
Pediatric Cancer Therapeutics Development pp 109–121 Cite as

Clinical Research Organizations
- Gregory A. Hale 6 &
- Jennifer Pullum 7
- First Online: 19 November 2022
226 Accesses
Part of the book series: Pediatric Oncology ((PEDIATRICO))
Contract research organizations, also known as clinical research organizations (CROs) or contract service organizations (CSO), or pharmaceutical development organizations, are established businesses that collaborate with pharmaceutical or medical device companies to assist them in the clinical development of their medication or device. While the sponsor retains responsibility for the conduct of the trial, CROs provide essential support services that may include regulatory affairs, regulatory submissions, budget generation, data management, biostatistics, medical monitoring, clinical monitoring, medical writing, and project management. CROs facilitate drug and medical device development by operationalizing clinical trials in accordance with Good Clinical Practice (GCP) guidelines, relying on their expertise in clinical trial conduct, operations experience, and close relationships with sites and investigators.
- Contract research organization
- Clinical research organization
- Clinical trial
- Data management
- Clinical monitoring
- Regulatory affairs
- Clinical research
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution .
Buying options
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Babiarz JC, Pisano D (2008) Overview of FDA and drug development. In: FDA regulatory affairs: a guide to prescription drug, medial devices, and biologics, 2nd edn. Informa Healthcare, New York City
Google Scholar
Babre D (2010) Perspect Clin Res 1:29–32
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Bhatt A (2012) Protocol deviation and violation. Perspect Clin Res 3:117
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Brody T (2009) Drug safety. In: Brody T (ed) Guide to drug development: a comprehensive review and assessment, 1st edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Brody T (2016a) Clinical trial design: amendments to the clinical study protocol. In: Brody T (ed) Clinical trials, 2nd edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Brody T (2016b) Regulatory approval. In: Brody T (ed) Clinical trials, 2nd edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Brody T (2016c) Package inserts. In: Brody T (ed) Clinical trials, 2nd edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Burks B (2020) Leave no site behind: how sites, sponsors, and CROs can speed clinical research together. Clinical Researcher. https://acrpnet.org/2020/01/14/leave-no-site-behind-how-sites-sponsors-and-cros-can-speed-clinical-research-together/ . Accessed 15 Jun 2020
Buvailo A (2020) The evolving pharma R&D outsourcing industry: a bird’s eye view. BioPharma Trend. https://www.biopharmatrend.com/post/146-the-evolving-pharma-rd-outsourcing-industry-a-birds-eye-view/ . Accessed 1 Nov 2020
Chiodin D, Cox EM, Edmund AV et al (2019) Regulatory affairs 101: introduction to investigational new drug applications and clinical trial applications. Clin Transl Sci 12:334–342
CREDEVO (2019) How to choose a CRO? Small and mid-size pharma companies. http://credevo.com/articles/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/howtochooseaCRO_small_medium_pharma_companies_credevo.png . Accessed 1 Sept 2020
Dirix P, Wyld L, Paluch-Simon S, Poortsmans P (2020) Time for more inclusive cancer trials. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 18:1431–1434. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2020.7652
Article Google Scholar
Eisenman D (2019) Established safety profiles allow for a gene therapy boom and streamlining of regulatory oversight. Clinical Researcher, vol 33
European Commission (n.d.) Substantial protocol amendments. https://ec.europa.eu/health/sites/health/files/files/clinicaltrials/docs/pc_rev3_2009-11/list_sa_uk_en.pdf
FDA (2003) Guidance for industry part 11, electronic records; electronic signatures-scope and application. US Dept. Health Human Services
FDA (2012) Guidance for industry and investigators. Safety reporting requirements for INDs and BA/BE studies. US Dept. Health Human Services
FDA (2018) E6 (R2) Good clinical practice: integrated addendum to ICH E6 (R1) Guidance for industry. US Dept. Health Human Services
FDA (2019) A risk-based approach to monitoring of clinical investigations. Questions and answers. Guidance for industry. US Dept. Health Human Services
FDA (2020) Enhancing the diversity of clinical trial populations-eligibility criteria, enrollment practices, and trials designs. Guidance for industry. US Dept. Health Human Services. http://www.fda.gov/drugs/guidance-compliance-regulatory-information/guidances-drugs . Accessed 1 Dec 2020.
FDA (2021) Investigational new drug (IND) application. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/investigational-new-drug-ind-application/ind-application-reporting-annual-reports . Accessed 1 Mar 2021
Gad SC, Spainhour CB, Serota DG (2020a) Introduction. In: Gad SC, Spainhour CB, Serota DG (eds) Contract research and development organizations—their history, selection, and utilization, 1st edn. Springer Nature, Cham
Chapter Google Scholar
Gad SC, Spainhour CB, Serota DG (2020b) Functions and types of contract support organizations (including CROs, CMDOs, packagers, and contract formulators). In: Gad SC, Spainhour CB, Serota DG (eds) Contract research and development organizations—their history, selection, and utilization, 1st edn. Springer Nature, Cham
Gad SC, Spainhour CB, Serota DG (2020c) Contract research and development organizations—their history, selection, and utilization, 1st edn. Springer Nature, Cham
Book Google Scholar
Gad SC, Spainhour CB, Serota DG (2020d) CROs in China, India, and elsewhere in the broader world: outsourcing science gone global. In: Gad SC, Spainhour CB, Serota DG (eds) Contract research and development organizations—their history, selection, and utilization, 1st edn. Springer Nature, Cham
Gad SC, Spainhour CB, Serota DG (2020e) Contracting, pricing, and cost or works performed by CROs. In: Gad SC, Spainhour CB, Serota DG (eds) Contract research and development organizations—their history, selection, and utilization, 1st edn. Springer Nature, Cham
Gad SC, Spainhour CB, Serota DG (2020f) Selection of CDROs. In: Gad SC, Spainhour CB, Serota DG (eds) Contract research and development organizations—their history, selection, and utilization, 1st edn. Springer Nature, Cham
Green S, Benedetti J, Smith A, Crowley J (2012a) Clinical trials in oncology, 3rd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Green S, Benedetti J, Smith A, Crowley J (2012b) Reporting of results. In: Green S, Benedetti J, Smith A, Crowley J (eds) Clinical trials in oncology, 3rd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Green S, Benedetti J, Smith A (2012c) Crowley data management and quality control. In: Green S, Benedetti J, Smith A, Crowley J (eds) Clinical trials in oncology, 3rd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Grignolo A, Choe S (2008) Meeting with the FDA. In: Pisano DL, Mantus DS (eds) FDA regulatory affairs: a guide to prescription drug, medical devices, and biologics, 2nd edn. Informa Healthcare, New York City
Hamrell MR (2008) IND. In: Pisano DJ, Mantus DS (eds) FDA regulatory affairs: a guide of prescription drug, medical devices, and biologics, 2nd edn. Informa Healthcare, New York City, p 20
Hulley SB, Newman TB, Cummings SR (2007) Choosing the study subjects: specification, sampling, and recruitment. In: Hulley SB, Cummings SR, Browner WS, Grady DG, Newman TB (eds) Designing clinical research, 3rd edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Jaoude JA, Kouzy R, Mainwaring W et al (2020) Performance status restriction in phase III cancer clinical trials. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 18:1322–1326. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2020.7578
Landhuis E (2018) Careers: the rise of outsourcing. Nature 556:263–265
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Masri MD, Ramirez B, Popescu C, Reggie EM (2012) Contract research organizations: an industry analysis. Int J Pharm Healthc Mark 6:336–350. https://doi.org/10.1108/17506121211283226
Passot C (2020) Trend of longer trial timelines is likely to continue. CenterWatch
Rajadhyaksha V (2010) Conducting feasibility in clinical trials: an investment to ensure a good study. Perspect Clin Res 3:106–109
Reist CJ, Rorick TL, Berdan LG, Lopes RD (2013) The role of academic research organization in clinical research. In: Lopes RD, Harrington RA (eds) Understanding clinical research, 1st edn. McGraw-Hill Medical, New York City
Rettig RA (2000) The industrialization of clinical research. Health Aff 19:129–146
Article CAS Google Scholar
Riddle WM (2018) Medical monitoring 101: providing medical expertise for clinical trials. C3isolutions.com/blog/meical-monitoring-101 . Accessed 12 Jul 2020
Rose L (2008) Pharmafile. http://www.pharmafile.com/news/stop-micro-managing-cros . Accessed 18 Aug 2020
Serota DG (2020a) The history of CROs: including CRO snapshots. In: Gad SC, Spainhour CB, Serota DG (eds) Contract research and development organizations—their history, selection, and utilization, 1st edn. Springer Nature, Cham
Serota DG (2020b) Study and project monitoring. In: Gad SC, Spainhour CB, Serota DG (eds) Contract research and development organizations—their history, selection, and utilization, 1st edn. Springer Nature, Cham
Sfera D, Sauber C (2019a) Regulations. In: Sfera D, Sauber C (eds) The comprehensive guide to clinical research. A practical handbook for gaining insight into the clinical research industry, 1st edn. Sweat Equity & Investments, LLC, East San Bernardino
Sfera D, Sauber C (2019b) Monitoring. In: Sfera D, Sauber C (eds) The comprehensive guide to clinical research. A practical handbook for gaining insight into the clinical research industry, 1st edn. Sweat Equity & Investments, LLC, East San Bernardino
Sfera D, Sauber C (2019c) Site level dynamics. In: Sfera D, Sauber C (eds) The comprehensive guide to clinical research. A practical handbook for gaining insight into the clinical research industry, 1st edn. Sweat Equity & Investments, LLC, East San Bernardino
Shih M (2015) Roles of contract research organizations in translational medicine. J Orthop Trans 3:85–88
Solarin O, Mohammed SI, Ndlovu N et al (2020) Partnerships and collaborations: the right alliances for clinical trials in Africa. JCO Glob Oncol 6:954–958. https://doi.org/10.1200/JGO.1900194
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Spilker B (2009a) Feasibility of multinational trials. In: Spilker B (ed) Guide to drug development: a comprehensive review and assessment, 1st edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Spilker B (2009b) Data management. In: Spilker B (ed) Guide to drug development: a comprehensive review and assessment, 1st edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Spilker B (2009c) Project management: balancing line function and matrix approaches. In: Spilker B (ed) Guide to drug development, 1st edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Medpace, Inc., Cincinnati, OH, USA
Gregory A. Hale
Clinical Trial Management, Medpace, Inc., Cincinnati, OH, USA
Jennifer Pullum
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Gregory A. Hale .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Clinical Development, Kronos Bio, San Mateo, CA, USA
Jorge DiMartino
Department of Pediatrics, George Washington University, Washington, DC, USA
Gregory H. Reaman
Medpace, Cincinnati, OH, USA
Franklin O. Smith
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter.
Hale, G.A., Pullum, J. (2022). Clinical Research Organizations. In: DiMartino, J., Reaman, G.H., Smith, F.O. (eds) Pediatric Cancer Therapeutics Development. Pediatric Oncology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-06357-2_8
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-06357-2_8
Published : 19 November 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-06356-5
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-06357-2
eBook Packages : Medicine Medicine (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Top 17 Clinical Research Organizations (CRO) in 2023
In clinical research and treatment development, clinical research organizations (CROs) are frequently a sponsor’s most important partner and ally.
Depending on the nature of the clinical trial, and your existing capabilities as a sponsor to run the trial, the CRO company of your choice will typically be responsible for facilitating most of the micro and macro processes that go into designing and running a successful clinical trial.
When contracting a CRO to help you with your trial, you are transferring over a large portion of responsibility into the hands of your clinical research partner. The CRO of your choice will have the responsibility to control a variety of factors and processes of a clinical trial, and depending on their expertise, team structures, service offerings, internal resources and many other capabilities.
Your ability to find and contract a top CRO company that is the right fit for your unique trial will be a determinant of whether or not you will be able to operate a high-quality clinical trial that meets your expected timelines, budget and delivers a top-notch patient experience.
At ClaraHealth (a patient-centric recruitment acceleration platform) , we have put together an extensive list of the top CRO companies in the US and around the world.
This is not a cro rankings list, but rather a compiled list of some of the top clinical research organizations around the world. We have highlighted their strengths and core service offerings to make it easier for you to find the right fit clinical research partner.
In addition, we’ve put together a list of 9 fundamental questions to ask the prospective clinical research organization , which will help you to save time and ensure a right fit in picking the CRO.
Formerly known as Quintiles and IMS Health, IQVIA is one of the largest CROs in the world, with a large range of service offerings to help advance clinical research.
The company was founded in North Carolina in 1982, and has since grown to over 88,000 employees in more than 100 countries.
Some clinical trial solutions offered by IQVIA include:
- Assistance with protocol design
- Design of phase 1 clinical trials
- Assessment and improvement of phase 2 and 3 clinical trials
- Site identification & selection
- Patient recruitment
- Access to global laboratories via their wholly owned subsidiary Q2 Solutions
Parexel is a global clinical research organization that was founded in 1982, and specializes in conducting clinical studies on behalf of its pharmaceutical partners in order to accelerate and ensure the drug approval process of up-and-coming potential treatments. It currently operates in more than 50 countries, and is run by more than 18,000 employees around the world.
The company has a wide range of service offerings, covering nearly every type of clinical trial service to assist sponsors in running successful clinical studies.
Some clinical trial solutions offered by Parexel include:
- Clinical trial design and development for early phase, phase 2 & 3, and late phase clinical trials
- Clinical data management
- Decentralized clinical trials
- Clinical supply chain management
- Medical writing
- Regulatory affairs consulting
- Pharmacovigilance
3. PRA Health Sciences
PRA Health Sciences is one of the largest contract research organizations in the world. Founded in 1976 under the name “Anti-Inflammatory Drug Study Group”, the company was renamed to PRA in 1982. PRA Health Sciences employees more than 17,000 people, and provides coverage to more than 90 countries.
In 2021, PRA Health Sciences was acquired by the Ireland-headquartered global CRO leader ICON, which is also reviewed in this list.
Some clinical trial solutions offered by PRA Health Sciences include:
- Decentralized Clinical Trials Platform
- Protocol Consultation & Study Design
- Onsite Support services
- Customized Solutions for Biotech (such as asset valuation, regulatory strategy, engagement and support, drug development strategy and funding solutions)
- Clinical Diagnostics
- Site Commercial Solutions
- PRA’s Laboratories for Drug Development
Headquartered in Ireland, ICON was founded in 1990 in Dublin by co-founders John Climax and Ronan Lambre. The company has since grown to be one of the largest CROs in the world. As of September 2020, the company employs more than 15,000 people in 94 locations and across 40 countries.
ICON offers clinical research services which include consulting, clinical development and commercialization across a wide range of therapeutic areas.
In 2021, ICON acquired PRA Health Sciences, which is another CRO and global leader in clinical research services.
Some clinical trial solutions offered by ICON:
- Commercial Positioning
- Early Phase
- Functional Services Provision
- Laboratories
- Language Services
- Medical Imaging
- Real World Intelligence
- Site & Patient Solutions
- COVID-19 Clinical Operations
5. Syneos Health
Formerly known as InVentiv Health Incorporated and INC Research, Syneos Health is a publicly listed and global contract research organization. The company is based in Morrisville, North Carolina, and specializes in assisting companies with late-stage clinical trials. Syneos Health currently employs more than 25,000 people, and has offices across 91 locations.
In early 2018, INC Research was acquired inVentiv Health, and the merged company was named Syneos Health.
Some clinical trial solutions offered by Syneos Health include:
- Decentralized Clinical Trials Solutions
- Bioanalytical Solutions
- Phase II-III/Phase IIIb-IIIV
- Medical Device Diagnostics
- Clinical Data Management
- Clinical Project Management
- Clinical Monitoring
- Drug Safety & Pharmacovigilance
- Site and Patient Access
6. Labcorp Drug Development (Formerly Covance)
Formerly known as Covance and renamed to Labcorp Drug Development in early 2021, this CRO is one of the largest contract research organizations in the world. The company claims to provide the world’s largest central laboratory network, and has been rated as one of the best places to work for LGBTQ+ equality by the Human Rights Campaign organization in 2018 to 2021. Currently, Labcorp employs over 70,000 people and is able to support clinical research efforts in almost 100 countries around the world.
Some clinical trial solutions offered by Labcorp Drug Development include:
- Preclinical Services
- Clinical Trials
- Clinical Trial Laboratory Services
- Post-Marketing Solutions
- Medical Devices
- Data & Technology
Also known as Pharmaceutical Product Development, PPD is a large global contract research organization headquartered in Wilmington, North Carolina. Started as a one-person consulting firm in 1985, PPD has grown to over 27,000 employees worldwide, and provides a wide range of clinical research services to pharmaceutical and biotech companies.
Some clinical trial solutions offered by PPD include:
- Clinical Development
- Early Development
- Peri- and Post-Approval
- PPD Biotech
- PPD Laboratories
- Product Development and Consulting
- Site and Patient Centric Solutions
8. Fisher Clinical Services
Part of Thermo Fisher Scientific, Fisher Clinical Services is a global clinical research organization with headquarters in Center Valley, Philadelphia.
The company has been in the business of clinical supply chain management for over 20 years, and is focused exclusively on working with the packaging and distribution requirements of clinical trials across the globe.
Some clinical trial solutions offered by Fisher Clinical Services include:
- Biologistics Management
- Cell & Gene Therapy
- Clinical Ancillary Management
- Clinical Label Services
- Clinical Trial Packaging & Storage
- Clinical Supply Optimization Services
- Cold Chain Management & Expertise
- Direct-to-Patient
- Distribution & Logistics
- Strategic Comparator Sourcing
- Public Health Research
Established in 1997 under the name Kiecana Clinical Research, KCR is a full-service contract research organization that provides a variety of services for clinical monitoring, safety & pharmacovigilance, clinical project management, quality assurance and regulatory affairs.
KCR operates globally, and has offices in North America, Western Europe, Central Europe and Eartern Europe. The company currently employs more than 700 staff.
Some clinical trial solutions offered by KCR include:
- Trial Execution
10. Medpace
Founded in 1992 and based in Cincinnati, Ohio, Medpace is a midsize clinical contract research organization. The company has operations in over 45 countries, and employs over 2,800 people. Medpace provides support services for Phase I-IV clinical trials for pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, which include central laboratory services and regulatory services.
Some clinical trial solutions offered by Medpace include:
- Biostatistics and Data Sciences
- Clinical Trial Management
- Drug Safety and Pharmacovigilance
- Medical Writing
- Quality Assurance
- Regulatory Affairs
- Risk-Based Monitoring
- Medpace Laboratories
11. Clintec
Now in business for over 22 years, Clintec is a medium-sized global contract research organization for pharmaceutical, biotech and medical device industries, with large expertise in oncology and rare diseases.
The company provides the flexibility and agility of a smaller-sized CRO, while also having a wide global coverage that large CRO companies are known for. Clintec is based in more than 50 countries, and was acquired by the leading global CRO IQVIA in late 2018.
Some clinical trial solutions offered by Clintec include:
- Project Management
- Data Management
- Biostatistics
- Global Feasibilities
- Patient Recruitment & Retention
12. Worldwide Clinical Trials
Bringing over 30 years of experience to the clinical research market, Worldwide Clinical Trials is a leading medium-sized global contract research organization. Founded by physicians with a dedication and commitment to advancing medical research, Worldwide Clinical Trials was the first customer-centric CRO.
Currently the company has coverage in more than 60 countries, and has extensive experience in a wide range of therapeutic areas, including central nervous system, metabolic, cardiovascular, oncology, rare diseases and general medicine.
Some clinical trial solutions offered by Worldwide Clinical Trials include:
- Bioanalytical Lab
- Early Phase Development
- Clinical Phase IIB-II Clinical Trials
- Phase IIIB-IV Clinical Trials
- Trial Management Technologies
Named #1 CRO in the world for operational excellence at the 2021 CRO Leadership Awards, CTI Clinical Trial And Consulting Services is a medium-sized global contract research organization that has been serving pharmaceutical companies since 1999.
Based in Covington, Kentucky, CTI has offices around the world in more than 60 countries, with coverage in North America, Europe, Latin America, Middle-East, Africa, and Asia-Pacific regions.
Some clinical trial solutions offered by CTI include:
- Feasibility
- Regulatory Affairs Study Start-Up
- Medical Monitoring
- Safety & Pharmacovigilance
- Clinical Services
14. Wuxi AppTec
Founded in 2000 as WuXi PharmaTech in the city of Wuxi, China, Wuxi AppTec has grown from a single laboratory into a leading global contract research organization with more than 28,000 employees, including 23,000 scientists and more than 30 research & development and manufacturing sites around the world.
With offices in Asia, U.S, Europe and the Middle East, the company is able to provide coverage to more than 30 countries around the world.
Some clinical trial solutions offered by Wuxi AppTec include:
- Small Molecule Drug R&D and Manufacturing
- Cell Therapy and Gene Therapy
- Drug R&D and Medical Device Testing
- Clinical Services (Phase I-IV)
15. Advanced Clinical
Founded in 1994 and based out of Deerfield, Illinois, Advanced Clinical is a midsize and full-service CRO that helps sponsors with running clinical trials. The company employs more than 700 staff, and offers a wide variety of services across many therapeutic areas. Advanced Clinical has global representation in over 50 countries around the world.
Some clinical trial solutions offered by Advanced Clinical include:
- eTMF & Document Management
- Global Medical Services
- Quality & Validation
16. Pharm-Olam
Pharm-Olam is a leading midsize CRO with global headquarters located in Houston, Texas and its European headquarters in Bracknell, United Kingdom. The company employs more than 800 staff, and has 25 offices around the world, with a global coverage in more than 60 countries.
The company has therapeutic expertise in 5 areas, including Rare & Orphan Disease, Infectious Disease & Vaccine, Oncology-Hematology, Allergy and Autoimmune.
Some clinical trial solutions offered by Pharm-Olam include:
- Study Feasibility
- Site Activation
- Patient Recruitment
- Medical Affairs
- Compliance & Training
- Clinical Monitoring & Operations
17. Clinipace
Founded in 2003 and based out of Morrisville, North Carolina, Clinipace is a global midsize full-service CRO with a focus on solution customization for clinical trials. The company has a large global coverage in more than 50 countries, and has offices in North America, South America, Europe and Asia-Pacific regions.
Clinipace’s therapeutic focus areas include Oncology, Nephrology and Urology, Rare Disease, Gastroenterology and Women’s Health. The company also has complete therapeutic expertise in Infectious Disease & Vaccines, Cardiology, CNS, Immunology, and Respiratory.
Some clinical trial solutions offered by Clinipace include:
- Clinical Analytics
- Clinical Technology and Ecosystem
- Functional Service Partnership (FSP)
- Regulatory & Strategic Product Development
9 Fundamental Questions To Ask A Top CRO Company Before Signing The Contract
1. which services does the cro provide.
CROs offload a lot of operational tasks from trial sponsors, which can touch any component of clinical trial operations. From formulating an overall study strategy and implementing technologies to support the operational processes of the trial, to picking and identifying sites, and supporting patients during the trial, the range of clinical services offered by a CRO tends to be vast and inclusive of all the typical services and support you will require for running a successful clinical trial.
However, not all CROs are the same in their service offerings, or are able to offer the same depth of capability within a seemingly same clinical trial support process. For this reason it is important to understand exactly which kind of clinical services and support you are looking to receive from the prospective CRO when running your clinical trial.
While services such as clinical monitoring and clinical trial management are offered by the majority of CROs, the specific needs of each trial are unique, and for this reason it is important to first identify what will be the unique services your trial requires. Completing this internal analysis first will help you to understand the extent to which a potential CRO partner will be able to provide all of these services.
Some CROs specialize in specific clinical trial functions which the company may label as a “core services”, in which case this is a sign the company will have more expertise, experience, and will be set up in a way to maximize their capabilities in providing support for these services compared to other services that the CRO offers.
For example, a CRO may include patient recruitment as part of its “core services”, which implies that they are highly skilled in and have the necessary infrastructure to design and implement a high-quality patient recruitment strategy.
Clara Health CRO Support Services: At Clara Health our specialty services include technology-augmented digital and patient advocacy recruitment, as well as patient support via our signature patient recruitment platform, which we use to upgrade clinical trials and deliver results sponsors look for in their recruitment and retention campaigns.
At Clara, we work alongside CROs to supplement and support clinical trials with modern and personalized capabilities that CROs do not typically have the bandwidth, corporate structure or infrastructure to support.
If you would like to learn more about exactly how our platform can upgrade your unique trial, feel free to book a Free 30 Minute Consultation Session Here with one of our in-house experts.
2. What Related Experience Does The CRO Have?
It is helpful to ask the prospective CRO company if they have any relevant experience in running clinical trials that would be an asset in designing and running your study. Previous experience in a related therapeutic area or in running a trial with a similar design allows CROs to have a deeper understanding into potential opportunities and challenges, increasing the likelihood of your clinical study being successful.
For example, if a sponsor is planning to run a trial in oncology, for the purpose of site identification and selection it would be valuable to partner with a CRO vendor that has expertise in this area, as they likely already have a good understanding of which sites will lead to optimal results.
However, it is also important to consider all factors when selecting a CRO vendor and not to rely on therapeutic experience as the sole qualifier for whether or not a potential CRO is a fit for your trial. While previous experience is beneficial, some sponsors close themselves off from working with vendors that have not worked in their therapeutic area, which significantly limits options when choosing a CRO partner that is truly a good fit for their clinical study.
This can impact the end result of your clinical study, as sponsors that are not successful in choosing a CRO vendor that is the right overall fit may face difficulties if the needs of their clinical study aren’t being properly met.
Clara Health: We have worked to provide support for clinical trials across a wide range of therapeutic areas and trial designs. Our specialty is filling in the gaps that CROs traditionally did not have to think about, which include digital patient recruitment, patient advocacy recruitment, and technology-augmented patient support.
Additionally, we are constantly building our proprietary data and running tests in a variety of therapeutic areas. These research efforts allow us to have a detailed understanding of the expected level of difficulty when recruiting particular patient populations, as well as allow us to predict with accuracy which segments of the targeted population will be likely to qualify in a particular study.
3. What Are The Communication Workflows & Expectations For Performing And Delivering Contracted Services?
It is important that you clarify what the expectations for communication will be between your prospective CRO vendor and your internal teams, as you will most likely be working with the CRO of your choice for the entire duration of your clinical trial.
There are a vast variety of factors and success determinants for a clinical trial, which are continuously undergoing change as the study unfolds. For this reason, it is recommended that you work with a CRO that is proactive in their communication, so that you are kept up to date with information about important changes as your clinical trial progresses.
A vendor that is proactive rather than reactive in their communication and approach to dealing with arising issues is one of the most important qualities in CRO. Challenging situations will naturally arise, and the promptness with which they are taken care of will significantly impact your clinical trial’s degree of success. Therefore, seeking a vendor that is able to match the standard of communication that you as a sponsor would like to experience throughout the duration of your partnership is one of the most critical steps in determining which CRO is the right fit for your clinical trial.
We’ve included a few additional questions pertaining to the communication structure and reporting expectations that you can ask a prospective CRO vendor to determine the degree of fit in this particular category:
Communication Expectations:
- If we were to move forward with you, which of your team members will be our main point of contact?
- How available will you be outside of the scheduled meetings to address any of our concerns or additional requests?
- What will be the frequency at which update meetings will be conducted, and who will be present at those meetings?
- Which clinical study processes will be reported on, and what will be the workflow for how we will receive this information?
- What will be the cadence at which we will receive progress reports?
- Would we be able to access metrics electronically via an interactive dashboard, or will you send us formal reports?
Clara Health: At Clara Health, we directly interact and actively work with several key stakeholders involved in running a clinical trial, which includes sponsors, CROs, sites, and patients. This unique position allows us to have a centralized perspective which helps us to see all the moving parts of a clinical trial at the same time, which helps to identify issues and relay this vital information and insight back to the sponsor (or other appropriate stakeholders) in the shortest time possible.
The ability to access this perspective allows us to gather the most accurate, complete, and up-to-date information about how the clinical trial is unfolding, and quickly becomes very valuable to sponsors for their clinical trial.
As an example, we may receive feedback from patients about having an unsatisfactory experience with a particular study site. We are able to aggregate and analyze this information, and relay our findings back to the sponsor and the study site to improve the experience for other patients.
4. What Is The CRO’s Client Satisfaction Record?
It is a good practice to request information or metrics from the prospective CRO vendor that can point to the degree of satisfaction of their past clients. Prior to signing the contract, vendors will naturally do their best to uplift their image and future value to you during their sales conversations with you and your team. It can be tricky to get an objective understanding of what the partnership experience will actually entail, especially when there are multiple vendors fighting for your commitment.
We recommend that you ask the prospective vendor to provide success metrics regarding areas of clinical trial operations that are going to be important for your trial.
For example, you may be interested in learning about the vendor’s relationship to finances, in which case it will be useful to ask them about situations in which they went over the planned budget, and investigate into the reasons behind that. Alternatively you may be concerned about potential delays in timelines, in which case it would be helpful to learn about metrics regarding the CRO’s ability to meet timeline expectations.
You may also request to talk to the prospective CRO’s past clients, which will help you to gain insight into what the relationship was like and give you the opportunity to examine if the way in which the particular CRO manages its relationships and performs its services meets the expectations that you would have for your potential relationship and for your clinical trial.
Clara Health: At Clara Health, our relationships with our partners and with our patients are most important to us. In the unique position where we fit in the clinical trial process, we have the opportunity to directly co-create the clinical trial patient experience with a variety of stakeholders, including sponsors, sites, CROs, and patients.
Our company’s values and culture have been directed and developed to be such that the client and patient experience is at the top of priority for all of our internal teams, and we work to provide the best quality of care to all stakeholders.
We have many testimonials from every type of partner we’ve worked with which we can happily share with you.
5. How Do You Adapt When Encountering Challenges With Running A Clinical Trial?
It is inevitable that challenges and unforeseen changes will arise throughout the operational clinical trial process, and for this reason it is important to work with a CRO vendor that can provide you with evidence of their flexibility and ability to adapt to sudden changes.
The ideal CRO partner is one that is highly consultative throughout the entire process, and has an ability and the initiative to deal with challenges at their seed stage, prior to them turning into major obstacles for the success of your trial.
CROs naturally have a large reach, and there are a lot of different clinical trial mechanisms and processes that are under their control. They are able to monitor and respond to what is going on in every key link in the chain of the clinical trial operation.
It is reasonable to expect this level of oversight from a CRO, and additional questions that can help you gain insight into this include:
- What are some examples where the CRO was effective at monitoring the health of clinical trials they’ve helped operate in the past?
- How quickly does the CRO respond to challenges or opportunities for improving the clinical trial experience?
- How well does the CRO gather & process information from study sites, study teams, patients & the sponsor, and what are their typical data analysis workflows?
It is also recommended to speak to the prospective CROs past clients to help you gain insight into how well they respond and adapt to the naturally arising challenges in clinical trials.
Clara Health: While CROs do have a large reach within the clinical trial, no CRO has complete visibility into every clinical process. They are not typically set up to support full visibility, which can manifest as a potential threat to your clinical trial as it unfolds. This is especially true for parts of the clinical trial processes that CROs naturally do not specialize and often subcontract, such as clinical trial recruitment.
At Clara, we are in a unique position in relation to other key partners involved in operating the clinical trial. We are in direct and frequent contact with patients, CROs, study sites, study teams, and the sponsor, and have a very deep understanding of the patient pipeline. This allows us the unique ability to go very deep into specific parts of the recruitment chain and investigate what is working and what is not working.
In addition, Clara functions as a resource for all partners in the clinical trial. For example, we work directly with site teams to ensure that they have access to a 3rd party that they can relay their needs to and receive fast support in case there is anything they require that can improve the patient recruitment process.
6. Which Parts Of Operating The Clinical Trial Will You Be Outsourcing?
Since there are so many processes and mechanisms that go into operating a clinical trial, CROs will always outsource some parts of running and managing the study. While you can expect that the prospective CRO will subcontract some of the work, it is important to find out which exact parts the clinical study will be outsourced.
There are certain basic and key clinical processes (such as site selection) that CROs almost always help with, and if you find that these parts of your trial are going to be subcontracted to another company, it is recommended to find out why the CROs operations are set up this way and how this would impact the service you will receive.
Ultimately what matters to you as a partner and client is that the quality of service and care that you will receive will be up to standard, and meet what was promised and what you are expecting. While this trust is important after you have signed the contract, it is recommended that prior to entering into such a significant commitment that you have evidence and the conviction that the CRO of your choice is truly the right fit and will deliver the quality of service that was being discussed.
Since it is impossible to predict exactly what the quality of this relationship and services performed will actually be like in practice, it is recommended that you understand the details of what will be done for your trial and how. Investigating how the CRO outsources and subcontracts services for a clinical trial will help you to gain necessary insight that you would need to make the correct vendor selection decision.
Clara Health: At Clara, we maximize the effectiveness of the digital component across the entire digital & recruitment spectrum, which is added on top of the existing capabilities of the CROs and other vendors involved in operating your clinical trial. In addition, we offer services that augment the CROs efforts, which has the potential to significantly improve the patient experience, operations flows, recruitment and retention performance, which is so important in ensuring the success of a clinical trial.
For example, if a CRO wants to have a great site relationship, we are able to come in as a third party on behalf of the sponsor and CRO and act as a resource and additional support for sites.
In another example, If a sponsor wants to have great relationships with the patient community, Clara is able to come in on behalf of the sponsor and develop these relationships while being perceived more neutrally by the patient community.
7. Do You Have Experience Running International Trials?
If you are planning on operating an international clinical trial, it is recommended to work with a CRO that has extensive experience in this area. While many CROs will offer near-global coverage, the level of experience with specific geographic locations can significantly vary from one vendor to another.
It is important to work with a CRO that has experience running clinical trials in the specific countries and regions you are planning to conduct your research in. Being compliant with the local rules and regulations for clinical testing is a very complex process that requires existing understanding and familiarity in order to ensure logistical smoothness and to mitigate legal risks. In operating a clinical trial, there are a multitude of clinical services and processes, which can greatly vary across the many regions in which you can conduct clinical testing.
A CRO that is lacking experience in operating international trials or operating in particular regions where you plan on conducting research may not be able to meet your desired quality and agility expectations, and therefore may not be the right fit for your international clinical trial.
Clara Health: In the past, we have provided international patient recruitment and digitally-augmented trial support services for clinical trials in the EU, Canada, UK, Australia and South America.
Clara Health is fully compliant to operate international studies everywhere in the world, with the exception of Russia and China.
8. What Is Your Relationship With Patients?
Patient-centric approach to designing and operating a clinical trial is becoming more and more crucial in the clinical research space. The ability of a sponsor and their CRO partner to understand the needs and characteristics of their target patient community is a significant determinant of whether or not the study will be a success.
A sponsor that has close and authentic relationships with the patient community tends to have a deeper understanding of how to create the best clinical trial experience that will attract patients and keep their interest throughout the clinical trial.
In addition, strong relationships with patients allow sponsors and CROs to forecast recruitment and patient retention pipeline with much higher accuracy. This ability is critical for ensuring the success of the trial and mitigating the risk of low enrollment. After an understanding of the patient population is acquired, sponsors gain the necessary insight to design a clinical trial that is not only favorable to their research results, but is also practical and will result in the enrollment numbers they are looking for.
While many CROs have already recognized the importance of patient-centricity and evolved the ways in which they design and operate clinical trials, other CROs have not yet made such a pivot in their values. It is important to understand the degree of importance the prospective CRO places on creating a favorable patient experience, and what kind of infrastructure the company has to support it.
At Clara, we recommend choosing a CRO partner that is adapting to the patient-centric model which is becoming more and more important for running a successful clinical trial.
Clara Health: Since early stages of our development, we’ve had a dedicated patient advocacy team that has been integral in shaping our company’s vision and operations. We have built our entire platform and recruitment infrastructure around creating the best experience for patients. Our teams, corporate values, service offerings and company infrastructure all work in the service of the patient.
In addition, over the many years of being in business we have heavily invested in building authentic patient community relationships that span across a variety of therapeutic areas. This has given us a unique ability to receive feedback directly from patients that is genuine and authentic around marketing materials, strategy for patient recruitment, and other services that we build for specific trials.
This ability to build partnerships with the patient community in an authentic way gives us a very unique ability to engage with the patient community on behalf of a pharmaceutical company, allowing our sponsor & CRO partners the opportunity to start conversations with patients through our in-house patient advocacy team.
If you would like to learn how Clara can help you to build a strong & authentic relationship with your target patient community, get in touch with us and we’d be happy to share our capabilities and previous results with you as they relate to your current or upcoming clinical trial.
9. How Is The CRO Going To Utilize Patient Input For Developing The Trial?
In the initial stages of clinical trial design, sponsors often determine the ideal patient profiles that would help them to drive the most favorable research outcomes for their study. While it is important for the success of your trial to determine who your ideal patients are, very often these projections do not match up with what is viable in practice.
At Clara, we often encounter study protocols that are not set up realistically for successful recruitment to be possible.
Common mistakes that are made when determining trial eligibility criteria and trial design include:
- Overestimating the interest in the clinical trial from the target patient population
- A lack of patient focus in the trial design
- A lack of convenience for patients in their participation
- Complicated and/or inefficient study experience flows
- Crafting the eligibility criteria around the patient population that is most likely to lead to favorable study outcomes, without conducting sufficient research to more accurately estimate the recruitment and retention difficulty of the group for a particular study
It is natural for there to be a “push & pull” between the research ideal and the real world practicality. It is important to determine the correct balance between these two sides for your trial, as going too far in either direction will decrease the chance of your clinical study’s success.
The nature of the industry as it is right now is such that there is excess research idealization and not enough emphasis on patient centricity. This distorted orientation has resulted in many clinical trials being unsuccessful, negatively impacting sponsors, patients and the entire clinical trials industry.
The ideal CRO partner should help you make sure that your protocol design sets your study up for success. The CRO should be able to help you determine the proper balance between the research ideal and the real world practicality, and back up their findings with sufficient research and patient data that can project your trial being a success.
Clara Health: When formulating a recruitment and retention plan for our clients, we begin with conducting thorough research into the target trial patient population. This allows us to get a clear understanding of which recruitment channels will yield the best results and what kind of marketing materials will resonate with the prospective study participants.
To ensure accuracy and real-world applicability of our research, we consult and collaborate with our internal patient advocacy and patient support teams, as well as with our clients and patients representing the target trial patient profiles. We then tie our findings back with any existing proprietary data that we have in connection with the therapeutic area or the prospective target patient group.
Our unique position within the clinical recruitment chain gives us the presence and deep-rooted access needed to effectively tap into any of the three patient traffic sources: digital recruitment, offline recruitment, or patient advocacy recruitment.
Once a recruitment campaign has gone live, we constantly monitor, analyze and optimize our performance to make sure that the processes we have in place are as efficient as possible and drive the greatest results. In addition, we have the capability to layer in any traditional advertising (such as billboard ads) if requested by the study sponsor.

2024: An Endeavor into the Enigma - Uncovering the Substance of CROs
Reflecting on the complexities inherent in the acronyms CRO (Clinical Research Organization) and CRA (Clinical Research Associate) indeed reveals a multifaceted landscape within the realm of clinical research. For those deeply entrenched in the nuances of clinical inquiry, understanding the operational mechanisms of CROs emerges as a pivotal journey delving into the uncharted territories of healthcare advancement. Whether venturing into the realms of clinical research for the first time or seeking a renewed perspective, delving into the semantic intricacies of CROs and unlocking their transformative potential in healthcare becomes an essential exploration, propelling organizations towards unparalleled developmental heights.
The Essence of a CRO:
Clinical Research Organizations, abbreviated as CROs, epitomize entities entrusted with the management of clinical trials on behalf of pharmaceutical and biotechnological giants. Their mandates encompass the selection of patients, procurement of informed consent, aggregation of data, and the persistent oversight of safety protocols. CROs are broadly categorized into two overarching classifications: full-service CROs, offering a spectrum of services essential for clinical trials, and specialized CROs, focusing their expertise on specific areas such as patient enrollment or data management.
The Era of CRO Dominance:
A seismic shift characterizes the ascendancy of CROs in recent chronicles. The tally of clinical trials orchestrated by CROs surged from 9,000 in 2006 to a staggering 26,000 in 2016. This remarkable ascent fundamentally attributes itself to the accessible expertise and efficiency that CROs demonstrate, all at a cost-effective rate compared to traditional avenues of research. Moreover, the integration of CROs into the operational framework enables pharmaceutical and biotechnological entities to sharpen their core competencies while concurrently mitigating the looming specter of clinical setbacks.
Navigating the Intersection of Costs and Benefits:
However, amidst the commendable merits inherent in CRO engagement, a caveat looms ominously. Skepticism burgeons regarding the equivalence of expertise, with concerns revolving around the potential discrepancy in data quality vis-à-vis conventional research entities. A lingering unease surfaces, questioning the parity of commitment to patient safety between CROs and their traditional counterparts. Navigating through the intricate labyrinth of CRO utilization necessitates a judicious assessment, a meticulous weighing of the benefits against the potential pitfalls in the steadfast pursuit of advancing the uncharted territories of healthcare improvement.
Clinical investigate organizations, recognized as contract inquire about substances, expand outsourced administrations to the pharmaceutical and biotechnology divisions. These organizations organize clinical trials for inventive pharmaceuticals and restorative approaches. The engagement of CROs can be started either by the pharmaceutical companies themselves or by the scholastic teach initiating the trials. The CRO industry has been encountering exponential development in later a long time. In 2024, the worldwide CRO administrations showcase gathered an evaluated $25.1 billion in 2024, with projections showing a compound yearly development rate of 7.5% over the resulting five a long time. Clinical inquire about administrations constituted the most considerable share of this advertise, measuring to $19.8 billion in 2024. Multiple variables contribute to the thriving of the CRO industry. At first, there has been a essential surge in the around the world conduct of clinical trials. Hence, a move from minute, casual trials to sweeping, formal trials overseen by commercial CROs has been watched. Thirdly, there is a recognizable uptick in the outsourcing slant among pharmaceutical and biotechnology enterprises. The essential on-screen characters in the CRO division include major multinational substances such as QuintilesIMS, Covance, and Parexel. At the same time, an developing unexpected of littler CROs specializes in specific restorative spaces or particular trial categories, extending the industry's scope and diversity. So, what absolutely constitutes the modus operandi of a CRO in 2024? In pith, a CRO outfits a comprehensive cluster of administrations including consider conceptualization, ponder execution, watchfulness, information administration, and expository interests. Furthermore, they habitually apportion administrative backing administrations like creating entries and conducting administrative audits. The vital advantage of locks in a CRO dwells in its capacity to speed up the medicate advancement direction. By subcontracting select or whole clinical trial endeavors, pharmaceutical enterprises in 2024 stand to abridge consumptions and rescue time. CROs, blessed with capability in executing clinical trials, adeptly encourage effective and compelling trial executions, subsequently progressing the field of pharmaceutical investigate.
What are the benefits of Clinical Research Organizations?
There are many benefits to working with a Clinical Research Organization (CRO). Perhaps the most important benefit is that CROs can help you to move your clinical research program forward faster and more efficiently. They have the experience and expertise to help you manage all aspects of your study, from start to finish. This can save you a lot of time and money, as CROs know how to navigate the complex world of clinical research.
Another major benefit of using a CRO is that they can help you to reduce risk. By using their experience and knowledge, CROs can help you to select the right study participants, design the study correctly, and implement best practices throughout the study. This can help to minimize any potential risks involved in conducting your study.
Finally, CROs can also help sponsors save money. They have established relationships with vendors and suppliers, so they can often get better deals on study materials and services than you would be able to negotiate on your own. This can result in significant cost savings for your clinical research program.
What are the challenges of Clinical Research Organizations?
The burgeoning domain of Clinical Investigate Organizations (CROs) experiences a heap of challenges in the year 2024. The quick development of this industry applies colossal weight on CROs to speed up and streamline considers, frequently coming about in hurried and substandard work. Concurrently, the basic to reduce costs holds on, coupled with the heightening complexities of administrative orders. Besides, hooking with furious competition from financially beneficial countries includes an extra layer of complexity, given their capacity to give cost-effective services.
These multifaceted challenges have accelerated various misgivings with respect to the quality and security guidelines inside the CRO space. A chronicled occasion in 2013 seen the FDA issuing a cautionary note to a CRO locked in in sedate company considers. The reprobation highlighted different deficiencies in the CRO's endeavors, including insufficient consider plan, subpar information administration, and a shortage of satisfactory observing protocols.
In a more later occurrence, circa 2013, another FDA caution resulted, provoked by a quiet casualty amid a clinical trial conducted by a CRO. The administrative body perceived insufficiencies in the CRO's oversight, showing in an insulant checked ponder and the disappointment to report grave antagonistic events.
These outlines only scratch the surface of the horde security worries that have tormented the CRO scene all through the a long time. The need of exacting quality control measures and inadequately observation can possibly result in extreme wounds or indeed fatalities for people taking an interest in clinical trials. Tending to these security concerns orders a concerted exertion. The FDA has spread direction archives and administrative goals pointed at improving the caliber of CRO endeavors. At the same time, pharmaceutical substances must work out increased acumen in selecting capable CROs whereas giving persevering oversight. Planned patients are empowered to attempt exhaustive investigate some time recently enlisting in clinical trials and ought to posture related inquiries with respect to the trial's procedural conduct.
Innovative Approaches to Better Clinical Research Organizations in the Year 2024
In the scene of clinical investigate organizations (CROs) as of 2024, there is a essential require for upgrade to guarantee the viability of clinical trials. The necessarily part of CROs in the arranging, execution, and documentation of clinical inquire about thinks about requires a sharp center on advancement strategies.
To move the advancement of CROs in 2024, one vital road includes the outsourcing of clinical inquire about preparing. By entrusting this pivotal viewpoint to outside substances, CROs can ensure comprehensive preparing in best hones, cultivating the conveyance of trials of the most elevated quality. This approach too serves to keep CROs side by side of cutting-edge advances and winning patterns inside the field, contributing to their ceaseless refinement.
Another essential road for the upgrade of CROs lies in the enlargement of straightforwardness. This means the basic of making operational subtle elements of CROs freely open. Such straightforwardness envelops illustrating the strategies utilized by CROs, uncovering the results of their considers, and uncovering the charge structures they execute. By grasping straightforwardness, the moral operation of CROs is shielded, guaranteeing impartial treatment of patients.
In the broader setting, the change of CROs in 2024 is a multifaceted endeavor. Outsourcing clinical inquire about preparing and cultivating straightforwardness rise as linchpin procedures to accomplish this overarching objective.
While CROs irrefutably constitute a significant aspect of the clinical inquire about prepare, their adequacy pivots on tending to characteristic challenges. Moved forward communication and straightforwardness with supports, destinations, and patients are basic for CRO viability. Emphasizing quality over amount is vital to maintain a sterling notoriety inside the industry. If diving more profound into the complexities of clinical investigate organizations interests you, consider selecting in our clinical inquire about certification course for an smart investigation of their working.
A Comprehensive Guide to PMP Certification
The meaning of triage: a guide for the clinical research professional.
Therapeutic Expertise
Participate

Explore end-to-end solutions throughout development — from portfolio optimization and regulatory strategy, to Phase I-IV clinical trials, market access planning, and more.
- Portfolio management and asset valuation
- Early development and innovation
- Integrated clinical development
- Approval and access
- Value substantiation lifecycle management
HOW WE DO IT
- Operational excellence
- Delivery models
- Building patient insights into assets, profile and claims
- Portfolio Optimization
- Asset Valuation and Indication Prioritization
- Early Evidence Review
- Model-Based Drug Development
- Integrated Development Strategy and Planning
- Phase I Clinical Trials
- Proof of Concept Studies: Phase IB-IIA
- Patient Engagement Strategy and Enrollment Solutions
- Patient Inclusion
- Site Alliance Network and KOL Engagement
- Protocol Optimization
- Regulatory Strategy
- Market Access Strategy and Delivery
- Biomarker and Genomic Medicine Strategy
- Clinical Trial Supply & Logistics
- Medical Communications
- Phase IIB-IV Clinical Trials
- Real World Evidence
- Protocol-Driven, Customized Site Solution Strategy
- Regulatory Strategy, Submissions, Compliance, and Outsourcing
- Clinical Development Technology Optimization
- Global Regulatory Submissions and Outsourcing
- Compliance and Risk Management
- Real-World Evidence, Market Access Strategy and Planning
- Regulatory Compliance, Drug Safety and Pharmacovigilance
- Lifecycle Optimization
- Leveraging AI and digital in clinical development
- Biotech Clinical Trial Solutions
- Gain an advantage through FSP

Utilize our expertise across therapeutic areas, combining innovative trial designs, leading clinical and regulatory expertise, global reach, and a passion for changing patient lives.
- Neuroscience
- General medicine
- Infectious disease & vaccines
- Inflammation & immunology
Cross-Therapeutic Expertise
- Cell & gene therapies
- Rare diseases

Our experts help you stay at the forefront of the industry - and ahead of change.
New Medicines, Novel Insights
- Advancing rare disease drug development
- Accelerating development of cell and gene therapies
- Achieving patient-guided drug development
Discussions on Diversity
- Chapter 1 Bridging the Gap
- Chapter 2 Beyond the Binary
The Regulatory Navigator
- Exploring ICH Q5A revision 2
- Potency assurance for CGT products: FDA's new draft guidance
- The FDA’s final guidance: CAR-T product development
Latest Report

New Medicines, Novel Insights: Achieving patient-guided drug development

Thinking about joining a clinical trial? Learn the drug development process, what it’s like to participate, how to find a trial, and answers to frequently asked questions.
INTERESTED IN PARTICIPATING?
- Healthy Volunteers
- Patient Volunteers
- Patient Advocacy Groups
HEAR FROM REAL PATIENTS
- Patient Stories
TRIAL SITES

Want to collaborate with us to offer clinical trials at your site? We would welcome the opportunity to discuss.
We are one of the largest CROs in the world, speeding life-changing medicine to market by engaging patients With Heart ™. Learn about who we are, what we do, and what we believe.
- Management team
- Global reach
Our DE&I strategy
- Compliance, Tax & Privacy
- Meet us at an event
- Jamie Macdonald
- Peyton Howell
- Michael Crowley
- Jonathan Shough
- Sheri McCoy
- Michael Bruun
- John Groetelaars
- Susan Salka
- Global Reach
- Our DE&I Strategy
Our ESG Strategy
- Compliance & Ethics
- Tax Strategy
- Privacy Policy
- Supplier Data Privacy Requirements
- Terms of Use
- French Gender Pay Data
- UK Gender Pay Data
- UK Modern Slavery Act Statement
- EU-U.S. Data Privacy Framework (EU-U.S. DPF)
- Supplier Diversity Policy
- World Vaccine Congress
- Patients as Partners U.S.
- MAPS Americas
- ASCPT 2024 Annual Meeting
- Managing Complexity in Cell and Gene Trials: Establishing an RBQM Strategy that Drives Better Performance
- EDI in clinical research: The case for adaptive strategies at every step
- 17th ISCR ANNUAL CONFERENCE 2024
- IncluDE Site Solutions Summit
- AAN Annual Meeting
- ASGCT Annual Meeting
- Dermatology Drug Development Summit EU
- World Orphan Drug Congress US
- AACR Annual Meeting
- BIO International Convention
- DIA Global Annual Meeting
- International Society for Cell & Gene Therapy
- Final countdown: How to transition your trials under EU-CTR
- SCRS: Oncology Site Solutions Summit
- Accelerating Vaccine Development Through Operational Excellence
- Alzheimer’s Disease vs Multiple Sclerosis Drug Development: Similarities, Differences & New Perspectives
What can we help you find today?
At Parexel, we speed your life-changing medicines to patients
Parexel is among the world’s largest clinical research organizations (CROs), providing the full range of Phase I to IV clinical development services to help lifesaving treatments reach patients faster. Leveraging the breadth of our clinical, regulatory, and therapeutic expertise, our team of more than 21,000 global professionals works in partnership with biopharmaceutical leaders, emerging innovators, and sites to design and deliver clinical trials with patients in mind, increasing access and participation to make clinical research a care option for anyone, anywhere.
Our depth of industry knowledge and strong track record gained over the past 40 years is moving the industry forward and advancing clinical research in healthcare’s most complex areas, while our innovation ecosystem offers quality solutions to make every phase of the clinical trial process more efficient. Our top-notch people, insight, and focus on operational excellence allow us to work every day to treat patients with dignity and continuously learn from their experiences, so every trial makes a difference.
This approach continues to earn us recognition industrywide, with Parexel being named “Best Contract Research Organization” in November 2023 by an independent panel for Citeline, “Top CRO to Work With” by investigative sites worldwide in the 2023 WCG CenterWatch Global Site Relationship Benchmark Survey and recipient of the 2023 Society for Clinical Research Sites (SCRS) Eagle Award for advancing the clinical research profession through strong site partnerships.
Read the transcript
It starts with people. They may come from anywhere. But they’re driven by a common goal: Their search for a brighter future.
They inspire us to learn from their lives across language and race, ability, ethnicity, and community.
So we design clinical trials that give them a voice, honor their sacrifice, and treat them as equals.
We are more than 21,000 professionals working with passion and perseverance to open doors. To lead change. And find new ways to work together.
We make participation easier and partnerships more productive to get to results faster and treatments sooner.
So every patient’s step forward brings them one step closer to a cure, to care, to hope.
Delivered with heart.

Leading the industry in trial inclusivity and accessibility
Within clinical research, patient diversity is critical. Inclusive studies move us closer to healthcare equity and more accurately reflect real-world populations — resulting in a far greater understanding of how the treatment will affect the people who need it. Our approach to designing more diverse, accessible trials is leading the industry forward.
Our family of brands
Parexel Academy
Your trusted partner in learning. Parexel Academy is committed to building and enhancing capabilities within the clinical research workforce so that, together, we make a positive impact on the lives of patients around the world.

Health Advances
As a trusted strategic advisor to healthcare and life science executives, Health Advances catalyzes your success with insight, innovation, and integrity.
The Medical Affairs Company
The industry’s leading provider of comprehensive outsourced medical affairs solutions.
Patients First
Empowerment and accountability.
Each of us, no matter what we do at Parexel, contributes to the development of a therapy that ultimately will benefit a patient. We take our work personally, we do it with empathy, and we're committed to making a difference.
From the smallest detail to the largest, we take quality seriously. We focus on the details while never losing sight of the big picture to drive the best possible outcome.
In our quest for innovation, we recognize and uphold the importance of all people, from our employees to our clients and the patients we all serve.
We follow our hearts, we do the right thing, and we have the courage to own the outcome.
Awards & Recognition
2024 ViE Best Contract Research Organization
Parexel was selected by a distinguished industry advisory board for its range of services in niche and core therapeutic areas, methods of performance improvement, attention to and quality of relationships with clients, reaching milestones and final outcomes, and building and maintaining existing and long-term partnerships. The annual ViE Awards, organized by Terrapin, celebrate the industry’s most outstanding achievements and showcase excellence in the global vaccine industry.
2023 Scrip Award
Parexel was named “Best Contract Research Organization” in the Full-Service Provider category at the 19th Annual Scrip Awards. The annual Scrip Awards, organized by Citeline, are designed to celebrate and recognize the very best innovations and achievements in global biopharma.
2023 HBA ACE Award
Parexel was recognized with the 2023 Healthcare Businesswomen’s Association’s (HBA) “Advancement. Commitment. Engagement (ACE) Award,” which recognizes companies for their creation and implementation of initiatives that deliver impactful outcomes designed to close the gender gap in the healthcare ecosystem. Parexel was one of two companies chosen as a result of the strong outcomes from its business initiative “Priority: Advancing Women in Leadership.”
2023 Eagle Award by Society of Clinical Research Sites
The SCRS Eagle Award recognizes the sponsor and CRO committed to outstanding leadership, professionalism, integrity, passion and dedication to advancing the clinical research profession through strong site partnerships. Recipients of the Eagle Award are selected based on votes cast from the global site community.
Ecovadis 2023
For the second year in a row, Parexel has received a “silver” rating in the 2023 EcoVadis Sustainability Rating Program. Ecovadis is the world’s largest and most trusted provider of business sustainability ratings. A silver rating is awarded to organizations with a structured and proactive sustainability approach with strong reporting on KPIs and actions.
2023 CRO Leadership Awards
Parexel has been recognized with CRO Leadership Awards for the 12 th consecutive year across all five categories – Capabilities, Compatibility, Expertise, Quality, and Reliability – for exceeding customer expectations in different customer segments. Winning CROs are chosen based on feedback from sponsor companies that they have worked on an outsourced project within the previous 18 months.
2023 WCG CenterWatch Global Site Relationship Benchmark Survey
Parexel was ranked as the “Top CRO to Work With” by investigative sites worldwide in the 2023 WCG CenterWatch Global Site Relationship Benchmark Survey for the second straight time. Among 34 CROs, Parexel received the highest average rating across all 26 performance attributes evaluated in the survey. In addition to receiving the highest average rating across all attributes, Parexel ranked highest on four out of the five attributes considered the most important to investigative sites and was selected as the CRO that investigative sites were most willing to recommend to a colleague.
2022 Catalyst Awards
Parexel was named a 2022 Catalyst Award winner by the global nonprofit organization Catalyst. Parexel was recognized for its Leveraging Gender Partnership to Advance Women in Leadership initiative that has evolved the company culture to one where women have the right resources and training to succeed.
FlexJobs’ Top 100 Companies to Watch for Remote Jobs in 2022
Parexel was recognized as a company to watch on FlexJobs' 10th annual list of the Top 100 Companies to Watch for Remote Jobs in 2023. Parexel is one of only five companies to have made the FlexJobs' list each year since its inception in 2014.
Human Rights Campaign Corporate Equality Index 2022
Parexel is proud to be featured on the Human Rights Campaign’s 2022 Corporate Equality Index, the premier survey benchmarking tool on how corporations across the US and beyond are adopting equitable workplace policies, practices and benefits for LGBTQ+ employees
Management Team
Meet our management team
Explore our environmental, social, and governance (ESG) report

Journey to Better Health Mobile Exhibit
Informing patients and families about clinical research.
The Center for Information and Study on Clinical Research Participation’s (CISCRP) core mission is to provide accessible, relevant, useful, high quality educational resources, programs, and services that increase awareness and understanding of the clinical research process; recognize and appreciate the unprecedented gift of participation in clinical trials; enhance and enrich the participation experience for patients and their families; and promote engagement and partnership between clinical research professionals, patients, and the public.

offerings for patients & families
Search Clinical Trials
services for professionals
Health Communication Services
Research services, patient diversity campaign, content licensing.

We Provide Services for Patients, Families, and Professionals
We are uniquely positioned to provide the public with clinical research information and offer industry services where we work with organizations on clinical research projects.
We Provide Services for the Public & Industry
offerings for the public
services for the industry
New Resources

The Importance of Diversity in Clinical Research Video

What is a Placebo? Brochure

Dee Burlile's Story, Scleroderma Clinical Trial Participant
Get involved.

search clinical trials

Your generous donations help increase and promote education about clinical research participation.

education center

Help plan, implement, and raise awareness for our educational programs and projects.
Latest News
Latest ciscrp patient survey reveals diversity gaps, yields 5 tips for improvement, round-up: highlighting recent health literacy educational materials, community trust: the foundation for fostering diversity in clinical trials, meet the ciscrp team at 2023 conferences, search clinical trials now, click on the resources listed below to download the full versions of biogen’s materials. .
Biogen’s Commitment to Build Trust and Diversity in Clinical Trials [VIDEO]
Biogen Trial Link
The TALLY Clinical Trial

The Hidden Face of MS

Click on the resources listed below to download the full versions of Drugviu’s materials.
Pandemic Response Network Flyer: English
Red de Respuesta a una Pandemia: Español

Click on the resources listed below to download the full versions of these materials.
Peer Plus: Mission and Capabilities

Latino Union of Chicago
Click on the resources listed below to download the full latino union of chicago annual report. .

Advocate Aurora Health
Click on the resources listed below to download the full versions of advocate’s materials. .
- Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer’s Network Trial Unit
Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer’s Disease Brochure Expanded Registry Flyer (English)
Enfermedad de Alzheimer de herencia dominante Expanded Registry Flyer (Spanish)
- Clarity AD Clinical Study Information
Forgetting the Little Things Concerned About Memory Loss?
- US POINTER Volunteer Study Brochure

Allergy & Asthma Network
Click on the resources listed below to download the full versions of the allergy & asthma network’s materials. , institute for population and precision health (ipph), click on the resources listed below to download the full versions of ipph’s materials. .
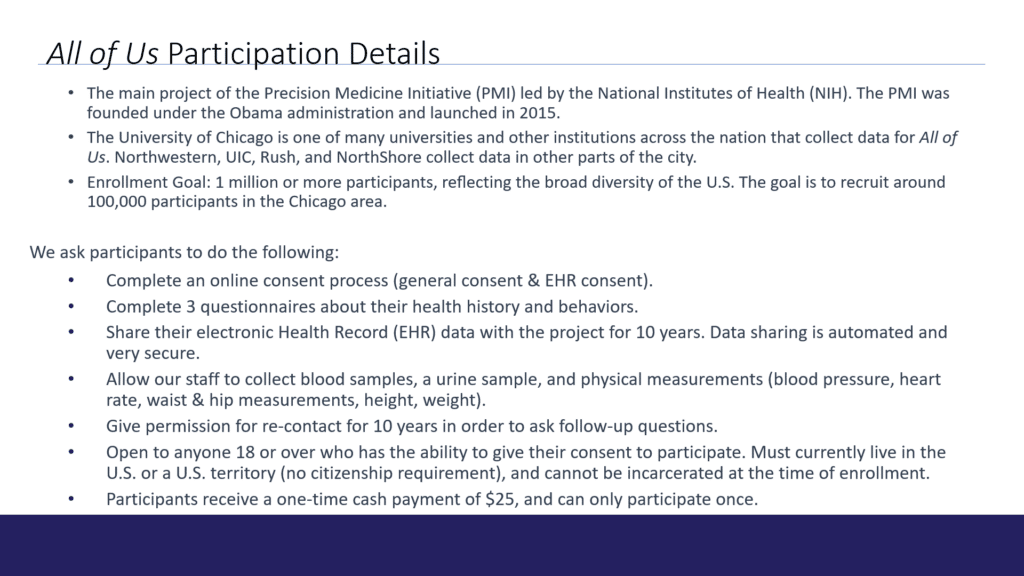
Einstein Healthcare Network
Click on the resources listed below to learn more about einsteing healthcare network’s resources. .
TREND Community
Click on the resources listed below to download the full versions of the trend community’s materials. , community voice report july 2020: covid-19 positive, community voice report august 2020: pericarditis, fox chase cancer center - temple health, click on the resources listed below to download the full versions of the fox chase cancer center’s materials. , be the breakthrough: understanding clinical trials.

Click on the resources listed below to download the full materials from Otsuka.
PsychU Brochure
NephU Brochure
PsychU App Flyer
PsychU Patient & Caregiver Collection Flyer
Collaborating for Improved ADPKD Management: Considerations for the Healthcare Team
Lung Cancer Initiative of North Carolina
Click on the resources listed below to view the full versions of LCI’s materials.
Lung Cancer Risk Assessment Handout
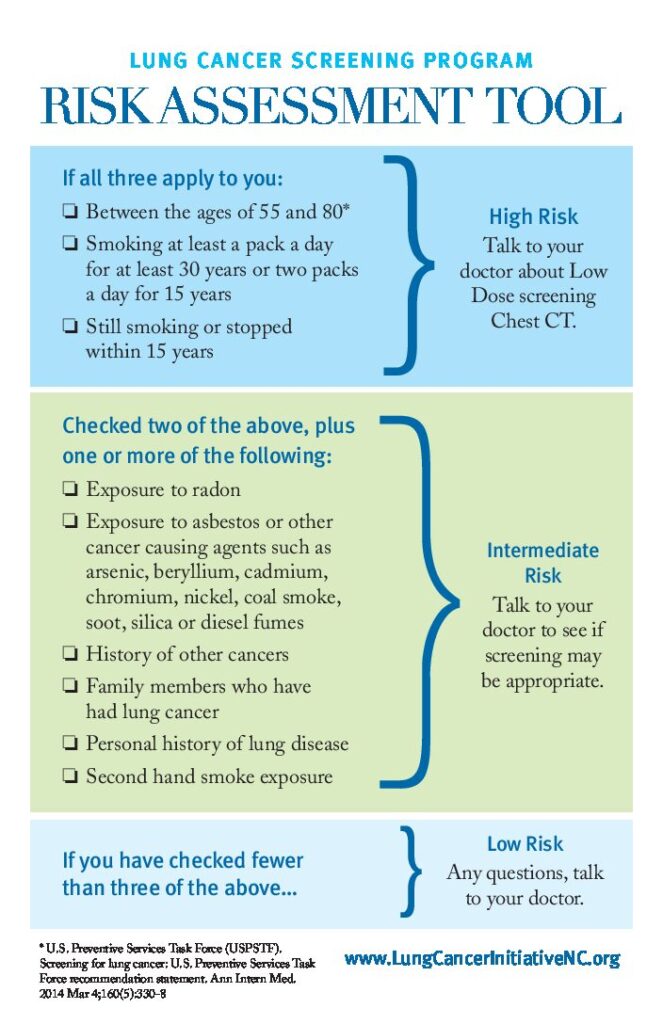
PRA Health Sciences
Click on the resources listed below to view the full versions of pra’s materials. .

wearestronger2gether.com

Duke Health
Click on the resources listed below to view the full versions of duke’s materials. .
Visit Discover Duke Research on Facebook
Download the handout below in English or Spanish

North Carolina Clinical Research
Visit north carolina clinical research’s website .

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Pharmacol
- v.44(2); Mar-Apr 2012
Data management in clinical research: An overview
Binny krishnankutty.
Global Medical Affairs, Dr. Reddy's Laboratories Ltd., Ameerpet, Hyderabad, India
Shantala Bellary
Naveen b.r. kumar, latha s. moodahadu.
Clinical Data Management (CDM) is a critical phase in clinical research, which leads to generation of high-quality, reliable, and statistically sound data from clinical trials. This helps to produce a drastic reduction in time from drug development to marketing. Team members of CDM are actively involved in all stages of clinical trial right from inception to completion. They should have adequate process knowledge that helps maintain the quality standards of CDM processes. Various procedures in CDM including Case Report Form (CRF) designing, CRF annotation, database designing, data-entry, data validation, discrepancy management, medical coding, data extraction, and database locking are assessed for quality at regular intervals during a trial. In the present scenario, there is an increased demand to improve the CDM standards to meet the regulatory requirements and stay ahead of the competition by means of faster commercialization of product. With the implementation of regulatory compliant data management tools, CDM team can meet these demands. Additionally, it is becoming mandatory for companies to submit the data electronically. CDM professionals should meet appropriate expectations and set standards for data quality and also have a drive to adapt to the rapidly changing technology. This article highlights the processes involved and provides the reader an overview of the tools and standards adopted as well as the roles and responsibilities in CDM.
Introduction
Clinical trial is intended to find answers to the research question by means of generating data for proving or disproving a hypothesis. The quality of data generated plays an important role in the outcome of the study. Often research students ask the question, “what is Clinical Data Management (CDM) and what is its significance?” Clinical data management is a relevant and important part of a clinical trial. All researchers try their hands on CDM activities during their research work, knowingly or unknowingly. Without identifying the technical phases, we undertake some of the processes involved in CDM during our research work. This article highlights the processes involved in CDM and gives the reader an overview of how data is managed in clinical trials.
CDM is the process of collection, cleaning, and management of subject data in compliance with regulatory standards. The primary objective of CDM processes is to provide high-quality data by keeping the number of errors and missing data as low as possible and gather maximum data for analysis.[ 1 ] To meet this objective, best practices are adopted to ensure that data are complete, reliable, and processed correctly. This has been facilitated by the use of software applications that maintain an audit trail and provide easy identification and resolution of data discrepancies. Sophisticated innovations[ 2 ] have enabled CDM to handle large trials and ensure the data quality even in complex trials.
How do we define ‘high-quality’ data? High-quality data should be absolutely accurate and suitable for statistical analysis. These should meet the protocol-specified parameters and comply with the protocol requirements. This implies that in case of a deviation, not meeting the protocol-specifications, we may think of excluding the patient from the final database. It should be borne in mind that in some situations, regulatory authorities may be interested in looking at such data. Similarly, missing data is also a matter of concern for clinical researchers. High-quality data should have minimal or no misses. But most importantly, high-quality data should possess only an arbitrarily ‘acceptable level of variation’ that would not affect the conclusion of the study on statistical analysis. The data should also meet the applicable regulatory requirements specified for data quality.
Tools for CDM
Many software tools are available for data management, and these are called Clinical Data Management Systems (CDMS). In multicentric trials, a CDMS has become essential to handle the huge amount of data. Most of the CDMS used in pharmaceutical companies are commercial, but a few open source tools are available as well. Commonly used CDM tools are ORACLE CLINICAL, CLINTRIAL, MACRO, RAVE, and eClinical Suite. In terms of functionality, these software tools are more or less similar and there is no significant advantage of one system over the other. These software tools are expensive and need sophisticated Information Technology infrastructure to function. Additionally, some multinational pharmaceutical giants use custom-made CDMS tools to suit their operational needs and procedures. Among the open source tools, the most prominent ones are OpenClinica, openCDMS, TrialDB, and PhOSCo. These CDM software are available free of cost and are as good as their commercial counterparts in terms of functionality. These open source software can be downloaded from their respective websites.
In regulatory submission studies, maintaining an audit trail of data management activities is of paramount importance. These CDM tools ensure the audit trail and help in the management of discrepancies. According to the roles and responsibilities (explained later), multiple user IDs can be created with access limitation to data entry, medical coding, database designing, or quality check. This ensures that each user can access only the respective functionalities allotted to that user ID and cannot make any other change in the database. For responsibilities where changes are permitted to be made in the data, the software will record the change made, the user ID that made the change and the time and date of change, for audit purposes (audit trail). During a regulatory audit, the auditors can verify the discrepancy management process; the changes made and can confirm that no unauthorized or false changes were made.
Regulations, Guidelines, and Standards in CDM
Akin to other areas in clinical research, CDM has guidelines and standards that must be followed. Since the pharmaceutical industry relies on the electronically captured data for the evaluation of medicines, there is a need to follow good practices in CDM and maintain standards in electronic data capture. These electronic records have to comply with a Code of Federal Regulations (CFR), 21 CFR Part 11. This regulation is applicable to records in electronic format that are created, modified, maintained, archived, retrieved, or transmitted. This demands the use of validated systems to ensure accuracy, reliability, and consistency of data with the use of secure, computer-generated, time-stamped audit trails to independently record the date and time of operator entries and actions that create, modify, or delete electronic records.[ 3 ] Adequate procedures and controls should be put in place to ensure the integrity, authenticity, and confidentiality of data. If data have to be submitted to regulatory authorities, it should be entered and processed in 21 CFR part 11-compliant systems. Most of the CDM systems available are like this and pharmaceutical companies as well as contract research organizations ensure this compliance.
Society for Clinical Data Management (SCDM) publishes the Good Clinical Data Management Practices (GCDMP) guidelines, a document providing the standards of good practice within CDM. GCDMP was initially published in September 2000 and has undergone several revisions thereafter. The July 2009 version is the currently followed GCDMP document. GCDMP provides guidance on the accepted practices in CDM that are consistent with regulatory practices. Addressed in 20 chapters, it covers the CDM process by highlighting the minimum standards and best practices.
Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium (CDISC), a multidisciplinary non-profit organization, has developed standards to support acquisition, exchange, submission, and archival of clinical research data and metadata. Metadata is the data of the data entered. This includes data about the individual who made the entry or a change in the clinical data, the date and time of entry/change and details of the changes that have been made. Among the standards, two important ones are the Study Data Tabulation Model Implementation Guide for Human Clinical Trials (SDTMIG) and the Clinical Data Acquisition Standards Harmonization (CDASH) standards, available free of cost from the CDISC website ( www.cdisc.org ). The SDTMIG standard[ 4 ] describes the details of model and standard terminologies for the data and serves as a guide to the organization. CDASH v 1.1[ 5 ] defines the basic standards for the collection of data in a clinical trial and enlists the basic data information needed from a clinical, regulatory, and scientific perspective.
The CDM Process
The CDM process, like a clinical trial, begins with the end in mind. This means that the whole process is designed keeping the deliverable in view. As a clinical trial is designed to answer the research question, the CDM process is designed to deliver an error-free, valid, and statistically sound database. To meet this objective, the CDM process starts early, even before the finalization of the study protocol.
Review and finalization of study documents
The protocol is reviewed from a database designing perspective, for clarity and consistency. During this review, the CDM personnel will identify the data items to be collected and the frequency of collection with respect to the visit schedule. A Case Report Form (CRF) is designed by the CDM team, as this is the first step in translating the protocol-specific activities into data being generated. The data fields should be clearly defined and be consistent throughout. The type of data to be entered should be evident from the CRF. For example, if weight has to be captured in two decimal places, the data entry field should have two data boxes placed after the decimal as shown in Figure 1 . Similarly, the units in which measurements have to be made should also be mentioned next to the data field. The CRF should be concise, self-explanatory, and user-friendly (unless you are the one entering data into the CRF). Along with the CRF, the filling instructions (called CRF Completion Guidelines) should also be provided to study investigators for error-free data acquisition. CRF annotation is done wherein the variable is named according to the SDTMIG or the conventions followed internally. Annotations are coded terms used in CDM tools to indicate the variables in the study. An example of an annotated CRF is provided in Figure 1 . In questions with discrete value options (like the variable gender having values male and female as responses), all possible options will be coded appropriately.

Annotated sample of a Case Report Form (CRF). Annotations are entered in coloured text in this figure to differentiate from the CRF questions. DCM = Data collection module, DVG = Discrete value group, YNNA [S1] = Yes, No = Not applicable [subset 1], C = Character, N = Numerical, DT = Date format. For xample, BRTHDTC [DT] indicates date of birth in the date format
Based on these, a Data Management Plan (DMP) is developed. DMP document is a road map to handle the data under foreseeable circumstances and describes the CDM activities to be followed in the trial. A list of CDM activities is provided in Table 1 . The DMP describes the database design, data entry and data tracking guidelines, quality control measures, SAE reconciliation guidelines, discrepancy management, data transfer/extraction, and database locking guidelines. Along with the DMP, a Data Validation Plan (DVP) containing all edit-checks to be performed and the calculations for derived variables are also prepared. The edit check programs in the DVP help in cleaning up the data by identifying the discrepancies.
List of clinical data management activities

Database designing
Databases are the clinical software applications, which are built to facilitate the CDM tasks to carry out multiple studies.[ 6 ] Generally, these tools have built-in compliance with regulatory requirements and are easy to use. “System validation” is conducted to ensure data security, during which system specifications,[ 7 ] user requirements, and regulatory compliance are evaluated before implementation. Study details like objectives, intervals, visits, investigators, sites, and patients are defined in the database and CRF layouts are designed for data entry. These entry screens are tested with dummy data before moving them to the real data capture.
Data collection
Data collection is done using the CRF that may exist in the form of a paper or an electronic version. The traditional method is to employ paper CRFs to collect the data responses, which are translated to the database by means of data entry done in-house. These paper CRFs are filled up by the investigator according to the completion guidelines. In the e-CRF-based CDM, the investigator or a designee will be logging into the CDM system and entering the data directly at the site. In e-CRF method, chances of errors are less, and the resolution of discrepancies happens faster. Since pharmaceutical companies try to reduce the time taken for drug development processes by enhancing the speed of processes involved, many pharmaceutical companies are opting for e-CRF options (also called remote data entry).
CRF tracking
The entries made in the CRF will be monitored by the Clinical Research Associate (CRA) for completeness and filled up CRFs are retrieved and handed over to the CDM team. The CDM team will track the retrieved CRFs and maintain their record. CRFs are tracked for missing pages and illegible data manually to assure that the data are not lost. In case of missing or illegible data, a clarification is obtained from the investigator and the issue is resolved.
Data entry takes place according to the guidelines prepared along with the DMP. This is applicable only in the case of paper CRF retrieved from the sites. Usually, double data entry is performed wherein the data is entered by two operators separately.[ 8 ] The second pass entry (entry made by the second person) helps in verification and reconciliation by identifying the transcription errors and discrepancies caused by illegible data. Moreover, double data entry helps in getting a cleaner database compared to a single data entry. Earlier studies have shown that double data entry ensures better consistency with paper CRF as denoted by a lesser error rate.[ 9 ]
Data validation
Data validation is the process of testing the validity of data in accordance with the protocol specifications. Edit check programs are written to identify the discrepancies in the entered data, which are embedded in the database, to ensure data validity. These programs are written according to the logic condition mentioned in the DVP. These edit check programs are initially tested with dummy data containing discrepancies. Discrepancy is defined as a data point that fails to pass a validation check. Discrepancy may be due to inconsistent data, missing data, range checks, and deviations from the protocol. In e-CRF based studies, data validation process will be run frequently for identifying discrepancies. These discrepancies will be resolved by investigators after logging into the system. Ongoing quality control of data processing is undertaken at regular intervals during the course of CDM. For example, if the inclusion criteria specify that the age of the patient should be between 18 and 65 years (both inclusive), an edit program will be written for two conditions viz . age <18 and >65. If for any patient, the condition becomes TRUE, a discrepancy will be generated. These discrepancies will be highlighted in the system and Data Clarification Forms (DCFs) can be generated. DCFs are documents containing queries pertaining to the discrepancies identified.
Discrepancy management
This is also called query resolution. Discrepancy management includes reviewing discrepancies, investigating the reason, and resolving them with documentary proof or declaring them as irresolvable. Discrepancy management helps in cleaning the data and gathers enough evidence for the deviations observed in data. Almost all CDMS have a discrepancy database where all discrepancies will be recorded and stored with audit trail.
Based on the types identified, discrepancies are either flagged to the investigator for clarification or closed in-house by Self-Evident Corrections (SEC) without sending DCF to the site. The most common SECs are obvious spelling errors. For discrepancies that require clarifications from the investigator, DCFs will be sent to the site. The CDM tools help in the creation and printing of DCFs. Investigators will write the resolution or explain the circumstances that led to the discrepancy in data. When a resolution is provided by the investigator, the same will be updated in the database. In case of e-CRFs, the investigator can access the discrepancies flagged to him and will be able to provide the resolutions online. Figure 2 illustrates the flow of discrepancy management.

Discrepancy management (DCF = Data clarification form, CRA = Clinical Research Associate, SDV = Source document verification, SEC = Self-evident correction)
The CDM team reviews all discrepancies at regular intervals to ensure that they have been resolved. The resolved data discrepancies are recorded as ‘closed’. This means that those validation failures are no longer considered to be active, and future data validation attempts on the same data will not create a discrepancy for same data point. But closure of discrepancies is not always possible. In some cases, the investigator will not be able to provide a resolution for the discrepancy. Such discrepancies will be considered as ‘irresolvable’ and will be updated in the discrepancy database.
Discrepancy management is the most critical activity in the CDM process. Being the vital activity in cleaning up the data, utmost attention must be observed while handling the discrepancies.
Medical coding
Medical coding helps in identifying and properly classifying the medical terminologies associated with the clinical trial. For classification of events, medical dictionaries available online are used. Technically, this activity needs the knowledge of medical terminology, understanding of disease entities, drugs used, and a basic knowledge of the pathological processes involved. Functionally, it also requires knowledge about the structure of electronic medical dictionaries and the hierarchy of classifications available in them. Adverse events occurring during the study, prior to and concomitantly administered medications and pre-or co-existing illnesses are coded using the available medical dictionaries. Commonly, Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA) is used for the coding of adverse events as well as other illnesses and World Health Organization–Drug Dictionary Enhanced (WHO-DDE) is used for coding the medications. These dictionaries contain the respective classifications of adverse events and drugs in proper classes. Other dictionaries are also available for use in data management (eg, WHO-ART is a dictionary that deals with adverse reactions terminology). Some pharmaceutical companies utilize customized dictionaries to suit their needs and meet their standard operating procedures.
Medical coding helps in classifying reported medical terms on the CRF to standard dictionary terms in order to achieve data consistency and avoid unnecessary duplication. For example, the investigators may use different terms for the same adverse event, but it is important to code all of them to a single standard code and maintain uniformity in the process. The right coding and classification of adverse events and medication is crucial as an incorrect coding may lead to masking of safety issues or highlight the wrong safety concerns related to the drug.
Database locking
After a proper quality check and assurance, the final data validation is run. If there are no discrepancies, the SAS datasets are finalized in consultation with the statistician. All data management activities should have been completed prior to database lock. To ensure this, a pre-lock checklist is used and completion of all activities is confirmed. This is done as the database cannot be changed in any manner after locking. Once the approval for locking is obtained from all stakeholders, the database is locked and clean data is extracted for statistical analysis. Generally, no modification in the database is possible. But in case of a critical issue or for other important operational reasons, privileged users can modify the data even after the database is locked. This, however, requires proper documentation and an audit trail has to be maintained with sufficient justification for updating the locked database. Data extraction is done from the final database after locking. This is followed by its archival.
Roles and Responsibilities in CDM
In a CDM team, different roles and responsibilities are attributed to the team members. The minimum educational requirement for a team member in CDM should be graduation in life science and knowledge of computer applications. Ideally, medical coders should be medical graduates. However, in the industry, paramedical graduates are also recruited as medical coders. Some key roles are essential to all CDM teams. The list of roles given below can be considered as minimum requirements for a CDM team:
- Data Manager
- Database Programmer/Designer
- Medical Coder
- Clinical Data Coordinator
- Quality Control Associate
- Data Entry Associate
The data manager is responsible for supervising the entire CDM process. The data manager prepares the DMP, approves the CDM procedures and all internal documents related to CDM activities. Controlling and allocating the database access to team members is also the responsibility of the data manager. The database programmer/designer performs the CRF annotation, creates the study database, and programs the edit checks for data validation. He/she is also responsible for designing of data entry screens in the database and validating the edit checks with dummy data. The medical coder will do the coding for adverse events, medical history, co-illnesses, and concomitant medication administered during the study. The clinical data coordinator designs the CRF, prepares the CRF filling instructions, and is responsible for developing the DVP and discrepancy management. All other CDM-related documents, checklists, and guideline documents are prepared by the clinical data coordinator. The quality control associate checks the accuracy of data entry and conducts data audits.[ 10 ] Sometimes, there is a separate quality assurance person to conduct the audit on the data entered. Additionally, the quality control associate verifies the documentation pertaining to the procedures being followed. The data entry personnel will be tracking the receipt of CRF pages and performs the data entry into the database.
CDM has evolved in response to the ever-increasing demand from pharmaceutical companies to fast-track the drug development process and from the regulatory authorities to put the quality systems in place to ensure generation of high-quality data for accurate drug evaluation. To meet the expectations, there is a gradual shift from the paper-based to the electronic systems of data management. Developments on the technological front have positively impacted the CDM process and systems, thereby leading to encouraging results on speed and quality of data being generated. At the same time, CDM professionals should ensure the standards for improving data quality.[ 11 ] CDM, being a speciality in itself, should be evaluated by means of the systems and processes being implemented and the standards being followed. The biggest challenge from the regulatory perspective would be the standardization of data management process across organizations, and development of regulations to define the procedures to be followed and the data standards. From the industry perspective, the biggest hurdle would be the planning and implementation of data management systems in a changing operational environment where the rapid pace of technology development outdates the existing infrastructure. In spite of these, CDM is evolving to become a standard-based clinical research entity, by striking a balance between the expectations from and constraints in the existing systems, driven by technological developments and business demands.
Source of Support: Nil.
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
A Comprehensive Guide to Clinical Research Organizations (CROs)

Clinical Research Organizations (CROs) play a crucial role in the pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device industries. They provide support to companies in the form of research services outsourced on a contract basis. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore what CROs are, who their clients are, the stages of the research process they are typically involved in, and delve into the exciting career opportunities within the field of clinical research.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Clinical Research Organizations (CROs) The Role of CROs in the Research Process Services Offered by CROs Clients and Partners of CROs Careers in Clinical Research Clinical Research Associate (CRA) Roles and Responsibilities Educational and Professional Requirements for Clinical Research Careers Advancement Opportunities in Clinical Research Tips for Success in Clinical Research Careers Resources and Professional Organizations Conclusion
Introduction to Clinical Research Organizations (CROs)
Clinical Research Organizations (CROs) are companies that provide support to the pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device industries in the form of research services outsourced on a contract basis. They offer a wide range of services , including biopharmaceutical development, clinical development, clinical trials management, and pharmacovigilance. CROs aim to simplify the entry into drug markets and streamline the drug development process by providing specialized expertise and resources.
The Role of CROs in the Research Process
CROs play a crucial role in the research process, from the early stages of drug discovery and development to the final stages of clinical trials and commercialization. They work closely with their clients to design and execute clinical trials, ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements and ethical standards. CROs also provide support in data management, statistical analysis, and the preparation of regulatory submissions.
Services Offered by CROs
CROs offer a wide range of services to their clients, including but not limited to:
Biopharmaceutical development : CROs assist in the development of new drugs, from preclinical studies to early-phase clinical trials. Clinical development: CROs design and manage clinical trials, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and ethical standards.
Clinical trials management: CROs oversee all aspects of clinical trials, including site selection, patient recruitment, data collection, and safety monitoring.
Pharmacovigilance : CROs monitor the safety of drugs and medical devices during clinical trials and after they are on the market.
Real-world evidence and outcomes research : CROs collect and analyze data from real-world sources, such as electronic health records, to generate evidence on the safety and effectiveness of drugs and medical devices. CROs conduct studies to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of drugs and medical devices in real-world settings.
Clients and Partners of CROs
CROs work with a diverse range of clients, including pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology firms, medical device manufacturers, research institutions, and government organizations . They collaborate closely with their clients to ensure that research studies are conducted efficiently, safely, and in compliance with regulatory requirements. CROs also partner with academic institutions and foundations to support their research initiatives.
Careers in Clinical Research
Clinical research offers exciting career opportunities for individuals interested in the scientific, regulatory, and operational aspects of drug development.
Careers in clinical research span a wide range of roles, including Clinical Research Associate (CRA), Clinical Project Manager, Data Manager, Biostatistician, and Medical Writer, among others. These roles require a combination of scientific knowledge, attention to detail, critical thinking, and strong communication skills.
Clinical Research Associate (CRA) Roles and Responsibilities
Clinical Research Associates (CRAs) play a crucial role in the execution and monitoring of clinical trials. Their responsibilities include site selection and initiation, monitoring study progress, ensuring compliance with protocols and regulatory requirements, and maintaining accurate and complete documentation. CRAs work closely with investigators, study coordinators, and other stakeholders to ensure that trials are conducted safely and efficiently.
Educational and Professional Requirements for Clinical Research Careers
Careers in clinical research typically require a strong educational background in life sciences or a related field. Many positions, such as CRAs, require a bachelor's or master's degree in a scientific discipline. Professional certifications, such as the Certified Clinical Research Associate (CCRA) certification, can enhance career prospects and demonstrate expertise in the field.
Advancement Opportunities in Clinical Research
Clinical research offers ample opportunities for career advancement and professional growth. Experienced professionals can progress to more senior roles, such as Clinical Project Manager or Clinical Operations Director, where they oversee the planning and execution of multiple clinical trials. Continuing education, networking, and staying updated with industry trends are essential for career advancement in clinical research.
Tips for success in seeking a Career in Clinical Research
To succeed in clinical research careers, professionals should continuously develop their scientific knowledge, stay updated with regulatory requirements, and enhance their communication and project management skills. Networking, building relationships with key stakeholders, and seeking mentorship can also contribute to career advancement in the field.
Resources and Professional Organizations for Clinical Research Professionals
Several resources and professional organizations cater to the needs of clinical research professionals. These include industry publications, online forums, conferences, and professional associations. Organizations such as the Association of Clinical Research Professionals (ACRP) and the Society of Clinical Research Associates (SoCRA) provide educational resources, networking opportunities, and professional certifications for clinical research professionals.
Clinical Research Organizations (CROs) play a vital role in the pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device industries by providing research services on a contract basis. They offer a wide range of services to support the development and execution of clinical trials, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and ethical standards.
Careers in clinical research offer exciting opportunities for individuals interested in the scientific, regulatory, and operational aspects of drug development. By partnering with CROs and pursuing careers in clinical research, professionals can contribute to the advancement of medical science and the development of innovative therapies.
If you're interested in exploring careers opportunities in clinical research, view our current vacancies at ICON today.
Sign up for post alerts
Icon & you the potential of together..
Careers that improve the lives of patients, our clients and each other. Are you ready to make a difference?
Related jobs
Clinical Monitoring
Remote Working
Office Based
Business Area
ICON Strategic Solutions
Job Categories
Description
Job Title: Clinical Research AssociateWorking model: Client office Based in Taiwan (Flexible WFH) ICON plc is a world-leading healthcare intelligence and clinical research organization. We’re proud to
2024-109665
Expiry date

2024-109664
Australia, Sydney
Hybrid: Office/Remote
ICON Full Service & Corporate Support
Study Start Up
At ICON, it’s our people that set us apart. Our diverse teams enable us to become a better partner to our customers and help us to fulfil our mission to advance and improve patients’ lives. Our ‘Own

Japan, Tokyo
Drug Safety
ICON plc is a world-leading healthcare intelligence and clinical research organisation. From molecule to medicine, we advance clinical research providing outsourced services to pharmaceutical, biotech

Related stories
.png)
Teaser label
Content type
Publish date
Introduction to the Clinical Research Supply Chain The clinical research supply chain plays a crucial role in the successful execution of clinical trials. It encompasses a complex network of activ
Discover the intricate workings of the clinical research supply chain in this comprehensive guide.

At ICON, a global leader in drug and device development services, Catherine Blake has found an environment that fosters career growth and inspires her to excel. As a Director of Clinical Data Sc
As Catherine reaches her 5 year work anniversary, she provides an insight into her personal career journey at ICON.

Exploring Lucy's Path: From Science to Communications Lucy's career journey is a testament to the power of adaptability and seizing opportunities as they arise. "I've been in Clinical Research si
We hear from Lucy on her varied career journey, who joined as a Clinical Research Associate in 2008.
Recently viewed jobs
A better career. A better world. A better you.
Browse popular job categories below or search all jobs above

What Is a CRO?
Pharmaceutical, biotechnology and medical device companies initiate, manage and fund clinical trials and are ultimately responsible for the clinical trial process. They are referred to as sponsors. Clinical trial sponsors also include government agencies, such as the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in the United States, and non-profit organizations.
The research and development process for a single drug can require the participation of thousands of people. It may take as long as 15 years to bring a new drug to market and the average cost can exceed $1 billion. It is a long, complex and expensive process, and many sponsors are not equipped, resourced or prepared to perform all trial-related duties and functions themselves.
For this reason, sponsors may choose to outsource all or part of the trial-related tasks to a company called a clinical research organization or contract research organization (CRO) to manage the clinical trial on their behalf, without sponsors having to maintain a staff for these services. CROs have the capacity to conduct the day-to-day research activities that are either not possible or too expensive for a sponsor to achieve in-house. CROs are experts in the space and active partners in clinical research.
- A CRO's Role in Pharmaceutical Development
- Functions of a CRO
- Clinical Research and Trial Management
- Global and Specialized CRO Services
“ It may take as long as 15 years to bring a new drug to market and the average cost can exceed $1 billion . “
CROs in the United States
the size that the global CRO market size is expected to reach, in dollars, in 2023
What Is a CRO’s role in pharmaceutical development?
CROs play a major role in ensuring safe, ethical clinical trials that are essential to developing new, life-changing drugs and medical devices that benefit millions of patients worldwide .
The services that a CRO may offer can cover the full timeline of the study:
- The development and revision of protocols for trials
- The adaptation of the necessary documentation to the applicable rules
- Obtaining the necessary approvals from clinical research ethics committees and regulatory authorities
- The design and preparation of case report forms
- The determination of the sample
- The selection of the best researchers and research centers
- The final negotiation of the contracts among all parties (the CRO, vendors and sites).
- Once regulatory approval is obtained and the trial begins with site selection and patient recruitment, the CRO can provide monitoring , which consists of controlling compliance with the protocol and the procedures established for the development of the study. Likewise, pharmacovigilance services include detection and action in case of any adverse event (AE).
- The last steps to ensure the success of any clinical study are the statistical analysis and management of the trial data , the generation of reports (including the clinical study report for submission to regulatory authorities for drug approval) and the control and storage of the documentation.
CRO structure
A Contract Research Organization (CRO) acts as a bridge between the sponsor, the one who contracts the services, and the rest of the actors involved in the clinical trial.
(Leon Research, https://leonresearch.com/what-is-a-cro-and-how-can-it-help-you-in-your-clinical-trial/ )
Functions of a Clinical Research Organization
Typically, a CRO provides scientific, clinical and business continuity for clinical trial sponsors. The CRO can be involved in a range of services from pre-clinical research (which takes place before human trials) to post-marketing surveillance (which takes place after a product has been approved for use).
Other administrative activities may include strategic consulting and protocol development, laboratory and analytical services, project management, trial logistics, medicine and disease coding, statistical analysis and reporting, validation programming, safety and efficacy summaries and the final study report.
Clinical research and trial management
A sponsor hires a CRO to plan, coordinate, execute and manage the life cycle of the clinical trial safely and efficiently. Serving as the main contact between the sponsor and other stakeholders throughout the trial, the CRO communicates with ethics and compliance committees, regulatory personnel, vendors, physicians and research coordinators.
Clinical trials conducted by CROs are completed on average 30 days faster than those conducted by sponsor companies. 1
Every day counts for both patients (who may be anxiously waiting on therapies that could improve or even save their lives) and sponsors (because time spent in the development process counts against the patent protection period after the drug goes to market, affecting sales revenue).
With more than 35 years of experience, the PPD clinical research business of Thermo Fisher Scientific offers an established drug development platform, patient enrollment expertise and robust laboratory services . Our broad range of clinical development, analytical and patient and advisory services – including full service to functional service provider services , digital and decentralized trials, and laboratories – enables customers to drive innovation and increase drug development productivity. We are recognized for accelerating promising medicines from early development through regulatory approval and market access. Our flexible, custom-tailored solutions serve pharmaceutical, biotech, medical device, academic, government and public health organizations in clinical research and development .
Global and specialized CRO services
Most large CROs are full-service, providing complete clinical trial management support, but there are some companies specializing in a specific type of study (e.g., research with medical devices or observational studies) and also CROs specializing in a specific therapeutic area, such as oncology or ophthalmology.
Global CROs, large companies with operations all over the world, provide greater, integrated geographical coverage, with more service offerings and capabilities, while local companies may sometimes have more in-depth knowledge of a particular country’s nuances and demographics as they relate to clinical development.
The global network consisting of clinical sites within the PPD clinical research business of Thermo Fisher Scientific and non-owned partner sites offers access to a diverse pool of healthy volunteers and specialty populations around the world. Our experienced staff provides external oversight of a trial, working directly with the institutions where clinical studies are conducted – hospitals and clinics, called investigational sites. We provide training to the principal investigator and the site staff, and ensure that the safety, rights and well-being of patients are protected; that the conduct of the trial is in compliance with regulatory requirements; and that reported trial data are accurate and complete.
What is the difference between a CRO and a sponsor?
Although the sponsoring company may transfer the trial functions to a CRO, the sponsor owns the investigational product and needs to ensure results are factual and scientifically backed.
According to the definition of the International Council on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) , a CRO is: “A person or an organization (commercial, academic or other) contracted by the sponsor to perform one or more of a sponsor’s trial-related duties and functions.”
The sponsor maintains a central role throughout the clinical trial process. Although regulatory tasks differ globally, they include initiating the trial process by submitting an application and ensuring approval is obtained (directly or indirectly).
The ICH Guideline for GCP specifies the responsibilities a CRO can take over from a sponsor :
- 5.2.1: A sponsor may transfer any or all of the sponsor’s trial-related duties and functions to a CRO, but the ultimate responsibility for the quality and integrity of the trial data always resides with the sponsor. The CRO should implement quality assurance and quality control.
- 5.2.2: Any trial-related duty and function that is transferred to and assumed by a CRO should be specified in writing. The sponsor should ensure oversight of any trial-related duties and functions carried out on its behalf, including trial-related duties and functions that are subcontracted to another party by the sponsor’s contracted CRO(s).
- 5.2.3: Any trial-related duties and functions not specifically transferred to and assumed by a CRO are retained by the sponsor.
- 5.2.4: All references to a sponsor in this guideline also apply to a CRO to the extent that a CRO has assumed the trial-related duties and functions of a sponsor.
What are the advantages of outsourcing to a CRO?
A CRO can offer substantial cost savings for a sponsor by reducing the time it takes to conduct a trial compared to a sponsor doing so in-house. This also eliminates the need for staff, infrastructure and lab and office space for the sponsor to run the trials themselves. Finally, a full-service CRO can provide access to a global network of clinical research sites, meaning it can quickly identify suitable sites for clinical trials in multiple countries. Geographical reach or therapeutic focus can be important in patient recruitment, especially in specific populations, such as underserved and diverse , or for rare diseases that affect a small subset of people.
Working with a CRO gives sponsors access to the most advanced technology and systems for data management, product development, research analysis and other clinical research services. CROs are quick to adopt the latest technologies, enabling them to provide strategic insights and advice, and to offer novel and distinctive ways to use advanced tools and adapt them to each sponsor’s needs to ensure optimal clinical trial performance. Given that CROs work with many different sponsors, they often have a breadth of experience beyond even a single large pharmaceutical company.
CROs adhere to clinical compliance on a daily basis, which requires intricate in-house knowledge of regulatory requirements and audits such as GCP (Good Clinical Practice) or GLP (Good Laboratory Practice) audits.
Sponsors conducting clinical research in a niche area such as rare disease may choose to work with a specialty CRO or a global CRO with offering such services.
Global Network
The PPD clinical research business of Thermo Fisher Scientific has an extensive global network of investigators, clinicians and partners with a wide range of products, technologies and services that can be leveraged for clinical trial conduct. Our goal is to deliver considerable time and cost savings in drug development, critical to accelerating the delivery of life-changing therapies. Our experts consider the end before the beginning by envisioning and planning for commercialization and market acceptance well before the first patient is enrolled in a clinical trial. And before trials are underway, we design for post-approval, real-world patient observation that provides support for payer authorizations and may lead to new ideas and products .
How does a sponsor select a CRO?
When selecting a CRO, here are some questions to consider:
- Can the CRO offer the services that the sponsor needs?
- Does the CRO have related experience and a good track record (i.e., similar projects and references or testimonials from satisfied clients)?
- Is the CRO financially stable?
- Does the CRO have a good system for employee training and a low staff turnover rate?
- Does the CRO have the key staff members required and can it set up a team to deliver qualified results?
- Does the CRO have the required infrastructure?
- Does the CRO have a robust quality assurance system?
- Is the CRO’s team responsive and willing to work with you and communicate throughout the project?
- Does the CRO have specialty services, laboratories, digital and decentralized solutions, a clinical supplies network and other capabilities important to your drug development program?
- Will the CRO help you recruit and manage safety boards or committees?
- Will the CRO conduct audits to help you prepare to pass FDA inspections?
- Can the CRO provide general site support and project management help in addition to clinical monitoring?
- Does the CRO function as a vendor or a true partner ?
Drive your drug development program forward
Partner with a leading, global CRO that leverages a proven track record and deep expertise to keep the patient at the forefront of your trial.
The PPD clinical research business of Thermo Fisher Scientific accelerates your success with a dynamic, forward-thinking approach, a comprehensive suite of capabilities and true partnership with our customers.

The Science-First CRO. ™
The scientific full service CRO and consultancy integrating strategic planning, regulatory strategy, and clinical trial execution to rapidly advance your complex or novel therapies.

READ THE PRESS RELEASE

Specialty Expertise
Our team of scientific experts is easy to work with, even for the rarest, most complex, and never done before novel therapies..
Driving Success
Advancing Novel Therapies to Success with Veristat READ SPONSOR SUCCESS STORIES

Phase I/II Trial After NH Trial

Rare Disease Gene Therapy Trial
Tackling problems big or small we can help.

What Are Your Challenges?

Be Part of the Team That Cares
At Veristat, we contribute and add value to our company’s mission - improving and saving lives. Whether you’re a scientific expert or an operations guru, explore the chance to become part of our fast-paced, agile team.

ACRP 2024 is where clinical researchers GO for inspiration, education, and connection. Join us from May 3 – 6 in Anaheim, CA!
ACRP Budget Buddy™
Budgeting for DCTs at your site just got a whole lot easier. Visit the new DCT Resource Center to get the new ACRP DCT Budget Buddy™.
Advancing People Advancing Health™
ACRP is moving the people and practice of clinical research forward™.
Check here for details on ACRP’s annual conference, May 3-6, 2024.
Become a Member
Connect with the resources and people you need for career success.
Get Certified
Apply now to take your exam from home, on-demand, 24/7.
Get Started

Simulated Informed Consent Training Can Lead to Real-World Improvements
Blog April 4, 2024

Global Clinical Scholars Research Training
Blog April 2, 2024

A Success Story of a Site-Centric Approach to Hybrid DCTs
Blog March 28, 2024
West Virginia Chapter: Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Applications in Healthcare
April 12 @ 12:00 pm
Join the West Virginia Chapter for a virtual presentation exploring how machine learning and Artificial Intelligence are impacting lives and individuals across diverse sectors.
Spring 2024 Certification Maintenance Regular Registration
Maintain your ACRP Certification by registering during the Spring 2024 registration window, April 16 – May 31, 2024. ACRP members save on recertification!
Upper Midwest Chapter: Collaborating for Success: Sites, CROs & Sponsors
April 19 @ 11:30 am
Join the Upper Midwest Chapter for an in-person event exploring how sites, sponsors, and CROs can collaborate to address common challenges encountered during feasibility, implementing sponsor-delivered technologies, and negotiating budgets.
View All Events
Clinical conferences for physicians: Who sets the agenda?
- PMID: 26639730
- DOI: 10.3233/JRS-150703
Background: Clinical conferences are generally defined as scheduled events at which practicing physicians themselves present to their colleagues interesting clinical cases, share their new experiences and learn about the latest achievements of medical science and practice. The value of a clinical conference is thought to be in direct communication between physicians, in analysis of topical issues in a given specialty with the aim to improve the quality of care. Speakers based on their own observations and studies reveal the most urgent problems, analyze results and offer potential decisions to their colleagues interested in the same questions. The event format may be different: workshops, highly specialized sections, round tables and seminars with participation of the leading specialists in a given field. These conferences are generally organised by the Ministries and Departments of Health, by leading research and/or educational institutions in the field, by recognised medical centres and other institutions. Recently pharmaceutical companies got actively involved in medical events, acting as sponsors of various scientific conferences and congresses, however threatening the mission of these events [1]. This brings up some uneasy questions: who are the medical conferences for? Who is in charge of setting the conference agenda? Do they contribute to evidence-based medicine; do they contribute to better health? Unfortunately, there is a trend to duplication or multiplication of conferences: various agencies and departments deliver the same conferences, presentations at which are often pre-arranged by pharmaceutical companies and do not have clear scientific novelty, while the conferences themselves have largely transformed into advertising of new pharmaceuticals or new technologies [2]. Pharmaceutical corporations sponsor invited speakers paying for their trips and paying honoraria, organising cocktail parties as part of medical activities. With the help of leading experts with impressive titles serving as speakers at the conferences, pharmaceutical companies are trying to be as close as possible to routine practice of prescribing of certain drugs, manipulating evidence, controlling scientific societies as well as the process of clinical guideline development and publication of research results [3]. The degree of expert involvement depends on their level of influence [4].
Objective: We aimed to study how often regular medical practitioners attend these conferences; to analyse who were keynote speakers and where they were coming from; to identify which organizations were responsible for organisation of these conferences and for sending out invitations to these conferences and for disseminating information about them.
Methods: We summarized all the invitations (printed on paper) received by one regular medical practitioner employed with the outpatient clinical of the city of Kazan for the period of two years (2012-2013).
Results: During the study period (2012-2013), a regular medical practitioner received 47 printed paper invitations to scientific conferences: 22 in 2012 and 25 in 2013. The conferences were not distributed evenly over the months of the years. November appeared to be the month with the highest density/number of medical conferences: 7 conferences in 2012 and 10 in 2013. If the distribution was even, then we could calculate the number per month dividing the number per year by 9 active months (excluding July, August and September). This resulted in 2.4 and 2.8 conferences per month. Among these studied conferences 4 were organized by public health agencies: invitation tickets were accompanied by the corresponding official order to organise a conference, issued by the Health Department. Noteworthy, that 2 of these conferences were held in conference rooms of the largest hotels of the city. Forty-one out of 47 medical conferences were sponsored by big pharma: either jointly with the major medical higher educational institutions of the city or plainly by pharmaceutical companies. Seventeen conferences were held during official working hours, in the first half of the day. Not only the logo of the pharmaceutical companies was printed on invitation tickets, but there was also an advert of the promoted pharmaceutical brand.Nine conference invitations contained invitation to dinner. In one of the invitations to a conference on neuroscience it was written: "dinner under the unforgettable music". Two conference invitations contained invitation to a lunch. Programs of 20 conferences (which were included) listed guest lecturers, coming from the leading medical universities in Moscow and St. Petersburg. Opinion leaders' involvement: some of the leading experts acted as speakers from 4 to 7 conferences a month in this sample conference invitations package of a regular polyclinic physician.
Conclusions: In 2012-2013 health practitioners were invited to attend medical conferences regularly, at least 2 times a month, with November being the busiest month. The keynote speakers were the opinion leaders from the local medical educational institutions and visitors from Moscow and St. Petersburg; their involvement with the conferences was repetitive. Governmental institutions jointly with big pharma were responsible for organisation of these conferences and attracting audience.Limitations of these observations:Unfortunately, the information on printed-paper conference invitations was not complete because not all tickets have survived. From the interview with the physician we know that in addition to these printed on paper invitations there were many invitations and alerts sent out by e-mail, SMS messages and personal phone calls, making the regularity of these conferences much higher. The physician, who kindly provided this information to us, asked not to be named or thanked in any public presentation of the results of these analyses.
Keywords: Conferences; health practitioners; opinion leaders; pharmaceutical companies; physicians.
Novotech Publishes Research Report on Acute Myeloid Leukaemia Clinical Trial Landscape for Clinical Stage Biotechs
BOSTON, April 10, 2024 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Novotech, the global full-service clinical Contract Research Organization (CRO) that partners with biotech companies to accelerate the development of advanced and novel therapeutics at every phase, has released an expert report, Acute Myeloid Leukaemia - Global Clinical Trial Landscape , offering critical data-backed analysis of the latest developments in Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) research.
The report presents a comprehensive look at the AML funding landscape, trial density, patient recruitment data across geographies, standard of care, emerging therapies, recent USFDA approvals, and regulatory trends. Importantly it also includes an in-depth SWOT analysis to guide strategic decision-making, prioritize research areas, and identify challenges for clinical stage biotechs.
AML is a malignant condition affecting blood-forming stem cells, marked by disrupted differentiation and uncontrolled growth of myeloid lineages, and is the second most prevalent leukemia in both adults and children.
The Acute Myeloid Leukaemia (AML) - Global Clinical Trial Landscape report notes that since 2019, the global biotech and biopharmaceutical industry initiated over 1,000 clinical trials for AML.
The clinical trial data shows:
- North America leads at 40%
- Asia-Pacific is second at 33%
- Europe stands third at 22%
- ROW contributes a moderate share of 5%.
“In North America, the United States holds a majority trial share at 86%, while in Europe, Spain, France, Germany, and Italy lead AML trials, showing the region's contribution to advancing research. Within the Asia-Pacific region, China and Australia collectively represent the highest trial share (around 65%). Among the ROW countries, Israel takes the lead with 55% of AML trials,” the report found.
The report includes an examination of the various AML risk factors, including age, gender, chemical exposure, smoking, previous cancer treatments, and genetic predisposition.
It also highlights that chemotherapy is typically used in conjunction with targeted drug therapy to treat AML, however it finds that the treatment paradigm is shifting “to personalized approaches guided by molecular and genetic profiles and incorporating targeted therapies. The goal is to advance precision medicine for AML by understanding its evolving molecular complexities.”
The report states, “Clinical trial initiatives in precision oncology for AML are revolutionizing treatment approaches, driving transformative advancements, and enhancing patient outcomes.”
The incidence data shows key disparities across regions, with Asia claiming almost half of worldwide diagnoses at 46.6% (Europe 22.1%, North America 14.7% and ROW 16.6%). As such, measures have been taken amongst medical professionals in Asia to aid in early detection and support the increasing burden in the region.
- Asia reported over 68,000 AML cases, with Mainland China, India, and Japan contributing approximately 30% to the global incidence in the Asia-Pacific region.
- Mainland China alone accounted for over 35% of the reported AML cases in Asia.
- Europe documented over 32,000 AML cases, constituting over 20% of the global incidence.
- North American countries specifically the United States and Canada, together accounted for around 15% of the global incidence, with over 21,000 AML cases.
Additional key data covered in the report includes:
- The United States leads with venture capital funding ($1786.7m), followed by China ($1218.5m), with a large gap between countries following this.
- Among the leading companies that received funding for AML were Opna Bio SA, Shorla Oncology, CytosinLab Therapeutics Co. Ltd., and OncoVerity Inc.
- The emergence of molecular studies has revolutionized the diagnostic and therapeutic landscape of AML.
- FDA-approved molecular targeted drugs, including FLT3, IDH1, and IDH2 inhibitors, alongside mutation-independent agents like venetoclax and gemtuzumab ozogamicin, highlight the precision focus in AML management.
- AML drug development data shows 105 drugs in preclinical stages, 113 in Phase I, 104 in Phase II, and 22 in Phase III.
- Marketed drugs for AML display a diverse array of molecule types. Small molecules constitute the majority (>65%) of these drugs, while Proteins and Antibody-Drug Conjugates make up the remaining portion.
- Ongoing research focuses on developing new agents and immunotherapies with improved efficacy and reduced toxicity profiles.
- Identifying reliable biomarkers can further personalise treatment strategies and predict response to specific agents.
- Research on early detection methods could improve prognosis and treatment outcomes.
FDA drug approvals received for AML over the last two years include ivosidenib particularly for its use in combination with azacitidine to treat newly diagnosed AML with a susceptible IDH1 mutation. Olutasidenib capsules received approval specifically for relapsed or refractory AML cases with a susceptible IDH1 mutation. Approval for quizartinib was received for the treatment of newly diagnosed FLT3 ITD-positive AML in adults. Additionally, the LeukoStrat CDx FLT3 Mutation Assay also gained approval as a companion diagnostic for quizartinib.
The Novotech research analyst team provides these expert reports on a monthly basis, completely free of charge. These reports offer current insights into global clinical trial activity, revealing which regions experience the highest trial volumes and the unique factors behind these trends. They tackle the potential and real hurdles faced by biotech firms in specific therapeutic areas in the hopes to positively impact and inform clinical trial decision making, eventually improving rates of success with new treatments.
Download the report here
About Novotech Novotech-CRO.com
Founded in 1997, Novotech is a global full-service clinical Contract Research Organization (CRO) focused on partnering with biotech companies to accelerate the development of advanced and novel therapeutics at every phase.
Recognized for its industry-leading contributions, Novotech has received numerous prestigious awards, including the CRO Leadership Award 2023, the Asia Pacific Cell & Gene Therapy Clinical Trials Excellence 2023, the Asia-Pacific Contract Research Organization Company of the Year Award since 2006.
The Company offers a comprehensive suite of services including laboratories, Phase I facilities, drug development consulting, regulatory expertise, and has experience with over 5,000 clinical projects, including Phase I to Phase IV clinical trials and bioequivalence studies. With a presence in 34 office locations and a dedicated team of 3,000+ professionals worldwide, Novotech is a trusted end-to-end strategic partner of choice.
For more information or to speak to an expert team member visit www.Novotech-CRO.com
A photo accompanying this announcement is available at https://www.globenewswire.com/NewsRoom/AttachmentNg/7825e3f7-01ff-4fa8-93c6-3eb8a863e82e


OCHIN Epic network welcomes 9 new health care organizations in 2024, bolstering patient access to care
April 10, 2024
MEDIA ADVISORY Contact: Kelsey Butz Email: [email protected] Phone: (518) 256-7540

PORTLAND, ORE. (April 10, 2024) — Seven ambulatory community health care organizations and two rural hospitals went live in the first quarter of 2024 with OCHIN Epic, an electronic health record (EHR) platform offered by OCHIN to help care teams manage and connect patient care, streamline clinical workflows, and improve the health of rural and medically underserved communities nationwide.
This quarter, the OCHIN network expanded into Kansas for the first time with the addition of Citizens Medical Center in Colby.
“We had a great go-live … Our collaboration with OCHIN will help us continue to provide access to care in rural Kansas in a safe and quality manner,” said Jenny Niblock, MSN, MBA, chief clinical officer of Citizens Health, the parent organization of Citizens Medical Center.

OCHIN Epic Ambulatory go-lives last quarter:
- Family Health Center of Marshfield — Marshfield, WI
- People’s Community Clinic — Austin, TX
- Central City Concern — Portland, OR
- Indian Health Board of Minneapolis — Minneapolis, MN
- Sacramento County Public Health — Sacramento, CA
- Radiant Health Centers — Irvine, CA
- Wilmington Community Clinic — Wilmington, CA
OCHIN Epic Acute go-lives last quarter:
- Citizens Medical Center — Colby, KS
- Riverwood Healthcare Center — Aitkin, MN
OCHIN expanded into acute care in 2023 to address persistent gaps in rural health care access and delivery, welcoming its first member hospital last summer. The expansion leverages OCHIN’s distinct knowledge of rural health challenges and more than 20 years of experience enabling community care organizations to transform care delivery through tailored insights and expertise.
The new members join OCHIN’s rapidly growing national network, which now reaches more than 5.9 million patients through about 32,000 providers at over 2,000 health care delivery sites nationwide. These include rural hospitals, rural health clinics, community health centers, tribal health organizations, school-based clinics, correctional facilities, behavioral health providers, dental clinics, public health departments, and HIV/AIDS care organizations.
For more information on OCHIN Epic, which has received Epic Gold Stars Level 9 distinction for two consecutive years, visit ochin.org.
Related Posts

OCHIN-led ADVANCE Clinical Research Network expands during its 10th anniversary, now represents 11+ million patients
New funding from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) is supporting the expansion of the OCHIN-led ADVANCE Clinical Research Network.

OCHIN receives $2 million to bolster Oregon’s health IT workforce
OCHIN has received a $2 million congressional appropriation to help bolster the health care workforce across Oregon.

OCHIN researchers find network patients lost health care coverage as continuous Medicaid policy ended
New OCHIN-led research found that the conclusion of a temporary Medicaid continuous coverage policy impacted the health care coverage of adults receiving care in the OCHIN network.

Vital care for vibrant communities: OCHIN’s impact in 2023
OCHIN is pleased to release our impact report for 2023, highlighting the shared progress of our growing member network to foster healthy, vibrant, and resilient communities nationwide.

EASE Act expands specialty health care options for rural communities
OCHIN is proud to support the EASE Act, new congressional legislation designed to address persistent community health care gaps through the creation of a national, virtual specialty care network.
We can help!
Trending posts.

Providing knowledge solutions to drive health equity
OCHIN, Inc. PO Box 5426 Portland, OR 97228-5426 (503) 943-2500
Important links
- Career Opportunities
- Advocacy and Development
- OCHIN HCCN Consultancy
Let's stay connected
- I am Not a Robot
- Health IT Solutions
- Workforce Solutions
- Operational Solutions
- National Network
- Annual Reports
- Our Purpose
- Our Approach
- Media Center
OCHIN Connections is a monthly newsletter featuring the latest OCHIN news and perspectives supporting our mission to drive health equity.
No thanks, I’m not interested at the moment
Study record managers: refer to the Data Element Definitions if submitting registration or results information.
Search for terms

- Advanced Search
- See Studies by Topic
- See Studies on Map
- How to Search
- How to Use Search Results
- How to Find Results of Studies
- How to Read a Study Record

- Learn About Studies
- Other Sites About Studies
- Glossary of Common Site Terms

- Submit Studies to ClinicalTrials.gov PRS
- Why Should I Register and Submit Results?
- FDAAA 801 and the Final Rule
- How to Apply for a PRS Account
- How to Register Your Study
- How to Edit Your Study Record
- How to Submit Your Results
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Support Materials
- Training Materials

- Selected Publications
- Clinical Alerts and Advisories
- Trends, Charts, and Maps
- Downloading Content for Analysis

- ClinicalTrials.gov Background
- About the Results Database
- History, Policies, and Laws
- ClinicalTrials.gov Modernization
- Media/Press Resources
- Linking to This Site
- Terms and Conditions
- Search Results
- Study Record Detail

An Open Comparative Study of the Effectiveness and Incomparable Study of the Immunogenicity and Safety of the Vaccine (CoviVac) for Adults Aged 60 Years and Older
- Study Details
- Tabular View
- No Results Posted

Inclusion Criteria:
Volunteers must meet the following inclusion criteria:
Type of participants
• Healthy volunteers or volunteers with a history of stable diseases that do not meet any of the criteria for non-inclusion in the study.
Other inclusion criteria
- Written informed consent of volunteers to participate in a clinical trial
- Volunteers who are able to fulfill the Protocol requirements (i.e., fill out a self-observation Diary, come to control visits).
Exclusion Criteria:
SARS-CoV-2 infection • A case of established COVID-19 disease confirmed by PCR and/or ELISA in the last 6 months.
Diseases or medical conditions
- Serious post-vaccination reaction (temperature above 40 C, hyperemia or edema more than 8 cm in diameter) or complication (collapse or shock-like condition that developed within 48 hours after vaccination; convulsions, accompanied or not accompanied by a feverish state) to any previous vaccination.
- Burdened allergic history (anaphylactic shock, Quincke's edema, polymorphic exudative eczema, serum sickness in the anamnesis, hypersensitivity or allergic reactions to the introduction of any vaccines in the anamnesis, known allergic reactions to vaccine components, etc.).
- Guillain-Barre syndrome (acute polyradiculitis) in the anamnesis.
- The axillary temperature at the time of vaccination is more than 37.0 ° C.
- Acute infectious diseases (recovery earlier than 4 weeks before vaccination) according to anamnesis.
- Donation of blood or plasma (in the amount of 450 ml or more) less than 2 months before inclusion in the study.
- Severe and/or uncontrolled diseases of the cardiovascular, bronchopulmonary, neuroendocrine systems, gastrointestinal tract, liver, kidneys, hematopoietic, immune systems.
- Is registered at the dispensary for tuberculosis, leukemia, oncological diseases, autoimmune diseases.
- Any confirmed or suspected immunosuppressive or immunodeficiency condition in the anamnesis.
- Splenectomy in the anamnesis.
- Neutropenia (decrease in the absolute number of neutrophils less than 1000/mm3), agranulocytosis, significant blood loss, severe anemia (hemoglobin less than 80 g/l) according to anamnesis.
- Anorexia according to anamnesis.
Prior or concomitant therapy
- Vaccination with any vaccine carried out within 30 days before vaccination / the first dose of the studied vaccine or planned administration within 30 days after vaccination / the last dose of the studied vaccine.
- Prior vaccination with an experimental or registered vaccine that may affect the interpretation of the study data (any coronavirus or SARS vaccines).
- Long-term use (more than 14 days) of immunosuppressants or other immunomodulatory drugs (immunoregulatory peptides, cytokines, interferons, immune system effector proteins (immunoglobulins), interferon inducers (cycloferon) during the six months preceding the study, according to anamnesis.
- Treatment with systemic glucocorticosteroids (≥ 20 mg of prednisone, or an analog, for more than 15 days during the last month).
- Volunteers who received immunoglobulin preparations or blood transfusion during the last 3 months prior to the start of the study according to anamnesis.
Other non-inclusion criteria
• Participation in any other clinical trial within the last 3 months.
Exclusion criteria:
- Withdrawal of Informed consent by a volunteer;
- The volunteer was included in violation of the inclusion/non-inclusion criteria of the Protocol;
- Any condition of a volunteer that requires, in the reasoned opinion of a medical researcher, the withdrawal of a volunteer from the study;
- Taking unauthorized medications (see section 6.2);
- The volunteer refuses to cooperate or is undisciplined (for example, failure to attend a scheduled visit without warning the researcher and/or loss of communication with the volunteer), or dropped out of observation;
- For administrative reasons (termination of the study by the Sponsor or regulatory authorities), as well as in case of gross violations of the Protocol that may affect the results of the study.
- For Patients and Families
- For Researchers
- For Study Record Managers
- Customer Support
- Accessibility
- Viewers and Players
- Freedom of Information Act
- HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
- U.S. National Library of Medicine
- U.S. National Institutes of Health
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Clinical research organizations (CROs) are independent companies that assist sponsors such as pharmaceutical, biotechnology, medical device companies, as well as universities and research organizations by providing trial management services outsourced by the sponsor under a contractual agreement (Gad et al. 2020a, b; Masri et al. 2012).CROs may also be referred to as contract service ...
Cu-Tech, a full-service contract clinical research organization (CRO), is uniquely specialized in the development of products related to dermatologic disease, and skin care. ... Jeffrey Buell formed sequence Development in 2012 as a commercial real estate development firm pledging to take an atypical perspective to properties in the 21st ...
9. KCR. Established in 1997 under the name Kiecana Clinical Research, KCR is a full-service contract research organization that provides a variety of services for clinical monitoring, safety & pharmacovigilance, clinical project management, quality assurance and regulatory affairs.
The Essence of a CRO: Clinical Research Organizations, abbreviated as CROs, epitomize entities entrusted with the management of clinical trials on behalf of pharmaceutical and biotechnological giants. Their mandates encompass the selection of patients, procurement of informed consent, aggregation of data, and the persistent oversight of safety ...
The clinical study is conducted by a sponsor or a clinical research organization (CRO). A perfect protocol, time limits, and regulatory requirements assume significance while planning a clinical trial. What, when, how, and who are clearly planned before the initiation of a study trial. ... Can Med Educ J. 2012; 3:82-84. [PMC free article ...
The Institute of Medicine (IOM) reports To Err Is Human: Building a Safer Health System (IOM, 2000) and Crossing the Quality Chasm: A New Health System for the 21st Century (IOM, 2001a), focused the nation's attention on concerns about the quality of health care in the United States. Since those reports were published, efforts have accelerated to develop a health care system that ...
Who we are. Parexel is among the world's largest clinical research organizations (CROs), providing the full range of Phase I to IV clinical development services to help lifesaving treatments reach patients faster. Leveraging the breadth of our clinical, regulatory, and therapeutic expertise, our team of more than 21,000 global professionals ...
INTRODUCTION. Contract research organizations (CROs) are private corporations that perform a wide variety of clinical research-related duties and functions on behalf of biotechnology, pharmaceutical, and medical device companies sponsoring studies in human subjects. 1 Because of economic and regulatory factors, CROs are playing an increasingly visible role in clinical research and the ...
ACRP supports individuals and life science organizations globally by providing community, education, and credentialing programs. Founded in 1976, ACRP is a registered 501 (c) (3) charitable organization whose mission is to promote excellence in clinical research and whose vision is that clinical research is performed ethically, responsibly, and ...
Clinical research is the comprehensive study of the safety and effectiveness of the most promising advances in patient care. Clinical research is different than laboratory research. It involves people who volunteer to help us better understand medicine and health. Lab research generally does not involve people — although it helps us learn ...
The Center for Information and Study on Clinical Research Participation's (CISCRP) core mission is to provide accessible, relevant, useful, high quality educational resources, programs, and services that increase awareness and understanding of the clinical research process; recognize and appreciate the unprecedented gift of participation in clinical trials; enhance and enrich the ...
Good Clinical Research Practice (GCP) is a process that incorporates established ethical and scientifi c quality standards for the design, conduct, recording and reporting of clinical research involving the participation of human subjects. Compliance with GCP provides public assurance that the rights, safety, and well-being of research
Clinical Data Management (CDM) is a critical phase in clinical research, which leads to generation of high-quality, reliable, and statistically sound data from clinical trials. This helps to produce a drastic reduction in time from drug development to marketing. Team members of CDM are actively involved in all stages of clinical trial right ...
Clinical Research Organizations (CROs) play a crucial role in the pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device industries. They provide support to companies in the form of research services outsourced on a contract basis. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore what CROs are, who their clients are, the stages of the research process ...
With more than 35 years of experience, the PPD clinical research business of Thermo Fisher Scientific offers an established drug development platform, patient enrollment expertise and robust laboratory services.Our broad range of clinical development, analytical and patient and advisory services - including full service to functional service provider services, digital and decentralized ...
A distinct clinical research organization, Veristat stands alone in combining industry-leading expertise with unwavering commitment to scientific integrity. ... (NDA) is the culmination of years of hard work and dedication by the Veristat team. I have truly come to rely on the clinical and statistical expertise of Veristat over the past decade ...
In the life sciences, a contract research organization (CRO) is a company that provides support to the pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device industries in the form of research services outsourced on a contract basis. A CRO may provide such services as biopharmaceutical development, biological assay development, commercialization, clinical development, clinical trials management ...
April 16. Maintain your ACRP Certification by registering during the Spring 2024 registration window, April 16 - May 31, 2024. ACRP members save on recertification! With more than 14,000 members, the Association of Clinical Research Professionals (ACRP) is the only non-profit organization solely dedicated to representing, supporting, and ...
Organizational Chart which depicts NIAID's Division of Clinical Research (DCR)
These conferences are generally organised by the Ministries and Departments of Health, by leading research and/or educational institutions in the field, by recognised medical centres and other institutions. Recently pharmaceutical companies got actively involved in medical events, acting as sponsors of various scientific conferences and ...
BOSTON, April 10, 2024 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Novotech, the global full-service clinical Contract Research Organization (CRO) that partners with biotech companies to accelerate the development of ...
PORTLAND, ORE. (April 10, 2024) — Seven ambulatory community health care organizations and two rural hospitals went live in the first quarter of 2024 with OCHIN Epic, an electronic health record (EHR) platform offered by OCHIN to help care teams manage and connect patient care, streamline clinical workflows, and improve the health of rural and medically underserved communities nationwide.
E A Sabel'nikova's 29 research works with 49 citations and 644 reads, including: Celiac disease associated with ulcerative colitis
Orlando-based clinical trials facilities network Alcanza Clinical Research has purchased a Florida site of Innovation Medical Research Center, the company announced in an April 9 press release ...
Recruitment of volunteers will be competitive. A maximum of 450 children aged 12 to 17 years inclusive will be screened in the study, of which it is planned to include and randomize 300 children who meet the criteria for inclusion in the study and do not have non-inclusion criteria, data on which will be used for subsequent safety and immunogenicity analysis.
Choosing to participate in a study is an important personal decision. Talk with your doctor and family members or friends about deciding to join a study. To learn more about this study, you or your doctor may contact the study research staff using the contacts provided below. For general information, Learn About Clinical Studies.