- Corrections

Search Help
Get the most out of Google Scholar with some helpful tips on searches, email alerts, citation export, and more.
Finding recent papers
Your search results are normally sorted by relevance, not by date. To find newer articles, try the following options in the left sidebar:
- click "Since Year" to show only recently published papers, sorted by relevance;
- click "Sort by date" to show just the new additions, sorted by date;
- click the envelope icon to have new results periodically delivered by email.
Locating the full text of an article
Abstracts are freely available for most of the articles. Alas, reading the entire article may require a subscription. Here're a few things to try:
- click a library link, e.g., "FindIt@Harvard", to the right of the search result;
- click a link labeled [PDF] to the right of the search result;
- click "All versions" under the search result and check out the alternative sources;
- click "Related articles" or "Cited by" under the search result to explore similar articles.
If you're affiliated with a university, but don't see links such as "FindIt@Harvard", please check with your local library about the best way to access their online subscriptions. You may need to do search from a computer on campus, or to configure your browser to use a library proxy.
Getting better answers
If you're new to the subject, it may be helpful to pick up the terminology from secondary sources. E.g., a Wikipedia article for "overweight" might suggest a Scholar search for "pediatric hyperalimentation".
If the search results are too specific for your needs, check out what they're citing in their "References" sections. Referenced works are often more general in nature.
Similarly, if the search results are too basic for you, click "Cited by" to see newer papers that referenced them. These newer papers will often be more specific.
Explore! There's rarely a single answer to a research question. Click "Related articles" or "Cited by" to see closely related work, or search for author's name and see what else they have written.
Searching Google Scholar
Use the "author:" operator, e.g., author:"d knuth" or author:"donald e knuth".
Put the paper's title in quotations: "A History of the China Sea".
You'll often get better results if you search only recent articles, but still sort them by relevance, not by date. E.g., click "Since 2018" in the left sidebar of the search results page.
To see the absolutely newest articles first, click "Sort by date" in the sidebar. If you use this feature a lot, you may also find it useful to setup email alerts to have new results automatically sent to you.
Note: On smaller screens that don't show the sidebar, these options are available in the dropdown menu labelled "Year" right below the search button.
Select the "Case law" option on the homepage or in the side drawer on the search results page.
It finds documents similar to the given search result.
It's in the side drawer. The advanced search window lets you search in the author, title, and publication fields, as well as limit your search results by date.
Select the "Case law" option and do a keyword search over all jurisdictions. Then, click the "Select courts" link in the left sidebar on the search results page.
Tip: To quickly search a frequently used selection of courts, bookmark a search results page with the desired selection.
Access to articles
For each Scholar search result, we try to find a version of the article that you can read. These access links are labelled [PDF] or [HTML] and appear to the right of the search result. For example:
A paper that you need to read
Access links cover a wide variety of ways in which articles may be available to you - articles that your library subscribes to, open access articles, free-to-read articles from publishers, preprints, articles in repositories, etc.
When you are on a campus network, access links automatically include your library subscriptions and direct you to subscribed versions of articles. On-campus access links cover subscriptions from primary publishers as well as aggregators.
Off-campus access
Off-campus access links let you take your library subscriptions with you when you are at home or traveling. You can read subscribed articles when you are off-campus just as easily as when you are on-campus. Off-campus access links work by recording your subscriptions when you visit Scholar while on-campus, and looking up the recorded subscriptions later when you are off-campus.
We use the recorded subscriptions to provide you with the same subscribed access links as you see on campus. We also indicate your subscription access to participating publishers so that they can allow you to read the full-text of these articles without logging in or using a proxy. The recorded subscription information expires after 30 days and is automatically deleted.
In addition to Google Scholar search results, off-campus access links can also appear on articles from publishers participating in the off-campus subscription access program. Look for links labeled [PDF] or [HTML] on the right hand side of article pages.
Anne Author , John Doe , Jane Smith , Someone Else
In this fascinating paper, we investigate various topics that would be of interest to you. We also describe new methods relevant to your project, and attempt to address several questions which you would also like to know the answer to. Lastly, we analyze …
You can disable off-campus access links on the Scholar settings page . Disabling off-campus access links will turn off recording of your library subscriptions. It will also turn off indicating subscription access to participating publishers. Once off-campus access links are disabled, you may need to identify and configure an alternate mechanism (e.g., an institutional proxy or VPN) to access your library subscriptions while off-campus.
Email Alerts
Do a search for the topic of interest, e.g., "M Theory"; click the envelope icon in the sidebar of the search results page; enter your email address, and click "Create alert". We'll then periodically email you newly published papers that match your search criteria.
No, you can enter any email address of your choice. If the email address isn't a Google account or doesn't match your Google account, then we'll email you a verification link, which you'll need to click to start receiving alerts.
This works best if you create a public profile , which is free and quick to do. Once you get to the homepage with your photo, click "Follow" next to your name, select "New citations to my articles", and click "Done". We will then email you when we find new articles that cite yours.
Search for the title of your paper, e.g., "Anti de Sitter space and holography"; click on the "Cited by" link at the bottom of the search result; and then click on the envelope icon in the left sidebar of the search results page.
First, do a search for your colleague's name, and see if they have a Scholar profile. If they do, click on it, click the "Follow" button next to their name, select "New articles by this author", and click "Done".
If they don't have a profile, do a search by author, e.g., [author:s-hawking], and click on the mighty envelope in the left sidebar of the search results page. If you find that several different people share the same name, you may need to add co-author names or topical keywords to limit results to the author you wish to follow.
We send the alerts right after we add new papers to Google Scholar. This usually happens several times a week, except that our search robots meticulously observe holidays.
There's a link to cancel the alert at the bottom of every notification email.
If you created alerts using a Google account, you can manage them all here . If you're not using a Google account, you'll need to unsubscribe from the individual alerts and subscribe to the new ones.
Google Scholar library
Google Scholar library is your personal collection of articles. You can save articles right off the search page, organize them by adding labels, and use the power of Scholar search to quickly find just the one you want - at any time and from anywhere. You decide what goes into your library, and we’ll keep the links up to date.
You get all the goodies that come with Scholar search results - links to PDF and to your university's subscriptions, formatted citations, citing articles, and more!
Library help
Find the article you want to add in Google Scholar and click the “Save” button under the search result.
Click “My library” at the top of the page or in the side drawer to view all articles in your library. To search the full text of these articles, enter your query as usual in the search box.
Find the article you want to remove, and then click the “Delete” button under it.
- To add a label to an article, find the article in your library, click the “Label” button under it, select the label you want to apply, and click “Done”.
- To view all the articles with a specific label, click the label name in the left sidebar of your library page.
- To remove a label from an article, click the “Label” button under it, deselect the label you want to remove, and click “Done”.
- To add, edit, or delete labels, click “Manage labels” in the left column of your library page.
Only you can see the articles in your library. If you create a Scholar profile and make it public, then the articles in your public profile (and only those articles) will be visible to everyone.
Your profile contains all the articles you have written yourself. It’s a way to present your work to others, as well as to keep track of citations to it. Your library is a way to organize the articles that you’d like to read or cite, not necessarily the ones you’ve written.
Citation Export
Click the "Cite" button under the search result and then select your bibliography manager at the bottom of the popup. We currently support BibTeX, EndNote, RefMan, and RefWorks.
Err, no, please respect our robots.txt when you access Google Scholar using automated software. As the wearers of crawler's shoes and webmaster's hat, we cannot recommend adherence to web standards highly enough.
Sorry, we're unable to provide bulk access. You'll need to make an arrangement directly with the source of the data you're interested in. Keep in mind that a lot of the records in Google Scholar come from commercial subscription services.
Sorry, we can only show up to 1,000 results for any particular search query. Try a different query to get more results.
Content Coverage
Google Scholar includes journal and conference papers, theses and dissertations, academic books, pre-prints, abstracts, technical reports and other scholarly literature from all broad areas of research. You'll find works from a wide variety of academic publishers, professional societies and university repositories, as well as scholarly articles available anywhere across the web. Google Scholar also includes court opinions and patents.
We index research articles and abstracts from most major academic publishers and repositories worldwide, including both free and subscription sources. To check current coverage of a specific source in Google Scholar, search for a sample of their article titles in quotes.
While we try to be comprehensive, it isn't possible to guarantee uninterrupted coverage of any particular source. We index articles from sources all over the web and link to these websites in our search results. If one of these websites becomes unavailable to our search robots or to a large number of web users, we have to remove it from Google Scholar until it becomes available again.
Our meticulous search robots generally try to index every paper from every website they visit, including most major sources and also many lesser known ones.
That said, Google Scholar is primarily a search of academic papers. Shorter articles, such as book reviews, news sections, editorials, announcements and letters, may or may not be included. Untitled documents and documents without authors are usually not included. Website URLs that aren't available to our search robots or to the majority of web users are, obviously, not included either. Nor do we include websites that require you to sign up for an account, install a browser plugin, watch four colorful ads, and turn around three times and say coo-coo before you can read the listing of titles scanned at 10 DPI... You get the idea, we cover academic papers from sensible websites.
That's usually because we index many of these papers from other websites, such as the websites of their primary publishers. The "site:" operator currently only searches the primary version of each paper.
It could also be that the papers are located on examplejournals.gov, not on example.gov. Please make sure you're searching for the "right" website.
That said, the best way to check coverage of a specific source is to search for a sample of their papers using the title of the paper.
Ahem, we index papers, not journals. You should also ask about our coverage of universities, research groups, proteins, seminal breakthroughs, and other dimensions that are of interest to users. All such questions are best answered by searching for a statistical sample of papers that has the property of interest - journal, author, protein, etc. Many coverage comparisons are available if you search for [allintitle:"google scholar"], but some of them are more statistically valid than others.
Currently, Google Scholar allows you to search and read published opinions of US state appellate and supreme court cases since 1950, US federal district, appellate, tax and bankruptcy courts since 1923 and US Supreme Court cases since 1791. In addition, it includes citations for cases cited by indexed opinions or journal articles which allows you to find influential cases (usually older or international) which are not yet online or publicly available.
Legal opinions in Google Scholar are provided for informational purposes only and should not be relied on as a substitute for legal advice from a licensed lawyer. Google does not warrant that the information is complete or accurate.
We normally add new papers several times a week. However, updates to existing records take 6-9 months to a year or longer, because in order to update our records, we need to first recrawl them from the source website. For many larger websites, the speed at which we can update their records is limited by the crawl rate that they allow.
Inclusion and Corrections
We apologize, and we assure you the error was unintentional. Automated extraction of information from articles in diverse fields can be tricky, so an error sometimes sneaks through.
Please write to the owner of the website where the erroneous search result is coming from, and encourage them to provide correct bibliographic data to us, as described in the technical guidelines . Once the data is corrected on their website, it usually takes 6-9 months to a year or longer for it to be updated in Google Scholar. We appreciate your help and your patience.
If you can't find your papers when you search for them by title and by author, please refer your publisher to our technical guidelines .
You can also deposit your papers into your institutional repository or put their PDF versions on your personal website, but please follow your publisher's requirements when you do so. See our technical guidelines for more details on the inclusion process.
We normally add new papers several times a week; however, it might take us some time to crawl larger websites, and corrections to already included papers can take 6-9 months to a year or longer.
Google Scholar generally reflects the state of the web as it is currently visible to our search robots and to the majority of users. When you're searching for relevant papers to read, you wouldn't want it any other way!
If your citation counts have gone down, chances are that either your paper or papers that cite it have either disappeared from the web entirely, or have become unavailable to our search robots, or, perhaps, have been reformatted in a way that made it difficult for our automated software to identify their bibliographic data and references. If you wish to correct this, you'll need to identify the specific documents with indexing problems and ask your publisher to fix them. Please refer to the technical guidelines .
Please do let us know . Please include the URL for the opinion, the corrected information and a source where we can verify the correction.
We're only able to make corrections to court opinions that are hosted on our own website. For corrections to academic papers, books, dissertations and other third-party material, click on the search result in question and contact the owner of the website where the document came from. For corrections to books from Google Book Search, click on the book's title and locate the link to provide feedback at the bottom of the book's page.
General Questions
These are articles which other scholarly articles have referred to, but which we haven't found online. To exclude them from your search results, uncheck the "include citations" box on the left sidebar.
First, click on links labeled [PDF] or [HTML] to the right of the search result's title. Also, check out the "All versions" link at the bottom of the search result.
Second, if you're affiliated with a university, using a computer on campus will often let you access your library's online subscriptions. Look for links labeled with your library's name to the right of the search result's title. Also, see if there's a link to the full text on the publisher's page with the abstract.
Keep in mind that final published versions are often only available to subscribers, and that some articles are not available online at all. Good luck!
Technically, your web browser remembers your settings in a "cookie" on your computer's disk, and sends this cookie to our website along with every search. Check that your browser isn't configured to discard our cookies. Also, check if disabling various proxies or overly helpful privacy settings does the trick. Either way, your settings are stored on your computer, not on our servers, so a long hard look at your browser's preferences or internet options should help cure the machine's forgetfulness.
Not even close. That phrase is our acknowledgement that much of scholarly research involves building on what others have already discovered. It's taken from Sir Isaac Newton's famous quote, "If I have seen further, it is by standing on the shoulders of giants."
- Privacy & Terms

Explore millions of high-quality primary sources and images from around the world, including artworks, maps, photographs, and more.
Explore migration issues through a variety of media types
- Part of The Streets are Talking: Public Forms of Creative Expression from Around the World
- Part of The Journal of Economic Perspectives, Vol. 34, No. 1 (Winter 2020)
- Part of Cato Institute (Aug. 3, 2021)
- Part of University of California Press
- Part of Open: Smithsonian National Museum of African American History & Culture
- Part of Indiana Journal of Global Legal Studies, Vol. 19, No. 1 (Winter 2012)
- Part of R Street Institute (Nov. 1, 2020)
- Part of Leuven University Press
- Part of UN Secretary-General Papers: Ban Ki-moon (2007-2016)
- Part of Perspectives on Terrorism, Vol. 12, No. 4 (August 2018)
- Part of Leveraging Lives: Serbia and Illegal Tunisian Migration to Europe, Carnegie Endowment for International Peace (Mar. 1, 2023)
- Part of UCL Press
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR.
Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals.
Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world’s leading museums, archives, and scholars.
Eight Ways (and More) To Find and Access Research Papers
This blog is part of our Research Smarter series. You’ll discover the various search engines, databases and data repositories to help you along the way. Click on any of the following links for in an in-depth look at how to find relevant research papers, journals , and authors for your next project using the Web of Science™. You can also check out our ultimate guides here , which include tips to speed up the writing process.
If you’re in the early stages of your research career, you’re likely struggling to learn all you can about your chosen field and evaluate your options. You also need an easy and convenient way to find the right research papers upon which to build your own work and keep you on the proper path toward your goals.
Fortunately, most institutions have access to thousands of journals, so your first step should be to be to check with library staff and find out what is available via your institutional subscriptions.
For those who may be unfamiliar with other means of access, this blog post – the first in a series devoted to helping you “research smarter” – will provide a sampling of established data sources for scientific research. These include search engines, databases, and data repositories.
Search Engines and Databases
You may have already discovered that the process of searching for research papers offers many choices and scenarios. Some search engines, for example, can be accessed free of charge. Others require a subscription. The latter group generally includes services that index the contents of thousands of published journals, allowing for detailed searches on data fields such as author name, institution, title or keyword, and even funding sources. Because many journals operate on a subscription model too, the process of obtaining full-text versions of papers can be complicated.
On the other hand, a growing number of publishers follow the practice of Open Access (OA) , making their journal content freely available. Similarly, some authors publish their results in the form of preprints, posting them to preprint servers for immediate and free access. These repositories, like indexing services, differ in that some concentrate in a given discipline or broad subject area, while others cover the full range of research.
Search Engines
Following is a brief selection of reputable search engines by which to locate articles relevant to your research.
Google Scholar is a free search engine that provides access to research in multiple disciplines. The sources include academic publishers, universities, online repositories, books, and even judicial opinions from court cases. Based on its indexing, Google Scholar provides citation counts to allow authors and others to track the impact of their work.
The Directory of Open Access Journals ( DOAJ ) allows users to search and retrieve the article contents of nearly 10,000 OA journals in science, technology, medicine, social sciences, and humanities. All journals must adhere to quality-control standards, including peer review.
PubMed , maintained by the US National Library of Medicine, is a free search engine covering the biomedical and life sciences. Its coverage derives primarily from the MEDLINE database, covering materials as far back as 1951.
JSTOR affords access to more than 12 million journal articles in upwards of 75 disciplines, providing full-text searches of more than 2,000 journals, and access to more than 5,000 OA books.
Selected Databases
The following selection samples a range of resources, including databases which, as discussed above, index the contents of journals either in a given specialty area or the full spectrum of research. Others listed below offer consolidated coverage of multiple databases. Your institution is likely subscribed to a range of research databases, speak to your librarian to see which databases you have access to, and how to go about your search.
Web of Science includes The Web of Science Core Collection, which covers more than 20,000 carefully selected journals, along with books, conference proceedings, and other sources. The indexing also captures citation data, permitting users to follow the thread of an idea or development over time, as well as to track a wide range of research-performance metrics. The Web of Science also features EndNote™ Click , a free browser plugin that offers one-click access to the best available legal and legitimate full-text versions of papers. See here for our ultimate guide to finding relevant research papers on the Web of Science .
Science.gov covers the vast territory of United States federal science, including more than 60 databases and 2,200-plus websites. The many allied agencies whose research is reflected include NASA, the US Department of Agriculture, and the US Environmental Protection Agency.
CiteSeerx is devoted primarily to information and computer science. The database includes a feature called Autonomous Citation Indexing, designed to extract citations and create a citation index for literature searching and evaluation.
Preprint and Data Repositories
An early form of OA literature involved authors, as noted above, making electronic, preprint versions of their papers freely available. This practice has expanded widely today. You can find archives devoted to a single main specialty area, as well as general repositories connected with universities and other institutions.
The specialty archive is perhaps best exemplified by arXiv (conveniently pronounced “archive,” and one of the earliest examples of a preprint repository). Begun in 1991 as a physics repository, ArXiv has expanded to embrace mathematics, astronomy, statistics, economics, and other disciplines. The success of ArXiv spurred the development of, for example, bioArXiv devoted to an array of topics within biology, and for chemistry, ChemRxiv .
Meanwhile, thousands of institutional repositories hold a variety of useful materials. In addition to research papers, these archives store raw datasets, graphics, notes, and other by-products of investigation. Currently, the Registry of Open Access Repositories lists more than 4,700 entries.
Reach Out Yourself?
If the resources above don’t happen to result in a free and full-text copy of the research you seek, you can also try reaching out to the authors yourself.
To find who authored a paper, you can search indexing platforms like the Web of Science , or research profiling systems like Publons™ , or ResearchGate , then look to reach out to the authors directly.
So, although the sheer volume of research can pose a challenge to identifying and securing needed papers, plenty of options are available.
Related posts
Demonstrating socioeconomic impact – a historical perspective of ancient wisdom and modern challenges.

Unlocking U.K. research excellence: Key insights from the Research Professional News Live summit

For better insights, assess research performance at the department level

Reference management. Clean and simple.
The top list of academic research databases

2. Web of Science
5. ieee xplore, 6. sciencedirect, 7. directory of open access journals (doaj), get the most out of your academic research database, frequently asked questions about academic research databases, related articles.
Whether you are writing a thesis , dissertation, or research paper it is a key task to survey prior literature and research findings. More likely than not, you will be looking for trusted resources, most likely peer-reviewed research articles.
Academic research databases make it easy to locate the literature you are looking for. We have compiled the top list of trusted academic resources to help you get started with your research:
Scopus is one of the two big commercial, bibliographic databases that cover scholarly literature from almost any discipline. Besides searching for research articles, Scopus also provides academic journal rankings, author profiles, and an h-index calculator .
- Coverage: 90.6 million core records
- References: N/A
- Discipline: Multidisciplinary
- Access options: Limited free preview, full access by institutional subscription only
- Provider: Elsevier
Web of Science also known as Web of Knowledge is the second big bibliographic database. Usually, academic institutions provide either access to Web of Science or Scopus on their campus network for free.
- Coverage: approx. 100 million items
- References: 1.4 billion
- Access options: institutional subscription only
- Provider: Clarivate (formerly Thomson Reuters)
PubMed is the number one resource for anyone looking for literature in medicine or biological sciences. PubMed stores abstracts and bibliographic details of more than 30 million papers and provides full text links to the publisher sites or links to the free PDF on PubMed Central (PMC) .
- Coverage: approx. 35 million items
- Discipline: Medicine and Biological Sciences
- Access options: free
- Provider: NIH
For education sciences, ERIC is the number one destination. ERIC stands for Education Resources Information Center, and is a database that specifically hosts education-related literature.
- Coverage: approx. 1.6 million items
- Discipline: Education
- Provider: U.S. Department of Education
IEEE Xplore is the leading academic database in the field of engineering and computer science. It's not only journal articles, but also conference papers, standards and books that can be search for.
- Coverage: approx. 6 million items
- Discipline: Engineering
- Provider: IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers)
ScienceDirect is the gateway to the millions of academic articles published by Elsevier, 1.4 million of which are open access. Journals and books can be searched via a single interface.
- Coverage: approx. 19.5 million items
The DOAJ is an open-access academic database that can be accessed and searched for free.
- Coverage: over 8 million records
- Provider: DOAJ
JSTOR is another great resource to find research papers. Any article published before 1924 in the United States is available for free and JSTOR also offers scholarships for independent researchers.
- Coverage: more than 12 million items
- Provider: ITHAKA
Start using a reference manager like Paperpile to save, organize, and cite your references. Paperpile integrates with PubMed and many popular databases, so you can save references and PDFs directly to your library using the Paperpile buttons:
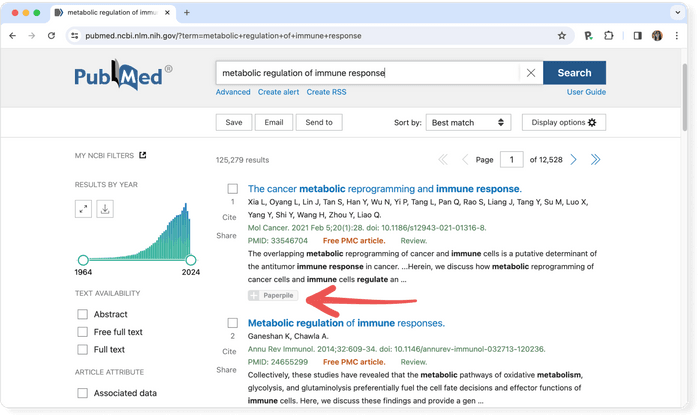
Scopus is one of the two big commercial, bibliographic databases that cover scholarly literature from almost any discipline. Beside searching for research articles, Scopus also provides academic journal rankings, author profiles, and an h-index calculator .
PubMed is the number one resource for anyone looking for literature in medicine or biological sciences. PubMed stores abstracts and bibliographic details of more than 30 million papers and provides full text links to the publisher sites or links to the free PDF on PubMed Central (PMC)
- Mission and history
- Platform features
- Library Advisory Group
- What’s in JSTOR
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
Open research reports
JSTOR hosts a growing curated collection of more than 50,000 open research reports from 187 think tanks and research institutes from around the world. These publications are freely accessible to everyone on JSTOR and discoverable as their own content type alongside journals, books, and primary sources. We update research reports on our platform each month as they become available through contributing institutes.
Download the list (xlsx) of contributing policy institutes.
Research reports provide current analysis on many of today’s most discussed and debated issues from a diversity of ideological and international perspectives representing 40 countries and 29 languages. A sample of topics would include: climate change, border security, fake news, cybersecurity, electric vehicles, artificial intelligence, energy policy, gender issues, terrorism, remote learning, recent trends in business and economics, and various public health issues, including COVID-19.
Although the briefs, papers, and reports published by these institutes are not peer-reviewed, they are written by policy experts and members of the academic community who are fellows in residence. This is content that impacts policy, both foreign and domestic. It is also increasingly used by faculty in their classrooms for its currency, breadth, and accessibility.
JSTOR’s research reports cover seven Areas of Focus: Business & Economics, Critical Race & Ethnic Studies, Education, Gender & Sexuality, Public Health, Security Studies, and Sustainability.
Browse research reports
Why research reports on JSTOR?
Input from faculty and librarians revealed that although research reports were for the most part freely available outside of JSTOR, they were hard to find and not easily discoverable alongside relevant material. It was also difficult for students to differentiate between the most credible research reports and a growing corpus of questionable sources on the Web.
JSTOR has attempted to redress these issues by centralizing a curated collection of think tank research reports on a single platform, making this content freely available to all JSTOR users, and enhancing its discoverability through comprehensive searching and the application of rich metadata.

Impossible? Let’s see.
Whether we're shaping the future of sustainability, or optimizing algorithms, or even exploring epidemiological studies, Google Research strives to continuously progress science, advance society, and improve the lives of billions of people.

Advancing the state of the art
Our teams advance the state of the art through research, systems engineering, and collaboration across Google. We publish hundreds of research papers each year across a wide range of domains, sharing our latest developments in order to collaboratively progress computing and science.
Learn more about our philosophy.
Watch the film
Link to Youtube Video
Read the latest

APR 19 · BLOG

APR 17 · BLOG

APR 16 · BLOG

APR 12 · BLOG

APR 11 · BLOG

MAR 29 · BLOG
Our research drives real-world change

Improving our LLM designed for the medical domain
- Large language models encode clinical knowledge Publication
- Towards Expert-Level Medical Question Answering with Large Language Models Publication
- Our latest health AI research updates Article
- Med-PaLM 2, our expert-level medical LLM Video
Project Contrails

A cost-effective and scalable way AI is helping to mitigate aviation’s climate impact
- A human-labeled Landsat-8 contrails dataset Dataset
- Can Google AI make flying more sustainable? Video
- Estimates of broadband upwelling irradiance fromm GOES-16 ABI Publication
- How AI is helping airlines mitigate the climate impact of contrails Blog
See our impact across other projects

Open Buildings

Project Relate

Flood Forecasting
We work across domains
Our vast breadth of work covers AI/ML foundations, responsible human-centric technology, science & societal impact, computing paradigms, and algorithms & optimization. Our research teams impact technology used by people all over the world.
One research paper started it all
The research we do today becomes the Google of the future. Google itself began with a research paper, published in 1998, and was the foundation of Google Search. Our ongoing research over the past 25 years has transformed not only the company, but how people are able to interact with the world and its information.

Responsible research is at the heart of what we do
The impact we create from our research has the potential to reach billions of people. That's why everything we do is guided by methodology that is grounded in responsible practices and thorough consideration.

Help us shape the future

We've been working alongside the academic research community since day one. Explore the ways that we collaborate and provide resources and support through a variety of student and faculty programs.

From Accra to Zürich, to our home base in Mountain View, we’re looking for talented scientists, engineers, interns, and more to join our teams not only at Google Research but all research projects across Google.
Explore our other teams and product areas
Google Cloud
Google DeepMind
- Follow us on Facebook
- Follow us on Twitter
- Criminal Justice
- Environment
- Politics & Government
- Race & Gender
Expert Commentary
How to find an academic research paper
Looking for research on a particular topic? We’ll walk you through the steps we use here at Journalist's Resource.

Republish this article

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License .
by David Trilling, The Journalist's Resource October 18, 2017
This <a target="_blank" href="https://journalistsresource.org/home/find-academic-research-paper-for-journalists/">article</a> first appeared on <a target="_blank" href="https://journalistsresource.org">The Journalist's Resource</a> and is republished here under a Creative Commons license.<img src="https://journalistsresource.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/cropped-jr-favicon-150x150.png" style="width:1em;height:1em;margin-left:10px;">
Journalists frequently contact us looking for research on a specific topic. While we have published a number of resources on how to understand an academic study and how to pick a good one — and why using social science research enriches journalism and public debate — we have little on the mechanics of how to search. This tip sheet will briefly discuss the resources we use.
Google Scholar
Let’s say we’re looking for papers on the opioid crisis. We often start with Google Scholar, a free service from Google that searches scholarly articles, books and documents rather than the entire web: scholar.google.com .
But a search for the keyword “opioids” returns almost half a million results, some from the 1980s. Let’s narrow down our search. On the left, you see options “anytime” (the default), “since 2013,” “since 2016,” etc. Try “since 2017” and the results are now about 17,000. You can also insert a custom range to search for specific years. And you can include patents or citations, if you like (unchecking these will slightly decrease the number of results).
Still too many results. To narrow the search further, try any trick you’d use with Google. (Here are some tips from MIT on how to supercharge your Google searches.) Let’s look for papers on opioids published in 2015 that look at race and exclude fentanyl (Google: “opioids +race -fentanyl”). Now we’re down to 2,750 results. Better.

Unless you tell Google to “sort by date,” the search engine will generally weight the papers that have been cited most often so you will see them first.
Try different keywords. If you’re looking for a paper that studies existing research, include the term “meta-analysis.” Try searching by the author’s name, if you know it, or title of the paper. Look at the endnotes in papers you like for other papers. And look at the papers that cited the paper you like; they’ll probably be useful for your project.
If you locate a study and it’s behind a paywall, try these steps:
- Click on “all versions.” Some may be available for free. (Though check the date, as this may include earlier drafts of a paper.)
- Reach out to the journal and the scholar. (The scholar’s email is often on the abstract page. Also, scholars generally have an easy-to-find webpage.) One is likely to give you a free copy of the paper, especially if you are a member of the press.
- In regular Google, search for the study by title and you might find a free version.
More tips on using Google Scholar from MIT and Google .
Other databases
- PubMed Central at the National Library of Medicine: If you are working on a topic that has a relationship to health, try this database run by the National Institutes of Health. This free site hosts articles or abstracts and links to free versions of a paper if they are available. Often Google Scholar will point you here.
- If you have online access to a university library or a local library, try that.
- Directory of Open Access Journals .
- Digital Public Library of America .
- Subscription services include org and Web of Science .
For more on efforts to make scholarly research open and accessible for all, check out SPARC , a coalition of university libraries.
Citations as a measure of impact
How do you know if a paper is impactful? Some scholars use the number of times the paper has been cited by other scholars. But that can be problematic: Some papers cite papers that are flawed simply to debunk them. Some topics will be cited more often than others. And new research, even if it’s high-quality, may not be cited yet.
The impact factor measures how frequently a journal, not a paper, is cited.
This guide from the University of Illinois, Chicago, has more on metrics.
Here’s a useful source of new papers curated by Boston Globe columnist Kevin Lewis for National Affairs.
Another way to monitor journals for new research is to set up an RSS reader like Feedly . Most journals have a media page where you can sign up for press releases or newsletters featuring the latest research.
Relevant tip sheets from Journalist’s Resource:
- 10 things we wish we’d known earlier about research
- How to tell good research from bad: 13 questions journalists should ask (This post also discusses how to determine if a journal is good.)
- Lessons on online search techniques, reading studies, understanding data and methods
- Guide to critical thinking, research, data and theory: Overview for journalists
About The Author
David Trilling
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

How and Where to Find Research Papers for Literature Reviews
The literature review is an integral part of the research process. Finding the correct research papers for a literature review can be a daunting task, especially for early career researchers. This is more so in the digital age, where the sheer quantum of research available can drown researchers who attempt to sift through case studies, journals, online platforms, repositories, and databases. Regardless of whether you are just starting a career in research or are a veteran in the field, looking for relevant sources for a literature review can be time-consuming and frustrating.
In this article, we will provide valuable tips and explore various resources to understand how to find research papers relevant to literature reviews efficiently.
Table of Contents
Academic Databases and Search Engines
To master how to find research papers, start with academic databases and search engines. Platforms such as Google Scholar, ResearchGate, and Scopus are indispensable for accessing a diverse array of scholarly articles. Enhance your search effectiveness by using advanced search options, employing specific keywords, and exploring related terms. Understanding and using the subject headings or descriptors provided by these databases is crucial for honing in on the most relevant papers quickly.
Reference Lists and Citation Networks
An effective strategy for finding research papers lies within the reference lists of the papers you already have. These lists can be gateways to additional, highly relevant sources. Similarly, investigating citation networks—observing which papers have cited key articles in your field—can unveil contemporary studies and emerging perspectives.
Accessing University Libraries
University libraries are a primary source of information on where you can find research papers. They offer access to a wealth of research papers and journals, including databases like JSTOR and ScienceDirect, for those seeking free resources. Library catalogs are instrumental in finding papers by title, author, or subject, and librarians can provide expert navigation through these resources.

Engaging with Online Academic Platforms
Platforms such as ResearchGate and Academia.edu, aside from being academic social networks, are valuable for finding research papers. They facilitate access to scholarly articles and enable researchers to share their work and connect with peers. Repositories like arXiv, bioRxiv, and SSRN provide early access to preprints across various disciplines, broadening your research scope.
Networking through Professional Associations and Conferences
For insights on where to find research papers, tap into professional associations and conferences. These platforms often grant members access to specialized publications and maintain online libraries of scholarly work. Conferences are also a goldmine for obtaining preprints or drafts of papers and for networking with fellow researchers.
Institutional Repositories
Institutional repositories are a go-to resource for finding research papers. These digital collections, hosted by academic institutions, offer open access to a variety of research outputs. Use keywords and subject categories to navigate these repositories for a rich selection of freely available scholarly material.
Government Reports and Policy Documents
Government agencies and research institutes are sometimes overlooked but can be significant sources of research papers. Their published reports and policy documents often include references to pertinent studies, providing valuable insights for your literature review.
By applying these expert strategies, you can streamline your search for relevant research papers. Remember, the quest is not just about where to find scientific articles; it’s about adopting a systematic and informed approach to locate the best resources. Utilizing targeted keywords, keeping abreast of the latest research, and exploring various sources will immensely enhance the quality of your literature reviews.
References:
- https://www.academictransfer.com/en/blog/how-to-find-papers-when-you-do-your-literature-review/
- https://www.scribendi.com/academy/articles/free_online_journal_and_research_databases.en.html
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading app that uses your interests to instantly create personalized reading feeds. Researchers can stay updated on the latest, most relevant content from its continually expanding library of 115M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef , Unpaywall , PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex as well as prestigious publishing houses like Springer Nature , JAMA , IOP, Taylor & Francis , NEJM, BMJ , Karger , SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more. The top-rated app in its space, R Discovery’s carefully curated features give you the power to choose what, where, and how you read research.
Try the app for free or upgrade to R Discovery Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, invite collaborators, auto sync with top reference managers, multiple feeds, and more. It’s like having the world of research at your fingertips ! Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Get R Discovery Prime now at just US $39 a year!
Related Posts

How to Read, Write, Promote Your Research Effectively: Timesaving Solution for Busy Researchers

Why You Need to Evaluate Sources in Research?
News Center
- Browse Archive
- Browse By Administrative Unit
- Browse By College/School
- Accomplishments
- Class Notes
- Experts Directory
- UNLV In The News
- UNLV Today Announcements
- UNLV Magazine
- Share a Story Idea
- Submit Class Note
- Submit a UNLV Today Accomplishment or Announcement
- Become a Speaker/Expert
- Directories
Quick Links
- Directories Home
- Colleges, Schools, and Departments
- Administrative Units
- Research Centers and Institutes
- Resources and Services
- Employee Directory
- Contact UNLV
- Social Media Directory
- UNLV Mobile Apps
- News Center Home
- Accomplishments Home
- Matthew Sheridan, Ao Li
Published: Matthew Sheridan, Ao Li
Matt Sheridan and Ao Li (both Chemistry and Biochemistry) published their research paper, "Reversible Amine-to-Imine Chemistry at a Covalent Organic Framework for Sustainable Uranium Redox Separation," in the journal of ACS Sustainable Chemistry and Engineering . This publication is a collaboration with Soochow and Fudan university focused on developing a rechargeable material to perform uranium photoreduction and separation without the use of sacrificial reagents using a covalent organic framework (COF) with reversible amine-to-imine bonds.
Campus Units:
People in the news.
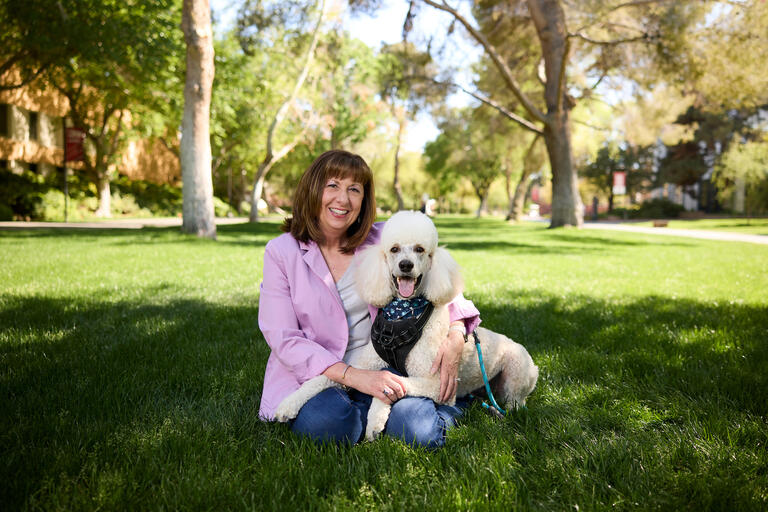

The Interview: Kim Kaplan
The human resources director for University Libraries finds magic in her Vegas life.
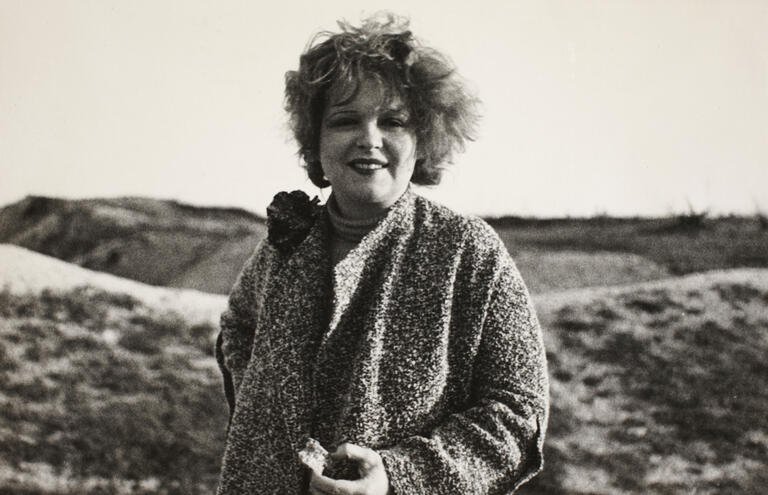

What Do We Know About Clara Bow?
The original 'It Girl' — and subject of Taylor Swift’s latest song — has strong ties to Southern Nevada. Discover more from the UNLV Special Collections & Archives.
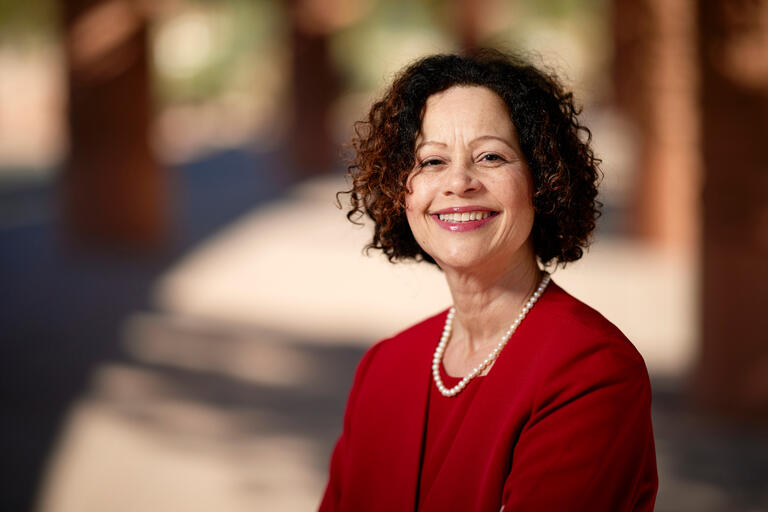

Advancing Legal and Human Rights
2024 Service-Learning Award recipient Rachel Anderson combines passions of community service and teaching for new legal clinic.
VASA-1: Lifelike Audio-Driven Talking Faces Generated in Real Time
- Follow on Twitter
- Like on Facebook
- Follow on LinkedIn
- Subscribe on Youtube
- Follow on Instagram
- Subscribe to our RSS feed
Share this page:
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Reddit
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- 15 April 2024
- Correction 22 April 2024
Revealed: the ten research papers that policy documents cite most
- Dalmeet Singh Chawla 0
Dalmeet Singh Chawla is a freelance science journalist based in London.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar

Policymakers often work behind closed doors — but the documents they produce offer clues about the research that influences them. Credit: Stefan Rousseau/Getty
When David Autor co-wrote a paper on how computerization affects job skill demands more than 20 years ago, a journal took 18 months to consider it — only to reject it after review. He went on to submit it to The Quarterly Journal of Economics , which eventually published the work 1 in November 2003.
Autor’s paper is now the third most cited in policy documents worldwide, according to an analysis of data provided exclusively to Nature . It has accumulated around 1,100 citations in policy documents, show figures from the London-based firm Overton (see ‘The most-cited papers in policy’), which maintains a database of more than 12 million policy documents, think-tank papers, white papers and guidelines.
“I thought it was destined to be quite an obscure paper,” recalls Autor, a public-policy scholar and economist at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge. “I’m excited that a lot of people are citing it.”
The most-cited papers in policy
Economics papers dominate the top ten papers that policy documents reference most.
Data from Overton as of 15 April 2024
The top ten most cited papers in policy documents are dominated by economics research; the number one most referenced study has around 1,300 citations. When economics studies are excluded, a 1997 Nature paper 2 about Earth’s ecosystem services and natural capital is second on the list, with more than 900 policy citations. The paper has also garnered more than 32,000 references from other studies, according to Google Scholar. Other highly cited non-economics studies include works on planetary boundaries, sustainable foods and the future of employment (see ‘Most-cited papers — excluding economics research’).
These lists provide insight into the types of research that politicians pay attention to, but policy citations don’t necessarily imply impact or influence, and Overton’s database has a bias towards documents published in English.
Interdisciplinary impact
Overton usually charges a licence fee to access its citation data. But last year, the firm worked with the publisher Sage to release a free web-based tool , based in Thousand Oaks, California, that allows any researcher to find out how many times policy documents have cited their papers or mention their names. Overton and Sage said they created the tool, called Sage Policy Profiles, to help researchers to demonstrate the impact or influence their work might be having on policy. This can be useful for researchers during promotion or tenure interviews and in grant applications.
Autor thinks his study stands out because his paper was different from what other economists were writing at the time. It suggested that ‘middle-skill’ work, typically done in offices or factories by people who haven’t attended university, was going to be largely automated, leaving workers with either highly skilled jobs or manual work. “It has stood the test of time,” he says, “and it got people to focus on what I think is the right problem.” That topic is just as relevant today, Autor says, especially with the rise of artificial intelligence.
Most-cited papers — excluding economics research
When economics studies are excluded, the research papers that policy documents most commonly reference cover topics including climate change and nutrition.
Walter Willett, an epidemiologist and food scientist at the Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health in Boston, Massachusetts, thinks that interdisciplinary teams are most likely to gain a lot of policy citations. He co-authored a paper on the list of most cited non-economics studies: a 2019 work 3 that was part of a Lancet commission to investigate how to feed the global population a healthy and environmentally sustainable diet by 2050 and has accumulated more than 600 policy citations.
“I think it had an impact because it was clearly a multidisciplinary effort,” says Willett. The work was co-authored by 37 scientists from 17 countries. The team included researchers from disciplines including food science, health metrics, climate change, ecology and evolution and bioethics. “None of us could have done this on our own. It really did require working with people outside our fields.”
Sverker Sörlin, an environmental historian at the KTH Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm, agrees that papers with a diverse set of authors often attract more policy citations. “It’s the combined effect that is often the key to getting more influence,” he says.

Has your research influenced policy? Use this free tool to check
Sörlin co-authored two papers in the list of top ten non-economics papers. One of those is a 2015 Science paper 4 on planetary boundaries — a concept defining the environmental limits in which humanity can develop and thrive — which has attracted more than 750 policy citations. Sörlin thinks one reason it has been popular is that it’s a sequel to a 2009 Nature paper 5 he co-authored on the same topic, which has been cited by policy documents 575 times.
Although policy citations don’t necessarily imply influence, Willett has seen evidence that his paper is prompting changes in policy. He points to Denmark as an example, noting that the nation is reformatting its dietary guidelines in line with the study’s recommendations. “I certainly can’t say that this document is the only thing that’s changing their guidelines,” he says. But “this gave it the support and credibility that allowed them to go forward”.
Broad brush
Peter Gluckman, who was the chief science adviser to the prime minister of New Zealand between 2009 and 2018, is not surprised by the lists. He expects policymakers to refer to broad-brush papers rather than those reporting on incremental advances in a field.
Gluckman, a paediatrician and biomedical scientist at the University of Auckland in New Zealand, notes that it’s important to consider the context in which papers are being cited, because studies reporting controversial findings sometimes attract many citations. He also warns that the list is probably not comprehensive: many policy papers are not easily accessible to tools such as Overton, which uses text mining to compile data, and so will not be included in the database.

The top 100 papers
“The thing that worries me most is the age of the papers that are involved,” Gluckman says. “Does that tell us something about just the way the analysis is done or that relatively few papers get heavily used in policymaking?”
Gluckman says it’s strange that some recent work on climate change, food security, social cohesion and similar areas hasn’t made it to the non-economics list. “Maybe it’s just because they’re not being referred to,” he says, or perhaps that work is cited, in turn, in the broad-scope papers that are most heavily referenced in policy documents.
As for Sage Policy Profiles, Gluckman says it’s always useful to get an idea of which studies are attracting attention from policymakers, but he notes that studies often take years to influence policy. “Yet the average academic is trying to make a claim here and now that their current work is having an impact,” he adds. “So there’s a disconnect there.”
Willett thinks policy citations are probably more important than scholarly citations in other papers. “In the end, we don’t want this to just sit on an academic shelf.”
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-00660-1
Updates & Corrections
Correction 22 April 2024 : The original version of this story credited Sage, rather than Overton, as the source of the policy papers’ citation data. Sage’s location has also been updated.
Autor, D. H., Levy, F. & Murnane, R. J. Q. J. Econ. 118 , 1279–1333 (2003).
Article Google Scholar
Costanza, R. et al. Nature 387 , 253–260 (1997).
Willett, W. et al. Lancet 393 , 447–492 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Steffen, W. et al. Science 347 , 1259855 (2015).
Rockström, J. et al. Nature 461 , 472–475 (2009).
Download references
Reprints and permissions
Related Articles

India’s 50-year-old Chipko movement is a model for environmental activism
Correspondence 23 APR 24
The Middle East’s largest hypersaline lake risks turning into an environmental disaster zone
More work is needed to take on the rural wastewater challenge

CERN’s impact goes way beyond tiny particles
Spotlight 17 APR 24
The economic commitment of climate change
Article 17 APR 24

Last-mile delivery increases vaccine uptake in Sierra Leone
Article 13 MAR 24
Postdoctoral Research Fellow
Description Applications are invited for a postdoctoral fellow position at the Lunenfeld-Tanenbaum Research Institute, Sinai Health, to participate...
Toronto (City), Ontario (CA)
Sinai Health
Postdoctoral Research Associate - Surgery
Memphis, Tennessee
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital (St. Jude)
Open Rank Faculty Position in Biochemistry and Molecular Genetics
The Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Genetics (www.virginia.edu/bmg) and the University of Virginia Cancer Center
Charlottesville, Virginia
Biochemistry & Molecular Genetics
Postdoctoral Position - Synthetic Cell/Living Cell Spheroids for Interactive Biomaterials
Co-assembly of artificial cells and living cells to make co-spheroid structures and study their interactive behavior for biomaterials applications.
Mainz, Rheinland-Pfalz (DE)
University of Mainz
2024 Recruitment notice Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology: Shenzhen, China
The wide-ranging expertise drawing from technical, engineering or science professions...
Shenzhen,China
Shenzhen Institute of Synthetic Biology
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Gender pay gap in U.S. hasn’t changed much in two decades
The gender gap in pay has remained relatively stable in the United States over the past 20 years or so. In 2022, women earned an average of 82% of what men earned, according to a new Pew Research Center analysis of median hourly earnings of both full- and part-time workers. These results are similar to where the pay gap stood in 2002, when women earned 80% as much as men.
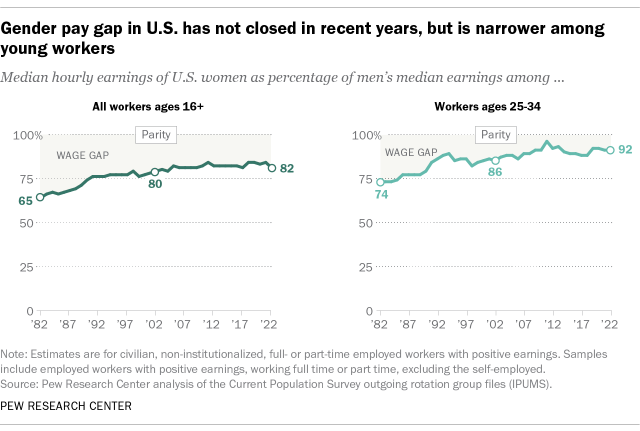
As has long been the case, the wage gap is smaller for workers ages 25 to 34 than for all workers 16 and older. In 2022, women ages 25 to 34 earned an average of 92 cents for every dollar earned by a man in the same age group – an 8-cent gap. By comparison, the gender pay gap among workers of all ages that year was 18 cents.
While the gender pay gap has not changed much in the last two decades, it has narrowed considerably when looking at the longer term, both among all workers ages 16 and older and among those ages 25 to 34. The estimated 18-cent gender pay gap among all workers in 2022 was down from 35 cents in 1982. And the 8-cent gap among workers ages 25 to 34 in 2022 was down from a 26-cent gap four decades earlier.
The gender pay gap measures the difference in median hourly earnings between men and women who work full or part time in the United States. Pew Research Center’s estimate of the pay gap is based on an analysis of Current Population Survey (CPS) monthly outgoing rotation group files ( IPUMS ) from January 1982 to December 2022, combined to create annual files. To understand how we calculate the gender pay gap, read our 2013 post, “How Pew Research Center measured the gender pay gap.”
The COVID-19 outbreak affected data collection efforts by the U.S. government in its surveys, especially in 2020 and 2021, limiting in-person data collection and affecting response rates. It is possible that some measures of economic outcomes and how they vary across demographic groups are affected by these changes in data collection.
In addition to findings about the gender wage gap, this analysis includes information from a Pew Research Center survey about the perceived reasons for the pay gap, as well as the pressures and career goals of U.S. men and women. The survey was conducted among 5,098 adults and includes a subset of questions asked only for 2,048 adults who are employed part time or full time, from Oct. 10-16, 2022. Everyone who took part is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the questions used in this analysis, along with responses, and its methodology .
The U.S. Census Bureau has also analyzed the gender pay gap, though its analysis looks only at full-time workers (as opposed to full- and part-time workers). In 2021, full-time, year-round working women earned 84% of what their male counterparts earned, on average, according to the Census Bureau’s most recent analysis.
Much of the gender pay gap has been explained by measurable factors such as educational attainment, occupational segregation and work experience. The narrowing of the gap over the long term is attributable in large part to gains women have made in each of these dimensions.
Related: The Enduring Grip of the Gender Pay Gap
Even though women have increased their presence in higher-paying jobs traditionally dominated by men, such as professional and managerial positions, women as a whole continue to be overrepresented in lower-paying occupations relative to their share of the workforce. This may contribute to gender differences in pay.
Other factors that are difficult to measure, including gender discrimination, may also contribute to the ongoing wage discrepancy.
Perceived reasons for the gender wage gap
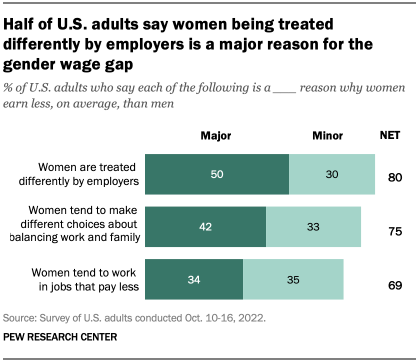
When asked about the factors that may play a role in the gender wage gap, half of U.S. adults point to women being treated differently by employers as a major reason, according to a Pew Research Center survey conducted in October 2022. Smaller shares point to women making different choices about how to balance work and family (42%) and working in jobs that pay less (34%).
There are some notable differences between men and women in views of what’s behind the gender wage gap. Women are much more likely than men (61% vs. 37%) to say a major reason for the gap is that employers treat women differently. And while 45% of women say a major factor is that women make different choices about how to balance work and family, men are slightly less likely to hold that view (40% say this).
Parents with children younger than 18 in the household are more likely than those who don’t have young kids at home (48% vs. 40%) to say a major reason for the pay gap is the choices that women make about how to balance family and work. On this question, differences by parental status are evident among both men and women.
Views about reasons for the gender wage gap also differ by party. About two-thirds of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents (68%) say a major factor behind wage differences is that employers treat women differently, but far fewer Republicans and Republican leaners (30%) say the same. Conversely, Republicans are more likely than Democrats to say women’s choices about how to balance family and work (50% vs. 36%) and their tendency to work in jobs that pay less (39% vs. 30%) are major reasons why women earn less than men.
Democratic and Republican women are more likely than their male counterparts in the same party to say a major reason for the gender wage gap is that employers treat women differently. About three-quarters of Democratic women (76%) say this, compared with 59% of Democratic men. And while 43% of Republican women say unequal treatment by employers is a major reason for the gender wage gap, just 18% of GOP men share that view.
Pressures facing working women and men
Family caregiving responsibilities bring different pressures for working women and men, and research has shown that being a mother can reduce women’s earnings , while fatherhood can increase men’s earnings .
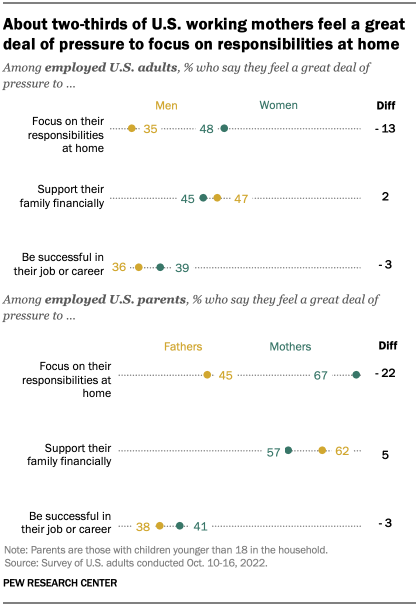
Employed women and men are about equally likely to say they feel a great deal of pressure to support their family financially and to be successful in their jobs and careers, according to the Center’s October survey. But women, and particularly working mothers, are more likely than men to say they feel a great deal of pressure to focus on responsibilities at home.
About half of employed women (48%) report feeling a great deal of pressure to focus on their responsibilities at home, compared with 35% of employed men. Among working mothers with children younger than 18 in the household, two-thirds (67%) say the same, compared with 45% of working dads.
When it comes to supporting their family financially, similar shares of working moms and dads (57% vs. 62%) report they feel a great deal of pressure, but this is driven mainly by the large share of unmarried working mothers who say they feel a great deal of pressure in this regard (77%). Among those who are married, working dads are far more likely than working moms (60% vs. 43%) to say they feel a great deal of pressure to support their family financially. (There were not enough unmarried working fathers in the sample to analyze separately.)
About four-in-ten working parents say they feel a great deal of pressure to be successful at their job or career. These findings don’t differ by gender.
Gender differences in job roles, aspirations
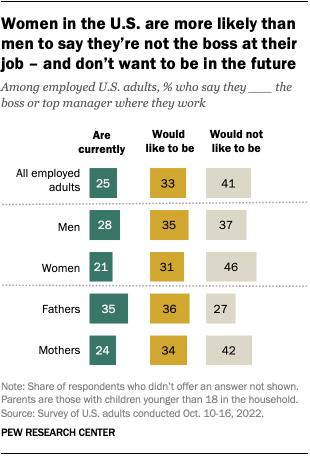
Overall, a quarter of employed U.S. adults say they are currently the boss or one of the top managers where they work, according to the Center’s survey. Another 33% say they are not currently the boss but would like to be in the future, while 41% are not and do not aspire to be the boss or one of the top managers.
Men are more likely than women to be a boss or a top manager where they work (28% vs. 21%). This is especially the case among employed fathers, 35% of whom say they are the boss or one of the top managers where they work. (The varying attitudes between fathers and men without children at least partly reflect differences in marital status and educational attainment between the two groups.)
In addition to being less likely than men to say they are currently the boss or a top manager at work, women are also more likely to say they wouldn’t want to be in this type of position in the future. More than four-in-ten employed women (46%) say this, compared with 37% of men. Similar shares of men (35%) and women (31%) say they are not currently the boss but would like to be one day. These patterns are similar among parents.
Note: This is an update of a post originally published on March 22, 2019. Anna Brown and former Pew Research Center writer/editor Amanda Barroso contributed to an earlier version of this analysis. Here are the questions used in this analysis, along with responses, and its methodology .
What is the gender wage gap in your metropolitan area? Find out with our pay gap calculator
- Gender & Work
- Gender Equality & Discrimination
- Gender Pay Gap
- Gender Roles

Women have gained ground in the nation’s highest-paying occupations, but still lag behind men
Diversity, equity and inclusion in the workplace, the enduring grip of the gender pay gap, more than twice as many americans support than oppose the #metoo movement, women now outnumber men in the u.s. college-educated labor force, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.
Find the research you need | With 160+ million publications, 1+ million questions, and 25+ million researchers, this is where everyone can access science
Google Scholar includes journal and conference papers, theses and dissertations, academic books, pre-prints, abstracts, technical reports and other scholarly literature from all broad areas of research. You'll find works from a wide variety of academic publishers, professional societies and university repositories, as well as scholarly articles ...
Get 30 days free. 1. Google Scholar. Google Scholar is the clear number one when it comes to academic search engines. It's the power of Google searches applied to research papers and patents. It not only lets you find research papers for all academic disciplines for free but also often provides links to full-text PDF files.
Access 160+ million publications and connect with 25+ million researchers. Join for free and gain visibility by uploading your research.
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR. Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals. Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world's leading museums, archives, and scholars. JSTOR is a digital library of academic journals ...
Ultrasound imaging of core muscles activity in multiparous women with vaginal laxity: a cross-sectional study. Doaa A. Abdel Hady. Omar M. Mabrouk. Doaa A. Osman. Article Open Access 20 Apr 2024.
Google Scholar is a free search engine that provides access to research in multiple disciplines. The sources include academic publishers, universities, online repositories, books, and even judicial opinions from court cases. Based on its indexing, Google Scholar provides citation counts to allow authors and others to track the impact of their work.
Elsevier Journal Finder helps you find journals that could be best suited for publishing your scientific article. Journal Finder uses smart search technology and field-of-research specific vocabularies to match your paper's abstract to scientific journals.
Read the latest Research articles from Nature. Datasets from in situ warming experiments across 28 arctic and alpine tundra sites covering a span of less than 1 year up to 25 years show the ...
DOAJ: Any document you find on this academic database is open access and can be accessed free of charge. 8. JSTOR. JSTOR is another great resource to find research papers. Any article published before 1924 in the United States is available for free and JSTOR also offers scholarships for independent researchers. Coverage: more than 12 million items
ACS Publications provides the most interesting, reliable, and relevant scientific content in the world. Students, faculty, staff, and scientists can find the information they need to spark their next influential research article, product, or discovery.
Browse the archive of articles on Nature. Genomic studies of Heliconius butterflies provide evidence that Heliconius elevatus is a hybrid species, and that its speciation was driven by ...
Publications. Our teams aspire to make discoveries that impact everyone, and core to our approach is sharing our research and tools to fuel progress in the field. Google publishes hundreds of research papers each year. Publishing our work enables us to collaborate and share ideas with, as well as learn from, the broader scientific community.
Open research reports. JSTOR hosts a growing curated collection of more than 50,000 open research reports from 187 think tanks and research institutes from around the world. These publications are freely accessible to everyone on JSTOR and discoverable as their own content type alongside journals, books, and primary sources. We update research ...
Explore and build more graphs for interesting papers that you find - soon you'll have a real, visual understanding of the trends, popular works and dynamics of the field you're interested in. Make sure you haven't missed an important paper In some fields like Machine Learning, so many new papers are published it's hard to keep track.
Research databases. You can search for scholarly sources online using databases and search engines like Google Scholar. These provide a range of search functions that can help you to find the most relevant sources. If you are searching for a specific article or book, include the title or the author's name. Alternatively, if you're just ...
OATD.org aims to be the best possible resource for finding open access graduate theses and dissertations published around the world. Metadata (information about the theses) comes from over 1100 colleges, universities, and research institutions. OATD currently indexes 7,439,716 theses and dissertations. About OATD (our FAQ). Visual OATD.org
Search Millions of Research Papers. This fulltext search index includes over 35 million research articles and other scholarly documents preserved in the Internet Archive. The collection spans from digitized copies of eighteenth century journals through the latest Open Access conference proceedings and preprints crawled from the World Wide Web.
One research paper started it all. The research we do today becomes the Google of the future. Google itself began with a research paper, published in 1998, and was the foundation of Google Search. Our ongoing research over the past 25 years has transformed not only the company, but how people are able to interact with the world and its information.
Journal Top 100 - 2022. This collection highlights our most downloaded* research papers published in 2022. Featuring authors from around the world, these papers highlight valuable research from an ...
Try searching by the author's name, if you know it, or title of the paper. Look at the endnotes in papers you like for other papers. And look at the papers that cited the paper you like; they'll probably be useful for your project. Paywalls. If you locate a study and it's behind a paywall, try these steps:
Accessing University Libraries. University libraries are a primary source of information on where you can find research papers. They offer access to a wealth of research papers and journals, including databases like JSTOR and ScienceDirect, for those seeking free resources. Library catalogs are instrumental in finding papers by title, author ...
The MeToo movement increased awareness around issues of gender discrimination in the workplace. This column studies the movement's impact on co-authorship in economics by analysing working papers published between January 2004 and December 2020. The authors find significant changes in the collaborative landscape of economists, particularly evident in a surge of new partnerships across ...
Matt Sheridan and Ao Li (both Chemistry and Biochemistry) published their research paper, "Reversible Amine-to-Imine Chemistry at a Covalent Organic Framework for Sustainable Uranium Redox Separation," in the journal of ACS Sustainable Chemistry and Engineering.This publication is a collaboration with Soochow and Fudan university focused on developing a rechargeable material to perform uranium ...
These numbers might differ from other published numbers due to slightly different choices in the evaluation. As is now standard, we use few-shot prompts to evaluate ... Papers), pages 2924-2936, 2019. [CTJ+21]Mark Chen, Jerry Tworek, Heewoo Jun, ... Open models based on gemini research and technology, 2024. 10 [VSP+17]Ashish Vaswani, Noam ...
We introduce VASA, a framework for generating lifelike talking faces of virtual characters with appealing visual affective skills (VAS), given a single static image and a speech audio clip. Our premiere model, VASA-1, is capable of not only producing lip movements that are exquisitely synchronized with the audio, but also capturing a large ...
The top ten most cited papers in policy documents are dominated by economics research; the number one most referenced study has around 1,300 citations. When economics studies are excluded, a 1997 ...
The gender gap in pay has remained relatively stable in the United States over the past 20 years or so. In 2022, women earned an average of 82% of what men earned, according to a new Pew Research Center analysis of median hourly earnings of both full- and part-time workers. These results are similar to where the pay gap stood in 2002, when women earned 80% as much as men.