Performance Appraisal on Employees’ Motivation: A Comprehensive Analysis
- Conference paper
- First Online: 20 September 2020
- Cite this conference paper

- Maryam Alsuwaidi ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9281-8560 19 ,
- Muhammad Alshurideh ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7336-381X 19 , 20 ,
- Barween Al Kurdi ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-0825-4617 21 &
- Said A. Salloum ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6073-3981 22
Part of the book series: Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing ((AISC,volume 1261))
Included in the following conference series:
- International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Systems and Informatics
4168 Accesses
39 Citations
Several analysis studies have been carried out with a view to providing valuable knowledge into the existing research outline of the performance appraisal and employee motivation. The current study systematically reviews and synthesizes the performance appraisal and employee motivation aiming to provide a comprehensive analysis of 27 articles from 2015 to 2020. The research will aim to establish the impact of performance appraisal fairness on the employees’ motivation in an organization. To achieve its objective, the study will adopt descriptive research. It will be informed of a survey, and there will be a sample selection to make the process economical. This shows that there will be a use of different techniques of information collection since the data to be collected a primary data. There will be interviewing of the sample size, and their responses will be noted down. The presence of the researcher may influence some people, and this necessitates the use of questionnaires for the respondents to fill on their own. In addition, most of the analyzed studies were conducted in Malaysia, China, Pakistan, and India. Besides, most of the analyzed studies were frequently conducted in job satisfaction and performance context, employee motivation followed by organizational effectiveness context. To that end, the findings of this review study provide an insight into the current trend of how performance appraisal affects employee’s motivation.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.

Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Alkalha, Z., Al-Zu’bi, Z., Al-Dmour, H., Alshurideh, M., Masa’deh, R.: Investigating the effects of human resource policies on organizational performance: an empirical study on commercial banks operating in Jordan. Eur. J. Econ. Finance Adm. Sci. 51 (1), 44–64 (2012)
Google Scholar
Ammari, G., Alkurdi, B., Alshurideh, M., Alrowwad, A.: Investigating the impact of communication satisfaction on organizational commitment: a practical approach to increase employees’ loyalty. Int. J. Mark. Stud. 9 (2), 113–133 (2017)
Article Google Scholar
ELSamen, A., Alshurideh, M.: The impact of internal marketing on internal service quality: a case study in a Jordanian pharmaceutical company. Int. J. Bus. Manag. 7 (19), 84–95 (2012)
Bowra, Z.A., Nasir, A.: Impact of fairness of performance appraisal on motivation and job satisfaction in banking sector of Pakistan. J. Basic Appl. Sci. Res. 4 (2), 16–20 (2014)
Alshurideh, M., Alhadid, A., Alkurdi, B.: The effect of internal marketing on organizational citizenship behavior an applicable study on the University of Jordan employees. Int. J. Mark. Stud. 7 (1), 138 (2015)
Obeidat, B., Sweis, R., Zyod, D., Alshurideh, M.: The effect of perceived service quality on customer loyalty in internet service providers in Jordan. J. Manag. Res. 4 (4), 224–242 (2012)
Alshraideh, A., Al-Lozi, M., Alshurideh, M.: The impact of training strategy on organizational loyalty via the mediating variables of organizational satisfaction and organizational performance: an empirical study on jordanian agricultural credit corporation staff. J. Soc. Sci. 6 , 383–394 (2017)
Obeidat, Z., Alshurideh, M., Al Dweeri., R., Masa’deh, R.: The influence of online revenge acts on consumers psychological and emotional states: does revenge taste sweet? In: 33 IBIMA Conference proceedings, Granada, Spain, 10–11 April 2019 (2019)
Abu Zayyad, H.M., Obeidat, Z.M., Alshurideh, M.T., Abuhashesh, M., Maqableh, M., Masa’deh, R.: Corporate social responsibility and patronage intentions: the mediating effect of brand credibility. J. Mark. Commun., 1–24 (2020)
Al-dweeri, R., Obeidat, Z., Al-dwiry, M., Alshurideh, M., Alhorani, A.: The impact of e-service quality and e-loyalty on online shopping: moderating effect of e-satisfaction and e-trust. Int. J. Mark. Stud. 9 (2), 92–103 (2017)
Alshurideh, M., Masa’deh, R., Alkurdi, B.: The effect of customer satisfaction upon customer retention in the Jordanian mobile market: an empirical investigation. Eur. J. Econ. Finance Adm. Sci. 47 (12), 69–78 (2012)
Hamid, S., Hamali, J.B.H., Abdullah, F.: Performance measurement for local authorities in Sarawak. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 224 , 437–444 (2016)
Ashurideh, M.: Customer service retention–a behavioural perspective of the UK mobile market. Durham University (2010)
Alshurideh, M.T.: Exploring the main factors affecting consumer choice of mobile phone service provider contracts. Int. J. Commun. Netw. Syst. Sci. 9 (12), 563–581 (2016)
Aburayya, A., Alshurideh, M., Albqaeen, A., Alawadhi, D., Ayadeh, I.: An investigation of factors affecting patients waiting time in primary health care centers: an assessment study in Dubai. Manag. Sci. Lett. 10 (6), 1265–1276 (2020)
Alshurideh, M.: A qualitative analysis of customer repeat purchase behaviour in the UK mobile phone market. J. Manag. Res. 6 (1), 109 (2014)
Teo, S.T.T., Bentley, T., Nguyen, D.: Psychosocial work environment, work engagement, and employee commitment: a moderated, mediation model. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 88 , 102415 (2019)
Sendawula, K., Nakyejwe Kimuli, S., Bananuka, J., Najjemba Muganga, G.: Training, employee engagement and employee performance: evidence from Uganda’s health sector. Cogent Bus. Manag. 5 (1), 1470891 (2018)
Alshurideh, M., et al.: Loyalty program effectiveness: theoretical reviews and practical proofs. Uncertain Supply Chain Manag. 8 (3), 1–10 (2020)
Alzoubi, H., Alshurideh, M., Al Kurdi, B., Inairata, M.: Do perceived service value, quality, price fairness and service recovery shape customer satisfaction and delight? A practical study in the service telecommunication context. Uncertain Supply Chain Manag. 8 (3), 1–10 (2020)
Alshurideh, M.T., et al.: The impact of Islamic bank’s service quality perception on Jordanian customer’s loyalty. J. Manag. Res. 9 , 139–159 (2017)
Al Dmour, H., Alshurideh, M., Shishan, F.: The influence of mobile application quality and attributes on the continuance intention of mobile shopping. Life Sci. J. 11 (10), 172–181 (2014)
Meng, F., Wu, J.: Merit pay fairness, leader-member exchange, and job engagement: evidence from Mainland China. Rev. Public Pers. Adm. 35 (1), 47–69 (2015)
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Lothian, N.: Measuring corporate performance: a guide to non-financial indicators. Chartered Institute of Management Accountants (1987)
Alshurideh, D.M.: Do electronic loyalty programs still drive customer choice and repeat purchase behaviour? Int. J. Electron. Cust. Relatsh. Manag. 12 (1), 40–57 (2019)
Harrington, J.R., Lee, J.H.: What drives perceived fairness of performance appraisal? Exploring the effects of psychological contract fulfillment on employees’ perceived fairness of performance appraisal in US federal agencies. Public Pers. Manag. 44 (2), 214–238 (2015)
Rubel, M.R.B., Kee, D.M.H.: High commitment compensation practices and employee turnover intention: mediating role of job satisfaction. Mediterr. J. Soc. Sci. 6 (6 S4), 321 (2015)
Edirisooriya, W.A.: Impact of rewards on employee performance: with special reference to ElectriCo. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Management and Economics, vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 311–318 (2014)
Sharma, N.P., Sharma, T., Agarwal, M.N.: Measuring employee perception of performance management system effectiveness. Empl. Relat. 38 , 224–247 (2016)
Martinic, M.K., Pieper, D., Glatt, A., Puljak, L.: Definition of a systematic review used in overviews of systematic reviews, meta-epidemiological studies and textbooks. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 19 (1), 203 (2019)
Arnăutu, E., Panc, I.: Evaluation criteria for performance appraisal of faculty members. Procedia-Social Behav. Sci. 203 , 386–392 (2015)
Salloum, S.A., Al-Emran, M., Shaalan, K.: The impact of knowledge sharing on information systems: a review. In: International Conference on Knowledge Management in Organizations, pp. 94–106 (2018)
Assad, N.F., Alshurideh, M.T.: Financial reporting quality, audit quality, and investment efficiency: evidence from GCC economies. WAFFEN-UND Kostumkd. J. 11 (3), 194–208 (2020)
Alshurideh, M.T., Assad, N.F.: Investment in context of financial reporting quality: a systematic review. WAFFEN-UND Kostumkd. J. 11 (3), 255–286 (2020)
Salloum, S.A., Alshurideh, M., Elnagar, A., Shaalan, K.: Mining in educational data: review and future directions. In: Joint European-US Workshop on Applications of Invariance in Computer Vision, pp. 92–102 (2020)
Salloum, S.A., Alshurideh, M., Elnagar, A., Shaalan, K.: Machine learning and deep learning techniques for cybersecurity: a review. In: Joint European-US Workshop on Applications of Invariance in Computer Vision, pp. 50–57 (2020)
Al-Emran, M., Mezhuyev, V., Kamaludin, A., Shaalan, K.: The impact of knowledge management processes on information systems: a systematic review. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 43 (July), 173–187 (2018)
Calabrò, A., Vecchiarini, M., Gast, J., Campopiano, G., De Massis, A., Kraus, S.: Innovation in family firms: a systematic literature review and guidance for future research. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 21 (3), 317–355 (2019)
Salloum, S.A., Al-Emran, M.: Factors affecting the adoption of e-payment systems by university students: extending the TAM with trust. Int. J. Electron. Bus. 14 (4), 371–390 (2018)
Alhashmi, S.F.S., Salloum, S.A., Abdallah, S.: Critical success factors for implementing Artificial Intelligence (AI) Projects in Dubai Government United Arab Emirates (UAE) health sector: applying the extended Technology Acceptance Model (TAM). In: International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Systems and Informatics, pp. 393–405 (2019)
Alshurideh, M., Al Kurdi, B., Salloum, S.: Examining the main mobile learning system drivers’ effects: a mix empirical examination of both the Expectation-Confirmation Model (ECM) and the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM). In: International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Systems and Informatics, pp. 406–417 (2019)
Al-Emran, M., Mezhuyev, V., Kamaludin, A.: Technology acceptance model in M-learning context: a systematic review. Comput. Educ. 125 , 389–412 (2018)
Nair, M.S., Salleh, R.: Linking performance appraisal justice, trust, and employee engagement: a conceptual framework. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 211 , 1155–1162 (2015)
Syafii, L.I., Thoyib, A., Nimran, U.: The role of corporate culture and employee motivation as a mediating variable of leadership style related with the employee performance (studies in Perum Perhutani). Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 211 , 1142–1147 (2015)
Khaskhelly, F.Z.: Investigating the impact of training on employee performance: a study of non-government organizations at Hyderabad division. University of Sindh, Jamshoro (2018)
Baleghi-Zadeh, S., Ayub, A.F.M., Mahmud, R., Daud, S.M.: Behaviour Intention to use the learning management: integrating technology acceptance model with task-technology fit. Middle-East J. Sci. Res. 19 (1), 76–84 (2014)
Kumar, R.: Research Methodology: A Step-by-step Guide for Beginners. Sage Publications Limited, Thousand Oaks (2019)
Imran, M., Hamid, S.N.B.A., Aziz, A.B., Wan, C.Y.: The effect of performance appraisal politics on employee performance in emergency services of Punjab, Pakistan. Acad. Strateg. Manag. J. 18 , 1–7 (2019)
Saether, E.A.: Motivational antecedents to high-tech R&D employees’ innovative work behavior: self-determined motivation, person-organization fit, organization support of creativity, and pay justice. J. High Technol. Manag. Res. 30 (2), 100350 (2019)
Shrivastava, A., Purang, P.: Performance appraisal fairness & its outcomes: a study of Indian banks. Indian J. Ind. Relat. 51 , 660–674 (2016)
Sattar, T., Ahmad, K., Hassan, S.M.: Role of human resource practices in employee performance and job satisfaction with mediating effect of employee engagement. Pak. Econ. Soc. Rev. 53 , 81–96 (2015)
Yang, J.-T., Wan, C.-S., Wu, C.-W.: Effect of internal branding on employee brand commitment and behavior in hospitality. Tour. Hosp. Res. 15 (4), 267–280 (2015)
Gollan, P.J., Kalfa, S., Agarwal, R., Green, R., Randhawa, K.: Lean manufacturing as a high-performance work system: the case of cochlear. Int. J. Prod. Res. 52 (21), 6434–6447 (2014)
Dobre, O.-I.: Employee motivation and organizational performance. Rev. Appl. Soc.-Econ. Res. 5 (1) (2013)
Jain, R.: Employee innovative behavior: a conceptual framework. Indian J. Ind. Relat. 51 , 1–16 (2015)
Schmidt, C.G., Foerstl, K., Schaltenbrand, B.: The supply chain position paradox: green practices and firm performance. J. Supply Chain Manag. 53 (1), 3–25 (2017)
Ren, T., Xiao, Y., Yang, H., Liu, S.: Employee ownership heterogeneity and firm performance in China. Hum. Resour. Manag. 58 (6), 621–639 (2019)
Kim, T., Wang, J., Chen, T., Zhu, Y., Sun, R.: Equal or equitable pay? Individual differences in pay fairness perceptions. Hum. Resour. Manag. 58 (2), 169–186 (2019)
Hanaysha, J.R.: An examination of the factors affecting consumer’s purchase decision in the Malaysian retail market. PSU Res. Rev. 2 , 7–23 (2018)
Hauff, S., Alewell, D., Hansen, N.K.: Further exploring the links between high-performance work practices and firm performance: a multiple-mediation model in the German context. Ger. J. Hum. Resour. Manag. 32 (1), 5–26 (2018)
Li, F., Chen, T., Lai, X.: How does a reward for creativity program benefit or frustrate employee creative performance? The perspective of transactional model of stress and coping. Gr. Organ. Manag. 43 (1), 138–175 (2018)
Ibrahim, Z., Ismail, A., Mohamed, N.A.K., Raduan, N.S.M.: Association of managers’ political interests towards employees’ feelings of distributive justice and job satisfaction in performance appraisal system. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 224 , 523–530 (2016)
Naeem, M., Jamal, W., Riaz, M.K.: The relationship of employees’ performance appraisal satisfaction with employees’ outcomes: evidence from higher educational institutes. FWU J. Soc. Sci. 11 (2), 71–81 (2017)
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Sharjah, Sharjah, UAE
Maryam Alsuwaidi & Muhammad Alshurideh
Faculty of Business, University of Jordan, Amman, Jordan
Muhammad Alshurideh
Amman Arab University, Amman, Jordan
Barween Al Kurdi
Research Institute of Sciences and Engineering, University of Sharjah, Sharjah, UAE
Said A. Salloum
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Said A. Salloum .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Faculty of Computers and Artificial Intelligence, Information Technology Department, and Chair of the Scientific Research Group in Egypt, Cairo University, Cairo, Egypt
Aboul Ella Hassanien
Department of Electronics and Computer Science, Koszalin University of Technology, Koszalin, Poland
Adam Slowik
Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, VŠB-Technical University of Ostrava, Ostrava-Poruba, Moravskoslezsky, Czech Republic
Václav Snášel
Rector of the Electronic Research Institute, Cairo, Egypt
Hisham El-Deeb
Faculty of computers and information, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt
Fahmy M. Tolba
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Editor(s) (if applicable) and The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Alsuwaidi, M., Alshurideh, M., Al Kurdi, B., Salloum, S.A. (2021). Performance Appraisal on Employees’ Motivation: A Comprehensive Analysis. In: Hassanien, A.E., Slowik, A., Snášel, V., El-Deeb, H., Tolba, F.M. (eds) Proceedings of the International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Systems and Informatics 2020. AISI 2020. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1261. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58669-0_61
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58669-0_61
Published : 20 September 2020
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-58668-3
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-58669-0
eBook Packages : Intelligent Technologies and Robotics Intelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Performance Appraisal Systems and Implementations: A Literature Review and Research Agenda

─Abstract ─ In recent years, a number of works have been published on different aspects of performance appraisal. Some of these works make literature review on performance management and performance measurement In this paper, we discuss the researchers and their works that shape current performance appraisal systems in the concept of historical development of the performance appraisal systems. Then, we make literature review for current stateof-the-art works in the performance appraisal systems. Therefore, we analyze 104 performance appraisal articles which are published in "Journal of Management" from 2000 to 2012 in our work. We classify the works with respect to its topic, publication year, sector, country and analysis techniques. Thus, we aim to determine current trends in the performance appraisal systems.
Related Papers
Syaza Noraliah
Busola Kehinde
Performance appraisal and performance management were one of the emerging issues since last decade. Many organizations have shifted from employee's performance appraisal system to employee's performance management system. This paper has focused to study the evolution of employee's performance appraisal system, critics the system suffered and how the performance management system came to the practice. The main purpose of this paper is to differentiate these two systems, employee's performance appraisal and management system. This paper uses a review of the literature to evaluate the development of appraisal system and argues the critic areas of appraisal system. The review identified as advancement in the management field and growing complexity in corporate sectors demand more capable HR, so mare appraisal of employee's performance is not sufficient. Employee's contribution should be aligned with organizational objectives and strategy. Performance management eliminates the shortcomings of performance appraisal system to the some extent.
Int. J. of HRM & Org. Bev.,
Dr Shaik R E H A N A Banu
Human Resource Management is concerned with employing the people, developing their resources, utilizing, maintaining and compensating their services in tune with the job and organizational requirements, human resources management may be defined as a set of policies, practices and programmers designed to maximize both personal and organizational goals. It is the process of binding people and organizations together so that the objectives of each are achieved. According to Flippo, personal management or human resources management is the planning, organizing, directing and controlling of the procurement, development, compensation, importance of HRM. The significance of HRM can be discussed at four levels-corporate, personal, social and national. HRM is the central subsystem of an organization overview of performance appraisal system. The history of performance appraisal is quite brief. Its roots in the early 20 th century can be traced to Taylor's pioneering time and motion studies. But this is not very helpful, for the same may be said about almost everything in the field of modern HRM. Performance Appraisal system began as simple methods of income justification. That is, Appraisal was used to decide whether or not the salary or wage of an individual employee was justified. The process was firmly linked to material outcomes. If and employee's performance was found to be less than ideal, a cut in pay would follow. On the other hand, if their performance was better than the supervisor expected, a pay rise was in order.
IAEME Publication
Performance Appraisal is vital for every person. It’s a taste of their performance. Henceforth the system needs to be effective enough to yield appropriate results. Modern Industries possess a saga of rigorous development as they are leading manufacturers railway wagons. They form one of the corner stone of nation’s development. They undertake numerous measures to make their employees trainings influential as it has been one of the finding of our paper that majority of them believe that their organization’s performance appraisal provides them overall development
IJMSBR Open Access Journal
Performance Appraisal is one the most widely accepted HR tool to assess the employee and organization performance. Selection of an appropriate performance appraisal technique has always been a point of apprehension for most of academicians as well as managers in each and every organization. The primary idea behind this study is to find out the most helpful and appropriate performance appraisal technique in education sector. The focus on this sector is primarily due to interest as well as prime occupational area of the researcher. To conduct and understand the concept and idea behind the appraisal system across various sectors several literatures were explored and reviewed. Evidences from majority of these literatures explain that the employees are more inclined towards online performance appraisal system than manual appraisal system. Moreover, the study also emphasizes on the fact that employee satisfaction can be improved through right kind of appraisal method. The present study analyses the appraisal system in education sector and tried to derive factors from the current appraisal system that can tighten the linkage between the current practices and the evolved practices. This will lead to strengthening of performance of employee and organization, reducing bias and creating positive work culture thus increasing organizational productivity.
Soma Bose Biswas
Identification and development of skill is highly related to the organizational success. Performance appraisal is a tool to identify required skill for the job. To prepare a bias free and an integrated system is of prime interest of the researchers. Modern corporate India is now attempting to use sophisticated performance management tool in order to attain business excellence and achieve organizational goal. There is absolute dearth of literature in the context of Indian practice of appraisal system. The qualitative research attempted to conceptualize the impact of Performance Appraisal System on Organizational Performance.. The paper examines and analyzes the evolutive perspective of performance appraisal systems through in depth study of literature. This paper also through analytical study conducted on Performance appraisal system (PAS) makes an attempt to find out if there is any linkage between organizational excellence and the performance appraisal system.
International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies [IJARCSMS] ijarcsms.com
Barbara Alston
PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL and MANAGEMENT
Hakan Nayır
Without a doubt in today's modern world, the competition between firms is getting tougher with each passing day; and thus, the means and methods employed in performance evaluation and management are becoming critically important. That is because the importance and impact of employees within the firm's mechanism as a result of current business dynamics have also exponentially increased. It is frequently observed that firms that are able to provide positive and fair conditions, improvement opportunities, compensations for their employees are much more likely to achieve better success. However, knowing that in today's economy resources are scarce, and implementing this well-known reality, to above mentioned concepts; it is obviously important to decide on the methods to efficiently increase the performance of employees and to determine the employees to invest in for the future. That's where and why creating and maintaining an effective performance management system have become key.
RELATED PAPERS
Marek Kejna
U.S.-Japan Women's Journal
Kimberly Kono
The Veterinary Clinics of North America Small Animal Practice
Spencer Johnston
Medical Principles and Practice
Suad AlFadhli
Nihon Rinsho Geka Gakkai Zasshi (Journal of Japan Surgical Association)
TERUMASA SAWADA
Roberto Amador
Antonio Alessi
JUAN CARLOS Carmona Echavarría
International Journal of Mobile Learning and Organisation
Michail Kalogiannakis
Bhagirath Baria
Journal of Instrumentation
Leonardo Cristella
Intan Kumalasari
Tatiane Cristina Dotta
EPI International Journal of Engineering
Wardi Wardi
Journal of Microbiology, Immunology and Infection
Loke Tim Khaw
Jurnal Akuntansi dan Manajemen PEMBNAS (JAM PEMBNAS)
desman nazara
Revista de Ciências Sociais
Nilson Almino de Freitas
Journal of the Formosan Medical Association
Rong-chi Chen
Nucleic Acids Research
Hugues Sicotte
Madan Bhandari Memorial College
Kashi Nath Khanal
Acta Mathematica Hungarica
Johann Davidov
Applied Sciences
elisabetta ferrara
Scientific reports
Britt van Hagen
Revista Latinoamericana de Herpetología
Antonio Esaú Valdenegro Brito
American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology
Laszlo Szalay
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
The Performance of Performance Appraisal Systems: A Theoretical Framework for Public Organizations
Performance appraisal (PA) plays a strategic role in public sector human resource management (HRM), acting as a driver for better performance. Drawing from previous theoretical research on the social context of performance appraisal systems and their effectiveness, the study develops a generalizable theoretical framework for classifying performance appraisal systems according to their structural and process proximal variables: purpose, rating source, and structured face-to-face feedback sessions. Through a multiple case study analysis, the theoretical framework has been applied to a sample of Italian PA systems for senior civil servants, aiming to explore the relationship between the structural and process proximal variables of PA systems and rating discriminability, intended as a measurement of performance effectiveness. The results show that the framework accurately represents the variation of the design of performance appraisal systems in the Italian context, highlighting the central role played by multi-source feedback and face-to-face rater-ratee interactions in promoting rating discriminability.
- Related Documents
Participation in the development of performance appraisal systems: A quasi-experiment
Exploring the relationship between corporate social responsibility actions and employee retention: a human resource management perspective.
BACKGROUND: This study builds on the little guidance in the existing literature to analyze the relationship between employee-oriented CSR actions and employee retention in a business context, while using Freeman stakeholders’ model as a theoretical research framework. This research also aims to shed light on significant behavioral factors facilitating the relationship between CSR endeavors and turnover rate. OBJECTIVE: This paper builds on the existing research gap in the literature and suggests that behavioral factors, including job satisfaction, organizational identification, and motivation facilitate the relationship between employee-oriented CSR actions and employee retention, which contributes to laying the foundations of a theoretical framework that has the potential to advance both theoretical and practitioner debates and disentangle the complexity of such a relationship, while offering strategically-focused development venues in CSR and HRM fields. METHODS: This research uses a single case study design to ensure an in-depth and detailed analysis of the phenomenon under scrutiny, while relying on a triangulation methodology for data collection, including a questionnaire used as exploratory approach, interviews to generate explanatory data, and archival data to bring confirmatory insights. Data analysis followed the procedures of a deductive approach. RESULTS: The research results show a positive relationship between employee-oriented CSR actions and employee retention, while demonstrating the facilitating role of job satisfaction, organizational identification, and motivation in moderating such a relationship. The findings also stress the importance of framing CSR interventions within the organization’s strategy and goals, while ensuring employee participation in such decision making processes to maximize the effect of CSR interventions on employee commitment and reduce turnover. CONCLUSIONS: This research has the potential to better clarify the nature of the relationship involving CSR interventions, from an employee perspective, retention, and turnover, while laying the foundations of a theoretical framework linking such constructs and other behavioral factors that underpin and support such a relationship. Building on the study’s findings and assumptions, future research is needed to gain a more comprehensive understanding of how HR-related CSR actions affect behavioral performance dimensions, resulting in employee commitment and retention. Future research should also consider multiple case study, multicultural, and ethnographic approaches for the sake of generalizability and theory building.
Incorporating Quality Performance Objectives into Performance Appraisal Systems
The association between performance appraisal systems, work-related attitudes and academic performance, developing building blocks for leading successful digital transformation: multiple case study analysis for 10 korean public corporations, conducting midterm performance reviews: an exercise for teaching performance management.
Although the annual performance review has received much criticism from practitioners and researchers alike, organizations continue to use coaching and/or reviews to maximize employee effectiveness and minimize liabilities. A semester class is a great context to practice skills relating to tracking and reviewing performance. This article describes how management instructors can implement performance reviews as an experiential exercise designed to improve students’ confidence related to receiving performance feedback. During a “Performance Appraisal Week,” instructors conduct individual performance reviews designed to discuss individual students’ class performance and elicit student–teacher feedback. Students experience the emotions of a professional face-to-face review, practice multiple-source and multiple-measure feedback interpretation, engage in performance-related dialogue, and consider plans to meet goals. During a full-class reflection and debrief, students apply concepts and discuss elements of performance management systems, and they build their confidence in how to navigate performance-related feedback discussions.
Dysfunctional schema modes in individuals with frontal lobe lesion; multiple CASE study analysis
Obstacles to innovation for smes: evidence from germany.
Achieving effective innovation is a complex task and during this process, firms [especially small and medium sized enterprises (SMEs)] often face obstacles. However, research into obstacles to innovation focusing on SMEs is very scarce. In this study, we propose a theoretical framework for describing these obstacles to innovation and investigate their influence on the innovative performance of SMEs. Data were collected in 2013 through face-to-face interviews with executives of 49 technology SMEs from Germany. The semi-structured interviews were designed on the basis of scales for measuring innovativeness, financial/competitive performance and obstacles to innovation, next to purely open questions. We find that the internal obstacles, lack of know-how, capacity overloading, unclear roles and tasks as well as the external obstacle governmental bureaucracy negatively influence innovative performance of SMEs. However, in contrast to prior findings, this study shows that cooperation ties of firms might also negatively influence the innovative performance.
The correlation between polygamy and educational achievement of children
Among themost efficient employee related management practices identified in both the developed and the developing nations is performance appraisal system, which is alsorecognized as a strong motivator for employees. It also enables smooth functioning of managerial decision making, administrative decision making and the employee development. The present study reviews prominent and key studies conducted in recent past systematically in order to assess how organizational performance appraisal systems and competency management frameworks affect employees’ work performance in the telecomsector.
Urban Visions. Beyond the Ideal City | Report from the Habitat III Village, Pop-up Public Space
<p>‘Urban Visions. Beyond the Ideal City’ was an event held at Habitat III, the United Nations conference on Housing and Sustainable Urban Development, in Ecuador, included in a series of meetings and events at the Pop-up Public Space, Habitat III Village, in Parque El Ejido in Quito. On 26<sup>th</sup> October 2016, we presented two research projects aiming at community engagement on issues related to the future of the urban environment:<br />- the "InstaBooth", a telephone booth-inspired portable structure developed at the Urban Informatics Lab of the Queensland University of Technology - <a href="http://www.urbaninformatics.net/projects/instabooth/">http://www.urbaninformatics.net/projects/instabooth/</a> - which uses tangible and hybrid interaction such as multi-touch screens and media façades to facilitate face-to-face and digitally mediated discussions;<br />- the cinematography competition "Urban Visions. Beyond the Ideal City", promoted by City Space Architecture - <a href="http://www.cityspacearchitecture.org/?p=urban-visions-beyond-the-ideal-city">http://www.cityspacearchitecture.org/?p=urban-visions-beyond-the-ideal-city</a> - which is the first film competition in the Italian context involving film-makers at a professional level on topics related to cities and urbanity.</p>
Export Citation Format
Share document.
- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file
People also looked at
Systematic review article, a systematic literature review on performance evaluation of power system from the perspective of sustainability.

- 1 College of Economics and Management, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, China
- 2 School of Economics and Management, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing, China
- 3 Business School, Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne, United Kingdom
- 4 School of Accounting, Nanjing Audit University, Nanjing, China
Sustainability is a comprehensive concept that integrates at least three dimensions of environment, economy and society. The power system is the primary source of greenhouse gas emissions, adversely impacting environmental sustainability. It also generates necessary energy supplies, which promote economic and social sustainable development. Based on the sustainability nature of power system, this study puts forward an improved methodology, namely “Planning-Searching-Screening-Reporting-Reflecting” (PSSRR Cycle) to review the literature systematically on power system performance evaluation from a sustainability perspective over the past 20 years, with the aim of describing the current state of the whole performance evaluation system including the evaluation framework, evaluation indicators and evaluation methods, and providing research suggestions for future research. This study finds in the current literature that the Triple Bottom Line theory is the most commonly used theoretical evaluation framework; environmental and economic sustainability indicators are more emphasized; the DEA and MCDM methods are the more common evaluation methods. This study presents some future research notes, including improving the Sustainable Balanced Scorecard as a sustainable performance evaluation framework, emphasizing more social sustainability indicators, and using a combination of existing evaluation methods to make performance evaluation more efficient and accurate.
1 Introduction
Driven by the deteriorating ecological environment, social change, and the attendant public interest, sustainability is becoming a key topic of discussion among the general public, governments, enterprises and academic scholars. There are many definitions of sustainability, among which one of the most widely accepted preliminary definitions was presented in the 1987 United Nations report “Our Common Future,” namely, “development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs” ( WCED, 1987 ). Since then, many dimensions of sustainability have been developed and discussed. In the late 1990s, the British scholar Elkington coins the phrase Triple Bottom Line (TBL), which measures sustainability by integrating the three dimensions of economic, environmental and social sustainability. That is, organizations pursuing their development require balanced development in economic prosperity, environmental protection and social welfare ( Elkington, 1997 ). The first dimension of sustainability is about the environment. Since the 1980s, environmental issues have become crucial to global sustainable development. Goodland (1995) puts forward the term environmental sustainability to refer to protecting human well-being by conserving natural resources and ensuring that the capacity to deal sustainably with human waste products is not exceeded. Diesendorf (2000) also states that environmental sustainability means that natural resources must be not harvested faster than regenerated. The second dimension of sustainability is about society. Social sustainability includes the concepts of equity, empowerment, accessibility, participation, cultural identity and institutional stability ( Daly, 1992 ). Saith (2006) argues that appropriate healthcare, education, gender equality, peace, and stability need to be used globally to promote social sustainability. Economic sustainability is the third dimension. Lobo et al. (2015) regard economic sustainability as a system of production that meets current levels of consumption without compromising future demand. Sheth et al. (2011) identify two different aspects of the economic dimension of sustainability, i.e., traditional financial performance and external economic benefits.
Power system has a significant impact on environmental, social and economic sustainability. Firstly, in terms of environmental sustainability, the carbon emission of power system accounts for more than 40% of total global carbon emissions due to over-reliance on fossil energy ( Climate Watch, 2021 ), which has had a massive impact on global climate change. Meanwhile, other gases produced by the power system also cause severe air pollution. For example, coal-fired power plants in China have caused severe pollution, resulting in large amounts of dangerous smog engulfing northern China ( Spegele and Abkowitz, 2015 ). Secondly, as for social sustainability, the value brought by the power system has permeated all aspects of people’s social life. Any failure of the power system will profoundly endanger the well-being of people and communities. For example, millions of homes and business entities were left without electricity, making millions of people live in the dark and cold due to a blizzard that devastated Texas in the United States ( Tribune, 2021 ). Thirdly, with regard to economic sustainability, the power system provides the electrical energy necessary for modern economic development. There is also a clear causal relationship between the production and consumption of electricity and the country’s economic development and prosperity ( Shiu and Lam, 2004 ; Ayres et al., 2007 ). Due to the power system’s impacts on sustainability and performance management requirements, it is crucial to understand the whole picture of performance evaluation of power system from the sustainability perspective. Therefore, a systematic literature review can be a suitable approach to acquire comprehensive knowledge and critical inspiration on the sustainability performance evaluation system of power system.
The notable difference from previous literature reviews is that this study evaluates existing literature on the performance evaluation system of power systems from three aspects, i.e. evaluation framework, evaluation indicators, and evaluation methods, which compose the whole performance evaluation system of the power system. Although there are a few existing literature reviews on the power system performance evaluation from the sustainable perspective, they only summarize one part of the performance evaluation system of the power system. For example, Wang et al. (2009) focus on an overview of Multi-Criteria Decision Making (MCDM) tools in sustainable energy decision-making. Martín-Gamboa et al. (2017) discuss the combined use of Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) and Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) methods in the sustainability assessment of power system. Campos-Guzmán et al. (2019) conduct a comprehensive literature review of the sustainability assessment method of renewable energy system over the past decade (2007–2017), which suggest that a methodological framework combining LCA and MCDM is the appropriate method for the sustainability assessment of renewable energy system. Varun I. K. et al. (2009) also review the application of LCA methods for renewable energy generation systems. These above literature reviews make some distinct contributions for summarizing the evaluation methods of performance evaluation system of power systems. However, they are more concerned with the evaluation methods and less concerned with other vital parts of the performance evaluation system of the power system, such as the evaluation framework and evaluation indicators.
Therefore, in this paper, a systematic literature review concerning the whole performance evaluation system of power system, with the aim of describing evaluation framework, evaluation indicators and evaluation methods, has been performed from the sustainability perspective during the past 20 years (2000–2020). This paper presents not only a holistic and systematic literature review to fully understand the current research status on the power system performance evaluation, but it also provides some critical inspiration and discussion for future research on the performance evaluation of the power system.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows with Section 2 spelling out a new systematic literature review methodology. Sections 3–5 show some description and discussion on the evaluation framework, evaluation indicators and evaluation methods of the power system’s performance evaluation system. Section 6 presents a critical discussion for future research and a conclusion.
2 Research Methodology
This paper adopts a systematic approach to implement the literature review. A systematic literature review is defined as an objective, transparent and complete method ( Tranfield et al., 2003 ; Cook et al., 1997 ). Precisely, a systematic literature review consists of a thorough search for outstanding contributions to a specific topic, which are assessed and synthesized according to a predefined and precise methodology. A series of specific stages are carefully implemented to ensure the validity and reliability of the literature review. Based on the systematic literature analysis framework proposed by Tranfield et al. (2003) , we put forward an improved methodology, namely “Planning-Searching-Screening-Reporting-Reflecting” (PSSRR Cycle, as shown in Figure 1 ), with five stages that form an integral logical loop.
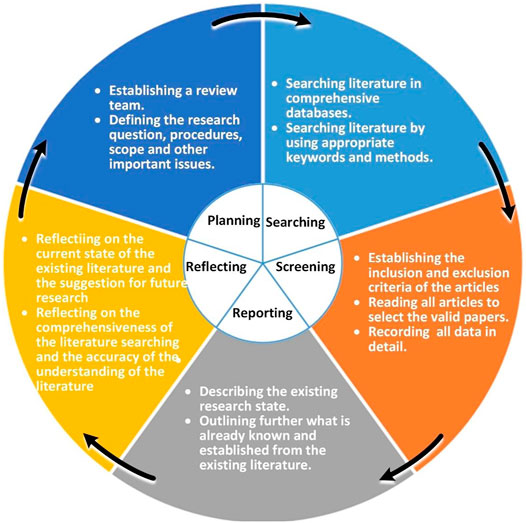
FIGURE 1 . The PSSRR Cycle of systematic literature review.
2.1 Planning
The first stage of a systematic literature review is to plan. According to the study by Tranfield et al. (2003) and Zhang et al. (2019) , we form a review team consisting of three scholars on power system’s performance evaluation research and three senior practitioners on power system’s performance evaluation and management. The review team define the research questions and solution ideas as follow after three-round discussions:
Q1. What are the current state and the trend of research on the performance evaluation of power system from the sustainability perspective?
This question will be answered through several steps: firstly, the existing literature will be searched by using appropriate keywords and methods in some databases as comprehensive as possible. Secondly, each article will be studied to find some features common to each piece of research literature and considered for inclusion in the thematic analysis. Thirdly, each article will be identified, and the research state of power system’s performance evaluation from the sustainability perspective will be summarized. Furthermore, the evaluation framework, evaluation indicators, and evaluation methods for performance evaluation of power system will be critically discussed in detail.
Q2. What are the possible research notes of the power system performance evaluation from the perspective of sustainability in the future?
This question will be resolved according to the answer of the former question. Firstly, after a dedicated thematic analysis, what is valuable about each article (e.g. sustainable relevance, evaluation framework, evaluation indicators and evaluation methods used) will be identified and summarized. Then, after reading all the literature, each member of our review team will bring forward valuable conclusions and discussions from existing studies. Finally, after a consensus consultation of the review team, the different views will be consolidated. Then, some discussions and future research suggestions will be conducted and re-refined to stimulate and support the in-depth future research on the sustainable development of power system.
2.2 Searching
Tranfield et al. (2003) argue that comprehensive, unbiased literature searching is one of the fundamental differences between the traditional literature review and the systematic literature review, which means the literature searching requires considerable time, patience and attention to the details ( Bom et al., 2019 ; Araujo et al., 2020 ). Our systematic literature searching begins with the identification of search keywords based on the scope of this study. Then, we decide on the searching keywords that were most appropriate for this study.
During the searching stage of this study, we make literature searching from Emerald, ELSEVIER Science Direct, SpringerLink, SCOPUS, JSTOR and Google Scholar, et al. The searching keywords include “performance assessment OR measurement OR evaluation” AND “power system OR energy system OR electricity system” AND “sustainable” which are limited to the article title, keywords and abstract. The searching is extended by using the Boolean search method (*) to identify all different forms of the above keywords. Finally, A total of 105 articles over the last 20 years are collected.
2.3 Screening
Tranfield et al. (2003) point out that the output of the literature searching should be a complete list of articles that is the basis of the literature review. Therefore, we screen those articles that meet all the inclusion criteria specified in the review protocol ( Milanesi et al., 2020 ). More than one author conducts this stage of this systematic review because whether articles should be included or excluded is relatively subjective. The disagreements about the literature screening are discussed and resolved by the review team.
In the screening stage of this study, we carefully screen the articles for in-depth analysis based on our inclusion and exclusion criteria (as shown in Table 1 ). All articles are read carefully by every author. Conference papers, book chapter sections (8 articles), and literature reviews (9 articles) are excluded. Finally, after literature screening, the remaining 88 articles on the power system’s performance evaluation are listed in an Excel workbook, which records all papers’ data in detail. The searching and screening process can be summarized in the PRISMA flow chart (as shown in Figure 2 ).

TABLE 1 . Inclusion and exclusion criteria of the literature.
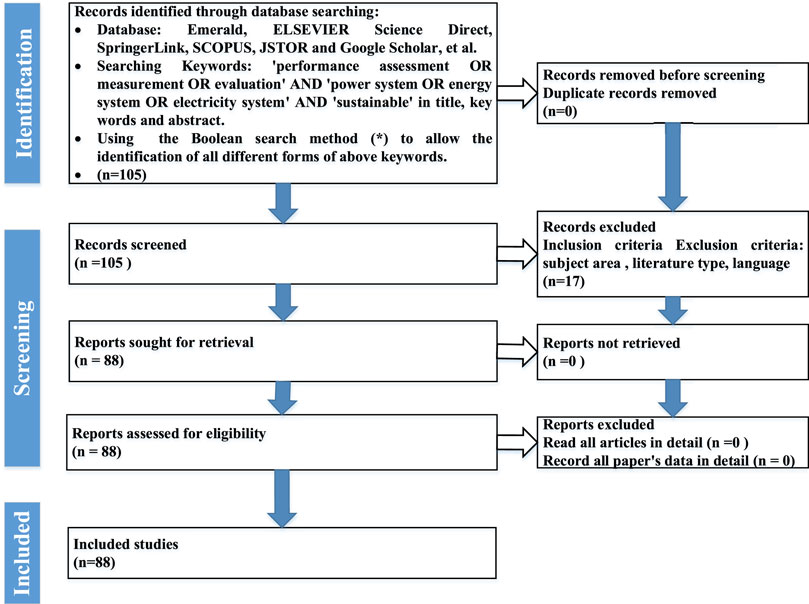
FIGURE 2 . PRISMA flow chart.
Eighty-eight articles are finally identified as shown in Figure 3 . After a plodding start, research on this topic is generally in a state of growth. Although there are some fluctuations, it is clear that academic interest in this issue has increased rapidly over the last few years. We may suggest at least three plausible reasons as follow. Firstly, in the light of the current carbon reduction targets proposed by countries around the world and the profound effect caused by climate change, there is a growing social awareness of the power system as a major source of carbon emission. Secondly, due to the rapid development of new energy technologies, scholars pay more and more attention to the contribution of technology to the sustainability of power system. Thirdly, the power system has an irreplaceable role in the development of national economies and societies.
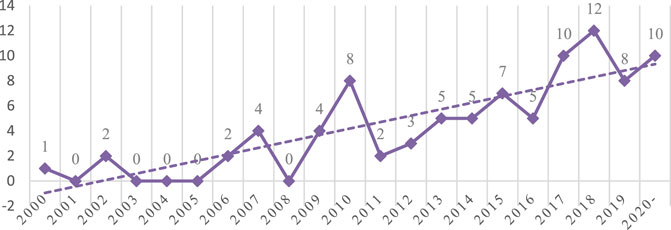
FIGURE 3 . Frequency distribution of publications by years.
Table 2 displays an overview of the articles published by journals. Energy and Energy Policy are the two most published journals on the performance evaluation of power system from the perspective of sustainability, both of which have titles related to energy, consistent with their aim of addressing and discussing sustainability issues. Figure 4 illustrates our ranking of the number of specific research subjects within the power system. It can be observed that most of the existing studies focus on the sustainability evaluation of power generation technologies and power generation enterprises, while there are fewer studies on the sustainability evaluation of the power supply chain. Figure 5 demonstrates the percentage of the screened literature that examines the number of different energy types. It is striking to see that the literature examining the sustainability of power generation from multiple energy sources is more predominant, followed by the literature examining the sustainability of power generation from renewable energy sources separately.

TABLE 2 . Journals ranked by number of articles.
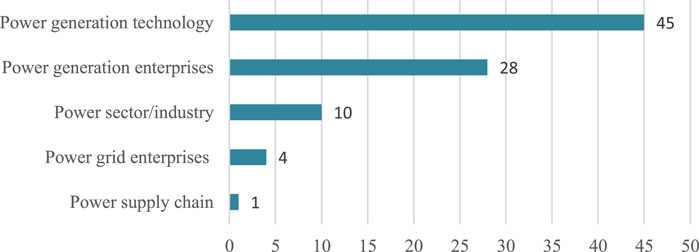
FIGURE 4 . Research subjects ranked by the number of articles.
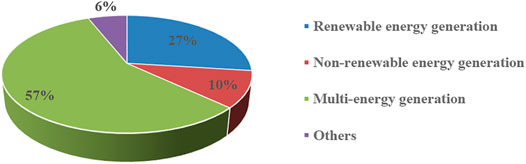
FIGURE 5 . Percentage of energy types studied.
2.4 Reporting
A successful systematic review should produce a clear report which can make the research more accessible to the readers by synthesizing a wide range of original research papers. The report firstly focuses on identifying the key themes and the degree of consensus between these different themes. Furthermore, the report outlines what is already known and established from the existing literature Tranfield et al., 2003 ; Zhang et al., 2019 ; Milanesi et al., 2020 . In this paper, we synthesize the selected articles so that the core contributions of the different articles. Then, the evaluation framework, evaluation indicators and evaluation methods as the three main themes of the power system’s performance evaluation system are discussed in detail.

2.5 Reflecting
Based on the systematic literature analysis framework that Tranfield et al. (2003) proposed, we add a Reflecting stage to form an integral logical loop. There are two parts in this stage as follow: firstly, reflecting critically on the current research state and the suggestion for future research; and secondly, reflecting on the limitations of this systematic review, with a focus on the comprehensiveness of the literature search and the accuracy of the understanding of the literature.
3 Evaluation Framework
The evaluation framework for performance evaluation refers to the conceptual dimensions of performance. Based on the existing literature, we have divided the evaluation framework into two categories from the sustainability perspective. The one is the evaluation framework with a single sustainability dimension, such as environmental, economic and social sustainability dimension. The other is the evaluation framework with multiple sustainability dimensions, which includes traditional triple bottom lines, extended triple bottom lines, sustainable balanced scorecards and a combination framework of different sustainability dimensions. As shown in Figure 6 , the proportion of the articles based on the evaluation framework with a single sustainability dimension is about 18%. About 82% of the articles are based on the evaluation framework with multiple sustainability dimensions. Among them, papers based on TBL and expanded TBL account for more than 52%.
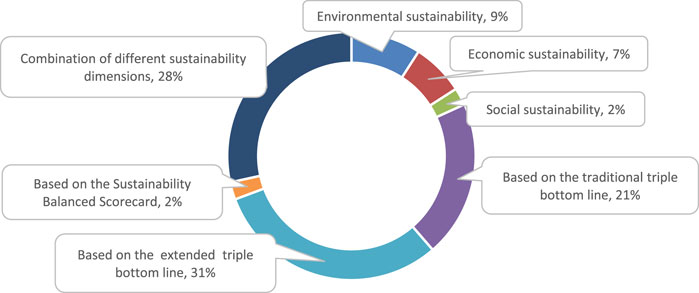
FIGURE 6 . Distribution of the evaluation framework.
3.1 Evaluation Framework With a Single Sustainability Dimension
3.1.1 single environment sustainability.
About 9% of the articles adopt a single environmental sustainability evaluation framework. Firstly, some articles have made attempts in research methods. For example, Xie et al. (2021) use a Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) game cross-efficiency model combined with a Malmquist index approach to study the dynamic environmental performance of Chinese power generators. Kouloumpis et al. (2015) present a combination of the life-cycle approach and scenario analysis to explore the impact of expected decarbonization of electricity supply on other environmental performance. Secondly, some scholars have explored the environmentally sustainable performance of power systems in the context of energy policy changes. For example, Zhang (2019) and Kaygusuz (2011) discuss the environmental sustainability performance of the power system in the circumstances of energy policy changes in China and Turkey. In addition, some scholars have explored the environmental sustainability performance of power system under certain energy technologies. For instance, Greening and Azapagic (2013) have explored the environmental sustainability performance of micro-wind turbines and the potential role in helping the UK meet its climate change targets. Diniz da Costa and Pagan (2006) evaluate the environmental sustainability performance of coal power generation in Australia. Shah and Unnikrishnan (2018) assess the environmental impacts of natural gas-fired power generation in India. The sustainability performance of the electricity supply chain in 24 Chinese provinces are evaluated mainly from the environmental perspective in the study by Sun et al. (2020) .
3.1.2 Single Economic Sustainability
Some articles directly use financial indicators to evaluate the economic sustainability performance of the power system. For example, Zhang and Qi (2020) use economic indicators such as carbon economic efficiency to evaluate the economic sustainability performance of the Chinese wind power industry. Si et al. (2020) utilize financial indicators such as short-term profitability, long-term profitability and RandD investment to evaluate economic sustainability performance. Employing financial metrics such as ROE and ROA, Schabek (2020) indicates solar power producers outperforms wind power by examining the economic sustainability performance of renewable energy companies from 16 emerging markets over the period 2000 to 2017. Paun (2017) also employs some financial indicators such as ROE and ROA to evaluate the economic sustainability performance of the renewable energy sector in Romania. Martí-Ballester (2017) applies ROE, Tobin’s Q and other financial indicators to evaluate economic sustainability performance. Deng et al. (2020) construct a financial performance evaluation system for nuclear-related enterprises from a sustainability perspective.
3.1.3 Single Social Sustainability
Only two articles assess the social sustainability of energy systems. Botelho et al. (2016) evaluate the social sustainability of renewable energy production facilities by using social indicators such as public familiarity with renewable energy generation facilities, the visibility of renewable energy generation facilities, and public opinion of renewable energy generation facilities. Gallego Carrera and Mack (2010) evaluate the social sustainability of energy technologies from stakeholders’ perspectives by applying some social indicators, such as security and reliability of energy supply, political stability and legitimacy, social and personal risk and quality of life.
3.2 Evaluation Framework With Multiple Sustainability Dimensions
3.2.1 traditional triple bottom line.
About 21% of the selected articles are based on the Triple Bottom Line. For example, Suomalainen and Sharp (2016) describe the shift of renewable energy policy in New Zealand and assess the sustainability performance of the power sector based on the TBL. Khan (2019) evaluate the sustainability performance of the Bangladesh Power System Master Plan through a multi-criteria decision analysis model using the social, environmental and economic dimensions of the TBL sustainability framework. This article notes that energy policy design needs to balance all three dimensions to ensure a sustainable power generation system in the future. Table 3 summarizes these articles using the traditional TBL to evaluate the performance of power system.
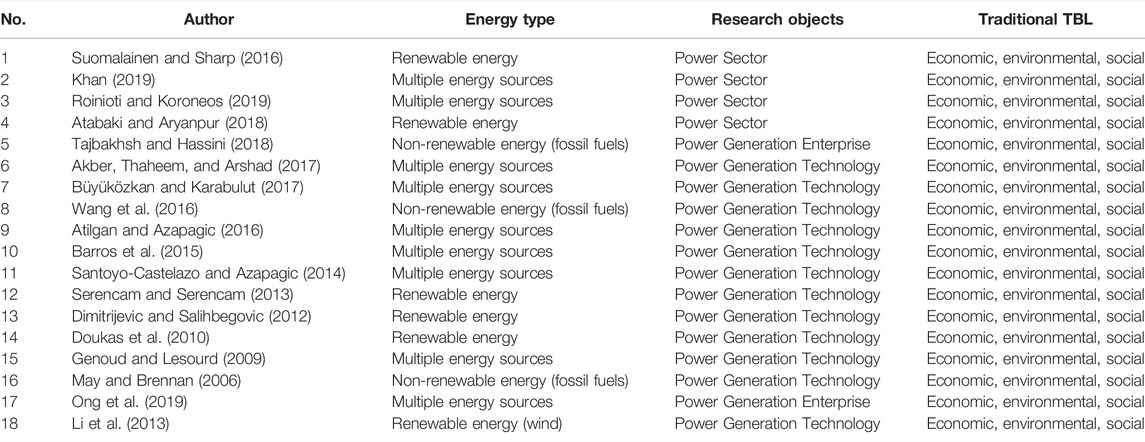
TABLE 3 . Summary of these articles using the traditional triple bottom line.
3.2.2 Extended Triple Bottom Line
Extended Triple Bottom Line is the most commonly used evaluation framework for power system performance evaluation. Extended Triple Bottom Line extends the TBL by adding some characteristics of power systems, i.e. technology, as a new extended dimension into the traditional TBL framework. For example, Rovere et al. (2010) extend the traditional triple bottom line framework by integrating four dimensions, i.e., social, economic, environmental and technological dimensions to evaluate the performance of small-scale hydro, wind, natural gas and nuclear power generation types. Similarly, for sustainable energy decision-making, Yilan et al. (2020) consider the economic, technical, environmental and socio-economic criteria to compare the performance of seven major power generation technologies in Turkey. In addition, some articles add to the traditional TBL framework by considering other dimensions such as Resources, Markets, Politics and Corporate Governance, etc. It describes these articles using the extended TBL to evaluate the performance of the power system in Table 4 .
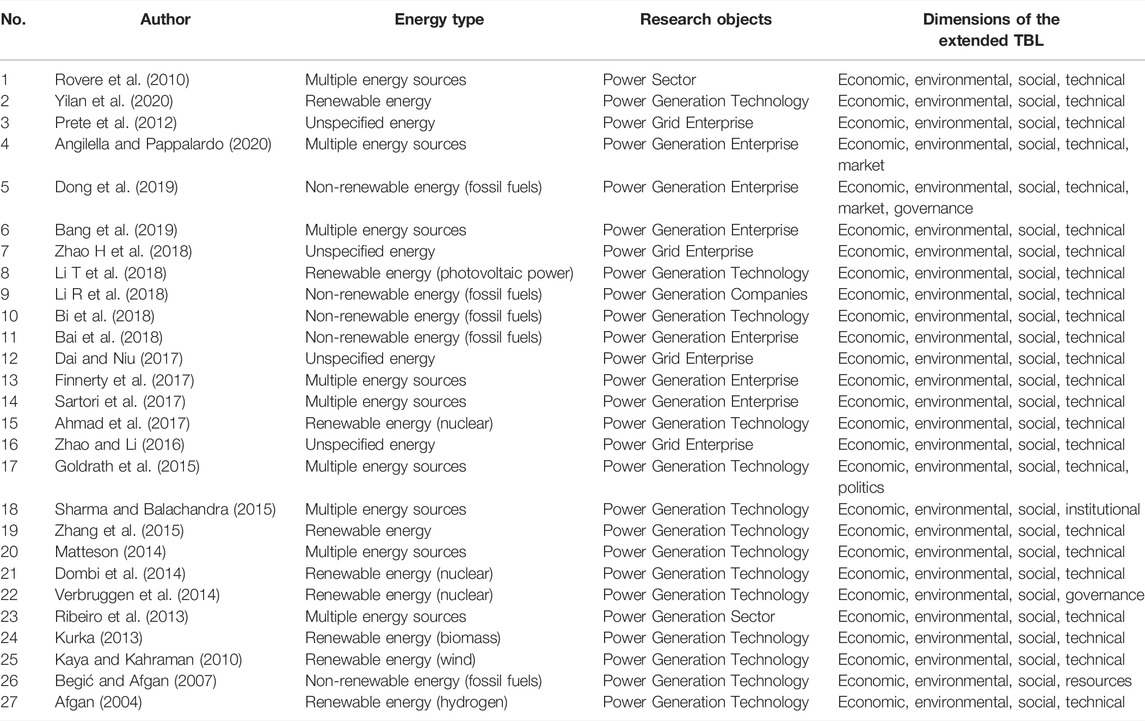
TABLE 4 . Summary of these articles using the extended triple bottom line.
3.2.3 Sustainable Balanced Scorecard
The Balanced Scorecard is a performance measurement and management system designed to balance financial and non-financial, short and long-term measures. A modification of the original Balanced Scorecard explicitly takes into account the environmental, social or ethical issues, which is referred to as Sustainable Balanced Scorecard (SBSC) ( Hansen and Schaltegger, 2016 ). SBSC is widely used in sustainability performance evaluation ( Deng et al., 2018 ; Mio et al., 2021 ). Only two papers are using the SBSC to measure the sustainable performance of power systems. For example, Sanjaranipour et al. (2018) measure the performance of the Iranian thermal power plant based on the SBSC framework. Based on the principles of the SBSC, Zhao and Li (2015) add the dimensions of Environment and Sustainability to the traditional BSC to assess and rank the performance of four power generation groups in China. A summary of these two articles using the SBSC is shown in Table 5 .

TABLE 5 . Summary of these articles using the SBSC.
3.2.4 Combination of Different Sustainability Dimensions
In this section, many articles assess the performance of power systems by relatively freely choosing an appropriate evaluation framework with a combination of different sustainability dimensions. This evaluation framework may include one or two sustainability dimensions of the TBL and other sustainability dimensions, such as technical sustainability, social sustainability, etc. For instance, Chai et al. (2019) evaluate the performance of listed companies in the thermal power sector by using an evaluation framework with the combination of different sustainability dimensions including the Technical dimension and the Environmental, Social dimensions, that stem from the traditional Triple Bottom Line. As shown in Table 6 , few articles deal with the social dimension in the combination of the different sustainability dimensions, while almost every article concerns environmental sustainability.
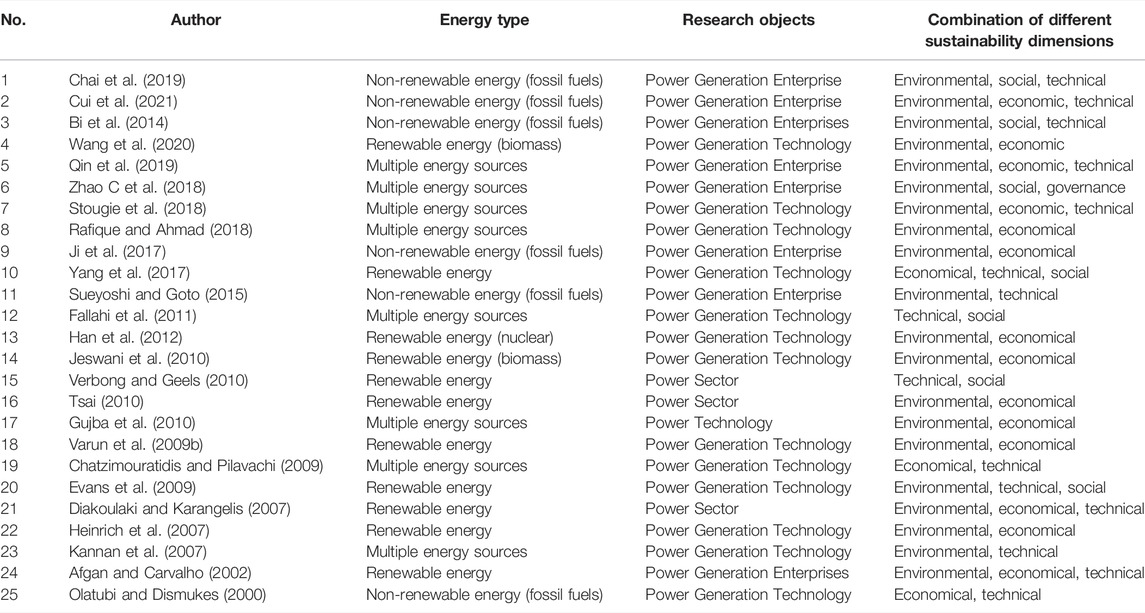
TABLE 6 . Summary of these articles using the Combination of different sustainability dimensions.
4 Evaluation Indicators
4.1 environmental sustainability indicators.
The environmental sustainability indicators can be divided into 13 indicator categories, as shown in Table 7 . In the articles selected in this paper, a total of 57 papers take Greenhouse Gas Emissions as their environmental sustainability indicator, which means Greenhouse Gas Emissions is the most considered environmental sustainability indicator. This finding is in line with the study of Campos-Guzmán et al. (2019) . The next more considered indicator categories are Acidification Potential and Human Toxicity Potential. The former includes sulfur dioxide emissions and their impact on atmospheric acidification. The latter includes emissions of harmful pollutants to human health (e.g., respirable particulate matter, carbon monoxide, etc.). The summary of environmental sustainability indicators and the frequency of each indicator category are shown in Figure 7 .
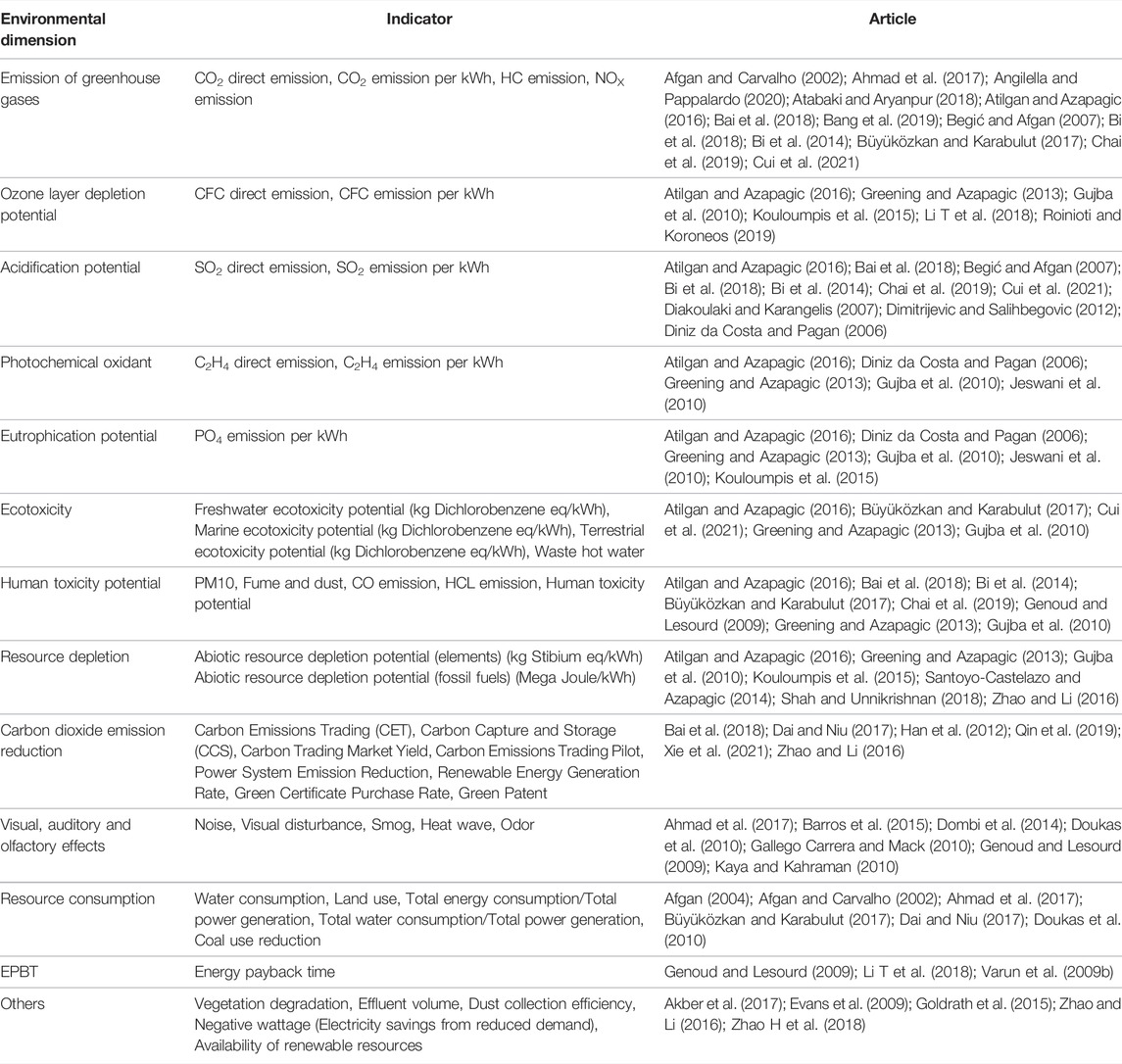
TABLE 7 . Summary of environmental sustainability indicators.
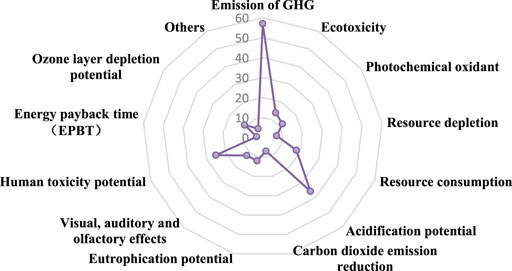
FIGURE 7 . Classification and frequency of environmental sustainability indicators.
4.2 Economic Sustainability Indicators
The economic sustainability indicators can be divided into 10 indicator categories, as shown in Table 8 . These indicators are mainly profitability indicators and cost-based indicators, which reflect how limited economic resources are allocated. Figure 8 describes the summary of economic sustainability indicators and the frequency of each indicator category.
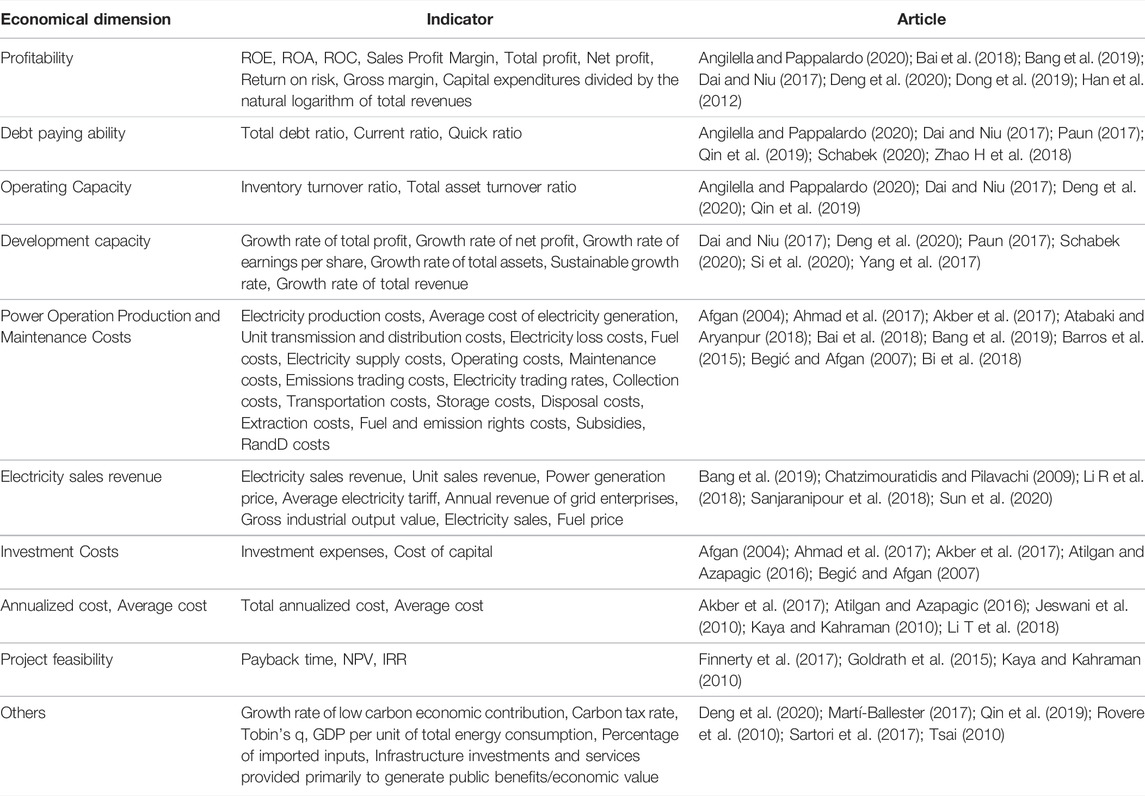
TABLE 8 . Summary of economic sustainability indicators.
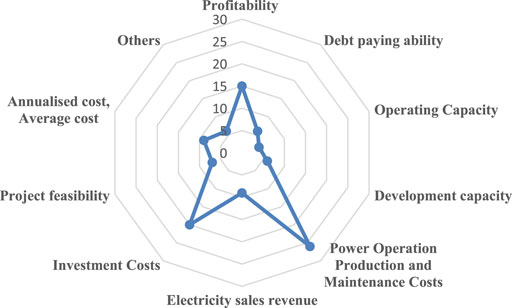
FIGURE 8 . Classification and frequency of economic sustainability indicators.
4.3 Social Sustainability Indicators
The social sustainability indicators can be divided into seven categories according to whether they are beneficial or harmful to humans, as shown in Table 9 . These social sustainability indicators show the issues that directly or indirectly affect the human and society. In most cases, they are qualitative indicators, implying the involvement of the public, experts and authorities. Employment and Job Creation is the most common social sustainability indicator, followed by other indicators such as Employee Care and Development and Risk. The summary of social sustainability indicators and the frequency of each indicator category are shown in Figure 9 .
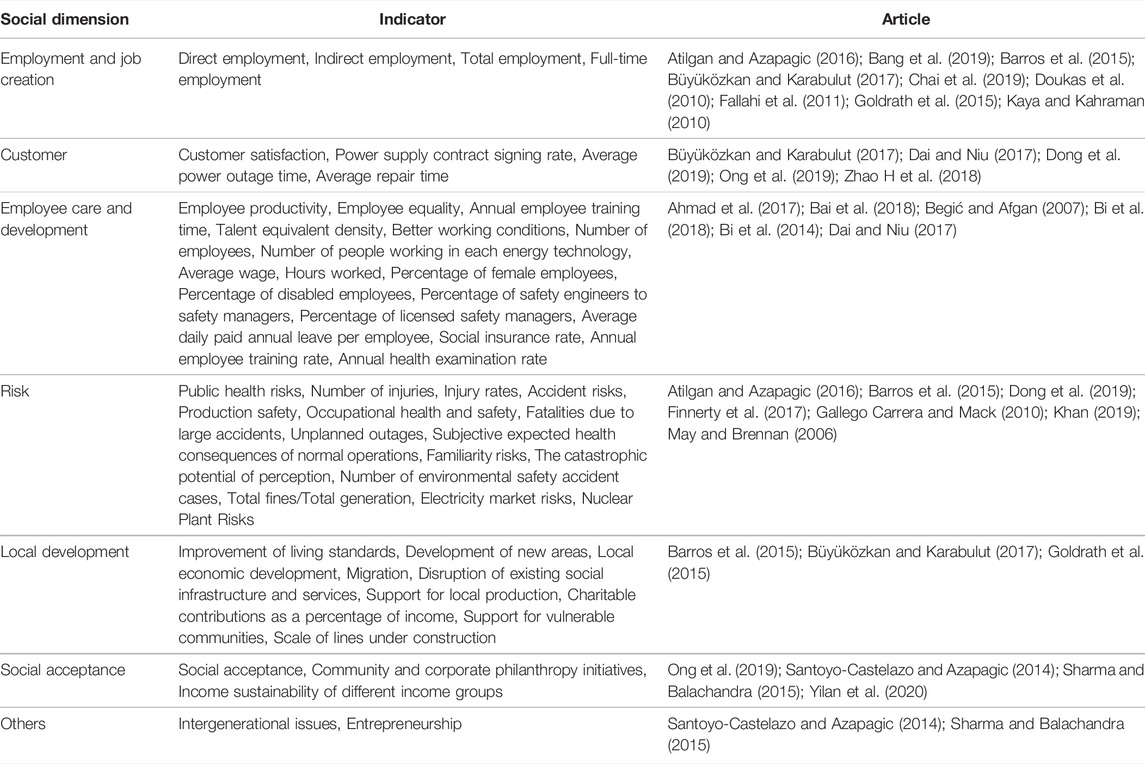
TABLE 9 . Summary of social sustainability indicators.
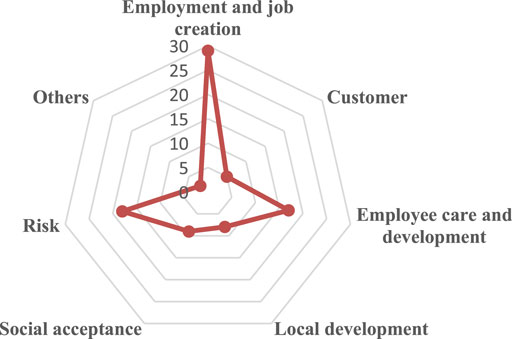
FIGURE 9 . Classification and frequency of social sustainability indicators.
4.4 Technical Sustainability Indicators
According to the indicators used in our selected articles, the technology sustainability indicators consist of 10 categories, as shown in Table 10 . Among these indicators, Efficiency is in the leading position, followed by Technical Innovation, Installed Capacity, Technical Reliability. Figure 10 illustrates the summary of technical sustainability indicators and the frequency of each indicator category.
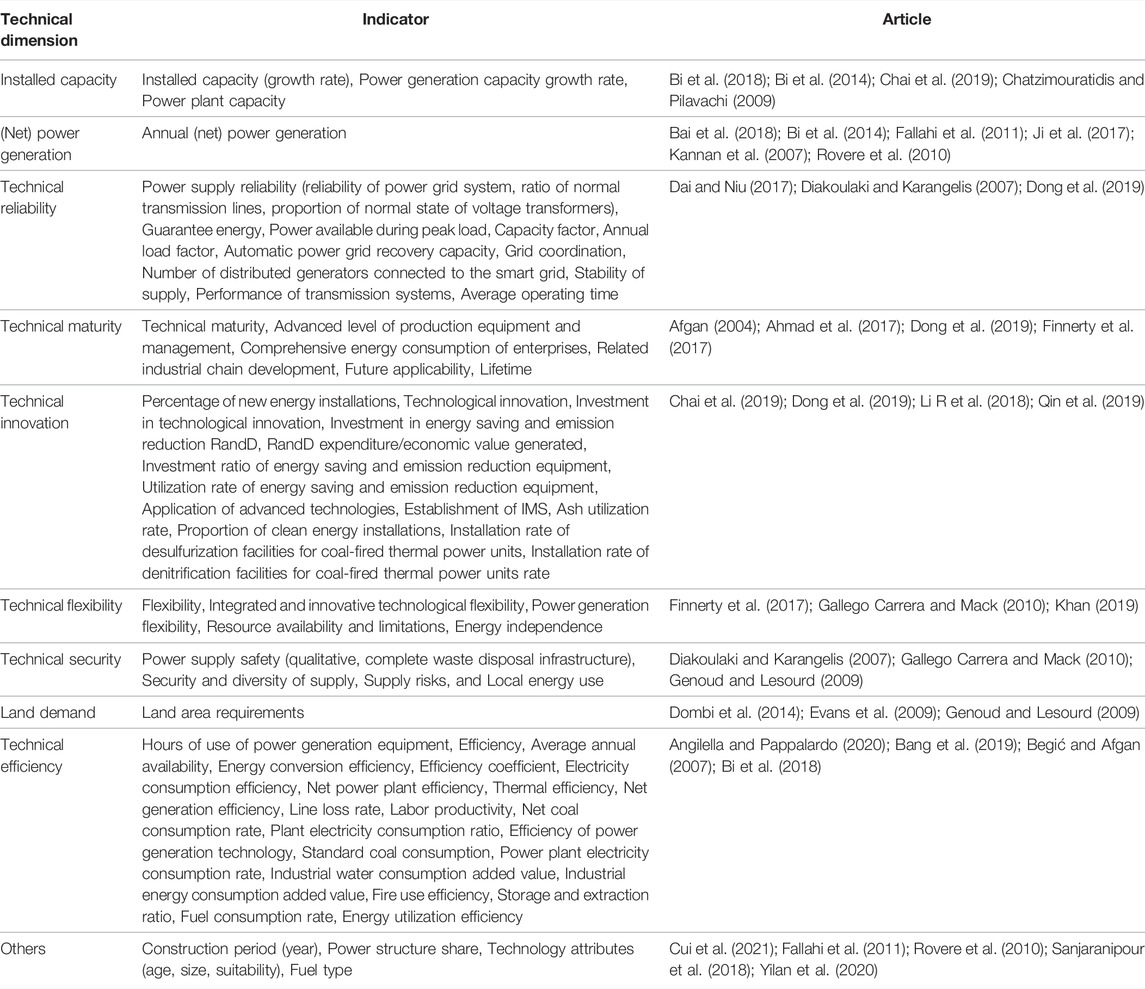
TABLE 10 . Summary of technical sustainability indicators.
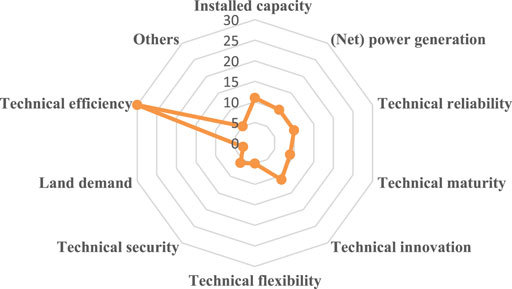
FIGURE 10 . Classification and frequency of technical sustainability indicators.
4.5 Other Sustainability Indicators
According to the previous Section 3, there are some other sustainability dimensions in addition to environmental, social, economic, and technical sustainability dimensions. Therefore, it is necessary to summarize the other sustainability dimensions, as shown in Table 11 .
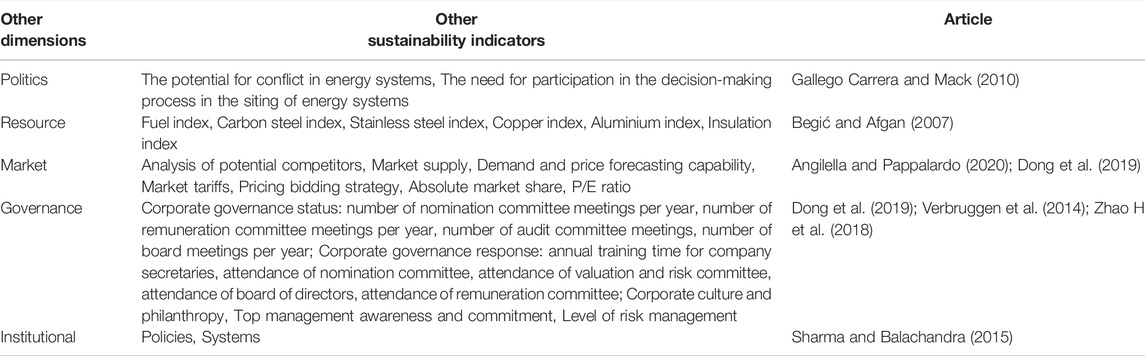
TABLE 11 . Summary of other sustainability indicators.
5 Evaluation Methods
5.1 data envelopment analysis.
In the early 2000s, Olatubi and Dismukes (2000) apply DEA methods to measure the cost performance of coal-fired generation facilities. Rovere et al. (2010) incorporate socio-environmental, technical and economic aspects into the performance evaluation to decide the power generation expansion based on the DEA approach. Fallahi et al. (2011) utilize the DEA methodology to measure efficiency and productivity changes in power generation management companies. Tajbakhsh and Hassini (2018) propose a two-stage DEA model to assess the sustainable performance of thermal power plants. Furthermore, Sun et al. (2020) introduce an improved DEA model to analyze the sustainable performance of Chinese electricity supply chain. Deng et al. (2020) combine DEA methods with MCDM methods such as Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) and Preference Ranking Organization Methods for Enrichment Evaluations (PROMETHEE) to study the financial sustainability performance of nuclear power companies. DEA methods are also often used in conjunction with statistical methods, such as Slacks-Based Measure (SBM) analysis ( Chai et al., 2019 ) and Tobit regression analysis ( Bang et al., 2019 ). The summary of the use of DEA methods is shown in Table 12 .

TABLE 12 . Summary of the use of DEA methods.
5.2 Multi-Criteria Decision Making Method
Due to the multidimensional nature of sustainability goals and the complexity of social, economic, and biophysical systems, Multi-Criteria Decision Making (MCDM) methods are becoming increasingly popular in performance evaluation for power system decision-making ( Wang et al., 2009 ). Chatzimouratidis and Pilavachi (2009) evaluate the technical, economic and sustainability performance of ten types of power plants by applying an Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) and find that renewable energy power plants are the best solution for the future. Li R et al. (2018) establish a new hybrid MCDM model by using AHP and fuzzy Vlsekriterijumska Optimizacija I Kompromisno Resenje (VIKOR) method to evaluate the performance of four large power generation companies. Dong et al. (2019) apply the extended MCDM model combined with fuzzy Delphi, Analytic Network Process (ANP) and fuzzy Decision-making Trial and Evaluation Laboratory (DEMATEL) to identify the key influences on the sustainability performance of conventional power generation groups in the market. Table 13 provides the summary of the application of MCDM methods.

TABLE 13 . Summary of the use of MCDM methods.
5.3 Life Cycle Assessment Method
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is an essential environmental management tool. Life cycle refers to the entire process of a product (or service) from the acquisition of raw materials, production, application to disposal. Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment (LCSA) is well suited for assessing environmental, economic and social sustainability ( Guinee et al., 2011 ). Stougie et al. (2018) assess the environmental and economic sustainability of five power generation systems: coal-fired power plants, coal-fired power plants including carbon capture and storage (CCS), biomass power plants, offshore wind farms, and photovoltaic parks. Li R et al. (2018) couple the LCA approach and sustainability theory to propose an integrated sustainability assessment model and then validated the model by applying it to a solar photovoltaics (PV) case study in the northeast of England.
LCA methods are often combined with MCDM methods. Atilgan and Azapagic (2016) combine the LCA approach with MAUT (Multi-Attribute Utility Theory) to assess the integrated life-cycle sustainability of power generators in Turkey. Genoud and Lesourd (2009) apply the LCA method and Elimination Et Choix Traduisant la R Ealité (ELECTRE) approach to evaluate the performance of power technology, such as Reservoir hydroelectricity, natural gas-fired power generation, etc. The articles using the LCA approach in combination with the MCDM approach are shown in Table 14 .

TABLE 14 . Summary of the application of LCA combined with MCDM methods.
5.4 Statistical Methods
The statistical method is a commonly used method of power system performance evaluation in some empirical research. For example, Si et al. (2020) employ factor analysis to investigate the interactive endogeneity relationship between RandD investment and financial sustainability performance and the moderate effect of executive incentives. Ong et al. (2019) conduct a self-administered questionnaire survey of 217 electrical and electronics companies and a hypotheses test through structural equation modelling (SEM) to identify critical success factors for sustainable performance measurement in Malaysian electrical and electronics companies. Yang et al. (2017) posit a new hybrid evaluation index system from sustainability and internal group management perspectives. In addition, the regression analysis method is more often applied to evaluate the economic sustainability performance of power listed companies, such as the articles studied by Schabek (2020) and Martí-Ballester (2017) . The summary of relevant articles of application the statistical methods is shown in Table 15 , Panel A.
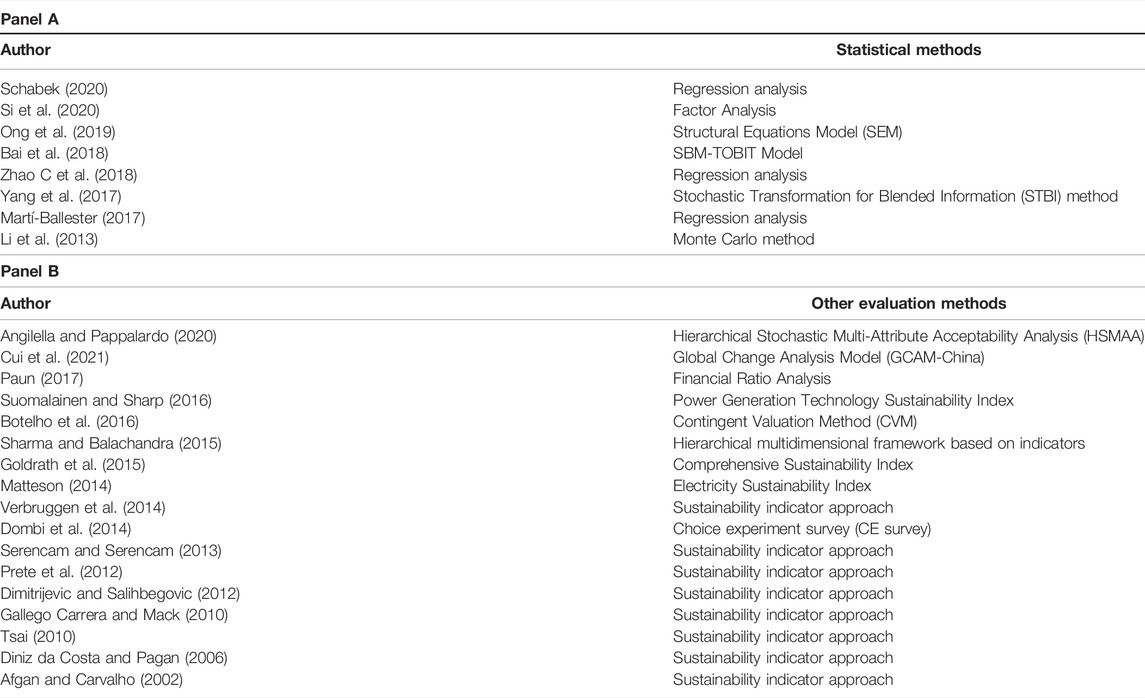
TABLE 15 . Summary of the application of statistical method and other evaluation methods.
5.5 Other Evaluation Methods
In addition to the above evaluation methods, some other evaluation methods are applied in some articles. For example, Botelho et al. (2016) adopt the Contingent Valuation Method (CVM) to evaluate the social sustainability performance of renewable energy in power generation. Dombi et al. (2014) define seven sustainability attributes to describe the sustainability performance of each renewable energy-based power and heat technology. The weight of these attributes is achieved through a Choice experiment survey conducted among Hungarian professionals. A summary of the application of other evaluation methods is shown in Table 15 , Panel B.
6 Critical Inspiration and Conclusion
Based on the above analysis, there are several research notes for future research on the performance evaluation of power systems. Firstly, under the circumstances of advocating global low-carbon development, research on performance evaluation of power systems is shifting from the traditional model to the sustainability model, which expands many research fields in the future. Especially, in order to explore the sustainable transformation and development of clean energy system from sustainability perspectives, performance evaluation of clean energy system is becoming a world research upsurge. Secondly, sustainable performance evaluation of power systems can adopt a combination of some management tools such as the sustainable balanced scorecard (SBSC). The SBSC combines the traditional balanced scorecard and the triple bottom line theoretical framework, combining strategy implementation tools, performance management tools and sustainability concepts. SBSC will vigorously promote sustainable performance evaluation and management practices in power systems. It should be noted that the difficulty of the SBSC lies in how to integrate the triple bottom line with the traditional BSC, which has two solution pathways requiring more rigorous theoretical and practical exploration. The one is to add more sustainability dimensions to the traditional four dimensions of the BSC, and the other is to integrate the sustainability concept into the four traditional BSC framework dimensions. Thirdly, while the environmental and economic sustainability performance of power systems has received widespread attention, the existing literature has paid relatively little attention to the issues of the social sustainability performance of power systems. The stability and safety of the power system have a significant impact on society. Furthermore, the social sustainability performance of the power system is also an essential expression of the power system’s social responsibility. Fourth, given the multidimensional nature and the complexity of the sustainable development of power systems, the MCDM is the most suitable evaluation method for the sustainability performance of power systems. Therefore, finding a suitable MCDM method according to the characteristics of the evaluation object is the critical issue for the performance evaluation of the power system. Future research should pay attention to the hybrid and application of MCDM method and other methods. Finally, in terms of the geographical distribution of research on the performance evaluation of power systems, future research should focus on the sustainable development of power systems in underdeveloped regions such as Africa. Moreover, although solar power, hydroelectric power, wind power and even nuclear power are currently more common research objects, it can be noted that biomass and straw energy has less attention. Therefore, the research of sustainability performance evaluation of power systems can also be broadened into these new fields in the future.
To sum up, this paper put forward a systematic methodology, namely “Planning-Searching-Screening-Reporting-Reflecting” (PSSRR Cycle), to review the articles on power system’s performance evaluation from a sustainable perspective. Some findings are revealed based on three main parts of the power system’s performance evaluation system: Evaluation Framework, Evaluation Indicators, and Evaluation Methods, respectively. Firstly, regarding the evaluation framework, the Triple Bottom Line theory is the most commonly used theoretical framework for evaluating the performance of power systems from a sustainability perspective. Almost all of the articles deal with the environmental aspects, which shows that the environmental sustainability caused by power systems have attracted the attention of the vast majority of scholars. In the Expanded Triple Bottom Line framework, technical sustainability is the most commonly considered aspect. It is worth noting that Evaluation Frameworks of the power system’s performance evaluation system are evolving ceaselessly. For example, a small number of studies have adopted the Sustainable Balanced Scorecard (SBSC) as the Evaluation Frameworks. SBSC is an organic blend of the traditional balanced scorecard and the triple bottom line. SBSC will be a powerful tool for evaluating sustainability performance and implementing the sustainable development strategy. For future research, the SBSC could be considered for sustainability performance evaluation of power systems, with continuous attempts to modify it so that the three dimensions of sustainability can be better balanced and expanded. Secondly, concerning the evaluation indicators, although the indicators used in each article are not the same, there are commonalities in these indicators that reflect which indicators are more commonly applied and valued. To a certain extent, the indicators used more frequently in articles are regarded as the more critical factors to evaluate the power system’s performance. Current research has placed more emphasis on environmental and economic sustainability indicators while neglecting social sustainability indicators. For the future research, the selection of indicators should follow corresponding principles, such as the ease of access to data, the comprehensiveness of the measurement and the high relevance to the content of the measurement, thus enhancing the diversity of the evaluation content. Furthermore, although some indicators are somewhat specific and rare, it does not mean that they are not essential because of the specificity of the research objects, which may also provide a reference for the related research in the future. Finally, as for evaluation methods, the DEA and MCDM methods are the more common performance evaluation methods of power systems. Many scholars can improve the DEA method to make the evaluation process and results more accurate. Many MCDM methods are often selected and efficient combined according to the advantages of these methods. In addition, the LCA method is also essential because it is widely used alone or in combination with DEA or MCDM methods. Although LCA is suitable for the characteristics of the power system, the requirements of data availability and accuracy are very high, which limits the application and development of this method. In the future studies, the use of multi-criteria decision making methods is more strongly recommended. A combination of different evaluation methods can be explored and even more precise evaluation methods can be developed.
The evaluation framework, evaluation indicators, and evaluation methods are the main three aspects of the whole performance evaluation system of the power system. This study distinguishes itself from existing reviews of power system performance evaluation in that it not only focus more on the description of the evaluation methods (e.g., Varun I. K. et al., 2009 ; Wang et al., 2009 ; Martín-Gamboa et al., 2017 ; Campos Guzmán et al., 2019 ), and it is also more concerned with other aspects of the evaluation system, such as the evaluation framework and evaluation indicators.
Of course, this paper is subject to several limitations. Firstly, although this paper tries to summarize all the evaluation framework, indicators, and methods as far as possible in the thematic analysis section, it is impossible to avoid some omissions. Secondly, some methodological limitations need to be considered when interpreting the study results. For example, book chapters, conference papers and books were excluded in this paper, which potentially creates a bias in the selection of literature. Finally, the keywords choice and literature screening are performed under our subjective conditions in this paper, which may lead to unexpected uncertainty due to the limitations of our knowledge.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by DD, CL, and YZ. JZ, SW, and LL commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
The work was supported by the Social Science Fund Project of Jiangsu Province of China (Grant no. 19EYB013), China National Social Science Fund Project (Grant no. 20FJYB026) and Youth Fund of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 72102108) and Jiangsu “333 Project” Scientific Research Support Project (Grant no. 2020-18).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Afgan, N. H., and Carvalho, M. G. (2002). Multi-criteria Assessment of New and Renewable Energy Power Plants. Energy 27 (8), 739–755. doi:10.1016/S0360-5442(02)00019-1
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Afgan, N. (2004). Sustainability Assessment of Hydrogen Energy Systems. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 29 (13), 1327–1342. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2004.01.005
Ahmad, S., Nadeem, A., Akhanova, G., Houghton, T., and Muhammad-Sukki, F. (2017). Multi-criteria Evaluation of Renewable and Nuclear Resources for Electricity Generation in Kazakhstan. Energy 141, 1880–1891. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2017.11.102
Akber, M. Z., Thaheem, M. J., and Arshad, H. (2017). Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment of Electricity Generation in Pakistan: Policy Regime for a Sustainable Energy Mix. Energy Policy 111, 111–126. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2017.09.022
Angilella, S., and Pappalardo, M. R. (2020). Performance Assessment of Energy Companies Employing Hierarchy Stochastic Multi-Attribute Acceptability Analysis. Oper. Res. Int. J. 22, 299–370. doi:10.1007/s12351-020-00567-5
Araújo, A. G., Pereira Carneiro, A. M., and Palha, R. P. (2020). Sustainable Construction Management: A Systematic Review of the Literature with Meta-Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 256, 120350. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120350
Atabaki, M. S., and Aryanpur, V. (2018). Multi-objective Optimization for Sustainable Development of the Power Sector: An Economic, Environmental, and Social Analysis of Iran. Energy 161, 493–507. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2018.07.149
Atilgan, B., and Azapagic, A. (2016). An Integrated Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment of Electricity Generation in Turkey. Energy Policy 93, 168–186. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2016.02.055
Ayres, R., Turton, H., and Casten, T. (2007). Energy Efficiency, Sustainability and Economic Growth. Energy 32 (5), 634–648. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2006.06.005
Bai, Y., Hua, C., Jiao, J., Yang, M., and Li, F. (2018). Green Efficiency and Environmental Subsidy: Evidence from Thermal Power Firms in China. J. Clean. Prod. 188, 49–61. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.03.312
Bang, Y.-Y., Lee, D. S., and Lim, S.-R. (2019). Analysis of Corporate CO2 and Energy Cost Efficiency: The Role of Performance Indicators and Effective Environmental Reporting. Energy Policy 133, 110897. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2019.110897
Begić, F., and Afgan, N. H. (2007). Sustainability Assessment Tool for the Decision Making in Selection of Energy System-Bosnian Case. Energy 32 (10), 1979–1985. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2007.02.006
Bi, G.-b., Shao, Y., Song, W., Yang, F., and Luo, Y. (2018). A Performance Evaluation of China's Coal-Fired Power Generation with Pollutant Mitigation Options. J. Clean. Prod. 171, 867–876. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.271
Bi, G.-B., Song, W., Zhou, P., and Liang, L. (2014). Does Environmental Regulation Affect Energy Efficiency in China's Thermal Power Generation? Empirical Evidence from a Slacks-Based DEA Model. Energy Policy 66, 537–546. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2013.10.056
Bom, S., Jorge, J., Ribeiro, H. M., and Marto, J. (2019). A Step Forward on Sustainability in the Cosmetics Industry: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 225, 270–290. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.03.255
Botelho, A., Pinto, L. M. C., Lourenço-Gomes, L., Valente, M., and Sousa, S. (2016). Social Sustainability of Renewable Energy Sources in Electricity Production: An Application of the Contingent Valuation Method. Sustain. Cities Soc. 26, 429–437. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2016.05.011
Büyüközkan, G., and Karabulut, Y. (2017). Energy Project Performance Evaluation with Sustainability Perspective. Energy 119, 549–560. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2016.12.087
Campos-Guzmán, V., García-Cáscales, M. S., Espinosa, N., and Urbina, A. (2019). Life Cycle Analysis with Multi-Criteria Decision Making: A Review of Approaches for the Sustainability Evaluation of Renewable Energy Technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 104, 343–366. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2019.01.031
Cartelle Barros, J. J., Lara Coira, M., de la Cruz López, M. P., and del Caño Gochi, A. (2015). Assessing the Global Sustainability of Different Electricity Generation Systems. Energy 89, 473–489. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2015.05.110
Chai, J., Fan, W., and Han, J. (2019). Does the Energy Efficiency of Power Companies Affect Their Industry Status? A DEA Analysis of Listed Companies in Thermal Power Sector. Sustainability 12 (1), 138. doi:10.3390/su12010138
Chatzimouratidis, A. I., and Pilavachi, P. A. (2009). Technological, Economic and Sustainability Evaluation of Power Plants Using the Analytic Hierarchy Process. Energy Policy 37 (3), 778–787. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2008.10.009
Climate Watch (2021). Historical GHG Emissions. Retrieved from https://www.climatewatchdata.org/ghg-emissions?source=CAIT .
Google Scholar
Cook, D. J., Mulrow, C. D., and Haynes, R. B. (1997). Systematic Reviews: Synthesis of Best Evidence for Clinical Decisions. Ann. Intern Med. 126 (5), 376–380. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-126-5-199703010-00006
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Cui, R. Y., Hultman, N., Cui, D., McJeon, H., Yu, S., Edwards, M. R., et al. (2021). A Plant-By-Plant Strategy for High-Ambition Coal Power Phaseout in China. Nat. Commun. 12 (1), 1468. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-21786-0
Dai, S., and Niu, D. (2017). Comprehensive Evaluation of the Sustainable Development of Power Grid Enterprises Based on the Model of Fuzzy Group Ideal Point Method and Combination Weighting Method with Improved Group Order Relation Method and Entropy Weight Method. Sustainability 9 (10), 1900. doi:10.3390/su9101900
Daly, H. E. (1992). U.N. Conferences on Environment and Development: Retrospect on Stockholm and Prospects for Rio. Ecol. Econ. 5 (1), 9–14. doi:10.1016/0921-8009(92)90018-N
Deng, D., Wen, S., Chen, F.-H., and Lin, S.-L. (2018). A Hybrid Multiple Criteria Decision Making Model of Sustainability Performance Evaluation for Taiwanese Certified Public Accountant Firms. J. Clean. Prod. 180, 603–616. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.107
Deng, Y., Zou, S., and You, D. (2020). Financial Performance Evaluation of Nuclear Power-Related Enterprises from the Perspective of Sustainability. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 27 (10), 11349–11363. doi:10.1007/s11356-019-07545-1
Diakoulaki, D., and Karangelis, F. (2007). Multi-criteria Decision Analysis and Cost-Benefit Analysis of Alternative Scenarios for the Power Generation Sector in Greece. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 11 (4), 716–727. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2005.06.007
Diesendorf, M. (2000). Sustainability: The Corporate Challenge of the 21st Century . NSW, Australia: Allen & Unwin .
Dimitrijevic, Z., and Salihbegovic, I. (2012). Sustainability Assessment of Increasing Renewable Energy Sources Penetration - JP Elektroprivreda B&H Case Study. Energy 47 (1), 205–212. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2012.09.010
Diniz da Costa, J. C., and Pagan, R. J. (2006). Sustainability Metrics for Coal Power Generation in Australia. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 84 (2), 143–149. doi:10.1205/psep.04126
Dombi, M., Kuti, I., and Balogh, P. (2014). Sustainability Assessment of Renewable Power and Heat Generation Technologies. Energy Policy 67, 264–271. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2013.12.032
Dong, J., Liu, D., Wang, D., and Zhang, Q. (2019). Identification of Key Influencing Factors of Sustainable Development for Traditional Power Generation Groups in a Market by Applying an Extended MCDM Model. Sustainability 11 (6), 1754. doi:10.3390/su11061754
Doukas, H., Karakosta, C., and Psarras, J. (2010). Computing with Words to Assess the Sustainability of Renewable Energy Options. Expert Syst. Appl. 37 (7), 5491–5497. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2010.02.061
Elkington, J. (1997). Cannibals with Forks: The Triple Bottom Line of Twenty-First Century Business . Oxford: Capstone .
Evans, A., Strezov, V., and Evans, T. J. (2009). Assessment of Sustainability Indicators for Renewable Energy Technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 13 (5), 1082–1088. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2008.03.008
Fallahi, A., Ebrahimi, R., and Ghaderi, S. F. (2011). Measuring Efficiency and Productivity Change in Power Electric Generation Management Companies by Using Data Envelopment Analysis: A Case Study. Energy 36 (11), 6398–6405. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2011.09.034
Finnerty, N., Sterling, R., Coakley, D., Contreras, S., Coffey, R., and Keane, M. M. (2017). Development of a Global Energy Management System for Non-energy Intensive Multi-Site Industrial Organisations: A Methodology. Energy 136, 16–31. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2016.10.049
Gallego Carrera, D., and Mack, A. (2010). Sustainability Assessment of Energy Technologies via Social Indicators: Results of a Survey Among European Energy Experts. Energy Policy 38 (2), 1030–1039. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2009.10.055
Genoud, S., and Lesourd, J.-B. (2009). Characterization of Sustainable Development Indicators for Various Power Generation Technologies. Int. J. Green Energy 6 (3), 257–267. doi:10.1080/15435070902880943
Goldrath, T., Ayalon, O., and Shechter, M. (2015). A Combined Sustainability Index for Electricity Efficiency Measures. Energy Policy 86, 574–584. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2015.08.013
Goodland, R. (1995). The Concept of Environmental Sustainability. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 26 (1), 1–24. doi:10.1146/annurev.es.26.110195.000245
Greening, B., and Azapagic, A. (2013). Environmental Impacts of Micro-wind Turbines and Their Potential to Contribute to UK Climate Change Targets. Energy 59, 454–466. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2013.06.037
Guinée, J. B., Heijungs, R., Huppes, G., Zamagni, A., Masoni, P., Buonamici, R., et al. (2011). Life Cycle Assessment: Past, Present, and Future. Environ. Sci. Technol. 45 (1), 90–96. doi:10.1021/es101316v
Gujba, H., Mulugetta, Y., and Azapagic, A. (2010). Environmental and Economic Appraisal of Power Generation Capacity Expansion Plan in Nigeria. Energy Policy 38 (10), 5636–5652. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2010.05.011
Han, J.-H., Ahn, Y.-C., and Lee, I.-B. (2012). A Multi-Objective Optimization Model for Sustainable Electricity Generation and CO2 Mitigation (EGCM) Infrastructure Design Considering Economic Profit and Financial Risk. Appl. Energy 95, 186–195. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.02.032
Hansen, E. G., and Schaltegger, S. (2016). The Sustainability Balanced Scorecard: A Systematic Review of Architectures. J. Bus. Ethics 133 (2), 193–221. doi:10.1007/s10551-014-2340-3
Heinrich, G., Basson, L., Cohen, B., Howells, M., and Petrie, J. (2007). Ranking and Selection of Power Expansion Alternatives for Multiple Objectives under Uncertainty. Energy 32 (12), 2350–2369. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2007.06.001
Jeswani, H. K., Gujba, H., and Azapagic, A. (2010). Assessing Options for Electricity Generation from Biomass on a Life Cycle Basis: Environmental and Economic Evaluation. Waste Biomass Valor 2 (1), 33–42. doi:10.1007/s12649-010-9057-z
Ji, X., Li, G., and Wang, Z. (2017). Impact of Emission Regulation Policies on Chinese Power Firms' Reusable Environmental Investments and Sustainable Operations. Energy Policy 108, 163–177. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2017.05.035
Kannan, R., Leong, K. C., Osman, R., and Ho, H. K. (2007). Life Cycle Energy, Emissions and Cost Inventory of Power Generation Technologies in Singapore. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 11 (4), 702–715. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2005.05.004
Kaya, T., and Kahraman, C. (2010). Multicriteria Renewable Energy Planning Using an Integrated Fuzzy VIKOR & AHP Methodology: The Case of Istanbul. Energy 35 (6), 2517–2527. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2010.02.051
Kaygusuz, K. (2011). The Paradigm of Sustainability in Turkey's Energy Sector. Energy Sources, Part B Econ. Plan. Policy 6 (1), 83–95. doi:10.1080/15567240802458906
Khan, I. (2019). Power Generation Expansion Plan and Sustainability in a Developing Country: A Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 220, 707–720. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.161
Kouloumpis, V., Stamford, L., and Azapagic, A. (2015). Decarbonising Electricity Supply: Is Climate Change Mitigation Going to Be Carried Out at the Expense of Other Environmental Impacts? Sustain. Prod. Consum. 1, 1–21. doi:10.1016/j.spc.2015.04.001
Kurka, T. (2013). Application of the Analytic Hierarchy Process to Evaluate the Regional Sustainability of Bioenergy Developments. Energy 62, 393–402. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2013.09.053
Li, H., Xie, M., and Zhang, T. (2013). Promote the Development of Renewable Energy: A Review and Empirical Study of Wind Power in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 22, 101–107. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2013.01.025
Li R, R., Dong, J., and Wang, D. (2018). Competition Ability Evaluation of Power Generation Enterprises Using a Hybrid MCDM Method under Fuzzy and Hesitant Linguistic Environment. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 10 (5), 055905. doi:10.1063/1.5043157
Li T, T., Roskilly, A. P., and Wang, Y. (2018). Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment of Grid-Connected Photovoltaic Power Generation: A Case Study of Northeast England. Appl. Energy 227, 465–479. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2017.07.021
Lo Prete, C., Hobbs, B. F., Norman, C. S., Cano-Andrade, S., Fuentes, A., von Spakovsky, M. R., et al. (2012). Sustainability and Reliability Assessment of Microgrids in a Regional Electricity Market. Energy 41 (1), 192–202. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2011.08.028
Lobo, M.-J., Pietriga, E., and Appert, C. (2015). “An Evaluation of Interactive Map Comparison Techniques,” in Paper Presented at the Proceedings of the 33rd Annual ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (Republic of Korea: ACM ). doi:10.1145/2702123.2702130
Martí-Ballester, C.-P. (2017). Sustainable Energy Systems and Company Performance: Does the Implementation of Sustainable Energy Systems Improve Companies' Financial Performance? J. Clean. Prod. 162, S35–S50. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.12.015
Martín-Gamboa, M., Iribarren, D., García-Gusano, D., and Dufour, J. (2017). A Review of Life-Cycle Approaches Coupled with Data Envelopment Analysis within Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis for Sustainability Assessment of Energy Systems. J. Clean. Prod. 150, 164–174. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.03.017
Matteson, S. (2014). Methods for Multi-Criteria Sustainability and Reliability Assessments of Power Systems. Energy 71, 130–136. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2014.04.042
May, J. R., and Brennan, D. J. (2006). Sustainability Assessment of Australian Electricity Generation. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 84 (2), 131–142. doi:10.1205/psep.04265
Milanesi, M., Runfola, A., and Guercini, S. (2020). Pharmaceutical Industry Riding the Wave of Sustainability: Review and Opportunities for Future Research. J. Clean. Prod. 261, 121204. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121204
Mio, C., Costantini, A., and Panfilo, S. (2021). Performance Measurement Tools for Sustainable Business: A Systematic Literature Review on the Sustainability Balanced Scorecard Use. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 9, 1–18. doi:10.1002/csr.2206
Olatubi, W. O., and Dismukes, D. E. (2000). A Data Envelopment Analysis of the Levels and Determinants of Coal-Fired Electric Power Generation Performance. Util. Policy 9 (2), 47–59. doi:10.1016/S0957-1787(01)00004-2
Ong, T., Teh, B., and Lee, A. (2019). Contingent Factors and Sustainable Performance Measurement (SPM) Practices of Malaysian Electronics and Electrical Companies. Sustainability 11 (4), 1058. doi:10.3390/su11041058
Paun, D. (2017). Sustainability and Financial Performance of Companies in the Energy Sector in Romania. Sustainability 9 (10), 1722. doi:10.3390/su9101722
Qin, Y., Li, M., De, G., Huang, L., Yang, S., Tan, Q., et al. (2019). Research on Green Management Effect Evaluation of Power Generation Enterprises in China Based on Dynamic Hesitation and Improved Extreme Learning Machine. Processes 7 (7), 474. doi:10.3390/pr7070474
Rafique, M. M., and Ahmad, G. (2018). Targeting Sustainable Development in Pakistan through Planning of Integrated Energy Resources for Electricity Generation. Electr. J. 31 (7), 14–19. doi:10.1016/j.tej.2018.08.001
Ribeiro, F., Ferreira, P., and Araújo, M. (2013). Evaluating Future Scenarios for the Power Generation Sector Using a Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis (MCDA) Tool: The Portuguese Case. Energy 52, 126–136. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2012.12.036
Roinioti, A., and Koroneos, C. (2019). Integrated Life Cycle Sustainability Assessment of the Greek Interconnected Electricity System. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assessments 32, 29–46. doi:10.1016/j.seta.2019.01.003
Rovere, E. L. L., Soares, J. B., Oliveira, L. B., and Lauria, T. (2010). Sustainable Expansion of Electricity Sector: Sustainability Indicators as an Instrument to Support Decision Making. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 14 (1), 422–429. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2009.07.033
Saith, A. (2006). From Universal Values to Millennium Development Goals: Lost in Translation. Dev. change 37 (6), 1167–1199. doi:10.1111/j.1467-7660.2006.00518.x
Sanjaranipour, N., Atabi, F., Momeni, M., Ghodousi, J., and Lahijanian, A. a.-M. (2018). Identification of Effective Components for Increasing the Sustainable Efficiency of Thermal Power Plants (With Emphasis on Air Pollution) Using the SBSC Technique. Ajw 15 (4), 57–68. doi:10.3233/ajw-180058
Santoyo-Castelazo, E., and Azapagic, A. (2014). Sustainability Assessment of Energy Systems: Integrating Environmental, Economic and Social Aspects. J. Clean. Prod. 80, 119–138. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.05.061
Sartori, S., Witjes, S., and Campos, L. M. S. (2017). Sustainability Performance for Brazilian Electricity Power Industry: An Assessment Integrating Social, Economic and Environmental Issues. Energy Policy 111, 41–51. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2017.08.054
Schabek, T. (2020). The Financial Performance of Sustainable Power Producers in Emerging Markets. Renew. Energy 160, 1408–1419. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2020.06.067
Serencam, H., and Serencam, U. (2013). Toward a Sustainable Energy Future in Turkey: An Environmental Perspective. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 27, 325–333. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2013.06.045
Shah, B., and Unnikrishnan, S. (2018). Sustainability Assessment of Gas Based Power Generation Using a Life Cycle Assessment Approach. Meq 29 (5), 826–841. doi:10.1108/meq-02-2018-0034
Sharma, T., and Balachandra, P. (2015). Benchmarking Sustainability of Indian Electricity System: An Indicator Approach. Appl. Energy 142, 206–220. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.12.037
Sheth, J. N., Sethia, N. K., and Srinivas, S. (2011). Mindful Consumption: a Customer-Centric Approach to Sustainability. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 39 (1), 21–39. doi:10.1007/s11747-010-0216-3
Shiu, A., and Lam, P.-L. (2004). Electricity Consumption and Economic Growth in China. Energy Policy 32 (1), 47–54. doi:10.1016/S0301-4215(02)00250-1
Si, K., Xu, X. L., and Chen, H. H. (2020). Examining the Interactive Endogeneity Relationship between R&D Investment and Financially Sustainable Performance: Comparison from Different Types of Energy Enterprises. Energies 13 (9), 2332. doi:10.3390/en13092332
Spegele, B., and Abkowitz, A. (2015). Beijing Steps up Smog Warnings . New York, NY: Wall Street Journal .
Stougie, L., Giustozzi, N., van der Kooi, H., and Stoppato, A. (2018). Environmental, Economic and Exergetic Sustainability Assessment of Power Generation from Fossil and Renewable Energy Sources. Int. J. Energy Res. 42 (9), 2916–2926. doi:10.1002/er.4037
Sueyoshi, T., and Goto, M. (2015). Environmental Assessment on Coal-Fired Power Plants in U.S. North-East Region by DEA Non-radial Measurement. Energy Econ. 50, 125–139. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2015.04.016
Sun, J., Xu, S., and Li, G. (2020). Analyzing Sustainable Power Supply Chain Performance. Jeim 34 (1), 79–100. doi:10.1108/JEIM-09-2019-0296
Suomalainen, K., and Sharp, B. (2016). Electricity Sector Transformation in New Zealand: A Sustainability Assessment Approach. J. Renew. Sustain. Energy 8 (3), 035902–035918. doi:10.1063/1.4950943
Tajbakhsh, A., and Hassini, E. (2018). Evaluating Sustainability Performance in Fossil-Fuel Power Plants Using a Two-Stage Data Envelopment Analysis. Energy Econ. 74, 154–178. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2018.05.032
Tranfield, D., Denyer, D., and Smart, P. (2003). Towards a Methodology for Developing Evidence-Informed Management Knowledge by Means of Systematic Review. Br. J. Manag. 14 (3), 207–222. doi:10.1111/1467-8551.00375
Tribune, T. T. (2021). “We’re in it Alone”: Power Outages Leave Millions of Texans Desperate for Heat and Safety. Retrieved from https://www.texastribune.org/2021/02/16/texans-weather-power-outage/?utm_source=articleshareandutm_medium=social .
Tsai, W.-T. (2010). Energy Sustainability from Analysis of Sustainable Development Indicators: A Case Study in Taiwan. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 14 (7), 2131–2138. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2010.03.027
Varun, , , Bhat, I. K., and Prakash, R. (2009a). LCA of Renewable Energy for Electricity Generation Systems-A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 13 (5), 1067–1073. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2008.08.004
Varun, , , Prakash, R., and Bhat, I. K. (2009b). Energy, Economics and Environmental Impacts of Renewable Energy Systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 13 (9), 2716–2721. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2009.05.007
Verbong, G. P. J., and Geels, F. W. (2010). Exploring Sustainability Transitions in the Electricity Sector with Socio-Technical Pathways. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 77 (8), 1214–1221. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2010.04.008
Verbruggen, A., Laes, E., and Lemmens, S. (2014). Assessment of the Actual Sustainability of Nuclear Fission Power. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 32, 16–28. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2014.01.008
Wang, J.-J., Jing, Y.-Y., Zhang, C.-F., and Zhao, J.-H. (2009). Review on Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis Aid in Sustainable Energy Decision-Making. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 13 (9), 2263–2278. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2009.06.021
Wang, S., Chu, C., Chen, G., Peng, Z., and Li, F. (2016). Efficiency and Reduction Cost of Carbon Emissions in China: a Non-radial Directional Distance Function Method. J. Clean. Prod. 113, 624–634. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.11.079
Wang, Z., Wang, Z., Xu, G., Ren, J., Wang, H., and Li, J. (2020). Sustainability Assessment of Straw Direct Combustion Power Generation in China: From the Environmental and Economic Perspectives of Straw Substitute to Coal. J. Clean. Prod. 273, 122890. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122890
WCED (1987). World Commission on Environment and Development. Our common future 17 (1), 1–91.
Xie, B.-C., Chen, Y.-F., Gao, J., and Zhang, S. (2021). Dynamic Environmental Efficiency Analysis of China's Power Generation Enterprises: a Game Cross-Malmquist Index Approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28 (2), 1697–1711. doi:10.1007/s11356-020-10237-w
Yang, W., Liu, L., and Yu, X. (2017). Evaluating the Comprehensive Benefit of Group-Affiliated New Energy Power Generation Enterprises for Sustainability: Based on a Combined Technique of STBI and TOPSIS. Sustainability 10 (1), 24. doi:10.3390/su10010024
Yilan, G., Kadirgan, M. A. N., and Çiftçioğlu, G. A. (2020). Analysis of Electricity Generation Options for Sustainable Energy Decision Making: The Case of Turkey. Renew. Energy 146, 519–529. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2019.06.164
Zhang, F., Cao, C., Li, C., Liu, Y., and Huisingh, D. (2019). A Systematic Review of Recent Developments in Disaster Waste Management. J. Clean. Prod. 235, 822–840. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.06.229
Zhang, H. (2019). Antinomic Policy-Making under the Fragmented Authoritarianism: Regulating China's Electricity Sector through the Energy-Climate-Environment Dimension. Energy Policy 128, 162–169. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2019.01.003
Zhang, L., Zhou, P., Newton, S., Fang, J.-x., Zhou, D.-q., and Zhang, L.-p. (2015). Evaluating Clean Energy Alternatives for Jiangsu, China: An Improved Multi-Criteria Decision Making Method. Energy 90, 953–964. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2015.07.124
Zhang, T., and Qi, X. (2020). Analysis of Performance Deviation of Wind Power Enterprises in China. Front. Energy Res. 8, 26–35. doi:10.3389/fenrg.2020.00126
Zhao C, C., Guo, Y., Yuan, J., Wu, M., Li, D., Zhou, Y., et al. (2018). ESG and Corporate Financial Performance: Empirical Evidence from China's Listed Power Generation Companies. Sustainability 10 (8), 2607. doi:10.3390/su10082607
Zhao H, H., Zhao, H., and Guo, S. (2018). Comprehensive Performance Evaluation of Electricity Grid Corporations Employing a Novel MCDM Model. Sustainability 10 (7), 2130. doi:10.3390/su10072130
Zhao, H., and Li, N. (2015). Evaluating the Performance of Thermal Power Enterprises Using Sustainability Balanced Scorecard, Fuzzy Delphic and Hybrid Multi-Criteria Decision Making Approaches for Sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 108, 569–582. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.07.141
Zhao, H., and Li, N. (2016). Performance Evaluation for Sustainability of Strong Smart Grid by Using Stochastic AHP and Fuzzy TOPSIS Methods. Sustainability 8 (2), 129. doi:10.3390/su8020129
Keywords: sustainability, performance evaluation, power system, systematic review, evaluation framework, evaluation indicators, evaluation methods
Citation: Deng D, Li C, Zu Y, Liu LYJ, Zhang J and Wen S (2022) A Systematic Literature Review on Performance Evaluation of Power System From the Perspective of Sustainability. Front. Environ. Sci. 10:925332. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.925332
Received: 21 April 2022; Accepted: 03 June 2022; Published: 18 July 2022.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2022 Deng, Li, Zu, Liu, Zhang and Wen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Deqiang Deng, [email protected] , [email protected]
Performance and application of the total-body PET/CT scanner: a literature review
Affiliations.
- 1 Department of Radiology, Shandong First Medical University & Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences, Taian, 271016, China.
- 2 Department of PET-CT, The First Affiliated Hospital of Shandong First Medical University, Shandong Provincial Qianfoshan Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University, Jinan, 250014, China.
- 3 Department of Radiology, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Shandong First Medical University, No. 366 Taishan Street, Taian, 271000, China. [email protected].
- PMID: 38607510
- PMCID: PMC11014840
- DOI: 10.1186/s13550-023-01059-1
Background: The total-body positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) system, with a long axial field of view, represents the state-of-the-art PET imaging technique. Recently, the total-body PET/CT system has been commercially available. The total-body PET/CT system enables high-resolution whole-body imaging, even under extreme conditions such as ultra-low dose, extremely fast imaging speed, delayed imaging more than 10 h after tracer injection, and total-body dynamic scan. The total-body PET/CT system provides a real-time picture of the tracers of all organs across the body, which not only helps to explain normal human physiological process, but also facilitates the comprehensive assessment of systemic diseases. In addition, the total-body PET/CT system may play critical roles in other medical fields, including cancer imaging, drug development and immunology.
Main body: Therefore, it is of significance to summarize the existing studies of the total-body PET/CT systems and point out its future direction. This review collected research literatures from the PubMed database since the advent of commercially available total-body PET/CT systems to the present, and was divided into the following sections: Firstly, a brief introduction to the total-body PET/CT system was presented, followed by a summary of the literature on the performance evaluation of the total-body PET/CT. Then, the research and clinical applications of the total-body PET/CT were discussed. Fourthly, deep learning studies based on total-body PET imaging was reviewed. At last, the shortcomings of existing research and future directions for the total-body PET/CT were discussed.
Conclusion: Due to its technical advantages, the total-body PET/CT system is bound to play a greater role in clinical practice in the future.
Keywords: Clinical application; Deep learning; Performance evaluation; Total-body PET/CT; uEXPLORER.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Publication types
Grants and funding.
- 2020GXRC018/Science and Technology Funding from Jinan
- 2019QL009/Academic Promotion Program of Shandong First Medical University
- TS201712065/Taishan Scholars Program of Shandong Province

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Abstract: The amount of research regarding t he topic "Performance Appraisal" is so vast. The paper which is based o n. an observational study of the r esearchers' daily work experiences a ...
The results show that the framework accurately represents the variation of the design of performance appraisal systems in the Italian context, highlighting the central role played by multi-source feedback and face-to-face rater-ratee interactions in promoting rating discriminability. ... The social context of performance appraisal: A review and ...
Models of PM effectiveness discuss the outcomes, or consequences, that flow from the evaluation of performance. In our review of the literature, a large number of articles (156 or 67.83%) examined this topic, with themes relating to linkage to other HRM systems and employee reaction being particularly prevalent.
The system of performance appraisal has manifested to be among the famous paradoxes in the effectiveness of human resource management in any of the world's organizations [1, 2]. ... The existing systematic literature review illustrates the importance of the performance appraisal fairness on employee's motivation, which is affected by other ...
The existing systematic literature review illustrates the importance of the performance appraisal fairness on employee's motivation, which is affected by other important ... In many organizations, one of the intrigues of management is the Performance Appraisal System, which aims at enhancing fairness, effectiveness as well as boost job
Chapter 2: 2.0 Literature Review Performance Appraisal is increasingly considered one of the most important human resource practices (Boswell and Boudreau 2002). The following section will show how appraisal, although only one part of the wider system described above, is central to the effectiveness of Performance Management (Piggot-Irvine 2003 ...
This section presents a review of literature to highlight : (i) the role of performance appraisal, (ii) what a good performance appraisal system should aim at, (iii) what are the major problems which make the present appraisal systems ineffective, and (iv) what strategies can be evolved to make performance appraisal more meaningful and productive.
There is no work which reflects current trend on the understanding of the performance appraisal in the literature and some of these works make literature review on performance management and performance measurement. In recent years, a number of works have been published on different aspects of performance appraisal. Some of these works make literature review on performance management and ...
A REVIEW OF LITERATURE ON THE PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL OF THE EMPLOYEES Balla Usha Sri*1 *1Research Scholar, Sanskriti University, Mathura, Uttar Pradesh, India. ... The study suggested for a comprehensive performance appraisal system which could include the developmental plans for the employees. (A.Bhurtel&EK.Adhikari, 2016) ...
The amount of research regarding the topic "Performance Appraisal" is so vast.The paper which is based on an observational study of the researchers' daily work experiences and review of literature identified constraints to performance appraisal in employees in the institutions, which includes the current knowledge in Performance Appraisal findings, as well as theoretical and ...
Performance Appraisal system began as simple methods of income justification. That is, Appraisal was used to decide whether or not the salary or wage of an individual employee was justified. The process was firmly linked to material outcomes. ... A REVIEW OF PERFORMANCE APPRAISAL LITERATURE BETWEEN 2000 AND 2012 During the last 30 years ...
During a "Performance Appraisal Week," instructors conduct individual performance reviews designed to discuss individual students' class performance and elicit student-teacher feedback. Students experience the emotions of a professional face-to-face review, practice multiple-source and multiple-measure feedback interpretation, engage in ...
ABSTRACT. Performance appraisal is one of the most important aspects of human resource management (HRM). Regardless of the technical soundness of the performance appraisal system, employees' reaction to the performance appraisal itself needs to be a concern. Employee satisfaction with performance appraisal plays a pivotal role in the long ...
impact of performance appraisal system and the competency management framework on the work performance of the employees in the telecom sector. 2. Literature review a) Importance and significance of performance appraisal systems In an organizational context employee motivation has great significance due to its ability to manage
that effective performance appraisal system is the sign of integral component of effectiveness of human resource management of an organization (Zapata-Phelan et al., 2009). Performance appraisal has been studied widely in ... Literature Review Employee performance appraisal is an effective tool or vehicle for assessment of employee ...
employee performance. From the review of literature carried out, it was discovered that gaps existed in literature regarding the ... measure employee and organizational performance. That notwithstanding, performance appraisal system is considered efficient enough and seem to be achieving good results for organizations. (Dauda & Luki, 2021)
2.1 Planning. The first stage of a systematic literature review is to plan. According to the study by Tranfield et al. (2003) and Zhang et al. (2019), we form a review team consisting of three scholars on power system's performance evaluation research and three senior practitioners on power system's performance evaluation and management.The review team define the research questions and ...
A performance appraisal is a regular review of a worker's job performance and overall contribution to ... An attempt was also made to identify the gaps in the literature. Muhammad Shaukat Malik et al. ... Dr. Prachi Singh et al. (2013) claimed that an appraisal system's primary goal should be to improve employee and organizational ...
2. Discussed and agreed individual performance targets that are aligned to the organisational goals and objectives. 3. S.M.A.R.T. Performance targets - specific, measurable, achievable, resourced and time-bound 4. Performance measures designed to track achievement of targets 5. Regular reviews, feedback on performance and adjustments where ...
This review collected research literatures from the PubMed database since the advent of commercially available total-body PET/CT systems to the present, and was divided into the following sections: Firstly, a brief introduction to the total-body PET/CT system was presented, followed by a summary of the literature on the performance evaluation ...