- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Law Studies

How to Analyze Case Law
Last Updated: January 21, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was written by Jennifer Mueller, JD . Jennifer Mueller is an in-house legal expert at wikiHow. Jennifer reviews, fact-checks, and evaluates wikiHow's legal content to ensure thoroughness and accuracy. She received her JD from Indiana University Maurer School of Law in 2006. There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 126,047 times.
When you hear the word "law," you may assume the word refers to statutes passed by Congress and state legislatures. But a major portion of American law actually is case law – the rules appellate judges distill from their interpretation of statutes and other sources. Accordingly, much of law school is spent learning how to analyze case law. However, attending law school isn't strictly necessary to acquire this valuable skill. You can teach yourself how to analyze case law, which begins – but doesn't end – with a thorough reading of the court's written opinion.
Summarizing the Facts

- The first time you read through a case, don't worry about trying to understand it. Just read for a sense of what's happening, who the major parties are, and what they want the court to do.
- Keep in mind that legal opinions aren't written for laypeople, or even for law students or attorneys – they are written for other judges. If you don't understand something (assuming you're not an appellate court judge), there's nothing wrong with that.
- You may have to go outside the opinion itself and look at other articles about the case, and then come back to it. For example, if you're reading a case that caused quite a stir in the media when it was decided, there will no doubt be newspaper and magazine articles about it. Reading those can help you better understand the court opinion.
- Many cases have summaries that appear before the case and let you know the basics of what happened, the issue before the court, and how the court resolved that issue. The summary can be helpful, but don't use it as a substitute for an initial read-through of the case.

- To make party identification even more confusing, party names may switch sides of the "v." in the case caption depending on who appealed. For example, suppose when a case began, Sally Sunshine sued Marvin Moon. The case's caption would be "Sunshine v. Moon." The trial court found in favor of Ms. Sunshine – but Mr. Moon appealed. The caption then became "Moon v. Sunshine."
- To continue the example, suppose the appellate court found in favor of Mr. Moon, but Ms. Sunshine appealed that ruling to a higher court. Now the case's caption is "Sunshine v. Moon" again.
- Since litigants in written opinions typically are only identified by their roles – appellant and appellee, for example – their names may only be mentioned once.

- Since the procedural history determines the role of the litigants, and thus what each of them is called throughout the written opinion, understanding how the case moved through the court system – who sued whom, and who appealed – is paramount to understanding the case.
- At the same time, you don't need to go into too much detail here. You just need to understand who filed the original lawsuit (which will help you understand the facts of the case), the decision at trial, and who appealed and why.

- At the appellate level, the courts are concerned with legal issues, not questions of fact. So, for example, if you are reading a case that came about as a result of a bar fight, the factual question of whether one party assaulted the other has already been resolved.
- In many cases, the initial facts that prompted the dispute may be summarized in a sentence or two. Often, what's really important is what happened afterward.
- Keep in mind that not all judges are the best writers. While you may be tempted to believe a particular fact is important because the judge who wrote the opinion spent several paragraphs discussing it, this is not necessarily the case.
- As you read more and more cases, particularly if the cases you read are focused on a particular court, you will become familiar with the styles of individual judges. This can make it easier for you to immediately notice when the judge is focusing on facts he or she believes are central to the case's holding.
Identifying the Issue and Decision

- Essentially, you're looking for what the person who appealed the lower court's ruling wanted to happen, that didn't. To find the issue, you must figure out what that person thought the lower court did wrong, and why.
- This usually isn't about something as simple as one person believing he should have been awarded more money, or a criminal defendant not wanting to go to jail. That might be part of an appellant's personal motivation, but to have a legitimate appeal you must be able to point to some way that the lower court made a legal error.
- In many cases, the legal error isn't an obvious error. The lower court may have applied the law correctly – but the appellant is arguing that her case is different from the cases that developed the rule the lower court used, or that the lower court should have used a different rule.
- Often in Supreme Court cases, there isn't a rule that can be handed down from previous cases and applied in this case, because no court has ever decided a case like this one. In these situations, it's up to the court to figure out how to tackle this new issue, and where it fits in to the long line of American jurisprudence.

- In some cases, the issue before the court involves multiple yes/no questions, or a follow-up question that is conditional on the answer to the first.
- This usually happens when a particular factual situation present in the case has never been explored by any other court. The court must first determine whether a particular law applies to that factual situation at all before it can decide how the law applies.
- For example, suppose a baker has been fined by the local government for creating cupcakes with expletives written in icing. The court may first have to determine whether icing on cupcakes is the sort of speech or expression protected by the First Amendment, before it can reach the real issue of whether the baker's First Amendment rights have been violated.

- Some judges have a very clear, straightforward writing style, and they'll phrase the issue as a question and answer it directly. However, this isn't usually the case. In most written opinions, you should expect to dig for the question and answer, which you'll have to craft yourself.
- When more than one question is asked, sometimes the answer to the first takes care of all the others. To look at the earlier cupcake-icing example, if the court had determined that no, icing on cupcakes is not protected by the First Amendment, the second question disappears. You don't have to consider whether the baker's First Amendment rights were violated by the fine, because she didn't have any First Amendment rights in the first place.
- When the answer is qualified with a "sometimes," any conditional questions that follow likewise will have qualifications. #Note any significant dissents. In many cases, particularly at the Supreme Court level, a justice who disagrees with the majority will issue a dissent. As time passes and court interpretation evolves, a significant dissent may end up being a majority opinion later on when the court reverses or overturns an earlier decision. [12] X Research source
- There also may be concurrences, which are separate opinions written by justices who agree with the ultimate outcome of the case, but not with the reasoning the majority applied to get there. Often a concurrence can help you understand the majority's reasoning, particularly if it seemed convoluted on first read.
- Unless you understand where the case you're reading falls in the history and development of that particular area of law, you may not be able to recognize which other opinions are important until you do further research.
- If you're unsure, it's best to simply note other opinions – be they dissents or concurrences – and the key difference between them and the majority's opinion.
- Especially if you're reading a Supreme Court case, you also should note which justice authored the dissent or concurrence. As justices leave the court and are replaced, the values and judicial temperament of the majority also can change.
- A dissent from a decade ago may become a majority opinion tomorrow – often written by the same justice, now carrying the majority where he or she once held a minority view.
Understanding the Reasoning

- Make note of the case from which the rule came, although typically it's not necessary for you to go back and read the case itself to understand the rule.
- However, if a significant portion of the opinion discusses the previous case, you may want to go back and read it as well so you have a better understanding of what the court is talking about.
- In some opinions (especially those penned by judges with straightforward writing styles), the rule used by the court will follow trigger phrases such as "the rule we apply is" or "we decide this case by applying the rule from" – phrases that alert you the court is about to tell you exactly what rule they used.
- Most opinions won't be this direct, and require a closer analysis of the language to ascertain the rule the court used. Sometimes you can figure this out by working backwards. Read the court's decision, and then follow the court's train of logic in reverse until you reach the rule.

- The application of a legal precedent to the facts of a case is the heart of legal analysis. This typically is done using similes. Seldom has the exact issue been presented before – to make a decision, the court must determine that this case is like a different case, and therefore the same rule should apply.
- Keep in mind that, especially if you're analyzing a Supreme Court case, the court wouldn't have accepted that case on appeal if it didn't present a new issue that had not already been decided in an earlier case.
- For this reason, there likely won't be a precedent that is entirely on point, or a previous case with the same fact pattern in which the same issue was raised and decided.
- Rather, the court must compare cases to find a rule that applies closely and is based on a similar situation that is analogous to the dispute presented.

- Sometimes the easiest way to locate the court's pivotal fact or facts is to consider what would have happened if they'd chosen to focus on a different fact.
- For example, if the court in the case of the beleaguered baker had decided to focus on the fact that cupcakes are food, and food has never been protected under the First Amendment, it might have arrived at a different decision than it did. Because the court focused instead on the fact that the baker wrote words with icing, just as writers write words in ink, and concluded that written words inarguably enjoy First Amendment protection.
- Although many other facts may be relevant, or important to some other aspect of the case, those aren't the facts that made the court rule the way it did.

- No court case exists in isolation. Once a court issues a decision, the legal interpretation and rules it establishes become part of the larger body of law devoted to that particular issue. Each opinion helps future courts understand more about the statute or constitutional provision at the heart of the case.
- You don't have to wait for future courts to apply the rule you've just learned to other cases, however. Take the facts in the original case and twist them slightly, then apply the rule yourself.
- Law professors call these imaginary cases "hypotheticals," and spend a good portion of class churning them out and asking their students to apply the rule they've learned to sometimes bizarre and convoluted stories.
Expert Q&A
You might also like.

- ↑ https://www.gareth-evans.com/how-to-read-understand-and-summarise-legal-cases/
- ↑ http://www.lexisnexis.com/en-us/lawschool/pre-law/reading-a-casebook.page
- ↑ https://www.monash.edu/learnhq/write-like-a-pro/annotated-assessment-samples/law/law-case-note
- ↑ https://utas.libguides.com/legal_research/caselaw
- ↑ http://www.cengage.com/resource_uploads/downloads/0324654553_91282.pdf
- ↑ https://lawschool.westlaw.com/marketing/display/SG/3
- ↑ http://www.csun.edu/~kkd61657/brief.pdf
About This Article

Case law refers to the decisions appellate judges make from their interpretations of former cases. To analyze specific case law, you’ll need to read the case through and try to get a feel for how the court made their decision. It can be pretty complex when you’re first reading a case, so jot down the main parties, the main dispute, and a brief history of the case to help yourself keep track. Once you understand the case, try to identify the legal rules the court used to make their decision. It’s also helpful to imagine different scenarios where the rule the case established could be applied, and whether or not the outcome would be the same. To learn how to focus on the most important facts of a case, read more from our Legal co-author! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Ibrahim Abubakar
May 8, 2021
Did this article help you?
Feb 6, 2019
Busisiwe Nyezi-Zikizela
Feb 9, 2020
Isreal Van de vaar
Mar 30, 2020
Sep 4, 2020

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter

Case Studies
The program’s portfolio of situational case studies presents narratives of real-life events and asks students to identify and analyze the relevant legal, social, business, ethical, and scientific issues involved. Playing the role of protagonist in each case study—such as a private attorney counseling a biotechnology company facing hazardous waste issues, or a federal official seeking to develop an effective fishery management plan—students formulate appropriate strategies for achieving workable solutions to conflicts, then discuss and debate their recommendations in class. This interactive approach to learning bolsters students’ acquisition of skills in critical areas: factual investigation, legal research, counseling, persuasive oral communication, and recognition and resolution of ethical dilemmas, to name a few.
The Stanford Law School Case Studies Collection is an exciting innovation in law school teaching designed to hone students’ problem-solving skills and stimulate creativity. The Collection includes situational case studies and interactive simulations (collectively referred to as “Case Materials”) that place students in the roles of lawyers and policy makers and teach fundamental lawyering skills such as investigating facts, counseling, and resolving ethical dilemmas.
In June of 1997 the Environmental and Natural Resources Law Policy Program hired an experienced environmental lawyer to develop “situational” case studies for use in classroom instruction to better prepare students for the practice of law in the real world. Most of the case studies have been field tested in the classroom and evaluated for effectiveness in increasing student mastery of fundamental lawyering skills and increasing student participation in classroom discussion. Feedback from students has been excellent. Stanford Law School plans to unveil case studies collections in the areas of Law and Business in the coming years.
You can use this site to download Case Materials for examination. With prior permission from Stanford Law School, instructors can also obtain copies of Case Materials they want to use in the classroom for free. This Case Studies Collection will be updated regularly as we add new Case Materials and revise existing Materials, so visit the site from time to time for new developments!
As used in our website, the phrase “case materials” refers to case studies and simulations, as well as accompanying exhibits and teaching notes. While both case studies and simulations can be used as tools in the “case study teaching method,” they are different in form and manner of use. A case study is a narrative that recounts the factual history of an event or series of events. It is typically used as the basis for in-class analysis and discussion. A simulation is a set of facts, roles and rules that establishes the framework for an in-class participatory exercise.
Research has shown that existing law school teaching methods and curricula do not adequately teach students the full complement of “lawyering” skills they need to competently practice law. The traditional appellate case method assumes that a problem has reached a point where litigation is the only alternative, and presents students with a scenario in which all relevant issues have been identified, the questions of law narrowly focused, and the questions of fact resolved. Skills-oriented courses and clinical programs (such as law clinics and externships) have made significant contributions to law schools’9 ability to teach lawyering skills. Their reach, however, has been limited by a combination of factors, including their high cost and the relatively few law students who actually take advantage of these programs.
While we do not envision the case study method displacing the appellate case method or clinical programs, we do believe that the case method can be used in conjunction with existing teaching methods to add considerable educational value. Case studies and simulations immerse students in real-world problems and situations, requiring them to grapple with the vagaries and complexities of these problems in a relatively risk-free environment – the classroom.
Incorporation of case studies and simulations into environmental law school curriculums can bolster student skill acquisition in the critical areas listed below. Based on a 1990-1991 American Bar Association questionnaire, the MacCrate Task Force concluded that traditional law school curricula and teaching methods fall short in teaching these fundamental lawyering skills:
- problem solving
- legal research
- factual investigation
- persuasive oral communications
- negotiation
- recognizing and resolving ethical dilemmas
- organization and management of legal work
The case study teaching method is adapted from the case method developed and used successfully for many years by the nation’s leading business schools. The method uses a narrative of actual events to teach and hone the skills students need to competently practice law. Students identify for themselves the relevant legal, social, business, and scientific issues presented, and identify appropriate responses regarding those issues. Suggested questions for class discussion are prepared in connection with each case study, itself the product of long, probing interviews of the people involved in the actual events. These narratives, or case studies, may be long or short, and portray emotion, character, setting and dialogue. Students present their thoughts on key issues during class discussion, usually from the viewpoint of the key protagonist in the case study.
Simulations are typically used to reinforce and synthesize concepts, skills and substantive law already covered in a course. The simulations are designed for limited instructor and maximum student involvement during the exercise itself. However, once the exercise has drawn to a close, ample time should be allotted for a debriefing session. During the debriefing, instructors and students can engage in a candid discussion of the relative effectiveness of different approaches used during the simulation, clear up any lingering questions about substantive issues, and probe ethical and/or policy issues raised by the simulation.
Requesting Permission to Copy or to Use Materials
Send your request for permission to use or copy Case Materials to [email protected] . To assist us in reviewing such requests and tracking the actual use of our Case Materials, please provide a description of the course (of up to 500 words) for which the Case Materials will be used. In addition, please include a brief description of the kind of course for which the Case Materials are intended, including:
- Whether the course is an elective or required course, undergraduate, graduate, or continuing education.
- The nature of the academic program and institution in which the course will be taught, such as law school, business school, Earth Sciences department, public interest law firm, etc.
- The number of times the course has been offered.
- Expected enrollment for the course.
- The history of the course’s development.
The Case Studies Blog | Harvard Law School

- Discussion Forum
- Worker Centers & OUR Walmart: Case studies on the changing face of labor in the United States

Photo credit: The All-Nite Images from NY, NY USA on Wikimedia Commons
A q&a with sharon block, executive director of the labor and worklife program and lecturer on law at harvard law school.
by: Lisa Brem*
Recently, HLS Case Writing Fellow Brittany Deitch and I worked with Sharon Block , Executive Director of the Labor and Worklife Program at Harvard Law School , to create two case studies for her spring 2018 seminar entitled “Organizing for Economic Justice in the New Economy”: the first case study — “ Worker Centers ” — explores how worker centers have grown in both numbers and power as they seek to fill the gaps left by the decline of the union movement in the United States. Part 1 of the case study examines the challenges and opportunities faced by the New Orleans Workers’ Center for Racial Justice and its affiliated National Guestworker Alliance. Part 2 gives a brief overview of the legal framework that defines and affects labor and workforce issues in the United States.
The second case study — “ OUR Walmart: Online-Offline Organizing ” — showcases a different model of worker organization that grew from employee activities at Walmart. Students reading both case studies will be able to analyze and draw conclusions about the efficacy of different types of worker centers and the roles they play in the larger workforce ecosystem.
Lisa Brem (LB): Why did you choose to create these case studies for your course?
Sharon Block (SB): One of my objectives in teaching this course was to demonstrate to students that this is a very exciting time for people interested in economic justice issues. Because of the historically low levels of union density in our country, more and more energy is going into testing how the law can facilitate new forms of worker organizations. There are a number of innovative and dynamic people leading these organizing efforts. They are confronting many new and challenging legal and strategic questions. With these case studies, I hoped to help students put themselves in the shoes of these leaders so they can appreciate how interesting work in these kinds of organizations can be.
LB: What challenges and opportunities did teaching these case studies present?
SB: One challenge presented by teaching these case studies is that they each capture a story that is on-going. Many case studies look back at a scenario that has already resolved so that students can see the outcome of the decisions that are the subject of the case studies. In contrast, these case studies address situations that are still unfolding – some consequences of the decisions analyzed are clear but many are not. Because I was able to have the principle players in the case study scenarios come to class, I hope that that challenge became an opportunity. The students were able to feel more involved in the scenarios and even feel like they may have an impact on the outcomes of these unfolding stories through the questions and issues they were able to raise with the principals who came to class.
LB: What are the major takeaways that students will learn by reading and discussing these case studies?
SB: I hope that the major takeaways that students will learn will be: (1) although laws may be enacted for a particular purpose, their impact may change over time, producing very different results than those intended; (2) creative lawyers can use the law as a tool to advance policy objectives that may be very different than those intended by the laws’ drafters; and (3) moments of crisis can create great opportunities for trying new solutions to old problems.
LB: How did the students react to the case studies?
SB: The students seemed to enjoy the immediacy of the situations covered in the case studies. I enjoyed seeing how the case studies gave them a new perspective on situations that were familiar to them. For example, all of the students were familiar with Walmart and many had patronized Walmart stores. The OUR Walmart case study gave them new insights into what it was like to work at a Walmart and the community among Walmart workers that would not be evident to customers. Similarly, most of the students knew generally about the impact of Hurricane Katrina on New Orleans but learned a great deal more about how long-standing and complex the impact of the storm was on the New Orleans labor market and the lives of the people who lived and worked there.
LB: What would you tell (advice you would give) other faculty looking to use these case studies?
SB: I would recommend that if faculty use these case studies with students who haven’t taken labor law, that they spend a little time helping students understand traditional worker organizing so that the students can appreciate how innovative the leaders featured in these cases studies are.
Learn more about the Worker Centers and OUR Walmart and download both case studies for free on our website.
Quick facts on Worker Centers:
Case Study length: 37 pages including attachments. The case study includes Part 1 (general background, 22 pages) and Part 2 (legal background, 15 pages).
Format: Worker Centers is best used to facilitate an 80- to 90-minute in-class discussion on worker centers in general, and the issues facing the New Orleans Center in particular. Some or all of the discussion questions listed in the teaching note can be provided to students prior to class along with the case study, to allow them to formulate ideas that they can share in class.
Quick facts on OUR Walmart:
Case Study length: 8 pages including attachments.
Format: OUR Walmart is best used to facilitate an 80- to 90-minute in-class discussion on worker centers in general, and the issues facing OUR Walmart in particular. Some or all of the discussion questions listed in the teaching note can be provided to students prior to class along with the case study, to allow them to formulate ideas that they can share in class.
Teaching Notes for both case studies are available for free download to qualified educators on Harvard Law School | The Case Studies website. Note that you must be logged in as a registered educator on our site to download teaching notes.
*Lisa Brem is the Managing Director of Teaching, Learning & Curriculum Solutions (TLC) at the HLS Library. The Case Studies Program and Case Development are integral parts of the TLC.
Share this:
- Robbing the Piggy Bank? Moving from mutual to stock form at Friendly Savings Bank

A Q&A with Harvard Law School Professor Holger Spamann
by: Lisa Brem
Corporations and corporate finance courses typically spend the majority of their time talking about the stock form of corporate organization, which makes sense, given that this is the dominant form used by businesses in capitalist economies. However, Harvard Law School Professor Holger Spamann spent his last Corporations class of the semester teaching a case study about something quite different: the mutual form. Yes, this is the organizational form memorialized in the classic film “It’s a Wonderful Life” in which Jimmy Stewart famously played the part of small community bank champion George Bailey. Why spend time in a corporations course talking about a mutual bank? We asked Professor Spamann about Friendly Savings Bank and why he and his co-author Stanley Ragalevsky created this case study.
Lisa Brem (LB): Why did you choose to create this case study for your course?
Holger Spamann (HS): I wanted something to engage broader questions about corporate organization and purpose. The mutual form presents a counter model to the shareholder(-value) driven corporate form, and it is successful at least in a limited realm. It is, therefore, a good launch pad for discussion. The case also raises questions about the role of the lawyer, particularly if one comes to believe that the management is essentially “robbing the bank” in this case.
LB: What challenges and opportunities did teaching the case study present?
HS: We try to draw students into the case by putting them in charge: they lead and present at the hearing. The risk is that you get off track, or rather off timing. It requires setting a strict timetable and reminding the students of it periodically.
LB: What are the major takeaways that students will learn by reading and discussing this case study?
HS: At a minimum, they will be aware that it is possible, at least in a limited realm, to have successful commercial entities that are not controlled by, and operated for, investors. Perhaps they will come to think that these entities have advantages in certain areas, and they may think that the bank lawyers in this case were operating in questionable territory. But that all depends on the view they end up taking on the merits of this case.
LB: How did the students react to the case study?
HS: Generally favorably. Some didn’t get the connection to the big question about entity structuring, which I will make sure to emphasize more next time.
LB: What would you tell (advice you would give) other faculty looking to use this case study?
HS: Watch the clock!
Learn more about the Friendly Savings Bank and download it for free on our website.
Quick facts on Friendly Savings Bank:
Case Study length: 39 pages including attachments.
Format: Can be taught in an 80 or 90-minute class discussion or taught as a role play simulation in a 2-hour class session. The simulation has three roles: lawyers for the Regulators, Bank Management, and Dissidents; the Management and Dissident groups take turns presenting their arguments to the Regulators, who make a final determination as to whether Friendly Savings Bank can convert from mutual to stock form.
Teaching Note available for free download to qualified educators on Harvard Law School | The Case Studies website . Note that you must be logged in as a registered educator on our site to download teaching notes.
- The Argument for Active Learning

Multiple studies have shown that active learning is more effective than lecturing at achieving educational outcomes. One large 2014 meta-analysis of STEM classes found that average student failure rates decreased from 34% to 22% and that average student performance improved by half a letter grade when active learning replaced traditional lecturing. Given these findings, imagine the savings in tuition dollars if active learning were to be widely implemented. When it comes to assessments, researchers looked at concept inventories (which measured higher-level cognitive skills) and course examinations (which measured lower-level cognitive skills). While both higher- and lower-level skills were improved, they found that “active learning has a greater impact on student mastery of higher-versus lower-level cognitive skills”. In addition, the authors found that active learning disproportionally benefitted female and disadvantaged students.

The case study method, which encourages students to step into the shoes of a case study protagonist to wrestle with a real-world dilemma, is a proven active learning pedagogy. The use of discussion and problem-solving via a case study can heighten student engagement, critical analysis, and reflection, thus creating conditions that foster transformative learning. This can be true for both small groups and large classes, either peer-directed or facilitated by an instructor.
By using these case studies in your classroom, you can encourage innovation and inclusivity while you watch student outcomes improve.
Freeman, S., S. L. Eddy, M. Mcdonough, M. K. Smith, N. Okoroafor, H. Jordt, and M. P. Wenderoth. “Active learning increases student performance in science, engineering, and mathematics.” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 111, no. 23 (2014): 8410-415. Accessed March 13, 2018. doi:10.1073/pnas.1319030111.
- Spotlight on: International and Comparative Law

Photo used under Creative Commons Licensing, Earth seen from the International Space Station.
“The flow of goods, technology, ideas, capital, and people across borders means that the work of lawyers, whether in private practice or public service, increasingly involves matters in which knowledge of legal systems beyond one’s own can prove important.” — from International and Comparative Law Overview, hls.harvard.edu.
HLS Case Studies authors have compiled several case studies that have an international or comparative law component. Continue reading to learn more about these case studies.
The WikiLeaks Incident is a workshop-based case study designed as a background document to set the stage for several hypothetical classroom exercises during which students play the roles of various stakeholders to broaden their understanding of the issues involved. The 2010 WikiLeaks shared leaked U.S. government documents, many of which were classified, resulting in legal maneuvering and tensions between Wikileaks, its critics, and its supporters. This case encourages students to ponder the question: What is the lawfulness and ethics of the actions taken? Students will analyze the government’s reaction to a large amount of classified material being published online, explore ways to respond appropriately to future leaks of sensitive material from the point of view of various stakeholders, and discuss ways in which the Internet as changed whistleblowing activity as well as the legal ramifications of these changes.
This case was developed for an Advanced Problem Solving Workshop in Cyberlaw and Intellectual Property, a second- or third-year elective course taught in the Harvard Law School J.D. program. The case can be taught in four 90-minute class sessions.
Sanctuary Cities asks students to engage in a legislative simulation before the House Subcommittee on Immigration and Border Security. The subcommittee hears testimony from various groups on a proposed House bill that would cut federal funding to sanctuary jurisdictions. Students play the roles of majority and minority members of the subcommittee, representatives of various organizations with an interest in the proposed legislation, and correspondents from different media outlets .
This simulation could be taught in Immigration Law courses, or seminars and clinical seminars on immigrant rights and advocacy. It could also be used in Legislation and Regulation courses.
“I wanted the students in my immigration law class to engage with the complex legal issues presented by the current debate over sanctuary policies and was eager to facilitate a productive debate.” – Professor Sabrineh Ardalan
Click here to read more on case Professor Ardalan’s comments about this case study.
The Case of the Lead Toys is a workshop-based case study that follows the story of toymaker Mattel that came under fire in 2007 when one of its European retailers found lead paint on some toys manufactured in China. The case asks students to play the role of the General Counsel for Mattel, determine what questions to ask their client, and draft a press release to communicate to the public about the crisis. The problem fits in the general category of avoiding trouble or distributing losses that have already occurred. Students will discuss whether lawyers should advise clients as if they were solely interested in taking maximum advantage of their legal rights or if their advice should encompass the full range of the client’s concerns, engaging the client’s moral compass in deciding whether it is right to pursue a legally-available objective.
This case was developed for the Problem Solving Workshop, a second-semester required course taught in the Harvard Law School first-year J.D. program. It has been used as the introductory case to highlight decisions faced by lawyers working directly for and with clients. The case can be taught in four hours over two sessions.
Ching Pow: Far East Yardies!! is a workshop-based case study based on the story of Jamaican filmmaker and entrepreneur Bruce Hart, who set out to make a low-budget box office hit called “Ching Pow: Far East Yardies!!,” a satirical redubbing of a kung fu movie that appeared to be in the public domain. However, with sponsorship secured and production underway, Hart discovered that there existed a copyright holder to the original film. This case follows Hart’s international quest to find the copyright holder and secure permissions to release his movie. Readers will take the stance of Bruce Hart’s lawyers and parse out the distinctions of derivative and orphan works in intellectual property law, identifying a systematic approach to problem-solving when faced with an unresolved issue.
This case was developed by Professor Charles Nesson for an elective course for the Harvard Law School J.D. program. Educators may want to pair this case study with a discussion of the United States’ unique policy of statutory damages in copyright infringement cases. This case can be taught in two 90-minute sessions.
So ma lia in Crisis: Famine, Counterterrorism, & Humanitarian Aid ( Part A , B1 , B2 ) is a free, 3-part case study that forefronts the 2011 Somalia famine to ground the teaching of International Humanitarian Law (IHL) with a real-world application.
Part A is a workshop-based case study that provides an opportunity for students to examine the potential impacts of U.S. material-support-to-terrorism laws in the context of humanitarian crises, through the lens of the Somalia famine. Participants are primed to problem solve, navigate potentially competing domestic and international law and policy, and make ethical and legal decisions in a high-pressure, complex international crisis. Then, in Parts B1 and B2, students will engage in role play exercises designed to expose the challenges in developing a consensus response among U.S. government agencies to a humanitarian crisis where a terrorist organization perceived as threatening U.S. security interests is involved.
Part B1 is best suited for two class periods spanning 90 minutes each. Part B2 can be taught in one or two class periods spanning 90 minutes each.
“…role-play exercises such as the Somalia Case Study help to contextualize IHL, introduce students to law’s real-world application, and potentially galvanize ideas about legal reform.” – Professor Rebecca Sutton
Check out our 4-part blog series about what students of Professor Rebecca Sutton’s Re-Imagining International Humanitarian Law course at the University of Western Ontario Law School thought about the use of this roleplay in a course on International Humanitarian Law. Read Part 1 , Part 2 , Part 3 , and Part 4 .
Want more? Browse through our 25 case studies that incorporate aspects of international and comparative law on our website .
Click here for more on International and Comparative Law at Harvard Law School and visit the Institute for Global Law and Policy .
- Fair Use Week: 5 Questions with Kyle Courtney
In honor of Fair Use Week , we are reposting our blog about our case study: How Fair is Fair Use? The Battle Over E-Reserves at GSU (A) and (B)
Since it was published, this case study has been downloaded 82 times.

Kyle Courtney, Copyright Advisor at Harvard University
Kyle K. Courtney, Harvard University’s Copyright Advisor in the Harvard Library Office for Scholarly Communication, wanted to develop a case study on the contentious institution of fair use at a university. He chose to focus on electronic reserves at Georgia State University, which faced a copyright infringement suit from Cambridge University Press, Oxford University Press, and Sage Publications. The case shows how the four factors of fair use, which are designed to support educational use and engender case-by-case analysis of copyrighted works, got caught in the crossfire between educators and publishers over extralegal, universal guidelines. What better format to bring fair use back to case-by-case analysis than a discussion-based case study?
Courtney first introduced the case study in his Copyright Immersion Program for Harvard University librarians designated as “Copyright First Responders.” Courtney has plans to use the case in his cyberlaw class at Northeastern University, which attracts students in law, criminal justice, and computer science. Courtney plans to teach the case in a continuing legal education program and to use taped segments of the Copyright Immersion Program for a massive open online course (MOOC). This case study could fit well in a number of other educational settings, such as intellectual property courses and professional development for general counsels or university officials.
Courtney shared with us his experiences as a first-time case study author:
EM: What inspired the case study?
KC: This was one of the most important library fair use cases in the last decade. It also marks a new era, one in which university presses sue university libraries. It’s a shift in the legal landscape.
This case involved a weighty decision for GSU: whether to go to trial and how to measure risk. It involved a lot of judgment, and judgment isn’t taught enough. This seemed like the ideal case for a teaching moment.
EM: What challenges and opportunities did the case writing process present?
KC: It was a challenge to lay out everything that happened before the suit: the GSU case itself represented a particular moment when decades of contention came to a head. There was very little precedent but so many forces at play: the libraries’ reliance on reserves, technological leaps, changing publishing models, and the challenges of copyright intersecting and sometimes interfering with education.
It was a rare opportunity to look inside at how these forces interact. It was a 353-page decision: you can’t not write a case study on that!
EM: What advice do you have for case writers and teachers in the legal classroom?
KC: Getting up to speed on the law can be complex. Spend time on the introduction: engagement with the first part is critical to having a good discussion because it sets the scene and establishes the foundation for the discussion. When I first taught the case, my students had to get up to speed on how the law had been interpreted in the past. For this reason, I’m not sure the case should be taught in one sitting.
I had my participants in teams representing multiple sides, because for them, identifying with libraries was already easy. By asking different teams to reach a middle ground you bring in negotiation. Where are there areas for wins? What do the sides have in common?
We also explored what other schools, like Cornell, have done with similar suits in the past and about what would happen if an institution chooses not to fight. I did this as a lark at the end, but it was a great exercise.
EM: How did the students react to the case study?
KC: They really liked it—even I was surprised at the amount of enthusiasm generated by something as routine as e-reserves. The case led to a robust discussion. I think the participants realized that their work today may have an impact on the law!
Case studies are great because they reflect the front-line problems that education has with copyright law. Capturing these problems is complex but proves that these issues can be reasoned, analyzed, and addressed. Cases give front-line people the sense that there is ground to be gained and that their newfound knowledge will serve them as better employees.
EM: What, if anything, would you do differently next time?
KC: I might spend more time hitting home the points in the introduction. With busy professionals, you can’t be sure they’ve read the whole case.
More generally, I think it helps to integrate case studies into classes where you’re building copyright law. Substantive legal courses don’t normally include opportunities for role play, but it’s a critical skill using the analytical side of your brain.
Our Bestselling Cases
Harvard Law School | The Case Studies has served 7,986 customers , published 220 cases , and fulfilled 8,152 orders over the last 6 years. Here is a list of our top 5 bestselling case studies:

2. Ernest Shackleton’s Journey to the Endurance describes the path that led Ernest Shackleton to embark on his epic voyage to the Antarctic aboard the Endurance in 1914. The case, a compelling saga of crisis and survival, allows instructors and students to review what happened during the voyage and explores what is required for effective teamwork and leadership in the face of turbulence.
3. William Fox follows the life and career path of William Fox, a mid-career partner at a prestigious law firm in London. This case enables participants to reflect on how to evaluate one’s career trajectory, the balance between commitments to work and personal life, and how the meaning of “success” might evolve over time.
4. Linklaters (A): Seeking Clear Blue Water follows Linklaters managing partner Tony Angel as he seeks to implement his vision for the global law firm. This case allows participants to discuss the importance of creating and articulating a clear strategy in a professional service firm, the challenges related to implementing such a strategy, and the considerations that lead to a successful change management.
5. How to Approach a Case Study in a Problem Solving Workshop is a free product that gives helpful tips for approaching problem-solving case studies and effectively reading these cases to prepare for discussions and exercises.
In 2017, HLS Case Studies published 16 new case studies , 11 of which are free to download . Browse all 40 free case studies , including Bank Secrecy Act, Anti-Money Laundering Law Compliance, and Blockchain Technology , the most popular case study published in 2017.
Negotiation instructors might want to review Mortgage Crisis Call , our most viewed new case, which has been viewed nearly 20,000 times since it was published in January 2017. This case is a multiparty negotiation scenario that provides an introduction to group decision making. It is set in the aftermath of the 2008 U.S. residential mortgage crisis, which left more than ten million homes foreclosed.
Please view the full catalog of cases published in 2017.
New Product: Sanctuary Cities: The Legislative Hearing

Photo used under Creative Commons Licensing, Statue of Liberty.
Q&A with Professor Sabrineh Ardalan
Harvard Law School | The Case Studies has published a new case study and classroom simulation developed by Sabrineh Ardalan, Assistant Clinical Professor at Harvard Law School and Assistant Director at the Harvard Immigration and Refugee Clinical Program, along with Brittany Deitch, J.D. Case Writing Fellow, and Lisa Brem, Managing Director of the Teaching, Learning and Curriculum group at HLS.
The case study includes a background note on sanctuary jurisdictions and a roles for six stakeholders who present comments and testimony at a mock legislative hearing on a bill affecting such jurisdictions.
Our Case Studies Program staff asked Professor Ardalan about her experience developing and teaching the case study. Read her answers to our questions below, and download free copies of Sanctuary Cities .
Why did you choose to create this simulation for your course?
I wanted the students in my immigration law class to engage with the complex legal issues presented by the current debate over sanctuary policies and was eager to facilitate a productive debate. A legislative simulation seemed like the ideal format for the class, particularly given the various legislative proposals introduced in Congress, as well as in city councils and states across the country.
What challenges and opportunities did teaching this simulation present?
The simulation allowed for both sides of the debate to have equal airtime so that students could fully understand the arguments for and against sanctuary-related policies and legislation. It was a challenge deciding what legislative initiative to use to allow students to explore the issues most fully, and we considered various bills pending at the state and federal level before making a decision.
What are the major takeaways that students will learn in this simulation?
Students will learn how to distill complicated legal arguments into clear, persuasive, and concise talking points and how to think through their strongest and weakest arguments in order to respond to questions and provide comments on testimony.
How did the students react to the simulation?
The students were very engaged both in the simulation itself and in the preparation for the simulation. They worked well in teams to develop testimony, arguments, and questions.
What would you tell (advice you would give) other faculty looking to use this simulation?
The more time you can allocate to debrief, the better. I wish I had built in additional space for a group discussion and feedback afterwards. Also, I would recommend bringing in advocates who have attended or testified at prior Congressional hearings to participate in the simulation, either by chairing the committee hearing or by commenting on the simulation and the issues presented after the fact.
Acknowledgments
I was lucky enough to have two amazing lawyers – JJ Rosenbaum , formerly the Legal Director with the New Orleans Workers’ Center for Racial Justice which led efforts in New Orleans and advocacy efforts at the Congressional hearings on New Orleans as a Sanctuary City , and Avideh Moussavian , who works on sanctuary issues at NILC – chair the hearing for the simulation, which greatly enhanced the experience for everyone involved.
Strategies for consensus-building and decision-making
Sabrina Bruno and Eric Blay
This is the fourth in a series on the use of Somalia in Crisis role play in a law school course on International Humanitarian Law. Read the Introduction.
The goal of the Somalia simulation was to help bring an end to the Somalia famine quickly without compromising American national security. There were numerous disagreements between opposing interest groups that necessitated consensus-building. While members of each of the parties were behaving as rational actors, individuals’ differing objectives led them to become quickly entrenched in their assigned positions. This tended to make them lose sight of the overall goal of the meeting, which was to develop a strategy for ending the famine in Somalia.
Our team played the advisory role of the intelligence agency. Striving to help build consensus with others while serving in an advisory role was challenging. It was imperative to remain in character—advocating the priorities of the intelligence agency—throughout the simulation. Differentiating between personal opinions and the insights that our assigned character was likely to espouse was challenging, but vital. In an advisory role, it is important to be aware of the seemingly incompatible agendas held by different parties. Equally necessary is to work with participants to identify underlying interests that might provide grounds for formulating solutions that meet everyone’s objectives to some extent. While each party held different principal priorities, their overarching goals seemed to converge. For instance, a central aim of all parties was to ensure the safety of American citizens, though each group differed as to how that safety could be achieved.
Reaching consensus among the groups was a difficult task. They became immersed in their assigned character roles and tended to focus on the issues that divided them rather than emphasizing what they had in common. It seemed that all parties felt that, despite being ordered to end the famine quickly, their specific interests ( i.e. legal, security, humanitarian, etc.) had to take up equal space at the bargaining table. In actual negotiations of this type one would hope that objective criteria, such as feasibility, would govern the final decisions, instead of having the final word going to the most forceful individuals who took the strictest hard-lined positions.
Allowing time for discussions amongst the representatives of the various teams was an effective strategy; it allowed multiple conversations to occur simultaneously, and created space for groups to identify similar interests as well as obstacles to reaching consensus. In comparison with the time spent having all participants met as one group, it seemed that the more chaotic intermingling of groups was much more efficient. Considerable decision-making work was done by group representatives who liaised with other interest groups to garner support for their position, or to collaborate on ideas for mutually acceptable solutions. This allowed them to present a united front to other, more ideologically opposed groups. A breakthrough came when groups accepted that compromises would have to be made by all parties. When given sufficient time to discuss amongst themselves, groups were able to create a unified plan, with the exception of concerns about fungible aid and the payment of access fees to FTOs. The result was a semi-secure and partially effective solution.
This simulation was a useful exercise for learning how human character and subjectivity influence policy-making processes. All aspects of strategy for the response to the Somalia famine were heavily influenced by the personalities and proclivities of the individuals who participated in the negotiation. The most significant thing we learned was that, in practice, the negotiation process is not ruled by objective criteria so much as the subjective views of participants. No matter what the nature of the factual scenario at hand is, it is clear that negotiation, mediation, and conciliation skills are crucial to navigating the entrenched positions of various stakeholders. Read Part 2 and Part 3 .
Written by law school students Sabrina Bruno and Eric Blay as part of the Re-Imagining International Humanitarian Law course at University of Western Ontario Law School.
Discerning the interests and priorities of diverse stakeholders
Katrina Younes, Rob Alfieri, Aaron Zaltzman
This is the third in a series on the use of Somalia in Crisis role play in a law school course on International Humanitarian Law. Read the Introduction.
During the simulation of a National Security Council (NSC) meeting regarding the 2011 Somalia Famine, we observed that the first step for building consensus between parties espousing disparate positions was to efficiently and accurately categorize the identities, key issues, and positions of the respective groups. The task of the NSC Committee Chair was to incorporate the competing views of 20 different voices, representing four distinct interest groups, and facilitate a consensus in just a few hours. While this extremely tight timeline made us nervous, the key to working effectively was the efficient management of the conversation.
One way we navigated these time constraints was by laying out a roadmap that outlined the policy points that were predicted to generate the most debate. This roadmap was developed after each team had been invited to specify which issues they believed could fairly easy garner consensus, versus the issues they felt would require further persuasion. The central aim of the NSC team, for example, was to end the famine and secure legal assurances that individuals would not be prosecuted for delivering life-saving humanitarian services to this end. This was their static position, from which they would not budge. The NSC team also identified lower-stakes positions that they were open to re-thinking—so long as their core static position was not compromised.
Once the respective views of each team had been expressed, the next task was to speak to other members of other teams to see what headway could be made. One of the groups—which consisted of U.S. Department of Defense, Joint Chiefs of Staff, Director of National Intelligence and Department of the Treasury—chose to focus on interacting with groups whose views were not in alignment with their own in order to see if there was any room to maneuver. It was during this part of the simulation exercise that it became clear just how entrenched various teams were in their positions. Upon a return to the plenary formation, the Chair of the NSC meeting quickly identified which policies had broad general support, and which were now proving to be the most contentious.
In the final round of negotiations, it was clear that all parties agreed that the Somalia famine represented an emergency that demanded immediate action. It was also evident that the idea of a humanitarian exemption to the counter-terrorism laws had some support, particularly if it could be executed in conjunction with a Partner Vetting System. The most contentious issue, it emerged, was whether NGOs should be permitted to pay access fees to FTOs if necessary. Ultimately, this issue consumed the bulk of the discussion. It also ended up standing in the way of a group consensus on the overall approach. However, since the various issues had been divided up and dealt with according to level of difficulty, many smaller and less divisive issues were still possible to agree upon. This enabled the parties to forego needless arguments over small points and focus on the more significant issues at hand. Read Part 2 and Part 4 .
Written by law school students Katrina Younes, Rob Alfieri, Aaron Zaltzman as part of the Re-Imagining International Humanitarian Law course at University of Western Ontario Law School.
Legal, political, strategic and ethical dimensions of the 2011 famine
Elspeth Graham & Laura Snowdon
This is the second in a series on the use of Somalia in Crisis role play in a law school course on International Humanitarian Law. Read the Introduction.
The United Nations declared a famine in Somalia in July 2011. The humanitarian response to this crisis was slowed by the presence of al-Shabaab, and the famine ultimately claimed the lives of nearly 260,000 people. Six years later, five teams of law students representing various U.S. government departments participated in a simulation exercise to negotiate the legal, strategic, ethical, and political concerns that arose in relation to the crisis. The five teams represented the National Security Council, Department of Defense, Department of Justice, Department of State, and Office of the Vice President, respectively.
Legal concerns regarding issues of enforceability and a lack of clarity in U.S. material-support-to-terrorism legislation hindered consensus-building amongst the negotiating parties. The representatives of each group recognized that the legal landscape governing humanitarian workers in Somalia was complex and unclear, resulting in a chilling effect on the provision of aid. A majority of representatives concluded that a temporally- and geographically-limited humanitarian exception was a feasible path forward: it could potentially balance the U.S.’s moral obligation to provide aid alongside its important national security concerns. They were persuaded to agree on a humanitarian exception on the basis of moral arguments, namely the moral obligation of the U.S. to help save the lives of Somali citizens in crisis. However, the team representing the Department of Defense was the lone holdout, preventing group consensus on this point. Given its mandate to prioritize national security, it voiced concerns that any humanitarian exception—however limited—might allow al-Shabaab to financially benefit from U.S. humanitarian assistance.
The likelihood of consensus could have been increased if those teams favouring a humanitarian exception had considered arrangements more sensitive to national security. A strong attempt at this argument was that the failure to provide a humanitarian exception could actually pose a greater security threat for the U.S., due to prospects of radicalization in the face of an increasingly grave humanitarian crisis. While the Department of Defense team recognized this risk, it still insisted that directly supporting terrorist organizations posed the greater threat. Arguably, other stakeholders could have challenged this set of assumptions more effectively. After further rounds of discussion, the representatives of the Department of Defense finally appeared open to a very limited humanitarian exception so that food and water could be delivered to Somali citizens. However, they maintained the view that their obligations to protect American citizens prevented them from permitting humanitarian aid workers to pay access fees to Foreign Terrorist Organizations (FTOs) such as al-Shabaab.
In terms of political concerns, the teams also considered how a potential humanitarian exception to the counter-terrorism legislation might affect international relations. During informal discussions, some argued that it was in the interest of the U.S. to allow humanitarian assistance: this would preserve its image and status in the international community. Otherwise, the U.S. might be viewed as weak, and even callous, for failing to assist in the response when it clearly had the capacity to do so. Cutting against this was the fear that allowing for a humanitarian exception could cause the U.S. to be viewed as a state that supports terrorist organizations.
The 2011 Somalia famine was an exceptionally problematic crisis, due to the need for humanitarian assistance in the context of an armed conflict involving a terrorist group. As a result of the intersection of these issues, decision-making in response to the famine was rendered even more complex. Only time will tell if the U.S. can learn from its past mistakes to coordinate an effective humanitarian response when similar crises unfold elsewhere in the world. Read Part 3 and Part 4 .
Written by law school students Elspeth Graham & Laura Snowdon as part of the Re-Imagining International Humanitarian Law course at University of Western Ontario Law School.
- Search for:
Subscribe to Blog via Email
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive weekly notifications of new posts by email.
Email Address
Follow HLS Case Studies
Subscribe to our newsletter
Subscribe to our RSS feed
- Et Seq., The Harvard Law School Library Blog
- Harvard Negotiation and Mediation Clinical Program
- HLS Berkman Center for Internet and Society
- HLS Forum on Corporate Governance and Financial Regulation
- HLS Program on the Legal Profession
- Program on Negotiation
Recent Posts
Top posts & pages.
- Leadership in Law Firms
- Why and How: Using the Case Study Method in the Law Classroom
- Summer Reading: Legal Education’s 9 Big Ideas, Part 3
- New Product: Allen & Overy: Surviving the Banking Crisis (A) and (B)
- Case Development Initiative Blog Posts
- Case Study Program Blog Posts
- Experiential Learning and the Case Study Method
- Harvard Negotiation and Mediation Clinical Program Blog Posts
- Legal News and Debate
- Problem Solving Workshop Blog Posts
- Program on International Law and Armed Conflict Blog Posts
- Uncategorized
Any opinions expressed herein do not necessarily reflect those of Harvard University.
Product names, logos, brands, and other trademarks featured or referred to within this manuscript are the property of their respective trademark holders. These trademark holders are not affiliated with the author or any of the author's representatives. They do not sponsor or endorse the contents and materials discussed in this blog.
Outside images are used under a Creative Commons license, and do not suggest the licensor's endorsement or affiliation.
Comments are encouraged. Blog administrators will use their discretion to remove any inappropriate, uncivil, slanderous, or spam comments.
Email the site administrator at [email protected]
Law Case Study – How To Answer Case Studies in Law
One of the major challenges students have in business law and other law courses are answering questions under the case study. In this article, I will explain how to answer any law case study question following the same rule you are aware of and which is generally recommended. The IRAC or IDAC Principle.
Law Case Study Tips
IRAC Principle is an acronym which depicts,
“I” for Identification
“R” for Rule(s)
“A” for Analysis
“C” for Conclusion
While the IDAC Principle depicts the same but “D” stands for Definition.
Law Case Study – Question 1
Chuddy requested Kris to transport goods from Lagos to Darlington’s estate in Enugu state for the sum of N200,000.00. Kris replied that he was only prepared to transport the goods for N300,000.00.
Chuddy wrote back to Kris asking him to reconsider the initial price, but Kris did not reply to his letter. Two days later, Chuddy delivered the goods to the business premises of Kris, who transported them to Darlington’s Estate in Enugu State.
Chuddy has refused to pay the N300,000.00 demand by Kris, saying that there was no concluded contract. Advise the party using relevant authorities.
[Question 1, First Semester Exam 2014/2015. BAM – YABATECH]
ANSWER/SOLUTION
Let’s make use of the IRAC Principle to answer this question, but before this, let me quickly explain how it works.
“I” – Identification.
First of all, you need to identify under which law the case falls, if it is LAW OF CONTRACT then you consider the elements of the law of contract which are Offer, Acceptance, Consideration, Invitation to treat etc…
- So, from the case above, after reading the question/case, you’ll find out that it is AN OFFER . An offer is a definite undertaking with the expectation that it will become binding when the person accepts but since there was no acceptance between Chuddy and Kris, it means that the offer was terminated.
“R” – Rules
From the above rule, we can say that the offer is a counter-offer because the terms [amount involved] were not accepted by both parties which also means that it was rejected.
So, what are the rules for termination of an offer?
- An offer can be terminated through or by Revocation by rejection, the death of either party, the lapse of time and counter-offer [it varies the terms of an offer]
“A” – Analysis
By Analysis, you are expected to analyze the case study on some facts and principles that are similar in the area of law . [Always remember to lay emphasis on established facts and principles]
Since we have identified the rules applicable stating that it is a counter-offer and it was rejected then let’s see what it means.
- Counter Offer: In a nutshell, counter offer varies the terms of an offer
- By rejection: It means the offeree did not accept the terms of the offer.
“C” – Conclusion
Here, you are expected to conclude your judgment based on legal facts and principles you have identified. Your conclusion should also entail which party has the right to sue or succeed if the matter is taken to court for legal actions.
- So, since a counteroffer cannot give rise to a binding agreement, it means that Kris should not take the issue to court because, by the means of a counteroffer, there was no agreement between both parties.
Related posts:
- Study In Canada Scholarships Financial Aid Visa Admissions
- Law of Contract
- Users of Accounting Information
- Importance of Accounting in an Economy
- Vitiating Factors – 5 Major Vitiating Factors
- UK Study Visa for International Students 2023
- Questions on Set Theory
- Overhead Costs Definition – What is Overhead Costs?
- AOC – Human Capital Management
- Ledger Accounts and Trial Balance +Video Guide
- Scholarships to Study in the UK for International Students
4 thoughts on “Law Case Study – How To Answer Case Studies in Law”
Thanks bro…. Bless you too
Wonderful! Am excited that u are doing this bro. God bless u
Nice one bro, good breakdown
Comments are closed.
Insert/edit link
Enter the destination URL
Or link to existing content
- RMIT Australia
- RMIT Europe
- RMIT Vietnam
- RMIT Global
- RMIT Online
- Alumni & Giving

- What will I do?
- What will I need?
- Who will help me?
- About the institution
- New to university?
- Studying efficiently
- Time management
- Mind mapping
- Note-taking
- Reading skills
- Argument analysis
- Preparing for assessment
- Critical thinking and argument analysis
- Online learning skills
- Starting my first assignment
- Researching your assignment
- What is referencing?
- Understanding citations
- When referencing isn't needed
- Paraphrasing
- Summarising
- Synthesising
- Integrating ideas with reporting words
- Referencing with Easy Cite
- Getting help with referencing
- Acting with academic integrity
- Artificial intelligence tools
- Understanding your audience
- Writing for coursework
- Literature review
- Academic style
- Writing for the workplace
- Spelling tips
- Writing paragraphs
- Writing sentences
- Academic word lists
- Annotated bibliographies
- Artist statement
- Case studies
- Creating effective poster presentations
- Essays, Reports, Reflective Writing
- Law assessments
- Oral presentations
- Reflective writing
- Art and design
- Critical thinking
- Maths and statistics
- Sustainability
- Educators' guide
- Learning Lab content in context
- Latest updates
- Students Alumni & Giving Staff Library
Learning Lab
Getting started at uni, study skills.
- Referencing
- When referencing isn't needed
- Integrating ideas
Writing and assessments
- Critical reading
- Poster presentations
- Postgraduate report writing
Subject areas
For educators.
- Educators' guide
- Answering a legal problem - IRAC
Proper planning is vital to successfully answering a legal problem. Below are some hints and tools using a problem from Company Law. When answering a legal problem, it is useful to apply the IRAC structure so that you address all areas required.
- IRAC structure
The IRAC method has four steps:
- Identify the issue
- Relevant law - Here you need to explain the law not just state it. This could be sections/s of the Corporations Act or case law
- Application to the facts - the law is applied to the facts of the problem
Use the following IRAC structure as a guide to answer case study questions.

- Issue: Define the legal relevant issue.
- Relevant law: Identify legal principles from cases and statutes. Explain the law, don't just state it.
- Apply to the facts: Develop legal arguments by applying the law to the facts.
- Conclusion: Arrive at a considered conclusion.
Note: Students gain the most marks by explaining the relevant law and then applying it to the facts.
Example question and answer
Bingo Ltd is a manufacturer of electrical goods. It entered into a contract with Melvin Ltd, a large discount retailer. Under this contract, Bingo Ltd was to supply its goods exclusively to Melvin Ltd. The directors of Melvin Ltd subsequently discover that a wholly-owned subsidiary of Bingo Ltd is selling identical electrical goods to competitors at cheaper prices. It appears that the subsidiary was incorporated to enable Bingo Ltd to avoid the effects of the contract with Melvin Ltd. Advise the directors.
(This a five-mark question)
Please note: This is a simple low mark answer (5 marks) to illustrate the use of IRAC only. Many Company Law problems will involve multiple issues. In these scenarios each issue would need to be addressed. For example: The first issue is... The second issue is whether...
1. Read the following question.
2. Now read the following text and try to identify the IRAC structure. Check your understanding by clicking on the buttons to reveal the IRAC structure.
Read the following question, then identify which part of the IRAC structure best fits each text excerpt by selecting from the drop down menu.
- Writing case notes
- Writing a legal memo
Still can't find what you need?
The RMIT University Library provides study support , one-on-one consultations and peer mentoring to RMIT students.
- Facebook (opens in a new window)
- Twitter (opens in a new window)
- Instagram (opens in a new window)
- Linkedin (opens in a new window)
- YouTube (opens in a new window)
- Weibo (opens in a new window)
- Copyright © 2024 RMIT University |
- Accessibility |
- Learning Lab feedback |
- Complaints |
- ABN 49 781 030 034 |
- CRICOS provider number: 00122A |
- RTO Code: 3046 |
- Open Universities Australia
- Privacy Policy

Home » Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation.
It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Case studies typically involve multiple sources of data, including interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which are analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and grounded theory. The findings of a case study are often used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Types of Case Study
Types and Methods of Case Study are as follows:
Single-Case Study
A single-case study is an in-depth analysis of a single case. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand a specific phenomenon in detail.
For Example , A researcher might conduct a single-case study on a particular individual to understand their experiences with a particular health condition or a specific organization to explore their management practices. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a single-case study are often used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Multiple-Case Study
A multiple-case study involves the analysis of several cases that are similar in nature. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to identify similarities and differences between the cases.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a multiple-case study on several companies to explore the factors that contribute to their success or failure. The researcher collects data from each case, compares and contrasts the findings, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as comparative analysis or pattern-matching. The findings of a multiple-case study can be used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Exploratory Case Study
An exploratory case study is used to explore a new or understudied phenomenon. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to generate hypotheses or theories about the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an exploratory case study on a new technology to understand its potential impact on society. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as grounded theory or content analysis. The findings of an exploratory case study can be used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Descriptive Case Study
A descriptive case study is used to describe a particular phenomenon in detail. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to provide a comprehensive account of the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a descriptive case study on a particular community to understand its social and economic characteristics. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a descriptive case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Instrumental Case Study
An instrumental case study is used to understand a particular phenomenon that is instrumental in achieving a particular goal. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand the role of the phenomenon in achieving the goal.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an instrumental case study on a particular policy to understand its impact on achieving a particular goal, such as reducing poverty. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of an instrumental case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Case Study Data Collection Methods
Here are some common data collection methods for case studies:
Interviews involve asking questions to individuals who have knowledge or experience relevant to the case study. Interviews can be structured (where the same questions are asked to all participants) or unstructured (where the interviewer follows up on the responses with further questions). Interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
Observations
Observations involve watching and recording the behavior and activities of individuals or groups relevant to the case study. Observations can be participant (where the researcher actively participates in the activities) or non-participant (where the researcher observes from a distance). Observations can be recorded using notes, audio or video recordings, or photographs.
Documents can be used as a source of information for case studies. Documents can include reports, memos, emails, letters, and other written materials related to the case study. Documents can be collected from the case study participants or from public sources.
Surveys involve asking a set of questions to a sample of individuals relevant to the case study. Surveys can be administered in person, over the phone, through mail or email, or online. Surveys can be used to gather information on attitudes, opinions, or behaviors related to the case study.
Artifacts are physical objects relevant to the case study. Artifacts can include tools, equipment, products, or other objects that provide insights into the case study phenomenon.
How to conduct Case Study Research
Conducting a case study research involves several steps that need to be followed to ensure the quality and rigor of the study. Here are the steps to conduct case study research:
- Define the research questions: The first step in conducting a case study research is to define the research questions. The research questions should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the case study phenomenon under investigation.
- Select the case: The next step is to select the case or cases to be studied. The case should be relevant to the research questions and should provide rich and diverse data that can be used to answer the research questions.
- Collect data: Data can be collected using various methods, such as interviews, observations, documents, surveys, and artifacts. The data collection method should be selected based on the research questions and the nature of the case study phenomenon.
- Analyze the data: The data collected from the case study should be analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, or grounded theory. The analysis should be guided by the research questions and should aim to provide insights and conclusions relevant to the research questions.
- Draw conclusions: The conclusions drawn from the case study should be based on the data analysis and should be relevant to the research questions. The conclusions should be supported by evidence and should be clearly stated.
- Validate the findings: The findings of the case study should be validated by reviewing the data and the analysis with participants or other experts in the field. This helps to ensure the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Write the report: The final step is to write the report of the case study research. The report should provide a clear description of the case study phenomenon, the research questions, the data collection methods, the data analysis, the findings, and the conclusions. The report should be written in a clear and concise manner and should follow the guidelines for academic writing.
Examples of Case Study
Here are some examples of case study research:
- The Hawthorne Studies : Conducted between 1924 and 1932, the Hawthorne Studies were a series of case studies conducted by Elton Mayo and his colleagues to examine the impact of work environment on employee productivity. The studies were conducted at the Hawthorne Works plant of the Western Electric Company in Chicago and included interviews, observations, and experiments.
- The Stanford Prison Experiment: Conducted in 1971, the Stanford Prison Experiment was a case study conducted by Philip Zimbardo to examine the psychological effects of power and authority. The study involved simulating a prison environment and assigning participants to the role of guards or prisoners. The study was controversial due to the ethical issues it raised.
- The Challenger Disaster: The Challenger Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Space Shuttle Challenger explosion in 1986. The study included interviews, observations, and analysis of data to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
- The Enron Scandal: The Enron Scandal was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Enron Corporation’s bankruptcy in 2001. The study included interviews, analysis of financial data, and review of documents to identify the accounting practices, corporate culture, and ethical issues that led to the company’s downfall.
- The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster : The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the nuclear accident that occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011. The study included interviews, analysis of data, and review of documents to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
Application of Case Study
Case studies have a wide range of applications across various fields and industries. Here are some examples:
Business and Management
Case studies are widely used in business and management to examine real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills. Case studies can help students and professionals to develop a deep understanding of business concepts, theories, and best practices.
Case studies are used in healthcare to examine patient care, treatment options, and outcomes. Case studies can help healthcare professionals to develop critical thinking skills, diagnose complex medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans.
Case studies are used in education to examine teaching and learning practices. Case studies can help educators to develop effective teaching strategies, evaluate student progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Social Sciences
Case studies are widely used in social sciences to examine human behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices. Case studies can help researchers to develop theories, test hypotheses, and gain insights into complex social issues.
Law and Ethics
Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case studies can help lawyers, policymakers, and ethical professionals to develop critical thinking skills, analyze complex cases, and make informed decisions.
Purpose of Case Study
The purpose of a case study is to provide a detailed analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. A case study is a qualitative research method that involves the in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular case, which can be an individual, group, organization, event, or community.
The primary purpose of a case study is to generate a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case, including its history, context, and dynamics. Case studies can help researchers to identify and examine the underlying factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and detailed understanding of the case, which can inform future research, practice, or policy.
Case studies can also serve other purposes, including:
- Illustrating a theory or concept: Case studies can be used to illustrate and explain theoretical concepts and frameworks, providing concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Developing hypotheses: Case studies can help to generate hypotheses about the causal relationships between different factors and outcomes, which can be tested through further research.
- Providing insight into complex issues: Case studies can provide insights into complex and multifaceted issues, which may be difficult to understand through other research methods.
- Informing practice or policy: Case studies can be used to inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
Advantages of Case Study Research
There are several advantages of case study research, including:
- In-depth exploration: Case study research allows for a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and its dynamics, which may not be possible through other research methods.
- Rich data: Case study research can generate rich and detailed data, including qualitative data such as interviews, observations, and documents. This can provide a nuanced understanding of the case and its complexity.
- Holistic perspective: Case study research allows for a holistic perspective of the case, taking into account the various factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Theory development: Case study research can help to develop and refine theories and concepts by providing empirical evidence and concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Practical application: Case study research can inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
- Contextualization: Case study research takes into account the specific context in which the case is situated, which can help to understand how the case is influenced by the social, cultural, and historical factors of its environment.
Limitations of Case Study Research
There are several limitations of case study research, including:
- Limited generalizability : Case studies are typically focused on a single case or a small number of cases, which limits the generalizability of the findings. The unique characteristics of the case may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, which may limit the external validity of the research.
- Biased sampling: Case studies may rely on purposive or convenience sampling, which can introduce bias into the sample selection process. This may limit the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the findings.
- Subjectivity: Case studies rely on the interpretation of the researcher, which can introduce subjectivity into the analysis. The researcher’s own biases, assumptions, and perspectives may influence the findings, which may limit the objectivity of the research.
- Limited control: Case studies are typically conducted in naturalistic settings, which limits the control that the researcher has over the environment and the variables being studied. This may limit the ability to establish causal relationships between variables.
- Time-consuming: Case studies can be time-consuming to conduct, as they typically involve a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific case. This may limit the feasibility of conducting multiple case studies or conducting case studies in a timely manner.
- Resource-intensive: Case studies may require significant resources, including time, funding, and expertise. This may limit the ability of researchers to conduct case studies in resource-constrained settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide

Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Template Lists
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business How to Present a Case Study like a Pro (With Examples)
How to Present a Case Study like a Pro (With Examples)
Written by: Danesh Ramuthi Sep 07, 2023

Okay, let’s get real: case studies can be kinda snooze-worthy. But guess what? They don’t have to be!
In this article, I will cover every element that transforms a mere report into a compelling case study, from selecting the right metrics to using persuasive narrative techniques.
And if you’re feeling a little lost, don’t worry! There are cool tools like Venngage’s Case Study Creator to help you whip up something awesome, even if you’re short on time. Plus, the pre-designed case study templates are like instant polish because let’s be honest, everyone loves a shortcut.
Click to jump ahead:
What is a case study presentation?
What is the purpose of presenting a case study, how to structure a case study presentation, how long should a case study presentation be, 5 case study presentation examples with templates, 6 tips for delivering an effective case study presentation, 5 common mistakes to avoid in a case study presentation, how to present a case study faqs.
A case study presentation involves a comprehensive examination of a specific subject, which could range from an individual, group, location, event, organization or phenomenon.
They’re like puzzles you get to solve with the audience, all while making you think outside the box.
Unlike a basic report or whitepaper, the purpose of a case study presentation is to stimulate critical thinking among the viewers.
The primary objective of a case study is to provide an extensive and profound comprehension of the chosen topic. You don’t just throw numbers at your audience. You use examples and real-life cases to make you think and see things from different angles.

The primary purpose of presenting a case study is to offer a comprehensive, evidence-based argument that informs, persuades and engages your audience.
Here’s the juicy part: presenting that case study can be your secret weapon. Whether you’re pitching a groundbreaking idea to a room full of suits or trying to impress your professor with your A-game, a well-crafted case study can be the magic dust that sprinkles brilliance over your words.
Think of it like digging into a puzzle you can’t quite crack . A case study lets you explore every piece, turn it over and see how it fits together. This close-up look helps you understand the whole picture, not just a blurry snapshot.
It’s also your chance to showcase how you analyze things, step by step, until you reach a conclusion. It’s all about being open and honest about how you got there.
Besides, presenting a case study gives you an opportunity to connect data and real-world scenarios in a compelling narrative. It helps to make your argument more relatable and accessible, increasing its impact on your audience.
One of the contexts where case studies can be very helpful is during the job interview. In some job interviews, you as candidates may be asked to present a case study as part of the selection process.
Having a case study presentation prepared allows the candidate to demonstrate their ability to understand complex issues, formulate strategies and communicate their ideas effectively.
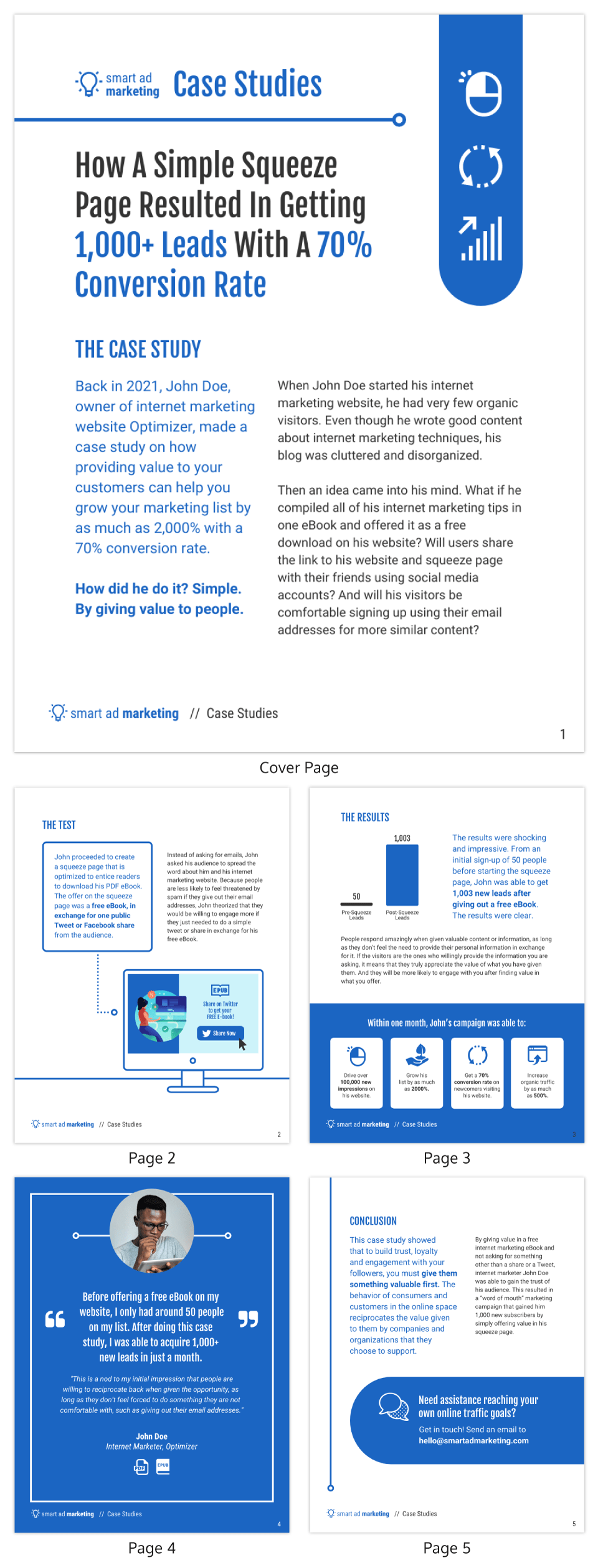
The way you present a case study can make all the difference in how it’s received. A well-structured presentation not only holds the attention of your audience but also ensures that your key points are communicated clearly and effectively.
In this section, let’s go through the key steps that’ll help you structure your case study presentation for maximum impact.
Let’s get into it.
Open with an introductory overview
Start by introducing the subject of your case study and its relevance. Explain why this case study is important and who would benefit from the insights gained. This is your opportunity to grab your audience’s attention.

Explain the problem in question
Dive into the problem or challenge that the case study focuses on. Provide enough background information for the audience to understand the issue. If possible, quantify the problem using data or metrics to show the magnitude or severity.

Detail the solutions to solve the problem
After outlining the problem, describe the steps taken to find a solution. This could include the methodology, any experiments or tests performed and the options that were considered. Make sure to elaborate on why the final solution was chosen over the others.

Key stakeholders Involved
Talk about the individuals, groups or organizations that were directly impacted by or involved in the problem and its solution.
Stakeholders may experience a range of outcomes—some may benefit, while others could face setbacks.
For example, in a business transformation case study, employees could face job relocations or changes in work culture, while shareholders might be looking at potential gains or losses.
Discuss the key results & outcomes
Discuss the results of implementing the solution. Use data and metrics to back up your statements. Did the solution meet its objectives? What impact did it have on the stakeholders? Be honest about any setbacks or areas for improvement as well.
Include visuals to support your analysis
Visual aids can be incredibly effective in helping your audience grasp complex issues. Utilize charts, graphs, images or video clips to supplement your points. Make sure to explain each visual and how it contributes to your overall argument.
Pie charts illustrate the proportion of different components within a whole, useful for visualizing market share, budget allocation or user demographics.
This is particularly useful especially if you’re displaying survey results in your case study presentation.
Stacked charts on the other hand are perfect for visualizing composition and trends. This is great for analyzing things like customer demographics, product breakdowns or budget allocation in your case study.
Consider this example of a stacked bar chart template. It provides a straightforward summary of the top-selling cake flavors across various locations, offering a quick and comprehensive view of the data.
Not the chart you’re looking for? Browse Venngage’s gallery of chart templates to find the perfect one that’ll captivate your audience and level up your data storytelling.
Recommendations and next steps
Wrap up by providing recommendations based on the case study findings. Outline the next steps that stakeholders should take to either expand on the success of the project or address any remaining challenges.
Acknowledgments and references
Thank the people who contributed to the case study and helped in the problem-solving process. Cite any external resources, reports or data sets that contributed to your analysis.
Feedback & Q&A session
Open the floor for questions and feedback from your audience. This allows for further discussion and can provide additional insights that may not have been considered previously.
Closing remarks
Conclude the presentation by summarizing the key points and emphasizing the takeaways. Thank your audience for their time and participation and express your willingness to engage in further discussions or collaborations on the subject.

Well, the length of a case study presentation can vary depending on the complexity of the topic and the needs of your audience. However, a typical business or academic presentation often lasts between 15 to 30 minutes.
This time frame usually allows for a thorough explanation of the case while maintaining audience engagement. However, always consider leaving a few minutes at the end for a Q&A session to address any questions or clarify points made during the presentation.
When it comes to presenting a compelling case study, having a well-structured template can be a game-changer.
It helps you organize your thoughts, data and findings in a coherent and visually pleasing manner.
Not all case studies are created equal and different scenarios require distinct approaches for maximum impact.
To save you time and effort, I have curated a list of 5 versatile case study presentation templates, each designed for specific needs and audiences.
Here are some best case study presentation examples that showcase effective strategies for engaging your audience and conveying complex information clearly.

1 . Lab report case study template
Ever feel like your research gets lost in a world of endless numbers and jargon? Lab case studies are your way out!
Think of it as building a bridge between your cool experiment and everyone else. It’s more than just reporting results – it’s explaining the “why” and “how” in a way that grabs attention and makes sense.
This lap report template acts as a blueprint for your report, guiding you through each essential section (introduction, methods, results, etc.) in a logical order.

Want to present your research like a pro? Browse our research presentation template gallery for creative inspiration!
2. Product case study template
It’s time you ditch those boring slideshows and bullet points because I’ve got a better way to win over clients: product case study templates.
Instead of just listing features and benefits, you get to create a clear and concise story that shows potential clients exactly what your product can do for them. It’s like painting a picture they can easily visualize, helping them understand the value your product brings to the table.
Grab the template below, fill in the details, and watch as your product’s impact comes to life!

3. Content marketing case study template
In digital marketing, showcasing your accomplishments is as vital as achieving them.
A well-crafted case study not only acts as a testament to your successes but can also serve as an instructional tool for others.
With this coral content marketing case study template—a perfect blend of vibrant design and structured documentation, you can narrate your marketing triumphs effectively.

4. Case study psychology template
Understanding how people tick is one of psychology’s biggest quests and case studies are like magnifying glasses for the mind. They offer in-depth looks at real-life behaviors, emotions and thought processes, revealing fascinating insights into what makes us human.
Writing a top-notch case study, though, can be a challenge. It requires careful organization, clear presentation and meticulous attention to detail. That’s where a good case study psychology template comes in handy.
Think of it as a helpful guide, taking care of formatting and structure while you focus on the juicy content. No more wrestling with layouts or margins – just pour your research magic into crafting a compelling narrative.
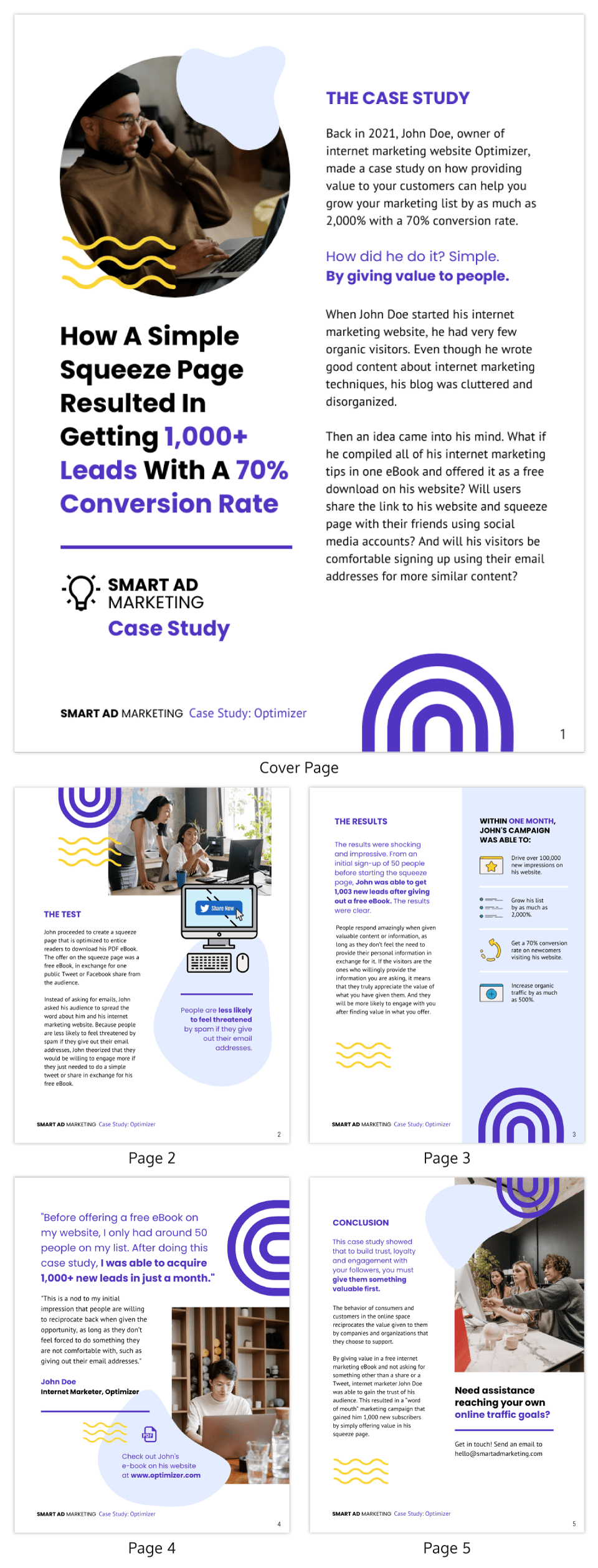
5. Lead generation case study template
Lead generation can be a real head-scratcher. But here’s a little help: a lead generation case study.
Think of it like a friendly handshake and a confident resume all rolled into one. It’s your chance to showcase your expertise, share real-world successes and offer valuable insights. Potential clients get to see your track record, understand your approach and decide if you’re the right fit.
No need to start from scratch, though. This lead generation case study template guides you step-by-step through crafting a clear, compelling narrative that highlights your wins and offers actionable tips for others. Fill in the gaps with your specific data and strategies, and voilà! You’ve got a powerful tool to attract new customers.
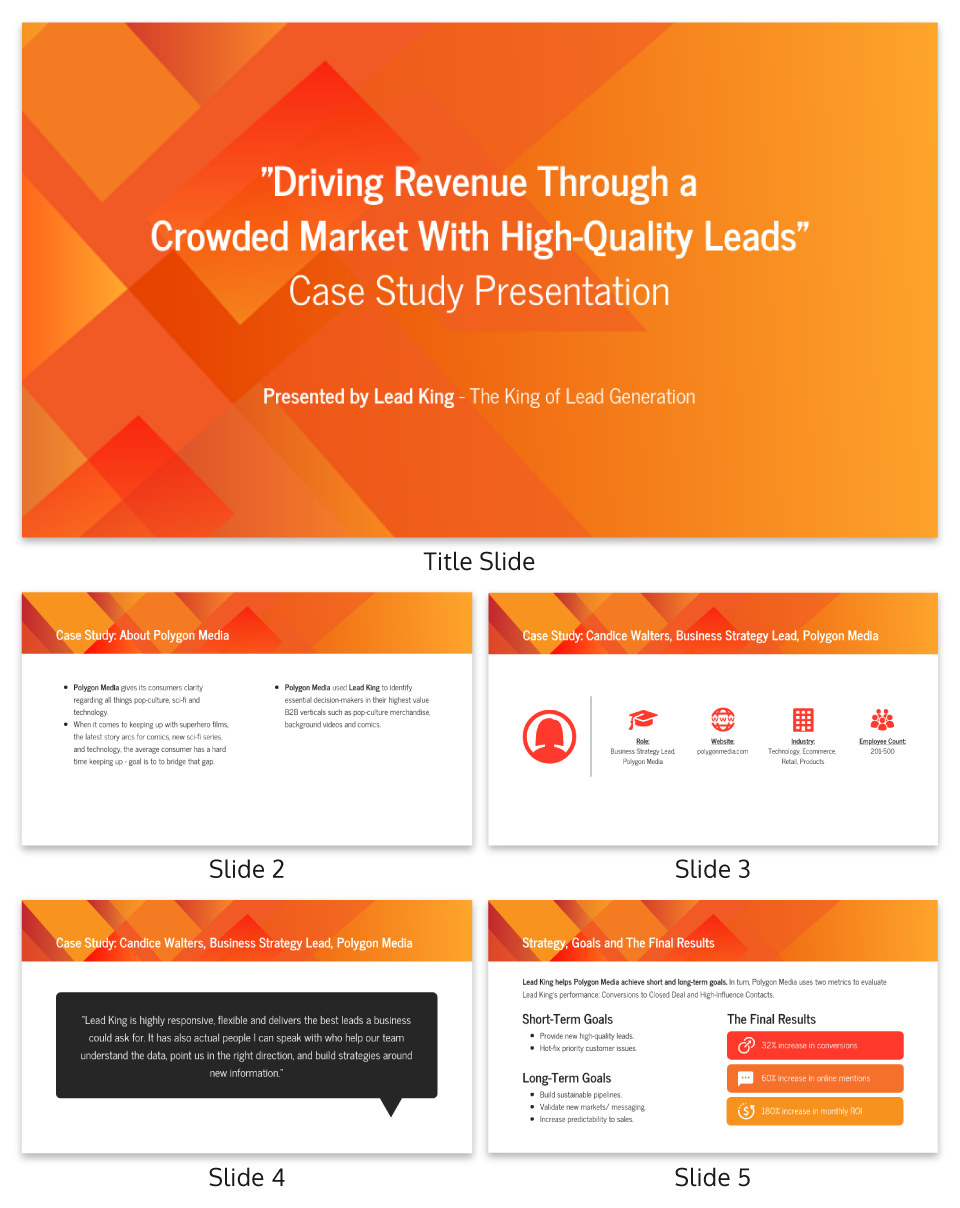
Related: 15+ Professional Case Study Examples [Design Tips + Templates]
So, you’ve spent hours crafting the perfect case study and are now tasked with presenting it. Crafting the case study is only half the battle; delivering it effectively is equally important.
Whether you’re facing a room of executives, academics or potential clients, how you present your findings can make a significant difference in how your work is received.
Forget boring reports and snooze-inducing presentations! Let’s make your case study sing. Here are some key pointers to turn information into an engaging and persuasive performance:
- Know your audience : Tailor your presentation to the knowledge level and interests of your audience. Remember to use language and examples that resonate with them.
- Rehearse : Rehearsing your case study presentation is the key to a smooth delivery and for ensuring that you stay within the allotted time. Practice helps you fine-tune your pacing, hone your speaking skills with good word pronunciations and become comfortable with the material, leading to a more confident, conversational and effective presentation.
- Start strong : Open with a compelling introduction that grabs your audience’s attention. You might want to use an interesting statistic, a provocative question or a brief story that sets the stage for your case study.
- Be clear and concise : Avoid jargon and overly complex sentences. Get to the point quickly and stay focused on your objectives.
- Use visual aids : Incorporate slides with graphics, charts or videos to supplement your verbal presentation. Make sure they are easy to read and understand.
- Tell a story : Use storytelling techniques to make the case study more engaging. A well-told narrative can help you make complex data more relatable and easier to digest.

Ditching the dry reports and slide decks? Venngage’s case study templates let you wow customers with your solutions and gain insights to improve your business plan. Pre-built templates, visual magic and customer captivation – all just a click away. Go tell your story and watch them say “wow!”
Nailed your case study, but want to make your presentation even stronger? Avoid these common mistakes to ensure your audience gets the most out of it:
Overloading with information
A case study is not an encyclopedia. Overloading your presentation with excessive data, text or jargon can make it cumbersome and difficult for the audience to digest the key points. Stick to what’s essential and impactful. Need help making your data clear and impactful? Our data presentation templates can help! Find clear and engaging visuals to showcase your findings.
Lack of structure
Jumping haphazardly between points or topics can confuse your audience. A well-structured presentation, with a logical flow from introduction to conclusion, is crucial for effective communication.
Ignoring the audience
Different audiences have different needs and levels of understanding. Failing to adapt your presentation to your audience can result in a disconnect and a less impactful presentation.
Poor visual elements
While content is king, poor design or lack of visual elements can make your case study dull or hard to follow. Make sure you use high-quality images, graphs and other visual aids to support your narrative.
Not focusing on results
A case study aims to showcase a problem and its solution, but what most people care about are the results. Failing to highlight or adequately explain the outcomes can make your presentation fall flat.
How to start a case study presentation?
Starting a case study presentation effectively involves a few key steps:
- Grab attention : Open with a hook—an intriguing statistic, a provocative question or a compelling visual—to engage your audience from the get-go.
- Set the stage : Briefly introduce the subject, context and relevance of the case study to give your audience an idea of what to expect.
- Outline objectives : Clearly state what the case study aims to achieve. Are you solving a problem, proving a point or showcasing a success?
- Agenda : Give a quick outline of the key sections or topics you’ll cover to help the audience follow along.
- Set expectations : Let your audience know what you want them to take away from the presentation, whether it’s knowledge, inspiration or a call to action.
How to present a case study on PowerPoint and on Google Slides?
Presenting a case study on PowerPoint and Google Slides involves a structured approach for clarity and impact using presentation slides :
- Title slide : Start with a title slide that includes the name of the case study, your name and any relevant institutional affiliations.
- Introduction : Follow with a slide that outlines the problem or situation your case study addresses. Include a hook to engage the audience.
- Objectives : Clearly state the goals of the case study in a dedicated slide.
- Findings : Use charts, graphs and bullet points to present your findings succinctly.
- Analysis : Discuss what the findings mean, drawing on supporting data or secondary research as necessary.
- Conclusion : Summarize key takeaways and results.
- Q&A : End with a slide inviting questions from the audience.
What’s the role of analysis in a case study presentation?
The role of analysis in a case study presentation is to interpret the data and findings, providing context and meaning to them.
It helps your audience understand the implications of the case study, connects the dots between the problem and the solution and may offer recommendations for future action.
Is it important to include real data and results in the presentation?
Yes, including real data and results in a case study presentation is crucial to show experience, credibility and impact. Authentic data lends weight to your findings and conclusions, enabling the audience to trust your analysis and take your recommendations more seriously
How do I conclude a case study presentation effectively?
To conclude a case study presentation effectively, summarize the key findings, insights and recommendations in a clear and concise manner.
End with a strong call-to-action or a thought-provoking question to leave a lasting impression on your audience.
What’s the best way to showcase data in a case study presentation ?
The best way to showcase data in a case study presentation is through visual aids like charts, graphs and infographics which make complex information easily digestible, engaging and creative.
Don’t just report results, visualize them! This template for example lets you transform your social media case study into a captivating infographic that sparks conversation.

Choose the type of visual that best represents the data you’re showing; for example, use bar charts for comparisons or pie charts for parts of a whole.
Ensure that the visuals are high-quality and clearly labeled, so the audience can quickly grasp the key points.
Keep the design consistent and simple, avoiding clutter or overly complex visuals that could distract from the message.
Choose a template that perfectly suits your case study where you can utilize different visual aids for maximum impact.
Need more inspiration on how to turn numbers into impact with the help of infographics? Our ready-to-use infographic templates take the guesswork out of creating visual impact for your case studies with just a few clicks.
Related: 10+ Case Study Infographic Templates That Convert
Congrats on mastering the art of compelling case study presentations! This guide has equipped you with all the essentials, from structure and nuances to avoiding common pitfalls. You’re ready to impress any audience, whether in the boardroom, the classroom or beyond.
And remember, you’re not alone in this journey. Venngage’s Case Study Creator is your trusty companion, ready to elevate your presentations from ordinary to extraordinary. So, let your confidence shine, leverage your newly acquired skills and prepare to deliver presentations that truly resonate.
Go forth and make a lasting impact!
Discover popular designs

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker

- Testimonial
- Web Stories
Learning Home

Not Now! Will rate later

MBA Case Studies - Solved Examples

Need of MBA Case Studies
Case i: chemco case.
- ChemCo is a quality leader in the U.K. car batteries market.
- Customer battery purchases in the automobile market are highly seasonal.
- The fork-lift business was added to utilize idle capacity during periods of inactivity.
- This is a low-growth industry (1% annual growth over the last two years)
- Large customers are sophisticated and buy based on price and quality. Smaller customers buy solely on price.
- There is a Spanish competitor in the market who offers low priced batteries of inferior quality.

Essential MBA GD Guide: Key Topics with Strategies Free
- Importance of Group Discussions
- Tips and Strategies to handle a GD
- Top 25 GD topics
- Free Download
- Established player in car batteries
- Losing heavily in fork-lift truck batteries
- Old fashioned owner resistance to change
- Low priced competitors
- Foreign competitors gaining market share
- Decisive Interview, GD & Essay prep
- GD: Topics 2021
- GD: Approach
- GD: Do's and Don'ts
- GD: Communications
- Solved GDs Topics
GD Introduction
- Types of GD topics: Techniques
- GD: Ettiquette
- GD: Content
- Solved Case Studies
- High quality product, but low end customers care more about price than quality
- Mismanaged product diversification in a price sensitive market
- Alternative 1: Establish an Off-Brand for the fork-lift business
- Alternative 2: Educate the customer market about product quality
- Alternative 3: Exit the fork-lift battery business
- Establishing the firm's quality image
- Increase in market share
- Increase in sales
- Cost of the product
- Protect firm's quality image in the automobile industry
- Redesigned product to reduce the cost of manufacture
- Low price to enable it to compete with Spanish producer
- Make use of the quality leadership in car batteries market
- Offer reliability testing, extended warranties etc. to promote quality image
- Set higher prices to extract surplus from these advantages
- A passive strategy, not proactive
- Recommendations: Alternative 1 is recommended in this case. Since the firm operates in an industry which has low growth, hence it can expand market share and sales only by taking the customers from other players. Hence, it needs to tackle the Spanish competitor head-on by aggressively pricing its product. At the same time, launching a low-priced product under the same brand name erodes the high quality image in the car batteries market. Hence, the best option is to go for an off-brand to target the fork-lift customers who are increasingly becoming price sensitive. This will enable the company to ward off the threat in short-term and build its position strongly in the long-term.

Case II: NAKAMURA LACQUER COMPANY
- The Nakamura Lacquer Company: The Nakamura Lacquer Company based in Kyoto, Japan was one of the many small handicraft shops making lacquerware for the daily table use of the Japanese people.
- Mr. Nakamura- the personality: In 1948, a young Mr. Nakamura took over his family business. He saw an opportunity to cater to a new market of America, i.e. GI's of the Occupation Army who had begun to buy lacquer ware as souvenirs. However, he realized that the traditional handicraft methods were inadequate. He was an innovator and introduced simple methods of processing and inspection using machines. Four years later, when the Occupation Army left in 1952, Nakamura employed several thousand men, and produced 500,000 pieces of lacquers tableware each year for the Japanese mass consumer market. The profit from operations was $250,000.
- The Brand: Nakamura named his brand “Chrysanthemum” after the national flower of Japan, which showed his patriotic fervor. The brand became Japan's best known and best selling brand, being synonymous with good quality, middle class and dependability.
- The Market: The market for lacquerware in Japan seems to have matured, with the production steady at 500,000 pieces a year. Nakamura did practically no business outside of Japan. However, early in 1960, when the American interest in Japanese products began to grow, Nakamura received two offers
- The Rose and Crown offer: The first offer was from Mr. Phil Rose, V.P Marketing at the National China Company. They were the largest manufacturer of good quality dinnerware in the U.S., with their “Rose and Crown” brand accounting for almost 30% of total sales. They were willing to give a firm order for three eyes for annual purchases of 400,000 sets of lacquer dinnerware, delivered in Japan and at 5% more than what the Japanese jobbers paid. However, Nakamura would have to forego the Chrysanthemum trademark to “Rose and Crown” and also undertaken to sell lacquer ware to anyone else the U.S. The offer promised returns of $720,000 over three years (with net returns of $83,000), but with little potential for the U.S. market on the Chrysanthemum brand beyond that period.
- The Semmelback offer: The second offer was from Mr. Walter Sammelback of Sammelback, Sammelback and Whittacker, Chicago, the largest supplier of hotel and restaurant supplies in the U.S. They perceived a U.S. market of 600,000 sets a year, expecting it to go up to 2 million in around 5 years. Since the Japanese government did not allow overseas investment, Sammelback was willing to budget $1.5 million. Although the offer implied negative returns of $467,000 over the first five years, the offer had the potential to give a $1 million profit if sales picked up as anticipated.
- Meeting the order: To meet the numbers requirement of the orders, Nakamura would either have to expand capacity or cut down on the domestic market. If he chose to expand capacity, the danger was of idle capacity in case the U.S. market did not respond. If he cut down on the domestic market, the danger was of losing out on a well-established market. Nakamura could also source part of the supply from other vendors. However, this option would not find favor with either of the American buyers since they had approached only Nakamura, realizing that he was the best person to meet the order.
- Decision problem: Whether to accept any of the two offers and if yes, which one of the two and under what terms of conditions?
- To expand into the U.S. market.
- To maintain and build upon their reputation of the “Chrysanthemum” brand
- To increase profit volumes by tapping the U.S. market and as a result, increasing scale of operations.
- To increase its share in the U.S. lacquerware market.
- Profit Maximization criterion: The most important criterion in the long run is profit maximization.
- Risk criterion: Since the demand in the U.S. market is not as much as in Japan.
- Brand identity criterion: Nakamura has painstakingly built up a brand name in Japan. It is desirable for him to compete in the U.S. market under the same brand name
- Flexibility criterion: The chosen option should offer Nakamura flexibility in maneuvering the terms and conditions to his advantage. Additionally, Nakamura should have bargaining power at the time of renewal of the contract.
- Short term returns: Nakamura should receive some returns on the investment he makes on the new offers. However, this criterion may be compromised in favor of profit maximization in the long run.?
- Reject both: React both the offers and concentrate on the domestic market
- Accept RC offer: Accept the Rose and Crown offer and supply the offer by cutting down on supplies to the domestic market or through capacity expansion or both
- Accept SSW: offer; accept the SSW offer and meet it through cutting down on supply to the domestic market or through capacity expansion or both. Negotiate term of supply.
- Reject both: This option would not meet the primary criterion of profit maximization. Further, the objective of growth would also not be met. Hence, this option is rejected.
- Accept RC offer: The RC offer would assure net returns of $283,000 over the next three yeas. It also assures regular returns of $240,000 per year. However, Nakamura would have no presence in the U.S. with its Chrysanthemum brand name The RC offer would entail capacity expansion, as it would not be possible to siphon of 275,000 pieces from the domestic market over three years without adversely affecting operations there. At the end of three years, Nakamura would have little bargaining power with RC as it would have an excess capacity of 275,000 pieces and excess labor which it would want to utilize. In this sense the offer is risky. Further, the offer is not flexible. Long-term profit maximization is uncertain in this case a condition that can be controlled in the SSW offer. Hence, this offer is rejected.
- Accept SSW offer: The SSW offer does not assure a firm order or any returns for the period of contract. Although, in its present form the offer is risky if the market in the U.S. does not pick up as expected, the offer is flexible. If Nakamura were to exhibit caution initially by supplying only 300,000 instead of the anticipated 600,000 pieces, it could siphon off the 175,000 required from the domestic market. If demand exists in the U.S., the capacity can be expanded. With this offer, risk is minimized. Further, it would be competing on its own brand name. Distribution would be taken care of and long-term profit maximization criterion would be satisfied as this option has the potential of $1 million in profits per year. At the time of renewal of the contract, Nakamura would have immense bargaining power.
- Negotiate terms of offer with SSW: The terms would be that NLC would supply 300,000 pieces in the first year. If market demand exists, NLC should expand capacity to provide the expected demand.
- Action Plan: In the first phase, NLC would supply SSW with 300,000 pieces. 125,000 of these would be obtained by utilizing excess capacity, while the remaining would be obtained from the domestic market. If the expected demand for lacquer ware exists in the U.S., NLC would expand capacity to meet the expected demand. The debt incurred would be paid off by the fifth year.
- Contingency Plan: In case the demand is not as expected in the first year, NLC should not service the U.S. market and instead concentrate on increasing penetration in the domestic market.
FAQs about MBA Case Studies
- Group Discussions
- Personality
- Past Experiences
Most Popular Articles - PS

100 Group Discussion (GD) Topics for MBA 2024

Solved GDs Topic

Top 50 Other (Science, Economy, Environment) topics for GD
5 tips for starting a GD

GD FAQs: Communication

GD FAQs: Content

Stages of GD preparation

Group Discussion Etiquettes

Case Study: Tips and Strategy

Practice Case Studies: Long

Practice Case Studies: Short
5 tips for handling Abstract GD topics
5 tips for handling a fish market situation in GD
5 things to follow: if you don’t know much about the GD topic

Do’s and Don’ts in a Group Discussion
5 tips for handling Factual GD topics

How to prepare for Group Discussion
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
- Your Health
- Treatments & Tests
- Health Inc.
- Public Health
Reproductive rights in America
What's at stake as the supreme court hears idaho case about abortion in emergencies.

Selena Simmons-Duffin

The Supreme Court will hear another case about abortion rights on Wednesday. Protestors gathered outside the court last month when the case before the justices involved abortion pills. Tom Brenner for The Washington Post/Getty Images hide caption
The Supreme Court will hear another case about abortion rights on Wednesday. Protestors gathered outside the court last month when the case before the justices involved abortion pills.
In Idaho, when a pregnant patient has complications, abortion is only legal to prevent the woman's death. But a federal law known as EMTALA requires doctors to provide "stabilizing treatment" to patients in the emergency department.
The Biden administration sees that as a direct conflict, which is why the abortion issue is back – yet again – before the Supreme Court on Wednesday.
The case began just a few weeks after the justices overturned Roe v. Wade in 2022, when the federal Justice Department sued Idaho , arguing that the court should declare that "Idaho's law is invalid" when it comes to emergency abortions because the federal emergency care law preempts the state's abortion ban. So far, a district court agreed with the Biden administration, an appeals court panel agreed with Idaho, and the Supreme Court allowed the strict ban to take effect in January when it agreed to hear the case.

Supreme Court allows Idaho abortion ban to be enacted, first such ruling since Dobbs
The case, known as Moyle v. United States (Mike Moyle is the speaker of the Idaho House), has major implications on everything from what emergency care is available in states with abortion bans to how hospitals operate in Idaho. Here's a summary of what's at stake.
1. Idaho physicians warn patients are being harmed
Under Idaho's abortion law , the medical exception only applies when a doctor judges that "the abortion was necessary to prevent the death of the pregnant woman." (There is also an exception to the Idaho abortion ban in cases of rape or incest, only in the first trimester of the pregnancy, if the person files a police report.)
In a filing with the court , a group of 678 physicians in Idaho described cases in which women facing serious pregnancy complications were either sent home from the hospital or had to be transferred out of state for care. "It's been just a few months now that Idaho's law has been in effect – six patients with medical emergencies have already been transferred out of state for [pregnancy] termination," Dr. Jim Souza, chief physician executive of St. Luke's Health System in Idaho, told reporters on a press call last week.
Those delays and transfers can have consequences. For example, Dr. Emily Corrigan described a patient in court filings whose water broke too early, which put her at risk of infection. After two weeks of being dismissed while trying to get care, the patient went to Corrigan's hospital – by that time, she showed signs of infection and had lost so much blood she needed a transfusion. Corrigan added that without receiving an abortion, the patient could have needed a limb amputation or a hysterectomy – in other words, even if she didn't die, she could have faced life-long consequences to her health.
Attorneys for Idaho defend its abortion law, arguing that "every circumstance described by the administration's declarations involved life-threatening circumstances under which Idaho law would allow an abortion."
Ryan Bangert, senior attorney for the Christian legal powerhouse Alliance Defending Freedom, which is providing pro-bono assistance to the state of Idaho, says that "Idaho law does allow for physicians to make those difficult decisions when it's necessary to perform an abortion to save the life of the mother," without waiting for patients to become sicker and sicker.
Still, Dr. Sara Thomson, an OB-GYN in Boise, says difficult calls in the hospital are not hypothetical or even rare. "In my group, we're seeing this happen about every month or every other month where this state law complicates our care," she says. Four patients have sued the state in a separate case arguing that the narrow medical exception harmed them.
"As far as we know, we haven't had a woman die as a consequence of this law, but that is really on the top of our worry list of things that could happen because we know that if we watch as death is approaching and we don't intervene quickly enough, when we decide finally that we're going to intervene to save her life, it may be too late," she says.
2. Hospitals are closing units and struggling to recruit doctors
Labor and delivery departments are expensive for hospitals to operate. Idaho already had a shortage of providers, including OB-GYNS. Hospital administrators now say the Idaho abortion law has led to an exodus of maternal care providers from the state, which has a population of 2 million people.
Three rural hospitals in Idaho have closed their labor-and-delivery units since the abortion law took effect. "We are seeing the expansion of what's called obstetrical deserts here in Idaho," said Brian Whitlock, president and CEO of the Idaho Hospital Association.
Since Idaho's abortion law took effect, nearly one in four OB-GYNs have left the state or retired, according to a report from the Idaho Physician Well-Being Action Collaborative. The report finds the loss of doctors who specialize in high-risk pregnancies is even more extreme – five of nine full time maternal-fetal medicine specialists have left Idaho.
Administrators say they aren't able to recruit new providers to fill those positions. "Since [the abortion law's] enactment, St. Luke's has had markedly fewer applicants for open physician positions, particularly in obstetrics. And several out-of-state candidates have withdrawn their applications upon learning of the challenges of practicing in Idaho, citing [the law's] enactment and fear of criminal penalties," reads an amicus brief from St. Luke's health system in support of the federal government.
"Prior to the abortion decision, we already ranked 50th in number of physicians per capita – we were already a strained state," says Thomson, the doctor in Boise. She's experienced the loss of OB-GYN colleagues first hand. "I had a partner retire right as the laws were changing and her position has remained open – unfilled now for almost two years – so my own personal group has been short-staffed," she says.
ADF's Bangert says he's skeptical of the assertion that the abortion law is responsible for this exodus of doctors from Idaho. "I would be very surprised if Idaho's abortion law is the sole or singular cause of any physician shortage," he says. "I'm very suspicious of any claims of causality."
3. Justices could weigh in on fetal "personhood"
The state of Idaho's brief argues that EMTALA actually requires hospitals "to protect and care for an 'unborn child,'" an argument echoed in friend-of-the-court briefs from the U.S. Conference of Catholic Bishops and a group of states from Indiana to Wyoming that also have restrictive abortion laws. They argue that abortion can't be seen as a stabilizing treatment if one patient dies as a result.
Thomson is also Catholic, and she says the idea that, in an emergency, she is treating two patients – the fetus and the mother – doesn't account for clinical reality. "Of course, as obstetricians we have a passion for caring for both the mother and the baby, but there are clinical situations where the mom's health or life is in jeopardy, and no matter what we do, the baby is going to be lost," she says.
The Idaho abortion law uses the term "unborn child" as opposed to the words "embryo" or "fetus" – language that implies the fetus has the same rights as other people.

Shots - Health News
The science of ivf: what to know about alabama's 'extrauterine children' ruling.
Mary Ziegler , a legal historian at University of California - Davis, who is writing a book on fetal personhood, describes it as the "North Star" of the anti-abortion rights movement. She says this case will be the first time the Supreme Court justices will be considering a statute that uses that language.
"I think we may get clues about the future of bigger conflicts about fetal personhood," she explains, depending on how the justices respond to this idea. "Not just in the context of this statute or emergency medical scenarios, but in the context of the Constitution."
ADF has dismissed the idea that this case is an attempt to expand fetal rights. "This case is, at root, a question about whether or not the federal government can affect a hostile takeover of the practice of medicine in all 50 states by misinterpreting a long-standing federal statute to contain a hidden nationwide abortion mandate," Bangert says.
4. The election looms large
Ziegler suspects the justices will allow Idaho's abortion law to remain as is. "The Supreme Court has let Idaho's law go into effect, which suggests that the court is not convinced by the Biden administration's arguments, at least at this point," she notes.

Trump backed a federal abortion ban as president. Now, he says he wouldn't sign one
Whatever the decision, it will put abortion squarely back in the national spotlight a few months before the November election. "It's a reminder on the political side of things, that Biden and Trump don't really control the terms of the debate on this very important issue," Zielger observes. "They're going to be things put on everybody's radar by other actors, including the Supreme Court."
The justices will hear arguments in the case on Wednesday morning. A decision is expected by late June or early July.
Correction April 23, 2024
An earlier version of this story did not mention the rape and incest exception to Idaho's abortion ban. A person who reports rape or incest to police can end a pregnancy in Idaho in the first trimester.
- Abortion rights
- Supreme Court

Supreme Court Has Three Ways to Resolve Donald Trump Case—Legal Analyst
T he U.S. Supreme Court has three ways to resolve former President Donald Trump 's presidential immunity claim, according to legal analyst Glenn Kirschner on Saturday.
Trump, the presumed 2024 GOP presidential nominee, has sought to use the presidential immunity defense to shield himself from a plethora of criminal and civil challenges. Most notably, he has sought the defense in his federal election interference case surrounding the events that led to the U.S. Capitol riot on January 6, 2021. That case was brought by Department of Justice (DOJ) special counsel Jack Smith .
Trump was charged in August with four federal felony counts : conspiracy to defraud the United States; conspiracy to obstruct an official proceeding; obstruction of and attempt to obstruct an official proceeding; and conspiracy against rights. He has pleaded not guilty to all charges against him and claims that the indictment is politically motivated.
The Supreme Court justices heard oral arguments on Thursday to rule whether or not presidential immunity protects Trump from facing criminal charges for actions he took while in office.
On Saturday, Kirschner, a former assistant U.S. attorney and frequent critic of the former president, posted a video to his YouTube channel in which he discussed the three possibilities the Court could take to resolve the former president's presidential immunity claim.
"I think at this point it's impossible to predict with any accuracy what this Supreme Court will do. But those three possibilities are: one, do what the Constitution provides and reject Donald Trump's claim that he has absolute immunity...The Constitution, of course, does not provide that a president is immune from prosecution, in fact it provides the exact opposite, expressly," he said.
He continued: "The second possibility is the Supreme Court justices can be so interested and enamored of this nonsensical argument of outer perimeter official acts of a president, maybe some light criminal treason around the edges by Donald Trump. Maybe those outer perimeter presidential acts should enjoy immunity from prosecution and if they so decide, then they probably have to return the case to judge Tanya Chutkan , the judge who is presiding in Donald Trump's federal prosecution in D.C."
"The third possibility is that they rule that the president does have absolute immunity and can commit all the crimes they want against the American people and they can't be prosecuted for it. They will march America straight back to the monarchy we fled and fought against...The only one that will pull America out of this march towards autocracy is if they rule that Donald Trump is not above the law."
Newsweek has reached out to the Supreme Court via online email form and Trump's spokesperson via email for comment.
Kirschner's comments come after Thursday's questioning, some of the top Court's justices appeared skeptical that presidents should have absolute immunity from criminal prosecution from private acts during their time as commander-in-chief. However, a majority of the justices appeared open to some type of immunity for official acts taken by a president.
The justices' remarks in the hearing led many analysts to predict that the Supreme Court may return the case to a lower court to distinguish whether the individual charges in Smith's case relate to official or private acts. As a result, many analysts expect Trump's trial in the federal case could be delayed and may not take place prior to the election.
Related Articles
- Videos: White Supremacist Patriot Front Group Marches Through City
- Lindsey Graham Confronted on Enquirer's 'Catch and Kill' Plot to Help Trump
- Steve Bannon Urges Donald Trump to 'Turn the Guns' on Joe Biden
Start your unlimited Newsweek trial

- --> Login or Sign Up
Shop by Author
- Harvard Law Case Studies A-Z
- Free Materials
- Workshop-Based Case Study
- Discussion-Based Case Study
- Sabrineh Ardalan
- Sharon Block
- Robert Bordone
- Emily M. Broad Leib
- Robert Clark
- John Coates
- Susan Crawford
- Alonzo Emery
- Philip B. Heymann
- Howell E. Jackson
- Wendy Jacobs
- Adriaan Lanni
- Jeremy McClane
- Naz Modirzadeh
- Catherine Mondell
- Ashish Nanda
- Charles R. Nesson
- John Palfrey
- Bruce Patton
- Todd D. Rakoff
- Lisa Rohrer
- Jeswald W. Salacuse
- James Sebenius
- Joseph William Singer
- Holger Spamann
- Carol Steiker
- Guhan Subramanian
- Lawrence Susskind
- David B. Wilkins
- Heidi Gardner
- Jonathan Zittrain
Shop by Brand
Howell Jackson
- Ashish Nanda and Nicholas Semi Haas
- Chad M. Carr
- John Coates, Clayton Rose, and David Lane
Ashish Nanda and Lauren Prusiner
- Ashish Nanda and Lisa Rohrer
- Ashish Nanda and Monet Brewerton
- View all Brands

Harvard Law School
The Case Studies

The Case Study
a valuable tool for experiential, participant-centered learning

Public Company Analysis
Understand the control structures within US public companies

Financial Regulation
Explore emerging challenges in regulating financial institutions

Mediation & Negotiation
Develop the theory and practice of negotiation and dispute resolution
Shop by Category
Featured items.

A Difficult Discussion with the Board (A)
John Coates, Karina Shaw, Nathan Cisneros

GE Capital after the Crisis
John Coates, John Dionne, David Scharfstein

Noorain Khan and Disability Inclusion at the Ford Foundation
Laura Winig and Susan Crawford

BYOB in Boston
Susan Crawford and Brittany Deitch
Current Top Sellers

Diego Primadonna
Robert Ricigliano

Lawrence Susskind and Eileen Babbitt

Ernest Shackleton's Journey to the Endurance
Ashish Nanda and Nicholas Tabor

Linklaters (A): Seeking Clear Blue Water
New products.

Hogan Lovells’ Sector-Focused Client Service Approach: Put to the Test During Covid
Heidi K. Gardner

First National Bank of Ames Corporation (Teaching Note)

Investor Access to Private Investment (Teaching Note)

Investor Access to Private Investment
Hannah Valentine under the supervision of Howell Jackson
Please note that each purchase of a product entitles the purchaser to one download and use. If you need multiple copies, please purchase the number of copies you need. For more information, see Copying Your Case Study .
Advertisement
Tracking Abortion Bans Across the Country
By The New York Times Updated May 1, 4:40 P.M. ET
- Share full article
Twenty-one states ban abortion or restrict the procedure earlier in pregnancy than the standard set by Roe v. Wade, which governed reproductive rights for nearly half a century until the Supreme Court overturned the decision in 2022.
In some states, the fight over abortion access is still taking place in courtrooms, where advocates have sued to block bans and restrictions. Other states have moved to expand access to abortion by adding legal protections.
Latest updates
- The Arizona state legislature voted to repeal an 1864 ban on nearly all abortions. Officials warned that the near-total ban may be briefly enforceable this summer until the repeal takes effect in the fall. A 15-week ban remains in effect.
- A ban on abortion after about six weeks of pregnancy took effect in Florida , following a ruling by the Florida Supreme Court that the privacy protections of the state’s Constitution do not extend to abortion.
The New York Times is tracking abortion laws in each state after the Supreme Court’s decision in Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization , which ended the constitutional right to an abortion.
Where abortion is legal
In a few states that have enacted bans or restrictions, abortion remains legal for now as courts determine whether these laws can take effect. Abortion is legal in the rest of the country, and many states have added new protections since Dobbs.
Ban in effect
Note: TK note here.
Legal for now
State details.
More details on the current status of abortion in each state are below.
An earlier version of this article misstated the legal status of abortion in Utah. As of 4 p.m. on June 24, the state attorney general had issued a statement saying the state’s abortion ban had been triggered, but it had not yet been authorized by the legislature’s general counsel. By 8:30 p.m., the counsel authorized the ban and it went into effect.
A table in an earlier version of this article misstated which abortion ban is being challenged in Texas state court. Abortion rights supporters are challenging a pre-Roe ban, not the state’s trigger ban.
An earlier version of this article referred incorrectly to the legal status of abortion in Indiana. While Indiana abortion providers stopped offering abortion services in anticipation of an abortion ban taking effect on Aug. 1, the law did not take effect.
- Election 2024
- Entertainment
- Newsletters
- Photography
- Personal Finance
- AP Investigations
- AP Buyline Personal Finance
- AP Buyline Shopping
- Press Releases
- Israel-Hamas War
- Russia-Ukraine War
- Global elections
- Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- Middle East
- Election Results
- Delegate Tracker
- AP & Elections
- Auto Racing
- 2024 Paris Olympic Games
- Movie reviews
- Book reviews
- Personal finance
- Financial Markets
- Business Highlights
- Financial wellness
- Artificial Intelligence
- Social Media
With homelessness on the rise, the Supreme Court weighs bans on sleeping outdoors

Rallies were held in various cities across the country as the Supreme Court considered the most significant case on homelessness in decades.

A challenge brought by Grants Pass, a small rural city in southern Oregon, is the most significant case in decades before the U.S. Supreme Court about homelessness. The case could upend how cities interact with people living in the streets. (AP Video by Claire Rush, Manuel Valdes)
Activists demonstrate at the Supreme Court as the justices consider a challenge to rulings that found punishing people for sleeping outside when shelter space is lacking amounts to unconstitutional cruel and unusual punishment, on Capitol Hill in Washington, Monday, April 22, 2024. (AP Photo/J. Scott Applewhite)
- Copy Link copied
Helen Cruz, who once lived on the streets in Grants Pass, Ore., speaks at a rally outside the Supreme Court as the justices hear arguments in the Grants Pass homeless case, on Capitol Hill in Washington, Monday, April 22, 2024. (AP Photo/J. Scott Applewhite)
WASHINGTON (AP) — The Supreme Court wrestled with major questions about the growing issue of homelessness on Monday as it considered whether cities can punish people for sleeping outside when shelter space is lacking.
It’s the most significant case before the high court in decades on the issue, and comes as record numbers of people are without a permanent place to live in the United States.
The case started in the rural Oregon town of Grants Pass , which began fining people $295 for sleeping outside as the cost of housing escalated and tents sprung up in the city’s public parks. The San Francisco-based U.S. 9th Circuit Court of Appeals struck down the law under its holding that banning camping in places without enough shelter beds amounts to cruel and unusual punishment.
The justices appeared to be leaning toward a narrow ruling in the case after hearing arguments that showed the stark terms of the debate over homelessness in Western states like California, which is home to one-third of the country’s homeless population.
Sleeping is a biological necessity, and people may be forced to do it outside if they can’t get housing or there’s no space in shelters, Justice Sonia Sotomayor said.
AP AUDIO: With homelessness on the rise, the Supreme Court will weigh bans on sleeping outdoors.
AP correspondent Jackie Quinn reports the U.S. Supreme Court is taking up a challenge by a city that wants to ban homeless people from sleeping outdoors.
“Where do we put them if every city, every village, every town lacks compassion and passes a law identical to this? Where are they supposed to sleep? Are they supposed to kill themselves, not sleeping?” she said.
Solving homelessness is a complicated issue, said Justice Brett Kavanaugh. He questioned whether ticketing people for camping helps if there aren’t enough shelter beds to hold everyone, but also raised concerns about federal courts “micromanaging” policy.
Other conservative justices asked how far Eighth Amendment legal protections should extend as cities struggle with managing homeless encampments that can be dangerous and unsanitary.
“How about if there are no public bathroom facilities, do people have an Eighth Amendment right to defecate and urinate outdoors?” said Justice Neil Gorsuch.
Other public-health laws cover that situation, Justice Department attorney Edwin Kneedler said. He argued people shouldn’t be punished just for sleeping outside, but said the ruling striking down the Grants Pass law should be tossed out because the court didn’t do enough to determine if people are “involuntarily homeless.”
Gorsuch and other justices also raised the possibility that other aspects of state or federal law could help sort through the issue, potentially without setting sweeping new legal precedent.
The question is an urgent one in the West, where a cross-section of Democratic and Republican officials contend that the 9th Circuit’s rulings on camping bans make it difficult for them to manage encampments. The appeals court has jurisdiction over nine states in the West.
Advocacy groups, on the other hand, argued that allowing cities to punish people who need a place to sleep will criminalize homelessness and ultimately make the crisis worse as the cost of housing increases.
Hundreds of demonstrators gathered outside the Supreme Court Monday morning to advocate for more affordable housing, holding silver thermal blankets and signs like “housing not handcuffs.”
Homelessness in the United States grew a dramatic 12% last year to its highest reported level, as soaring rents and a decline in coronavirus pandemic assistance combined to put housing out of reach for more people.
More than 650,000 people are estimated to be homeless, the most since the country began using the yearly point-in-time survey in 2007. Nearly half of them sleep outside. Older adults, LGBTQ+ people and people of color are disproportionately affected, advocates said.
In Oregon, a lack of mental health and addiction resources has also helped fuel the crisis. The state has some of the highest rates of homelessness and drug addiction in the nation, and ranks near the bottom in access to treatment, federal data shows.
The court is expected to decide the case by the end of June.
Rush reported from Portland, Oregon.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
1. Read the case. You should read the case through at least once from beginning to end until you attempt to figure out which facts are most important or analyze the court's holding. It's difficult to correctly determine what was central to the court's reasoning until you've read it all the way through.
Harvard Education Press provides access to cases in higher education and K-12 education. Topics include administration and finance, curriculum development, external relations and public affairs, faculty, human resources, leadership, marketing, planning, student affairs, data use, and community organizing. Harvard Kennedy School Case Program.
The Case Study Teaching Method. It is easy to get confused between the case study method and the case method, particularly as it applies to legal education. The case method in legal education was invented by Christopher Columbus Langdell, Dean of Harvard Law School from 1870 to 1895. Langdell conceived of a way to systematize and simplify legal ...
The ABA's LEAPS Project has a comprehensive list of objections to practical problem solving in the classroom: materials are time consuming and expensive to create and deploy; addition of a case study or simulation to a syllabus inherently displaces other material; and there are few incentives from law school leaders to introduce this type of ...
Problem Solving Workshop modules. The Problem Solving Workshop curriculum is designed to expose 1L students to a variety of legal roles. Through decision-making, legal writing, and teamwork, students learn how to think like lawyers and solve a client's problem. Below are Harvard Law School's 2014 PSW modules. Alternative cases are noted as well.
The Stanford Law School Case Studies Collection is an exciting innovation in law school teaching designed to hone students' problem-solving skills and stimulate creativity. The Collection includes situational case studies and interactive simulations (collectively referred to as "Case Materials") that place students in the roles of lawyers ...
- Introduction to legal case-solving (Prac tical Case-solving in European Law), page 2 - A. The methods and techniques of legal case-solving I. The analysis of the facts and question of the case1 1) The apprehension of the facts of the case At the beginning of every case-solving grasp at first carefully the facts of the case (the "story").
The use of discussion and problem-solving via a case study can heighten student engagement, critical analysis, and reflection, thus creating conditions that foster transformative learning. ... Harvard Law School | The Case Studies has served 7,986 customers, published 220 cases, and fulfilled 8,152 orders over the last 6 years. Here is a list ...
FREE. All content is free for all to use, as we are supported by our strategic partners who utilize Casebriefs ™ to connect to the Higher Education and Professional Markets. Access the world's largest database of Free Case Briefs for Law Students. Curated from law school case books, includes links for optimal case understanding.
Law Case Study - Question 1. Chuddy requested Kris to transport goods from Lagos to Darlington's estate in Enugu state for the sum of N200,000.00. Kris replied that he was only prepared to transport the goods for N300,000.00. Chuddy wrote back to Kris asking him to reconsider the initial price, but Kris did not reply to his letter.
Identify the key problems and issues in the case study. Formulate and include a thesis statement, summarizing the outcome of your analysis in 1-2 sentences. Background. Set the scene: background information, relevant facts, and the most important issues. Demonstrate that you have researched the problems in this case study. Evaluation of the Case
Activity 1. Activity 2. The IRAC method has four steps: Identify the issue. Relevant law - Here you need to explain the law not just state it. This could be sections/s of the Corporations Act or case law. Application to the facts - the law is applied to the facts of the problem. Conclusion.
Legal problem solving is a common format of assessments in law. It involves reading a fact scenario ('the problem') and explaining the possible legal outcomes of the issues in the fact scenario. Legal problem solving is an essential skill for the study and practice of law. To do this, you'll need to: provide a conclusion on each legal ...
If you're new to creating legal case studies, learn below how writing a case study builds client trust, as well as tips for writing a compelling case study, including: Getting permission from your client. Choosing the right case. Making your case study easy to read. Providing easy access to your case study. Telling a compelling story.
Case studies are widely used in business and management to examine real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills. Case studies can help students and professionals to develop a deep understanding of business concepts, theories, and best practices. ... Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case ...
The Problem Solving Workshop encourages the use of case studies throughout the HLS curriculum. Now, several faculty initiatives produce case studies at Harvard Law School. The Case Development Initiative . The Case Development Initiative creates case studies for J.D. and Executive Education classes. HLS faculty use case studies to teach a ...
How To Solve Law Case Study | CA Foundation Law Dec 23 | How To Score Good Marks In CA Law ExamsIn this video, we will discuss How to Solve Case Study for CA...
Title slide: Start with a title slide that includes the name of the case study, your name and any relevant institutional affiliations. Introduction: Follow with a slide that outlines the problem or situation your case study addresses. Include a hook to engage the audience.
Advertise with GPSolo. Contact MCI for opportunities to reach GPSolo's 20,000+ members. GPSolo Magazine contains articles exploring a particular topic of interest to solo, small firm and general practice lawyers, as well as columns on technology and law practice management.
We are looking for content geared toward solos, small firm lawyers, law students and young lawyers. Articles can be on substantive areas of the law, trending technology, helpful tips for daily issues as well as unexpected cases. It could even be a checklist to reference when working on a case. Contact us for more details before submitting an ...
Prepare for B-school admission rounds, with these MBA case study examples. It is common for B-schools to incorporate a case-based discussion in the group exercise round or give a case study in a personal interview. So, here we have presented two popular MBA case study examples, with analysis and solution.
Jenny Kane/AP. In a major case on homelessness, the U.S. Supreme Court on Monday appeared to side with an Oregon city's crackdown on sleeping in public. The decision could have sweeping ...
The case, known as Moyle v.United States (Mike Moyle is the speaker of the Idaho House), has major implications on everything from what emergency care is available in states with abortion bans to ...
The U.S. Supreme Court has three ways to resolve former President Donald Trump 's presidential immunity claim, according to legal analyst Glenn Kirschner on Saturday. Trump, the presumed 2024 GOP ...
Case Studies and Other Experiential Learning Tools from Harvard Law School
While legal design thinking can bring tremendous value to a law firm that is stuck with a current practice problem (associate attrition, failed technology adoption, losing clients), it is uniquely suited to think through future practice problems--in other words, developing a succession process. It is becoming a game changer because legal ...
A 15-week ban remains in effect. A ban on abortion after about six weeks of pregnancy took effect in Florida, following a ruling by the Florida Supreme Court that the privacy protections of the ...
The case started in the rural Oregon town of Grants Pass, which began fining people $295 for sleeping outside as the cost of housing escalated and tents sprung up in the city's public parks. The San Francisco-based U.S. 9th Circuit Court of Appeals struck down the law under its holding that banning camping in places without enough shelter ...
Tip 3: Tell human stories. One key strength of our Airbnb case study was storytelling. Even though we followed a standard case study structure, we told the story in a very human and engaging way which made it easy to follow and memorable. Here are 4 practical tips to improve storytelling in your case study: