach. Together with the development of machine learning algorithms, the proliferation of EMIs is more plausible. This is very important to enhance the personalization of possible treatments.
Regarding data collection, there are now software solutions that are opening up unprecedented opportunities for future research. Older studies usually included PDAs or similar devices, which implies not only spending more resources to implement an AA study but also some degree of training in order for participants to be able to use these devices. Currently, there are studies that harness existing survey platforms such as Qualtrics to program either random or fixed prompts without the need for any specifically developed software.
Given that most of the studies were conducted in the United States and the rest were conducted in other Western high-income countries, the results should be generalized to other contexts. Cultural and contextual factors are determinant in all psychopathological conditions, and SAD is not an exception [ 106 ]. The proliferation of open-source platforms (eg, m-Path [ 107 ]) will permit the dissemination of this methodology to researchers without large budgets, such as researchers from low- and middle-income countries. This is crucial to guarantee that knowledge is not restricted to certain populations, fundamentally populations from Western, educated, industrialized, rich, and democratic countries. In addition, most of the studies (54/70, 77%) paid the participants to enhance the compliance rates, which turned out to be in line with the average compliance in AA literature (approximately 75% [ 108 ]). However, this should be considered in future research on AA that seeks to increase the external validity by means of ecological designs.
Methodological Design
Regarding the methodological design of the studies included in this systematic review, there are important aspects to discuss. Most of the studies were well designed; advanced statistical strategies were applied; and, accordingly, most of this research was published in journals with a high impact factor. However, there is a methodological pitfall in AA research that revolves around the lack of psychometrically sound instruments, usually because of trying to reduce participant burden as much as possible. According to Hopwood et al [ 109 ], four aspects are essential when discussing the theoretical and methodological implications for AA research: (1) How should time be scaled? (2) How many assessments are needed? (3) How frequently should assessments be conducted? and (4) When should the assessments occur? Researchers using AA methods to conduct research on SA and SAD should carefully consider these questions both theoretically and empirically. Moreover, there is a wider consensus on the need to conduct more theory-driven hypothesis testing [ 110 ]. All these methodological aspects should be considered with caution together with the importance of increasing the transparency of reporting the results of AA research [ 111 ].
Power analysis was revealed as a weak methodological aspect, with many of the studies not calculating the required sample sizes to anticipate the number of needed participants. Potential limitations concerning the quality of the studies seem to be related to the lack of clear guidelines and standards, which have only recently started to emerge [ 112 ].
Regarding the data analysis, most of the studies used multilevel or hierarchical linear models [ 113 ]. Indeed, in cases in which ANOVAs or ordinary least squares models were used instead of hierarchical models, the results should be interpreted with more caution. They do not account for the dependency of the data, and in longitudinal assessments such as AA in which data are essentially nested, using these strategies may yield inaccurate pictures of the data [ 114 ]. In addition, AAs generally entail mounting random missing data, and multilevel mixed models are appropriate to deal with that data structure.
Future studies need to incorporate new modalities of data analysis that might provide more complex information to understand the dynamics of SA. For example, multilevel network analyses [ 115 ] would allow for shedding light not only on the nested structure of the symptoms but also on the interconnectedness at every moment of the individuals’ experiences and behaviors. In addition, new-generation time-series analyses such as the time-varying change point autoregressive models would allow for the detection of gradual and abrupt changes in SA markers over the course of the AAs [ 116 ]. Furthermore, the recently developed dynamic structural equation modeling method [ 117 ] is particularly suitable for intensive longitudinal data from AA. This method allows for a more accurate estimation of individual differences in means and autoregressive effects from AA data. Finally, machine learning strategies will be paramount not only to build predictive models that can better explain SA but also to implement EMIs based on people’s needs [ 118 ]. In the field of SAD, there is a dearth of studies on EMIs, which is surprising given the ample evidence that has been found using AA.
Limitations
The results of this review should be considered in light of certain limitations. The first limitation concerns the inclusion criteria. Gray literature, including dissertations and preprint depositories, was not considered. Given the growing interest in this topic, we may have missed other relevant studies from these sources. However, this decision had the main aim of ensuring the rigor of including articles that had undergone a peer review process. In addition, we only included revised articles published in English, excluding articles published in different languages.
A second limitation is that this is the first synthesis that summarizes the literature on AA for SA, but further quantitative syntheses (ie, meta-analyses) should be conducted on the specific topics identified in this study. Thus, a qualitative review is a first step that contributes to taking stock of the principal topics studied in the field of SA and AA, but no conclusive statements should be drawn.
Conclusions
This systematic review shows that AA constitutes a very powerful modality to grasp SA from a complementary perspective to laboratory experiments and usual self-report measures. Over the last few years, mounting research has been conducted showing important trends that are shedding light on the understanding of SA and SAD using this ecological tool that is revolutionizing the field.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Margarita Salas postdoctoral contracts MGS/2021/37 (UP2021-021) and MGS/2022/18 (UP2022-024) financed by the European Union NextGenerationEU. This study was also funded by the Prometeo Programme grant for Research Groups of Excellence (CIPROM/2021/041—Project “IMPULSA”), Conselleria d’Innovació, Universitats, Ciència i Societat Digital, Generalitat Valenciana. Finally, this work was supported by the Generalitat Valenciana through the Santiago Grisolía predoctoral program (GRISOLIAP/2021/009).
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
Conflicts of Interest
None declared.
Syntax used in database searches.
Characteristics of the included studies.
Social anxiety disorder ambulatory assessment research design overview.
PRISMA Checklist.
- Gilboa-Schechtman E, Shachar I, Sahar Y. Positivity impairment as a broad-based feature of social anxiety. In: Weeks JW, editor. The Wiley Blackwell Handbook of Social Anxiety Disorder. Hoboken, NJ. John Wiley & Sons; 2014;409-432.
- Morrison AS, Heimberg RG. Social anxiety and social anxiety disorder. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. Mar 28, 2013;9(1):249-274. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Shiffman S, Stone AA, Hufford MR. Ecological momentary assessment. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. Apr 2008;4(1):1-32. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kuppens P, Oravecz Z, Tuerlinckx F. Feelings change: accounting for individual differences in the temporal dynamics of affect. J Pers Soc Psychol. Dec 2010;99(6):1042-1060. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Trull TJ, Ebner-Priemer UW. Using experience sampling methods/ecological momentary assessment (ESM/EMA) in clinical assessment and clinical research: introduction to the special section. Psychol Assess. Dec 2009;21(4):457-462. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Colombo D, Suso-Ribera C, Fernández-Álvarez J, Cipresso P. Technology based ecological momentary assessment in clinical psychology. In: Asmundson JG, editor. Comprehensive Clinical Psychology. New York, NY. Elsevier Academic Press; 2022;106-120.
- Fonseca-Pedrero E, Ródenas-Perea G, Pérez-Albéniz A, Al-Halabí S, Pérez M, Muñiz J. La hora de la evaluación ambulatoria. Pap Psicol. 2021;42(2):21-28. [ CrossRef ]
- Palmier-Claus JE, Myin-Germeys I, Barkus E, Bentley L, Udachina A, Delespaul PA, et al. Experience sampling research in individuals with mental illness: reflections and guidance. Acta Psychiatr Scand. Jan 2011;123(1):12-20. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Wright AG, Woods WC. Personalized models of psychopathology. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. May 07, 2020;16:49-74. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Myin-Germeys I, Kasanova Z, Vaessen T, Vachon H, Kirtley O, Viechtbauer W, et al. Experience sampling methodology in mental health research: new insights and technical developments. World Psychiatry. Jun 24, 2018;17(2):123-132. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ. Jul 21, 2009;339(jul21 1):b2535. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Social anxiety is experienced in the wild: a protocol for a systematic review of studies using ambulatory assessment. Open Science Framework. URL: https://osf.io/47hc8/ [accessed 2024-02-17]
- Asher M, Asnaani A, Aderka IM. Gender differences in social anxiety disorder: a review. Clin Psychol Rev. Aug 2017;56:1-12. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Blalock DV, Kashdan TB, Farmer AS. Trait and daily emotion regulation in social anxiety disorder. Cogn Ther Res. Dec 8, 2015;40(3):416-425. [ CrossRef ]
- Blalock DV, Kashdan TB, McKnight PE. High risk, high reward: daily perceptions of social challenge and performance in social anxiety disorder. J Anxiety Disord. Mar 2018;54:57-64. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Farmer AS, Kashdan TB. Affective and self-esteem instability in the daily lives of people with generalized social anxiety disorder. Clin Psychol Sci. Mar 01, 2014;2(2):187-201. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Goodman FR, Kashdan TB, Stiksma MC, Blalock DV. Personal strivings to understand anxiety disorders: social anxiety as an exemplar. Clin Psychol Sci. Nov 14, 2018;7(2):283-301. [ CrossRef ]
- Goodman FR, Kashdan TB, İmamoğlu A. Valuing emotional control in social anxiety disorder: a multimethod study of emotion beliefs and emotion regulation. Emotion. Jun 2021;21(4):842-855. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kashdan TB, Farmer AS. Differentiating emotions across contexts: comparing adults with and without social anxiety disorder using random, social interaction, and daily experience sampling. Emotion. Jun 2014;14(3):629-638. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kashdan TB, Farmer AS, Adams LM, Ferssizidis P, McKnight PE, Nezlek JB. Distinguishing healthy adults from people with social anxiety disorder: evidence for the value of experiential avoidance and positive emotions in everyday social interactions. J Abnorm Psychol. Aug 2013;122(3):645-655. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kashdan TB, Goodman FR, Machell KA, Kleiman EM, Monfort SS, Ciarrochi J, et al. A contextual approach to experiential avoidance and social anxiety: evidence from an experimental interaction and daily interactions of people with social anxiety disorder. Emotion. Aug 2014;14(4):769-781. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Daniel KE, Larrazabal MA, Boukhechba M, Barnes LE, Teachman BA. State and trait emotion regulation diversity in social anxiety. Clin Psychol Sci. Sep 28, 2023;11(5):894-909. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Beltzer ML, Ameko MK, Daniel KE, Daros AR, Boukhechba M, Barnes LE, et al. Building an emotion regulation recommender algorithm for socially anxious individuals using contextual bandits. Br J Clin Psychol. Jan 14, 2022;61 Suppl 1(S1):51-72. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Daniel KE, Baee S, Boukhechba M, Barnes LE, Teachman BA. Do I really feel better? Effectiveness of emotion regulation strategies depends on the measure and social anxiety. Depress Anxiety. Dec 25, 2019;36(12):1182-1190. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Daros AR, Daniel KE, Meyer MJ, Chow PI, Barnes LE, Teachman BA. Impact of social anxiety and social context on college students’ emotion regulation strategy use: an experience sampling study. Motiv Emot. May 27, 2019;43(5):844-855. [ CrossRef ]
- Ladis I, Toner ER, Daros AR, Daniel KE, Boukhechba M, Chow PI, et al. Assessing emotion polyregulation in daily life: who uses it, when is it used, and how effective is it? Affect Sci. Jun 08, 2023;4(2):248-259. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Doorley JD, Volgenau KM, Kelso KC, Kashdan TB, Shackman AJ. Do people with elevated social anxiety respond differently to digital and face-to-face communications? Two daily diary studies with null effects. J Affect Disord. Nov 01, 2020;276:859-865. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Doorley JD, Goodman FR, Disabato DJ, Kashdan TB, Weinstein JS, Shackman AJ. The momentary benefits of positive events for individuals with elevated social anxiety. Emotion. Apr 2021;21(3):595-606. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Goodman FR, Kashdan TB. The most important life goals of people with and without social anxiety disorder: focusing on emotional interference and uncovering meaning in life. J Posit Psychol. Nov 11, 2021;16(2):272-281. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Goodman FR, Rum R, Silva G, Kashdan TB. Are people with social anxiety disorder happier alone? J Anxiety Disord. Dec 2021;84:102474. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Goodman FR, Kelso KC, Wiernik BM, Kashdan TB. Social comparisons and social anxiety in daily life: an experience-sampling approach. J Abnorm Psychol. Jul 2021;130(5):468-489. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Goodman FR, Daniel KE, Eldesouky L, Brown BA, Kneeland ET. How do people with social anxiety disorder manage daily stressors? Deconstructing emotion regulation flexibility in daily life. J Affect Disord Rep. Dec 2021;6:100210. [ CrossRef ]
- Oren-Yagoda R, Aderka IM. The medium is the message: effects of mediums of communication on perceptions and emotions in social anxiety disorder. J Anxiety Disord. Oct 2021;83:102458. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Oren-Yagoda R, Paz N, Aderka IM. Pride in social anxiety disorder. J Anxiety Disord. Oct 2023;99:102759. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Oren-Yagoda R, Schwartz M, Aderka IM. The grass is always greener: envy in social anxiety disorder. J Anxiety Disord. Aug 2021;82:102445. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Oren-Yagoda R, Melamud-Ganani I, Aderka IM. All by myself: loneliness in social anxiety disorder. J Psychopathol Clin Sci. Jan 2022;131(1):4-13. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- O’Toole MS, Jensen MB, Fentz HN, Zachariae R, Hougaard E. Emotion differentiation and emotion regulation in high and low socially anxious individuals: an experience-sampling study. Cogn Ther Res. Mar 13, 2014;38(4):428-438. [ CrossRef ]
- O'Toole MS, Zachariae R, Mennin DS. Social anxiety and emotion regulation flexibility: considering emotion intensity and type as contextual factors. Anxiety Stress Coping. Nov 30, 2017;30(6):716-724. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Villanueva J, Meyer AH, Miché M, Wersebe H, Mikoteit T, Hoyer J, et al. Social interaction in major depressive disorder, social phobia, and controls: the importance of affect. J Technol Behav Sci. Dec 10, 2019;5(2):139-148. [ CrossRef ]
- Rinner MT, Meyer AH, Mikoteit T, Hoyer J, Imboden C, Hatzinger M, et al. General or specific? The memory-experience gap for individuals diagnosed with a major depressive disorder or a social phobia diagnosis, and individuals without such diagnoses. Memory. Oct 16, 2019;27(9):1194-1203. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Katz DE, Cassin S, Weerasinghe R, Rector NA. Changes in post-event processing during cognitive behavioural therapy for social anxiety disorder: a longitudinal analysis using post-session measurement and experience sampling methodology. J Anxiety Disord. Aug 2019;66:102107. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Lee MR, Okazaki S, Yoo HC. Frequency and intensity of social anxiety in Asian Americans and European Americans. Cultur Divers Ethnic Minor Psychol. Apr 2006;12(2):291-305. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Naragon-Gainey K. Affective models of depression and anxiety: extension to within-person processes in daily life. J Affect Disord. Jan 15, 2019;243:241-248. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Russell JJ, Moskowitz DS, Zuroff DC, Bleau P, Pinard G, Young SN. Anxiety, emotional security and the interpersonal behavior of individuals with social anxiety disorder. Psychol Med. May 12, 2010;41(3):545-554. [ CrossRef ]
- Park J, Naragon-Gainey K. Daily experiences of emotional clarity and their association with internalizing symptoms in naturalistic settings. Emotion. Aug 2019;19(5):764-775. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Helbig-Lang S, von Auer M, Neubauer K, Murray E, Gerlach AL. Post-event processing in social anxiety disorder after real-life social situations - an ambulatory assessment study. Behav Res Ther. Sep 2016;84:27-34. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Jacobson NC, Summers B, Wilhelm S. Digital biomarkers of social anxiety severity: digital phenotyping using passive smartphone sensors. J Med Internet Res. May 29, 2020;22(5):e16875. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Seah TH, Aurora P, Coifman KG. Emotion differentiation as a protective factor against the behavioral consequences of rumination: a conceptual replication and extension in the context of social anxiety. Behav Ther. Jan 2020;51(1):135-148. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Arch JJ, Wilcox RR, Ives LT, Sroloff A, Andrews-Hanna JR. Off-task thinking among adults with and without social anxiety disorder: an ecological momentary assessment study. Cogn Emot. Mar 19, 2021;35(2):269-281. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Badra M, Schulze L, Becker ES, Vrijsen JN, Renneberg B, Zetsche U. The association between ruminative thinking and negative interpretation bias in social anxiety. Cogn Emot. Sep 2017;31(6):1234-1242. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Bailey T, Shahabi L, Tarvainen M, Shapiro D, Ottaviani C. Moderating effects of the valence of social interaction on the dysfunctional consequences of perseverative cognition: an ecological study in major depression and social anxiety disorder. Anxiety Stress Coping. Mar 22, 2019;32(2):179-195. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Battista SR, MacKinnon SP, Sherry SB, Barrett SP, MacNevin PD, Stewart SH. Does alcohol reduce social anxiety in daily life? A 22-day experience sampling study. J Soc Clin Psychol. Jun 2015;34(6):508-528. [ CrossRef ]
- Boukhechba M, Chow P, Fua K, Teachman BA, Barnes LE. Predicting social anxiety from global positioning system traces of college students: feasibility study. JMIR Ment Health. Jul 04, 2018;5(3):e10101. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Brown LH, Silvia PJ, Myin-Germeys I, Kwapil TR. When the need to belong goes wrong: the expression of social anhedonia and social anxiety in daily life. Psychol Sci. Sep 06, 2007;18(9):778-782. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Brown BA, Rottenberg J, Goodman FR. Social anxiety and interpersonal risk for suicidal ideation: a longitudinal daily diary analysis. Suicide Life Threat Behav. Dec 28, 2023;53(6):968-980. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Buckner JD, Crosby RD, Wonderlich SA, Schmidt NB. Social anxiety and cannabis use: an analysis from ecological momentary assessment. J Anxiety Disord. Mar 2012;26(2):297-304. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Buckner JD, Langdon KJ, Jeffries ER, Zvolensky MJ. Socially anxious smokers experience greater negative affect and withdrawal during self-quit attempts. Addict Behav. Apr 2016;55:46-49. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Chow PI, Fua K, Huang Y, Bonelli W, Xiong H, Barnes LE, et al. Using mobile sensing to test clinical models of depression, social anxiety, state affect, and social isolation among college students. J Med Internet Res. Mar 03, 2017;19(3):e62. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Čolić J, Bassett TR, Latysheva A, Imboden C, Bader K, Hatzinger M, et al. Depersonalization and derealization in embarrassing social interactions: an experience sampling study in social phobia, major depression and controls. J Anxiety Disord. Mar 2020;70:102189. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Di Matteo D, Fotinos K, Lokuge S, Mason G, Sternat T, Katzman MA, et al. Automated screening for social anxiety, generalized anxiety, and depression from objective smartphone-collected data: cross-sectional study. J Med Internet Res. Aug 13, 2021;23(8):e28918. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Farmer AS, Kashdan TB. Social anxiety and emotion regulation in daily life: spillover effects on positive and negative social events. Cogn Behav Ther. 2012;41(2):152-162. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Geyer EC, Fua KC, Daniel KE, Chow PI, Bonelli W, Huang Y, et al. I did ok, but did I like it? Using ecological momentary assessment to examine perceptions of social interactions associated with severity of social anxiety and depression. Behav Ther. Nov 2018;49(6):866-880. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Goodman FR, Stiksma MC, Kashdan TB. Social anxiety and the quality of everyday social interactions: the moderating influence of alcohol consumption. Behav Ther. May 2018;49(3):373-387. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Goodman FR, Brown BA, Silva GM, Bradford DE, Tennen H, Kashdan TB. Motives and consequences of alcohol use in people with social anxiety disorder: a daily diary study. Behav Ther. Jul 2022;53(4):600-613. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hannah Lee J. Perceptions towards an interaction partner predict social anxiety: an ecological momentary assessment study. Cogn Emot. Dec 30, 2021;35(8):1479-1498. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hur J, DeYoung KA, Islam S, Anderson AS, Barstead MG, Shackman AJ. Social context and the real-world consequences of social anxiety. Psychol Med. Aug 19, 2019;50(12):1989-2000. [ CrossRef ]
- Jacobson NC, Bhattacharya S. Digital biomarkers of anxiety disorder symptom changes: personalized deep learning models using smartphone sensors accurately predict anxiety symptoms from ecological momentary assessments. Behav Res Ther. Feb 2022;149:104013. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kane L, Ashbaugh AR. Ecological momentary assessment of post-event processing in between two speech tasks: relationships with cognitive and affective factors involved in the maintenance of social anxiety. Behav Res Ther. Dec 2022;159:104208. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kashdan TB, Steger MF. Expanding the topography of social anxiety. An experience-sampling assessment of positive emotions, positive events, and emotion suppression. Psychol Sci. Feb 06, 2006;17(2):120-128. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kashdan TB, Collins RL. Social anxiety and the experience of positive emotion and anger in everyday life: an ecological momentary assessment approach. Anxiety Stress Coping. May 2010;23(3):259-272. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kashdan TB, Adams L, Savostyanova A, Ferssizidis P, McKnight PE, Nezlek JB. Effects of social anxiety and depressive symptoms on the frequency and quality of sexual activity: a daily process approach. Behav Res Ther. May 2011;49(5):352-360. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kivity Y, Huppert JD. Does cognitive reappraisal reduce anxiety? A daily diary study of a micro-intervention with individuals with high social anxiety. J Consult Clin Psychol. Mar 2016;84(3):269-283. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kim S, Kwon JH. The impact of negative emotions on drinking among individuals with social anxiety disorder in daily life: the moderating effect of maladaptive emotion regulation strategies. Cogn Ther Res. Oct 09, 2019;44(2):345-359. [ CrossRef ]
- Nanamori M, Tomita N, Kametani C, Matsuda N, Kumano H. Triggers of self-focused attention: an ecological momentary assessment study. Biopsychosoc Med. Apr 23, 2023;17(1):16. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- O'Grady MA, Cullum J, Armeli S, Tennen H. Putting the relationship between social anxiety and alcohol use into context: a daily diary investigation of drinking in response to embarrassing events. J Soc Clin Psychol. Jun 2011;30(6):599-615. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Papp LM, Kouros CD, Witt HK, Curtin JJ, Blumenstock SM, Barringer A. Real-time momentary mood as a predictor of college students’ prescription drug misuse in daily life: direct links and the moderating role of background mental health. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. Dec 2022;30(6):787-796. [ CrossRef ]
- Piccirillo ML, Rodebaugh TL. Personalized networks of social anxiety disorder and depression and implications for treatment. J Affect Disord. Feb 01, 2022;298(Pt A):262-276. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Reichenberger J, Smyth JM, Blechert J. Fear of evaluation unpacked: day-to-day correlates of fear of negative and positive evaluation. Anxiety Stress Coping. Mar 09, 2018;31(2):159-174. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Saulnier KG, Saulnier SJ, Allan NP. Cognitive risk factors and the experience of acute anxiety following social stressors: an ecological momentary assessment study. J Anxiety Disord. May 2022;88:102571. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Walukevich-Dienst K, Calhoun BH, Fairlie AM, Cadigan JM, Patrick ME, Lee CM. Using substances to cope with social anxiety: associations with use and consequences in daily life. Psychol Addict Behav. Jun 2023;37(4):581-591. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Wilson GA, Koerner N, Antony MM. An examination of feedback seeking in individuals with social anxiety disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, or no history of mental disorder using a daily diary method. J Cogn Psychother. Apr 01, 2018;32(1):15-37. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Daniel KE, Mendu S, Baglione A, Cai L, Teachman BA, Barnes LE, et al. Cognitive bias modification for threat interpretations: using passive Mobile Sensing to detect intervention effects in daily life. Anxiety Stress Coping. May 31, 2022;35(3):298-312. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Daniel KE, Daros AR, Beltzer ML, Boukhechba M, Barnes LE, Teachman BA. How anxious are you right now? Using ecological momentary assessment to evaluate the effects of cognitive bias modification for social threat interpretations. Cogn Ther Res. Mar 11, 2020;44(3):538-556. [ CrossRef ]
- Rozen N, Aderka IM. Emotions in social anxiety disorder: a review. J Anxiety Disord. Apr 2023;95:102696. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Dryman MT, Heimberg RG. Emotion regulation in social anxiety and depression: a systematic review of expressive suppression and cognitive reappraisal. Clin Psychol Rev. Nov 2018;65:17-42. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Ford BQ, Gross JJ, Gruber J. Broadening our field of view: the role of emotion polyregulation. Emot Rev. Jun 23, 2019;11(3):197-208. [ CrossRef ]
- Aldao A, Sheppes G, Gross JJ. Emotion regulation flexibility. Cogn Ther Res. Jan 1, 2015;39(3):263-278. [ CrossRef ]
- Tamir M, Mitchell C, Gross JJ. Hedonic and instrumental motives in anger regulation: research report. Psychol Sci. Apr 01, 2008;19(4):324-328. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- De castella K, Goldin P, Jazaieri H, Ziv M, Heimberg RG, Gross JJ. Emotion beliefs in social anxiety disorder: associations with stress, anxiety, and well‐being. Aust J Psychol. Nov 20, 2020;66(2):139-148. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ]
- McRae K, Zarolia P. Cognition and emotion in emotion dysregulation. In: Beauchaine TP, Crowell SE, editors. The Oxford Handbook of Emotion Dysregulation. Oxford, UK. Oxford University Press; 2018;39-52.
- Gohm CL, Clore GL. Individual differences in emotional experience: mapping available scales to processes. Pers Soc Psychol Bull. Jul 02, 2016;26(6):679-697. [ CrossRef ]
- Barrett LF, Gross J, Christensen TC, Benvenuto M. Knowing what you're feeling and knowing what to do about it: mapping the relation between emotion differentiation and emotion regulation. Cogn Emot. Nov 2001;15(6):713-724. [ CrossRef ]
- Ottaviani C, Couyoumdjian A. Pros and cons of a wandering mind: a prospective study. Front Psychol. 2013;4:524. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- McEvoy PM, Erceg-Hurn DM, Barber KC, Dupasquier JR, Moscovitch DA. Transportability of imagery-enhanced CBT for social anxiety disorder. Behav Res Ther. Jul 2018;106:86-94. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hirsch CR, Clark DM, Mathews A, Williams R. Self-images play a causal role in social phobia. Behav Res Ther. Aug 2003;41(8):909-921. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Clark DM, Wells A. A cognitive model of social phobia. PsycNET. URL: https://psycnet.apa.org/record/1995-98887-004 [accessed 2024-09-15]
- Moscovitch DA. What is the core fear in social phobia? A new model to facilitate individualized case conceptualization and treatment. Cogn Behav Pract. May 2009;16(2):123-134. [ CrossRef ]
- Rapee RM, Heimberg RG. A cognitive-behavioral model of anxiety in social phobia. Behav Res Ther. Aug 1997;35(8):741-756. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Weeks JW, Howell AN. Fear of positive evaluation: the neglected fear domain in social anxiety. In: Weeks JW, editor. The Wiley Blackwell Handbook of Social Anxiety Disorder. Hoboken, NJ. John Wiley & Sons; 2014.
- Mather M, Thayer JF. How heart rate variability affects emotion regulation brain networks. Curr Opin Behav Sci. Feb 2018;19:98-104. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Zilcha-Mano S. Toward personalized psychotherapy: the importance of the trait-like/state-like distinction for understanding therapeutic change. Am Psychol. Apr 2021;76(3):516-528. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Sedano-Capdevila A, Porras-Segovia A, Bello HJ, Baca-García E, Barrigon ML. Use of ecological momentary assessment to study suicidal thoughts and behavior: a systematic review. Curr Psychiatry Rep. May 18, 2021;23(7):41. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Buckner JD, Lemke AW, Jeffries ER, Shah SM. Social anxiety and suicidal ideation: test of the utility of the interpersonal-psychological theory of suicide. J Anxiety Disord. Jan 2017;45:60-63. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- de Jong K, Conijn JM, Gallagher RA, Reshetnikova AS, Heij M, Lutz MC. Using progress feedback to improve outcomes and reduce drop-out, treatment duration, and deterioration: a multilevel meta-analysis. Clin Psychol Rev. Apr 2021;85:102002. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Bringmann LF, van der Veen DC, Wichers M, Riese H, Stulp G. ESMvis: a tool for visualizing individual experience sampling method (ESM) data. Qual Life Res. Nov 22, 2021;30(11):3179-3188. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Soto JA, Dawson-Andoh NA, BeLue R. The relationship between perceived discrimination and generalized anxiety disorder among African Americans, Afro Caribbeans, and non-Hispanic Whites. J Anxiety Disord. Mar 2011;25(2):258-265. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Mestdagh M, Verdonck S, Piot M, Niemeijer K, Tuerlinckx F, Kuppens P, et al. m-Path: an easy-to-use and highly tailorable platform for ecological momentary assessment and intervention in behavioral research and clinical practice. PsyArXiv. Preprints posted online January 25, 2022. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wrzus C, Neubauer AB. Ecological momentary assessment: a meta-analysis on designs, samples, and compliance across research fields. Assessment. Apr 11, 2023;30(3):825-846. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hopwood CJ, Bleidorn W, Wright AG. Connecting theory to methods in longitudinal research. Perspect Psychol Sci. May 05, 2022;17(3):884-894. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Kuppens P, Dejonckheere E, Kalokerinos EK, Koval P. Some recommendations on the use of daily life methods in affective science. Affect Sci. Jun 19, 2022;3(2):505-515. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hall M, Scherner PV, Kreidel Y, Rubel JA. A systematic review of momentary assessment designs for mood and anxiety symptoms. Front Psychol. May 17, 2021;12:642044. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Trull TJ, Ebner-Priemer UW. Ambulatory assessment in psychopathology research: a review of recommended reporting guidelines and current practices. J Abnorm Psychol. Jan 2020;129(1):56-63. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Raudenbush SW, Bryk AS. Hierarchical Linear Models: Applications and Data Analysis Methods. 2nd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA. Sage Publications; 2002.
- Gómez Penedo JM, Muiños R, Hirsch P, Roussos A. La aplicación de modelos lineales jerárquicos para el estudio de la eficacia en psicoterapia. Rev Argent Cienc Comport. Apr 24, 2019;11(1):25. [ CrossRef ]
- Bringmann LF, Vissers N, Wichers M, Geschwind N, Kuppens P, Peeters F, et al. A network approach to psychopathology: new insights into clinical longitudinal data. PLoS One. Apr 4, 2013;8(4):e60188. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hehlmann MI, Schwartz B, Lutz T, Gómez Penedo JM, Rubel JA, Lutz W. The use of digitally assessed stress levels to model change processes in CBT - a feasibility study on seven case examples. Front Psychiatry. Mar 9, 2021;12:613085. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hamaker EL, Asparouhov T, Brose A, Schmiedek F, Muthén B. At the frontiers of modeling intensive longitudinal data: dynamic structural equation models for the affective measurements from the COGITO study. Multivariate Behav Res. Apr 06, 2018;53(6):820-841. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Delgadillo J. Machine learning: a primer for psychotherapy researchers. Psychother Res. Jan 29, 2021;31(1):1-4. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
Abbreviations
Edited by J Torous; submitted 17.02.23; peer-reviewed by K Daniel, T Ranjan; comments to author 03.09.23; revised version received 28.01.24; accepted 07.02.24; published 04.04.24.
©Javier Fernández-Álvarez, Desirée Colombo, Juan Martín Gómez Penedo, Maitena Pierantonelli, Rosa María Baños, Cristina Botella. Originally published in JMIR Mental Health (https://mental.jmir.org), 04.04.2024.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work, first published in JMIR Mental Health, is properly cited. The complete bibliographic information, a link to the original publication on https://mental.jmir.org/, as well as this copyright and license information must be included.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
This article is part of the research topic.
Exploring STEM Environments that Broaden Participation
Facilitating Collaboration Between Japanese High Schools and Universities: A Qualitative Exploration of the Role of Education Outreach Coordinators Provisionally Accepted

- 1 The University of Tokyo, Japan
The final, formatted version of the article will be published soon.
In recent years, universities have been expected to participate in Japanese high school education, especially in the "period for inquiry-based cross-disciplinary study." Despite various university faculties engaging in diverse educational practices, there is insufficient research on human resource development and the creation of mechanisms to ensure continuous development.This study conducted semi-structured interviews from July to November 2023, with 15 educators from universities and high schools, among others, to explore the current state of educational collaborations between these institutions and identify potential solutions.A reflective thematic analysis of the interview identified two key themes: the significance of university involvement in high school education and conflict areas generated from this collaboration. The findings suggest that the success of these initiatives relies on the involvement of coordinators who possess a high level of expertise and competencies.Discussion: These coordinators, who work in the "third space" in universities, are crucial for realizing the ideal outcomes of educational collaborations between universities and high schools in Japan's new educational environment.In the Japanese education system, particularly at the high school level, there is an increasing expectation for more university involvement.
Keywords: qualitative research, school-university collaboration, Coordinator, third space professionals, Japan
Received: 28 Feb 2024; Accepted: 03 Apr 2024.
Copyright: © 2024 Mori. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Mx. Akiko Mori, The University of Tokyo, Bunkyo, Japan
People also looked at
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.37(16); 2022 Apr 25

A Practical Guide to Writing Quantitative and Qualitative Research Questions and Hypotheses in Scholarly Articles
Edward barroga.
1 Department of General Education, Graduate School of Nursing Science, St. Luke’s International University, Tokyo, Japan.
Glafera Janet Matanguihan
2 Department of Biological Sciences, Messiah University, Mechanicsburg, PA, USA.
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. Consequently, these objectives determine the study design and research outcome. The development of research questions is a process based on knowledge of current trends, cutting-edge studies, and technological advances in the research field. Excellent research questions are focused and require a comprehensive literature search and in-depth understanding of the problem being investigated. Initially, research questions may be written as descriptive questions which could be developed into inferential questions. These questions must be specific and concise to provide a clear foundation for developing hypotheses. Hypotheses are more formal predictions about the research outcomes. These specify the possible results that may or may not be expected regarding the relationship between groups. Thus, research questions and hypotheses clarify the main purpose and specific objectives of the study, which in turn dictate the design of the study, its direction, and outcome. Studies developed from good research questions and hypotheses will have trustworthy outcomes with wide-ranging social and health implications.
INTRODUCTION
Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses. 1 , 2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results. 3 , 4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the inception of novel studies and the ethical testing of ideas. 5 , 6
It is crucial to have knowledge of both quantitative and qualitative research 2 as both types of research involve writing research questions and hypotheses. 7 However, these crucial elements of research are sometimes overlooked; if not overlooked, then framed without the forethought and meticulous attention it needs. Planning and careful consideration are needed when developing quantitative or qualitative research, particularly when conceptualizing research questions and hypotheses. 4
There is a continuing need to support researchers in the creation of innovative research questions and hypotheses, as well as for journal articles that carefully review these elements. 1 When research questions and hypotheses are not carefully thought of, unethical studies and poor outcomes usually ensue. Carefully formulated research questions and hypotheses define well-founded objectives, which in turn determine the appropriate design, course, and outcome of the study. This article then aims to discuss in detail the various aspects of crafting research questions and hypotheses, with the goal of guiding researchers as they develop their own. Examples from the authors and peer-reviewed scientific articles in the healthcare field are provided to illustrate key points.
DEFINITIONS AND RELATIONSHIP OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
A research question is what a study aims to answer after data analysis and interpretation. The answer is written in length in the discussion section of the paper. Thus, the research question gives a preview of the different parts and variables of the study meant to address the problem posed in the research question. 1 An excellent research question clarifies the research writing while facilitating understanding of the research topic, objective, scope, and limitations of the study. 5
On the other hand, a research hypothesis is an educated statement of an expected outcome. This statement is based on background research and current knowledge. 8 , 9 The research hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a new phenomenon 10 or a formal statement on the expected relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. 3 , 11 It provides a tentative answer to the research question to be tested or explored. 4
Hypotheses employ reasoning to predict a theory-based outcome. 10 These can also be developed from theories by focusing on components of theories that have not yet been observed. 10 The validity of hypotheses is often based on the testability of the prediction made in a reproducible experiment. 8
Conversely, hypotheses can also be rephrased as research questions. Several hypotheses based on existing theories and knowledge may be needed to answer a research question. Developing ethical research questions and hypotheses creates a research design that has logical relationships among variables. These relationships serve as a solid foundation for the conduct of the study. 4 , 11 Haphazardly constructed research questions can result in poorly formulated hypotheses and improper study designs, leading to unreliable results. Thus, the formulations of relevant research questions and verifiable hypotheses are crucial when beginning research. 12
CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Excellent research questions are specific and focused. These integrate collective data and observations to confirm or refute the subsequent hypotheses. Well-constructed hypotheses are based on previous reports and verify the research context. These are realistic, in-depth, sufficiently complex, and reproducible. More importantly, these hypotheses can be addressed and tested. 13
There are several characteristics of well-developed hypotheses. Good hypotheses are 1) empirically testable 7 , 10 , 11 , 13 ; 2) backed by preliminary evidence 9 ; 3) testable by ethical research 7 , 9 ; 4) based on original ideas 9 ; 5) have evidenced-based logical reasoning 10 ; and 6) can be predicted. 11 Good hypotheses can infer ethical and positive implications, indicating the presence of a relationship or effect relevant to the research theme. 7 , 11 These are initially developed from a general theory and branch into specific hypotheses by deductive reasoning. In the absence of a theory to base the hypotheses, inductive reasoning based on specific observations or findings form more general hypotheses. 10
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions and hypotheses are developed according to the type of research, which can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative research. We provide a summary of the types of research questions and hypotheses under quantitative and qualitative research categories in Table 1 .
Research questions in quantitative research
In quantitative research, research questions inquire about the relationships among variables being investigated and are usually framed at the start of the study. These are precise and typically linked to the subject population, dependent and independent variables, and research design. 1 Research questions may also attempt to describe the behavior of a population in relation to one or more variables, or describe the characteristics of variables to be measured ( descriptive research questions ). 1 , 5 , 14 These questions may also aim to discover differences between groups within the context of an outcome variable ( comparative research questions ), 1 , 5 , 14 or elucidate trends and interactions among variables ( relationship research questions ). 1 , 5 We provide examples of descriptive, comparative, and relationship research questions in quantitative research in Table 2 .
Hypotheses in quantitative research
In quantitative research, hypotheses predict the expected relationships among variables. 15 Relationships among variables that can be predicted include 1) between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable ( simple hypothesis ) or 2) between two or more independent and dependent variables ( complex hypothesis ). 4 , 11 Hypotheses may also specify the expected direction to be followed and imply an intellectual commitment to a particular outcome ( directional hypothesis ) 4 . On the other hand, hypotheses may not predict the exact direction and are used in the absence of a theory, or when findings contradict previous studies ( non-directional hypothesis ). 4 In addition, hypotheses can 1) define interdependency between variables ( associative hypothesis ), 4 2) propose an effect on the dependent variable from manipulation of the independent variable ( causal hypothesis ), 4 3) state a negative relationship between two variables ( null hypothesis ), 4 , 11 , 15 4) replace the working hypothesis if rejected ( alternative hypothesis ), 15 explain the relationship of phenomena to possibly generate a theory ( working hypothesis ), 11 5) involve quantifiable variables that can be tested statistically ( statistical hypothesis ), 11 6) or express a relationship whose interlinks can be verified logically ( logical hypothesis ). 11 We provide examples of simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative, causal, null, alternative, working, statistical, and logical hypotheses in quantitative research, as well as the definition of quantitative hypothesis-testing research in Table 3 .
Research questions in qualitative research
Unlike research questions in quantitative research, research questions in qualitative research are usually continuously reviewed and reformulated. The central question and associated subquestions are stated more than the hypotheses. 15 The central question broadly explores a complex set of factors surrounding the central phenomenon, aiming to present the varied perspectives of participants. 15
There are varied goals for which qualitative research questions are developed. These questions can function in several ways, such as to 1) identify and describe existing conditions ( contextual research question s); 2) describe a phenomenon ( descriptive research questions ); 3) assess the effectiveness of existing methods, protocols, theories, or procedures ( evaluation research questions ); 4) examine a phenomenon or analyze the reasons or relationships between subjects or phenomena ( explanatory research questions ); or 5) focus on unknown aspects of a particular topic ( exploratory research questions ). 5 In addition, some qualitative research questions provide new ideas for the development of theories and actions ( generative research questions ) or advance specific ideologies of a position ( ideological research questions ). 1 Other qualitative research questions may build on a body of existing literature and become working guidelines ( ethnographic research questions ). Research questions may also be broadly stated without specific reference to the existing literature or a typology of questions ( phenomenological research questions ), may be directed towards generating a theory of some process ( grounded theory questions ), or may address a description of the case and the emerging themes ( qualitative case study questions ). 15 We provide examples of contextual, descriptive, evaluation, explanatory, exploratory, generative, ideological, ethnographic, phenomenological, grounded theory, and qualitative case study research questions in qualitative research in Table 4 , and the definition of qualitative hypothesis-generating research in Table 5 .
Qualitative studies usually pose at least one central research question and several subquestions starting with How or What . These research questions use exploratory verbs such as explore or describe . These also focus on one central phenomenon of interest, and may mention the participants and research site. 15
Hypotheses in qualitative research
Hypotheses in qualitative research are stated in the form of a clear statement concerning the problem to be investigated. Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes. 2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed-methods research question can be developed. 1
FRAMEWORKS FOR DEVELOPING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions followed by hypotheses should be developed before the start of the study. 1 , 12 , 14 It is crucial to develop feasible research questions on a topic that is interesting to both the researcher and the scientific community. This can be achieved by a meticulous review of previous and current studies to establish a novel topic. Specific areas are subsequently focused on to generate ethical research questions. The relevance of the research questions is evaluated in terms of clarity of the resulting data, specificity of the methodology, objectivity of the outcome, depth of the research, and impact of the study. 1 , 5 These aspects constitute the FINER criteria (i.e., Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant). 1 Clarity and effectiveness are achieved if research questions meet the FINER criteria. In addition to the FINER criteria, Ratan et al. described focus, complexity, novelty, feasibility, and measurability for evaluating the effectiveness of research questions. 14
The PICOT and PEO frameworks are also used when developing research questions. 1 The following elements are addressed in these frameworks, PICOT: P-population/patients/problem, I-intervention or indicator being studied, C-comparison group, O-outcome of interest, and T-timeframe of the study; PEO: P-population being studied, E-exposure to preexisting conditions, and O-outcome of interest. 1 Research questions are also considered good if these meet the “FINERMAPS” framework: Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, Relevant, Manageable, Appropriate, Potential value/publishable, and Systematic. 14
As we indicated earlier, research questions and hypotheses that are not carefully formulated result in unethical studies or poor outcomes. To illustrate this, we provide some examples of ambiguous research question and hypotheses that result in unclear and weak research objectives in quantitative research ( Table 6 ) 16 and qualitative research ( Table 7 ) 17 , and how to transform these ambiguous research question(s) and hypothesis(es) into clear and good statements.
a These statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
b These statements are direct quotes from Higashihara and Horiuchi. 16
a This statement is a direct quote from Shimoda et al. 17
The other statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
CONSTRUCTING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
To construct effective research questions and hypotheses, it is very important to 1) clarify the background and 2) identify the research problem at the outset of the research, within a specific timeframe. 9 Then, 3) review or conduct preliminary research to collect all available knowledge about the possible research questions by studying theories and previous studies. 18 Afterwards, 4) construct research questions to investigate the research problem. Identify variables to be accessed from the research questions 4 and make operational definitions of constructs from the research problem and questions. Thereafter, 5) construct specific deductive or inductive predictions in the form of hypotheses. 4 Finally, 6) state the study aims . This general flow for constructing effective research questions and hypotheses prior to conducting research is shown in Fig. 1 .

Research questions are used more frequently in qualitative research than objectives or hypotheses. 3 These questions seek to discover, understand, explore or describe experiences by asking “What” or “How.” The questions are open-ended to elicit a description rather than to relate variables or compare groups. The questions are continually reviewed, reformulated, and changed during the qualitative study. 3 Research questions are also used more frequently in survey projects than hypotheses in experiments in quantitative research to compare variables and their relationships.
Hypotheses are constructed based on the variables identified and as an if-then statement, following the template, ‘If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.’ At this stage, some ideas regarding expectations from the research to be conducted must be drawn. 18 Then, the variables to be manipulated (independent) and influenced (dependent) are defined. 4 Thereafter, the hypothesis is stated and refined, and reproducible data tailored to the hypothesis are identified, collected, and analyzed. 4 The hypotheses must be testable and specific, 18 and should describe the variables and their relationships, the specific group being studied, and the predicted research outcome. 18 Hypotheses construction involves a testable proposition to be deduced from theory, and independent and dependent variables to be separated and measured separately. 3 Therefore, good hypotheses must be based on good research questions constructed at the start of a study or trial. 12
In summary, research questions are constructed after establishing the background of the study. Hypotheses are then developed based on the research questions. Thus, it is crucial to have excellent research questions to generate superior hypotheses. In turn, these would determine the research objectives and the design of the study, and ultimately, the outcome of the research. 12 Algorithms for building research questions and hypotheses are shown in Fig. 2 for quantitative research and in Fig. 3 for qualitative research.

EXAMPLES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS FROM PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Descriptive research question (quantitative research)
- - Presents research variables to be assessed (distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes)
- “BACKGROUND: Since COVID-19 was identified, its clinical and biological heterogeneity has been recognized. Identifying COVID-19 phenotypes might help guide basic, clinical, and translational research efforts.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Does the clinical spectrum of patients with COVID-19 contain distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes? ” 19
- EXAMPLE 2. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Shows interactions between dependent variable (static postural control) and independent variable (peripheral visual field loss)
- “Background: Integration of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive sensations contributes to postural control. People with peripheral visual field loss have serious postural instability. However, the directional specificity of postural stability and sensory reweighting caused by gradual peripheral visual field loss remain unclear.
- Research question: What are the effects of peripheral visual field loss on static postural control ?” 20
- EXAMPLE 3. Comparative research question (quantitative research)
- - Clarifies the difference among groups with an outcome variable (patients enrolled in COMPERA with moderate PH or severe PH in COPD) and another group without the outcome variable (patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH))
- “BACKGROUND: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) in COPD is a poorly investigated clinical condition.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Which factors determine the outcome of PH in COPD?
- STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: We analyzed the characteristics and outcome of patients enrolled in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) with moderate or severe PH in COPD as defined during the 6th PH World Symposium who received medical therapy for PH and compared them with patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) .” 21
- EXAMPLE 4. Exploratory research question (qualitative research)
- - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated (perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment) to have a deeper understanding of the research problem
- “Problem: Interventions for children with obesity lead to only modest improvements in BMI and long-term outcomes, and data are limited on the perspectives of families of children with obesity in clinic-based treatment. This scoping review seeks to answer the question: What is known about the perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment? This review aims to explore the scope of perspectives reported by families of children with obesity who have received individualized outpatient clinic-based obesity treatment.” 22
- EXAMPLE 5. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Defines interactions between dependent variable (use of ankle strategies) and independent variable (changes in muscle tone)
- “Background: To maintain an upright standing posture against external disturbances, the human body mainly employs two types of postural control strategies: “ankle strategy” and “hip strategy.” While it has been reported that the magnitude of the disturbance alters the use of postural control strategies, it has not been elucidated how the level of muscle tone, one of the crucial parameters of bodily function, determines the use of each strategy. We have previously confirmed using forward dynamics simulations of human musculoskeletal models that an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. The objective of the present study was to experimentally evaluate a hypothesis: an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. Research question: Do changes in the muscle tone affect the use of ankle strategies ?” 23
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESES IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Working hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory
- “As fever may have benefit in shortening the duration of viral illness, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response when taken during the early stages of COVID-19 illness .” 24
- “In conclusion, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response . The difference in perceived safety of these agents in COVID-19 illness could be related to the more potent efficacy to reduce fever with ibuprofen compared to acetaminophen. Compelling data on the benefit of fever warrant further research and review to determine when to treat or withhold ibuprofen for early stage fever for COVID-19 and other related viral illnesses .” 24
- EXAMPLE 2. Exploratory hypothesis (qualitative research)
- - Explores particular areas deeper to clarify subjective experience and develop a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach
- “We hypothesized that when thinking about a past experience of help-seeking, a self distancing prompt would cause increased help-seeking intentions and more favorable help-seeking outcome expectations .” 25
- “Conclusion
- Although a priori hypotheses were not supported, further research is warranted as results indicate the potential for using self-distancing approaches to increasing help-seeking among some people with depressive symptomatology.” 25
- EXAMPLE 3. Hypothesis-generating research to establish a framework for hypothesis testing (qualitative research)
- “We hypothesize that compassionate care is beneficial for patients (better outcomes), healthcare systems and payers (lower costs), and healthcare providers (lower burnout). ” 26
- Compassionomics is the branch of knowledge and scientific study of the effects of compassionate healthcare. Our main hypotheses are that compassionate healthcare is beneficial for (1) patients, by improving clinical outcomes, (2) healthcare systems and payers, by supporting financial sustainability, and (3) HCPs, by lowering burnout and promoting resilience and well-being. The purpose of this paper is to establish a scientific framework for testing the hypotheses above . If these hypotheses are confirmed through rigorous research, compassionomics will belong in the science of evidence-based medicine, with major implications for all healthcare domains.” 26
- EXAMPLE 4. Statistical hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - An assumption is made about the relationship among several population characteristics ( gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD ). Validity is tested by statistical experiment or analysis ( chi-square test, Students t-test, and logistic regression analysis)
- “Our research investigated gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD in a Japanese clinical sample. Due to unique Japanese cultural ideals and expectations of women's behavior that are in opposition to ADHD symptoms, we hypothesized that women with ADHD experience more difficulties and present more dysfunctions than men . We tested the following hypotheses: first, women with ADHD have more comorbidities than men with ADHD; second, women with ADHD experience more social hardships than men, such as having less full-time employment and being more likely to be divorced.” 27
- “Statistical Analysis
- ( text omitted ) Between-gender comparisons were made using the chi-squared test for categorical variables and Students t-test for continuous variables…( text omitted ). A logistic regression analysis was performed for employment status, marital status, and comorbidity to evaluate the independent effects of gender on these dependent variables.” 27
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESIS AS WRITTEN IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES IN RELATION TO OTHER PARTS
- EXAMPLE 1. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “Pregnant women need skilled care during pregnancy and childbirth, but that skilled care is often delayed in some countries …( text omitted ). The focused antenatal care (FANC) model of WHO recommends that nurses provide information or counseling to all pregnant women …( text omitted ). Job aids are visual support materials that provide the right kind of information using graphics and words in a simple and yet effective manner. When nurses are not highly trained or have many work details to attend to, these job aids can serve as a content reminder for the nurses and can be used for educating their patients (Jennings, Yebadokpo, Affo, & Agbogbe, 2010) ( text omitted ). Importantly, additional evidence is needed to confirm how job aids can further improve the quality of ANC counseling by health workers in maternal care …( text omitted )” 28
- “ This has led us to hypothesize that the quality of ANC counseling would be better if supported by job aids. Consequently, a better quality of ANC counseling is expected to produce higher levels of awareness concerning the danger signs of pregnancy and a more favorable impression of the caring behavior of nurses .” 28
- “This study aimed to examine the differences in the responses of pregnant women to a job aid-supported intervention during ANC visit in terms of 1) their understanding of the danger signs of pregnancy and 2) their impression of the caring behaviors of nurses to pregnant women in rural Tanzania.” 28
- EXAMPLE 2. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “We conducted a two-arm randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate and compare changes in salivary cortisol and oxytocin levels of first-time pregnant women between experimental and control groups. The women in the experimental group touched and held an infant for 30 min (experimental intervention protocol), whereas those in the control group watched a DVD movie of an infant (control intervention protocol). The primary outcome was salivary cortisol level and the secondary outcome was salivary oxytocin level.” 29
- “ We hypothesize that at 30 min after touching and holding an infant, the salivary cortisol level will significantly decrease and the salivary oxytocin level will increase in the experimental group compared with the control group .” 29
- EXAMPLE 3. Background, aim, and hypothesis are provided
- “In countries where the maternal mortality ratio remains high, antenatal education to increase Birth Preparedness and Complication Readiness (BPCR) is considered one of the top priorities [1]. BPCR includes birth plans during the antenatal period, such as the birthplace, birth attendant, transportation, health facility for complications, expenses, and birth materials, as well as family coordination to achieve such birth plans. In Tanzania, although increasing, only about half of all pregnant women attend an antenatal clinic more than four times [4]. Moreover, the information provided during antenatal care (ANC) is insufficient. In the resource-poor settings, antenatal group education is a potential approach because of the limited time for individual counseling at antenatal clinics.” 30
- “This study aimed to evaluate an antenatal group education program among pregnant women and their families with respect to birth-preparedness and maternal and infant outcomes in rural villages of Tanzania.” 30
- “ The study hypothesis was if Tanzanian pregnant women and their families received a family-oriented antenatal group education, they would (1) have a higher level of BPCR, (2) attend antenatal clinic four or more times, (3) give birth in a health facility, (4) have less complications of women at birth, and (5) have less complications and deaths of infants than those who did not receive the education .” 30
Research questions and hypotheses are crucial components to any type of research, whether quantitative or qualitative. These questions should be developed at the very beginning of the study. Excellent research questions lead to superior hypotheses, which, like a compass, set the direction of research, and can often determine the successful conduct of the study. Many research studies have floundered because the development of research questions and subsequent hypotheses was not given the thought and meticulous attention needed. The development of research questions and hypotheses is an iterative process based on extensive knowledge of the literature and insightful grasp of the knowledge gap. Focused, concise, and specific research questions provide a strong foundation for constructing hypotheses which serve as formal predictions about the research outcomes. Research questions and hypotheses are crucial elements of research that should not be overlooked. They should be carefully thought of and constructed when planning research. This avoids unethical studies and poor outcomes by defining well-founded objectives that determine the design, course, and outcome of the study.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Conceptualization: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Methodology: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - original draft: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - review & editing: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Qualitative Research Topics. Qualitative Research Topics are as follows: Understanding the lived experiences of first-generation college students. Exploring the impact of social media on self-esteem among adolescents. Investigating the effects of mindfulness meditation on stress reduction. Analyzing the perceptions of employees regarding ...
While many books and articles guide various qualitative research methods and analyses, there is currently no concise resource that explains and differentiates among the most common qualitative approaches. We believe novice qualitative researchers, students planning the design of a qualitative study or taking an introductory qualitative research course, and faculty teaching such courses can ...
This article therefore proceeds as follows: First, we provide examples from our own qualitative research experiences, working on a variety of sensitive, challenging, and difficult topics, from across the social and health science disciplines; and second, we provide an eight-point guide for how best to support researchers who undertake these ...
Qualitative Research is a peer-reviewed international journal that has been leading debates about qualitative methods for over 20 years. The journal provides a forum for the discussion and development of qualitative methods across disciplines, publishing high quality articles that contribute to the ways in which we think about and practice the craft of qualitative research.
American Journal of Qualitative Research (AJQR) is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal that publishes qualitative research articles from a number of social science disciplines such as psychology, health science, sociology, criminology, education, political science, and administrative studies.The journal is an international and interdisciplinary focus and greatly welcomes papers from all ...
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research. Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and ...
Abstract. This paper aims to provide an overview of the use and assessment of qualitative research methods in the health sciences. Qualitative research can be defined as the study of the nature of phenomena and is especially appropriate for answering questions of why something is (not) observed, assessing complex multi-component interventions ...
February 2015. by Erin E. Toolis and Phillip L. Hammack. Lifetime Activism, Marginality, and Psychology: Narratives of Lifelong Feminist Activists Committed to Social Change (PDF, 93KB) August 2014. by Anjali Dutt and Shelly Grabe. Qualitative Inquiry in the History of Psychology (PDF, 82KB) February 2014. by Frederick J. Wertz.
Qualitative research involves the studied use and collection of a variety of empirical materials - case study, personal experience, introspective, life story, interview, observational, historical, interactional, and visual texts - that describe routine and problematic moments and meanings in individuals' lives.
Qualitative research applied to public health: new topics and insight. The concept of public health refers to the science and art of preventing diseases and promoting, protecting, and improving health ( 1 ). The essential functions of public health include monitoring the health of the population, keeping watch on risk factors, guaranteeing ...
1: Journal Article Reporting Standards for Qualitative Research in Psychology. This American Psychologist open-access article lays out—for the first time—journal article reporting standards for qualitative research in psychology (Levitt, H.M., et al., Vol. 73, No. 1). The voluntary guidelines are designed to help authors communicate their work clearly, accurately and transparently.
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems.[1] Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervene or introduce treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypotheses as well as further investigate and understand quantitative data. Qualitative research gathers participants ...
This article presents a list of 130-plus qualitative research topic ideas to help learners that struggle to get titles for their papers. It is helpful because many learners have difficulties picking titles that will make their essays impressive to educators. But before presenting the topics, this article defines qualitative research.
This review aims to synthesize a published set of evaluative criteria for good qualitative research. The aim is to shed light on existing standards for assessing the rigor of qualitative research encompassing a range of epistemological and ontological standpoints. Using a systematic search strategy, published journal articles that deliberate criteria for rigorous research were identified. Then ...
Here are fantastic examples of qualitative research titles: Female harm: how it is influenced by culture. The socioeconomic impacts of free education. The link between food insecurity and poor performance in schools. Alcoholism among college students: a critical study. How to mitigate child labor in our society.
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems. Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervene or introduce treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypotheses as well as further investigate and understand quantitative data.
Qualitative research is the methodology researchers use to gain deep contextual understandings of users via non-numerical means and direct observations. Researchers focus on smaller user samples—e.g., in interviews—to reveal data such as user attitudes, behaviors and hidden factors: insights which guide better designs.
Within the context of pharmacy practice research, qualitative approaches have been used to examine a diverse array of topics, including the perceptions of key stakeholders regarding prescribing by pharmacists and the postgraduation employment experiences of young pharmacists (see "Further Reading" section at the end of this article ...
This research topic promotes research on qualitative research focusing on: • Prevention/mitigation of risks in communicable, neglected, or high-prevalence diseases. • Social and environmental determinants, • Nutrition, physical exercise, and quality of life. • Expectations of populations on the promotion of physical, mental, sexual and ...
Qualitative Research Topics: Psych, Education, Health, Medicine & More. Wandering around the internet looking for qualitative research topics can be exhausting. We are writing this article to make it a one-stop solution for you. There is enough inspiration to come up with the most suitable topic for you, no matter your academic area.
QD is a valuable method for master's-level students and research trainees as it provides a practical, accessible, and flexible approach to qualitative research (Bradshaw et al., 2017), fostering the development of important research skills and contributing to the scientific integrity of their work. The disciplines in which QD research fits ...
Introduction. Research in Political Science is increasingly based on qualitative and interpretative methods. Document analyses, discourse analyses or ethnographic studies have become more and more common (Halperin and Heath Citation 2020; Silverman Citation 2021).However, the application of these methods confronts researchers with a number of principled questions and challenges that concern ...
Despite existing knowledge on this topic, assessing nurses' environmental awareness and behavior, including the barriers they face, is crucial with regard to improving sustainable health care practices. ... By conducting qualitative analysis, this research also identified multiple barriers to the adoption of sustainable practices among nurses ...
Qualitative research has ample possibilities within the arena of healthcare research. This article aims to inform healthcare professionals regarding qualitative research, its significance, and applicability in the field of healthcare. ... They are normally built around a specific topic and are considered as the best approach to gather data on ...
The qualitative synthesis of these studies showed that AA permitted the exploration of the emotional, cognitive, and behavioral dynamics associated with the experience of SA and SAD. ... substance use, and interactional patterns were the principal topics of the included studies. In addition, the incorporation of AA to study psychological ...
In recent years, universities have been expected to participate in Japanese high school education, especially in the "period for inquiry-based cross-disciplinary study." Despite various university faculties engaging in diverse educational practices, there is insufficient research on human resource development and the creation of mechanisms to ensure continuous development.This study conducted ...
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...