Informative Essay — Purpose, Structure, and Examples


What is informative writing?
Informative writing educates the reader about a certain topic. An informative essay may explain new information, describe a process, or clarify a concept. The provided information is objective, meaning the writing focuses on presentation of fact and should not contain personal opinion or bias.
Informative writing includes description, process, cause and effect, comparison, and problems and possible solutions:
Describes a person, place, thing, or event using descriptive language that appeals to readers’ senses
Explains the process to do something or how something was created
Discusses the relationship between two things, determining how one ( cause ) leads to the other ( effect ); the effect needs to be based on fact and not an assumption
Identifies the similarities and differences between two things; does not indicate that one is better than the other
Details a problem and presents various possible solutions ; the writer does not suggest one solution is more effective than the others

Purpose of informative writing
The purpose of an informative essay depends upon the writer’s motivation, but may be to share new information, describe a process, clarify a concept, explain why or how, or detail a topic’s intricacies.
Informative essays may introduce readers to new information .
Summarizing a scientific/technological study
Outlining the various aspects of a religion
Providing information on a historical period
Describe a process or give step-by-step details of a procedure.
How to write an informational essay
How to construct an argument
How to apply for a job
Clarify a concept and offer details about complex ideas.

Explain why or how something works the way that it does.
Describe how the stock market impacts the economy
Illustrate why there are high and low tides
Detail how the heart functions
Offer information on the smaller aspects or intricacies of a larger topic.
Identify the importance of the individual bones in the body
Outlining the Dust Bowl in the context of the Great Depression
Explaining how bees impact the environment
How to write an informative essay
Regardless of the type of information, the informative essay structure typically consists of an introduction, body, and conclusion.
Introduction
Background information
Explanation of evidence
Restated thesis
Review of main ideas
Closing statement

Informative essay introduction
When composing the introductory paragraph(s) of an informative paper, include a hook, introduce the topic, provide background information, and develop a good thesis statement.
If the hook or introduction creates interest in the first paragraph, it will draw the readers’ attention and make them more receptive to the essay writer's ideas. Some of the most common techniques to accomplish this include the following:
Emphasize the topic’s importance by explaining the current interest in the topic or by indicating that the subject is influential.
Use pertinent statistics to give the paper an air of authority.
A surprising statement can be shocking; sometimes it is disgusting; sometimes it is joyful; sometimes it is surprising because of who said it.
An interesting incident or anecdote can act as a teaser to lure the reader into the remainder of the essay. Be sure that the device is appropriate for the informative essay topic and focus on what is to follow.

Directly introduce the topic of the essay.
Provide the reader with the background information necessary to understand the topic. Don’t repeat this information in the body of the essay; it should help the reader understand what follows.
Identify the overall purpose of the essay with the thesis (purpose statement). Writers can also include their support directly in the thesis, which outlines the structure of the essay for the reader.
Informative essay body paragraphs
Each body paragraph should contain a topic sentence, evidence, explanation of evidence, and a transition sentence.

A good topic sentence should identify what information the reader should expect in the paragraph and how it connects to the main purpose identified in the thesis.
Provide evidence that details the main point of the paragraph. This includes paraphrasing, summarizing, and directly quoting facts, statistics, and statements.
Explain how the evidence connects to the main purpose of the essay.
Place transitions at the end of each body paragraph, except the last. There is no need to transition from the last support to the conclusion. A transition should accomplish three goals:
Tell the reader where you were (current support)
Tell the reader where you are going (next support)
Relate the paper’s purpose
Informative essay conclusion
Incorporate a rephrased thesis, summary, and closing statement into the conclusion of an informative essay.
Rephrase the purpose of the essay. Do not just repeat the purpose statement from the thesis.
Summarize the main idea found in each body paragraph by rephrasing each topic sentence.
End with a clincher or closing statement that helps readers answer the question “so what?” What should the reader take away from the information provided in the essay? Why should they care about the topic?
Informative essay example
The following example illustrates a good informative essay format:


How to Write an Informative Essay: Everything You Need to Know

Did you know that informative essays aren't just for school? They're also used in jobs like journalism, marketing, and PR to explain complex ideas and promote things. This shows how useful they are outside of the classroom.
So, if you're planning to write one, that's a great choice! It's interesting but can be tough. To do it well, you need to plan, research, and organize carefully. Keep your tone balanced, give clear info, and add your own thoughts to stand out.
In this guide, our essay writer will give you tips on starting and organizing your essay effectively. At the end, you'll also find interesting essay samples. So, let's jump right into it.
What is an Informative Essay
To give a good informative essay definition, imagine them as windows to new knowledge. Their main job is to teach others about a particular topic. Whether it's for a school project or something you stumble upon online, these essays are packed with interesting facts and insights.
Here's a simple breakdown from our admission essay writing service of what makes an informative essay tick:

- Keeping It Real: These essays are all about the facts. No opinions allowed. We want to keep things fair and honest.
- Topics Galore: You can write about anything you find interesting, from science and history to things about different cultures.
- Where You Find Them: Informative essays can pop up anywhere, from your classroom assignments to the pages of magazines or even online articles.
- Research: Like a good detective, informative essays rely on solid evidence. That means digging into trustworthy sources to gather reliable information.
- Stay Neutral: To keep things fair, informative essays don't take sides. They present the facts and let readers draw their own conclusions.
- Structure: These essays have a clear roadmap. They start with an introduction to set the stage, then present the main points with evidence, and wrap up with a summary to tie it all together.
- Write for Your Audience: Keep your writing simple and easy to understand. Think about who will be reading it.
- Give Just Enough Detail: Don't overload people with info. Find the right balance so it's interesting but not overwhelming.
Ready to Ignite Minds with Your Informative Essay?
Our qualified writers are here to craft a masterpiece tailored to your needs worthy of an A+
Reasons to Write an Informative Essay
Writing informative essays, whether following the IEEE format or another style, is a great way to teach and share ideas with others. Here's why it's worth giving it a try:
.webp)
- Make Complex Ideas Easy : Informative essays simplify complicated topics so everyone can understand them. They break down big ideas into simple parts, helping more people learn and share knowledge.
- Encourage Thinking : When you read these essays, you're encouraged to think for yourself. They give you facts and evidence so you can form your own opinions about different topics. This helps you become better at understanding the world around you.
- Inspire Doing : They can motivate people to take action and make positive changes by raising awareness about important issues like the environment, fairness, or health. By reading these essays, people might be inspired to do something to help.
- Leave a Mark : When you write informative essays, you're leaving a legacy of knowledge for future generations. Your ideas can be read and learned from long after you're gone, helping others understand the world better.
How to Start an Informative Essay
If you're still doubting how to start with an informative essay outline, no worries! Here's a step-by-step guide to help you tackle this task like a pro. Alternatively, you can simply order essay and have it done by experts.

- Choose an Exciting Topic : Pick something that really grabs your attention. Writing about what you're genuinely interested in makes the whole process way more fun. Plus, it's easier to write confidently about things you know a bit about.
- Dig into Research : Spend some quality time digging up info from reliable sources. Take good notes, so you have all the facts you need to back up your essay. The better your research, the stronger your essay will be.
- Set Your Essay's Goal : Decide what you want your essay to do. Are you explaining something, analyzing a problem, or comparing ideas? Knowing your goal helps you focus your writing.
- Sketch Out Your Essay : Make a simple plan for your essay. Start with an intro that grabs attention and states your main idea. Then, map out your main points for the body paragraphs and plan a strong finish for your conclusion.
- Kick Off with an Awesome Introduction : Start with a killer opening line to hook your readers. Give a bit of background on your topic and clearly state your main idea.
- Flesh Out Your Body Paragraphs : In each paragraph, cover one key point backed up with evidence from your research. Keep it clear and simple, and don't forget to cite your sources.
- Wrap Up Strong : Sum up your main points in your conclusion and restate your main idea in a memorable way. Leave your readers with something to think about related to your topic.
Informative Essay Outline
Many students don't realize how helpful outlining can be for writing an informative essay. Spending a bit of time on it can actually save you loads of time later on when you're writing. To give you a head start, here's a simple format from our term paper writing services :
I. Introduction
- Start with something catchy to grab attention
- Give a little background info on your topic
- State your main idea clearly in your thesis statement
II. Body Paragraphs
A. Talk about your first main idea
- Share evidence or facts that support this idea
- Explain what the evidence means
- Transition smoothly to the next point
B. Move on to your second main idea
- Provide evidence or facts for this point
- Explain why this evidence matters
- Transition to the next paragraph
C. Address your third main idea
- Offer supporting evidence or facts
- Explain the significance of this evidence
- Transition to the next part
III. Conclusion
- Restate your thesis statement to remind readers of your main point
- Summarize the key points you've covered in the body paragraphs
- Leave readers with some final thoughts or reflections to ponder
IV. Optional: Extra Sections
- Consider addressing counterarguments and explaining why they're not valid (if needed)
- Offer suggestions for further research or additional reading
- Share personal anecdotes or examples to make your essay more relatable (if it fits)
Informative Essay Structure
Now that you've got a plan and know how to start an essay let's talk about how to organize it in more detail.
Introduction :
In your informative essay introduction, your aim is to grab the reader's interest and provide a bit of background on your topic. Start with something attention-grabbing, like a surprising fact or a thought-provoking question. Then, give a quick overview of what you'll be talking about in your essay with a clear thesis statement that tells the reader what your main points will be.
Body Paragraphs:
The body paragraphs of an informative essay should dive into the main ideas of your topic. Aim for at least three main points and back them up with evidence from reliable sources. Remember the 'C-E-E' formula: Claim, Evidence, Explanation. Start each paragraph with a clear point, then provide evidence to support it, and finally, explain why it's important. Mastering how to write an informative essay also requires smooth transitions from one section to the next, so don't forget to use transition words.
Conclusion :
You may already guess how to write a conclusion for an informative essay, as it's quite similar to other writing types. Wrap up by summarizing the main points you've made. Restate your thesis to remind the reader what your essay was all about. Then, leave them with some final thoughts or reflections to think about. Maybe suggest why your topic is important or what people can learn from it.

Informative Essay Examples
Essay examples show how theoretical ideas can be applied effectively and engagingly. So, let's check them out for good structure, organization, and presentation techniques.
Additionally, you can also explore essay writing apps that offer convenience and flexibility, allowing you to work on assignments wherever you are.
7 Steps for Writing an Informative Essay
Before you leave, here are 7 simple yet crucial steps for writing an informative essay. Make sure to incorporate them into your writing process:
.webp)
- Choose Your Topic: If you're given the freedom to choose your topic, opt for something you're passionate about and can explain effectively in about five paragraphs. Begin with a broad subject area and gradually narrow it down to a specific topic. Consider conducting preliminary research to ensure there's enough information available to support your essay.
- Do Your Research: Dive deep into your chosen topic and gather information from reliable sources. Ensure that the sources you use are credible and can be referenced in your essay. This step is crucial for building a solid foundation of knowledge on your topic.
- Create an Outline: Once you've collected your research, organize your thoughts by creating an outline. Think of it as a roadmap for your essay, briefly summarizing what each paragraph will cover. This step helps maintain coherence and ensures that you cover all essential points in your essay.
- Start Writing: With your outline in hand, begin drafting your essay. Don't strive for perfection on the first attempt; instead, focus on getting your ideas down on paper. Maintain an objective and informative tone, avoiding overly complex language or unnecessary embellishments.
- Revise Your Draft: After completing the initial draft, take a break before revisiting your work. Read through your essay carefully, assessing how well your arguments are supported by evidence and ensuring a smooth flow of ideas. Rewrite any sections that require improvement to strengthen your essay's overall coherence and clarity.
- Proofread: Once you've revised your essay, thoroughly proofread it to catch any spelling or grammar errors. Additionally, verify the accuracy of the facts and information presented in your essay. A polished and error-free essay reflects positively on your attention to detail and credibility as a writer.
- Cite Your Sources: Finally, include a citations page to acknowledge the sources you've referenced in your essay. Follow the formatting guidelines of the chosen citation style, whether it's MLA, APA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and proper credit to the original authors. This step is essential for maintaining academic integrity and avoiding plagiarism accusations.
Final Remarks
Fantastic! Now that you know how to write an informative essay and absorbed the essentials, let's recap the key points:
- You've learned the basics of informative essay writing.
- Ready to choose an interesting topic that connects with your audience.
- You've understood how to organize your essay clearly, with each paragraph serving a purpose.
- You have step-by-step guidance for writing engagingly.
- You've gained valuable tips to improve your writing skills and make your essay stand out.
By applying these insights, you're set to write an engaging essay that informs and inspires your readers!
Want to Unleash the Brilliance of Your Ideas?
Claim your expertly crafted informative essay today and command attention with your brilliant insights!
Related Articles
.webp)
Informative Essay

What is an Informative Essay and How to Write One?
11 min read
Published on: Aug 11, 2021
Last updated on: Jan 31, 2024

People also read
Good Informative Essay Topics for All Academic Levels
Share this article
Have you been assigned an informative essay but don’t know where to start? This guide has got you covered!
An informative essay is a common assignment for school or college students. The goal is to provide detailed information to the readers about the specific topic.
Read on to find simple step-by-step instructions for writing an interesting and engaging informative essay. You’ll also get to read helpful examples and tips you can follow to make your essay even better!
Let’s dive in!
On This Page On This Page -->
Informative Essay Definition
The informative essay can be simply defined as,
"A form of essay writing that aims to educate and inform the reader about a specific topic."
Informative essays can cover a variety of topics. It could be written about a particular thing, event, or natural phenomenon, etc.
This type of essay highlights the objective facts and evidence without reflecting the writer's subjective point-of-view about the topic.
What is the Purpose of an Informative Essay?
An informative essay presents objective and verifiable information about a topic. It relies on factual evidence and reliable sources.
The main goal of writing an informative essay is to;
- Inform the reader about something.
- Explain a particular subject.
- Transmit verified knowledge clearly and concisely.
Types of Informative Essay
There are several types of informative essays, and each type has its own purpose and style. Here are some of the informative essay types that you need to know.
- Descriptive Essay
A descriptive essay is an essay that describes something about an event, person, place, or idea in detail. The descriptive essay aims to provide enough information to the readers to visualize or imagine the matter described.
Want to know more about descriptive essays? Check out this descriptive essay writing blog to learn more.
- Cause and Effect Essay
The cause and effect essay describes the cause of an event or idea and then explains its effects on todayâs world and people. Also, this type of essay is a common form of organization in academic writing.
However, the cause-and-effect essay requires strong research skills. Without them, your essay will not become a successful piece of writing.
- Compare and Contrast Essay
In a compare and contrast essay, the writer discusses the similarities and differences between two or more things. This type of essay also requires strong critical thinking skills.
Therefore, when you start writing the compare and contrast essay , you should identify and analyze the subject from all angles and characteristics.
- Process Essay
The process essay is also known as the "How-To" essay. This essay provides information about how a process occurs or about the process of doing something.
- Problem-Solution Essay
A problem-solution essay is another common type of informative essay in which you describe a problem and then propose its solution. Its main purpose is to educate the readers on the problem and its significance.
Looking for more information? Visit our problem-solution essay guide and learn to write perfect problem solution essays.
- Expository Essay
The expository essay explains, illustrates, or interprets something in a way that becomes easy for the readers. This essay provides a fair analysis of the subject based on facts without the writerâs opinions.
Here is a simple video that explains informative writing:
How to Start an Informative Essay?
Before you can start writing, you have to do some "rewriting." Here are the steps involved in prewriting:
- Brainstorm Ideas
Brainstorming is the first step in writing any type of essay. Here, you brainstorm several topic ideas and generate a list of potential topics.
So think about all the possible ideas that are related to your interest and subject. This will help you choose an interesting topic for your essay.
- Choose a Topic
Choosing the right topic is essential for writing a great essay. A good topic will not only make your writing process easy but also make the research phase interesting.
So choose a topic you can easily write about and support it with facts, evidence, and statistics. In short, the topic should be interesting and easy to research.
- Know Your Target Audience
Your audience determines the style and tone of your essay. Consider who will be reading your essay and what their background, knowledge, and interests might be.
For instance, if you are writing for school children, your language should be simple, easy, and interesting. Meanwhile, writing for a professional audience requires you to use technical terminology and jargon.
So always think about who you are writing for and determine your audience before proceeding.
- Do the Research
You have to do some research to gather information for your essay. Make sure the information that you collect is reliable and accurate.
Use a variety of sources for research, including research articles, books, documentaries, etc. You should also take detailed and organized notes to keep track of the information you find, so you can use it later.
- Create an Outline
An essay outline helps the writer keep their focus strong and narrow. With the help of an outline, you will easily organize your thoughts and ideas.
So create an outline of your essay to lay out a structure.
Don't know how to make an informative essay outline? Donât worry, read on to find out.

Paper due? Why Suffer? That's our job.
Informative Essay Outline
Crafting a well-structured essay involves planning what points to include and how it all ties together. Creating an outline is the best way to ensure that your work is well-structured.
An informative essay outline is outlined in the following way:
Letâs discuss these outline parts in detail.
Introduction
- Start with a captivating hook that grabs the reader's attention. It could be an intriguing fact, a relevant quote, or a thought-provoking question.
- State your thesis statement . It is the last part of the introduction that clearly presents the main idea or argument of your essay. It should reflect the informative nature of your essay and guide the reader on what to expect.
- Divide the body of your essay into several paragraphs. Each paragraph should focus on one specific aspect or subtopic related to your main thesis.
- Start each paragraph with a topic sentence that introduces the main point of that paragraph.
- Analyze and discuss your supporting evidence. They could be examples, facts, or statistics that provide informative content.
Conclusion
- Summarize the main points covered in your essay.
- End with a thought-provoking statement, a call to action, or a suggestion for further exploration of the topic.
Here is an example outline template that you can use to write your informative essay outline
Informative Essay Outline Template
Creating an outline is necessary for writing any type of essay. Check out our 10+ essay outline templates and make excellent outlines with ease!
How to Write an Informative Essay?
Once you have done the prewriting, you have got everything you need to start. Following the steps below will help you write a great informative essay.
How to Write an Informative Essay Introduction?
The introduction of an essay sets the tone of the essay and provides an overview of the topic. Here are some key elements you need to include when writing an informative essay introduction:
- Attention-Grabber / Hook:
The hook is the first line of the essay that aims to pique the readersâ interest. This can be:
- An interesting fact,
- A thought-provoking question,
- Or a compelling anecdote related to your topic, etc.
The hook should be related to your topic and should be engaging enough to grab the reader's attention.
Struggling to come up with a good hook? These 200+ hook examples will help you craft an excellent hook!
- Background Information:
After grabbing the readerâs attention, you have to them to your topic. Discuss some background details on the topic to provide context.
Also, discuss the relevance or importance of the subject matter. This helps the reader understand the significance of the information you're about to present. Moreover, use clear and concise language to provide essential and interesting details to make the reader want to continue reading.
- Thesis Statement:
The thesis statement presents the main topic or idea of the essay in a concise and clear way. It provides an overview of what will be covered.
The thesis statement is the last part of the introduction. It should be specific, focused, and encompass the main ideas you'll be discussing in the body of the essay.
How to Write an Informative Essay Body Paragraphs?
The body paragraphs are the major chunk of your essay. They provide all the information about your chosen topic. There should be at least three body paragraphs in your essay, although there can be more depending on your topic.
Here are the key elements of the informative essay body paragraphs:
- Topic Sentence
Begin each body paragraph with a clear topic sentence that introduces the main point you will be discussing in that paragraph. It is the first sentence of the paragraph and should be clearly related to the thesis.
- Provide Information and Evidence
In an informative essay, information and evidence should be presented clearly and logically. So present the facts, examples, statistics, or quotations that inform the reader about the topic. This information should come from reliable and credible sources.
- Discuss and Elaborate
After presenting the evidence, explain and discuss them to ensure a thorough understanding of the information. Clarify any complex terms, concepts, or ideas that may require explanation for understanding the topic effectively.
- Use Transitional Phrases:
Use transitional phrases or sentences to connect paragraphs and ideas. This helps maintain a cohesive flow of information throughout the essay.
For instance, transitional words such as "moreover," "furthermore," "on the other hand," or "in addition to" can be used to link ideas logically.
Having a difficult time with smooth transitions? Here’s a list of transition words for essays to help you out!
How to Write an Informative Essay Conclusion?
In an essay conclusion , you wrap up the essay and provide a sense of closure. Writing the informative essay conclusion includes the following steps:
- Summarize the Main Points:
Revisit the main points covered in your essay's body paragraphs and provide a concise summary of the information presented. Do not introduce any new information or arguments in the conclusion.
- Restate your Thesis Statement
Begin your conclusion by restating your thesis statement in a slightly different way. This helps remind the reader of the main objective of your essay.
- Provide a Thought-Provoking Statement:
End your conclusion with a thought-provoking statement, reflection, or question that leaves a strong impression on the reader. This can help inspire them to continue exploring the topic beyond your essay.
Edit and Proofread the Essay
Once you are done with your first draft, take some time to proofread and revise you essay. Check for grammar and spelling, format, logical coherence, and clarity. Remove any repetitive statements or unnecessary details.
Revising your essay will make it even better and more interesting to read.
Informative Essay Examples
Reading some good examples will make writing an informative essay easier for you. Here are a few short informative essay examples that demonstrate how it looks like. Be sure to read them out.
Informative Essay about Stress
Informative Essay on Diabetes
Informative Essay on Netflix
Informative Essay on Tree in Winter
Informative Essay Topics
A good essay topic is a key to a successful essay. Here are a few ideas that will get you inspired:
- The Benefits of Regular Exercise
- The Importance of Recycling
- The Process of Photosynthesis
- What was the Big Bang?
- The History of the Internet
- How did the Dinosaurs go extinct?
- The Benefits of Meditation
- The Impact of Climate Change on Ecosystems
- The Role of Technology in Education
Stuck on choosing your topic? Don’t worry! Check out our list 200 informative essay topics to get inspiration!
To Sum Up,
This guide introduced everything you needed to start writing an informative essay. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can confidently embark on your informative writing journey.
Are you in a race against the deadline and need professional help? Weâve got you covered!
We are a legit essay writing service with professional essay writers. Our team of experts writes high-quality, original, and customized essays tailored to your unique requirements.
Our essay writing service has worked on informative essays and academic papers on various topics, with a high rate of customer satisfaction!
You can also maximize the benefits of our AI writing tool to polish and refine your writing skills.
Frequently Asked Questions
What should be included in an informative essay.
Here are some points that should be included in an informative essay.
- Thesis statement
- Strong evidence
- Examples
What is the main topic of an informative essay?
The main topic of an informative essay is to educate the readers on a specific topic.
Nova A. (Literature, Marketing)
As a Digital Content Strategist, Nova Allison has eight years of experience in writing both technical and scientific content. With a focus on developing online content plans that engage audiences, Nova strives to write pieces that are not only informative but captivating as well.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Keep reading

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
Mar 20, 2023
How to Write an Informative Essay | Outlines and Examples
Discover the Art of Informative Essays: Engage, Learn, and Be Inspired by These Compelling Examples – Read on to Elevate Your Writing Skills!
An informative essay is written to disseminate knowledge about a specific subject. These writings will typically address one of the five W's (who, what, where, when, and why) in a given topic. Naturally, they can also respond with "how," suggesting a method.
Opinions and attempts to persuade readers to adopt your point of view have no place in informative writing. Only argumentative writing is allowed to play that part. If your instructive essay is particularly engaging, it may inspire your readers to pursue further research on the topic; however, they will have to make that decision independently.
To get you started, we've provided some informative essay samples as well as resources to help you select a subject and craft your paper.
What Is an Informative Essay?
An informative essay is a type of academic writing that explains about a particular topic or subject. The primary goal of an informative essay is to provide information on a topic, idea, or concept in a clear, concise, and organized manner. The purpose of the essay is to increase the reader's knowledge and understanding of the subject matter.
An informative essay is different from other types of essays, such as persuasive or argumentative essays. While persuasive essays aim to convince the audience to take a particular viewpoint or to take action, informative essays are written solely to provide information. This means that the essay should be unbiased, objective, and free from personal opinions or biases.
When writing an informative essay, it is essential to choose a topic that is interesting and relevant to the audience. It is also essential to conduct thorough research on the topic and to use credible sources, such as academic journals, books, and reputable websites. It is also essential to use a formal tone, clear language, and appropriate grammar and punctuation.
An informative essay is a type of academic writing that aims to provide information on a particular topic or subject in a clear, concise, and organized manner. The essay should be unbiased, objective, and free from personal opinions or biases.
The structure of an informative essay typically follows a basic format, including an introduction that provides background details and a distinct thesis statement, body paragraphs that outlines key arguments along with supporting proof, and a conclusion that offers a synopsis of the information presented. When writing an informative essay, it is essential to choose a topic that is interesting and relevant to the audience and to use credible sources and a formal tone.
How to Create an Informative Essay Outline?
Writing an informative essay outline is an essential step in the essay writing process. An outline provides a structure and a framework for the essay, allowing the writer to organize their thoughts and ideas before beginning to write. A good outline will help to ensure that the essay is clear, concise, and well-structured.
The outline for an informative essay typically includes the following sections: introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Each section has a specific purpose and should be structured in a particular way.
I. Introduction
The introduction of an informative essay should provide background information on the topic and introduce the thesis statement, which is the main idea of the essay. The introduction should also capture the reader's attention and motivate them to continue reading.
A. Hook: The hook is the opening sentence or two of the essay. It should be attention-grabbing and relevant to the topic.
B. Background information: The background information provides context for the topic and helps the reader understand why the topic is important.
C. Thesis statement: The thesis statement is the main idea of the essay. It should be clear, concise, and specific.
II. Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs of an informative essay provide detailed information on the topic. Each paragraph should focus on a particular aspect of the topic and be organized in a logical and coherent manner.
A. Topic sentence: The topic sentence is the first sentence of each body paragraph. It should clearly state the main point of the paragraph.
B. Supporting details: The supporting details provide evidence and examples to support the topic sentence.
C. Transitions: Transitions help to connect the paragraphs and make the essay flow smoothly.
III. Conclusion
The conclusion of an informative essay summarizes the main points of the essay and restates the thesis statement in a new way. The conclusion should also leave a lasting impression on the reader.
A. Restate thesis statement: The thesis statement should be restated in a new way to remind the reader of the main idea of the essay.
B. Summarize main points: The main points of the essay should be summarized in a concise and clear manner.
C. Final thoughts: The conclusion should end with final thoughts that leave a lasting impression on the reader.
Crafting an outline for an informative essay is a crucial stage in the process of essay writing. The purpose of creating an outline for an informative essay is to establish the topics you aim to address and to structure ideas accordingly.
The outline should include an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion, each with a specific purpose and structure. By following these guidelines, writers can create an informative essay that is clear, concise, and well-structured.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Writing an Informative Essay Format
Despite the fact that all essays have a similar structure, each type has its own distinctive features and peculiarities. It is a must to be aware of them in order to create a well-structured informative research paper outline. Structuring an informative essay outline can help you organize your thoughts and ideas and ensure that you cover all the necessary information.
Here are 7 steps to help you create a well-structured informative essay outline:
Choose a Topic
Select a topic that you are familiar with and that you find interesting. Ensure that the topic is suitable for an informative essay and that there is enough information available for you to research.
Conduct Research
Research your topic thoroughly using reputable sources such as academic journals, books, and websites. Gather information that will help you to support your arguments and make your essay more persuasive.
Create a Thesis Statement
Write a clear thesis statement that summarizes the main argument or purpose of your essay. Your thesis statement should be concise and focused, and it should provide a clear direction for your essay.
Create an Introduction
Begin your essay with an introduction that provides background information on your topic and introduces your thesis statement. Your introduction should be engaging and informative, and it should capture the reader's attention.
Create Body Paragraphs
The body of your essay should consist of several paragraphs, each of which should focus on a specific point or argument. Use clear and concise language to convey your ideas, and support your arguments with evidence such as examples, statistics, and other forms of evidence.
Create a Conclusion
Conclude your essay with a summary of your main points and a restatement of your thesis statement. Your conclusion should provide closure to your essay and leave a lasting impression on your reader.
Proofread and Edit
Edit and proofread your essay for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors. Ensure that your essay is well-structured, easy to read, and well-supported with evidence.
Overall, following these seven steps will help you create a well-structured informative essay outline that will guide you in writing an effective and persuasive essay.
Comprehensive Analysis of All of the Outline's Subsections
Outlines for informative papers typically consist of the same five or six parts as those for other kinds of essays. This type of writing task usually requires a specific structure. Begin with a one-paragraph opening, then move on to the body—which should be at least three paragraphs long—and end with a closing. It's likely that this will appear recognizable to you.
Let's read more carefully through the parts of the research report. See to it that you have painted a distinct image of the content that each paragraph will address.
Introduction:
In the introduction of your informative essay structure, you should define your subject in simple terms. Rather than relying on your own assumptions, check that you are using the actual definitions provided by reputable sources. The so-called "prehistory" of the subject can be included, as it often contains fascinating tidbits that aren't common knowledge.
To back up the thesis assertion made at the outset of the paper, you should provide arguments in the body of your work. It is suggested to devote each paragraph to a single subject idea, so the number of body paragraphs will be determined by the number of arguments.
Controversial Arguments:
Before responding to an opponent's claims, make sure you've done your homework and collected all the information you'll need to present a well-reasoned response. There will be more than one way to look at the heart of any given subject. It is for this reason that you must exercise caution when gathering evidence and showing your opponent's arguments.
Each line needs to not only make a case but also provide proof to back up that case. Include the identities of the scientists and scholars who created the relevant references in your citation. Paint a vivid image of the subject at hand. That's why it's up to you to clarify everything that's crucial.
The Conclusion:
Many students make the mistake of thinking that the conclusion section of a summary must be a direct reiteration of the thesis statement. In the final section, you should restate the processed data and direct the reader's attention to the most important parts of the study.
The most important guideline to follow is to explain in the conclusion how the reader can profit from the study findings.
2 Informative Essay Examples
The Key Causes Resulting in Water Pollution
Water pollution is a serious environmental issue that poses a significant threat to human health and the ecosystem. It occurs when harmful substances are introduced into water bodies such as rivers, lakes, oceans, and groundwater, making them unsuitable for human consumption and other uses.
The causes of water pollution are diverse, ranging from industrial and agricultural practices to household activities. This essay examines the key causes of water pollution and their impacts on the environment and human health.
Industrial activities:
Industrial activities are a significant cause of water pollution, especially in developed countries. Industries such as mining, manufacturing, and oil drilling often release harmful chemicals and waste into water bodies, contaminating them with toxic substances.
For instance, the discharge of untreated wastewater from factories and refineries leads to high levels of pollutants in water bodies. These pollutants can cause waterborne diseases, kill aquatic plants and animals, and render water unsafe for human consumption.
Agricultural practices:
Agricultural activities are another significant cause of water pollution. The use of fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides in farming has led to the contamination of water bodies. When these chemicals are washed away by rain or irrigation, they end up in rivers and lakes, causing water pollution. Excessive use of fertilizers, in particular, has been linked to the eutrophication of water bodies.
Eutrophication is a process in which excessive nutrients in water promote the growth of algae, which reduces the amount of oxygen available for other aquatic organisms, leading to the death of fish and other aquatic life.
Household activities:
Household activities are also responsible for water pollution. These activities include the disposal of household waste, cooking oils, and detergents into water bodies. Septic systems and faulty sewer lines also contribute to water pollution. When households dispose of their waste improperly, it ends up in water bodies, contaminating them with harmful substances.
Detergents contain phosphates, which can cause eutrophication when they enter water bodies. Moreover, septic systems and faulty sewer lines can cause water contamination when they leak or overflow.
Mining activities:
Mining activities, particularly those involving open-pit mines, can cause significant water pollution. Open-pit mines generate large amounts of waste, which is often dumped into nearby water bodies. This waste contains toxic substances such as heavy metals, which can contaminate water and cause severe health problems.
The use of chemicals such as cyanide and mercury in mining operations also contributes to water pollution. These chemicals are used to extract gold and other minerals from ores, but they can contaminate water bodies if not handled properly.
Oil spills:
Oil spills are one of the most devastating causes of water pollution. When oil spills occur, they can have catastrophic effects on the environment and the economy. Oil spills can result from accidents involving oil tankers, pipeline leaks, and offshore drilling.
The spilt oil can spread over large areas, contaminating water bodies and killing aquatic plants and animals. The toxic substances in the oil can also pose a significant health risk to humans who come into contact with them.
Impacts of water pollution:
Water pollution has severe impacts on the environment and human health. For instance, water pollution can lead to the death of fish and other aquatic organisms, reducing biodiversity. Water pollution can also make water unsafe for human consumption, leading to waterborne diseases such as cholera and typhoid fever.
Furthermore, water pollution can lead to the destruction of ecosystems, reducing the ability of natural systems to provide essential services such as water purification, flood control, and erosion prevention.
In conclusion, water pollution is a significant environmental problem that can have severe consequences for aquatic life and humans. The causes of water pollution are diverse and can come from industrial and agricultural practices, household activities, mining activities, and oil spills.
To prevent water pollution, it is crucial to implement measures that reduce the release of pollutants into water bodies, such as improved industrial processes, sustainable agriculture practices, proper disposal of household hazardous waste, responsible mining practices, and oil spill prevention measures.
By working together to address water pollution, we can protect our water resources and ensure a healthier future for ourselves and the environment.
The Importance of Education in the 21st Century
Education is a fundamental pillar of society, and it plays a crucial role in the development of individuals and nations. In the 21st century, education has become more critical than ever before, given the rapid pace of technological advancements and globalization. This essay discusses the importance of education in the 21st century and how it impacts individuals and society as a whole.
Globalisation and Technological Advancements:
The 21st century is marked by a new era of globalization, characterized by the integration of economies, cultures, and societies across the world. Technological advancements, such as the internet and social media, have made it easier for people to communicate and access information, breaking down traditional barriers and boundaries.
In this context, education is essential for individuals to acquire the knowledge and skills necessary to navigate this new world successfully. Education enables individuals to communicate, think critically, and adapt to changes in the environment, including technological advancements.
Employability:
In the 21st century, the job market is highly competitive, and employers demand a skilled and knowledgeable workforce. Education plays a crucial role in ensuring that individuals are equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge to meet the demands of the job market.
Education enables individuals to acquire specialized knowledge and skills in their fields of interest, making them more competitive in the job market. Additionally, education fosters the development of soft skills, such as communication, teamwork, and problem-solving, which are highly valued by employers.
Personal Development:
Education is not just about acquiring knowledge and skills; it is also about personal development. Education enables individuals to develop a sense of identity, values, and beliefs, shaping their character and worldview. Education also promotes personal growth by exposing individuals to new ideas, perspectives, and cultures, broadening their horizons and promoting tolerance and diversity.
Social Development:
Education is critical for social development, promoting social mobility and reducing inequalities. Education enables individuals from different backgrounds and social classes to access the same opportunities and pursue their dreams, irrespective of their socioeconomic status.
Education also promotes social cohesion and community building by fostering a sense of civic responsibility and promoting active participation in society.
Environmental Sustainability:
In the 21st century, environmental sustainability is a crucial global issue that requires urgent action. Education plays a crucial role in promoting environmental awareness and sustainability. Education enables individuals to understand the impact of human activities on the environment and develop strategies to mitigate these impacts.
Education also promotes a culture of environmental stewardship, encouraging individuals to take responsibility for their actions and work towards a sustainable future.
Innovation and Creativity:
Innovation and creativity are critical drivers of economic growth and social progress in the 21st century. Education plays a crucial role in promoting innovation and creativity by fostering a culture of experimentation and risk-taking. Education enables individuals to develop critical thinking skills, think outside the box, and come up with creative solutions to complex problems.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, education is critical for the development of individuals and society in the 21st century. It enables individuals to acquire the knowledge and skills necessary to navigate a rapidly changing world, compete in the job market, and pursue personal and social goals. Education also promotes environmental sustainability, innovation, and creativity, promoting economic growth and social progress.
As such, investing in education is essential for building a better future for individuals and society as a whole.
In conclusion, writing an informative essay can be a rewarding experience, as it allows you to share your knowledge on a particular topic with others. By following the steps outlined in this article and utilizing the examples provided, you can create a well-structured and informative essay that will captivate your audience. Remember to thoroughly research your topic, organize your ideas, and use clear and concise language to convey your message. If you're looking for additional support in creating high-quality essays, sign up for jenni.ai ! Our AI-powered writing assistant can help you generate ideas, structure your essay, and even provide autocompletion suggestions to help you write faster. With jenni.ai, you can create engaging and informative essays with ease. Don't hesitate, click the button below to sign up for jenni.ai today and start writing your best essays yet!
Try Jenni for free today
Create your first piece of content with Jenni today and never look back

Writing an Informative Essay
Informative essays engage readers with new, interesting, and often surprising facts and details about a subject. Informative essays are educational; readers expect to learn something new from them. In fact, much of the reading and writing done in college and the workplace is informative. From textbooks to reports to tutorials like this one, informative writing imparts important and useful information about a topic.
This tutorial refers to the sample informative outline and final essay written by fictional student Paige Turner.
Reasons to Write Informatively
Your purpose for writing and the audience for whom you are writing will impact the depth and breadth of information you provide, but all informative writing aims to present a subject without opinions or bias. Some common reasons to write informatively are to
- report findings that an audience would find interesting,
- present facts that an audience would find useful, and
- communicate information about a person, place, event, issue, or change that would improve an audience’s understanding.
Characteristics of Informative Essays
Informative essays present factual information and do not attempt to sway readers’ opinions about it. Other types of academic and workplace writing do try to influence readers’ opinions:
- Expository essays aim to expose a truth about an issue in order to influence how readers view the issue.
- Persuasive essays aim to influence readers’ opinions, so they will adopt a particular position or take a certain course of action.
Expository and persuasive essays make “arguments.” The only argument an informative essay makes is that something exists, did exist, is happening, or has happened, and the point of the essay is not to convince readers of this but to tell them about it.
- Informative essays seek to enlighten and educate readers, so they can make their own educated opinions and decisions about what to think and how to act.
Strategies for Writing Informatively
Informative essays provide useful information such as facts, examples, and evidence from research in order to help readers understand a topic or see it more clearly. While informative writing does not aim to appeal emotionally to readers in order to change their opinions or behaviors, informative writing should still be engaging to read. Factual information is not necessarily dry or boring. Sometimes facts can be more alarming than fiction!
Writers use various strategies to engage and educate readers. Some strategies include
- introducing the topic with an alarming fact or arresting image;
- asserting what is true or so about the subject in a clear thesis statement;
- organizing the paragraphs logically by grouping related information;
- unifying each paragraph with a topic sentence and controlling idea;
- developing cohesive paragraphs with transition sentences;
- using precise language and terminology appropriate for the topic, purpose, and audience; and
- concluding with a final idea or example that captures the essay’s purpose and leaves a lasting impression.
Five Steps for Getting Started
1. Brainstorm and choose a topic.
- Sample topic : The opioid epidemic in the United States.
- The opiod epidemic or even opiod addiction would would be considered too broad for a single essay, so the next steps aim to narrow this topic down.
2. Next, write a question about the topic that you would like to answer through research.
- Sample question : What major events caused the opioid crisis in the United States?
- This question aims to narrow the topic down to causes of the epidemic in the US.
3. Now go to the Purdue Global Library to find the answers to your research question.
As you begin reading and collecting sources, write down the themes that emerge as common answers. Later, in step four, use the most common answers (or the ones you are most interested in writing and discussing) to construct a thesis statement.
- Sample answers: aggressive marketing, loopholes in prescription drug provider programs, and economic downturn.
4. Next, provide purpose to your paper by creating a thesis statement.
The thesis attempts to frame your research question. The sample thesis below incorporates three of the more common answers for the research question from step two: What caused the opioid crisis in the United States?
- Thesis Statement : Aggressive marketing, loopholes in prescription drug provider programs, and economic downturn contributed to the current opioid crisis in the United States.
- Writing Tip : For additional help with thesis statements, please visit our Writing a Thesis Statement article. For help with writing in 3rd person, see our article on Formal Vs. Informal Writing .
5. Now follow each numbered step in the “Suggested Outline Format and Sample” below.
Sample answers have been provided for “I. Introduction” and “II. First Cause.” A complete sample outline can be seen here. A complete sample informative essay can be seen here.
Suggested Outline Format and Sample
I. INTRODUCTION
A. First provide a topic sentence that introduces the main topic: Sample topic sentence : There is a current prescription pain medication addiction and abuse epidemic possibly caused by an excessive over prescription of these medications.
B. Now provide a couple sentences with evidence to support the main topic: Sample sentence one with evidence to support the main topic : According to Dr. Nora Volkow, Director of National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), in testimony before the 115th Congress, “In 2016, over 11 million Americans misused prescription opioids … and 2.1 million had an opioid use disorder due to prescription opioids” (Federal Efforts to Combat the Opioid Crisis, 2017, p. 2).
C. Sample sentence two with evidence to support the main topic : Volkow indicated “more than 300,000 Americans have died of an opioid overdose” since 2013 (Federal Efforts to Combat the Opioid Crisis, 2017, p.2).
D. Sample sentence three with evidence to support the main topic : According to Perez-Pena (2017), the Center for Disease Control and Prevention reported more than 25,000 people in the United States died in 2015 from overdosing on opioids Fentanyl, Oxycodone, and Hydrocodone.
E. Toward the end of the introduction, include your thesis statement written in the 3rd-person point-of-view: Sample thesis statement : Potential solutions to the growing opioid epidemic may be illuminated by examining how opioid addiction is triggered through aggressive pharmaceutical marketing, how opioid addiction manifests among prescribed patients, and how economic downturns play a role in the increase of opioid addiction.
F. Write down the library sources you can use in this introductory paragraph to help support the main topic.
- Federal Efforts to Combat the Opioid Crisis, 2017
- Perez-Pena, 2017
- Writing Tip : For more help writing an introduction, please refer to this article on introductions and conclusions .
II. FIRST CAUSE
A. First provide a topic sentence that introduces the first cause of the opioid epidemic: Sample topic sentence that introduces the first cause : One issue that helped contribute to the opioid epidemic is aggressive marketing by pharmaceutical manufacturers.
B. Now provide sentences with evidence to support the first cause: Sample sentence one with evidence that supports the first cause : Perez-Pena (2017) concluded that while the healthcare industry was attempting to effectively and efficiently treat patients with chronic pain, pharmaceutical companies were providing funding to prominent doctors, medical societies, and patient advocacy groups in order to win support for a particular drug’s adoption and usage.
C. Sample sentence two with evidence to support the first cause : In fact, pharmaceutical companies continue to spend millions on promotional activities and materials that deny or trivialize any risks of opioid use while at the same time overstating each drug’s benefit (Perez-Pina, 2017).
D. Next, add more information or provide concluding or transitional sentences that foreshadows the upcoming second cause: Sample concluding and transitional sentence that foreshadow the second cause : Although aggressive marketing by pharmaceutical companies played a large role in opioid addiction, patients are to blame too, as many take advantage of holes in the healthcare provider system in order to remedy their addiction.
E. Write down the library sources you can use in this body paragraph to help support the first cause:
- Writing Tip : For more assistance working with sources, please visit the Using Sources page here.
III. SECOND CAUSE
A. First provide a topic sentence that introduces the second cause.
B. Now provide sentences with evidence to support the second cause.
C. Next, add more information or provide concluding or transitional sentences that foreshadows the upcoming third cause.
D. Write down the library sources you can use in this body paragraph to help support the second cause:
- Writing Tip : Listen to Writing Powerful Sentences for information and features of effective writing.
IV. THIRD CAUSE
A. First provide a topic sentence that introduces the third cause.
B. Now provide sentences with evidence to support the third cause.
C. Next, add more information or provide a concluding sentence or two.
D. Write down the library sources you can use in this body paragraph to help support the third cause:
V. CONCLUSION: Summary of key points and evidence discussed.
- Writing Tip : For more help writing a conclusion, refer to this podcast on endings .
- Writing Tip : Have a question? Leave a comment below or Purdue Global students, click here to access the Purdue Global Writing Center tutoring platform and available staff.
- Writing Tip : Ready to have someone look at your paper? Purdue Global students, click here to submit your assignment for feedback through our video paper review service.
See a Sample Informative Essay Outline here .
See a sample informative essay here., share this:.
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
2 Responses
- Pingbacks 0
dang bro i got an A
Having faith with all this mentioned, that i will pass my english class at a college. Thank you for posting.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Follow Blog via Email
Enter your email address to follow this blog and receive email notifications of new posts.
Email Address
- RSS - Posts
- RSS - Comments
- COLLEGE WRITING
- USING SOURCES & APA STYLE
- EFFECTIVE WRITING PODCASTS
- LEARNING FOR SUCCESS
- PLAGIARISM INFORMATION
- FACULTY RESOURCES
- Student Webinar Calendar
- Academic Success Center
- Writing Center
- About the ASC Tutors
- DIVERSITY TRAINING
- PG Peer Tutors
- PG Student Access
Subscribe to Blog via Email
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
- College Writing
- Using Sources & APA Style
- Learning for Success
- Effective Writing Podcasts
- Plagiarism Information
- Faculty Resources
- Tutor Training
Twitter feed
My Speech Class
Public Speaking Tips & Speech Topics
Informative Essay Outline – Ultimate Guide & Examples

Amanda Green was born in a small town in the west of Scotland, where everyone knows everyone. I joined the Toastmasters 15 years ago, and I served in nearly every office in the club since then. I love helping others gain confidence and skills they can apply in every day life.
Writing an informative essay requires excellent research skills to educate your audience; I know this from first-hand experience. But creating an outline for your paper is easier said than done. I promise!
I created this guide to show you the correct outline for writing an informative essay with examples. Follow my tips so you can organize your thoughts and ideas.
What Is an Informative Essay?

An informative essay’s purpose is to inform and educate readers on a specific topic. Some reports seek to define a term, while others compare and contrast different objects. Some informative essays analyze data or provide procedures for doing something.
It’s the type of essay that should present something other than an opinion. That means you should omit personal pronouns “I” and “me” on the paper. You should also not persuade your reader in an informative essay.
Informational Essay Outline
Most essays and speeches follow four parts: an introduction, thesis, body, and conclusion. The main purpose is to help the writer connect all the information and support their thesis statement. Below is an outline for an informative essay structure with examples.
- Introduction
The essay introduction is where you introduce the topic of your choice. It should be shorter than the body paragraphs because it merely provides a background of your informative essay topic. Give the readers an overview of the body paragraph.
This part also includes the relevance of your topic. Ask yourself why you are writing about this subject. What makes it timely?
Can We Write Your Speech?
Get your audience blown away with help from a professional speechwriter. Free proofreading and copy-editing included.
Here’s an example:
“Tobacco, a plant that contains an addictive drug called nicotine, kills over 8 million people worldwide annually. It occurs as individuals inhale and exhale the burning plant material’s fumes.”
The thesis statement is often part of the introduction. It’s a complete sentence at the end of the first paragraph discussing what the informative essay will inform its readers. The thesis should be brief, concise, and written in simple terms.
For example:
“Smoking is the major cause of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, such as cancer, diabetes, and stroke.”
- Body paragraphs
The main body of the essay includes a paragraph for every supporting detail. Teachers usually require students to have three points in this section. For every target point, the writer should support it with facts.
The target point is also known as the topic sentence. This statement will serve as the basis of the paragraph for cohesion. After that, support the sentence with facts and studies. Don’t forget to cite your sources to avoid plagiarism.
Don’t forget to summarize each point after every body paragraph to tie everything together.
Below is an example of a body paragraph about one target point.
“Smoking can cause cancer because it weakens the body’s immune system or damages a cell’s DNA. According to the US Department of Health and Human Services (2014), nearly 9 out of 10 deaths caused by lung cancer are caused by smoking cigarettes or exposure to second-hand smoke. Although treatments are advancing, it continues killing more people than other types of cancer.”
The informative essay conclusion summarizes the entire essay, highlighting the key points. Here, you should restate your thesis statement and the paper’s purpose. Do not introduce any new ideas or recommendations.
Here is a quick sample informative essay conclusion.
“Smoking is responsible for a majority of cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. It increases the risk of cancer, stroke, and diabetes. Nevertheless, people consume it because of the adrenaline rush that creates short-term energy and pleasure. With an effective action plan, anyone can quit this bad habit for good.”
How to Write an Informative Essay: The Writing Process

Now that you know the correct structure of an informative essay, here are some tips for writing one.
Review the Instructions
If you’re writing an informative essay for school, the teacher might have specific instructions for the activity or topic. Find out what you should write about and what they want to read from your paper.
Then, learn the required word and paragraph count. Some professors also have instructions for the writing style guide you should follow.
Formatting guidelines are also common among high school and college professors. Make sure to follow the font style, spacing, and size instructions.
A good essay is about more than just content. Teachers also grade these aspects to help you practice formality in writing. Don’t hesitate to ask questions if you’re unclear about the instructions.
Choose a Narrow Topic
Broad themes like love, weather, music, and technology are not recommended when writing an informative essay. Pick a topic that does not include general knowledge.
Consider smoking, for example. This topic is too broad for a 500-word essay. Try focusing on a subtopic, such as the diseases it causes or why people smoke. Perhaps you can also write about the correlation between smoking and poverty.
Create a Logical Thesis Before Writing the Body
You can only create subtopics for your informative essay if you already have a solid topic and thesis statement. Consider what you want your reader to know and why you choose this subject.
Start with a question in mind and write an initial answer. Research the topic, then formulate a tentative response. Make sure it’s based on facts with credible sources and summarizes your overall exposition. A logical thesis statement for this essay type also doesn’t include an opinion.
Create Several Drafts
Whether you’re asked to submit drafts or not, making several versions of your paper is crucial to ensure its quality. After every draft, you should create a more improved version of it with a better structure and fewer errors.
If you have to submit every draft, the lecturer may write their comments and return the paper for revision. Revising is the process of adding or removing information, fixing sentences, rearranging, or changing your evidence. It helps make your writing more understandable.
Here are some guide questions when revising your informative essay.
- Are some parts of your informative essay in proportion with others?
- Do you spend too much time on general knowledge and less on evidence?
- Does the paper follow the thesis statement?
- Is the formality appropriate?
- Does the essay follow a logical pattern?
- Are all the facts accurate?
- Have you cited all information appropriately?
Write a Successful Conclusion
Your outline for an informative essay should include a successful conclusion. It wraps up what you have been informing your readers. You can take from general to specific information while focusing on restating your topic.
Do not add extra information to your conclusion unless it’s a call to action for possible future research. In general, this part of the essay should restate your thesis statement, explain why the topic is essential, and address your main points.
One tip for writing a successful conclusion is to use your introductory paragraph as a guide. It also contains the thesis statement and main points. So, you can reword it and add a closing sentence. Provide closure to the reader, leaving them with a significant impression.
Proofread Your Paper
Proofreading is the final stage in the essay writing process before submitting your informative paper or persuasive essay. This step is crucial because professors also grade your essay or academic paper based on a technicality in informative writing. Check for grammar, punctuation, formatting, and spelling errors to make your writing more precise and accurate.
Review from the larger aspects of your text to the narrow ones. Check your complex sentence constructions, variety, vocabulary, and repetitive phrases. You also want to review your list of references. Are you using the correct style guide?
Learn More Writing Tips for Essay Writers
Writing an informative essay takes more than just research skills. You also need to ensure clarity, organization, and coherence in your work. Take a moment and read some informative essay examples you can find online.
The best method to write an informative essay is to have a specific thesis statement which you can expand in the body paragraphs. Revise, edit, and proofread your work before submitting the final draft. I hope my guide and tips helped you on your way!
How to Write a Best Man Speech – Ideas, Tips & Examples
How to Write a High School Graduation Speech (+ Examples)
Leave a Comment
I accept the Privacy Policy
Reach out to us for sponsorship opportunities
Vivamus integer non suscipit taciti mus etiam at primis tempor sagittis euismod libero facilisi.
© 2024 My Speech Class
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write an Informative Essay
Last Updated: February 14, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Megan Morgan, PhD . Megan Morgan is a Graduate Program Academic Advisor in the School of Public & International Affairs at the University of Georgia. She earned her PhD in English from the University of Georgia in 2015. There are 12 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 243,052 times.
An informative essay educates the reader about a topic. You'll need to know a good deal about your subject and convey information in a clear, organized fashion. If it seems overwhelming at first, remember to take it step by step. Working methodically can help you write a successful paper, and you may even enjoy the process!
Selecting and Researching Your Topic

- Be sure you know how your teacher wants you to cite your sources so you can keep track of what you research. Some schools provide reference software like EndNote or RefWorks, which can make collecting and keeping track of research sources easier.
- Be aware of any formatting requirements. The essay prompt will often tell you things such as whether the essay needs to be handwritten or typed, and what font type and size to use. If it doesn't stipulate, the safe choice is a standard, readable 12-pt font such as Times New Roman or Arial. Avoid using "cute" or "quirky" fonts in an academic paper unless given specific permission to do so.
- Know the due date! Get started early so that you have plenty of time to complete the essay.

- The topic should not be too broad or too narrow. See Write an Essay for more information. There should be enough information about the topic to write about, but not so much that you can't present clear, concise information. For example, writing on "the history of animal shelters" is probably much too broad, while "the history of Sunny Days Animal Shelter in X County" is probably too narrow. A happy medium might be "the history of breed-specific animal shelters in America."
- The topic should be appropriate and interesting to your audience. Think in advance about who might be reading your essay. Obviously, if this is for school, your teacher is your primary audience, but you should always have a target audience in mind. What will they want to know? What do they probably not know already that your essay will provide?
- Ideally, the topic should be one that interests you. This will make the writing process that much easier, and you can pass your enthusiasm on to your reader.

- For best results, try to find online sources from reputable organizations, government agencies, and universities. Google Scholar can be a good place to start.

- For your informative essay, you will need an introduction, at least three main points, and a conclusion. You may want to make these sections and write notes down under the section where you expect it to go.

- Make an ideas map. Put your topic in a circle at the center of a piece of paper, then write down the most important pieces of information or ideas related to it in circles surrounding the topic. Make lines connecting each idea to the topic. Next, add details around each idea, circling them and making lines to show connections. There may be lines connecting ideas to each other, as well, or between supporting details.
- Make a list. If you prefer the linear format of a list, write down your topic at the top and then below it any ideas you have. Under the ideas, add extra details that support them. Don't worry about putting them in specific order - that comes next.
- Free write. Free writing can help you generate ideas, even if it usually doesn't provide polished prose you'll use in your final draft. Set a short time limit, such as 15 minutes, and then write whatever comes to mind about your topic. Don't stop to edit or change spelling, and keep writing even if you aren't sure you have anything to say. The important thing is to write for all 15 minutes.
Making an Outline

- Don't worry about getting your thesis just right at this point - that comes later. If you don't feel ready to write the thesis out, jot down some notes in the introductory part of your outline. At the very least, you need some idea of what you want to say in your essay.
- While it may seem odd to summarize your essay before you've begun, writing your thesis at the beginning of your outline will help you organize your ideas and select the most important details that you want to present.

- The number of details you use depends on the paper length: if you're writing a five-paragraph essay, then you have three paragraphs for the body, so you'll need three main ideas.
- Make sure you choose the most important details, and that they are all distinct from one another.
- Details used to support your thesis are also called "evidence."

- Make sure you have enough supporting details for each paragraph. If you don't have enough to say about the paragraph's main topic, consider changing the topic or combining it with another paragraph. Alternatively, you can research a bit more to find additional supporting details for the paragraph.

Writing Your Essay

- Do not worry about spelling errors or mistakes. Remember that this is just a rough draft, not your final copy. Just focus on writing it down, and later you can fix mistakes.
- Write your rough draft by hand or type it - whichever is easier for you.

- For example, a topic/transition sentence might look like this: "While some factories allow union labor, others, such as those in X, argue that unionizing harms the workplace." This sentence gives a clear direction for the paragraph (some factories argue against unionizing) and links it to the paragraph before it (which was probably about pro-union factories).
- Remember: each paragraph needs unity (a single central idea), clear relation to the thesis , coherence (logical relationship of ideas within the paragraph), and development (ideas are clearly explained and supported). [11] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source

- Make sure you're clear about what the idea of each paragraph is. To keep yourself on track, refer to your outline as you write.

- Have you told the reader everything you need to about your topic?
- Do you have a clear thesis statement, expressed in two to three sentences?
- Do all your paragraphs relate to the thesis?
- Does each paragraph have one main idea, supported by accurate, objective details?
- Does your conclusion summarize your thoughts on the topic without adding new information or opinions?
- How does the paper flow? Are there clear, logical transitions between paragraphs?
- Have you used clear, concise prose and avoided flowery language?
- Did the reader learn something new from the essay? Is it presented in an interesting way?
- Have you cited sources as instructed by your teacher?

- As you write your final draft, keep track of coherence in particular. Rough drafts often have all of their ideas jumbled up without a clear, logical progression. A key difference between a rough draft and a final draft is that the final draft should offer its information in a smooth, clear, easy-to-read fashion that builds on previous points as it goes along. Keeping an eye out to make sure you've followed the C-E-E- formula will help you.

- Also keep an eye out for word echoes, or words that show up many times within the space of a few sentences or paragraphs. If you use the word discusses multiple times in the same paragraph, it will make your writing seem clunky and unpolished.

- Sometimes our eyes "fix" mistakes for us as we read, so it's hard to catch mistakes reading silently. Reading aloud helps you find mistakes your eye might not.
Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/understanding-assignments/
- ↑ https://library.carleton.ca/guides/help/choosing-essay-topic
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/subject_specific_writing/writing_in_literature/writing_in_literature_detailed_discussion/conducting_research.html
- ↑ https://advice.writing.utoronto.ca/researching/notes-from-research/
- ↑ https://libguides.rio.edu/c.php?g=620382&p=4320145
- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/brainstorming/
- ↑ https://examples.yourdictionary.com/20-compelling-hook-examples-for-essays.html
- ↑ https://examples.yourdictionary.com/examples-of-informative-essays.html
- ↑ https://wts.indiana.edu/writing-guides/paragraphs-and-topic-sentences.html
- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/paragraphs/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/revising-drafts/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
About This Article

To write an informative essay, start with an introduction that presents a thesis statement articulating your argument in 2-3 concise sentences. For the body of the essay, focus on one main idea per paragraph and start each paragraph with a topic sentence that establishes that main idea. Then, follow the topic sentence with cited evidence and explanatory detail. Finish up with a conclusion that summarizes your main points and restates your thesis. Don't forget to proofread carefully before turning in your essay! For helpful tips on researching and using good sources, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Britney Montgomery
Dec 8, 2016
Did this article help you?

David Lewis
Nov 27, 2016
Heather Young
Oct 19, 2016
Colleen Borgese
Feb 27, 2017
Feb 28, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
EssayEmpire
How to write an informative essay.

How to write an informative essay? An informative essay is a form of writing that teaches the reader about a topic in an unbiased manner. Typically, this type of essay will include an introduction, a few body paragraphs, and a conclusion. The body of the essay generally will contain facts that are well-researched and come from reliable sources.
How to Write an Informative Essay:
Informative essay structure, informative essays subjects, informative essay topics, informative essay format, informative essay writing tips, informative essay ideas.

The basic structure of an informative essay is very simple. It needs to have a beginning, middle, and end.
- The beginning (introduction) needs to present the topic and grab the attention of the audience. It needs to include the focus sentence for the entire essay.
- The middle (body paragraphs) will be the main bulk of the essay and it will contain all the important facts that you are covering. This is where the audience will get their questions answered. Remember to answer these questions: who, what, where, when, why, and how.
- The end is a conclusion where you will summarize the essay. It should spur the reader or listener to learn more about the topic.
The introduction section in this type of essay typically is the first paragraph of the paper and offers a brief overview of the paper’s topic. It may also present a surprising fact, geared to hook the reader and encourage him to read the rest of the essay. The last sentence of the opening paragraph will usually contain the point of the informative essay, also called the thesis statement. Generally, it is the most important sentence in the entire essay, as it sets forth the direction for the rest of the paper.
The body paragraphs of an informative essay will typically contain the facts that support the thesis statement, presenting the reader with information about the topic in an organized manner. The facts may answer questions that the reader might have about the topic, for instance. This can be done through examples, step-by-step analysis, or by presenting expert opinions. Generally, each fact should refer back to and support the opening thesis statement. The writer must make sure not to express his thoughts or opinions, even in a subtle fashion, since all facts and discussion of the facts must be done in an unbiased manner.
At the end of the informative essay, the writer will have a concluding paragraph. This paragraph typically summarizes the facts that were discussed throughout the body of the essay. It can also restate the thesis sentence. The writer should make sure that he does not introduce any new points or facts in this paragraph — if there are additional facts that the writer feels are important for the essay, they should be included in the body paragraphs.
Informative essays, sometimes called expository essays, can be used for many purposes. They can compare viewpoints on a controversial subject as long as they don’t include the author’s opinions. They may analyze data, like in a cause and effect situation, or educate the audience on ways to do something, like solving a certain kind of problem.
For example:
- An informative essay might explain the pros and cons of the death penalty, using statistics on crime rate reduction as a pro and statistics on innocent men being found guilty as a con.
- An informative essay might analyze whether lack of education is a cause of homelessness by using statistics and information about the educational attainment of homeless men and women.
- An informative essay might educate the audience on how to open a bank account.
To help you get a better idea of the different types of informative essays, here are some possible titles for this type of essay:
- Understanding the Link between Cholesterol and Heart Disease
- How to Buy a House
- Understanding Your Credit Score
- Defining Poverty in the City of Chicago
- The Health Benefits of a Vegetarian Diet
- The Importance of Regular Daily Exercise
- The Causes of Global Warming
- Reducing Carbon Emissions with Alternative Fuels
- Cost Savings of Hybrid Vehicles
- Understanding Geothermal Heating and Cooling
- Why Cleaning Your Ducts is Important
- Qualifications of Contractors
- How to Get your Commercial Driver’s License
An informative essay is the best way to explain something that is complicated…in an uncomplicated way.
See more Informative Essay Topics .
After narrowing your topic somewhat and doing some brain-teaser lists, you can invent your own scratch outline for the material. But here are six common structuring and thinking devices people use to convey information:
The Process or “How-To”
The essentials or “what-is”, causes or “why”, effects or “what’s next”.
- Comparison or Contrast
Classification
If you start with one of these approaches early in your prewriting, focusing and structuring your informative writing will be easier. This is not to say you should always rely on these devices—the most creative topics often break new ground. Let’s look at each in some detail.
One way of focusing and organizing information is to present it as a process. Imagine yourself telling the reader how to do something: “How to Skydive,” “How to Win at Poker,” “How to Teach Children Manners.” Process can also be used to focus on issues simply for understanding: “How Refugees Become Terrorists,” “The Stages of Juvenile Delinquency,” or “How the West was Persuaded to Invade Iraq.” Your scratch outline will consist of chronological steps. Try several scratch outlines until you’re satisfied. If, for instance, you find yourself with three stages that have very little information and one bloated with examples and ideas, you probably need to divide that step and combine the smaller ones. If I were writing on skydiving, for instance, I don’t think the following outline would work well:
- Saying goodbye to family
- Arriving at the airport
- Preparing your equipment
- The flight up
- Cleaning up
The first, second, and last items don’t deserve full steps in the process. They can be brief transitions. Preparing equipment seems reasonable as a main heading, but the dive seems most important and ought to be divided into several stages itself: the (gulp!) leap, the free fall, opening the chute, and the landing. Organizing chronologically does not imply that you must give equal time to each element. Focus on the key moments. Slowing time down at a key moment can heighten the informative effect.
The Georgia Paramedics Against Drunk Driving, for instance, published a brochure that describes the process of an accident at 55 mph. This brochure describes the one second after a car smashes into a solid object. In the first tenth of the second, the bumper and grille collapse. In the second tenth, the hood crumples and hits the windshield. The car frame stops, but the rest of the car still travels at 55 mph. The driver braces his legs, but they snap at the knee. In the third tenth of the second, the steering wheel shatters. In the fourth, the front two feet of the car collapse while the rest still moves at 35 mph. The driver is still traveling 55. In the fifth tenth, the driver is impaled on the steering column and blood fills his lungs. In the sixth tenth, the impact can rip his feet out of tightly laced shoes, the brake pedal snaps off, and the driver’s head strikes the windshield. In the seventh tenth of the second, hinges pop and seats break free, hitting the driver—who is now dead.
This approach informs a reader of essential characteristics of your topic. For example: “The Essentials of a Good Photograph,” “Problems Children Have When Parents Divorce,” “What’s Really Bad About Rats,” or “What Is Unique About Adrienne Rich’s Poetry.” Your scratch outline consists of each key element you will explain. For instance, for children involved in divorces, you might have:
- Loss of a father/mother figure
- Dealing with parental sorrow and grief
- Feelings of guilt about causing the parents’ divorce
- Loss of home if property is sold and divided
- New “uncle-daddies”/“aunt-mommies” in the home
- Loss of friends if the family moves
Under each of these you can list the examples, facts, questions, or bug items from your brain teasers. If you find some items have little information, omit them. If one item draws most of your attention, you might focus more exclusively on it. For instance, one common thread I notice in my list of ideas is loss. I might decide at this point to focus on “Things Children Lose During Divorce.”
The topic on good photographs and the one on divorce would also be possible as process essays, describing the stages of taking a good photo or the stages children go through during a divorce. The organization of the paper changes, but it might be equally effective. On the other hand, the topic on rats might not work so well as process— unless you wanted to tell the story of one incident (“Our Apartment Building’s Battle with Rats” or “Chicago’s History of Rat Control”). The real point here is having a plan that does not mix approaches. That might confuse a reader—and you.
Organize your paper by informing the reader of the causes of a particular situation. Here are the same topics from cause perspectives:
- What motivates (causes) a person to skydive?
- What were some less obvious reasons that the United States and its allies invaded Iraq?
- What causes a rat infestation?
- Why do children feel guilty during a divorce?
- How are juvenile delinquents created?
List as many causes (reasons or motivations) for the situation. Each may become an outline heading and eventually a paragraph in the paper.
Instead of looking backward for the source of the situation, look forward to the effects or consequences of a situation. Explaining our topics from this perspective we have:
- Long-term effects of skydiving on your body
- How terrorism affects American foreign policy with other countries
- The psychological effects of rat bites
- When children of divorce marry
- The effects juvenile delinquents have on their peers
Reasonable causes and effects: Suggesting causes and effects for events may be controversial or lead to logical errors. The informative writer must try to avoid arguing and instead suggest all reasonable causes and effects without bias. For instance, the following would be reasonable causes of the computer revolution:
- To improve business efficiency and reduce human errors
- To reduce information storage space
- To speed up communications
- To save money by eliminating jobs
But how about these:
- To bend the minds of children away from religion
- To help government gain secret control of people’s finances
The last two demand a lot of arguing to prove they’re true and are more appropriate for persuasive papers than informative ones. “But,” someone might say, “Look how children are turning away from religion just as computers became widespread! It’s a fact!” No, it’s an opinion without the widespread acceptance the first four causes would have.
Comparison and Contrast
Let’s try our topic list for comparative structure:
- Skydiving is safer than hang gliding
- Afghanistan and Iraq: Two ways of handling the media
- Rats vs. cockroaches: If you had to choose
- Is it worse for a parent to die or to divorce?
- Teaching manners to kids in the United States and in Italy
- Gangs today and five years ago
Next you would list your points of comparison as headings and support each point with details.
Here are some of the topics structured by classification:
- Three types of terrorist strategies
- Four kinds of excuses to give professors
- Five skydiving styles
- Three common reaction patterns for children of divorce
- Types of female gang members
After deciding on your main points, fill in each category with details describing it. In your draft, each heading will become a paragraph.
Most college graduates are surprised by how much writing is required in their careers. Nurses, social workers, police officers, technicians, and businesspeople discover writing fills far more job time than they ever anticipated. One engineer recently estimated that she spends 50 percent of her office time writing, not calculating or sketching plans. And of the writing you will do as a college graduate, more will be informative than any other kind: technical and business reports, memos, brochures, summaries of meetings, letters, speeches, and perhaps research projects or articles for professional journals newsletters in your field. The person who can convey instructions, facts, summaries, and analyses concisely, clearly, and vividly will have an edge in becoming a valued employee or leader.
Audience and Tone
Informative writing strives for objectivity. This means a reader must be moved by your information, not by your opinions. Using facts to support personal opinions on controversial topics or to make new proposals is persuasive writing—discussed in the next chapter. In informative writing your tone should be unbiased; you should not think of yourself as converting your audience but rather as educating it. On the most basic level, you can simply report—as in a research report, a summary of an article your professor asked you to read, or a report of what happened at the student senate meeting. But in college most informative essays you’ll be asked to write must analyze a situation—use your reasoning and interpretive skills to explain. This kind of informative writing is traditionally called expository writing—you expose what might not be obvious. At some point, of course, it can cross a murky line into persuasive writing. This happens all the time in published writing, and it’s only wrong if you try to hide propaganda behind a façade of objectivity.
For example, your informative report may explain how an abortion is done or contrast the pro-life and pro-choice positions without any personal opinions. An analytical informative paper could go further. It might explain the effects abortions have on women or the reasons men tend to lead anti-abortion activities, but you would cross into persuasion if you try to tell the reader to oppose or support abortion laws. In other words, you should restrain your personal opinions in informative writing. If in describing the process of an abortion, you write, “the baby is then ripped in agony from his mother’s womb,” you have loaded the dice with opinion. Likewise, if you write “the reproductive wastage is cleaned from the uterine wall,” you load the dice the other way.
While personal anecdotes and personal knowledge can provide great detail in informative writing as elsewhere, be sure to keep the focus on the topic and not yourself. It may be tempting to describe the abortion process by telling the story of a friend who had one, but you will risk falling into storytelling and becoming too opinionated if you rely only on your friend’s story.
Another aspect of objectivity is your obligation to present all major legitimate viewpoints where there is difference of opinion. Which are legitimate? They must be either widely accepted or verifiable through science or direct observation. In the abortion debate, many people believe that a newly conceived fetus has a human soul, so, even though we cannot prove it scientifically, you ought to include that viewpoint somewhere in an informative paper contrasting positions on abortion. However, you do not have to include the supermarket tabloid claim that aborted fetuses are being implanted with computers and grown to be robotic servants of the FBI. The source is untrustworthy and the claim has not been verified by reputable observers. Scientists do disagree, however, about whether a fetus feels pain during an abortion. They debate how developed the nervous system is at various stages, so both theories should be presented.
But don’t think of informative writing as dull or boring, a mere reciting of facts. The writer’s job—always—is to keep the reader awake, no matter what the topic. Unless your audience requires stiff formality—as in a lab or business report, for instance—occasional humor, vivid anecdotes, and lively words are usually welcome.
Writers do adjust their tone in informative writing for the audience. The amount and kind of information you might use writing about an archaeological dig will vary greatly depending on whether you write a paper for your anthropology professor, a letter to your mother, or a section of a job application. The professor will want technical and interpretive information; your mother may find the events of the trip more important; a potential employer may be most interested in the skills you learned and how well you meshed with the rest of the team.
Suppose you are writing an informative paper entitled “The Gift of Life”— donating your organs to sick people when you die. How would your tone and information differ for the following audiences?
- A sociology professor
- Transplant surgeons
- The family of a dying person
- The general public
To illustrate, here are some details about the procedure. Which of the preceding audiences especially would or would not want to know the following?
- Organ donation allows part of the dying person to continue living.
- The donor is usually brain dead (a flat EEG line), but the heart still beats and a ventilator keeps the person breathing during the removal of transplant organs (organs deteriorate quickly without blood and oxygen).
- A neurologist is consulted to declare the person brain dead.
- The transplant doctor does not decide when to take the organs.
- The hospital does notify transplant doctors of likely cases so they can contact the receiving family and wait anxiously with equipment poised for permission to begin removing organs.
- The Uniform Anatomical Gift Act allows your spouse, child over 18, parent, or adult sibling to donate your body even if you have not signed a donor card.
- Doctors refer to these as “organ harvests.”
- It is a rapid operation without anesthetics. The body is simply sliced open— “peeled back” as one doctor said in a professional journal—to save time. The desired organs are quickly removed. Then the breathing machine is turned off and the person dies.
- The body cavity can be packed and stitched up for a funeral.
As you can see from the facts just listed, an informative writer must be sensitive to the intended audience.
Packing in Details
There’s no way to write well without details, and the informative essay should bristle with them. Stimulate your brain by asking reporters’ questions. You might start with this overall one: “What would I want to know about this topic if I could ask any expert?” Suppose your topic is the effects of a nuclear war.
Ask personal questions: What would happen to me if a nuclear bomb struck a half-mile away, a mile away, 5 miles, 50 miles? Ask for graphic details— what would happen to my skin, bones, hair, eyes, sexual function, and digestion? How would it affect me if I survived? How would I eat? Who would live with me? What would be the odds of finding friends or family? What aspects of society would remain? Suppose it was a terrorist’s nuclear “dirty bomb?”
Ask less personal questions: How would the living deal with all the dead and dying? Would society revert to a primitive cave culture as some people predict? Would the survivors be inspired to deeper comradery? Would there be just a few bombs or would the warring countries let loose dozens? Would the atmosphere be poisoned for all life on earth as in Nevil Shute’s On the Beach? How likely is the nuclear winter that Carl Sagan and other experts predicted—should the sun be blocked by billions of tons of dust thrown into the atmosphere? How would we respond if it was terrorism and not war? Can you add three or four questions to this list? Try it now for practice.
It’s easier to ask questions, of course, than to answer them, but in asking sometimes answers emerge. In asking you also mark which territory you will be able to handle best when you focus the topic more. So the first step is to ask the honest questions—the ones you really care about. Tough questions require tough, gutsy details. They’ll help point you toward a good paper.
Surprise Value
Good informative reports or essays should surprise the reader with new information. If you only tell us what we already know, you are not informing us of anything. For instance, most people know that nuclear bombs generate great heat and do awful things to human flesh. But when you read John Hersey’s book Hiroshima, you learn that some people caught within a quarter mile of the blast of the bomb dropped on August 6, 1945, were vaporized so suddenly that they didn’t even have time to scream or turn away. How do we know? Because they stood between concrete walls and the blast, and exact, perfect outlines of their bodies are preserved on the concrete—a painter raising his brush, a mother straightening the blanket on her baby. Their bodies shielded the wall from the intense heat just enough to imprint their silhouette.
That is information. Give your reader the same kind of essential, inside information. “General” information and “official” information usually tell readers only what they already know, unless you pick exotic topics—such as spelunking (cave exploring), cooking Indonesian food, or teaching sign language to the deaf.
Do you have to do original research to write informative essays? In a sense, yes. However, you don’t have to travel to Japan or work ten years in a lab. Your eyes, ears, fingers, and brain are researching the world every day. If you can imagine a world without electricity, family, schools, police, hospitals, or law enforcement, you may be able to create a plausible essay on the world after nuclear war. If you can use your human experience to imagine what it might be like to see a dying relative put on a respirator and can honestly picture a doctor asking you to sign over the person’s organs, you can write about some of the issues in the “gift of life” topic.
- List five topics on which you think you can write a nonresearched, informative essay. Highlight the ones you think will offer the most surprise value for a general audience.
- Write a brain-teaser list of questions (with answers) and one other brainteaser list for two of the best topics from number 1.
- Narrow the best topic further and write three scratch outlines (just main headings). Use three different organizing patterns.
- Using the same topic, decide which organization plan conveys your message best and fill it in with details from your brain-teaser lists.
- Write the paper and revise it.
- Audience and Tone: Suppose you were writing an informative letter entitled “My First Semester at College.” How would your tone and information included differ depending on to whom you were writing?
- The college president
- Your boss (who reimburses your tuition)
- Your best friend (who is not attending college)
- Make a list of information for each letter.
- Rewrite these weak topics into sharper, more interesting ones still related to the originals; give two alternatives for each:
- How to bowl
- Today’s music
- How to balance a checkbook
- Police brutality
- Smoking is bad for your health
- Ask five tough questions about each of the following topics, questions that will lead to surprise value information:
- Teenage marriages
- The future of gasoline consumption in the United States
- Community colleges vs. four-year colleges
- Television satellite dishes or cable television
- Write a process or how-to essay, packing as much information as you can into one or two pages. Concentrate on vivid details and smooth organization.
- How to drink with style
- How to meet men or women at college
- How to deal with a sexist (or a racist or homophobic) boss
- How to give an “A” oral report
- Explain how a process works that you know well, but which most people don’t understand—a CD burner, sink trap, spark plug, antibody, therapy for autistic children. No more than 250 words.
- Class Exercise in Process Writing: Create a diagram or doodle of your own of about the same complexity as this one: Write a process description of it so someone else can draw it without seeing the doodle. Proportion is important, but actual size is not. You will have ten minutes. Members of the class will try to draw it only from the read-aloud instructions—no changes allowed from your written text.
- Write an Essentials essay on one of the following, packing as much information as possible into one or two pages:
- A good love letter
- A top action film
- The most common clichés of television situation comedies
- Handling being an older adult student in college
- Create a brochure for an organization or cause you believe in. Explain its essential features in no more than 250 words.
- Inform a person you’re attracted to of your essential personality features. This should not be a sell, but an honest appraisal. Offer at least three key aspects about yourself that a future spouse should be aware of. Pack in vivid, supporting detail.
- Write an informative essay on the essentials of a career you’re considering. Interview a person in the field, asking real questions you have. Here are some all-purpose starter questions:
- What do you like best about your job?
- What one piece of advice would you give to someone wanting to enter this career?
- What qualities are most important to be a successful ______________?
- What are you most proud of in your career?
- What part of your job would you gladly give to someone?
- What most frustrates or disappoints you about it?
- Write a cause essay on one of these topics. Your job is to consider less obvious reasons as well as ones most people are aware of:
- Why people get body piercings
- Why SUVs are so popular
- Why the drug Ecstasy is popular among younger teens
- Why divorce is more socially acceptable today
- Why Physical Education is required in college
- Imagine altering one “law of nature” (such as eliminating winter or not having to kill to eat). Start by explaining why you might change it (the causes) and then forecast possible effects. Look for both positive and negative effects.
- Write a one- to two-page informative essay comparing or contrasting two of your current textbooks. Evaluate them based on the standards established in this chapter for conveying information: adaptation to audience, surprise value, and covering the tough questions readers have. Quote examples to support your views.
- Write a classification essay on one of the following, packing as much information as possible in one or two pages:
- Male attitudes toward women
- Female attitudes toward men
- Levels of racism
- Student clothing styles
- Types of video game players
- The class will be divided into six groups. Each will apply a different one of the six informative organizing patterns to the same topic. Each group should write a focus sentence, an outline, and some details for each heading.
Also, check our Informative Essay Examples .
- http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-an-informative-essay.htm
- http://examples.yourdictionary.com/examples-of-informative-essays.html
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

Special offer!
GET 10% OFF WITH 24START DISCOUNT CODE
Related posts.

At LanguageHumanities, we're committed to delivering accurate, trustworthy information. Our expert-authored content is rigorously fact-checked and sourced from credible authorities. Discover how we uphold the highest standards in providing you with reliable knowledge.
Learn more...
What Is an Informative Essay?
An informative essay is a form of writing that teaches the reader about a topic in an unbiased manner. Typically, this type of essay will include an introduction, a few body paragraphs, and a conclusion. The body of the essay generally will contain facts that are well-researched and come from reliable sources.
There are many uses for an informative essay. For example, it may be used to inform readers about a product, a process, a person, or an event. Although it may be used to discuss a controversial issue, it may not be used to express the writer's opinion about that issue. In those cases, the writer should present both sides of the issue in an unbiased manner — the reader should not be able to infer the writer's opinion on the topic after reading an informative essay.
The introduction section in this type of essay typically is the first paragraph of the paper and offers a brief overview of the paper's topic. It may also present a surprising fact, geared to hook the reader and encourage him to read the rest of the essay. The last sentence of the opening paragraph will usually contain the point of the informative essay, also called the thesis statement . Generally, it is the most important sentence in the entire essay, as it sets forth the direction for the rest of the paper.
The body paragraphs of an informative essay will typically contain the facts that support the thesis statement, presenting the reader with information about the topic in an organized manner. The facts may answer questions that the reader might have about the topic, for instance. This can be done through examples, step-by-step analysis, or by presenting expert opinions. Generally, each fact should refer back to and support the opening thesis statement. The writer must make sure not to express his thoughts or opinions, even in a subtle fashion, since all facts and discussion of the facts must be done in an unbiased manner.
At the end of the informative essay, the writer will have a concluding paragraph. This paragraph typically summarizes the facts that were discussed throughout the body of the essay. It can also restate the thesis sentence. The writer should make sure that he does not introduce any new points or facts in this paragraph — if there are additional facts that the writer feels are important for the essay, they should be included in the body paragraphs.
Dee is a freelance writer based in Colorado. She has a B.A. in English Literature, as well as a law degree. Dee is especially interested in topics relating to medicine, legal issues, and home improvement, which are her specialty when contributing to LanguageHumanities.
AS FEATURED ON:

Related Articles
- What Is an Analysis Essay?
- What Is a Process Analysis Essay?
- How Do I Write a Funny Essay?
- What Are the Best Tips for Writing an Essay Conclusion?
- What Is an Opinion Essay?
- What Are the Best Tips for Writing an Essay Introduction?
- What is a Narrative Thesis?
Discussion Comments
Post your comments.
- By: AlexOakenman An informative essay is a form of writing that informs the reader about a topic in an unbiased manner.
- By: vivalapenler Although informative essays may be used to discuss a controversial issue, they should not contain the writer's opinion about that issue.
- By: malekas Informative essays generally contain facts that are well-researched and come from reliable sources.
- By: serkucher Brainstorming with pen and paper may be helpful for writers preparing to create an informative essay.

Informative Essay

An Informative Essay stands out in the academic world as a tool for students to elaborate on specific topics with depth and clarity. By incorporating factual details and supporting evidence, these essays educate and enlighten the reader. This guide, enriched with practical essay examples , is tailored to assist students in mastering the art of crafting compelling and informative essays. Whether for school assignments or personal exploration, these examples provide valuable insights into effective informative essay writing.
What is an Informative Essay?
An informative essay is a genre of writing aimed at educating the audience on a particular topic or subject. This type of essay doesn’t just offer facts but also provides insights and explanations to help readers understand the subject matter more deeply. Unlike persuasive essays, which aim to convince readers of a particular viewpoint, informative essays are neutral; they do not express the writer’s personal opinions or arguments.

Download Informative Essay Bundle
You may have already been flooded with all these load of essays that your teacher asked you to write. You are probably thinking of a clever way on how to get away from the situation where you probably have not ever dreamed of. However, it is a task that we should all be thankful for. Essay writing actually brings more benefits than browsing through those social media platforms that you have already memorized. It does not only sharpen your minds and makes you more creative than putting likes and hitting shares of your friends’ post. The ability to share something from your mind is definitely a plausible act.
Informative Essay Format
Crafting an informative essay requires a structured approach to organize the wealth of information in a way that’s easily understandable to the reader. The format of an informative essay typically consists of three main parts: the introduction, the body, and the conclusion. Following this format helps in developing a coherent and logically flowing essay that effectively informs the reader.
Introduction
The introduction sets the stage for the entire essay. It should start with a hook that grabs the reader’s attention, such as a surprising fact, a question, or a vivid description of the topic. Following the hook, provide some background information to help readers understand the context of the essay. Finally, the introduction should end with a clear and concise thesis statement that outlines the main points or aspects of the topic that will be discussed. This statement acts as a roadmap for the essay, guiding the reader through the information presented.
Components of the Introduction: Hook : Engages the reader’s interest. Background Information : Provides context for the topic. Thesis Statement : Outlines the main points to be discussed.
Body Paragraphs
The body of an informative essay is where the main information is presented. It should be divided into paragraphs, with each paragraph focusing on a specific point or aspect of the topic. Start each paragraph with a topic sentence that introduces the point to be discussed. Follow this with supporting details, such as facts, examples, statistics, and quotes from credible sources. Each paragraph should be coherent and focused, contributing to the overall argument or presentation of the topic.
Structure of Body Paragraphs: Topic Sentence : Introduces the main idea of the paragraph. Supporting Details : Facts, examples, and evidence supporting the topic sentence. Transition : Smoothly connects to the next paragraph or point.
The conclusion of an informative essay wraps up the essay by summarizing the main points discussed. It should restate the thesis statement in a new way, reflecting the information presented in the essay. The conclusion can also highlight the importance or relevance of the topic, offering final insights or thoughts for the reader to consider. This section should leave the reader with a clear understanding of the topic and its significance. Elements of the Conclusion: Restatement of Thesis : Reflects the main points made in the essay. Summary of Main Points : Briefly recaps the key information discussed. Final Insight : Offers closing thoughts or implications of the topic.
Formatting Tips:
Use clear and concise language throughout the essay. Ensure each paragraph flows logically to the next. Cite sources where necessary to back up facts and claims. Keep the essay focused on informing the reader, avoiding personal opinions.
Types of Informative Essay
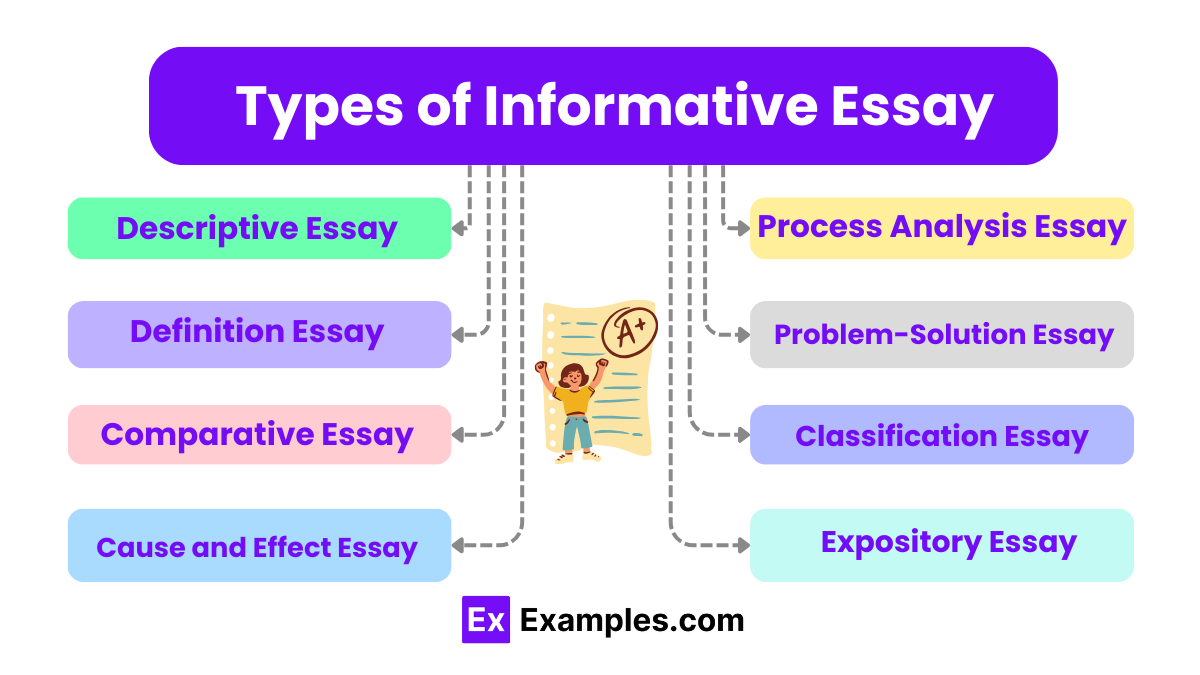
Download This Image
- Descriptive Essay : Provides a detailed description of a person, place, object, or event, using sensory details to paint a vivid picture for the reader.
- Definition Essay : Explores the meaning, history, and implications of a complex concept or term, offering a deep and thorough understanding beyond basic definitions.
- Compare and Contrast Essay : Analyzes two or more subjects by comparing their similarities and contrasting their differences, highlighting the nuances between them.
- Cause and Effect Essay : Examines the reasons why something happened (cause) and the outcomes that followed (effect), aiming to establish a clear relationship between events.
- Process Analysis Essay : Explains how something is done, how something occurs, or how something works, in a step-by-step format, providing clear instructions or insights.
- Problem-Solution Essay : Identifies a specific problem and proposes one or more solutions, focusing on presenting viable and effective ways to address the issue at hand.
- Classification Essay : Organizes or sorts different subjects or objects into categories based on shared characteristics, providing a clear understanding of their relationships and differences.
- Expository Essay : Presents a balanced analysis of a topic, using facts, statistics, and examples, aiming to explain or clarify a subject in a straightforward, unbiased manner.
How is an Informative Essay Structured?
An informative essay is structured in a clear, organized manner to effectively convey information to the reader. This structure consists of three main parts: the introduction, the body paragraphs, and the conclusion. Here’s how each part is typically organized:
- Hook : Begins with a captivating opening to grab the reader’s attention. This could be an interesting fact, a question, or a startling statistic related to the topic.
- Background Information : Provides context for the topic being discussed. This section gives the reader any necessary background information to understand the essay.
- Thesis Statement : Concludes the introduction with a clear, concise statement that outlines the main points or focus of the essay. This statement guides the rest of the essay.
- Topic Sentence : Each body paragraph starts with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea of the paragraph, relating back to the thesis statement.
- Supporting Details : These are facts, examples, or explanations that provide evidence to support the topic sentence. This may include statistics, quotes from credible sources, or logical arguments.
- Analysis : This section interprets the supporting details, explaining how they relate to the topic and the thesis statement. It’s where the writer’s insight comes into play, providing depth to the information presented.
- Transition : Each paragraph ends with a sentence that provides a smooth transition to the next paragraph, maintaining the flow of the essay.
- Summary of Main Points : Begins by briefly summarizing the key points or information presented in the body paragraphs, reinforcing the essay’s main ideas.
- Restatement of the Thesis : Reiterates the thesis statement in light of the information and analysis provided, emphasizing the essay’s main argument or focus.
- Closing Statement : Concludes with a final thought or call to action, leaving the reader with something to ponder or suggesting steps for further exploration of the topic
7 steps for Writing an Informative Essay
- Choose Your Topic : Select a topic that interests you and meets the assignment’s criteria. Ensure it is broad enough to research but narrow enough to be covered in your essay.
- Conduct Research : Gather information from reliable sources to understand your topic thoroughly. Look for facts, statistics, and examples that will provide a solid foundation for your essay.
- Create an Outline : Organize your thoughts and research into an outline. This will help structure your essay logically, ensuring a clear flow of ideas from the introduction through the body paragraphs to the conclusion.
- Write the Introduction : Begin with a hook to capture the reader’s interest, followed by background information to set the context for your topic. Conclude the introduction with a thesis statement that presents the main focus or argument of your essay.
- Develop Body Paragraphs : Each paragraph should focus on a single main idea that supports your thesis. Start with a topic sentence, followed by evidence and examples. Include your analysis to explain how this evidence relates to your topic.
- Conclude Your Essay : Summarize the main points of your essay, restate your thesis in light of the information provided, and offer a final thought or call to action. This is your chance to reinforce the importance of your topic and the information you’ve presented.
- Revise and Edit : Review your essay for any errors or unclear parts. Check for grammar, punctuation, and spelling mistakes. Ensure your writing is clear, concise, and logically organized. It may help to get feedback from others or to step away from your essay for a while before reviewing it again.
Purpose of Informative Essays
Informative essays serve a foundational role in educational and communication contexts, aiming to enlighten the reader on a specific topic or subject matter. The core purpose of these essays is to inform, explain, and educate without presenting the author’s opinion or persuading the reader to adopt a particular viewpoint. Here’s a deeper look into the primary objectives of informative essays:
Educate the Reader
The most direct purpose of an informative essay is to educate its audience. By presenting facts, data, and detailed explanations, the essay seeks to expand the reader’s knowledge on a given subject. This is particularly valuable in academic settings, where understanding diverse topics is essential to a well-rounded education.
Provide Clarity and Insight
Informative essays often tackle complex subjects that may be difficult to understand at first glance. Through clear writing and structured explanation, these essays break down intricate concepts into digestible parts, offering insight and clarity. They help the reader grasp the nuances of topics ranging from scientific theories to historical events and beyond.
Enhance Critical Thinking
By presenting information from various angles and including detailed analyses, informative essays encourage readers to engage in critical thinking. Readers are prompted to consider the hows and whys of the subject matter, analyze the information presented, and connect it to broader contexts or their personal knowledge.
Stimulate Interest
Although the primary aim is to inform, a well-crafted informative essay can also spark interest in the topic. By uncovering intriguing facts or presenting the subject in a compelling manner, the essay can motivate readers to explore the topic further on their own, fostering a culture of learning and curiosity.
Support Academic and Professional Success
In academic settings, informative essays are a tool for students to demonstrate their understanding of a topic, their ability to conduct thorough research, and their proficiency in communicating complex ideas. Professionally, these essays contribute to knowledge sharing within industries, helping individuals stay informed about current trends, innovations, and foundational concepts.
Build Foundation for Further Exploration
Informative essays lay the groundwork for deeper research and exploration. By providing a comprehensive overview of a topic, they equip readers with the basic knowledge necessary to delve into more specialized studies or related subjects, serving as a stepping stone for academic and personal growth.
10+Informative Essay Samples
15+ informative essay examples.

Free Download
Informative Essay Outline


School Informative Essay

Informative Essay Example

Expository Informative Example

Student Informative Sample

Short Informative Essay

What Is an Informative Essay?
Informative essay is a written as literary essay piece with the purpose of educating a target audience or readers regarding a certain topic or subject.
It is intended to present or expose something while at the same time avoiding to present arguments or personal opinion from the writer. An informative essay is also sometimes called an expository essay in the sense that it also aims to expose or display an information which will be beneficial for the reader.
It does not present bias judgments nor favorable ideas. It does not also dwell in the concept of convincing readers to do things that are contrary to their will.
How to Write an Informative Essay
Writing an informative essay is like telling a blind person what is the color of the sky or telling a kid what are ice creams made of. You simply just have to present a topic and expand.
- Think of a topic. The first thing that you have to do is think of a topic that you want to right about. It would be good if it is something that you are most passionate about so you can write in great details.
- Create a format. The most effective format is using the essential parts of an essay .
- Present your ideas. After choosing the topic, start writing your ideas. Try to present it in a way that you are educating the readers.
College Informative Essay

Middle School Informative

Narrative Informative Example
Informative Essay Example

Sample Informative Essay

Informative Organizer Essay
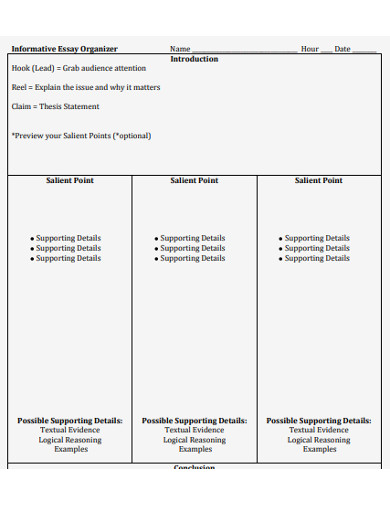
Informative Assignment Essay

Uses of Informative Essay
1. educational tools.
- Learning and Teaching : Informative essays are widely used in educational settings to teach students about specific topics. They serve as a means for students to research, organize, and present information, enhancing their learning process. For educators, these essays are a tool to assess students’ understanding and ability to communicate knowledge effectively.
2. Enhancing Understanding
- Complex Concept Clarification : These essays break down complex concepts into more understandable parts, making it easier for readers to grasp difficult subjects. They can demystify scientific principles, historical events, or technological advancements, providing clarity and insight.
3. Communication of Ideas
- Knowledge Sharing : In professional and academic communities, informative essays facilitate the sharing of knowledge and ideas. They allow experts to communicate findings, theories, and analyses, contributing to the collective understanding of a field.
4. Awareness and Information Dissemination
- Public Awareness : Informative essays play a crucial role in raising awareness about important issues, such as health, environmental concerns, and social justice. By presenting facts and information, they help inform public opinion and encourage informed decision-making.
5. Basis for Further Research
- Foundation for Exploration : These essays provide a foundation for further research. By offering a comprehensive overview of a topic, they can inspire readers to explore subjects in greater depth, paving the way for advanced studies and discoveries.
6. Professional Development
- Skill Enhancement : Writing informative essays helps individuals develop valuable skills, including research, critical thinking, organization, and writing. These skills are essential in many professional contexts, enhancing career prospects and professional competence.
7. Decision Making and Problem Solving
- Informed Decisions : In the business world and personal life, informative essays can provide the necessary background to make informed decisions. Understanding all aspects of a situation or topic can lead to better problem-solving strategies and outcomes.
8. Cultural and Social Engagement
- Cultural Insight : Essays about cultural practices, societal trends, and historical backgrounds offer readers insights into different ways of life and perspectives, promoting cultural understanding and empathy.
9. Personal Growth
- Intellectual Stimulation : Reading and writing informative essays can be intellectually stimulating, encouraging curiosity and a love for learning. They can broaden one’s horizons and foster a more informed and thoughtful perspective on the world.
Importance of Informative Essay
- Facilitates Learning and Education : They are essential tools in educational settings, helping students learn and understand various topics across different subjects.
- Promotes Critical Thinking : Writing and reading informative essays encourage critical thinking by requiring analysis and synthesis of information.
- Enhances Research Skills : The process of writing an informative essay improves research skills, teaching individuals how to gather, evaluate, and organize information effectively.
- Improves Writing and Communication Skills : Informative essays help in honing writing skills, including structuring arguments, maintaining clarity, and engaging the audience with informative content.
- Encourages Intellectual Curiosity : They stimulate curiosity about the world, encouraging readers and writers to explore topics deeply and broadly.
- Supports Informed Decision Making : By presenting facts and data, informative essays enable readers to make decisions based on knowledge and insights rather than assumptions or misinformation.
- Builds a Foundation for Further Study : They lay the groundwork for more in-depth research and analysis, serving as a stepping stone to more specialized studies.
- Spreads Awareness on Important Issues : Informative essays are a powerful medium for raising awareness about social, environmental, and health-related issues, contributing to public education and action.
- Promotes Cultural Understanding and Empathy : Essays on cultural and societal topics promote understanding and empathy towards different communities and ways of life.
- Contributes to Professional Development : The skills gained from researching and writing informative essays are valuable in professional settings, enhancing abilities in documentation, presentation, and critical analysis.
- Serves as a Source of Inspiration : Reading informative essays can inspire new ideas, hobbies, or even career paths by introducing readers to previously unknown subjects or deeper aspects of familiar topics.
- Facilitates Clear and Effective Information Dissemination : In both academic and professional contexts, the ability to clearly and effectively disseminate information is critical, and informative essays are an excellent medium for this purpose.
How Do You Start an Informative Essay Sentence?
Start an informative essay sentence with a hook such as a surprising fact, a question, or a quote to grab the reader’s attention and draw them into the topic.
How Do You Structure an Informative Essay?
Structure an informative essay with an introduction that includes a hook and thesis statement, body paragraphs that explore the topic in detail, and a conclusion that summarizes the main points.
What Should Each Body Paragraph Begin With?
Each body paragraph should begin with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea of the paragraph, directly supporting the thesis statement.
What Are the Informative Writing Techniques?
Informative writing techniques include using clear and concise language, organizing information logically, employing facts and data for support, and incorporating visuals like charts or graphs to enhance understanding.
How Do You Start an Informative Letter?
Start an informative letter with a polite greeting, followed by a clear introduction of the purpose of the letter. Provide the necessary information in a concise and organized manner.
What Are the Parts of an Informative Essay?
The parts of an informative essay include the introduction with a hook and thesis statement, body paragraphs with topic sentences and supporting details, and a conclusion that summarizes the essay’s main points.
The basic parts or elements of an essay are the introduction, the body, and the conclusion. These are all important parts which of course constitutes the wholeness of your essay.
So each part has to be given with special importance. The conclusion of essay , which is the last part, should be your chance to make your readers understand the whole point of your topic.
This is the chance for you to clarify some important things that you want to highlight. It is advisable that you write at least three to five sentences for your conclusion in order for it not to become too explanatory which you have already done on the previous part.
Informative Essay Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Crafting the Perfect Thesis for Your Informative Essay
How to Research Effectively for an Informative Essay
Structuring Your Informative Essay: A Step-by-Step Guide
Selecting the Best Topic for Your Informative Essay
The Importance of Editing Your Informative Essay
Incorporating Visuals into Your Informative Essay
Tips for Writing an Engaging Informative Essay Introduction
Developing Strong Arguments in Your Informative Essay
Informative Essay Conclusion: Leaving a Lasting Impression
Avoiding Plagiarism in Your Informative Essay
How to Write an Informative Essay? (Step-by-Step)
Have you been asked to pen an informative essay? You will undoubtedly have a loose idea of what you are supposed to do — that is, to produce a coherent, well-organized, and deeply-researched and fact-checked text about a particular topic.
Although you are most certainly off to a good start if you keep those essentials in mind, you may not quite know what kinds of sections you should include, what aspects of the topic to cover, to what extent it is acceptable to bring personal opinions or experiences into your essay, or even how long the essay should be.
We’re here to help you gain the tools you need to start your informative essay with confidence and excitement — and to make it great.
Informative Essay Basics
The essay has, as a form of writing, existed for centuries — where it has typically been used in academic (specifically philosophical or scientific) circles to advance debates on a particular topic. In the modern world, essays have a place within all levels of education.
In elementary school, essays can be used as a vehicle to help students practice their budding writing skills, as well as to demonstrate that they have understood a particular topic as essays serve to produce a summary of the materials that were covered. At higher levels, in high school as well as at college, essays have a different purpose. They are a wonderful place to hone critical thinking skills and to begin disseminating entirely original ideas.
Even outside of education and academia, essays have a place in the media and even on corporate blogs. The word “essay” is derived from the French essayer , which means “to attempt” — and that does describe how many students feel while writing these papers, but it also shows the purpose of these texts. Essays center on a single topic, but many different types exist. The informative essay, also sometimes called the expository essay, is one of the most important of these.
What precisely are informative essays, you wonder, and what sets them apart from other types of essays? Informative essays:
- Are meant to convey objective and true information about a single topic — such as the history of ice cream cones in London, the reasons behind the fact that alligator lizards are endangered, the physical health benefits of yoga, or the cultural significance of George Orwell’s 1984 .
- This information is typically conveyed in a neutral tone; informative essays stick to the facts and are not narrative or argumentative in nature. These essays have more in common with encyclopedia entries than any other type of essay.
- Informative essays need to be well-researched — any information therein must be backed up with sources that support the information offered within the essay. This may not be true in elementary school, however; students are often expected to write about something they learned about in school recently, instead.
- Informative essays have the goal of educating readers about the topic in question, or at least to convince the grading educator that the author has thoroughly researched the topic and succeeded in writing a compelling essay.
All these factors set informative essays apart from other types of essays, which include:
- Argumentative essays, in which the author attempts to convince readers that the viewpoint they are arguing in favor of is correct. Unlike informative essays, argumentative essays make a particular claim, which is then debated.
- Narrative essays, in which the author shares an experience or story from someone else’s life. These essays can be used to help readers learn more about the author, they can be entertaining or emotional, and they are highly subjective in nature.
- Descriptive essays, which use vivid or precise words to describe the topic with the goal of immersing the reader.
All types of essays contain information — but other types of essays have primary goals besides simply sharing information. Informative essays are unique in that they are written in order to educate, and aim to be objective.
A Look at the Different Types of Informative Essays
While all informative essays are written in order to inform readers about a particular topic, this goal can be achieved by means of a variety of different formats and structures. Let’s take a look at the different strategies that can be employed in crafting an informative essay — which is particularly important for students who have been given a lot of free reign in deciding what they can write about, and how they can go about that.
Informative essays may be:
- Straight-up summaries of the information the student has gathered about the topic they are choosing to write on. This kind of essay is not typically offered a name, so we’ll call it the “today I learned” essay. These essays are often assigned in elementary school, but can also be employed at the high school level. In the first case, the topic may be as simple as “tigers” or “cotton”. In high school, topics become more complex, covering, for instance, the history of the local town hall that is now rumored to be haunted.
- Contrast and compare essays. A staple in high school, these informative essays cover two different things and examine the similarities and differences — such as, for instance, the views of Hobbes vs Locke.
- How-to essays. These essays describe how to achieve a particular goal, like caring for a wounded sparrow or setting up a Twitter account. These essays are also called process essays.
- Cause and effect essays explain how one phenomenon or event caused another; how and why did the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand lead to the first world war?
- Problem-solution essays are also often said to be informative essays. At first glance, they lay out a particular problem and explain how this problem could be solved. In practice, however, such essays often become argumentative in nature. Take, for instance, topics like “how affordable housing could create job opportunities”.
How to Write an Informative Essay: A Step-by-Step Guide
Are you ready to sink your teeth into the brainstorming process? Should you still be feeling lost, here’s a handy step-by-step that will help you get started. Read the entire guide before you begin researching, and definitely before you start writing, for the best results!
- Choose a Topic for Your Informative Essay
You may have been given a very narrow assignment, like “choose two enlightenment philosophers to compare and contrast”, or even “discuss the factors leading up to the formation of the United Nations”. You may also have a much looser topic, like “write any informative essay about any aspect of Victorian England of your choosing”.
If you have not been given a definitive topic, you will have the freedom to narrow your options down on your own. As you decide on a good topic for your informative essay, you have two basic choices:
- You can decide to explore an aspect of the subject matter that you are genuinely interested in and would love the opportunity to learn more about, through the process of researching and writing your informative essay.
- You can also choose to write on a topic that you are already fairly deeply familiar with, in order to build confidence that you can write a well-researched essay that is factually correct. This is often a solid choice for students who do not have much time to write their essays.
- Keep Your Audience in Mind
Not all informative essays are written by students — some may be created to be published on the internet, while others may even appear in newspapers. If you are a student, you already know who your audience is; the grading teacher or professor. You will want to keep their particular likes and dislikes into account as you write the essay, in terms of the format and structure you choose.
- Begin Researching for Your Essay
You can begin by brainstorming aspects of the topic you are already familiar with, and would like to include in your essay — make a mindmap, and jot down any source materials you already know you would like to include. Next, use the library or the internet to track down further sources you may wish to call on in your essay.
Collect all the information you have and find in a word-processing document (or on paper if you prefer), and make a note of any gaps you discover, so that you can continue your research. Highlight quotes you would like to include in your essay.
- Where Relevant, Decide on a Structure for Your Informative Essay
With some research under your belt, you will have a better idea about the structure you may like to follow. You may decide on a compare and contrast essay, for instance. In this case, you will know that you can choose from among a few different structural options, depending on the points you would like to emphasize:
- You may like to write an introduction, followed by a thesis statement, and then (continuing with the Hobbes vs Locke topic we mentioned earlier) highlight the unique views of each, followed by the reasons these philosophers are often said to hold wildly-opposing perspectives on human nature, and ultimately explaining how the two influential philosophers also share a lot of commonalities.
- You could also follow your introduction and thesis statement with commonalities before explaining why the two are ultimately very different — creating an informative essay with an entirely different view.
Similarly, in the case of a simple expository essay that only aims to offer more information about the chosen topic, you can explore different formatting options. To take “tigers”, for instance, you could lead with their physical features, evolutionary history, or different species of tigers. The structure you choose greatly impacts the tone of your final essay.
- Commit to an Outline and Begin Writing
Once you have played around with different options, settle on an outline by creating subheads for each section. You can now tackle each section as a “mini essay” of its own.
The introduction should generally be compelling, leading with an interesting fact. Follow this with a main idea, or thesis statement, and then continue to write the body of your essay by tackling each section — in order, or by beginning with the sections you already have sufficient information for. Finish the essay with a conclusion that either summarizes the information covered, or invites the reader to keep on learning more. The conclusion should leave the reader feeling like the essay is indeed finished; end on a strong note, but never introduce new information at this point.
If, as you write, you discover that you do not have all the answers, pause your writing process to keep researching. This will likely happen, and your essay will begin shaping itself as you write.
- Edit and Proofread Your Essay
These steps cannot be skipped, and form an integral part of the essay-writing process.
The editing stage should include:
- Reading your essay from start to finish, without pausing to correct typos or sentences you are not quite happy with, and assessing if you are satisfied with the structure of the essay. If you are not, make changes here before you do anything else.
- Assessing what is still missing, or what information you offer in your informative essay that does not truly belong there (and that should be removed).
- Read your essay to see whether you offer opinions — these should usually be removed from an informative essay.
- Next, assess whether the paragraphs are coherent and flow smoothly. Make changes where necessary, ensuring that all information presented in a single paragraph is related.
- If you are still happy, you can now take a closer look at the sentences within your essay, seeing where you can make them stronger or more compelling.
- Wherever you are not sure whether a statement you have made is correct, now is the time to fact-check it thoroughly.
The proofreading phase focuses on spelling and sentences. If you have been asked to follow a certain style guide, check that your essay complies with it — looking everything you are not sure about up.
Tips to Help You Write a Compelling Informative Essay
Are you still not quite sure whether you are on the right track? To make sure that you have the chance to write the best possible essay, try to make sure that you choose a topic you are genuinely passionate about, or would truly like to learn more about.
Unless you are already a subject-matter expert, doing research — that is, learning enough about the topic to write a compelling expository essay — will take up much more time than writing the essay. To ensure that you make the most of the research you do, organize it neatly so that you will easily be able to find everything you are planning to incorporate nicely.
If you have been asked to include footnotes and in-text citations, it will often help to place these into the correct format right away; this will save you time later.
The fact that you are writing an informative essay does not mean that the text has to be dry; you can still choose engaging and interesting words, and make use of literary techniques such as hooks to keep your readers focused. Unlike in an encyclopedia entry, those writing informative essays should also make use of creative transitions that will make the paragraphs flow more smoothly.
Where possible, avoid these common mistakes when you are writing your informative essay:
- Being too wordy — if you can make your point in a single sentence, there is no need to use three.
- Relying on tried and true tropes excessively — even if you are writing an informative essay for high school, set yourself the challenge of including information that your grading teacher has likely never been introduced to before. Informative essays aim to inform, and if you can achieve this goal, you’re a step ahead of the rest.
- Writing a boring essay. Information doesn’t have to be dry; you can still entertain in subtle ways.
- Being overly formal; always try to find your own authentic writing voice, even if you have been instructed to write an academic text.
- Waiting too long to start. If your essay is a long one, the deadline may seem to be far away. The sooner you get started on doing your research and writing your essay, the more likely it is to truly excel.
- If you have been given a word count, or a number of pages to write, do not strive to pad a modest amount of information out with additional words. Instead, add more information. It’s better to find yourself in a place where you feel the need to be more succinct, because you still have more to say, than one where you try your best to add verbal padding to meet the requirements.
In Conclusion
Writing an informative essay offers a wonderful opportunity to teach others what you know, or indeed to learn more about any given topic yourself. While it may be daunting at first, the essay will start building itself once you have the right information and have settled on an appropriate structure. If you have a little extra time, do make use of it by editing your essay to perfection; you’ll be pleased with the results.
Related posts:
- 14 Tips to Help you Write An Essay Fast
- How to Write an LEQ Essay? (Step-byStep)
- How to Write a Concluding Sentence in an Essay?
- How to Write a DBQ (APUSH) Essay?
- How to Write an Effective Counterclaim in 5 Steps
- How to Write a Policy Brief (Step-by-Step)
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

What Is Informative Writing?

Written by Rebecca Turley

“Atticus told me to delete the adjectives and I’d have the facts.” ~ To Kill a Mockingbird , Harper Lee
The purpose of informative writing is to share information without any opinion or bias. In informative writing, there’s no room for your personal insights, feelings, and attitudes about the subject. The task is clear: educate the reader by conveying factually accurate and relevant information.
It may be presented in the form of an essay, an article, a textbook, a biography, a nonfiction book, how-to guide, a report, and more.
Also called explanatory or expository writing, informative writing comes down to writing about the facts, for the facts, with only the facts in mind.

Here’s what you’ll want to keep in mind as you craft informative pieces:
Informative writing:
- Provides facts and details about a topic using examples and evidence from research
- Educates the reader
- Reports new or interesting findings
- Seeks to improve the reader’s understanding about a topic
Informative writing does not :
- Seek to change the reader’s opinion
- Persuade the reader
- Present an argument
What Is the Purpose of Informative Writing?
Informative writing can accomplish one or more goals:
Describe Something or Share Information
Informative writing may provide a detailed description of something – a person, an event, a thing, a place. “What to do at Yellowstone National Park,” “An examination of Post-WWII Japan,” or “A look at the lifecycle of a Monarch butterfly” – these are all examples of using informative writing to describe a place, thing, or event.
Analyze Cause and Effect
You can use informative writing to describe the effect of something or the how and the why behind things that take place. When addressing the why piece while establishing cause and effect, it’s easy to slip into persuasive or argumentative writing. So it’s important that in your description of cause and effect, you focus on providing factual information that reveals a connection between two factors, not an interpretation based on anything outside of the facts at hand. “How does stress impact your health?” and “What changes did the Civil Rights Movement bring about?” both provide an opportunity to explore cause and effect, and both also present a real challenge when it comes to putting feelings aside to tell the story.
Compare and Contrast
Informative writing is often used to compare similarities or differences between two things. While comparing and contrasting can easily become argumentative (“Why premium gas is better for your car than standard unleaded gas”), it can also be structured in an informative, unbiased fashion (“Comparing the difference between premium gas and standard unleaded gas”).
Explain a Process
“How to change your car’s oil” or “How the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel was pained” are a couple of wildly different examples of how informative writing can provide readers with an in-depth description of a process. How-to guides and step-by-step tutorials are good examples of explaining a process.
Provide an Answer or Solution to a Problem
With this type of write-up, you identify a problem and then its solution. You can highlight one solution to the problem without showing a bias or preference, or you can provide several solutions to the problem at hand. Informative writing in this context provides one or more solutions to questions concerning practical matters like “How do I save money on my heating bill?” or “How do I find the best mortgage rate?”
Answer Why or How
Informative writing can detail how things work or why things happen using clear, unbiased, informative language. For example, “Why does the presidential election in the U.S. rely on using the Electoral College?” and “How does an internal combustion engine work?” both seek to answer a question.
The Best Way to Structure a Piece of Informative Writing

While this type of writing lends itself to a more formal presentation, you can keep the read interesting and engaging by switching up sentence structure and using a variety of bullet points, headings, and subheadings. Keep the flowery language at bay and watch your use of adjectives and adverbs because they can often take an informative piece or an expository or argumentative one.
Informative writing is best organized by providing:
- A strong, opening paragraph that introduces the topic to be discussed
- Supporting paragraphs that include topic sentences, followed by supporting evidence
- A concluding paragraph that provides a summary of key points and evidence
Because informative writing is all about sharing detailed information and facts, it’s a good practice to keep each supporting paragraph organized and focused on just one point, detail, or aspect. It’s also important to present the information in a clear, organized manner that’s accessible to readers unfamiliar with the topic.
Veracity is King in Informative Writing

Citing credible sources helps give informative writing its own credibility. Without source citations, your informative writing piece won’t come across as a reliable, trustworthy read.
Don’t guess, don’t assume, and don’t take something you’ve heard as fact. Verify it, cite it, and use reliable sources.
Your best bet? Government sites (ending in .gov), academic sites (ending in .edu), scholarly journals, and trusted new sites.
- Clerc Center | PK-12 & Outreach
- KDES | PK-8th Grade School (D.C. Metro Area)
- MSSD | 9th-12th Grade School (Nationwide)
- Gallaudet University Regional Centers
- Parent Advocacy App
- K-12 ASL Content Standards
- National Resources
- Youth Programs
- Academic Bowl
- Battle Of The Books
- National Literary Competition
- Youth Debate Bowl
- Bison Sports Camp
- Discover College and Careers (DC²)
- Financial Wizards
- Immerse Into ASL
- Alumni Relations
- Alumni Association
- Homecoming Weekend
- Class Giving
- Get Tickets / BisonPass
- Sport Calendars
- Cross Country
- Swimming & Diving
- Track & Field
- Indoor Track & Field
- Cheerleading
- Winter Cheerleading
- Human Resources
- Plan a Visit
- Request Info

- Areas of Study
- Accessible Human-Centered Computing
- American Sign Language
- Art and Media Design
- Communication Studies
- Data Science
- Deaf Studies
- Early Intervention Studies Graduate Programs
- Educational Neuroscience
- Hearing, Speech, and Language Sciences
- Information Technology
- International Development
- Interpretation and Translation
- Linguistics
- Mathematics
- Philosophy and Religion
- Physical Education & Recreation
- Public Affairs
- Public Health
- Sexuality and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Theatre and Dance
- World Languages and Cultures
- B.A. in American Sign Language
- B.A. in Art and Media Design
- B.A. in Biology
- B.A. in Communication Studies
- B.A. in Communication Studies for Online Degree Completion Program
- B.A. in Deaf Studies
- B.A. in Deaf Studies for Online Degree Completion Program
- B.A. in Education with a Specialization in Early Childhood Education
- B.A. in Education with a Specialization in Elementary Education
- B.A. in English
- B.A. in Government
- B.A. in Government with a Specialization in Law
- B.A. in History
- B.A. in Interdisciplinary Spanish
- B.A. in International Studies
- B.A. in Interpretation
- B.A. in Mathematics
- B.A. in Philosophy
- B.A. in Psychology
- B.A. in Psychology for Online Degree Completion Program
- B.A. in Social Work (BSW)
- B.A. in Sociology
- B.A. in Sociology with a concentration in Criminology
- B.A. in Theatre Arts: Production/Performance
- B.A. or B.S. in Education with a Specialization in Secondary Education: Science, English, Mathematics or Social Studies
- B.S in Risk Management and Insurance
- B.S. in Accounting
- B.S. in Accounting for Online Degree Completion Program
- B.S. in Biology
- B.S. in Business Administration
- B.S. in Business Administration for Online Degree Completion Program
- B.S. in Information Technology
- B.S. in Mathematics
- B.S. in Physical Education and Recreation
- B.S. In Public Health
- General Education
- Honors Program
- Peace Corps Prep program
- Self-Directed Major
- M.A. in Counseling: Clinical Mental Health Counseling
- M.A. in Counseling: School Counseling
- M.A. in Deaf Education
- M.A. in Deaf Education Studies
- M.A. in Deaf Studies: Cultural Studies
- M.A. in Deaf Studies: Language and Human Rights
- M.A. in Early Childhood Education and Deaf Education
- M.A. in Early Intervention Studies
- M.A. in Elementary Education and Deaf Education
- M.A. in International Development
- M.A. in Interpretation: Combined Interpreting Practice and Research
- M.A. in Interpretation: Interpreting Research
- M.A. in Linguistics
- M.A. in Secondary Education and Deaf Education
- M.A. in Sign Language Education
- M.S. in Accessible Human-Centered Computing
- M.S. in Speech-Language Pathology
- Master of Social Work (MSW)
- Au.D. in Audiology
- Ed.D. in Transformational Leadership and Administration in Deaf Education
- Ph.D. in Clinical Psychology
- Ph.D. in Critical Studies in the Education of Deaf Learners
- Ph.D. in Hearing, Speech, and Language Sciences
- Ph.D. in Linguistics
- Ph.D. in Translation and Interpreting Studies
- Ph.D. Program in Educational Neuroscience (PEN)
- Individual Courses and Training
- Summer On-Campus Courses
- Summer Online Courses
- Certificates
- Certificate in Sexuality and Gender Studies
- Educating Deaf Students with Disabilities (online, post-bachelor’s)
- American Sign Language and English Bilingual Early Childhood Deaf Education: Birth to 5 (online, post-bachelor’s)
- Peer Mentor Training (low-residency/hybrid, post-bachelor’s)
- Early Intervention Studies Graduate Certificate
- Online Degree Programs
- ODCP Minor in Communication Studies
- ODCP Minor in Deaf Studies
- ODCP Minor in Psychology
- ODCP Minor in Writing
- Online Degree Program General Education Curriculum
- University Capstone Honors for Online Degree Completion Program
Quick Links
- PK-12 & Outreach
- NSO Schedule

Guide to Different Kinds of Essays
202.448-7036
An essay is a paper that discusses, describes or analyzes one topic. It can discuss a subject directly or indirectly, seriously or humorously. It can describe personal opinions, or just report information. An essay can be written from any perspective, but essays are most commonly written in the first person ( I ), or third person (subjects that can be substituted with the he, she, it, or they pronouns).
There are many different kinds of essays. The following are a some of the most common ones:
Descriptive Cause/Effect Argumentative Definition Narrative Critical Compare/Contrast Process
Descriptive:
Examples: A descriptive essay could describe . . .
The descriptive essay provides details about how something looks, feels, tastes, smells, makes one feel, or sounds. It can also describe what something is, or how something happened. These essays generally use a lot of sensory details. The essay could be a list-like description that provides point by point details. Or, it could function as a story, keeping the reader interested in the plot and theme of the event described.
Definition:
Examples: A definition essay may try and define . . .
A definition essay attempts to define a specific term. It could try to pin down the meaning of a specific word, or define an abstract concept. The analysis goes deeper than a simple dictionary definition; it should attempt to explain why the term is defined as such. It could define the term directly, giving no information other than the explanation of the term. Or, it could imply the definition of the term, telling a story that requires the reader to infer the meaning.
Compare/Contrast:
Examples:A compare/contrast essay may discuss . . .
The compare/contrast essay discusses the similarities and differences between two things, people, concepts, places, etc. The essay could be an unbiased discussion, or an attempt to convince the reader of the benefits of one thing, person, or concept. It could also be written simply to entertain the reader, or to arrive at an insight into human nature. The essay could discuss both similarities and differences, or it could just focus on one or the other. A comparison essay usually discusses the similarities between two things, while the contrast essay discusses the differences.
Cause/Effect:
Examples:A cause/effect essay may explain . . .
The cause/effect essay explains why or how some event happened, and what resulted from the event.
This essay is a study of the relationship between two or more events or experiences. The essay could discuss both causes and effects, or it could simply address one or the other. A cause essay usually discusses the reasons why something happened. An effect essay discusses what happens after a specific event or circumstance.
The example below shows a cause essay, one that would explain how and why an event happened.
If this cause essay were about a volcanic eruption, it might go something like this: “Pressure and heat built up beneath the earth’s surface; the effect of this was an enormous volcanic eruption.”
The next example shows an effect essay, one that would explain all the effects that happened after a specific event, like a volcanic eruption.
If this effect essay were about a volcanic eruption again, it might go something like this:
“The eruption caused many terrible things to happen; it destroyed homes, forests, and polluted the atmosphere.”
Examples:A narrative essay could tell of . . .
The narrative essay tells a story. It can also be called a “short story.” Generally, the narrative essay is conversational in style and tells of a personal experience. It is most commonly written in the first person (uses I ). This essay could tell of a single, life-shaping event, or simply a mundane daily experience.
Examples: A process essay may explain . . .
A process essay describes how something is done. It generally explains actions that should be performed in a series. It can explain in detail how to accomplish a specific task, or it can show how an individual came to a certain personal awareness. The essay could be in the form of step-by-step instructions, or in story form, with the instructions/explanations subtly given along the way.
Argumentative:
Examples: An argumentative essay may persuade a reader that . . .
An argumentative essay is one that attempts to persuade the reader to the writer’s point of view. The writer can either be serious or funny, but always tries to convince the reader of the validity of his or her opinion. The essay may argue openly, or it may attempt to subtly persuade the reader by using irony or sarcasm.
Examples: A critical essay may analyze . . .
A critical essay analyzes the strengths, weaknesses, and methods of someone else’s work. Generally, these essays begin with a brief overview of the main points of the text, movie, or piece of art, followed by an analysis of the work’s meaning. It should then discuss how well the author/creator accomplishes his/her goals and makes his/her points. A critical essay can be written about another essay, story, book, poem, movie, or work of art.
202-448-7036
At a Glance
- Quick Facts
- University Leadership
- History & Traditions
- Accreditation
- Consumer Information
- Our 10-Year Vision: The Gallaudet Promise
- Annual Report of Achievements (ARA)
- The Signing Ecosystem
- Not Your Average University
Our Community
- Library & Archives
- Technology Support
- Interpreting Requests
- Ombuds Support
- Health and Wellness Programs
- Profile & Web Edits
Visit Gallaudet
- Explore Our Campus
- Virtual Tour
- Maps & Directions
- Shuttle Bus Schedule
- Kellogg Conference Hotel
- Welcome Center
- National Deaf Life Museum
- Apple Guide Maps
Engage Today
- Work at Gallaudet / Clerc Center
- Social Media Channels
- University Wide Events
- Sponsorship Requests
- Data Requests
- Media Inquiries
- Gallaudet Today Magazine
- Giving at Gallaudet
- Financial Aid
- Registrar’s Office
- Residence Life & Housing
- Safety & Security
- Undergraduate Admissions
- Graduate Admissions
- University Communications
- Clerc Center

Gallaudet University, chartered in 1864, is a private university for deaf and hard of hearing students.
Copyright © 2024 Gallaudet University. All rights reserved.
- Accessibility
- Cookie Consent Notice
- Privacy Policy
- File a Report
800 Florida Avenue NE, Washington, D.C. 20002
- Words with Friends Cheat
- Wordle Solver
- Word Unscrambler
- Scrabble Dictionary
- Anagram Solver
- Wordscapes Answers
Make Our Dictionary Yours
Sign up for our weekly newsletters and get:
- Grammar and writing tips
- Fun language articles
- #WordOfTheDay and quizzes
By signing in, you agree to our Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy .
We'll see you in your inbox soon.
Examples of Informative Essays

- DESCRIPTION Woman Typing an Essay
- SOURCE paulaphoto / iStock / Getty Images Plus
- PERMISSION Used under Getty Images license
The purpose of an informative essay is to educate others on a certain topic. Typically, these essays will answer one of the five Ws: who, what, where, when, and why. Of course, they can also answer "how," indicating how to do something.
Informative essays must never express your opinion or try to convince others to take a certain action or stance. That role is expressly reserved for persuasive essays . Of course, if your informative essay is interesting enough, it may move readers to learn more about the subject, but they'll have to come to that on their own, thanks to the wealth of interesting information you present.
Read our examples of informative essays and learn more about choosing a topic and how to write an informative essay to help you get started.
Structure of an Informative Essay
The basic structure of an informative essay is very simple. It needs to have a beginning, middle, and end. These are known more formally as the introduction, body, and conclusion, respectively.
The Introduction
The beginning, otherwise known as the introduction, is your opportunity to present your thesis statement and grab the attention of the reader. Your thesis statement must be one sentence, making it very clear what the reader will be informed about.
The introduction can be anywhere from a paragraph to a page, depending on the requirements and circumstances. Use this opportunity to introduce the main idea, provide any pertinent definitions, and briefly describe what will be covered. Above all else, the introduction must clearly state what readers are about to explore. Be sure to steer clear of any evidence of your opinion on the topic.
Below, you'll find two informative essay introduction examples to help you brainstorm your own ideas.
Sample Introduction #1 : This essay discusses the topic of donating blood.
When you woke up this morning, did you think today would be the day you save a life? In fact, it's quite easy to save a life and it only takes a little bit of your time. You don't even need to be a paramedic or firefighter. All you have to do is set aside approximately one hour to donate blood. This essay will explore how to donate blood, whom it benefits, and how often you can contribute to these life-saving measures.
Sample Introduction #2: This essay explores the history of Ireland from the perspective of its iconic castles.
Ireland is a country steeped in history. In fact, its history dates beyond 3,000 B.C, when the megalithic tombs were constructed in Newgrange. Throughout the country's expansive evolution, the Irish fought time and again to maintain their independence as a sovereign nation. Evidence of the rich history is clearly visible through its many castles, including Leighlinbridge Castle and Carlow Castle, two of Ireland's oldest establishments.
The middle, otherwise known as the body, is your opportunity to expound upon the thesis statement and grab the attention of the audience with solid facts, statistics, statements , and other supporting details.
The body will be several paragraphs long, comprising the bulk of the essay. This is where you'll provide further details about the main idea. Be sure you delve deeply into every area previously outlined in the introduction.
The Conclusion
The end, otherwise known as the conclusion , is your opportunity to summarize the essay in a paragraph or two. It should spur the reader to want to learn more about the topic. Be sure to reiterate the thesis statement clearly. In your introduction, you may have laid out what would be covered in the essay. Offer a sentence or two reiterating what was learned about those topic areas.
After that, offer up a few closing remarks that gloss over the most important elements. End on a high note, encouraging your readers to learn more or contemplate the most important elements of your essay. You may even pose a rhetorical question.
Below, you'll find two sample conclusions to help you brainstorm your own ideas.
Sample Conclusion #1 : This concludes the essay example above on the topic of donating blood. Note how it emphasizes the simplicity of the process.
The process of donating blood is decidedly simple. Many folks carry out the process while reading a chapter from a new book or watching an episode of their favorite TV show. Indeed, the infinitesimal amount of time it takes to donate blood can transfer into a lifetime of happiness for the recipient. Remember to bring juice or something sugary to keep your glucose levels high at the end of the procedure. Then, hold your head up high, knowing there's a life out there that's about to be saved by you.
Sample Conclusion #2 : This conclusion to the Ireland essay example reiterates the "ferocity of its people."
If Ireland isn't an example of a rebel nation, what is? The ferocity of its people is clearly evidenced by the fact that Leighlinbridge Castle was built and rebuilt three times before it was finally sacked by the Cromwellians. Carlow Castle's staggering history earmarks Ireland's triumphant history too, starting as a mighty fortress and surviving numerous rebellions. Indeed, Ireland is a country storied in history and its many castles are the tellers of its tale.
Sample Informative Essay
In the sample below, note a few things as you read. Try to keep an eye out for the thesis statement in the first paragraph. Then, note the transition words in two of the body paragraphs. They are, "Also in line with safety…" and "In terms of fun…" Finally, in-text citations will vary, based on your teacher's style guide, so be sure to double-check those. Download the PDF version below the essay to keep as a handy reminder.
The title of the following essay is "How to Travel Solo Successfully."
James Baldwin said it best. "I met a lot of people in Europe. I even encountered myself" (Baldwin, 2014). Solo travel will not only reveal colorful new heights, it will also introduce you to yourself - your resiliency, your sense of adventure, your independence. Learning how to travel solo is as intrinsic as tying your shoes, and it is something that can be learned today. The first, most obvious, way to travel solo successfully is to research your area. The number one indicator of a tourist is someone stopped in the middle of the sidewalk scanning the GPS on their phone. According to World Travel News Report, four in fifteen tourists will be pickpocketed if they stand still on a busy street (Parker, 2019). Arrive well-informed on the area. Understand the public transportation system to the point where you can blend in as a local. Also in line with safety, you may want to splurge on accommodations. You can stay alone in a hostel, but read the reviews carefully. Make sure it is in a safe area and security is a priority for them. You might even want to consider a private room, some of which include a private bath. In terms of fun, pack for your lack of companionship. Bring a blank journal to record your adventures. Pack a paperback to enjoy while you wait out a rainstorm in a coffee shop. World traveler Samantha Byrnes says, "I never travel with friends. When I'm exploring a new continent, my journal is my only sidekick" (Byrnes, 2018). This allows her to absorb her new surroundings, make new acquaintances, and focus on the act of encountering herself. Byrnes continues, "We lost sight of ourselves in the day-to-day. We focus on work, family, to-do lists, chores. Solo travel allows us to return to ourselves so that, when we resume our day-to-day activities, we can give our all" (Byrnes, 2018). Learning how to travel solo successfully is an achievable feat. You can stay safe if you remain knowledgeable on the area and choose your accommodations wisely. Beyond that, you can experience true transformation through the simple act of carrying a tattered old journal. What do you say? Will you explore solo travel? Choose wisely, for it just might change your life forever.

Example Informative Essay
Subject matter.
Have you been tasked with writing an informative essay? If the topic is open, the first thing you must ask yourself is, "What interests me the most?" This will make the task far less laborious. Take something you're already knowledgeable about and share it with the world, citing other sources and stating current facts and statistics.
This is your chance to add to others' viewpoints on a subject as long as you don't include your own opinions. Allow them to analyze the data, perhaps in a cause and effect layout. Or, you can educate them on how to do something, create something, or solve a problem.
Here are some examples of informative essay topics to get your creative juices flowing:
- How to open a bank account
- World poverty
- Procrastination and its effects
- Homelessness
- Air pollution
- Dream interpretation
- History of women's right to vote
- Foreign cultures
- U.S. stock market
- Biographies
- Architecture in Paris
- History of the Titanic
Example Essay Titles
While your introduction must be carefully crafted in order to reel readers in, your essay title is the first thing they encounter, and it needs to be enticing. Formulate a clear title, indicating what's about to be discussed. Find a way to invite others to want to learn more. Remember to follow these rules for capitalization in titles .
Here are some possible titles for inspiration:
- How to Donate Blood
- A Brief History of Ireland
- Understanding the Link Between Cholesterol and Heart Disease
- How to Buy a House
- Understanding Your Credit Score
- Defining Poverty in the City of Chicago
- The Health Benefits of a Vegetarian Diet
- The Importance of Regular Daily Exercise
- Top Three Causes of Global Warming
- Reducing Carbon Emissions With Alternative Fuels
- The Many Cost Savings of Hybrid Vehicles
- Understanding Geothermal Heating and Cooling
- Why Cleaning Your Air Ducts Is Important
- Qualifications for Contractors
- How to Get a Commercial Driver's License
Essay Writing Steps
Most of the work on an informative essay is done before you actually sit down to type.
- Select an appropriate topic.
- Research and gather ideas about the subject. See what you already know about the subject as you uncover other areas you still need to research.
- Make a list of these important facts. Be sure all the facts are accurate. This is a good time to craft your thesis statement as well as a topic sentence for each fact you'd like to include.
- Create an outline that will organize your facts in a logical way. After this, you'll be ready to make your first draft.
- Write your essay based on the outline you've created. Ensure that one section naturally flows into the next.
- Proofread and edit your work. Editing is an important step for any writing project. Reading your essay out loud will help you notice areas where your writing may be unclear or awkwardly worded.
If possible, have someone else read your essay and offer their ideas for improvement. Of course, don't forget to pay attention to grammar, punctuation, spelling, capitalization, and other errors as well.
Knowledge Is Power
An informative essay is the best way to explain something complicated - in an uncomplicated way. Even though you're (hopefully) writing on a topic of interest to you, be sure to back up each claim with substantial facts and statistics. Let the content speak for itself, inviting readers to learn more.
Informative essays are powerful, persuasive essays are moving, but have you ever been tasked with a narrative essay? Enjoy the wonders of this third form of essay writing in Narrative Essay Examples and let the endless exchange of knowledge begin!
How To Write An Informative Essay
- Essay Writing Guides

If you have been looking at the blank MS Word document for a couple of hours attempting to write something meaningful in your informative essay, you’re in the right place. Today, you will learn the informative essay definition, master this paper with ease, and get the highest grades. Read the guide from our essay service to discover how to craft a worthy informative essay.
What is an Informative Essay?
An informative essay is a paper that provides information on a specific topic. In other words, it educates the reader about a particular thing, be it a term, event, natural phenomenon, etc.
An informative essay doesn’t contain the author’s evaluation or analysis. Instead, it aims to describe a subject. What does this essay look like? In essence, most Wikipedia articles are informative essays since they provide you with information on a particular topic .
Due to this, you might be lucky if you are assigned to write an informative essay, since it’s one of the simplest academic writing tasks.
Informative Essay Purpose
The informative essay aims to explain a particular subject. But what does it mean? It means you need to tell your reader about the topic’s origin, causes, effects, etc. Let’s exemplify it with some historical events, like WW2:
- When did WW2 start?
- Who and why did initiate it?
- What are the main WW2 events?
- How did it end?
- What countries did engage in WW2?
- What implications did it involve?
Informative Essay Outline
All essay types share the same logic when it comes to outlining. Therefore, your informative essay structure must contain the following elements:
Introduction
Essays share some introduction features. Informative one is no exception: your introduction must contain a hook, background facts, a thesis statement, and the transition sentence.
What is an essay hook? It is a couple of the very first sentences of your essay introduction that spark your readers’ interest. You can include some eye-opening statistics and add some wordplay. After that, you may want to add background information that will evolve into the thesis statement.
Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is the main topic your essay will revolve around. A good rule of thumb is to narrow down your thesis statement so that you can fit into the required word count without compromising your research quality. After writing a thesis statement, you need to include a logical transition to your essay body.
You will describe your topic in the essay body. Usually, it will contain several paragraphs, depending on your topic complexity and the required word count. The crucial point is to follow the sequence of events and make logical transitions between the essay parts. Consequently, each body paragraph must contain:
- A topic sentence that explains the paragraph’s main point and connects it to the previous one.
- Information: facts, statistics, and thesis-supporting evidence.
- Mini-conclusion. Summarize your paragraph and add a transition to the next one.
Repeat this pattern while writing each body paragraph to make your essay sound clear and logical.
An informative essay conclusion contains the following elements:
- The restated thesis statement.
- A summary of body paragraphs.
- The final word.
How to Write an Informative Essay Introduction?
How to start an informative essay? First and foremost, it doesn’t require proving or debunking some beliefs or analyzing something. That’s why popular hooks like provocative rhetorical questions may not be suitable for this paper.
However, you may want to play with the readers’ awareness. Take a look at the introduction hook example on the global deforestation topic: Do you know that people remove 40,000 square miles (the size of Iceland) of forest each year? By wrapping striking facts into rhetorical questions, you can quickly grab your readers’ attention.

Need expert help with your essays, but also want to save some money?

How to Write an Informative Essay Thesis?
The thesis statement can render the meaning of your paper title. For example, your topic is Amazonian deforestation.
Think of what to write about: when Amazonian deforestation started, what countries remove the most trees, what implications deforestation involves, etc.
In this case, you have to provide a thesis statement that will set a direction for your paper so that you can uncover more and more details in your essay body.
So the thesis statement for this topic might sound like this: Deforestation of the Amazonian rainforest makes an unprecedented impact on the local biodiversity and climate . At this point, you have defined your essay’s direction: you will mention extinct species, changing rain patterns, rainforest loss rates, etc.
Note that you should make your thesis statement sound non-controversial. It has to be a fact (like deforestation implications) rather than an opinion/argument.
Remember that informative essays don’t involve debates.
How to Write an Informative Essay Body?
The essay body aims to bring more details to your thesis statement. It would be much better if you added headings for each part of your subject. In this way, it will be much easier for you to follow the essay direction. Also, you can use headings from H1 to H4. Take a look at the example on how to do that:
- H1 Amazonian Rainforest Deforestation: Causes and Implications .
- H2 When Did the Amazonian Deforestation Start ?
- H2 Main Amazonian Deforestation Drivers
- H2 Rainforest Loss Rates
- H3 Brazilian Rainforest Loss Rates
- H2 Amazonian Rainforest Deforestation Implications
- H3 Global Temperature Rise
- H3 Global Sea Level Rise
- H3 Massive Extinction of Rainforest Species
- H2 The Bottom Line.
Are you ready to get things finally done?

How to Write an Informative Essay Conclusion?
The essay conclusion should provide a sense of completeness. For this, you should rephrase the thesis statement first. Please note that you need to give your rephrased thesis statement a new meaning based on the provided facts and conclusions.
After that, summarize your essay body in a couple of sentences. At the end of your conclusion, sum up the whole paper within the final line.
How to Choose a Topic for an Informative Essay?
Usually, professors provide their students with essay topics. But if you are free to choose one on your own, you are lucky. Check these tips for choosing informative essay topics:
- Check for informative essay ideas on the web. Many websites list hundreds of topics for all academic levels.
- Select narrow topics instead of broad ones if you wish to get a meaningful, well-researched essay – it’s impossible to cover a general topic.
- Make sure you can find enough information on your subject. For this, do a quick research on a couple of topics before writing an informative essay.
Informative Essay Examples
Here are some informative paper examples you can use anytime you feel uncertain about how to properly organize and write your paper:
- The War Within
- The Miracle Worke
- An informative essay about traveling
Informative Essay Writing Tips
Feel free to check the following tips if you wish to write an outstanding informative essay and get the highest grade for it:
Note Your Ideas
You may struggle to keep in mind all the ideas regarding your essay. So it would be excellent to note and list them before writing your first draft.
Make Up an Outline
Research your selected subject and draft your essay outline first to save you time. Once you get a clear and logical paper structure, you will write your essay step-by-step without a problem.
Use Writing Tools
Using citation machines is the best way to follow the required informative essay format and list all the used sources with ease. You can also use grammar checkers like Grammarly and plagiarism detection software to polish your paper.
Proofread Your Essay the Next Day
You might not notice all the errors in your essay right after completing your draft. Due to this, you may want to let your vision and mind have a rest. For this, proofread your piece the next day.
Write My Informative Essay for Me, Please!
Writing an informative essay is easier than you think. This academic paper requires you to describe a given or chosen topic in detail, with facts, statistics, and explanations. If you still struggle to grasp the informative essay meaning or have no time for it, you can ask professional Ph.D. writers from our essay writing service to craft this paper for you. All you need to do is create an account, place an order, and wait for the delivery.
- Academic Writing Guides
- Citation Guides
- Essay Samples
- Essay Topics
- Research Paper Topics
- Research Paper Writing Guides
- Study Tips and Tricks
Featured articles

Strategies for Writing a Great Problem Solution Essay
Composing an assignment on a problem and solution essay topic allows you to demonstrate your ability to resolve human challenges. It helps you understand human problems and how to be a part of the solution instead of allocating blame and pointing fingers. So, how do you compose a great problem solutions essay? This post has […]
Author: Marina Kean

Your Complete Guide to Writing a Compelling Leadership Essay
True leadership lies at the heart of human well-being and success. Every positive step humanity ever took required great and responsible leadership. Therefore, people have studied leadership for many edges to unravel its different underlying factors. But how do you write a great essay that demonstrates your grasp of this sacred call? This post shares […]
- Plagiarism check
- AI Check New
- Get premium
14 Do's and Don'ts When Writing an Informative Essay
##14 Do’s and Don’ts for When Writing an Informative Essay
Writing a high-quality informative essay can be straightforward when you know what to do and what to avoid in your process.
Wondering what to do and what to avoid in your informative essay-writing process? When writing one, we’ve compiled a comprehensive list of do’s and don’ts.
Keep reading to learn more!
Here is our list of do’s for when writing an informative essay:
Research the Topic Thoroughly
Search for related topics on Google Scholar . This can help you find additional sources and articles to gain more information from. Also, you can use the search engine to give you the keywords you need for your paper.
It is easy to get overwhelmed with the whole research process. However, it is important to remember that you are not expected to read everything you find. Instead, use the keywords that you find in Google Scholar to help you narrow down your search for information.
You should only spend a little bit of time reading articles on subjects that are relevant to your topic. This will help you save time and improve your writing since you are providing relevant information to your readers.
Brainstorm Ideas for Your Informative Essay
Brainstorming is an essential part of the writing process. It can help you generate ideas and discover a topic that interests you. It can also help you plan your ideas and organize your essay. Many students need help with knowing where to start when writing an essay. Brainstorming can help you get started.
Brainstorming can help you:
Discover a topic that interests you Plan your ideas and organize your essay Organize your ideas and research Get started writing your essay
Brainstorming can help you plan and organize your essay, but it's just one part of the writing process. It should not replace other important writing steps such as pre-writing, drafting, and editing
Organize Your Thoughts and Ideas
The best way to organize ideas is to write them down. You can write them in a journal or use a word processing program. Using a word processing program, you can use the outlining feature to organize your thoughts. Outlines are a great way to organize your ideas. Outlines can be used in a variety of ways. For example, some people use them to write essays and reports.
Others use them to plan speeches or presentations. No matter how you use an outline, it will help you organize your thoughts and ideas. Outlining is a great way to start writing. It helps you think about your topic and write your thoughts down. Once you have an outline, you can start writing.
You can start by writing the introduction and filling in each point from your outline. This will help you write a strong paper that is organized and coherent. Outlining is a great way if you want to write an organized paper.
Select a Focus and Make a Thesis Statement
Allowing yourself a thesis statement can help when it comes to writing. Whether it's a 1,000-word essay or a 100-word paragraph, it makes the writing process easier. However, writing 1,000 words without a thesis statement can be daunting, so it's best to start by making one.
Having a thesis statement lets you narrow down the topic and write about it more easily. You'll be able to connect your ideas and tell your reader what you want to say. Start with a thesis statement to make writing a seamless process.
Include Relevant Facts and Data
What is the context of the writing? What is the author trying to convey and why? What is the purpose of the text, and what is the author's intention? Before evaluating the content, dig a little to understand the background.
Ask yourself: Is the text written for a specific publication? Is it a college writing assignment? Is it an online tutorial? How is the author trying to engage the reader? What is the author's purpose? What kind of audience is the author trying to reach? The more you know about the text itself, the easier it will be to understand what is being said and how the author is saying it.
Support Your Arguments with Evidence
It’s easy to get caught up in what you’re trying to say and forget to back it up with evidence. Writing is an act of communication, and to be truly effective, you need to make sure your audience understands where you are coming from and why you are making the points you are.
Citing evidence is important for a few reasons. First of all, it demonstrates that you understand the context of your argument and are capable of keeping your perspective in mind as you dive into the details. Secondly, citing evidence shows your audience how you came to that conclusion and gives them a path to follow if they want to come to the same conclusion themselves.
Finally, citing evidence shows your audience that you are not afraid to admit your sources and creates a sense of trust that you are presenting what you know to be true rather than making unfounded assumptions.
Use a Logical Structure
A logical structure starts with fundamental concepts and builds toward more complex ideas. This is the most important thing to consider when creating a logical structure for your essay. The first sentence of an essay should always provide the reader with the most essential information to help them understand the rest of the essay.
This sentence should provide the reader with the main idea and help them understand the structure of the essay. It should lead into the next paragraph, further elaborating on the main idea. Stay consistent with your main idea, and don’t go off on tangents.
An effective essay has a logical structure, meaning it starts with the most important information and builds upon it with each subsequent paragraph. A logical structure can be achieved in many ways, but the most important thing is to stay consistent with your main idea.
Don’t go off on tangents or try to include too much information. A logical structure will help you convey your main idea clearly and concisely to your audience.
Use Simple and Clear Language
The best writing is clear and concise. Readers don’t want to be confused, and they certainly don’t want to re-read paragraphs or sentences to understand your message. So, use simple and clear language. The best way to do this is to avoid using big words when small ones will do, and to keep your sentences short and to the point.
Writing that’s complex or difficult to read can often be simplified, so never fear doing that. Instead, you’ll end up with writing that is clear and easy to understand, which is exactly what your readers want.
Use a Variety of Sentence Structures
This means using the correct punctuation. For example, if you are making a statement, use a period to finish it. Do not use a question mark. This is incorrect punctuation. When asking a question, use a question mark at the end of your sentence. It is important to use the correct punctuation as it is an important part of writing.
Cite Your Sources Properly
If we are not certain of the credibility of a source, we should not use it. It is a common mistake for students to cite dubious sources when they are unsure if the source is credible. This can result in a plagiarized paper with references that do not support the author’s observations or opinions. Checking the source’s credibility prevents such situations from happening.
In addition, the student should always ensure that the source they use is relevant to the topic. This can prevent unnecessary repetition of information, which can be a telltale sign of plagiarism. Furthermore, it helps us to stay focused on the essence of the topic and present our ideas more creatively and innovatively.
Check Your Work for Accuracy
Many teachers primarily focus on the content of a student’s writing, particularly when it comes to essay writing. An essay’s content is the most important, and it’s the hardest thing to master. It’s easier to work on your grammar skills and ensure your writing is error-free.
That way, you’ll be well prepared to write an essay that will get you the desired results with the least amount of stress. It’s a good idea to focus on what’s important and ensure your content is interesting, engaging, and informative before worrying about grammar and spelling.
Proofread and Edit Your Informative Essay
The combination of writing an essay and balancing a hectic schedule can be quite overwhelming. Mistakes like grammatical, spelling, and punctuation errors are bound to happen. Proofreading and editing your essay is a great way to go about it.
You can use Rephrasely’s Grammar Corrector, a free online tool that helps in identifying grammatical errors and helps in fixing them. Once you're done with your draft, you can use the tool to proofread your essay.
Ask Someone Else to Review Your Informative Essay
It means that your writing is so off-base that you can’t even convince a stranger that your writing is good. That’s a problem. It could be that your writing is just plain bad, or it could be that you’ve been so consumed by your ideas that you can’t even see them objectively.
This is a clear sign that you need to get someone else to review your writing. Either that, or you need to take a break, walk away from your writing for a bit, and come back to it with a fresh mind.
Revise and Refine Your Informative Essay
Student writing can be hard to come to terms with because it’s not always clear exactly what the teacher is looking for. “Revise and refine” can be tricky because it’s hard to know where to start. Is it a case of just putting some ‘revise and refine’ at the top and hoping for the best? Well, sort of.
It’s hard to know exactly what your teachers are looking for, so it’s always best to start with a rough draft of your essay and then revise and refine it from there. Revising and refining your writing can be just as important as the initial draft, so make sure your essay is well-structured, well-researched, and well-written.
Here is our list of don’ts for writing an informative essay:
Don't Copy and Paste from Other Sources
While students may not have the essay writing skills to create a compelling argument, they can at least give themselves a fighting chance by avoiding plagiarism . By not copying and pasting content from other sources, students can at least be confident that the content they are presenting is original and accurate.
Some students may have the misconception that using other content is fine as long as they cite it, but they must remember that they are risking their academic standing by doing so.
Don't Use Biased Language
If you are writing a research paper, ensure that the material you are using is cited properly. This includes the titles, the authors, and the publishers. If you do not do this, you are guilty of plagiarism. Therefore, make sure that you are properly citing your sources so that you can avoid being accused of plagiarism.
When you are not properly citing your sources, you steal someone else’s work. When you are accused of plagiarism, you are accused of stealing someone else’s work.
Don't Make Baseless Claims
One of my biggest pet peeves is when students make claims that aren’t backed up by facts. For example, if a student were to write, “The Beatles were the most influential band of all time,” but didn’t offer any evidence to support this claim, it would leave the reader wondering if this statement is true or just an opinion.
As a writer, it’s important to back up your claims with examples, statistics, or any other evidence proving your point. By doing this, you’re ensuring that your argument is sound and well-supported, which will help your readers understand your point of view and make them more likely to agree with you.
Don't Use Jargon or Complex Terminology
Using jargon or complex terminology may make you seem authoritative, but can also make you seem inaccessible to the reader. If your writing is filled with unfamiliar terms that the average reader will not understand, they will be unable to follow your argument. Instead, consider the average reader and write in a style that is easy to understand and engaging.
Don't Use First-Person Pronouns
Many students have a habit of using first-person pronouns in their written assignments. For example, they will use ‘I,’ ‘me,’ ‘my,’ ‘mine,’ ‘myself’ or ‘our’, etc., in their written assignments so that it becomes distracting to the reader. It doesn’t look professional, and it is better to avoid it.
While you may want to use them, you should ask yourself, “is it important to know who is saying this?” If it isn’t, then don’t mention it. Just write your thoughts. It is much more professional and easier to follow if you do. It may take a while to get used to, but it is worth it!
Don't Exaggerate or Make Assumptions
Students should use evidence to support their arguments rather than exaggerating or making assumptions to get their point across. In the context of student writing, this means that students should provide concrete evidence for their arguments rather than just stating opinions.
For example, if a student is writing an essay about why the death penalty should be abolished, they shouldn't just state that it's immoral and unjust; they should provide specific examples and evidence to support their argument.
Don't Provide False Information
Writers should never include false information. Instead, they should write about their experiences in a way that is honest and engaging without exaggerating or including things that never happened. Never underestimate your reader and their ability to detect misinformation!
Don't Use Too Many Quotes
Quoting is a great way to show that expert opinions support your research and can also be a great way to add some personality to your writing. However, you want to make sure that you don't go overboard and quote too much. Otherwise, your writing can end up sounding dry and uninteresting, which is the opposite of what you're trying to achieve. So as with all things, moderation is key.
Don't Be Afraid to Be Opinionated
Students are often too afraid to be opinionated. They’re worried about coming across as too confident or even arrogant. When students are afraid to express their own opinions, their writing suffers. This is because they aren’t trying to engage with the text.
Instead, they’re simply regurgitating what the author has already said. When students are more willing to share their opinions, they have more to say about the text. This leads to more engaging writing, which is exactly what you want your writing to be. So, don’t be afraid to be opinionated! Be confident in your ideas and share them with the world.
Don't Forget to Include a Conclusion
The conclusion is the final part of a student's essay. It summarizes what the writer said in the essay’s body, and gives the reader a sense of completeness and closure. Conclusions add to the essay's structure and organization. It also helps the reader remember what the writer said in the essay.
The conclusion should not be a summary of the body. Instead, it should be a new and original thought that ties together the main ideas of the body. A conclusion should also leave the reader with an understanding of how the writer's point of view affects their life.
The conclusion should be concise and to the point. It should be between one and three sentences long. It should avoid being overly long or overly complicated. The conclusion should also have a transition sentence leading to the essay's body.
Don't Ignore the Purpose of Your Informative Essay
The best essay writing services could help you improve your writing without changing your original voice. They want your essay to sound like you wrote it. They just want to help you become a better writer. It's a very rewarding experience that can help you build confidence in your writing abilities.
You'll see how your writing has grown and how much progress you've made due to the essay writing service's help. It's a win-win.
Don't Be Afraid to Ask for Help
If you're writing a paper with someone and you're stuck, don't be afraid to ask for help. Your partner might have a different perspective than you, and they can provide some insight that you haven't considered. Even if they can't help, they'll probably be glad to know they're not the only ones struggling!
Don't Forget to Check the Formatting Requirements
All academic papers are required to be formatted and structured in a particular way. It is essential to follow these guidelines to ensure your professor can easily read and assess your work. Furthermore, by taking the time and effort to format your papers properly, you will not only impress your professor but also improve your chances of receiving a good grade.
Not sure how to format your paper? Don't worry - plenty of resources online can help you get it right. A quick Google search will reveal many websites and apps showing you exactly how to format your paper in MLA, APA, or Chicago Style.
By taking the time to format and structure your paper properly, you will ensure that it is easy to read and understand, which will ultimately lead to better results.
Don't Wait Until the Last Minute to Write Your Informative Essay
Many students believe they can write a good essay only in the last minutes before the deadline. And they are right. If they don't take care to arrange their ideas and get the first draft done before the deadline, they will be writing from scratch at the last minute. It is better to dedicate time to writing the first draft of your essay and then go over it and edit it on time.
If you are stuck for ideas, try brainstorming or using some of the effective writing prompts available online. It helps to have a first draft ready before the deadline and then go over it for editing. This way, you save time on writing from scratch and can focus on perfecting your informative essay.
Final Thoughts
Following our list of do’s and don’ts for writing an informative essay will help you score top marks.
Here is our list of do’s for writing an informative essay:
Research the topic thoroughly Brainstorm ideas for your informative essay Organize your thoughts and ideas Select a focus and make a thesis statement Include relevant facts and data Support your arguments with evidence Use a logical structure Use simple and clear language Use a variety of sentence structures Cite your sources properly Check your work for accuracy Proofread and edit your informative essay Ask someone else to review your informative essay Revise and refine your informative essay
Don't copy and paste from other sources Don't use biased language Don't make baseless claims Don't use jargon or complex terminology Don't use first-person pronouns Don't exaggerate or make assumptions Don't provide false information Don't use too many quotes Don't be afraid to be opinionated Don't forget to include a conclusion Don't ignore the purpose of your informative essay Don't be afraid to ask for help Don't forget to check the formatting requirements Don't wait until the last minute to write your informative essay
We hope you’ve found our article helpful. Don’t forget to share it with a fellow student!
Works Cited: How to improve your writing. Rephrasely. (n.d.). Retrieved January 17, 2023, from https://rephrasely.com/blog/how-to-improve-your-writing Google scholar. (n.d.). Retrieved January 17, 2023, from https://scholar.google.com/ 20 important questions to consider when writing an essay. Rephrasely. (n.d.). Retrieved January 17, 2023, from https://rephrasely.com/blog/20-important-questions-to-consider-when-writing-an-essay Google. (n.d.). My word! Google Books. Retrieved January 17, 2023, from https://books.google.co.za/books?hl=en&lr=&id=J3uv5MQsdIkC&oi=fnd&pg=PA1&dq=plagiarism&ots=ef7kSH9Gv7&sig=TN6K7esNMRglDoWhQwQ_XP_O0IE&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=plagiarism&f=false
About Rephrasely
Getting your wording just right.
Paraphrasing is a natural part of the writing process as it helps you clarify your thinking and suit your words to your audience. Using a Rephrasely helps structure and streamline this work, and our paraphrase tool offers 20 modes, many of them free, for accomplishing just this. The 20 modes we offer are diverse, including a summarize tool, a free grammar checker, a mode to simplify text, and a sentence shortener. There are sentence rephrasers and paraphrase rephrase tools, and we pride ourselves on having both, since our reword generator accounts for context at both the sentence and paragraph levels.
When you google paraphrase you will get a variety of results, from a free Rephrasely , to an article spinner, to a general phrase tool, and it can be hard to determine which of these rephrase tools will best help you complete your work. If you simply need to get a word rephrase, that is, reword only small elements within the sentence, many tools will suffice, but there is the risk that you end up with a tool that does not consider context and produces very awkward and ungrammatical sentences. Rephrasing is very much an art, and we’ve built our paraphrase bot to produce the most correct results in 20 modes in over 100 languages, making it the best paraphrasing tool at an exceptionally low cost. So whether you need to paraphrase deutsch, paraphrase greek, or paraphrase bahasa melayu, the next time you think, I need something to paraphrase this for me, you’ll know where to turn.
From keywords to paragraphs
Generating paragraphs with unique ideas can be challenging, and too often writers get stuck at this stage of the writing process. With our paragraph tool, you can enter keywords and let our AI generate paragraphs for you, so that you can have something to work with, refine the output, and become more engaged in your writing.
A paragraph generator creates links between your ideas, such that the output is sensible, unique, and stimulating, very close to what you would expect a thoughtful human paragraph writer to produce.
Paragraph makers are nice, but what about a short story generator? Because our AI is generalized, it serves a story generator, an essay generator, a poem generator, and much more. To generate compelling stories, you should provide the story generator with useful keywords from which it can develop plot elements, including characters, setting details, and any situational information. To generate reasonably good essays, you should likewise provide the essay maker with details around argumentative positions and any other pertinent ideas. If you more specifically want an introduction paragraph generator or conclusion paragraph generator, you can provide starter text and keywords that will best enable our essay creator to produce them.
You may well ask, “is this essay generator free?” Everything on this site is free within a 3-day trial, so you can test and develop confidence in our products. You may also be wondering where this is an essay automatic writer or if it will take a while to get results. All results appear within a matter of seconds, so you can move through your work as quickly as possible.
You may have professional needs for creating paragraphs as well, such as those needed for cover letter. Most of the time a cover letter template includes information that is not relevant to you; by using your own keywords, we can produce cover letter examples that are relevant to your use case and often require very little editing. By using this service, you can also learn how to write a cover letter and achieve the cover letter format you need.
Plagiarism checker free
Like everything else on our site, you can check plagiarism free within a trial, which is a great opportunity for those who want to check a paper for plagiarism without committing to paying before they see results. This free plagiarism checker is great for students and clearly indicates how to check for plagiarism by highlighting areas of similarity between the two texts. Just to be sure you are not accidentally plagiarizing, be sure to check all of your paraphrases as well.
- How to Cite
- Language & Lit
- Rhyme & Rhythm
- The Rewrite
- Search Glass
Elements of an Informational Narrative
An informational narrative is used when the writer is trying to inform others about a particular subject of which they may not be familiar. Informative essays can also be called an expository or explanatory essays. This kind of essay is aimed at presenting information in a clear and concise manner so the reader can learn about the subject matter.
Basics of an Informational Narrative
An informational narrative is written using a variety of resources to present information. It consists of an introduction with a thesis, the body of the text with cited information supporting the thesis, and the conclusion which sums up the points presented in the narrative.
When writing an informational narrative, avoid using the personal pronoun 'I,' and do not use contractions. Because this is a narrative which is supposed to present an idea, you will need to a method to cite the source where you obtained information and ideas that inspired your own thoughts. This is important so the reader can go back to the sources cited and confirm what was written is in fact what the source states.
Elements of the Introduction
The introduction is where the writer presents the thesis which the narrative will be based around. The thesis is the central argument in which the body of the narrative will be supporting. When writing an introduction attempt to get to the thesis in the first or second sentence of the narrative. The narrative is a tool to inform the reader about the thesis of the paper. Realize that the reader is more concerned about the thesis and less about beautiful prose. Present your argument in the thesis as soon as possible.
Body of the Narrative
The body of the narrative is where you present the information which you have obtained in your research and supports the thesis which was presented in the introduction. The body of the text can be as long or as short as required to complete the narrative, but in general they are at least three paragraphs long. When writing you will want to present a single idea which relates to the thesis in each paragraph along with the required citations. Do not present more than a single idea in each paragraph. Otherwise the paragraph can seem cluttered.
Conclusion of the Narrative
Concluding the narrative is not about just simply restating the thesis in the introduction. Summarize the information which was presented in the body of the narrative in relation to the thesis, creating a synthesis of information which the reader can conclude that what was presented supports the thesis which you presented. At the very most a conclusion should only be several paragraphs unless the narrative is extremely long or complex. Never introduce new information in the conclusion. If the information is important enough to include in the conclusion it should have been included in the body of the narrative.
Tips for an informational narrative
The informational narrative is about informing the reader in a clear and concise manner the thesis of the paper. Again, concise and precise wording is more important in this sort of narrative than lyrical language. Think about the audience of the narrative as well. This will affect how you write the narrative. Writing to an audience who does not understand the thesis presented will require more information and explanation than writing for a group of experts in the field which the subject matter is part of their career. Finally, the flow of the narrative should include transitions between each paragraph. Transitions are sentences or phrases that help the reader move smoothly between your ideas.
- Purdue University Online Writing Lab: What is an informational essay?
- Purdue University Online Writing Lag: Expository Essay
Damian Miller has been a writer since 2002. He has published the ebooks "End of the Rainbow" and "Guide to Cold Weather Hiking." Miller is an Eagle Scout and holds a master's degree in history and Bachelor of Arts degrees in anthropology/sociology and in history from Purdue University.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Purpose of informative writing. The purpose of an informative essay depends upon the writer's motivation, but may be to share new information, describe a process, clarify a concept, explain why or how, or detail a topic's intricacies. Informative essays may introduce readers to new information. Summarizing a scientific/technological study.
An expository essay is also intended to inform readers, but it is a much more complex essay that uses lots of evidence and facts to back up the main topic. ... Informative essays can be found in ...
Keeping It Real: These essays are all about the facts. No opinions allowed. We want to keep things fair and honest. Topics Galore: You can write about anything you find interesting, from science and history to things about different cultures. Where You Find Them: Informative essays can pop up anywhere, from your classroom assignments to the pages of magazines or even online articles.
A well-written informative essay should include an introduction (hook, bridge, thesis), a body (topic sentence, research, explanation), and a conclusion (reframed thesis and call to action). While ...
Informative Essay Definition. The informative essay can be simply defined as, "A form of essay writing that aims to educate and inform the reader about a specific topic." Informative essays can cover a variety of topics. It could be written about a particular thing, event, or natural phenomenon, etc.
The conclusion should also leave a lasting impression on the reader. A. Restate thesis statement: The thesis statement should be restated in a new way to remind the reader of the main idea of the essay. B. Summarize main points: The main points of the essay should be summarized in a concise and clear manner.
Informal Writing. 5. Now follow each numbered step in the "Suggested Outline Format and Sample" below. Sample answers have been provided for "I. Introduction" and "II. First Cause.". A complete sample outline can be seen here. A complete sample informative essay can be seen here.
An informative essay, also called expository, is a piece that strives to inform the reader about a specific subject. When writing an informative essay, the writer should use their rationale, collect the necessary data, analyze, and synthesize it. They should also provide accurate, understandable, and, most importantly, unbiased information on ...
Writing an informative essay takes more than just research skills. You also need to ensure clarity, organization, and coherence in your work. Take a moment and read some informative essay examples you can find online. The best method to write an informative essay is to have a specific thesis statement which you can expand in the body paragraphs.
Your essay will need, at minimum, an introductory paragraph, a body, and a conclusion. Each body paragraph should follow the "C-E-E" formula: Claim + Evidence + Explanation. Use supporting details and your own thoughts to expand on the paragraph's topic or idea.
The last sentence of the opening paragraph will usually contain the point of the informative essay, also called the thesis statement. Generally, it is the most important sentence in the entire essay, as it sets forth the direction for the rest of the paper. ... Informative essays, sometimes called expository essays, can be used for many ...
An informative essay is a form of writing that informs the reader about a topic in an unbiased manner. The introduction section in this type of essay typically is the first paragraph of the paper and offers a brief overview of the paper's topic. It may also present a surprising fact, geared to hook the reader and encourage him to read the rest ...
An informative essay is also sometimes called an expository essay in the sense that it also aims to expose or display an information which will be beneficial for the reader. It does not present bias judgments nor favorable ideas. It does not also dwell in the concept of convincing readers to do things that are contrary to their will.
These essays are also called process essays. Cause and effect essays explain how one phenomenon or event caused another; how and why did the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand lead to the first world war? Problem-solution essays are also often said to be informative essays. At first glance, they lay out a particular problem and explain ...
It may be presented in the form of an essay, an article, a textbook, a biography, a nonfiction book, how-to guide, a report, and more. Also called explanatory or expository writing, informative writing comes down to writing about the facts, for the facts, with only the facts in mind. ... Informative writing can pack a punch by employing an ...
The narrative essay tells a story. It can also be called a "short story." Generally, the narrative essay is conversational in style and tells of a personal experience. It is most commonly written in the first person (uses I). This essay could tell of a single, life-shaping event, or simply a mundane daily experience.
Informative essays must be educational and objective. Follow a guide to structuring one, download a sample essay, or pick a topic from our list of examples. ... Understand the public transportation system to the point where you can blend in as a local. Also in line with safety, you may want to splurge on accommodations. You can stay alone in a ...
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays. Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and ...
The crucial point is to follow the sequence of events and make logical transitions between the essay parts. Consequently, each body paragraph must contain: A topic sentence that explains the paragraph's main point and connects it to the previous one. Information: facts, statistics, and thesis-supporting evidence. Mini-conclusion.
Brainstorm Ideas for Your Informative Essay. Brainstorming is an essential part of the writing process. It can help you generate ideas and discover a topic that interests you. It can also help you plan your ideas and organize your essay. Many students need help with knowing where to start when writing an essay. Brainstorming can help you get ...
informational essay. 2. Ask students if they can describe an informational essay, or if they've ever written one. Listen to response. Clarify or explain that the purpose of an informative essay, sometimes called an expository essay, is to provide factual information about a certain topic. It has to be a nonfictiontopic, such
An informational narrative is used when the writer is trying to inform others about a particular subject of which they may not be familiar. Informative essays can also be called an expository or explanatory essays. This kind of essay is aimed at presenting information in a clear and concise manner so the reader can learn about the subject matter.