Unemployment Essay
500+ words essay on unemployment.
Unemployment is a serious problem among young people. There are thousands of people who do not have any work to do and cannot find work for themselves. Unemployment refers to the situation where a person wants to work but cannot find employment in the labour market. One of the major reasons that contribute to unemployment is the large population of India and the limited availability of resources. In this essay on unemployment, we will discuss all these issues responsible for unemployment in India and how we can overcome this problem. Students must go through this unemployment essay to get ideas on how to write an effective essay on the topic related to unemployment. Also, they can practice more CBSE essays on different topics to boost their writing skills.
Unemployment is measured by the unemployment rate, defined as the number of people actively looking for a job as a percentage of the labour force. The unemployment rate for the year 2013-14 in rural India was 4.7%, whereas it was 5.5% for urban India. In the short term, unemployment significantly reduces a person’s income and, in the long term, it reduces their ability to save for retirement and other goals. Unemployment is a loss of valuable productive resources to the economy. The impact of job loss in rural and regional areas flows through the local community, damaging businesses.

Reason for Unemployment
An unemployed person is one who is an active member of the labour force and is seeking work but is unable to find any work for himself. There are multiple reasons behind the unemployment of a person. One of them is the slow economic growth, due to which jobs in adequate numbers are not created. Excessive dependence on agriculture and slow growth of non-farm activities also limit employment generation. Unemployment in urban areas is mainly the result of substantial rural migration to urban areas. This has also resulted in a labour workforce in cities. The lack of technology and proper machinery has also contributed to unemployment.
The present educational system is based on theoretical knowledge instead of practical work. Thus, it lacks the development of aptitude and technical qualifications required for various types of work among job seekers. This has created a mismatch between the need and availability of relevant skills and training. This results in unemployment, especially among the youth and educated people with high degrees and qualifications. Apart from it, the lack of investment and infrastructure has led to inadequate employment opportunities in different sectors.
Steps to Eliminate Unemployment
Various strategies and proposals have been implemented to generate employment. Many Employment programmes and policies have been introduced and undertaken to boost self-employment and help unemployed people engage in public works. The Government of India has taken several policy measures to fight the problem of unemployment. Some of the measures are the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA), National Skill Development Mission, Swarna Jayanti Shahari Rozgar Yojana (SJSRY), Regional Rural Banks (RRBs).
Despite the measures taken by the government, India remains a country experiencing severe unemployment problems. It can be resolved by imparting education in such a way that youth get the necessary skills so as to get employment easily. Setting up various vocational training and vocational courses for undergraduate and postgraduate students will help in finding employment for youth. The government needs to emphasise these courses at the primary level and make them a compulsory part of the curriculum to make students proficient in their early stages of life. Career counselling should be provided within schools and colleges so that students can choose a better career option based on their interests and ability. Government should create more job opportunities for the youth and graduates.
India is a fast-growing economy. There is an enormous scope for improvement in the unemployment sector. The various measures and steps taken by the government to increase the employment rate have succeeded to a great extent. The widespread skill development programmes have gained popularity across the nation. With better enforcement of the strategies, the employment level can be significantly improved. Although, we have to go a long way before we can say that all the people in India will get employment.
We hope this essay on unemployment must have helped students in boosting their essay-writing skills. Keep learning and visiting the BYJU’S website for more study material.
Frequently Asked Questions on Unemployment Essay
Is unemployment still an existing problem in india.
Yes, unemployment is still a serious issue in our country. Steps need to be taken by the government and also by the youngsters in India to improve this situation.
Is it necessary for schoolchildren to be informed about unemployment?
Students at this young age should definitely be informed about this topic as it will motivate them to study and aim for higher scores in exams.
What points are to be added to an essay topic on Unemployment?
Add details about different age groups of people suffering from this state of employment. You can focus on the fact that poverty is an indirect reason for unemployment and vice-versa. Then, suggest steps that can be taken to bring about an improvement in education and increase the percentage of literacy.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Counselling

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

22.1: Introduction to Unemployment
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 4465

Defining Unemployment
Unemployment, also referred to as joblessness, occurs when people are without work and actively seeking employment.
learning objectives
- Classify the different measures and types of unemployment
Unemployment, also referred to as joblessness, occurs when people are without work and are actively seeking employment. During periods of recession, an economy usually experiences high unemployment rates. There are many proposed causes, consequences, and solutions for unemployment.
Types of Unemployment
- Classical: occurs when real wages for jobs are set above the market-clearing level. It causes the number of job seekers to be higher than the number of vacancies.
- Cyclical: occurs when there is not enough aggregate demand in the economy to provide jobs for everyone who wants to work. Demand for goods and services decreases, less production is needed, and fewer workers are needed.
- Structural: occurs when the labor market is not able to provide jobs for everyone who wants to work. There is a mismatch between the skills of the unemployed workers and the skills needed for available jobs. It differs from frictional unemployment because it lasts longer.
- Frictional: the time period in between jobs when a worker is searching for work or transitioning from one job to another.
- Hidden: the unemployment of potential workers that is not taken into account in official unemployment statistics because of how the data is collected. For example, workers are only considered unemployed if they are looking for work so those without jobs who have stopped looking are no longer considered unemployed.
- Long-term: usually defined as unemployment lasting longer than one year.
Measuring Unemployment
Unemployment is calculated as a percentage by dividing the number of unemployed individuals by the number of all individuals currently employed in the workforce. The final measurement is called the rate of unemployment.
Unemployment Rate : Unemployment is calculated as a percentage by dividing the number of unemployed individuals by the number of individual employed in the labor force.
Effects of Unemployment
When unemployment rates are high and steady, there are negative impacts on the long-run economic growth. Unemployment wastes resources, generates redistributive pressures and distortions, increases poverty, limits labor mobility, and promotes social unrest and conflict. The effects of unemployment can be broken down into three types:
- Individual: people who are unemployed cannot earn money to meet their financial obligations. Unemployment can lead to homelessness, illness, and mental stress. It can also cause underemployment where workers take on jobs that are below their skill level.
- Social: an economy that has high unemployment is not using all of its resources efficiently, specifically labor. When individuals accept employment below their skill level the economies efficiency is reduced further. Workers lose skills which causes a loss of human capital.
- Socio-political: high unemployment rates can cause civil unrest in a country.
Reducing Unemployment
There are numerous solutions that can help reduce the amount of unemployment:
- Demand side solutions: many countries aid unemployed workers through social welfare programs. Individuals receive unemployment benefits including insurance, compensation, welfare, and subsidies to aid in retraining. An example of a demand side solution is government funded employment of the able-bodied poor.
- Supply side solutions: the labor market is not 100% efficient. Supply side solutions remove the minimum wage and reduce the power of unions. The policies are designed to make the market more flexible in an attempt to increase long-run economic growth. Examples of supply side solutions include cutting taxes on businesses, reducing regulation, and increasing education.
Defining Full Employment
Full employment is defined as an acceptable level of unemployment somewhere above 0%; there is no cyclical or deficient-demand unemployment.
- Define full employment
Full Employment
In macroeconomics, full employment is the level of employment rates where there is no cyclical or deficient-demand unemployment. Mainstream economists define full employment as an acceptable level of unemployment somewhere above 0%. Full employment represents a range of possible unemployment rates based on the country, time period, and political biases.
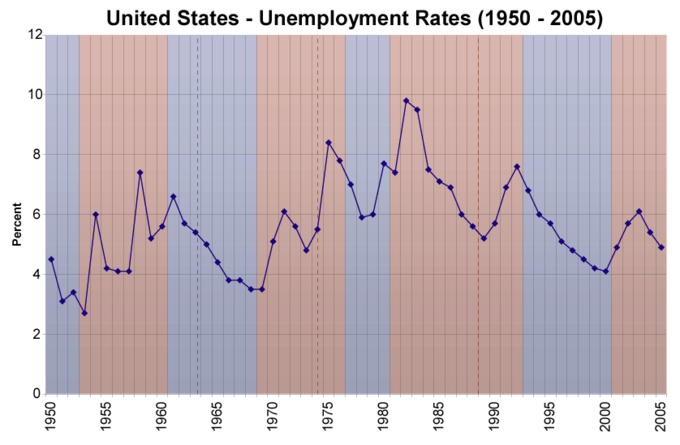
U.S. Unemployment : The graph shows the unemployment rates in the United States. Full employment is defined as “ideal” unemployment. It is important because it keeps inflation under control.
Ideal Unemployment
Full employment is often seen as an “ideal” unemployment rate. Ideal unemployment excludes types of unemployment where labor-market inefficiency is reflected. Only some frictional and voluntary unemployment exists, where workers are temporarily searching for new jobs. This classifies the unemployed individuals as being without a job voluntarily. Ideal unemployment promotes the efficiency of the economy.
Lord William Beveridge defined “full employment” as the situation where the number of unemployed workers equaled the number of job vacancies available. He preferred that the economy be kept above the full employment level to allow for maximum economic production.
Non-Accelerating Inflation Rate of Unemployment (NAIRU)
The full employment unemployment rate is also referred to as “natural” unemployment. In an effort to avoid this normative connotation, James Tobin introduced the term “Non-Accelerating Inflation Rate of Unemployment” also known as the NAIRU. It corresponds to the level of unemployment when real GDP equals potential output. The NAIRU has been called the “inflation threshold. ” The NAIRU states the inflation does not rise or fall when unemployment equals the natural rate.
As an example, the United States is committed to full employment. The “Full Employment Act” was passed in 1946 and revised in 1978. It states that full employment in the United States is no more than 3% unemployment for persons 20 and older, and 4% for persons aged 16 and over.
Types of Unemployment: Frictional, Structural, Cyclical
In economics, unemployment is occurs when people are without work while actively searching for employment.
- Discuss structural unemployment, frictional unemployment, and the natural unemployment rate
Unemployment
In economics, unemployment occurs when people are without work while actively searching for employment. The unemployment rate is a percentage, and calculated by dividing the number of unemployed individuals by the number of all currently employed individuals in the labor force. The causes, consequences, and solutions vary based on the specific type of unemployment that is present within a country.
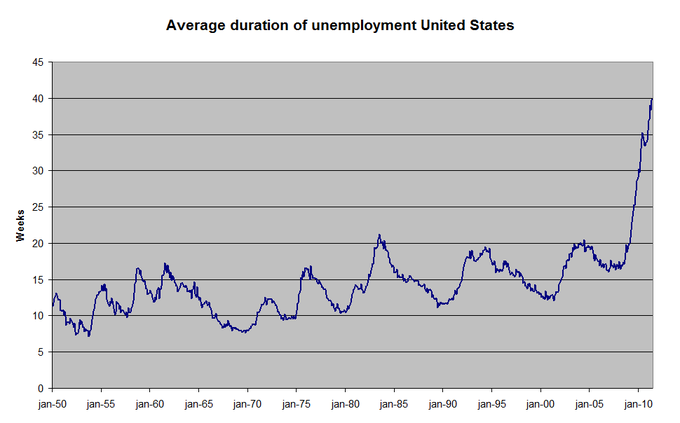
U.S. Unemployment : This graph shows the average duration of unemployment in the United States from 1950-2010. Unemployment occurs when there are more individuals seeking jobs than there are vacancies.
Structural Unemployment
Structural unemployment is one of the main types of unemployment within an economic system. It focuses on the structural problems within an economy and inefficiencies in labor markets. Structural unemployment occurs when a labor market is not able to provide jobs for everyone who is seeking employment. There is a mismatch between the skills of the unemployed workers and the skills needed for the jobs that are available. It is often impacted by persistent cyclical unemployment. For example, when an economy experiences long-term unemployment individuals become frustrated and their skills become obsolete. As a result, when the economy recovers they may not fit the requirements of new jobs due to their inactivity.

Retraining : When there is structural unemployment, workers may seek to learn different skills so that they can apply to new types of jobs.
Frictional Unemployment
Frictional unemployment is another type of unemployment within an economy. It is the time period between jobs when a worker is searching for or transitioning from one job to another. Frictional unemployment is always present to some degree in an economy. It occurs when there is a mismatch between the workers and jobs. The mismatch can be related to skills, payment, work time, location, seasonal industries, attitude, taste, and other factors. Frictional unemployment is influenced by voluntary decisions to work based on each individual’s valuation of their own work and how that compares to current wage rates as well as the time and effort required to find a job.
Cyclical Unemployment
Cyclical unemployment is a type of unemployment that occurs when there is not enough aggregate demand in the economy to provide jobs for everyone who wants to work. In an economy, demand for most goods falls, less production is needed, and less workers are needed. With cyclical unemployment the number of unemployed workers is greater that the number of job vacancies.
The Natural Unemployment Rate
The natural unemployment rate, sometimes called the structural unemployment rate, was developed by Friedman and Phelps in the 1960s. It represents the hypothetical unemployment rate that is consistent with aggregate production being at a long-run level. The natural rate of unemployment is a combination of structural and frictional unemployment. It is present in an efficient and expanding economy when labor and resource markets are at equilibrium. The natural unemployment rate occurs within an economy when disturbances are not present.
- Types of unemployment determine what the causes, consequences, and solutions. The types of unemployment include: classical, cyclical, structural, frictional, hidden, and long-term.
- Unemployment is calculated as a percentage by dividing the number of unemployed individuals by the number of all the individuals currently employed in the work force.
- When unemployment rates are high and steady, there are negative impacts on the long-run economic growth.
- Demand side and supply side solutions are used to reduce unemployment rates.
- Full employment represents a range of possible unemployment rates based on the country, time period, and political biases.
- Full employment is often seen as an “ideal” unemployment rate. Ideal unemployment excludes types of unemployment where labor-market inefficiency is reflected.
- The full employment unemployment rate is also referred to as “natural” unemployment.
- The Non-Accelerating Inflation Rate of Unemployment (NAIRU) corresponds to the unemployment rate when real GDP equals potential output.
- Structural unemployment focuses on the structural problems within an economy and inefficiencies in labor markets.
- Frictional unemployment is the time period between jobs when a worker is searching for or transitioning from one job to another.
- Cyclical unemployment is a type of unemployment that occurs when there is not enough aggregate demand in the economy to provide jobs for everyone who wants to work.
- Classical unemployment occurs when real wages for a jobs are set above the marketing clearing level.
- The natural unemployment rate represents the hypothetical unemployment rate that is consistent with aggregate production being at a long-run level.
- unemployment : The state of being jobless and looking for work.
- full employment : A state when an economy has no cyclical or deficient-demand unemployment.
- structural unemployment : A mismatch between the requirements of the employers and the properties of the unemployed.
- frictional unemployment : When people being temporarily between jobs, searching for new ones.
LICENSES AND ATTRIBUTIONS
CC LICENSED CONTENT, SPECIFIC ATTRIBUTION
- unemployment. Provided by : Wiktionary. Located at : en.wiktionary.org/wiki/unemployment . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Unemployment. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Unemplo...ull_employment . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Boundless. Provided by : Boundless Learning. Located at : www.boundless.com//economics/...n/unemployment . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Us unemployment rates 1950 2005. Provided by : Wikimedia. Located at : commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Us_unemployment_rates_1950_2005.png . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- full employment. Provided by : Wiktionary. Located at : en.wiktionary.org/wiki/full_employment . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Full employment. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Full_employment . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Boundless. Provided by : Boundless Learning. Located at : www.boundless.com//economics/...ull-employment . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Map of U.S. states by unemployment rate. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Map_of_U.S._states_by_unemployment_rate.png . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Unemployment types. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Unemplo...l_unemployment . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Natural rate of unemployment. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Natural_rate_of_unemployment . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Unemployment. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Unemplo...l_unemployment . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- frictional unemployment. Provided by : Wiktionary. Located at : en.wiktionary.org/wiki/frictional_unemployment . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- structural unemployment. Provided by : Wiktionary. Located at : en.wiktionary.org/wiki/structural_unemployment . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- All sizes | Stone Hall Adult Education Centre, Warwick Road, Acocks Green - sign | Flickr - Photo Sharing!. Provided by : Flickr. Located at : www.flickr.com/photos/ell-r-b...n/photostream/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- US average duration of unemployment. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/File:US_average_duration_of_unemployment.png . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- US & World Economies
- Unemployment
What Is Unemployment?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ScreenShot2020-03-23at2.04.43PM-59de96b153e540c498f1f1da8ce5c965.png)
How Unemployment Works
Example of unemployment, types of unemployment, disadvantages of unemployment, frequently asked questions (faqs).
The Balance / Daniel Fishel
Unemployment refers to the number of people who are available and looking for work but who are unable to find jobs. Unemployment impacts not only individuals, but communities, regions, and the overall economy as well.
Key Takeaways
- Unemployment occurs when someone is able to work and wants to work but is unable to find employment.
- The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) specifically defines unemployed persons as those who don't have a job but are available for work and have looked for work in the past four weeks.
- Unemployment on a national level is caused by a slowing economy. Competition in particular industries, advancing technology, and outsourcing can also cause unemployment.
- Unemployment has both individual and broader economic consequences.
Economic slowdowns are the primary cause of unemployment on a national level. Businesses are forced to cut costs when the economy slows by reducing payroll expenses.
The COVID-19 outbreak created higher employment rates than the Great Recession of 2007 to 2009. In fact, during the first few months of the pandemic, they were actually closer to the unemployment rates experienced during the Great Depression. The history of recessions shows that an increase in the unemployment rates has always accompanied them.
Competition in particular industries or companies can also cause unemployment. Advanced technology, such as computers or automation, can cause unemployment by replacing workers who normally handle tasks with machines.
There are several sub-types of unemployment. It's referred to as "structural unemployment" when technology replaces people and results in job loss.
Unemployment isn't evenly distributed among the population. The rate of unemployment can be higher or lower for certain groups, depending on multiple factors, including:
- Socioeconomic class
You're considered to be unemployed when you can work, and you want to work, but you can't find a suitable job. The term "unemployment" quantifies or measures a group of unemployed people. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) has a more specific definition: the number of people who don't have a job, have actively looked for work in the past four weeks, and are available for work.
The BLS also includes in unemployment statistics people who are temporarily laid off and are waiting to be called back to their jobs.
The BLS reports unemployment statistics in its U-3 report, part of the monthly jobs report . It measures unemployment through monthly household surveys referred to as the Current Population Survey (CPS). The CPS has been conducted every month since 1940. It was originally part of the government's response to the Great Depression, and it's been modified several times since then.
The BLS doesn't count residents of any institution as being unemployed, including prisons, jails, mental facilities, and homes for the aged. It doesn't count those on active military duty, either.
A major redesign of the CPS occurred in 1994. The questionnaire was revamped, and computer-assisted interviewing was used. Some of the labor force concepts were also revised.
The BLS doesn't count everyone who is jobless as being unemployed. It excludes those who haven't looked for work within the last four weeks. The BLS also removes them from the labor force, which includes both the employed and unemployed.
Most people who voluntarily leave the labor force do so because of:
- A disability that keeps them from working
- Family responsibilities
- Lack of need or interest in working
The BLS also doesn't include in the labor force those people who would like to work but aren't actively looking for work. They may have stopped looking due to school, health problems, transportation issues, or a lack of available jobs.
But the BLS does track these people in the U-6 unemployment rate. Some people call this the " real unemployment rate ." It includes those who have looked for work in the past 12 months, but not the past four weeks. The BLS identifies people in this group as "marginally attached to the labor force." " Discouraged workers " are a subset of the marginally attached. They've given up looking, because they don't think there are jobs out there for them.
Those younger than age 16 aren't included in the American labor force, even if they're working.
The consequences of unemployment are financially and emotionally destructive for individuals. Long-term unemployment can lead to financial instability or poverty, which can also cause physical and mental health problems.
The consequences can be harmful to the economy when unemployment rises above 5% or 6%. The economy loses one of its key growth drivers when that many people are unemployed: consumer spending . Workers have less money to spend until they find another job.
Lower consumer spending reduces business revenue, and this forces companies to cut more payroll to reduce their costs. It can contribute to a downward economic spiral.
Those who are unemployed long-term may find that their job skills no longer match the requirements of jobs being offered. This is called "structural unemployment." Many who are facing this type of unemployment are age 55 or older. This group may not be able to get good jobs, despite laws prohibiting age discrimination. They may get part-time or low-paying entry-level jobs to make ends meet until they can take early Social Security benefits at age 62.
It can deepen a recession or depression when high national unemployment continues.
Who counts as unemployed?
BLS says you are considered unemployed when you don't have a job, have actively looked for work in the past four weeks, and are available for work.
How does the BLS define the unemployment rate?
The unemployment rate is the percentage of the total labor force that is unemployed.
Pew Research Center. " Unemployment Rose Higher in Three Months of COVID-19 Than It Did in Two Years of the Great Recession ."
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. " How the Government Measures Unemployment ."
U.S. Bureau of Labor and Statistics. " History of the Current Population Survey ."
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. " How the Government Measures Unemployment ." Pages 2, 4.
Center for American Progress. " An Unequal Division of Labor ."
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. " Alternative Measures of Labor Underutilization for States, 2021 Annual Averages ."
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. " How the Government Measures Unemployment ," Page 4.
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. " What Is the Lowest Level of Unemployment That the U.S. Economy Can Sustain? "
National Center for Biotechnology Information. " Unemployment Among Younger and Older Individuals: Does Conventional Data About Unemployment Tell Us the Whole Story? "
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/what-is-unemployment-3306222_FINAL-blank-d5eae495a96a485a9f2940abc7542df6-b7a8b9905ef843858d4e50fad2b1c170.png)
- 7 Causes of Unemployment 2 of 16
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/unemployment-rate-falls-to-3-9-percent--stocks-close-higher-954724928-5b374c43c9e77c0037dc233a.jpg)
What Is Unemployment? Causes, Types, and Measurement
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is Unemployment?
- How It Works
- Measuring Unemployment
The Bottom Line
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
Yarilet Perez is an experienced multimedia journalist and fact-checker with a Master of Science in Journalism. She has worked in multiple cities covering breaking news, politics, education, and more. Her expertise is in personal finance and investing, and real estate.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/YariletPerez-d2289cb01c3c4f2aabf79ce6057e5078.jpg)
How is Unemployment Defined?
The term unemployment refers to a situation where a person actively searches for employment but is unable to find work. Unemployment is considered to be a key measure of the health of the economy.
The most frequently used measure of unemployment is the unemployment rate . It's calculated by dividing the number of unemployed people by the number of people in the labor force.
Many governments offer unemployment insurance to certain unemployed individuals who meet eligibility requirements.
Key Takeaways
- Unemployment occurs when workers who want to work are unable to find jobs.
- High rates of unemployment signal economic distress while extremely low rates of unemployment may signal an overheated economy.
- Unemployment can be classified as frictional, cyclical, structural, or institutional.
- Unemployment data is collected and published by government agencies in a variety of ways.
- Many governments offer unemployed individuals a small amount of income through unemployment insurance, as long as they meet certain requirements.
Michela Buttignol
Understanding Unemployment
Unemployment is a key economic indicator because it signals the ability (or inability) of workers to obtain gainful work and contribute to the productive output of the economy. More unemployed workers mean less total economic production.
The unemployment definition doesn't include people who leave the workforce for reasons such as retirement, higher education, and disability.
Sign of Economic Distress
Unemployed workers must maintain at least subsistence consumption during their period of unemployment. This means that an economy with high unemployment has lower output without a proportional decline in the need for basic consumption.
High, persistent unemployment can signal serious distress in an economy and even lead to social and political upheaval.
Sign of an Overheating Economy
A low unemployment rate, on the other hand, means that the economy is more likely to be producing near its full capacity, maximizing output, driving wage growth, and raising living standards over time.
However, extremely low unemployment can also be a cautionary sign of an overheating economy, inflationary pressures, and tight conditions for businesses in need of additional workers.
Categories of Unemployment
While the definition of unemployment is clear, economists divide unemployment into many different categories. The two broadest categories are voluntary and involuntary unemployment. When unemployment is voluntary, it means that a person left their job willingly in search of other employment. When it is involuntary, it means that a person was fired or laid off and must now look for another job.
Types of Unemployment
Both voluntary and involuntary unemployment can be broken down into four types.
Frictional Unemployment
This type of unemployment is usually short-lived. It is also the least problematic from an economic standpoint. It occurs when people voluntarily change jobs. After a person leaves a company, it naturally takes time to find another job. Similarly, graduates just starting to look for jobs to enter the workforce add to frictional unemployment.
Frictional unemployment is a natural result of the fact that market processes take time and information can be costly. Searching for a new job, recruiting new workers, and matching the right workers to the right jobs all take time and effort. This results in frictional unemployment.
Cyclical Unemployment
Cyclical unemployment is the variation in the number of unemployed workers over the course of economic upturns and downturns, such as those related to changes in oil prices. Unemployment rises during recessionary periods and declines during periods of economic growth.
Preventing and alleviating cyclical unemployment during recessions is one of the key reasons for the study of economics and the various policy tools that governments employ to stimulate the economy on the downside of business cycles.
Structural Unemployment
Structural unemployment comes about through a technological change in the structure of the economy in which labor markets operate. Technological changes can lead to unemployment among workers displaced from jobs that are no longer needed. Examples of such changes include the replacement of horse-drawn transport with automobiles and the automation of manufacturing.
Retraining these workers can be difficult, costly, and time-consuming. Displaced workers often end up either unemployed for extended periods or leaving the labor force entirely.
Institutional Unemployment
Institutional unemployment results from long-term or permanent institutional factors and incentives in the economy.
The following can all contribute to institutional unemployment:
- Government policies, such as high minimum wage floors, generous social benefits programs, and restrictive occupational licensing laws
- Labor market phenomena, such as efficiency wages and discriminatory hiring
- Labor market institutions, such as high rates of unionization
How to Measure Unemployment
In the United States, the government uses surveys, census counts, and the number of unemployment insurance claims to track unemployment.
The U.S. Census conducts a monthly survey called the Current Population Survey (CPS) on behalf of the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) to produce the primary estimate of the nation’s unemployment rate. This survey has been done every month since 1940.
The sample consists of about 60,000 eligible households. That translates to about 110,000 people each month. The Census changes a quarter of the sampled households each month so that no household is represented for more than four consecutive months. This is meant to strengthen the reliability of the estimates.
Many variations of the unemployment rate exist, with different definitions of who is an unemployed person and who is in the labor force.
The BLS commonly cites the U-3 unemployment rate (defined as the total unemployed as a percentage of the civilian labor force) as the official unemployment rate; however, this definition does not include discouraged unemployed workers who are no longer looking for work.
Other categories of unemployment include discouraged workers and part-time or underemployed workers who want to work full-time but, for economic reasons, are unable to do so.
History of Unemployment
Although the U.S. government began tracking unemployment in the 1940s, the highest rate of unemployment to date occurred during the Great Depression, when unemployment rose to 24.9% in 1933.
Between 1931 and 1940, the unemployment rate remained above 14% but subsequently dropped down to the single digits. It remained there until 1982 when it climbed above 10%.
In 2009, during the Great Recession, unemployment again rose to 10%. In April 2020, amid the COVID-19 pandemic, unemployment hit 14.8%. As of February 2024, the unemployment rate was 3.9%.
What Are the Main Causes of Unemployment?
There are many reasons for unemployment. These include recessions, depressions, technological improvements, job outsourcing, and voluntarily leaving one job to find another.
What Are the 3 Types of Unemployment?
Today's economists point to three main types of unemployment: frictional, structural, and cyclical. Frictional unemployment is the result of voluntary employment transitions within an economy. Frictional unemployment naturally occurs, even in a growing, stable economy as workers change jobs.
Structural unemployment can produce permanent disruptions due to fundamental and permanent changes that occur in the structure of the economy. These changes can marginalize a group of workers. They include technological changes, a lack of relevant skills, and jobs moving overseas to another country. Cyclical unemployment relates to the loss of jobs that occurs during changes in business cycles.
What Is the Strict Definition of Unemployment?
The official unemployment definition comes from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, which states that "people are classified as unemployed if they do not have a job, have actively looked for work in the prior four weeks, and are currently available for work."
Unemployment is when an individual who is not employed and is seeking employment, cannot find work. Unemployment is a key indicator of the health of an economy. A low unemployment rate represents a strong economy while a high unemployment rate represents a weak economy.
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. “ How the Government Measures Unemployment ."
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. " Concepts and Definitions (CPS) ."
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. " Alternative Measures of Labor Underutilization for States, 2023 Annual Averages ."
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. “ Table A-15. Alternative Measures of Labor Underutilization .”
U.S. Census Bureau. " Chapter D, Labor: Labor Force (Series D 1-682) ." Page 135.
Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis, FRED. “ Unemployment Rate .”
- What Is Unemployment? Causes, Types, and Measurement 1 of 43
- What Does Termination of Employment Mean? 2 of 43
- What Is an Unemployment Claim? 3 of 43
- Unemployment Compensation: Definition, Requirements, and Example 4 of 43
- What Is Severance Pay? Definition and Why It's Offered 5 of 43
- The Layoff Payoff: A Severance Package 6 of 43
- 7 Considerations When You Negotiate Severance 7 of 43
- 7 Effective Ways to Prepare for a Layoff 8 of 43
- Unemployment Insurance (UI): How It Works, Requirements, and Funding 9 of 43
- How to Apply for Unemployment Insurance Now 10 of 43
- Who Doesn't Get Unemployment Insurance? 11 of 43
- What Was Private Unemployment Insurance? 12 of 43
- How to Pay Your Bills When You Lose Your Job 13 of 43
- Can I Access Money in My 401(k) If I Am Unemployed? 14 of 43
- All About COBRA Health Insurance 15 of 43
- Medical Debt: What to Do When You Can’t Pay 16 of 43
- Help, My Unemployment Benefits Are Running Out 17 of 43
- What Is the Unemployment Rate? Rates by State 18 of 43
- How Is the U.S. Monthly Unemployment Rate Calculated? 19 of 43
- Unemployment Rates: The Highest and Lowest Worldwide 20 of 43
- What You Need to Know About the Employment Report 21 of 43
- U-3 vs. U-6 Unemployment Rate: What's the Difference? 22 of 43
- Participation Rate vs. Unemployment Rate: What's the Difference? 23 of 43
- What the Unemployment Rate Does Not Tell Us 24 of 43
- How the Unemployment Rate Affects Everybody 25 of 43
- How Inflation and Unemployment Are Related 26 of 43
- How the Minimum Wage Impacts Unemployment 27 of 43
- The Cost of Unemployment to the Economy 28 of 43
- Okun’s Law: Economic Growth and Unemployment 29 of 43
- What Can Policymakers Do To Decrease Cyclical Unemployment? 30 of 43
- What Happens When Inflation and Unemployment Are Positively Correlated? 31 of 43
- The Downside of Low Unemployment 32 of 43
- Frictional vs. Structural Unemployment: What’s the Difference? 33 of 43
- Structural vs. Cyclical Unemployment: What's the Difference? 34 of 43
- Cyclical Unemployment: Definition, Cause, Types, and Example 35 of 43
- Disguised Unemployment: Definition and Different Types 36 of 43
- Employment-to-Population Ratio: Definition and What It Measures 37 of 43
- Frictional Unemployment: Definition, Causes, and Quit Rate Explained 38 of 43
- Full Employment: Definition, Types, and Examples 39 of 43
- Labor Force Participation Rate: Purpose, Formula, and Trends 40 of 43
- Labor Market Explained: Theories and Who Is Included 41 of 43
- What Is the Natural Unemployment Rate? 42 of 43
- Structural Unemployment: Definition, Causes, and Examples 43 of 43
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/job-hunt-game-5bfc2d3e4cedfd0026c16b2d.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
AP®︎/College Macroeconomics
Course: ap®︎/college macroeconomics > unit 2.
- Unemployment rate primer
- Natural, cyclical, structural, and frictional unemployment rates
- Worked free response question on unemployment
Lesson summary: Unemployment
- Unemployment
- Types of unemployment and the natural rate of unemployment
Lesson overview
Key takeaways, the labor force participation rate (lfpr), limitations of the unemployment rate, three types of unemployment, the natural rate of unemployment, changes in the natural rate of unemployment (nru), key equations, the labor force:, the unemployment rate (ur), common misperceptions.
- Not everyone who is out of work is unemployed. In order to be counted as unemployed you have to be out of work, looking for work, and able to accept a job if one is offered to you. If you are out of work and not looking, then you are considered “not in the labor force” rather than unemployed.
- We tend to think of unemployment as an undesirable thing, but a certain amount of unemployment is actually part of a healthy economy. Structural unemployment occurs when new industries are created and old industries become obsolete. For example, when we moved from using horses and buggies to using cars to get around, this put a lot of buggy makers in the structurally unemployed category.
- Frictional unemployment might not seem very fun, but consider what it means to have zero unemployment—nobody ever looks for a job, they just remain in whatever job they are given! In fact, a number of dystopian novels have been written in which everyone in a society is automatically assigned a fixed career (such as the Divergent series). Those societies have zero frictional unemployment, but they are also quite unpleasant if you are unhappy with that career!
- A decrease in the unemployment rate isn’t necessarily a sign of an improving economy. When people stop looking for jobs and drop out of the labor force as discouraged workers, the unemployment rate will decrease even though the true employment situation hasn’t gotten any better. This is why it is important to look at both changes in the unemployment rate and changes in the labor force participation rate. Looking at both changes let’s you get a more complete idea about changes in the employment situation.
Discussion Questions:
- An inventor in Burginville developed a fantastic new dictation machine that perfectly records speech and turns it into a typed document. Unfortunately, that meant that unemployment increased among typists working in offices. Which type of unemployment is this? Explain. Solution, please. This is structural unemployment because typists skills are no longer desired. The changing structure of office work has resulted in people losing their jobs.
- The nation of Fitlandia has 120 , 000 people. Of these, 20 , 000 are children under the age of 16, 72,000 have jobs, 8,000 don’t have jobs and are looking for work, and 20,000 people are retired. Assuming that these are all noninstitutionalized civilians, calculate the labor force participation rate and the unemployment rate. I think I got it. Can I check my work? L F = # Employed + # Unemployed = 72,000 + 8,000 = 80,000 L F P R = L F Eligible Population × 100 % = 80,000 100,000 × 100 % = 80 % U R = # Unemployed # Labor Force × 100 % = 8,000 80,000 × 100 % = 10 %
- Explain why a decrease in the unemployment rate can actually signal a tough job market.
Want to join the conversation?
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

Essays About Unemployment: Top 6 Examples and 5 Prompts
Read our guide to see helpful essay examples and prompts to further your understanding and write essays about unemployment.
Unemployment is an unfortunate circumstance many find themselves in; it is a challenge that civilized society faces today. When people are unemployed, they look for jobs but cannot get them. As a result, they are left without a source of income and cannot adequately provide for themselves and their families. This, in turn, can lead to various issues, including depression.
Unemployment is a social, economic, and political issue. It leaves many people in poverty and prevents people from obtaining a source of income. As a result, politicians capture the eyes of voters by promising to lower the unemployment rate to get elected.
You can get started by reading these essay examples if you are writing essays about unemployment.
6 Examples of Essays About Unemployment
1. unemployment reflection by christopher haynes, 2. what i learned from nearly a year of unemployment by becca slaughter, 3. why aren’t europe and canada in the same boat as u.s. for unemployment by glen hendrix, 4. a global dilemma: how unemployment creates poverty by tess hinteregger, 5. why has covid-19 been especially harmful for working women by nicole bateman and martha ross, 6. youth day and ordeal of nigerian youth by utomi jerome-mario, essay prompts about unemployment, 1. unemployment during the covid-19 pandemic, 2. the connection between unemployment and crime, 3. unemployment: whose fault is it, 4. the causes of unemployment, 5. the effects of unemployment.
“In order to secure work, we must be prepared to change or upgrade our skills and be willing to relocate if necessary. But some people are not interested in retraining to find work in another field, some people do not have the confidence to go out and look for work, and some refuse to accept a job they feel is below their level. Unless people like this change their attitudes, they will not be able to find work.”
Haynes provides two perspectives on unemployment; first, that the government should do more to address it, and second, that if people want work, they must adjust to make a living. He believes that many are unemployed because they are unwilling to change their skillset or relocate to get a job. Therefore, more should be done to reduce unemployment, but it goes both ways; everyone must put in the effort.
“I remember feeling embarrassed and powerless. I was angry it wasn’t my decision. I was happy I didn’t have to go back there, yet I was stressed about not having anywhere to go. Ultimately, I felt an overwhelming sadness that left me terrified. While I was overflowing with confusing and contradicting emotions, I somehow felt empty.”
In her essay, Slaughter reflects on her unemployed time and how it changed her. Her previous job was long and stressful, but whenever someone would ask her what she did for a living, she was embarrassed and regretful for not being there anymore. In addition to losing her job, she feels like she lost a part of herself at that time. Thankfully, she got a new job, one less taxing than her previous one.
“You would think paying all that money year after year to a government whose purpose is to “establish justice, insure domestic tranquility, provide for the common defense, promote the general welfare, and secure the blessings of liberty to ourselves and our posterity” would entitle that person to a modicum of “blessings” to insure his “tranquility” and “general welfare” in case of some stupid virus pandemic. It would certainly be the “just” thing to do. And that person’s “posterity” might look a bit less bleak. European governments and Canada did just that. And it’s not even explicitly stated in the preamble to their constitution.”
Hendrix criticizes the United States’ response to the unemployment problem caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, saying that Canada and European nations have done a much better job. He discusses how much better their unemployment benefit system is compared to the U.S. and how it is ironic that the United States, whose constitution says all of these things promoting justice and wellbeing, cannot provide that for its citizens during a global pandemic.
“While unemployment can create poverty, poverty also reduces the chance of being employed. To ensure that those who are affected by unemployment do not fall into the negative cycle, researchers believe that governments should focus on improving quality education and training all young people so they remain in school.”
Hinteregger, in her essay, explains the link between unemployment and poverty, writing that it leads to the loss of income. People will also have to raise their families in poverty, which perpetuates the cycle of poverty. In addition, the poor may resort to violence to make a living. She points out the sheer irony of this issue, as unemployment causes poverty while poverty may also reduce the chance of being employed.
“COVID-19 is hard on women because the U.S. economy is hard on women, and this virus excels at taking existing tensions and ratcheting them up. Millions of women were already supporting themselves and their families on meager wages before coronavirus-mitigation lockdowns sent unemployment rates skyrocketing and millions of jobs disappeared. And working mothers were already shouldering the majority of family caregiving responsibilities in the face of a childcare system that is wholly inadequate for a society in which most parents work outside the home.”
Bateman and Ross write about the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on women. Many women are forced to go through so much to provide for their families; however, the lockdowns led to many of them losing their jobs. The unemployment rate for women rose dramatically, by 12 percent, from February to April of 2020. It has been difficult for them to balance work with taking care of their families, women’s primary role as dictated by society.
“Youth unemployment is potentially dangerous as it sends a signal to all segments of the Nigerian Society. Here in Nigeria, the rate of youth unemployment is high, even at the period of economic normalcy i.e. the oil boom of the 1970s (6.2 per cent); 1980s (9.8 per cent) and the 1990s (11.5 per cent). Youth unemployment therefore is not a recent phenomenon. But if what happened in the 1980s/90s were a challenge of sorts, what is happening presently, going by the latest report by the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), is a challenge.”
Jerome-Mario’s essay focuses on several issues affecting the Nigerian youth, including unemployment. The country has a high unemployment rate; over a fourth of the youth population is unemployed. He stresses the importance of the youth using their voice to make a change and to persuade the government to care for its citizens more.

The pandemic and its lockdown policies have undoubtedly caused many people to lose jobs. Look into the impact of COVID-19 on the unemployment rate, particularly during the early months of the pandemic. Which sectors were most affected? Pull data and statistics to show how the public was affected by the covid-19 pandemic in terms of unemployment.
Many say that unemployment leads to higher crime rates. Do you believe this is true? Research how unemployment is linked to crime; examine the effects of unemployment on mental health; and conclude whether this may contribute to the increased likelihood of committing a crime.
In Haynes’ essay, he claims that employers/the government, and workers are to blame for unemployment. After reading his essay and both arguments, who do you believe is at fault? Explain your response in detail, and make sure to provide a solid base of evidence.
Unemployment has many contributing causes. Assuming a non-pandemic setting, research what causes unemployment and list them down in your essay. Elaborate on each one and, if you can draw connections, explain them as well.
As a grave issue, unemployment has many severe effects, notably poverty. For your essay, write about the effects of unemployment on a person, both physical and mental. How are they connected? What secondary effects might they produce? For a compelling and argumentative essay, answer these questions using research material and interview data.
For help with this topic, read our guide explaining what is persuasive writing ?If you are interested in learning more, check out our essay writing tips !

Martin is an avid writer specializing in editing and proofreading. He also enjoys literary analysis and writing about food and travel.
View all posts
Economics: Unemployment, Its Causes and Types
This essay sample explores solutions, types, and causes of unemployment. Read it to get ideas for your essay about unemployment.
Unemployment Essay Introduction
Unemployment, types of unemployment, causes of unemployment, conclusion for unemployment essay.
Unemployment has become a major problem in almost every society. The challenges posed by unemployment are both social and economical in nature. Under normal circumstances, unemployment leads to despondency since a section of society lacks ways of earning a living.
This affects not only the economic status of the society but also the political and social aspects. It is against this background that a lot of efforts are put in place so as to address the issue of unemployment. Job creation is one sure way of ensuring that unemployment is under control.
This involves concerted efforts to bring about opportunities to work through which income can be generated. However, unemployment is of different types, and a better understanding of the same is crucial in the event of finding a meaningful solution.
Furthermore, unemployment is caused by several factors which are responsible for the whole situation. The aim of this paper is to navigate through the light of unemployment, thoroughly analyzing the causes and types of the same.
Unemployment refers to a situation in which qualified people are seeking employment but remain unemployed. This is primarily due to the scarcity of job opportunities or other different causes. Unemployment, therefore, leads to a lack of a source of income, thus affecting the economic condition of the society. Unemployment takes different forms and shapes (Harris, 2001).
The condition of unemployment differs from society to society, depending on the factors responsible for the situation. This brings out the fact that unemployment does not occur in a uniform manner; it rather takes different forms depending on the various forces in the social, economic, and political arenas.
Unemployment is a major problem that needs to be addressed by all means. However, a better understanding of the causes and types of unemployment is necessary for the event of finding an appropriate solution to the whole situation.
Unemployment occurs in different forms. Under normal circumstances, the type of unemployment is denoted by the nature of factors that have brought about the situation. As a result, unemployment is categorized by forces that play a role in the creation of the situation (Hooks 2003).
Another important factor in the categorization of unemployment is the manner in which the situation occurs and for how long it occurs. In such a situation, certain forms of unemployment tend to be repetitive in nature, while others only take place once.
The seriousness of the unemployment problem also forms a good basis for its categorization. Under normal circumstances, unemployment is categorized in economic terms. Therefore the dynamics of economics play an important role in the whole scenario.
There are several types of unemployment that occur in different forms and are brought about by different situations and circumstances. The following are the types of unemployment;
- Hidden unemployment
- Cyclical unemployment
- Seasonal unemployment
- Long-term unemployment
- Underemployment
- Hardcore unemployment
- Structural unemployment
- Frictional unemployment
Hidden unemployment refers to cases of unemployment that are not represented in the official records of unemployment. This happens since many cases of unemployment are unreported, and statistics given by government agencies don’t represent them. Seasonal unemployment, on the other hand, refers to those jobs that are seasonal in nature.
These kinds of jobs only operate during certain times and not others (Abbot 2010). During the seasons, when the jobs are not on, the workers are considered unemployed. When there are certain structural changes in the status of the economy, there are kinds of changes that take place, which lead to loss of jobs and a reduction of opportunities for work.
This situation is referred to as structural unemployment. It is brought about by structural changes in the economy. Unemployment caused by personal reasons is called hardcore unemployment.
These reasons might be mental, psychological, or physical in nature. Individuals who engage in two different careers can find themselves unemployed due to the nature of their occupation. This kind of unemployment is called frictional unemployment. It is brought about by the conflict between two different jobs rendering people unemployed.
Unemployment is caused by several factors, and there is no single factor that is responsible for unemployment. As a result, there are a number of factors that combine to bring about a lack of opportunities and the fact of qualified people remaining unemployed (Symes 1995).
Fundamentally the causes of unemployment are economic in nature. As such, the plight of unemployment is brought about by factors that are inherently economic in nature. Economic forces and activities, to a large extent, determine the nature and cause of most unemployment problems. Also, factors that deal with labor and personnel are responsible for a large number of unemployment cases.
The following are causes of unemployment;
- Economic growth
- Microeconomic policies
- Constraints in economic growth
The process of economic growth has a lot of relevance to the plight of unemployment. Under normal circumstances, unemployment is an economic problem. The forces that bring about unemployment are economic in nature.
Economic growth, for instance, has a lot of significance to the whole situation of unemployment. The level of economic activity prevailing at any given moment has a lot of significance on the state of unemployment at the time.
During the process of economic growth, there is a trend that follows; this normally involves a decrease in employment opportunities. This automatically leads to a rise in the levels of unemployment. Therefore economic growth has a negative effect on the rate of unemployment in the economy. Technology also leads to high levels of unemployment; this is primarily due to the replacement of humans with machines.
With the increase in the innovation of technology, more tasks are performed by machines making it unnecessary to employ people. This makes people lose their jobs to machines since it becomes cheaper to use machines than employ people. Another factor in the same vein of technology is the use of the capital intensive mechanism. As a result, the jobs that can be performed by people are done by machines (Stretton 1999).
The role played by policies of microeconomic nature in the creation of unemployment in society cannot be underestimated. These policies normally lead to a sudden change in the economic environment making certain adjustments that lead to unemployment.
This happens when new policies are set out in place. During the initial times of implementation, the economic environment responds with fear and panic, thus causing a sudden disappearance of opportunities for career.
Constraints in economic growth lead to uncertainty among various economic players making the chances of unemployment to reduce. There is usually rampant unemployment during times of economic uncertainty. Two reasons, first, most companies won’t employ anyone during the times of economic constraints. Secondly, many companies lay off their staff during times of slackness and low economic activity.
Unemployment is a problem that is economic in nature. Most of the factors that bring about unemployment have an economic connotation. However, the effects of unemployment go beyond the economic arena. There are several types of unemployment that are grouped according to various factors that cause the plight.
Furthermore, unemployment is not caused by one single factor; there are several forces that cause unemployment in different ways. The paper has taken an analytical look at the whole concept of unemployment. Priority has been given to the causes and types of unemployment.
The paper thus found out that unemployment is caused by various forces that are economical, social, and political in nature. At the same time, the paper found out that there is a different categorization of unemployment. This is normally done with the purpose of defining the essence of the unemployment problem in question.
Abbot, L. (2010). Theories of the Labour Market and Employment: A Review. Washington: Industrial Systems Research.
Harris, N. (2001). Business economics: theory and application. London: Butterworth-Heinemann.
Hooks, J. (2003). Economics: fundamentals for financial services providers. Washington: Kogan Page Publishers.
Stretton, H. (1999). Economics: a new introduction . Washington: Pluto Press.
Symes, V. (1995). Unemployment in Europe: problems and policies. New York: Routledge.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2020, January 12). Economics: Unemployment, Its Causes and Types. https://studycorgi.com/economics-unemployment-its-causes-and-types/
"Economics: Unemployment, Its Causes and Types." StudyCorgi , 12 Jan. 2020, studycorgi.com/economics-unemployment-its-causes-and-types/.
StudyCorgi . (2020) 'Economics: Unemployment, Its Causes and Types'. 12 January.
1. StudyCorgi . "Economics: Unemployment, Its Causes and Types." January 12, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/economics-unemployment-its-causes-and-types/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "Economics: Unemployment, Its Causes and Types." January 12, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/economics-unemployment-its-causes-and-types/.
StudyCorgi . 2020. "Economics: Unemployment, Its Causes and Types." January 12, 2020. https://studycorgi.com/economics-unemployment-its-causes-and-types/.
This paper, “Economics: Unemployment, Its Causes and Types”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: June 12, 2022 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- School Education /
Essay on Unemployment: 100 to 300 Words
- Updated on
- Sep 7, 2023

Writing an essay on unemployment provides an opportunity to explore a critical issue affecting societies worldwide. Unemployment, a multifaceted problem, has far-reaching consequences that touch upon various aspects of individuals, families, and nations. In this essay, we will delve into the complexities of unemployment, examine its causes and consequences, discuss government initiatives, and shed light on potential solutions.
This Blog Includes:
Essay on unemployment in 100 words, essay on unemployment in 200 words, essay on unemployment in 300 words, tips to ace in writing an essay.
Must Read: The Beginner’s Guide to Writing an Essay
Unemployment refers to the condition when individuals, capable and willing to work, are unable to secure gainful employment. It is a pervasive issue across the globe, with varying degrees of impact on societies. Unemployment results in financial instability, and emotional distress, and hampers individual growth. Governments and organizations must collaborate to create opportunities for employment through skill development and policy implementation.
Unemployment, a pressing concern globally, stems from multiple factors that hinder the workforce’s engagement in productive activities. It affects both developed and developing nations, contributing to economic imbalances and social disparities. The consequences of unemployment include reduced income levels, increased poverty rates, and strained government resources. Moreover, the psychological toll it takes on individuals and families can be severe, leading to stress, depression, and strained relationships.
The intricate web of unemployment is spun from a mix of causes, ranging from economic fluctuations to structural shifts in industries. Cyclical unemployment, driven by economic downturns, and structural unemployment, resulting from a mismatch between skills and job openings, are widespread forms. Additionally, technological advancements lead to technological unemployment as machines replace human labour.
Unemployment has cascading effects on societies. Diminished purchasing power affects market demand, thereby impacting economic growth. As unemployment rates rise, so does the burden on social welfare programs and the healthcare system. The phenomenon also fuels social unrest and political instability, making it a challenge governments cannot ignore.
Governments worldwide have initiated strategies to tackle unemployment. Skill development programs, vocational training, and entrepreneurship initiatives are designed to equip individuals with market-relevant skills. Furthermore, promoting labour-intensive industries and investing in sectors with growth potential can generate employment opportunities.
In conclusion, unemployment is a complex issue that necessitates a multi-pronged approach. Governments, industries, and individuals must collaborate to alleviate its impact. Effective policy implementation, education reforms, and the cultivation of entrepreneurial spirit can pave the way towards reducing unemployment rates and fostering a more stable and prosperous society.
Before we dive into the specifics of unemployment, let’s briefly discuss some tips to enhance your essay-writing skills:
- Understand the Prompt: Ensure a clear understanding of the essay prompt to address all its components effectively.
- Research Thoroughly: Gather relevant information from credible sources to build a comprehensive and informed essay.
- Organize Your Thoughts: Create an outline to structure your essay logically, allowing your ideas to flow coherently.
- Introduction and Conclusion: Craft a compelling introduction to engage your readers, and a succinct conclusion to summarize your key points.
- Use Clear Language: Express your ideas using clear and concise language, avoiding jargon or overly complex vocabulary.
- Provide Examples: Illustrate your points with real-life examples to enhance understanding and credibility.
- Edit and Proofread: Revise your essay for grammar, punctuation, and coherence to ensure a polished final draft.
Also Read: Unemployment v/s Underemployment – What’s Worse?
Unemployment refers to the state in which individuals who are willing and able to work are without gainful employment opportunities. It is a condition where individuals seek jobs but are unable to secure them, leading to financial instability and societal challenges.
Unemployment, as discussed in the essay, is a multifaceted issue encompassing the lack of employment opportunities for willing and capable individuals. It explores various forms of unemployment, its causes, far-reaching consequences on economies and societies, and the role of governments in implementing solutions to mitigate its impact.
Unemployment is the term used to describe the situation where individuals of working age are actively seeking employment but are unable to find suitable job opportunities. It signifies a gap between the available workforce and available jobs, often leading to economic and social challenges within a society.
Unemployment emerges as a prominent thread, influencing economic, social, and psychological realms. As we’ve explored in this essay, comprehending the causes and consequences of unemployment is pivotal in devising solutions. Governments, institutions, and individuals must strive collectively to unravel this issue’s complexities and weave a fabric of employment opportunities, stability, and progress. We hope that this essay blog on Unemployment helps. For more amazing daily reads related to essay writing , stay tuned with Leverage Edu .
Manasvi Kotwal
Manasvi's flair in writing abilities is derived from her past experience of working with bootstrap start-ups, Advertisement and PR agencies as well as freelancing. She's currently working as a Content Marketing Associate at Leverage Edu to be a part of its thriving ecosystem.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today.

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out
Home — Essay Samples — Economics — Unemployment — Unemployment: Causes, Effects, and Solutions
Unemployment: Causes, Effects, and Solutions
- Categories: Unemployment
About this sample

Words: 685 |
Published: Jan 30, 2024
Words: 685 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read
Table of contents
Introduction, causes of unemployment, effects of unemployment, solutions to combat unemployment, a. economic factors.
- Global recession: During economic downturns, companies may reduce employment to cut costs and remain competitive.
- Automation and technological advancements: The use of machines and technology may replace human workers in some industries, leading to job losses.
- Outsourcing of jobs: Companies may choose to outsource jobs to other countries where labor costs are lower, leaving domestic workers unemployed.
B. Societal Factors
- Lack of education and skills: Individuals without proper education and job training may be ill-equipped to meet the demands of a constantly evolving job market.
- Discrimination in hiring processes: Certain groups, such as women, minorities, and older workers, may face barriers in securing employment due to discrimination.
- Dependency on welfare programs: Some individuals may choose to remain on welfare programs due to a lack of incentive to enter the workforce or because they cannot find suitable employment.
A. Economic Effects
- Reduction in consumer spending: Without a steady income, unemployed individuals may have less money to spend, resulting in a decline in consumer spending.
- Decline in government revenue: With fewer people working, the government may see a decline in tax revenue, which can impact its ability to provide necessary services and promote economic growth.
- Increase in social welfare expenses: The government may need to allocate more funds toward social welfare programs, such as unemployment benefits and food assistance, to support those who are unemployed.
B. Social Effects
- Increase in crime rates: Individuals who are unemployed may resort to criminal activities to make ends meet, leading to a rise in crime rates.
- Mental health issues: Unemployment can cause stress, anxiety, and depression, which can negatively impact an individual's mental health.
- Strained relationships and family instability: Unemployment may cause financial strain and tension within families, leading to relationship problems and instability.
A. Economic Solutions
- Encouraging entrepreneurship and small business development: Providing resources and support for individuals to start their own businesses can lead to job creation and economic growth.
- Promoting vocational training and skill development programs: Ensuring that individuals have access to education and training programs can increase their job readiness and competitiveness in the job market.
- Implementing balanced trade policies: Creating policies that promote fair trade and reduce job outsourcing can protect domestic jobs and promote job growth.

B. Social Solutions
- Addressing educational disparities and providing access to quality education: Providing quality education to disadvantaged communities can improve their job readiness and reduce unemployment rates.
- Combating discrimination in the workplace: Enforcing anti-discrimination laws and promoting diversity and inclusion in the workplace can reduce barriers to employment for certain groups.
- Strengthening social safety net programs: Ensuring that social welfare programs are designed to incentivize work and provide support to those in need can promote economic stability and reduce poverty.
- Bureau of Labor Statistics. (2021, October 8). Employment Situation Summary. https://www.bls.gov/news.release/empsit.nr0.htm

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Economics

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 665 words
3 pages / 1230 words
2 pages / 1193 words
3 pages / 1311 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Unemployment
The economy is a complex and constantly changing entity that can be difficult to understand, especially for college students who are just beginning to explore the intricacies of macroeconomics. One of the most fundamental [...]
In today's fast-paced and competitive economy, the issue of unemployment remains a pressing concern for individuals and societies alike. The reasons for unemployment are multifaceted and complex, ranging from structural and [...]
Sociological imagination is a concept put forward by the sociologist C. Wright Mills in 1959. It refers to the ability to see the intersection between personal troubles and public issues, and to understand how these two are [...]
Unemployment has become a pervasive issue in societies worldwide, presenting both social and economic challenges. The lack of employment opportunities leads to despair among individuals who are unable to earn a living. This not [...]
It is no secret that entrepreneurs square measure important to making wealth and driving economic process, innovation and employment. With the most recent federal budget saying that it'll support little businesses there has [...]
In Malaysia, there are graduates remain unemployed need more concern by the government because it have become a serious case in Malaysia. In year 2015 involving 132,900 graduates from institutions of higher learning all over [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
Undoing the Stigma of Unemployment

W ith the looming 2024 elections in mind, one of the most discussed puzzles of our time is why Americans report feeling economically anxious despite a low unemployment rate, declining inflation, and other positive economic indicators. My research on American workers points to one of the root causes of this anxiety. It focuses on the kind of workers we might expect to have little to worry about—experienced, college-educated, white-collar professionals—including some with advanced degrees from elite universities like Harvard and MIT. Focusing on this group reveals that in the contemporary United States the careers of even the most privileged workers are anxiety-filled and precarious.
Regardless of prestigious degrees and impressive work experience, the careers of almost all American workers are made unpredictable by routine layoffs. It was not always like this. In the post-World War II era white-collar workers at large companies could reasonably expect to stay at one company for decades. But since the 1980s job security has crumbled, and currently about 3 out of 4 American workers become unemployed at some point in their career.
Yet, economic anxiety extends beyond mere layoffs. It is foremost rooted in the fear of not being able to bounce back after a layoff, and getting trapped in long-term unemployment or low-wage work. This fear is well-founded, even for experienced college-educated professionals. A 2013 study by the Economic Policy Institute reveals that if a college-educated worker becomes unemployed they are as likely as any other worker—of whatever level of education—to get trapped in long-term unemployment. Even after a prolonged search, many get stuck in low-wage jobs. Downward mobility does not show up in unemployment statistics, but it shatters lives.
American workers are anxious because anyone can fall. There are no reliable shields against an invisible but powerful force which can rapidly erase past educational and professional achievements: stigma. Once a worker becomes unemployed they are stigmatized in the eyes of potential employers. This can be clearly seen in studies where researchers send fake resumes to companies with real job openings. These resumes are identical in terms of skills and qualifications and differ only in whether or not the applicant has a current employment gap. From these studies, we know that employers are far less likely to invite unemployed applicants for job interviews.
Read More: The U.S. Spends Less Than Nearly Every Country on Unemployment. That’s Why People Can’t Get Jobs.
I interviewed recruiters to gain a better understanding of the unemployment stigma. After assuring them that they will remain anonymous, the recruiters openly discussed the widely shared assumptions of employers about unemployed applicants. One recruiter explained: “A company could lay off people for a wide variety of reasons. But there is that perception that very often those folks who have been laid off or out of work for any length of time are not going to be the top people out there.” In practice, this perception often translates to an employer preference for “passive jobseekers,” referring to workers currently working and not actively looking for work; or in other words, workers who are not unemployed. Here is how one recruiter succinctly summed up the widely shared sentiment underlying the preference for passive jobseekers: “The sense is that if someone is good, they would be working.” When reflecting on it, this recruiter acknowledged that “this logic is crap,” recalling his own experience: “I was a top-performer and the whole group was laid off.” But, nonetheless, even this recruiter who recognized employers’ flawed logic, felt compelled to follow the preference of his employer clients for passive jobseekers.
It is not only employers who stigmatize. As the unemployed workers I’ve interviewed in the course of my research repeatedly emphasized, they experienced the unemployment stigma in every realm of their life, including when trying to network with former colleagues, or even when turning to their spouses or close friends for support.
The stigma of unemployment is everywhere because most of us want to believe in the myth of meritocracy—the false assumption that one’s position reflects one’s merit. The pull of this myth is evident whenever I share stories from my research. Take for example the story of Ron, one of the people I interviewed. Ron is a Harvard graduate who worked in finance for over three decades, most recently at a large and prestigious bank. After a layoff he spent three years unsuccessfully trying to get another job in banking. Today, Ron earns poverty-level wages at a department store.
When I share Ron’s story, I am inevitably asked for more details about his particular situation. A story like Ron’s is terrifying to all who hear it because if his career can go off a cliff, so can anyone’s. The thread connecting the various questions is the search for something faulty about Ron, which would reduce the anxiety of the person asking the questions about whether the same fate may await them. I am almost never asked about the hiring process or employer stigmas that may underlie Ron’s difficulties.
The questions’ focus on finding something faulty about Ron show how tenaciously we want to hold on to the belief in meritocratic predictability, that if you do the “right” things, study hard, go to a good college, and get a good job, you’ll do okay. But the dark flipside of this belief is the stigmatization of those who experience unemployment or downward mobility. Hanging on to this belief motivates us to find some reason why the unemployed are at fault for their unemployment, and hence we lead with skeptical questions—which mirror those of employers—about the talent or motivation of anyone who is out of work or has experienced downward mobility.
Ironically, while we cling to the myth of a predictable meritocracy as a way of coping with our anxiety, the myth leaves in place institutions and employer practices that guarantee our perpetual anxiety. The myth of meritocracy means that we judge and stigmatize each other, even our friends and loved ones, instead of providing empathetic support. It means that we blame individuals for what are societal shortcomings, and these shortcomings remain untouched. And ultimately, it means we remain trapped in an economic system in which we are all one layoff away from potential disaster.
The way out of this trap is to confront it head on and shine a bright light on the assumption that unemployment necessarily reflects anything about the unemployed person as opposed to the economy, employers, and the hiring system. Until we do so, we will continue to experience perpetual economic anxiety, regardless of topline economic indicators.
More Must-Reads From TIME
- Biden’s Campaign Is In Trouble. Will the Turnaround Plan Work?
- Why We're Spending So Much Money Now
- The Financial Influencers Women Actually Want to Listen To
- Breaker Sunny Choi Is Heading to Paris
- The UAE Is on a Mission to Become an AI Power
- Why TV Can’t Stop Making Silly Shows About Lady Journalists
- The Case for Wearing Shoes in the House
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Contact us at [email protected]
- Liberty Fund
- Adam Smith Works
- Law & Liberty
- Browse by Author
- Browse by Topic
- Browse by Date
- Search EconLog
- Latest Episodes
- Browse by Guest
- Browse by Category
- Browse Extras
- Search EconTalk
- Latest Articles
- Liberty Classics
- Search Articles
- Books by Date
- Books by Author
- Search Books
- Browse by Title
- Biographies
- Search Encyclopedia
- #ECONLIBREADS
- College Topics
- High School Topics
- Subscribe to QuickPicks
- Search Guides
- Search Videos
- Library of Law & Liberty
- Home /
ECONLIB Guides
Employment and Unemployment

Introduction
Definitions and basics.
Unemployment , from the Concise Encyclopedia of Economics
Each month, the federal government’s Bureau of Labor Statistics randomly surveys sixty thousand individuals around the nation. If respondents say they are both out of work and seeking employment, they are counted as unemployed members of the labor force. Jobless respondents who have chosen not to continue looking for work are considered out of the labor force and therefore are not counted as unemployed….
Full Employment: : Business Cycles , from the Concise Encyclopedia of Economics
Just as there is no regularity in the timing of business cycles, there is no reason why cycles have to occur at all. The prevailing view among economists is that there is a level of economic activity, often referred to as full employment, at which the economy theoretically could stay forever. Full employment refers to a level of production at which all the inputs to the production process are being used, but not so intensively that they wear out, break down, or insist on higher wages and more vacations. If nothing disturbs the economy, the full-employment level of output, which naturally tends to grow as the population increases and new technologies are discovered, can be maintained forever. There is no reason why a time of full employment has to give way to either a full-fledged boom or a recession….
Unemployment Insurance , from the Concise Encyclopedia of Economics
The United States unemployment insurance program is intended to offset income lost by workers who lose their jobs as a result of employer cutbacks. The program, launched by the Social Security Act of 1935, is the government’s single most important source of assistance to the jobless. A second goal of the program is to counter the negative impacts on the national economy, and especially on local economies, of major layoffs, seasonal cutbacks, or a recession. Unemployment benefits help sustain the level of income and hence the demand for goods and services in areas hard hit by unemployment. In short, unemployment insurance supports consumer buying power….
Welfare , from the Concise Encyclopedia of Economics
… in 1996, Congress passed and President Bill Clinton signed the Personal Responsibility and Work Opportunity Reconciliation Act, which replaced AFDC with TANF. Under the new program, the federal government eliminated the entitlement to cash welfare, placed limits on the length of time families could collect benefits, and introduced work requirements. By law, a family cannot receive TANF benefits for more than a lifetime limit of five years, cumulative across welfare spells. Regarding work requirements, TANF mandated that at least 50 percent of recipients participate in “work” activities by 2002, with activities including employment, on-the-job training, vocational EDUCATION, job search, and community service….
New Keynesian Economics , from the Concise Encyclopedia of Economics
The primary disagreement between new classical and new Keynesian economists is over how quickly wages and prices adjust. New classical economists build their macroeconomic theories on the assumption that wages and prices are flexible. They believe that prices “clear” markets–balance supply and demand–by adjusting quickly. New Keynesian economists, however, believe that market-clearing models cannot explain short-run economic fluctuations, and so they advocate models with “sticky” wages and prices. New Keynesian theories rely on this stickiness of wages and prices to explain why involuntary unemployment exists and why monetary policy has such a strong influence on economic activity….
Labor Unions , from the Concise Encyclopedia of Economics
Many unions have won higher wages and better working conditions for their members. In doing so, however, they have reduced the number of jobs available….
In the News and Examples
Russ Roberts on the Least Pleasant Jobs . Podcast on EconTalk, April 21, 2008.
EconTalk host Russ Roberts talks about the claim that for capitalism to succeed there have to be people at the bottom to do the unpleasant tasks and that the rich thrive because of the suffering of those at the bottom. He critiques the idea that capitalism is a zero sum game where to get ahead, someone has to fall back. He also looks at the evolution of the least pleasant jobs over time and how technology interacts with rising productivity to make the least pleasant jobs more pleasant….
The Broken Window Fallacy , a LearnLiberty video.
Do natural disasters, terrorist attacks, and wars, create jobs? Prof. Art Carden answers this question, along with many others, in this video.
What’s behind the slow U.S. economic recovery from the recent recession? Mulligan on Redistribution, Unemployment, and the Labor Market . Podcast on EconTalk, December 3, 2012.
Casey Mulligan of the University of Chicago and the author of The Redistribution Recession, talks with EconTalk host Russ Roberts about the ideas in the book. Mulligan argues that increases in the benefits available to unemployed workers explains the depth of the Great Recession that began in 2007 and the slowness of the recovery particularly in the labor market. Mulligan argues that other macroeconomic explanations ignore the microeconomic incentives facing workers and employers.
Bhide on Outsourcing, Uncertainty, and the Venturesome Economy . Podcast at EconTalk.
Amar Bhidé, of Columbia University and author of The Venturesome Economy, talks with EconTalk host Russ Roberts about the role of entrepreneurship and innovation in a global economy. Bhidé argues that the worries about outsourcing and America’s alleged declining leadership in technology are misplaced. He argues that the source of prosperity is not technology per se but the application of technology to actual products that improve our lives and that the American venture system and labor market are very effective at the application of technology. The end of the conversation turns to the role of uncertainty in both venture capital and entrepreneurship but also to the role of financial institutions and financial innovation.
Ed Leamer on Outsourcing and Globalization . Podcast on EconTalk, July 09, 2007.
Is outsourcing good for America? How does foreign competition affect wages in the United States? Ed Leamer, professor of economics at UCLA, talks about the effects of outsourcing on wages, jobs, and the U.S. standard of living….
Minimum Wages , from the Concise Encyclopedia of Economics
Minimum wage laws set legal minimums for the hourly wages paid to certain groups of workers. In the United States, amendments to the Fair Labor Standards Act have increased the federal minimum wage from $.25 per hour in 1938 to $5.15 in 1997. Minimum wage laws were invented in Australia and New Zealand with the purpose of guaranteeing a minimum standard of living for unskilled workers. Most noneconomists believe that minimum wage laws protect workers from exploitation by employers and reduce poverty. Most economists believe that minimum wage laws cause unnecessary hardship for the very people they are supposed to help….
Wages and Working Conditions , from the Concise Encyclopedia of Economics
CEOs of multinational corporations, exotic dancers, and children with lemonade stands have at least one thing in common. They all expect a return for their effort. Most workers get that return in a subtle and ever-changing combination of money wages and working conditions. This article describes how they changed for the typical U.S. worker during the twentieth century…. Surely the single most fundamental working condition is the chance of death on the job. In every society workers are killed or injured in the process of production. While occupational deaths are comparatively rare overall in the United States today, they still occur with some regularity in ocean fishing, the construction of giant bridges and skyscrapers, and a few other activities.
A Little History: Primary Sources and References
Great Depression , from the Concise Encyclopedia of Economics
A worldwide depression struck countries with market economies at the end of the 1920s. Although the Great Depression was relatively mild in some countries, it was severe in others, particularly in the United States, where, at its nadir in 1933, 25 percent of all workers and 37 percent of all nonfarm workers were completely out of work. Some people starved; many others lost their farms and homes…. By June 1937, the recovery–during which the unemployment rate had fallen to 12 percent–was over. Two policies, labor cost increases and a contractionary monetary policy, caused the economy to contract further. Although the contraction ended around June 1938, the ensuing recovery was quite slow. The average rate of unemployment for all of 1938 was 19.1 percent, compared with an average unemployment rate for all of 1937 of 14.3 percent. Even in 1940, the unemployment rate still averaged 14.6 percent.
Phillips Curve , from the Concise Encyclopedia of Economics
The Phillips curve represents the relationship between the rate of inflation and the unemployment rate…. At the height of the Phillips curve’s popularity as a guide to policy, Edmund Phelps and Milton Friedman independently challenged its theoretical underpinnings. They argued that well-informed, rational employers and workers would pay attention only to real wages–the inflation-adjusted purchasing power of money wages. In their view, real wages would adjust to make the supply of labor equal to the demand for labor, and the unemployment rate would then stand at a level uniquely associated with that real wage–the “natural rate” of unemployment….
John Maynard Keynes , biography from the Concise Encyclopedia of Economics
Keynes’s ideas took a dramatic change, however, as unemployment in Britain dragged on during the interwar period, reaching levels as high as 20 percent. Keynes investigated other causes of Britain’s economic woes, and The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money was the result….
Advanced Resources
Related topics.
Productive Resources Business Cycles Inflation Roles of Government Insurance Price Controls, Price Ceilings, and Price Floors
Unemployment Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on unemployment.
Unemployment is a very serious issue not only in India but in the whole world. There are hundreds and thousands of people out there who do not have employment . Besides, the problems of unemployment are very severe in India because of the growing population and demand for jobs. Moreover, if we neglect this problem then it will be going to become the reason for the doom of the nation.

What is Unemployment?
Unemployment refers to a situation in which a skilled and talented people wanted to do a job. But cannot find a proper job due to several reasons.
Types of Unemployment
Now we know what is unemployment but unemployment does not only mean that the person does not have a job. Likewise, unemployment also includes people working in areas out of their expertise.
The various types of unemployment include disguised unemployment, seasonal unemployment, open unemployment, technological unemployment, structural unemployment. Besides, some other unemployment is cyclic unemployment, educated unemployment, underemployment, frictional unemployment, chronic unemployment, and casual unemployment.
Above all, seasonal unemployment, under unemployment, and disguised unemployment are the most common unemployment that is found in India.
Reasons for Unemployment
In a country like India, there is much reason for a large section of the population for being unemployed. Some of these factors are population growth, slow economic growth , seasonal occupation, slow growth of the economic sector, and fall in the cottage industry.
Moreover, these are the major reason for unemployment in India. Also, the situation has become so drastic that highly educated people are ready to do the job of a sweeper. Besides, the government is not doing his work seriously.
Apart from all these, a large portion of the population is engaged in the agricultural sector and the sector only provides employment in harvest or plantation time.
In addition, the biggest reason of unemployment in India is its vast population which demands a large number of jobs every year which the government and authorities are unable to provide.
Consequences of Unemployment
If things will go on like the current scenario then unemployment will become a major issue. Apart from this, the following things happen in an economy which is an increase in poverty, an increase in crime rate, exploitation of labor, political instability, mental health, and loss of skills. As a result, all this will eventually lead to the demise of the nation.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Initiative by Government
The government has taken the problem very seriously and have taken measures to slowly reduce unemployment. Some of these schemes includes IRDP (Integrated Rural Development Programme), DPAP (Drought Prone Area Programme), Jawahar Rozgar Yojana, Employment Assurance Scheme, NRY (Nehru Rozgar Yojana), Training for self-Employment, PMIUPEP (Prime Minister’s Integrated Urban Poverty Eradication Program), employment exchange, Employment Guarantee Scheme, development of organized sector, small and cottage industries, employment in forging countries, and Jawahar Gram Samridhi Yojana and few more.
Besides, these schemes the government also make some rules flexible, so that employment can be created in the private sector also.
To conclude, we can say that the problem of unemployment in India has reached a critical stage. But, now the government and local authorities have taken the problem seriously and working on it to reduce unemployment. Also, to completely solve the issue of unemployment we have to tackle the main issue of unemployment that is the vast population of India.
FAQs about Unemployment
Q.1 Why there is a problem of unemployment in India? A.1 Due to overpopulation and lack of proper skills there is a problem of unemployment in India.
Q.2 Define Disguised unemployment? A.2 Disguised unemployment refers to a form of employment in which more than the required numbers of people work in industry or factory. And removing some employee will not affect productivity.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Unemployment Essay Sample
Unemployment is the state of being jobless and seeking employment, or not having a job. It’s one of the most terrifying things that can happen to an individual. The number of unemployed people in the US is increasing and it’s time we took a closer look at what this means for our society. This essay will explore its causes and inferences.
Here is a sample essay on unemployment given by the experts to students. It could be used as a standard essay to write such other essays for the assignments.
Essay Example on Unemployment
- Thesis Statement of Unemployment Essay
- Introduction of Unemployment Essay
- Cause of Unemployment in the World
- Inferences of the Unemployment in a society of Nation
- How to deter the Problem of Unemployment at Global Scale
Thesis Statement of Unemployment Essay Unemployment gives rise to anarchy, terrorism, and a threat to the internal security of a nation. I ntroduction of Unemployment Essay Today the most fundamental problem that is engulfing society is the issue of unemployment. People are not able to manage two squares of meals per day. This issue cannot be ignored by us at any point as it is eating the structure of our society like a termite thus making it hollow from the inside. There are many problems that arise due to unemployment like terrorism in society which is dangerous for humankind. The issue could be addressed at the most be getting solutions on the problem of unemployment in society, which acts as the causing effect of terrorism and other problems. Main Body of Unemployment Essay Cause of Unemployment in the World The major cause of unemployment in society is the improper management of resources and giving unequal status to the people of society. Here are some major causes of unemployment given below. Unequal Distribution of resources The economic resources are unequally distributed among the people in a society of the nation at large. As a consequence of which some sections get mighty wealth as compared to others. Excessive deflation Another biggest cause that lies behind the cause of unemployment in society is the excessive deflation in the country. When people have to sell their products below the manufacturing cost they find no profit in the business. There comes a time when this business is closed by the businessmen due to lack of profit in the work. Many people lose their employment due to this reason. Mismanagement of the Banking and Financial Institution Loan and other Financial Help are given to the businessmen easily as compared to the common masses. As a result of which there is not a development of the poor people as they cannot invest money for any innovative purpose by owing a loan from the bank. This corruption is the cause of unemployment in a poor section of society. Get Non-Plagiarized Custom Essay on Unemployment in USA Order Now Inferences of the Unemployment in a society of Nation Here are the main results of unemployment in a given nation of a particular society. Students become the enemy of other’s lives in these states. Terrorism – In the scarcity of jobs youth people join many terrorist groups for the sake of earning livelihood for their families. Thus the rise of terrorism could be backed by the unemployment problem. Human Trafficking – The biggest issue of human trafficking is unemployment; many women and men are being transferred across the national and international boundaries for this reason. People do not have enough money to rare their families and thus get involved in such anti-social practices to earn money. Social Riots – Social riots are also the conclusion of unemployment as communities get irritated when other people from a different community get employment. This emotion of wrath and jealously is very strong which even kills the lives of many innocent. Communal Issues – Many times it also gives rise to the communal issue when social riots take their final destination. It could be the most serious result of unemployment in any society. How to deter the Problem of Unemployment at Global Scale The issue of unemployment is not a small problem that could be easily uprooted by society. Its roots had gone very deep into society and it is very difficult to eradicate them. It could be done by making certain efforts by every person in the world. Here are some points that could be considered by the people to eradicate the unemployment problem from society or the world at large. Equal Distribution of Economic Resources The economic resources must be equally distributed among the people so that this issue of unemployment and accumulation of wealth could be solved. Though it is a difficult thing to do but still if we make some plans for it, success could be achieved in it. Reduction in Corruption Corruption is a major issue that causes a huge part of the unemployment problems. This could be reduced by the efficient bureaucrats of the nation. Skill Oriented study The education should be skilled oriented so that people can work easily to save their livelihood. The education system should also encourage students to create new jobs and employment generation. Buy Customized Essay on Unemployment At Cheapest Price Order Now Conclusion The above discussions and arguments about unemployment draw a conclusion that though the issue is very big it could be solved by making efforts. Certain plans and strategies are needed to achieve the dream of eradicating the unemployment issue from society. Intelligentsia of the society needs to pay big attention towards this field of unemployment. Thus we can save our world from ill practices like terrorism and riots.
Hire essay writers to get professional essay writing at an affordable price
This essay has attempted to provide an overview of the causes and consequences of unemployment.
Looking for a professional essay writer to write your assignment? Hire our USA based essay writers to get excellent services with no plagiarism and affordable rates.
Students can get free essay samples to understand how to write an effective essay. Some of the essay samples are Space Exploration Essay , Capital Punishment Essay Example , Nuclear Power Essay Sample , and so on.
Students Assignment Help also offers multiple academic writing help and services for USA students such as custom writing services , assignment proofreading services , report writing help , etc. You can contact our experts any time to get instant and fastest academic help.
Explore More Relevant Posts
- Nike Advertisement Analysis Essay Sample
- Mechanical Engineer Essay Example
- Reflective Essay on Teamwork
- Career Goals Essay Example
- Importance of Family Essay Example
- Causes of Teenage Depression Essay Sample
- Red Box Competitors Essay Sample
- Deontology Essay Example
- Biomedical Model of Health Essay Sample-Strengths and Weaknesses
- Effects Of Discrimination Essay Sample
- Meaning of Freedom Essay Example
- Women’s Rights Essay Sample
- Employment & Labor Law USA Essay Example
- Sonny’s Blues Essay Sample
- COVID 19 (Corona Virus) Essay Sample
- Why Do You Want To Be A Nurse Essay Example
- Family Planning Essay Sample
- Internet Boon or Bane Essay Example
- Does Access to Condoms Prevent Teen Pregnancy Essay Sample
- Child Abuse Essay Example
- Disadvantage of Corporate Social Responsibilities (CSR) Essay Sample
- Essay Sample On Zika Virus
- Wonder Woman Essay Sample
- Teenage Suicide Essay Sample
- Primary Socialization Essay Sample In USA
- Role Of Physics In Daily Life Essay Sample
- Are Law Enforcement Cameras An Invasion of Privacy Essay Sample
- Why Guns Should Not Be Banned
- Neolithic Revolution Essay Sample
- Home Schooling Essay Sample
- Cosmetology Essay Sample
- Sale Promotion Techniques Sample Essay
- How Democratic Was Andrew Jackson Essay Sample
- Baby Boomers Essay Sample
- Veterans Day Essay Sample
- Why Did Japan Attack Pearl Harbor Essay Sample
- Component Of Criminal Justice System In USA Essay Sample
- Self Introduction Essay Example
- Divorce Argumentative Essay Sample
- Bullying Essay Sample
Get Free Assignment Quote
Enter Discount Code If You Have, Else Leave Blank

Encyclopedia of Quality of Life and Well-Being Research pp 6766–6767 Cite as
Unemployment
- Rainer Winkelmann 3
- Reference work entry
616 Accesses
1 Citations
Layoff ; Out of work ; Redundancy and work ; Work displacement
Unemployment is a state where a person wants to work but is unable to find a job. According to the formal OECD definition, the unemployed comprise all persons above a specified age, who during the reference period (typically a week or a month) were not in paid employment or self-employment, available for work, and actively seeking work. An important distinction is between long-term unemployment (with a duration of 6 months or more) and short-term unemployment. Unemployment is different from nonemployment, as the latter includes those not available for, and seeking, work, including students and retirees.
Description
There is universal agreement, backed up by decades of empirical research covering many countries and time periods, that unemployment, in particular if prolonged, is detrimental to quality of life. At the same time, the perceived reasons for such an adverse effect, as well as the assessment of its...
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Clark, A. (2003). Unemployment as a social norm: Psychological evidence from panel data. Journal of Labor Economics, 21 , 323–351.
Google Scholar
Clark, A. (2006). Unhappiness and unemployment duration. Applied Economics Quarterly, 52 , 291–308.
Diener, E. D., & Suh, E. (1997). Measuring quality of life: Economic, social, and subjective indicators. Social Indicators Research, 40 , 189–216.
Jahoda, M., Lazarsfeld, P.F., Zeisel, H. (1975). Die Arbeitslosen von Marienthal. Ein soziographischer Versuch über die Wirkungen langandauernder Arbeitslosigkeit, Edition Suhrkamp.
Kuhn, A., Lalive, R., & Zweimüller, J. (2009). The public health costs of unemployment. Journal of Health Economics, 28 , 1099–1115.
Lalive, R., & Stutzer, A. (2004). The role of social work norms in job searching and subjective well-being. Journal of the European Economic Association, 2 , 696–719.
Luechinger, S., Stutzer, A., & Meier, S. (2010). Why does unemployment hurt the employed? Evidence from the life satisfaction gap between the public and the private sector. Journal of Human Resources, 45 , 998–1045.
Wilkinson, R., & Pickett, K. (2009). The spirit level: Why more equal societies almost always do better . London: Allen Lane.
Winkelmann, L., & Winkelmann, R. (1998). Why are the unemployed so unhappy? Evidence from Panel Data. Economica, 65 , 1–15.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Economics, University of Zurich, Zuerichbergstr. 14, Zuerich, Switzerland
Rainer Winkelmann
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Rainer Winkelmann .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
University of Northern British Columbia, Prince George, BC, Canada
Alex C. Michalos
(residence), Brandon, MB, Canada
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Winkelmann, R. (2014). Unemployment. In: Michalos, A.C. (eds) Encyclopedia of Quality of Life and Well-Being Research. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-0753-5_3078
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-0753-5_3078
Publisher Name : Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN : 978-94-007-0752-8
Online ISBN : 978-94-007-0753-5
eBook Packages : Humanities, Social Sciences and Law
Share this entry
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Call us Topics in English
- Privacy Policy
- terms of use
Topics in English Topics in english to learn and fluent pronunciation and writing and facilitate conversation between you and others, whether in school, work or daily life

Essay on unemployment 15 Models
Last updated Friday , 15-03-2024 on 11:20 am
Essay on unemployment is important for every student, and we will write several models for essay on unemployment, such as a short essay on unemployment or a paragraph, or a 250-word essay, a long essay on unemployment.
Unemployment is a serious social problem and has negative effects on both the individual and society. Therefore, we find that writing an essay about it is important and should deal with an introduction and a conclusion as well, and we will present an essay on unemployment with the elements.
There are several models to suit all students, in the primary, preparatory and secondary levels.
Essay on unemployment
Unemployment is one of the biggest problems facing countries, and this problem has increased recently as a result of the spread of the Corona virus (Covid-19), as many factories, companies and stores were closed, export and import stopped, and the tourism sector and other government institutions. stopped working
The high unemployment rate in some countries was a clear indication of the deterioration of their economy and the low level of per capita income.
The government is working to solve this problem to avoid the negative effects that result from it, because unemployment has negative effects on both the individual and society.
Definition of unemployment
Unemployment is defined as the increase in the number of people looking for a job over the number of jobs offered in the labor market.
The unemployment rate is determined by calculating the percentage by dividing the number of job seekers by the number of the labor force. The labor force means the sum of working people and people looking for jobs.
Undoubtedly, the higher the unemployment rate in society, the more this indicates the existence of major economic problems.
Therefore, we find that there is a continuous follow-up to determine the unemployment rate in society, and to try to develop solutions to this problem.
The main types of unemployment
There is no doubt that every young man dreams of having a job after graduating from university, but this dream is not easily achieved, and the percentage of the unemployed has increased.
And we can define the unemployed as the one who is looking for a job and wants it but does not find it, and we do not mean by it those who do not want to work, such as some rich young people or the elderly and those who receive a pension, and the young people who are still studying, all of these are not from the unemployed, and they are not counted in the unemployment rate in society.
Among the most important types of unemployment are the following:
1- Classic unemployment among young people
Unemployment among young people is one of the most dangerous types of unemployment, because young people are the energy of society, and they are able to work well.
A job is the dream of every young man after he finishes his studies. But often young people are shocked by the bitter reality, after he finished his studies, he could not find any suitable job for him. As a result, young people are forced to do much less work than they had previously dreamed of. In most cases, they are jobs that do not require a great deal of education.
And some of the young people refuse to work, and keep looking for their dream job, and in many cases they do not find it.
2- Disguised unemployment
The name disguised unemployment is called the increase in the number of people who work in a job, more than the number required to complete that work, We see this clearly in government institutions and bodies. Where it is overcrowded with employees and there is no real production commensurate with their number.
Accordingly, the numbers in excess of the need for work are unemployed people, but they receive salaries. The state cannot take measures against them (such as dismissing them or firing them from work) in order to take into account their social conditions.
3- Seasonal unemployment
Seasonal unemployment is unemployment that recurs permanently, because there are some jobs associated with certain times of the year, or related to some projects. Many workers work in this business. When the project or work season ends, these people become unemployed.
4- Long-term unemployment
The number of citizens looking for work is monitored through labor offices and other government institutions.
The numbers who join a job, and the numbers that did not find a job, are monitored. People who are looking for work and they did not find during a period of more than 27 weeks they are called long-term unemployment.
5- Short-term unemployment
The number of citizens looking for work is also monitored through labor offices and other government institutions.
The numbers who join a job, and the numbers that did not find a job, are monitored. Individuals who are looking for work and have not found a job within a period of less than 27 weeks is called short-term unemployment.
6- Cyclical unemployment
Cyclical unemployment also occurs in a large proportion, and it is due to the capital cycle, or because a person moves from one job to another. But in most cases, the period of unemployment is limited, and the individual can join work again.
Causes of unemployment
- The gap between the number of job seekers and the number of existing jobs. Some may attribute this reason to the increase in population. But we must benefit from human wealth by preparing and training them, and providing job opportunities that benefit both the individual and society.
- The mismatch between the skills of individuals and the skills required for the labor market. The state bears the biggest mistake in this matter, as the academic preparation of students does not comply with the requirements of the labor market.
- The high interest rate, which is one of the reasons for the high unemployment rate in society. As businessmen and the rich prefer to put their money in banks if the interest is high, Thus, they do not invest in agriculture, industry, or trade. All of this leads to a lack of job opportunities and an increase in the unemployment rate.
- Natural disasters, which are also one of the factors that increase the unemployment rate, For example, earthquakes, volcanoes, tsunamis, hurricanes, heavy rain, drought, desertification and other natural phenomena, all of these phenomena have an impact on human life and may lead to unemployment of many of them. Where many people lose their jobs and money as a result of natural disasters.
- The spread of epidemics is one of the factors that increase the unemployment rate, and we have recently witnessed the impact of the Corona epidemic (Covid-19) on the economy of countries, especially developing countries, where their economy has deteriorated, and many people have lost their jobs and money.
- Technological development and machine solutions in place of labor was one of the most important causes of the unemployment problem. The problem of unemployment appeared after the Industrial Revolution, in which the machine became more widely used, and the labor force was laid off. The greater the technological progress, the greater the layoff, and the greater the unemployment.
- Internal or external migration is one of the causes of unemployment. This is like the migration of citizens from the countryside to the cities, which makes the number of people looking for work much greater than the number of jobs.
- The global recession greatly affects the economy of all countries, especially developing countries, as the world has become intertwined in economic matters, and the movement of trade, import and export, and others. When the economy is weak and buying is scarce, many people lose their jobs and join the unemployed.
The effects of unemployment on the individual
Unemployment has many negative effects on the individual, as it affects all aspects of his life, especially if he is married and has a family he is responsible for.
The biggest problem that a person can face is his inability to provide the necessary money to buy his basic needs and the needs of his family.
1- The low level of income and consequently the deterioration of living conditions, which puts the person under severe psychological pressure.
2- Increasing the financial burden, as the unemployed person cannot compensate for the money he spends, and therefore he will spend all his savings, and after that he will not find what to spend.
3 – Borrowing and the accumulation of debts, happen a lot because there are basic requirements, and it is impossible to dispense with them.
4- The high rate of mental and physical diseases. Undoubtedly, the unemployed person is under great psychological and nervous pressure, which causes him psychological diseases such as depression, stress and anxiety. In addition, he suffers from other diseases such as high pressure, heart disease and others.
5- The tendency to commit suicide is the most dangerous effect caused by unemployment, because the unemployed person who is unable to provide for the needs of his family is under great nervous and psychological pressure, which may lead him to commit suicide if he does not find a solution to his problem.
6- Hatred of society is one of the negative effects resulting from unemployment, because the unemployed person will hate others, and hatred will spread among members of society.
7- Lack of loyalty to the homeland is one of the most dangerous negative effects of unemployment, as a person will hate his homeland and search for another country that provides him with a better living.
The effects of unemployment on society
Unemployment has negative effects on society, as unemployment is closely related to the economy. The stronger the economy, the more projects and job opportunities, and thus the lower the unemployment rate in society.
Certainly, the economy is a sign of the strength or weakness of the state. In recent times, wars have become very economic.
Among the negative effects of unemployment on society are the following:
1- The loss of political stability, and this is a dangerous thing because political instability will lead to a deterioration in the state of the economy.
2- The high crime rate is one of the negative effects of unemployment, as some individuals resort to theft, bribery and other crimes to get money.
3- Family disintegration and the high rate of divorce, as a result of the man’s inability to provide for the family’s needs.
4- Searching for illegal ways to immigrate, and this is what young people always think of without caring about the risks that may take their lives.
5- Weakness of the economy as a result of not benefiting from the workforce.
6- Skilled migration abroad in search of good job opportunities.
7- Increasing financial allocations for subsidy, which helps the economy deteriorate rapidly.
8- The spread of poverty among the classes of citizens and the arrival of large numbers of citizens below the poverty line.
The effect of unemployment on the economy
There is no doubt that the relationship between the economy and unemployment is close, as unemployment is an important indicator of the strength or weakness of the economy.
The higher the unemployment rate, the weaker the economy, and the lower the economic growth. While the low unemployment rate indicates the recovery and strength of the economy.
Among the negative effects of unemployment are:
- Lack of production, and not benefiting from the unemployed workforce.
- Consumption of products, and the need to import larger quantities.
- Increase aid, and borrow from abroad.
All of these negative effects exacerbate economic problems, which may eventually lead to the state’s inability to pay its foreign debts.
The policy adopted to solve the unemployment problem
Encouraging the private sector.
Encouraging small businesses.
Develop education according to the required jobs.
Investing the components of the state to provide job opportunities for young people, such as investing waste lands in agriculture and animal investment, or encouraging small industries that complement other industries.
At the end of a topic about unemployment and its negative effects on both the individual and society, we must advise young people to acquire the largest number of experiences in order to be able to find a job for themselves.
Also, small projects, in which several people participate, are a good solution.
It is also important in order to eliminate the phenomenon of unemployment to study the needs of the labor market, and to make education in line with these needs.
Unemployment Essay in English
Many people suffer from difficulty in getting a good job opportunity. This is because job opportunities are much less than the number of people willing to work. Some of these people prefer unemployment rather than working in jobs below their educational level.
There are some tips that young people should follow in order to get a good job. Including self-development through the diversity of experiences in their specialization.
University study is no longer sufficient, but the young man must develop himself through specialized courses, learn more than one language, learn computer science and other modern sciences.
This is what every individual should do after job opportunities have become few, because unemployment has a negative impact on an individual’s life, whether in the economic, social and health aspects.
Paragraph on unemployment
The problem of unemployment arose with the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, as the machine became more widely used, and thus labor was largely dispensed with. This problem is exacerbated by increasing technological progress. As a result, a large number of individuals cannot find suitable work for them.
And the jobs required a special quality of employees, and they were required to be fully acquainted with the English language and computer science.
Therefore, young people must gain several experiences in order to get a good job, and there is a great development in the requirements of the labor market.
Trade, for example, through the Internet (online shopping) has become the most prevalent, and technology has become more widely used in agriculture and industry as well.
Unemployment solutions essay
The problem of unemployment has become a global problem, and it is important that we look for realistic solutions to this problem. Among these solutions is the encouragement of small projects, which are managed by one individual or a group of individuals, in addition to encouraging investors to establish huge projects that provide many job opportunities for young people.
It is important that education at the secondary and university levels meet the demands of the labor market, so that the student will not be shocked after graduating from university that what he has studied has nothing to do with the needs of the labor market.
Also, allocating funds to subsidize non-workers until they find a job is necessary, in order to avoid the risks that result from the high rate of unemployment in society, such as the high crime rate in society, family disintegration and other social and health problems.
Unemployment Essay in English 250 Words
The problem of unemployment has become a global problem, and it is a serious problem that affects both the individual and society. Therefore, the causes of this problem are studied and followed up, in order to find real solutions.
The causes of the unemployment problem differ from one society to another. There are societies that attribute this phenomenon to overpopulation, and thus encourage families to control birth, provide them with the necessary medicines for this, and use the media to direct families to birth control.
While other countries encourage national and foreign investment, in order to provide job opportunities for their citizens. Other countries encourage the establishment of projects that require many labors, and thus we find that there are many solutions to overcome the problem of unemployment.
It is important for each country to study this phenomenon separately, and to know what its causes are, so that it can develop appropriate solutions to solve the problem of unemployment. Individuals must also develop their skills, and have multiple experiences that qualify them to join the work.
The existence of solutions to the problem of unemployment is very important, because unemployment has negative effects on both the individual and society, and unemployment is considered an indicator of the strength or weakness of the state’s economy.
Unemployment essay introduction
Undoubtedly, the problem of unemployment troubles many countries, especially developing countries. This is because the high rate of unemployment in society leads to political instability.
When the government cannot provide the needs of citizens, by providing them with job opportunities, and they receive a salary sufficient to purchase their needs, then demonstrations, crimes and other acts of violence and sabotage will increase, and all this leads to political instability.
While the rich countries solve this problem by giving unemployment aid, which is an amount of money that is sufficient to purchase the needs of individuals, and is given to unemployed people until they find a suitable job for them.
The high unemployment rate among members of society will lead to an increase in poverty and the spread of psychological and mental illnesses.
Youth unemployment essay
Undoubtedly, young people are the most important group in society, and they must hold great hopes for nations.
Young people are characterized by strength, enthusiasm, and aspiration for a better future. Therefore, the government must provide job opportunities for young people, so that these opportunities are appropriate to their scientific abilities.
It is desirable for young people to arm themselves with science, and to acquire all the experiences that qualify them for the labor market. It has become necessary to learn modern sciences, especially technological sciences, and computer science. English language proficiency has also become a requirement for most jobs. The government must look for real solutions to solve the unemployment problem, because the risks of unemployment are very bad for both the individual and society.
Short essay on unemployment
The unemployment rate is a real indicator of the state’s economy. When the economy is strong, there are huge projects in various fields. Thus, job opportunities will be available to many of the unemployed.
A strong economy is followed by a circulation of money, sales increase, and imports and exports increase. All of this provides many job opportunities for the unemployed youth. Therefore, there must be projects that absorb the unemployed labor force.
The work is beneficial to both the individual and society, whereby the individual can live a decent life and provide for his family’s needs easily. The society can advance economically, and thus it can progress in all other areas, such as health, education and services.
Technology and unemployment essay
Technology has caused the disappearance of many jobs. The machine has become more accurate and faster than the human being. This made many people lose their jobs, especially in the agricultural and industrial fields. Where the agricultural and industrial sectors absorb large numbers of workers and employees. As for today, it has become mainly dependent on machines.
Also, modern jobs require that the employee be qualified to deal with modern technology, Therefore, young people must develop themselves and learn modern sciences, especially technological sciences.
The educational curricula should also be developed, and provide students with skills required in the labor market.
If everyone does what he should do, the unemployment rate in society will decrease.
Unemployment as a social problem essay
Undoubtedly, unemployment is a social problem that affects not only the individual but also his family, and unemployment has negative effects on society as a whole. The causes of unemployment differ from one society to another. But we can define unemployment as the increase in the number of people looking for a job over the number of people required for this job.
In this case, the person may accept a job that is less than his ambitions, and may refrain from working until he finds a job suitable for his academic qualification.
In all cases, there must be various solutions to this problem, such as encouraging foreign investment, establishing large projects, encouraging the private sector, encouraging self-projects and small projects.
All the previous solutions help to solve the unemployment problem to a large extent.
Problem of unemployment essay
There are negative effects of unemployment, some of which pertain to the individual and others to society.
One of the serious negative effects that the individual is exposed to is his lack of money to buy his basic needs and the needs of his family.
At that time, we expect the person to react badly. He may accept a bribe, steal, or kill in order to get money.
Thus, the crime rate in society will increase.
As a result, investors will flee to safer countries. Thus, job opportunities will decrease further, and thus the unemployed will increase and crimes will increase, and so on. The unemployment problem will only get worse if it is not resolved quickly.
One of the problems facing society as a result of the increase in the unemployment rate is the spread of poverty, and thus the increase in financial allocations to provide aid to unemployed people, and this becomes a burden on the economy of poor countries.
Essay on unemployment in 250 words
Unemployment may signal the beginning of the end of the state. In many countries that collapse and declare bankruptcy, the beginning of the matter is the high unemployment rate in them.
When there are fewer projects, less investment and production, and import becomes much greater than export, it will be difficult to solve the problem of unemployment.
As a result, the crime rate in society increases, and it is difficult to control citizens. Demonstrations and anti-government revolutions erupt, causing the state to collapse.
Therefore, the government must find real solutions to the unemployment problem. Such as encouraging the private sector to set up projects that require a lot of manpower, or allow citizens to immigrate to other countries with good job opportunities.
The damages of unemployment do not affect society only, but also affect the individual, causing him economic problems and represented in his inability to provide for his family’s needs, which causes him psychological and nervous pressure. In many cases, people commit suicide because of their inability to earn enough money for their lives.
Dear student, a basic form was submitted for the topic on unemployment, In addition to many other models such as, Essay on unemployment, The main types of unemployment, The main types of unemployment. If you prefer to add any other topic, you can contact us through the comments of this article and we will study your request and add it as soon as possible. To read more related articles, you can click on the following links below the article.
- Paragraph on my family
- Speech on discipline
- Philosophy in life essay
Related Articles

Essays On My Hobby 2 Models

Essay on old age home

Essay on farmer
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Definition of Unemployment and Its Types Essay
The high level of employment in any nation promotes the sound of the economy. When youths and women are in full employment, the country social, political, and economic aspects are in a better position. Through a high level of employment, the government gets wide ways of obtaining taxes, as the product output is increased.
Through an increment of government revenue and increased output in productivity, there is growth in the economy and poverty reduction (Boyes and Melvin 312). In a country where the level of economy growth is high, there are more and more opportunities.
High levels of employment make the economy stable and help in recovering damaged parts. Even if the terms of employment are short or long they tend to boost the economy a great deal. Other benefits related to the employments are high levels of entrepreneurship due to the increased participation of young and energetic people in the labor market. Economists say that well paying jobs improves the overall incomes and social money spending of poor people, and assists a great deal in financing social activities.
Unemployment is an economic condition that occurs when an individual or a group of people seek jobs to no success. In every country, the level of unemployment depends on some factors such as the status of the economy, market and commerce forces.
There are five main types of unemployment (Baumol and Blinder 630). To begin with, there is frictional unemployment that is a temporary status of the job seekers. This condition occurs when a person takes a break from his or her current job and start looking for another opportunity somewhere.
This period when one shifts from one point of work to the other is the one that creates frictional unemployment. In most of the developed countries that have advancement in various ways, there is a high probability of one securing another job after leaving one. The major challenge is in the developing and in the underdeveloped countries where if one quits from one job, getting another one is a problem.
The issue of frictional unemployment can have a solution through employment insurance programs. This program offers support and temporary sources of income to the people who in several occasions become unemployed. In most cases, people do not quit from their jobs voluntarily but because of some circumstances like nursing a sickness, giving birth, or other critical issues in the family.
Through this insurance program, the unemployed people are still made to earn some income to continue supporting their families, and meeting their needs (Tucker 380). During this period, the unemployed people face their challenges with more confidence. The government should concentrate on empowering these insurance programs such that they are in a position to meet even large group of the frictional unemployment cases.
The employees who mostly benefit from this program are those who quit their jobs due to good reason like shortage of work, or sudden break of the job management. The government should also come up with a policy of encouraging the idea of permanent jobs to avoid such breaks. If one is in a permanent job, and well paid, it would be hard for one to quit from such a job. Taxation should be favorable to some salaries, as the net salary is so small unable to sustain ones life.
With reasonable tax on salaries, employees will have a good amount of salary to manage their lives without any need of quitting. The major limitation of the insurance programs policy is that the employees have to make regular contributions of some amount to the program. However, there is no guarantee of receiving this compensation after quitting a job. Compensation depends on the reason of quitting.
The second type of unemployment is structural unemployment that happens due to major changes in the economy. The major reason behind this type of unemployment is when the job in question requires more skilled workers than the current ones.
In addition, this form of unemployment may occur because of the difficulties of moving to a new working location, or challenges of learning new skills to meet the needs of the available jobs. Sometimes, the economy may advance greatly making use of new machines and technologies replacing some employees.
Structural unemployment in most cases occurs due to creation of new job opportunities to meet the labor demands in the market. This type of unemployment is very common as far as the economy of the country is flexible whereby when there are some firms going down, there are others that are in need of other skills and expands at the same time (Gwartney, Stroup and Sobel 516).
The rate at which the technological advancement of the nation is developing and globalization, the need for a more advanced labor is required. The nation cannot avoid be prohibited from advancing in technology or in its economy but there can be a solution for this type of unemployment.
The fact is that every nation is subject to some ways of advancement, and because of this advancement, a continuous mismatch of labor and the skills required is inevitable. As far as the government acts fairly to all sectors in the economy, there is need for special attention to service based sectors, such that it will be possible for them to accommodate as many employees as possible. Policies to increase job opportunities in service sectors can help many people to secure jobs in these sectors.
The rest of people, who may not fit in service industries, will then find some places in the industrial sectors. Some policies of regular training of employees in industrial sectors are also very important (Tucker 89). These sectors should emphasis on conducting regular trainings to keep their employees updated and matching with the current changes.
Before an industry purchase a modern machine that may require new skills, there is need to equip the current employees with the necessary skills as long as they are ready to learn. Most of these employees will be ready to learn to secure their jobs. It can be much disappointing if an industry can lay off more than 85% of its employees because they lack the necessary skills.
The only group that may deserve dismissal is of those who may find it hard to learn those new skills due to their education levels. If such policies may put into action, a country can only be experiencing very few cases of structural unemployment. If government supports service sectors fully and other business departments there will be more job opportunities for the citizens to choose where they fit best (Campbell and Craig 203).
Advancement of the country’s economy and its technological levels should be an opportunity for job creation but not a way of dismissing workers. Advancement is worth celebration but not an issue causing such disappointments of joblessness. Government may be much willing to support service industries, but there is need to distribute resources uniformly hence putting a limitation to that policy. If it supports one industry more than the rest, it may seem like discrimination.
Another type of unemployment is classical also called real wage and occurs as result of trade unions and other labor organizations actions. Severally, trade unions fight for the rights of the employees especially if the salary they are getting is not worth their responsibilities at their working places. When they realize that a certain company is underpaying the employees or the working conditions are not favorable for them, it is their duties and responsibility to fight for the rights of those employees.
To some extent, they calls for a bigger salary increment that the company may not afford to pay, and in return, the company decides to reduce labor and pay the few that it can afford. Although there is right for the trade unions to fight for the rights of the employees, the type and the status of the company should also be a factor to consider before taking actions. It is better to receive little salary than to survive without any money to support personal and family needs.
The government may try as much as possible to curb this type of unemployment through some policies like a minimum amount of wages than any company should not go below, and the minimum salary for the employees. Those terms can only be ignored incase there is a special arrangement between the employer and the employee. Sometimes it can be challenging to the government to take hard measures on some companies, as they also have their own rights in operations (Baumol and Blinder 420).
The trade unions should be taking some time to talk with the employees first before they take any action of salary negotiations. The employee should be ready to take the risks of the negotiation outcome if it will be necessary for that salary complaint. As much as the government tries to put some limitations on the wages that the company should pay its employees, some companies object and decide to negotiate with its employees.
The other type of unemployment is seasonal that mostly occurs in industries that deals with seasonal customers or products. For instance, tourism industries work only during the periods when there are expecting tourists. When these jobs are out of season the employees stays unemployed (Tucker 113). The employer may engage these employees in other minor jobs, even if with relatively lower salaries during the off-season as they wait for the peak of the season.
On the other hand, the government may provide these employees with some reserve works in the public sectors to keep them going during the hard seasons. This can only be possible if the country’s economy is doing well and the government has enough money to take care of these situations. Although it may be hard to take care of every individual, but the majority should benefit and earn something during such seasons.
Those people, who suffer from seasonal unemployment, are at an advantage on the other hand. When their job is on season, they earn much money that may take them through the off peak seasons or invest in other fields to keep on earning.
During this period when they are not officially working, they can also look for other seasonal jobs before they resume to their normal fields. Even if the government can try to accommodate those people during the off-season periods into public sectors, it cannot afford to absorb all of them, hence putting a limitation to this policy.
Disguised unemployment is another type most common in the underdeveloped countries. The major problem in these countries that results to this type of unemployment is the slow growth of capital stock.
The rate of population growth is much higher than the capital stock growth, hence becoming very hard for the country to offer a reliable type of employment (Gwartney, Stroup and Sobel 121). A country with such a problem is realized through a high number of unemployed people in the urban areas especially cities. In such countries most of the young energetic people end up in agricultural activities where the name disguised unemployment comes from.
The people who finally end up in agriculture do not add any value as they do this work unwillingly, as they have little knowledge on how agricultural activities operate. The government can only solve this problem through establishing more sectors by adding spending to create job opportunities, although the overall Gross Domestic Product of the nation limits this policy sometimes.
The last type of unemployment is cyclical that occurs during recession. At times, the economy of a nation may be so down whereby the demand of the goods and services is also down hence pulling down the need for labor in industries and other sectors.
During such a period, most company’s have no other option other than firing any surplus labor. It is a hard moment of every company as they wonder on what criteria they will suck the excess employees. Most of them make use of the education levels and the acquired skills of the employees as the best factor of elimination.
When the country’s economy is in recession, the government can only be the savior. The government may decide to lower both the tax and interests rates, which will in return boost the consumer spending as well as the demands of various goods and services. This act by the government will create more job opportunities that creation of cyclical unemployment. Prolonged reduction of the government revenue may limit this policy, as the government also requires money for its operations.
In conclusion, the government does not set any target in its operations for the unemployment cases. Its main objective for its citizens is to have enough jobs in the market offering opportunities to everyone who is in need of work. The government aims at equalizing the demand and the supply policies between its citizens and the industrial needs to make both benefits from one another (Gwartney, Stroup and Sobel 701).
To some extent there are inevitable limits that the government cannot exceed as far as controlling unemployment cases is concerned. In several cases, the policies that are looked upon to improve the levels of employment in a nation may be very expensive and on the other hand, they have an opportunity cost for them to be successful.
Works Cited
Baumol, William and Alan Blinder. Economics: principles and policy . New York: Cengage Learning, 2008.
Boyes, William and Michael Melvin. Economics. New York: Cengage Learning, 2006.
Campbell, David and Tom Craig. Organisations and the business environment . London: Butterworth-Heinemann, 2005.
Gwartney, James, et al. Economics: private and public choice. New York : Cengage Learning, 2008.
Tucker, Irvin . Macroeconomics for Today . New York : Cengage Learning, 2008.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2019, March 13). Definition of Unemployment and Its Types. https://ivypanda.com/essays/unemployment-4/
"Definition of Unemployment and Its Types." IvyPanda , 13 Mar. 2019, ivypanda.com/essays/unemployment-4/.
IvyPanda . (2019) 'Definition of Unemployment and Its Types'. 13 March.
IvyPanda . 2019. "Definition of Unemployment and Its Types." March 13, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/unemployment-4/.
1. IvyPanda . "Definition of Unemployment and Its Types." March 13, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/unemployment-4/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Definition of Unemployment and Its Types." March 13, 2019. https://ivypanda.com/essays/unemployment-4/.
- Business Cycle and Unemployment
- Macroeconomics in Unemployment
- Vector Mechanics for Engineers
- Unemployment and Inflation Relation
- Measuring Unemployment Issues in Society
- Unemployment Values: Types and Impacts
- Unemployment and Business Cycle in Australia
- Unemployment Causes and Effects Essay
- Public Administration: Unemployment Economic Impact
- Unemployment Disparity Affecting African Americans
- Theory of Effective Demand
- Economic of Immigration and Economics of Mexico
- Repercussion of Great Depression
- Unemployment in UK
- The Economic Impact of the Icelandic Volcano Eruptions on the International Economy
Does the surprise fall in unemployment mean the Albanese government's 'full employment' ambitions are working?
Analysis Does the surprise fall in unemployment mean the Albanese government's 'full employment' ambitions are working?
The unemployment rate fell to 3.7 per cent in February , from 4.1 per cent in January.
It was a surprisingly large decline, but does it mean we're moving closer to full employment?
When Treasurer Jim Chalmers released his Employment White Paper last year, he unveiled a new definition of "full employment."
He said we had to think about more than the headline unemployment rate.
He said when an economy's operating at full employment, workers should be getting the hours they want, with fair pay.
It shouldn't take long for people to find a job, or to switch jobs.
Long-term unemployment should be minimal, and barriers to youth employment should be few.
In short, he said we had to look at a broader suite of measures to gauge the true extent of labour's under-utilisation in the economy.
So, let's see what that looks like.
Here are some interactive templates of key labour market data that we'll be including in our stories on the unemployment rate every month.
They'll help us to track the Albanese government's full employment ambitions, and to make better sense of any surprise movements in single numbers each month.
Templates for a labour market in full employment
The treasurer's definition of full employment is different from the Reserve Bank's.
The RBA uses a technical and more narrow definition: it says full employment is the level of unemployment that's consistent with stable wage or price inflation.
From the RBA's perspective, we have over-full employment at the moment, which means it thinks the level of unemployment is so low it's contributing to wage and price inflation.
Currently, the headline unemployment rate is 3.7 per cent.
The RBA thinks we'll probably enjoy a sustainable level of "full employment" when the unemployment rate increases to be sitting somewhere around 4.25 to 4.5 per cent.
The template below shows us what other employment indicators look like when the unemployment rate moves around.
Scroll your cursor over one of the lines, and you'll notice how the numbers in all four boxes move in sync with each other.
The unemployment rate refers to the number of people who are actively looking for work but haven't found a job yet, expressed as a percentage of the labour force.
The underemployment rate refers to the number of underemployed workers (workers who aren't getting the hours they want), expressed as a percentage of the labour force.
When you add those two rates together — the unemployment rate plus the underemployment rate — you get the underutilisation rate , which reflects the large proportion of people in the labour force who aren't working as much as they would like, either because they don't have enough hours or don't have a job at all.
In the template above, notice how long-term unemployment (unemployed for 52 weeks or more) fell to a multi-decade low in April last year, but it's been increasing as those broader measures of underutilisation have been increasing.
Next, we'll track some other indicators.
The participation rate and employment-to-population ratio both picked up in February, and they're sitting very close to record highs.
We'll also monitor the time it's taking people to find a job.
The median duration of job search , which we've smoothed out using a 12-month average, is sitting around 11 weeks nationally. In the years before the pandemic, it was averaging between 15 and 16 weeks.
And finally, another important indicator of labour market "tightness" is the relationship between job vacancies and unemployment.
Employers like it when lots of people are applying for each job. Workers prefer the opposite.
When we experienced the peak of labour market tightness in September 2022, there was practically one unemployed person for every job vacancy.
As a worker, that was a great time to be choosy about where you wanted to work, and to haggle for a pay increase.
But after the RBA rapidly hiked rates, and borders were reopened and population growth picked up again, the number of unemployed people began increasing as job vacancies fell.
We're still a long way away from our pre-pandemic scenario, when there were 700,000 unemployed people and only 220,000 job vacancies, but we may be heading there again.
On Thursday, Abhijit Surya from Capital Economics said the sharp fall in the unemployment rate in February was probably a "blip" rather than a trend, and pointed to job vacancies as evidence.
"With job vacancies continuing to fall, we suspect the unemployment rate will rise anew in the months ahead," he said.
"That said, the labour market is still tighter than most had thought [... ] although the RBA dialled back its hawkish bias at its meeting yesterday, it will probably wait for further data to confirm that there are no risks to the inflation outlook from a stronger-than-expected labour market.
"The upshot is that we still expect the Bank to hand down its first rate cut only in August, with risks tilted towards policy being loosened later," he said.
So, the RBA will keep relying on its more narrow definition of full employment to guide its decisions on interest rates, while the Albanese government says it will focus on removing structural barriers to employment so the "sustainable" level of unemployment can be lower than it has been in recent decades.
The templates above will track how that effort goes in coming years.
- X (formerly Twitter)
Related Stories
Huge jobs gains raise risk of higher interest rates for longer, economists warn.
'Full employment' will be redefined to reflect modern labour market, the Employment White Paper has found
Is the Albanese government's vision of full employment a flop?
- Economic Growth
- Economic Indicator
- Economic Trends
- Employment Statistics
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
Why Are Lawmakers Trying to Ban TikTok Instead of Doing What Voters Actually Want?

By Julia Angwin
Ms. Angwin is a contributing Opinion writer and an investigative journalist.
America is politically polarized. But there is an issue on which both sides agree: We need more privacy, and TikTok should not be banned.
A record 72 percent of Americans want “more government regulation” of what companies can do with their data, according to an October report from Pew Research Center . And only 31 percent of Americans favor a nationwide ban on TikTok, according to a February Associated Press/NORC opinion poll .
Despite public sentiment, the U.S. House passed legislation on Wednesday by an overwhelming majority that could force TikTok to divest from control by its Chinese parent company or be banned. Its fate in the Senate is not clear.
TikTok’s parent company, ByteDance, is based in China, and American lawmakers say they are pursuing a ban in the name of protecting U.S. data from the Chinese government. But lawmakers are not pursuing comprehensive federal privacy legislation that would protect Americans’ data on all the apps they use.
This is, sadly, just more evidence of how removed federal lawmaking has become from the will of the people. Issues with wide popular support such as abortion access and gun control remain unaddressed at the federal level. And a majority of Americans say that government policies do not reflect public opinion on key issues.
Despite this growing divide, it is truly stunning that lawmakers feel comfortable pushing a TikTok ban during a high-stakes election year. After all, one-third of U.S. adults say they use the site , and one-third of U.S. adults under 30 say they regularly get their news on TikTok . Even President Biden, despite saying he would sign the ban into law if it made it to his desk, just started a TikTok channel for his re-election campaign .
Some members of Congress, such as Representative Jeff Jackson, a North Carolina Democrat, regularly use TikTok to communicate with their constituents. Mr. Jackson, who voted for the bill, has 2.5 million followers on the site. “My message to TikTok: break up with the Chinese Communist Party or lose access to your American users,” said Representative Mike Gallagher, a Wisconsin Republican and one of the bill’s sponsors.
The legislation seeks to bar the distribution within the United States of “foreign adversary controlled applications such as TikTok” unless it sells itself within six months to a buyer that is approved by the U.S. president.
The rush to pass this bill is particularly odd because the federal government already has a process for dealing with foreign entities buying stakes in domestic companies. The Committee on Foreign Investment in the United States is an interagency body that reviews foreign investments for national security concerns. For instance, it was a review by the committee that caused a Chinese buyer to reverse its acquisition of the dating app Grindr in 2020.
The committee and TikTok have been negotiating for years over how to mitigate the national security concerns. After Donald Trump while president ordered the committee to investigate , TikTok offered a plan that would have transferred all its data on U.S. citizens to a U.S. subsidiary that would be overseen by Oracle. Oracle would have also overseen TikTok’s algorithms and content takedown decisions on behalf of the U.S. government. But the U.S. government rejected it for reasons that have not been disclosed, and it appears the negotiations have reached an impasse.
But the tricky thing is that forcing TikTok to sell would not solve the problems that lawmakers claim they are trying to address. Selling TikTok to a big tech company such as Google, Meta or Microsoft — after all, who else could afford its estimated price of $84 billion ? — would not make U.S. users’ data more secure. In fact, it would simply give the tech giant buying it a new trove of information about all of us that the new owner could use to enhance its already astoundingly detailed portraits.
Right now, for example, Google has most of my email, my documents, my web-browsing behavior and my search queries. The videos I watch on TikTok are, in fact, among the few things it doesn’t have. Adding those videos would add valuable new data to its dossier on me and allow it to monetize it with advertisers, data brokers and anyone else that uses its self-service online advertising platforms and services.
Sure, maybe in the worst-case scenario, the Chinese government is spying on my viewing of TikTok videos. (TikTok, of course, says that its Chinese parent company is entirely separate from the U.S. entity.) But TikTok doesn’t have much more data than any other app; all it knows is that I spend too much time watching cooking videos and makeup tutorials. This information probably helps China in its endless quest to provide all of the material goods that I buy, from kitchen equipment to makeup brushes, but it was already manufacturing those goods anyway, so my feeling is that my viewing data is just additional information about potential future demand for products.
OK, fine, you say, but what about the Chinese propaganda that is being spread through TikTok? I’ve read the same scare stories, and all I can say is that they aren’t that convincing. Referring to the People’s Republic of China, the Office of the Director of National Intelligence stated in its February threat assessment that “TikTok accounts run by a P.R.C. propaganda arm reportedly targeted candidates from both political parties during the U.S. midterm election cycle in 2022.”
That sounds terrifying until you consider that anyone can set up a TikTok account to target anyone during an election. We know, for instance, that Russians set up accounts on Facebook to try to influence U.S. elections in 2016. And they didn’t have to buy Facebook to do that. It’s also worth noting that the threat assessment does not allege that TikTok’s algorithm promoted the People’s Republic of China accounts — and I’m guessing that if the director of national intelligence’s office had evidence of that, it would have stated it.
And it’s not clear that the intelligence community has better evidence that it is providing behind closed doors. After a national security briefing on TikTok for members of Congress, Representative Sara Jacobs, Democrat of California, told The Associated Press : “Not a single thing that we heard in today’s classified briefing was unique to TikTok. It was things that happen on every single social media platform.”
Meanwhile, China appears to be having plenty of success pushing its political agenda through influencers on YouTube, Facebook and Instagram , according to a 2022 Associated Press investigation.
And that’s my point. All of the social media platforms are information minefields, rife with deceptive content from state actors, corporations, paid influencers and others. Their algorithms fuel our worst impulses by highlighting content that promotes anger and outrage. They strip mine our data to make money.
Forcing TikTok to merge with another data-hungry social media platform won’t solve any of that. What will make a difference is establishing base-line privacy rules that prohibit companies from exploiting our data and that give us control over the algorithms used to manipulate us.
The Times is committed to publishing a diversity of letters to the editor. We’d like to hear what you think about this or any of our articles. Here are some tips . And here’s our email: [email protected] .
Follow the New York Times Opinion section on Facebook , Instagram , TikTok , WhatsApp , X and Threads .
Julia Angwin, a contributing Opinion writer and the founder of Proof News , writes about tech policy. You can follow her on Twitter or Mastodon or her personal newsletter .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The unemployment rate for the year 2013-14 in rural India was 4.7%, whereas it was 5.5% for urban India. In the short term, unemployment significantly reduces a person's income and, in the long term, it reduces their ability to save for retirement and other goals. Unemployment is a loss of valuable productive resources to the economy.
Firstly, the essay provides the definition of unemployment. Secondly, it describes a current situation regarding unemployment rate in the United States of America. Thirdly, it focuses on the explanation of reasons for this phenomenon. Fourthly, negative and positive consequences and effect of unemployment on American society are discovered.
Types of Unemployment. Classical: occurs when real wages for jobs are set above the market-clearing level. It causes the number of job seekers to be higher than the number of vacancies. Cyclical: occurs when there is not enough aggregate demand in the economy to provide jobs for everyone who wants to work. Demand for goods and services decreases, less production is needed, and fewer workers ...
Unemployment occurs when someone is able to work and wants to work but is unable to find employment. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) specifically defines unemployed persons as those who don't have a job but are available for work and have looked for work in the past four weeks. Unemployment on a national level is caused by a slowing ...
Unemployment is a phenomenon that occurs when a person who is actively searching for employment is unable to find work. Unemployment is often used as a measure of the health of the economy. The ...
Lesson summary: Unemployment. In this lesson summary review and remind yourself of the key terms and calculations used in measuring unemployment, the labor force, the unemployment rate, the labor force participation rate, and the natural rate of unemployment. Topics include cyclical, seasonal, frictional, and structural unemployment.
6 Examples of Essays About Unemployment. 1. Unemployment Reflection by Christopher Haynes. "In order to secure work, we must be prepared to change or upgrade our skills and be willing to relocate if necessary. But some people are not interested in retraining to find work in another field, some people do not have the confidence to go out and ...
This is primarily due to the scarcity of job opportunities or other different causes. Unemployment, therefore, leads to a lack of a source of income, thus affecting the economic condition of the society. Unemployment takes different forms and shapes (Harris, 2001). The condition of unemployment differs from society to society, depending on the ...
We will write a custom essay on your topic. I have chosen the unemployment situation because of the increasing and prevalent unemployment rates in various countries. Recent statistics indicate that, the rate of unemployment is on the increase and there is a lot of information to cover the complex area of unemployment.
Essay on Unemployment in 100 words. Unemployment refers to the condition when individuals, capable and willing to work, are unable to secure gainful employment. It is a pervasive issue across the globe, with varying degrees of impact on societies. Unemployment results in financial instability, and emotional distress, and hampers individual growth.
The purpose of this essay is to examine the causes and effects of unemployment, as well as provide potential solutions to address this issue. Thesis statement: Unemployment is caused by economic and societal factors, and it leads to negative economic and social consequences.
The stigma of unemployment is everywhere because most of us want to believe in the myth of meritocracy—the false assumption that one's position reflects one's merit. The pull of this myth is ...
Essay Writing Service. High unemployment rate in a country leads to social and economic problems in the community as a whole. Economic problems result in less production of goods and services, less distribution of income, loss of tax revenues, fall in GDP rate etc. (www.economywatch.com). Social problems cause's social ills and shows effect ...
Get custom essay. The first effect is loss of income. Unemployment results in individuals losing their source of income and livelihood. Most people in employment use their incomes to get mortgages and other forms of financing (Stone 69). Loss of income leads to poor living standards and increased risk on health.
This essay sample was donated by a student to help the academic community. Papers provided by EduBirdie writers usually outdo students' samples. Unemployment has been an issue and a concern in most counties across the world, including the US, but unemployment is at the lowest it has ever been in 50 years. The factors include demographics, level ...
Introduction Definitions and Basics Unemployment, from the Concise Encyclopedia of Economics Each month, the federal government's Bureau of Labor Statistics randomly surveys sixty thousand individuals around the nation. If respondents say they are both out of work and seeking employment, they are counted as unemployed members of the labor force. Jobless respondents who have chosen […]
500+ Words Essay on Unemployment. Unemployment is a very serious issue not only in India but in the whole world. There are hundreds and thousands of people out there who do not have employment.Besides, the problems of unemployment are very severe in India because of the growing population and demand for jobs.
Essay Example on Unemployment Thesis Statement of Unemployment Essay. Unemployment gives rise to anarchy, terrorism, and a threat to the internal security of a nation. Introduction of Unemployment Essay. Today the most fundamental problem that is engulfing society is the issue of unemployment. People are not able to manage two squares of meals ...
Unemployment is a state where a person wants to work but is unable to find a job. According to the formal OECD definition, the unemployed comprise all persons above a specified age, who during the reference period (typically a week or a month) were not in paid employment or self-employment, available for work, and actively seeking work.
Abstract. Youth unemployment is a major challenge especially in emerging economies like South Africa characterised by a young and growing population. Taking into account relevant literature (this ...
There are several models to suit all students, in the primary, preparatory and secondary levels. Essay on unemployment. Unemployment is one of the biggest problems facing countries, and this problem has increased recently as a result of the spread of the Corona virus (Covid-19), as many factories, companies and stores were closed, export and import stopped, and the tourism sector and other ...
Definition. Unemployment is a key financial pointer since it flags the (in)ability of laborers to promptly get beneficial work to add to the profitable yield of the economy. ... Discursive Essay on Hispanic Unemployment[ESSAY] Related documents. Essay About Unemployment Problems[ESSAY] Poverty, Illiteracy and Unemployment, or Why Does Education ...
The meaning of work (or work meaning), as defined by Pratt and Ashforth (Citation 2003), refers to the significance individuals attribute to work within the context of their lives.This concept is crucial as it is closely linked to people's decisions to enter or leave the workforce and provides insights into how organizations can motivate their employees (O'reilly & Caldwell, Citation 1980 ...
Unemployment is an economic condition that occurs when an individual or a group of people seek jobs to no success. In every country, the level of unemployment depends on some factors such as the status of the economy, market and commerce forces. There are five main types of unemployment (Baumol and Blinder 630).
The uncertainty surrounding the Preamble may be surprising, as the Constitution's introduction would seem central to any debate over the document's meaning. And, in fact, at least two of the Founding Fathers appeared to view the Preamble as an important feature of the document critical to the legal framework it established.
The unemployment rate fell to 3.7 per cent in February, from 4.1 per cent in January.. It was a surprisingly large decline, but does it mean we're moving closer to full employment? When Treasurer ...
Footnotes Jump to essay-1 At least one of the Framers defined legislative power as the power to prescribe rules for the regulation of society. The Federalist No. 75 (Alexander Hamilton). See also John Locke, Two Treatises of Government 382 (Peter Laslett ed., Cambridge Univ. Press 1967) (1690) (defining the legislative power as that which has a right to direct how the Force of the Commonwealth ...
They are forecasting robust growth, low unemployment and inflation that slowly but surely glides closer to the Fed's 2 percent target rate. March 20, 2024, 2:13 p.m. ET
Several of the papers feature the government's plan to introduce a new definition of extremism. The Daily Telegraph says Muslim groups that incite hatred will be named and shamed.
Ms. Angwin is a contributing Opinion writer and an investigative journalist. America is politically polarized. But there is an issue on which both sides agree: We need more privacy, and TikTok ...