Problems & Exercises
1.2 physical quantities and units.
The speed limit on some interstate highways is roughly 100 km/h. (a) What is this in meters per second? (b) How many miles per hour is this?
A car is traveling at a speed of 33 m/s 33 m/s size 12{"33"" m/s"} {} . (a) What is its speed in kilometers per hour? (b) Is it exceeding the 90 km/h 90 km/h size 12{"90"" km/h"} {} speed limit?
Show that 1 . 0 m/s = 3 . 6 km/h 1 . 0 m/s = 3 . 6 km/h size 12{1 "." 0`"m/s"=3 "." "6 km/h"} {} . Hint: Show the explicit steps involved in converting 1 . 0 m/s = 3 . 6 km/h. 1 . 0 m/s = 3 . 6 km/h. size 12{1 "." 0`"m/s"=3 "." "6 km/h"} {}
American football is played on a 100-yd-long field, excluding the end zones. How long is the field in meters? (Assume that 1 meter equals 3.281 feet.)
Soccer fields vary in size. A large soccer field is 115 m long and 85 m wide. What are its dimensions in feet and inches? (Assume that 1 meter equals 3.281 feet.)
What is the height in meters of a person who is 6 ft 1.0 in. tall? (Assume that 1 meter equals 39.37 in.)
Mount Everest, at 29,028 feet, is the tallest mountain on the Earth. What is its height in kilometers? (Assume that 1 kilometer equals 3,281 feet.)
The speed of sound is measured to be 342 m/s 342 m/s size 12{"342"" m/s"} {} on a certain day. What is this in km/h?
Tectonic plates are large segments of the Earth’s crust that move slowly. Suppose that one such plate has an average speed of 4.0 cm/year. (a) What distance does it move in 1 s at this speed? (b) What is its speed in kilometers per million years?
(a) Refer to Table 1.3 to determine the average distance between the Earth and the Sun. Then calculate the average speed of the Earth in its orbit in kilometers per second. (b) What is this in meters per second?

1.3 Accuracy, Precision, and Significant Figures
Express your answers to problems in this section to the correct number of significant figures and proper units.
Suppose that your bathroom scale reads your mass as 65 kg with a 3% uncertainty. What is the uncertainty in your mass (in kilograms)?
A good-quality measuring tape can be off by 0.50 cm over a distance of 20 m. What is its percent uncertainty?
(a) A car speedometer has a 5.0 % 5.0 % size 12{5.0%} {} uncertainty. What is the range of possible speeds when it reads 90 km/h 90 km/h size 12{"90"" km/h"} {} ? (b) Convert this range to miles per hour. 1 km = 0.6214 mi 1 km = 0.6214 mi size 12{"1 km" "=" "0.6214 mi"} {}
An infant’s pulse rate is measured to be 130 ± 5 130 ± 5 size 12{"130" +- 5} {} beats/min. What is the percent uncertainty in this measurement?
(a) Suppose that a person has an average heart rate of 72.0 beats/min. How many beats does he or she have in 2.0 y? (b) In 2.00 y? (c) In 2.000 y?
A can contains 375 mL of soda. How much is left after 308 mL is removed?
State how many significant figures are proper in the results of the following calculations: (a) 106 . 7 98 . 2 / 46 . 210 1 . 01 106 . 7 98 . 2 / 46 . 210 1 . 01 size 12{ left ("106" "." 7 right ) left ("98" "." 2 right )/ left ("46" "." "210" right ) left (1 "." "01" right )} {} (b) 18 . 7 2 18 . 7 2 size 12{ left ("18" "." 7 right ) rSup { size 8{2} } } {} (c) 1 . 60 × 10 − 19 3712 1 . 60 × 10 − 19 3712 size 12{ left (1 "." "60" times "10" rSup { size 8{ - "19"} } right ) left ("3712" right )} {} .
(a) How many significant figures are in the numbers 99 and 100? (b) If the uncertainty in each number is 1, what is the percent uncertainty in each? (c) Which is a more meaningful way to express the accuracy of these two numbers, significant figures or percent uncertainties?
(a) If your speedometer has an uncertainty of 2 . 0 km/h 2 . 0 km/h size 12{2 "." 0" km/h"} {} at a speed of 90 km/h 90 km/h size 12{"90"" km/h"} {} , what is the percent uncertainty? (b) If it has the same percent uncertainty when it reads 60 km/h 60 km/h size 12{"60"" km/h"} {} , what is the range of speeds you could be going?
(a) A person’s blood pressure is measured to be 120 ± 2 mm Hg 120 ± 2 mm Hg size 12{"120" +- 2" mm Hg"} {} . What is its percent uncertainty? (b) Assuming the same percent uncertainty, what is the uncertainty in a blood pressure measurement of 80 mm Hg 80 mm Hg size 12{"80"" mm Hg"} {} ?
A person measures his or her heart rate by counting the number of beats in 30 s 30 s size 12{"30"" s"} {} . If 40 ± 1 40 ± 1 size 12{"40" +- 1} {} beats are counted in 30 . 0 ± 0 . 5 s 30 . 0 ± 0 . 5 s size 12{"30" "." 0 +- 0 "." 5" s"} {} , what is the heart rate and its uncertainty in beats per minute?
What is the area of a circle 3 . 102 cm 3 . 102 cm size 12{3 "." "102"" cm"} {} in diameter?
If a marathon runner averages 9.5 mi/h, how long does it take him or her to run a 26.22-mi marathon?
A marathon runner completes a 42 . 188 -km 42 . 188 -km size 12{"42" "." "188""-km"} {} course in 2 h 2 h size 12{2" h"} {} , 30 min, and 12 s 12 s size 12{"12"" s"} {} . There is an uncertainty of 25 m 25 m size 12{"25"" m"} {} in the distance traveled and an uncertainty of 1 s in the elapsed time. (a) Calculate the percent uncertainty in the distance. (b) Calculate the uncertainty in the elapsed time. (c) What is the average speed in meters per second? (d) What is the uncertainty in the average speed?
The sides of a small rectangular box are measured to be 1 . 80 ± 0 . 01 cm 1 . 80 ± 0 . 01 cm size 12{1 "." "80" +- 0 "." "01"" cm"} {} , {} 2 . 05 ± 0 . 02 cm, and 3 . 1 ± 0 . 1 cm 2 . 05 ± 0 . 02 cm, and 3 . 1 ± 0 . 1 cm size 12{2 "." "05" +- 0 "." "02"" cm, and 3" "." 1 +- 0 "." "1 cm"} {} long. Calculate its volume and uncertainty in cubic centimeters.
When non-metric units were used in the United Kingdom, a unit of mass called the pound-mass (lbm) was employed, where 1 lbm = 0 . 4539 kg 1 lbm = 0 . 4539 kg size 12{1" lbm"=0 "." "4539"`"kg"} {} . (a) If there is an uncertainty of 0 . 0001 kg 0 . 0001 kg size 12{0 "." "0001"`"kg"} {} in the pound-mass unit, what is its percent uncertainty? (b) Based on that percent uncertainty, what mass in pound-mass has an uncertainty of 1 kg when converted to kilograms?
The length and width of a rectangular room are measured to be 3 . 955 ± 0 . 005 m 3 . 955 ± 0 . 005 m size 12{3 "." "955" +- 0 "." "005"" m"} {} and 3 . 050 ± 0 . 005 m 3 . 050 ± 0 . 005 m size 12{3 "." "050" +- 0 "." "005"" m"} {} . Calculate the area of the room and its uncertainty in square meters.
A car engine moves a piston with a circular cross section of 7 . 500 ± 0 . 002 cm 7 . 500 ± 0 . 002 cm size 12{7 "." "500" +- 0 "." "002"`"cm"} {} diameter a distance of 3 . 250 ± 0 . 001 cm 3 . 250 ± 0 . 001 cm size 12{3 "." "250" +- 0 "." "001"`"cm"} {} to compress the gas in the cylinder. (a) By what amount is the gas decreased in volume in cubic centimeters? (b) Find the uncertainty in this volume.
1.4 Approximation
How many heartbeats are there in a lifetime?
A generation is about one-third of a lifetime. Approximately how many generations have passed since the year 0 AD?
How many times longer than the mean life of an extremely unstable atomic nucleus is the lifetime of a human? (Hint: The lifetime of an unstable atomic nucleus is on the order of 10 − 22 s 10 − 22 s size 12{"10" rSup { size 8{ - "22"} } " s"} {} .)
Calculate the approximate number of atoms in a bacterium. Assume that the average mass of an atom in the bacterium is ten times the mass of a hydrogen atom. (Hint: The mass of a hydrogen atom is on the order of 10 − 27 kg 10 − 27 kg size 12{"10" rSup { size 8{ - "27"} } " kg"} {} and the mass of a bacterium is on the order of 10 − 15 kg. 10 − 15 kg. size 12{"10" rSup { size 8{ - "15"} } "kg"} {} )
Approximately how many atoms thick is a cell membrane, assuming all atoms there average about twice the size of a hydrogen atom?
(a) What fraction of Earth’s diameter is the greatest ocean depth? (b) The greatest mountain height?
(a) Calculate the number of cells in a hummingbird assuming the mass of an average cell is ten times the mass of a bacterium. (b) Making the same assumption, how many cells are there in a human?
Assuming one nerve impulse must end before another can begin, what is the maximum firing rate of a nerve in impulses per second?
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/college-physics/pages/1-introduction-to-science-and-the-realm-of-physics-physical-quantities-and-units
- Authors: Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: College Physics
- Publication date: Jun 21, 2012
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/college-physics/pages/1-introduction-to-science-and-the-realm-of-physics-physical-quantities-and-units
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/college-physics/pages/1-problems-exercises
© Mar 3, 2022 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.1: The Basics of Physics
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 14431

\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Introduction: Physics and Matter
Physics is a study of how the universe behaves.
learning objectives
- Apply physics to describe the function of daily life
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through space and time, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the study of nature in an attempt to understand how the universe behaves.
What is Physics? : Mr. Andersen explains the importance of physics as a science. History and virtual examples are used to give the discipline context.
Physics uses the scientific method to help uncover the basic principles governing light and matter, and to discover the implications of those laws. It assumes that there are rules by which the universe functions, and that those laws can be at least partially understood by humans. It is also commonly believed that those laws could be used to predict everything about the universe’s future if complete information was available about the present state of all light and matter.
Matter is generally considered to be anything that has mass and volume. Many concepts integral to the study of classical physics involve theories and laws that explain matter and its motion. The law of conservation of mass, for example, states that mass cannot be created or destroyed. Further experiments and calculations in physics, therefore, take this law into account when formulating hypotheses to try to explain natural phenomena.
Physics aims to describe the function of everything around us, from the movement of tiny charged particles to the motion of people, cars, and spaceships. In fact, almost everything around you can be described quite accurately by the laws of physics. Consider a smart phone; physics describes how electricity interacts with the various circuits inside the device. This knowledge helps engineers select the appropriate materials and circuit layout when building the smart phone. Next, consider a GPS system; physics describes the relationship between the speed of an object, the distance over which it travels, and the time it takes to travel that distance. When you use a GPS device in a vehicle, it utilizes these physics equations to determine the travel time from one location to another. The study of physics is capable of making significant contributions through advances in new technologies that arise from theoretical breakthroughs.
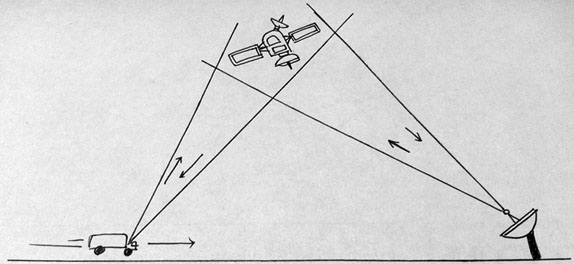
Global Positioning System : GPS calculates the speed of an object, the distance over which it travels, and the time it takes to travel that distance using equations based on the laws of physics.
Physics and Other Fields
Physics is the foundation of many disciplines and contributes directly to chemistry, astronomy, engineering, and most scientific fields.
- Explain why the study of physics is integral to the study of other sciences
Physics and Other Disciplines
Physics is the foundation of many important disciplines and contributes directly to others. Chemistry deals with the interactions of atoms and molecules, so it is rooted in atomic and molecular physics. Most branches of engineering are applied physics. In architecture, physics is at the heart of structural stability and is involved in acoustics, heating, lighting, and the cooling of buildings. Parts of geology rely heavily on physics, such as the radioactive dating of rocks, earthquake analysis, and heat transfer in the Earth. Some disciplines, such as biophysics and geophysics, are hybrids of physics and other disciplines.
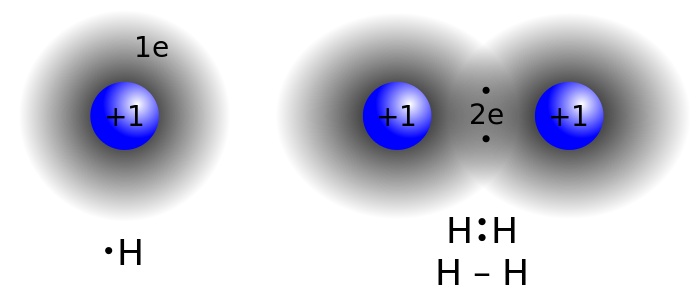
Physics in Chemistry : The study of matter and electricity in physics is fundamental towards the understanding of concepts in chemistry, such as the covalent bond.
Physics has many applications in the biological sciences. On the microscopic level, it helps describe the properties of cell walls and cell membranes. On the macroscopic level, it can explain the heat, work, and power associated with the human body. Physics is involved in medical diagnostics, such as X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and ultrasonic blood flow measurements. Medical therapy sometimes directly involves physics: cancer radiotherapy uses ionizing radiation, for instance. Physics can also explain sensory phenomena, such as how musical instruments make sound, how the eye detects color, and how lasers can transmit information.
The boundary between physics and the other sciences is not always clear. For instance, chemists study atoms and molecules, which are what matter is built from, and there are some scientists who would be equally willing to call themselves physical chemists or chemical physicists. It might seem that the distinction between physics and biology would be clearer, since physics seems to deal with inanimate objects. In fact, almost all physicists would agree that the basic laws of physics that apply to molecules in a test tube work equally well for the combination of molecules that constitutes a bacterium. What differentiates physics from biology is that many of the scientific theories that describe living things ultimately result from the fundamental laws of physics, but cannot be rigorously derived from physical principles.
It is not necessary to formally study all applications of physics. What is most useful is the knowledge of the basic laws of physics and skill in the analytical methods for applying them. The study of physics can also improve your problem-solving skills. Furthermore, physics has retained the most basic aspects of science, so it is used by all of the sciences. The study of physics makes other sciences easier to understand.
Models, Theories, and Laws
The terms model , theory , and law have exact meanings in relation to their usage in the study of physics.
- Define the terms model, theory, and law
Definition of Terms: Model, Theory, Law
In colloquial usage, the terms model , theory , and law are often used interchangeably or have different interpretations than they do in the sciences. In relation to the study of physics, however, each term has its own specific meaning.
The laws of nature are concise descriptions of the universe around us. They are not explanations, but human statements of the underlying rules that all natural processes follow. They are intrinsic to the universe; humans did not create them and we cannot change them. We can only discover and understand them. The cornerstone of discovering natural laws is observation; science must describe the universe as it is, not as we may imagine it to be. Laws can never be known with absolute certainty, because it is impossible to perform experiments to establish and confirm a law in every possible scenario without exception. Physicists operate under the assumption that all scientific laws and theories are valid until a counterexample is observed. If a good-quality, verifiable experiment contradicts a well-established law, then the law must be modified or overthrown completely.
A model is a representation of something that is often too difficult (or impossible) to display directly. While a model’s design is justified using experimental information, it is only accurate under limited situations. An example is the commonly used “planetary model” of the atom, in which electrons are pictured as orbiting the nucleus, analogous to the way planets orbit the Sun. We cannot observe electron orbits directly, but the mental image helps explain the observations we can make, such as the emission of light from hot gases. Physicists use models for a variety of purposes. For example, models can help physicists analyze a scenario and perform a calculation, or they can be used to represent a situation in the form of a computer simulation.
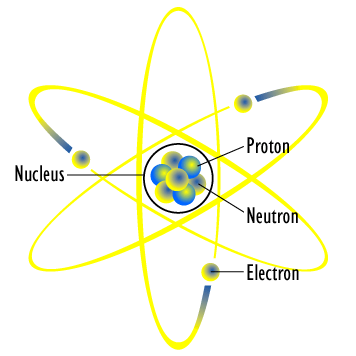
Planetary Model of an Atom : The planetary model of the atom in which electrons are pictured as orbiting the nucleus, analogous to the way planets orbit the Sun
A theory is an explanation for patterns in nature that is supported by scientific evidence and verified multiple times by various groups of researchers. Some theories include models to help visualize phenomena, whereas others do not . Newton’s theory of gravity, for example, does not require a model or mental image, because we can observe the objects directly with our own senses. The kinetic theory of gases, on the other hand, makes use of a model in which a gas is viewed as being composed of atoms and molecules. Atoms and molecules are too small to be observed directly with our senses—thus, we picture them mentally to understand what our instruments tell us about the behavior of gases.
A law uses concise language to describe a generalized pattern in nature that is supported by scientific evidence and repeated experiments. Often, a law can be expressed in the form of a single mathematical equation. Laws and theories are similar in that they are both scientific statements that result from a tested hypothesis and are supported by scientific evidence. However, the designation law is reserved for a concise and very general statement that describes phenomena in nature, such as the law that energy is conserved during any process, or Newton’s second law of motion, which relates force, mass, and acceleration by the simple equation \(F=ma\). A theory, in contrast, is a less concise statement of observed phenomena. For example, the Theory of Evolution and the Theory of Relativity cannot be expressed concisely enough to be considered a law. The biggest difference between a law and a theory is that a law is much more complex and dynamic, and a theory is more explanatory. A law describes a single observable point of fact, whereas a theory explains an entire group of related phenomena. And, whereas a law is a postulate that forms the foundation of the scientific method, a theory is the end result of that process.
- Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through space and time, along with related concepts such as energy and force.
- Matter is generally considered to be anything that has mass and volume.
- Scientific laws and theories express the general truths of nature and the body of knowledge they encompass. These laws of nature are rules that all natural processes appear to follow.
- Many scientific disciplines, such as biophysics, are hybrids of physics and other sciences.
- The study of physics encompasses all forms of matter and its motion in space and time.
- The application of physics is fundamental towards significant contributions in new technologies that arise from theoretical breakthroughs.
- Concepts in physics cannot be proven, they can only be supported or disproven through observation and experimentation.
- A model is an evidence-based representation of something that is either too difficult or impossible to display directly.
- A theory is an explanation for patterns in nature that is supported by scientific evidence and verified multiple times by various groups of researchers.
- A law uses concise language, often expressed as a mathematical equation, to describe a generalized pattern in nature that is supported by scientific evidence and repeated experiments.
- matter : The basic structural component of the universe. Matter usually has mass and volume.
- scientific method : A method of discovering knowledge about the natural world based in making falsifiable predictions (hypotheses), testing them empirically, and developing peer-reviewed theories that best explain the known data.
- application : the act of putting something into operation
- Model : A representation of something difficult or impossible to display directly
- Law : A concise description, usually in the form of a mathematical equation, used to describe a pattern in nature
- theory : An explanation for patterns in nature that is supported by scientific evidence and verified multiple times by various groups of researchers
LICENSES AND ATTRIBUTIONS
CC LICENSED CONTENT, SHARED PREVIOUSLY
- Curation and Revision. Provided by : Boundless.com. License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
CC LICENSED CONTENT, SPECIFIC ATTRIBUTION
- scientific method. Provided by : Wiktionary. Located at : http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/scientific_method . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Provided by : Light and Matter. Located at : http://lightandmatter.com/lma.pdf . License : CC BY: Attribution
- OpenStax College, College Physics. September 17, 2013. Provided by : OpenStax CNX. Located at : http://cnx.org/content/m42092/latest/?collection=col11406/1.7 . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Matter. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : http://en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Matter . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Physics. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : http://en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Physics . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- matter. Provided by : Wiktionary. Located at : en.wiktionary.org/wiki/matter . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- What is Physics?. Located at : http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=az5dZOVsoww . License : Public Domain: No Known Copyright . License Terms : Standard YouTube license
- Boundless. Provided by : Amazon Web Services. Located at : s3.amazonaws.com/figures.boundless.com/5078e0f6e4b04e6a3fb83a94/gps.jpg . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Boundless. Provided by : Boundless Learning. Located at : www.boundless.com//physics/definition/application . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Covalent bond. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/Covalent_bond . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Boundless. Provided by : Boundless Learning. Located at : www.boundless.com//physics/definition/law . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Boundless. Provided by : Boundless Learning. Located at : www.boundless.com//physics/definition/model . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- theory. Provided by : Wikipedia. Located at : en.Wikipedia.org/wiki/theory . License : CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Provided by : Wikimedia. Located at : http://upload.wikimedia.org/Wikipedia/commons/d/d8/Atom_diagram.png . License : CC BY: Attribution
- TPC and eLearning
- What's NEW at TPC?
- Read Watch Interact
- Practice Review Test
- Teacher-Tools
- Subscription Selection
- Seat Calculator
- Ad Free Account
- Edit Profile Settings
- Classes (Version 2)
- Student Progress Edit
- Task Properties
- Export Student Progress
- Task, Activities, and Scores
- Metric Conversions Questions
- Metric System Questions
- Metric Estimation Questions
- Significant Digits Questions
- Proportional Reasoning
- Acceleration
- Distance-Displacement
- Dots and Graphs
- Graph That Motion
- Match That Graph
- Name That Motion
- Motion Diagrams
- Pos'n Time Graphs Numerical
- Pos'n Time Graphs Conceptual
- Up And Down - Questions
- Balanced vs. Unbalanced Forces
- Change of State
- Force and Motion
- Mass and Weight
- Match That Free-Body Diagram
- Net Force (and Acceleration) Ranking Tasks
- Newton's Second Law
- Normal Force Card Sort
- Recognizing Forces
- Air Resistance and Skydiving
- Solve It! with Newton's Second Law
- Which One Doesn't Belong?
- Component Addition Questions
- Head-to-Tail Vector Addition
- Projectile Mathematics
- Trajectory - Angle Launched Projectiles
- Trajectory - Horizontally Launched Projectiles
- Vector Addition
- Vector Direction
- Which One Doesn't Belong? Projectile Motion
- Forces in 2-Dimensions
- Being Impulsive About Momentum
- Explosions - Law Breakers
- Hit and Stick Collisions - Law Breakers
- Case Studies: Impulse and Force
- Impulse-Momentum Change Table
- Keeping Track of Momentum - Hit and Stick
- Keeping Track of Momentum - Hit and Bounce
- What's Up (and Down) with KE and PE?
- Energy Conservation Questions
- Energy Dissipation Questions
- Energy Ranking Tasks
- LOL Charts (a.k.a., Energy Bar Charts)
- Match That Bar Chart
- Words and Charts Questions
- Name That Energy
- Stepping Up with PE and KE Questions
- Case Studies - Circular Motion
- Circular Logic
- Forces and Free-Body Diagrams in Circular Motion
- Gravitational Field Strength
- Universal Gravitation
- Angular Position and Displacement
- Linear and Angular Velocity
- Angular Acceleration
- Rotational Inertia
- Balanced vs. Unbalanced Torques
- Getting a Handle on Torque
- Torque-ing About Rotation
- Properties of Matter
- Fluid Pressure
- Buoyant Force
- Sinking, Floating, and Hanging
- Pascal's Principle
- Flow Velocity
- Bernoulli's Principle
- Balloon Interactions
- Charge and Charging
- Charge Interactions
- Charging by Induction
- Conductors and Insulators
- Coulombs Law
- Electric Field
- Electric Field Intensity
- Polarization
- Case Studies: Electric Power
- Know Your Potential
- Light Bulb Anatomy
- I = ∆V/R Equations as a Guide to Thinking
- Parallel Circuits - ∆V = I•R Calculations
- Resistance Ranking Tasks
- Series Circuits - ∆V = I•R Calculations
- Series vs. Parallel Circuits
- Equivalent Resistance
- Period and Frequency of a Pendulum
- Pendulum Motion: Velocity and Force
- Energy of a Pendulum
- Period and Frequency of a Mass on a Spring
- Horizontal Springs: Velocity and Force
- Vertical Springs: Velocity and Force
- Energy of a Mass on a Spring
- Decibel Scale
- Frequency and Period
- Closed-End Air Columns
- Name That Harmonic: Strings
- Rocking the Boat
- Wave Basics
- Matching Pairs: Wave Characteristics
- Wave Interference
- Waves - Case Studies
- Color Addition and Subtraction
- Color Filters
- If This, Then That: Color Subtraction
- Light Intensity
- Color Pigments
- Converging Lenses
- Curved Mirror Images
- Law of Reflection
- Refraction and Lenses
- Total Internal Reflection
- Who Can See Who?
- Formulas and Atom Counting
- Atomic Models
- Bond Polarity
- Entropy Questions
- Cell Voltage Questions
- Heat of Formation Questions
- Reduction Potential Questions
- Oxidation States Questions
- Measuring the Quantity of Heat
- Hess's Law
- Oxidation-Reduction Questions
- Galvanic Cells Questions
- Thermal Stoichiometry
- Molecular Polarity
- Quantum Mechanics
- Balancing Chemical Equations
- Bronsted-Lowry Model of Acids and Bases
- Classification of Matter
- Collision Model of Reaction Rates
- Density Ranking Tasks
- Dissociation Reactions
- Complete Electron Configurations
- Elemental Measures
- Enthalpy Change Questions
- Equilibrium Concept
- Equilibrium Constant Expression
- Equilibrium Calculations - Questions
- Equilibrium ICE Table
- Intermolecular Forces Questions
- Ionic Bonding
- Lewis Electron Dot Structures
- Limiting Reactants
- Line Spectra Questions
- Mass Stoichiometry
- Measurement and Numbers
- Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids
- Metric Estimations
- Metric System
- Molarity Ranking Tasks
- Mole Conversions
- Name That Element
- Names to Formulas
- Names to Formulas 2
- Nuclear Decay
- Particles, Words, and Formulas
- Periodic Trends
- Precipitation Reactions and Net Ionic Equations
- Pressure Concepts
- Pressure-Temperature Gas Law
- Pressure-Volume Gas Law
- Chemical Reaction Types
- Significant Digits and Measurement
- States Of Matter Exercise
- Stoichiometry Law Breakers
- Stoichiometry - Math Relationships
- Subatomic Particles
- Spontaneity and Driving Forces
- Gibbs Free Energy
- Volume-Temperature Gas Law
- Acid-Base Properties
- Energy and Chemical Reactions
- Chemical and Physical Properties
- Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory
- Writing Balanced Chemical Equations
- Mission CG1
- Mission CG10
- Mission CG2
- Mission CG3
- Mission CG4
- Mission CG5
- Mission CG6
- Mission CG7
- Mission CG8
- Mission CG9
- Mission EC1
- Mission EC10
- Mission EC11
- Mission EC12
- Mission EC2
- Mission EC3
- Mission EC4
- Mission EC5
- Mission EC6
- Mission EC7
- Mission EC8
- Mission EC9
- Mission RL1
- Mission RL2
- Mission RL3
- Mission RL4
- Mission RL5
- Mission RL6
- Mission KG7
- Mission RL8
- Mission KG9
- Mission RL10
- Mission RL11
- Mission RM1
- Mission RM2
- Mission RM3
- Mission RM4
- Mission RM5
- Mission RM6
- Mission RM8
- Mission RM10
- Mission LC1
- Mission RM11
- Mission LC2
- Mission LC3
- Mission LC4
- Mission LC5
- Mission LC6
- Mission LC8
- Mission SM1
- Mission SM2
- Mission SM3
- Mission SM4
- Mission SM5
- Mission SM6
- Mission SM8
- Mission SM10
- Mission KG10
- Mission SM11
- Mission KG2
- Mission KG3
- Mission KG4
- Mission KG5
- Mission KG6
- Mission KG8
- Mission KG11
- Mission F2D1
- Mission F2D2
- Mission F2D3
- Mission F2D4
- Mission F2D5
- Mission F2D6
- Mission KC1
- Mission KC2
- Mission KC3
- Mission KC4
- Mission KC5
- Mission KC6
- Mission KC7
- Mission KC8
- Mission AAA
- Mission SM9
- Mission LC7
- Mission LC9
- Mission NL1
- Mission NL2
- Mission NL3
- Mission NL4
- Mission NL5
- Mission NL6
- Mission NL7
- Mission NL8
- Mission NL9
- Mission NL10
- Mission NL11
- Mission NL12
- Mission MC1
- Mission MC10
- Mission MC2
- Mission MC3
- Mission MC4
- Mission MC5
- Mission MC6
- Mission MC7
- Mission MC8
- Mission MC9
- Mission RM7
- Mission RM9
- Mission RL7
- Mission RL9
- Mission SM7
- Mission SE1
- Mission SE10
- Mission SE11
- Mission SE12
- Mission SE2
- Mission SE3
- Mission SE4
- Mission SE5
- Mission SE6
- Mission SE7
- Mission SE8
- Mission SE9
- Mission VP1
- Mission VP10
- Mission VP2
- Mission VP3
- Mission VP4
- Mission VP5
- Mission VP6
- Mission VP7
- Mission VP8
- Mission VP9
- Mission WM1
- Mission WM2
- Mission WM3
- Mission WM4
- Mission WM5
- Mission WM6
- Mission WM7
- Mission WM8
- Mission WE1
- Mission WE10
- Mission WE2
- Mission WE3
- Mission WE4
- Mission WE5
- Mission WE6
- Mission WE7
- Mission WE8
- Mission WE9
- Vector Walk Interactive
- Name That Motion Interactive
- Kinematic Graphing 1 Concept Checker
- Kinematic Graphing 2 Concept Checker
- Graph That Motion Interactive
- Two Stage Rocket Interactive
- Rocket Sled Concept Checker
- Force Concept Checker
- Free-Body Diagrams Concept Checker
- Free-Body Diagrams The Sequel Concept Checker
- Skydiving Concept Checker
- Elevator Ride Concept Checker
- Vector Addition Concept Checker
- Vector Walk in Two Dimensions Interactive
- Name That Vector Interactive
- River Boat Simulator Concept Checker
- Projectile Simulator 2 Concept Checker
- Projectile Simulator 3 Concept Checker
- Hit the Target Interactive
- Turd the Target 1 Interactive
- Turd the Target 2 Interactive
- Balance It Interactive
- Go For The Gold Interactive
- Egg Drop Concept Checker
- Fish Catch Concept Checker
- Exploding Carts Concept Checker
- Collision Carts - Inelastic Collisions Concept Checker
- Its All Uphill Concept Checker
- Stopping Distance Concept Checker
- Chart That Motion Interactive
- Roller Coaster Model Concept Checker
- Uniform Circular Motion Concept Checker
- Horizontal Circle Simulation Concept Checker
- Vertical Circle Simulation Concept Checker
- Race Track Concept Checker
- Gravitational Fields Concept Checker
- Orbital Motion Concept Checker
- Angular Acceleration Concept Checker
- Balance Beam Concept Checker
- Torque Balancer Concept Checker
- Aluminum Can Polarization Concept Checker
- Charging Concept Checker
- Name That Charge Simulation
- Coulomb's Law Concept Checker
- Electric Field Lines Concept Checker
- Put the Charge in the Goal Concept Checker
- Circuit Builder Concept Checker (Series Circuits)
- Circuit Builder Concept Checker (Parallel Circuits)
- Circuit Builder Concept Checker (∆V-I-R)
- Circuit Builder Concept Checker (Voltage Drop)
- Equivalent Resistance Interactive
- Pendulum Motion Simulation Concept Checker
- Mass on a Spring Simulation Concept Checker
- Particle Wave Simulation Concept Checker
- Boundary Behavior Simulation Concept Checker
- Slinky Wave Simulator Concept Checker
- Simple Wave Simulator Concept Checker
- Wave Addition Simulation Concept Checker
- Standing Wave Maker Simulation Concept Checker
- Color Addition Concept Checker
- Painting With CMY Concept Checker
- Stage Lighting Concept Checker
- Filtering Away Concept Checker
- InterferencePatterns Concept Checker
- Young's Experiment Interactive
- Plane Mirror Images Interactive
- Who Can See Who Concept Checker
- Optics Bench (Mirrors) Concept Checker
- Name That Image (Mirrors) Interactive
- Refraction Concept Checker
- Total Internal Reflection Concept Checker
- Optics Bench (Lenses) Concept Checker
- Kinematics Preview
- Velocity Time Graphs Preview
- Moving Cart on an Inclined Plane Preview
- Stopping Distance Preview
- Cart, Bricks, and Bands Preview
- Fan Cart Study Preview
- Friction Preview
- Coffee Filter Lab Preview
- Friction, Speed, and Stopping Distance Preview
- Up and Down Preview
- Projectile Range Preview
- Ballistics Preview
- Juggling Preview
- Marshmallow Launcher Preview
- Air Bag Safety Preview
- Colliding Carts Preview
- Collisions Preview
- Engineering Safer Helmets Preview
- Push the Plow Preview
- Its All Uphill Preview
- Energy on an Incline Preview
- Modeling Roller Coasters Preview
- Hot Wheels Stopping Distance Preview
- Ball Bat Collision Preview
- Energy in Fields Preview
- Weightlessness Training Preview
- Roller Coaster Loops Preview
- Universal Gravitation Preview
- Keplers Laws Preview
- Kepler's Third Law Preview
- Charge Interactions Preview
- Sticky Tape Experiments Preview
- Wire Gauge Preview
- Voltage, Current, and Resistance Preview
- Light Bulb Resistance Preview
- Series and Parallel Circuits Preview
- Thermal Equilibrium Preview
- Linear Expansion Preview
- Heating Curves Preview
- Electricity and Magnetism - Part 1 Preview
- Electricity and Magnetism - Part 2 Preview
- Vibrating Mass on a Spring Preview
- Period of a Pendulum Preview
- Wave Speed Preview
- Slinky-Experiments Preview
- Standing Waves in a Rope Preview
- Sound as a Pressure Wave Preview
- DeciBel Scale Preview
- DeciBels, Phons, and Sones Preview
- Sound of Music Preview
- Shedding Light on Light Bulbs Preview
- Models of Light Preview
- Electromagnetic Radiation Preview
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Preview
- EM Wave Communication Preview
- Digitized Data Preview
- Light Intensity Preview
- Concave Mirrors Preview
- Object Image Relations Preview
- Snells Law Preview
- Reflection vs. Transmission Preview
- Magnification Lab Preview
- Reactivity Preview
- Ions and the Periodic Table Preview
- Periodic Trends Preview
- Intermolecular Forces Preview
- Melting Points and Boiling Points Preview
- Reaction Rates Preview
- Ammonia Factory Preview
- Stoichiometry Preview
- Nuclear Chemistry Preview
- Gaining Teacher Access
- Tasks and Classes
- Tasks - Classic
- Subscription
- Subscription Locator
- 1-D Kinematics
- Newton's Laws
- Vectors - Motion and Forces in Two Dimensions
- Momentum and Its Conservation
- Work and Energy
- Circular Motion and Satellite Motion
- Thermal Physics
- Static Electricity
- Electric Circuits
- Vibrations and Waves
- Sound Waves and Music
- Light and Color
- Reflection and Mirrors
- About the Physics Interactives
- Task Tracker
- Usage Policy
- Newtons Laws
- Vectors and Projectiles
- Forces in 2D
- Momentum and Collisions
- Circular and Satellite Motion
- Balance and Rotation
- Electromagnetism
- Waves and Sound
- Atomic Physics
- Forces in Two Dimensions
- Work, Energy, and Power
- Circular Motion and Gravitation
- Sound Waves
- 1-Dimensional Kinematics
- Circular, Satellite, and Rotational Motion
- Einstein's Theory of Special Relativity
- Waves, Sound and Light
- QuickTime Movies
- About the Concept Builders
- Pricing For Schools
- Directions for Version 2
- Measurement and Units
- Relationships and Graphs
- Rotation and Balance
- Vibrational Motion
- Reflection and Refraction
- Teacher Accounts
- Task Tracker Directions
- Kinematic Concepts
- Kinematic Graphing
- Wave Motion
- Sound and Music
- About CalcPad
- 1D Kinematics
- Vectors and Forces in 2D
- Simple Harmonic Motion
- Rotational Kinematics
- Rotation and Torque
- Rotational Dynamics
- Electric Fields, Potential, and Capacitance
- Transient RC Circuits
- Light Waves
- Units and Measurement
- Stoichiometry
- Molarity and Solutions
- Thermal Chemistry
- Acids and Bases
- Kinetics and Equilibrium
- Solution Equilibria
- Oxidation-Reduction
- Nuclear Chemistry
- Newton's Laws of Motion
- Work and Energy Packet
- Static Electricity Review
- NGSS Alignments
- 1D-Kinematics
- Projectiles
- Circular Motion
- Magnetism and Electromagnetism
- Graphing Practice
- About the ACT
- ACT Preparation
- For Teachers
- Other Resources
- Solutions Guide
- Solutions Guide Digital Download
- Motion in One Dimension
- Work, Energy and Power
- Algebra Based Physics
- Other Tools
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Purchasing the Download
- Purchasing the CD
- Purchasing the Digital Download
- About the NGSS Corner
- NGSS Search
- Force and Motion DCIs - High School
- Energy DCIs - High School
- Wave Applications DCIs - High School
- Force and Motion PEs - High School
- Energy PEs - High School
- Wave Applications PEs - High School
- Crosscutting Concepts
- The Practices
- Physics Topics
- NGSS Corner: Activity List
- NGSS Corner: Infographics
- About the Toolkits
- Position-Velocity-Acceleration
- Position-Time Graphs
- Velocity-Time Graphs
- Newton's First Law
- Newton's Second Law
- Newton's Third Law
- Terminal Velocity
- Projectile Motion
- Forces in 2 Dimensions
- Impulse and Momentum Change
- Momentum Conservation
- Work-Energy Fundamentals
- Work-Energy Relationship
- Roller Coaster Physics
- Satellite Motion
- Electric Fields
- Circuit Concepts
- Series Circuits
- Parallel Circuits
- Describing-Waves
- Wave Behavior Toolkit
- Standing Wave Patterns
- Resonating Air Columns
- Wave Model of Light
- Plane Mirrors
- Curved Mirrors
- Teacher Guide
- Using Lab Notebooks
- Current Electricity
- Light Waves and Color
- Reflection and Ray Model of Light
- Refraction and Ray Model of Light
- Classes (Legacy Version)
- Teacher Resources
- Subscriptions

- Newton's Laws
- Einstein's Theory of Special Relativity
- About Concept Checkers
- School Pricing
- Newton's Laws of Motion
- Newton's First Law
- Newton's Third Law
- Sample Problems and Solutions
- Kinematic Equations Introduction
- Solving Problems with Kinematic Equations
- Kinematic Equations and Free Fall
- Kinematic Equations and Kinematic Graphs

Check Your Understanding
Answer: d = 1720 m
Answer: a = 8.10 m/s/s
Answers: d = 33.1 m and v f = 25.5 m/s
Answers: a = 11.2 m/s/s and d = 79.8 m
Answer: t = 1.29 s
Answers: a = 243 m/s/s
Answer: a = 0.712 m/s/s
Answer: d = 704 m
Answer: d = 28.6 m
Answer: v i = 7.17 m/s
Answer: v i = 5.03 m/s and hang time = 1.03 s (except for in sports commericals)
Answer: a = 1.62*10 5 m/s/s
Answer: d = 48.0 m
Answer: t = 8.69 s
Answer: a = -1.08*10^6 m/s/s
Answer: d = -57.0 m (57.0 meters deep)
Answer: v i = 47.6 m/s
Answer: a = 2.86 m/s/s and t = 30. 8 s
Answer: a = 15.8 m/s/s
Answer: v i = 94.4 mi/hr
Solutions to Above Problems
d = (0 m/s)*(32.8 s)+ 0.5*(3.20 m/s 2 )*(32.8 s) 2
Return to Problem 1
110 m = (0 m/s)*(5.21 s)+ 0.5*(a)*(5.21 s) 2
110 m = (13.57 s 2 )*a
a = (110 m)/(13.57 s 2 )
a = 8.10 m/ s 2
Return to Problem 2
d = (0 m/s)*(2.60 s)+ 0.5*(-9.8 m/s 2 )*(2.60 s) 2
d = -33.1 m (- indicates direction)
v f = v i + a*t
v f = 0 + (-9.8 m/s 2 )*(2.60 s)
v f = -25.5 m/s (- indicates direction)
Return to Problem 3
a = (46.1 m/s - 18.5 m/s)/(2.47 s)
a = 11.2 m/s 2
d = v i *t + 0.5*a*t 2
d = (18.5 m/s)*(2.47 s)+ 0.5*(11.2 m/s 2 )*(2.47 s) 2
d = 45.7 m + 34.1 m
(Note: the d can also be calculated using the equation v f 2 = v i 2 + 2*a*d)
Return to Problem 4
-1.40 m = (0 m/s)*(t)+ 0.5*(-1.67 m/s 2 )*(t) 2
-1.40 m = 0+ (-0.835 m/s 2 )*(t) 2
(-1.40 m)/(-0.835 m/s 2 ) = t 2
1.68 s 2 = t 2
Return to Problem 5
a = (444 m/s - 0 m/s)/(1.83 s)
a = 243 m/s 2
d = (0 m/s)*(1.83 s)+ 0.5*(243 m/s 2 )*(1.83 s) 2
d = 0 m + 406 m
Return to Problem 6
(7.10 m/s) 2 = (0 m/s) 2 + 2*(a)*(35.4 m)
50.4 m 2 /s 2 = (0 m/s) 2 + (70.8 m)*a
(50.4 m 2 /s 2 )/(70.8 m) = a
a = 0.712 m/s 2
Return to Problem 7
(65 m/s) 2 = (0 m/s) 2 + 2*(3 m/s 2 )*d
4225 m 2 /s 2 = (0 m/s) 2 + (6 m/s 2 )*d
(4225 m 2 /s 2 )/(6 m/s 2 ) = d
Return to Problem 8
d = (22.4 m/s + 0 m/s)/2 *2.55 s
d = (11.2 m/s)*2.55 s
Return to Problem 9
(0 m/s) 2 = v i 2 + 2*(-9.8 m/s 2 )*(2.62 m)
0 m 2 /s 2 = v i 2 - 51.35 m 2 /s 2
51.35 m 2 /s 2 = v i 2
v i = 7.17 m/s
Return to Problem 10
(0 m/s) 2 = v i 2 + 2*(-9.8 m/s 2 )*(1.29 m)
0 m 2 /s 2 = v i 2 - 25.28 m 2 /s 2
25.28 m 2 /s 2 = v i 2
v i = 5.03 m/s
To find hang time, find the time to the peak and then double it.
0 m/s = 5.03 m/s + (-9.8 m/s 2 )*t up
-5.03 m/s = (-9.8 m/s 2 )*t up
(-5.03 m/s)/(-9.8 m/s 2 ) = t up
t up = 0.513 s
hang time = 1.03 s
Return to Problem 11
(521 m/s) 2 = (0 m/s) 2 + 2*(a)*(0.840 m)
271441 m 2 /s 2 = (0 m/s) 2 + (1.68 m)*a
(271441 m 2 /s 2 )/(1.68 m) = a
a = 1.62*10 5 m /s 2
Return to Problem 12
- (NOTE: the time required to move to the peak of the trajectory is one-half the total hang time - 3.125 s.)
First use: v f = v i + a*t
0 m/s = v i + (-9.8 m/s 2 )*(3.13 s)
0 m/s = v i - 30.7 m/s
v i = 30.7 m/s (30.674 m/s)
Now use: v f 2 = v i 2 + 2*a*d
(0 m/s) 2 = (30.7 m/s) 2 + 2*(-9.8 m/s 2 )*(d)
0 m 2 /s 2 = (940 m 2 /s 2 ) + (-19.6 m/s 2 )*d
-940 m 2 /s 2 = (-19.6 m/s 2 )*d
(-940 m 2 /s 2 )/(-19.6 m/s 2 ) = d
Return to Problem 13
-370 m = (0 m/s)*(t)+ 0.5*(-9.8 m/s 2 )*(t) 2
-370 m = 0+ (-4.9 m/s 2 )*(t) 2
(-370 m)/(-4.9 m/s 2 ) = t 2
75.5 s 2 = t 2
Return to Problem 14
(0 m/s) 2 = (367 m/s) 2 + 2*(a)*(0.0621 m)
0 m 2 /s 2 = (134689 m 2 /s 2 ) + (0.1242 m)*a
-134689 m 2 /s 2 = (0.1242 m)*a
(-134689 m 2 /s 2 )/(0.1242 m) = a
a = -1.08*10 6 m /s 2
(The - sign indicates that the bullet slowed down.)
Return to Problem 15
d = (0 m/s)*(3.41 s)+ 0.5*(-9.8 m/s 2 )*(3.41 s) 2
d = 0 m+ 0.5*(-9.8 m/s 2 )*(11.63 s 2 )
d = -57.0 m
(NOTE: the - sign indicates direction)
Return to Problem 16
(0 m/s) 2 = v i 2 + 2*(- 3.90 m/s 2 )*(290 m)
0 m 2 /s 2 = v i 2 - 2262 m 2 /s 2
2262 m 2 /s 2 = v i 2
v i = 47.6 m /s
Return to Problem 17
( 88.3 m/s) 2 = (0 m/s) 2 + 2*(a)*(1365 m)
7797 m 2 /s 2 = (0 m 2 /s 2 ) + (2730 m)*a
7797 m 2 /s 2 = (2730 m)*a
(7797 m 2 /s 2 )/(2730 m) = a
a = 2.86 m/s 2
88.3 m/s = 0 m/s + (2.86 m/s 2 )*t
(88.3 m/s)/(2.86 m/s 2 ) = t
t = 30. 8 s
Return to Problem 18
( 112 m/s) 2 = (0 m/s) 2 + 2*(a)*(398 m)
12544 m 2 /s 2 = 0 m 2 /s 2 + (796 m)*a
12544 m 2 /s 2 = (796 m)*a
(12544 m 2 /s 2 )/(796 m) = a
a = 15.8 m/s 2
Return to Problem 19
v f 2 = v i 2 + 2*a*d
(0 m/s) 2 = v i 2 + 2*(-9.8 m/s 2 )*(91.5 m)
0 m 2 /s 2 = v i 2 - 1793 m 2 /s 2
1793 m 2 /s 2 = v i 2
v i = 42.3 m/s
Now convert from m/s to mi/hr:
v i = 42.3 m/s * (2.23 mi/hr)/(1 m/s)
v i = 94.4 mi/hr
Return to Problem 20

25+ Most Important Physics Topics For Students
“Physics: the mysterious subject for students.”
It is great to make a command on basics first if you want to master that subject. It is the scenario with every field of study. Someone who wants to study physics must clear his/her basic concepts and be familiar with its topics like kinetic energy, potential energy, statistical mechanics, etc.
“Curiosity is the road that leads you to learn physics.”
In this blog, we will tell you what physics is and some important physics topics that will help in your daily life. We will tell you what physics is and how you can understand it.
Physics students learn about important physics topics by reading this blog. So, hang on and know everything about physics!
Get experts help to get top-notch Physics help online that will help you to improve your grades on your assignment.
What Is Physics?
Table of Contents
When we look at the things around us, many questions are in our minds. Physics gives the answers to all these questions. You all must have heard about chemistry and biology. There are a lot of applications of physics with different aspects of nature.

Chemistry tells us about the results of things, and biology studies the processes of real life. But only physics tells us how things work. And if you need chemistry assignment help , you can contact our experts.
For example: As you look at a car running on the road, the question comes to your mind how does this car run on the road, how does its engine work, and how does a small brake pedal stop the entire car? The answer to all these questions is physics. Also, angular momentum is part of physics.
Physics tells us how things work. Many physics topics help us to understand the concept of nature and the universe. From the galaxy to the small atom, we can understand all these through physics.
The term physics is derived from the Greek word PHUSIKE, which means nature and its study. Energy, force, light, and time are all very basic concepts that we study in physics.
What Are The Topics Of Basic Physics?
These are the following topics of basic physics, and it is such as;
Subject Matter Topics for Introductory Physics
The following are the subject matter topics for introductory physics. It is also the best Physics topics for College students.
Reasons: Why do students choose to study physics in their higher education?
A physics degree helps you explore the world in every aspect- from the galaxy and the small atom with electronic structure. It equips you with techniques that help you to solve complex problems. It lets you know about some beautiful things and the plain ugly truth that rule our world. In reality, analyzing physics provides you with a deep knowledge of how the world works.
With the help of physics knowledge, many students want to pursue it by taking a postgraduate course related to it. It describes the various physics mysteries.
Five reasons to study physics at college-
- Experimental Physics encourages you to know the world around you and answer your curiosity.
- Analyzing physics improves your problem-solving and critical-thinking skills.
- Versatility is the essence of physicists, which opens a broad range of future careers.
- Physics is applied everywhere and gives you a chance to work internationally.
- Physics encourages technological progress, influencing society, the economy, and the environment.
List Of Important School Physics Topics
- History of quantum mechanics
- Newton’s Laws Of Motion
- Vectors And Projectiles
- Work And Energy
- Circular Motion And Gravitation
Electric Circuits
Thermal physics.
- Vibrations And Waves
- Refraction And Lenses
There are many branches of Physics, one of which is named Mechanics, and Mechanics has three branches, one of which is named Kinematics. Kinematics is one of the most important physics topics.
Kinematics means describing the motion of an object. In kinematics, we only study the object’s motion, why that object, and who brings it into action is not related to kinematics.
Kinematics also has four parameters: velocity, displacement, acceleration, and time. With the help of these four parameters, we can describe motion in kinematics. For any assignment or homework above the kinematics subject, you can take help from our experts.

Newton’s Laws of Motion
Newton’s Law is One of the Most Important Physics Topics. Newton’s Law of Motion consists of three laws, based on which all things related to motion can be known. Newton’s law of motion consists of three laws. From these laws, we can know all things related to motion.
The first law of Newton’s law states Uniform Motion and is also called the Law of inertia. In the second Newton’s Law, the force is said to be, which is directly proportional to the square of acceleration. And in the third Newton’s law, it is said that every action has an equal and opposite reaction.
These three newton’s law of motion is a very important part of physics topics. If you are studying physics, then definitely read this topic, if any problem arises, you can take help related to physics assignments and homework from our experts.
Vectors and Projectiles
Vectors and Projectiles are one of the third most important physics topics. Vectors and projectiles both have different meanings, but they are related to each other, only then they are considered to be the same topic.
Arrows represent vectors. The length of the Arrow is Proportional to the Magnitude, and the Direction of the Arrow is to be the Direction of the Vector that defines the vector. And projectile means that after throwing any object, it goes down due to gravity.
This is a very interesting topic, if you are a student of physics, then you must read this topic, and if you need help with any assignment or homework related to it, then you can take it from our experts.
Work and Energy
Work and energy are the two words that we often use in everyday life, but this is a very important physics topic. Work and energy have different meanings in physics.
Work means that energy is transferred by force, and energy means the ability to work. Each other’s words are fulfilling the meaning of these two. It is a very interesting physics topic, on top of which you can also write many assignments.
Circular Motion and Gravitation
Circular Motion and Gravitation are very interesting physics topics. It is said that forces can be used in circular motion and gravitation.
Circular motion means when a body moves in a circular path at a content speed and constant direction. And gravitation means that if we throw an object upwards, that object will go back to the top of the force according to the Cause of Gravity.
Electric circuits are one of the physics topics that tell us in detail about electric circuits. Both positive and negative are electric field circuits. This is explained by what works and how they work.
Electric circuits refer to the positive current coming out of a cell and generator with a wire connected to the negative circuit with the help of a wire. This is a very interesting chapter for physics students and can also offer many models and assignments on this topic.
Thermal physics is also a very important part of physics topics. Thermal physics is a topic that exposes students to many new things.
The study of thermal physics is done by heat. Heat energy and thermal energies are the motions and vibrations of molecules in terms of the energy activity of any substance or system. If there are more molecules in it, the same energy will be found in it. This is a very interesting topic for students, and many assignments can be made on it.
Vibrations and Waves
Vibrations and Waves On hearing this word, your mind must have heard thoughts related to the sound. But vibrations and waves are also part of physics topics. Vibrations and waves are very important in physics. Also, know How do convex mirrors impact your reflection?
Vibrations mean that if we shake with a big pay force, then that body keeps vibrating for some time due to that force, that vibration is called vibration. A wave can be described as a disturbance that travels from one medium to another through a medium. They are both from advance quantum physics , and students can make many models and assignments on them to get the aim of physics.

Refraction and Lenses
Refraction and lenses are some of the most interesting and important physics topics. All this topic is based on refraction and lenses. Students need to know how light lanes affect refraction through their theoretical physicist.
We can determine whether the light will reflect or refract by placing the ray of light on the lens in the refraction and lenses. It is also one of the interesting topics for the students, and with the help of this topic, students can also make many physics assignments.
Bonus point: list of interesting topics for a physics research project-
Here we mention some physics research topics that you can take and prepare a project on it-
- Nanoscience and Nanotechnology
- Optical Physics and Quantum Information Science
- Astrophysics, Fusion, and Plasma Physics
- Create a project on physics history
- Climate-related topic
- Linear motion.
- Circular and Rotational Motion.
- Interactions and Force.
- Motion in Two-Dimensions.
Physics topics for assignment
Follow the below-given physics topics list for the assignment.
- Unit dimensions and Error.
- Conservation of Momentum.
- Laws of Motion.
- Circular Motion.
- Motion in two dimensions.
- Work power and energy.
What is the best topic for physics project?
The best topic for the physics project for science and engineering practices: analyzing and s below.
Physics Topics Grade 11
Following are the topics in physics with their chapter name.
Physics topics for Class 12
Following are the physics topics are given below for the 12th grade.
Which topic is best for research in physics?
Follow the below-given points to know the physics topics for research.
- Optical Physics and Quantum Information Science.
- Astrophysics, Fusion, and Plasma Physics.
- Microfluidics and Microsystems.
- Nanoscience and Nanotechnology.
- Condensed Matter and Materials Physics.
- Energy Systems.
- Biophysics.
Interesting topics for physics presentation
Best physics topics on mcat.
These are the following best physics topics for MCAT.
- Electrostatics.
- Atomic and Nuclear Phenomena.
- Kinematics.
- Light and Optics.
- Thermodynamics.
How is physics used in daily life?
Physics captures our daily life. It explains the motion, forces, and internal energy behind ordinary works. For example, various actions like driving a car, walking, or using a phone call include advances in physics.
Let’s understand it through examples-
1. Example of heat
Heat is a kind of energy that carries from a warm object to a cold object. For example, when you use the stove for cooking, the flame transfers the heat to the utensil put on top of it. As a result, food gets heat from utensils. Physical optics must account for the more subtle properties of visible light in its waveform.
2. Example of a ballpoint pen
The use of a ballpoint pen is inevitable whether you are in school or at the workplace. If physics is not there, then you are not able to write on paper. The physics topics of gravity come when we talk about writing through a ballpoint pen.
As you press the pen on the paper to write, the ball turns, or gravity pushes the ink down on the ball top, from where it is transferred to the paper.
Useful point for students-
Job opportunities after studying physics-
A physics degree opens the door to various post for students-
- Academic researcher
- Acoustic consultant
- Clinical scientist, medical physics
- Geophysicist
- Higher education lecturer
- Metallurgist
- Meteorologist
- Nanotechnologist
- Radiation protection practitioner
- Research scientist (physical sciences)
- Secondary school teacher
- Sound engineer
- Technical author
What are the 5 laws of physics?
These are the 5 laws of physics, it is given below.
- Pascal’s Law
- Newton’s Laws
- Coulomb’s Law
- Stefan’s Law
- Avagadro’s Law
Quick Links
- A Brief Knowledge Of Kinematics Physics Equations
- The Definitive Guide On What Is Cartesian Equation
In this blog, we have explained what Physics means and which important Physics topics are there, which students can study with great interest. These all are 20th century physics topics. Moreover, many such physics topics have been told about which students can make their physics assignments and research projects. Moreover, if you need help with physics assignments, our experts offer Physics assignment help or physics homework help online free at very low prices.
Who is the father of physics?
The title “father of physics” has not been assigned to a particular person. Galileo Galilei, Sir Isaac, Albert Einstein, and Newton have all been considered the father of physics in western cultures.
What are the physics concepts everyone should know?
1. Classical mechanics (the laws of motion) 2. Electromagnetism 3. Relativity 4. Thermodynamics
What are the three main topics of physics?
The three main topics of physics are given below. Circular Motion (one-dimensional motion, two-dimensional motion, random motion, Harmonic motion) and Gravitation. Electric Circuits. Refraction and Lenses.
Which topic is hard in physics?
The hardest topic of physics is Quantum physics, pressure, and energy, work, etc.
Similar Articles

How To Do Homework Fast – 11 Tips To Do Homework Fast
Homework is one of the most important parts that have to be done by students. It has been around for…

How to Write an Assignment Introduction – 6 Best Tips
In essence, the writing tasks in academic tenure students are an integral part of any curriculum. Whether in high school,…
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
StudyMonkey
Your personal ai physics tutor.
Learn Smarter, Not Harder with Physics AI
Introducing StudyMonkey, your AI-powered Physics tutor .
StudyMonkey AI can tutor complex Physics homework questions, enhance your essay writing and assess your work—all in seconds.
No more long all-nighters
24/7 solutions to Physics questions you're stumped on and essays you procrastinated on.
No more stress and anxiety
Get all your Physics assignments done with helpful answers in 10 seconds or less.
No more asking friends for Physics help
StudyMonkey is your new smart bestie that will never ghost you.
No more staying after school
AI Physics tutoring is available 24/7, on-demand when you need it most.
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force.
AI Tutor for any subject
American college testing (act), anthropology, advanced placement exams (ap exams), arabic language, archaeology, biochemistry, chartered financial analyst (cfa) exam, communications, computer science, certified public accountant (cpa) exam, cultural studies, cyber security, dental admission test (dat), discrete mathematics, earth science, elementary school, entrepreneurship, environmental science, farsi (persian) language, fundamentals of engineering (fe) exam, gender studies, graduate management admission test (gmat), graduate record examination (gre), greek language, hebrew language, high school entrance exam, high school, human geography, human resources, international english language testing system (ielts), information technology, international relations, independent school entrance exam (isee), linear algebra, linguistics, law school admission test (lsat), machine learning, master's degree, medical college admission test (mcat), meteorology, microbiology, middle school, national council licensure examination (nclex), national merit scholarship qualifying test (nmsqt), number theory, organic chemistry, project management professional (pmp), political science, portuguese language, probability, project management, preliminary sat (psat), public policy, public relations, russian language, scholastic assessment test (sat), social sciences, secondary school admission test (ssat), sustainability, swahili language, test of english as a foreign language (toefl), trigonometry, turkish language, united states medical licensing examination (usmle), web development, step-by-step guidance 24/7.
Receive step-by-step guidance & homework help for any homework problem & any subject 24/7
Ask any Physics question
StudyMonkey supports every subject and every level of education from 1st grade to masters level.

Get an answer
StudyMonkey will give you an answer in seconds—multiple choice questions, short answers, and even an essays are supported!
Review your history
See your past questions and answers so you can review for tests and improve your grades.
It's not cheating...
You're just learning smarter than everyone else
How Can StudyMonkey Help You?
Hear from our happy students.
"The AI tutor is available 24/7, making it a convenient and accessible resource for students who need help with their homework at any time."
"Overall, StudyMonkey is an excellent tool for students looking to improve their understanding of homework topics and boost their academic success."
Upgrade to StudyMonkey Premium!
Why not upgrade to StudyMonkey Premium and get access to all features?
Browse Course Material
Course info.
- Prof. Markus Klute
Departments
As taught in.
- Nuclear Physics
- Particle Physics
Learning Resource Types
Introduction to nuclear and particle physics, assignments, problem sets, paper presentation.
Below is a list of seminal papers in nuclear and particle physics. You are asked to form a team of two and pick a paper (first come first served). Please review the paper and prepare a 20-minute presentation summarizing the paper and also setting it into context. You can also suggest a paper not listed below.
Parity Violation
Experimental Test of Parity Conservation in Beta Decays
CP Violation
Evidence for the \(2\pi\) Decays of the \(K_2^0\) Meson
Observation of Single Isolated Electrons of High Transverse Momentum in Events with Missing Transverse Energy at the CERN pp Collider
Experimental Observation of Lepton Pairs of Invariant Mass around 95 GeV/c 2 at the CERN SPS Collider
Neutrino Oscillations
Evidence for Oscillation of Atmospheric Neutrinos
Higgs Boson
Observation of a New Boson at a Mass of 125 GeV with the CMS Experiment at the LHC
Observation of a New Particle in the Search for the Standard Model Higgs Boson with the ATLAS Detector at the LHC
Possible Existence of a Neutron
Fermi’s Theory of Beta Decay
Fermi’s Theory of Beta Decay (PDF)

You are leaving MIT OpenCourseWare
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Class 11 Physics Assignments
We have provided below free printable Class 11 Physics Assignments for Download in PDF. The Assignments have been designed based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 11 Physics . These Assignments for Grade 11 Physics cover all important topics which can come in your standard 11 tests and examinations. Free printable Assignments for CBSE Class 11 Physics , school and class assignments, and practice test papers have been designed by our highly experienced class 11 faculty. You can free download CBSE NCERT printable Assignments for Physics Class 11 with solutions and answers. All Assignments and test sheets have been prepared by expert teachers as per the latest Syllabus in Physics Class 11. Students can click on the links below and download all Pdf Assignments for Physics class 11 for free. All latest Kendriya Vidyalaya Class 11 Physics Assignments with Answers and test papers are given below.
Physics Class 11 Assignments Pdf Download
We have provided below the biggest collection of free CBSE NCERT KVS Assignments for Class 11 Physics . Students and teachers can download and save all free Physics assignments in Pdf for grade 11th. Our expert faculty have covered Class 11 important questions and answers for Physics as per the latest syllabus for the current academic year. All test papers and question banks for Class 11 Physics and CBSE Assignments for Physics Class 11 will be really helpful for standard 11th students to prepare for the class tests and school examinations. Class 11th students can easily free download in Pdf all printable practice worksheets given below.
Topicwise Assignments for Class 11 Physics Download in Pdf
Advantages of Class 11 Physics Assignments
- As we have the best and largest collection of Physics assignments for Grade 11, you will be able to easily get full list of solved important questions which can come in your examinations.
- Students will be able to go through all important and critical topics given in your CBSE Physics textbooks for Class 11 .
- All Physics assignments for Class 11 have been designed with answers. Students should solve them yourself and then compare with the solutions provided by us.
- Class 11 Students studying in per CBSE, NCERT and KVS schools will be able to free download all Physics chapter wise worksheets and assignments for free in Pdf
- Class 11 Physics question bank will help to improve subject understanding which will help to get better rank in exams
Frequently Asked Questions by Class 11 Physics students
At https://www.cbsencertsolutions.com, we have provided the biggest database of free assignments for Physics Class 11 which you can download in Pdf
We provide here Standard 11 Physics chapter-wise assignments which can be easily downloaded in Pdf format for free.
You can click on the links above and get assignments for Physics in Grade 11, all topic-wise question banks with solutions have been provided here. You can click on the links to download in Pdf.
We have provided here topic-wise Physics Grade 11 question banks, revision notes and questions for all difficult topics, and other study material.
We have provided the best collection of question bank and practice tests for Class 11 for all subjects. You can download them all and use them offline without the internet.
Related Posts

Class 11 Mathematics Limits And Derivatives Assignments

Class 11 Mathematics Binomial Theorem Assignments

Class 11 Chemistry Assignments
Why Study Physics?
Want to know “how” and “why” learn physics..

Physics is crucial to understanding the world around us, the world inside us, and the world beyond us. It is the most fundamental science.
Physics challenges our imaginations with concepts like relativity and string theory. It leads to great discoveries that, in turn, bring life-changing technologies, like computers, GPS, and lasers. Physicists also work to solve some of the greatest challenges of our times by finding ways to cure cancer, heal joints, or develop solutions for sustainable energy.
Learn more about the work that physicists do by reading stories from real physicists on our Physicists Profiles and Career Options pages.
If you’re an educator looking for resources to incorporate into your middle or high school classroom, review APS’s PhysicsQuest and STEP UP projects.
Like science? It begins with physics
Physics encompasses the study of the universe from the largest galaxies to the smallest (subatomic!) particles.
Moreover, physics is the basis for many other sciences, including chemistry, oceanography, seismology, and astronomy, as well as the applied sciences, like the various branches of engineering. The principles of physics are also applied in many areas of biology and biomedical science. Advanced education in all of these areas — and more! — is possible with a bachelor’s degree in physics.
Want to learn real-world skills? Study physics!
Physicists are problem solvers. Their analytical skills make them versatile and adaptable, so physicists often work interesting jobs in interesting places. You can find physicists in industrial and government labs, on college campuses, in the astronaut corps, and consulting for the special effects in TV shows and movies. In addition, many physics grads work for engineering or consulting firms, at newspapers and magazines, in government, for non-profits, in data science and app development roles, and even on Wall Street — places where their ability to think analytically is a great asset.
In general, though, most physics majors continue in STEM-related careers or careers that require strong problem-solving skills. Data shows that nearly 4 in 10 physics majors continue in engineering professions, while 1 in 4 go into computer or information systems. Another 1 in 4 physics majors continue in another STEM pathway or a non-STEM career where they regularly solve technical problems.
Want a job? People hire physicists
Physics brings a broad perspective to any problem. Because physicists learn how to critically analyze and breakdown even the most complex problems, they are not bound by context. This form of inventive thinking makes physicists desirable in any field. A bachelor’s degree in physics is a great foundation for careers in:
- Computer Science
- Data Science
- Engineering
Want a good salary? Physics tops the sciences
Even when the job market is slow, physicists get well-paying job offers. Employers know that a physicist brings additional skills and expertise — and they pay accordingly! That's why physics graduates can expect career salaries similar to those of computer science and engineering majors.
As of 2020, data shows the mean starting salary for a physics major taking a job in the STEM private sector was about $65k annually, with students who chose non-STEM technical pathways earning slightly less, at about $50k. But some physics majors, depending on their interests and skills acquired during college, start at much higher salaries — $80k or more.
Like most fields of STEM, if you pursue advanced education, your salary increases . After completing a master’s degree, physicists earn an average of about $90k annually, and after a doctorate, physicists earn a starting salary of roughly $120k.
View physics career statistical data

Five Myths About High School Physics
There are a lot of misconceptions about taking physics in high school — here are the facts.

Physicist Profiles
Discover how much you can do with a degree in physics by seeing how others have put theirs to use.

Career Navigator
Discover your path to career success, your comprehensive companion offering valuable insights, practical tools, and personalized guidance.

Physics Careers and Education
APS supports physicists and other scientists from the beginning of their education to every stage of their careers.
Join your Society
If you embrace scientific discovery, truth and integrity, partnership, inclusion, and lifelong curiosity, this is your professional home.
Spectrometer

Spectrometer is a spectroscope equipped with devices for measuring the frequencies of the radiation observed by it. Spectrometers were developed in early studies of physics, astronomy, and chemistry. It is the study of interactions between light and matter, and the reactions and measurements of radiation intensity and wavelength. The concept of a spectrometer now encompasses instruments that do not examine light.

While it provided a theoretical backing to early quantum research in radiation and atomic structure, it also has a staggering number of other applied uses; Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and X-ray machines utilise a form of radio-frequency spectroscopy, we measure the unique makeup and physical properties of distant astral bodies through their spectra and wavelength, and it’s even used to test doping in sports.
Spectrometers the chief instrument used in spectrometric analysis, which are specialised pieces of equipment that measure radiation types and wavelength. Spectrometers separate particles, atoms, and molecules by their mass, momentum, or energy. These types of spectrometers are used in chemical analysis and particle physics.
Types of Spectrometer
There are multiple fields of spectroscopy. Some of the potential fields and applications include:
Mass Spectronomy – Sorts and measures masses within a chemical sample through their mass-to-charge ratio. This is usually done by ionizing the particles with a shower of electrons, then passing them through a magnetic field to separate them into different stages of deflection.
Once the particles are separated, they’re measured by an electron multiplier, and we can identify the makeup of the sample through the weight of each ion’s mass. Practical uses of Mass Spectronomy include isotope dating and protein characterisation. Independant roving space exploration robots such as the Mars Phoenix Lander also carry mass spectrometers for analysis of foreign soils.
Matter and Energy – Spectrometry is based on interactions between matter and energy. A sample stimulated with a specific kind of energy will respond in a way that is characteristic of the sample. Depending on the method, a sample responds to an energy input by absorbing energy, releasing energy or perhaps even by undergoing a permanent physical change. If a sample gives no response in a particular instrument, there is information in that result as well.
Biomedical Spectroscopy – This is a great example of the multidisciplinary nature of spectroscopy. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (a subset of MRI) is often used to diagnose and study chemical changes in the brain which can cause anything from depression to physical tumours, as well as analyse the metabolic structure of muscle. This works by mapping a spectrum of wavelengths in the brain that correspond to the known spectrum, and carefully analysing patterns and aberrations in those patterns.
Ultraviolet (UV) Spectrometers – Ultraviolet (UV) spectroscopy works on a principle similar to that of colorimetry, except it uses ultraviolet light. UV spectroscopy is also called electronic spectroscopy, because the results depend on the electrons in the chemical bonds of the sample compound. Researchers use UV spectrometers to study chemical bonding and to determine the concentrations of substances (nucleic acids for example) that do not interact with visible light.
Atomic Spectrometers – Atomic spectrometers are used to find the elemental composition of samples and to determine the concentrations of each element. There are two basic types of atomic spectrometers: emission and absorbance. In either case a flame burns the sample, breaking it down into atoms or ions of the elements present in the sample. An emission instrument detects the wavelengths of light released by the ionized atoms. In an absorbance instrument, light of specified wavelengths passes through the energized atoms to a detector. The wavelengths of the emissions or absorbances are characteristic of the elements present.
Modern Spectrometry
The study of spectrometry dates back to the 1600s, when Isaac Newton first discovered that focusing a light through glass split it into the different colours of the rainbow, also known as the spectrum of visible light. The spectrum itself is an obviously visible phenomenon; it’s makes up the colours of the rainbow and creates the sheen we will see on the surface of a puddle, but it took centuries of piecemeal research to develop the study of this phenomenon into a coherent field that could be used to draw usable conclusions.
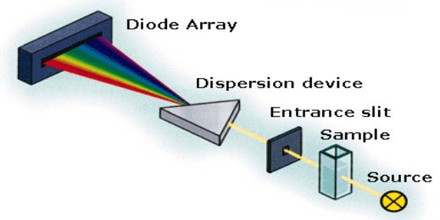
Simply put, as natural light filters from space from celestial bodies such as the sun, it goes through various reactions in our atmosphere. Each chemical element reacts slightly differently in this process, some visibly, those on the 390-700mm wavelength which detectable to the human eye and some invisibly.
Reference: atascientific.com , sciencing.com , dictionary.com , wikipedia .

Researchers Used Machine Learning, a Type of Artificial Intelligence (AI), to Anticipate Undiscovered Connections Between Known Viruses and Vulnerable Mammalian Species

Rejuvenation
Scientific Inquiry

Difference between Physical Change and Chemical Change

Biodiversity can Benefit from Parasites and they Might be Essential to Preserving it

Annual Report 2013 of Habib Metropolitan Bank

According to Research, Moderate Physical Activity benefits the Brain

Write A Letter To College-Going Brother
Structure of a Flower

Antarctica has been Discovered to have the World’s Largest Fish Breeding Area
Latest post.
Metamaterial Absorber
Regenerative Braking – an energy recovery mechanism

Researchers Investigate how we Experience Bitter Tastes

Researchers discovered the Oldest Undisputed evidence of Earth’s Magnetic Field

Negative Thermal Expansion (NTE)

Thermal Expansion

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
AP Physics 1 concept review: Review for AP Physics 1 exam AP Physics 1 free response questions 2015: Review for AP Physics 1 exam. Community questions. Our mission is to provide a free, world-class education to anyone, anywhere. Khan Academy is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization. Donate or volunteer today! Site Navigation. About. News;
Figure 1.3 The Apple iPhone is a common smart phone with a GPS function, sophisticated camera, haptic (vibration) capabilities, and many other functions. Physics describes the way that electricity flows through the circuits of this device. Engineers use their knowledge of physics to construct an iPhone with features that consumers will enjoy.
A collection of classroom ready worksheets for use by teachers with their classes. Pages are synchronized to readings from The Physics Classroom Tutorial and to assignments of The Minds On Physics Internet Modules. And now teachers can purchase The Solutions Guide containing complete answers, explanations and solutions to all worksheets.
Select amount. $10. $20. $30. $40. Other. AP®︎/College Physics 1 5 units · 27 skills. Course challenge. Test your knowledge of the skills in this course.
Quantum Physics I. Menu. More Info Syllabus Calendar Readings Lecture Notes Lecture Videos Assignments Exams Study Materials Assignments. problems solutions Problem Set 1 (PDF) ... assignment_turned_in Problem Sets with Solutions. Download Course. Over 2,500 courses & materials
Teacher Support. To help meet the multimodal needs of classrooms today, OpenStax Tutor's Physics provides Teacher Support tips for on-level [OL], below-level [BL], and above-level [AL] students. [OL] Pre-assessment for this section could involve asking students the definition of matter, atoms, electrons, protons, neutrons, subatomic particles, and energy.
Introduction to Dynamics: Newton's Laws of Motion; 4.1 Development of Force Concept; 4.2 Newton's First Law of Motion: Inertia; 4.3 Newton's Second Law of Motion: Concept of a System; 4.4 Newton's Third Law of Motion: Symmetry in Forces; 4.5 Normal, Tension, and Other Examples of Forces; 4.6 Problem-Solving Strategies; 4.7 Further Applications of Newton's Laws of Motion
20. Kinetic Energy and Work in 1D. Problem Set 7 (PDF) Block Going Down a Ramp. Collision and Sliding on a Rough Surface. 21. Kinetic Energy and Work in 2D and 3D. 22. Conservative and Non-conservative Forces.
First and foremost, we'd wanna include Isaac Newton. Especially when you start to study physics, you're starting to understand the world as Newton understood it. He understood, "Hey, you know, "things don't fall to the ground "just 'cause they always fall to, "just 'cause that's the way the universe is.
Even though Quantum Physics is a challenging branch to study, consider looking into these interesting Physics topics for assignments: The Pauli exclusion principle and the factor of quantum indeterminacy. An infrared divergence and transition amplitude calculation when dealing with soft photons. The Bohr model and the Quantum Mechanical ...
Lesson 1 - Basic Terminology and Concepts. Definition and Mathematics of Work. Calculating the Amount of Work Done by Forces. Potential Energy. Kinetic Energy. Mechanical Energy. Power. Lesson 2 - The Work-Energy Relationship. Internal vs. External Forces.
In architecture, physics is at the heart of structural stability and is involved in acoustics, heating, lighting, and the cooling of buildings. Parts of geology rely heavily on physics, such as the radioactive dating of rocks, earthquake analysis, and heat transfer in the Earth. Some disciplines, such as biophysics and geophysics, are hybrids ...
Kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another. Each equation contains four variables. The variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final velocity (vf), and initial velocity (vi). If values of three variables are known, then the others can be calculated using the equations. This page demonstrates the process with 20 sample problems and accompanying ...
28. Poynting Vector: Energy, Power and Momentum of Radiation, Magnetic Properties of Materials. Transmission Lines. Problem set 11 due. Some of the problems are assigned from the course textbook: Purcell, E. M. Electricity and Magnetism. 2nd ed. Vol. 2. Berkeley Physics Course. The problem sets were handed out in the sessions noted in the table.
In this physics science project, you will investigate how far a ball bearing launched by a Gauss rifle will fly, depending on how many magnetic acceleration stages are in the setup and the ball bearing's initial velocity.…. Read more. Rainbow Fire Science Project. Add Favorite More Menu.
These all are 20th century physics topics. Moreover, many such physics topics have been told about which students can make their physics assignments and research projects. Moreover, if you need help with physics assignments, our experts offer Physics assignment help or physics homework help online free at very low prices. FAQ
An algebra-based, introductory college-level physics course that explores topics such as fluid statics and dynamics; thermodynamics with kinetic theory; PV diagrams and probability; electrostatics; electrical circuits with capacitors; magnetic fields; electromagnetism; physical and geometric optics; and a whole lot more.
David Morin, [email protected] This chapter gives a brief introduction to quantum mechanics. Quantum mechanics can be thought of roughly as the study of physics on very small length scales, although there are also certain macroscopic systems it directly applies to. The descriptor \quantum" arises
Now, with expert-verified solutions from Exercises for the Feynman Lectures on Physics 1st Edition, you'll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems. Our resource for Exercises for the Feynman Lectures on Physics includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step.
A 24/7 free Physics homework AI tutor that instantly provides personalized step-by-step guidance, explanations, and examples for any Physics homework problem. Improve your grades with our AI homework helper! ... Get all your Physics assignments done with helpful answers in 10 seconds or less. No more asking friends for Physics help.
Paper Presentation. Below is a list of seminal papers in nuclear and particle physics. You are asked to form a team of two and pick a paper (first come first served). Please review the paper and prepare a 20-minute presentation summarizing the paper and also setting it into context. You can also suggest a paper not listed below.
All Assignments and test sheets have been prepared by expert teachers as per the latest Syllabus in Physics Class 11. Students can click on the links below and download all Pdf Assignments for Physics class 11 for free. All latest Kendriya Vidyalaya Class 11 Physics Assignments with Answers and test papers are given below.
Learn physics. Physics is crucial to understanding the world around us, the world inside us, and the world beyond us. It is the most fundamental science. Physics challenges our imaginations with concepts like relativity and string theory. It leads to great discoveries that, in turn, bring life-changing technologies, like computers, GPS, and lasers.
Definition. Spectrometer is a spectroscope equipped with devices for measuring the frequencies of the radiation observed by it. Spectrometers were developed in early studies of physics, astronomy, and chemistry. It is the study of interactions between light and matter, and the reactions and measurements of radiation intensity and wavelength.