
CREATE ACCOUNT LOG IN


Writing: Essay Questions and APA Style
Introduction, example of formatting, writing strategy, questions within questions.
- Writing Support Home This link opens in a new window
- APA Citation Home This link opens in a new window
- CORE Library Home This link opens in a new window
Some courses may require you to write application papers that respond to prompts, similar to a question and answer format. In these cases, use the following formatting rules unless otherwise specified by your instructor:
To format questions and answers in APA format:
- Begin the question on a new line and type number 1 followed by a period.
- Type the discussion question in an approved font and size. Use the correct punctuation at the end -- a question mark if the prompt is a question; a period if it is a statement.
- Use double spacing and one inch margins.
- Separate the answer from the question by beginning the answer on a new line.
- Always answer in complete sentences. If your answer is lengthy, it is okay to start a new paragraph.
- Incorporate in-text citations as needed, with a references page at the end.
- Continue to use the same format for fonts and spacing for the whole document.
- Continue the list of questions on a new line and align the number 2 under the 1.
If the Instructor has specific instructions about bold type, follow their preference, but APA does not require it.
Use an academic tone; avoid "I" statements such as "I think" or "I believe" or "My opinion is..."
These types of papers are typically not essays that require an introduction and conclusion. However, you will still need to retain the usual APA components: proper formatting, a title page, a references page, and in-text citations.
When in doubt, ask your instructor!
1. Discuss the approaches psychologists have taken to understand human perception.
Psychologists have taken three main approaches in their efforts to understand human perception. First, is the computational approach. These psychologists try to determine the computations that a machine would have to perform to solve perceptual problems in an effort to help explain how complex computations within the human nervous system might turn raw sensory stimulation into a representation of the world. The computational approach owes much to two earlier approaches .... (and so on and so forth).
Imagine that you've been asked to respond to the following question:
A solid writing strategy for responding to essay questions is the following:
Answer the Question + At Least One Reason + Closing Statement
Keep your responses focused, structured, and prove your points with evidence.
Here's how to do it.
1) Begin with a direct answer to the question. The easiest way to do this is to restate the question in a way that incorporates your answer. If you will give more than one reason or address more than one topic in your response, pre-outline the topics/reasons you will discuss in order.
2) Address your reason(s) in order.
A. Use transitions to move smoothly between reasons.
B. Incorporate examples to amplify your reasoning.
C. Use signal phrases and in-text citations to identify your sources.
3. End with a closing statement that wraps up your response and reminds the reader of your position on the question.
Thanks to Texas State University for the example here.
Sometimes an instructor will prepare a prompt that is more than one question, and may require a response that tackles more than one topic. Here's an example:
This is actually two related questions -- a main question and then a subset of that main question.
Adjust your strategy as follows:
1) Prepare a direct response that focuses on the general main topic or question.
2) Respond to each question in the prompt as a separate paragraph under the restatement of the question. Use a transitional sentence to move smoothly from the first paragraph of response to the second.
3) Wrap it up with a concluding sentence at the end of the final paragraph.
Note: Latin "Lorem ipsum" text is used in lieu of real responses, as you may encounter this question in one of your courses!
- Answering the Short Answer Essay Exam From the University of Arkansas. Printable document that contains tips for writing effective answers to essay questions.
- Next: Writing Support Home >>
- Last Updated: Dec 24, 2020 5:03 AM
- URL: https://azhin.org/cummings/apa_questions
© 2015 - 2024
- Research Guides
- Vanderbilt University Libraries
- Peabody Library
Peabody Library Research Channel
Questions on the format of an apa paper.
- New to Vanderbilt: Start Here!
- The Research Process
- Select a Topic
- Find Background Information
- Refine Research Question
- Create an Outline
- Locate & Retrieve Materials
- Read Articles
- Conduct a Literature Review This link opens in a new window
- Evaluate Information
- Write Paper
General Questions on APA Style
APA Style FAQs
Questions on Citing Sources
- Questions on the Format of References
- Citing Sources This link opens in a new window
- After Vanderbilt
- Need Research Help?
In the entries below, the relevant section of the APA publication manual is given in parentheses after each answer.
What are the main parts of an APA paper? There are four main parts of a standard APA paper: the title page, the abstract, the text of the paper, and the references. The title page is page 1, the abstract is page 2, and the text of the paper begins on page 3. The references begin on the first new page after the end of the body of the paper. Papers can also include tables and figures, which may be placed after the references or embedded in the text; and appendices, which are placed after the reference list. (Sections 2.1 and 2.2)
What goes on the title page? APA 7 gives examples of a title page for a professional paper (Figure 2.1) and a student paper (Figure 2.2). See examples here . A title page for a student paper will typically have, in this order, the title of your paper, your departmental affiliation (if any), your name, the course name, the instructor’s name, and the date—all on separate lines and centered on the page. (Section 2.3)
Does my paper really need an abstract? And what’s an abstract? An abstract is a brief (usually no more than 250-word) one-paragraph summary of your paper. A student paper does not always require an abstract (consult your instructor); a professional paper typically does. In APA style, the abstract is sole tenant of the second page of the paper. If you write an abstract, remember that it is not simply the introductory paragraph of your paper, but neither should it include information not to be found elsewhere in the paper. It is a summary of your paper’s content—its main purpose, methods, and conclusions. (See section 3.3 of the APA guide for detailed abstract-writing instructions for different types of papers). Many will write the abstract last, after the body of the paper is complete. (Sections 2.9 and 3.3)
Can I use headings to mark off sections of the body of my paper? Yes. APA style allows for many levels of headings. See a very helpful example paper . (Section 2.27)
Can I use footnotes in APA style? You can, if your instructor or the journal you are submitting to permits, but references and citations do not go in footnotes in an APA paper. APA is in this way distinct from MLA, Chicago, and many other styles. Citations go directly in the text. Footnotes are used only for supplementary information or asides. Most APA papers have no footnotes. (Section 2.13)
What font should I use? APA does not prescribe a font style or size, but recommends a font that is “accessible to all users.” Calibri 11-point or Times New Roman 12-point are examples of acceptable fonts. Zapf Dingbats is discouraged. A consistent font should be used throughout a paper. Your instructor may have more restrictive requirements. (Section 2.19)
What sized margins should I use? One-inch margins at top, bottom, left, and right. (Section 2.22)
Should my paper be double-spaced? Yes. Everything in an APA paper should be double-spaced, including block quotes, the abstract, and the reference list. Rare exceptions include text to accompany a figure (which may be single-spaced) and footnotes (also single-spaced). (Section 2.21)
When should I use block quotes? Block quotes, which are set off from the main text and indented half an inch, should be used for quotations longer than 40 words. Like all quotes, they should either be followed by a parenthetical citation (with a page number) or be introduced with a narrative citation and followed by a page number in parentheses. Do not put quotation marks around a block quote. Block quotes are double-spaced. See examples here . (Section 8.27)
Do I need to put a page number on every page of my paper? Yes. The page number, beginning with the title page as “1,” goes at the top right of each page. Use just the number; do not write the word “page.” Use your word processor to create a header that reproduces automatically on every page—don’t try to type in the page number on each page. (Section 2.18)
What’s a “running head”? Do I need one at the top of my paper? A running head is your paper title, or a shortened version of it, that traditionally goes at the top left of every page of your paper. APA no longer requires student papers (as opposed to professional papers) to have a running head, but its use is so longstanding that it may remain a de facto standard for some time. Consult your instructor.
If you use a running head, put it in ALL CAPS and ensure it is no longer than 50 characters long. It should be on the same line as your page number. You should create the running using the “header” function of your word processor so that it reproduces automatically on every page. (Section 2.8)
When do I need to put the words “Running head” at the top of my paper? Never—even if you are using a running head in your paper. This maddening rule, which bedeviled generations of students, has been done away with in APA 7.
Questions on APA Paper Format
Questions on APA Reference Format
- << Previous: General Questions on APA Style
- Next: Questions on Citing Sources >>
- Last Updated: May 3, 2024 2:04 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.library.vanderbilt.edu/peabodyresearch

APA Style 7th Edition: Citing Your Sources
Apa 7th edition, what is the purpose, quick links.
- In Text Quick View
- Block Quotes
- Books & eBooks
- Thesis/Dissertation
- Audiovisual
- Conference Presentations
- Social Media
- Legal References
- Reports and Gray Literature
- Academic Integrity and Plagiarism
- Additional Resources
- Reference Page
APA Publications in the Library
This guide pertains to the 7th edition of the APA Manual.
This guide is designed to support the citation and reference needs of USC students, staff, and faculty. The 7th edition of the manual does make distinctions between formatting certain components for academic use over publication. This guide will distinguish student/academic formatting where applicable.
This guide is designed as a "quick" reference to common APA citation, reference and formatting criteria. When in doubt, we encourage users to consult with the APA publication manual or APA website for further clarification as the authority on formatting.
Attribution for guide: Adapted from American Psychological Association. (2020). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed). https://doi.org/10.1037/0000165-000
What is the purpose of citations?
Citations help readers locate your sources. They help to continue the scholarly conversation. To learn more about how citations can help you avoid plagiarism, view this interactive tutorial:
USC Library Lessons: Avoiding Plagiarism through Citations
When considering citations and references for your papers, you can ask yourself, "could someone find this information in the future?"
A client's personal file would not need a citation because your reader cannot go find that information again. Census statistics would require a citation because your reader could go locate that information again.
APA requires FOUR ELEMENTS of every citation:
- Who- Author of content
- When- Date content was published
- What- Title of content
- Where- Publication information. This can be the website you got it from or the journal or book's publication information.
If any of the elements listed above are unavailable, check out "Missing Reference Information" from APA for more information.
- APA Style Website As part of our Style and Grammar Guidelines, we explain the basics of paper format, grammar, punctuation, in-text citations, references, bias-free language, and more. Much of what you used to find on the sixth edition blog, you can now find on the APA Style website.
- Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper by Robert V. Labaree Last Updated May 6, 2024 623241 views this year
- Owl Purdue 7th Edition Style Guide and Formatting Writing guide from Owl Purdue covering the 7th edition of the APA Manual
- Quick Reference Guide Quick guide on how to identify components to configure a reference for Journal article, book, and chapter from an edited book.
- Annotated Sample Student Paper Sample student paper with formatting annotations.
- Sample student paper
- Annotated Sample Professional Paper Sample professional paper with formatting annotations
- Sample professional paper
- USC Libraries APA Style Quick Guide
- Next: In Text Citations >>
- Last Updated: Apr 22, 2024 9:37 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/APA7th

How to Format Your Research Paper
Writing your paper: apa 7th edition, apa style papers 7th edition.
- MLA Paper Format
- Chicago Paper Format
- Hanging Indents
- Ask a Librarian
APA 7th Edition Resources
- APA Style Blog The style and grammar guidelines pages present information about APA Style as described in the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, Seventh Edition.
- Purdue OWL: APA Style Guide This Purdue OWL style guide will help you in citing your sources in the APA Style commonly used to cite sources within the area of social sciences.
Printable APA 7th Edition Guides
Creating citations using APA 7th Edition:
- APA 7th Edition Citations - PDF
- APA 7th Edition Citations - Word
Creating in-text citations using APA 7th Edition:
- APA 7th In-Text Citations - PDF
- APA 7th In-Text Citations - Word
Integrating sources into the text of your paper using signal phrases:
- Integrating Sources - PDF
- Integrating Sources - Word
Things to know before you begin:
- Sans serif fonts: Arial (11-point), Calibri (11-point), or Lucinda Sans Unicode (10-point)
- Serif fonts: Times New Roman (12-point), Georgia (11-point), or Computer Modern (10-point)
- Margins: 1 inch on all sides
- Paragraphs: All paragraphs (except in the Abstract) should be indented
- Spacing: All of the text in your paper should be double-spaced (title page included)
Typical APA style papers have four main sections:
See the tabs below for a breakdown of how each portion should be formatted.
- Paper Templates
- Sample Papers
- APA 7 Citations
Below you will find templates for APA Style papers. Click the link to make a copy of the file.
- Google Docs : To make a copy of these templates you must first sign in to your Google account. After you’re signed in, click "File" and then click “Make a Copy.”
- Microsoft Word : To make a copy of these templates download the file.
- APA Style Student Paper Template (7th Edition) - Word Download a copy of this Word Doc and change the pre-filled information to your own.
APA Style Report Templates: These templates include multiple heading levels and should be used for report style papers.
- APA Style Student Report Template (7th Edition) - Word Download a copy of this Word Doc and change the pre-filled information to your own.
Below you will find an example of an accurately formatted APA Style student paper.
- APA Style Student Paper Sample (7th Edition) - PDF Click here to see a sample of an accurately formatted APA style student paper.
- APA Style Student Paper Sample (7th Edition) - Word Click here to see a sample of an accurately formatted APA style student paper.

Place only page numbers in the header.
Your paper should have the full title in bold. Place an extra space beneath the title and before your name.
Your name, your affiliation, the course title, professor’s name, and due date should be double spaced beneath the title.
All of this should be in the center of the title page.

- Put the word “Abstract” on the top of the page. Be sure it is center-aligned and in bold.
- Do not indent any paragraphs on this page.
Indent all other paragraphs throughout the body of the paper.

- Place the entire title of your paper in Title Case on the top line of a new page.
- Be sure it is center-aligned and in bold.

- Center-align the word “References” on the first line of a new page, be sure that it is in bold.
- Your citations should be alphabetized.
- Entries are double-spaced with no extra lines between them.
- Be sure to use a hanging indent for any citations that require more than one line.
Need help formatting your APA style citations using the 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association ? Click the image or link below to go to the citation guide.

- APA 7th Edition Citations
Need help learning what hanging indents are and how to create them using Google Docs or Microsoft Word?

- Hanging Indents This page gives a brief description of what they are, where to find information on when and how to properly use them, and also video tutorials on how to create them.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: MLA Paper Format >>
- Last Updated: Mar 29, 2024 2:49 PM
- URL: https://necc.mass.libguides.com/formatting
To cite this LibGuide use the following templates:
APA : Northern Essex Community College Library. (Date updated). Title of page . Title of LibGuide. URL
MLA : Northern Essex Community College Library. "Title of Page." Title of LibGuide, Date updated, URL.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 11: Presenting Your Research
Writing a Research Report in American Psychological Association (APA) Style
Learning Objectives
- Identify the major sections of an APA-style research report and the basic contents of each section.
- Plan and write an effective APA-style research report.
In this section, we look at how to write an APA-style empirical research report , an article that presents the results of one or more new studies. Recall that the standard sections of an empirical research report provide a kind of outline. Here we consider each of these sections in detail, including what information it contains, how that information is formatted and organized, and tips for writing each section. At the end of this section is a sample APA-style research report that illustrates many of these principles.
Sections of a Research Report
Title page and abstract.
An APA-style research report begins with a title page . The title is centred in the upper half of the page, with each important word capitalized. The title should clearly and concisely (in about 12 words or fewer) communicate the primary variables and research questions. This sometimes requires a main title followed by a subtitle that elaborates on the main title, in which case the main title and subtitle are separated by a colon. Here are some titles from recent issues of professional journals published by the American Psychological Association.
- Sex Differences in Coping Styles and Implications for Depressed Mood
- Effects of Aging and Divided Attention on Memory for Items and Their Contexts
- Computer-Assisted Cognitive Behavioural Therapy for Child Anxiety: Results of a Randomized Clinical Trial
- Virtual Driving and Risk Taking: Do Racing Games Increase Risk-Taking Cognitions, Affect, and Behaviour?
Below the title are the authors’ names and, on the next line, their institutional affiliation—the university or other institution where the authors worked when they conducted the research. As we have already seen, the authors are listed in an order that reflects their contribution to the research. When multiple authors have made equal contributions to the research, they often list their names alphabetically or in a randomly determined order.
In some areas of psychology, the titles of many empirical research reports are informal in a way that is perhaps best described as “cute.” They usually take the form of a play on words or a well-known expression that relates to the topic under study. Here are some examples from recent issues of the Journal Psychological Science .
- “Smells Like Clean Spirit: Nonconscious Effects of Scent on Cognition and Behavior”
- “Time Crawls: The Temporal Resolution of Infants’ Visual Attention”
- “Scent of a Woman: Men’s Testosterone Responses to Olfactory Ovulation Cues”
- “Apocalypse Soon?: Dire Messages Reduce Belief in Global Warming by Contradicting Just-World Beliefs”
- “Serial vs. Parallel Processing: Sometimes They Look Like Tweedledum and Tweedledee but They Can (and Should) Be Distinguished”
- “How Do I Love Thee? Let Me Count the Words: The Social Effects of Expressive Writing”
Individual researchers differ quite a bit in their preference for such titles. Some use them regularly, while others never use them. What might be some of the pros and cons of using cute article titles?
For articles that are being submitted for publication, the title page also includes an author note that lists the authors’ full institutional affiliations, any acknowledgments the authors wish to make to agencies that funded the research or to colleagues who commented on it, and contact information for the authors. For student papers that are not being submitted for publication—including theses—author notes are generally not necessary.
The abstract is a summary of the study. It is the second page of the manuscript and is headed with the word Abstract . The first line is not indented. The abstract presents the research question, a summary of the method, the basic results, and the most important conclusions. Because the abstract is usually limited to about 200 words, it can be a challenge to write a good one.

Introduction
The introduction begins on the third page of the manuscript. The heading at the top of this page is the full title of the manuscript, with each important word capitalized as on the title page. The introduction includes three distinct subsections, although these are typically not identified by separate headings. The opening introduces the research question and explains why it is interesting, the literature review discusses relevant previous research, and the closing restates the research question and comments on the method used to answer it.
The Opening
The opening , which is usually a paragraph or two in length, introduces the research question and explains why it is interesting. To capture the reader’s attention, researcher Daryl Bem recommends starting with general observations about the topic under study, expressed in ordinary language (not technical jargon)—observations that are about people and their behaviour (not about researchers or their research; Bem, 2003 [1] ). Concrete examples are often very useful here. According to Bem, this would be a poor way to begin a research report:
Festinger’s theory of cognitive dissonance received a great deal of attention during the latter part of the 20th century (p. 191)
The following would be much better:
The individual who holds two beliefs that are inconsistent with one another may feel uncomfortable. For example, the person who knows that he or she enjoys smoking but believes it to be unhealthy may experience discomfort arising from the inconsistency or disharmony between these two thoughts or cognitions. This feeling of discomfort was called cognitive dissonance by social psychologist Leon Festinger (1957), who suggested that individuals will be motivated to remove this dissonance in whatever way they can (p. 191).
After capturing the reader’s attention, the opening should go on to introduce the research question and explain why it is interesting. Will the answer fill a gap in the literature? Will it provide a test of an important theory? Does it have practical implications? Giving readers a clear sense of what the research is about and why they should care about it will motivate them to continue reading the literature review—and will help them make sense of it.
Breaking the Rules
Researcher Larry Jacoby reported several studies showing that a word that people see or hear repeatedly can seem more familiar even when they do not recall the repetitions—and that this tendency is especially pronounced among older adults. He opened his article with the following humourous anecdote:
A friend whose mother is suffering symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) tells the story of taking her mother to visit a nursing home, preliminary to her mother’s moving there. During an orientation meeting at the nursing home, the rules and regulations were explained, one of which regarded the dining room. The dining room was described as similar to a fine restaurant except that tipping was not required. The absence of tipping was a central theme in the orientation lecture, mentioned frequently to emphasize the quality of care along with the advantages of having paid in advance. At the end of the meeting, the friend’s mother was asked whether she had any questions. She replied that she only had one question: “Should I tip?” (Jacoby, 1999, p. 3)
Although both humour and personal anecdotes are generally discouraged in APA-style writing, this example is a highly effective way to start because it both engages the reader and provides an excellent real-world example of the topic under study.
The Literature Review
Immediately after the opening comes the literature review , which describes relevant previous research on the topic and can be anywhere from several paragraphs to several pages in length. However, the literature review is not simply a list of past studies. Instead, it constitutes a kind of argument for why the research question is worth addressing. By the end of the literature review, readers should be convinced that the research question makes sense and that the present study is a logical next step in the ongoing research process.
Like any effective argument, the literature review must have some kind of structure. For example, it might begin by describing a phenomenon in a general way along with several studies that demonstrate it, then describing two or more competing theories of the phenomenon, and finally presenting a hypothesis to test one or more of the theories. Or it might describe one phenomenon, then describe another phenomenon that seems inconsistent with the first one, then propose a theory that resolves the inconsistency, and finally present a hypothesis to test that theory. In applied research, it might describe a phenomenon or theory, then describe how that phenomenon or theory applies to some important real-world situation, and finally suggest a way to test whether it does, in fact, apply to that situation.
Looking at the literature review in this way emphasizes a few things. First, it is extremely important to start with an outline of the main points that you want to make, organized in the order that you want to make them. The basic structure of your argument, then, should be apparent from the outline itself. Second, it is important to emphasize the structure of your argument in your writing. One way to do this is to begin the literature review by summarizing your argument even before you begin to make it. “In this article, I will describe two apparently contradictory phenomena, present a new theory that has the potential to resolve the apparent contradiction, and finally present a novel hypothesis to test the theory.” Another way is to open each paragraph with a sentence that summarizes the main point of the paragraph and links it to the preceding points. These opening sentences provide the “transitions” that many beginning researchers have difficulty with. Instead of beginning a paragraph by launching into a description of a previous study, such as “Williams (2004) found that…,” it is better to start by indicating something about why you are describing this particular study. Here are some simple examples:
Another example of this phenomenon comes from the work of Williams (2004).
Williams (2004) offers one explanation of this phenomenon.
An alternative perspective has been provided by Williams (2004).
We used a method based on the one used by Williams (2004).
Finally, remember that your goal is to construct an argument for why your research question is interesting and worth addressing—not necessarily why your favourite answer to it is correct. In other words, your literature review must be balanced. If you want to emphasize the generality of a phenomenon, then of course you should discuss various studies that have demonstrated it. However, if there are other studies that have failed to demonstrate it, you should discuss them too. Or if you are proposing a new theory, then of course you should discuss findings that are consistent with that theory. However, if there are other findings that are inconsistent with it, again, you should discuss them too. It is acceptable to argue that the balance of the research supports the existence of a phenomenon or is consistent with a theory (and that is usually the best that researchers in psychology can hope for), but it is not acceptable to ignore contradictory evidence. Besides, a large part of what makes a research question interesting is uncertainty about its answer.
The Closing
The closing of the introduction—typically the final paragraph or two—usually includes two important elements. The first is a clear statement of the main research question or hypothesis. This statement tends to be more formal and precise than in the opening and is often expressed in terms of operational definitions of the key variables. The second is a brief overview of the method and some comment on its appropriateness. Here, for example, is how Darley and Latané (1968) [2] concluded the introduction to their classic article on the bystander effect:
These considerations lead to the hypothesis that the more bystanders to an emergency, the less likely, or the more slowly, any one bystander will intervene to provide aid. To test this proposition it would be necessary to create a situation in which a realistic “emergency” could plausibly occur. Each subject should also be blocked from communicating with others to prevent his getting information about their behaviour during the emergency. Finally, the experimental situation should allow for the assessment of the speed and frequency of the subjects’ reaction to the emergency. The experiment reported below attempted to fulfill these conditions. (p. 378)
Thus the introduction leads smoothly into the next major section of the article—the method section.
The method section is where you describe how you conducted your study. An important principle for writing a method section is that it should be clear and detailed enough that other researchers could replicate the study by following your “recipe.” This means that it must describe all the important elements of the study—basic demographic characteristics of the participants, how they were recruited, whether they were randomly assigned, how the variables were manipulated or measured, how counterbalancing was accomplished, and so on. At the same time, it should avoid irrelevant details such as the fact that the study was conducted in Classroom 37B of the Industrial Technology Building or that the questionnaire was double-sided and completed using pencils.
The method section begins immediately after the introduction ends with the heading “Method” (not “Methods”) centred on the page. Immediately after this is the subheading “Participants,” left justified and in italics. The participants subsection indicates how many participants there were, the number of women and men, some indication of their age, other demographics that may be relevant to the study, and how they were recruited, including any incentives given for participation.
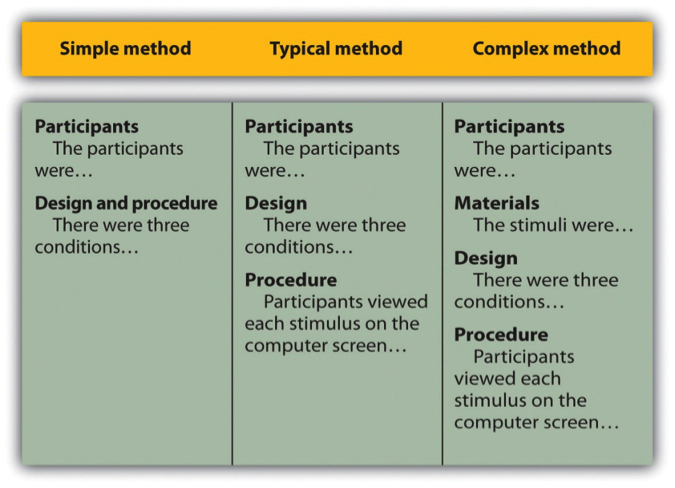
After the participants section, the structure can vary a bit. Figure 11.1 shows three common approaches. In the first, the participants section is followed by a design and procedure subsection, which describes the rest of the method. This works well for methods that are relatively simple and can be described adequately in a few paragraphs. In the second approach, the participants section is followed by separate design and procedure subsections. This works well when both the design and the procedure are relatively complicated and each requires multiple paragraphs.
What is the difference between design and procedure? The design of a study is its overall structure. What were the independent and dependent variables? Was the independent variable manipulated, and if so, was it manipulated between or within subjects? How were the variables operationally defined? The procedure is how the study was carried out. It often works well to describe the procedure in terms of what the participants did rather than what the researchers did. For example, the participants gave their informed consent, read a set of instructions, completed a block of four practice trials, completed a block of 20 test trials, completed two questionnaires, and were debriefed and excused.
In the third basic way to organize a method section, the participants subsection is followed by a materials subsection before the design and procedure subsections. This works well when there are complicated materials to describe. This might mean multiple questionnaires, written vignettes that participants read and respond to, perceptual stimuli, and so on. The heading of this subsection can be modified to reflect its content. Instead of “Materials,” it can be “Questionnaires,” “Stimuli,” and so on.
The results section is where you present the main results of the study, including the results of the statistical analyses. Although it does not include the raw data—individual participants’ responses or scores—researchers should save their raw data and make them available to other researchers who request them. Several journals now encourage the open sharing of raw data online.
Although there are no standard subsections, it is still important for the results section to be logically organized. Typically it begins with certain preliminary issues. One is whether any participants or responses were excluded from the analyses and why. The rationale for excluding data should be described clearly so that other researchers can decide whether it is appropriate. A second preliminary issue is how multiple responses were combined to produce the primary variables in the analyses. For example, if participants rated the attractiveness of 20 stimulus people, you might have to explain that you began by computing the mean attractiveness rating for each participant. Or if they recalled as many items as they could from study list of 20 words, did you count the number correctly recalled, compute the percentage correctly recalled, or perhaps compute the number correct minus the number incorrect? A third preliminary issue is the reliability of the measures. This is where you would present test-retest correlations, Cronbach’s α, or other statistics to show that the measures are consistent across time and across items. A final preliminary issue is whether the manipulation was successful. This is where you would report the results of any manipulation checks.
The results section should then tackle the primary research questions, one at a time. Again, there should be a clear organization. One approach would be to answer the most general questions and then proceed to answer more specific ones. Another would be to answer the main question first and then to answer secondary ones. Regardless, Bem (2003) [3] suggests the following basic structure for discussing each new result:
- Remind the reader of the research question.
- Give the answer to the research question in words.
- Present the relevant statistics.
- Qualify the answer if necessary.
- Summarize the result.
Notice that only Step 3 necessarily involves numbers. The rest of the steps involve presenting the research question and the answer to it in words. In fact, the basic results should be clear even to a reader who skips over the numbers.
The discussion is the last major section of the research report. Discussions usually consist of some combination of the following elements:
- Summary of the research
- Theoretical implications
- Practical implications
- Limitations
- Suggestions for future research
The discussion typically begins with a summary of the study that provides a clear answer to the research question. In a short report with a single study, this might require no more than a sentence. In a longer report with multiple studies, it might require a paragraph or even two. The summary is often followed by a discussion of the theoretical implications of the research. Do the results provide support for any existing theories? If not, how can they be explained? Although you do not have to provide a definitive explanation or detailed theory for your results, you at least need to outline one or more possible explanations. In applied research—and often in basic research—there is also some discussion of the practical implications of the research. How can the results be used, and by whom, to accomplish some real-world goal?
The theoretical and practical implications are often followed by a discussion of the study’s limitations. Perhaps there are problems with its internal or external validity. Perhaps the manipulation was not very effective or the measures not very reliable. Perhaps there is some evidence that participants did not fully understand their task or that they were suspicious of the intent of the researchers. Now is the time to discuss these issues and how they might have affected the results. But do not overdo it. All studies have limitations, and most readers will understand that a different sample or different measures might have produced different results. Unless there is good reason to think they would have, however, there is no reason to mention these routine issues. Instead, pick two or three limitations that seem like they could have influenced the results, explain how they could have influenced the results, and suggest ways to deal with them.
Most discussions end with some suggestions for future research. If the study did not satisfactorily answer the original research question, what will it take to do so? What new research questions has the study raised? This part of the discussion, however, is not just a list of new questions. It is a discussion of two or three of the most important unresolved issues. This means identifying and clarifying each question, suggesting some alternative answers, and even suggesting ways they could be studied.
Finally, some researchers are quite good at ending their articles with a sweeping or thought-provoking conclusion. Darley and Latané (1968) [4] , for example, ended their article on the bystander effect by discussing the idea that whether people help others may depend more on the situation than on their personalities. Their final sentence is, “If people understand the situational forces that can make them hesitate to intervene, they may better overcome them” (p. 383). However, this kind of ending can be difficult to pull off. It can sound overreaching or just banal and end up detracting from the overall impact of the article. It is often better simply to end when you have made your final point (although you should avoid ending on a limitation).
The references section begins on a new page with the heading “References” centred at the top of the page. All references cited in the text are then listed in the format presented earlier. They are listed alphabetically by the last name of the first author. If two sources have the same first author, they are listed alphabetically by the last name of the second author. If all the authors are the same, then they are listed chronologically by the year of publication. Everything in the reference list is double-spaced both within and between references.
Appendices, Tables, and Figures
Appendices, tables, and figures come after the references. An appendix is appropriate for supplemental material that would interrupt the flow of the research report if it were presented within any of the major sections. An appendix could be used to present lists of stimulus words, questionnaire items, detailed descriptions of special equipment or unusual statistical analyses, or references to the studies that are included in a meta-analysis. Each appendix begins on a new page. If there is only one, the heading is “Appendix,” centred at the top of the page. If there is more than one, the headings are “Appendix A,” “Appendix B,” and so on, and they appear in the order they were first mentioned in the text of the report.
After any appendices come tables and then figures. Tables and figures are both used to present results. Figures can also be used to illustrate theories (e.g., in the form of a flowchart), display stimuli, outline procedures, and present many other kinds of information. Each table and figure appears on its own page. Tables are numbered in the order that they are first mentioned in the text (“Table 1,” “Table 2,” and so on). Figures are numbered the same way (“Figure 1,” “Figure 2,” and so on). A brief explanatory title, with the important words capitalized, appears above each table. Each figure is given a brief explanatory caption, where (aside from proper nouns or names) only the first word of each sentence is capitalized. More details on preparing APA-style tables and figures are presented later in the book.
Sample APA-Style Research Report
Figures 11.2, 11.3, 11.4, and 11.5 show some sample pages from an APA-style empirical research report originally written by undergraduate student Tomoe Suyama at California State University, Fresno. The main purpose of these figures is to illustrate the basic organization and formatting of an APA-style empirical research report, although many high-level and low-level style conventions can be seen here too.

Key Takeaways
- An APA-style empirical research report consists of several standard sections. The main ones are the abstract, introduction, method, results, discussion, and references.
- The introduction consists of an opening that presents the research question, a literature review that describes previous research on the topic, and a closing that restates the research question and comments on the method. The literature review constitutes an argument for why the current study is worth doing.
- The method section describes the method in enough detail that another researcher could replicate the study. At a minimum, it consists of a participants subsection and a design and procedure subsection.
- The results section describes the results in an organized fashion. Each primary result is presented in terms of statistical results but also explained in words.
- The discussion typically summarizes the study, discusses theoretical and practical implications and limitations of the study, and offers suggestions for further research.
- Practice: Look through an issue of a general interest professional journal (e.g., Psychological Science ). Read the opening of the first five articles and rate the effectiveness of each one from 1 ( very ineffective ) to 5 ( very effective ). Write a sentence or two explaining each rating.
- Practice: Find a recent article in a professional journal and identify where the opening, literature review, and closing of the introduction begin and end.
- Practice: Find a recent article in a professional journal and highlight in a different colour each of the following elements in the discussion: summary, theoretical implications, practical implications, limitations, and suggestions for future research.
Long Descriptions
Figure 11.1 long description: Table showing three ways of organizing an APA-style method section.
In the simple method, there are two subheadings: “Participants” (which might begin “The participants were…”) and “Design and procedure” (which might begin “There were three conditions…”).
In the typical method, there are three subheadings: “Participants” (“The participants were…”), “Design” (“There were three conditions…”), and “Procedure” (“Participants viewed each stimulus on the computer screen…”).
In the complex method, there are four subheadings: “Participants” (“The participants were…”), “Materials” (“The stimuli were…”), “Design” (“There were three conditions…”), and “Procedure” (“Participants viewed each stimulus on the computer screen…”). [Return to Figure 11.1]
- Bem, D. J. (2003). Writing the empirical journal article. In J. M. Darley, M. P. Zanna, & H. R. Roediger III (Eds.), The compleat academic: A practical guide for the beginning social scientist (2nd ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association. ↵
- Darley, J. M., & Latané, B. (1968). Bystander intervention in emergencies: Diffusion of responsibility. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 4 , 377–383. ↵
A type of research article which describes one or more new empirical studies conducted by the authors.
The page at the beginning of an APA-style research report containing the title of the article, the authors’ names, and their institutional affiliation.
A summary of a research study.
The third page of a manuscript containing the research question, the literature review, and comments about how to answer the research question.
An introduction to the research question and explanation for why this question is interesting.
A description of relevant previous research on the topic being discusses and an argument for why the research is worth addressing.
The end of the introduction, where the research question is reiterated and the method is commented upon.
The section of a research report where the method used to conduct the study is described.
The main results of the study, including the results from statistical analyses, are presented in a research article.
Section of a research report that summarizes the study's results and interprets them by referring back to the study's theoretical background.
Part of a research report which contains supplemental material.
Research Methods in Psychology - 2nd Canadian Edition Copyright © 2015 by Paul C. Price, Rajiv Jhangiani, & I-Chant A. Chiang is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
What is the proper formatting for research questions (e.g. RQ1) and hypotheses (e.g. H1) in APA?
In APA style, research questions and hypotheses should be formatted in a clear and concise manner. Here are the guidelines for formatting research questions and hypotheses in APA:
Research Questions:
- Begin with the phrase "Research Question" or "RQ" followed by the corresponding number. For example, "Research Question 1" or "RQ1."
- State the research question in a clear and specific manner, using interrogative sentence format.
- Use proper punctuation, capitalization, and grammar.
Example: Research Question 1: What is the relationship between marital conflict and behavior problems in school-aged children? [2]
Hypotheses:
- Begin with the phrase "Hypothesis" or "H" followed by the corresponding number. For example, "Hypothesis 1" or "H1."
- State the hypothesis in a clear and concise manner, using declarative sentence format.
- If you have multiple hypotheses, number them accordingly.
Example: Hypothesis 1: Marital conflict predicts behavior problems in school-aged children. [2]
Learn more:
- APA Stylistics: Basics - Purdue OWL® - Purdue University
- Writing Resources - How to Write an APA Research Paper - Hamilton College
- Writing a Research Report in American Psychological Association (APA) Style - Research Methods in Psychology - 2nd Canadian Edition
Continue the conversation
Explore more.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn how to format your research paper in seventh edition APA Style with these sample papers. Download Word templates and PDF annotations for different paper types and purposes.
Media Files: APA Sample Student Paper , APA Sample Professional Paper This resource is enhanced by Acrobat PDF files. Download the free Acrobat Reader. Note: The APA Publication Manual, 7 th Edition specifies different formatting conventions for student and professional papers (i.e., papers written for credit in a course and papers intended for scholarly publication).
To format questions and answers in APA format: Begin the question on a new line and type number 1 followed by a period. Type the discussion question in an approved font and size. Use the correct punctuation at the end -- a question mark if the prompt is a question; a period if it is a statement. Use double spacing and one inch margins.
Connect everything back to your research questions, purpose statement, and hypotheses. • Use any theoretical framework/s to interpret the data collected. • Discuss the potential biases or limitations that may have impacted the results of your research or your conclusions. • Talk about the implications for future research.
Learn how to format your paper according to APA 7th edition guidelines. Find out how to set up page margins, headings, title page, abstract, reference page, and more.
Basic guidelines for formatting the reference list at the end of a standard APA research paper Author/Authors Rules for handling works by a single author or multiple authors that apply to all APA-style references in your reference list, regardless of the type of work (book, article, electronic resource, etc.)
Indent the first line of every paragraph of text 0.5 in. using the tab key or the paragraph-formatting function of your word-processing program. Page numbers: Put a page number in the top right corner of every page, including the title page or cover page, which is page 1. Student papers do not require a running head on any page.
This article walks through the formatting steps needed to create an APA Style student paper, starting with a basic setup that applies to the entire paper (margins, font, line spacing, paragraph alignment and indentation, and page headers). It then covers formatting for the major sections of a student paper: the title page, the text, tables and ...
Use one-inch margins on all sides of the paper. 3. The text should be left-justified (a straight line), and the right side should be "ragged" (do not justify on both sides) 4. Paragraphs should be indented at the beginning (please use paragraphs!) 5.
Documenting Sources in APA Format Research is both the activity of gathering the information needed to answer a research question and the work of building the answer to the question from the information you gathered. Therefore, a research paper has three goals: 1) to state the one-sentence answer to the question,
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
There are four main parts of a standard APA paper: the title page, the abstract, the text of the paper, and the references. The title page is page 1, the abstract is page 2, and the text of the paper begins on page 3. The references begin on the first new page after the end of the body of the paper. Papers can also include tables and figures ...
The 7th edition of the manual does make distinctions between formatting certain components for academic use over publication. This guide will distinguish student/academic formatting where applicable. This guide is designed as a "quick" reference to common APA citation, reference and formatting criteria.
papers (a change from APA 6). Page numbers begin on the first page and follow on every subsequent page without interruption. No other information (e.g., authors' last names) is required. Note: your instructor may ask for a running head or your last name before the page number. You can look at the APA professional sample paper for guidelines on ...
Get help formatting your research papers. Things to know before you begin: Font & Font Size: Be sure to use the same font throughout your entire paper.APA 7th Edition allows for the use of the fonts listed below.
Sample Student Paper (continued) 66 • PAPER ELEMENTS AND FORMAT journal article reference, 10.1 YouTube video reference, 10.12 short URL, 9.36 book reference, 10.2 report reference, 10.4 blog post reference, 10.1 conference presentation reference, 10.5 edited book chapter reference, 10.3 shortDOI, 9.36 ELEMENTS & FORMAT
The opening introduces the research question and explains why it is interesting, the literature review discusses relevant previous research, and the closing restates the research question and comments on the method used to answer it. ... Sample APA-Style Research Report. Figures 11.2, 11.3, 11.4, and 11.5 show some sample pages from an APA ...
The sections in APA-style paper are as follows: 1. Title Page. As per the APA research paper format, the title should be between 10-12 words and should reflect the essence of the paper. After writing the title, write your name followed by name of the college.
Research papers in the social and natural sciences often follow APA style. This article focuses on reporting quantitative research methods. In your APA methods section, you should report enough information to understand and replicate your study, including detailed information on the sample, measures, and procedures used.
Here are the guidelines for formatting research questions and hypotheses in APA: Research Questions: Begin with the phrase "Research Question" or "RQ" followed by the corresponding number. For example, "Research Question 1" or "RQ1." State the research question in a clear and specific manner, using interrogative sentence format.
Headings and subheadings provide structure to a document. They signal what each section. is about and allow for easy navigation of the document. APA headings have five possible levels. Each heading level is formatted differently. Note: Title case simply means that you should capitalize the first word, words with four or more letters, and all ...
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue.
Understanding how objective quantities are translated into subjective evaluations has long been of interest to social scientists, medical professionals, and policymakers with an interest in how people process and act on quantitative information. The theory of decision by sampling proposes a comparative procedure: Values seem larger or smaller based on how they rank in a comparison set, the ...
The following questions test your knowledge of seventh edition APA Style. The 45 questions assess APA Style paper format, in-text citations, references, numbers, lists, spelling, capitalization, and abbreviations. The numbers in parentheses after most questions indicate the sections where you can find more information about the topic in the ...
APA Style uses the author-date citation system, in which a brief in-text citation directs readers to a full reference list entry. The in-text citation appears within the body of the paper (or in a table, figure, footnote, or appendix) and briefly identifies the cited work by its author and date of publication.