- Games, topic printables & more
- The 4 main speech types
- Example speeches
- Commemorative
- Declamation
- Demonstration
- Informative
- Introduction
- Student Council
- Speech topics
- Poems to read aloud
- How to write a speech
- Using props/visual aids
- Acute anxiety help
- Breathing exercises
- Letting go - free e-course
- Using self-hypnosis
- Delivery overview
- 4 modes of delivery
- How to make cue cards
- How to read a speech
- 9 vocal aspects
- Vocal variety
- Diction/articulation
- Pronunciation
- Speaking rate
- How to use pauses
- Eye contact
- Body language
- Voice image
- Voice health
- Public speaking activities and games
- About me/contact

How to write a good speech in 7 steps
By: Susan Dugdale
- an easily followed format for writing a great speech
Did you know writing a speech doesn't have be an anxious, nail biting experience?
Unsure? Don't be.
You may have lived with the idea you were never good with words for a long time. Or perhaps giving speeches at school brought you out in cold sweats.
However learning how to write a speech is relatively straight forward when you learn to write out loud.
And that's the journey I am offering to take you on: step by step.
To learn quickly, go slow
Take all the time you need. This speech format has 7 steps, each building on the next.
Walk, rather than run, your way through all of them. Don't be tempted to rush. Familiarize yourself with the ideas. Try them out.
I know there are well-advertised short cuts and promises of 'write a speech in 5 minutes'. However in reality they only truly work for somebody who already has the basic foundations of speech writing in place.
The foundation of good speech writing
These steps are the backbone of sound speech preparation. Learn and follow them well at the outset and yes, given more experience and practice you could probably flick something together quickly. Like any skill, the more it's used, the easier it gets.
In the meantime...
Step 1: Begin with a speech overview or outline
Are you in a hurry? Without time to read a whole page? Grab ... The Quick How to Write a Speech Checklist And come back to get the details later.
- WHO you are writing your speech for (your target audience)
- WHY you are preparing this speech. What's the main purpose of your speech? Is it to inform or tell your audience about something? To teach them a new skill or demonstrate something? To persuade or to entertain? (See 4 types of speeches: informative, demonstrative, persuasive and special occasion or entertaining for more.) What do you want them to think, feel or do as a result of listening the speech?
- WHAT your speech is going to be about (its topic) - You'll want to have thought through your main points and have ranked them in order of importance. And have sorted the supporting research you need to make those points effectively.
- HOW much time you have for your speech eg. 3 minutes, 5 minutes... The amount of time you've been allocated dictates how much content you need. If you're unsure check this page: how many words per minute in a speech: a quick reference guide . You'll find estimates of the number of words required for 1 - 10 minute speeches by slow, medium and fast talkers.
Use an outline
The best way to make sure you deliver a perfect speech is to start by carefully completing a speech outline covering the essentials: WHO, WHY, WHAT and HOW.
Beginning to write without thinking your speech through is a bit like heading off on a journey not knowing why you're traveling or where you're going to end up. You can find yourself lost in a deep, dark, murky muddle of ideas very quickly!
Pulling together a speech overview or outline is a much safer option. It's the map you'll follow to get where you want to go.
Get a blank speech outline template to complete
Click the link to find out a whole lot more about preparing a speech outline . ☺ You'll also find a free printable blank speech outline template. I recommend using it!
Understanding speech construction
Before you begin to write, using your completed outline as a guide, let's briefly look at what you're aiming to prepare.
- an opening or introduction
- the body where the bulk of the information is given
- and an ending (or summary).
Imagine your speech as a sandwich

If you think of a speech as a sandwich you'll get the idea.
The opening and ending are the slices of bread holding the filling (the major points or the body of your speech) together.
You can build yourself a simple sandwich with one filling (one big idea) or you could go gourmet and add up to three or, even five. The choice is yours.
But whatever you choose to serve, as a good cook, you need to consider who is going to eat it! And that's your audience.
So let's find out who they are before we do anything else.
Step 2: Know who you are talking to
Understanding your audience.
Did you know a good speech is never written from the speaker's point of view? ( If you need to know more about why check out this page on building rapport .)
Begin with the most important idea/point on your outline.
Consider HOW you can explain (show, tell) that to your audience in the most effective way for them to easily understand it.
Writing from the audience's point of view

To help you write from an audience point of view, it's a good idea to identify either a real person or the type of person who is most likely to be listening to you.
Make sure you select someone who represents the "majority" of the people who will be in your audience. That is they are neither struggling to comprehend you at the bottom of your scale or light-years ahead at the top.
Now imagine they are sitting next to you eagerly waiting to hear what you're going to say. Give them a name, for example, Joe, to help make them real.
Ask yourself
- How do I need to tailor my information to meet Joe's needs? For example, do you tell personal stories to illustrate your main points? Absolutely! Yes. This is a very powerful technique. (Click storytelling in speeches to find out more.)
- What type or level of language is right for Joe as well as my topic? For example if I use jargon (activity, industry or profession specific vocabulary) will it be understood?
Step 3: Writing as you speak
Writing oral language.
Write down what you want to say about your first main point as if you were talking directly to Joe.
If it helps, say it all out loud before you write it down and/or record it.
Use the information below as a guide

(Click to download The Characteristics of Spoken Language as a pdf.)
You do not have to write absolutely everything you're going to say down * but you do need to write down, or outline, the sequence of ideas to ensure they are logical and easily followed.
Remember too, to explain or illustrate your point with examples from your research.
( * Tip: If this is your first speech the safety net of having everything written down could be just what you need. It's easier to recover from a patch of jitters when you have a word by word manuscript than if you have either none, or a bare outline. Your call!)
Step 4: Checking tone and language
The focus of this step is re-working what you've done in Step 2 and 3.
You identified who you were talking to (Step 2) and in Step 3, wrote up your first main point. Is it right? Have you made yourself clear? Check it.

How well you complete this step depends on how well you understand the needs of the people who are going to listen to your speech.
Please do not assume because you know what you're talking about the person (Joe) you've chosen to represent your audience will too. Joe is not a mind-reader!
How to check what you've prepared
- Check the "tone" of your language . Is it right for the occasion, subject matter and your audience?
- Check the length of your sentences. You need short sentences. If they're too long or complicated you risk losing your listeners.
Check for jargon too. These are industry, activity or group exclusive words.
For instance take the phrase: authentic learning . This comes from teaching and refers to connecting lessons to the daily life of students. Authentic learning is learning that is relevant and meaningful for students. If you're not a teacher you may not understand the phrase.
The use of any vocabulary requiring insider knowledge needs to be thought through from the audience perspective. Jargon can close people out.
- Read what you've written out loud. If it flows naturally, in a logical manner, continue the process with your next main idea. If it doesn't, rework.
We use whole sentences and part ones, and we mix them up with asides or appeals e.g. "Did you get that? Of course you did. Right...Let's move it along. I was saying ..."
Click for more about the differences between spoken and written language .
And now repeat the process
Repeat this process for the remainder of your main ideas.
Because you've done the first one carefully, the rest should follow fairly easily.
Step 5: Use transitions
Providing links or transitions between main ideas.
Between each of your main ideas you need to provide a bridge or pathway for your audience. The clearer the pathway or bridge, the easier it is for them to make the transition from one idea to the next.

If your speech contains more than three main ideas and each is building on the last, then consider using a "catch-up" or summary as part of your transitions.
Is your speech being evaluated? Find out exactly what aspects you're being assessed on using this standard speech evaluation form
Link/transition examples
A link can be as simple as:
"We've explored one scenario for the ending of Block Buster 111, but let's consider another. This time..."
What follows this transition is the introduction of Main Idea Two.
Here's a summarizing link/transition example:
"We've ended Blockbuster 111 four ways so far. In the first, everybody died. In the second, everybody died BUT their ghosts remained to haunt the area. In the third, one villain died. His partner reformed and after a fight-out with the hero, they both strode off into the sunset, friends forever. In the fourth, the hero dies in a major battle but is reborn sometime in the future.
And now what about one more? What if nobody died? The fifth possibility..."
Go back through your main ideas checking the links. Remember Joe as you go. Try each transition or link out loud and really listen to yourself. Is it obvious? Easily followed?
Keep them if they are clear and concise.
For more about transitions (with examples) see Andrew Dlugan's excellent article, Speech Transitions: Magical words and Phrases .
Step 6: The end of your speech
The ideal ending is highly memorable . You want it to live on in the minds of your listeners long after your speech is finished. Often it combines a call to action with a summary of major points.

Example speech endings
Example 1: The desired outcome of a speech persuading people to vote for you in an upcoming election is that they get out there on voting day and do so. You can help that outcome along by calling them to register their support by signing a prepared pledge statement as they leave.
"We're agreed we want change. You can help us give it to you by signing this pledge statement as you leave. Be part of the change you want to see!
Example 2: The desired outcome is increased sales figures. The call to action is made urgent with the introduction of time specific incentives.
"You have three weeks from the time you leave this hall to make that dream family holiday in New Zealand yours. Can you do it? Will you do it? The kids will love it. Your wife will love it. Do it now!"
How to figure out the right call to action
A clue for working out what the most appropriate call to action might be, is to go back to your original purpose for giving the speech.
- Was it to motivate or inspire?
- Was it to persuade to a particular point of view?
- Was it to share specialist information?
- Was it to celebrate a person, a place, time or event?
Ask yourself what you want people to do as a result of having listened to your speech.
For more about ending speeches
Visit this page for more about how to end a speech effectively . You'll find two additional types of speech endings with examples.
Write and test
Write your ending and test it out loud. Try it out on a friend, or two. Is it good? Does it work?
Step 7: The introduction
Once you've got the filling (main ideas) the linking and the ending in place, it's time to focus on the introduction.
The introduction comes last as it's the most important part of your speech. This is the bit that either has people sitting up alert or slumped and waiting for you to end. It's the tone setter!
What makes a great speech opening?
Ideally you want an opening that makes listening to you the only thing the 'Joes' in the audience want to do.
You want them to forget they're hungry or that their chair is hard or that their bills need paying.
The way to do that is to capture their interest straight away. You do this with a "hook".
Hooks to catch your audience's attention
Hooks come in as many forms as there are speeches and audiences. Your task is work out what specific hook is needed to catch your audience.

Go back to the purpose. Why are you giving this speech?
Once you have your answer, consider your call to action. What do you want the audience to do, and, or take away, as a result of listening to you?
Next think about the imaginary or real person you wrote for when you were focusing on your main ideas.
Choosing the best hook
- Is it humor?
- Would shock tactics work?
- Is it a rhetorical question?
- Is it formality or informality?
- Is it an outline or overview of what you're going to cover, including the call to action?
- Or is it a mix of all these elements?
A hook example
Here's an example from a fictional political speech. The speaker is lobbying for votes. His audience are predominately workers whose future's are not secure.
"How's your imagination this morning? Good? (Pause for response from audience) Great, I'm glad. Because we're going to put it to work starting right now.
I want you to see your future. What does it look like? Are you happy? Is everything as you want it to be? No? Let's change that. We could do it. And we could do it today.
At the end of this speech you're going to be given the opportunity to change your world, for a better one ...
No, I'm not a magician. Or a simpleton with big ideas and precious little commonsense. I'm an ordinary man, just like you. And I have a plan to share!"
And then our speaker is off into his main points supported by examples. The end, which he has already foreshadowed in his opening, is the call to vote for him.
Prepare several hooks
Experiment with several openings until you've found the one that serves your audience, your subject matter and your purpose best.
For many more examples of speech openings go to: how to write a speech introduction . You'll find 12 of the very best ways to start a speech.
That completes the initial seven steps towards writing your speech. If you've followed them all the way through, congratulations, you now have the text of your speech!
Although you might have the words, you're still a couple of steps away from being ready to deliver them. Both of them are essential if you want the very best outcome possible. They are below. Please take them.
Step 8: Checking content and timing
This step pulls everything together.
Check once, check twice, check three times & then once more!
Go through your speech really carefully.
On the first read through check you've got your main points in their correct order with supporting material, plus an effective introduction and ending.
On the second read through check the linking passages or transitions making sure they are clear and easily followed.
On the third reading check your sentence structure, language use and tone.
Double, triple check the timing
Now go though once more.
This time read it aloud slowly and time yourself.
If it's too long for the time allowance you've been given make the necessary cuts.
Start by looking at your examples rather than the main ideas themselves. If you've used several examples to illustrate one principal idea, cut the least important out.
Also look to see if you've repeated yourself unnecessarily or, gone off track. If it's not relevant, cut it.
Repeat the process, condensing until your speech fits the required length, preferably coming in just under your time limit.
You can also find out how approximately long it will take you to say the words you have by using this very handy words to minutes converter . It's an excellent tool, one I frequently use. While it can't give you a precise time, it does provide a reasonable estimate.

Step 9: Rehearsing your speech
And NOW you are finished with writing the speech, and are ready for REHEARSAL .

Please don't be tempted to skip this step. It is not an extra thrown in for good measure. It's essential.
The "not-so-secret" secret of successful speeches combines good writing with practice, practice and then, practicing some more.
Go to how to practice public speaking and you'll find rehearsal techniques and suggestions to boost your speech delivery from ordinary to extraordinary.
The Quick How to Write a Speech Checklist
Before you begin writing you need:.
- Your speech OUTLINE with your main ideas ranked in the order you're going to present them. (If you haven't done one complete this 4 step sample speech outline . It will make the writing process much easier.)
- Your RESEARCH
- You also need to know WHO you're speaking to, the PURPOSE of the speech and HOW long you're speaking for
The basic format
- the body where you present your main ideas
Split your time allowance so that you spend approximately 70% on the body and 15% each on the introduction and ending.
How to write the speech
- Write your main ideas out incorporating your examples and research
- Link them together making sure each flows in a smooth, logical progression
- Write your ending, summarizing your main ideas briefly and end with a call for action
- Write your introduction considering the 'hook' you're going to use to get your audience listening
- An often quoted saying to explain the process is: Tell them what you're going to tell them (Introduction) Tell them (Body of your speech - the main ideas plus examples) Tell them what you told them (The ending)
TEST before presenting. Read aloud several times to check the flow of material, the suitability of language and the timing.

- Return to top
speaking out loud
Subscribe for FREE weekly alerts about what's new For more see speaking out loud

Top 10 popular pages
- Welcome speech
- Demonstration speech topics
- Impromptu speech topic cards
- Thank you quotes
- Impromptu public speaking topics
- Farewell speeches
- Phrases for welcome speeches
- Student council speeches
- Free sample eulogies
From fear to fun in 28 ways
A complete one stop resource to scuttle fear in the best of all possible ways - with laughter.

Useful pages
- Search this site
- About me & Contact
- Blogging Aloud
- Free e-course
- Privacy policy
©Copyright 2006-24 www.write-out-loud.com
Designed and built by Clickstream Designs

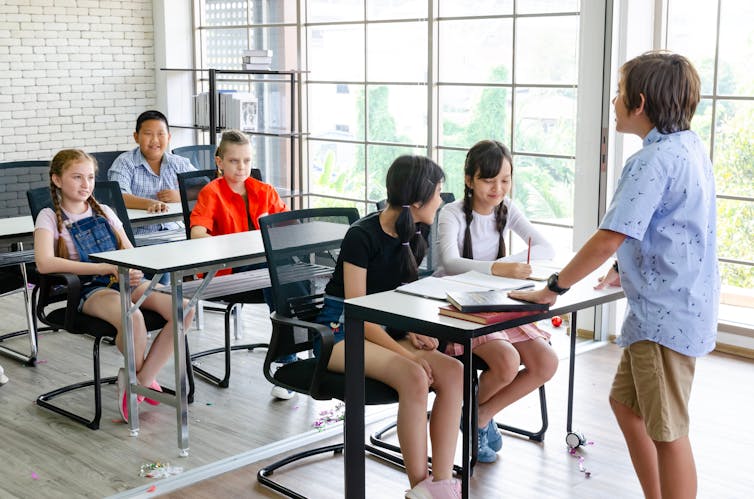
Speech for Elementary Students

Speech writing and delivery can be a daunting task for many students. Not only should you pick a good topic for listeners to relate to, but you must also create an interesting and well-structured content for the speech to make sense.
- Speech Templates and Examples
- Welcome Speech Examples & Samples
It is an imaginative art form that allows a speaker to be creative with their words and the manner in which they present their pieces. For this reason, knowing the proper way to compose and deliver a speech is essential in the craft.

How to Choose the Perfect Topic
Choosing a topic that appeals to you is a significant ingredient for effective speech writing. You need to choose a topic that you’re comfortable with and possess certain knowledge about. This will serve as a foundation for your formal speech in order to attain a quick and easy writing process.
When choosing a suitable topic for your speech, consider the following tips:
1. Consider different options.
It’s always good to focus on subjects that you’re most passionate about. This includes hobbies, interests, and personal favorites that might be compelling enough to talk about in front of a crowd. If the assignment does not require a specific topic to tackle, then you are free to choose something out of your own interest. You may also see how to start a speech .
You can start by creating a list of these potential topics, and then researching about any relevant information that may be shared. Make sure you gather enough details that could form major points for your speech.
2. Avoid overused topics.
You may want to steer clear from subject matters that have been presented for over a thousand times. Chances are, your audience may know more about the topic than you do, or perhaps they already possess a clear idea of where your speech is headed. But since it’s nearly impossible to find an original topic these days, it would be best to choose something more specific instead. You can narrow down these options to something fresh and interesting to spark curiosity among listeners. You may also like tribute speech examples & samples .
3. Do your research.
Once the topic has been finalized, you can then move on to one of the important steps of planning process: the research procedure.
This step involves a lot — and we mean A WHOLE LOT — of reading to complete. A visit to your local library will make it easier to collect information from a variety of sources. Here, you can gain in-depth knowledge on a particular topic, as well as a few theories and concepts provided by some authors. The internet also has its own reading materials to offer in case a trip to the library isn’t possible. You may also check out appreciation speech examples & samples .
4. Deliver well.
Body language says a lot about what goes on inside your head. Your nerves and emotions can sometimes radiate in the room if you fail to compose yourself properly. Proper posture and appearance are just a some factors that can affect your delivery. In most cases, a speech must be kept short and to-the-point as well, especially when time is a major issue. With this in mind, consider timing your delivery during practice and adjusting it accordingly to the time limit given. You might be interested in dedication speech examples .
High School President Speech Example

Size: 161 KB
Short Application Essay for Students Example

Size: 243 KB
Informative Speech for Students Example

Size: 53 KB
Speech Contest for Elementary School Students

Size: 132 KB
Popular Speech Topics for Elementary Students
Speech topics can vary from simple to complex themes that include social problems or political issues in today’s society. These may either form a persuasive speech or an informative speech, or possibly a combination of both types.
But when it comes to speech topics for grade school or elementary students, choosing a topic that is simple yet relatable is extremely important. Given the age bracket of this particular group, the topic chosen or provided by the teacher must cover familiar grounds. These topics are often more subjective in nature, wherein an extensive research process isn’t necessary. You may also see presentation speech examples & samples .
The subject of family is probably the most popular speech topic there is. Since it’s about something you’re completely accustomed to, it wouldn’t be hard to find the right words to complete your speech.
Say for example, you could make a speech about an unforgettable memory with your family. This could be about a vacation out of town, a fun get-together over the holidays, or maybe a significant event in your life that your family was a huge part of. Anything you wish to share about your family, as long as it conveys a moral value, would be a good option for your speech topic. You may also like how do you write a speech?
2. Dreams & Ambitions
What do you want to be when you grow older? What are your dreams and aspirations? Where do you see yourself twenty years from now?
The answer to these questions can help you construct a strong topic for your speech. This could be about the things you’ve imagined yourself doing in the near future or the direction you wish to take. To fill the rest of your speech, you can also add a little backstory as to why this has become one of your goals, as well as your means of reaching these ambitions. Including other major points that are closely related to the topic is also advised. You may also check out thank-you speech examples & samples .
3. Hobbies & Interests
If you’re into sports and other recreational activities that go beyond the academic circle, then consider this as an opportunity for you to draw attention towards the things you deeply love and enjoy doing. Talk about your strengths in the said field, and the limitations you wish to improve on. Turn this into a learning experience by sharing to the group how it has shaped you into a becoming the person you are today. You may even connect this to the dreams you wish to achieve one day. You might be interested in speech examples for students .
For example, making a speech about basketball and its principles apart from being a regular pastime is a great way to let listeners view the subject matter from a different perspective. Composing a speech about something that means a lot to you can be less intimidating in most instances.
4. About Yourself
Although not everyone would be too keen about putting themselves in the center of a speech, it’s still a recommendable topic to consider.
The great thing about topics that focus on your personal life is that they can be very broad. So instead of making a speech about your likes and dislikes, you can go deeper with some intriguing thoughts that fill your mind. You can talk about your fears, along with the things you wish to change in the world. This is a great way to go out of the norm and take on speech topics that some people may consider as taboo. You may also see launch speech examples .
Opening Speech for Students Example

Size: 96 KB
Elevator Speech for Students Example

Size: 111 KB
Student Graduation Speech

Size: 75 KB
Useful Speech Planning & Delivery Tips for Students
There are two things that matter most in speech planning and delivery: the content of your speech and your ability to broadcast it to a group of individuals. But to ensure that your message reaches its audience, you must tailor your speech accordingly with the help of the following tactics:
1. Planning the Content
- Define your goals. What is the purpose of your speech? Apart from it being a requirement in class, you must identify what your end goal actually is. Will it educate listeners? Or create awareness regarding a specific topic? This would also depend on who your listeners are. Keep in mind that the content of your speech should convey a message that listeners can grasp and learn from. You may also see youth speech examples .
- Prepare your material. Never settle for an impromptu speech, or you may end up regretting it when you’re standing in front of an audience with dead air filling the atmosphere. It’s always important to create a speech outline to organize thoughts and ideas accordingly. This way, you can easily point out grammar mistakes or statements that don’t make proper sense when read aloud.
- Observe others. If you’re struggling with your speech presentation , try watching a few videos online and observe how these speakers deliver their piece. Take note of their body language as well as how they utter each word.
- Follow a logical flow of ideas. Don’t make it hard for listeners to understand the main point of your speech. Ensure that your speech consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. Kick off with your strongest arguments followed by the subpoints that support the main thought.
- Practice. Stand in front of a mirror and begin delivering your speech. You need to practice how you could transmit information from your speech to the minds of your listeners. This will also help you specify any qualities about your delivery that must be enhanced. You may also like leadership speech examples & samples .
2. Delivering the Content
- Maintain eye contact with your audience. Building a connection with every member of your audience can be achieved through proper eye contact. This will you capture the attention of each individual in order to encourage them to listen attentively to what you have to say.
- Engage actively with listeners. Another reason why preparing your material beforehand is a must, is for you to actively engage with members of the audience. If you pay attention to what people are doing, then they’re bound to pay attention to you as well. Along with your speech, you can also conduct interactive activities or use visual materials to engross listeners. You may also see wedding speech examples & samples .
- Be time-conscious. Watch the time. Given the short attention span of the average person, you must keep your speech short and direct to the point. Refrain from exceeding the allotted time given, or you may end up damaging the whole presentation.
- Don’t read. There’s nothing wrong with bringing a copy of the speech for you to refer to, until it turns into a distraction instead of a useful tool. Rather, you can take a few glances every now and then to see where you are in your speech, and what point to emphasize next. You may also like campaign speech examples .
- Entertain questions. Take the time to address questions and concerns that audience members may have. But instead of holding a Q&A session by the very end of your speech, you can invite people to ask questions during certain parts of your presentation. This will serve as a breather to allow interaction between the speaker and the listeners.
Essay Speech for Students Example

Size: 643 KB
Demonstration Speech for Students Example

Size: 99 KB
Valedictory Speech for Students Example

Student Speech at Elementary School

And there you have it! With the help of these tips and techniques, you can prepare and deliver the best speech possible to leave a lasting impact with your audience.
Speech Generator for Elementary Students
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a speech for elementary students on the importance of reading
Help me write a speech for elementary students on staying active

Public Speaking Tips For Kids
The speeches are written and practiced at home. This year I created a template for the kids to help make a start on their speech. The template not only helps them plan out the content for their speech, but gives them tips on how to define the purpose, research and practise their speech.
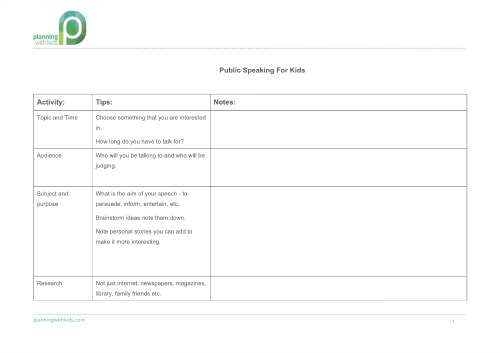
I used this template with all three kids – prep, year three and year five. The level of guidance needed by each child varied and I naturally I spent the most time with the six year old as this is the first time he has had to write and present a speech.
Not every element of the template will necessarily need to be completed and depends on the topic. For example the prep child chose “Kids have fun when….” from the list of topics for his class. This topic requires no research to be done as he is an expert in knowing how kids have fun!
The kids may also need more room than for the “middle” section, depending on how long their speech is to be. We simply turned over the page and wrote on the back.
Public Speaking Tips For Kids – A Checklist
I have listed below the elements the template covers:
- Topic and Time: Choose something that you are interested in.
- How long do you have to talk for?
- Audience: Who will you be talking to and who will be judging.
- Subject and purpose: What is the aim of your speech – to persuade, inform, entertain, etc. Brainstorm ideas note them down. Note personal stories you can add to make it more interesting.
- Research: Not just internet, newspapers, magazines, library, family friends etc.
- Structure: Ask yourself the question – ‘At the end of the speech I would like my audience to…….
- Beginning: Brief, capture the attention of the audience and establish the subject and purpose of the speech. Don’t just restate the topic. Add your personality and make it unique, many others may be talking on the same topic.
- Middle: Sets out your ideas, shares your research, includes examples to support your topic. For your time limit work out how many points / paragraphs you can include. Work on having a powerful statement to lead into each new point / paragraph.
- End: Short statement relating back to the topic and sums up the subject and purpose of the speech. Make it brief, but memorable. Try including a memorable line that the audience can take away with them. Memorise your conclusion, so your last couple of sentences can be delivered with confidence and with full eye contact with the audience.
- Practice: By yourself first. Time it and edit your content so it first with the time restraints.
- Palm Cards: Then make palm cards for key points only. Keep cards to a minimum and number them.
- Dress rehearsal: Practice using palm cards, first by yourself, then either in front of family or even video your self.
Are school mornings stressful for you?

Are any of these scenarios familiar to you:
- Are your school mornings currently a harder version of Groundhog Day?
- Do you sleep a bit longer than planned in the mornings then rush to get you and the kids ready?
- Do you wake up to a house that is already in a state of mild chaos?
- Do the kids end up buying their lunches more than you planned because you ran out of time or food?
- Do you drop the kids off at school with you feeling frazzled and the kids grumpy?
Then my super simple system will help revolutionise your school mornings! Sign up to my E-news and receive my guide here .

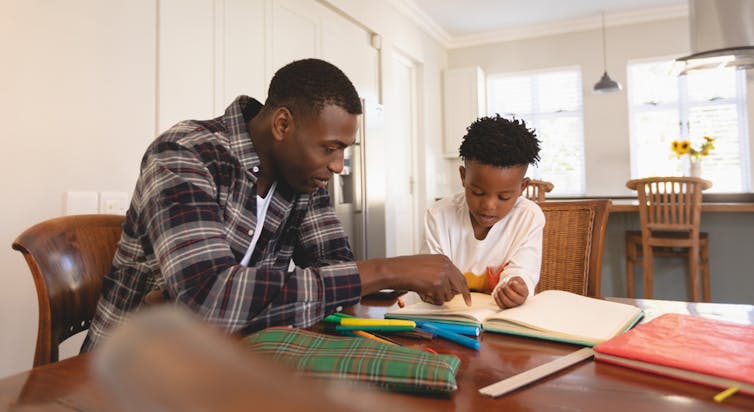
How to help your child write a speech (without doing it for them)
Associate Professor in Education, Deakin University
Disclosure statement
Joanne O'Mara receives funding from The Australian Research Council and the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada.
Deakin University provides funding as a member of The Conversation AU.
View all partners
It’s hard for parents to help kids with homework without doing it for them . It can be especially difficult to work out where to start when your child is preparing a speech for school.
You might find your child is procrastinating more about getting started with a speech than about other homework. This could be because they are anxious about it.
Having something that they want to say to their class can help to increase your child’s confidence and motivation when they deliver the speech. A positive speechmaking experience can increase confidence for next time, which is why some schools teach public speaking in a systematic way.
It’s important to keep in mind that public speaking has two parts to it: writing the speech, and delivering it.
Here are some tips for how to help your kid with both aspects of preparation.

Read more: What's the point of homework?
Writing the speech
First, help your child find something they want to say to their audience.
When a child is delivering a speech to the class, they are being listened to, observed, and watched by their peers. Most other classwork is only read by the teacher. In a speech, they are sharing their ideas with the whole class.
That’s why it is really important they own what they are saying, and say it in their own words.
It’s key they own the topic (if it is a free choice of topic) or that they own the stance they are taking (if the topic is set by the teacher).
As a parent, it’s tricky to support your child to find their own words to say – but it’s very important you don’t write the speech for them.
Help them to think about what they care about and what they think is important to share with their class.
Apart from the fact the teacher will spot a parent-written speech a mile away, if your child has no ownership of their speech, they will not care about communicating the ideas to the class.
Next, help your child to think about organising their ideas.
It’s good to have a hook or a catchy introduction into the main idea of the speech. That could be a rhetorical question, an anecdote or an amazing fact. They can then think of around three main points about the topic.
Ask your child questions that help them to think about some examples or evidence that support their ideas.
Finally, help them to finish their speech. Often, the ending might return to the beginning to round off the point being made – a kind of “I told you so”!

Delivering the speech – 4 tips for parents
1. Encourage your child to focus on communicating their idea to their audience.
If they focus on sharing their ideas, rather than worrying about themselves, everything will come together. Encourage them to think about looking at the audience and making sure everyone can hear them.
2. Practise the speed of delivery and time their speech.
One of the easiest things to practise that makes a big difference to the delivery of the speech is the pacing.
The big tip is to slow down. When speakers feel nervous they tend to speed up, sometimes just a little — but often students will deliver their speeches at breakneck speed, racing to just get it done so they can go and sit down.
I’ve listened to thousands of student speeches and have never heard one delivered too slowly. But I have heard many that sound like a horse-race call.
3. Be an affirmative audience to their speech.
Listen to your child practise when they feel ready to share with you, but don’t push them if they are resistant.
Focus on building their confidence by talking to them about the moments you felt they were connecting with you as an audience member. Be appreciative of their jokes or show you share their feelings about ideas they care about.
Your children seek your approval – don’t be stingy with it.
4. If they are feeling confident, suggest they work on nuancing their delivery.
Once they are feeling confident about delivering the speech, the child can add variety and texture.
For instance, they might slow down for emphasis on certain words, add a pause after asking a question, or think about some moments where they might speak more softly or loudly.
Variation will add interest to the delivery of the speech and help to grab and keep the audience’s attention. It also helps further convey your child’s ideas.

Good support takes time
It’s hard to get the balance right when supporting your child to prepare their speech. The trick is to understand that it will take more than one sitting.
So, plan for a few chunks of time, and work on building their ideas and enthusiasm.
Read more: Should parents help their kids with homework?
- Primary school
- Speech writing
- Primary schooling
- Children's literacy

Assistant Editor - 1 year cadetship

Program Development Officer - Business Processes

Executive Dean, Faculty of Health

Lecturer/Senior Lecturer, Earth System Science (School of Science)

Sydney Horizon Educators (Identified)
- Speech Topics For Kids
- How To Write A Speech
How to Write a Speech: A Guide to Enhance Your Writing Skills
Speech is a medium to convey a message to the world. It is a way of expressing your views on a topic or a way to showcase your strong opposition to a particular idea. To deliver an effective speech, you need a strong and commanding voice, but more important than that is what you say. Spending time in preparing a speech is as vital as presenting it well to your audience.
Read the article to learn what all you need to include in a speech and how to structure it.
Table of Contents
- Self-Introduction
The Opening Statement
Structuring the speech, choice of words, authenticity, writing in 1st person, tips to write a speech, frequently asked questions on speech, how to write a speech.
Writing a speech on any particular topic requires a lot of research. It also has to be structured well in order to properly get the message across to the target audience. If you have ever listened to famous orators, you would have noticed the kind of details they include when speaking about a particular topic, how they present it and how their speeches motivate and instill courage in people to work towards an individual or shared goal. Learning how to write such effective speeches can be done with a little guidance. So, here are a few points you can keep in mind when writing a speech on your own. Go through each of them carefully and follow them meticulously.
Self Introduction
When you are writing or delivering a speech, the very first thing you need to do is introduce yourself. When you are delivering a speech for a particular occasion, there might be a master of ceremony who might introduce you and invite you to share your thoughts. Whatever be the case, always remember to say one or two sentences about who you are and what you intend to do.
Introductions can change according to the nature of your target audience. It can be either formal or informal based on the audience you are addressing. Here are a few examples.
Addressing Friends/Classmates/Peers
- Hello everyone! I am ________. I am here to share my views on _________.
- Good morning friends. I, _________, am here to talk to you about _________.
Addressing Teachers/Higher Authorities
- Good morning/afternoon/evening. Before I start, I would like to thank _______ for giving me an opportunity to share my thoughts about ________ here today.
- A good day to all. I, __________, on behalf of _________, am standing here today to voice out my thoughts on _________.
It is said that the first seven seconds is all that a human brain requires to decide whether or not to focus on something. So, it is evident that a catchy opening statement is the factor that will impact your audience. Writing a speech does require a lot of research, and structuring it in an interesting, informative and coherent manner is something that should be done with utmost care.
When given a topic to speak on, the first thing you can do is brainstorm ideas and pen down all that comes to your mind. This will help you understand what aspect of the topic you want to focus on. With that in mind, you can start drafting your speech.
An opening statement can be anything that is relevant to the topic. Use words smartly to create an impression and grab the attention of your audience. A few ideas on framing opening statements are given below. Take a look.
- Asking an Engaging Question
Starting your speech by asking the audience a question can get their attention. It creates an interest and curiosity in the audience and makes them think about the question. This way, you would have already got their minds ready to listen and think.
- Fact or a Surprising Statement
Surprising the audience with an interesting fact or a statement can draw the attention of the audience. It can even be a joke; just make sure it is relevant. A good laugh would wake up their minds and they would want to listen to what you are going to say next.
- Adding a Quote
After you have found your topic to work on, look for a quote that best suits your topic. The quote can be one said by some famous personality or even from stories, movies or series. As long as it suits your topic and is appropriate to the target audience, use them confidently. Again, finding a quote that is well-known or has scope for deep thought will be your success factor.
To structure your speech easily, it is advisable to break it into three parts or three sections – an introduction, body and conclusion.
- Introduction: Introduce the topic and your views on the topic briefly.
- Body: Give a detailed explanation of your topic. Your focus should be to inform and educate your audience on the said topic.
- Conclusion: Voice out your thoughts/suggestions. Your intention here should be to make them think/act.
While delivering or writing a speech, it is essential to keep an eye on the language you are using. Choose the right kind of words. The person has the liberty to express their views in support or against the topic; just be sure to provide enough evidence to prove the discussed points. See to it that you use short and precise sentences. Your choice of words and what you emphasise on will decide the effect of the speech on the audience.
When writing a speech, make sure to,
- Avoid long, confusing sentences.
- Check the spelling, sentence structure and grammar.
- Not use contradictory words or statements that might cause any sort of issues.
Anything authentic will appeal to the audience, so including anecdotes, personal experiences and thoughts will help you build a good rapport with your audience. The only thing you need to take care is to not let yourself be carried away in the moment. Speak only what is necessary.
Using the 1st person point of view in a speech is believed to be more effective than a third person point of view. Just be careful not to make it too subjective and sway away from the topic.
- Understand the purpose of your speech: Before writing the speech, you must understand the topic and the purpose behind it. Reason out and evaluate if the speech has to be inspiring, entertaining or purely informative.
- Identify your audience: When writing or delivering a speech, your audience play the major role. Unless you know who your target audience is, you will not be able to draft a good and appropriate speech.
- Decide the length of the speech: Whatever be the topic, make sure you keep it short and to the point. Making a speech longer than it needs to be will only make it monotonous and boring.
- Revising and practicing the speech: After writing, it is essential to revise and recheck as there might be minor errors which you might have missed. Edit and revise until you are sure you have it right. Practise as much as required so you do not stammer in front of your audience.
- Mention your takeaways at the end of the speech: Takeaways are the points which have been majorly emphasised on and can bring a change. Be sure to always have a thought or idea that your audience can reflect upon at the end of your speech.
How to write a speech?
Writing a speech is basically about collecting, summarising and structuring your points on a given topic. Do a proper research, prepare multiple drafts, edit and revise until you are sure of the content.
Why is it important to introduce ourselves?
It is essential to introduce yourself while writing a speech, so that your audience or the readers know who the speaker is and understand where you come from. This will, in turn, help them connect with you and your thoughts.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Personal Development
- School Leadership
How to Write a Student Council Speech
Last Updated: April 24, 2024 Approved
This article was co-authored by Patrick Muñoz . Patrick is an internationally recognized Voice & Speech Coach, focusing on public speaking, vocal power, accent and dialects, accent reduction, voiceover, acting and speech therapy. He has worked with clients such as Penelope Cruz, Eva Longoria, and Roselyn Sanchez. He was voted LA's Favorite Voice and Dialect Coach by BACKSTAGE, is the voice and speech coach for Disney and Turner Classic Movies, and is a member of Voice and Speech Trainers Association. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. This article has 127 testimonials from our readers, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 2,027,018 times.
Being a member of the student council can help you help your school. However, it takes hard work to get into the student council . You need to craft a good speech that gives your classmates incentives to vote for you.
Your Student Council Speech
Use a strong, attention-grabbing opening. Discuss your qualifications briefly, then move on. Focus your speech on your passion and present a blueprint to achieve your goals. Close with a strong summary and call to vote for you.
Sample Speeches

Writing the Introduction

- Do not merely start by saying, "My name is ___ and I'm running for student council." Your classmates will already know as much and this is not really a unique statement. There will be time to state the basic information after you've got the class's attention. [1] X Research source
- You can open with a question. Something like, "If there was one thing you could change about this school, what would it be?" Or a question that adds some humor , like, "I know what you're thinking. Why should I listen to this person?" and then proceed to lay out your credentials. Quotes on leadership, power, and guidance would also make good openings. However, make sure to double-check your sources and especially if you're finding quotes online. Many online quote databases, like Quote Garden or Brainy Quote, sometimes attribute quotes to the wrong sources. [2] X Research source
- If you're stuck, look up and read famous speeches. You can find many speeches from presidents, world leaders, civil rights activists, and others online. Pay attention to how they opened their speeches and ask yourself, "Was this interesting? Do I want to keep reading/listening? Why?" [3] X Research source

- State your name and grade in school. This may feel somewhat unnecessary if you go to a small school, but it's considered a formality. If you're missing this part of the speech, you may end up looking sloppy in comparison to other students. [5] X Research source
- State what you want. That is, what you're running for. Do you want to be the president , vice president , treasurer, secretary? Even if you think most students are aware of what position you're running for, make sure you state it here to remind them. [6] X Research source
- Try to keep this section brief as it's not as important as your qualifications and plans to improve the school . Even one sentence would suffice. For example, "My name is Ramona Hart, I'm in the 11th grade, and I'm running for treasurer of the student council."

- Any accomplishments relevant to the position warrant mentioning here. If you're running for secretary, for example, talk about your summer job filing papers in your uncle's law firm. If you're running for student council president, talk about your leadership experience being captain of the swim team. [7] X Research source
- While this section is important, try to keep it minimal. A couple of sentences laying out your qualifications is enough as the body of your speech is where you should spend the most time. For example, let's go back to the above example. From there, we could say, "I am currently enrolled in advanced placement algebra and I have been an honor roll student for three years. This knowledge of numbers and diligence qualifies me to have responsibility for finances for our student council." [8] X Research source
Writing the Body of the Speech

- You should list your ideas and then expand on them later in the body. It might take a bit of research to figure out what you want to change. Ask around the school, talking to students and teachers, and see where there's room for improvement. What are the concerns of the students? What are people happy with regarding the school? What would they like to see change? Asking these questions can help you get a sense of your audience and community.
- Remember, you should not make promises you cannot keep. Do not say anything just to get elected. While many students might want gum-chewing policies eliminated or for the lunch period to run twice as long, this is probably not necessary or possible. Try to focus on areas that seem important to keep your school running safely and efficiently. Concerns about things like bullying , academic standards, and extracurricular activities should be your concern over fun and games. [10] X Research source
- A good opening statement for your body would state the causes important to you and what you plan to do about them. For example, if you were running for president, you could say something like, "I understand we need to improve how we handle bullying, increase interest in extracurricular activities, and expand access to AP courses throughout the school. As your president, I would work to bring in speakers to talk about sensitivity in the classroom, increase advertising for basketball games and quiz bowl tournaments, and start a tutoring program to help students struggling with certain subjects." [11] X Research source

- Using the school library or computers, figure out the best means to tackle certain problems many schools face. How have other schools dealt with bullying? Poor test scores? Low interest in extracurricular activities? What can you reasonably do as a student council member to address these problems? [12] X Research source
- You do not have to have a point-by-point plan laid out, but a few sentences on some preliminary ideas can help you stand out from your peers. People are more inclined to vote for someone who's thought about how to solve problems in addition to identifying problems. [13] X Research source

Ending with a Strong Conclusion

- Do summarize, briefly, your qualifications but do not put the main focus on them. This is where you should sincerely state your passion. Students should not just vote for you because you'd do a good job but because you genuinely care about the school. State your passion for your community and how much you want to see other students succeed. Lots of students have high qualifications. You can set yourself apart by being a candidate who really cares. [16] X Research source

- Research what other student council speeches are like on video websites. This could help give you ideas.
Expert Q&A

- Only promise to do things that you really can do. Thanks Helpful 4 Not Helpful 0
- Practice reading your speech a few times, as you'll likely be nervous before giving it. Thanks Helpful 4 Not Helpful 0

- Even if you write a great speech, understand you may lose. Be prepared to lose graciously and sincerely congratulate the winning candidate. Thanks Helpful 104 Not Helpful 16
- Unlike in a governmental election, student council candidates should not attack each other, previous leaders, or other students. Otherwise, you could get into trouble and leave a bad impression on voters. Thanks Helpful 78 Not Helpful 16
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.studentcouncilpro.com/student-council-speeches.html
- ↑ http://www.write-out-loud.com/student-council-speeches.html
- ↑ Patrick Muñoz. Voice & Speech Coach. Expert Interview. 12 November 2019.
About This Article

To write a student council speech, start with an attention-grabbing statement such as a question or a powerful quote about leadership. Next, briefly explain who you are, what position you are running for, and why you are running. Then list any relevant qualifications, such as a summer job. In the body of the speech, discuss at least 3 ways to improve the school. For this section, make sure not to make any promises you can’t keep. Finally, end by briefly reiterating your main points and asking for the students’ vote. To learn more about how to support your ideas and research for your speech, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Did this article help you?

Mihrimah G.
Sep 27, 2017
Kyla Harvie
Jun 11, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get the best dating & love tips
wikiHow's Relationships Newsletter
Speech Topics for Grade 3
Erin schreiner.

Most third-graders have little experience with public speaking. Up to this point in their education, they have had few instances in which they were required to show their smarts in front of peers through the presentation of a speech. While these early learners will likely not yet be adept public speakers, it is advantageous to begin the process of practicing speaking in public. By engaging your students in the composition and presentation of speeches, you give them the opportunity to build their confidence and prepare for the public speaking-related challenges they will face later in their education.
Explore this article
- My Family Vacation
- If I Could Be a Superhero
- Traveling to Space
- Book Commercial
1 My Family Vacation
Ask your third-graders to recount a fun time they had with their family members by instructing them to compose speeches in which they describe their family vacation experiences. Instruct each pupil to select a memorable vacation and describe it in as much detail as possible. Assist students in composing their explanations by guiding them through the prewriting process and ask them to create webs containing details about their adventure. Encourage students to adopt a chronological structure when composing their speeches to make their explanations clear and easy to follow.
2 If I Could Be a Superhero
Many third-graders have a preoccupation with superheroes. Tap into this natural interest by asking students to compose speeches in which they explain what they would most like about being a superhero. Begin this speech assignment creatively by asking pupils to draw pictures of themselves as superheroes. After this introduction, ask students to use their pictures as inspiration and compose an explanation of whom they would be if they were a superhero. Remind students to include in their speeches their superhero names, what their costumes would look like and what powers they would possess.
3 Traveling to Space
While none of your third-graders have taken off into space, the prospect of doing so is likely thrilling. Ask each of your pupils to compose a space-related speech and present it to the class. Allow each pupil to select a topic relevant to space travel, such as man's first walk on the moon or space stations. Provide students with print media related to space for them to use in their research efforts. After all the students have researched their selected topics and composed their speeches, allow them to present to the class.
4 Book Commercial
Get your third-graders excited about reading by allowing them to compose and present book commercials. Ask each student to select a book that he particularly enjoyed. Instruct the student to compose a short speech in which he outlines the strong points of the book and encourages his peers to read it. Encourage the students to integrate visual aids into their commercials by bringing in their featured books to hold up to their classmates or dressing as a character from the story.
- 1 Best Speech Topics: Elementary School Speech Topics

About the Author
Erin Schreiner is a freelance writer and teacher who holds a bachelor's degree from Bowling Green State University. She has been actively freelancing since 2008. Schreiner previously worked for a London-based freelance firm. Her work appears on eHow, Trails.com and RedEnvelope. She currently teaches writing to middle school students in Ohio and works on her writing craft regularly.
Related Articles

Good Speech Topics for Grade 8 Students

How to Teach Children to Write the Introduction to...

Public Speaking Activities for Kids

Teaching 4th Graders to Write a Biography

Fun Ideas for a 10-Minute Show & Tell

How to Teach English With Ludic Activities

Essay Topics for Third Graders

Activities to Do Instead of Book Reports

How to Teach the Civil War to a Fifth-Grade Class

How to Teach Public Speaking to Children

Reading Activities for "The Bravest Dog Ever: The True...

How to Teach Alliteration -- A Lesson Plan

Harlem Renaissance Art Activities for Fifth Grade

Warm-Up Activities for English Class

The Difference Between a Tall Tale and a Folktale

Free Team Building Activities for a High School Classroom

How to Give a Good Lecture

How to Write an Eagle Scout Speech

How to Write a Conclusion for a Book Report

Picture Book Activities for Middle School Students
Regardless of how old we are, we never stop learning. Classroom is the educational resource for people of all ages. Whether you’re studying times tables or applying to college, Classroom has the answers.
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright Policy
- Manage Preferences
© 2020 Leaf Group Ltd. / Leaf Group Media, All Rights Reserved. Based on the Word Net lexical database for the English Language. See disclaimer .
3-minute speeches: Complete guide on writing, preparing and delivering (with examples)
Hrideep barot.
- Body Language & Delivery , Presentation , Public Speaking , Speech Topics , Speech Writing

Although 3-minute speeches may seem brief, a lot of words and ideas may be said at that time. Despite the time constraint, if you are conversant with the subject matter, you may prepare for your three-minute speech swiftly. The secret is to create a strong outline that allows you to add or remove details based on how much time you have left.
Words in a 3-minute speech
An average speech of three minutes in length would have roughly 390 words at a regular speech rate of 130 words per minute (wpm) .
Daphne Gray-Grant, a speech and writing coach, discovered that the typical speaking tempo is 125 to 150 words per minute or 375 to 450 words for a three-minute speech .
Read this article for more information: How long should a speech be?
Writing 3-minute speeches
An engaging speech may capture the attention of the crowd and properly capture the spirit of the event. On the other side, if it is poorly written or disorganised, a dozing audience will miss your point. There is no one ideal structure for a speech. You should instead choose what will resonate with your audience the most.
1. Importance of Stories
Beginning with a story engages the audience, and using stories to break up your speech illustrates the concepts you’re talking about using instances from real life. You might also choose to tell snippets of a single story throughout your speech to illustrate your point. If you’re speaking to a group of professional women with kids, for instance, a story about work-life balance is appropriate. Pick a story that is relevant to your audience. Infrequently, if ever, are overtly political or religious statements appropriate.
2. Simply the Facts
It could be advisable to stick to only the facts while presenting a subject while looking for methods to make them applicable to your audience. But no matter what you talk about, keep your speech’s goal in mind at all times. You run the risk of losing the attention of your audience, and making a point with a long, winding speech isn’t particularly effective.
3. Ordered Chronologically
Your tale or the information you’re conveying must make sense in the order you present it, which typically entails using chronological order. If you’re discussing company law, for instance, you should start with earlier laws and tell a tale about how those rules have been modified or updated. It is feasible to deliver a speech in reverse chronological sequence, but you must make sure your audience understands this to avoid misunderstanding. Give the audience frequent dates or other points of reference to serve as the context for the timing of your speech.
4. Organizing Advice
By outlining your speech, you can make sure that you follow the proper flow and concentrate on the most important points rather than getting lost in the weeds of details. Make a rough draught of your speech, then practise it so that it flows naturally before you give it. Take a list of the key points you want to discuss in your speech and consult a subject-matter expert for any information that is either missing or superfluous to ensure that you cover what you need to.
5. Use of Diction
We select our words based on the circumstances we find ourselves in and the audience we are speaking to. The language you would use with your friends might not be appropriate for your boss. Pick the appropriate words for your audience in order to deliver a speech that is effective. The language you use must be clear to them. It is preferable to stay away from using slang because your language must also be acceptable for the topic. You do not need to poke fun at the audience or try to be amusing. Since audiences are able to tell when a speaker isn’t being sincere, speak from the heart and don’t just say what you think the audience wants to hear. You’ll be able to express yourself more strongly and with more emotion as a result.

6. Speech Patterns
Different speeches are needed for different circumstances. A three-minute presentation in class about your ideal job has a different format than a speech to your graduating class. Learning the appropriate format for various speech kinds is simple. There are various varieties of speeches, all of them ranging in form and length. Impromptu, demonstration, educational, persuading, or tribute speeches are a few examples. Each speech is appropriate for a particular situation in life. Select the speech structure that best fits your circumstance, then formats your speech in line with it. Be mindful of your introduction. Strong opening approaches, sometimes known as “hooks,” come in a variety of forms, including tales, rhetorical questions, shocking claims, striking facts, or simply acting in an unexpected or out-of-the-ordinary manner.
Preparing 3-minute speeches
One of the best strategies to make sure you deliver a compelling presentation is to practise your speech beforehand. Consider using these hints to aid in your preparation:
- Your speech should be organised logically with an introduction, body, and conclusion.
- Before giving a speech, frequently practise and rehearse it. Try practising in front of a mirror or with friends acting as your audience. Use a timer to help you pace your speech, and be careful to do so.
- Learn about the podium or other location where the speech will be delivered. Find out the size of the stage, the location of any steps or impediments, and the best places to enter and exit.
- Always keep a professional impression while dressing comfortably .
- Regardless of whether a speech is humorous, serious, or technical, visual aids should fit it. The primary function of visual aids is to facilitate audience comprehension and reinforce key ideas of a speech in distinctive and engaging ways.

Practising 3-minute speeches
It’s common for jittery, distracting body language and a lack of preparation to ruin otherwise effective speeches. Practice your speech after you’ve planned and written it. You have not practised enough if you need to read your speech word-for-word from your notes. You will feel more assured as you practise more. The best way to get rid of tense body language is to have a buddy videotape you speaking so you can see it repeatedly. While speaking, pay attention to how your hands are moving; they should be at ease.
Pay attention to how you stand; you should be tall and straight. Be mindful of your eye contact. Keep your eyes off of your notes, the floor, or the ceiling. Change your jewellery if it is noisy. Don’t touch your face or hair. Do not clasp your hands behind or in front of your back, and refrain from putting your hands in your pockets. Before giving your speech, repeat this procedure multiple times to make sure you have broken these undesirable habits.
The Big Day
Arrive early at the location on the day of your presentation. Wear clean, acceptable apparel, and go for the look that gets you the most compliments. Make sure your cell phone is off and remove any large objects from your pockets. Check your loudness in the room before you start to make sure you are loud enough. Make sure you can make eye contact with those seated at the audience’s margins by paying attention to where they are seated. Check the location in advance to make sure there are no obstacles like wires or cables that could cause you to trip if you wish to move while speaking. All of these actions will support your confidence grows.
Don’t try to improvise during your speech; instead, speak as you did when you were practising. Keep in mind that feeling anxious before, during, and especially after your speech is natural. This is neither a flaw nor a weakness. Use your anxious energy to make your speech lively and engaging if you have done your preparation and practising well.
Delivering 3-minute speeches
Public speaking that is effective and confident should appear natural. In truth, it takes most people a lot of time and practice before they feel comfortable speaking in front of an audience. To overcome stage anxiety, present yourself with confidence, and keep your audience interested, you can employ a variety of tactics.
1. Avoid showing any nervousness while speaking.
Imagine yourself as someone who is imparting knowledge to others who are willing to listen. Don’t worry too much about how you’ll come across while nervous: When a speaker claims to be really frightened, audiences can not help but notice their anxiety. You perceive it as far worse than your listeners do. It doesn’t really matter whether you’re anxious as long as you act calm.
2. Create positive body language
The grin is the most significant facial expression. This forges an immediate connection with your audience and will win them over. Use your facial expressions to emphasise important points: Your speech will look more believable as a result.
It’s important to stand up straight, space your feet slightly apart, and keep your arms at your sides. Do not sway or place your hands on your hips when speaking. You’ll come across as more assured and credible if you appear grounded. Avoid making “closed” motions like crossing your arms or knees or posing for a picture with your arms behind your back. A mental barrier is put up between you and your audience as a result.
3. Use gestures for achievement
To make your message easier for the audience to follow, use your arms and hands. Effective, self-assured body language captures listeners’ attention. Together, your body and words can convey a potent statement. Make sure to vary your gestures to avoid coming out as a robot.
To effectively emphasise ideas, adjust your body language to the size of the area you are working in. Make powerful motions when giving a speech! Tentative, hesitant acts might give you a doubtful, unconvincing appearance.
4. Make eye contact to captivate others.
Make as much eye contact with your audience as you can to engage them (and appear interested in them). Don’t only focus on one welcoming face. Make sure you engage the entire audience by looking at the folks at the rear and on the sides in addition to the front. Observe the crowd more intently than your notes. Not something you read from, notes should be prompt.

How to make a 3-minute speech interesting?
People worry that they will have to “dumb down” their important research due to time constraints, however, this is not the case!
A punchy message and an engaging brief speech can shed light on the breadth of your research and make the worth of your thoughts clear.
If you make the most of your three minutes and plan your speech effectively, you will have plenty of time to accomplish this.
- Deliver a message that is quite obvious.
- Present a “top and tail” component.
- To clarify a complex concept, use metaphors and other verbal illustrations.
- Instead of “making a formal speech,” speak as if you are having a conversation with your listeners.
General topics for 3-minute speeches
3-minute speeches for students.
Everyone has interests, and everyone enjoys discussing them. You know, hobbies could also be passions. Simple inquiries to pose include:
- What interests you?
- Why are your activities so appealing to you?
- When do you engage in these pastimes?
- What are your hobbies, how long have you been doing them, and how did you start?
- What pastimes did you once enjoy but no longer do?
- Is it necessary to engage in hobbies? Why or why not?
Everyone enjoys music, and the majority of people have extremely strong feelings about it, especially when it comes to the music they enjoy (or detest) the most. Simple inquiries to make include the following:
- What genres of music do you enjoy or find boring?
- What emotions do various musical genres evoke in you?
- What genres of music are produced in your nation?
- What song, artist, or album is your favourite?
- What music is now in vogue in your nation?
3. Motivation
Whether or whether the pupils are motivated, it is a good idea to talk about motivation in order to motivate them. Examples of questions are:
- In general, how motivated are you?
- What spurs you on to action?
- What inspires people to accomplish the most?
- What actions do you do when you lack motivation?
- How can one effectively inspire others?
Everybody has objectives, and discussing them really makes us more motivated to take action. Goal-setting can be aided by sharing them with others. An excellent set of inquiries are:
- What are your present life objectives?
- How are your goals going to be attained?
- How frequently do you set yourself goals?
- What objectives have you previously set and attained?
- How do you feel after achieving your objectives?
Everyone has dreams, sometimes on a nightly basis, and discussing them in class is a terrific activity since it encourages pupils to be imaginative and even whimsical. Excellent inquiries on this subject include:
- How would you characterise your dreams?
- What do dreams represent to you?
- What percentage of your dreams can you recall? Why?
- What are your thoughts about prophecies? Are they genuine?
- What are some instances of your most cherished dreams?
Go through this article for more valuable insights: Speech titles and topics: Everything you need to know
Examples of 3-minute speeches
- A 3-minute speech on the topic “Life”.
Good morning to everyone in this room. I’m here today to speak about life and share my opinions with all of you. Life is a never-ending process that must come to an end eventually. Life is all about creating and adoring oneself. a quotation for you: “Life can only be comprehended by living it backwards.” The potential to live a meaningful life and help others do the same is presented by life itself. It makes no difference how long you live. However, how well you lead a good life matter. Death is a constant menace to our life. Everyone will eventually die, but that doesn’t mean we should stop trying to live life to the fullest or pursue our ambitions. A person is only intelligent when they are prepared to face their destiny when it calls, but in the meantime, they should cherish every moment. There is an air of preparation. Every person goes through a journey in life where they must cross the bridge of death in order to awaken to eternal life. Life itself is a genuinely priceless gift. Every moment we have in our life gives us the chance to do something to grow and display our virtues. Every instant unlocks the path for us to accept blessings. The reality is that both good and bad things happen to us in life. What matters most is how we respond. God has given us life as a gift in the hope that we will do our best to make it meaningful. Each of us is a special individual. Respect your uniqueness since no one was born exactly like you and no one ever will be. I frequently come across people who accuse God of something they themselves do not possess. They constantly curse their lives. But do they understand how priceless this life is in and of itself? If we make life worthwhile and strive diligently for positivity. Finally, I’ll say that we ought to make life valuable. Life should be made beautiful by the affection of our family and friends. By carrying out our responsibilities in our families, our workplaces, society, and the larger globe, life can be more beautiful and meaningful.
2. A 3-minute speech by Aaron Beverly who was the 2 nd place winner of the 2016 World Championship of Public Speaking
3. A 3-minute speech by Emma Watson on Gender Equality
Final words
Speaking for three minutes is undoubtedly difficult to master. You must unquestionably conduct an adequate study and choose crucial issues to include in your speech. It is crucial to realise that you must deliver the most essential information first while speaking in a restricted amount of time, such as a 3-minute speech.
A three-minute speech is undoubtedly a wonderful starting point for public speaking. This is because you need to communicate with your audience more effectively when you just have a short amount of time. The speech ought to be concise, pertinent, and clear. Be more relatable to the audience and speak for them. To be the best, you must improve your communication abilities.
Read this article for more useful information: Writing and delivering spectacular short speeches: A-Z guide
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

7 Keys to Emcee Like a Pro: Unlock Your Hosting Potential

8 Ways to Rise Above the Noise to Communicate Better

How to Negotiate: The Art of Getting What You Want

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved
Kindly drop your contact details so that we can arrange call back
Select Country Afghanistan Albania Algeria AmericanSamoa Andorra Angola Anguilla Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile China Christmas Island Colombia Comoros Congo Cook Islands Costa Rica Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Mexico Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island Northern Mariana Islands Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Romania Rwanda Samoa San Marino Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands South Africa South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Tajikistan Thailand Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Wallis and Futuna Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe land Islands Antarctica Bolivia, Plurinational State of Brunei Darussalam Cocos (Keeling) Islands Congo, The Democratic Republic of the Cote d'Ivoire Falkland Islands (Malvinas) Guernsey Holy See (Vatican City State) Hong Kong Iran, Islamic Republic of Isle of Man Jersey Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Republic of Lao People's Democratic Republic Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Macao Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav Republic of Micronesia, Federated States of Moldova, Republic of Mozambique Palestinian Territory, Occupied Pitcairn Réunion Russia Saint Barthélemy Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan Da Cunha Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Martin Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Sao Tome and Principe Somalia Svalbard and Jan Mayen Syrian Arab Republic Taiwan, Province of China Tanzania, United Republic of Timor-Leste Venezuela, Bolivarian Republic of Viet Nam Virgin Islands, British Virgin Islands, U.S.


How to Write an Effective Speech Outline: A Step-by-Step Guide
- The Speaker Lab
- March 8, 2024
Table of Contents
Mastering the art of speaking starts with crafting a stellar speech outline. A well-structured outline not only clarifies your message but also keeps your audience locked in.
In this article, you’ll learn how to mold outlines for various speech types, weaving in research that resonates and transitions that keep listeners on track. We’ll also show you ways to spotlight crucial points and manage the clock so every second counts. When it’s time for final prep, we’ve got smart tips for fine-tuning your work before stepping into the spotlight.
Understanding the Structure of a Speech Outline
An effective speech outline is like a map for your journey as a speaker, guiding you from start to finish. Think of it as the blueprint that gives shape to your message and ensures you hit all the right notes along the way.
Tailoring Your Outline for Different Speech Types
Different speeches have different goals: some aim to persuade, others inform or celebrate. Each type demands its own structure in an outline. For instance, a persuasive speech might highlight compelling evidence while an informative one focuses on clear explanations. Crafting your outline with precision means adapting it to fit these distinct objectives.
Incorporating Research and Supporting Data
Your credibility hinges on solid research and data that back up your claims. When writing your outline, mark the places where you’ll incorporate certain pieces of research or data. Every stat you choose should serve a purpose in supporting your narrative arc. And remember to balance others’ research with your own unique insights. After all, you want your work to stand out, not sound like someone else’s.
The Role of Transitions in Speech Flow
Slick transitions are what turn choppy ideas into smooth storytelling—think about how bridges connect disparate land masses seamlessly. They’re not just filler; they carry listeners from one thought to another while maintaining momentum.
Incorporate transitions that feel natural yet keep people hooked. To keep things smooth, outline these transitions ahead of time so nothing feels left up to chance during delivery.
Techniques for Emphasizing Key Points in Your Outline
To make certain points pop off the page—and stage—you’ll need strategies beyond bolding text or speaking louder. Use repetition wisely or pause strategically after delivering something significant. Rather than go impromptu, plan out what points you want to emphasize before you hit the stage.
Timing Your Speech Through Your Outline
A watchful eye on timing ensures you don’t overstay—or undercut—your moment under the spotlight. The rhythm set by pacing can be pre-determined through practice runs timed against sections marked clearly in outlines. Practice will help ensure that your grand finale isn’t cut short by surprise.
What Type Of Speaker Are You?
Click below to discover your Speaker Archetype and how to start getting booked and paid to speak!
Depending on the type of speech you’re giving, your speech outline will vary. The key ingredients—introduction, body, and conclusion—are always there, but nuances like tone or message will change with each speaking occasion.
Persuasive Speeches: Convincing With Clarity
When outlining a persuasive speech, arrange your arguments from strong to strongest. The primacy effect works wonders here, so make sure to start off with a strong point. And just when they think they’ve heard it all, hit them with an emotional story that clinches the deal.
You might start by sharing startling statistics about plastic pollution before pivoting to how individuals can make a difference. Back this up with data on successful recycling programs which demonstrate tangible impact, a technique that turns facts into fuel for action.
Informative Speeches: Educating Without Overwhelming
An informative speech shouldn’t feel like drinking from a fire hose of facts and figures. Instead, lay out clear subtopics in your outline and tie them together with succinct explanations—not unlike stepping stones across a stream of knowledge.
If you’re talking about breakthroughs in renewable energy technology, use bullet points to highlight different innovations then expand upon their potential implications one at a time so the audience can follow along without getting lost in technical jargon or complexity.
Ceremonial Speeches: Creating Moments That Matter
In a ceremonial speech you want to capture emotion. Accordingly, your outline should feature personal anecdotes and quotes that resonate on an emotional level. However, make sure to maintain brevity because sometimes less really is more when celebrating milestones or honoring achievements.
Instead of just going through a hero’s whole life story, share the powerful tales of how they stepped up in tough times. This approach hits home for listeners, letting them feel the impact these heroes have had on their communities and sparking an emotional bond.
Incorporating Research in Your Speech Outline
When you’re crafting a speech, the backbone of your credibility lies in solid research and data. But remember, it’s not just about piling on the facts. It’s how you weave them into your narrative that makes listeners sit up and take notice.
Selecting Credible Sources
Finding trustworthy sources is like going on a treasure hunt where not all that glitters is gold. To strike real gold, aim for academic journals or publications known for their rigorous standards. Google Scholar or industry-specific databases are great places to start your search. Be picky. Your audience can tell when you’ve done your homework versus when you’ve settled for less-than-stellar intel.
You want to arm yourself with evidence so compelling that even skeptics start nodding along. A well-chosen statistic from a reputable study does more than decorate your point—it gives it an ironclad suit of armor.
Organizing Information Effectively
Your outline isn’t just a roadmap; think of it as scaffolding that holds up your argument piece by piece. Start strong with an eye-opening factoid to hook your audience right off the bat because first impressions matter—even in speeches.
To keep things digestible, group related ideas together under clear subheadings within your outline. Stick to presenting data that backs up each key idea without wandering down tangential paths. That way, everyone stays on track.
Making Data Relatable
Sure, numbers don’t lie but they can be hard to connect to. If you plan on using stats in your speech, make them meaningful by connecting them to relatable scenarios or outcomes people care about deeply. For instance, if you’re talking health statistics, relate them back to someone’s loved ones or local hospitals. By making the personal connection for your audience, you’ll get their attention.
The trick is using these nuggets strategically throughout your talk, not dumping them all at once but rather placing each one carefully where its impact will be greatest.
Imagine your speech as a road trip. Without smooth roads and clear signs, the journey gets bumpy, and passengers might miss the scenery along the way. That’s where transitions come in. They’re like your speech’s traffic signals guiding listeners from one point to another.
Crafting Seamless Bridges Between Ideas
Transitions are more than just linguistic filler. They’re strategic connectors that carry an audience smoothly through your narrative. Start by using phrases like “on top of this” or “let’s consider,” which help you pivot naturally between points without losing momentum.
To weave these seamlessly into your outline, map out each major turn beforehand to ensure no idea is left stranded on a tangent.
Making Use of Transitional Phrases Wisely
Be cautious: overusing transitional phrases can clutter up your speech faster than rush hour traffic. Striking a balance is key—think about how often you’d want to see signposts on a highway. Enough to keep you confident but not so many that it feels overwhelming.
Pick pivotal moments for transitions when shifting gears from one major topic to another or introducing contrasting information. A little direction at critical junctures keeps everyone onboard and attentive.
Leveraging Pauses as Transition Tools
Sometimes silence speaks louder than words, and pauses are powerful tools for transitioning thoughts. A well-timed pause lets ideas resonate and gives audiences time to digest complex information before moving forward again.
This approach also allows speakers some breathing room themselves—the chance to regroup mentally before diving into their next point with renewed vigor.
Connecting Emotional Threads Throughout Your Speech
Last but not least, don’t forget emotional continuity, that intangible thread pulling heartstrings from start-to-finish. Even if topics shift drastically, maintaining an underlying emotional connection ensures everything flows together cohesively within the larger tapestry of your message.
Techniques for Emphasizing Key Points in Your Speech Outline
When you’re crafting your speech outline, shine a spotlight on what matters most so that your audience doesn’t miss your key points.
Bold and Italicize for Impact
You wouldn’t whisper your punchline in a crowded room. Similarly, why let your main ideas get lost in a sea of text? Use bold or italics to give those lines extra weight. This visual cue signals importance, so when you glance at your notes during delivery, you’ll know to emphasize those main ideas.
Analogies That Stick
A good analogy is like super glue—it makes anything stick. Weave them into your outline and watch as complex concepts become crystal clear. But remember: choose analogies that resonate with your target audience’s experiences or interests. The closer home it hits, the longer it lingers.
The Power of Repetition
If something’s important say it again. And maybe even once more after that—with flair. Repetition can feel redundant on paper, but audiences often need to hear critical messages several times before they take root.
Keep these strategies in mind when you’re ready to dive into your outline. You’ll transform those core ideas into memorable insights before you know it.
Picture this: you’re delivering a speech, and just as you’re about to reach the end, your time’s up. Ouch! Let’s make sure that never happens. Crafting an outline is not only about what to say but also how long to say it.
Finding Balance in Section Lengths
An outline isn’t just bullet points; it’s a roadmap for pacing. When outlining your speech, make sure to decide how much time you’d like to give each of your main points. You might even consider setting specific timers during rehearsals to get a real feel for each part’s duration. Generally speaking, you should allot a fairly equal amount of time for each to keep things balanced.
The Magic of Mini Milestones
To stay on track, a savvy speaker will mark time stamps or “mini milestones” on their outline. These time stamps give the speaker an idea of where should be in their speech by the time, say, 15 minutes has passed. If by checkpoint three you should be 15 minutes deep and instead you’re hitting 20 minutes, it’s time to pick up the pace or trim some fat from earlier sections. This approach helps you stay on track without having to glance at the clock after every sentence.
Utilizing Visual Aids and Multimedia in Your Outline
Pictures speak louder than words, especially when you’re on stage. Think about it: How many times have you sat through a presentation that felt like an eternity of endless bullet points? Now imagine if instead, there was a vibrant image or a short video clip to break up the monotony—it’s game-changing. That’s why integrating visual aids and multimedia into your speech outline isn’t just smart. It’s crucial for keeping your audience locked in.
Choosing Effective Visuals
Selecting the right visuals is not about flooding your slides with random images but finding those that truly amplify your message. Say you’re talking about climate change. In this case, a graph showing rising global temperatures can hit hard and illustrate your chosen statistic clearly. Remember, simplicity reigns supreme; one powerful image will always trump a cluttered collage.
Multimedia Magic
Videos are another ace up your sleeve. They can deliver testimonials more powerfully than quotes or transport viewers to places mere descriptions cannot reach. But be warned—timing is everything. Keep clips short and sweet because no one came to watch a movie—they came to hear you . You might highlight innovations using short video snippets, ensuring these moments serve as compelling punctuations rather than pauses in your narrative.
The Power of Sound
We often forget audio when we think multimedia, yet sound can evoke emotions and set tones subtly yet effectively. Think striking chords for dramatic effect or nature sounds for storytelling depth during environmental talks.
Audiences crave experiences they’ll remember long after they leave their seats. With well-chosen visuals and gripping multimedia elements woven thoughtfully into every section of your speech outline, you’ll give them exactly that.
Rehearsing with Your Speech Outline
When you’re gearing up to take the stage, your speech outline is a great tool to practice with. With a little preparation, you’ll give a performance that feels both natural and engaging.
Familiarizing Yourself with Content
To start off strong, get cozy with your outline’s content. Read through your outline aloud multiple times until the flow of words feels smooth. This will help make sure that when showtime comes around, you can deliver those lines without tripping over tough transitions or complex concepts.
Beyond mere memorization, understanding the heart behind each point allows you to speak from a place of confidence. You know this stuff—you wrote it. Now let’s bring that knowledge front and center in an authentic way.
Mimicking Presentation Conditions
Rehearsing under conditions similar to those expected during the actual presentation pays off big time. Are you going to stand or roam about? Will there be a podium? Think about these details and simulate them during rehearsal because comfort breeds confidence—and we’re all about boosting confidence.
If technology plays its part in your talk, don’t leave them out of rehearsals either. The last thing anyone needs is tech trouble during their talk.
Perfecting Pace Through Practice
Pacing matters big time when speaking. Use timed rehearsals to nail down timing. Adjust speed as needed but remember: clarity trumps velocity every single time.
You want people hanging onto every word, which is hard to do if you’re talking so fast they can barely make out what you’re saying. During rehearsals, find balance between pacing and comprehension; they should go hand-in-hand.
Finalizing Your Speech Outline for Presentation
You’ve poured hours into crafting your speech, shaping each word and idea with precision. Now, it’s time to tighten the nuts and bolts. Finalizing your outline isn’t just about dotting the i’s and crossing the t’s. It’s about making sure your message sticks like a perfectly thrown dart.
Reviewing Your Content for Clarity
Your first task is to strip away any fluff that might cloud your core message. Read through every point in your outline with a critical eye. Think of yourself as an editor on a mission to cut out anything that doesn’t serve a purpose. Ask yourself if you can explain each concept clearly without needing extra words or complex jargon. If not, simplify.
Strengthening Your Argument
The meat of any good presentation lies in its argument, the why behind what you’re saying. Strengthen yours by ensuring every claim has iron-clad backing—a stat here, an expert quote there. Let this be more than just facts tossed at an audience; weave them into stories they’ll remember long after they leave their seats.
Crafting Memorable Takeaways
Audiences may forget details but never how you made them feel—or think. Embed memorable takeaways throughout your outline so when folks step out into fresh air post-talk, they carry bits of wisdom with them.
This could mean distilling complex ideas down to pithy phrases or ending sections with punchy lines that resonate. It’s these golden nuggets people will mine for later reflection.
FAQs on Speech Outlines
How do you write a speech outline.
To craft an outline, jot down your main ideas, arrange them logically, and add supporting points beneath each.
What are the 3 main parts of a speech outline?
An effective speech has three core parts: an engaging introduction, a content-rich body, and a memorable conclusion.
What are the three features of a good speech outline?
A strong outline is clear, concise, and structured in logical sequence to maximize impact on listeners.
What is a working outline for a speech?
A working outline serves as your blueprint while preparing. It’s detailed but flexible enough to adjust as needed.
Crafting a speech outline is like drawing your map before the journey. It starts with structure and flows into customization for different types of talks. Remember, research and evidence are your compass—they guide you to credibility. Transitions act as bridges, connecting one idea to another smoothly. Key points? They’re landmarks so make them shine.
When delivering your speech, keep an eye on the clock and pace yourself so that every word counts.
Multimedia turns a good talk into a great show. Rehearsing polishes that gem of a presentation until it sparkles.
Last up: fine-tuning your speech outline means you step out confident, ready to deliver something memorable because this isn’t just any roadmap—it’s yours.
- Last Updated: March 5, 2024

Explore Related Resources
Learn How You Could Get Your First (Or Next) Paid Speaking Gig In 90 Days or Less
We receive thousands of applications every day, but we only work with the top 5% of speakers .
Book a call with our team to get started — you’ll learn why the vast majority of our students get a paid speaking gig within 90 days of finishing our program .
If you’re ready to control your schedule, grow your income, and make an impact in the world – it’s time to take the first step. Book a FREE consulting call and let’s get you Booked and Paid to Speak ® .
About The Speaker Lab
We teach speakers how to consistently get booked and paid to speak. Since 2015, we’ve helped thousands of speakers find clarity, confidence, and a clear path to make an impact.
Get Started
Let's connect.
Copyright ©2023 The Speaker Lab. All rights reserved.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Kids Learning
Myself Essay in English for Class 3 Students | Easy Essay on Myself
Introduction.
A student learns to get a grasp from his or her surroundings and decides to express them through words. Speech helps them in moments like this but when it comes to recording them, students find themselves in a bind. They turn to writing for help and discover that they can express themselves more clearly. Essay writing is one of the many writing exercises where the student gains insight into his or her perspective by writing on their desired topics.
Among many such topics, the most commonly used for writing essays is writing about oneself. “Myself” is a theme that can be used for students of Class 3. Essays about “Myself” typically include the basic information about the writer, such as their name, their age, family’s information, the school they go to, and their hobbies and leisure activities.
Here is one type of essay students in grade 3 can write about. Try to focus on the details.
My name is Hana Jay. My father’s name is Hare Ju and my mother’s name is Kuni Jya. I am 8 years old. I live in Supriya Bhatt Apartments in Mumbai. My father is a stockbroker, but I don’t know what that means. My mother is a teacher. I know what a teacher is. I have one brother and one sister. My sister is the oldest, then there is my brother. I am the youngest. I go to Dexter School. It is close to home. It takes 10 minutes to reach school by walking. I like going to school regularly because we learn something new every day. My favourite subject is English. I like English because it makes it easy for me to express my thoughts. I love to play video games with my brother and sister. We play Mario Kart a lot though I am better than them. I have many friends in school and in the neighbourhood. In the evenings on our way back home, we go to the library and read some storybooks. My favourite fairy tale is “The Wolf and The Red Riding Hood”. I love the story and can read it every day. My favourite food is mutton biryani. When I grow up I want to make the world’s best biryani.
Essay on Myself for Class 3 Students
Essay writing tasks are included in the curriculum of the junior school so as to inculcate good communication skills among the kids. Some kids are fond of writing essays and are able to express themselves with fluidity, while some kids struggle with essay writing. The only thing that will help these kids to improve their writing skills is a set of easy to understand guidelines. Here you can find two easy to understand essays on the topic ‘Myself’ for class 3, which will set the guidelines for your kids to write similar essays on their own.
Essay on Myself
My name is Aarohi Sharma and I am eight years old. I stay at Lavelle Road in Bangalore and I study in Baldwin Girls’ High School. I am in class 3 and I love going to school every day. My father’s name is Rohan Sharma and he works in an IT organization. My mother’s name is Mansi Sharma and she is a homemaker.
My favourite subjects are Maths and English. I have a lot of indoor games that help me to improve my mental math skills. I love solving puzzle games and Sudokus. Every day, when I return from school, my grandfather and I sit together to solve the Sudoku puzzle from the newspaper. I like to read storybooks that have amazing colorful pictures in it. ‘Rapunzel’ is my favorite storybook and I like the blonde hair that she lets down from the tower window.
I like to watch cartoons and I try to paint the cartoon characters in my drawing book. My favourite cartoon character is Doraemon and I also have a soft toy of Doraemon. I love to have chocolates and my mother brings me yummy chocolates whenever I get a good grade at school. I like swimming very much and I never miss my swimming classes. My friend Aarti and I go to swimming classes together. I also like playing basketball and I take basketball classes on the weekends. I love watching airplanes flying high in the sky until they disappear in the clouds. I aspire to become a pilot when I grow up.
My name is Arjun Sen and I am eight years old. I stay at Richmond Circle, Bangalore. I study at St. Joseph’s Boys High School and I am in class 3. My father’s name is Gautam Sen and he works in the Indian Navy. My mother’s name is Mira Sen and she works in an NGO. I have an elder sibling, Rahul and he is in class 9.
My favourite subjects are Maths and English. I like to practice maths every day and my elder brother helps me learn new English words. We have a room full of bookshelves at our home and during vacations, our father makes us read a few old books from there.
I am also very fond of painting and poetry. My elder brother writes his own poems and I like to read his poems. My favourite pastime is painting and I spend most of my time painting scenery on the weekends. I love painting the sceneries of sunset in which the sky is orange.
My favourite food is Pasta and my mother prepares very delicious pasta dishes on Sundays. On Sunday evenings, she plays the piano and my brother recites his poetry along with it. My favourite sport is tennis and I take coaching classes for tennis every Wednesday and Friday. Roger Federer is my favourite tennis player. I also like to play football and I am a part of the football team in our school’s junior section. I aspire to become a tennis player when I grow up and play it as well as Roger Federer.
FAQs on Myself Essay in English for Class 3 Students | Easy Essay on Myself
1. What is an essay? How are they useful?
An essay is a long descriptive piece of writing where a writer’s thoughts are expressed about a certain topic. Essays are an efficient way of getting young children into expressing themselves through writing. According to statistics, kids who start writing - along with reading for leisurely means - early in their childhood, are proven to be smarter and have more IQ (intelligent quotient) than those who don’t. It also helps them in gaining clarity of their thoughts which leads to better concentration on other tasks.
2. Where can I learn to write a Myself Essay in English for Class 3?
Vedantu provides a comprehensive guide for students to understand the basics of writing an essay. Different types of essays are taught in an easy way that could be comprehended by Class 3 students. A Myself Essay requires a basic introduction about the student, their hobbies, their likes and dislikes. Such personal information about the student should be structured logically and coherently to produce an effective descriptive essay. The language of the essay should be minimal and clear as it should be written by Class 3 students.
3. What are the different types of essays?
There are predominantly four types of essay:
Argumentative Essay: This essay is written for forming an opinion about a certain topic after lots of research. Its purpose is to build an evidence-based argument.
Expository Essay: This essay explores what the writer knows about the topic. Its purpose is to inform others about the topic.
Narrative Essay: This essay uses creative language. It is about narrating a compelling story or experience to the readers.
Descriptive Essay: This essay uses creative language as well. Its focus is more on the sensory details and thoughts to let the readers feel the exact emotions as the writer.
4. What are the advantages of Essay Writing?
Essay writing has many advantages. To begin with, students can learn to write several simple and complex sentences at an early age. It is also one of the easiest topics to talk about since the children know what they think about themselves and their immediate surroundings. Additionally, they can discover many types of interests they may have. Furthermore, they can enhance their thinking process by imagining their future as the essay requires discussing their aspirations. This practice helps them in knowing themselves and deciding on their future goals.
5. What are the main features of writing a Myself Essay in English for Class 3 students?
A Myself essay should include personal information about the student. It should introduce the student, their family, their likes, their dislikes, their hobbies, their favourite pastime, their favourite books, favourite places, etc. The student can also write about their dreams, goals, aspirations, their understanding of the incidents, places and people around them. It should be informal and descriptive. The language should be smooth and easy to understand. The usage of words in the essay should be used creatively and in the right places.
6. How to write an essay on ‘Myself’ for class 3?
While writing essays on Myself, the kids will have to introduce themselves in the first paragraph. Some basic details like his name, his father’s name, mother’s name, etc are to be written in the first paragraph. In the next two paragraphs, kids will have to write about themselves. They may mention some hobbies, their favourite food, their favourite sport, etc.
7. What are the important points that have to be written in the essay on ‘Myself’, for class 3?
‘Myself’ is one of the easiest topics that kids may get to write an essay on in class 3. The following points may guide them to frame the essay easily.
What is your name?
How old are you?
What are your father’s name and mother’s name?
Which school do you go to?
Which class are you studying in?
What are your favourite subjects?
What is your favourite sport?
What is your favourite pastime?
What is your favourite food?
Kids-learning • Class 3
ATLANTA, MAY 23-24 PUBLIC SPEAKING CLASS IS ALMOST FULL! RESERVE YOUR SPOT NOW

- Public Speaking Classes
- Corporate Presentation Training
- Online Public Speaking Course
- Northeast Region
- Midwest Region
- Southeast Region
- Central Region
- Western Region
- Presentation Skills
- 101 Public Speaking Tips
- Fear of Public Speaking
How to Write a Graduation Speech (Graduation Speech Examples)

Have you been asked to deliver a commencement speech? Or have you worked your butt off to become valedictorian or salutatorian, and now you have to deliver a graduation speech? In this post, we will cover one of the more challenging types of presentation creation: How to Write a Graduation Speech . (By the way, I have also included a few popular graduation speech examples as a guide for you.)
This post is a continuation of our How to Create a Presentation series. We are going to break this post down into three parts, though. We will show you how to create a commencement speech in this post. Next week, I’ll show you how to write a valedictorian speech and how to deliver a salutatorian speech. Each of these graduation speeches has a slightly different purpose, but all of them need to be inspirational and funny.
How to Write a Commencement Speech
The commencement speech is often the keynote speech of the graduation ceremony. This presentation should be uplifting and entertaining, but this graduation speech should also teach a life lesson to the graduating students. If you do a search on YouTube of the best graduation speeches, many of these speakers will be famous comedians. When a comedian delivers a commencement speech, and the speech is posted on YouTube, it will always get a ton of views. The humor alone will make people want to watch the video. Three of the most popular of these speeches are by Conan O’Brien, Will Ferrell, and Ellen DeGeneres. The interesting thing about the speeches from these famous comedians is that, yes, they are funny, but the inspiration comes from what they learned from their failures.
“There is no such thing as failure. Failure is just life life trying to push you in another direction.” Oprah Winfrey, Harvard University Commencement Speech
A Good Structure When You Write a Commencement Address
Thank the crowd.

Start with Something Funny

Be Inspirational
The inspirational part of your commencement speech will come from the theme of the graduation speech . (For Sample Graduation Speech Themes , see the section below.) The easiest way to develop a theme is to look for an inspirational famous quote about success. You can do this by just going to Google and type in “success quotes”. Once you come up with a great quote, you can either paraphrase the quote and make it your own or quote the original speaker.

Tell Stories from Your Own Experience Related to Your Quote (Theme).
This the most important part of how to write a graduation speech. The stories and examples are what the audience will remember. These stories add emotion and inspiration to your graduation speech. They also help you build rapport with the audience. Finally, these stories make your delivery much easier. You don’t have to memorize a lot of material. Instead, just play the video in your head of what happened and describe the incident to the graduates.
For a great example of this, watch the YouTube video on Stanford University’s channel where Steve Jobs gives the commencement speech. I love this speech, because Jobs skips the introduction and the funny stuff and starts his speech with the following. “I’m going to tell you three stories.” It’s simple, and the crowd loves him.
End with an Inspirational Call to Action.

So as you go on to the next stage in your life and you experience failure… because you will experience failure, use that as a stepping stone to your next success. Persevere. Don’t rest on that success. Use it as a stepping stone to your next success. Persevere, and you will experience a series of successes and failures that will allow you to accomplish something great!”
Use this outline to create a simple 20 to 30 minute speech. (The shorter the better… No one gets a diploma until you finish.)
Sample Graduation Speech Themes

If you are having trouble coming up with a theme for your graduation speech, here are a few Sample Commencement Speech Themes. As you read through them, think about which them or quote has been most applicable in your career? Once you choose a graduation speech them, use the outline above to create your speech.
- Hard Work Leads to Success
“I find that the harder I work, the more luck I seem to have.” — Coleman Cox
- Create Your Own Path.
“It is better to fail in originality than to succeed in imitation.” — Herman Melville
- Make Things Happen.
“Success usually comes to those who are too busy to be looking for it.” — Henry David Thoreau
- Don’t Settle for Average. Strive for Greatness.
“Don’t be afraid to give up the good to go for the great.” –John D. Rockefeller
- Don’t Wait for the Perfect Opportunity. Look for a Way to Create Your Own Opportunity.
“Opportunities don’t happen. You create them.” — Chris Grosser/blockquote> The Road Ahead is Hard, But It Leads to Success. “Successful people do what unsuccessful people are not willing to do. Don’t wish it were easier; wish you were better.” — Jim Rohn
- Focus on Your Dream.
“The successful warrior is the average man, with laser-like focus.” — Bruce Lee
- Learn from Every Mistake to Move Toward Success.
“Success seems to be connected with action. Successful people keep moving. They make mistakes, but they don’t quit.” — Conrad Hilton
- When Your Why is Big Enough, Your How Will Appear.
“If you really want to do something, you’ll find a way. If you don’t, you’ll find an excuse.” — Jim Rohn
- Happiness is the Key to Success.
“Success is not the key to happiness. Happiness is the key to success. If you love what you are doing, you will be successful.” — Albert Schweitzer
Use the Speech Creator as a Guide to How to Create a Graduation Speech
Once you have chosen a them, and you have a few stories to inspire your audience, use our Online Speech Writer to help you organize your thoughts. (It’s free.)

Free Public Speaking Tips , Podcasts
View More Posts By Category: Free Public Speaking Tips | leadership tips | Online Courses | Past Fearless Presentations ® Classes | Podcasts | presentation skills | Uncategorized

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Use conversational language rather than formal. In your mind choose a child to give your speech to. This will help you keep it 'real'. Limit the number of main points you wish to make about your topic to one or two. Keep the formal or structured part of your speech brief. Allow time for, and encourage questions.
Tell them (Body of your speech - the main ideas plus examples) Tell them what you told them (The ending) TEST before presenting. Read aloud several times to check the flow of material, the suitability of language and the timing. Return to top. A step by step guide for writing a great speech.
1. Family. The subject of family is probably the most popular speech topic there is. Since it's about something you're completely accustomed to, it wouldn't be hard to find the right words to complete your speech. Say for example, you could make a speech about an unforgettable memory with your family.
Using powerful language. The language used in a speech should be interesting for the listeners. The acronym A FOREST is an easy way to make sure your language is powerful. It stands for: Watch ...
The opening. Start with an opening that hooks your audience before making the overall topic of your speech clear. Get their attention and prepare them to focus on the words that will follow. For ...
8. Conclude your speech with a call-to-action. As you near the end of your speech, your audience should be excited by your topic and ready to act. Encourage your audience to find out more and participate in a solution to the problem you have described by telling them how they can do so.
7. Practice in front of a test audience. Gather together your family members or friends and ask them to listen to your practice. You'll probably feel nervous, but the practice will make you more confident for the actual speech. Try to make eye contact with different members of your audience throughout the speech.
Beginning: Brief, capture the attention of the audience and establish the subject and purpose of the speech. Don't just restate the topic. Add your personality and make it unique, many others may be talking on the same topic. Middle: Sets out your ideas, shares your research, includes examples to support your topic.
Delivering the speech - 4 tips for parents. 1. Encourage your child to focus on communicating their idea to their audience. If they focus on sharing their ideas, rather than worrying about ...
When given a topic to speak on, the first thing you can do is brainstorm ideas and pen down all that comes to your mind. This will help you understand what aspect of the topic you want to focus on. With that in mind, you can start drafting your speech. An opening statement can be anything that is relevant to the topic.
This handy Speech Writing Guide PDF will help you to teach your class how to write their own speeches, using strong techniques and persuasive language. It comes with separate pages on guidance, planning and writing, making it a brilliant introduction for those who are new to this kind of writing. The templates provided will take away the pressure that comes with having a blank page, while the ...
3. Keep your ideas short but very strongly worded. Your body should be about two paragraphs of 5 to 6 sentences each. This might sound brief, considering how much information you'll have to get across, but you have limited time and must keep people's attention.
Plan where you want to finish your speech and how you will get there before you start writing . The structure of a speech is often in three parts. For example: 1. an opening that grabs your audience's attention and makes the overall topic of your speech clear - for example, pose a question to the audience where you can predict the answer. 2.
a grade 3 learner takes a good step to present a speech on behalf of their classmates with full confidence and support from their teacher
Most third-graders have little experience with public speaking. Up to this point in their education, they have had few instances in which they were required to show their smarts in front of peers through the presentation of a speech. While these early learners will likely not yet be adept public speakers, it is ...
Writing 3-minute speeches. An engaging speech may capture the attention of the crowd and properly capture the spirit of the event. On the other side, if it is poorly written or disorganised, a dozing audience will miss your point. There is no one ideal structure for a speech. You should instead choose what will resonate with your audience the most.
When outlining your speech, make sure to decide how much time you'd like to give each of your main points. You might even consider setting specific timers during rehearsals to get a real feel for each part's duration. Generally speaking, you should allot a fairly equal amount of time for each to keep things balanced.
HOW TO WRITE A SPEECHWhether you're writing a letter, dissertation, email or even a tweet, the structure of your language is important so that your reader ca...
What is a Speech?A Speech is a formal address or discourse delivered to an audience.The speech is structured around a purpose.It aims to convey that purpose ...
Speech helps them in moments like this but when it comes to recording them, students find themselves in a bind. ... Here is one type of essay students in grade 3 can write about. Try to focus on the details. Example 1: ... Essay on Myself for Class 3 Students. Essay writing tasks are included in the curriculum of the junior school so as to ...
When planning, remember to: Underline key words from the question and blurb. Underline the audience you will be delivering your speech to. Decide on your "voice" and point of view. Write a one-sentence statement that summarises your point of view. Note down the points you can develop to support your point of view.
Thank the principal/dean for the invitation to speak. Next, thank the administration. Then, thank the faculty. Thank the parents and distinguished alumni. And, finally, thank the class of [year]. Many speakers will add in a little humor here by poking fun at the typical words used in this thanks.
Listen to this episode from My Blog » Vultix on Spotify. To Download or Read Spectrum Language Arts Grade 3, Grammar Workbook, Writing Practice, Punctuation Activity ...